Page 1

Agilent Technologies
E1465A/E1466A/E1467A
Relay Matrix Switch Modules
User’s Manual
Manual Part Number: E1465-90013
Printed in U.S.A. E0301
Page 2

Page 3

Contents
E1465A/E1466A/E1467A Relay Matrix Switch Modules User’s Manual
Front Matter....................................................................................................................... 7
Agilent Technologies Warranty Statement ................................................................... 7
U.S. Government Restricted Rights ............................................................................. 7
Safety Symbols ............................................................................................................ 8
Warnings ...................................................................................................................... 8
Documentation History................................................................................................. 8
Declaration Of Conformity ............................................................................................ 9
Chapter 1 - Getting Started ........................................................................................... 11
Using This Chapter .................................................................................................... 11
Matrix Modules Description ........................................................................................ 11
Programming the Matrix Modules .............................................................................. 15
Addressing the Modules ..................................................................................... 15
Example: Closing Relays (BASIC) ..................................................................... 16
Example: Closing Relays (Turbo C) ................................................................... 17
Chapter 2 - Configuring the Matrix Modules ............................................................... 19
Using This Chapter .................................................................................................... 19
WARNINGS and CAUTIONS..................................................................................... 19
Configuring the Switch Module .................................................................................. 20
Switch Module Connectors ................................................................................. 20
Setting the Logical Address Switch .................................................................... 21
Setting the Interrupt Level .................................................................................. 21
Installing the Switch Module in a Mainframe ...................................................... 23
Configuring the Terminal Modules.............................................................................. 24
Terminal Module Connectors .............................................................................. 24
Wiring the Terminal Modules .............................................................................. 27
Attaching the Terminal Modules to the Switch Module ....................................... 29
Configuring Larger Matrixes....................................................................................... 30
Creating Larger Matrixes .................................................................................... 30
Creating a 32x32 Matrix ..................................................................................... 30
Creating a 4x256 Matrix ..................................................................................... 32
Creating an 8x96 Matrix ..................................................................................... 33
Creating Larger Matrixes with Multiple Mainframes ........................................... 34
Chapter 3 - Using the Matrix Modules ......................................................................... 35
Using This Chapter .................................................................................................... 35
Matrix Modules Commands ....................................................................................... 35
Power-on and Reset Conditions ................................................................................ 36
Matrix Modules Identification...................................................................................... 36
Example: Matrix Module Identification (BASIC) .................................................. 36
Example: Matrix Module Identification (TURBO C) ............................................ 37
Switching Channels ................................................................................................... 38
Example: Opening/Closing Channels (BASIC) ................................................... 38
Example: Channel Sequencing (BASIC) ............................................................ 38
3
Page 4

Scanning Channels .................................................................................................... 39
Example: Scanning Channels Using TTL Triggers (BASIC) ............................... 39
Example: Scanning Using Trig In/Out Ports (BASIC) ........................................ 41
Querying Matrix Modules ........................................................................................... 42
Example: Querying Channel Closure (BASIC) ................................................... 42
Using the Scan Complete Bit ..................................................................................... 42
Example: Using the Scan Complete Bit (BASIC) ............................................... 43
Saving and Recalling States ...................................................................................... 44
Example: Saving and Recalling States (BASIC) ................................................. 44
Detecting Error Conditions ......................................................................................... 45
Example: Detecting Error Conditions (BASIC) ................................................... 45
Example: Detecting Error Conditions (TURBO C) .............................................. 45
Synchronizing Matrix Modules ................................................................................... 46
Example: Synchronizing a Matrix Module (BASIC) ............................................ 46
Understanding Matrix Modules .................................................................................. 47
Advantages of Latching Relays .......................................................................... 47
Matrix Module Operations .................................................................................. 47
Chapter 4 - Matrix Modules Command Reference ...................................................... 49
Using This Chapter .................................................................................................... 49
Command Types........................................................................................................ 49
Common Command Format ............................................................................... 49
SCPI Command Format ..................................................................................... 49
SCPI Command Reference ................................................................................. 51
ABORt ........................................................................................................................ 52
ARM ........................................................................................................................... 53
ARM:COUNt ....................................................................................................... 53
ARM:COUNt? ..................................................................................................... 54
DISPlay ...................................................................................................................... 55
DISPlay:MONitor:CARD ..................................................................................... 55
DISPlay:MONitor[:STATe] ................................................................................... 56
INITiate....................................................................................................................... 57
INITiate:CONTinuous ......................................................................................... 57
INITiate:CONTinuous? ....................................................................................... 58
INITiate[:IMMediate] ........................................................................................... 58
OUTPut ...................................................................................................................... 59
OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe] .................................................................................. 59
OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe]? ................................................................................ 60
OUTPut[:STATe] ................................................................................................. 60
OUTPut[:STATe]? ............................................................................................... 61
OUTPut:TTLTrgn[:STATe] ................................................................................... 61
OUTPut:TTLTrgn[:STATe]? ................................................................................. 62
[ROUTe:] .................................................................................................................... 63
[ROUTe:]CLOSe ................................................................................................. 63
[ROUTe:]CLOSe? ............................................................................................... 64
[ROUTe:]OPEN ................................................................................................... 65
[ROUTe:]OPEN? ................................................................................................. 66
[ROUTe:]SCAN ................................................................................................... 66
STATus....................................................................................................................... 68
STATus:OPERation:CONDition? ........................................................................ 70
STATus:OPERation:ENABle ............................................................................... 70
STATus:OPERation:ENABle? ............................................................................. 70
4
Page 5

STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]? ............................................................................ 71
STATus:PRESet ................................................................................................. 71
SYSTem ..................................................................................................................... 72
SYSTem:CDEScription? ..................................................................................... 72
SYSTem:CPON .................................................................................................. 73
SYSTem:CTYPe? ............................................................................................... 73
SYSTem:ERRor? ................................................................................................ 74
TRIGger ..................................................................................................................... 75
TRIGger[:IMMediate] .......................................................................................... 75
TRIGger:SOURce ............................................................................................... 76
TRIGger:SOURce? ............................................................................................. 77
SCPI Commands Quick Reference............................................................................ 78
IEEE 488.2 Common Commands Reference ............................................................ 79
Appendix A - Matrix Modules Specifications .............................................................. 81
Appendix B - Register-Based Programming ............................................................... 83
About This Appendix .................................................................................................. 83
Register Programming vs. SCPI Programming.......................................................... 83
Addressing the Registers ........................................................................................... 83
The Base Address .............................................................................................. 84
Register Offset .................................................................................................... 84
Register Descriptions ................................................................................................. 86
Reading and Writing to the Registers ................................................................. 86
Manufacturer Identification Register ................................................................... 86
Device Type Register ......................................................................................... 86
Status/Control Register ....................................................................................... 86
Relay Control Register ....................................................................................... 88
Programming Examples ............................................................................................. 90
Example: Reading the Registers (BASIC) .......................................................... 90
Example: Reading the Registers (C/HP-UX) ...................................................... 91
Example: Making Measurements (BASIC) ......................................................... 92
Example: Making Measurements (C/HP-UX) ..................................................... 93
Example: Scanning Channels (BASIC) .............................................................. 95
Example: Scanning Channels (C/HP-UX) .......................................................... 96
Appendix C - Matrix Modules Error Messages ........................................................... 99
Error Types ................................................................................................................ 99
Error Messages........................................................................................................ 100
Appendix D - Relay Life .............................................................................................. 101
Replacement Strategy.............................................................................................. 101
Relay Life Factors .................................................................................................... 101
End-of-Life Determination ........................................................................................ 101
Index ............................................................................................................................. 103
5
Page 6

6
Page 7

AGILENT TECHNOLOGIES WARRANTY STATEMENT
AGILENT PRODUCT: E1465A/E1466A/E1467A Relay Matrix Switch Modules DURATION OF WARRANTY: 3 years
1. Agilent Technologies warrants Agilent hardware, accessories and supplies against defects in materials and workmanship for the period
specified above. If Agilent receives notice of such defects during the warranty period, Agilent will, at its option, either repair or replace
products which prove to be defective. Replacement products may be either new or like-new.
2. Agilent warrants that Agilent software will not fail to execute its programming instructions, for the period specified above, due to
defects in material and workmanship when properly installed and used. If Agilent receives notice of such defects during the warranty
period, Agilent will replace software media which does not execute its programming instructions due to such defects.
3. Agilent does not warrant that the operation of Agilent products will be interrupted or error free. If Agilent is unable, within a reasonable
time, to repair or replace any product to a condition as warranted, customer will be entitled to a refund of the purchase price upon prompt
return of the product.
4. Agilent products may contain remanufactured parts equivalent to new in performance or may have been subject to incidental use.
5. The warranty period begins on the date of delivery or on the date of installation if installed by Agilent. If customer schedules or delays
Agilent installation more than 30 days after delivery, warranty begins on the 31st day from delivery.
6. Warranty does not apply to defects resulting from (a) improper or inadequate maintenance or calibration, (b) software, interfacing, parts
or supplies not supplied by Agilent, (c) unauthorized modification or misuse, (d) operation outside of the published environmental
specifications for the product, or (e) improper site preparation or maintenance.
7. TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THE ABOVE WARRANTIES ARE EXCLUSIVE AND NO OTHER
WARRANTY OR CONDITION, WHETHER WRITTEN OR ORAL, IS EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED AND AGILENT
SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY, SATISFACTORY
QUALITY, AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
8. Agilent will be liable for damage to tangible property per incident up to the greater of $300,000 or the actual amount paid for the product
that is the subject of the claim, and for damages for bodily injury or death, to the extent that all such damages are determined by a court
of competent jurisdiction to have been directly caused by a defective Agilent product.
9. TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THE REMEDIES IN THIS WARRANTY STATEMENT ARE CUSTOMER’S
SOLE AND EXLUSIVE REMEDIES. EXCEPT AS INDICATED ABOVE, IN NO EVENT WILL AGILENT OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE
LIABLE FOR LOSS OF DATA OR FOR DIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL (INCLUDING LOST PROFIT OR
DATA), OR OTHER DAMAGE, WHETHER BASED IN CONTRACT, TORT, OR OTHERWISE.
FOR CONSUMER TRANSACTIONS IN AUSTRALIA AND NEW ZEALAND: THE WARRANTY TERMS CONTAINED IN THIS
STATEMENT, EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT LAWFULLY PERMITTED, DO NOT EXCLUDE, RESTRICT OR MODIFY AND ARE
IN ADDITION TO THE MANDATORY STATUTORY RIGHTS APPLICABLE TO THE SALE OF THIS PRODUCT TO YOU.
U.S. Government Restricted Rights
The Software and Documentation have been developed entirely at private expense. They are delivered and licensed as "commercial
computer software" as defined in DFARS 252.227- 7013 (Oct 1988), DFARS 252.211-7015 (May 1991) or DFARS 252.227-7014 (Jun
1995), as a "commercial item" as defined in FAR 2.101(a), or as "Restricted computer software" as defined in FAR 52.227-19 (Jun
1987)(or any equivalent agency regulation or contract clause), whichever is applicable. You have only those rights provided for such
Software and Documentation by the applicable FAR or DFARS clause or the Agilent standard software agreement for the product
involved.
E1465A/E1466A/E1467A Relay Matrix Switch Modules User’s Manual
Copyright © 1991, 1993, 1995, 1996, 2001 Agilent Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Edition 7
7
Page 8
Documentation History
All Editions and Updates of this manual and their creation date are listed below. The first Edition of the manual is Edition 1. The Edition
number increments by 1 whenever the manual is revised. Updates, which are issued between Editions, contain replacement pages to
correct or add additional information to the current Edition of the manual. Whenever a new Edition is created, it will contain all of the
Update information for the previous Edition. Each new Edition or Update also includes a revised copy of this documentation history page.
Edition 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . July, 1991
Edition 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . July, 1993
Edition 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . June, 1995
Edition 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . January, 1996
Edition 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . May, 1996
Edition 6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . November, 1996
Edition 7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . March, 2001
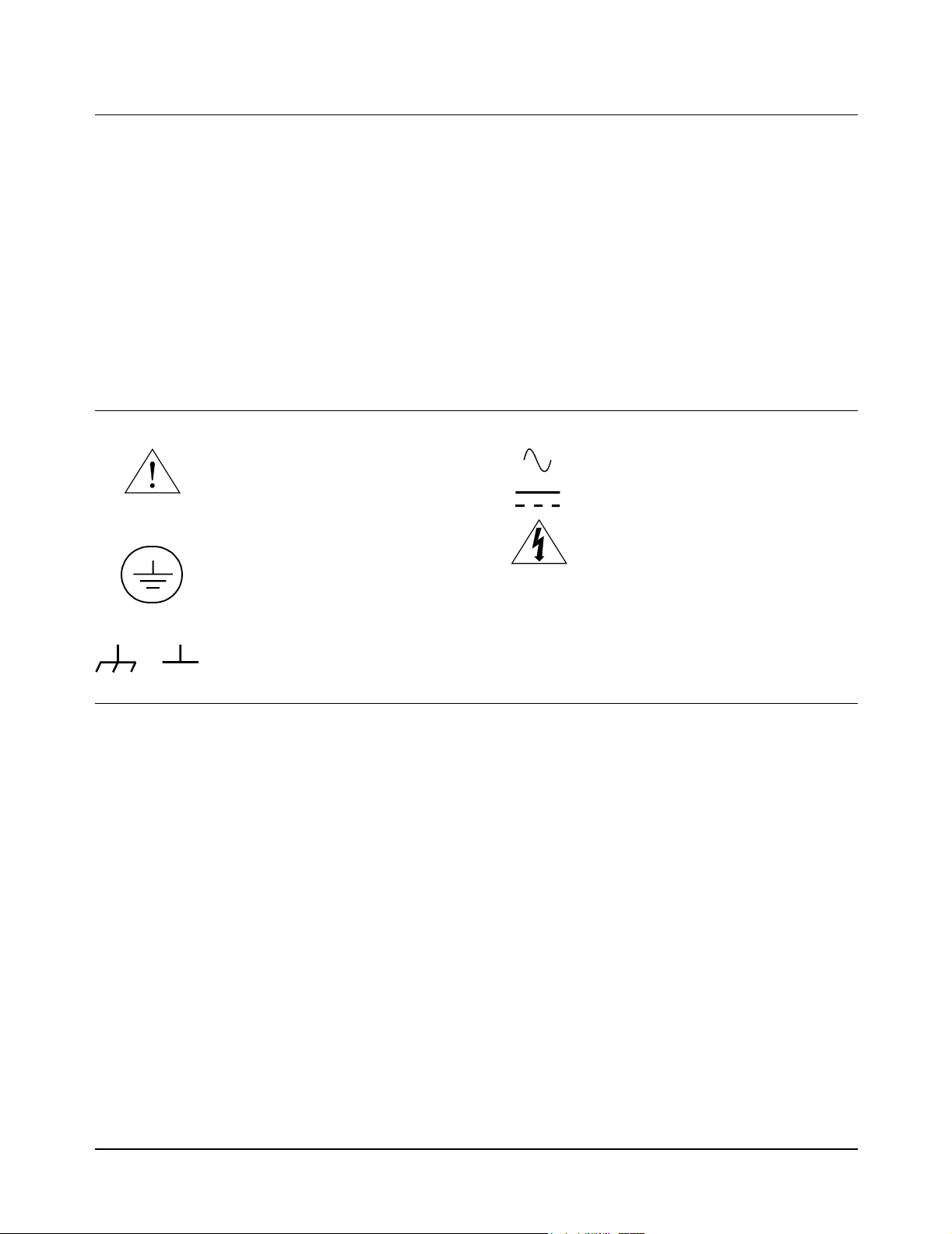
Safety Symbols
Instruction manual symbol affixed to
Instruction manual symbol affixed to
product. Indicates that the user must refer to
product. Indicates that the user must refer to
the manual for specific WARNING or
the manual for specific WARNING or
CAUTION information to avoid personal
CAUTION information to avoid personal
injury or damage to the product.
injury or damage to the product.
Indicates the field wiring terminal that must
be connected to earth ground before
operating the equipment — protects against
electrical shock in case of fault.
WARNING
Alternating current (AC)
Direct current (DC).
Warning. Risk of electrical shock.
Calls attention to a procedure, practice, or
condition that could cause bodily injury or
death.
or
Frame or chassis ground terminal—typically
connects to the equipment's metal frame.
CAUTION
Calls attention to a procedure, practice, or
condition that could possibly cause damage to
equipment or permanent loss of data.
WARNINGS
The following general safety precautions must be observed during all phases of operation, service, and repair of this product. Failure to
comply with these precautions or with specific warnings elsewhere in this manual violates safety standards of design, manufacture, and
intended use of the product. Agilent Technologies assumes no liability for the customer's failure to comply with these requirements.
Ground the equipment: For Safety Class 1 equipment (equipment having a protective earth terminal), an uninterruptible safety earth
ground must be provided from the mains power source to the product input wiring terminals or supplied power cable.
DO NOT operate the product in an explosive atmosphere or in the presence of flammable gases or fumes.
For continued protection against fire, replace the line fuse(s) only with fuse(s) of the same voltage and current rating and type. DO NOT
use repaired fuses or short-circuited fuse holders.
Keep away from live circuits: Operating personnel must not remove equipment covers or shields. Procedures involving the removal of
covers or shields are for use by service-trained personnel only. Under certain conditions, dangerous voltages may exist even with the
equipment switched off. To avoid dangerous electrical shock, DO NOT perform procedures involving cover or shield removal unless you
are qualified to do so.
DO NOT operate damaged equipment: Whenever it is possible that the safety protection features built into this product have been
impaired, either through physical damage, excessive moisture, or any other reason, REMOVE POWER and do not use the product until
safe operation can be verified by service-trained personnel. If necessary, return the product to Agilent for service and repair to ensure that
safety features are maintained.
DO NOT service or adjust alone: Do not attempt internal service or adjustment unless another person, capable of rendering first aid and
resuscitation, is present.
DO NOT substitute parts or modify equipment: Because of the danger of introducing additional hazards, do not install substitute parts
or perform any unauthorized modification to the product. Return the product to Agilent for service and repair to ensure that safety features
are maintained.
8
Page 9
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
According to ISO/IEC Guide 22 and CEN/CENELEC EN 45014
Manufacturer’s Name: Agilent Technologies, Inc.
Manufacturer’s Address: Basic, Emerging and Systems Technologies Product Generation Unit
815 14
Loveland, CO 80537 USA
Declares, that the product
Product Name: Relay Matrix Switch Modules
Model Number: E1465A/E1466A/E1467A
Product Options: This declaration includes all options of the above product(s).
Conforms with the following European Directives:
The product herewith complies with the requirements of the Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC and the EMC Directive 89/336/EEC
and carries the CE Marking accordingly.
Conforms with the following product standards:
EMC Standard Limit
IEC 61326-1:1997 + A1:1998 / EN 61326-1:1997 + A1:1998
CISPR 11:1997 + A1:1997 / EN 55011-1991 Group 1, Class A
IEC 61000-4-2:1995+A1998 / EN 61000-4-2:1995 4 kV CD, 8 kV AD
IEC 61000-4-3:1995 / EN 61000-4-3:1995 3 V/m, 80-1000 MHz
IEC 61000-4-4:1995 / EN 61000-4-4:1995 0.5 kV signal lines, 1 kV power lines
IEC 61000-4-5:1995 / EN 61000-4-5:1995 0.5 kV line-line, 1 kV line-ground
IEC 61000-4-6:1996 / EN 61000-4-6:1996 3 V, 0.15-80 MHz
IEC 61000-4-11:1994 / EN 61000-4-11:1994 1 cycle, 100%
th
Street S.W.
[1]
Canada: ICES-001:1998
Australia/New Zealand: AS/NZS 2064.1
Safety IEC 61010-1:1990+A1:1992+A2:1995 / EN 61010-1:1993+A2:1995
Canada: CSA C22.2 No. 1010.1:1992
UL 3111-1
Supplemental Information:
[1] The product was tested in a typical configuration with Agilent Technologies test systems.
September 5, 2000
Date Name
Quality Manager
Title
Authorized EU-representative: Agilent Technologies Deutschland GmbH, Herrenberger Stra>e 130, D 71034 Böblingen, Germany
For further information, please contact your local Agilent Technologies sales office, agent or distributor.
Revision: A.03 Issue Date: 09/05/00
9
Page 10
Notes:
10
Page 11

Using This Chapter
This chapter gives guidelines to get started using the E1465A, E1466A, and
E1467 Relay Matrix Switch Modules (matrix modules), including:
• Matrix Modules Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
• Programming the Matrix Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
Matrix Modules Description
The E1465A, E1466A, and E1467A Relay Matrix Switch modules are
VXIbus C-Size register-based modules that can operate with a command
module, such as an E1406A. Four 4x16 submatrixes are implemented on
the PC board with 256 latching relays. Terminal modules convert the submatrixes into 4x64 (E1466A), 8x32 (E1467A), or 16x16 (E1465A) matrixes.
Agilent plug-in modules installed in an mainframe or used with a command
module are treated as independent instruments, each having a unique
secondary GPIB address. Each instrument is assigned a dedicated error
queue, input and output buffers, status registers, and if applicable,
dedicated mainframe/command module memory space for readings or data.
An instrument may be composed of a single plug-in module or multiple
plug-in modules.
Chapter 1
Getting Started
NOTE The matrix model number is determined by the terminal module connected
to the PC board. If no terminal module is connected, the relay matrix switch
module defaults to an E1466A. To program the E1465A and E1467A, make
certain the terminal module is connected.
E1465A Relay Matrix module (Figure 1-1) provides a 16x16 two-wire
The
crosspoint matrix. This 16x16 matrix is created by connecting the terminal
module. The terminal module connects the columns of the submatrixes of
A, B, C, and D.
The
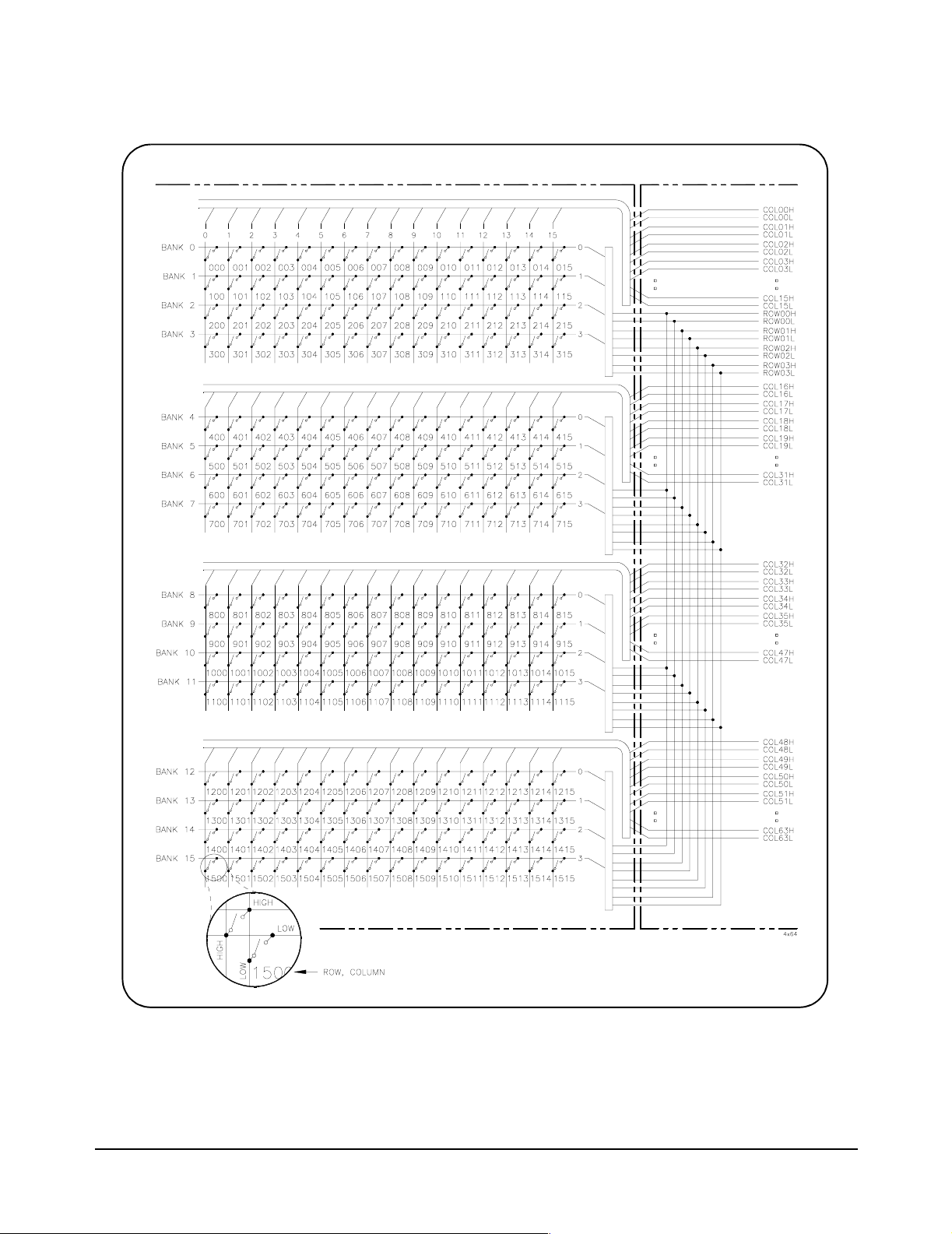
E1466A Relay Matrix module (Figure 1-2) provides a 4x64 two-wire
crosspoint matrix. This 4x64 matrix is created by connecting the terminal
module. The terminal module connects the rows of submatrixes A, B, C,
and D.
The
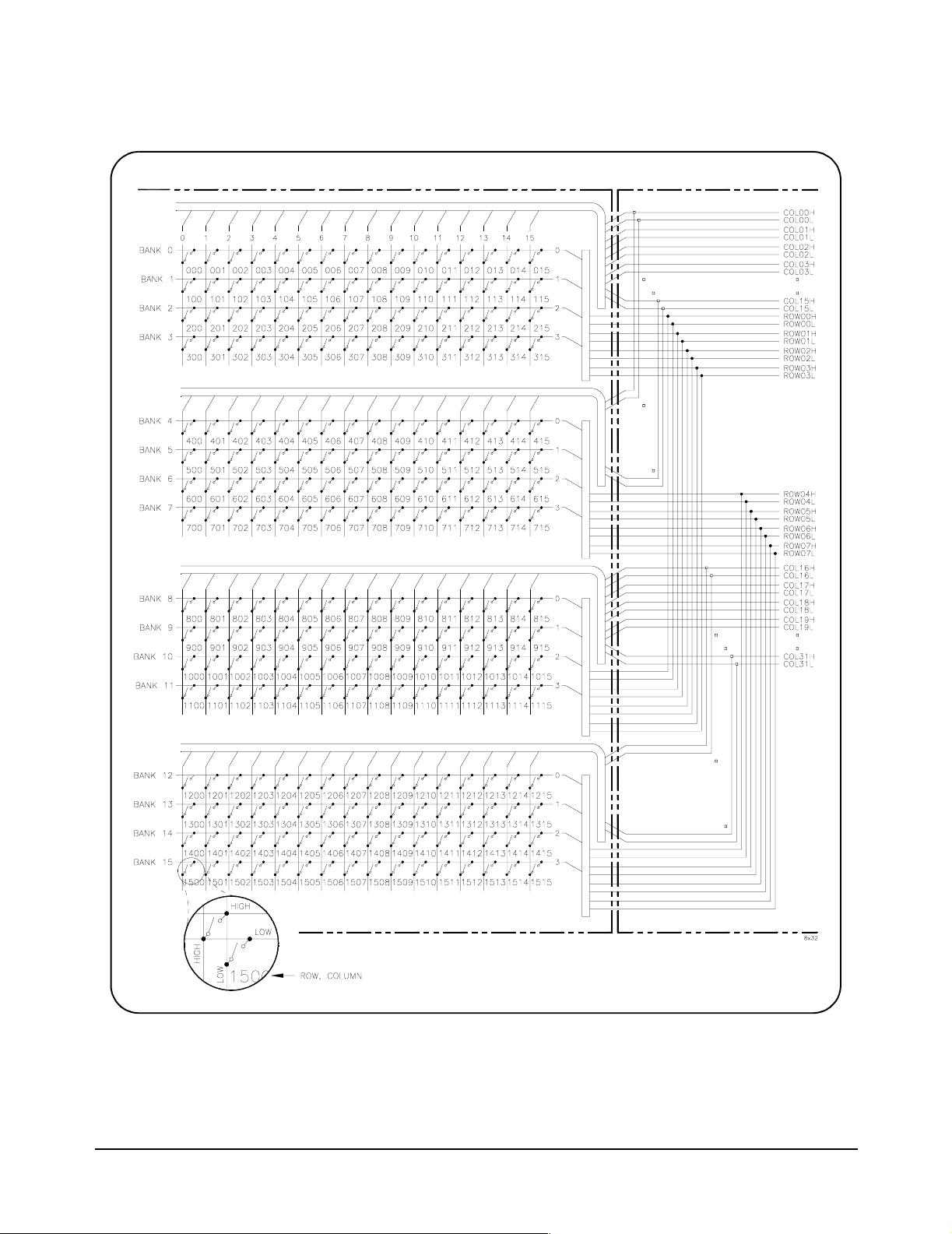
E1467A Relay Matrix module (Figure 1-3) provides an 8x32 two-wire
crosspoint matrix. This 8x32 matrix is created by connecting the terminal
module. The terminal module connects the rows of submatrixes A and C,
and rows of submatrixes B and D. The columns of submatrixes A and B,
and columns of submatrixes C and D are also connected.
Getting Started 11Chapter 1
Page 12
TERMINAL MODULEMATRIX MODULE
A
B
C
D
Figure 1-1. E1465A 16x16 Relay Matrix Module
12 Getting Started Chapter 1
Page 13
TERMINAL MODULEMATRIX MODULE
A
B
C
D
Figure 1-2. E1466A 4x64 Relay Matrix Module
Getting Started 13Chapter 1
Page 14
TERMINAL MODULEMATRIX MODULE
A
B
C
D
Figure 1-3. E1467A 8x32 Relay Matrix Module
14 Getting Started Chapter 1
Page 15

Programming the Matrix Modules
There are several ways you can program the matrix modules. One way is
to write directly to the registers. This method can provide better throughput
speed, but requires more knowledge of the matrix design. See Appendix B
for information on register-based programming.
Another way to program the matrix module is to use a command module and
Standard Commands for Programmable Instruments (SCPI). With SCPI
commands, the command module parses the commands and writes to the
appropriate relay module register. The examples in this manual use the
SCPI programming language. See Appendix B for examples on writing
directly to the registers.
Addressing the
Modules
Channel List The channel_list is a combination of the card number and the channel
Card Number The card number (ss of the channel_list) identifies the switch module
To address specific channels (relays) within a matrix module, you specify
the SCPI command and matrix module channel list. The following are the
most commonly used SCPI commands:
• CLOSe channel_list Closes the relays specified
• OPEN channel_list Opens the relays specified
• SCAN channel_list Closes the relays specified, one at a time
numbers. The channel_list takes the form of @ssrrcc where ss = matrix
module card number (00-99), rr = row number of the matrix module, and
cc = column number of the matrix module.
within a switchbox. The card number assigned depends on the switch
configuration used. Leading zeroes can be ignored for the card number.
For a single-module switchbox configuration, the card number is always 01.
For a multiple-module switchbox configuration, multiplexer modules are set
to successive logical addresses. The multiplexer module with the lowest
logical address is always card number 01. The card number with the next
successive logical address is 02, etc.
Figure 1-4 illustrates card numbers and logical addresses of a typical
multiple-module switchbox configuration. Chapter 2 shows an example of
addressing a switchbox configuration.
Channel Addresses The channel address is the rrcc of the channel_list. This address determines
which relay will be addressed. Use a comma (,) to form a channe list or
use a colon (:) to form a channel range. You can address single channels
(@ssrrcc), multiple channels (@ssrrcc,ssrrcc,...), sequential channels
(@ssrrcc:ssrrcc), groups of sequential channels (@ssrrcc:ssrrcc,
ssrrcc:ssrrcc), or any combination.
Only valid channels can be accessed in a channel list or channel range.
Also, the channel range must be from a lower channel number to a higher
channel number. For example, CLOS (@10000:20303) is acceptable, but
CLOS (@20303:10000) generates an error. Table 1-1 shows the matrix
modules channel numbers for the three matrix modules.
Getting Started 15Chapter 1
Page 16
Command
Module
Table 1-1. Matrix Modules Channel Numbers
Matrix Module Rows (rr) Columns (cc)
E1465A 16x16 Relay Matrix Switch 00 - 15 00 - 15
E1466A 4x64 Relay Matrix Switch 00 - 03 00 - 63
E1467A 8x32 Relay Matrix Switch 00 - 07 00 - 31
Multiple-Module Switchbox Card Numbers
Card Number 01
Multiplexer Module
Logical Address = 120
1
4
8
6
2
2
1
2
1
2
4
1
3
6
2
4
8
6
4
3
6
1
4
8
2
6
4
3
1
6
Secondary Address = 15
8
2
1
Card Number 02
Multiplexer Module
Logical Address = 121
8
2
1
Card Number 03
Multiplexer Module
Logical Address = 122
8
2
1
Example: Closing
Relays (BASIC)
Note: Physical placement of the Module in the Logical Address
order is not required, but is recommended.
Figure 1-4. Card Numbers in a Multiple-Module Switchbox
This example assumes a PC running BASIC and a GPIB interface. The
program closes row 03, column 12 of an E1465A 16x16 matrix module at
logical address 120 (secondary address = 120/8 = 15) and queries the
result. The result is returned to the controller and displayed (1 = relay closed,
0 = relay open). See Chapter 4 for information on the SCPI commands.
10 OUTPUT 70915; "*RST"
20 OUTPUT 70915; "CLOS (@10312)"
! Resets the module
! Closes row 03, column 12 on
module number 1
30 OUTPUT 70915; "CLOS? (@10312)"
40 ENTER 70915; Value
50 PRINT Value
! Query channel 10312
! Enter result into variable Value
! Print results (should print "1"
to indicate that the channel is
closed)
60 END
! Terminate program
16 Getting Started Chapter 1
Page 17

Example: Closing
Relays (Turbo C)
This example assumes a PC with a GPIB Interface card (with command
library) running Borland Turbo C. The program closes row 03, column 12 of
an E1465A 16x16 matrix module at logical address 120 (secondary address
= 120/8 = 15) and queries the result. The result is returned to the controller
and displayed (1 = relay closed, 0 = relay open). See Chapter 4 for
information on the SCPI commands.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <chpib.h> /*Include file for GPIB*/
#define ISC 7L
#define MATRIX 70915L /*Matrix default address*/
#define TASK1 "*RST" /*Reset*/
#define TASK2 "CLOS (@10312)" /*Close row 3, column 12*/
#define TASK3 "CLOS? (@10312)" /*Query row 3, column 12*/
main()
{
char into[257];
int length = 256;
/*Output commands to matrix module*/
error_handler (IOTIMEOUT (7L,5.0), "TIMEOUT");
error_handler (IOOUTPUTS (MATRIX, TASK1, 4), "OUTPUT command");
error_handler (IOOUTPUTS (MATRIX, TASK2, 15), "OUTPUT
command");
error_handler (IOOUTPUTS (MATRIX, TASK3, 15), "OUTPUT
command");
/*Enter from matrix*/
error_handler (IOENTERS (MATRIX, into, &length), "ENTER command");
printf("Now let's see if the switch is closed: %s",into);
return;
}
int error_handler (int error, char *routine)
{
char ch;
if (error != NOERR)
{
printf ("\n Error %d %s \n", error, errstr(error));
printf (" in call to GPIB function %s \n\n", routine);
printf ("Press 'Enter' to exit: ");
scanf ("%c", &ch);
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}
Getting Started 17Chapter 1
Page 18

Notes:
18 Getting Started Chapter 1
Page 19

Configuring the Matrix Modules
Using This Chapter
This chapter gives guidelines to connect external wiring to the E1465A,
E1466A, and E1467A Relay Matrix Switch modules (matrix module) and
shows how to connect multiple modules together to form larger matrixes.
This chapter includes:
• WARNINGS and CAUTIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
• Configuring the Switch Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
• Configuring the Terminal Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
• Configuring Larger Matrixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
WARNINGS and CAUTIONS
WARNING SHOCK HAZARD. Only service-trained personnel who are
aware of the hazards involved should install, remove, or
configure matrix modules. Remove all power sources from the
mainframe and installed modules before installing or removing
a module.
Chapter 2
CAUTION MAXIMUM INPUTS. The maximum voltage that can be applied to
any terminal is 200 Vdc/170 Vrms. The maximum current that can
be applied to any row or column is 1 A dc or ac peak. The maximum
power that can be applied to any terminal is 30 W or 62.5 VA
(resistive).
CAUTION STATIC ELECTRICITY. Static electricity is a major cause of
component failure. To prevent damage to the electrical components
in a matrix module, observe anti-static techniques when removing or
installing the module or when working on the module.
Configuring the Matrix Modules 19Chapter 2
Page 20
Configuring the Switch Module
This section gives guidelines to configure the E1465A/E1466A/E1467A
switch module, including:
• Switch Module Connectors
• Setting the Logical Address Switch
• Setting the Interrupt Level
• Installing the Switch Module in a Mainframe
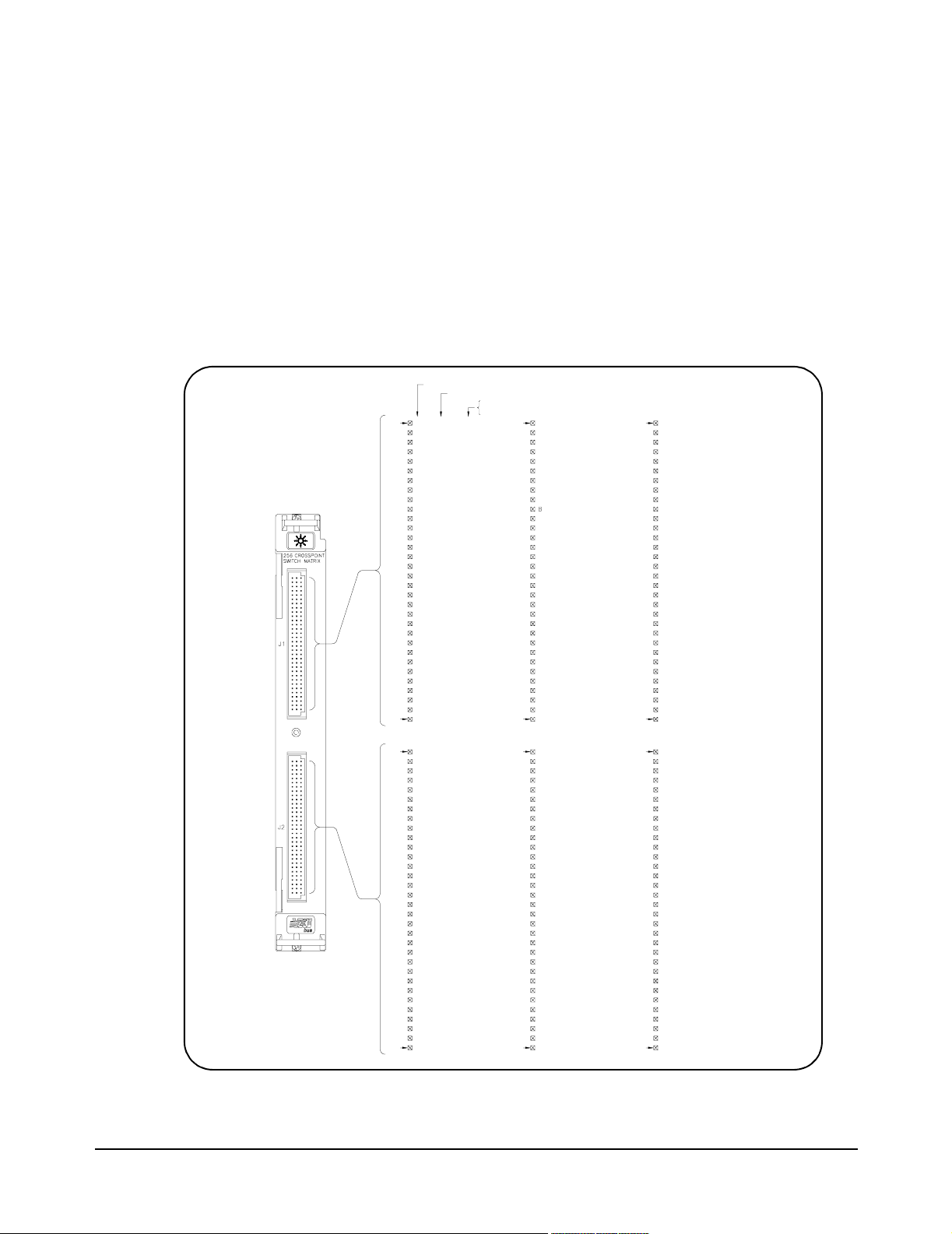
Switch Module
Connectors
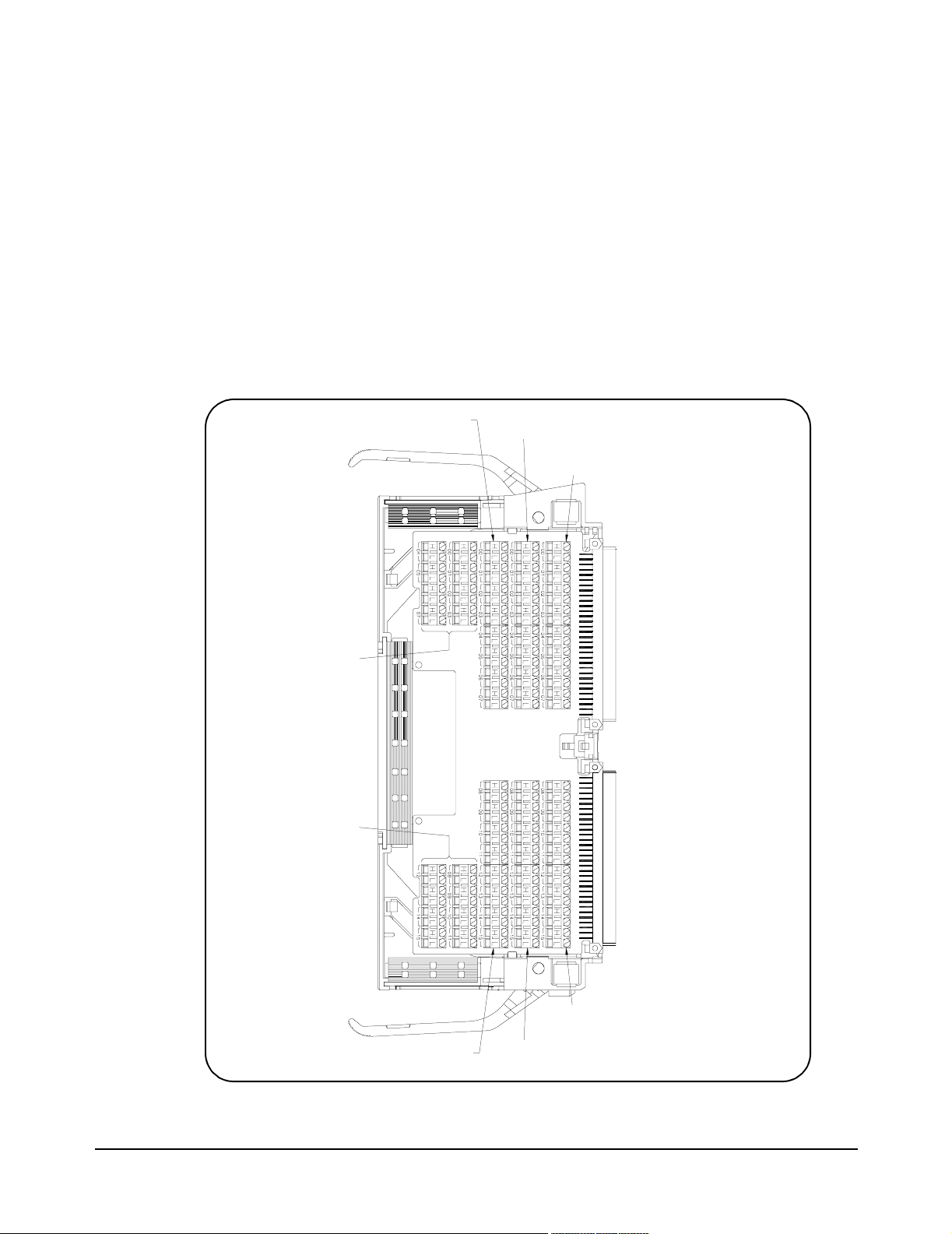
Figure 2-1 shows the front panel of the E1465/66/67A switch module and
the connector pin-out that mates to the terminal module.
Bank
Row/Column
L=Low
02H
02L
05H
05L
08H
08L
11H
11L
14H
14L
01H
01L
04H
04L
07H
07L
10H
10L
13H
13L
00H
03H
06LCOL
09H
09L
12H
12L
15H
15L
02H
02L
05H
05L
08H
08L
11H
11L
14H
14L
H=High
Pin
GND
64
GND
A
0H
0L
3H
3L
2H
2L
2H
2L
ROW
A
ROW1H1L
0H
ROW
B
ROW
B
B
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
Pin
B
33
Pin
C
64
CCCOL
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
CCROW
C
C
D
D
3H
ROW
ROW
COL
00H
COL
00L COL
03H
COL
03L
COL
06H
COL
06L
COL
09HCOLA
09L
COL
12H
COL
COL
12L
15H
COL
15L
COL
02H
COL
02L
COL
COL
05H
COL
05L
08H
COL
COL
08L
COL
11H
11L
COL
COL
14H
COL
14L
COL
01H
COL
01L
04H
04L
COL
07H
COL
07L
COL
10H
COL
10L
COL
13H
COL
13L
COL
00H
COL
00L
COL
03H
COL
03L
COL
06H
COL
06L
COL
09H
COL
09L
COL
12H
COL
12L
COL
15H
COL
15L
COL
ROW0H0L
3H
ROW
ROW
2H
ROW
ROW
Pin
GND
96
GND
ROW
ROW
ROW
ROW
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COLA
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
COL
ROW
ROW
ROW
ROW
ROW
ROW
01H
01L
04H
04L
07H
07L
10H
10L
13H
13L
00H
00L
03H
03L
06H
06L
09H
09L
12H
12L
15H
15L
02H
02L
05H
05L
08H
08L
11H
11L
14H
14L
01H
01L
04H
04L
07H
07L
10H
10L
13H
13L
2H
2L
1H
1L
1H
1L
0H
0L
3H
3L
A
A
0L
3L
3L
2L
B
B
NC
NC
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
Pin
B
65
Pin
C
96
CCCOL
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
D
NC
NC
C
C
D
D
D
D
Pin
32
Pin
Pin
32
1
GND
GND
ROW
A
ROW
A
ROW
A
ROW
A
ROWB
BNCROW
NC
AACOL
COL
AACOL
COL
AACOL
COL
COL
A
A
COL
A
COL
A
COL
B
COL
B
COL
B
COL
B
COL
B
COL
B
COL
B
COL
B
COL
BBCOL
COL
CCOL
C
COL 00L
CCOL
C
COL 03L
C
COL 06H
C
C
COL
C
COL
C
COL
C
COL
COL
CCCOL
D
COL
D
COL
D
COL
COL
D
D
COL
D
COL
D
COL
D
COL
D
COL
D
COL
NC
NC
C
ROW
C
ROW
D
ROW
D
ROW1H1L
GND
Pin
CF(10)
1
CF(13)
Pin
CF(11)
33
GND
Pin
CF(12)
65
Figure 2-1. Relay Matrix Switch Module Pin-out
20 Configuring the Matrix Modules Chapter 2
Page 21
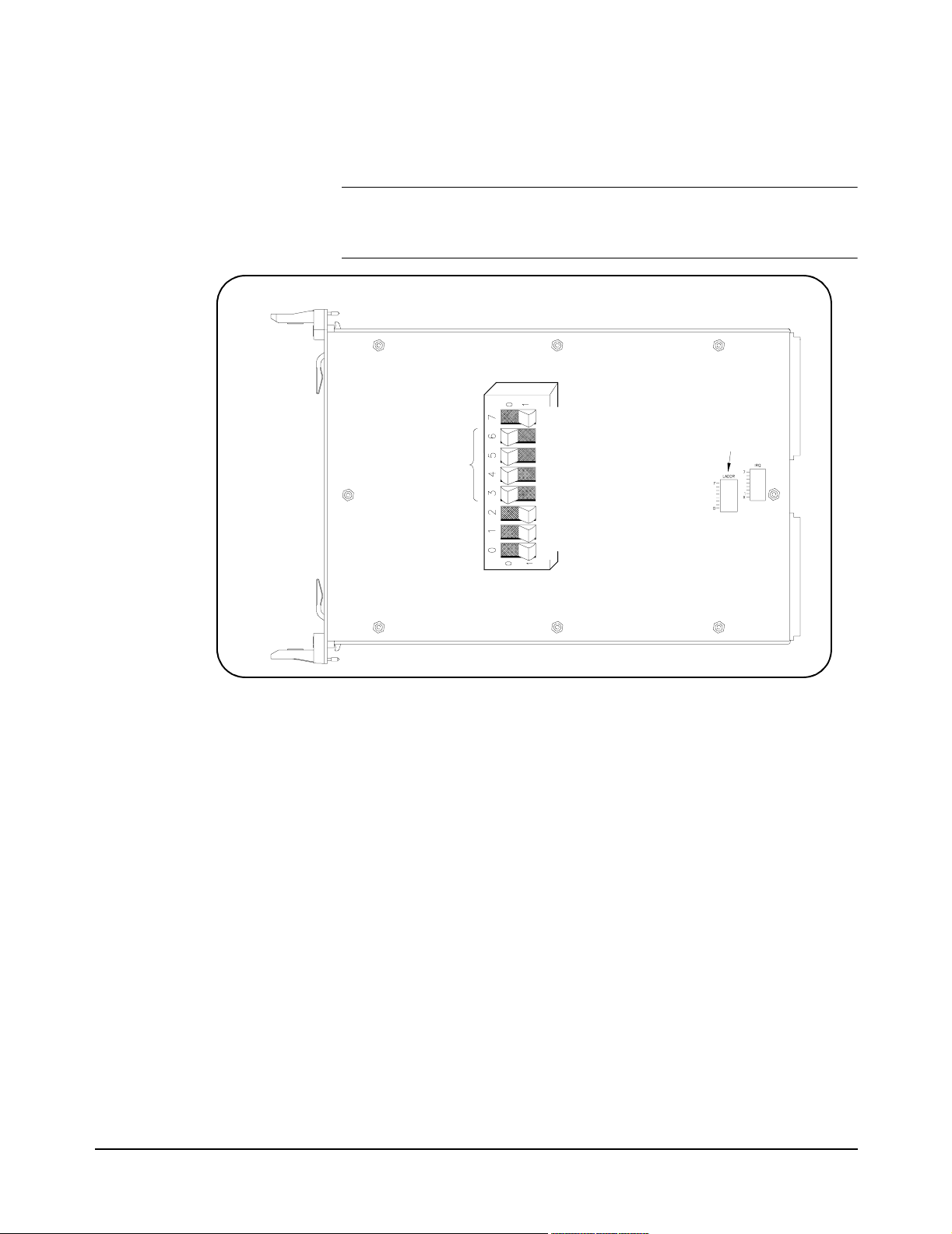
Setting the Logical
Address Switch
NOTE The address switch selected value must be a multiple of 8 if the module is
The logical address switch (LADDR) factory setting is 120. Valid address
values are from 1 to 255. The matrix module can be configured as a single
instrument or as a switchbox. See Figure 2-2 for switch position information.
the first module in a switchbox used with a VXIbus command module and
is being instructed by SCPI commands.
Logical Address = 120
Setting the Interrupt
Level
8+16+32+64=120
128
64
32
16
8
4
2
1
N
D
E
P
O
CLOSED = Switch Set To 1 (ON)
E
S
OPEN = Switch Set To 0 (OFF)
O
L
C
Logical Address
Switch Location
Figure 2-2. Setting the Module Logical Address
The matrix module generates an interrupt after a channel has been closed.
These interrupts are sent to, and acknowledgements are received from, the
command module (such as an E1406A) via the VXIbus backplane interrupt
lines. For applications where the matrix module is installed in a C-Size
mainframe and is a servant of the command module, the interrupt line
jumper does not have to be moved. See Figure 2-3 to change the interrupt
line.
You can select seven different interrupt line levels. Line X disables the
interrupt and should not be used. The module's factory setting is line 1.
To change the setting, remove the four-pin jumper (part number 1258-0247)
from the old line location and reinstall the jumper in the new line location.
If you are setting the interrupt line to something other than 1, see the
E1406A Command Module User's Manual for additional information. If the
four-pin jumper is not used, the two jumper locations must have the same
interrupt line selected.
Configuring the Matrix Modules 21Chapter 2
Page 22
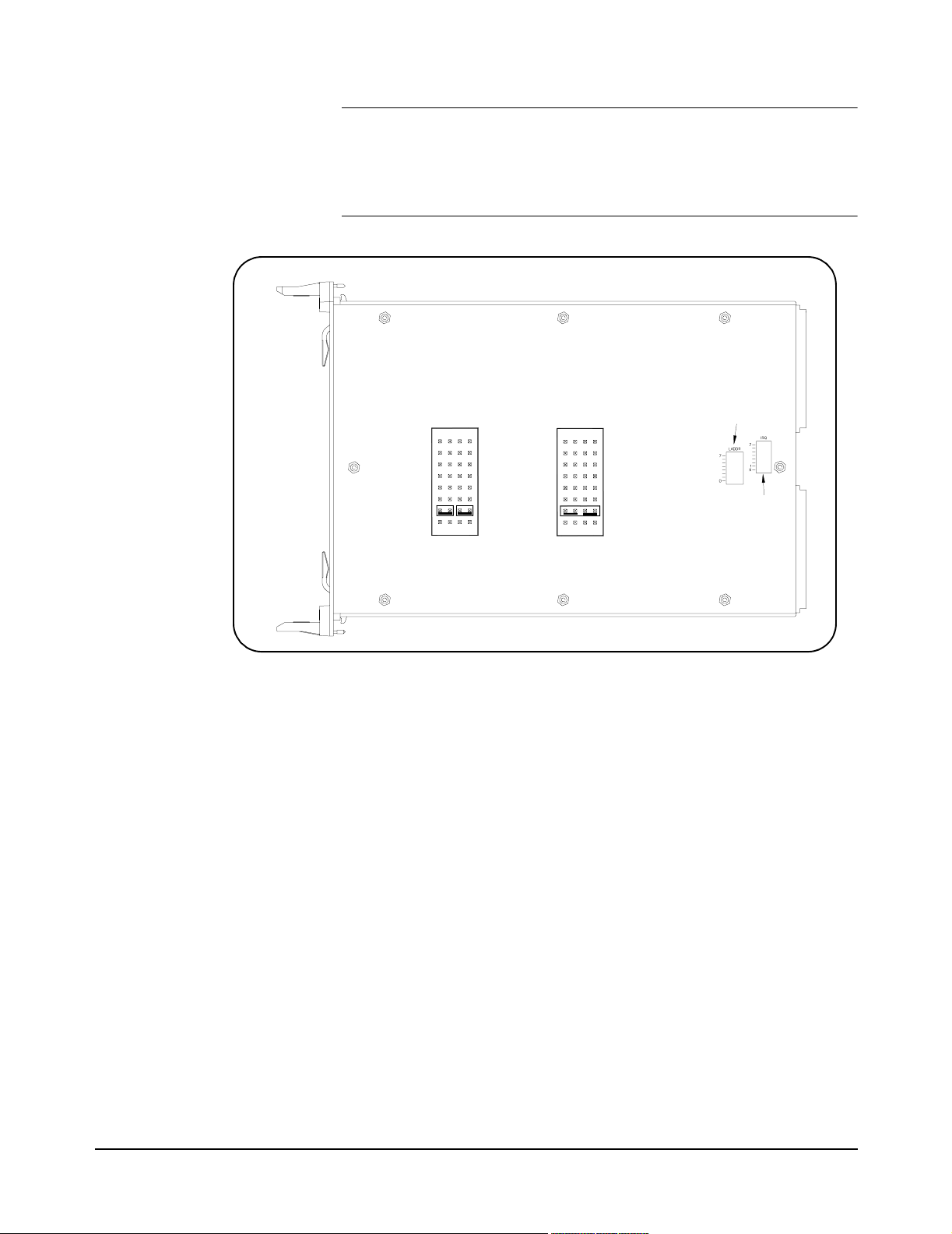
NOTE When the E1406A Command Module is the resource manager, the
interrupt line jumper must be installed in position 1. However, if you are
using an embedded computer with the E1406A Command Module,
interrupt line 2 should be selected. The Level X interrupt line should not
be used under normal operating conditions.
Using 2-Pin
IRQ
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
X
Using 4-Pin
JumperJumper
IRQ
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
X
Figure 2-3. Setting the Interrupt Level
Logical Address
Switch Location
Interrupt
Priority
Location
22 Configuring the Matrix Modules Chapter 2
Page 23
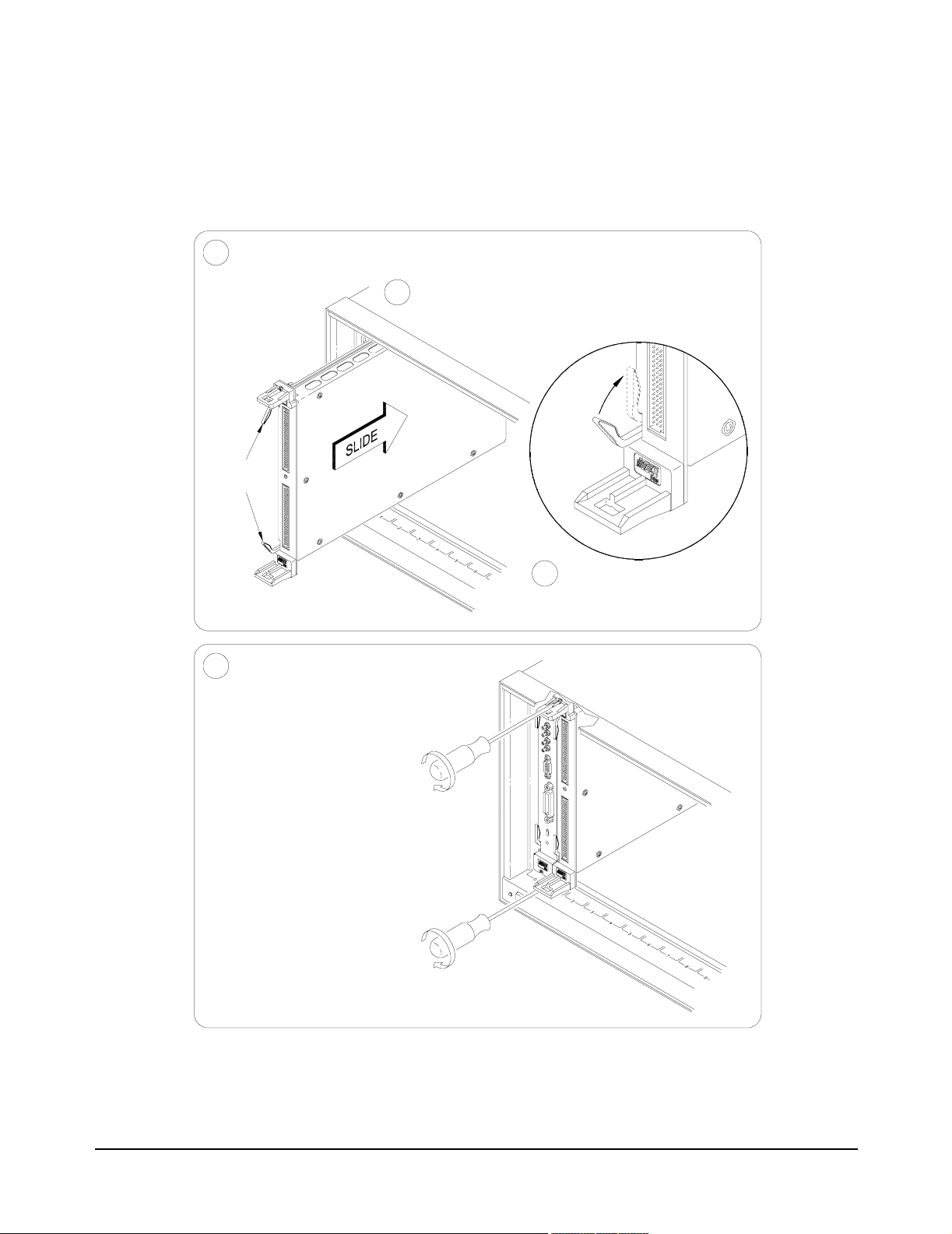
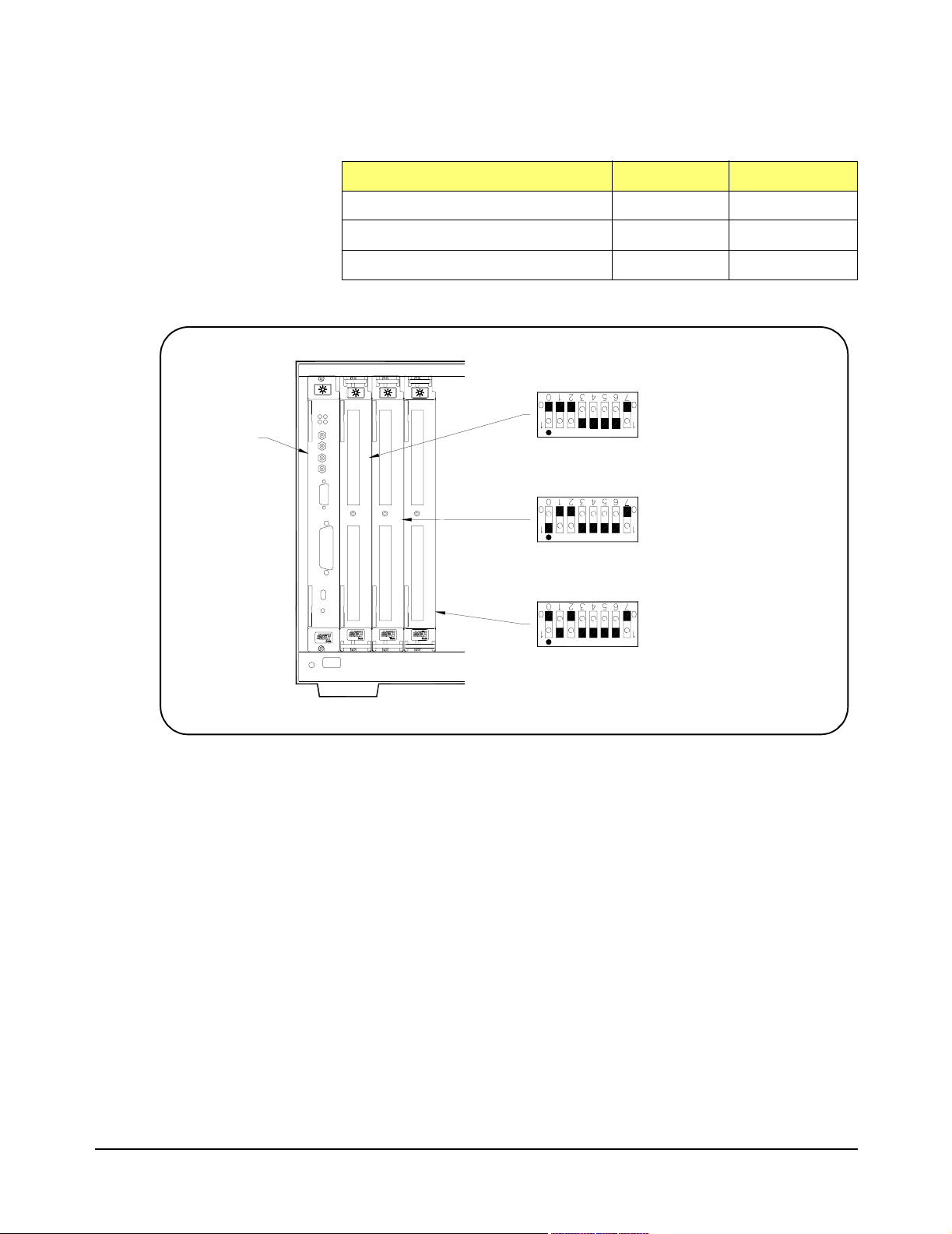
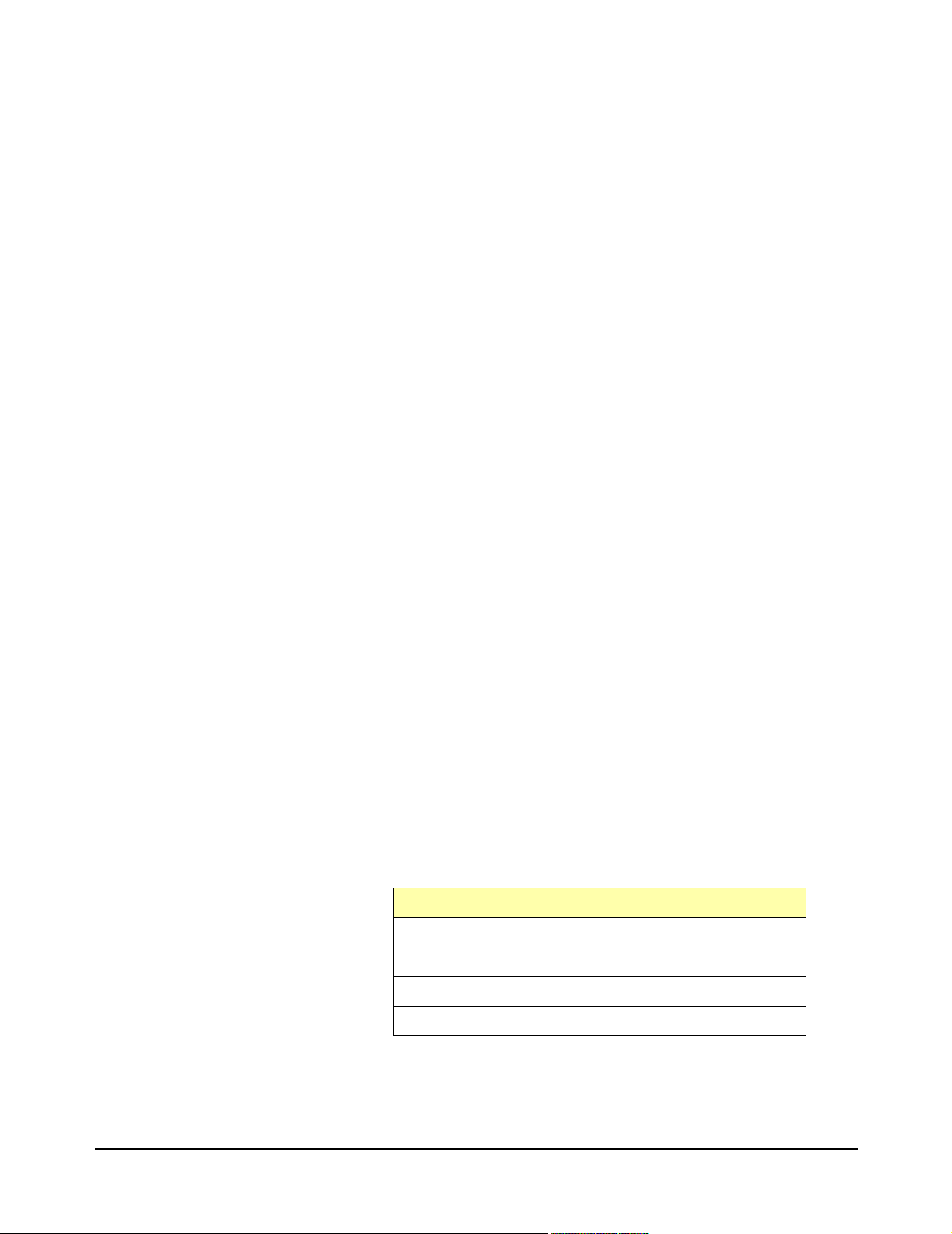
Installing the
Switch Module in a
Mainframe
Set the extraction levers out.
1
Extraction
Levers
E1465/66/67A Relay Matrix Switch modules may be installed in any slot
(except slot 0) in a C-size VXIbus mainframe. See Figure 2-4 to install the
module in a mainframe.
2
Slide the module into any slot (except slot 0)
until the backplane connectors touch.
4
Tighten the top and bottom screws
to secure the module to the
mainframe.
NOTE: The extraction levers will not
seat the backplane connectors on older
VXIbus mainframes. You must manually
seat the connectors by pushing in the
module until the module's front panel is
flush with the front of the mainframe. The
extraction levers may be used to guide or
remove the switch module.
To remove the module from the mainframe,
reverse the procedure.
3
Seat the module into the
mainframe by pushing in
the extraction levers.
Figure 2-4. Installing the Switch Module in a VXIbus Mainframe
Configuring the Matrix Modules 23Chapter 2
Page 24
Configuring the Terminal Modules
This section gives guidelines to configure the E1465A/E1466A/E1467A
terminal modules, including:
• Terminal Module Connectors
• Wiring Terminal Modules
• Connecting Terminal Modules to the Switch Module
Terminal Module
Connectors
Figure 2-5 shows the E1465A terminal module connectors and associated
row/column designators. Figure 2-6 shows the E1466A terminal module
connectors and associated row/column designators. Figure 2-7 shows
the E1467A terminal module connectors and associated row/column
designators.
Rows
(00-07)
Daisy Chain
Row (00-07)
Column
(00-07)
Daisy Chain
Column
(00-07)
Rows
(08-15)
Daisy Chain
Coumn
(08-15)
Daisy Chain
Row (08-15)
Column
(08-15)
Figure 2-5. E1465A Terminal Module
24 Configuring the Matrix Modules Chapter 2
Page 25
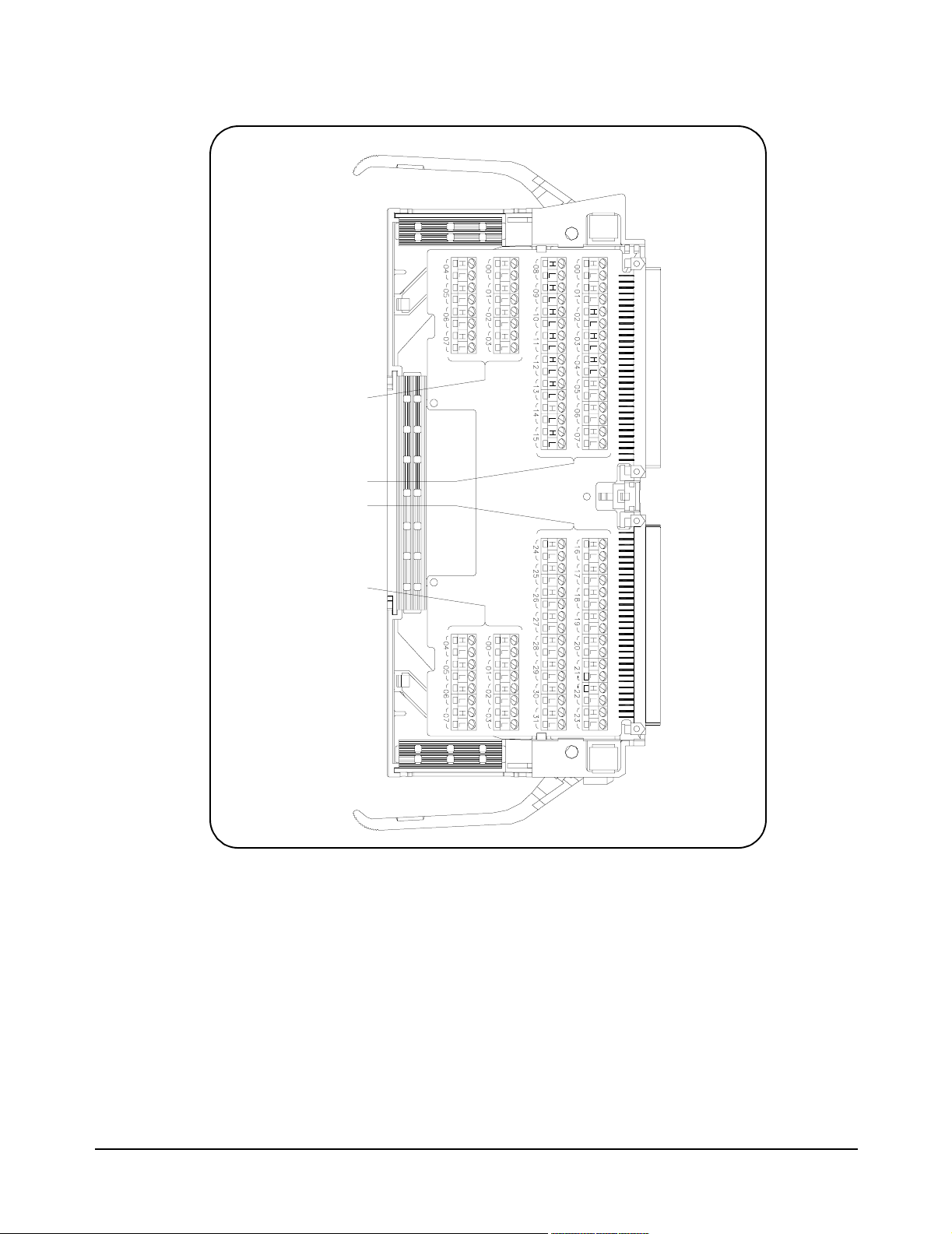
Rows
(00-03)
Daisy Chain Rows
for Expansion
Columns
(00-31)
Columns
(32-63)
Figure 2-6. E1466A Terminal Module
Configuring the Matrix Modules 25Chapter 2
Page 26
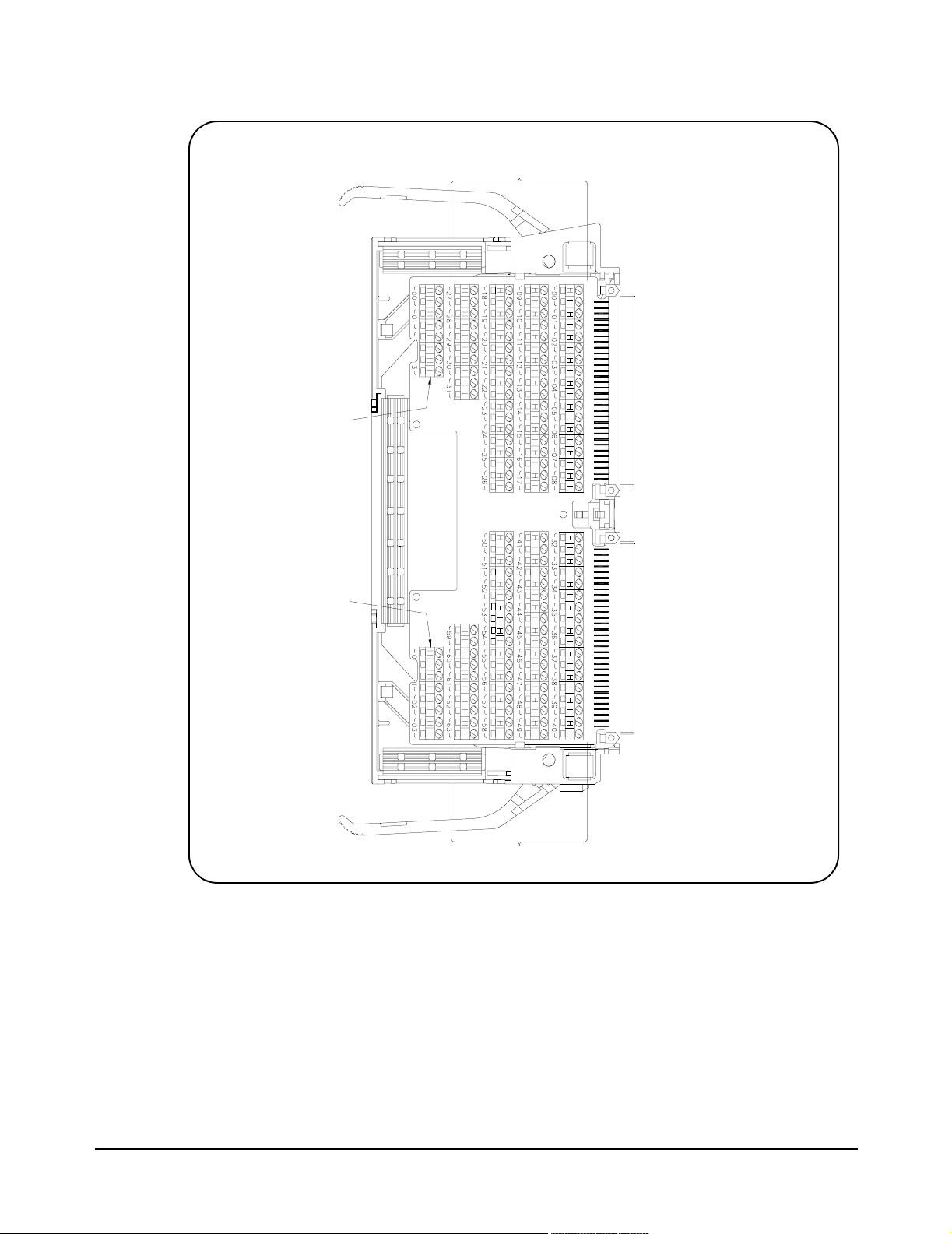
Rows (00-07)
Columns (00-15)
Columns (16-31)
Daisy Chain Rows
for Expansion
Figure 2-7. E1467A Terminal Module
26 Configuring the Matrix Modules Chapter 2
Page 27
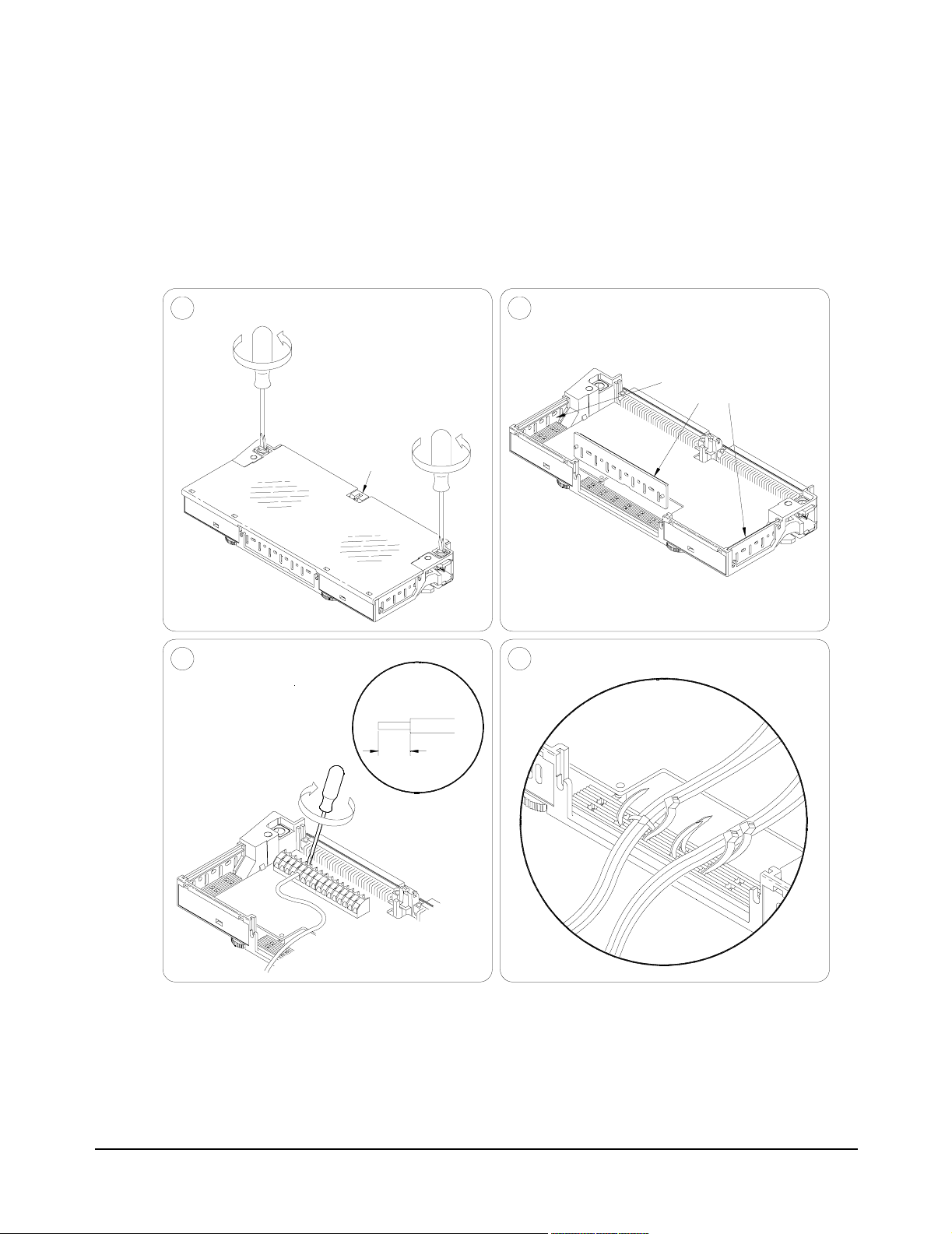
Wiring the Terminal
Modules
Remove clear cover.1 Remove and retain wiring exit panel.2
Figures 2-8 and 2-9 give guidelines to connect user wiring to the terminal
module assembly. Expansion connectors allow you to create larger
matrixes. See "Configuring Larger Matrixes" for details.
User wiring to the matrix modules is to the High (H) and Low (L) terminal
connections. Maximum terminal wire size is No. 16 AWG. Wire ends should
be stripped 6 mm (0.25 in.) and tinned. When wiring all channels, use a
smaller gauge wire (No. 20 - 22 AWG).
A. Release screws.
B. Press tab forward
and release.
Tab
Make connections.3 Route wiring.4
Screw type
Use wire
size 16-26
AWG
5mm
0.2"
VW1 Flammability
Rating
Remove 1 of the 3
wire exit panels.
Tighten wraps to
secure wires.
Insert wire into terminal.
Tighten screw.
Figure 2-8. Wiring the Terminal Module
Continued on next page
Configuring the Matrix Modules 27Chapter 2
Page 28
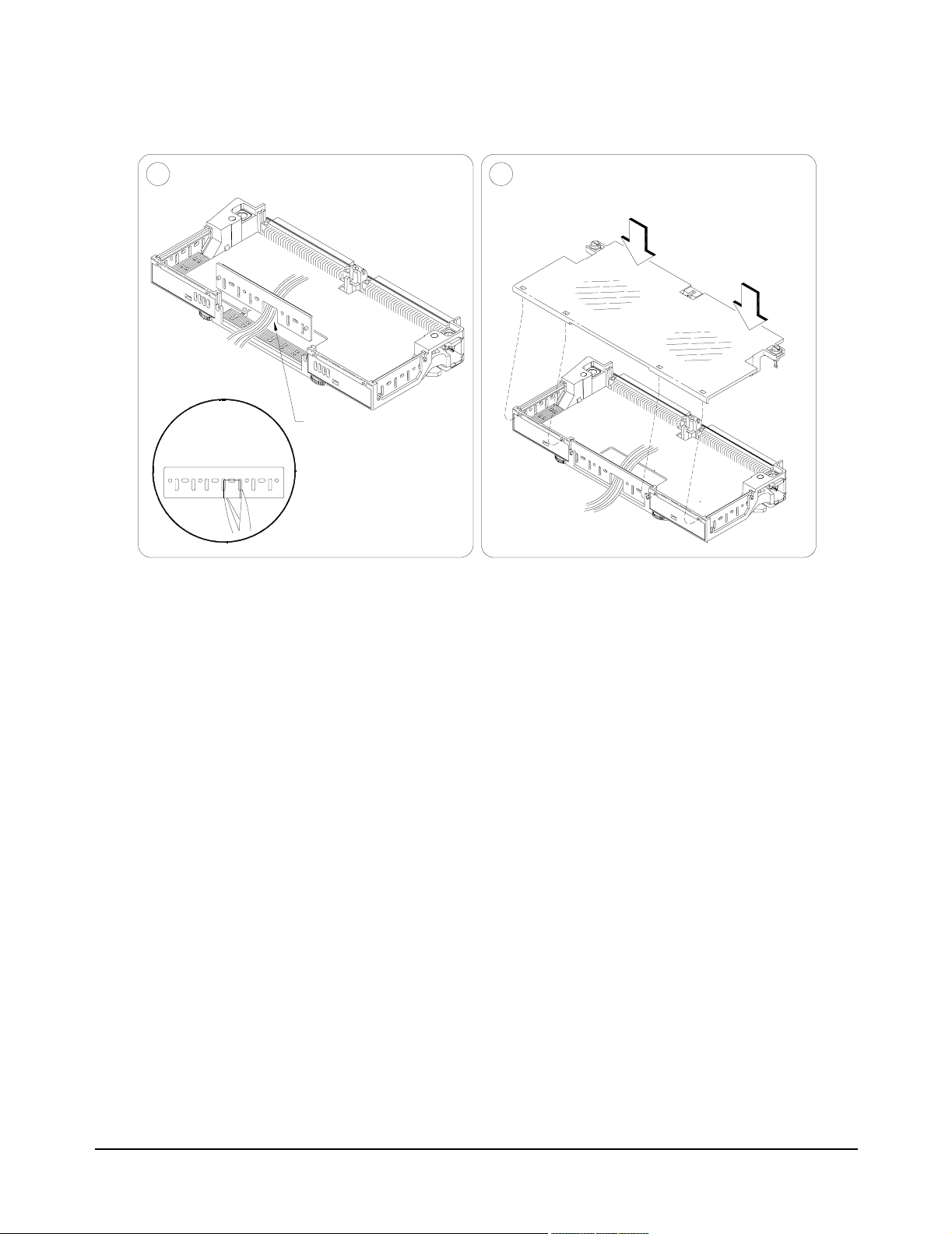
5
Replace wiring exit panel.
Replace clear cover.6
A. Hook in the top cover tabs
onto the fixture.
B. Press down and
tighten screws.
Cut required
holes in panels.
for wire exit
Keep wiring exit panel
hole as small as
possible.
Figure 2-9. Wiring the Terminal Module
Continued from previous page
28 Configuring the Matrix Modules Chapter 2
Page 29
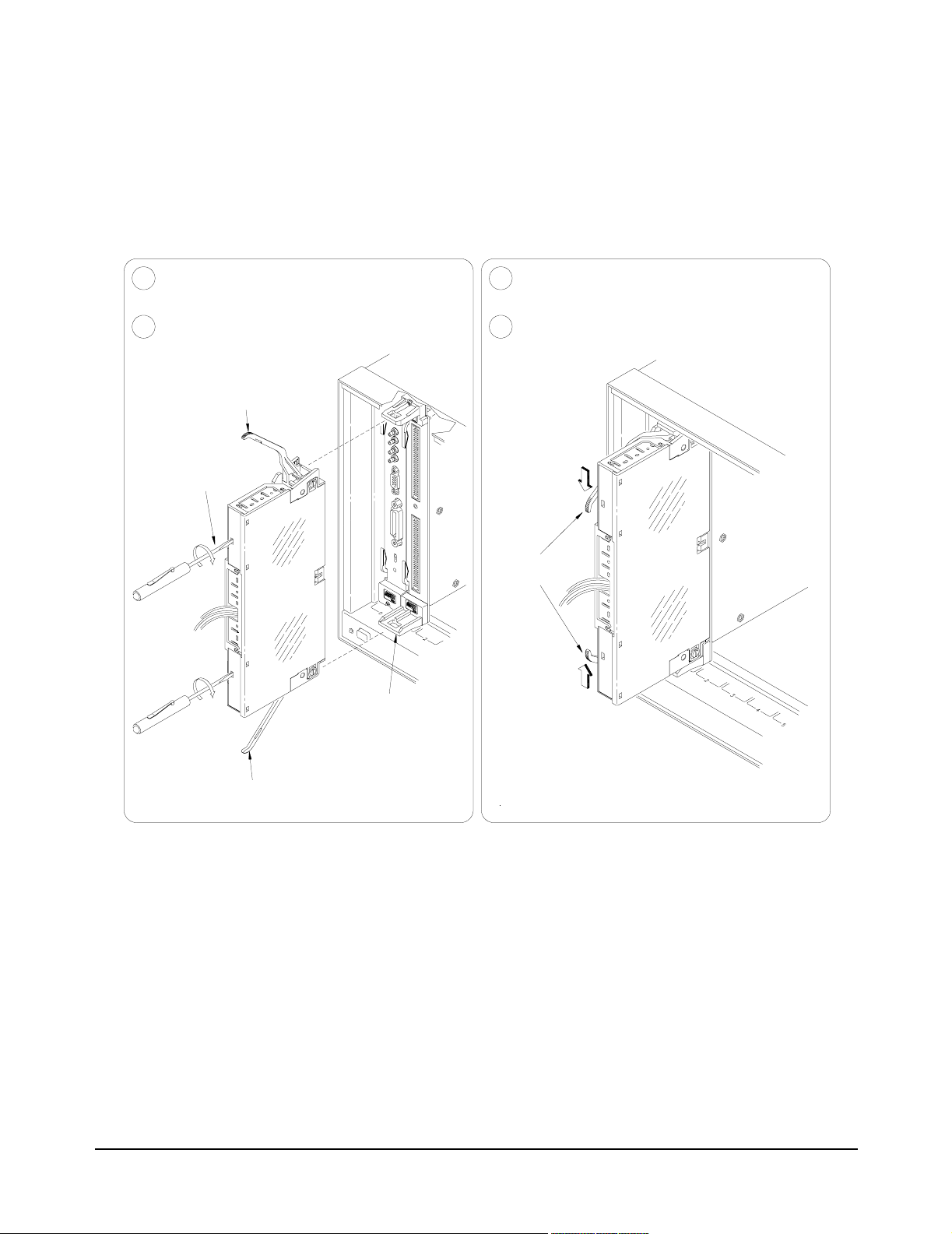
Attaching the
Terminal Modules
to the Switch
Module
Figure 2-10 shows how to attach the E1465A, E1466A, or E1467A terminal
modules to the switch module.
Extend the extraction levers on the terminal13
module.
2
Align the terminal module connectors to the
Relay Marix Switch Module.
Extraction Lever
Use small screwdriver
to release the two
extraction levers
E1466A
Module
Extraction Lever
Apply gentle pressure to attach the terminal
module to the Relay Matrix Switch Module.
4
Push in the extraction levers to lock the
terminal module onto the Relay Matrix Switch
Module.
Extraction
Levers
To remove the terminal
module from the Relay Matrix
Switch Module, use a small screwdriver to release the two extraction
levers and push both levers out simultaneously
to free it from the Relay Matrix Switch Module.
Figure 2-10. Attaching the Terminal Modules to the Switch Module
Configuring the Matrix Modules 29Chapter 2
Page 30
Configuring Larger Matrixes
This section gives guidelines to create larger matrixes, including:
• Creating Larger Matrixes
• Creating a 32x32 Matrix
• Creating a 4x256 Matrix
• Creating an 8x96 Matrix
• Creating Larger Matrixes with Multiple Mainframes
Creating Larger
Matrixes
Creating a 32x32
Matrix
You can create larger matrixes with the matrix modules by using the
E1466-80002 Daisy Chain Expansion cable. With larger matrixes, more
crosspoints become available. A C-Size mainframe can have up to 3,072
two-wire crosspoints. You can make a larger matrix by connecting the rows
or columns of one terminal module to the corresponding rows or columns of
the next terminal module. Only the E1465A has a column expansion. You
can also create larger matrixes by connecting multiple mainframes together.
When using multiple modules, the modules should be configured as a
switchbox. That is, the first switch card (module) has a logical address that
is a multiple of 8 and succeeding switch cards have sequential logical
addresses. For example, if you use the matrix default address of 120 for the
first card, the remaining cards in the switchbox would have logical addresses
of 121, 122, 123, etc.
When using multiple modules configured as a switchbox, you must address
the modules as a switchbox. For example, if you want to close row 00,
column 05 on the second card, use CLOSe @20005).
Figure 2-11 shows how to connect four E1465A 16x16 modules to create a
32-row by 32-column matrix. This configuration requires 16 E1466-80002
Daisy Chain Expansion cables. The daisy chain rows of modules 1 and 3
are connected to the rows of cards 2 and 4 to increase the number of
columns.
The daisy chain columns of cards 1 and 3 are connected together and the
daisy chain columns of cards 2 and 4 are connected together. For example,
to connect row 16 to column 15 use CLOSe (@30015). This command will
close the relay on card 3, row 00, column 15. The following table shows
which cards support applicable rows and columns.
Cards (Modules) Rows/Columns
Cards 1 and 2 Rows 00 - 15
Cards 3 and 4 Rows 16 - 31
Cards 1 and 3 Columns 00 - 15
Cards 2 and 4 Columns 16 - 31
30 Configuring the Matrix Modules Chapter 2
Page 31

E1465A TERMINAL MODULES
Daisy Chain Cable
Daisy
Chain
Rows
(00-07)
MODULE 1 MODULE 2
Rows
(00-07)
Daisy
Chain
Rows
(08-15)
Daisy
Chain
Rows
(16-23)
Daisy Chain
Columns
(00-15)
Rows
(08-15)
Rows
(16-23)
Daisy Chain
Columns
(16-31)
MODULE 4MODULE 3
Daisy
Chain
Rows
(24-31)
Daisy Chain
Columns
(00-15)
Rows
(24-31)
Figure 2-11. Creating a 32x32 Matrix
Configuring the Matrix Modules 31Chapter 2
Daisy Chain
Columns
(16-31)
Page 32

Creating a 4x256
Matrix
Figure 2-12 shows how to connect four E1466A 4x64 modules to create a
4-row by 256-column matrix. This configuration requires three E1466-80002
Daisy Chain Expansion cables. The daisy chain rows of the first module are
connected to the rows of the next module. The daisy chain rows of the
second module are then connected to the rows of the next module, etc.
You can continue this pattern to create even larger matrixes. For example,
to connect row 03 to column 255, use CLOSe (@40363). This command will
close the relay on card 4, row 3, column 63.
)
3
0
(
s
w
o
R
Columns
(0-63)
Daisy
Chain
Row
Daisy Chain Cable
)
3
0
(
s
w
o
R
Columns
(64-127)
Daisy
Chain
Row
Daisy Chain Cable
)
3
0
(
s
w
o
R
Columns
(128-191)
Daisy
Chain
Row
Daisy Chain Cable
Figure 2-12. Creating a 4x256 Matrix
)
3
0
(
s
w
o
R
Daisy
Chain
Row
Columns
(192-255)
32 Configuring the Matrix Modules Chapter 2
Page 33

Creating an 8x96
Matrix
Figure 2-13 shows how to connect three E1467A 8x32 modules to create an
8-row by 96-column matrix. This configuration requires four E1466-80002
Daisy Chain Expansion cables. The daisy chain rows of the first module are
connected to the rows of the next module. The daisy chain rows of the
second module are then connected to the rows of the next module, etc.
You can continue this pattern to create even larger matrixes. For example,
to connect row 4 to column 32, use CLOSe (@20400). This command
closes the relay on card 2, row 4, column 00.
Rows
(4-7) (0-3)
Daisy
Chain
Row
Rows
Daisy
Chain
Row
Columns
(0-31)
Daisy Chain Cable
Rows
Daisy Daisy
Chain
Row
Rows
(0-3)(4-7)
Columns
(32-63)
Chain
Row Row
Daisy Chain Cable
Rows
(4-7) (0-3)
Daisy Daisy
Chain
Rows
Columns
(64-95)
Chain
Row
Figure 2-13. Creating an 8x96 Matrix
Configuring the Matrix Modules 33Chapter 2
Page 34

Creating Larger
Matrixes with
Multiple Mainframes
Figure 2-14 shows one way to connect C-Size mainframes together using
GPIB. The matrix switch modules in each mainframe are then configured as
switchboxes. The switchbox card numbers are 1, 2, 3, etc. in each
mainframe and each mainframe has a different address.
For example, to address the second module in the second mainframe, use
OUTPUT 70815; "CLOSe (@20001)", where the interface select code is 7,
the command module primary address is 08, and and the matrix module's
secondary address is 15. This address selects card 2, row 00, column 01.
Command Module
E1406A
(Primary Address = 09)
E1406A
Command Module
(Primary Address = 08)
E1466A (Logical Address = 120. Secondary Address = 15)
E1466A (Logical Address = 121)
E1466A (Logical Address = 122)
E1466A (Logical Address = 120. Secondary Address = 15)
E1466A (Logical Address = 121)
E1466A (Logical Address = 122)
Command Module
E1406A
(Primary Address = 07)
GPIB
E1466A (Logical Address = 120. Secondary Address = 15)
E1466A (Logical Address = 121)
E1466A (Logical Address = 122)
Figure 2-14. Creating Larger Matrixes with Multiple Mainframes
34 Configuring the Matrix Modules Chapter 2
Page 35

Using This Chapter
Chapter 3
Using the Matrix Modules
This chapter uses typical examples to show ways to use the E1465A,
E1466A, and E1467A Relay Matrix Switch modules (matrix modules).
See Chapter 4 for command information. Chapter contents are:
• Matrix Modules Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
• Power-on and Reset Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
• Matrix Modules Identification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .36
• Switching Channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .38
• Scanning Channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
• Querying Matrix Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
• Using the Scan Complete Bit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
• Saving and Recalling States. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
• Detecting Error Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
• Synchronizing Matrix Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
• Understanding Matrix Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
NOTE All examples in this chapter use GPIB select code 7, primary address 09,
and secondary address 15 (LADDR = 120) for the matrix modules.
Matrix Modules Commands
Table 3-1 explains some of the SCPI commands used in this chapter.
See Chapter 4 for more information on these commands.
Table 3-1. Matrix Modules Commands Used in Chapter 3
SCPI Command Command Description
[ROUTe:]CLOSe <
[ROUTe:]CLOSe? <
[ROUTe:]OPEN <
[ROUTe:]OPEN? <
[ROUTe:]SCAN <
INITiate[:IMMediate] Starts scan sequence and closes first channel in the <channel_list>
TRIGger:SOURce <
channel_list>
channel_list>
channel_list>
channel_list>
channel_list>
source
> Selects the trigger source to advance the scan
Closes the channels in the <channel_list>
Queries the state of the channels in the <channel_list>
Opens the channels in the <channel_list>
Queries the state of the channels in the <channel_list>
Closes the channels in the <channel_list>, one at a time
Using the Matrix Modules 35Chapter 3
Page 36

Power-on and Reset Conditions
The matrix modules use latching relays and the relay state remains
unchanged during power-up and power-down. However, if an E1406A
Command Module is used, the firmware opens all relays during power-up
and a when *RST (reset) is executed. See Table 3-2 for default values.
Table 3-2. *RST (Reset) Default Conditions
Parameter Default Description
ARM:COUNt
TRIGger:SOURce IMM Will advance scanning cycles automatically
INITiate:CONTinuous
OUTPut[:STATe]
1
OFF
OFF
Matrix Modules Identification
The following programs use the *RST, *CLS, *IDN?, CTYP?, and CDES?
commands to reset and identify the matrix modules. For example, a typical
printout for the E1465A 16x16 matrix module will be similar to:
HEWLETT-PACKARD,SWITCHBOX,0,A.04.00
16 x 16 Matrix Switch
HEWLETT-PACKARD,E1465A,0,A.04.00
Example: Matrix
Module
Identification
(BASIC)
10 DIM A$[50], B$[50], C$[50]
20 OUTPUT 70915;"*RST; *CLS"
30 OUTPUT 70915; "*IDN?"
40 ENTER 70915; A$
50 OUTPUT 70915; "SYST:CDES? 1"
60 ENTER 70915; B$
70 OUTPUT 70915; "SYST:CTYP? 1"
80 ENTER 70915; C$
90 PRINT A$, B$, C$
100 END
Number of scanning cycles is 1
Number of scanning cycles is set by ARM:COUNt
Trigger output from EXT or TTL sources is disabled
I Dimensions three string
variables to fifty characters
! Outputs the commands to reset
and clears the status register
! Queries for module identification
I Enters the results into A$
! Outputs the command for a card
description
! Enters the results into B$
! Outputs the command for the
card type
! Enters the results into C$
! Prints the contents of variables
A$, B$, and C$
36 Using the Matrix Modules Chapter 3
Page 37

Example: Matrix
Module
Identification
(TURBO C)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <chpib.h> /*
#define ISC 7L
#define MATRIX 70915L /*
#define TASK1 "*RST;*CLS;*IDN?" /*
#define TASK2 "SYST:CDES? 1" /*
#define TASK3 "SYST:CTYP? 1" /*
main( )
{
char into1[51], into2[51], into3[51];
int length = 50;
/*
Output and enter commands to matrix module
error_handler (IOTIMEOUT (7L,5.0), "TIMEOUT");
error_handler (IOOUTPUTS (MATRIX, TASK1, 15), "OUTPUT command");
error_handler (IOENTERS (MATRIX, into1, &length), "ENTER command");
error_handler (IOOUTPUTS (MATRIX, TASK2, 12), "OUTPUT command");
error_handler (IOENTERS (MATRIX, into2, &length), "ENTER command");
error_handler (IOOUTPUTS (MATRIX, TASK3, 12), "OUTPUT command");
error_handler (IOENTERS (MATRIX, into3, &length), "ENTER command");
Include file for GPIB
Matrix default address
Reset, clear, and query id
*/
*/
*/
Command for card description
Command for card type
*/
*/
*/
printf("IDENTIFICATION: %s",into1);
printf("CARD DESCRIPTION: %s",into2);
printf("CARD TYPE: %s",into3);
return;
}
int error_handler (int error, char *routine)
{
char ch;
if (error != NOERR)
{
printf ("\n Error %d %s \n", error, errstr(error));
printf (" in call to GPIB function %s \n\n", routine);
printf ("Press 'Enter' to exit: ");
scanf ("%c", &ch);
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}
Using the Matrix Modules 37Chapter 3
Page 38

Switching Channels
Use CLOSe <channel_list> to close one or more matrix module channels
and OPEN <channel_list> to open the channel(s). channel_list has the
form @ssrrcc where ss = card number (01-99), rr is the row number, and
cc = column number. See Table 3-3 for row and column definitions for the
modules.
To OPEN or CLOSe multiple channels, place a comma (,) between the
channel numbers. For example, to close channels 10103 and 10201,
execute CLOS (@10103,10201). To OPEN or CLOSe a continuous range
of channels, place a colon (:) between the first and last channel numbers.
Table 3-3. Matrix Modules Channel Numbers
Matrix Module Rows (rr) Columns (cc)
E1465A 16 x 16 Relay Matrix 00 - 15 00 - 15
E1466A 4 x 64 Relay Matrix 00 - 03 00 - 63
E1467A 8 x 32 Relay Matrix 00 - 07 00 - 31
Example:
Opening/Closing
Channels (BASIC)
Example: Channel
Sequencing
(BASIC)
This BASIC program shows one way to close and open row 2, column 14
on an E1466A matrix module (card #1). In the program, implied commands
are those that appear in square brackets ([ ]) in the command syntax. The
brackets are not part of the command and are not sent to the instrument.
For example, in the following program, ROUTe can be eliminated and
just the CLOSe or OPEN command can be used.
10 DISP "TEST E1465A Matrix"
20 OUTPUT 70915; "ROUT:CLOS (@10214)"
30 OUTPUT 70915; "ROUT:OPEN (@10214)"
40 END
This example BASIC program sequences through each channel on an
E1466A 4x64 matrix module.
10 OUTPUT 70915;"*RST"
20 FOR Row = 0 TO 3
30 FOR Col = 0 TO 63
40 Addr=10000+100*row+Col
50 OUTPUT 70915; "CLOS (@ ";Addr;")"
60 NEXT Col
70 NEXT Row
80 END
! Reset the module
! Loop to step through all
rows in the matrix
! Loop to step through all
columns in the matrix
! Calculates channel to close
! Closes the channel
! Sequences through each
column in the matrix
! Sequences through each row
in the matrix
38 Using the Matrix Modules Chapter 3
Page 39

Scanning Channels
Scanning matrix module channels consists of closing a sequence of
channels one channel at a time. Single scan, multiple scans, or continuous
scanning modes are available. TRIGger:SOURce specifies the source to
advance the scan. OUTPut can be used to enable the E1406A Command
Module Trig Out port or TTL Trigger bus lines (0-7).
Example: Scanning
Channels Using
TTL Triggers
(BASIC)
E1406A
Command Module
TTLTrg0
This example uses the E1406A Command Module TTL Trigger Bus Lines
to synchronize matrix module channel closures to an E1412A system
multimeter. For measurement synchronization, the E1406A TTL Trigger
Bus Line 0 is used by the matrix module to trigger the multimeter to perform
a measurement. The E1406A TTL Trigger Bus Line 1 is used by the
multimeter to advance the matrix module channel scan.
Note that these trigger bus lines are not actual hardware connections.
Triggering is accomplished by the E1406A firmware. Row 00 (High and Low)
of an E1465A 16x 6 matrix module is connected to the voltmeter's High and
Low. The columns are then scanned, switching in different DUTs (devices
under test).
Figure 3-1 shows how to connect the matrix module to the multimeter
module. The connections shown with dotted lines are not actual hardware
connections, but indicate how the firmware operates to accomplish the
triggering.
TTLTrg1
E1466A
Matrix Module
E1412A
Multimeter Module
Trigger
E1466A
Terminal Module
TTLTrg1
VM
Complete
HI
LO
Row 00H
Row 00L
Figure 3-1. Example: Scanning Using TTL Triggers
Using the Matrix Modules 39Chapter 3
TTLTrg0
Page 40

This BASIC example program sets up the multimeter (GPIB address 70903)
to scan making two-wire resistance measurements. The E1465A matrix
module is set to scan row 00, columns 00 to 15.
10 ALLOCATE REAL Rdgs(1:16)
20 OUTPUT 70915; "*RST;*CLS"
30 OUTPUT 70903; "*RST;*CLS"
40 OUTPUT 70903; "ABORT;:TRIG:SOUR TTLTRG0"
50 OUTPUT 70903; "OUTP:TTLTRG1:STAT ON"
60 OUTPUT 70903; "CONF:RES AUTO,DEF"
70 OUTPUT 70903; "TRIG:DEL 0;COUN 16;:CAL:ZERO:AUTO ON"
80 OUTPUT 70903; "*OPC?"
90 ENTER 70903; Check
100 OUTPUT 70903; "INIT"
110 OUTPUT 70915; "TRIG:SOUR TTLTRG1"
120 OUTPUT 70915; "OUTPUT:TTLT0:STATE ON"
130 OUTPUT 70915; "SCAN (@10000:10015
140 OUTPUT 70915; "INIT"
150 OUTPUT 70903; "FETCH?"
160 ENTER 70903; Rdgs(*)
170 PRINT Rdgs(*)
180 END
! Reset and clear the matrix
module
! Reset and clear the multimeter
! Multimeter triggers on TTL
Trigger line 0
! Multimeter pulses TTL Trigger
line 1 on measurement
complete
! Set multimeter function to
Resistance
! Set multimeter Range, NPLC
functions
! Check to see if multimeter ready
! When multimeter is ready,
initialize trigger
! Set matrix module to be
triggered by TTL Trigger line 1
! Matrix module pulses TTL
Trigger line 0 on channel closed
! Scan list is Row 0, Columns
0 to 15
! Initiate scan
! Enter readings
! Print readings
40 Using the Matrix Modules Chapter 3
Page 41

Example: Scanning
Using Trig In/Out
Ports (BASIC)
+5V
This example uses the E1406A Command Module Trig In and Trig Out ports
to synchronize the matrix module channel closures to an external 3457A
voltmeter at address 722. Figure 3-2 shows how to connect the voltmeter to
the command module and to the matrix module.
E1406A
Command
Module
+5V
0V
Trig
In
3457A Multimeter (Rear View)
Figure 3-2. Example: Scanning Using Trig In and Trig Out Ports
0V
Voltmeter External
Complete
Row 00L
Row 00H
Trigger
Terminal Module
10 OUTPUT 722; "TRIG EXT; DCV;MEM FIFO"
20 OUTPUT 70915; "*RST;*CLS"
30 OUTPUT 70915; "OUTP ON"
40 OUTPUT 70915; "TRIG:SOUR:EXT"
50 OUTPUT 70915; "SCAN (@10000:10015)"
60 OUTPUT 70915; "INIT"
70 WAIT 2
80 FOR Channels = 1 to 16
90 ENTER 722;Results
100 PRINT Results
110 NEXT Channels
120 END
Trig
Out
E1466A
Matrix Module
E1466A
! Set voltmeter for external
trigger, DCV measurements,
memory first in, first out storage
! Reset and clear the matrix
module
! Enable the E1406A Trig Out port
! Set trigger source to external
triggering
! Set matrix measurement mode
and define channel list
! Initiate scan
! Wait 2 seconds
Using the Matrix Modules 41Chapter 3
Page 42

Querying Matrix Modules
All query commands end with a "?". These commands are used to determine
a specific state of the matrix module. Data are sent to the output buffer
where it can be retrieved into a computer. CLOSe? <channel_list> and
OPEN? <channel_list> return the current state of the specified channel.
These commands return "1" if the operation is true and return "0" if the
operation is false. A maximum of 128 channels can be queried at one time.
Therefore, to query more than 128 channels, you must enter the query data
in two separate commands. See Chapter 4 for more information on query
commands.
Example: Querying
Channel Closure
(BASIC)
This BASIC example program closes a range of channels on an E1467A
8x32 matrix module and queries the results.
10 DIM Chan1$[128], Chan2$[128]
20 OUTPUT 70915;"CLOS (@10000:10731)"
30 OUTPUT 70915; "CLOS? (@10000:10331)"
40 ENTER 70915; Chan1$
50 OUTPUT 70914; "CLOS? (@10400:10731)"
60 ENTER 70915; Chan2$
70 PRINT "Channels closed";Chan1$, Chan2$
80 END
! Dimensions two string variables
to 128 characters each
! Closes rows 00 through 07 and
columns 00 through 31
! Queries rows 00 through 03
and columns 00 through 31
! Enters the results of the first
128 channel closures
! Queries rows 04 through 07
and columns 00 through 31
! Enters the results of the second
128 channel closures
! Prints all channels closed
(should print 1s)
Using the Scan Complete Bit
The Scan Complete Bit (bit 8) in the OPERation Status Register (in the
command module) can be used to determine when a scanning cycle
completes. (No other bits in this register apply to the switchbox.) Bit 8
has a decimal value of 256 and can be read directly using STAT:OPER?.
See STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]? in Chapter 4.
When enabled by STAT:OPER:ENAB 256, the Scan Complete Bit is
reported as Bit 7 of the Status Byte Register. You can use the GPIB Serial
Poll or the IEEE 488.2 Common command *STB? to read the Status
Register.
42 Using the Matrix Modules Chapter 3
Page 43

When Bit 7 of the Status Byte Register is enabled by *SRE 128 to assert a
GPIB Service Request (SRQ), the computer can be interrupted when the
Scan Complete Bit is set, after the scanning cycle completes. This allows
the controller to do other operations while the scanning cycle is in progress.
Example: Using the
Scan Complete Bit
(BASIC)
This example monitors bit 7 in the Status Byte Register to determine when
the scanning cycle is complete. The computer interfaces with an E1406A
Command Module over GPIB. The GPIB select code is 7, primary address
is 09, and secondary address is 15.
10 OUTPUT 70915;"*RST; *CLS"
20 OUTPUT 70915; "STATUS:OPER:ENABLE 256"
30 OUTPUT 70915; "TRIG:SOUR IMM"
40 OUTPUT 70915; "SCAN (@10000:10015)"
50 OUTPUT 70915; "*OPC?"
60 ENTER 70915; A$
70 PRINT "*OPC? = ";A$
80 OUTPUT 70915; "STAT:OPER:ENAB?"
90 ENTER 70915; A$
100 PRINT "STAT:OPER:ENAB? = ";A$
110 OUTPUT 70915; "*STB?"
120 ENTER 70915; A$
130 PRINT "Switch Status = ";A$
140 OUTPUT 70915; "INIT"
150 I = 0
160 WHILE (I=0)
170 I = SPOLL(70915)
180 PRINT "Waiting for scan to complete: SPOLL = ";I
190 END WHILE
200 I = SPOLL(70915)
210 PRINT "Scan complete: SPOLL = ";I
220 END
! Reset and clear the matrix
module
! Enable Scan Complete Bit
! Set matrix module for
continuous triggering
! Select channels to scan
! Wait for operation complete
! Query OPERation Status
register contents
! Query Status Byte register
contents
! Start scan cycle
! Initialize counter value
! Stay in loop until value is
returned from SPOLL (70915)
Using the Matrix Modules 43Chapter 3
Page 44

Saving and Recalling States
*SAV <numeric_state> stores the current state of the matrix modules
channels. Up to 10 states can be stored by specifying <numeric_state> as
an integer 0 through 9. The following states are stored: Channel relay states
(open or closed), ARM:COUNt, TRIGger:SOURce, OUTPut[:STATe], and
INITiate:CONTinuous.
*RCL <numeric_state> recalls the specified previously stored state. If the
specified <numeric_state> does not exist, the matrix module configures to
its power-on/reset states (see Table 3-2).
Example: Saving
and Recalling
States (BASIC)
This program shows one way to save and recall matrix modules states.
10 DIM A$[30]
20 OUTPUT 70915; "CLOS (@10000:10015)
30 OUTPUT 70915; "*SAV 5"
40 OUTPUT 70915; "*RST; *CLS"
50 OUTPUT 70915; "CLOS? (@10000:10020)"
60 ENTER 70915;A$
70 PRINT "Channels Closed:";A$
80 OUTPUT 70915; "*RCL 5"
90 OUTPUT 70915; "CLOS? (@10000:10200)"
100 ENTER 70915; A$
110 PRINT "Channels Closed:";A$
120 END
! Dimensions string variable
A$ to 30 characters
! Closes channels on a matrix
module
! Saves state as numeric state 5
! Resets and clears the matrix
module
! Query to see which channels
are closed
! Recall numeric state 5
! Check if recalled channels are
closed
! Prints 1s for first 16 channels
closed and 0s for remaining 5
channels
44 Using the Matrix Modules Chapter 3
Page 45

Detecting Error Conditions
SYSTem:ERRor? requests a value from instrument's error register. This
register contains an integer in the range [-32768 to 32767]. The response
takes the form <err_number>,<err_message>, where <err_number> is the
value of the instrument's error and <err_message> is a short description of
the error.
If no error occurs, the switchbox responds with 0,"No error". If there has
been more than one error, the instrument will respond with the first error in
its error queue. Subsequent queries continue to read the error queue until it
is empty. The maximum <err_message> string length is 255 characters.
Example: Detecting
Error Conditions
(BASIC)
Example: Detecting
Error Conditions
(TURBO C)
This BASIC example program attempts an illegal channel closure for the
E1466A 4x64 matrix module and polls for the error message.
10 DIM Err_num$[256]
20 OUTPUT 70915; "CLOS (@10500)"
30 OUTPUT 70915; "SYST:ERR?"
40 ENTER 70915; Err_num$
50 PRINT Err_num$
60 END
This Turbo C example program attempts an illegal channel closure for the
E1466A 4x64 matrix module and polls for the error message.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <chpib.h> /*
#define ISC 7L
#define MATRIX 70915L /*
#define TASK1 "CLOSE (@10500)" /*
#define TASK2 "SYST:ERR?" /*
! Dimensions Err_num$ for 256
characters
! Try to close an illegal channel
! Check for a system error
! Enter the errors into Err_num$
! Prints error +2001, "Invalid
channel number"
Include file for GPIB
Matrix module default address
Command for illegal switch closure
Command for system error
*/
*/
*/
*/
main()
{
char into[257];
int length = 256;
/*
Output commands to matrix module
error_handler (IOTIMEOUT (7L,5.0), "TIMEOUT");
error_handler (IOOUTPUTS (MATRIX, TASK1, 15), "OUTPUT
command");
error_handler (IOOUTPUTS (MATRIX, TASK2, 9), "OUTPUT command");
Using the Matrix Modules 45Chapter 3
*/
Page 46

Enter from matrix module
/*
error_handler (IOENTERS (MATRIX, into, &length), "ENTER command");
printf("Print the errors: %s",into);
return;
}
int error_handler (int error, char *routine)
{
char ch;
if (error != NOERR)
{
printf ("\n Error %d %s \n", error, errstr(error));
printf (" in call to GPIB function %s \n\n", routine);
printf ("Press 'Enter' to exit: ");
scanf ("%c", &ch);
exit(0);
}
return 0;
}
Synchronizing Matrix Modules
This section gives guidelines to synchronize matrix modules with
measurement instruments.
*/
Example:
Synchronizing a
Matrix Module
(BASIC)
This BASIC example program shows how to synchronize matrix modules
with measurement instruments. In this example, a matrix module switches a
signal to a multimeter. The program verifies that the channel is closed before
the multimeter begins its measurement.
10 OUTPUT 70915; "*RST"
20 OUTPUT 70915; "CLOS (@10012)"
30 OUTPUT 70915; "*OPC?"
40 ENTER 70915; Opc_value
50 OUTPUT 70915; "CLOS? (@10012)"
60 ENTER 70915;A
70 IF A=1 THEN
80 OUTPUT 70903;"MEAS:VOLT:DC?"
90 ENTER 70903; Meas_value
100 PRINT Meas_value
110 ELSE
120 PRINT "Channel did not close"
130 END IF
140 END
! Reset the module
! Close a channel
! Wait for operation complete
!Test that the channel is closed
! When channel is closed,
measure the voltage
! Print the measured value
46 Using the Matrix Modules Chapter 3
Page 47

Understanding Matrix Modules
This section provides internal configuration details about the E1465,
E1466A, and E1467A matrix modules, including advantages of latching
relays and module operation.
Advantages of
Latching Relays
There are several advantages to using the E1465A/E1466A/E1467A
latching relays, as follows. The main disadvantage of latching relays is
that the relay state is unchanged at power-on, power-off, or following a reset.
Therefore, the device's firmware must ensure that all relays are open
following these conditions.
• With 256 relays on the dense matrix relay module, latching relays
prevent excessive current being drawn from the power supply if
the user closes too many relays accidentally. Energy is saved
since power is not continually applied to keep a latching relay
closed.
• By not continually applying power, the relay coil does not heat up.
This is important because the two metal contacts inside the relay,
in effect, form a thermocouple. Thus, temperature differences on
the relay contacts cause thermal EMF (electromotive force) to be
generated.
• The life of a latching relay is usually longer than that of a
nonlatching relay because of the power that must be continually
applied to close a nonlatching relay.
• In conventional switch module designs, the module interrupts the
central processing unit (CPU) each time a relay is opened or
closed. For the E1465A/E1466A/E1467A matrix relay modules,
the CPU is interrupted one time after all relays in the specified
channel list have been opened or closed. Thus, system
throughput speed is increased.
Matrix Module
Operations
The following paragraphs describe matrix module operations (see Figure
3-3).
• A command is sent to the matrix module and is stored in FIFO
memory.
• Once the data is in memory, the VME Timing PAL (programmable
array logic) asserts DTACK*. This signals the CPU on the matrix
module's commander that it is now free to service other tasks.
• The VME Timing PAL signals the FIFO Interface PAL to execute
the command. During execution, the Data Bus FIFO EMPTY*
flag signals the FIFO Interface PAL to read the Data Bus and
Address Bus FIFO and generate 7 msec pulses to activate the
relays. Only one 7 msec pulse is required per relay bank (up to
16 relays).
Using the Matrix Modules 47Chapter 3
Page 48

• The FIFO Interface PAL reads the Data Bus and Address Bus
FIFO until the EMPTY* flag signals the FIFO Interface PAL the
FIFO memory is empty.
• When the FIFO is empty, the FIFO Interface PAL signals the VME
Timing PAL which asserts IRQ*. This interrupts the command
module CPU after the last relay has been activated.
• Because the matrix module asserts IRQ* after the last relay is
activated, the CPU is not continually interrupted. Thus, system
throughput is enhanced.
Power
Add
Bus
Sysreset
& Control
Bus
DTACK
IRQ*
Data
Bus
Card
Add
Detector
Card
Reset &
Logic
VME
Timing
PAL
Data
Bus
Buffer
Address
Card Reset*
Device
Register
Bus
FIFO
Data
Bus
FIFO
ID
Empty *
Add
Decoder
Driver
& One Shot
FIFO
Interface
PAL
Data
Bus
Driver
Power
FIFO-Write
FIFO-Read
Latching
Relay
Ground
Status &
Control
Register
Figure 3-3. Matrix Modules Block Diagram
48 Using the Matrix Modules Chapter 3
Page 49

Matrix Modules Command Reference
Using This Chapter
Command Types
Chapter 4
This chapter describes Standard Commands for Programmable Instruments
(SCPI) and summarizes IEEE 488.2 Common (*) commands applicable to
the E1465A, E1466A, and E1467A Relay Matrix Switch modules. This
chapter contains the following sections:
• Command Types. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
• SCPI Command Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
• SCPI Commands Quick Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78
• IEEE 488.2 Common Commands Reference. . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Commands are separated into two types: IEEE 488.2 Common commands
and SCPI commands.
Common Command
Format
SCPI Command
Format
The IEEE 488.2 standard defines the Common commands that perform
functions like reset, self-test, status byte query, etc. Common commands
are four or five characters in length, always begin with the asterisk character
(*), and may include one or more parameters. The command keyword is
separated from the first parameter by a space character. Some examples
of Common commands are shown below:
*RST *ESR 32 *STB?
The SCPI commands perform functions like closing switches, opening
switches, scanning channels, querying instrument states or retrieving data.
A subsystem command structure is a hierarchical structure that usually
consists of a top level (or root) command, one or more lower-level
commands, and their parameters. The following example shows part of a
typical subsystem:
[ROUTe:]
CLOSe<channel_list>
SCAN <channel_list>
[ROUTe:] is the root command, CLOSe and SCAN are second-level
commands with parameters. There must be a space between the
second-level command (such as CLOSe) and the parameter
(<channel_list>).
Matrix Modules Command Reference 49Chapter 4
Page 50

Command Separator A colon (:) always separates one command from the next lower-level
command as shown below:
[ROUTe:]SCAN
Colons separate the root command from the second-level command
([ROUTe:]SCAN).
Abbreviated Commands The command syntax shows most commands as a mixture of upper- and
lowercase letters. The uppercase letters indicate the abbreviated spelling for
the command. For shorter program lines, send the abbreviated form. For
better program readability, you may send the entire command. The
instrument will accept either the abbreviated form or the entire command.
For example, if the command syntax shows TRIGger, then TRIG and
TRIGGER are both acceptable forms. Other forms of TRIGger, such as
TRIGG or TRIGGE will generate an error. You may use uppercase or
lowercase letters. Therefore, TRIGGER, trigger, and TrigGeR are all
acceptable.
Implied Commands Implied commands are those that appear in square brackets ([ ]) in the
command syntax. (The brackets are not part of the command and are not
sent to the instrument.) Suppose you send a second-level command but do
not send the preceding implied command. In this case, the instrument
assumes you intend to use the implied command and it responds as if you
had sent it. Examine the portion of the [ROUTe:] subsystem shown below:
[ROUTe:]
CLOSe<channel_list>
The root command [ROUTe:] is an implied command (indicated by square
brackets ([ ])). To make a query about a channel’s present status, you can
send either of the following command statements:
ROUT:CLOSe? <channel_list> or CLOSe? <channel_list>
Linking Commands Linking IEEE 488.2 Common Commands with SCPI Commands. Use a
semicolon (;) between the commands. For example, *RST;OUTP ON or
TRIG:SOUR HOLD;:*RST.
Linking Multiple SCPI Commands. Use both a semicolon (;) and a colon (:)
between the commands, such as ARM:COUN 1;:TRIG SOUR EXT.
50 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
Page 51

Parameters The following table contains explanations and examples of parameter types
you might see later in this chapter.
Type Explanations and Examples
Boolean Represents a single binary condition that is either true or
false (ON, OFF, 1.0). Any non-zero value is considered
true.
Discrete Selects from a finite number of values. These parameters
use mnemonics to represent each valid setting. An
example is the TRIGger:SOURce <source> command
where <source> can be BUS, EXTernal, HOLD,
IMMediate, or TTLTrgn.
Numeric Commonly used decimal representations of numbers
including optional signs, decimal points, and scientific
notation. Examples are 123, 123E2, -123, -1.23E2, .123,
1.23E-2, 1.23000E-01. Special cases include MINimum,
MAXimum, DEFault and INFinity.
Optional
SCPI Command Reference
This section describes the Standard Commands for Programmable
Instruments (SCPI) commands for the E1465A, E1466A, and E1467A Relay
Matrix Switch Modules. Commands are listed alphabetically by subsystem
and within each subsystem.
Parameters shown within square brackets ([ ]) are optional
parameters. (The brackets are not part of the command
and are not sent to the instrument.) If you do not specify a
value for an optional parameter, the instrument chooses a
default value.
For example, consider the ARM:COUNt? [<MIN | MAX>]
command. If you send the command without specifying a
parameter, the present ARM:COUNt value is returned. If
you send the MIN parameter, the command returns the
minimum count available. If you send the MAX parameter,
the command returns the maximum count available. Be
sure to place a space between the command and the
parameter.
Matrix Modules Command Reference 51Chapter 4
Page 52

ABORt
Subsystem Syntax ABORt
The ABORt command stops a scan in progress when the scan is enabled
via the interface and the trigger source is TRIGger:SOURce BUS or
TRIGger:SOURce HOLD.
Comments ABORt Actions: The ABORt command terminates the scan and invalidates
the current channel list.
Stopping Scan Enabled Via Interface: When a scan is enabled via an
interface, an interface CLEAR command can be used to stop the scan.
When the scan is enabled via the interface and TRIG:SOUR BUS or HOLD
is set, you can use ABORt to stop the scan.
Restarting a Scan: Use INIT to restart the scan.
Related Commands: ARM, INITiate:CONTinuous,[ROUTe:]SCAN, TRIGger
Example Stopping a Scan with ABORt
This example stops a (continuous) scan in progress.
TRIG:SOUR BUS
INIT:CONT ON
SCAN(@10000:10003)
INIT
.
.
ABOR
! Trigger command will be via
backplane (bus) interface
(*TRG generates trigger)
! Set continuous scanning
! Scan channels 00 to 03
! Start scan, close channel 00
! Abort scan in progress
52 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
Page 53

ARM
Subsystem Syntax ARM
ARM:COUNt
Parameters
The ARM subsystem selects the number of scanning cycles (1 to 32,767)
for each INITiate command.
:COUNt <number> MIN | MAX
:COUNt? [<MIN | MAX>]
ARM:COUNt <number> MIN | MAX allows scanning to occur a multiple of
times (1 to 32,767) with one INITiate command when INITiate:CONTinuous
OFF | 0 is set. MIN sets 1 cycle and MAX sets 32,767 cycles.
Name Type Range of Values Default Value
<number> numeric
1 - 32,767 | MIN | MAX
1
Comments Number of Scans: Use only numeric values between 1 and 32767, MIN, or
MAX for the number of scanning cycles.
Related Commands: ABORt, INITiate[:IMMediate]
*RST Condition: ARM:COUNt 1
Example Setting Ten Scanning Cycles
This example sets a relay matrix for 10 scans of channels 10000 through
10003. When the scan sequence completes, channels 10000 through
10003 are closed.
ARM:COUN 10
SCAN(@10000:10003)
INIT
! Set 10 scans per INIT command
! Scan channels 10000-10003
! Start scan, close channel 10000
Matrix Modules Command Reference 53Chapter 4
Page 54

ARM:COUNt?
Parameters
ARM:COUNt? [<MIN | MAX>] returns the current number of scanning cycles
set by ARM:COUNt. The current number of scan cycles is returned when
MIN or MAX is not specified. With MIN or MAX as a parameter, MIN returns
"1" and MAX returns "32,767".
Name Ty pe Range of Values Default Value
MIN | MAX
numeric
MIN = 1, MAX = 32,767
Comments Related Commands: INITiate[:IMMediate]
Example Querying Number of Scans
This example sets a switchbox for 10 scanning cycles and queries the
number of scan cycles set. The ARM:COUN? command returns 10.
ARM:COUN 10
ARM:COUN?
current cycle
! Set 10 scans per INIT
! Query number of scans
54 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
Page 55

DISPlay
The DISPlay subsystem monitors the channel state of the selected module
in a switchbox. This subsystem operates with an E1406A Command Module
when a display terminal is connected.
Subsystem Syntax DISPlay
DISPlay:MONitor:CARD
DISPlay:MONitor:CARD <number> | AUTO selects the module in a switchbox
to be monitored.
Parameters
:MONitor
:CARD <number> | AUTO
[:STATe] <mode>
Name Type Range of Values Default Value
<number> | AUTO numeric
1 - 99
AUTO
Comments Selecting a Specific Module to be Monitored: Use DISPlay:MONitor:CARD
to send the card number for the switchbox to be monitored.
Selecting the Present Module to be Monitored: Use DISPlay:MONitor:CARD
AUTO to select the last module addressed by a switching command (for
example, [ROUTe:]CLOSe).
*RST Conditions: DISPlay:MONitor:CARD AUTO
Example Select Module #2 in a Switchbox for Monitoring
DISP:MON:CARD 2
! Selects module #2 in a switchbox
Matrix Modules Command Reference 55Chapter 4
Page 56

DISPlay: MONitor [:STATe]
DISPlay:MONitor[:STATe] <mode> turns the monitor mode ON or OFF.
Parameters
Name Type Range of Values Default Value
<mode>boolean
ON | OFF | 1 | 0 OFF | 0
Comments Monitoring Switchbox Channels: DISPlay:MONitor:STATe ON or
DISPlay:MONitor:STATe 1 turns the monitor mode ON to show the
channel state of the selected module. DISPlay:MONitor:STATe OFF or
DISPlay:MONitor:STATe 0 turns the channel monitor OFF.
Selecting the Module to be Monitored: Use DISPlay:MONitor:CARD
<number> AUTO to select the module.
Monitor Mode with a Matrix Module: When monitoring mode is turned ON, a
hexadecimal number representing the channels closed will be displayed at
the bottom of the display terminal. For example, for an E1466A with row 0,
columns 0-3 closed, will look like the following:
R0: 0000 0000 0000 000F R1: 0000 0000 0000 0000 R2: 0000 0000 ... etc.
*RST Condition: DISPlay:MONitor[:STATe]OFF | 0
Example Enabling Monitor Mode
DISP:MON:CARD 2
DISP:MON 1
! Select module #2 in a switchbox
! Turn monitor mode ON
56 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
Page 57

INITiate
Subsystem Syntax INITiate
INITiate:CONTinuous
Parameters
The INITiate command subsystem selects continuous scanning cycles and
starts the scanning cycle.
:CONTinuous <mode>
:CONTinuous?
[:IMMediate]
INITiate:CONTinuous <mode> enables or disables continuous scanning
cycles for the matrix modules.
Name Type Range of Values Default Value
<mode>boolean
ON | OFF | 1 | 0 OFF | 0
Comments Continuous Scanning Operation: Continuous scanning is enabled with
INITiate:CONTinuous ON or INITiate:CONTinuous 1. Sending
INITiate:IMMediate closes the first channel in the channel list. Each trigger
from the source specified by TRIGger:SOURce advances the scan through
the channel list. A trigger at the end of the channel list closes the first
channel in the channel list and the scan cycle repeats.
Noncontinuous Scanning Operation: Noncontinuous scanning is enabled
with INITiate:CONTinuous OFF or INITiate:CONTinuous 0. Sending
INITiate:IMMediate closes the first channel in the channel list. Each trigger
from the source specified by TRIGger:SOURce advances the scan through
the channel list. At the end of the scanning cycle, the last channel in the
channel list is opened.
Stopping Continuous Scan: See the ABORt command.
Related Commands: ABORt, ARM:COUNt, TRIGger:SOURce
*RST Condition: INITiate:CONTinuous OFF | 0
Matrix Modules Command Reference 57Chapter 4
Page 58

Example Enabling Continuous Scanning
This example enables continuous scanning of channels 10000 through
10003 of a single-module switchbox. Since TRIGger:SOURce IMMediate
(default) is set, use an interface clear command (such as CLEAR) to stop
the scan.
INITiate:CONTinuous?
Example Querying Continuous Scanning State
INITiate[:IMMediate]
INIT:CONT ON
SCAN(@10000:10003)
INIT
INITiate:CONTinuous? queries the scanning state. With continuous scanning
enabled, the command returns "1" (ON). With continuous scanning
disabled, the command returns "0" (OFF).
This example enables continuous scanning of a matrix module and queries
the state. Since continuous scanning is enabled, INIT:CONT? returns "1".
INIT:CONT ON
INIT:CONT?
! Enable continuous scanning
! Define channel list
! Start scan cycle, close channel
10000
! Enable continuous scanning
! Query continuous scanning state
INITiate[:IMMediate] starts the scanning process and closes the first channel
in the channel list. Successive triggers from the source specified by
TRIGger:SOURce advance the scan through the channel list.
Comments Starting the Scanning Cycle: INITiate:IMMediate starts scanning by closing
the first channel in the channel list. Each trigger received advances the scan
to the next channel in the channel list. An invalid channel list definition
causes an error (see [ROUTe:]SCAN).
Stopping Scanning Cycles: See the ABORt command.
Example Enabling a Single Scan
This example enables a single scan of channels 10000 through 10003 of a
matrix module. The trigger source to advance the scan is immediate
(internal) triggering set with TRIGger:SOURce IMMediate (default).
SCAN(@10000:10003)
INIT
! Scan channels 10000 - 10003
! Begin scan, close channel 10000
(use immediate triggering)
58 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
Page 59

OUTPut
The OUTPut command subsystem enables or disables the different trigger
lines of the E1406A Command Module.
Subsystem Syntax OUTPut
OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe]
OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe] <mode> enables or disables the "Trig Out" port on
the E1406A Command Module to output a trigger when a channel is closed
during a scan. ON | 1 enables the port and OFF | 0 disables the port.
:EXTernal
[:STATe] <mode>
[:STATe]?
[:STATe] <mode>
[:STATe]?
:TTLTrgn (:TTLTrg0 through :TTLTrg7)
[:STATe] <mode>
[:STATe]?
Parameters
Name Type Range of Values Default Value
<mode>boolean
ON | OFF | 1 | 0 OFF | 0
Comments Enabling "Trig Out" Port: When enabled, a pulse is output from the "Trig Out"
port after each scanned switchbox channel is closed. If disabled, a pulse is
not output from the port after channel closures. The output pulse is a +5V
negative-going pulse.
"Trig Out" Port Shared by Switchboxes: When enabled, the "Trig Out" port is
pulsed by any switchbox each time a scanned channel is closed. To disable
the output for a specific module, send OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe] OFF or
OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe] 0 for that module.
One Output Selected at a Time: Only one output (TTLTrg or EXTernal) can be
enabled at one time. Enabling a different output source will automatically
disable the active output.
Related Commands: [ROUTe:]SCAN, TRIGger:SOURce
*RST Condition: OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe] OFF (port disabled)
Matrix Modules Command Reference 59Chapter 4
Page 60

Example Enabling "Trig Out" Port
OUTP:EXT ON
OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe]?
OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe]? queries the present state of the "Trig Out" port
on the E1406A Command Module. The command returns "1" if the port is
enabled or "0" if the port is disabled.
Example Query "Trig Out" Port Enable State
This example enables the "Trig Out" port and queries the enable state.
OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe]? returns "1" since the port is enabled.
OUTP:EXT ON
OUTP:EXT?
OUTPut[:STATe]
OUTPut[:STATe] <mode> enables or disables the "Trig Out" port on the
E1406A Command Module. OUTPut[:STATe] ON | 1 enables the port and
OUTPut[:STATe] OFF | 0 disables the port. This command functions the
same as OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe].
! Enable "Trig Out" port to output
pulse after each scanned
channel is closed
! Enable E1406A "Trig Out" port
! Query port enable state
Parameters
Name Type Range of Values Default Value
<mode>boolean
ON | OFF | 1 | 0 OFF | 0
Comments *RST Condition: OUTPut[:STATe] OFF (port disabled)
Example Enabling "Trig Out" Port
OUTP ON
! Enable "Trig Out" port to output
pulse after each scanned
channel is closed
60 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
Page 61

OUTPut[:STATe]?
Example Query "Trig Out" Port Enable State
OUTPut[:STATe]? queries the present state of the E1406A Command
Module "Trig Out" port. The command returns "1" if the port is enabled
or "0" if the port is disabled. This command functions the same as
OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe]?.
This example enables the E1406A Command Module "Trig Out" port and
queries the enable state. OUTPut[:STATe]? returns "1" since the port is
enabled.
OUTP ON
OUTP?
OUTPut:TTLTrgn[:STATe ]
OUTPut:TTLTrgn[:STATe] <mode> selects and enables which TTL Trigger
bus line (0 to 7) will output a trigger when a channel is closed during a scan.
This is also used to disable a selected TTL Trigger bus line. "n" specifies the
TTL Trigger bus line (0 to 7) and <mode> enables (ON or 1) or disables
(OFF or 0) the specified TTL Trigger bus line.
Parameters
Comments Enabling TTL Trigger Bus: When enabled, a pulse is output from the selected
TTL Trigger bus line (0 to 7) after each channel in the switchbox is closed
during a scan. If disabled, a pulse is not output. The output is a
negative-going pulse.
! Enable "Trig Out" port
! Query port enable state
Name Type Range of Values Default Value
n numeric 0 to 7 N/A
<mode>boolean
ON | OFF | 1 | 0 OFF | 0
One Output Selected at a Time: Only one output (TTLTrg or EXTernal) can be
enabled at one time. Enabling a different output source will automatically
disable the active output. For example, if TTLTrg1 is the active output and
TTLTrg4 is enabled, TTLTrg1 will become disabled and TTLTrg4 will
become the active output.
Related Commands: [ROUTe:]SCAN, TRIGger:SOURce,
OUTPut:TTLTrgn[:STATe]?
*RST Condition: OUTPut:TTLTrgn[:STATe] OFF (disabled)
Matrix Modules Command Reference 61Chapter 4
Page 62

Example Enabling TTL Trigger Bus Line 7
OUTP:TTLT7:STAT 1
OUTPut:TTLTrgn[:STATe ]?
OUTPut:TTLTrgn[:STATe]? queries the present state of the specified TTL
Trigger bus line. The command returns "1" if the specified TTLTrg bus line
is enabled or "0" if disabled.
Example Query TTL Trigger Bus Enable State
This example enables TTL Trigger bus line 7 and queries the enable state.
OUTPut:TTLTrgn? returns "1" since the port is enabled.
OUTP:TTLT7:STAT 1
OUTP:TTLT 7?
! Enable TTL Trigger bus line 7 to
output pulse after each scanned
channel is closed
! Enable TTL Trigger bus line 7
! Query bus enable state
62 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
Page 63

[ROUTe:]
Subsystem Syntax [ROUTe:]
[ROUTe:]CLOSe
The [ROUTe:] command subsystem controls switching and scanning
operations for relay matrix switch modules in a switchbox.
CLOSe <channel_list>
CLOSe? <channel_list>
OPEN <channel_list>
OPEN? <channel_list>
SCAN <channel_list>
NOTE There must be a space between the second level command (CLOSe, for
example) and the parameter <channel_list>.
[ROUTe:]CLOSe <channel_list> closes the relay matrix channels specified
by <channel_list>. <channel_list> has the form (@ssrrcc) where ss = matrix
module card number (01-99), rr = matrix module row number, and cc =
matrix module column number.
Parameters
Comments
Name Typ e Range of Values Default Value
<channel_list> numeric E1465A: rr: 00 - 15
cc: 00 - 15
E1466A
cc: 00 - 63
E1467A
cc: 00 - 31
Closing Channels:
: rr: 00 - 03
: rr: 00 - 07
• To close a single channel use ROUT:CLOS (@ssrrcc)
• To close multiple channels use ROUT:CLOS (@ssrrcc,ssrrcc,...)
• To close sequential channels use ROUT:CLOS (@ssrrcc:ssrrcc)
• To close groups of sequential channels use ROUT:CLOS
(@ssrrcc:ssrrcc,ssrrcc:ssrrcc)
• or any combination of the above
N/A
Matrix Modules Command Reference 63Chapter 4
Page 64

NOTE Closure order for multiple channels with a single command is not
guaranteed. Channel numbers can be in the <channel_list> in any
random order.
Related Commands: [ROUTe:]OPEN, [ROUTe:]CLOSe?
*RST Condition: All channels open.
Example Closing Matrix Modules Channels
This example closes channels 10100 and 20013 of a two-module switchbox
(card numbers 01 and 02).
[ROUTe:]CLOSe?
Comments Query is Software Readback: ROUTe:CLOSe? returns the current software
Example Querying Channel Closure
CLOS(@10100,20013)
[ROUTe:]CLOSe? <channel_list> returns the current state of the channel(s)
queried. <channel_list> has the form (@ssrrcc) where cc = card number
(01-99) and nn = channel number (00-31). The command returns "1" if
channel(s) are closed or returns "0" if channel(s) are open.
state of the channel(s) specified. It does not account for relay hardware
failures.
A maximum of 128 channels can be queried at one time. If you want to query
more than 128 channels, you must enter the query data in two separate
commands.
This example closes channels 100 and 213 of a two-module switchbox and
queries channel closure. Since the channels are programmed to be closed
"1,1" is returned as a string.
! Closes row 1, column 00 of card
#1 and row 00, column 13 of card
#2.
CLOS(@100,213)
CLOS?(@100,213)
64 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
!Close channels 100 and 213
!Query channels 100 and 213
state
Page 65

[ROUTe:]OPEN
Parameters
[ROUTe:]OPEN <channel_list> opens the relay matrix channels specified by
<channel_list>. <channel_list> has the form (@ssrrcc) where ss = matrix
module card number (01-99), rr = matrix module row number, and cc =
matrix module column number.
Name Typ e Range of Values Default Value
<channel_list> numeric E1465A
Comments Opening Channels:
• To open a single channel use ROUT:OPEN (@ssrrcc)
• To open multiple channels use ROUT:OPEN (@ssrrcc,ssrrcc,...)
• To open sequential channels use ROUT:OPEN (@ssrrcc:ssrrcc)
• To open groups of sequential channels use ROUT:OPEN
(@ssrrcc:ssrrcc,ssrrcc:ssrrcc)
• or any combination of the above
Opening Order: Opening order for multiple channels with a single command
is not guaranteed.
Related Commands: [ROUTe:]CLOSe, [ROUTe:]OPEN?
*RST Condition: All channels open.
: rr: 00 - 15
cc: 00 - 15
E1466A
cc: 00 - 63
E1467A
cc: 00 - 31
: rr: 00 - 03
: rr: 00 - 07
N/A
Example Opening Matrix Modules Channels
This example opens channels 10100 and 20013 of a two-module switchbox
(card numbers 01 and 02).
OPEN(@10100,20013)
Matrix Modules Command Reference 65Chapter 4
! Opens channels 10100 and
20013
Page 66

[ROUTe:]OPEN?
Comments Query is Software Readback: ROUTe:OPEN? returns the current software
Example Querying Channel Open State
[ROUTe:]OPEN? <channel_list> returns the current state of the channel(s)
queried. <channel_list> has the form (@ssrrcc) where ss = matrix module
card number (01-99), rr = matrix module row number, and cc = matrix
module column number. The command returns "1" if channel(s) are open or
returns "0" if channel(s) are closed.
state of the channel(s) specified. It does not account for relay hardware
failures.
A maximum of 128 channels can be queried at one time: If you want to query
more than 128 channels, you must enter the query data in two separate
commands.
This example opens channels 10100 and 20013 of a two-module switchbox
and queries channel 20013 state. Since channel 20013 is programmed to
be open, "1" is returned.
[ROUTe:]SCAN
Parameters
OPEN(@10100,20013)
OPEN?(@20013)
[ROUTe:]SCAN <channel_list> defines the channels to be scanned.
<channel_list> has the form (@ssrrcc) where cc = card number 01-99) and
nn = channel number (00-31).
Name Typ e Range of Values Default Value
<channel_list> numeric E1465A
! Open channels 10100 and 20013
! Query channel 20013 state
: rr: 00 - 15
cc: 00 - 15
E1466A
cc: 00 - 63
E1467A
cc: 00 - 31
: rr: 00 - 03
: rr: 00 - 07
N/A
Comments Defining Scan List: When ROUTe:SCAN is executed, the channel list is
checked for valid card and channel numbers. An error is generated for an
invalid channel list.
66 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
Page 67

Scanning Channels:
• To scan a single channel use ROUT:SCAN (@ssrrcc)
• To scan multiple channels use ROUT:SCAN (@ssrrcc,ssrrcc,...)
• To scan sequential channels use ROUT:SCAN (@ssrrcc:ssrrcc)
• To scan groups of sequential channels use ROUT:SCAN
(@ssrrcc:ssrrcc,ssrrcc:ssrrcc)
• or any combination of the above
NOTE Channel numbers can be in the <channel_list> in any random order.
Scanning Operation: When a valid channel list is defined,
INITiate[:IMMediate] begins the scan and closes the first channel in the
<channel_list>. Successive triggers from the source specified by
TRIGger:SOURce advance the scan through the <channel list>. At the
end of the scan, the last trigger opens the last channel.
Stopping Scan: See ABORt
Related Commands: TRIGger, TRIGger:SOURce
*RST Condition: All channels open.
Example Scanning Using External Device
See "Scanning Channels" in Chapter 3 for examples of scanning programs
using external instruments.
Matrix Modules Command Reference 67Chapter 4
Page 68

STATus
Subsystem Syntax STATus
The STATus subsystem reports the bit values of the OPERation Status
Register. It also allows you to unmask the bits you want reported from the
Standard Event Status Register and to read the summary bits from the
Status Byte Register.
:OPERation
:CONDition?
:ENABle <unmask>
:ENABle?
[:EVENt?]
:PRESet
As shown in Figure 3-1, the STATus subsystem for the E1463A Form C
Switch includes the Status Byte Register, the Standard Event Status
Register, OPERation Status Register, and Output Queue. The Standard
Event Status Register (*ESE?) and the Status Byte Register (*STB?) are
under IEEE 488.2 control.
Status Byte Register
In the Status Byte register, the Operation Status bit (OPR), Request Service
bit (RQS), Standard Event bit (ESB), Message Available bit (MAV) and
Questionable Data bit (QUE) (bits 7, 6, 5, 4 and 3 respectively) can be
queried with the *STB? command.
Standard Event Status Register
In the Standard Event Status Register, you can use *ESE? to query the
"unmask" value (the bits to be logically ORed into the Summary bit).
The registers are queried using decimal-weighted bit values. Decimal
equivalents for bits 0 through 15 are shown in Figure 3-1.
OPERation Status Register
Using STATus:OPERation:ENABle 256 allows only bit 8 to generate a
Summary bit from the OPERation Status Register, since the decimal value
for bit 8 is 256. The decimal values can also used in the inverse manner to
determine the bits set from the value returned by
STATus:OPERation:EVENt? or STATus:OPERation:CONDition?.
The Form C switch driver uses only bit 8 of OPERation Status Register.
This bit is called the Scan Complete bit and is set whenever a scan operation
completes. Since completion of a scan operation is an event in time, bit 8
will never appear set when STATus:OPERation:CONDition? is queried.
However, you can find bit 8 set by using STATus:OPERation:EVENt?.
68 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
Page 69

Automatically Set at
Power On Conditions
Automatically Set by
Related Commands
are *OPC? and *WAI
Parser
Set by *OPC
Scan Complete
Output Queue
Standard Event Status Register
Power On
User Request
Command Error
Execution Error
Device Dependent Error
Query Error
Request Control
Operation Complete
OPERation Status Register
STATus:OPERation:CONDition?
STATus:OPERation:EVENt?
STATus:OPERation:ENABle
STATus:OPERation:ENABle?
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
CEV EN
<1>
<2>
<4>
<8>
<16>
<32>
<64>
<128>
<256>
<512>
<1024>
<2048>
<4096>
<8192>
<16384>
<32768>
STATus:PRESet
*ESR?
0
<1>
1
<2>
<4>
2
<8>
3
<16>
4
<32>
5
<64>
6
<128>
7
EV EN
"OR"
+
*ESE <unmask>
*ESE?
"OR"
Summary
Summary
Bit
NOTE:
QUE = Questionable Data
MAV = Message Available
ESB = Standard Event
RQS = Request S ervice
OPR = Operation Status
C = Condition Register
EV = Event Register
EN = Enable Register
SRQ = Interface Bus
Service Request
Status Byte Register
*STB?
SPOLL
+
Bit
MAV
ESB
RQS
OPR
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Status
Byte
Summary Bit
<1>
<2>
<4>
<8>
<16>
<32>
<128>
EN
*SRE <unmask>
*SRE?
"OR"
SRQ
+
System
Controller
Interface Bus
SRQ Line
SRQ
Other
Instrument
SRQ
Other
Instrument
unmask examples:
Register
Operation Complete <128>7
*ESE 61 unmasks standard event register bits 0,
2, 3, 4 and 5 (*ESE 128 only unmasks bit 7).
*SRE 128 unmasks the OPR bit (operation) in
the status byte regist er. This is effective
only if the STAT:OPER:ENAB 25 6 command
is executed.
STAT:QUES:ENAB 256 unmasks t he "Scan Complete"
bit.
unmask
decimal
bit
weight
"OR"
ESB
+
Figure 4-1. E1465A/E1466A/E1467A Status System Register Diagram
Matrix Modules Command Reference 69Chapter 4
Page 70

STATus:OPERation:CONDition?
STATus:OPERation:CONDition? returns the state of the Condition Register
in the OPERation Status Register. The state represents conditions that are
part of the instrument's operation. The switch module driver does not set bit
8 in the OPERation Status Register (see STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]?).
STATus:OPERation:ENABle
STATus:OPERation:ENABle <unmask> sets an enable mask to allow events
recorded in the Event Register of the OPERation Status Register to send a
Summary bit to the Status Byte Register (bit 7). For matrix modules, when
bit 8 in the OPERation Status Register is set to 1 and bit 8 is enabled by
STATus:OPERation:ENABle, bit 7 in the Status Byte Register is set to 1.
Parameters
Name Typ e Range of Values Default Value
<unmask> numeric
Comments Setting Bit 7 of the Status Byte Register: STATus:OPERation:ENABle 256
sets bit 7 (OPR) of the Status Byte Register to 1 after bit 8 (Scan Complete)
of the OPERation Status Register is set to 1.
Related Commands: [ROUTe:]SCAN
Example Enabling OPERation Status Register Bit 8
STAT:OPER:ENAB 256
STATus:OPERation:ENABle?
STATus:OPERation:ENABle? returns the bit value of the Enable Register
within the OPERation Status Register.
Comments Output Format: STATus:OPERation:ENABle? returns a decimal-weighted
value from 0 to 65,535 indicating the bits set to true.
0 through 65,535 N/A
! Enable bit 8 of the OPERation
Status Register to be reported to
bit 7 (OPR) in the Status Byte
Register
Maximum Value Returned: The value returned is the value set by
STATus:OPERation:ENABle <unmask>. However, the maximum
decimal-weighted value used in this module is 256 (bit 8 in the Condition
Register within the OPERation Status Register is set to true).
70 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
Page 71

Example Querying the Enable Register in the OPERation Status Register
STAT:OPER:ENAB?
STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]?
STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]? returns which bits in the Event Register within
the OPERation Status Register are set. The Event Register indicates that
a time-related instrument event has occurred.
Comments Setting Bit 8 of the OPERation Status Register: Bit 8 (Scan Complete) is set
to 1 after a scanning cycle completes. Bit 8 returns to 0 (zero) after sending
STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]?.
Returned Data after sending STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]?: The command
returns "+256" if bit 8 of the OPERation Status Register is set to 1. The
command returns "+0" if bit 8 of the OPERation Status Register is set to 0.
Event Register Cleared: Reading the Event Register within the OPERation
Status Register with STATus:OPERation:EVENt? clears the Event Register.
Aborting a Scan: Aborting a scan will leave bit 8 set to 0.
! Query the Enable Register in the
OPERation Status Register
Example Reading the OPERation Status Register After a Scanning Cycle
STATus:PRESet
Related Commands: [ROUTe:]SCAN
STAT:OPER?
read the register value
STATus:PRESet affects only the Enable Register within the OPERation
Status Register by setting all Enable Register bits to 0. It does not affect
either the Status Byte Register or the Standard Event Status Register.
STATus:PRESet does not clear any of the Event Registers.
! Return the bit values of the Event
Register within the OPERation
Status Register
+ 256 shows bit 8 is set to 1.
+0 shows bit 8 is set to 0.
Matrix Modules Command Reference 71Chapter 4
Page 72

SYSTem
The SYSTem subsystem returns the error numbers and error messages in
the error queue of a switchbox. It can also return the types and descriptions
of modules (cards) in a switchbox.
Subsystem Syntax SYSTem
SYSTem:CDEScription?
SYSTem:CDEScription? <number> returns the description of a selected
module (card) in a switchbox.
Parameters
:CDEScription? <number>
:CPON <number> | ALL
:CTYPe? <number>
:ERRor?
Name Typ e Range of Values Default Value
<number> numeric
1 through 99 N/A
Comments E1465A Module Description: SYSTem:CDEScription? returns:
"16 x 16 Matrix Switch"
E1466A Module Description: SYSTem:CDEScription? returns:
"4 x 64 Matrix Switch"
E1467A Module Description: SYSTem:CDEScription? returns:
"8 x 32 Matrix Switch"
Example Reading the Description of a Module
SYST:CDES? 1
! Return description of module
card #1
72 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
Page 73

SYSTem:CPON
Parameters
SYSTem:CPON <number> | ALL sets the selected module (card) in a
switchbox to its power-on state.
Name Typ e Range of Values Default Value
Comments Matrix Module Power-on State: The power-on state is all channels (relays)
Example Setting Module to Power-on State
SYSTem:CTYPe?
Parameters
<number> numeric
open. *RST opens all channels of all modules in a switchbox, while
SYSTem:CPON <number> opens the channels in only the module (card)
specified in the command.
SYST:CPON 1
SYSTem:CTYPe? <number> returns the module (card) type of a selected
module in a switchbox.
Name Typ e Range of Values Default Value
<number> numeric
1 through 99 | ALL N/A
! Set card #1 to power-on state
1 through 99 N/A
Comments
E1465A Matrix Module Model Number: SYSTem:CTYPe? <number> returns:
HEWLETT-PACKARD,E1465A,0,A.04.00
where the 0 after E1465A is the module serial number (always 0) and
A.04.00 is an example of the module revision code number.
E1466A Matrix Module Model Number: SYSTem:CTYPe? <number> returns:
HEWLETT-PACKARD,E1466A,0,A.04.00
where the 0 after E1466A is the module serial number (always 0) and
A.04.00 is an example of the module revision code number.
Matrix Modules Command Reference 73Chapter 4
Page 74

E1467A Matrix Module Model Number: SYSTem:CTYPe? <number> returns:
HEWLETT-PACKARD,E1467A,0,A.04.00
where the 0 after E1467A is the module serial number (always 0) and
A.04.00 is an example of the module revision code number.
Example Reading the Model Number of a Module
SYSTem:ERRor?
Comments Error Numbers/Messages in the Error Queue: Each error generated by a
SYST:CTYP? 1
SYSTem:ERRor? returns the error numbers and corresponding error
messages in the error queue of a matrix module. See Appendix C for a
listing of matrix module error numbers and messages.
matrix module stores an error number and corresponding error message
in the error queue. The error message can be up to 255 characters long.
Clearing the Error Queue: An error number/message is removed from the
queue each time SYSTem:ERRor? is sent. The errors are cleared first-in,
first-out. When the queue is empty, each following SYSTem:ERRor?
command returns +0, "No error". To clear all error numbers/messages in
the queue, execute *CLS.
Maximum Error Numbers/Messages in the Error Queue: The queue holds a
maximum of 30 error numbers/messages for each switchbox. If the queue
overflows, the last error number/message in the queue is replaced by -350,
"Too many errors". The least recent error numbers/messages remain in the
queue and the most recent errors are discarded.
! Returns the model number
Example Reading the Error Queue
SYST:ERR?
74 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
! Query the error queue
Page 75

TRIGger
Subsystem Syntax TRIGger
TRIGger[:IMMediate]
Comments Executing TRIGger[:IMMediate]: Before TRIGger[:IMMediate] will execute,
The TRIGger command subsystem controls the triggering operation of
matrix modules in a switchbox.
[:IMMediate]
:SOURce <source>
:SOURce?
TRIGger[:IMMediate] causes a trigger event to occur when the defined trigger
source is TRIGger:SOURce BUS or TRIGger:SOURce HOLD.
a channel list must be defined with [ROUTe:]SCAN <channel_list> and an
INITiate[:IMMediate] must be executed
BUS or HOLD Source Remains: If selected, TRIGger:SOURce BUS or
TRIGger:SOURce HOLD remains in effect after triggering a switchbox with
TRIGger[:IMMediate].
Related Commands: INITiate, [ROUTe:]SCAN
Example Advancing Scan Using TRIGger
This example scans a single-module switchbox from channel 10000 through
10003. Since TRIGger:SOURce HOLD is set, the scan is advanced one
channel each time TRIGger is executed.
TRIG:SOUR HOLD
SCAN(@10000:10003)
INIT
loop statement
TRIG
increment loop
! Set trigger source to HOLD
! Define channel list
! Begin scan, close channel 10000
! Start count loop
! Advance scan to next channel
! Increment loop count
Matrix Modules Command Reference 75Chapter 4
Page 76

TRIGger:SOURce
Parameters
Comments Enabling the Trigger Source: TRIGger:SOURce only selects the trigger
TRIGger:SOURce <source> specifies the trigger source to advance the
<channel_list> during scanning.
Parameter Name Parameter Type Parameter Description
BUS discrete *TRG or GET command
EXTernal discrete "Trig In" port
HOLD discrete Hold Triggering
IMMediate discrete Immediate Triggering
TTLTrgn numeric TTL Trigger Bus Line 0 - 7
source. INITiate[:IMMediate] enables the trigger source.
Using the TRIGger Command: You can use TRIGger[:IMMediate] to advance
the scan when TRIGger:SOURce BUS or TRIGger:SOURce HOLD is
selected.
Using External Trigger Inputs: With TRIGger:SOURce EXTernal selected,
only one switchbox at a time can use the external trigger input at the E1406A
"Trig In" port. The trigger input is assigned to the first switchbox requesting
the external trigger source (with a TRIGger:SOURce EXTernal command).
Assigning External Trigger: A switchbox assigned with TRIGger:SOURce
EXTernal remains assigned to that source until the switchbox trigger source
is changed to BUS, HOLD, or IMMediate. When the source is changed, the
external trigger source is available to the next switchbox requesting it (with
a TRIGger:SOURce EXTernal command). If a switchbox requests an
external trigger input already assigned to another switchbox, an error is
generated.
Using Bus Triggers: To trigger the switchbox with bus triggers when
TRIGger:SOURce BUS selected, use the IEEE 488.2 common command
*TRG or the GPIB Group Execute Trigger (GET) command.
"Trig Out" Port Shared by Switchboxes: When enabled, the E1406A
Command Module "Trig Out" port is pulsed by any switchbox each time a
scanned channel is closed. To disable the output for a specific module
send OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe] OFF or OUTPut:EXTernal[:STATe] 0 for
that module.
One Output Selected at a Time: Only one output (TTLTrg or EXTernal) can be
enabled at one time. Enabling a different output source will automatically
disable the active output.
76 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
Page 77

Related Commands: ABORt, [ROUTe:]SCAN, OUTPut
*RST Condition: TRIGger:SOURce IMMediate
Example Scanning Using External Triggers
This example uses external triggering (TRIGger:SOURce EXTernal) to scan
channels 0000 through 0003 of a single-module switchbox. The trigger
source to advance the scan is the input to the "Trig In" port on the E1406A
Command Module. When INIT is executed, the scan is started and channel
0000 is closed. Then, each trigger received at the "Trig In" port advances the
scan to the next channel.
TRIG:SOUR EXT
SCAN(@10000:10003)
INIT
trigger externally
Example Scanning Using Bus Triggers
This example uses bus triggering (TRIG:SOUR BUS) to scan channels 0000
through 0003 of a single-module switchbox. The trigger source to advance
the scan is the *TRG command (as set with TRIGger:SOURce BUS). When
INIT is executed, the scan is started and channel 0000 is closed. Then, each
*TRG command advances the scan to the next channel.
TRIG:SOUR BUS
SCAN(@10000:10003)
INIT
loop statement
*TRG
increment loop
! Select external triggering
! Scan channels 0000 - 0003
! Begin scan, close channel 0000
! Advance scan to next channel
! Select interface (bus) triggering
! Scan channels 0000 - 0003
! Begin scan, close channel 0000
! Loop to scan all channels
! Advance scan using bus
triggering
! Increment loop count
TRIGger:SOURce?
Example Querying the Trigger Source
TRIGger:SOURce? returns the current trigger source for the switchbox.
The command returns BUS, EXT, HOLD, IMM, or TTLT for sources BUS,
EXTernal, HOLD, IMMediate, or TTLTrgn, respectively.
This example sets external triggering and queries the trigger source.
Since external triggering is set, TRIG:SOUR? returns "EXT".
TRIG:SOUR EXT
TRIG:SOUR?
Matrix Modules Command Reference 77Chapter 4
! Set external trigger source
! Query trigger source
Page 78

SCPI Commands Quick Reference
The following table summarizes the SCPI Commands for the E1465A,
E1466A, and E1467A Relay Matrix Switch Modules.
Command Description
ABORt ABORt Aborts a scan in progress
ARM :COUNt
:COUNt? [MIN|MAX]
DISPlay :MONitor:CARD
:MONitor[:STATe] <
INITiate :CONTinuous <
:CONTinuous?
[:IMMediate]
OUTPut [:EXTernal][:STATe] <
[:EXTernal][:STATe]?
[:STATe] <
[:STATe]?
:TTLTrgn[:STATe] <
:TTLTrg
[ROUTe:] CLOSe
CLOSe?
OPEN
OPEN?
SCAN
STATus :OPERation:CONDition?
:OPERation:ENABle <
:OPERation:ENABle?
:OPERation[:EVENt]?
:PRESet
<number>
<number>
mode
mode
mode
>
n
[:STATe]?
<channel _list>
<channel _list>
<channel_list>
<channel _list>
<channel_list>
MIN | MAX
>
mode
| AUTO
>
mode
>
unmask
Multiple scans per INIT command
Queries number of scans
Selects module to be monitored
Turns monitor mode on or off
Enables/disables continuous scanning
Queries continuous scan state
Starts a scanning cycle
>
>
Enables/disables the Trig Out port on the E1406
Queries port enable state
Enables/disables the Trig Out port on the E1406
Queries port enable state
Enables/disables TTL trigger bus line pulse
Queries TTL trigger bus line state
Closes channel(s)
Queries channel(s) closed
Opens channel(s)
Queries channel(s) opened
Defines channels for scanning
Returns status of the Condition Register
Enables the Operation Event Register to set a bit in the
Status Register
Query the contents in the Operation Status Register
Returns status of the Operation Status Register
Sets Enable Register to 0
SYSTem :CDEScription?
:CTYPe?
:CPON
<number>
:ERRor?
TRIGger [:IMMediate]
:SOURce BUS
:SOURce EXTernal
:SOURce HOLD
:SOURce IMMediate
:SOURce TTLTrg
:SOURce?
<number>
<number>
n
| ALL
Returns description of module in a switchbox
Returns the module type
Sets specified module to its power-on state
Returns error number/message to error queue
Causes a trigger to occur
Trigger source is *TRG
Trigger source is Trig In (on the E1406)
Hold off triggering
Continuous (internal) triggering
Trigger source is TTL trigger bus line (0 - 7)
Query scan trigger source
78 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
Page 79

IEEE 488.2 Common Commands Reference
The following table lists the IEEE 488.2 Common (*) commands that apply
to the E1465A, E1466A, and E1467A Relay Matrix Switch Modules. The
operation of some of these commands is described in Chapter 3 of this
manual. For more information on Common commands, refer to the user’s
manual for your mainframe or to the ANSI/IEEE Standard 488.2-1987.
Command Title Command Description
*CLS Clear Status Register Clears all status registers (see STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]?).
*ESE Event Status Enable Enables Status Register bits.
*ESE? Event Status Enable Query Queries the current contents in the Standard Event Status Register
*ESR? Event Status Register Query Queries and clears the current contents in the Standard Event Status
Register
*IDN? Identification Query Returns identification string of the Switchbox.
*OPC Operation Complete Sets the Request for OPC flag when all pending operations have
completed. Also, sets OPC bit in the Standard Event Status Register.
*OPC? Operation Complete Query Returns a "1" to the output queue when all pending operations have
completed. Used to synchronize between multiple instruments.
*RCL Recall Instrument State Recalls previously stored configuration.
*RST Reset Opens all channels and sets the module to a known state.
*SAV Save Instrument State Stores the current configuration in specified memory.
*SRE Service Request Enable Sets the Service Request Enable Register bits and corresponding
Serial Poll Status Register bits to generate a service request.
*SRE? Service Request Enable
Query
*STB? Read Status Byte Query Queries the current contents in the Status Byte Register.
*TRG Trigger Triggers the module to advance the scan when scan is enabled and
*TST? Self-Test Query Returns +0 if self-test passes.
*WAI Wait to Continue Prevents an instrument from executing another command until the
Queries the current contents in the Service Request Enable Register.
trigger source is TRIGger:SOURce BUS.
Returns +cc01 for firmware error.
Returns +cc02 for bus error.
Returns +cc10 if an interrupt was expected but not received.
Returns +cc11 if the busy bit was not held for 10 msec.
operation caused by the previous command is finished. Since all
instruments normally perform sequential operations, executing this
command causes no change.
Matrix Modules Command Reference 79Chapter 4
Page 80

Notes:
80 Matrix Modules Command Reference Chapter 4
Page 81

General
Appendix A
Matrix Modules Specifications
Module Size/Device Type:
C-size VXIbus, Register based, A16/D16, Interrupter
(levels 1-7, jumper selectable)
Power Requirements:
Voltage: +5 V
Peak Module Current (A) 0.10 0.18
Terminals:
Screw type, maximum wire size 18 AWG
+12 V
Input Characteristics
Maximum Voltage Terminal to Terminal:
200 Vdc or 170 Vac
Maximum Current per Channel (non-inductive):
1 Adc or 1 A ac peak
(238 Vac peak to peak)
rms
DC Performance
Closed Channel Resistance:
Initial: <4.0
End of Life: <10.0 W
Thermal Offset per Channel:
<5
mV (differential H-L)
W
Relay Life:
@ No Load: 5 x 107 Operations
@ Full Load: 10
Watts/slot: 5 W
Cooling/slot: 0.08 mm H
Operating Temperature: 0
Operating Humidity: 65% RH, 0
Maximum Voltage Terminal to Chassis:
200 Vdc or 170 Vac
Maximum Power per Channel:
30 Wdc or 62.5 VA ac resistive load
Insulation Resistance
(between any two points, single module):
8
W at 40°C, 95% RH
10
9
10
W at 25°C, 40% RH
5
Operations
0 @ 0.42 Liter/sec for 10oC rise
2
°
- 55°C
(238 Vac peak to peak)
rms
°
- 40°C
AC Performance
Bandwidth (-3 dB): Zload = Zsource = 50 W
>10 MHz (for worst crosspoint)
Crosstalk between Channels:
See tables on next page
Closed Channel Capacitance (Hi-Low, Lo-Chassis):
HI to Lo: <270 pF
Hi to GND: <430 pF
Lo to GND: <440 pF
Matrix Modules Specifications 81Appendix A
Page 82

E1465A Crosstalk Between Channels
Specifications are for 16 x 16 matrix, for Z(load) = Z(source) = 50
crosspoint closed per row or column. Typical is defined as the worst crosspoint test result from one or two matrix
modules.
Within a Card (worst path)
Closed Path to Closed Path (typical)
Open Row to Open Row (typical)
Open Row to Open Column (typical)
Open Column to Open Column (typical)
Module to Module (Represents 16 x 32 Configuration)*
Closed Path to Closed Path (typical)
Open Row to Open Row (typical)
Open Row to Open Column (typical)
Open Column to Open Column (typical)
E1466A Crosstalk Between Channels
Specifications are for 4 x 64 matrix, for Z(load) = Z(source) = 50
crosspoint closed per row or column. Typical is defined as the worst crosspoint test result from one or two matrix
modules.
Within a Card (worst path)
Closed Path to Closed Path (typical)
Open Row to Open Row (typical)
Open Row to Open Column (typical)
Open Column to Open Column (typical)
W. AC specifications apply with no more than one
<10 kHz
- 78 dB
- 93 dB
- 84 dB
- 86 dB
<10 kHz
- 78 dB
- 84 dB
- 84 dB
- 93 dB
<100 kHz
- 57 dB
- 73 dB
- 63 dB
- 65 dB
<100 kHz
- 55 dB
- 66 dB
- 63 dB
- 72 dB
<1 MHz
- 41 dB
- 56 dB
- 47 dB
- 48 dB
<1 MHz
- 43 dB
- 52 dB
- 48 dB
- 48 dB
W. AC specifications apply with no more than one
<10 kHz
- 72 dB
- 73 dB
- 84 dB
- 92 dB
<100 kHz
- 50 dB
- 52 dB
- 64 dB
- 70 dB
<1 MHz
- 34 dB
- 37 dB
- 47 dB
- 52 dB
Module to Module (Represents 4 x 128 Configuration)*
Closed Path to Closed Path (typical)
Open Row to Open Row (typical)
Open Row to Open Column (typical)
Open Column to Open Column (typical)
E1467A Crosstalk Between Channels
Specifications are for 8 x 32 matrix, for Z(load) = Z(source) = 50
crosspoint closed per row or column. Typical is defined as the worst crosspoint test result from one or two matrix
modules.
Within a Card (worst path)
Closed Path to Closed Path (typical)
Open Row to Open Row (typical)
Open Row to Open Column (typical)
Open Column to Open Column (typical)
Module to Module (Represents 8 x 64 Configuration)*
Closed Path to Closed Path (typical)
Open Row to Open Row (typical)
Open Row to Open Column (typical)
Open Column to Open Column (typical)
*Chaining Cable (part number E1466-80002) used to connect modules
<10 kHz
- 66 dB
- 68 dB
- 84 dB
- 92 dB
<100 kHz
- 45 dB
- 46 dB
- 64 dB
- 71 dB
<1 MHz
- 29 dB
- 29 dB
- 48 dB
- 52 dB
W. AC specifications apply with no more than one
<10 kHz
- 75 dB
- 91 dB
- 85 dB
- 92 dB
<10 kHz
- 72 dB
- 74 dB
- 92 dB
- 82 dB
<100 kHz
- 54 dB
- 59 dB
- 64 dB
- 71 dB
<100 kHz
- 51 dB
- 53 dB
- 72 dB
- 64 dB
<1 MHz
- 38 dB
- 43 dB
- 47 dB
- 54 dB
<1 MHz
- 33 dB
- 38 dB
- 56 dB
- 50 dB
82 Matrix Modules Specifications Appendix A
Page 83

Register-Based Programming
About This Appendix
This appendix contains information you can use for register-based
programming of the E1465A, E1466A, and E1467A Relay Matrix Switch
modules. The contents include:
• Register Programming vs. SCPI Programming . . . . . . . . . . . .83
• Addressing the Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
• Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
• Programming Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .90
Register Programming vs. SCPI Programming
The E1465A Relay Matrix Switch modules are register-based modules that
do not support the VXIbus word serial protocol. When a SCPI command is
sent to the module, the E1406 Command Module parses the command and
programs the switch at the register level.
Appendix B
NOTE If SCPI is used to control this module, register programming is not
recommended. The SCPI driver maintains an image of the card state.
The driver will be unaware of changes to the card state if you alter the
card state by using register writes.
Register-based programming is a series of reads and writes directly to
the module registers. This increases throughput speed since it eliminates
command parsing and allows the use of an embedded controller. Also, if
slot 0, the resource manager, and the computer GPIB interface are provided
by other devices, a C-size system can be downsized by removing the
command module.
Addressing the Registers
Register addresses for register-based devices are located in the upper
25% of VXI A16 address space. Every VXI device (up to 256 devices) is
allocated a 32-word (64-byte) block of addresses. With 19 registers, the
E1465A/E1466A/E1467A modules each use 19 of the 64 addresses
allocated.
Register-Based Programming 83Appendix B
Page 84

The Base Address When reading or writing to a switch register, a hexadecimal or decimal
register address is specified. This address consists of a base address plus
a register offset. The base address used in register-based programming
depends on whether the A16 address space is outside or inside the
E1406 Command Module.
Figure B-1 shows the register address location within A16 as it might be
mapped by an embedded controller. Figure B-2 shows the location of A16
address space in the E1406 Command Module.
A16 Address Space
Outside the Command
Module
A16 Address Space
Inside the Command
Module or Mainframe
When the E1406 Command Module is not part of your VXIbus system (see
Figure B-1), the switch’s base address is computed as:
Command Module Address + C000
+ (LADDR * 64)
16
16
or
Command Module Address + 49,152 + (LADDR * 64)
where C000
(49,152) is the starting location of the register addresses,
16
LADDR is the matrix module’s logical address, and 64 is the number of
address bytes per VXI device. For example, the matrix module’s factory-set
logical address is 120 (78
). If this address is not changed, the switch will
16
have a base address of:
C000
+ (120 * 64)16 = C00016 + 1E0016 = DE00
16
16
or
49,152 + (120 * 64) = 49,152 + 7680 = 56,832
When the A16 address space is inside the E1406 Command Module
(see Figure B-2), the matrix module’s base address is computed as:
1FC000
+ (LADDR * 64)16
16
or
2,080,768 + (LADDR * 64)
where 1FC000
(2,080,768) is the starting location of the VXI A16
16
addresses, LADDR is the matrix module’s logical address, and 64 is the
number of address bytes per register-based device. Again, the matrix
module’s factory-set logical address is 120. If this address is not changed,
the switch module will have a base address of:
1FC000
+ (120 * 64)16 = 1FC00016 + 1E0016 = 1FDE00
16
16
or
2,080,768 + (120 * 64) = 2,080,768 + 7680 = 2,088,448
Register Offset The register offset is the register’s location in the block of 64 address bytes.
For example, the matrix module’s Status Register has an offset of 04
When you write a command to this register, the offset is added to the base
address to form the register address:
1FDE00
+ 0416 = 1FDE04
16
16
or
2,088,448 + 4 = 2,088,452
84 Register-Based Programming Appendix B
16
.
Page 85

FFFF
COOO
OOOO
Register
Offset
3E
16
3C
or
16
16
2E
16
2C
16
2A
16
16
16
16
16
16
06
16
16
16
16
16
*
16
*
10
30
28
26
24
22
20
1E
04
02
00
16
FFFF
16
16
REGISTER
ADDRESS
SPACE
A16
*
ADDRESS
SPACE
C000
16
(49,152)
16
*
16
+ (Logical Address 64)Base Address = COOO
49,152 + (Logical Address 64)
16-BIT WORDS
Bank 8 Control Register
Bank 7 Control Register
Bank 6 Control Register
Bank 5 Control Register
Bank 4 Control Register
Bank 3 Control Register
Bank 2 Control Register
Bank 1 Control Register
Bank 0 Control Register
Not Used
Status/Control Register
Device Type Register
ID Register
E1465A/66A/67A
A16 Register Map
Register Address = Base address + Register Offset
Figure B-1. Registers Within A16 Address Space
FFFFFF
EOOOOO
200000
IF0000
000000
16
16
16
16
16
E1406A
ADDRESS MAP
A24
ADDRESS
SPACE
Register
Offset
3E
16
3C
16
200000
16
IFCOOO
16
A16
ADDRESS
SPACE
IFOOOO
16
Base Address = IFC000
*
16
2,080,768 + (Logical Address 64)
200000
16
REGISTER
ADDRESS
SPACE
*
IFCOOO
16
(2,080,768)
+ (Logical Address 64)
or
*
16
*
10
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
16
06
16
16
16
16
30
2E
2C
2A
28
26
24
22
20
1E
16
04
02
00
Register Address = Base address + Register Offset
Figure B-2. Registers Within the E1406 A16 Address Space
Bank 8 Control Register
Bank 7 Control Register
Bank 6 Control Register
Bank 5 Control Register
Bank 4 Control Register
Bank 3 Control Register
Bank 2 Control Register
Bank 1 Control Register
Bank 0 Control Register
Not Used
Status/Cont rol Register
Device Type Register
ID Register
E1465A/66A/67A
A16 Register Map
Register-Based Programming 85Appendix B
Page 86

Register Descriptions
Each matrix module contains two read registers, one read/write register, and
16 write registers. This section describes each matrix module register.
Reading and
Writing to the
Example programs are provided at the end of this appendix that show how
to read and write to these registers. You can read or write to the following
matrix module registers.
Registers
• Manufacturer Identification Register (read only)
• Device Type Register (base + 02
• Status/Control Register (base + 04
• 16 Relay Control Registers (write only)
Manufacturer
Identification
The Manufacturer Identification Register is at offset address 0016 and
returns FFFF
the module is an A16 register-based module. This register is read only.
. This shows that Hewlett-Packard is the manufacturer and
16
Register
b+00
16
Write Undefined
Read
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Manufacturer ID - Returns FFFF16 = Hewlett-Packard A16 only register-based device.
Device Type
Register
The Device Type Register is at offset address 0216 and returns 012216 for
an E1465A/E1466A/E1467A module. This register is read only.
) (read only)
16
) (read or write)
16
b+02
16
Write Undefined
Read 0122
b+04
16
Write Not Used E Not Used SR
Read
86 Register-Based Programming Appendix B
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
16
Status/Control
Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
MS Module ID XXBEXX1 1XX
X
The Status/Control Register is at offset address 0416 and informs the user
about the module’s status and configuration. This register is read and write.
Page 87

Reading the
Status/Control Register
For Status/Control register reads, three bits are defined as follows.
• MODID (bit 14): 0 indicates the module has been selected by
MODID (module ID) and a 1 indicates the module has not been
selected. For example, if an E1466A matrix module is not busy
(bit 7 = 1) and the interrupt is enabled (bit 6 = 0), a read of the
Status/Control Register (base + 04
) returns DBBF.
16
• Module ID (bits 10 - 13): The following bit representations determine
the module configuration (E1465A/66A/67A determined by the
terminal module attached).
Model/Bits (13) (12) (11) (10)
E1465A 1 0 0 1
E1466A 0 1 1 0
E1467A 0 1 0 1
• Busy (bit 7): 0 indicates the module is busy. Each relay requires
about 7 ms execution time during which time the matrix module
is busy. Bit 7 of this register is used to inform the user of a busy
condition.
Writing to the
Status/Control Register
NOTE When writing to the registers it is necessary to write "0" to bit 0 after the
• Enable (bit 6): 0 indicates the interrupt is enabled. The interrupt
generated after a channel has been closed can be disabled. Bit 6
of this register is used to inform the user of the interrupt status.
You can only write to bits 0 and 6 of the Status/Control Register.
• Enable (bit 6): Writing a "1" to this bit disables the interrupt function
of the module.
• Soft Reset (bit 0): Writing a "1" to this bit does not soft reset the
module. To reset each relay in register-based programming, you
must write all 0s to all 16 banks to open all relays.
reset has been performed before any other commands can be programmed
and executed. SCPI commands take care of this automatically.
Register-Based Programming 87Appendix B
Page 88

Relay Control
Register
There are 16 relay control registers: Bank 0 Relay Control Register (base +
) through Bank 15 Relay Control Register 2 (base + 3E16). These
20
16
registers are used to open and close the specified matrix relays. Reading
any Relay Control Register will always return FFFF
regardless of the
16
channel states.
The numbers in the register maps indicate the channel number to be
written to. To close a relay, you must write a 1 to the bit. For example,
WRITEIO-16,(DE00
DE00
is the base address, 2016 is the offset address, and 0010 is the
16
);001016 closes bit 4 of bank 0 (channel 004), where
16
hexadecimal number to send a 1 to bit 4.
Bank 0 Relay Control Register
Address
Base+20
Address
Base+22
Address
Base+24
Address
Base+26
Address
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
015 014 013 012 011 010 009 008 007 006 005 004 003 002 001 000
16
Bank 1 Relay Control Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
115 114 113 112 111 111 109 108 107 106 105 104 103 102 101 100
16
Bank 2 Relay Control Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
215 214 213 212 211 210 209 208 207 206 205 204 203 202 201 200
16
Bank 3 Relay Control Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
315 314 313 312 311 310 309 308 307 306 305 304 303 302 301 300
16
Bank 4 Relay Control Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Base+28
415 414 413 412 411 410 409 408 407 406 405 404 403 402 401 400
16
Bank 5 Relay Control Register
Address
Base+2A
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
515 514 513 512 511 510 509 508 507 506 505 504 503 502 501 500
16
Bank 6 Relay Control Register
Address
Base+2C
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
615 614 613 612 611 610 609 608 607 606 605 604 603 602 601 600
16
88 Register-Based Programming Appendix B
Page 89

Bank 7 Relay Control Register
Address
Base+2E
Address
Base+30
Address
Base+32
Address
Base+34
Address
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
715 714 713 712 711 710 709 708 707 706 705 704 703 702 701 700
16
Bank 8 Relay Control Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
815 814 813 812 811 810 809 808 807 806 805 804 803 802 801 800
16
Bank 9 Relay Control Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
915 914 913 912 911 910 909 908 907 906 905 904 903 902 901 900
16
Bank 10 Relay Control Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1015 1014 1013 1012 1011 1010 1009 1008 1007 1006 1005 1004 1003 1002 1001 1000
16
Bank 11 Relay Control Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Base+36
Address
Base+38
Address
Base+3A
Address
Base+3C
Address
Base+3E
1115 1114 1113 1112 1111 111 0 110 9 1108 110 7 11 06 1105 11 04 110 3 1102 11 01 110 0
16
Bank 12 Relay Control Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1215 1214 1213 1212 1211 1210 1209 1208 1207 1206 1205 1204 1203 1202 1201 1200
16
Bank 13 Relay Control Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1315 1314 1313 1312 1311 1310 1309 1308 1307 1306 1305 1304 1303 1302 1301 1300
16
Bank 14 Relay Control Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1415 1414 1413 1412 1411 1410 1409 1408 1407 1406 1405 1404 1403 1402 1401 1400
16
Bank 15 Relay Control Register
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1515 1514 1513 1512 1511 1510 1509 1508 1507 1506 1505 1504 1503 1502 1501 1500
16
Register-Based Programming 89Appendix B
Page 90

Programming Examples
This section provides example programs in BASIC and C/HP-UX, including:
• Example: Reading the Registers (BASIC)
• Example: Reading the Registers (C/HP-UX)
• Example: Making Measurements (BASIC)
• Example: Making Measurements (C/HP-UX)
• Example: Scanning Channels (BASIC)
• Example: Scanning Channels (C/HP-UX)
Example: Reading
the Registers
(BASIC)
This BASIC programming example reads the Manufacturer ID Register,
Device Type Register and Status Register on the E1466A matrix module.
10 !*****************************************************
20 ! ****** READREG *****
30 !*****************************************************
40 OPTION BASE 1
50 !
60 DIM Reg_name$(1:3)[32], Reg_addr(1:3)
70 !
80 !
90 READ Reg_name$(*)
100 READ Reg_addr(*)
110 !
120 !
130 Base_addr = DVAL("DE00",16)
140 !
150 !
160 !
170 CONTROL 16,25;2
180 !
190 Read_regs(Base_addr, Reg_name$(*), Reg_addr(*))
200 !
210 DATA Identification register, Device register, Status register
220 DATA 00, 02, 04
230 END
300 !
310 !
320 SUB Read_regs(Base_addr, Reg_name$(*), Reg_addr(*))
330 !
340 For Number = 1 to 3
350 Register = READIO(-16,Base_addr + Reg_addr(number))
360 PRINT Reg_name$(number); " = "; IVAL$(Register,16)
370 Next Number
380 SUBEND
Set up arrays to store register names and addresses
Read register names and addresses into the arrays
Set base address variable
Map the A16 address space in the controller
Call the subprogram Read_regs
.
.
.
This subprogram steps through a loop that reads each register
and prints its contents
90 Register-Based Programming Appendix B
Page 91

Example: Reading
the Registers
This C/HP-UX programming example reads the Manufacturer ID Register,
Device Type Register and Status Register on the E1466A matrix module.
(C/HP-UX)
/***************************************************/
/****** readreg.c ******/
/**************************************************/
#include <sys/vxi.h> /*source file for controller VXI drivers*/
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define logical_address 120 /*logical address of the matrix module*/
int fd;
typedef unsigned short word;
typedef struct dev_regs{ /*set up pointers*/
unsigned short id_reg;
unsigned short device_type;
unsigned short status_reg;
unsigned short bank0_channels;
} DEV_REGS;
main( )
{
/*open the controller VXI interface*/
fd=open("/dev/vxi/primary",O_RDWR);
if (fd){
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
/*retrieve the A16 pointers*/
dev=(struct dev_regs *)vxi_get_a16_addr(fd,logical_address);
/*sub to read the registers*/
read_reg(dev);
/*END of main program*/
}
/*SUB READ_REG*/
int read_reg(reg_ptr)
DEV_REGS *reg_ptr;
{
/*read the ID register*/
printf("\n ID Register = 0x%x\n",reg_ptr->id_reg);
/*read the Device Type register*/
printf("\n Device Type Register = 0x%x\n",reg_ptr->device_type);
/*read the Status register*/
printf("\n Status Register = 0x%x\n",reg_ptr->status_reg);
return;
}
Register-Based Programming 91Appendix B
Page 92

Example: Making
Measurements
(BASIC)
This BASIC programming example closes bit 1 on bank 0, waits for a
measurement to be made, and then opens the channel. You must insert
your own programming code for the measurement part of this program. For
example, if you are using the E1411B, see the E1326B/E1411B Multimeter
User's Manual for programming examples.
10 !***************************************************
20 !***** MAKEMEAS *****
30 !***************************************************
40 OPTION BASE 1
50 !
60 DIM Reg_name$(1:1)[32], Reg_addr(1:1)
70 !
80 !
90 READ Reg_name$(*)
100 READ Reg_addr(*)
110 !
120 !
130 Base_addr = DVAL("DE00",16)
140 !
150 !
160 CONTROL 16,25;2
170 !
180 Make_meas(Base_addr, Reg_addr(*))
190 !
200 DATA Bank0 channels register
210 DATA 06
220 END
280 !
290 !
300 !
310 SUB Make_meas(Base_addr, Reg_addr(*))
320 !
330 WRITEIO -16, Base_addr + Reg_addr(1); 1
340 REPEAT
350 UNTIL BIT(READIO(-16,Base_addr+4),7)
380 WRITEIO -16, Base_addr + Reg_addr(1);0
390 SUBEND
Set up arrays to store register names and addresses
Read register names and address into the arrays
Set base address variable
Map the A16 address space in the controller
Call the subprogram Make_meas
.
.
.
This subprogram closes bit 1 of bank0 channels, waits for the
channel to be closed, makes a measurement, and then opens
the relay
.
.
.!
.
Make Measurements
92 Register-Based Programming Appendix B
Page 93

Example: Making
Measurements
(C/HP-UX)
This C/HP-UX programming example closes bit 1 on bank 0, waits for a
measurement to be made, and then opens the channel. You must insert
your own programming code for the measurement part of this program. For
example, if you are using the E1411B, see the E1326B/E1411B Multimeter
User's Manual for programming examples.
The sub ver_time allows time for switch closures. This sub should print a
time around 7 ms. If the time is less, you must change the value of j in
the for loop. For example, instead of 7000, you might need to use 10000.
/******************************************************/
/*** makemeas.c ***/
/******************************************************/
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/vxi.h> /*source file for controller VXI drivers*/
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define logical_address 120 /*logical address of matrix module*/
int fd;
typedef unsigned short word;
typedef struct dev_regs{ /*set up pointers*/
unsigned short id_reg;
unsigned short device_type;
unsigned short status_reg;
unsigned short bank0_channels;
} DEV_REGS;
main( )
{
/*open the controller VXI interface*/
fd=open("/dev/vxi/primary",O_RDWR);
if (fd){
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
/*retrieve the A16 pointers*/
dev=(struct dev_regs *)vxi_get_a16_addr(fd,logical_address);
/*sub to verify the time to close the switch*/
ver_time( );
/*sub to close switch and make measurement*/
make_meas(dev);
} /* *END of main program*/
Continued on next page
Register-Based Programming 93Appendix B
Page 94

/*SUB VER_TIME*/
ver_time( )
{
struct timeval first,
second,
lapsed;
struct timezone tzp;
gettimeofday(&first,&tzp);
for (j=0; j<=7000; j ++);
gettimeofday ($second,&tzp);
if (first.tv_usec > second.tv_usec)
{
second.tv_usec +=1000000;
second.tv_sec--;
}
lapsed.tv_usec = second.tv_usec - first.tv_usec;
lapsed.tv_sec = second.tv_sec - first.tv_sec;
printf("Elapsed time for closing a channel is: %ld sec %ld usec \n",
lapsed.tv_sec, lapsed.tv_usec);
}
/*SUB MAKE_MEAS*/
int make_meas(reg_ptr)
DEV_REGS *reg_ptr;
{
/*close bit 1 of bank0 */
reg_ptr->bank0_channels=0x0001;
for (j=0; j<=7000; j ++); /*wait for switch to close*/
printf("\n Making Measurement");
.
. /*make measurements*/
.
/*open bit 1 of bank0*/
reg_ptr->bank0_channels=0x0000;
return;
}
94 Register-Based Programming Appendix B
Page 95

Example: Scanning
Channels (BASIC)
This BASIC programming example scans through the bank 0 channels
(closing one switch at a time) and makes measurements between switch
closures. You must insert your own programming code for the measurement
part of this program. For example, if you are using the E1411B, see the
E1326B/E1411B Multimeter User's Manual for programming examples.
10 !**************************************************
20 !***** SCANNING *****
30 !**************************************************
40 OPTION BASE 1
50 !
60 DIM Reg_name$(1:1)[32], Reg_addr(1:1)
70 !
80 !
90 READ Reg_name$(*)
100 READ Reg_addr(*)
110 !
120 Base_addr = DVAL("DE00",16)
130 !
140 !
150 CONTROL 16,25;2
160 !
170 Scan_meas(Base_addr, Reg_addr(*))
180 !
190 DATA Bank0 channels register
200 DATA 06
210 END
270 !
280 !
290 !
300 SUB Scan_meas(Base_addr, Reg_addr(*))
310 !
320 WRITEIO -16, Base_addr + Reg_addr(1);0
330 FOR I= 0 to 15
340 WRITEIO -16, Base_addr + Reg_addr(1);2^I
350 REPEAT
360 UNTIL BIT(READIO(-16,Base_addr+4),7)
370 PRINT "Making Measurements"
420 NEXT I
430 WRITEIO -16,Base_addr + Reg_addr(1);0
440 SUBEND
Set up arrays to store register names and addresses
Read register names and addresses into the arrays
Set base address variable
Map the A16 address space in the controller
Call the subprogram Scan_meas
.
.
.
This subprogram sets all bits in bank0 open then scans through
bank 0, closing one channel at a time (waits for the channel to
be closed) so a measurement can be made.
.
. !
.
Make Measurements
Register-Based Programming 95Appendix B
Page 96

Example: Scanning
Channels (C/HP-UX)
NOTE The sub ver_time allows time for the switches to close. The program should
This C/HP-UX programming example scans through the bank 0 channels
(closing one switch at a time) and makes measurements between switch
closures. You must insert your own programming code for the measurement
part of this program. For example, if you are using the E1411B, see the
E1326B/E1411B Multimeter User's Manual for programming examples.
print a time around 7 ms. If the time is less, you must change the value of j
in the for loop. For example, instead of 7000, you might need to use 10000.
The math.h include file requires a -lm option when compiling this program.
/******************************************************/
/*** scanning.c ***/
/******************************************************/
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h> /*file to perform math functions*/
#include <sys/vxi.h> /*source file for controller VXI drivers*/
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define logical_address 120 /*logical address of Form C Switch*/
#define lastch 15
int fd, i, j, reg;
double y;
typedef unsigned short word;
typedef struct dev_regs{ /*set up pointers*/
unsigned short id_reg;
unsigned short device_type;
unsigned short status_reg;
unsigned short dummy[13];
unsigned short bank0_channels;
} DEV_REGS;
main( )
{
/*open the controller VXI interface*/
fd=open("/dev/vxi/primary",O_RDWR);
if (fd) {
perror("open");
exit(1);
}
/*retrieve the A16 pointers*/
dev=(struct dev_regs*)vxi_get_a16_addr(fd,logical_address);
Continued on next page
96 Register-Based Programming Appendix B
Page 97

/*sub to verify the time to close the switch*/
ver_time( );
/*sub to close a set of switches and make measurements*/
scan_meas(dev);
} /*END of main program*/
/*SUB VER_TIME*/
ver_time( )
{
struct timeval first,
second,
lapsed;
struct timezone tzp;
gettimeofday(&first,&tzp);
for (j=0; j<=7000; j ++);
gettimeofday ($second,&tzp);
if (first.tv_usec > second.tv_usec)
{
second.tv_usec +=1000000;
second.tv_sec--;
}
lapsed.tv_usec = second.tv_usec - first.tv_usec;
lapsed.tv_sec = second.tv_sec - first.tv_sec;
printf("Elapsed time for closing a channel is: %ld sec %ld usec \n",
lapsed.tv_sec, lapsed.tv_usec);
}
/*SUB SCAN_MEAS*/
int scan_meas(reg_ptr)
DEV_REGS *reg_ptr;
{
/*set bank0 to 000 */
reg_ptr->bank0_channels=0x000;
i=0;
for (i=0;i=lastch;i ++)
{
y=i;
reg=pow(2.0,y);
reg_ptr-bank0_channels=reg;
for (j=0; j<=7000; j ++); /*wait for switch to be closed*/
printf("\n Making Measurement");
.
. /*make measurements*/
.
}
return;
}
Register-Based Programming 97Appendix B
Page 98

Notes:
98 Register-Based Programming Appendix B
Page 99

Error Types
Appendix C
Matrix Modules Error Messages
Table C-2 lists the error messages generated by the E1465A, E1466A, or
E1467A Relay Matrix Switch modules firmware when programmed by SCPI.
Errors with negative values are governed by the SCPI standard and are
categorized in Table C-1. Error numbers with positive values are not
governed by the SCPI standard. See the E1406A Command Module
User’s Manual for further details on these errors.
Table C-1. Error Types
Range Error Types Description
-199 to -100 Command Errors (syntax and parameter errors).
-299 to -200 Execution Errors (instrument driver detected errors)
-399 to -300 Device Specific Errors (instrument driver errors that
are not command nor execution errors).
-499 to -400 Query Errors (problem in querying an instrument)
Matrix Modules Error Messages 99Appendix C
Page 100

Error Messages
Table C-2. Error Messages
Code
-109 Missing Parameter Sending a command requiring a channel list without the channel list.
-211 Trigger Ignored Trigger received when scan not enabled. Trigger received after scan
-213 INIT Ignored Attempting to execute an INIT command when a scan is already in
-224 Illegal Parameter Value Attempting to execute a command with a parameter not applicable to
-310 System Error Too many characters in the channel list expression.
+1500 External Trigger Source
Already Allocated
+2000 Invalid Card Number Addressing a module (card) in a switchbox that is not part of the
+2001 Invalid Channel Number Attempting to address a channel of a module in a switchbox that is not
+2006 Command Not Supported On
This Card
+2008 Scan List Not Initialized Executing an INIT without a channel list defined.
+2009 Too Many Channels In Channel
List
Error Message
Potential Cause(s)
complete. Trigger too fast.
progress.
the command.
Assigning an external trigger source to a switchbox when the trigger
source has already been assigned to another switchbox.
switchbox.
supported by the module (e.g., channel 99 of matrix module).
Sending a command to a module (card) in a switchbox that is
unsupported by the module.
Attempting to address more channels than available in the switchbox.
+2011 Empty Channel List No valid channels are specified in the <channel_list>.
+2012 Invalid Channel Range Invalid channel(s) specified in SCAN <channel_list> command.
Attempting to begin scanning when no valid <channel_list> is defined.
+2600 Function Not Supported On
This Card
Sending a command to a module (card) in a switchbox that is not
supported by the module or switchbox.
100 Matrix Modules Error Messages Appendix C
 Loading...
Loading...