Page 1

Part No. 060202-10 , Rev. D
June 2007
Alcatel OS-LS-6200
User Guide
www.alcatel.com
Page 2

An Alcatel service agreement brings your company the assurance of 7x24 no-excuses technical
support. You’ll also receive regular software updates to maintain and maximize your Alcatel
product’s features and functionality and on-site hardware replacement through our global network
of highly qualified service delivery partners. Additionally, with 24-hour-a-day access to Alcatel’s
Service and Support web page, you’ll be able to vi ew and update any case (open or clos ed) that you
have reported to Alcatel’s technical support, open a new case or access helpful release notes,
technical bulletins, and manuals. For more information on Alcatel’s Service Programs, see our web
page at www.ind.alcatel.com, call us at 1-800-995-2696, or email us at support@ind.alcatel.com.
This Manual documents Alcatel 6200 hardware and software.
The functionality described in this Manual is subject to change without notice.
©
Copyright
reproduced in whole or in part without the express written permission of Alcatel Internetworking, Inc.
Alcatel
OmniSwitch
SwitchExpert
are trademarks of their respective companies.
2007 by Alcatel Internetworking, Inc. All rights reserved. This document may not be
®
and the Alcatel logo are registered trademarks of Compagnie Financiére Alcatel, Paris, France.
®
and OmniStack® are registered trademarks of Alcatel Internetworking, Inc. Omni Switch/Router™,
SM
, the Xylan logo are trademarks of Alcatel Internetworking, Inc. All other brand and product names
26801 West Agoura Road
Calabasas, CA 91301
(818) 880-3500 FAX (818) 880-3505
info@ind.alcatel.com
US Customer Support-(800) 995-2696
International Customer Support-(818) 878-4507
Internet-http://eservice.ind.alcatel.com
Page 3

Warning
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for Class A digital
device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and,
if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions in this guide, may cause interference to
radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference,
in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
The user is cautioned that changes and modifications made to the equipment without
approval of the manufacturer could void the user’s authority to operate this equipment. It is suggested
that the user use only shielded and grounded cables to ensure compliance with FCC Rules.
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio noise emissions from
digital apparatus set out in the radio interference regulations of the Canadian department of
communications.
Le present appareil numerique níemet pas de bruits radioelectriques depassant les limites applicables
aux appareils numeriques de la Class A prescrites dans le reglement sur le brouillage radioelectrique
edicte par le ministere des communications du Canada.
Utilice sólo adaptadores con las siguientes características eléctricas y que estén debidamente
certificados de acuerdo a la legislación vigente. El uso de otros adaptadores podría dañar el dispositivo
y anular la garantía además de provocar riesgos al usuario.
OS-LS-6224P AC100/115/220/230V; 50/60Hz; 2.0/1.7/0.9/
OS-LS-6248P AC100/115/220/230V; 50/60Hz; 4.0/3.4/1.8/
OS-LS-6224 AC 100/115/220/230V; 50/60Hz; 0.4/0.4/0.2/
OS-LS-6248 AC100/115/220/230V; 50/60Hz; 0.6/0.6/0.4/
OS-LS-6224U AC 100/115/220/230V 50/60Hz 1.0/1.0/0.5/
Adaptador:
OS-LS-6224P OS-LS-62BP-P 3Y Power
OS-LS-6248P OS-LS-62BP-P Alcatel
OS-LS-6248 OS-LS-62BP-DC & OS-LS-62BP Accton & 3Y Power
OS-LS-6224 OS-LS-62BP-DC & OS-LS-62BP Accton & 3Y Power
Características de entrada: Características de salida:
0.9A; Clase I
1.8A; Clase I
0.2A; Clase I
0.4A; Clase I
0.5A Clase I
Modelo: Marca comercial:
DC 12V, 4.0A; -50V, 3.6A
DC 12V, 7.5A; -50V, 7.5A
DC 12V, 4.5A
DC 12V, 4.5A
DC 12V , 4.5A
Page 4

Page 5

Contents
Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction 1
Key Features ........................................................................................................1
Description of Software Features .........................................................................3
System Defaults .............................................................. ... ................................. .9
Chapter 2: Initial Configuration 13
General Configuration Information .....................................................................14
Auto-Negotiation 15
Device Port Default Settings 15
Booting the Switch ..............................................................................................16
Configuration Overview ......................................................................................18
Initial Configuration .............................................................................................18
Static IP Address and Subnet Mask 18
User Name 19
SNMP Community Strings 19
Advanced Configuration .....................................................................................21
Retrieving an IP Address From a DHCP Server 21
Receiving an IP Address From a BOOTP Server 22
Security Management and Password Configuration ..........................................23
Configuring Security Passwords Introduction 23
Configuring an Initial Console Password 24
Configuring an Initial Telnet Password 24
Configuring an Initial SSH password 24
Configuring an Initial HTTP Password 25
Configuring an initial HTTPS Password 25
Software Download and Reboot .........................................................................25
Software Download through XModem 25
Software Download Through TFTP Server 26
Boot Image Download 27
Startup Menu Functions .....................................................................................28
Chapter 3: Configuring the Switch 33
Using the Web Interface .....................................................................................33
Navigating the Web Browser Interface ...............................................................33
Home Page 33
Configuration Options 34
Panel Display 35
Main Menu 35
Managing Device Information ............................................................................. 36
Managing Stacking .............................................................................................37
Understanding the Stack Topology 38
Stacking Failover Topology 38
v
Page 6

Contents
Stacking Members and Unit ID 38
Removing and Replacing Stacking Members 39
Exchanging Stacking Members 40
Switching between the Stacking Master and the Secondary Master 40
Configuring Stacking 41
Resetting the Stack 42
Managing System Logs ......................................................................................43
Enabling System Logs 43
Viewing Memory Logs 45
Viewing the Device FLASH Logs 47
Remote Log Configuration 48
Configuring SNTP ................................................................. ..............................51
Polling for Unicast Time Information 51
Polling for Anycast Time Information 51
Polling For Broadcast Time Information 52
Defining SNTP Global Settings 52
Defining SNTP Authentication 53
Defining SNTP Servers 54
Defining SNTP Interface Settings 56
Configuring System Time ...................................................................................57
Configuring Daylight Savings Time 57
Managing System Files ......................................................................................61
Downloading System Files 62
Uploading System Files 64
Copying Files 65
Active Image 66
TCAM Resources ...............................................................................................67
Configuring Interfaces .........................................................................................69
Configuring Interface Connections 69
Creating Trunks (LAGs) 72
Configuring LACP 73
Displaying Port Statistics ................................................ ... .................................75
Interface Statistics 76
Etherlike Statistics 77
Configuring IP Information ..................................................................................80
Defining IP Addresses 80
Defining Default Gateways 81
Configuring DHCP 82
Configuring ARP 83
Configuring Domain Name Service ....................................................................85
Configuring General DNS Server Parameters 86
Configuring Static DNS Host to Address Entries 87
Configuring SNMP ....................................................... ... ... .................................88
Enabling SNMP 89
Defining SNMP Users 90
vi
Page 7

Contents
Defining SNMP Group Profiles 92
Defining SNMP Views 93
Defining SNMP Communities 95
Defining SNMP Notification Recipients 96
Defining SNMP Notification Global Parameters 98
Defining SNMP Notification Filters 100
Configuring User Authentication .......................................................................101
Defining Local Users Passwords 101
Defining Line Passwords 102
Defining Enable Passwords 103
Configuring Authentication Methods ................................................................104
Defining Access Profiles 104
Defining Profile Rules 107
Defining Authentication Profiles 109
Mapping Authentication Methods 112
Defining TACACS+ Methods 114
Defining RADIUS Settings 115
Managing RMON Statistics ..............................................................................118
Viewing RMON Statistics 118
Defining RMON History Control 120
Viewing the RMON History Table 121
Defining RMON Events Control 124
Viewing the RMON Events Logs 125
Defining RMON Alarms 126
Alcatel Mapping Adjacency Protocol (AMAP) ...................................................128
Configuring AMAP 128
Viewing Adjacent Devices 130
Configuring LLDP .............................................................................................131
Defining LLDP Port Settings 132
Defining Media Endpoint Discovery Network Policy 133
Defining LLDP MED Port Settings 134
Viewing the LLDP Neighbor Information 135
Viewing Neighbor Information Details 136
Managing Power-over-Ethernet Devices .......................................................... 139
Defining PoE System Information 139
Defining PoE Interfaces 140
Device Diagnostic Tests ...................................................................................142
Configuring Port Mirroring 142
Viewing Integrated Cable Tests 144
Viewing Optical Transceivers 145
Viewing Device Health 147
Configuring Traffic Control ...............................................................................149
Enabling Storm Control 149
Configuring Port Security 151
802.1X Port-Based Authentication ...................................................................153
vii
Page 8

Contents
Advanced Port-Based Authentication 154
Defining Network Authentication Properties 155
Defining Port Authentication 157
Modify Port Authentication Page 158
Configuring Multiple Hosts 160
Defining Authentication Hosts 162
Viewing EAP Statistics 164
Defining Access Control Lists ...........................................................................167
Configuring Access Control Lists 167
Binding Device Security ACLs 168
Defining IP Based Access Control Lists 169
Defining MAC Based Access Control Lists 171
DHCP Snooping ...............................................................................................173
DHCP Snooping Properties 174
Defining DHCP Snooping on VLANs 175
Defining Trusted Interfaces 176
Binding Addresses to the DHCP Snooping Database 177
Configuring Option 82 .......................................................................................178
Dynamic ARP Inspection ..................................................................................179
ARP Inspection Properties 180
ARP Inspection Trusted Interface Settings 181
Defining ARP Inspection List 182
Assigning ARP Inspection VLAN Settings 183
IP Source Guard ...............................................................................................184
Configuring IP Source Guard Properties 185
Defining IP Source Guard Interface Settings 185
Adding Interfaces to the IP Source Guard Database 186
Defining the Forwarding Database ...................................................................188
Defining Static Forwarding Database Entries 188
Defining Dynamic Forwarding Database Entries 189
Configuring Spanning Tree ...............................................................................191
Defining Spanning Tree 192
Defining STP on Interfaces 194
Defining Rapid Spanning Tree 197
Defining Multiple Spanning Tree 199
Defining MSTP Instance Settings 200
Defining MSTP Interface Settings 201
Configuring VLANs .......................................................................... ... .. ............204
Assigning Ports to VLANs 204
Tagged/Untagged VLANs 206
Displaying Basic VLAN Information 206
Defining VLAN Membership 207
Defining VLAN Interface Settings 210
Defining Customer Mapping for Multicast TV 211
Mapping CPE VLANs 212
viii
Page 9

Contents
Defining VLAN Groups ...................................... ... .. ..................................... .....213
Configuring MAC Based VLAN Groups 213
Configuring Subnet Based VLAN Groups 214
Configuring Protocol Based VLAN Groups 215
Mapping Groups to VLANs 216
Defining GARP 217
Defining GVRP 219
Viewing GVRP Statistics 220
Multicast Filtering ............................................................................................223
Defining IGMP Snooping 223
Specifying Static Interfaces for a Multicast Group 225
Displaying Interfaces Attached to a Multicast Router 227
Configuring Multicast TV 228
Defining Multicast TV Membership 229
Configuring Triple Play .....................................................................................230
Configuring Quality of Service ..........................................................................231
Access Control Lists 232
Mapping to Queues 233
QoS Modes 234
Enabling QoS 235
Defining Global Queue Settings 236
Defining Bandwidth Settings 237
Configuring VLAN Rate Limit 239
Mapping CoS Values to Queues 240
Mapping DSCP Values to Queues 241
Defining Basic QoS Settings 242
Defining QoS DSCP Rewriting Settings 243
Defining QoS DSCP Mapping Settings 244
Defining QoS Class Maps 245
Defining Policies 246
Defining Tail Drop 248
Viewing the Policy Table 248
Viewing Policy Bindings 250
Chapter 4: Command Line Interface 253
Using the Command Line Interface ..................................................................253
Accessing the CLI 253
Console Connection 253
Telnet Connection 253
Entering Commands .........................................................................................255
Keywords and Arguments 255
Minimum Abbreviation 255
Command Completion 255
Getting Help on Commands 255
ix
Page 10

Contents
Partial Keyword Lookup 257
Negating the Effect of Commands 257
Using Command History 257
Understanding Command Modes 257
Exec Commands 258
Configuration Commands 258
Command Line Processing 259
Command Groups ................................. ... ........................................................261
802.1x Commands .................................... ........................................................263
aaa authentication dot1x 264
dot1x system-auth-control 265
dot1x port-control 266
dot1x re-authentication 267
dot1x timeout re-authperiod 268
dot1x re-authenticate 269
dot1x timeout quiet-period 269
dot1x timeout tx-period 270
dot1x max-req 271
dot1x timeout supp-timeout 272
dot1x timeout server-timeout 273
show dot1x 274
show dot1x users 277
show dot1x statistics 279
ADVANCED FEATURES 281
dot1x auth-not-req 281
dot1x multiple-hosts 282
dot1x single-host-violation 283
dot1x guest-vlan 284
dot1x guest-vlan enable 285
dot1x mac-authentication 285
show dot1x advanced 2 86
AAA Commands ...............................................................................................288
aaa authentication login 288
aaa authentication enable 290
login authentication 291
enable authentication 292
ip http authentication 293
ip https authentication 294
show authentication methods 294
password 296
enable password 296
username 297
show users accounts 298
ACL Commands ...............................................................................................300
ip-access-list 300
x
Page 11

Contents
permit (ip) 301
deny (IP) 304
mac access-list 306
permit (MAC) 307
deny (MAC) 308
service-acl 310
show access-lists 310
show interfaces access-lists 311
Address Table Commands ...................................................... .........................313
bridge address 314
bridge multicast filtering 315
bridge multicast address 316
bridge multicast forbidden address 317
bridge multicast forward-all 318
bridge multicast forbidden forward-all 319
bridge aging-time 320
clear bridge 320
port security 321
port security mode 321
port security max 322
port security routed secure-address 323
show bridge address-table 324
show bridge address-table static 325
show bridge address-table count 326
show bridge multicast address-table 327
show bridge multicast address-table static 328
show bridge multicast filtering 329
show ports security 330
show ports security addresses 331
LLDP Commands .............................................................................................333
lldp optional-tlv 333
lldp med enable 334
lldp med network-policy (global) 334
lldp med network-policy (interface) 335
lldp med location 335
clear lldp rx 336
show lldp configuration 337
show lldp med configuration 337
show lldp local 338
show lldp neighbors 340
AMAP Commands ................................................ ............................................345
amap enable 345
amap discovery time 346
amap common time 346
show amap 346
xi
Page 12

Contents
Clock Commands .............................................................................................348
349
clock set 349
clock source 350
clock timezone 350
clock summer-time 351
sntp authentication-key 353
sntp authenticate 353
sntp trusted-key 354
sntp client poll timer 355
sntp broadcast client enable 356
sntp anycast client enable 357
sntp client enable (Interface) 357
sntp unicast client enable 358
sntp unicast client poll 359
sntp server 360
show clock 361
show sntp configuration 362
show sntp status 363
Configuration and Image File Commands ........................................................365
copy 365
delete 368
dir 369
more 370
rename 371
boot system 372
show running-config 373
show startup-config 373
show bootvar 374
Ethernet Configuration Commands ..................................................................376
interface ethernet 376
interface range ethernet 377
shutdown 378
description 379
speed 380
duplex 381
negotiation 382
flowcontrol 383
mdix 383
back-pressure 384
clear counters 385
set interface active 386
show interfaces advertise 386
show interfaces configuration 388
show interfaces status 390
xii
Page 13

Contents
show interfaces description 392
show interfaces counters 392
port storm-control broadcast enable 395
port storm-control broadcast rate 396
show ports storm-control 397
GVRP Commands ................................................ ............................................399
gvrp enable (Global) 399
gvrp enable (Interface) 400
garp timer 401
gvrp vlan-creation-forbid 402
gvrp registration-forbid 402
clear gvrp statistics 403
show gvrp configuration 404
show gvrp statistics 405
show gvrp error-statistics 406
IGMP Snooping Commands .............................................................................408
ip igmp snooping (Global) 408
ip igmp snooping (Interface) 409
ip igmp snooping host-time-out 410
ip igmp snooping mrouter-time-out 410
ip igmp snooping leave-time-out 411
ip igmp snooping multicast-tv 412
ip igmp snooping querier enable 413
ip igmp snooping querier address 413
ip igmp snooping querier version 414
show ip igmp snooping mrouter 414
show ip igmp snooping interface 415
show ip igmp snooping groups 416
IP Addressing Commands ................................................................................418
ip address 418
ip address dhcp 419
ip default-gateway 420
show ip interface 421
arp 422
arp timeout 423
clear arp-cache 424
show arp 424
ip domain-lookup 425
ip domain-name 426
ip name-server 426
ip host 427
clear host 428
clear host dhcp 429
show hosts 429
LACP Commands ...................................................... .................................. ... ..431
xiii
Page 14

Contents
lacp system-priority 431
lacp port-priority 432
lacp timeout 4 32
show lacp ethernet 433
show lacp port-channel 435
Line Commands ................................................................................................437
line 437
speed 438
autobaud 439
exec-timeout 439
history 440
history size 440
terminal history 441
terminal history size 442
show line 443
Management ACL Commands .........................................................................445
management access-list 445
permit (Management) 446
deny (Management) 447
management access-class 448
show management access-list 449
show management access-class 450
PHY Diagnostics Commands ................................. .. ..................................... ...451
test copper-port tdr 451
show copper-ports tdr 452
show copper-ports cable-length 452
show fiber-ports optical-transceiver 453
Port Channel Commands .................................................................................455
interface port-channel 455
interface range port-channel 455
channel-group 456
show interfaces port-channel 457
Port Monitor Commands ...................................................................................458
port monitor 458
show ports monitor 459
Power over Ethernet Commands ......................................................................460
power inline 460
power inline powered-device 461
power inline priority 462
power inline usage-threshold 462
power inline traps enable 463
show power inline 464
QoS Commands ......................................... .................................. ... ... ..............467
qos 468
show qos 469
xiv
Page 15

Contents
class-map 469
show class-map 470
match 471
policy-map 472
class 472
rate-limit 473
rate-limit (VLAN) 474
show policy-map 474
trust cos-dscp 475
set 476
police 477
service-policy 478
qos aggregate-policer 478
show qos aggregate-policer 480
police aggregate 481
wrr-queue cos-map 481
priority-queue out num-of-queues 482
traffic-shape 483
show qos interface 484
qos wrr-queue threshold 486
qos map dscp-dp 487
qos map policed-dscp 487
qos map dscp-queue 488
qos trust (Global) 489
qos trust (Interface) 490
qos cos 490
qos dscp-mutation 491
qos map dscp-mutation 492
show qos map 493
RADIUS Commands ........................................................................................495
radius-server host 495
radius-server key 497
radius-server retransmit 497
radius-server source-ip 498
radius-server timeout 499
radius-server deadtime 500
show radius-servers 501
RMON Commands ...........................................................................................503
show rmon statistics 503
rmon collection history 505
show rmon collection history 506
show rmon history 507
rmon alarm 510
show rmon alarm-table 511
show rmon alarm 512
xv
Page 16

Contents
rmon event 514
show rmon events 514
show rmon log 515
rmon table-size 517
SNMP Commands ...................................................................................... ... ...518
snmp-server community 519
snmp-server view 520
snmp-server group 521
snmp-server user 522
snmp-server engineID local 523
snmp-server enable traps 525
snmp-server filter 525
snmp-server host 526
snmp-server v3-host 528
snmp-server trap authentication 529
snmp-server contact 529
snmp-server location 530
snmp-server set 531
show snmp 531
show snmp engineid 533
show snmp views 534
show snmp groups 535
show snmp filters 536
show snmp users 536
Spanning-Tree Commands ..................................... .. ..................................... ...538
spanning-tree 539
spanning-tree mode 540
spanning-tree forward-time 541
spanning-tree hello-time 542
spanning-tree max-age 543
spanning-tree priority 544
spanning-tree disable 544
spanning-tree cost 545
spanning-tree port-priority 546
spanning-tree portfast 547
spanning-tree link-type 548
spanning-tree pathcost method 549
spanning-tree bpdu 550
clear spanning-tree detected-protocols 551
spanning-tree mst priority 551
spanning-tree mst max-hops 552
spanning-tree mst port-priority 553
spanning-tree mst cost 554
spanning-tree mst configuration 556
instance (mst) 556
xvi
Page 17

Contents
name (mst) 558
revision (mst) 558
show (mst) 559
exit (mst) 561
abort (mst) 561
spanning-tree guard root 562
spanning-tree bpduguard 563
dot1x bpdu 563
show dot1x bpdu 564
show spanning-tree 564
SSH Commands ...............................................................................................580
ip ssh port 580
ip ssh server 581
crypto key generate dsa 581
crypto key generate rsa 582
ip ssh pubkey-auth 583
crypto key pubkey-chain ssh 584
user-key 585
key-string 586
show ip ssh 587
show crypto key mypubkey 588
show crypto key pubkey-chain ssh 589
Syslog Commands ............................................................... ............................591
logging on 591
logging 592
logging console 593
logging buffered 594
logging buffered size 595
clear logging 595
logging file 596
clear logging file 597
aaa logging 597
file-system logging 598
management logging 598
show logging 599
show logging file 601
show syslog-servers 603
System Management Commands ...................................... .. ............................604
ping 604
traceroute 606
telnet 608
resume 611
reload 612
hostname 612
stack master 613
xvii
Page 18

Contents
stack reload 614
stack display-order 614
show stack 615
show users 617
show sessions 617
show system 618
show version 619
service cpu-utilization 620
show cpu utilization 6 21
TACACS+ Commands ......................................................................................622
tacacs-server host 622
tacacs-server key 623
tacacs-server timeout 624
tacacs-server source-ip 625
show tacacs 625
Triple Play Commands .....................................................................................627
switchport customer vlan 627
switchport customer multicast-tv vlan 627
ip igmp snooping map cpe vlan 628
show ip igmp snooping cpe vlans 629
show ip igmp snooping interface 629
DHCP Snooping, IP Source Guard and ARP Inspection Commands ..............631
ip dhcp snooping 632
ip dhcp snooping vlan 633
ip dhcp snooping trust 634
ip dhcp information option allowed-untrusted 634
ip dhcp information option 635
ip dhcp snooping verify 635
ip dhcp snooping database 636
ip dhcp snooping database update-freq 636
ip dhcp snooping binding 637
clear ip dhcp snooping database 638
show ip dhcp snooping 638
show ip dhcp snooping binding 639
ip source-guard (global) 640
ip source-guard (interface) 640
ip source-guard binding 641
ip source-guard tcam retries-freq 642
ip source-guard tcam locate 643
show ip source-guard 643
show ip source-guard inactive 644
ip arp inspection 645
ip arp inspection vlan 646
ip arp inspection trust 646
ip arp inspection validate 647
xviii
Page 19

Contents
ip arp inspection list create 648
ip mac 648
ip arp inspection list assign 649
ip arp inspection logging interval 650
show ip arp inspection 650
show ip arp inspection list 651
User Interface Commands ...................................................... ... ......................652
do 652
enable 653
disable 654
login 654
configure 655
exit (Configuration) 655
exit 656
end 657
help 657
terminal datadump 658
show history 659
show privilege 659
VLAN Commands ................................................... .................................. ... ... ..661
vlan database 662
vlan 663
default-vlan vlan 664
interface vlan 664
interface range vlan 665
name 666
map protocol protocols-group 666
switchport general map protocols-group vlan 667
switchport mode 668
switchport access vlan 669
switchport trunk allowed vlan 670
switchport trunk native vlan 671
switchport general allowed vlan 672
switchport general pvid 673
switchport general ingress-filtering disable 674
switchport general acceptable-frame-type tagged-only 675
switchport forbidden vlan 676
map mac macs-group 677
switchport general map macs-group vlan 677
map subnet subnets-group 678
switchport general map subnets-group vlan 679
switchport protected 680
ip internal-usage-vlan 681
show vlan 682
show vlan internal usage 683
xix
Page 20

Contents
show interfaces switchport 684
switchport access multicast-tv vlan 687
show vlan protocols-groups 688
show vlan macs-groups 688
show vlan subnets-groups 689
show vlan multicast-tv 690
Web Server Commands ...................................................................................691
ip http server 691
ip http port 692
ip http exec-timeout 693
ip https server 693
ip https port 694
ip https exec-timeout 695
crypto certificate generate 695
crypto certificate request 6 96
crypto certificate import 698
ip https certificate 699
show crypto certificate mycertificate 699
show ip http 700
show ip https 701
Appendix A. Configuration Examples 703
Configuring QinQ ...................................................... ........................................704
Configuring Customer VLANs using the CLI ....................................................707
Configuring Multicast TV ..................................................................................709
Configuring Customer VLANs ...........................................................................716
Configuring Customer VLANs Using the Web Interface ...................................716
Appendix B. Software Specifications 721
Software Features ............................................................................................721
Management Features ......................................................................................722
Standards .........................................................................................................722
Management Information Bases .......................................................................723
Appendix C. Troubleshooting 725
Problems Accessing the Management Interface ..............................................725
Using System Logs ................................... ........................................................726
Appendix D. Glossary 727
xx
Page 21

Figures
Figures
Figure 2-1. Installation and Configuration 14
Figure 2-2. Send File window 29
Figure 3-3. Home Page 34
Figure 3-4. Ports Panel 35
Figure 3-5. System Information Page 37
Figure 3-6. Stack Management Topology Page 41
Figure 3-7. Stack Management - Reset Page 42
Figure 3-8. Logs Settings Page 44
Figure 3-9. Memory Page 46
Figure 3-10. FLASH Logs Page 48
Figure 3-11. Remote Log Page 49
Figure 3-12. SNTP Configuration Page 53
Figure 3-13. SNTP Authentication Page 54
Figure 3-14. SNTP Servers Page 55
Figure 3-15. SNTP Interface Page 56
Figure 3-16. Clock Time Zone Page 61
Figure 3-17. File Download Page 63
Figure 3-18. File Upload Page 65
Figure 3-19. Copy Files Page 66
Figure 3-20. Active image Page 67
Figure 3-21. TCAM Resources Page 69
Figure 3-22. Interface Configuration Page 71
Figure 3-23. LAG Membership Page 73
Figure 3-24. Interface LACP Configuration Page 75
Figure 3-25. Statistics Interface Page 77
Figure 3-26. Statistics Etherlike Page 78
Figure 3-27. IP Interface Page 81
Figure 3-28. Default Gateway Page 82
Figure 3-29. DHCP Page 83
Figure 3-30. ARP Page 84
Figure 3-31. DNS Server Page 86
Figure 3-32. DNS Host Mapping Page 88
Figure 3-33. Engine ID Pag e 90
Figure 3-34. SNMP Users Page 92
Figure 3-35. SNMP Groups Page 93
Figure 3-36. SNMP Views Page 94
Figure 3-37. SNMP Communities Page 96
Figure 3-38. SNMP Trap Station Management Page 98
Figure 3-39. SNMP Global Trap Settings Page 99
Figure 3-40. Trap Filter Settings Page 100
Figure 3-41. Local Users Page 102
Figure 3-42. Line Page 103
xxi
Page 22

Figures
Figure 3-43. Enable Page 104
Figure 3-44. Access Profiles Page 107
Figure 3-45. Profiles Rules Page 109
Figure 3-46. Authentication Profiles Page 110
Figure 3-47. Authentication Mapping Page 113
Figure 3-48. TACACS+ Page 115
Figure 3-49. RADIUS Page 117
Figure 3-50. RMON Statistics Page 119
Figure 3-51. History Control Page 121
Figure 3-52. History Table Page 122
Figure 3-53. Events Control Page 125
Figure 3-54. Events Logs Page 126
Figure 3-55. Alarm Page 128
Figure 3-56. AMAP Settings Page 129
Figure 3-57. AMAP Adjacencies Page 130
Figure 3-58. LLDP Properties Page 132
Figure 3-59. LLDP Port Settings Page 133
Figure 3-60. MED Networking Policy Page 134
Figure 3-61. MED Port Settings Page 135
Figure 3-62. LLDP Neighbor Information Page 136
Figure 3-63. Details Neighbor Information Page 138
Figure 3-64. Properties Page 140
Figure 3-65. PoE Interface Page 142
Figure 3-66. Port Mirroring Page 144
Figure 3-67. Copper Cable Page 145
Figure 3-68. Optical Transceiver Page 146
Figure 3-69. Health Page 148
Figure 3-70. Storm Control Page 150
Figure 3-71. Port Security Page 153
Figure 3-72. System Information Page 156
Figure 3-73. Port Authentication Page 160
Figure 3-74. Multiple Hosts Page 162
Figure 3-75. Authentication Host Page 163
Figure 3-76. Statistics Page 166
Figure 3-77. ACL Binding Page 169
Figure 3-78. IP Based ACL Page 171
Figure 3-79. MAC Based ACL Page 173
Figure 3-80. DHCP Snooping Properties Page 175
Figure 3-81. VLAN Settings Page 176
Figure 3-82. Trusted Interface Page 177
Figure 3-83. Binding Database Page 178
Figure 3-84. DHCP Option 82 Page 179
Figure 3-85. ARP Inspection Properties Page 181
Figure 3-86. ARP Inspection Trusted Interface Page 182
Figure 3-87. ARP Inspection List Page 183
xxii
Page 23

Figures
Figure 3-88. VLAN Settings Page 184
Figure 3-89. IP Source Guard Properties Page 185
Figure 3-90. Interface Settings Page 186
Figure 3-91. IP Source Guard Binding Database Page 187
Figure 3-92. Static Addresses Page 189
Figure 3-93. Dynamic Addresses Page 190
Figure 3-94. STP General Page 194
Figure 3-95. Interface Configuration Page 197
Figure 3-96. RSTP Page 199
Figure 3-97. MSTP General Page 200
Figure 3-98. MSTP Instance Settings Page 201
Figure 3-99. MSTP Interface Settings Page 203
Figure 3-100. VLAN Basic Information Page 207
Figure 3-101. Current Table Page 209
Figure 3-102. Interface Configuration Page 211
Figure 3-103. Customer Multicast TV VLAN Page 212
Figure 3-104. CPE VLANs Mapping Page 213
Figure 3-105. MAC-Based Groups Page 214
Figure 3-106. Subnet-Based Groups Page 215
Figure 3-107. Protocol Based Groups Page 216
Figure 3-108. Mapping Groups to VLAN Page 217
Figure 3-109. GARP Configuration Page 218
Figure 3-110. GVRP Parameters Page 220
Figure 3-111. GVRP Statistics Page 221
Figure 3-112. IGMP Snooping Page 225
Figure 3-113. Multicast Group Page 226
Figure 3-114. Multicast Forward All Page 228
Figure 3-115. IGMP Snooping Mapping Page 229
Figure 3-116. Multicast TV Membership Page 230
Figure 3-117. CoS Mode Page 236
Figure 3-118. Queue Priority Page 237
Figure 3-119. Bandwidth Configuration Page 239
Figure 3-120. VLAN Rate Limit Page 240
Figure 3-121. CoS to Queue Page 241
Figure 3-122. DSCP Priority Page 242
Figure 3-123. QoS General Page 243
Figure 3-124. DSCP Rewrite Page 244
Figure 3-125. DSCP Mapping Page 245
Figure 3-126. Class Map Page 246
Figure 3-127. Aggregate Policer Page 247
Figure 3-128. Tail Drop Page 248
Figure 3-129. Policy Table Page 249
Figure 3-130. Policy Binding Page 251
Figure 1. VLAN Basic Information Page 704
Figure 2. Add 802.1q VLAN Page 705
xxiii
Page 24

Figures
Figure 3. VLAN Interface Configuration Page 705
Figure 4. Modify VLAN Interface Configuration Page 706
Figure 5. VLAN Current Table 707
Figure 6. QinQ Configuration Example 707
Figure 7. Triple Play Configuration 709
Figure 8. Add VLAN Membership Page 712
Figure 9. CPE VLAN Mapping Page 713
Figure 10. CPE VLAN Mapping Page 714
Figure 11. VLAN Interface Settings Page 715
Figure 12. Customer Multicast TV VLAN Page 716
Figure 13. VLAN Basic Information Page 717
Figure 14. Add VLAN Page 717
Figure 15. VLAN Interface Configuration Page 718
Figure 16. Modify VLAN Interface Configuration Page 718
Figure 17. VLAN Current Table 719
xxiv
Page 25

Chapter 1: Introduction
The OmniStack® 62 00 series has seven platforms:
• OS-LS-6212 –
combo uplink ports (with SFP or 10/100/1000Base-TX interfaces) and two ports
full-duplex Gigabit stacking
• OS-LS-6212P –
standard-based Power over Ethernet, two Gigabit combo uplink ports (with SFP or 10/
100/1000Base-TX interfaces) and two ports full-duplex Gigabit stacking
• OS-LS-6224 – Ethernet based switch with 24 RJ-45 10/100Base-TX ports, two
Gigabit combo uplink ports (with SFP or 10/1 00/1000Base-TX interf aces) and two
ports full-duplex Gigabit stacking (optional DC power source)
• OS-LS-6224P – Ethernet based switch with 24 RJ-45 10/100Base-TX ports
providing standard-based Power over Ethernet, two Gigabit combo uplink ports
(with SFP or 10/100/1000Base-TX interfaces) and two ports full-duplex Gigabit
stacking
• OS-LS-6248 – Ethernet based switch with 48 RJ-45 10/100Base-TX ports, two
Gigabit combo uplink ports (with SFP or 10/1 00/1000Base-TX interf aces) and two
ports full-duplex Gigabit stacking (optional DC power source)
• OS-LS-6248P – Ethernet based switch with 48 RJ-45 10/100Base-TX ports
providing standard-based Power over Ethernet, two Gigabit combo uplink ports
(with SFP or 10/100/1000Base-TX interfaces) and two ports full-duplex Gigabit
stacking
• OS-LS-6224U – Ethernet based switch with 24 100Base-FX external SFP ports,
two Gigabit combo ports with assicuated Mini-GBIC slots or RJ-45 ports and two
1000Base-T stacking ports
All devices have a management port which is used for debuggi ng an d manag ement
purposes.
This switch provides a broad range of features for switching. It includes a
management agent that allows you to configure the features listed in this manual.
The default configuration can be used for most of the features provided by t his
switch. However, there are many options that you should configure to maximize the
switch’s performance for your particular network environment.
Ethernet based switch with 12 RJ-45 10/100Base-TX ports, two Gigabit
Ethernet based switch with 12 RJ-45 10/100Base-TX ports providing
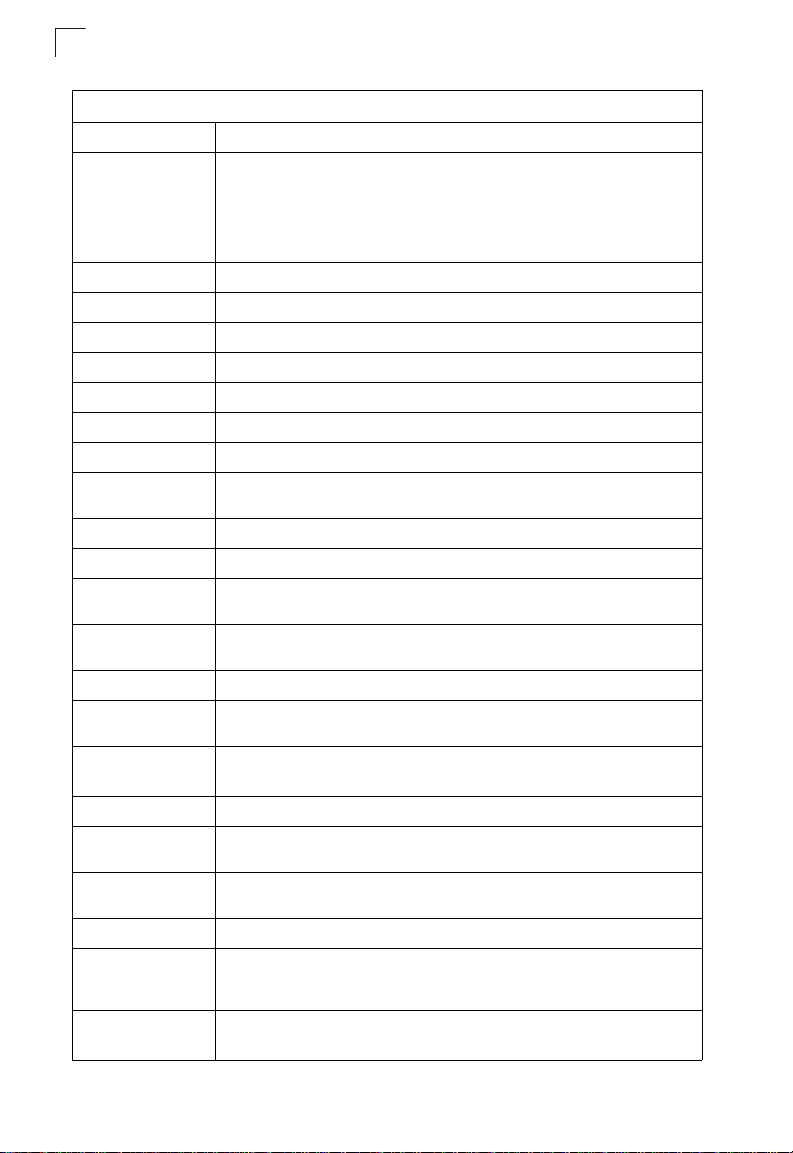
Key Features
Feature Description
Configuration Backup
and Restore
Backup to TFTP server
Table1-1. Key Features
1
Page 26
Introduction
1
Table1-1. Key Features
Feature Description
Authentication Console, Telnet, web – User name / password, RADIUS, TACACS+
Web – HTTPS; Telnet – SSH
SNMP v1/2c - Community strings
SNMP version 3 – MD5 or SHA password
Port – IEEE 802.1x
Access Control Lists Supports up to 1K IP or MAC ACLs
DHCP Client Supported
DNS Server Supported
Port Configuration Speed, duplex mode and flow control
Rate Limiting Input and output rate limiting per port
Port Mirroring One or more ports mirrored to single analysis port
Port Trunking Supports up to 8 trunks using either static or dynamic trunking (LACP)
Broadcast Storm
Control
Static Address Up to 16K MAC addresses in the forwarding table
IEEE 802.1D Bridge Supports dynamic data switching and addresses learning
Store-and-Forward
Switching
Spanning Tree
Protocol
Virtual LANs Up to 255 using IEEE 802.1Q, port-based, protocol-based, or private VLANs GVRP
Traffic Prioritization Default port priority, traffic class map, queue scheduling, IP Precedence, or
STP Root Guard Prevents devices outside the network core from being assigned the
STP BPDU Guard Used as a security mechanism to protect the network from invalid configurations.
802.1x - MAC
Authentication
DHCP Snooping Expands network security by providing a firewall security between untrusted
DHCP Option 82 Enables to add information for the DHCP server on request.
IP Source Address
Guard
ARP Inspection Classic Address Resolution Protocol is a TCP/IP protocol that translates IP
Supported
Supported to ensure wire-speed switching while eliminating bad frames
Supports standard STP, Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), Multiple Spanning
Trees (MSTP).
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) and TCP/UDP Port
spanning tree root.
MAC authentication ensures that end-user stations meet security policies criteria,
and protects networks from viruses.
interfaces and DHCP servers.
Restricts IP traffic on non-routed, Layer 2 interfaces by f ilterin g traffic. This feature
is based on the DHCP snooping binding database and on manually configured IP
source bindings.
addresses into MAC addresses.
2
Page 27
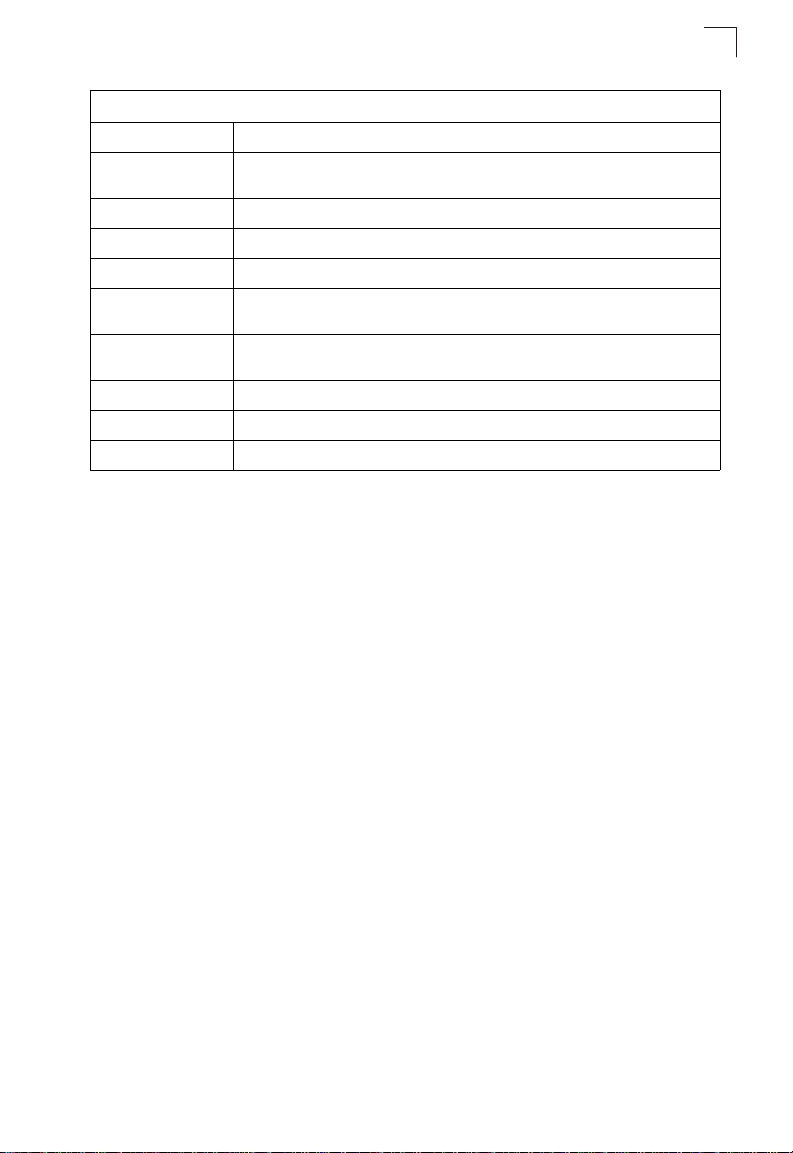
Description of Software Features
Table1-1. Key Features
Feature Description
LLDP-MED Increases network flexibility by allowing different IP systems to co-exist on a single
QoS Supports Quality of Service (QoS).
Multicast Filtering Supports IGMP snooping and query.
Power over Ethernet Enables PoE support.
Multicast TV VLAN Supplies multicast transmissions to L2-isolated subscribers, without replicating the
IP Subnet-Based
VLANs
MAC-Based VLANs Packets are classified according to MAC address
Jumbo Frames Support of mini jumbo frames allows forwarding of packets up to 1632 bytes.
QinQ Allows network managers to add an additional tag to previously tagged packets
network.
multicast transmissions for each subscriber VLAN.
Packets are classified according to the packet’s source IP subnet in its IP header
1
Description of Software Features
The switch provides a wide range of advanced performance enhancing features.
Flow control eliminates the loss of packets due to bottlenecks caused by port
saturation. Broadcast storm suppression prevents broadcast traffic storms from
engulfing the network. Port-based and protocol-based VLANs, plus support for
automatic GVRP VLAN registration provide traffic security and efficient use of
network bandwidth. CoS priority queueing ensures the minimum delay for moving
real-time multimedia data across the network. While multicast filtering provides
support for real-time network applications. Some of the management features are
briefly described below.
Configuration Backup and Restore – You can save the current configuration
settings to a file on a TFTP server, and later download this file to restore the switch
configuration settings.
Authentication – This switch authenticates management access via the console
port, T eln et or web browser . User names and pa sswords can be configured locally or
can be verified via a remote authentication server (i.e., RADIUS or TACACS+).
Port-based and MAC-based authentication is also supported via the IEEE 802.1x
protocol. This protocol uses the Extensible Authentication Protocol over LANs
(EAPOL) to request user credentials from the 802.1x client, and then verifies the
client’s right to access the network via an authentication server.
Other authentication options include HTTPS for secure management ac cess via t he
web, SSH for secure management access over a Telnet-e quivalent connection,
SNMP version 3, IP address filtering for SNMP/web/Telnet management access,
and MAC address filtering for port access.
3
Page 28

Introduction
1
MAC Address Capacity Support – The device supports up to 16K MAC
addresses. The device reserves specific MAC addresses for system use.
Self-Learning MAC Addresses – The device enables automatic MAC addresses
learning from incoming packets.
Automatic Aging for MAC Addresses – MAC addresses from which no traffic is
received for a given period are aged out. This prevents the Bridging Table from
overflowing.
Static MAC Entries – User defined static MAC entries are stored in the Bridging
Table, in addition to the Self Learned MAC addresses.
VLAN-Aware MAC-based Switching – Packets arriving from an unknown source
address are sent to the CPU. When source addresses are added to the Hardware
Table, packets addressed to this address are then forwarded straight to
corresponding port.
MAC Multicast Support – Multicast service is a limited broadcast service, which
allows one-to-many and many-to-many connections for information distribut ion.
Layer 2 multicast service is where a single frame is address ed to a speci fic multicast
address, and copies of the frame transmitted to relevant all relevan t ports.
Address Resolution Protocol –
switches to inter-communicate using various routing protocols to discover network
topology and define Routing tables. Device Next-Hop MAC addresses are
automatically derived by ARP. This includes directly attached end systems. Users can
override and supplement this by defining additional ARP Table entries.
QinQ tagging – QinQ tagging allows network managers to add an additional tag to
previously tagged packets. Adding additional tags to the packets helps create more
VLAN space. The added tag provides an VLAN ID to each customer, this ensures
private and segregated network traffic.
Port Configuration – You can manually configure the speed, duplex mode, and
flow control used on specific ports, or use auto-negotiation to detect the connection
settings used by the attached device. Use the full-duplex mode on ports whenever
possible to double the throughput of switch connecti ons. Flow control should also be
enabled to control network traffic during periods of congestion and prevent the loss
of packets when port buff er thresholds are exceeded. The switch supports flow
control based on the IEEE 802.3x standard.
Rate Limiting – This feature controls the maximum rate for traffic transmitted or
received on an interface. Rate limiting is configured on interfaces at the edge of a
network to limit traffic into o r out of the network. T r affic th at falls within t he rate limit is
transmitted, while packets that exceed the acceptable amount of traffic are dropped.
Port Mirroring – The switch can unobtrusively mirror traffic from any port to a
monitor port. You can then attach a protocol analyzer or RMON probe to this port to
perform traffic analysis and verify connection integrity.
Port Trunking – Ports can be combined into an aggregate connection. Trunks can
be manually set up or dynamically configured using I EEE 802. 3ad Lin k Ag gregatio n
IP routing generally utilizes routers and Layer 3
4
Page 29

Description of Software Features
Control Protocol (LACP). The additional ports dramatically increase the throughput
across any connection, and provide redundancy by taking over the load if a port in
the trunk should fail. The switch supports up to 6 trunks.
Broadcast Storm Control – Broadcast s uppress ion preve nts broadcast traffic from
overwhelming the network. When enabled on a port, the level of broadcast traffic
passing through the port is restricted. If broadcast traffic rises above a pre-defined
threshold, it will be throttled until the level falls back beneath the threshold.
Static Addresses – A st atic MAC address ca n be assigned to a specific inte rface on
this switch. Static addresses are bound to the assigned interface and will not be
moved. When a static address is seen on another interface, the address will be
ignored and will not be written to th e a ddress table. Static addresses can be used to
provide network security by restricting access for a known host to a specific port.
STP BPDU Guard – Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDU) Guard expands network
adminstrator’s ablility to enforce STP borders and maintain STP top ologies
realibility. BPDU is utilized when Fast Link ports is enabled and/or if the Spanning
Tree Protocol is disabled on ports. If a BPDU message is sent to a port on which
STP is disabled, BPDU Guard shuts down the port, and generates a SNMP
message.
STP Root Guard – Spanning Tree Root Guard is used to prevent an unauthorized
device from becoming the root of a spanning tree. Root guard functionality enables
detection and resolution of misconfigurations, while preventing loops or loss of
connectivity.
802.1x - MAC Authentication – MAC authentication like the 802.1X allows network
access to a device, for example, printers and IP phones, that do not have the 802.1X
supplicant capability. MAC authentication uses the MAC address of the connecting
device to grant or deny network access.
To support MAC authentication, the RADIUS authentication server maintains a
database of MAC addresses for devices that require access to th e netwo rk. In order
for the feature to be active, 802.1x must be in auto-mode.
User then can enable the MAC authentication feature in one of following modes:
• MAC Only – Where only MAC authentication is enabled
• MAC + 802.1x (In that case 802.1x takes precedence)
The feature can be enabled per port. The port must be a member of a guest VLAN
prior of activating the feature.
DHCP Snooping – DHCP Snooping expands network security by providing a
firewall security between untrusted interfaces and DHCP serv ers. By enabling
DHCP Snooping network administrators can identify between trusted interfaces
connected to end-users or DHCP Servers, and untrusted interface located beyond
the network firewall. DHCP Snooping creates and maintains a DHCP Snooping
Table which contains information received from untrusted packets. Interfaces are
untrusted if the packet is received from an interface from out side the network or from
a interface beyond the network firewall.
1
5
Page 30

Introduction
1
DHCP Option 82 – DHCP server can insert information into DHCP requests. The
DHCP information is used to assign IP addresses to network interfaces.
IP Source Address Guard – IP source guard stops malignant network users from
using unallocated network IP addresses. IP Sou rce Guard ensures that only packet s
with an IP address stored in the DHCP Database are forwarded. IP address stored
in the DHCP Snooping Database are either statically configured by the network
administrator or are retrieved using DHCP. IP source guard can be enabled only on
DHCP snooping untrusted interface.
Dynamic ARP Inspection – ARP Inspection eliminates man-in-the-middle attacks,
where false ARP packets are inserted into the s ubnet. ARP req uests and responses
are inspected, and their MAC Address to IP Address binding is checked. Packets
with invalid ARP Inspection Bindings are logged and dro pped. Packet s are classified
as:
• Trusted — Indicates that the interface IP and MAC address are recognized, and
recorded in the ARP Inspec-tion List. Trusted packets are forward without ARP
Inspection.
• Untrusted — Indicates that the packet arrived fro m an interface that does no t have
a recognized IP and MAC addresses. The packet is checked for:
• Source MAC — Compares the packet’s source MAC address against the
sender’s MAC address in the ARP request. This check is performed on both
ARP requests and responses.
• Destination MAC — Compares the packet’s destination MAC address again st
the destination interface’s MAC address. This check is performed for ARP
responses.
• IP Addresses — Compares the ARP body for invalid and unexpected IP
addresses. Addresses include 0.0.0.0, 255.255.255.25 5, a nd al l I P Multi cas t
addresses. If the packet’s IP address was not found in the ARP Inspection
List, and DHCP snooping is enabled for a VLAN, a search of the DHCP
Snooping Database is performed. If the IP address i s found the packet is valid,
and is forwarded. ARP inspection is performed only on untrusted interfaces.
LLDP - The Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) allows network managers to
troubleshoot and enhance network management by discovering and maintaining
network topologies over multi-vendor environments. LLDP discovers network
neighbors by standardizing methods for network devices to advertise themselves to
other system, and to store discovered information. Device discovery information
includes:
• Device Identification
• Device Capabilities
• Device Configuration
The advertising device transmits multiple advertisement message sets in a single
LAN packet. The multiple advertisement sets are sent in the packet Type Length
Val ue (TLV) field. LLDP devices must support chassis and port ID advertisement, as
well as system name, system ID, system description, and system capability
6
Page 31

Description of Software Features
advertisements
LLDP-MED – LLDP Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED) increases network
flexibility by allowing different IP systems to co-exist on a single network. Provides
detailed network topology information, including what device are located on the
network, and where the devices are located. For example, which IP phone is
connect to what port, which software is running on what switch, and which port is
connected to what PC.
Spanning Tree Protocol – The switch supports these spanning tree protocols:
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP, IEEE 802.1D) – This protocol adds a level of fault
tolerance by allowing two or more redundant connections to be created between a
pair of LAN segments. When there are multiple physical paths between segments,
this protocol will choose a single path and disable all others to ensure that only one
route exists between any two stations on the network. This prevents the creation of
network loops. However, if the chosen path should fail for any reason, an alternate
path will be activated to maintain the connection.
Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP, IEEE 802.1w) – This protocol reduces the
convergence time for network topology changes to about 10% of tha t required by the
older IEEE 802.1D STP standard. It is intended as a compl ete replac ement fo r STP,
but can still interoperate with switches running the older standard by automatically
reconfiguring ports to STP-compliant mode if they detect STP protocol messages
from attached devices.
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP, IEEE 802.1s) – This protocol is a direct
extension of RSTP. It can provide an independent spanning tree for dif ferent VLANs.
It simplifies network management, provides for even faster conv ergence than RSTP
by limiting the size of each region, and prevents VLAN members from being
segmented from the rest of the group (as sometimes occurs with IEEE 802 .1D STP).
Virtual LANs – The switch supports up to 255 VLANs. A Virtual LAN is a collection
of network nodes that share the same broadcast domain rega rdless of the ir physical
location or connection point in the network. The switch supports tagged VLANs
based on the IEEE 802.1Q standard. Members of VLAN groups can be dynamically
learned via GVRP, or ports can be manually assigned to a specific set of VLANs.
This allows the switch to restrict traffic to the VLAN groups to which a user has been
assigned. By segmenting your network into VLANs, you can:
• Eliminate broadcast storms which severely degrade performance in a flat network.
• Simplify network management for node changes/moves by remotely configuring
VLAN membership for any port, rather than having to manually change the network
connection.
• Provide data security by restricting all traffic to the originating VLAN.
• Use private VLANs to restrict traffic to pass only between data ports and the upli nk
ports, thereby isolating adjacent ports within t he s ame VL AN, and al l owing you to
limit the total number of VLANs that need to be configured.
•
Use protocol VLANs to restrict traffic to specified interfaces based on protocol type.
1
7
Page 32

Introduction
1
Traffic Prioritization – This switch prioritizes each packet based on the requi red
level of service, using eight priority queues with strict or Weighted Round Robin
Queuing. It uses IEEE 802.1p and 802.1Q tags to prioritize inc oming traffic based on
input from the end-station application. These functions can
independent priorities for delay-sensitive data and best-effort data.
This switch also supports several common methods of prioritizing layer 3/4 traffic to
meet application requirements. Traffic can be prioritized based on the priority bits in
the IP frame’s Type of Service (ToS) octet or the number of the TCP/UDP port.
When these services are enabled, the priorities are mapped to a Class of Service
value by the switch, and the traffic then sent to the corresponding output queue.
Multicast Filtering – Specific mul ticast traffic can be assigned to it s own VLAN to
ensure that it does not interfere with normal network traffic and to guarantee
real-time delivery by setting the required priority level for the designated VLAN. The
switch uses IGMP Snooping and Query to manage multicast group registration.
Virtual Cable Testing (VCT) – VCT
occurrences, such as open cables and cable shorts.
MDI/MDIX Support – The device supports auto-detection between crossed and
straight-through cables. S tandard wiring for end stations is Media-Dependent
Interface (MDI) and the standard wiring for hubs and switches is known as
Media-Dependent Interface with Crossover (MDIX).
Quality of Service (QoS) Support – Network traffic is usually unpredictable, and
the only basic assurance that can be offered is Best Effort traffic delivery. To
overcome this challenge, Quality of Service (QoS) is applied throughout th e net wo rk.
This ensures that network traffic is prioritized accord ing to specified crit eria, and that
specific traffic receives preferen tial treat ment. QoS in the network opti mizes network
performance. The device supports the following QoS modes:
•Basic
• Advanced
Class Of Service 802.1p Support – The IEEE 802.1p signaling technique is an OSI
Layer 2 standard for marking and prioritizing network traffic at the data link/MAC
sub-layer. 802.1p traffic is classified and sent to the destination. No bandwidth
reservations or limits are established or enforced. 802.1p is a spin-off of the 802.1Q
(Vlans) standard. 802.1p establishes eight levels of priority, similar to the IP
Precedence IP Header bit-field.
Quality of Service Basic Mode – In the Basic QoS mode, it i s possible to a ctivate a
trust mode (to trust VPT, DSCP, TCP/UDP or none). In addition, a single Access
Control List can be attached to an interface.
Web Based Management – With web based management, the system can be
managed from any web browser. Th e s ystem contains an Embedded Web Server
(EWS), which serves HTML pages, through which the system can be monitored an d
configured. The system internally converts web-based input into configuration
commands, MIB variable settings and other management-related settings.
detects and reports copper link cabling
be used to provide
8
Page 33

System Defaults
Remote Monitoring – Remote Monitoring (RMON) is an extension to SNMP,
which provides comprehensive network traff ic mon itoring cap abilities (a s opposed to
SNMP which allows network device management and monitoring). RMON is a
standard MIB that defines current and historical MAC-layer statistics and control
objects, allowing real-time information to be cap tured across the entire network.
VLAN Groups – Provides VLAN classification by MAC address, subnet , and
protocol groups.
Multicast TV – Supplies multicast transmis sions to L2-isolated subscribers, without
replicating the multicast transmissions for each subscriber VLAN
Port Based Authentication – Port based authentication enables authenticating
system users on a per-port basis via an external server. Only authenticated and
approved system users can transmit and receive data. Ports are authenticated via
the Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS) server using the
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP).
1
System Defaults
The device is configured with default settings. To reset the device to the default
settings, delete the startup configura tion. The following table lists some of the basic
system defaults.
Table1-2. System Defaults
Function Parameter Default
Console Port
Connection
Authentication Privileged Exec Level no password
Baud Rate 9600
Data bits 8
Stop bits 1
Parity 0
Local Console Timeout 10
Normal Exec Level no password
Enable Privileged Exec from Normal
Exec Level
RADIUS Authentication disabled
TACACS Authentication disabled
802.1x Port Authentication disabled
HTTPS disabled
SSH disabled
Port Security disabled
no password
9
Page 34

Introduction
1
Table1-2. System Defaults
Function Parameter Default
SNMP Community Strings no SNMP communities
Traps disabled
SNMP V3 View:
Port Configuration Admin Status enabled
Auto-negotiation on
Flow Control off
Port Capability list of all capabilities on port
AMAP Status enabled
Common Phase Timeout Interval 300 sec.
Discovery Phase Timeout Interval 30 sec.
Rate Limiting Input and output limits disabled
Port Trunking Static Trunks up to 8 port in 8 trunks can be defined
LACP system priority 1
LACP Port-priority 1
LACP long
Broadcast Storm
Protection
Spanning Tree
Protocol
Address Table Aging Time 300 seconds
Virtual LANs Default VLAN 1
Status disabled
Broadcast Limit Rate 100 kbps
Status enabled
Spanning Tree Mode STP
Fast Forwarding (Edge Port) enabled
PVID 1
Acceptable Frame Type all
Ingress Filtering on
Switchport Mode (Egress Mode) hybrid (tagged/untagged)
GVRP (global) disabled
GVRP (port interface) disabled
local engine ID of device is comprised of
IANA Private Enterprise number & MAC
address of device
10
Page 35

Table1-2. System Defaults
Function Parameter Default
Quality of Service QoS Mode disabled
CoS Mapping Cos 0 - queue 1; CoS 1 - queue 1; Cos 2 -
Scheduling all queues are expedite queues
IP Settings IP Address none
Subnet Mask none
Default Gateway none
DHCP disabled
BOOTP enabled if configuration is empty and there is
DNS Server Domain Lookup enabled
Multicast Filtering IGMP Snooping disabled
System Log S ta tu s on
Messages Logged 200
Messages Logged to Flash 200
SNTP Clockset 0:00 Jan 1, 2000
Clock source internal
Daylight Savings disabled
SNTP no servers defined
Port Security Port Lock disabled
DHCP Snooping disabled
DHCP Option 82 disabled
STP BPDU Guard disabled
ARP Inspection disabled
IP Source Address Guard disabled
Root Guard disabled
Multicast Forwarding IGMP Snooping (Global) disabled
IGMP Snooping (Interface) disabled
Multicast TV VLAN disabled
SSH Server enabled
queue 1
Cos 3 - queue 1; CoS 4 - queue 2; Cos 5 queue 2
Cos 6 - queue 3; CoS 7 - queue 3;
no command line activity within 60 seconds
System Defaults
1
11
Page 36

Introduction
1
Table1-2. System Defaults
Function Parameter Default
SSL Server enabled
RADIUS RADIUS server none defined
TACACS+ TACACS+ server none defined
12
Page 37

Chapter 2: Initial Configuration
This section describes the initial device configuration and includes the following
topics:
• General Configuration Information
• Booting the Switch
• Configuration Overview
• Advanced Configuration
• Software Download and Reboot
• Startup Menu Functions
After completing all external connections, connect a terminal to the device to monitor
the boot and other procedures. The order of installation and configuration
procedures is illustrated in the following figure. For the initial configuration, the
standard device configuration is performed. Other functio ns can be performed, but
doing so suspends the installation process and causes a system reboot.
Performing other functions is described later in this section.
13
Page 38

2
Initial Configuration
Figure 2-1. Installation and Configuration
General Configuration Information
Your device has predefined features and setup configuration.
14
Page 39

General Configuration Information
2
Auto-Negotiation
Auto-negotiation allows a device to advertise modes of operation and share
information with another device that shares a point-to-point link segment. This
automatically configures both devices to take maximum advantage of their abilities.
Auto-negotiation is performed completely within the physical layers during link
initiation, without any additional overhead to either the MAC or higher protocol
layers. Auto-negotiation allows the ports to do th e following:
• Advertise their abilities
• Acknowledge receipt and understanding of the common modes of operation that
both devices share
• Reject the use of operational modes that are not shared by both devices
• Configure each port for the highest-level operation al mode that both ports can
support
If connecting a port of the switch to the network interface card (NIC) of a terminal
that does not support auto-negotiation or is not set to auto-negotiation, both the
device port and the NIC must be manual ly set wi th the Web browser interfa ce or CLI
commands to the same speed and duplex mode.
Note:
If the station on the other side of the link attempts to auto-negotiate with a port that
is manually configured to full duplex, the auto-negotiation results in the station
attempting to operate in half duplex. The resulting mismatch may lead to
significant frame loss. This is inherent in the auto-negotiation standard.
Device Port Default Settings
The following table describes the device port default settings.
Function Default Settings
Port speed and mode 100 M or 1000M Auto-negotiation
Port forwarding state Enabled
Head of line blocking prevention On (Enabled)
Flow Control Off
Back Pressure Off
These default settings can be modified once the device is installed.
Note:
The following is an example for changing the port speed on port g1 using CLI
commands:
Console (config)# interface ethernet g1 4-376
Console (config-if)#
speed 100 4-380
15
Page 40

2
Initial Configuration
The following is an example for enabling flow control on port e1 using CLI
commands:
Console (config)# interface ethernet e1 4-376
Console (config-if)#
flowcontrol on 4-383
The following is an example for enabling back pressure on port e1 using CLI
commands.
Console (config)#
Console (config-if)#
Console (config-if)#
interface ethernet e1 4-376
speed 10 4-380
back-pressure 4-384
Booting the Switch
To boot the switch, perform the following:
1. Ensure that the device console is connected to a VT100 terminal device or
VT100 terminal emulator.
2. Deactivate the AC power receptacle.
3. Connect the device to the AC receptacle.
4. Activate the AC power receptacle.
When the power is turned on with the local terminal already connect ed, the switch
goes through Power On Self Test (POST). POST runs every time the device is
initialized and checks hardware components to determine if the device is fully
operational before completely booting. If a critical problem is detected, the program
flow stops. If POST passes successfully, a valid executable image is loaded into
RAM. POST messages are displayed on the terminal and indicate test success or
failure.
As the switch boots, the bootup test first counts the device memory availability and
then continues to boot. The following screen is an example of the displayed POST.
------ Performing the Power-On Self Test (POST) ------
Boot1 Checksum Test...............................PASS
Boot2 Checksum Test...............................PASS
Flash Image Validation Test.......................PASS
BOOT Software Version x.x.x.xx Built 07-Jan-200x 10:53:05
Processor: xxxxxx xxxxx xxxx, xx MByte SDRAM.
I-Cache 8 KB. D-Cache 8 KB. Cache Enabled.
Autoboot in 2 seconds - press RETURN or Esc. to abort and enter prom.
The boot process runs approximately 30 seconds.
16
Page 41

Booting the Switch
2
The auto-boot message that appears at the end of POST (see the last lines)
indicates that no problems were encountered during boot.
During boot, the St artup menu can be accessed if necessary to run special
procedures. To enter the Startup menu, press <Esc> or <Enter> within the first two
seconds after the auto-boot message is displayed. For information on the Startup
menu, see "Startup Menu Functions."
If the system boot is not interrupted by pressing <Esc> or <Enter>, the system
continues operation by decompressing and loading the code into RAM. The code
starts running from RAM and the list of numbered system ports and their states (up
or down) are displayed.
Note:
The following screen is an example configuration. Items such as addresses,
versions, and dates may differ for each device.
Preparing to decompress...
Decompressing SW from image-1
638000
OK
Running from RAM...
*********************************************************************
*** Running SW Ver. x.x.x.x Date 11-Jan-200x Time 15:43:13 ***
*********************************************************************
HW version is
Base Mac address is: 00:00:b0:24:11:80
Dram size is: xxM bytes
Dram first block size is: 47104K bytes
Dram first PTR is: 0x1200000
Flash size is: xM
Devices on SMI BUS:
------------------smi dev id = 16, dev type=0xd0411ab, dev revision=0x1
Device configuration:
Prestera based - Back-to-back system
Slot 1 - DB-DX240-24G HW Rev. xx.xx
Tapi Version: xx.x.x-x
Core Version: xx.x.x-x
01-Jan-200x 01:01:22 %INIT-I-InitCompleted: Initialization task is
completed
Console> 01-Jan-200x 01:01:23 %LINK-I-Up: e1
01-Jan-200x 01:01:23 %LINK-W-Down: e2
01-Jan-200x 01:01:23 %LINK-I-Up: Vlan 1
01-Jan-200x 01:01:23 %LINK-W-Down: e4
.
.
.
01-Jan-200x 01:01:23 %LINK-W-Down: e46
01-Jan-200x 01:01:23 %LINK-W-Down: e47
01-Jan-200x 01:01:23 %LINK-W-Down: e48
After the switch boots successfully, a system prompt appears (console>) and the
local terminal can be used to begin configuring the switch. However, before
17
Page 42

2
Initial Configuration
configuring the switch, ensure that the sof tware version inst alled on the devi ce is the
latest version. If it is not the latest version, down load and install the latest version.
See "Software Download and Reboot."
Configuration Overview
Before assigning a static IP address to the device, obtain the following information
from the network administrator:
• A specific IP address allocated by the network administrator for the switch to be
configured
• Network mask for the network
There are two types of configuration: Initial configuration consists of configuration
functions with basic security considerations, whereas advanced configuration
includes dynamic IP configuration and more advanced security considerations.
After making any configuration changes, the new configuration must be saved
before rebooting. To save the configuration, enter the following CLI command:
Console# copy running-config startup-config 4-365
Initial Configuration
Initial configuration, which starts after the device has booted successfully, includes
static IP address and subnet mask configuration, and setting user name and
privilege level to allow remote management. If the device is to be managed from an
SNMP-based management station, SNMP community strings must also be
configured. The following configurations are completed:
• Static IP Address and Subnet Mask
• Static Route Configuration
•User Name
• SNMP Community strings
Static IP Address and Subnet Mask
IP interfaces can be configured on each interface of the device. After entering the
configuration command, it is recommended to check if a interface was configured
with the IP address by entering the show ip interface command.
The commands to configure the device are interface specific.
To manage the switch from a remote network, a static route must be configured,
which is an IP address to where packets are sent when no entries are found in the
device tables. The configured IP address must belo ng to the same subne t as one of
the device IP interfaces.
18
Page 43

Initial Configuration
2
T o confi gure a static route, enter the command at the system prompt as shown in the
following configuration example where 101.1.1.2 is the speci fic management stati on:
Console# configure
Console(config)# interface vlan 1 4-664
Console(config-if)#
Console(config-if)#
Console(config)#
ip address 100.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 4-418
exit 4-656
ip default-gateway 100.1.1.10 4-420
.
Gateway IP Address
Gateway IP
Address
10.7.1.1 Static Active
IP Address Interface Type
----------- ----------- -------------
10.7.1.192/24 VLAN1 static
10.7.2.192/24 VLAN2 DHCP
Type Activity Status
User Name
A user name is used to manage the device remotely, for example through SSH,
Telnet, or the Web interface. To gain complete administrative (super-user) control
over the device, the highest privilege level 15 must be specif ied.
Note:
Only the administrator (super-user) with the highest privilege level (15) is allowed
to manage the device through the Web browser interface.
For more information about the privilege level, see the Command Line Interface.
The configured user name is entered as a login name for remote management
sessions. To configure user name and privilege level, enter the command at the
system prompt as shown in the configuration example:
Console> enable
Console# configure
Console(config)# username admin password lee privilege 15
SNMP Community Strings
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) provides a method for managing
network devices. Devices supporting SNMP run a local software (agent ). The SNMP
agents maintain a list of variables, used to manage the device. The variables are
defined in the Management Information Base (MIB). The MIB present s the variables
controlled by the agent. The SNMP agent defines the MIB specification format, as
well as the format used to access the information over the network.
Access rights to the SNMP agents are controlled by access strings and SNMP
community strings.
The device is SNMP-compliant and contains an SNMP agent that supports a set of
standard and private MIB variables. Developers of management st ations require t he
19
Page 44

2
Initial Configuration
exact structure of the MIB tree and receive the complete private MIBs information
before being able to manage the MIBs.
All parameters are manageable from any SNMP management platform, except the
SNMP management station IP address and community (community name and
access rights). The SNMP management access to the switch is disabled if no
community strings exist.
Note:
The device switch is delivered with no community strings configured.
The following screen displays the default device configuration:
Console#
Community-String Community-Access IP address
---------------- ---------------- ----------
System Contact:
System Location:
show snmp 4-531
The community-string, community-access, and IP address can be configured
through the local terminal during the initial configuration procedure.
The SNMP configuration options for the Community String are as follows:
• Access rights options: ro (read only), rw (read-and-write) or su (super).
• An option to configure IP address or not: If an IP address is not configured, it
means that all community members having the same community name a re granted
the same access rights.
Common practice is to use two community strings for the switch one (public
community) with read-only access and the other (priva te community) with re ad-write
access. The public string allows authorized management stations to retrieve MIB
objects, while the private string allows authorized management statio ns to retrieve
and modify MIB objects.
During initial configuration, it is recommended to configure the device according to
the network administrator requirements, in accordance with using an SNMP-based
management station.
To configure SNMP station IP address and community string(s) perform the
following:
1. At the console prompt, enter the command Enable. The prompt is disp layed as
#.
2. Enter the command configure and press <Enter>.
3. In the configuration mode, enter the SNMP configuration command with the
parameters including community name (privat e), community access right (read
and write) and IP address, as shown in the following example:
20
Page 45

Advanced Configuration
Console# configure
Config(config)# snmp-server community private rw 11.1.1.2 type
router 4-519
Config(config)#
Console(config)#
Community-String Community-Access IP address
---------------- ---------------- ----------
private readWrite 11.1.1.2
Traps are enabled.
Authentication-failure trap is enabled.
Trap-Rec-Address Trap-Rec-Community Version
---------------- ------------------ -------
System Contact:
System Location:
exit 4-656
show snmp 4-531
2
This completes the initial configuration of the device from a local terminal. The
configured parameters enable furth er dev ice con figurat io n fr om an y remote loc ati on.
Advanced Configuration
This section provides information about dynamic allocation of IP addresses and
security management based on the authentication, authorization, and accounting
(AAA) mechanism, and includes the following topics:
• Configuring IP Addresses through DHCP
• Configuring IP Addresses through BOOTP
• Security Management and Password Configuration
When configuring/receiving IP addresses through DHCP and BOOTP, the
configuration received from these servers includes the IP address, and may include
subnet mask and default gateway.
Retrieving an IP Address From a DHCP Server
When using the DHCP protocol to retrieve an IP address, the device acts as a
DHCP client. To retrieve an IP address from a DHCP server, perform the following
steps:
1. Select and connect any port to a DHCP server or to a subnet that has a DHCP
server on it, in order to retrieve the IP address.
2. Enter the following commands to use the selected port for receiving the IP
address. In the following example, the commands are based on the port type
used for configuration.
21
Page 46

2
Initial Configuration
• Assigning Dynamic IP Addresses:
console# configure
console(config)# interface ethernet e1 4-376
console(config-if)#
console(config-if)#
console(config)#
ip address dhcp hostname sales 4-419
exit 4-656
The interface receives the IP address automatically.
3. To verify the IP address, enter the show ip interface command at the system
prompt as shown in the following example.
Console#
Gateway IP
Address
-------- ------ ---------------
10.7.1.1 Static Active
IP address Interface Type Directed Broadcast
------------- --------- ------- --------
10.7.1.192/24 VLAN 1 Static
Notes: 1.
show ip interface
Type Activity status
The device configuration does not have to be deleted to retrieve an IP
address for the DHCP server.
2. When copying configuration files, avoid using a configuration file that
contains an instruction to enable DHCP on an interface that connects to the
same DHCP server, or to one with an identical configuration. In this instance,
the switch retrieves the new configuration file and boots from it. The device
then enables DHCP as instructed in the new configuration file, and the
DHCP instructs it to reload the same file again.
Receiving an IP Address From a BOOTP Server
The standard BOOTP protocol is supported and enables the swi t ch to aut omatic all y
download its IP host configuration from any stan dard BOOTP server in t he network.
In this case, the device acts as a BOOTP client.
To retrieve an IP address from a BOOTP server:
1. Select and connect any port to a BOOTP server or subnet containing such a
server, to retrieve the IP address.
2. At the system prompt, enter the delete startup con figuration command to delete
the startup configuration from flash. The device reboots with no configuration
22
Page 47

Security Management and Password Configuration
and in 60 seconds starts sending BOOTP requests. The device receives the IP
address automatically.
Note:
When the device reboot begins, any input at the ASCII terminal or keyboard
automatically cancels the BOOTP process before completion and the device does
not receive an IP address from the BOOTP server.
The following example illustrates the process:
2
Console> enable 4-368
Console#
Startup file was deleted
Console#
You haven’t saved your changes. Are you sure you want to continue (y/
n)[n]?
This command will reset the whole system and disconnect your current
session.Do you want to continue (y/n)[n]?
******************************************************
/*the device reboots */
delete startup-config 4-368
reload 4-612
To verify the IP address, enter the show ip interface command. The device is now
configured with an IP address.
Security Management and Password Configuration
System security is handled through the AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and
Accounting) mechanism that manages user access rights, privileges, and
management methods. AAA uses both local and remote user databases. Data
encryption is handled through the SSH mechanism.
The system is delivered with no default password configured; all passwords are
user-defined. If a user-defined password is lost, a p assword recovery procedure c an
be invoked from the S tartup menu. The proce dure is appli cable for the l ocal termi nal
only and allows a one-time access to the device from the local terminal with no
password entered.
Configuring Security Passwords Introduction
The security passwords can be configured for the following services:
• Console
•Telnet
•SSH
•HTTP
•HTTPS
Passwords are user-defined.
When creating a user name, the default priority is "1," which allows access but not
configuration rights. A priority of "15" must b e set to enable access an d configuration
rights to the device. Although user names can be assigned pri vilege lev el 15 without
23
Page 48

2
Initial Configuration
a password, it is recommended to always assign a password. If there is no specified
password, privileged users can access the Web interface wit h any password.
Configuring an Initial Console Password
To configure an initial console password, enter the following commands:
Console(config)# aaa authentication login default line 4-288
Console(config)#
Console(config)#
Console(config-line)#
Console(config-line)#
Console(config-line)#
aaa authentication enable default line 4-290
line console 4-437
login authentication default 4-291
enable authentication default 4-292
password george 4-296
When initially logging on to a device through a console session, enter george at the
password prompt.
When changing a device’s mode to enable, enter george at the password prompt.
Configuring an Initial Telnet Password
To configure an initial Telnet password, enter the following commands:
Console(config)#
Console(config)#
Console(config)#
Console(config-line)#
Console(config-line)#
Console(config-line)#
aaa authentication login default line 4-288
aaa authentication enable default line 4-290
line telnet 4-437
login authentication default 4-291
enable authentication default 4-292
password bob 4-296
When initially logging onto a device through a Telnet session, enter bob at the
password prompt.
When changing a device mode to enable, enter bob.
Configuring an Initial SSH password
To configure an initial SSH password, enter the following commands:
Console(config)#
Console(config)#
Console(config)#
Console(config-line)#
Console(config-line)#
Console(config-line)#
aaa authentication login default line 4-288
aaa authentication enable default line 4-290
line ssh 4-437
login authentication default 4-291
enable authentication default 4-292
password jones 4-296
When initially logging onto a device through a SSH session, enter jones at the
password prompt.
When changing a device mode to enable, enter jones.
24
Page 49

Software Download and Reboot
Configuring an Initial HTTP Password
To configure an initial HTTP password, enter the following commands:
2
Console(config)# ip http authentication local 4-293
Console(config)#
username admin password user1 level 15 4-297
Configuring an initial HTTPS Password
To configure an initial HTTPS password, enter the following commands:
Console(config)#
Console(config)#
ip https authentication local 4-294
username admin password user1 level 15 4-297
Enter the following commands once when configuring to use a console, a Telnet, or
an SSH session in order to use an HTTPS session.
In the Web browser enable SSL 2.0 or greater for the content of the page to appear.
Console(config)# c
Console(config)#
rypto certificate generate key_generate 4-695
ip https server 4-693
When initially enabling an http or https session, enter admin for user name and
user1 for password.
Note:
HTTP and HTTPS services require level 15 access and connect directly to the
configuration level access.
Software Download and Reboot
Software Download through XModem
This section contains instructions for downloading device sof tware (system and boot
images) using XModem, which is a data transfer protocol for updating back-up
configuration files.
To download a boot file using XModem:
1. Enter the command “xmodem:boot”. The switch is ready to receive the file via
the XModem protocol and displays text similar to the following:
Console# copy xmodem:boot 4-365
Please download program using XMODEM.
console#
2. Speci fy the path of the source file within 20 seconds. If t he p at h is not spe cif ie d
within 20 seconds, the command times out.
To download a software image file using XModem:
1. Enter the command “xmodem:image”. The switch is ready to receive the file via
25
Page 50

2
Initial Configuration
the XModem protocol.
2. Speci fy the path of the source file to begin t he transfer process. The following is
an example of the information that appears:
Console# copy xmodem:image 4-365
Please download program using XMODEM
console#
Software Download Through TFTP Server
This section contains instructions for downloading device sof tware (system and boot
images) through a TFTP server. The TFTP server must be configured before
downloading the software.
The switch boots and runs when decompressing the system image from the flash
memory area where a copy of the system image is stored. When a new image is
downloaded, it is saved in the other area allocated for the additional system image
copy.
On the next boot, the switch decompresses and runs the currently active system
image unless chosen otherwise.
To download an image through the TFTP server:
1. Ensure that an IP address is configured on one of the device ports and pings
can be sent to a TFTP server.
2. Ensure that the file to be downloaded is saved on the TFTP server (the Image
file).
3. Enter the command “show version” to verify which software version is currently
running on the device. The following is an example of the information that
appears:
Console# show version 4-619
SW version x.xx.xx (date xx-xxx-2004 time 13:42:41)Boot version
x.xx.x (date x-xxx-2003 time 15:12:20) HW version
4. Enter the command “show bootvar” to verify which system image is currently
active. The following is an example of the information that appears:
Console# show bootvar 4-374
Images currently available on the Flash Image-1 active (selected
for next boot)Image-2 not active
Console#
5. Enter the command “copy tftp://{tftp address}/{file name} image” to copy a new
system image to the device. When the new image is downloaded , i t is saved in
26
Page 51

Software Download and Reboot
the area allocated for the other copy of system image (image-2, as given in the
example). The following is an example of the informa tion that appears:
Console# copy tftp://176.215.31.3/file1 image Accessing file
file1 on 176.215.31.3... 4-365
Loading file1 from
176.215.31.3:!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!
Copy took 00:01:11 [hh:mm:ss]
Exclamation symbols indicate that a copying process is in progress. A period
indicates that the copying process is timed out. Many periods in a row indicate
that the copying process failed.
6. Select the image for the next boot by entering the boot system command.
After this command, enter the command show bootvar to verify that the copy
indicated as a parameter in the boot system command is selected for the
next boot. The following is an example of the information that appears:
Console# boot system image-2 4-372
Console# show bootvar 4-374
Images currently available on the Flash
Image-1 active Image-2 not active (selected for next boot)
If the image for the next boot is not selected by entering the boot system
command, the system boots from the currently active image (image-1,as given
in the example).
7. Enter the command “reload”. The following message is displayed:
2
Console# reload 4-612
This command will reset the whole system and disconnect your
current session.Do you want to continue (y/n)[n]?
8. Enter “Y” to reboot the switch.
Note:
For information on downloading software to stacking units, see "Configuring
Stacking".
Boot Image Download
Loading a new boot image from the TFTP server and programming it into the flash
updates the boot image. The boot image is loaded when the switch is powered on.
To download a boot file through the TFTP server:
1. Ensure that an IP address is configured on one of the device ports and pings
can be sent to a TFTP server .
2. Ensure that the file to be downloaded (the .rfb fi le) is saved on the TFTP serv er.
27
Page 52

2
Initial Configuration
3. Enter the command “show version” to verify which boot version is currently
running on the device. The following is an example of the information that
appears:
Console# show version 4-619
SW version x.xx.xx (date xx-xxx-2004 time 13:42:41)Boot version
x.xx.xx (date xx-xx-2004 time 15:12:20)HW version xx.xx.xx (date
xx-xxx-2004 time 12:12:20)
4. Enter the command “copy tftp://{tftp address}/{file name} boot” to copy the boot
image to the switch. The following is an example of the information that
appears:
Console# copy tftp://176.215.31.3/6024_boot-10013.rfb 4-365
boot
Erasing file
...done.!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!Copy:393232 bytes copied in 00:00:05 [hh:mm:ss]
5. Enter the command “reload”. The following message is displayed:
Console# reload 4-612
This command will reset the whole system and disconnect your
current session. Do you want to continue (y/n)[n]?
6. Enter “Y” to reboot the switch.
Startup Menu Functions
Additional configuration functions can be performed from the Startup menu.
To display the Startup menu:
1. During the boot process, after the first part of the POST is completed press
<Esc> or <Enter> within two seconds after the foll owing message is displ ayed:
Autoboot in 2 seconds -press RETURN or Esc.to abort and enter prom.
The Startup menu is displayed and contains the following configuration
functions:
[1]Download Software
[2]Erase Flash File
[3]Erase Flash Sectors
[4]Password Recovery Procedure
[5]Enter Diagnostic Mode
[6]Back Enter your choice or press 'ESC' to exit:
28
Page 53

Startup Menu Functions
The following sections describe the Startup menu options. If no selection is made
within 25 seconds (default), the switch times out and the device continues to load
normally.
Only technical support personnel can operate the Diagnostics Mode. For th is
reason, the Enter Diagnostic Mode option of the Startup menu is not described in
this guide.
Download Software
Use the software download option when a new software version must be
downloaded to replace corrupted files, update, or upgrade the system software.
To download software from the Startup menu:
1. On the Startup menu, press “1”.
The following prompt is displayed:
Downloading code using XMODEM
2. When using HyperTerminal, click Transfer on the HyperTerminal menu bar.
3. From the Transfer menu, click Send File. The Send File window is displayed.
2
Figure 2-2. Send File window
4. Enter the file path for the file to be downloaded.
5. Ensure the protocol is defined as Xmodem.
6. Click Send.
The software is downloaded. Software downloa ding takes severa l minutes. The
terminal emulation application, such as HyperTerminal, may display the
progress of the loading process.
29
Page 54

2
Initial Configuration
After software downloads, the device reboots automatically.
Erase FLASH File
In some cases, the device configuration must be erased. If the configuration is
erased, all parameters configured via CLI, Web brows er interface, or SNMP must be
reconfigured.
To erase the device configuration:
1. From the Startup menu, press “2” within 6 seconds to erase flash file. The
following message is displayed:
Warning! About to erase a Flash file.
Are you sure (Y/N)?y
2. Press “Y”.
Note:
Do not press <Enter>.
The following message is displayed.
Write Flash file name (Up to 8 characters, Enter for none.):config
File config (if present) will be erased after system initialization
========Press Enter To Continue ========
3. Enter config as the name of the flash file. The configuration is erased and the
device reboots.
4. Perform the switch’s initial configuration.
Erase FLASH Sectors
For troubleshooting purposes, the flash sectors may need to be erased. If the flash
is erased, all software files must be downloaded and installed again.
To erase the FLASH:
1. From the Startup menu, press “3” within 6 seconds. The following message is
displayed:
Warning! About to erase Flash Memory! FLASH size =16252928.blocks =64
Are you sure (Y/N)
2. Confirm by pressing <Y>. The following message is displayed:
Enter First flash block (1 -63):
3. Enter the first flash block to be erased and press <Enter>. The following
message is displayed:
Enter Last flash block (1 -63):
30
Page 55

Startup Menu Functions
2
4. Enter the last flash block to be erased and press <Enter>. The following
message is displayed:
Are you sure (Y/N)
5. Confirm by pressing <Y>. The following message is displayed:
Erasing flash blocks 1 -63: Done.
Password Recovery
If a password is lost, use the Password Recovery option on the Startup menu. The
procedure enables the user to enter the device once without a password.
To recover a lost password for the local terminal only:
1. From the St artup menu, select “4” and press <Enter>. The p assword is deleted.
2. To ensure device security, reconfigure passwords for applicable management
methods.
31
Page 56

2
Initial Configuration
32
Page 57

Chapter 3: Configuring the Switch
Using the Web Interface
This switch provides an embedded HTTP Web agent. Using a We b browser you can
configure the switch and view statistics to monitor network activity. The Web agent
can be accessed by any computer on the network using a standard Web browser
(Internet Explorer 6.0 or above, or Netscape Navigator 6.2 or above).
You can also use the Command Line Interface (CLI) to manage the switch over a
Note:
serial connection to the console port or via Telnet. For more information on using
the CLI, refer to Chapter 4: “Command Line Interface.”
Prior to accessing the switch from a Web browser, be sure you have first performed
the following tasks:
1. Configure the switch with a valid IP address, subnet mask, and defaul t gateway
using an out-of-band serial connection, BOOTP or DHCP protocol.
2. Set user names and passwords using an out-of-band serial connection. Access
to the Web agent is controlled by the same user names and passwords as the
onboard configuration program.
3. After you enter a user name and password, you wil l hav e access to the system
configuration program.
Notes: 1.
If you log into the CLI interface as guest (Normal Exec level), you can view
the configuration settings or change the guest password. If you log in as
“admin” (Privileged Exec level), you can change the settings on any page.
2. If the path between your management station and this switch does not pass
through any device that uses the Spanning Tree Algorithm, then you can set
the switch port attached to your management station to fast forwarding (i.e.,
enable Admin Edge Port) to improve the switch’s response time to
management commands issued through the web interface.
Navigating the Web Browser Interface
To access the web-browser interface you must first enter a user name and
password. The administrator has Read/Write access to all co nfigurat i on p arame ters
and statistics.
Home Page
When your web browser connects with the switch’s web agent, the home page is
displayed as shown below. The home page displays the Main Menu on the lef t side
of the screen and System Information on the right side. The Main Menu links are
33
Page 58

Configuring the Switch
3
used to navigate to other menus, and display configuration parameters and
statistics.
Figure 3-3. Home Page
Configuration Options
Configurable parameters have a dialog box or a drop-down list. Once a conf iguration
change has been made on a page, be sure to click on the “Apply” or “Apply
Changes” button to confirm the new set ting. The following t able summarizes the web
page configuration buttons:
Table 3-1.
Add Adds new device configuration information.
Modify Modifies existing device configuration information.
Apply Saves new or modified configuration information to the device.
Delete Checkbox Delet es current device configuration information.
Test Now Performs either copper or fiber cabl e te s t s .
Clear Counters Clears device statistics.
Notes: 1.
34
To ensure proper screen refresh, be sure that Internet Explorer 5.x is
configured as follows: Under the menu “Tools / Internet Options / General /
Temporary Internet Files / Settings,” the setting for item “Check for newer
versions of stored pages” should be “Every visit to the page.”
2. When using Internet Explorer 5.0, you may have to manually refresh the
screen after making configuration changes by pressing the browser’s refresh
button.
Page 59

Navigating the Web Browser Interface
3
Panel Display
The web agent displays an image of the switch’s ports. The Mode can be set to
display different information for the ports, including Active (i.e., up or down), Duplex
(i.e., half or full duplex, or Flow Control (i.e., with or without flow control). Cli cking on
the image of a port opens the Interface Configuration Page as described on page
3-71.
Figure 3-4. Ports Panel
Main Menu
Using the onboard web agent, you can define system parameters, manage and
control the switch, and all its ports, or monitor network conditions. The following
table briefly describes the selections available from this program:
Table 3-2. EWS Menu Options
System
System Management Provides system information including the general device
Interfaces Provides information for configuring the device interfaces.
IP Addressing Provides information for configuring IP addressing. In additi on, this
SNMP Provides information for configuring SNMP.
Web View Management Provides information for configuring system passwords, and web
RMON Provides information for viewing RMON statistics.
Network Discovery Provides Information for configuring the LLDP and the AMAP
Physical Provides information for managing Power-over-Ethernet devices
Ethernet Provides information for managing PoE devices and viewing PoE
Diagnostics Provides information for performing copper and f iber cable tests,
Security
information, stacking information, system logs, system time
parameters, and parameters for managing system files.
section contains information for defining ARP, DHCP, and DNS
settings.
access.
protocols.
and system diagnostics.
statistics.
performing port mirroring, and viewing device health information.
35
Page 60

Configuring the Switch
3
Table 3-2. EWS Menu Options
Traffic Control Provides in formation for configuring Broadcast Storm Control and
802.1X Provides information for configuring 802.1X port authentication.
Access Control Provides information for configuring Access Control Lists and
DHCP Snooping Builds and maintains a binding table used b y DHCP Sn ooping , th e
Layer 2
Address Tables Provides information for defining static and dynamic addresses.
Spanning Tree Provides information for configuring the Spanning Tree Protocol,
VLAN Provides information for defining VLANs, including VLAN groups,
Multicast Provides information for configuring Multicast Groups, Multicast
Policy
General QoS Provides information for configuring the QoS general mode
Basic Mode Provides information for configuring the QoS basic mode.
Advanced Mode Provides information for configuring the QoS advanced mode.
port security.
Access Control Entries, as well as, information for binding ACLs to
interfaces.
ARP Inspection and IP Source Guard features.
the Rapid Spanning Tree, and Multiple Spanning T ree.
GARP, and GVRP.
Forwarding, and IGMP snooping.
Managing Device Information
In the System Information Page, you can easily identify the syste m by disp laying the
device name, location and contact information.
Command Attributes
• Model Name — Displays the device model number and name.
• System Name — Defines the user-defined device name. The field range is 0-160
characters.
• System Location — Defines the location where the system is currently running.
The field range is 0-160 characters.
• System Contact — Defines the name of the contact person. The field range is
0-160 characters.
• System Object ID — Displays the vendor’s authoritative identification of the
network management subsystem contained in the entity.
• System Up Time — Displays the amount of time since the most recent device
reset. The system time is displayed in the following format: Days, Hours, Minutes ,
and Seconds. For example, 41 days, 2 hours, 22 minutes and 15 seconds.
• Base MAC Address — Displays the device MAC address.
• Hardware Version — Displays the installed device hardware version number.
36
Page 61

Managing Stacking
• Software Version — Displays the installed software version number.
• Boot Version — Displays the current boot version running on the device.
Web – Click System, System Management, System Information. Spe cify the system
name, location, and contact information for the system administrator, then click
Apply.
Figure 3-5. System Information Page
3
CLI – The following is an example of the CLI System Information commands:
console# show system
4-618
Managing Stacking
Stacking provides multiple switch management through a single point as if all stack
members are a single unit. All stack members are accessed through a single IP
address through which the stack is managed. The stack is managed from the
following:
• Web-based interface
• SNMP Management Station
• Command Line Interface (CLI)
Devices support stacking up to six units per stack, or can operate as stand-alone
units.
During the Sta cking setup, one switch is selected as the Stacking Master and
another stacking member can be selected as the Secondary Master. All other
devices are selected as stack members, and assigned a unique Unit ID.
37
Page 62

Configuring the Switch
3
Switch software is downloaded separately for each stack members. However, all
units in the stack must be running the same software version.
Switch stacking and configuration is maintained by the Stacking Master. The
Stackin g Master det ects and configures the ports with minimal ope ra tiona l impact in
the event of:
• Unit Failure
• Inter-unit Stacking Link Failure
•Unit Insertion
• Removal of a Stacking Unit
This section provides an introduction to the user interface, and includes the following
topics:
• Understanding the Stack Topology
• Stacking Failover Topology
• Stacking Members and Unit ID
• Removing and Replacing Stacking Members
• Exchanging Stacking Members
• Switching between the Stacking Master and the Secondary Master
Understanding the Stack Topology
The devices operate in a Ring topology. A stacked Ring topology is where all
devices in the stack are connect ed to each other formi ng a circl e. Each device in the
stack accepts data and sends it to the device to which it is attached. The packet
continues through the stack until it reache s its des tination. The system discovers the
optimal path on which to send traffic.
Most difficulties incurred in Ring topologies occ ur when a device in t he ring becomes
non-functional, or a link is severed. In a stack, the system automatically switches to
a Stacking Failover topology without any system downtime. An SNMP message is
automatically generated, but no stack managemen t action is requ ired. However, the
stacking link or stacking member must be rep aired to ensure the stacking integrity.
After the stacking issues are resolved, the device can be reconnected to the stack
without interruption, and the Ring topology is restored.
Stacking Failover Topology
If a failure occurs in the stacking topology, the stack reverts to Stacking Failover
Topology. In the Stacking Failover topology, devices operate in a chain formation.
The Stackin g Master determines where the packet s are sent. Each unit is conne cted
to two neighboring devices, except for the top and bottom units.
Stacking Members and Unit ID
Stackin g Unit I Ds a re esse nt ial t o t he stacking configuration. The stacking operation
is determined during the boot process. The operation mode is determined by the
Unit ID selected during the initialization process. Stacking LEDs are dual mode
38
Page 63

Managing Stacking
LEDS. During bootup, the Stacking LEDs indicate the stacking Unit number. When
the device is running, the stack ID selector displays the unit ID number. Pressing a
second time displays the port speed. For example, if the user selected s tand-alone
mode, the device boots in the boot-up process as a stand-alone device.
The device units are shipped with a default Unit ID of the stand-alone unit. If the
device is operating as a stand-alone unit , all stacking LEDs are off.
Once the user selects a different Unit ID, it is not erased, and remains valid, even if
the unit is reset.
Unit ID 1 and Unit ID 2 are reserved for Master enabled units. Unit IDs 3 to 8 can be
defined for stack members.
When the Master unit boots or when inserting or removing a stack member, the
Master unit initiates a stacking discovering process.
Note:
If two members are discovered with the same Unit ID the stack continues to
function, however only the unit with the older join time joins the stack. A message
is sent to the user, notifying that a unit failed to join the stack.
3
Removing and Replacing Stacking Members
Stackin g member 1 and Stacking member 2 are Stacking Master enabled units. Unit
1 and Unit 2 are either designated as Master Unit or Secondary Master Unit. The
Stacking Master assignment is performed during the configuration process. One
Master enabled stack member is elected Master, and the other Master enabled
stack member is elected Secondary Master, according to the following decision
process:
• If only one Stacking Master enabled unit is present, it is elected Stacking Master.
• If two Stacking Masters enabled stacking members are present, and one has been
manually configured as the Stacking Master, the manually configured member is
elected Stacking Master.
• If two Master enabled units are present and neither has been manuall y configured
as the Stacking Master, the one with the longer up-t ime is elected Stacking Maste r.
• If the two Master enabled stacking members are the same age, Unit 1 is elected
Stacking Master.
• Two stacking member are considered the same age if they were insert ed within the
same ten minute interval.
For example, Stack member 2 is inserted in the first minute of a ten-minute cycle,
and Stack member 1 is i nserted in fifth minute of the same cycle, the units are
considered the same age. If there are two Master enabled units tha t are the same
age, then Unit 1 is elected Stacking Master.
The Stacking Master and the Secondary Master maintain a Warm Standby. The
Warm Standby ensures that the Secondary Master takes over for the Stacking
Master if a failover occurs. This guarantees that the stack continues to operate
normally.
During the Warm Standby, the Master and the Secondary Master are synchronized
with the static configuration only. When the Stacking Master is configured, the
39
Page 64

Configuring the Switch
3
Stacking Master must synchronize the Stacking Secondary Master. The Dynamic
configuration is not saved, for exampl e, dynamically l earned MAC addresses are n ot
saved.
Each port in the stack has a specific Unit ID, port type, and port number, which is
part of both the configuration commands and the configuration files. Configuration
files are managed only from the device Stacking Master, including:
• Saving to the FLASH
• Uploading Configuration files to an external TFTP Server
• Downloading Configuration files from an external TFTP Server
Whenever a reboot occurs, topology discovery is performed, and the master learns
all units in the stack. Unit IDs are sa ved in the un it and are l earned t hrough t opolog y
discovery. If a unit attempts to boot without a selected Master, and the unit is not
operating in stand-alone mode, the unit does not boot.
Configuration files are changed only through explicit user configuration.
Configuration files are not automatically modified when:
• Units are Added
• Units are Removed
• Units are reassigned Unit IDs
• Units toggle between Stacking Mode and Stand-alone Mode
Each time the system reboots, the Startup Configuration file in the Master unit is
used to configure the stack. If a stack member is removed from the stack, and then
replaced with a unit with the same Unit ID, the stack member is configured with the
original device configuration. Only ports which are physically present are displayed
in the home page, and can be configured through the WebViewMgmt system.
Non-present ports are configured through the CLI or SNMP interfaces.
Exchanging Stacking Members
If a stack member with the same Unit ID replaces an existing Unit ID with the same
Unit ID, the previous device configurati on is a ppl ied to the i nse rt ed st a ck me mber. If
the new inserted device has either more than or less ports than t he previous device,
the relevant port configuration is applied to the new stack member.
Switching between the Stacking Master and the Secondary Master
The Secondary Master replaces the Stacking Master if the following events occur:
• The Stacking Master fails or is removed from the stack.
• Links from the Stacking Master to the stacking members fails.
• A soft switchover is performed with either via web interface or the CLI.
Switching between the Stacking Master and the Secondary Master results in a
limited service loss. Any dynamic tables are relearned if a failure occurs. The
running configuration file is synchronized between Stacking Master and the
Secondary Master, and continues running on the Secondary Master.
40
Page 65

Managing Stacking
3
Configuring Stacking
The St ack Management Topology Page allows network managers to either reset the
entire stack or a specific device. Device configuration changes that are not saved
before the device is reset are not saved. If the Stacking Master is reset, the entire
stack is reset.
Command Attributes
• Top Unit — Indicates the first stack member’s number. Possible values are Master
and 1-8.
• Bottom Unit — Indicates the second stack member’s number. Possible values are
Master and 1-8.
• Stack Order — Displays the number of the unit within the stack.
• Neighbor 1 — Indicates the first stack member of the stack.
• Neighbor 2 — Indicates the second stack member of the stack.
• Switch Stack Control from Unit 1 to Unit 2 — Switches the stack control from
the Stack Master to the Secondary Stack Master. The possible field values are:
• Checked — Enables switching the st ack control to the Secondary Stack Maste r.
• Unchecked — Maintains the current stacking control.
Web – Click System, System Management, Stack Management, Topology. Specify
the upper and lower stacking members, then click Apply.
Figure 3-6. Stack Management Topology Page
It is recommended to upgrade software on all units in a stack simultaneously. Use
the following steps:
41
Page 66

Configuring the Switch
3
1. Download the file
2. Open the File Download Page.
3. Select the Firmware Download field.
4. Enter full path and file name of software to be downloaded to device.
5. Select Download to all Units.
6. Reset the stack.
CLI – The following is an example of stack management commands:
Console(config)# stack master unit 2
4-613
Console(config)# stack display-order top 6 bottom 1
4-614
Resetting the Stack
The Stack Management - Reset Page resets the stack.
Command Attributes
• Reset Unit No — Indicates the unit to be reset.
Web – Click System, System Management, Stack Management, Reset page. Click
the Reset button.
42
Figure 3-7. Stack Management - Reset Page
Page 67

Managing System Logs
CLI – The following is an example of stack reset commands:
Console(config)# stack reload unit 2
4-614
3
Managing System Logs
The switch allows you to control the loggi ng of error messages, i ncludi ng th e type of
events that are recorded in switch memory, logging to a remote System Log (syslog)
server, and di splays a list of recent event messages.
The default for all logs is information, with the exception of logs in the Remote Log
Server, which are errors.
Level Severity Name Des cription
7 Debug Debugging messages
6 Informational Informational messages only
5 Notice Normal but significant condition, such as cold
4 Warning Warning conditions (e.g., return false,
3 Error Error conditions (e.g., invalid input, default
2 Critical Critical conditions (e.g., memory allocation, or
1 Alert Immediate action needed
0 Emergency System unusable
start
unexpected return)
used)
free memory error - resource exhausted)
Enabling System Logs
The Logs Settings Pagecontains fields for defining which events are recorded to
which logs. It contains fields for enabling logs globally, and parameters for defining
logs. The Severity log messages are listed from the highest severity to the lowest.
When a severity level is selected, all severity level choices above the selection are
selected automatically.
Command Attributes
• Enable Logging — Indicates if devic e global logs for Cache and File are enabled.
Console logs are enabled by default. The possible field values are:
• Checked — Enables device logs.
• Unchecked — Disables device logs.
• Severity — The following are the available severity logs:
43
Page 68

Configuring the Switch
3
• Emergency — Indicates the highest warning level. If the device i s do wn or not
functioning properly, an emergency log message is saved to the specified
logging location.
• Alert — Indicates the second highest warning level. An alert log is saved, if there
is a serious device malfunction; for example, all device features are down.
• Critical — Indicates the third highest warning level. A critical log is saved if a
critical device malfunction occurs; for example, two device ports are not
functioning, while the rest of the device ports remain functional.
• Error — Indicates that a device error has occurred, for example, if a single port
is offline.
• Warning — Indicates the lowest level of a device warning. The device is
functioning, but an operational problem has occurred.
• Notice — Provides device information, for example, a port is not operating.
• Informational — Provides device information.
• Debug — Provides debugging messages.
• Console — Defines the minimum severity level from which logs are sent to the
console.
• RAM Logs — Defines the minimum severity level from which logs are sent to the
Event Log kept in RAM (Cache).
• Log File — Defines the minimum severity level from which logs are sent to the
Message Log kept in FLASH memory.
Web – Click System, System Management, Logs, Log Settings, and enable logs.
Figure 3-8. Logs Settings Page
CLI – The following is an example of the CLI commands used to view system logs:
44
Page 69

console# config
4-655
console(config)# logging on
4-591
console(config)# logging console errors
4-593
console(config)# logging buffered debugging
4-594
console(config)# logging file alert
4-594
console(nconfig)# exit
4-656
console# clear logging file
4-595
Clear Logging File [y/n]y
Managing System Logs
3
Viewing Memory Logs
The system allows you to enable or disable event logging, and specify which levels
are logged to the RAM (Cache).
Severe error messages that are logged to the RAM are permanently stored in the
switch to assist in troubleshooting network problems. When a severity level is
selected, all severity level choices above the selection are selected automatically.
The Memory Page allows you to configure and limit system messages that are
logged to the RAM.
Command Attributes
• Log Index — Displays the log number.
• Log Time — Displays the time at which the log was generated.
• Severity — The following are the available log severity levels:
• Emergency — The highest warning level. If t he device is down or not functioning
properly, an emergency log message is saved to the specified l ogging locati on.
• Alert — The second highest warning level. An alert log is saved, if there is a
serious device malfunction; for example, all device features are down.
• Critical — The third highest warning level. A critical log is saved if a critical
device malfunction occurs; for example, two device ports are not functioning,
while the rest of the device ports remain functional.
• Error — A device error has occurred, for example, if a single port is offline.
• Warning — The lowest level of a device warning. The device is functio ning, but
an operational problem has occurred.
• Notice — Provides device information.
• Informational — Provides device information.
• Debug — Provides debugging messages.
• Description — Displays the log message text.
Web – Click System, System Management, Logs, Memory.
45
Page 70

Configuring the Switch
3
Figure 3-9. Memory Page
46
Page 71

Managing System Logs
3
CLI – The following is an example of the CLI comma nds used to vie w me mory logs:
Console# show logging
4-599
Logging is enabled.
Console logging: level debugging. Console Messages: 0 Dropped
(severity).
Buffer logging: level debugging. Buffer Messages: 11 Logged, 200 Max.
File logging: level notifications. File Messages: 0 Dropped (severity).
Syslog server 192.180.2.27 logging: errors. Messages: 6 Dropped
(severity).
Syslog server 192.180.2.28 logging: errors. Messages: 6 Dropped
(severity).
2 messages were not logged (resources)
Application filtering control
Application Event Status
----------- ----- -----AAA Login Enabled
File system Copy Enabled
File system Delete-Rename Enabled
Management ACL Deny Enabled
Buffer log:
11-Aug-2004 15:41:43: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed
state to up
11-Aug-2004 15:41:43: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Ethernet1/0, changed
state to up
11-Aug-2004 15:41:43: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Ethernet1/1, changed
state to up
11-Aug-2004 15:41:43: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Ethernet1/2, changed
state to up
11-Aug-2004 15:41:43: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Ethernet1/3, changed
state to up
11-Aug-2004 15:41:43: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from memory by console
11-Aug-2004 15:41:39: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
11-Aug-2004 15:41:39: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
Ethernet1/0, changed state to down
11-Aug-2004 15:41:39: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
Ethernet1/1, changed state to down
11-Aug-2004 15:41:39: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
Ethernet1/2, changed state to down
11-Aug-2004 15:41:39: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
Viewing the Device FLASH Logs
The FLASH Logs Page contains all system logs in a chronological order that are
saved in FLASH memory.
Command Attributes
• Log Index — Displays the log number.
• Log Time — Displays the time at which the log was generated.
• Severity — Displays the log severity.
• Description — Displays the log message text.
47
Page 72

Configuring the Switch
3
Web – Click System, System Management, Logs, Flash.
Figure 3-10. FLASH Logs Page
CLI – The following is an example of the CLI commands used to display FLASH
logs:
Console# show logging file 4-601
Logging is enabled.
Console Logging: Level info. Console Messages: 0 Dropped.
Buffer Logging: Level info. Buffer Messages: 62 Logged, 62 Displayed, 2 00
Max.
File Logging: Level debug. File Messages: 11 Logged, 51 Dropped.
SysLog server 12.1.1.2 Logging: warning. Messages: 14 Dropped.
SysLog server 1.1.1.1 Logging: info. Messages: 0 Dropped.
01-Jan-2000 01:12:01:%COPY-W-TRAP: The copy operation was completed
successfully
01-Jan-2000 01:11:49:%LINK-I-Up: 1/e11
01-Jan-2000 01:11:46:%LINK-I-Up: 1/e12
01-Jan-2000 01:11:42:%LINK-W-Down: 1/e13
Remote Log Configuration
The Remote Log Page allows you to configure the logging of messages that are
sent to syslog servers or other management stations. You can also limit the event
messages sent to only those messages at or above a specified level.
Command Attributes
• Server — Specifies the IP address of the server to which logs can be sent.
• UDP Port — Defines the UDP port to which the server logs are sent. The possible
range is 1 - 65535. The default value is 514.
• Facility — Defines an application from which system logs are sent to the remote
server. Only one facility can be assigned t o a single server. If a second facil ity level
48
Page 73

Managing System Logs
is assigned, the first facility is overridden. All applications defined for a device
utilize the same facility on a server. The field default is Local 7. The possible field
values are Local 0 - Local 7.
• Description— Displays the user-defined server description.
• Minimum Severity — Indicates the minimum severity from which logs are sent to
the server. For example, if Notice is selec ted, all logs with a severity level of Notice
and higher are sent to the remote server.
• Remove — Deletes the currently selected server from the Servers list. The
possible field values are:
• Checked — Removes the selected server from the Remote Log Page. Once
removed, logs are no longer sent to the removed server.
• Unchecked — Maintains the remote servers.
Web – Click System, System Management, Logs, Remote Logs. Specify Remote
Log Statu s.
3
Figure 3-11. Remote Log Page
CLI – Enable system logging and then specify the level of messa ges to be logged to
remote logs. Use the show logging command to display the current settings.
49
Page 74

Configuring the Switch
3
Console# show logging file
4-601
Logging is enabled.
Console logging: level debugging. Console Messages: 0 Dropped
(severity).
Buffer logging: level debugging. Buffer Messages: 11 Logged, 200 Max.
File logging: level notifications. File Messages: 0 Dropped (severity).
Syslog server 192.180.2.27 logging: errors. Messages: 6 Dropped
(severity).
Syslog server 192.180.2.28 logging: errors. Messages: 6 Dropped
(severity).
2 messages were not logged (resources)
Application filtering control
Buffer log:
11-Aug-2004 15:41:43:%LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface FastEthernet0/0, changed
state to up
11-Aug-2004 15:41:43:%LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Ethernet1/0, changed
state to up
11-Aug-2004 15:41:43:%LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Ethernet1/1, changed
state to up
11-Aug-2004 15:41:43:%LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Ethernet1/2, changed
state to up
11-Aug-2004 15:41:43:%LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Ethernet1/3, changed
state to up
11-Aug-2004 15:41:43:%SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from memory by console
11-Aug-2004 15:41:39:%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
FastEthernet0/0, changed state to up
11-Aug-2004 15:41:39:%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
Ethernet1/0, changed state to down
11-Aug-2004 15:41:39:%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
Ethernet1/1, changed state to down
11-Aug-2004 15:41:39:%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
Ethernet1/2, changed state to down
11-Aug-2004 15:41:39:%LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
Ethernet1/3, changed state to down
50
Page 75

Configuring SNTP
3
Configuring SNTP
Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) allows the switch to set its internal clock
based on periodic updates from a time server (SNTP or NTP). Maintaining an
accurate time on the switch enables the system log to record meaningful dates and
times for event entries. You can also manually set the clock using the CLI. If the
clock is not set, the switch will only record the time from th e factory defa ult set at t he
last bootup.
Note:
The system time is not saved in NVRAM.
The device can poll the following server types for the server time:
• Unicast
• Anycast
• Broadcast
Time sources are established by stratums. Stratums define the accuracy of the
reference clock. The higher the stratum (where zero is the highest), the more
accurate the clock is. The device receives time from stratum 1 and above.
The following is an example of stratums:
• Stratum 0 — A real time clock (such as a GPS system) is used as the time
source.
• Stratum 1 — A server that is directly linked to a Stratum 0 time source is used.
Stratum 1 time servers provide primary network time standards.
• Stratum 2 — The time source is distanced from the Stratum 1 server over a
network path. For example, a Stratum 2 server receives the time over a network
link, via NTP, from a Stratum 1 server.
Information received from SNTP servers is evaluated based on the Time level and
server type. SNTP time definitions are assessed and determined by the following
time levels:
• T1 — The time at which the original request was sent by the client.
• T2 — The time at which the original request was received by the server.
• T3 — The time at which the server sent the client a reply.
• T4 — The time at which the client received the server's reply.
Polling for Unicast Time Information
Polling for Unicast information is used for polling a server for which the IP addre ss is
known. T1 - T4 are used to determine the server time. This is the preferred method
for synchronizing device time.
Polling for Anycast Time Information
Polling for Anycast information is used when the server I P add ress i s unknown . The
first Anycast server to return a response is used to set the time va lue. T ime levels T3
and T4 are used to determine the server time. Using Anycast time information for
synchronizing device time is preferred to using Broadcast time information.
51
Page 76

Configuring the Switch
3
Polling For Broadcast Time Information
Broadcast information is used when the server IP address is unknown. When a
broadcast message is sent from an SNTP server, the SNTP client listens for the
response. The SNTP client neither sends time information requests nor receives
responses from the Broadcast server.
Message Digest 5 (MD5) Authentication safeguards de vice synchronizatio n paths to
SNTP servers. MD5 is an algorithm that produces a 128 -bit hash. MD5 is a variat ion
of MD4, and increases MD4 security. MD5 verifies the integrity of the
communication, authenticates the origin of the communi cation.
Defining SNTP Global Settings
The SNTP Configuration Page provides information for defining SNTP parameters
globally.
Command Attributes
• Poll Interval — Defines the interval (in seconds) at which the SNTP server is
polled for Unicast information. The Poll Interval default is 1024 seconds.
• Enable Receive Broadcast Servers Up da tes — Defines whether or not the
device monitors the SNTP servers for the interface’s Broadcast server time
information. The possible values are:
• Checked — Enables the device to receive Broadcast server updates.
• Unchecked — Disables the device from receiving Broadcast server updates.
• Enable Receive Anycast Servers Updates — Defines whethe r or not the device
polls the SNTP server for Anycast server time information. If both the Enable
Receive Anycast Servers Update and the Enable Receive Broadcast Servers
Update fields are enabled, the system time is set according the Anycast server time
information. The possible values are:
• Checked — Enables the device to receive Anycast server updates.
• Unchecked — Disables the device from receiving Anycast server updates.
• Enable Receive Unicast Servers Updates — Defines whether or not the devi ce
polls the SNTP server for Unicast server time information. If the Enable Receive
Broadcast Servers Updates, Enable Receive Anycast Servers Updates, and
Enable Receive Unicast Servers Updates fields a re all enabled, the system time is
set according the Unicast server time information. The possible values are:
• Checked — Enables the device to receive Unicast server updates.
• Unchecked — Disables the device from receiving Unicast server updates.
• Enable Poll Unicast Servers — Defines whether or not the device sends SNTP
Unicast forwarding information to the SNTP server. The possible values are:
• Checked — Enables the device to receive Poll Unicast server updates.
• Unchecked — Disables the device from receiving Poll Unicast server updates.
Web – Select System, System Management, SNTP, Configuration. Define the fields
and click Apply.
52
Page 77

Configuring SNTP
Figure 3-12. SNTP Configuration Page
CLI - The following is an example of the SNTP global parameters commands:
Console(config)# sntp client poll timer 120
4-355
Console(config)# sntp Broadcast client enable
4-356
Console(config)# sntp unicast client enable
4-358
Console(config)# sntp anycast client enable
4-357
Console(config)# sntp unicast client poll
4-359
3
Defining SNTP Authentication
The SNTP Authentication Page provides parameters for defining the means by
which the SNTP server is authenticated.
Command Attributes
• Enable SNTP Authentication — Indicates if authenticating an SNTP session
between the device and an SNTP server is enabled on the device. The possible
field values are:
• Checked — Authenticates SNTP sessions between the device and SNTP
server.
• Unchecked — Disables authenticating SNTP sessions between the device and
SNTP server.
• Encryption Key ID — Indicates if the encryption key identification is used to
authenticate the SNTP server and device. The field value is up to 4294967295.
53
Page 78

Configuring the Switch
3
• Authentication Key — Indicates the key used for authentication.
• Trusted Key — Indicates the encryption key used (Unicast/Anycast) or elected
(Broadcast) to authenticate the SNTP server.
• Remove — Removes Encryption Key IDs. The possible field values are:
• Checked — Removes the selected Encryption Key ID
• Unchecked — Maintains the Encryption Key IDs. This is the default value.
Web – Select System, System Management , SNTP, Authentication. Define the fields
and click Apply.
Figure 3-13. SNTP Authentication Page
CLI - The following is an example of the SNTP authentication commands:
Console(config)# sntp authentication-key 8 md5 ClkKey
4-353
Console(config)# sntp trusted-key 8
4-354
Console(config)# sntp authenticate
4-353
Defining SNTP Servers
The SNTP Servers Page cont ains in formation for enabli ng SNTP servers, as well as
adding new SNTP servers. In addition, the SNTP Servers Page enables the device
to request and accept SNTP traffic from a server.
Command Attributes
• SNTP Server — Displays user-defined SNTP server IP addresses. Up to eight
SNTP servers can be defined.
• Poll Interval — Indicates whether or not the device polls t he selected SNTP server
for system time information.
54
Page 79

Configuring SNTP
• Encryption Key ID — Displays the encryption key identification used to
communicate between the SNTP server and device. The field range is
1-4294967295.
• Preference — Indicates the SNTP server providing SNTP system time
information. The possib le fie l d v al u es are:
• Primary — Indicates the primary server provides SNTP information.
• Secondary — Indicates the backup server provides SNTP information.
• Status — Displays the SNTP server operating status.
• Last Response — Displays the last time a response was received from t he SNTP
server.
• Offset — Indicates the time difference between the device local clock and the
acquired time from the SNTP server.
• Delay — Indicates the amount of time it takes for a device request to reach the
SNTP server.
• Remove — Removes SNTP servers from the SNTP server list. The possible field
values are:
• Checked — Removes the SNTP server.
• Unchecked — Maintains the SNTP server.
Web – Select System, System Management, SNTP, Servers. Define the fields and
click Apply.
3
Figure 3-14. SNTP Servers Page
55
Page 80

Configuring the Switch
3
CLI - The following is an example of the SNTP server commands:
Console(config)# sntp server 192.1.1.1
4-360
Defining SNTP Interface Settings
The SNTP Interface Page contains fields for setting SNTP on different interfaces.
Command Attributes
• Interface — Indicates the interface on which SNTP can be enabled. The poss ible
field values are:
• Port — Indicates the specific port number on which SNTP is enabled.
• LAG — Indicates the specific LAG number on which SNTP is enabled.
• VLAN — Indicates the specific VLAN number on which SNTP is enabled.
• Receive Servers Updates — Enables the interface to receive or not recei ve
updates.
• Remove — Removes SNTP interfaces.
• Checked — Removes the selected SNTP interface.
• Unchecked — Maintains the selected SNTP interfaces.
Web – Select System, System Management, SNTP, Interface. Define the fields and
click Apply.
Figure 3-15. SNTP Interface Page
CLI - The following is an example of the SNTP interface commands:
Console(config)# interface ethernet 1/e3 4-376
Console(config-if)# sntp client enable 4-357
56
Page 81

Configuring System Time
3
Configuring System Time
Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) allows the switch to set its internal clock
based on periodic updates from a time server (SNTP or NTP). Maintaining an
accurate time on the switch enables the system log to record meaningful dates and
times for event entries. You can also manually set the clock using the CLI. If the
clock is not set and the time cannot be established from a SNTP server, the switch
will only record the time from the factory default set at the last bootup.
When the SNTP client is enabled, the switch periodically sends a request for a time
update to a configured time server. You can configure up to eight time server IP
addresses. The switch attempts to poll each server in the configured sequence.
Polling can be enabled per interface.
Configuring Daylight Savings Time
The Clock Time Zone Page contains fields for defining system time parameters for
both the local hardware clock and the extern al SNTP clock. If the system time is kept
using an external SNTP clock, and the external SNTP clock fails, the system time
reverts to the local hardware clock. Daylight Savings Time can be enabled on the
device.
The following is a list of Daylight Savings Time start and end times in specific
countries:
• Albania — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Australia — From the end of October until the end of March.
• Australia - Tasmania — From the beginning of October until the end of March.
• Armenia — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Austria — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Bahamas — From April to October, in conjunction with Daylight Savings Time in
the United States.
• Belarus — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Belgium — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Brazil — From the third Sunday in October until the third Saturday in March. During
the period of Daylight Saving Time, Brazilian clocks go forward one hour in most
of the Brazilian southeast.
• Chile — In Easter Island, from March 9 until October 12. In the rest of t he country,
from the first Sunday in March or after 9th March.
• China — China does not use Daylight Saving Time.
• Canada — From the first Sunday in April until the last Sunday of October. Daylight
Saving Time is usually regulated by provincial and territorial governments.
Exceptions may exist in certain municipalities.
• Cuba — From the last Sunday of March to the last Sunday of October.
• Cyprus — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Denmark — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
57
Page 82

Configuring the Switch
3
• Egypt — From the last Friday in April until the last Thursday in September.
• Estonia — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Finland — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• France — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Germany — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Greece — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Hungary — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• India — India does not use Daylight Saving Time.
• Iran — From Farvardin 1 until Mehr 1.
• Iraq — From April 1 until October 1.
• Ireland — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Israel — Varies year-to-year.
• Italy — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Japan — Japan does not use Daylight Saving Time.
• Jordan — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of Octo ber.
• Latvia — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Lebanon — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Lithuania — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Luxembourg — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of
October.
• Macedonia — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Mexico — From the first Sunday in April at 02:00 to the last Sunday in October at
02:00.
• Moldova — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Montenegro — From the last weekend of March until t he last weekend of October.
• Netherlands — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of Octobe r.
• New Zealand — From the first Sunday in October until the first Sunday on or after
March 15.
• Norway — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Paraguay — From April 6 until September 7.
• Poland — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Portugal — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Romania — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Russia — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Serbia — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Slovak Republic
October.
• South Africa — South Africa does not use Daylight Saving Time.
• Spain — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Sweden — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
- From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of
58
Page 83

Configuring System Time
• Switzerland — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• Syria — From March 31 until October 30.
• Taiwan — Taiwan does not use Daylight Saving Time.
• Turkey — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of October.
• United Kingdom — From the last weekend of March until the last weekend of
October.
• United States of America — From the first Sunday in April at 02:00 to the last
Sunday in October at 02:00.
Command Attributes
• Clock Source — The source used to set the system clock. The possible field
values are:
• None — Indicates that a clock source is not used. The clock is set locally.
• SNTP — Indicates that the system time is set via an SNTP server.
• Date — The system date. The field format is Day/Month/Year. For example: 04/
May/50 (May 4, 2050).
• Local Time — The system time. The field format is HH:MM:SS. For example:
21:15:03.
• Time Zone Offset — The difference between Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) and
local time. For example, the Time Zone Offset for Paris i s GMT +1, while the Time
Zone Offset for New York is GMT –5.
• Daylight Savings — Enables automatic Daylight Savings Time (DST) on the
device based on the device’s location. There are two types of daylight settings,
either by a specific date in a particular year or a recurring setting irrespective of the
year. For a specific setting in a particular year complete the Dayli ght Savings area,
and for a recurring setting, complete the Recurring area. The possi ble field values
are:
• USA — Enables switching to DST at 2:00 a.m. on the first Sunday of April, and
reverts to standard time at 2:00 a.m. on the last Sunday of October.
• European — Enables switching to DST at 1:00 am on the last Sunday in March
and reverts to standard time at 1:00 am on the last Sunday in October. The
European option applies to EU members, and other European countries using
the EU standard.
• Other — Indicates the DST definitions are user-defined based on the device
locality. If Other is selected, the From and To fields must be defined.
• Time Set Offset (1-1440) — Used for non-USA and European countries to set the
amount of time for DST (in minutes). The default time is 60 minutes.
• From — Indicates the time that DST begins in countries other than the USA and
Europe, in the format Day/Month/Year in one field and HH:MM in another. For
example, if DST begins on October 25, 2007 at 5:00 am, the two fields should be
set to 25/Oct/07 and 05:00. The possible field values are:
• Date — The date on which DST begins. The possible field range is 1-31.
• Month — The month of the year in which DST begins. The possible field range
is Jan-Dec.
3
59
Page 84

Configuring the Switch
3
• Year — The year in which the configured DST begins.
• Time — The time at which DST begins. The field f ormat is HH:MM. For example:
05:30.
• To — Indicates the time that DST ends in countries other than the USA and
Europe, in the format Day/Month/Year in one field and HH:MM in another. For
example, if DST ends on March 23, 2008 at midnight, the two fields should be 23/
Mar/08 and 00:00. The possible field values are:
• Date — The date on which DST ends. The possible field range is 1-31.
• Month — The month of the year in which DST ends. The possible field range is
Jan-Dec.
• Year— The year in which the configured DST ends.
• Time — The time at which DST starts. The field format is HH:MM. For example:
05:30.
• Recurring — Enables user-defined DST for countries in which DST is constant
from year to year, other than the USA and Europe.
• From — The time that DST begins each year. In the example, DST begins l ocally
every first Sunday in April at midnight. The possible field values are:
• Day — The day of the week from which DST begins every year. The possible
field range is Sunday-Saturday.
• Week — The week within the month from which DST begins every year. The
possible field range is 1-5.
• Month — The month of the year in which DST begins every year. The possible
field range is Jan-Dec.
• Time — The time at which DST begins every year. The field format is
Hour:Minute. For example: 02:10.
• To — The time that DST ends each year. In the example, DST e nds loca ll y ev ery
first Sunday in October at midnight. The possible field values are:
• Day — The day of the week at which DST ends every year. The possible field
range is Sunday-Saturday.
• Week — The week within the month at which DST ends every year. The
possible field range is 1-5.
• Month — The month of the year in which DST ends every year. The possible
field range is Jan-Dec.
• Time — The time at which DST ends every year. The field format is HH:MM. For
example: 05:30.
Web – Select System, System Management, SNTP, Clock Time Zone. Define the
fields and set the offset for your time zone relative to the UTC, and click Apply.
60
Page 85

Managing System Files
Figure 3-16. Clock Time Zone Page
CLI - The following is an example of the system clock commands:
Console# clock set 13:32:00 7 Mar 2002
4-349
Console# configure 4-655
Console(config)# clock source sntp
4-350
Console(config)# clock timezone -6 zone CST
4-350
Console(config)# clock summer-time recurring first sun apr 2:00 last sun
oct 2:00
4-351
3
Managing System Files
You can upload/download firmware to or from a TFTP server. By saving runtime
code to a file on a TFTP server, that file can later be downloaded to the switch to
restore operation. You can set the switch to use new firmware without overwriting
the previous version.
The system run-time software and configuration information is kept in files which
may be saved, copied, uploaded for host-based storage and manipulation. The
system files include:
• Boot Files — The system uses two identical copies of the boot image, stored in
flash. The first copy is used when the system comes up.
• Software Image Files — two images are stored. The device boots f rom one , and
the other is used as a redundant backup.
61
Page 86

Configuring the Switch
3
• Startup Configuration File — Contains the commands required to reconfigure the
device to the same settings as when the device is powered down or rebooted. The
Startup file is created by copying the configuration commands from the Running
Configuration file or the Backup Configuration file.
• Running Configuration File — Contains all conf iguration file comma nds, as we ll
as all commands entered during the current session. After the device is powered
down or rebooted, all commands stored in the Running Configu ration fi le are lost.
During the startup process, all commands in the Startup file are copied to the
Running Configuration File and applied to the device. During the session, all new
commands entered are added to the commands existing in the Running
Configuration file. Commands are not overwritten. To update the Startup file,
before powering down the device, the Runnin g Configuration file must be copied
to the Startup Configuration file. The next time the device is restarted, the
commands are copied back into the Running Configuration file from the Startup
Configuration file.
• Image files — Software upgrades are used when a new version file is downloaded.
The file is checked for the right format, and that it is complete. After a successful
download, the new version is marked, and is used after the device is reset.
Downloading System Files
There are two types of files, firmware files and configuration files. The firmware f iles
manage the device, and the configuration files configure the device for
transmissions. Only one type of download can be performed at any one time. File
names cannot contain slashes (\ or /), the leading letter of the file name should not
be a period (.), and the maximum length for file names on the TFTP server is 127
characters or 31 characters for files on the switch. (Valid characters: A-Z, a-z, 0-9,
“.”, “-”, “_”). The File Download Page contains parameters for downloading system
files.
Command Attributes
• Firmware Download/Configuration Download — Indicates whether a firmware
file or a configuration is being do wnloa ded. I f Firmware Download is sel ect ed, t he
Configuration Download fields are grayed out. If Configuration Download is
selected, the Firmware Download fields are grayed out.
• TFTP Server IP Address — Specifies the TFTP Server IP Address from which
files are downloaded.
• Source File Name — Specifies the file to be downloaded.
• Destination File — Specifies the destination file type to which to the file is
downloaded. The possible field values are:
• Software Image — Downloads the Image file.
• Boot Code — Downloads the Boot file.
• Download to Master Only — Downloads the system file only to the Master.
• Download to All Units — Downloads the system file to all units.
62
Page 87

Managing System Files
• Configuration Download — Indicates that the download is for configuration files.
If Configuration Download is selected, the Firmware Download fields are grayed
out.
• Configuration TFTP Server IP Address — Specifies the TFTP Server IP Address
from which the configuration files are downloaded.
• Configuration Source File Name — Specifies the configuration files to be
downloaded.
• Configuration Destination File — Specifies the destination file to which to the
configuration file is downloaded. The possible field values are:
• Running Configuration — Downloads commands into the Running
Configuration file.
• Startup Configuration — Downloads the Startup Configuration file, and
overwrites the old Startup Configuration file.
Web – Click System, System Management, File Management, File Download.
Define the fields. Click Apply.
3
Figure 3-17. File Download Page
CLI – The following is an example of downloading system files using CLI
63
Page 88

Configuring the Switch
3
commands:
Console# copy tftp://172.16.101.101/file1 image
4-365
Accessing file 'file1' on 172.16.101.101..
Loading file1 from 172.16.101.101:
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!! [OK]
Copy took 0:01:11 [hh:mm:ss]
Uploading System Files
The File Upload Page contains fields for uploading the software from the device to
the TFTP server.
Command Attributes
• Firmware Upload — Specifies that the software image file is uploaded. If
Firmware Upload is selected, the Configuration Upload fields are grayed out.
• Configuration Upload — Specifies that the Configuration file is uploaded. If
Configuration Upload is selected, the Soft ware Image Upload fields are grayed out.
• Software TFTP Server IP Address — Specifies the TFTP Server IP Address to
which the Software Image is uploaded.
• Software Destination File Name — Specifies the software image file path to
which the file is uploaded.
• Configuration TFTP Server IP Address — Specifies the TFTP Server IP Address
to which the Configuration file is uploaded.
• Configuration Destination File Name— Specifies the file name to which the
Startup Configuration file is uploaded.
• Configuration Transfer file name — Specifies the Configuration file name that is
uploaded. The possible field values are:
• Running Configuration — Uploads the Running Configuration file.
• Startup Configuration — Uploads the Startup Configuration file.
Web – Click System, System Management, File Management, File Upload. Define
64
Page 89

Managing System Files
the fields. Click Apply.
Figure 3-18. File Upload Page
CLI – The following is an example of downloading system files using CLI
commands:
Console# copy tftp://172.16.101.101/file1 image
4-365
Accessing file 'file1' on 172.16.101.101..
Loading file1 from 172.16.101.101:
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!! [OK]
Copy took 0:01:11 [hh:mm:ss]
3
Copying Files
Files can be copied and deleted from the Copy Files Page.
Command Attributes
• Copy Master Firmware — Copies the Firmware file currently running on the
Stacking Master. The possible field values are selected from the following list
boxes:
• Source — Select if the Software Image or Bootcode file will be copied.
• Destination Unit — Select the stacking member to whic h the firmware is copied,
the possible field values are All, Backup, and stacking members 1-4.
• Copy Configuration — Copies the Running Configurati on File. The possible field
values are: The possible field values are:
• Source — Select if the Starting Configuration file , the Running Configuration file,
65
Page 90

Configuring the Switch
3
or the Backup file will be copied.
• Destination — Specifies t he usage for the source fil e after it is copied. It may be
used as a Starting Configuration file, the Running Confi guration file, the Backup
file, or as a configuration file with a new name.
• Restore Configuration Factory Defaults — Resets the Configuration file to the
factory defaults. The factory defaults are reset after the device is reset. When
unselected, the device maintains the current Configuration file.
Web – System, System Management, File Management, Copy Files. Define the
fields. Click Apply.
Figure 3-19. Copy Files Page
CLI – The following is an example of downloading system files using CLI
commands:
Console# copy running-config startup-config
4-365
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!! [OK]
Copy took 0:01:11 [hh:mm:ss]
Active Image
The Active Image Page allows network managers to select and reset the Image
files. The Active Image file for each unit in a stacking configuration can be
individually selected.
Command Attributes
• Image – Binary file that contains executable code
66
Page 91

TCAM Resources
• Filename – The name of the file
• Version – Binary code version
• Date – Version’s date
• Status – Indicates Image status
• Image After Reset – The Image file which is active on the unit after the device is
reset. The possible field values are:
• Image 1 — Activates Image file 1 after the device is reset.
• Image 2 — Activates Image file 2 after the device is reset.
Web – System, System Management, File Management, Active Image. Define the
fields. Click Apply.
3
Figure 3-20. Active imag e Pa g e
TCAM Resources
The TCAM Resources Page display the availability of TCAM resources (Ternary
Content Addressable Memory
searching throughout the stack, in order to perform securit y, QoS, and other types of
applications. In contrast with binary CAM, TCAM allows a third ma tching st ate o f “X”
or “Don’t Care” bits in data searches ( the first two bit types are “0” and “1”), adding
more flexibility to searches. However, the need to encode three possible states
instead of two also adds greater resource costs.
The maximum number of rules that may be allocated by all applications on the
device is 1024.
The following table lists all applications that can allocate TCAM rules. Each
allocation has its specific allocation policy.
) across the stack. TCAM is used for high-speed
67
Page 92

Configuring the Switch
3
Note: Some applications allocate rules upon their initiation. Additionally, applications that
initialize during system boot use some of their rules during the startup process.
Table3-3. TCAM Allocation
Application Per
QoS
Advanced
Mode rules
Access
Control
Rules
PVE Port 2/port
IP Subnet
VLAN
Protocol
Based VLAN
MAC Based
VLAN
DHCP
Snooping
IP Source
Guard
ARP
Inspection
VLAN Rate
Limiting
Port/
Device
Port 6/
Port 6/
Port 0 255 2 or 4 Rules are duplicated
Port 0 No limit 1 or 2 Rules are duplicated
Port 0 432 1 or 2 Rules are duplicated
Device 2/
Port 0 No limit 1 TCAM entry/1 IP
Device 2/
Both 0 255 1 global rule/1 VLAN
Per
Alloca
tion
on
Activa
tion
device
device
or
LAG
device
device
Application
Upper Limit
No limit 1 or 2 TCAM entries
No limit 1 or 2 TCAM entries
--- --- Feature is activated
No limit 8 TCAM entries/1
128 4 TCAM entries/1
TCAM rules per
User ACL
per each rule.
per each rule.
DHCP Snooping rule
Source Guard entry
ARP Inspection rule
Rate Limit.
Additional rule is
created for each
“permit” rule on the
interface.
Comments
Feature is activated
by default.
Feature is activated
by default.
by default.
Allocation done only
during initialization.
for both IP and MAC
based VLANs.
for both IP and MAC
based VLANs.
for both IP and MAC
based VLANs.
Command Attributes
• Stack Unit – Indicates the stacking member for which TCAM resource usage is
displayed.
• TCAM Utilization – Percentage of the available TCAM resources which are used.
For example, if more ACLs and policy maps are defined, the system will use more
TCAM resources.
68
Page 93

Configuring Interfaces
Figure 3-21. TCAM Resources Page
Configuring Interfaces
The Interfaces pages provide detailed information about each interface on the
switch, such as administrative status, input/output packets, packet errors and
discards.
3
Configuring Interface Connections
You can use the Interface Configuration Page to enable/disable an interface, set
auto-negotiation and the interface capabilities to advertise, or manually fix the
speed, duplex mode, and flow control. Interfaces can also be designated as PVE
ports. PVE ports bypass the Forwarding Database (FDB), and forward all Unicast,
Multicast and Broadcast traffic to an uplink. A single uplink can be defined for a
protected port.
Command Attributes
• Unit No. — Indicates the stacking member for which the interface configuration
information is displayed.
• Interface — Indicates the stacking member for which the interface configuration
information is displayed.
• Name — Displays the port number.
• Port Type — Displays the port type. The possible field values are:
• Copper — Indicates the port has a copper port connection.
• Fiber — Indicates the port has a fiber optic port connection.
69
Page 94

Configuring the Switch
3
• Port Status — Indicates whether the port is currently operational or
non-operational. The possible field values are:
• Up — Indicates the port is currently operating.
• Down — Indicates the port is currently not operating.
• Port Speed — Displays the configured rate for the port. The port type determines
what speed setting options are available. Port speeds can only be configured when
auto negotiation is disabled. The possible field values are:
• 10M — Indicates the port is currently operating at 10 Mbps.
• 100M — Indicates the port is currently operating at 100 Mbps.
• 1000M — Indicates the port is currently operating at 1000 Mbps.
• Duplex Mode — Displays the port duplex mode. This field is configurable only
when auto negotiation is disabled, and the port speed is set to 10M or 100 M. This
field cannot be configur e d on LA Gs. The possible field val ues are:
• Full — The interface supports transmission between the device and its link
partner in both directions simultaneously.
• Half — The interface supports transmission between the device and the client
in only one direction at a time.
• Auto Negotiation — Displays the auto negotiation status on the port. Auto
negotiation is a protocol between two link partners that enabl es a port to a dvertise
its transmission rate, duplex mode, and flow control abilities to its partner.
• Advertisement — Defines the auto negotiation setting the port advertises. The
possible field values are:
• Max Capability — Indicates that all port speeds and duplex mode settings are
accepted.
• 10 Half — Indicates that the port advertises for a 10 Mbps speed port and half
duplex mode setting.
• 10 Full — Indicates that the port advertises for a 10 Mbps speed port and full
duplex mode setting.
• 100 Half — Indicates that the port adver tises for a 100 Mbps speed port and half
duplex mode setting.
• 100 Full — Indicates that the port advertises for a 100 Mbps speed port and ful l
duplex mode setting.
• 1000 Full — Indicates that the port advertises for a 1000 Mbps speed port and
full duplex mode setting
• Back Pressure — Displays the back pressure mode on the Port. Back pressure
mode is used with half duplex mode to disable ports from receiving messages.
• Flow Control — Displays the flow control status on the port. Operates when the
port is in full duplex mode.
• MDI/MDIX — Displays the MDI/MDIX status on the port. Hubs and switches are
deliberately wired opposite the way end stati ons are wired, so that when a hub or
switch is connected to an end station, a straight through Ethernet cable can be
used, and the pairs are matched up properly. When two hubs or switches are
connected to each other, or two end stations are connected to each other, a
70
Page 95

Configuring Interfaces
crossover cable is used to ensure that the correct pairs are connected. The
possible field values are:
• Auto — Use to automatically detect the cable type.
• MDI (Media Dependent Interface) — Use for end stations.
• MDIX (Media Dependent Interface with Crossover) — Use for hubs and
switches.
• LAG — Indicates the LAG of which the port is a member.
• PVE — Enables a port to be a Private VLAN Edge (PVE) port. When a port is
defined as PVE, it bypasses the Forwarding Database (FDB), and forwards all
Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast traffic to an uplink (except MAC-to-me packet s).
Uplinks can be a port or GE port. Traffic from the uplink is distributed to all
interfaces.
Only one uplink can be defined for a protected port. Private VLANs cannot be
configured on ports on which IGMP snooping or Multicast TV VLAN has been
configured. An IP address cannot be configured on the VLAN of which a protected
port is a member. Only one uplink can be defined for a protected port. Private
VLANs cannot be configured on ports on which IGMP snooping or Mul ticast TV
VLAN has been configured. An IP address cannot be configured on the VLAN of
which a protected port is a member .
Web – Click System, Interfaces, Interface, Interface Configuration. Modify the
required interface settings, and click Apply.
3
Figure 3-22. Interface Configuration Page
71
Page 96

Configuring the Switch
3
CLI – The following is an example of the Port Configuration CLI commands:
Console# set interface active ethernet 1/e5 4-386
Console#
Console(config)#
Console(config-if)#
Console(config-if)#
Console(config-if)#
Console(config-if)#
Console(config-if)#
Console(config-if)#
Console(config-if)# back-pressure 4-384
configure
interface ethernet
description
speed 100 4-380
duplex full 4-381
negotiation 4-382
flowcontrol on 4-383
mdix auto 4-383
1/e5
"RD SW#3"
4-376
4-379
Creating Trunks (LAGs)
Link Aggregation optimizes port usage by linking a group of port s tog eth er to form a
single LAG (aggregated group). Aggregating port s multiplies the b andwidth bet ween
the devices, increases port flexibility, and provides link redundancy. The device
supports up to eight ports per LAG, and eight LAGs per system.
The device supports both static LAGs and Link Aggregation Control Protoc ol (LACP)
LAGs. LACP LAGs negotiate aggregating ports’ links with other LACP po rt s l ocated
on a different device. If the other device ports are also LACP ports, the devices
establish a LAG between them.
• Consider the following when aggregating ports:
• All ports within a LAG must be the s ame m ed i a ty p e.
• A VLAN is not configured on the port.
• The port is not assigned to a different LAG.
• Auto-negotiation mode is not configured on the port.
• The port is in full-duplex mode.
• All ports in the LAG have the same ingress filtering and tagged modes.
• All ports in the LAG have the same back pressure and flow control modes.
• All ports in the LAG have the sam e prio ri ty .
• All ports in the LAG have the same transceiver type.
• The device supports up to eight LAGs, and eight ports in each LAG.
• Ports can be configured as LACP ports only if the ports are not part of a previous ly
configured LAG.
• Ports added to a LAG lose their individual port configuration. When ports are
removed from the LAG, the original port configuration is applied to the port s.
The device uses a hash function to determine which packets are carried on which
aggregated-link member. The hash function statistically load-balances the
aggregated link members. The device considers an Aggregated Link as a single
logical port.
Note: To avoid creating a loop in the network, be sure you add a static trunk via the
configuration interface before connecting the ports, and also disconnect the
ports before removing a static trunk via the configuration interface.
72
Page 97

Configuring Interfaces
The LAG Membership Page contains parameters for defining LAG and LACP ports.
Command Attributes
• LAG Port — Displays the LAG number.
• Name — Displays the user-defined port name.
• Link State — Displays the link operational status.
• Member — Displays the ports configured to the LAG.
• Remove — Removes the LAG. The possible field values:
• Checked — Removes the selected LAG.
• Unchecked — Maintains the LAGs.
Web – Click System, Interfaces, Interface, LAG Membership. Define the fields and
click Apply.
3
Figure 3-23. LAG Membership Page
CLI – The following is an example of the CLI commands for aggregating ports:
Console(config-if)# channel-group 1 mode on 4-456
Configuring LACP
Aggregate ports can be linked into link-aggregation port-groups. Each group is
comprised of ports with the same speed, set to full-duplex operations.
LAG ports can contain different media types if the ports are operating at the same
speed. Aggregated links can be set up manually or automatically established by
enabling Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) on t he re le vant links . Aggreg ate
ports can be linked into link-aggregation port -groups. Each group is comprised of
73
Page 98

Configuring the Switch
3
ports with the same speed.
• Ports assigned to a common port channel must meet the following criteria:
• Ports must have the same LACP System Priority.
Notes: 1.
The Interface LACP Configuration Page contains parameters for defining the LACP
ports.
Command Attributes
• LACP System Priority — Determines the link aggregation group (LAG)
membership, and to identify this device to other swi tches during LAG negotiations.
Ports must be configured with the same system priority to join the same LAG.
System priority is combined with the switch’s MAC address to form the LAG
identifier. This identifier is used to indicate a specific LAG during LACP
negotiations with other systems. The field range is 1 - 65535, and the default is 1.
• Unit No. — Displays the stacking member for which the LACP parameters are
displayed
• Port — Displays the port number to which timeout and priority values are assigned.
• Port-Priority — Displays the LACP priority value for the port. The field range is
1-65535.
• LACP Timeout — Displays the administrative LACP timeout.
Web – Click System, Interfaces, Interface, LACP Configuration. Define the
LACP parameters and click Apply.
If the port channel admin key is not set (through the CLI) when a channel
group is formed (i.e., it has a null value of 0), this key is set to the same value
as the port admin key used by the interfaces that joined the group (lacp
admin key).
2. To avoid creating a loop in the network, be sure you enable LACP before
connecting the ports, and also disconnect the ports before disabling LACP.
3. If the target switch has also enabled LACP on the connected ports, the trunk
will be activated automatically.
4. A trunk formed with another switch using LACP will automatically be
assigned the next available trunk ID.
5. All ports on both ends of an LACP trunk must be configured for full duplex,
either by forced mode or auto-negotiation.
port
74
Page 99

Displaying Port Statistics
Figure 3-24. Interface LACP Configuration Page
CLI – The following is an example of the LACP interface CLI commands:
Console(config)#
4-431
Console(config)#
4-376
Console(config-if)#
4-432
Console(config-if)#
4-432
lacp system-priority
interface ethernet 1/e6
lacp port-priority
lacp timeout long
120
247
3
Displaying Port Statistics
You can display standard statistics on network traffic from the Interfaces Group and
Ethernet-like MIBs, as well as a detailed breakdown of traffic based on the RMON
MIB. Interfaces and Ethernet-like statisti cs display errors on the traffic passing
through each port. This information can be used to identify potential problems with
the switch (such as a faulty port or unusually heavy loading). RMON statistics
provide access to a broad range of statistics, including a total count of different
frame types and sizes passing through each port. All values di splayed have been
accumulated since the last system reboot, and are shown as counts per second.
75
Page 100

Configuring the Switch
3
Interface Statistics
Command Attributes
• Unit No. — Displays the stacking member for which the Interface Statistics are
displayed.
• Interface — Indicates the device for which statistics are displayed. The possible
field values are:
• Port — Defines the specific port for which interface statistics ar e d isplayed.
• LAG — Defines the specific LAG for which interface statistics are displayed.
• Refresh Rate — Defines the amount of time that passes before the interface
statistics are refreshed. The possible field values are:
• 15 Sec — Indicates that the Interface statistics are ref reshed every 15 seconds.
• 30 Sec — Indicates that the Interface statistics are ref reshed every 30 seconds.
• 60 Sec — Indicates that the Interface statistics are ref reshed every 60 seconds.
• No Refresh — Indicates that the Interface statistics are not refreshed.
Receive Statistics
• Total Bytes (Octets) — Displays the number of octets received on the selected
interface.
• Unicast Packets — Displays the number of Unicast packets received on the
selected interface.
• Multicast Packets — Displays the number of Multicast packets received on the
selected interface.
• Broadcast Packets — Displays the number of Broadcast packet s received on the
selected interface.
• Packets with Errors — Displays the number of error packets received from the
selected interface. Packet with Errors counts all errors without the CRC errors.
Transmit Statistics
• Total Bytes (Octets) — Displays the number of octets transmitted from the
selected interface.
• Unicast Packets — Displays the number of Unicast packets transmit ted from the
selected interface.
• Multicast Packets — Displays the number of Multicast packets transmitted from
the selected interface.
• Broadcast Packets — Displays the number of Broadcast packets transmitted
from the selected interface.
76
 Loading...
Loading...