Page 1

Acer ARMC/2
User’s Guide
MAN-840
07/09/04
Page 2
© Copyright 1998-2004 American Megatrends, Inc.
All rights reserved.
American Megatrends, Inc.
6145-F Northbelt Parkway
Norcross, GA 30071
This publication contains propriet ary in f ormation which is protected by copyright . No
part of this publication can be reproduced, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system,
translated into any language or computer language, or transmitted in any form
whatsoever without the prior written consent of the publisher, American Megatrends, Inc.
American Megatrends, Inc. acknowledges the following trademarks:
Intel is a registered trademark of the Intel Corporation.
MS-DOS and Microsoft are registered trademarks of the Microsoft Corporation.
Microsoft Windows is a trademark of the Microsoft Corporation.
IBM, AT, VGA, PS/2, and OS/2 are registered trademarks and XT and CGA are
trademarks of the International Business Machines Corporation.
Other trademarks and trade names may be used in this document to refer to either the
entities claiming the marks and names or their products. American Megatrends, Inc.
disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
Revision History
02/25/04 Preliminary release
03/15/04 Updated GUI
04/02/04 Updated ARMC2RMseek Utility instructions
05/04/04 Password/User Name length changed to max 32 characters
05/14/04 Added Full Screen Toolbar & ARMC2ConfigApp FW Flash Module
06/04/04 Removed Battery Backup Unit Information
07/09/04 Removed Optional Modem Information
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
ii
Page 3

Table of Contents
Revision History............................................................................................................................ii
Table of Contents.........................................................................................................................iii
Disclaimer ....................................................................................................................................vi
Optional Components.................................................................................................................vii
FCC Class B Statement..............................................................................................................vii
Chapter 1 Introduction.......................................................................................................... 1
Features....................................................................................................................................... 1
Important NOTES: ......................................................................................................................... 3
Chapter 2 Installing Your ARMC/2 Card ............................................................................. 4
Before You Start ..........................................................................................................................4
Avoid Electro-Static Discharge (ESD)...................................................................................... 4
ARMC/2 Installation and Setup.................................................................................................... 4
Step 1 Unpack the ARMC/2 Card (and check jumper settings) .................................................. 5
ARMC/2 Card Layout............................................................................................................... 5
ARMC/2 MAC Address............................................................................................................. 5
JP4 and JP5 Chassis/Motherboard Power Switch................................................................... 6
JP6 ARMC/2 Reset Button....................................................................................................... 6
JP7 and JP8 Chassis/Motherboard Reset Switch.................................................................... 6
JP11 Flash Write Enable/Disable............................................................................................. 6
JP12 Diagnostic and Recovery Mode Jumper......................................................................... 7
JP13 and JP14 PCI Bus SMB Data and Clock Jumper........................................................... 7
Step 2 Plug in the ARMC/2 Card into the Host System and Attach Internal Cables................... 7
J3 Service Connector............................................................................................................... 7
J4 JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) ICE (In-Circuit Emulator) Connector................................ 7
J5 IPMB (Intelligent Platform Management Bus)..................................................................... 8
IPMB (Intelligent Platform Management Bus).......................................................................... 8
J9 ARMC/2 Feature Connector................................................................................................ 9
JP2 Serial Port Connector........................................................................................................ 9
JP3 Service Connector............................................................................................................. 9
JP4 and JP5 Chassis/Motherboard Power Switch................................................................. 10
JP6 ARMC/2 Reset Button..................................................................................................... 10
JP7 and JP8 Chassis/Motherboard Reset Switch.................................................................. 10
Step 3 Connect External Cables................................................................................................ 10
Step 4 Confirm the Motherboard’s BIOS Settings..................................................................... 11
Step 5 Install the Operating System and ARMC/2 Drivers........................................................ 11
Installing Virtual Floppy Drivers on Microsoft® Windows Operating Systems....................... 12
Step 6 Install the Acer ARMC/2 Windows Software Components............................................. 15
Step 7 Setup Your Client Internet Browser................................................................................ 19
Step 8 Connect to the ARMC/2 from a Client System............................................................... 23
Step 9 Load the ARMC/2 SDR and Soft Processor (SP) File for Your Server Board Model.... 27
Chapter 3 Locating Your ARMC/2 Card ............................................................................ 31
Overview.................................................................................................................................... 31
Locating Your ARMC/2 Card ..................................................................................................... 31
IP Address Range...................................................................................................................... 35
Usage.........................................................................................................................................37
Chapter 4 Using Your ARMC/2........................................................................................... 39
ARMC/2 GUI Overview.............................................................................................................. 39
Default User Name and Password ............................................................................................ 39
ARMC/2 GUI Explained............................................................................................................. 40
Menu Bar................................................................................................................................ 40
Preface
iii
Page 4

Quick Launch Icons................................................................................................................ 41
Session Information................................................................................................................ 41
Manage Group...........................................................................................................................42
Remote Console........................................................................................................................ 43
Redirection................................................................................................................................. 44
Setting up Internet Explorer....................................................................................................44
Staring Redirection................................................................................................................. 48
Remote Console Shortcut Key Combinations........................................................................ 50
Console Redirection Window................................................................................................. 51
Console Redirection Toolbar.................................................................................................. 54
Console Redirection Toolbar Status ...................................................................................... 54
Console Redirection Toolbar Toggle Buttons ........................................................................ 55
Start CD-ROM Drive Redirection ........................................................................................... 56
Stop CD-ROM Drive Redirection............................................................................................ 59
Start Floppy Drive Redirection ............................................................................................... 61
Stop Floppy Drive Redirection................................................................................................ 64
ARMC2 Floppy Image Creator............................................................................................... 66
Creating a Floppy Image........................................................................................................ 66
Transferring a Floppy Image to a Floppy Disk....................................................................... 69
Remote Power Control............................................................................................................... 74
Upgrade Firmware..................................................................................................................... 75
Updating Your ARMC/2’s Firmware....................................................................................... 76
Reset ARMC/2........................................................................................................................... 81
Configure Group ........................................................................................................................83
Users.......................................................................................................................................... 84
Adding Users.......................................................................................................................... 85
Removing Users..................................................................................................................... 86
Viewing and Editing Users ..................................................................................................... 87
Network...................................................................................................................................... 88
Firewall....................................................................................................................................... 90
Alert Notification......................................................................................................................... 92
Date & Time............................................................................................................................... 93
Serial Port .................................................................................................................................. 94
SSL Certificate...........................................................................................................................95
PMCP File Upload .....................................................................................................................97
IPMI Configuration................................................................................................................... 102
Server OS Monitoring & Recovery........................................................................................... 103
View Group .............................................................................................................................. 104
ARMC/2 Card Health............................................................................................................... 105
Event Log................................................................................................................................. 106
Server Health...........................................................................................................................107
General Information................................................................................................................. 108
General Information : Version .............................................................................................. 108
General Information : Features ............................................................................................ 109
General Information : Detailed Versions.............................................................................. 109
Last Saved Crash Screen........................................................................................................ 110
Appendix A ARMC/2 Universal Cable................................................................................. 111
ARMC/2 Universal Cable Layout............................................................................................. 111
Appendix B ARMC2ConfigApp ........................................................................................... 113
Overview.................................................................................................................................. 113
ARMC2ConfigApp.................................................................................................................... 113
User Manager Tab ...............................................................................................................115
Adding a User....................................................................................................................... 116
User Properties ....................................................................................................................117
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
iv
Page 5

Network Configuration Tab................................................................................................... 118
Advanced Tab ...................................................................................................................... 119
WinCuri .................................................................................................................................... 120
WinCuri.exe Help File........................................................................................................... 120
LinCuri......................................................................................................................................122
LinCuri Help File................................................................................................................... 123
Appendix C ARMC/2 Remote Recovery Application (RRA) ............................................. 125
ARMC/2 Card Remote Recovery Application (RRA)............................................................... 125
Appendix D Troubleshooting.............................................................................................. 132
Screen Distortion .....................................................................................................................132
Problem................................................................................................................................ 132
Symptom .............................................................................................................................. 132
Solution................................................................................................................................. 133
BMC Not Responding.............................................................................................................. 134
Problem................................................................................................................................ 134
Symptom .............................................................................................................................. 134
Solution................................................................................................................................. 134
Cannot Power On the Host System Remotely......................................................................... 135
Problem................................................................................................................................ 135
Symptom .............................................................................................................................. 135
Solution................................................................................................................................. 135
Complete Flash........................................................................................................................ 135
Problem................................................................................................................................ 135
Symptom .............................................................................................................................. 135
Solution................................................................................................................................. 135
Appendix E Serial Over LAN ............................................................................................... 137
Hardware Setup....................................................................................................................... 137
BIOS..................................................................................................................................... 138
Appendix F Port Usage........................................................................................................ 139
Port Usage Table..................................................................................................................... 139
Appendix G MAC Address Map........................................................................................... 141
Appendix H Tree Structure and Description of CD Contents.......................................... 142
ARMC/2 CD ............................................................................................................................. 142
ARMC/2 CD Image............................................................................................................... 142
CD Contents......................................................................................................................... 142
Appendix I GtkRConsoleARMC2 for Linux ...................................................................... 144
Installation................................................................................................................................ 144
Notes........................................................................................................................................ 145
Limited Warranty
The buyer agrees that if this product proves to be defective, American Megatrends is only
obligated to repair or replace this product at American Megatrends’ discretion according
to the terms and conditions of the warranty registration card that accompanies this
product. American Megatrends shall not be liable in tort or contract for any loss or
damage, direct, incidental or consequential resulting from the use of this product. Please
see the Warranty Registration Card shipped with this product for full warranty details.
Preface
v
Page 6
Technical Support
Please contact your local Acer Authorized Reseller for technical support.
Disclaimer
This manual describes the operation of the Acer ARMC/2 card. Although efforts have
been made to assure the accuracy of the information contained here, Acer expressly
disclaims liability for any error in this information, and for damages, whether direct,
indirect, special, exemplary, consequential or otherwise, that may result from such error,
including but not limited to the loss of profits resulting from the use or misuse of the
manual or information contained therein (even if Acer has been advised of the possibility
of such damages). Any questions or comments regarding this document or its contents
should be addressed to Acer at the address shown on the inside of the front cover.
Acer provides this publication “as is” without warranty of any kind, either expressed or
implied, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability or fitness
for a specific purpose.
Some states do not allow disclaimer of express or implied warranties or the limitation or
exclusion of liability for indirect, special, exemplary, incidental or consequential
damages in certain transactions; therefore, this statement may not apply to you. Also, you
may have other rights which vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction.
This publication could include technical inaccuracies or typographical errors. Changes
are periodically made to the information herein; these changes will be incorporated in
new editions of the publication. Acer may make improvements and/or revisions in the
product(s) and/or the program(s) described in this publication at any time.
Requests for technical information about Acer products should be made to your Acer
authorized reseller or marketing representative.
Retail Packing List
You should have received the following:
• a ARMC/2 card
• one USB cable
• one universal cable
• a warranty card
• this ARMC/2 User's Guide (located on the ARMC/2 CD)
• a ARMC/2 Quick Installation Guide
• a ARMC/2 CD
• a ARMC/2 external power adapter
Note: Your ARMC/2 may or may not ship with everything listed in the Retail Packing List.
Contact your Acer authorized reseller to find out what is shipped with your ARMC/2.
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
vi
Page 7
Optional Components
The following component does not come with your ARMC/2 card. You must order this
component separately.
• Power cable
FCC Class B Statement
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device
must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installatio n. This
equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the
user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Warning
Changes or modifications to this device not expressly approved by American
Megatrends could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Preface
vii
Page 8

Page 9
Chapter 1 Introduction
Features
Feature Description
Key Feature
Soft Processor
Remote Client
Processor System On
Chip (SOC)
Memory
Flash
Ethernet LAN
I2C Controller Hardware
Monitor (OEM version
feature)
Power Supply
Form Factor
Environmental
Specifications
Monitoring
• 100% out-of-band
• 100% operating system independent
• provides out-of-band connectivity
• plugs into a mission critical server
• half-sized PCI form factor plugs into any PCI slot
• industry standard Internet browser (any JavaScript 1.2 capable)
• manage the server from anywhere in the world
• SSL v3 for secure connection
• 32-Bit 266 MHz ~ 400 MIPS MMU
• 16 K I-cache
• 16 K D-cache
• 32 megabyte PC-133 MHz SDRAM standard (soldered on PCB, you cannot
upgrade or remove)
• 16 bit, 16 megabyte flash ROM (soldered on PCB, you cannot upgrade or
remove)
• integrated SOC 10/100 MAC
• external level one 10/100 BASE-TX Ethernet
• ambient temperature monitoring
• PCI voltages monitoring
• card internal voltages monitoring
• RTC
• external RTC for time stamp of events
• switching logic between optional 6 V wall adapter, 5 V PCI, and 3.3 V PCI
• half-size standard PCI card
• storage temperature: -20 degrees to 80 degrees C
• relative humidity: 5 to 80 percent non-condensing @ 40 degrees
• operating temperature: 0 to 45 degrees C
• vibration: 2.5G acceleration over 2000 Hz sine wave, 2oct/mian sine sweep
• shock: 20G; 11 msec duration, half-sine shock sweep
• IPMI 1.5 compliant (OEM version feature)
• I2C sensors (OEM version feature)
• SDR and Soft Processor (SP) file support for easy customization (OEM
version feature)
• OEM specific
Cont’d
Chapter One : Introduction
1
Page 10

Features, Continued
Feature Description
Communication
USB Device Controller
for Mouse/Keyboard
USB Device Controller
for CD-ROM
USB Device Controller
for FDD
USB Hub
Serial Port X 3
Debug Support
Alert Notification
Console Redirection
Security
Virtual Boot
Host Side Operating
System Support
Platform Management
Configuration Program
(PMCP)
• 10/100 megabit Ethernet LAN
• TCP/IP
• DHCP enabled
• SNMP
• web-based interface
• USB 1.1 device controller
• USB 2.0 device controller
• USB 1.1 device controller
• USB 2.0 hub
• debug port
• RS485
• one external
• Jtag ICE
• SNMP trap up to eight destinations
• email notification
• via 10/100 megabit Ethernet LAN
• up to three multiple redirection sessions
• up to 15 screens per second high speed redirection hardware engine
• no overhead on the host system, complete operating system independence
• redirect BIOS screens and setup screens
• seamless text and graphics transition
• SSL (Secured Socket Layer) 3.0 (Pass-phrase encrypted certificates are not
supported)
• DAA (Digestive Authentication Access)
• MD-5
• USB 2.0 CD-ROM
• USB floppy
• supports boot to image
• allows remote operating system boot up and installation
Note: For information on how to create a bootable CD, visit nero.com or
roxio.com. You can do a search on how to create a bootable CD using their
products. You can also consult your CD writer's documentation.
• Windows 2000/2003 and above
• RedHat Linux 9.0; Enterprise Linux 3.0, AS; Enterprise Linux 3.0 Update2,
AS
• Available
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
2
Page 11

Important NOTES:
There are some NOTES for ARMC/2.
NOTE1.
This note applies to the Altos G520/G710/R710/R510 with Redhat Enterprise Linux 3.0
and Altos G520/R510 with Redhat 9.0. Because these server can not detect the virtual
device (keyboard/mouse/CDROM/Floppy) in Redhat Enterpeise Linux 3.0 and Redhat
Linux 9.0. These some methods can solve this issue.
Method 1.
. Disable the USB 2.0 controller in BIOS (only for G520, R510 and R710)
Method 2.
. Connect a external USB 1.1 hub to server, then connect the ARMC/2 USB
cable behind the USB 1.1 hub.
Method 3.
. Users can unplug and plug ARMC/2 USB cable then server can recognizes
virtual device in Linux. But if you shutdown or restart the server, you must unplug and plug
ARMC/2 USB cable again.
NOTE2.
For “Full Screen function key (Alt + F) issue if client computer OS is Linux:”
IF client computer OS is RH9.0 or RH Enterprise 3.0 Update 1, the function key
is no problem. But it is other Linux version; please use toolbar to control the
Full Screen mode.
NOTE3.
For “Use Mazilla browser of Linux OS on client computer to login ARMC/2 website”
IF client computer OS is Linux, please use the Mazilla browser version to 1.6 or later to login
ARMC/2 website.
NOTE4.
For “Must connect external power with ARMC/2.”
IF ARMC/2 does not connect external power, it will bring about the system
cannot power on by pressing power button.
NOTE5.
“The host heartbeat function is ONLY supported under Windows OS.”
Chapter Two : Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
3
Page 12

Chapter 2 Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
Before You Start
Avoid Electro-Static Discharge (ESD)
Electro-Static Discharge (ESD) can damage the ARMC/2 card and other system
components. Keep your ARMC/2 card in its anti-static bag until it is to be installed.
Avoid contact with any component or connector on any adapter card, printed circuit
board, or memory module. Handle these components by the mounting bracket.
Perform all unpacking and installation procedures on a ground-connected anti-static mat.
Wear an anti-static wristband grounded at the same point as the anti-static mat. You can
also use a sheet of conductive aluminum foil grounded through a one megaohm resistor
instead of the anti-static mat. Similarly, a strip of conductive aluminum foil wrapped
around the wrist and grounded through a one megaohm resistor serves the same purpose
as a wristband.
ARMC/2 Installation and Setup
Use the following steps to install the ARMC/2 card into the host system.
Step Action
1 Unpack the ARMC/2 card (and check jumper settings)
2 Plug in the ARMC/2 card into the host system and attach internal cables
3 Connect external cables
4 Confirm the motherboard’s BIOS settings
5 Install the operating system and ARMC/2 card’s drivers
6 Install all ARMC/2 Windows Software Components
7 Setup your client system’s Internet browser
8 Connect to the ARMC/2 from a client system
9 Load the ARMC/2 SDR and Soft Processor (SP) File for your motherboard or
server board model
Note: Inspect the cardboard carton for obvious damage.
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
4
Page 13
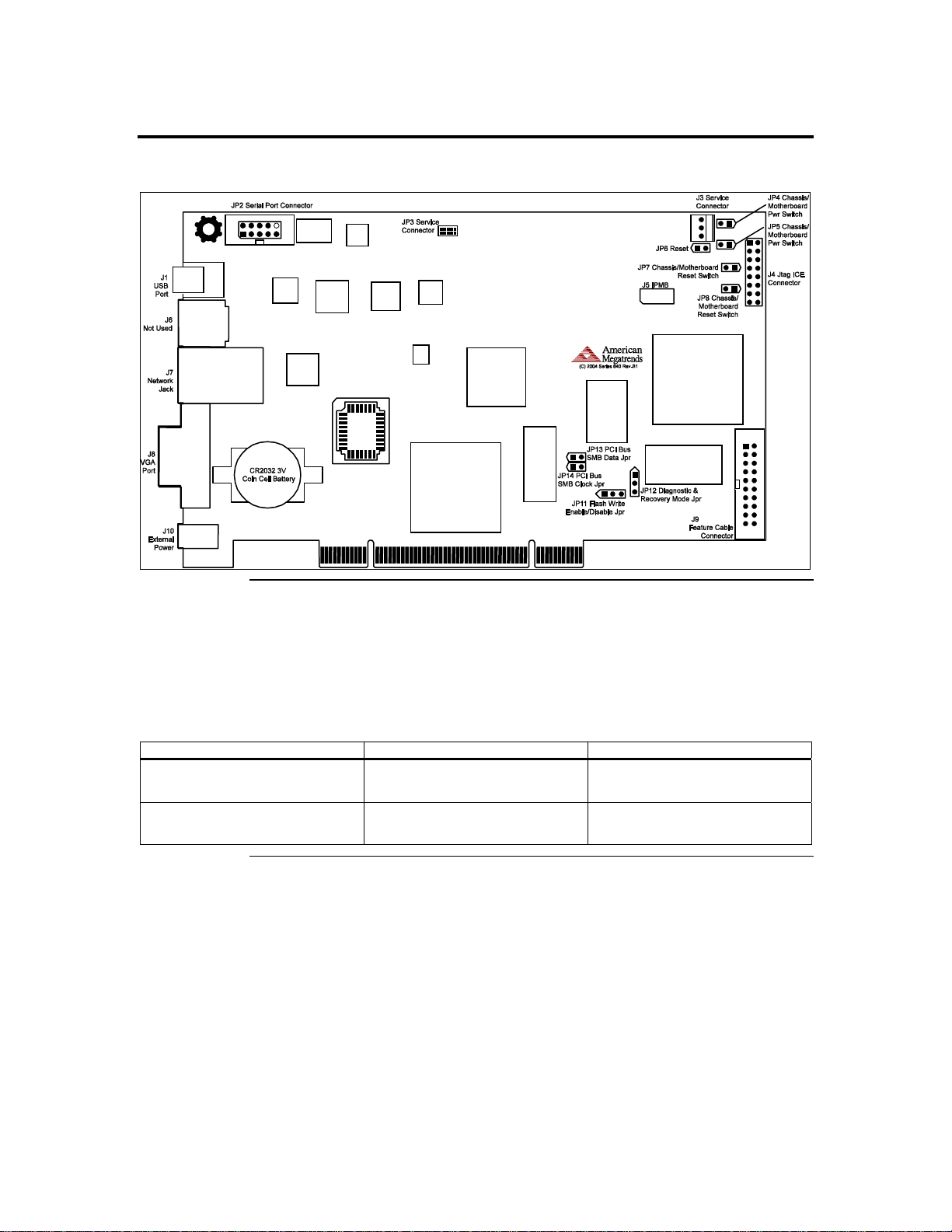
Step 1 Unpack the ARMC/2 Card (and check jumper settings)
ARMC/2 Card Layout
ARMC/2 MAC Address
Your ARMC/2 card has a unique MAC address. The MAC address is the only way to
distinguish one ARMC/2 card from another when you run programs such as Remote
Recovery Application (RRA) and ARMC2RMseek Locator. You can write down your
ARMC/2 card’s MAC address in the table below or in Appendix H, MAC Address Map.
See the first line for an example.
MAC Address Location Description
00-40-D9-02-9B-3C Server Room, Rack 2, 5
Windows 2003 Advanced
Server, Mail Server
Cont’d
Chapter Two : Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
5
Page 14
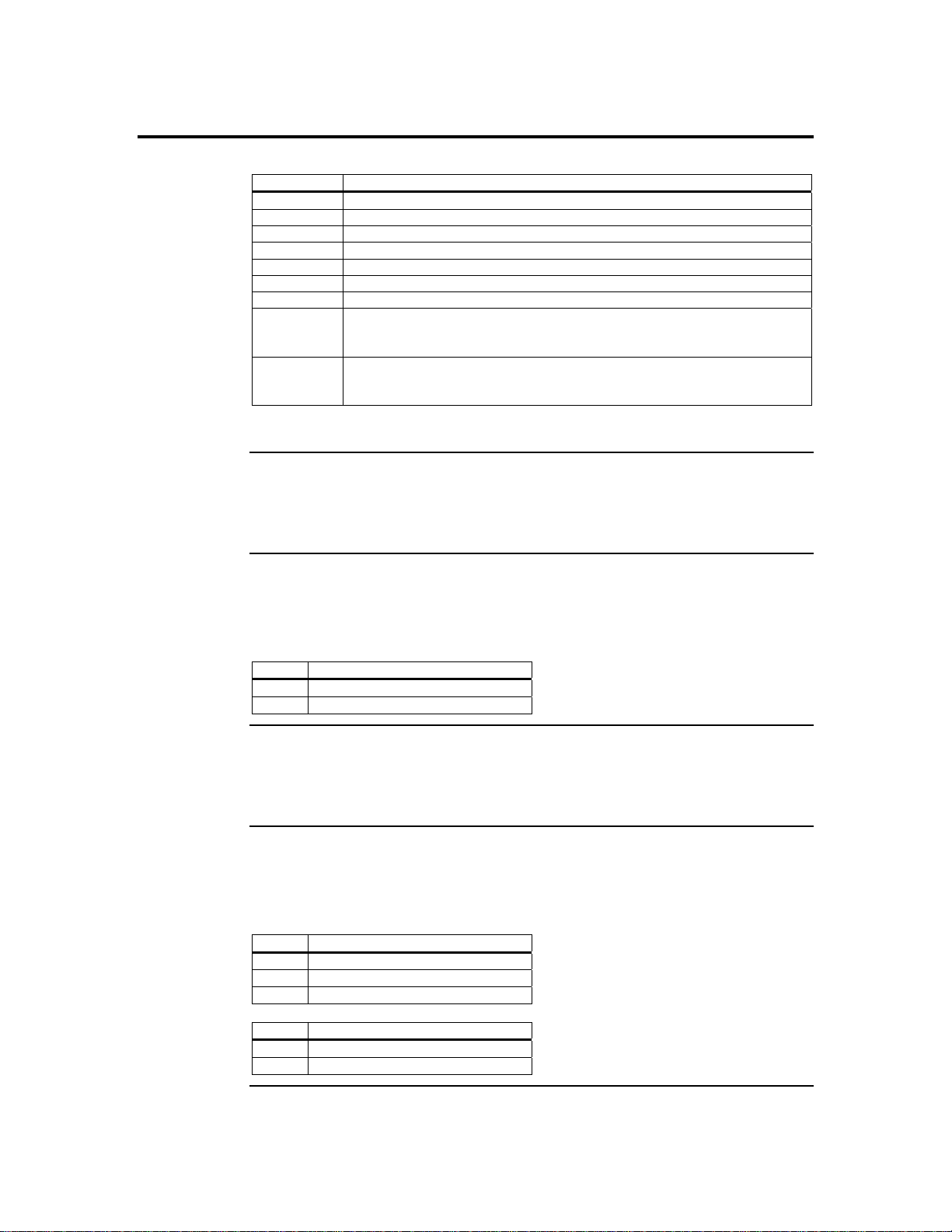
Step 1 Unpack the ARMC/2 Card (and check jumper settings), Continued
Check the following jumpers:
Jumper Setting
JP4 Confirm that pins one and two are open.
JP5 Confirm that pins one and two are open.
JP6 Confirm that pins one and two are open.
JP7 Confirm that pins one and two are open.
JP8 Confirm that pins one and two are open.
JP11 Confirm that pins one and two are shorted.
JP12 Confirm that pins one, two and three are open.
JP13 If your hosts system’s motherboard has support for I2C on the PCI slots,
place a short pins one and two. If not, confirm that pins one and two are
open.
JP14 If your hosts system’s motherboard has support for I2C on the PCI slots,
place a short pins one and two. If not, confirm that pins one and two are
open.
Note: The ARMC/2 cards have these two jumpers, JP13 and JP14.
JP4 and JP5 Chassis/Motherboard Power Switch
JP6 ARMC/2 Reset Button
JP7 and JP8 Chassis/Motherboard Reset Switch
JP11 Flash Write Enable/Disable
Verify that there is no jumper on JP4 and JP5. These two headers are to be used with a
cable, not a jumper.
You can temporarily short this jumper to reset your ARMC/2 card. For normal operations,
verify that there is no jumper on JP6.
Pin Description
1 Ground
2 Reset #
Verify that there is no jumper on JP7 and JP8. These two headers are to be used with a
cable, not a jumper.
You can write-protect your ARMC/2 card’s firmware so that it cannot be flashed. By
default, pins one and two are shorted so that you can flash the firmware.
Pin Description
1 VCC3
2 Write-Protect Enabled
3 Ground
Pin Description
1-2 Flash Write Enable
2-3 Flash Write Disable
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
6
Page 15
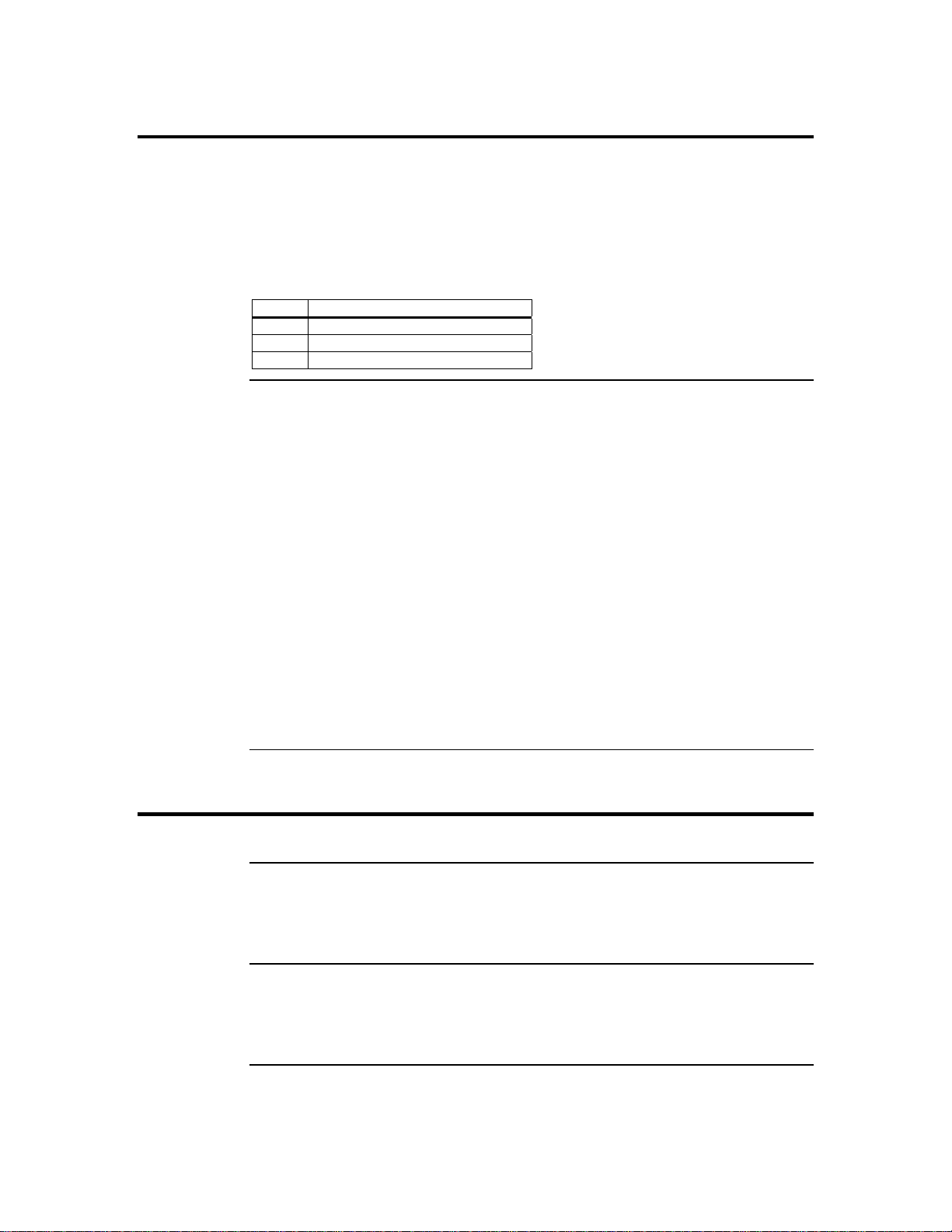
Step 1 Unpack the ARMC/2 Card (and check jumper settings), Continued
JP12 Diagnostic and Recovery Mode Jumper
This jumper is primarily used to recover a failed flash attempt. By shorting pins one and
two, you can place your ARMC/2 card into Diagnostics Mode. By shorting pins two and
three, you can place your ARMC/2 card into Recovery Mode. See Appendix C, Remote
Recovery Application (RRA) for more information on how to recover your ARMC/2 card.
By default, pins one, two and three are open.
Pin Description
1 GP I/O PA7
2 Ground
3 GP I/O PA10
JP13 and JP14 PCI Bus SMB Data and Clock Jumper
These two headers allow your ARMC/2 card to read I2C bus information. If your hosts
system’s motherboard has support for I2C on the PCI slots, place a jumper on these two
headers. By default th ese headers are open.
Note: Only revision B1 and newer revisions of the ARMC/2 cards have these two jumpers.
Revisions A and B do not have JP13 and JP14.
Note: Most PCI slots have a “floating” I2C bus. A “floating” I2C bus means that there is no
physical connection between the two I2C pins on the PCI slot and the motherboard’s I2C
bus. Shorting JP13 and JP14 would be useless in this case.
Note: JP13 and JP14 can be used in place of the ARMC/2 Universal Cable to gather I2C bus
information from the motherboard.
Note: Only the OEM version can utilize the hardware health monitoring capabilities of
ARMC/2 card. The hardware health monitoring function requires an OEM specific cable
and Sensor Definition Kit (SDK/SDR) file and Soft Processor (SP) file.
Step 2 Plug in the ARMC/2 Card into the Host System and Attach Internal
Cables
Physically plug in the ARMC/2 card into any available PCI slot inside the host system.
J3 Service Connector
This jumper is used exclusively for servicing the ARMC/2 card. J3 is not described in
this document.
J4 JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) ICE (In-Circuit Emulator) Connector
This header is used to debug and service the ARMC/2 card. J4 is not described in this
document.
Cont’d
Chapter Two : Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
7
Page 16
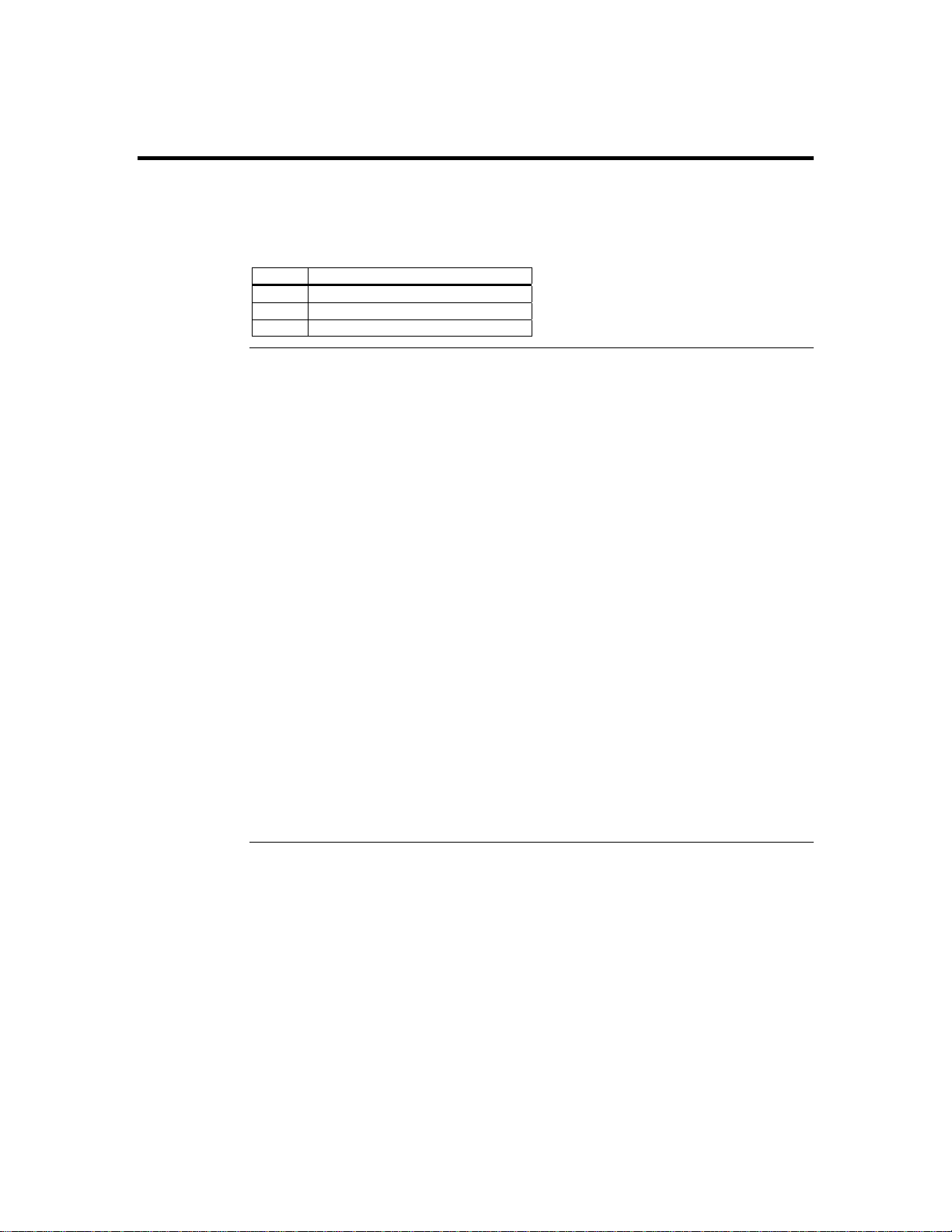
Step 2 Plug in the ARMC/2 Card into the Host System and Attach Internal
Cables,
J5 IPMB (Intelligent Platform Management Bus)
IPMB (Intelligent Platform Management Bus)
Continued
If your motherboard has an IPMB connector, you can connect a cable from J5 on the
ARMC/2 card to the IPMB connector on your motherboard.
Pin Description
1 Positive Signal
2 Ground
3 Negative Signal
The IPMI specification was developed by Intel, Dell, Hewlett-Packard, and NEC to
provide a standard interface to be used for monitoring server items such as temperature,
voltage, fans, power supplies, and chassis. IPMI is comprised of three specifications
Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI), Intelligent Platform Management Bus
(IPMB) and Intelligent Chassis Management Bus (ICMB). The IPMI specification
defines the interface between management software and chassis management hardware.
The IPMB specification defines the internal Intelligent Platform Management Bus. The
ICMB specification defines an external bus for connecting additional IPMI enabled
systems.
The electrical interconnect for system management is based on the inter-IC (I2C) bus.
This bus is a two wire serial interface (clock, data) driven by open-collector drivers.
Devices arbitrate for the bus based on a collision detection mechanism. The I2C data and
I2C clock signals are referred to as an IPMB.
The IPMB connector can be used to read IPMI information from the motherboard's
System Management Controller. The format and definition of the IPMI information must
be based on the IPMI v1.5 Specification.
The IPMI specification was architected around the server motherboard environment. In a
typical motherboard, the Management Controller connects to a variety of dumb sensors
located on the motherboard and within the chassis. The command set contains commands
tailored to this environment and are intended to handle sensors, data repositories, even t
logs and watchdog timers.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
8
Page 17
Step 2 Plug in the ARMC/2 Card into the Host System and Attach Internal
Cables,
J9 ARMC/2 Feature Connector
Note: JP13 and JP14 can be used in place of the ARMC/2 Universal Cable to gather I2C bus
Note: JP4 and JP5 can be used in place of the ARMC/2 Universal Cable to power on, power off,
Note: JP7 and JP8 can be used in place of the ARMC/2 Universal Cable to reset the
Note: Only the OEM version can utilize the hardware health monitoring capabilities of
Note: IPMI support is an OEM version feature.
Note: This cable is an optional component and must be cu stom made for your specific
JP2 Serial Port Connector
JP3 Service Connector
Continued
This feature connector is primarily used for operating the host system’s motherboard
power and reset switch. It can also be used to gather I2C bus information from the
motherboard.
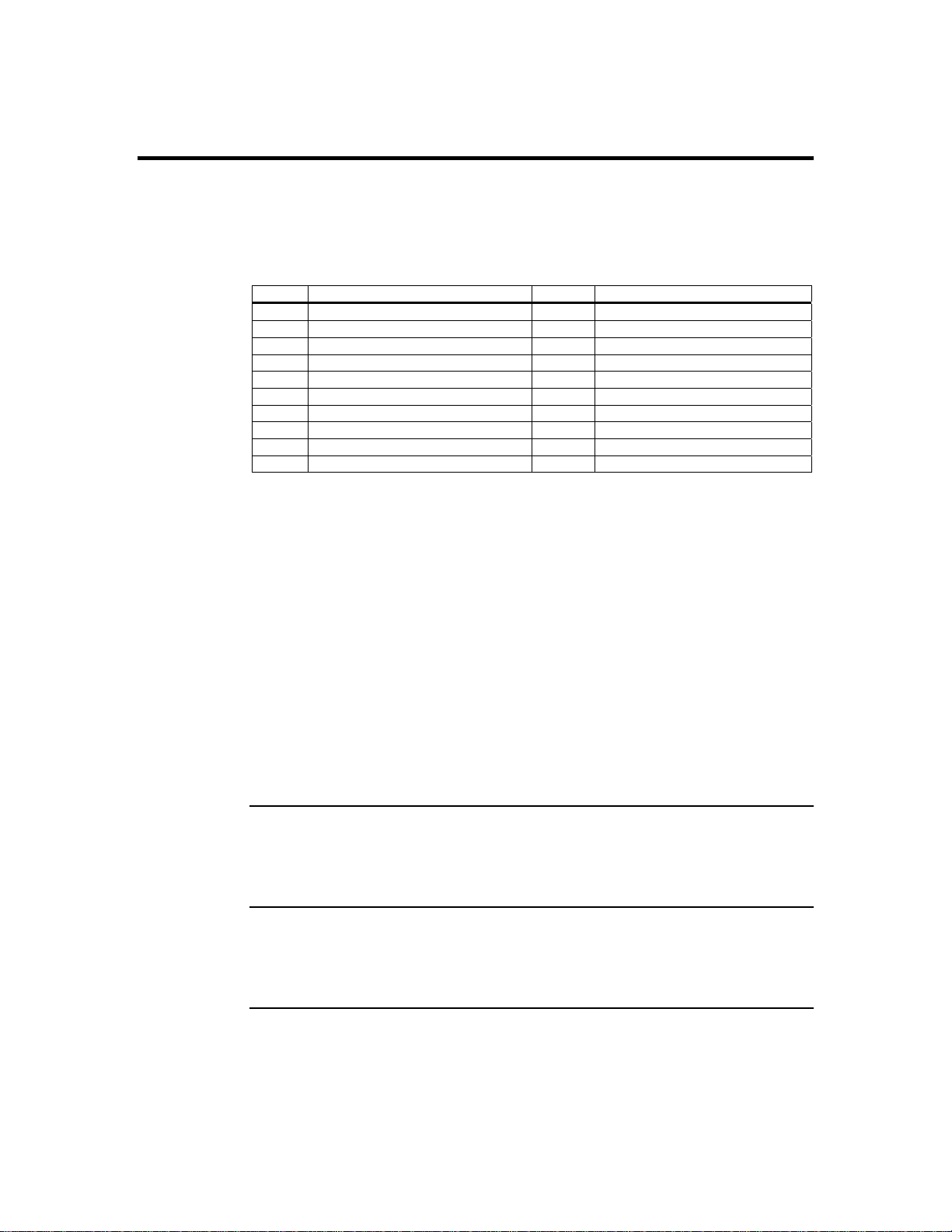
Pin Description Pin Description
1 Not Connected 11 Reset_Host #
2 I2C Clock 12 Ground
3 Not Connected 13 Ground
4 Not Connected 14 Not Connected
5 Power_Off # 15 Not Connected
6 I2C Data 16 Ground
7 Not Connected 17 Not Connected
8 Not Connected 18 Not Connected
9 Not Connected 19 Not Connected
10 Not Connected 20 Ground
information from the motherboard.
and power cycle the motherboard.
motherboard.
ARMC/2 card. The hardware health monitoring function requires an OEM specific cable
and Sensor Definition Kit (SDK/SDR) file and Soft Processor (SP) file.
configuration.
You can connect an external 9 pin serial port connector to this header. This header is
primarily used to text redirect over the serial port.
This jumper is used exclusively for servicing the ARMC/2 card. JP3 is not described in
this document.
Cont’d
Chapter Two : Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
9
Page 18
Step 2 Plug in the ARMC/2 Card into the Host System and Attach Internal
Cables,
JP4 and JP5 Chassis/Motherboard Power Switch
Note: JP4 and JP5 can be used in place of the ARMC/2 Universal Cable to power on, power
JP6 ARMC/2 Reset Button
JP7 and JP8 Chassis/Motherboard Reset Switch
Note: JP7 and JP8 can be used in place of the ARMC/2 Universal Cable to reset the
Continued
JP4 and JP5 can be used in place of the ARMC/2 Universal Cable to power on, power off,
and power cycle the motherboard.
Connect a two pin cable from the motherboard’s Power (Soft On/Off) header to JP4 on
your ARMC/2 card. Connect the chassis power switch to JP5 on your ARMC/2 card.
off, and power cycle the motherboard.
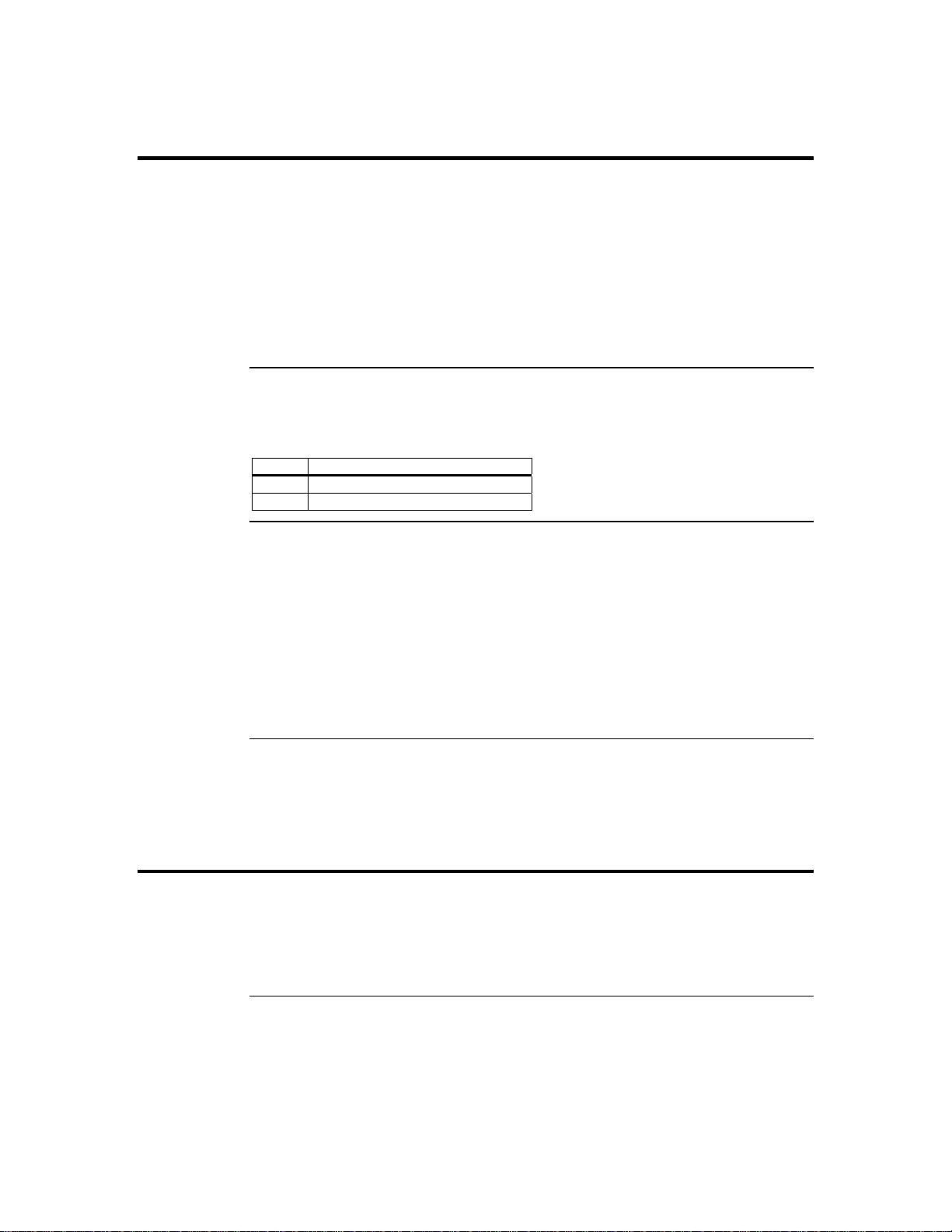
You can short this jumper to reset your ARMC/2 card.
Pin Description
1 Ground
2 Reset #
JP7 and JP8 can be used in place of the ARMC/2 Universal Cable to reset the
motherboard.
Connect a two pin cable from the motherboard’s Reset header to JP7 on your ARMC/2
card. Connect the chassis reset switch to JP8 on your ARMC/2 card.
motherboard.
Step 3 Connect External Cables
• Connect the USB cable from the back of the ARMC/2 card to the motherboard’s
USB port.
• Connect your VGA monitor to your ARMC/2 card.
• Connect the RJ45 LAN cable from your local network to your ARMC/2 card.
• Connect your AC adapter. (Only if the AC Adapter is part of your ARMC/2 kit)
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
10
Page 19
Step 4 Confirm the Motherboard’s BIOS Settings
Power on the motherboard and enter the BIOS. Using the following table, confirm that
your motherboard’s BIOS settings are correct.
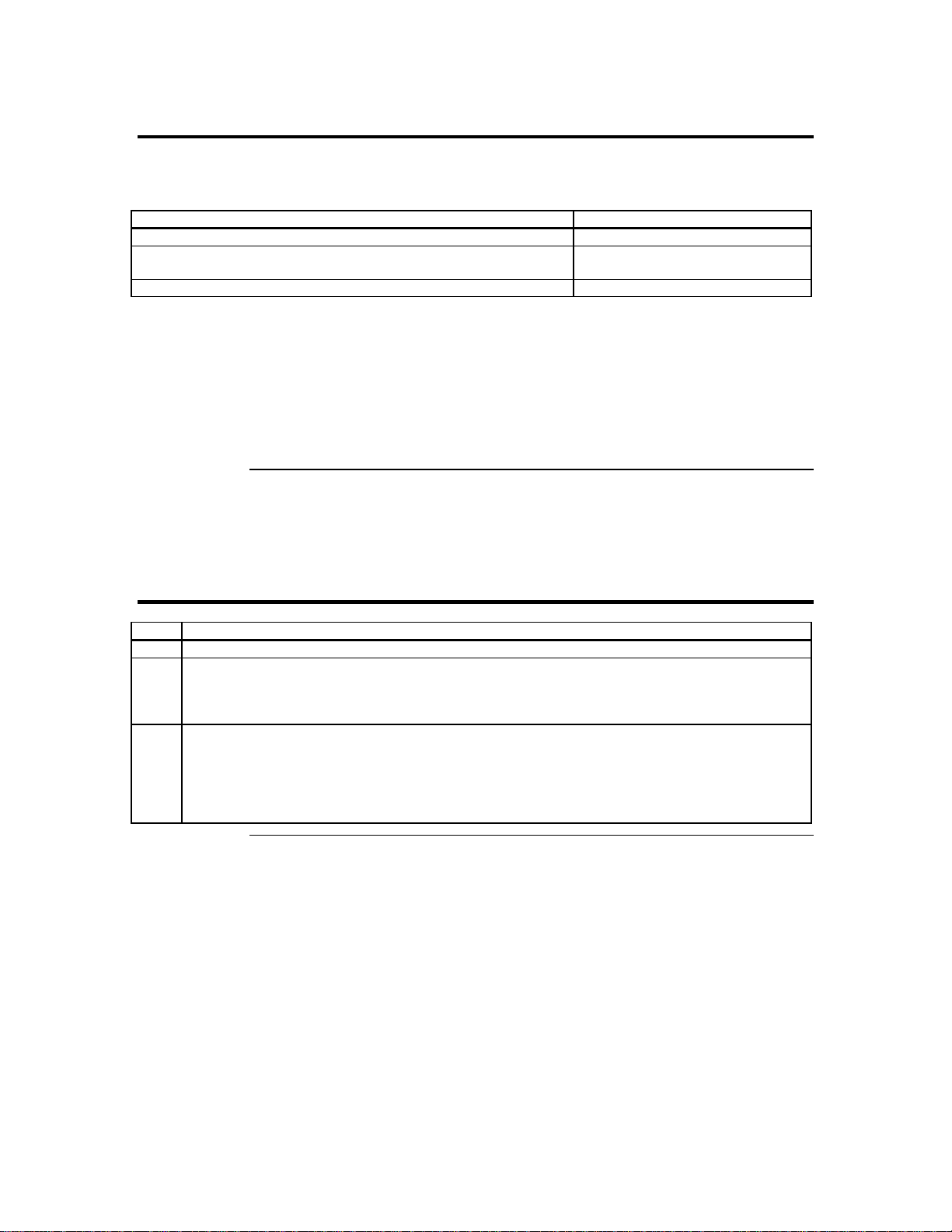
BIOS Section Setting
Boot Options> Removable Devices Virtual Floppy or USB Boot Device
Boot Options> ATAPI CDROM Virtual CDROM or USB Boot
Device
Advanced> PCIPnP> Configuration> Legacy USB Support Enable
Save the BIOS settings and restart the computer.
Note: Make sure that your motherboard BIOS supports Legacy USB devices, USB Boot or Boot
to USB.
Note: On some motherboards and server boards, depress the <CTRL>, <ALT>, and <ESC>
keys simultaneously to enter the BIOS. On others use the <F2> keys. See your server’s
documentation for more information on entering the BIOS setup.
Step 5 Install the Operating System and ARMC/2 Drivers
Step Action
1 Install the operating system (if applicable) on the host system.
2 (Windows 2000/2003 only) When prompted for the AMI Virtual Floppy drivers, install the ARMC/2
card’s AMI Virtual Floppy drivers located on the ARMC/2 CD in the INF folder.
3 (Windows 2000/2003 only) When prompted for the virtual CD-ROM drivers, install the Windows
default CD-ROM drivers.
Note: Do not use the amivirtfl.inf when prompted to install the virtual CD-ROM drivers. The
Virtual CD-ROM device does not require any special drivers. You can select the default option
Microsoft Windows provides.
Cont’d
Chapter Two : Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
11
Page 20
Step 5 Install the Operating System and ARMC/2 Drivers, Continued
Installing Virtual Floppy Drivers on Microsoft® Windows Operating Systems
Microsoft® Windows 2000/2003 operating systems need an .INF for the AMI Virtual
Floppy device exposed by the ARMC/2 card.
Note: This installation procedure needs to be done one time only on the host sys t em. Once the
Virtual Floppy is properly loaded, you can perform floppy redirection without going
through any extra steps.
Step Action
1 Microsoft® Windows 2000/2003 operating systems for the Virtual Floppy device .INF file the first
time you install the ARMC/2 card on the server.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
12
Page 21
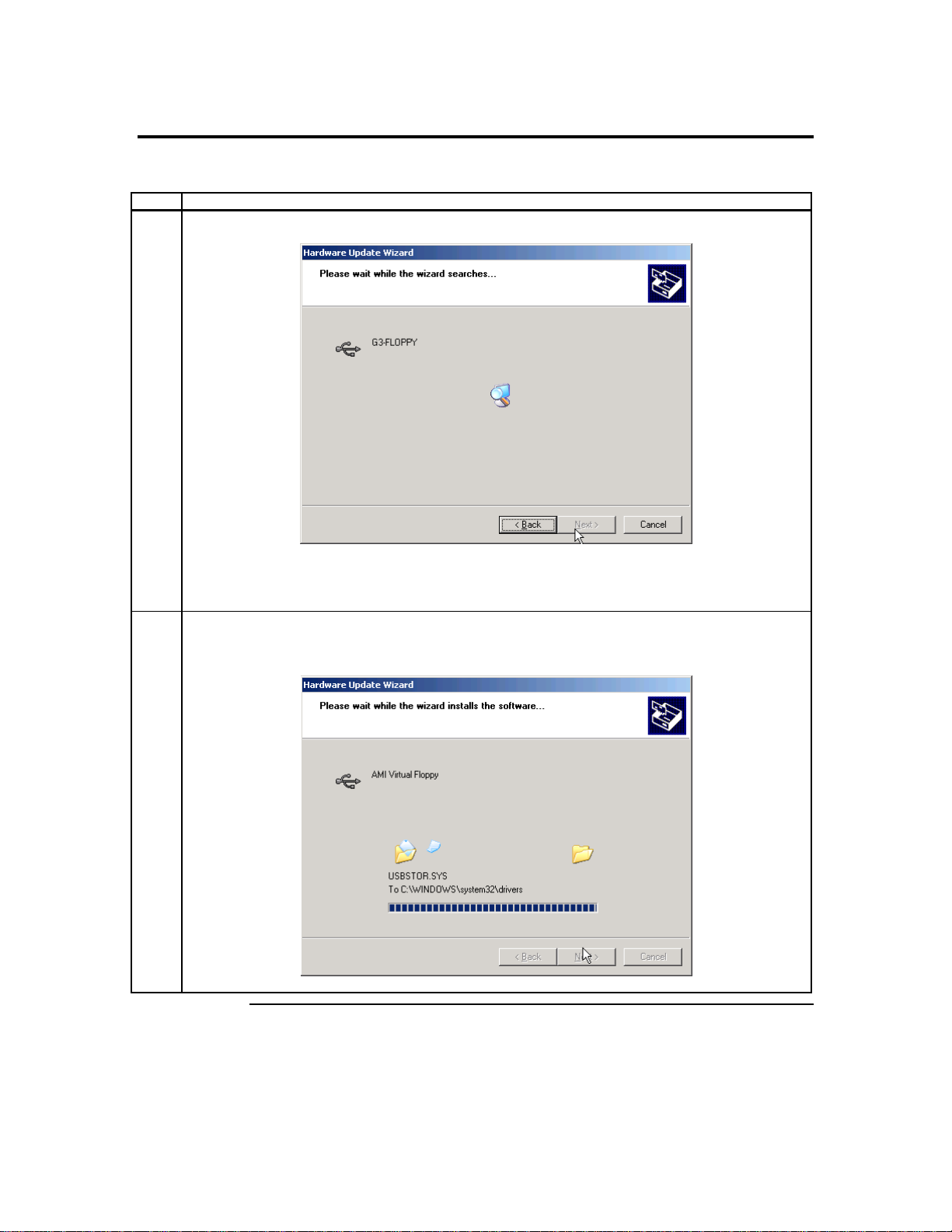
Step 5 Install the Operating System and ARMC/2 Drivers, Continued
Installing Virtual Floppy Drivers on Microsoft® Windows Operating Systems, Continued
Step Action
2 The Hardware Update Wizard begins to search for the drives on the ARMC/2 CD.
Note: Do NOT use the default file that the Microsoft® Windows operating system presents when it is
searching for the Virtual Floppy driver. Instead, select the Specify a Location option and select
the .INF file located in the ARMC/2 CD called amivirtfl.inf in the INF directory.
3 The Hardware Update Wizard begins to load the Virtual Floppy driver from the ARMC/2 CD. Its status
is displayed.
Cont’d
Chapter Two : Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
13
Page 22
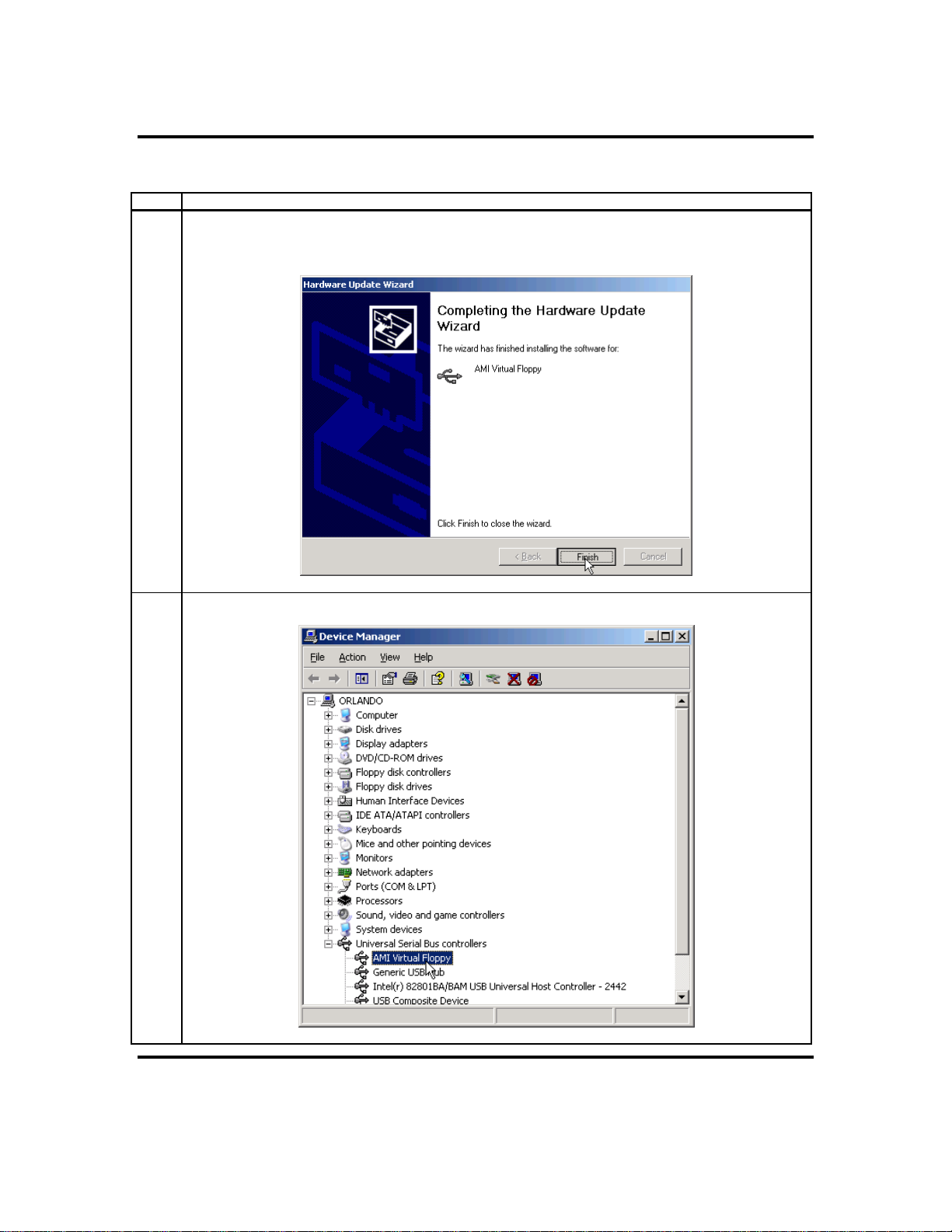
Step 5 Install the Operating System and ARMC/2 Drivers, Continued
Installing Virtual Floppy Drivers on Microsoft® Windows Operating Systems, Continued
Step Action
4 Once this file is loaded and recognized by the Microsoft® Windows operating system, left click the
Finish button. The Microsoft® Windows operating system may require a reboot of the host system
after the installation of the Virtual Floppy driver.
5 Congratulations! You have successfully installed the Virtual Floppy driver.
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
14
Page 23
Step 6 Install the Acer ARMC/2 Windows Software Components
Acer ARMC/2 Windows Software Components is a collection of ARMC/2 host-side and
remote access components. These programs are briefly explained in the following table:
Program Description
ARMC2ConfigApp The ARMC2ConfigApp program allows you to configure the ARMC/2 card from the
host system or from a client system.
WinCuri The WinCuri program is a command prompt-based program that you can use to
configure the ARMC/2 card. It allows you all the functionality of both the Internet
browser-based Remote Access Companion for ARMC/2 and the ARMC2ConfigApp
program.
HostHeartbeat HostHeartbeat is installed as a service in Windows. It is used to tell whether the
operating system on the host system is operating or not. It can also detect whether the
operating system was shutdown normally or abruptly.
Floppy Image
Creator
Remote Recovery
Application
(RRA)
ARMC2RMseek In order to configure your ARMC/2 card completely, you must access the ARMC/2 from
Floppy Image Creator allows you to create bootable floppy image files that you can use to
boot the ARMC/2 card from.
The Remote Recovery Application (RRA) is a recovery tool that can be executed from a
remote client system located on the same network as the ARMC/2 card. You can use it to
recover a failed flash attempt.
Note: You must physically set the ARMC/2 card you want to recover into Recovery Mode.
To do this, simply short pins two and three on jumper JP12 on your ARMC/2 card.
Note: Your ARMC/2 card must be write enabled before you can flash an image to it.
Confirm that pins one and two on jumper JP11 are shorted on your ARMC/2 card.
Note: The firmware upgrade process is a crucial operation. Make sure that the chances of a
power or connectivity loss are minimal when performing this operation.
another system on the same network. To do this, you must know the ARMC/2 card’s IP
address. If you have installed the ARMC/2 on a network that uses DHCP, you can
search the network for the ARMC/2 card. To locate and find out its IP address, you can
use ARMC2RMseek.
Cont’d
Chapter Two : Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
15
Page 24
Step 6 Install the Acer ARMC/2 Windows Software Components, Continued
Follow the steps outlined in the following table to install the Acer ARMC/2 Windows
Software Components:
Step Description
1 Insert your ARMC/2 CD into the host system. The host system is the system that has the ARMC/2
card installed into it. Browse to the following folder and file:
CDROM\ServerTools\Win32\Setup.exe
2 Double left click the Setup.exe icon to begin the installation of the Acer ARMC/2 Windows Host
Component.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
16
Page 25
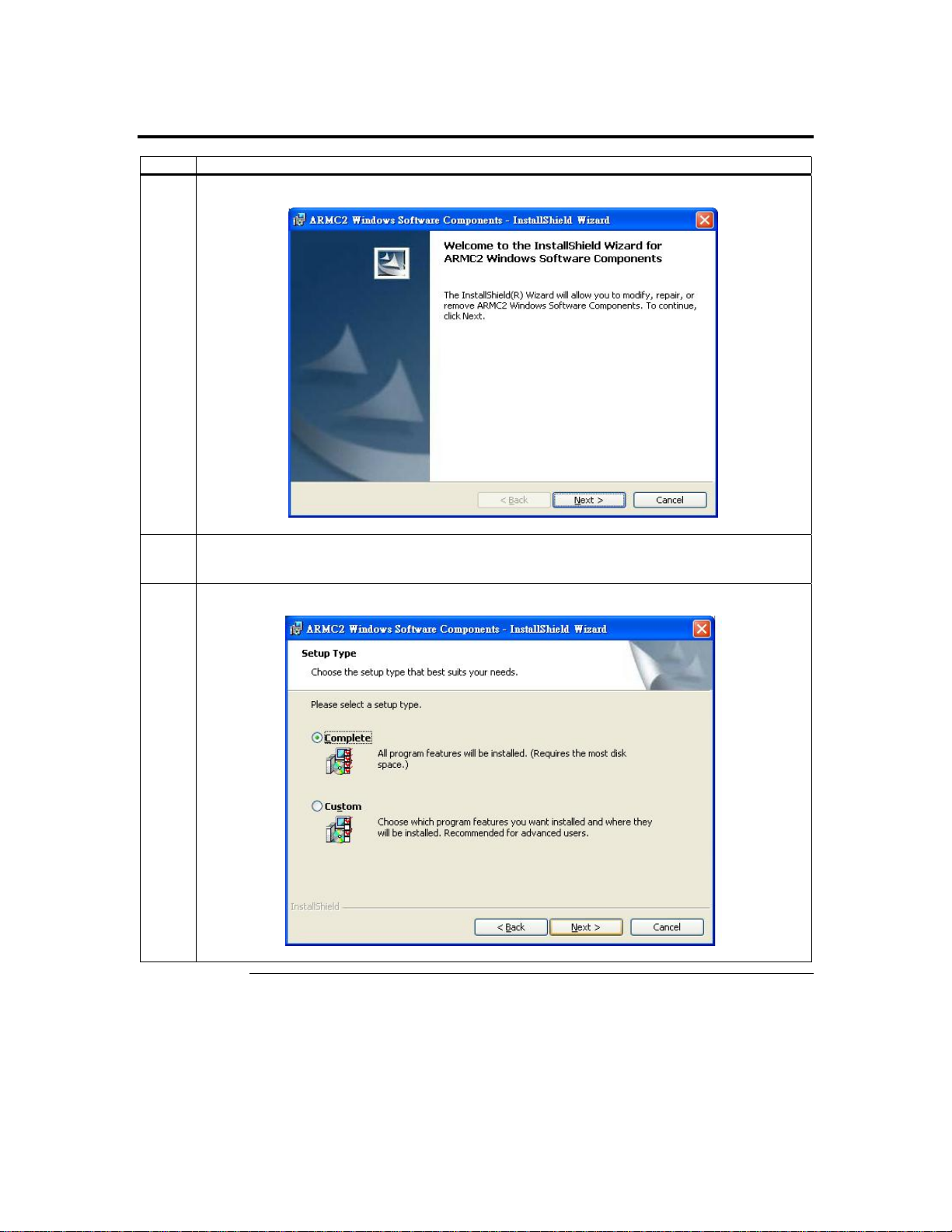
Step 6 Install the Acer ARMC/2 Windows Software Components, Continued
Step Description
3 The Acer ARMC/2 Windows Host Component setup window opens. Left click the Next button.
4 Skip this step unless the Customer Information window opens. Enter your name and your
organization’s name in the appropriate fields. Select the option for Install this application for and
left click the Next button.
5 The Setup Type window opens. Select the Complete setup option. Left click the Next button.
Cont’d
Chapter Two : Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
17
Page 26
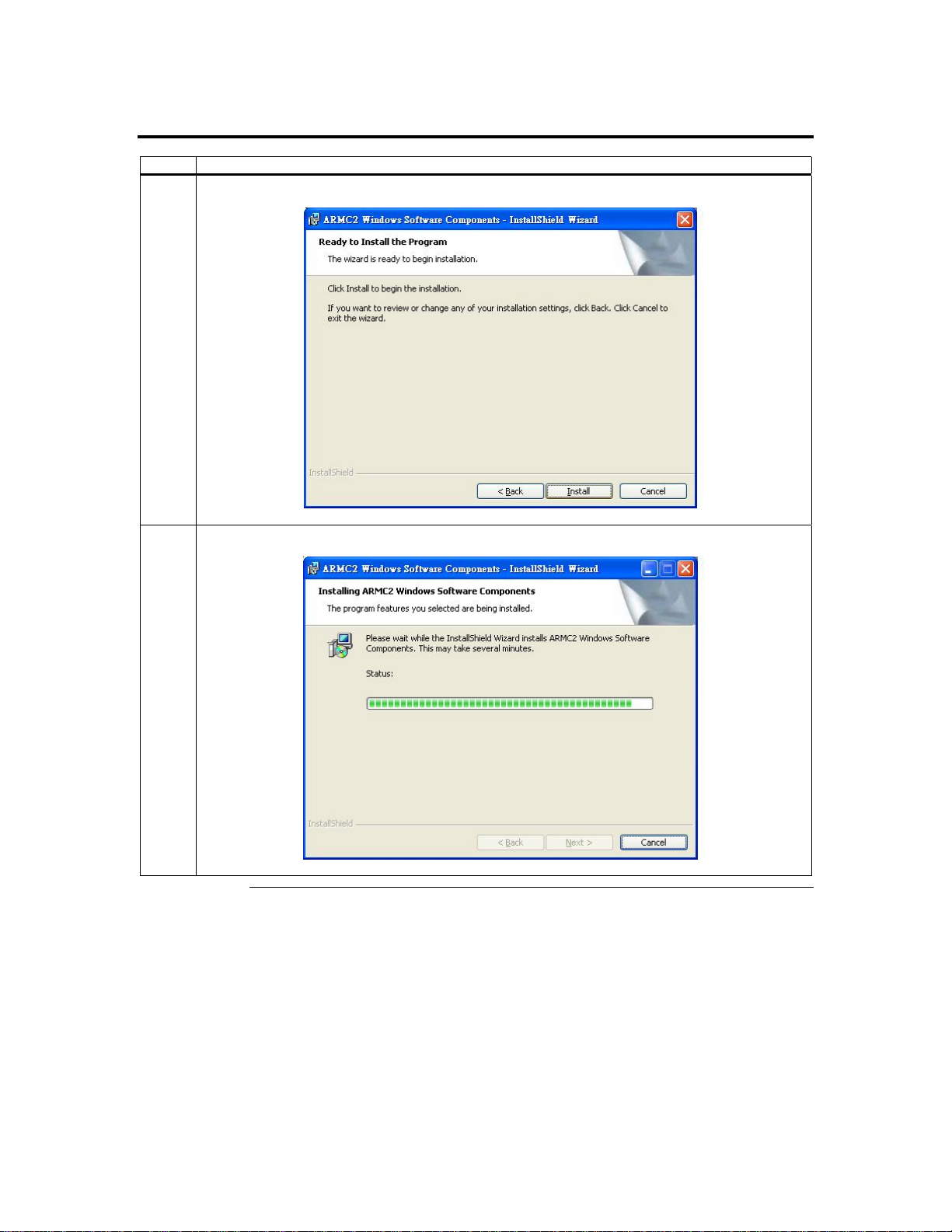
Step 6 Install the Acer ARMC/2 Windows Software Components, Continued
Step Description
6 The Install Program window opens. Left click the Install button.
7 The Installation Progress window opens.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
18
Page 27
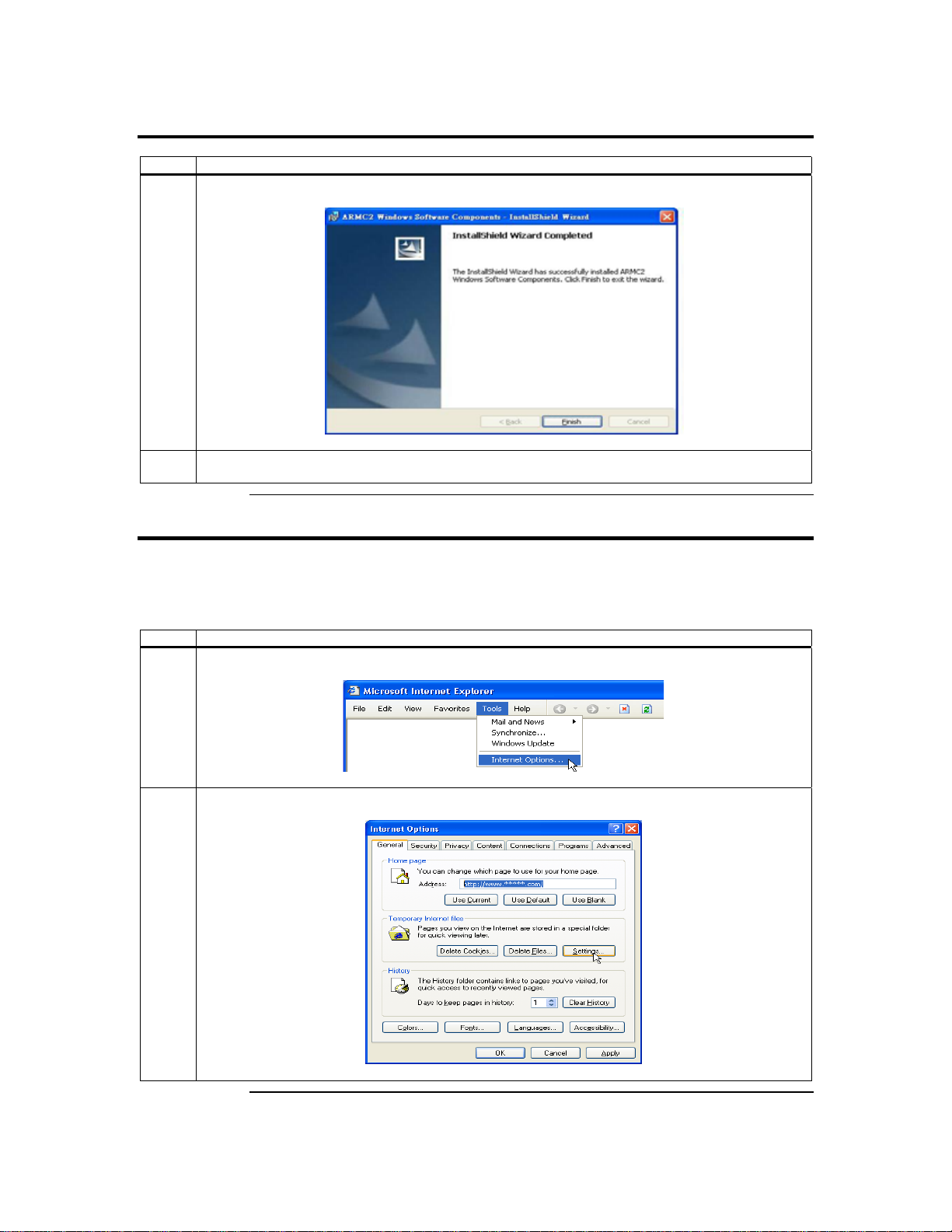
Step 6 Install the Acer ARMC/2 Windows Software Components, Continued
Step Description
8 The installation is complete. Left click the Finish button.
9 Repeat steps 1 through 8 on a local network computer that you want to use to access the host
system.
Step 7 Setup Your Client Internet Browser
You must first setup your Internet browser on the client system before you can redirect
the host system’s console or view the Crash screen. Follow the instructions in the table
below:
Step Description
1 Open Internet Options. To get there, open your Internet Explorer browser, left click Tools and then
Internet Options.
2 The Internet Options window opens. Left click the Settings button.
Cont’d
Chapter Two : Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
19
Page 28
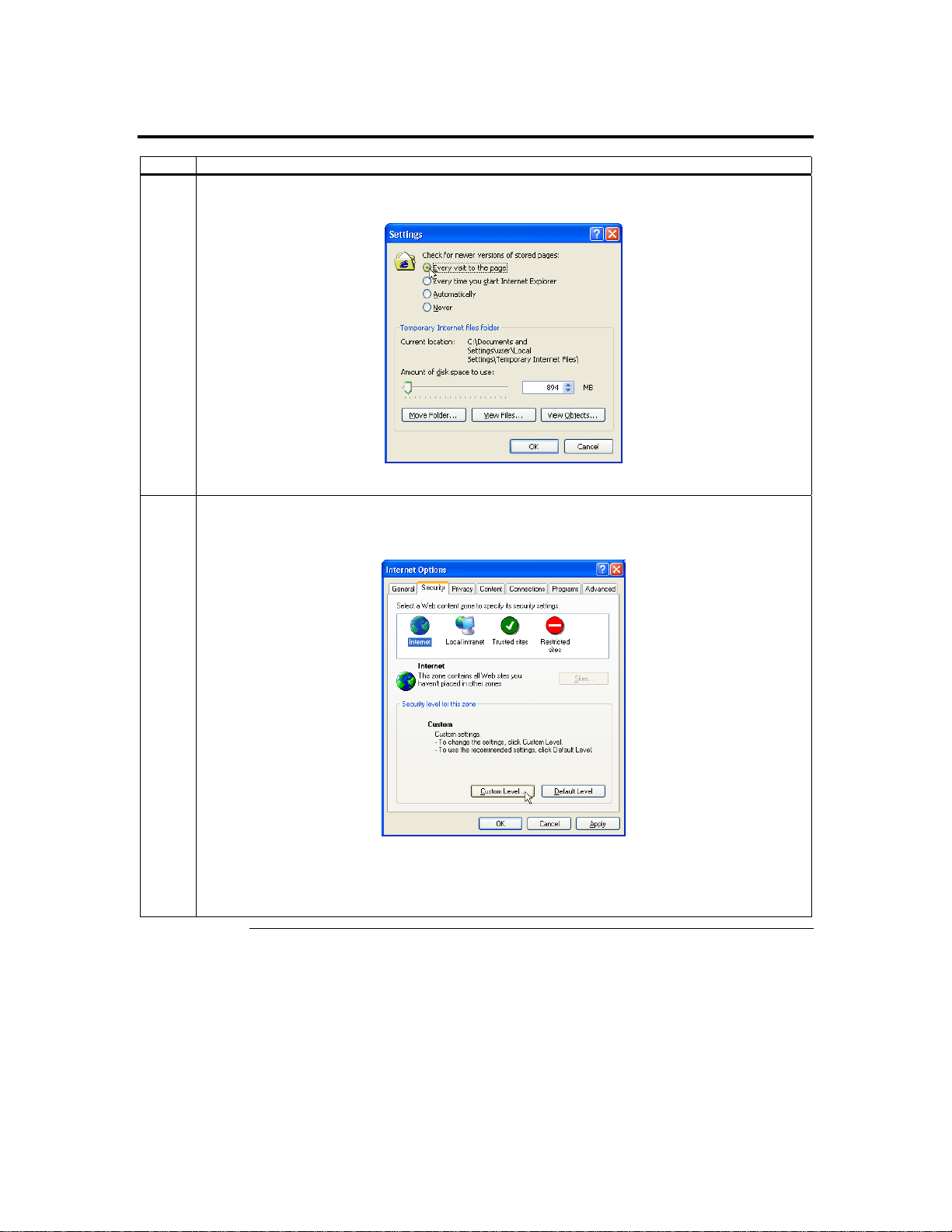
Step 7 Setup Your Client Internet Browser, Continued
Step Description
3 The Settings window opens. Left click the Every visit to the page button or Automatically button. Left
click the OK button to apply the change and to go back to the Internet Options window.
Note: Other settings can cause old data to be displayed when performing operations on the ARMC/2.
4 Next, you must setup Internet Explorer to allow the downloading of Signed ActiveX controls and
also allow it to run Signed ActiveX controls. To do this, left click the Security tab and then the
Custom Level button.
Note: In Microsoft Windows 2003 server operating systems, the default security setting is High, and
this disables many items (besides the Active X ones mentioned in this document) that are
necessary to even access the ARMC/2 GUI. The security settings for a Microsoft Windows
2003 server operating system remote client must be on Medium or Low.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
20
Page 29
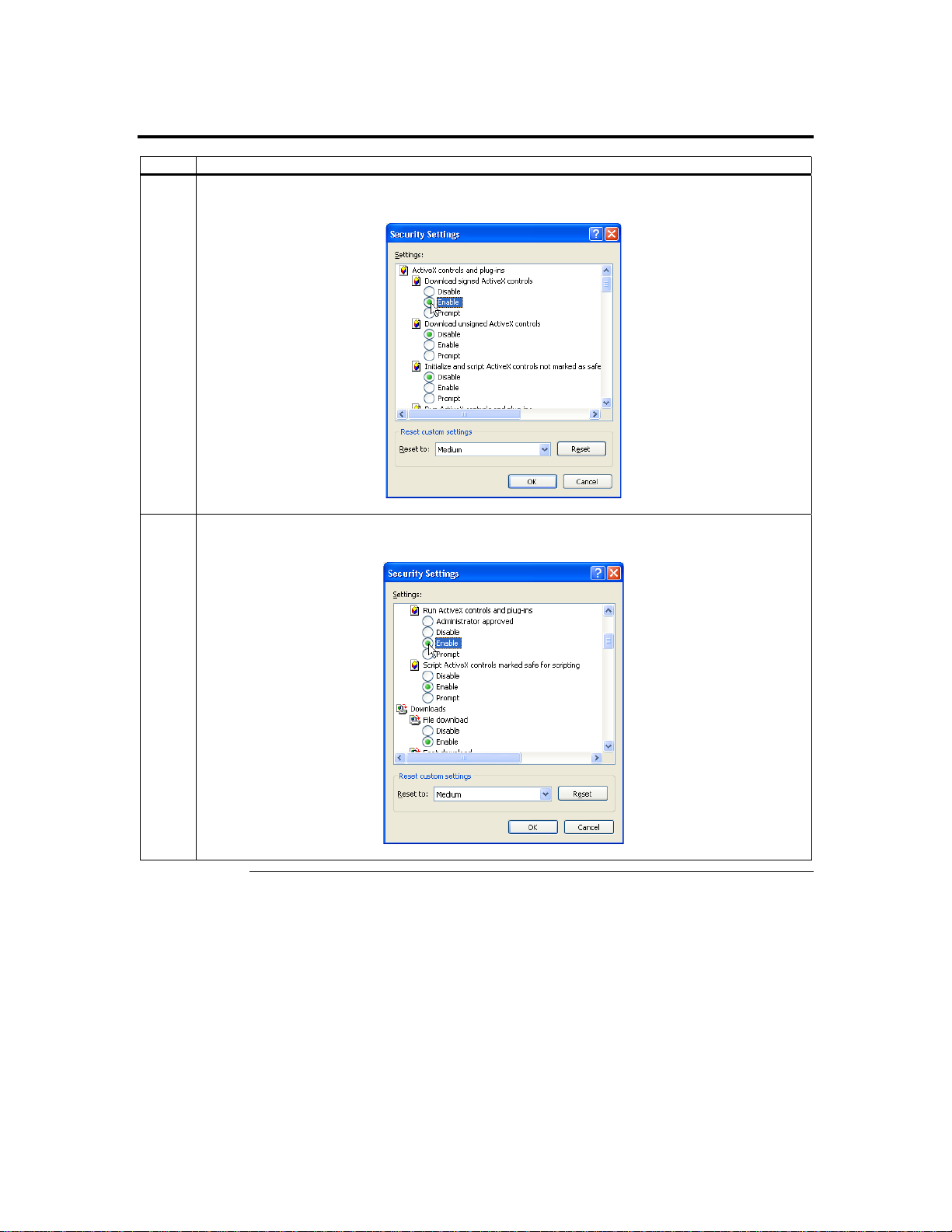
Step 7 Setup Your Client Internet Browser, Continued
Step Description
5 The Security Settings window opens. Left click the Enable button under the Download signed ActiveX
controls section.
6 Scroll down and left click the Enable button under the Run ActiveX controls and plug-ins section.
Left click the OK button.
Cont’d
Chapter Two : Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
21
Page 30
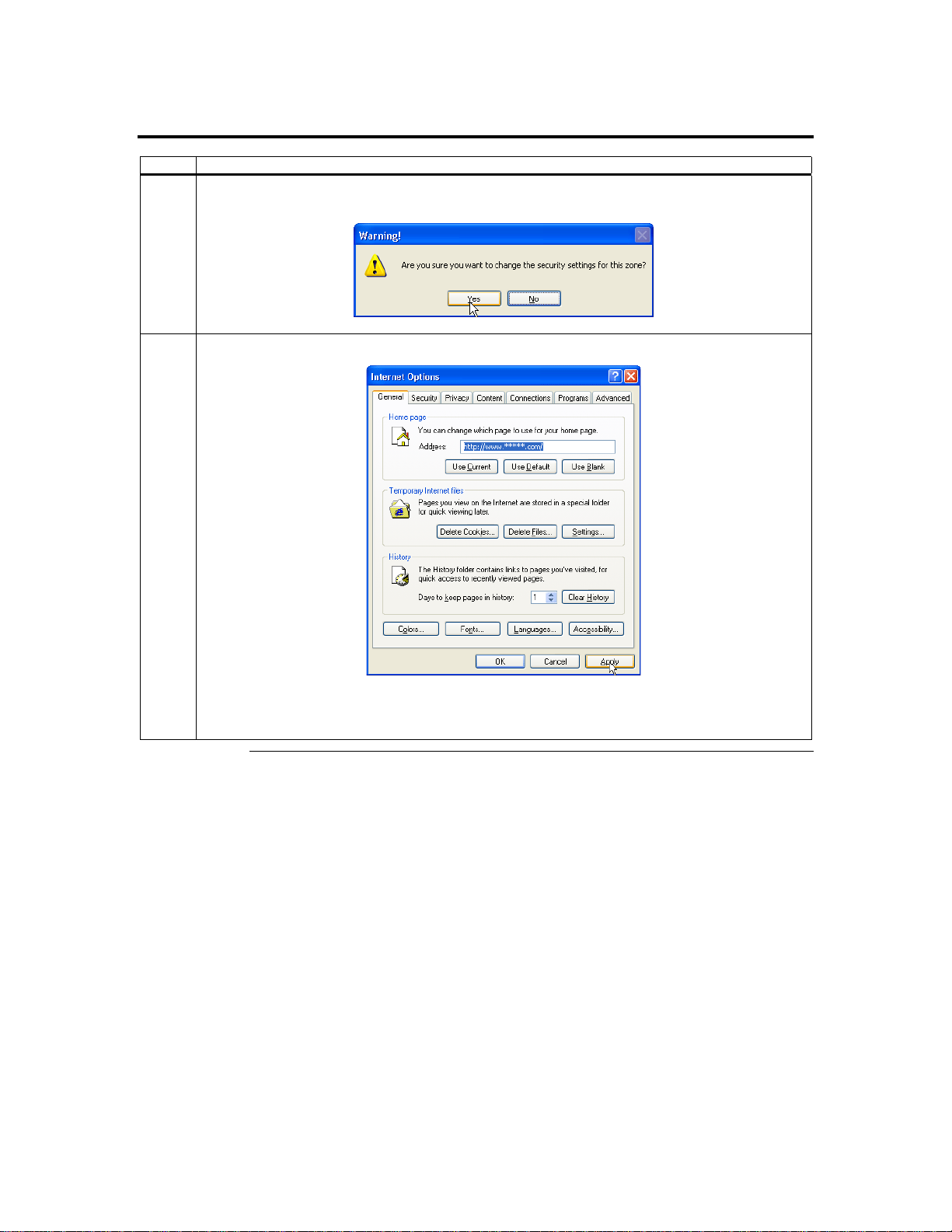
Step 7 Setup Your Client Internet Browser, Continued
Step Description
7 You are prompted with a Warning window. Left click the Yes button to accept the changes to the
Internet zone and to go back to the Internet Options window.
8 Left click the Apply button and then the OK button to make the changes.
Note: You must restart Internet Explorer before the changes take effect.
Note: Remote Console cannot run with any other security settings in Internet Explorer.
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
22
Page 31

Step 8 Connect to the ARMC/2 from a Client System
In order to connect to the ARMC/2 card, you must access the ARMC/2 from another
system on the same network. This document refers to this other system as the client
system. To do this, you must know the ARMC/2 card’s IP address. If you have installed
the ARMC/2 on a network that uses DHCP, you can search the network for the ARMC/2
card. To locate and find out its IP address, you must run ARMC2RMseek Locator.
Note: To get or set the IP address on your ARMC/2 card in a Windows 2000 environment, you
can also run the ARMC2ConfigApp program on the host system. See Appendix B,
ARMC2ConfigApp for more information on how to use the ARMC2ConfigApp program.
Note: Make sure that you have already installed the ARMC/2 Windows Software Components
on the system that you want to use to locate the ARMC/2 card.
Follow the steps in the table below to connect to the ARMC/2 from a remote client
system:
Step Description
1 Locate the ARMC2RMseek Locator program on your remote client system. Run the
ARMC2RMseek Locator program by double left clicking on it.
Path : Press “Start” -> Programs -> ARMC2 Remote Tools -> ARMC2RMseek
2 Left click on the Next button when you see this screen.
Cont’d
Chapter Two : Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
23
Page 32

Step 8 Connect to the ARMC/2 from a Client System, Continued
Step Description
3 Type in your Network Name. In this example, Your Network Name is the Network Name. Next,
you must enter a range of IP addresses that you want to search. In this example, the ARMC/2
card’s IP address is between 172.16.2.200 to 172.16.2.255. Left click the Add>> button when
finished.
4 The name and IP range of the ARMC/2 will display in the right field. Place a check in the box next
to the range of IP addresses. Left click on the Next button.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
24
Page 33

Step 8 Connect to the ARMC/2 from a Client System, Continued
Step Description
5 The name and IP range of the ARMC/2 will display in the Selected IP Range window. Left click on
the Next button.
6 If the IP range is correct, ARMC2RMseek Locator will locate the ARMC/2 card. It will list all
ARMC/2 cards it has discovered.
Note: If more than one ARMC/2 card is found, you can distinguish them by the ARMC/2 card’s
name. The ARMC/2 card’s name consists of the words ARMC2 and the IP address of the
ARMC/2 card’s NIC.
Cont’d
Chapter Two : Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
25
Page 34

Step 8 Connect to the ARMC/2 from a Client System, Continued
Step Description
7 In this example, the ARMC/2 card’s IP address is 172.16.2.243. Double left click on the IP address
to start managing the ARMC/2 card and write down its IP address. Left click on the Finish button
after ARMC2RMseek Locator discovers all ARMC/2 cards.
8
When prompted for the user name and password, enter the following:
Left click the OK button. After you successfully log into your ARMC/2 card, you are greeted with
the Welcome to ARMC/2 screen.
Field Default
User Name root
Password
superuser
Note: The default user name and password are in lower-case characters.
Note: When you log in using the root user name and password, you have full administrative
powers. It is advised that once you log in, you change the root password. See the
Administrator Setup subsection under the ARMC/2
Configurations section of this chapter.
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
26
Page 35

Step 9 Load the ARMC/2 SDR and Soft Processor (SP) File for Your Server
Board Model
The following table is a pictorial description of how to load an SDR and Soft Processor
(SP) File:
Step Description
1 The menu bar on the top bar of the GUI has a series of section buttons. Left click on the Configure
dropdown menu and then left click the PMCP File Upload menu item.
2 The Host Health Monitoring Files dialog box opens. Left click the Browse button.
Cont’d
Chapter Two : Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
27
Page 36

Step 9 Load the ARMC/2 SDR and Soft Processor (SP) File for Your Server
Board Model,
Step Description
3 Insert the ARMC/2 and browse to it. Select the SDR>G520> directory. .
Continued
Note: You can create your own SDR and Soft Processor (SP) Files using the
Configuration Program (PMCP) tool
Note: The Choose File browse window differs from operating system to operating system. However,
the procedure is similar.
4 Select the SDR and Soft Processor (SP) File with the BIN file extension and left click the Open
button.
.
Platform Management
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
28
Page 37

Step 9 Load the ARMC/2 SDR and Soft Processor (SP) File for Your Server
Board Model,
Step Description
5 Left click the Upload button.
Continued
6 Once the SDR and Soft Processor (SP) File is uploaded, you are prompted with verification that the
SDR and Soft Processor (SP) File uploaded.
7 Select the Soft Processor (SP) file with the BIN file extension and left click the Open button.
Cont’d
Chapter Two : Installing Your ARMC/2 Card
29
Page 38

Step 9 Load the ARMC/2 SDR and Soft Processor (SP) File for Your Server
Board Model
Step Description
8 Left click the Upload button.
Continued
9 Once the Soft Processor (SP) file is uploaded, you are prompted with verification that the Soft
Processor (SP) file uploaded.
You can close the Host Health Monitoring Files dialog box by left clicking the close icon on the upper
right corner of the dialog box.
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
30
Page 39

Chapter 3 Locating Your ARMC/2 Card
Overview
The Acer ARMC family of server and system remote management cards can be accessed
from anywhere on your Intranet through an Internet browser. This is a great way to
maintain your critical server when you are nowhere near it.
This chapter explains how to locate your ARMC/2 card on your local network.
Locating Your ARMC/2 Card
In order to connect to the ARMC/2 card, you must access the ARMC/2 from another
system on the same network. This document refers to this other system as the client
system. To do this, you must know the ARMC/2 card’s IP address. If you have installed
the ARMC/2 on a network that uses DHCP, you can search the network for the ARMC/2
card. To locate and find out its IP address, you must run ARMC2RMseek Locator.
Note: To get or set the IP address on your ARMC/2 card in a Windows 2000 environment, you
can also run the ARMC2ConfigApp program on the host system. See Appendix B,
ARMC2ConfigApp for more information on how to use the ARMC2ConfigApp program.
Note: Make sure that you have already installed the ARMC/2 Windows Software Components
on the system that you want to use to locate the ARMC/2 card.
Follow the steps in the table below to connect to the ARMC/2 from a remote client
system:
Step Description
1 Locate the ARMC2RMseek program on your remote client system. Run the ARMC2RMseek
program by double left clicking on it.
Path : Press “Start” -> Programs -> ARMC2 Remote Tools -> ARMC2RMseek
Cont’d
Chapter Three : Locating Your ARMC/2 Card
31
Page 40

Locating Your ARMC/2 Card, Continued
Step Description
2 Left click on the Next button when you see this screen.
3 Type in your Network Name. In this example, Your Network Name is the Network Name. Next,
you must enter a range of IP addresses that you want to search. In this example, the ARMC/2
card’s IP address is between 172.16.2.200 to 172.16.2.255. Left click the Add>> button when
finished.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
32
Page 41

Locating Your ARMC/2 Card, Continued
Step Description
4 The name and IP range of the ARMC/2 will display in the right field. Place a check in the box next
to the range of IP addresses. Left click on the Next button.
5 The name and IP range of the ARMC/2 will display in the Selected IP Range window. Left click on
the Next button.
Cont’d
Chapter Three : Locating Your ARMC/2 Card
33
Page 42

Locating Your ARMC/2 Card, Continued
Step Description
6 If the IP range is correct, ARMC2RMseek Locator will locate the ARMC/2 card. It will list all
ARMC/2 cards it has discovered.
Note: If more than one ARMC/2 card is found, you can distinguish them by the ARMC/2 card’s
name. The ARMC/2 card’s name consists of the words ARMC2 and the IP address of the
ARMC/2 card’s NIC.
7 In this example, the ARMC/2 card’s IP address is 192.168.0.36. Double left click on the IP address
to start managing the ARMC/2 card and write down its IP address. Left click on the Finish button
after ARMC2RMseek Locator discovers all ARMC/2 cards.
Congratulations! You have successfully located your ARMC/2 card.
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
34
Page 43

IP Address Range
Type in a unique name for this IP range in the Network Name field. In this example,
Your Network Name is the Network Name. Next, you must enter a range of IP
addresses that you want to search. In this example, the ARMC/2 card’s IP address is
between 172.16.2.200 to 172.16.2.2 5 5. Left cl i c k the Add>> button when fini s hed .
Cont’d
Chapter Three : Locating Your ARMC/2 Card
35
Page 44

IP Address Range, Continued
Note: The Start and End IP addresses can be the same if you only wish to scan for one ARMC/2
card with that specific IP address.
When you have finished entering all the IP address ranges to be scanned, make sure that
they appear correctly in the list box. Confirm that the checkbox next to the IP range you
want to search is checked.
At this point, you have two options. You can choose to run the scan immediately by left
clicking on the Next button.
The name and IP range of the ARMC/2 card will display in the Selected IP Range
window. Left click on the Next button.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
36
Page 45

IP Address Range, Continued
If the IP range is correct, ARMC2RMseek Locator locates all ARMC/2 cards. It lists all
ARMC/2 cards it has discovered. Left click on the Finish button after ARMC2RMseek
Locator discovers all ARMC/2 cards.
Usage
Once the program has been installed and setup, you can access it any time by double left
clicking on its icon on the task bar. The screen that was last viewed will appear.
Chapter Three : Locating Your ARMC/2 Card
37
Page 46

Note: To close the ARMC2RMseek Locator utility you must right click on the ARMC2RMseek
Locator icon from the task bar and left click the Exit menu option.
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
38
Page 47

Chapter 4 Using Your ARMC/2
ARMC/2 GUI Overview
The ARMC/2 has a user-friendly Graphics User Interface (GUI) called the ARMC/2 GUI.
It is designed to be easy to use. It has a low learning curve because it uses a standard
Internet browser. You can expect to be up and running in less than five minutes.
This chapter allows you to become familiar with the ARMC/2 GUI’s various functions.
Each function is described in detail.
Default User Name and Password
When you first try to access your ARMC/2, you will be prompted to enter a user name
and password. The default user name and passwor d a re as foll ow s:
Field Default
User Name root
Password
superuser
Note: The default user name and password are in lower-case characters.
Note:
When you log in using the root user name and password, you have full administrative powers. It
is advised that once you log in, you change the root password.
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
39
Page 48

ARMC/2 GUI Explained
After you successfully log into your ARMC/2, you are greeted with the ARMC/2 GUI.
Menu Bar Quick Launch Icons
Session
Information
Menu Bar
There is a menu bar located at the top of the ARMC/2 GUI. It lists the following groups:
• Manage Group
• Configure Group
• View Group
You can navigate the menu bar by left clicking on one of the menu items. A drop down
menu will appear for each Group.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
40
Page 49

ARMC/2 GUI Explained, Continued
Quick Launch Icons
There is a quick launch icon section located on the upper area of the ARMC/2 GUI. It lists
the following icons:
• Remote Console
• General Information
• User Management
• Power Control
You can navigate these icons with your mouse (or other pointing device) and select th em
by left clicking on one of the icons.
Session Information
This section of the ARMC/2 GUI allows you to view your user name and permission level.
Session Information
You are currently logged in as: root
Current permission level: Administrator
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
41
Page 50

Manage Group
You can left click on the Manage menu item from the menu bar. The following table
gives you a brief description of each menu item. Each menu item is explained in more
detail further in this section.
Function Description
Remote
Console
Remote Power
Control
Upgrade
Firmware
Reset
ARMC/2
This menu item allows you to start a Remote Console session with the
host system.
This menu item allows you to power on, power off, power cycle, and reset
the host system.
This menu item allows you to update your ARMC/2’s firmware.
This menu item allows you to reset your ARMC/2 card.
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
42
Page 51

Remote Console
Remote Console is a subsection of the Manage group. The following table describes the
information listed in this subsection in detail:
Item Description
High Color Quality
(16-bit) for fast/LAN
Connection
Low Color Quality
(8-bit) for fast/LAN
Connection
Low Color Quality
(8-bit) for
slow/WAN/DSL
Connection
This option allows the ARMC/2 to send 16 bits per pixel color.
This setting is recommended for faster connection speeds or over
a LAN connection.
This option allows the ARMC/2 to send 8 bits per pixel color.
This setting is recommended for lower connection speeds or over
a WAN connection.
When using Low Color Quality (8-bit) for fast/LAN Connection,
you can opt not to use software compression. Compression can
increase the frame rates. Best used for slower connections.
This option allows the ARMC/2 to send 8 bits per pixel color.
This setting is recommended for lower connection speeds or over
a WAN connection.
When using Low Color Quality (8-bit) for slow/WAN/DSL
Connection, you can also use software compression. Compression
can increase the frame rates. Best used for slower connections,
such as DSL.
Note: The Low Color Quality (8-bit) for slow/WAN/DSL Connection mode is recommended for
low speed connections such as those over a Wide Area Network or home DSL. If you are
connecting over a LAN at high speeds you can use High Color Quality (16-bit) for
fast/LAN Connection mode. In order to change modes you must stop redirection, close
the browser, and reconnect in the appropriate mode.
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
43
Page 52

Redirection
The most powerful feature of your ARMC/2 is the ability to redirect the host system’s
console. To redirect the host system’s console is the ability to manage your host system
as if it were physically in front of you, but not.
Setting up Internet Explorer
You must first setup your Internet browser before you can redirect the host system’s
console.
Step Description
1 Open Internet Options. To get there, open your Internet Explorer browser, left click Tools and then
Internet Options.
2 The Internet Options window opens. Left click the Settings button.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
44
Page 53

Redirection, Continued
Setting up Internet Explorer, Continued
Step Description
3 The Settings window opens. Left click the Every visit to the page button or Automatically button. Left
click the OK button to apply the change and to go back to the Internet Options window.
Note: Other settings can cause old data to be displayed when performing operations on the
4 Next, you must setup Internet Explorer to allow the downloading of Signed ActiveX controls and
also allow it to run Signed ActiveX controls. To do this, left click the Security tab and then the
Custom Level button.
ARMC/2.
Note: In Microsoft Windows 2003 server operating systems, the default security setting is High, and
this disables many items (besides the Active X ones mentioned in this document) that are
necessary to even access the ARMC/2 GUI. The security settings for a Microsoft Windows
2003 server operating system remote client must be on Medium or Low.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
45
Page 54

Redirection, Continued
Setting up Internet Explorer, Continued
Step Description
5 The Security Settings window opens. Left click the Enable button under the Download signed ActiveX
controls section.
6 Scroll down and left click the Enable button under the Run ActiveX controls and plug-ins section.
Left click the OK button.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
46
Page 55

Redirection, Continued
Setting up Internet Explorer, Continued
Step Description
7 You are prompted with a Warning window. Left click the Yes button to accept the changes to the
Internet zone and to go back to the Internet Options window.
8 Left click the Apply button and then the OK button to make the changes.
Note: You must restart Internet Explorer before the changes take effect.
Note: Remote Console cannot run with any other security settings in Internet Explorer.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
47
Page 56

Redirection, Continued
Staring Redirection
Follow the steps in the table below to begin Console Redirection:
Step Description
1 Left click the Manage menu item from the ARMC/2 menu bar. Left click the Remote Console menu
item from the drop down menu. Left click the Remote Console mode that you want to use.
2 The ARMC/2 Console Redirection status window opens.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
48
Page 57

Redirection, Continued
Staring Redirection, Continued
Step Description
3 The Authentication window opens. Type your Username and Password and click the Login button.
4 The Console Redirection window opens.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
49
Page 58

Redirection, Continued
Remote Console Shortcut Key Combinations
The most powerful feature of your ARMC/2 is the ability to redirect the host system’s
console. To redirect the host system’s console is the ability to manage your host system
as if it were physically in front of you, but not. The following table is a list of basic
keystrokes and their functions:
Keystroke Description
<ATL> + <S> Start Console Redirection
<ATL> + <T> Stop Console Redirection
<ATL> + <R> Restart Console Redirection
<ATL> + <F> Toggle Full Screen Mode
<ATL> +
<M>
<ATL> + <A> Hold/Unhold Right <ATL> Key
<ATL> + <B> Hold/Unhold Left <ATL> Key
<ATL> + <L> Hold/Unhold Right <CTRL> Key
<ATL> + <N> Hold/Unhold Left <CTRL> Key
<ATL> + <D> Ge nerate <CTRL>, <ATL>, + <DEL>
<ATL> + <E> Start/Stop CD-ROM Drive Redirection
<ATL> + <P> Start/Stop Fl oppy Drive Redirection
Synchronize Mouse
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
50
Page 59

Redirection, Continued
Console Redirection Window
Dropdown
Menu Item
Console
Redirection
Description
This dropdown menu contains the following dropdown menu items:
Start Console Redirection
Stop Console Redirection
Restart
Full Screen
Sync Cursor
CDROM Redirection
Floppy Redirection
This menu item can be used to begin Console Redirection.
This menu item can be used to halt Console Redirection.
This menu item can be used to stop Console Redirection and
then start Console Redirection again.
This menu item can be used to view the Console Redirection in
Full Screen mode.
Note: Set your client system’s screen resolution to 1024 x
768 so that you can view the host system in true full screen.
This menu item can be used to synchronize or unsynchronize
the mouse cursor.
This menu item can be used to start or stop the redirection of
the CD-ROM drive.
This menu item can be used to start or stop the redirection of
the floppy drive.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
51
Page 60

Redirection, Continued
Console Redirection Window, Continued
Dropdown
Menu Item
Keyboard
Description
This dropdown menu contains the following dropdown menu items:
Hold Right CTRL Key
Hold Right ALT Key
Hold Left CTRL Key
Hold Left ALT Key
Left Windows Key
Right Windows Key
ALT+CTRL+DEL
Auto Key-Break Mode
This menu item can be used to act as the right-side <CTRL>
key when in Console Redirection.
This menu item can be used to act as the right-side <ALT> key
when in Console Redirection.
This menu item can be used to act as the left-side <CTRL> key
when in Console Redirection.
This menu item can be used to act as the left-side <ALT> key
when in Console Redirection.
This menu item can be used to access the left-side
<WINDOWS> key during a Console Redirection session. The
following actions can be performed:
• Hold Down
• Press and Release
This menu item can be used to access the right-side
<WINDOWS> key during a Console Redirection session. The
following actions can be performed:
• Hold Down
• Press and Release
This menu item can be used to act as if you depressed the
<CTRL>, <ALT> and <DEL> keys down simultaneously on
the host system that you are redirecting.
This feature is used to avoid repeated keystrokes over slow
connections.
Note: Sometimes when performing redirection over a slow
connection, you may see multiple repetitions of a single
key stroke on the host system. If you are experiencing
this type of situation, enable Auto Key-Break Mode.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
52
Page 61

Redirection, Continued
Console Redirection Window, Continued
Dropdown
Menu Item
View This dropdown menu item contains the Toolbar menu item that allows you to start the Console
Description
Redirection toolbar.
The following window is a screen capture of the Console Redirection toolbar.
Macros This dropdown menu item contains the Record New Macro menu item that allows you to
record a set of keystrokes. A good example is when using the ARMC/2 in conjunction with a
KVM. Normally, you must use a key sequence to switch systems. If yo u pr ogrammed a macro,
you would be able to switch systems by selecting a preprogrammed macro.
Help This dropdown menu item contains the About RConsoleOCX Control menu item that allows
you to view the RConsoleOCX Control version number and copyright information.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
53
Page 62

Redirection, Continued
Console Redirection Toolbar
The Console Redirection toolbar allows you to use Console Redirection more easily in
full screen mode. The Console Redirection toolbar is a great GUI to use especially if you
are not familiar with the shortcut key combinations.
Follow the steps in the table below to begin the Console Redirection toolbar:
Step Description
1 Left click the View dropdown menu. The dropdown menu will open. Left click on the Toolbar menu
item.
2 The Console Redirection toolbar will open.
Note: You can left click the down arrow to see the Console Redirection Status information.
Console Redirection Toolbar Status
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
54
Status Item Description
Compression This field displays if you are using compression
or not.
Resolution This field displays if you are using high or low
color mode during your redirection.
Frame Rate This field displays the current frame rate you
are getting.
Active
Clients
This field displays how many users are currently
accessing the ARMC/2.
Cont’d
Page 63

Redirection, Continued
Console Redirection Toolbar Toggle Buttons
Icon Description
When you see this icon, it means that the Console Redirection is on. You can left
click this icon to stop Console Redirection.
When you see this icon, it means that Console Redirection is stopped. You can left
click this icon to start Console Redirection.
Left click to start mouse synchronization or press the <ALT> <M> keys.
Left click to stop mouse synchronization or press the <ALT> <M> keys.
Left click to view the redirected host system’s console in full screen mode.
Note: Set your client system’s screen resolution to 1024 x 768 so that you can view
the host system in true full screen.
Left click to view the redirected host system’s console in a window.
Left click to toggle the use of the <CTRL> key.
Left click to toggle the use of the <ALT> key.
Left click to use the <CTRL> <ALT> <DEL> keys together.
When you see this icon, it means that CD-ROM device redirection is stopped.
You can left click this icon to start CD-ROM redirection.
When you see this icon, it means that CD-ROM redirection is currently on. You
can left click this icon to stop CD-ROM redirection.
When you see this icon, it means that floppy device redirection is stopped. You
can left click this icon to start floppy redirection.
When you see this icon, it means that floppy redirection is currently on. You can
left click this icon to stop floppy redirection.
Left click this icon to Power Control screen.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
55
Page 64

Redirection, Continued
Start CD-ROM Drive Redirection
Note: You must be logged in as an administrator on the windows client to perform CD-ROM
drive and Floppy drive redirection.
There are a number of ways to start CD-ROM Drive Redirection. See the following table:
Method Description
1 Use the keyboard shortcut keys, <ATL> + <E>, to open the CD-ROM Drive Redirection Dialog
Box.
2 Use the Console Redirection toolbar to open the CD-ROM Drive Redirection Dialog Box.
3 Use the CDROM Redirection dropdown menu to open the CD-ROM Drive Redirection Dialog
Box.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
56
Page 65

Redirection, Continued
Start CD-ROM Drive Redirection, Continued
Note: For information on how to create a bootable CD, visit nero.com or roxio.com. You can
do a search on how to create a bootable CD using their products. You can also consult
your CD writer's documentation.
Once you open the CD-ROM Drive Redirection Dialog Box, follow the steps below:
Step Description
1 Select whether you want to redirect the CD-ROM drive or a CD image file. Left click the OK button.
2 Select the CD-ROM Drive you want to redirect. Left click the OK button. CD-ROM Drive Redirection
will begin immediately.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
57
Page 66

Redirection, Continued
Start CD-ROM Drive Redirection, Continued
Step Description
3 If you used the Console Redirection toolbar to start the CD-ROM Drive Redirection, you will see the
following:
Notice that the CDROM Drive Redirection icon changes. If you used the dropdown menu, there is a
check next to the CDROM Redirection menu item.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
58
Page 67

Redirection, Continued
Stop CD-ROM Drive Redirection
There are a number of ways to stop CD-ROM Drive Redirection. See the following table:
Method Description
1 Use the keyboard shortcut keys, <ATL> + <E>, to stop CD-ROM Drive Redirection.
2 Use the Console Redirection toolbar. Simply left click the CD-ROM Drive Redirection icon.
3 Use the Console Redirection dropdown menu. Left click the Console Redirection dropdown menu.
You will notice a check next to the CDROM Redirection menu item. Left click the CDROM
Redirection menu item to stop the CD-ROM Drive Redirection.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
59
Page 68

Redirection, Continued
Stop CD-ROM Drive Redirection, Continued
The Console Redirection status dialog box appears as it stops device redirection.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
60
Page 69

Redirection, Continued
Start Floppy Drive Redirection
Note: You must be logged in as an administrator on the windows client to perform CD-ROM
drive and Floppy drive redirection.
There are a number of ways to start Floppy Redirect io n . See the following table:
Method Description
1 Use the keyboard shortcut keys, <ATL> + <P>.
2 Use the Console Redirection toolbar.
3 Use the Floppy Redirection dropdown menu.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
61
Page 70

Redirection, Continued
Start Floppy Drive Redirection, Continued
Once you open the Floppy Redirection Dialog Box, follow the steps below:
Step Description
1 Select whether you want to redirect the floppy drive or a floppy image file. Left click the OK button.
2 Select the Floppy Drive you want to redirect. Left click the OK button. Floppy Drive Redirection will
begin immediately.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
62
Page 71

Redirection, Continued
Start Floppy Drive Redirection, Continued
Step Description
3 If you used the Console Redirection toolbar to start the Floppy Drive Redirection, you will see the
following:
Notice that the Floppy Drive Redirection icon changes. If you used the dropdown menu, there is a
check next to the Floppy Redirection menu item.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
63
Page 72

Redirection, Continued
Stop Floppy Drive Redirection
There are a number of ways to stop Floppy Redi recti o n . See the following table:
Method Description
1 Use the keyboard shortcut keys, <ATL> + <P>, to stop Floppy Redirection.
2 Use the Console Redirection toolbar. Simply left click the Floppy Redirection icon.
3 Use the Console Redirection dropdown menu. Left click the Console Redirection dropdown menu.
You will notice a check next to the Floppy Redirection menu item. Left click the Floppy
Redirection menu item to stop Floppy Redirection.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
64
Page 73

Redirection, Continued
Stop Floppy Drive Redirection, Continued
The Console Redirection status dialog box appears as it stops device redirection.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
65
Page 74

Redirection, Continued
ARMC2 Floppy Image Creator
Creating a Floppy Image
Follow the steps in the table below to create a floppy image to use during device
redirection.
Using an image file is desirable because it is faster than redirecting from the actual floppy
disk. It is also more convenient to have a series of floppy images stored on a CD or on a
local or networked hard disk drive.
Step Description
1 Open the Floppy Image Creator program.
2 Select Create an Image file from a Floppy Media and left click the Next button.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
66
Page 75

Redirection, Continued
Creating a Floppy Image, Continued
Step Description
3 Select the floppy drive that you want to create the floppy image from. Select a location where you
want the image to be stored and give it a file name. In this example, the file name is
SampleImage.dat. Left click the Start button to begin the floppy image creation.
4 A progress dialog box opens displaying the status of the image creation.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
67
Page 76

Redirection, Continued
Creating a Floppy Image, Continued
Step Description
5 Once the floppy image is created, a confirmation dialog box opens. Left click the OK button.
6 Congratulations! You have successfully created a floppy image to use to during device redirection.
Left click the Exit button to close the Floppy Image Creator program.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
68
Page 77

Redirection, Continued
Transferring a Floppy Image to a Floppy Disk
Follow the steps in the table below to transfer a floppy image to a floppy disk.
Step Description
1 Open the Floppy Image Creator program.
2 Select Transfer an Image file from a file to a Floppy Media and left click the Next button.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
69
Page 78

Redirection, Continued
Transferring a Floppy Image to a Floppy Disk, Continued
Step Description
3 Left click the Browse button to locate the floppy image file that you want to copy to the floppy disk.
4 In this example, the file name is SampleImage.dat. Left click the image file to select it and left
click the Open button.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
70
Page 79

Redirection, Continued
Transferring a Floppy Image to a Floppy Disk, Continued
Step Description
5 Left click the Start button to begin the image transfer to the floppy disk.
6 A progress dialog box opens displaying the status of the image transfer.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
71
Page 80

Redirection, Continued
Transferring a Floppy Image to a Floppy Disk, Continued
Step Description
7 Once the floppy image is transferred, a confirmation dialog box opens. Left click the OK button.
8 Congratulations! You have successfully transferred a floppy image to a floppy disk. Left click the
Exit button to close the Floppy Image Creator program.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
72
Page 81

Redirection, Continued
Follow the steps in the table below to stop Console Redirection:
Step Description
1 Left click the Console Redirection dropdown menu item from the toolbar. The dropdown menu will
appear. Left click Stop Console Redirection.
Note: You can press the <ALT> key and the <T> key to stop Console Redirection.
Note: You can left click on the Stop Redirection icon on the toolbar to stop Console Redirection.
2 The following Console Redirection message box will appear.
3 Once Console Redirection has stopped, you can close both the Console Redirection window. You can
also leave the window open and start redirection again once you are ready.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
73
Page 82

Remote Power Control
The Control Host Power dialog box is a subsection of the Manage group. The Control
Host Power allows you to reset, power off, power on, and power cycle the host system
remotely.
Name Icon Description
Reset
Power Off
Power On
Power
Cycle
Current
System
State
none This displays the power status of the
Left click this button to reset the host
system.
Left click this button to power down the
host system.
Left click this button to power up the
host system.
Left click this button to power cycle the
host system.
host system. It can either be in an On
state or Off state.
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
74
Page 83

Upgrade Firmware
The Upgrade Firmware Wizard dialog box is a subsection of the Manage group. The
Upgrade Firmware Wizard will help you upgrade your ARMC/2’s firmware.
•
Warning
DO NOT CLOSE THE WINDOW USING THE CLOSE BUTTON (X) ON THE TITLE
BAR WHEN THE ARMC/2 IS IN UPGRADE MODE. USE THE CANCEL BUTTON
ONLY!
Note: The firmware upgrade process is a crucial operation. Make sure that the chances of a
power or connectivity loss are minimal when performing this operation.
Note: You can use the Cancel button at this time to abort the upgrade process. By doing so, the
ARMC/2 card resets itself (except in Step 1 of 4).
Note: Once you enter into Flash Mode and choose to cancel the firmware flash operation, the
ARMC/2 must be reset. This means that you must close the Internet browser and log back
onto the ARMC/2 before you can perform any other types of operations.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
75
Page 84

Upgrade Firmware, Continued
Updating Your ARMC/2’s Firmware
Follow the steps in the table below to update your ARMC/2’s firmware:
Step Description
1 Left click the Enter Upgrade Mode button.
2 The following dialog appears:
Preparing to upgrade firmware. Please wait…
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
76
Page 85

Upgrade Firmware, Continued
Updating Your ARMC/2’s Firmware, Continued
Step Description
3 Left click the Browse button to locate the firmware (*.IMA) update file.
4 Locate the firmware file and select it. Left click the Open button.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
77
Page 86

Upgrade Firmware, Continued
Updating Your ARMC/2’s Firmware, Continued
Step Description
5 Left click the Upload button to go to the next step.
6 The ARMC/2 firmware wizard will begin to check the existing firmware against the firmware file
you are trying to load.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
78
Page 87

Upgrade Firmware, Continued
Updating Your ARMC/2’s Firmware, Continued
Step Description
7 Once it verifies the image, the following dialog box appears:
Left click the OK button.
8 If the dialog box prompted that an update is necessary, left click the Flash button. If the wizard
determined that no flash is necessary, you can left click the Cancel button.
Note: Even if you choose to cancel the firmware flash operation, the
means that you must close the Internet browser and log back onto the ARMC/2 before you can
perform any other types of operations.
Note: You can place a check next to Preserve Config if you want to flash the firmware but retain your
original configuration.
9 Left click the OK button.
ARMC/2 must be reset. This
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
79
Page 88

Upgrade Firmware, Continued
Updating Your ARMC/2’s Firmware, Continued
Step Description
10 When you see this screen, it means that the firmware image is being upgraded. Once the upgrade’s
progress reaches 100%, it is complete. The ARMC/2 will reset itself. You must close the browser
and reconnect to the ARMC/2 once this process is complete.
11 After the Firmware Upgrade Wizard has been completed successfully, the ARMC/2 will
automatically reset itself. This is done in order for the image upgrade to take effect. You cannot
perform any other operation within your current Internet browser session
Close your Internet browser session and reconnect to your ARMC/2.
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
80
Page 89

Reset ARMC/2
The Reset ARMC/2 menu item is a subsection of the Manage group. The Reset ARMC/2
is used to reset your ARMC/2 card.
Follow the steps in the table below to reset your ARMC/2 card:
Step Description
1 Left click the Manage menu item and then the Reset ARMC/2 menu item.
2 A confirmation dialog box opens. Left click the OK button to verify that you want to reset the
ARMC/2 card.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
81
Page 90

Reset ARMC/2, Continued
Step Description
3 The ARMC/2 card resets itself. You are prompted to close Internet Explorer and log back into the
ARMC/2 card. Left click the Close button.
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
82
Page 91

Configure Group
You can left click on the Configure menu item from the menu bar. The following table
gives you a brief description of each menu item. Each menu item is explained in more
detail further in this section.
Function Description
Users This menu item allows you to administer users that can access the
ARMC/2 and host system.
Network This menu item allows you to configure the network parameters of the
ARMC/2.
Firewall This menu item allows you to allow and restrict the IP addresses that can
access the ARMC/2.
Alert
Notification
Date & Time This menu item allows you to configure the time on the ARMC/2 card.
Serial Port This menu item allows you to configure Serial Over LAN access on your
SSL
Certificate
PMCP File
Upload
IPMI
Configuration
Server OS
Monitoring &
Recovery
This menu item allows you to configure how alerts are sent.
ARMC/2 card.
This menu item allows you to upload a Digital Certificate and Private
Key to the ARMC/2 card.
Note: The ARMC/2 does not support pass-phrase encrypted certificates.
This menu item allows you to upload a platform management file for
your motherboard/ server board.
This menu item allows you to configure the ARMC/2 card to read data
from an onboard baseboard management controller (BMC) on the
motherboard/ server board.
This menu item allows you to configure operating system monitoring and
recovery methods.
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
83
Page 92

Users
The Users screen is a subsection of the Configure group. This page allows you to
configure the administrators who have access to the ARMC/2.
The following table describes the information listed in this subsection in detail:
Item Description
Username This field displays a list of all users who are able to access this ARMC/2.
Note: The default administrator is root. It is prudent for you to change the root
password.
Description This field displays the Username’s description that you entered when you created the
account for each Username in the list.
Add Button This button allows you to add and configure a new user account to your ARMC/2.
Remove Button This button allows you to eliminate an account from your ARMC/2’s access list.
Properties Button This button allows you to view and edit an account.
Close Button This button allows you to exit the User dialog box.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
84
Page 93

Users, Continued
Adding Users
Follow the steps in the table below to add an account:
Step Description
1 Left click the Add button.
2 Enter a user name in the Username field. Your user name must be at least four characters long and
no more than 32 characters long. User names are case-sensitive and must start with an alphabetical
character. You can also enter a short description of the account in the Description field. Enter a
password in the Password field. Your password must be at least eight characters long. Confirm your
password by entering your password again in the Confirm Password field.
Note: The password must be a minimum of eight characters and a maximum of 32 characters. Use a
mixture of alphanumeric and special characters for better security. The password is casesensitive.
Assign permissions and access rights. After you enter the new administrator’s information, left click
the OK button.
Note: Only user accounts with administrative rights are allowed to add, edit, and remove users. Non-
administrator users can only change their own password. If a new user is given administrative
privileges, permissions are automatically granted for all interfaces.
Cont’d
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
85
Page 94

Users, Continued
Removing Users
Follow the steps in the table below to remove an account:
Step Description
1 Left click an account from the Username field. Once the account that you want to remove is
highlighted, left click the Remove button.
2 A confirmation dialog box opens. Left click the OK button to confirm deletion or left click the
Cancel button to cancel.
Cont’d
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
86
Page 95

Users, Continued
Viewing and Editing Users
Follow the steps in the table below to view and edit an account’s access rights and
properties:
Step Description
1 Left click an account from the Username field. Once the account you want to view and edit is
highlighted, left click the Properties button.
2 Here you can change the password, description, permissions, and acc e ss r ights. After you have
viewed and edited the account information, left click the OK button.
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
87
Page 96

Network
Left click the Network menu item to configure the Network parameters of the ARMC/2.
The Network Settings dialog box opens:
The following table describes the information listed in this subsection in detail:
Item Description
MAC Address This field displays the ARMC/2’s MAC address.
Configuration
Method
This field allows you to configure the ARMC/2’s IP address statically or dynamically.
Obtain IP address
automatically
This option allows the ARMC/2’s IP to be configured by a
DHCP server (dynamically).
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
88
Cont’d
Page 97

Network, Continued
Item Description
Use the following IP
address
This option allows you to configure the ARMC/2’s IP address
with a static IP. The IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway
fields will become editable when this option is selected.
IP Address This field allows you to set the ARMC/2’s IP address.
Subnet Mask This field allows you to set the Subnet Mask The ARMC/2 resides on.
Gateway This field allows you to set the ARMC/2’s Gateway access address.
Apply Button This button allows you to save your configuration.
Note: You are prompted to close your Internet browser and reconnect to the new IP address if
you make changes to the Networking Information screen.
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
89
Page 98

Firewall
Left click the Firewall menu item to configure the IP access parameters of the ARMC/2.
The Firewall Settings dialog box opens. Here you can enter IP addresses to block or
allow. You can also specify which ports to block or allow.
Left click the Blocked Sites tab to enter a range of IP addresses that you want to block.
Left click the Trusted Sites tab to enter a range of IP addresses that you want to always
allow.
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
90
Cont’d
Page 99

Firewall, Continued
Once you left click the Add button on either the Blocked Sites or Trusted Sites, the
following dialog box opens.
Item Description
Start IP Address This fie l d allows you to enter the start address of the subnet you want to either block
or always allow.
Subnet Mask This field allows you to enter the specific subnet of the IP address range that y ou wa nt
to use.
Protocol This drop down box allows you select either the UDP protocol or TCP protocol. The
ARMC/2 can be configured to accept or ignore packets based on the type of packet.
All Ports This setting allows the ARMC/2 to accept or ignore ports 1 through 65535.
Ports Range This setting allows you to select the specific range of ports that you want the ARMC/2
to accept or ignore.
Starting Port This field allows you to enter the first port of the port range that you want the
ARMC/2 to accept or ignore.
Ending Port This field allows you to enter the last port of the port range that you want the
ARMC/2 to accept or ignore.
OK button Left click the OK button when you are satisfied with the information entered.
Cancel button Left click the Cancel button to discard changes and exit.
Note: You can edit any of the IP address ranges by selecting the IP address range from the main
Firewall Dialog Window. You can enter your adjustments and left clicking on the Modify
button for the changes to take effect.
Chapter Four : Using Your ARMC/2
91
Page 100

Alert Notification
Left click the Alert Notification menu item to configure how alerts are sent from the
ARMC/2 card. The Alert Notification dialog box opens. Here you can set SNMP
destinations and email destinations.
ARMC/2 User’s Guide
92
 Loading...
Loading...