Page 1

AR180 F1 Series
User Guide
Page 2

Copyright © 2010. All Rights Reserved.
Acer AR180 F1 Series
User Guide
Acer AR180 F1
Model Number :
Serial Number:
Purchase Date:
Place of Purchase:
Page 3

iii
Information for your safety and comfort
Safety instructions
Read these instructions carefully. Keep this document for future
reference. Follow all warnings and instructions marked on the product.
Turning the product off before cleaning
Unplug this product from the wall outlet before cleaning. Do not use
liquid cleaners or aerosol cleaners. Use a damp cloth for cleaning.
CAUTION for plug as disconnecting device
Observe the following guidelines when connecting and disconnecting
power to the power supply unit:
• Install the power supply unit before connecting the power cord to
the AC power outlet.
• Unplug the power cord before removing the power supply unit
from the computer.
• If the system has multiple sources of power, disconnect power
from the system by unplugging all power cords from the power
supplies.
CAUTION for accessibility
Be sure that the power outlet you plug the power cord into is easily
accessible and located as close to the equipment operator as possible.
When you need to disconnect power to the equipment, be sure to
unplug the power cord from the electrical outlet.
Warnings
• Do not use this product near water.
• Do not place this product on an unstable cart, stand or table. If the
product falls, it could be seriously damaged.
Page 4

iv
• Slots and openings are provided for ventilation to ensure reliable
operation of the product and to protect it from overheating.
These openings must not be blocked or covered. The openings
should never be blocked by placing the product on a bed, sofa, rug
or other similar surface. This product should never be placed near
or over a radiator or heat register, or in a built-in installation
unless proper ventilation is provided.
• Never push objects of any kind into this product through cabinet
slots as they may touch dangerous voltage points or short-out
parts that could result in a fire or electric shock. Never spill liquid
of any kind onto or into the product.
• To avoid damage of internal components and to prevent battery
leakage, do not place the product on a vibrating surface.
• Never use it under sporting, exercising, or any vibrating
environment which will probably cause unexpected short current
or damage rotor devices, HDD, Optical drive, and even exposure
risk from lithium battery pack.
• This product is not suitable for use with visual display workplace
devices according to B2 of the German Ordinance for Work with
Visual Display Units.
Using electrical power
• This product should be operated from the type of power indicated
on the marking label. If you are not sure of the type of power
available, consult your dealer or local power company.
• Do not allow anything to rest on the power cord. Do not locate
this product where people will walk on the cord.
• If an extension cord is used with this product, make sure that the
total ampere rating of the equipment plugged into the extension
cord does not exceed the extension cord ampere rating. Also,
make sure that the total rating of all products plugged into the
wall outlet does not exceed the fuse rating.
• Do not overload a power outlet, strip or receptacle by plugging in
too many devices. The overall system load must not exceed 80% of
the branch circuit rating. If power strips are used, the load should
not exceed 80% of the power strip's input rating.
• This product's power supply is equipped with a three-wire
grounded plug. The plug only fits in a grounded power outlet.
Make sure the power outlet is properly grounded before inserting
the power supply plug. Do not insert the plug into a non-
Page 5

v
grounded power outlet. Contact your electrician for details.
Warning! The grounding pin is a safety feature. Using a power outlet that is
not properly grounded may result in electric shock and/or injury.
Note: The grounding pin also provides good protection from unexpected
noise produced by other nearby electrical devices that may interfere with
the performance of this product.
• Use the product only with the supplied power supply cord set. If
you need to replace the power cord set, make sure that the new
power cord meets the following requirements: detachable type,
UL listed/CSA certified, VDE approved or its equivalent, 4.6 meters
(15 feet) maximum length.
Product servicing
Do not attempt to service this product yourself, as opening or
removing covers may expose you to dangerous voltage points or other
risks. Refer all servicing to qualified service personnel.
Unplug this product from the wall outlet and refer servicing to
qualified service personnel when:
• the power cord or plug is damaged, cut or frayed
• liquid was spilled into the product
• the product was exposed to rain or water
• the product has been dropped or the case has been damaged
• the product exhibits a distinct change in performance, indicating a
need for service
• the product does not operate normally after following the
operating instructions
Note: Adjust only those controls that are covered by the operating
instructions, since improper adjustment of other controls may result in
damage and will often require extensive work by a qualified technician to
restore the product to normal condition.
This server must be placed in a restricted access location.
CAUTION: Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the
Page 6

vi
manufacturer. Dispose of used batteries according to the
manufacturer’s instructions.
Page 7

vii
Additional safety information
Your device and its enhancements may contain small parts. Keep them
out of the reach of small children.
Disposal instructions
Do not throw this electronic device into the trash when
discarding. To minimize pollution and ensure utmost
protection of the global environment, please recycle. For
more information on the Waste from Electrical and
Electronics Equipment (WEEE) regulations, visit
http://www.acer-group.com/public/Sustainability/sustainability01.htm.
Mercury advisory
For projectors or electronic products containing an LCD/CRT
monitor or display: Lamp(s) inside this product contain
mercury and must be recycled or disposed of according to local, state
or federal laws. For more information, contact the Electronic Industries
Alliance at www.eiae.org. For lamp-specific disposal information,
check www.lamprecycle.org.
Tips and information for comfortable use
Computer users may complain of eyestrain and headaches after
prolonged use. Users are also at risk of physical injury after long hours
of working in front of a computer. Long work periods, bad posture,
poor work habits, stress, inadequate working conditions, personal
health and other factors greatly increase the risk of physical injury.
Incorrect computer usage may lead to carpal tunnel syndrome,
tendonitis, tenosynovitis or other musculoskeletal disorders. The
following symptoms may appear in the hands, wrists, arms, shoulders,
neck or back:
• numbness, or a burning or tingling sensation
• aching, soreness or tenderness
• pain, swelling or throbbing
• stiffness or tightness
• coldness or weakness
Page 8

viii
If you have these symptoms, or any other recurring or persistent
discomfort and/or pain related to computer use, consult a physician
immediately and inform your company's health and safety
department.
The following section provides tips for more comfortable computer
use.
Finding your comfort zone
Find your comfort zone by adjusting the viewing angle of the monitor,
using a footrest, or raising your sitting height to achieve maximum
comfort. Observe the following tips:
• refrain from staying too long in one fixed posture
• avoid slouching forward and/or leaning backward
• stand up and walk around regularly to remove the strain on your
leg muscles
• take short rests to relax your neck and shoulders
• avoid tensing your muscles or shrugging your shoulders
• install the external display, keyboard and mouse properly and
within comfortable reach
• if you view your monitor more than your documents, place the
display at the center of your desk to minimize neck strain
Taking care of your vision
Long viewing hours, wearing incorrect glasses or contact lenses, glare,
excessive room lighting, poorly focused screens, very small typefaces
and low-contrast displays could stress your eyes. The following sections
provide suggestions on how to reduce eyestrain.
Eyes
• Rest your eyes frequently.
• Give your eyes regular breaks by looking away from the monitor
and focusing on a distant point.
• Blink frequently to keep your eyes from drying out.
Display
• Keep your display clean.
Page 9

ix
• Keep your head at a higher level than the top edge of the display
so your eyes point downward when looking at the middle of the
display.
• Adjust the display brightness and/or contrast to a comfortable
level for enhanced text readability and graphics clarity.
• Eliminate glare and reflections by:
• placing your display in such a way that the side faces the
window or any light source
• minimizing room light by using drapes, shades or blinds
• using a task light
• changing the display's viewing angle
• using a glare-reduction filter
• using a display visor, such as a piece of cardboard extended
from the display's top front edge
• Avoid adjusting your display to an awkward viewing angle.
• Avoid looking at bright light sources, such as open windows, for
extended periods of time.
Developing good work habits
Develop the following work habits to make your computer use more
relaxing and productive:
• Take short breaks regularly and often.
• Perform some stretching exercises.
• Breathe fresh air as often as possible.
• Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy body.
Warning! We do not recommend using the computer on a couch
or bed. If this is unavoidable, work for only short periods, take
breaks regularly, and do some stretching exercises.
Page 10

x
Regulations and safety notices
FCC notice
This device has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class A digital device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This device generates, uses,
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used
in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If this device does cause harmful interference to
radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the
device off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the device and receiver.
• Connect the device into an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician
for help.
Notice: Shielded cables
All connections to other computing devices must be made using
shielded cables to maintain compliance with FCC regulations. In
compliance with FCC regulations, use shielded cables to connect to
other computing devices. A dual-link cable is recommended for DVI
output.
Notice: Peripheral devices
Only peripherals (input/output devices, terminals, printers, etc.)
certified to comply with the Class A limits may be attached to this
equipment. Operation with non-certified peripherals is likely to result
in interference to radio and TV reception.
Page 11

xi
Caution
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the manufacturer
could void the user's authority, which is granted by the Federal
Communications Commission, to operate this computer.
Operation conditions
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject
to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Notice: Canadian users
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Remarque à l'intention des utilisateurs canadiens
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme a la norme NMB003 du Canada.
Compliant with Russian regulatory certification
Notice for Australia
For safety reasons, only connect headsets with a telecommunications
compliance label. This includes customer equipment previously labelled
permitted or certified.
Notice for New Zealand
1 The grant of a Telepermit for any item of terminal equipment
indicates only that Telecom has accepted that the item complies
with minimum conditions for connection to its network. It
indicates no endorsement of the product by Telecom, nor does it
provide any sort of warranty. Above all, it provides no assurance
that any item will work correctly in all respects with another item
of Telepermitted equipment of a different make or model, nor
does it imply that any product is compatible with all of Telecom's
network services.
2 This equipment is not capable, under all operating conditions, of
correct operation at the higher speeds for which it is designed.
Page 12

xii
Telecom will accept no responsibility should difficulties arise in
such circumstances.
3 Some parameters required for compliance with Telecom's
Telepermit requirements are dependent on the equipment (PC)
associated with this device. The associated equipment shall be set
to operate within the following limits for compliance with
Telecom's Specifications:
a There shall be no more than 10 call attempts to the same number
within any 30 minute period for any single manual call initiation, and
b The equipment shall go on-hook for a period of not less than 30
seconds between the end of one attempt and the beginning of the
next call attempt.
4 Some parameters required for compliance with Telecom's
Telepermit requirements are dependent on the equipment (PC)
associated with this device. In order to operate within the limits
for compliance with Telecom's specifications, the associated
equipment shall be set to ensure that automatic calls to different
numbers are spaced such that there is not less than 5 seconds
between the end of one call attempt and the beginning of
another.
5 This equipment shall not be set up to make automatic calls to
Telecom's 111 Emergency Service.
6 This device is equipped with pulse dialing while the Telecom
standard is DTMF tone dialing. There is no guarantee that Telecom
lines will always continue to support pulse dialing.
7 Use of pulse dialing, when this equipment is connected to the
same line as other equipment, may give rise to bell tinkle or noise
and may also cause a false answer condition. Should such problems
occur, the user should NOT contact the telecom Fault Service.
8 This equipment may not provide for the effective hand-over of a
call to another device connected to the same line.
9 Under power failure conditions this appliance may not operate.
Please ensure that a separate telephone, not dependent on local
power, is available for emergency use.
Page 13

xiii
Notice: BSMI
Power Supply Unit (PSU) statement
Power supply unit (PSU) redundancy claim ensures that the system may
continue to run normally in the event one power supply unit becomes
inoperable. Under normal operation, both power supplies share the
system loading.
Laser compliance statement
The CD or DVD drive used with this computer is a laser product.
The CD or DVD drive's classification label (shown below) is located on
the drive.
CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT
CAUTION: INVISIBLE LASER RADIATION WHEN OPEN. AVOID
EXPOSURE TO BEAM.
Appareil à laser de classe 1
Attention: Radiation laser visible et invisible en cas d’ouverture. Éviter
toute exposition aux rayons.
Laserprodukt der Klasse 1
Achtung: Beim Öffnen werden unsichtbare Laserstrahlen freigelegt.
Setzen Sie sich diesen Strahlen nicht aus.
Prodotto laser di classe 1
Attenzione: Radiazioni laser invisibili in caso d’apertura. Evitare
l’esposizione ai raggi.
Producto láser de Clase 1
Precaución: Cuando está abierta, hay radiación láser. Evite una
exposición al haz de luz.
Produto Laser de Classe 1
Precaução: Radiação laser invisível quando aberto. Evite exposição ao
feixe.
Page 14

xiv
Laserproduct klasse 1
Voorzichtig: Onzichtbare laserstraling indien geopend. Voorkom
blootstelling aan straal.
Declaration of Conformity for EU countries
Hereby, Acer, declares that this system is in compliance with the
essential requirements and other relevant provisions of Directive 1999/
5/EC.
List of applicable countries
This device must be used in strict accordance with the regulations and
constraints in the country of use. For further information, please
contact local office in the country of use. Please see
http://ec.europa.eu/enterprise/rtte/implem.htm for the latest country
list.
Page 15

1 System tour 1
Overview 2
External and internal structure 3
Front panel 3
Rear panel 6
Internal components 8
Mainboard 9
2 System setup 15
Setting up the system 16
Pre-installation requirements 16
Connecting peripherals 17
Turning on the system 18
To power on the system: 18
Power-on problems 18
Configuring the system OS 20
Turning off the system 21
3 System upgrades 23
Installation precautions 24
ESD precautions 24
Pre-installation instructions 24
Post-installation instructions 25
Opening the server 26
Configuring the storage devices 28
Accessing the drive bays 28
Hard disk drive configuration guidelines 28
Determining drive status 29
Removing and installing a 3.5” hard disk drive 30
Installing and removing the power supply 32
Power supply failure 33
Replacing the power supply 33
Removing and installing the air duct 34
Replacing a system fan 35
Replacing the processor and heatsink 37
Removing the heatsink 37
Installing a heatsink 38
Upgrading the processor 40
Upgrading the system memory 43
Installing a memory module: 48
Removing a memory module: 49
Installing an expansion card 51
Contents
Page 16

xvi
Installing a SAS card 51
Installing the rear SAS card 52
Installing the right riser card 54
4 System BIOS 57
Introduction 58
The BIOS setup utility 58
Changing configuration data 58
Main setup 60
Advanced Settings 62
Boot Features 62
Processor & Clock Options 64
Advanced Chipset Control 67
IDE/SATA configuration 71
PCI/PnP configuration 74
Super IO Configuration 75
Hardware Health Configuration 76
ACPI configuration 79
Security Settings 81
System Management Settings 84
Product Information 84
Remote Access Configuration 86
DMI Event Logging 87
Boot Settings 89
Boot Device Priority 89
Hard Disk Drives 90
CD/DVD Drive 90
Exit 91
5 System troubleshooting 95
Resetting the system 96
Initial system startup problems 96
BIOS error beep codes 97
Initial troubleshooting checklist 98
Hardware diagnostic testing 99
Checking the boot-up status 99
Verifying the condition of the storage devices 100
Confirming loading of the operating system 100
Specific problems and corrective actions 101
Appendix A: Server management tools 105
Server management overview 106
Page 17

RAID configuration utilities 107
Intel onboard SATA RAID Creation 107
Adaptec onboard SATA RAID Creation 109
Configuring LSI MegaRAID SAS 8204ELP 111
MEGARAID SAS 8708EM2 RAID CREATION 113
FLEX IO LSI 1078 SAS RAID CREATION 115
Appendix B: Rack mount configuration 117
Rack installation information 118
System rack installation 120
Vertical mounting hole pattern 121
Installing the system into the rack 122
Appendix C: Acer Smart Console 129
Using Acer Smart Console 130
Software requirements 130
Accessing Acer Smart Console 131
Acer Smart Console user interface 132
System Information 132
Server Health 133
Configuration 135
Remote Control 145
Launch SOL 147
Virtual Media 148
Maintenance 150
KVM function description 151
Exit 157
xvii
Index 159
Page 18

xviii
Page 19

1 System tour
Page 20

2
1 System tour
Overview
The AR180 F1 is a high-performance 2U rack-mount dual-socket server
that supports up to two new generations of Intel architecture
processors (Intel® Xeon 5500 series and Intel® Xeon 5600 series
processors), DDR3 memory technology, PCI Express Gen2 (5.0Gb/s) dual
onboard gigabit Ethernet ports with Intel
Technology (IOAT), VT-d and iSCSI boot and integrated BMC
management feature.
The AR180 F1 targets medium businesses that require server solution
combined with performance, reliability and expandability to support
applications such as FTP server, file/printer server, data center, data
center and Internet/Intranet server. The AR180 F1 is a flexible and
highly reliable rack-mount server that satisfy growing businesses and
customers’ needs.
System features and support
• Up to twelve 3.5-inch SAS/SATA hard disk drives.
• Hot-plug system fans
®
•Dual Intel
• Twelve DIMM slots that support a maximum of 192 GB (registered)
or 48 GB (unbuffered) memory
Xeon 5500 / 5600 processors
®
I/O Acceleration
Page 21
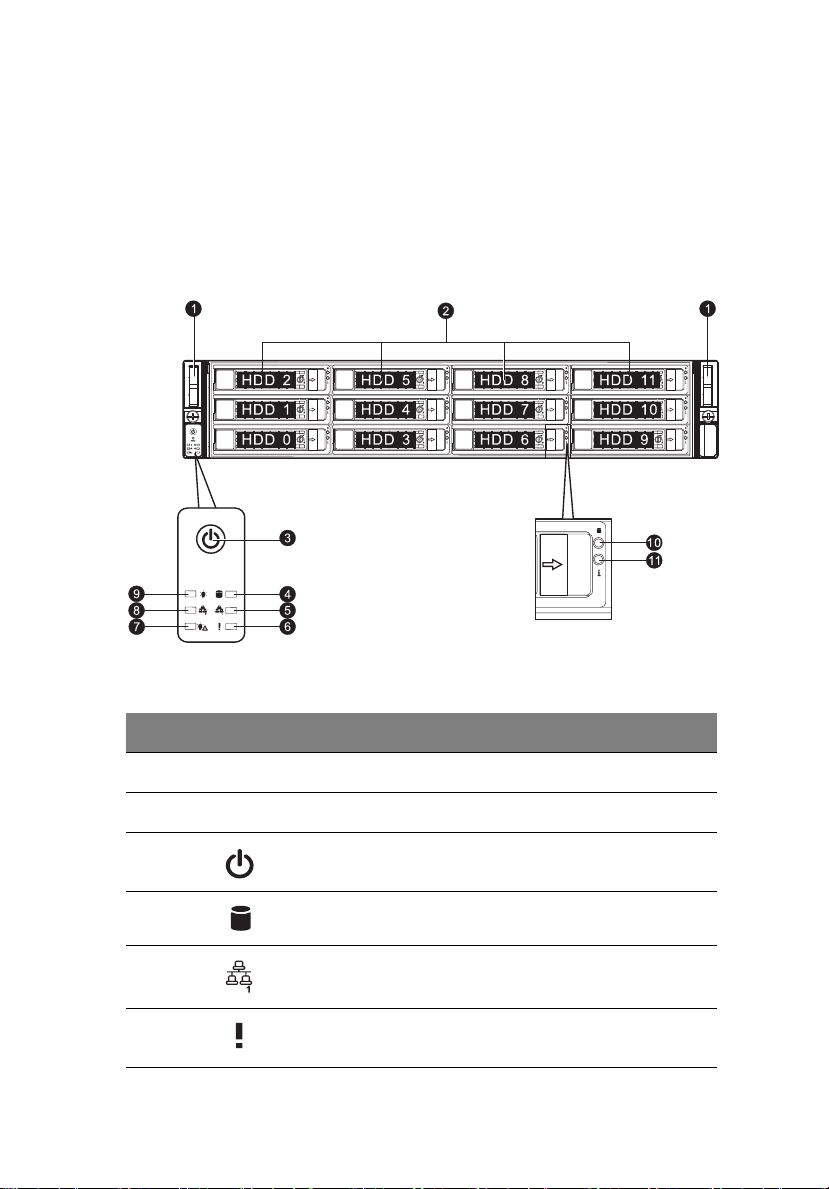
3
External and internal structure
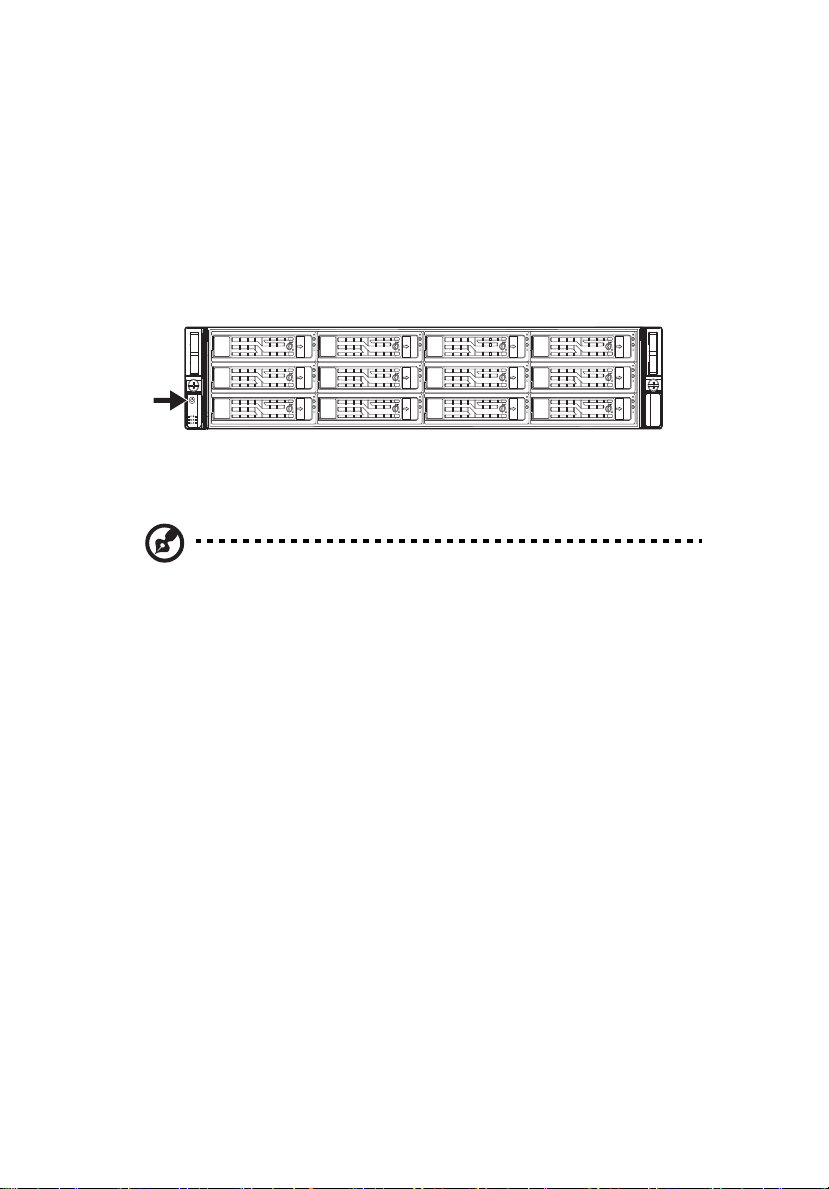
Front panel
The illustration below shows the system front panel.
With 3.5-inch HDD bays
No. Icon Component
1 Rack handles
2 3.5-inch hard disk drive (HDD) bays
3 Power button
4 HDD activity indicator
5 LAN1 activity indicator
6 Status / fault indicator
Page 22

4
No. Icon Component
7 Power failure indicator
8 LAN2 activity indicator
9 Power indicator
10 Hot-plug HDD activity indicator
11 Hot-plug HDD status indicator
Front panel LED indicator status
LED indicator LED color LED state Status
1 System tour
Power
indicator
HDD activity
indicator (on
board SATA)
Status / fault
indicator
Green On S0: Power ON
Green Blinking (1 Hz at
50% duty cycle)
N/A Off S4
N/A Off S5
Amber Blinking HDD access
N/A Off No access
Red On CPU overheat
Red Fast Blink (1x/sec) Fan failure
Red Slow Blink (1x/4sec) Power failure
S1: Sleep
Page 23

5
LED indicator LED color LED state Status
LAN activity
indicators
(LAN1,
LAN2)
Green On LAN Link / No Access
Green Blinking LAN Access
N/A Off Disconnect / Idle
Page 24
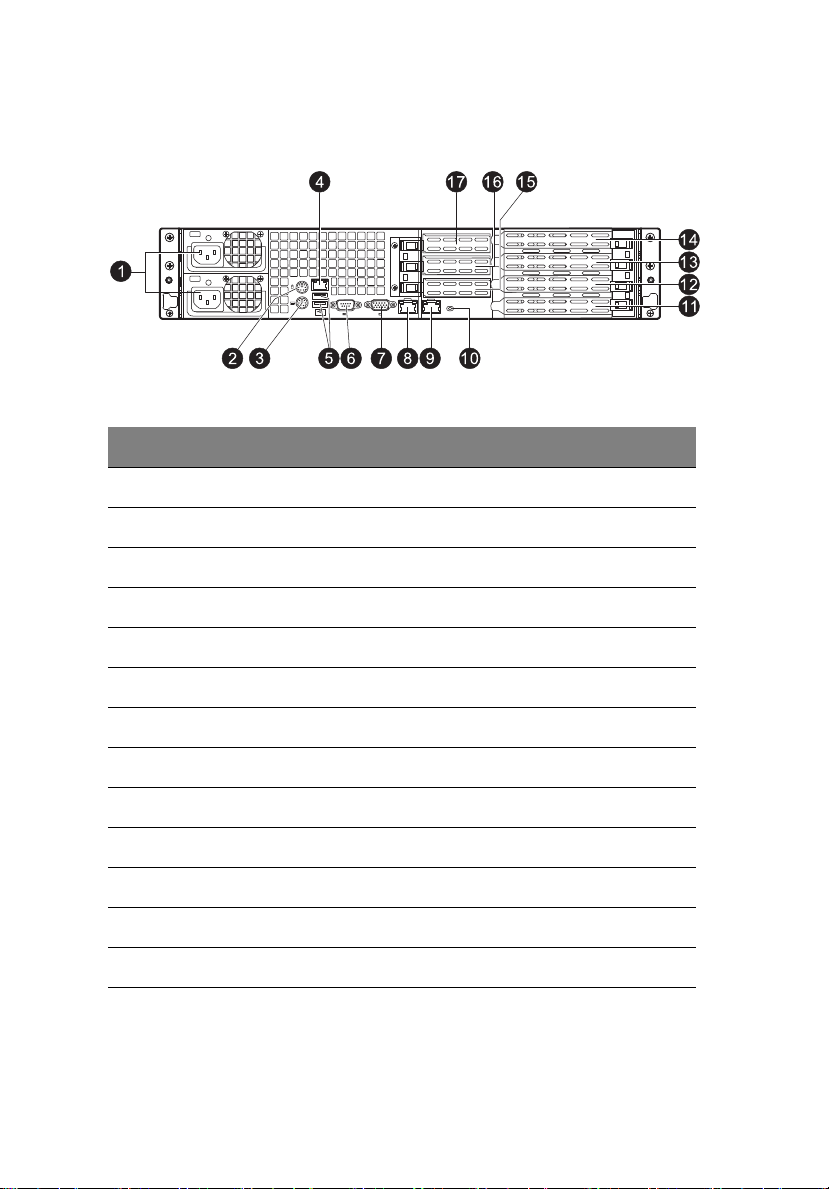
6
Rear panel
No. Component
1 Power supply modules
2 PS/2 mouse port
3 PS/2 keyboard port
4 Server management port (RJ-45) (10/100 Mbps)
1 System tour
5 USB 2.0 ports
6COM port
7 Monitor port
8-9 Gigabit LAN1 - 2 ports (10/100/1000 Mbps)
10 System ID indicator
11 Flex I/O expansion slot
12-13 Full-height PCI Express 2.0 x8 (x4 link) expansion slots
14 Full-height PCI Express 2.0 x16 (x8 link) expansion slot
15-17 Low-profile PCI Express 2.0 x8 (x4 link) expansion slots
Page 25
7
Rear panel LED indicator status
LED indicator LED color LED state Status
System ID LED N/A Off Normal
Blue On System ID button pressed
Blue Blinking IPMI-activated system ID
LAN port LED indicators
LED indicator LED color LED state Status
RJ45 LED (Left) N/A Off No connection or 10 Mbps
Green On 100 Mbps
Amber On 1000 Mbps
RJ45 LED (Right) Green On Active connection
Green Blinking Transmit/Receive activity
Page 26
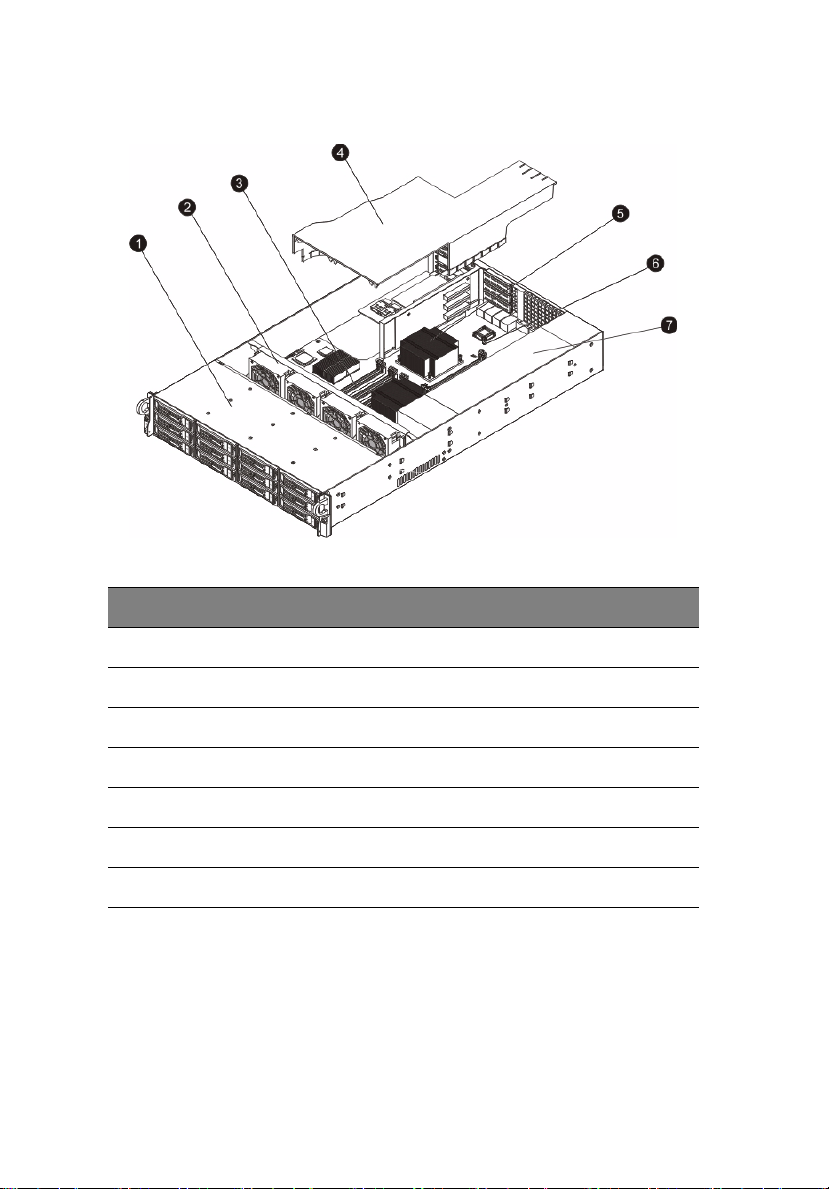
8
Internal components
No. Component
1 System tour
1 Hard disk drive bay
2System fan modules
3 Memory modules
4 Air duct
5 PCI riser board bracket assembly
6 Mainboard
7 Power supply module
Page 27
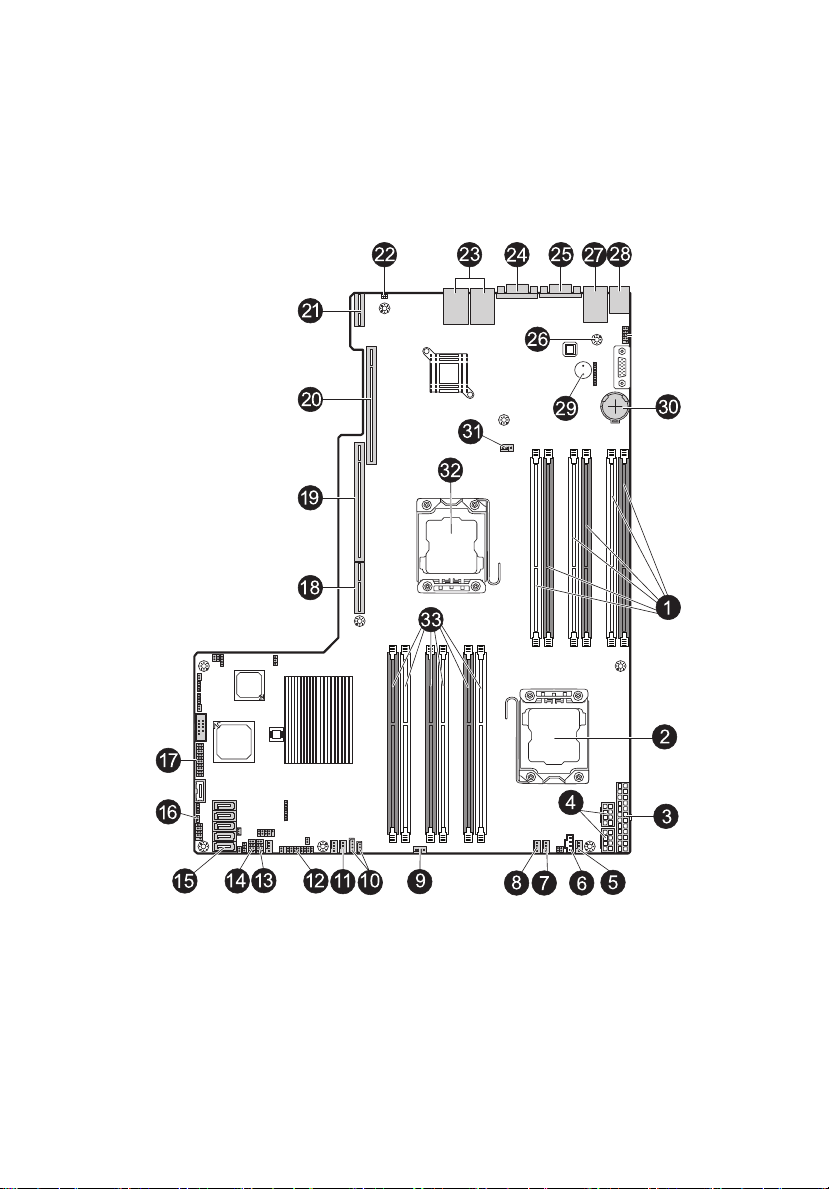
9
Mainboard
The mainboard becomes accessible once you open the system. It should
look like the figure shown below.
Page 28

10
No. Connector Description
1 System tour
1 P1-DIMM3A
P1-DIMM3B
P1-DIMM2A
P1-DIMM2B
P1-DIMM1A
P1-DIMM1B
2 CPU2 Processor 2 socket
3 JPW1 ATX 24-pin power connector
4 JPW2/JPW3 12V 8-pin power connectors
5 FAN1 Chassis fan 1
6 JPI2C Power supply SMB bus I2C header
7 FAN7 CPU2 FAN (Reserved)
8 FAN2 Chassis fan 2
9 FAN3 Chassis fan 3
10 IPMB1/
JIPMB2
11 FAN4 Chassis fan 4
DDR3 sockets for processor1
4-pin/3-pin external BMC I2C header
12 JF1 Front panel control header
13 T-SGPIO2 Serial General Purpose Input/Output header 2
14 T-SGPIO1 Serial General Purpose Input/Output header 1
15 I-SATA0~5 SATA ports
16 JL1 Chassis intrusion
17 JTPM Trusted platform module header (JP8)
18 SXB 3 Left side riser card slot
Page 29

11
No. Connector Description
19 SXB1 Left side riser card slot
20 SXB2 Right side riser card slot
21 UIOP Left side riser card slot
22 ID System ID LED
23 LAN1/LAN2 G-bit ethernet ports 1/2
24 VGA1 Rear VGA port
25 COM1 COM1 serial connection
26 IPMI LAN IPMI dedicated LAN
27 USB 0/1 Back panel USB 0/1
28 KB/MS PS2 keyboard/mouse
29 SP1 Onboard buzzer
30 JBT1 Onboard battery
31 FAN8 CPU1 FAN (Reserved)
32 CPU1 Processor 1 socket
33 P2-DIMM3A
P2-DIMM3B
P2-DIMM2A
P2-DIMM2B
P2-DIMM1A
P2-DIMM1B
DDR3 sockets for processor2
Page 30
12
Mainboard jumper settings
1 System tour
No. Jumper Description Default Setting
1 JBT1 Clear CMOS Instead of pins, this jumper consists
2JI2C1/
JI2C2
3 JP3 ME Mode Select Pins 2~3 (disable)
4 JP5 ME Recovery Open (normal)
SMB to PCI-E slots Off (disable)
of contact pads to prevent accidental
clearing of the CMOS contents. To
clear CMOS, disconnect the power
and short the CMOS pads with a
metal object such as a small
screwdriver.
Page 31

13
No. Jumper Description Default Setting
5 JPB BMC Enabled Pins 1~2 (enable)
6 JPG1 VGA Enable Pins 1~2 (enable)
7 JPL1 GLAN1 Enable Pins 1 (enable)
8 JPRST1 BMC/PHY Enable Pins 1~2 (enable)
9 JWD Watch Dog Pins 1~2 (reset)
Note: Jumpers not indicated are for test purposes only.
Page 32
14
Mainboard LEDs
1 System tour
No. LED Description State Status
1 D20 BMC heartbeat
LED
2 LE1 Standby power
LED
3 LE11 System ID LED Solid blue System ID
Green blinking Normal
Solid green Power on
Page 33

2 System
setup
Page 34

16
2 System setup
Setting up the system
Pre-installation requirements
Selecting a site
Before unpacking and installing the system, select a suitable site for
the system for maximum efficiency. Consider the following factors
when choosing a site for the system:
• Near a grounded power outlet.
• Clean and dust-free.
• Stable surface free from vibration.
• Well-ventilated and away from sources of heat.
• Protected from electromagnetic fields produced by electrical
devices such as air conditioners, radio and TV transmitters, etc.
Package contents
Ensure you have the following items:
• Acer AR180 system
• Acer AR180 accessory box
If any of the above items is damaged or missing, contact your dealer
immediately.
Save the boxes and packing materials for future use.
Page 35
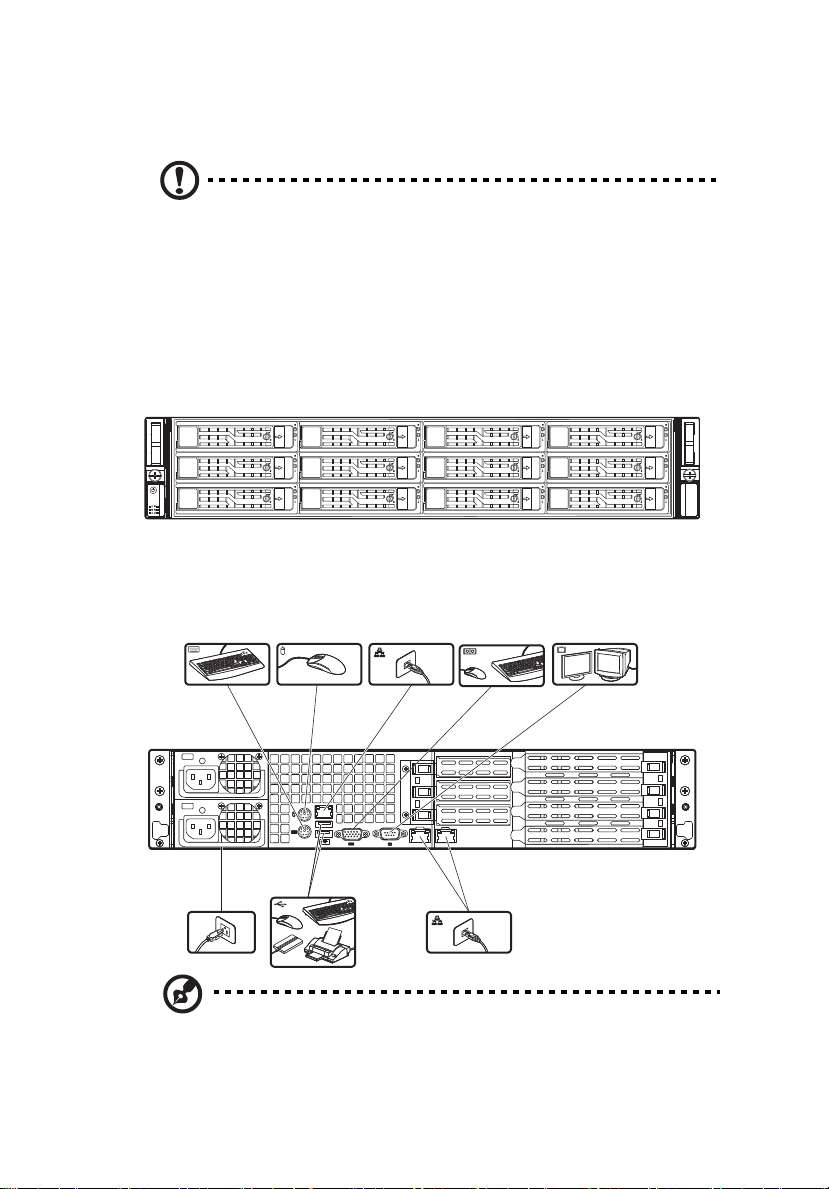
17
Connecting peripherals
Caution! The server operates on 100-240 VAC only. Do not
connect the system to an incorrect voltage source.
Refer to the illustration below for specific connection instructions on
the peripherals you want to connect to the system.
Front connections
Rear connections
Note: Consult the operating system manual for information on
how to configure the network setup.
Page 36
18
2 System setup
Turning on the system
After making sure that you have properly set up the system and
connected all the required cables, you can now power on the system.
To power on the system:
After plugging in the power cord, press the power button.
The system starts up and displays a welcome message on the monitor.
After that, a series of POST messages appears. The POST messages
indicate if the system is running well or not.
Note: If the system does not turn on or boot after pressing the
power button(s), go to the next section for the possible causes of
the boot failure.
Aside from the POST messages, you can determine if the system is in
good condition by checking if the following occurred.
• The power indicator on the front panel lights up green.
• The Num Lock, Caps Lock, and Scroll Lock indicators on the
keyboard light up.
Power-on problems
If the system does not boot after you have applied power, check
thefollowing factors that might have caused the boot failure.
• The external power cord may be loosely connected.
Check the power cord connection from the power source to the
power supply module AC input connector on the rear panel. Make
sure that the power cord is properly connected to the power
source and to the AC input connector.
• No power comes from the grounded power outlet.
Page 37
19
Have an electrician check your power outlet.
• Loose or improperly connected internal power cables.
Check the internal cable connections. If you are not confident to
perform this step, ask a qualified technician to assist you.
Warning! Make sure all power cords are disconnected from the
electrical outlet before performing this task.
Note: If you have gone through the preceding actions and the
system still fails to boot, ask your dealer or a qualified technician
for assistance.
Page 38
20
2 System setup
Configuring the system OS
Acer Smart Setup assists you to conveniently install your choice of
operating system.
To start using Smart Setup, follow the steps below.
1 Locate the Smart Setup included in the system package.
2 If an optional DVD drive is not installed in the server, connect an
external DVD drive to your system. Press the Stop/Eject button on
the DVD drive to eject the disc tray.
3 When the disc tray slides open, insert the Smart Setup DVD with
the label or title side of the disc facing upward.
Note: When handling the disc, hold it by the edges to avoid
smudges or fingerprints.
4 Gently press the disc down to make sure that it is properly
inserted.
Caution! While pressing the disc, be careful not to bend the disc
tray. Make sure that the disc is properly inserted before closing
the disc tray. Improper insertion may damage both the disc and
the CD-ROM drive.
5 Gently press the drive Stop/Eject button again to close the disc
tray.
6 On the Acer Smart Setup window, select OS Installation.
7 Follow all onscreen instructions.
For more information, refer to the Smart Setup Help file.
Note: The Windows or Linux OS disc is needed when you install
the OS with the Smart Setup.
Page 39

21
Turning off the system
There are two ways to turn off the server — via software or via
hardware. The software procedure below applies to a system running
the Windows operating system. For further operating system
shutdown procedures, refer to the related user documentation.
To turn off the system via software:
1 Press <Ctrl> + <Alt> + <Delete> on the attached keyboard or click
Start on the Windows taskbar.
2 Select Shut Down.
3 Select Shut down from the drop-down window then click on OK.
To turn off the system via hardware:
If you cannot shut down the server using the software, press and hold
the power button for at least four seconds. Quickly pressing the button
may put the server in a Suspend mode only.
Page 40

22
2 System setup
Page 41

3 System
upgrades
Page 42

24
3 System upgrades
Installation precautions
Before you install any server component, we recommend that you read
the following sections. These sections contain important ESD
precautions along with pre-installation and post-installation
instructions.
ESD precautions
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage the processor, disk drives,
expansion boards, mainboard, memory modules and other server
components. Always observe the following precautions before you
install a server component:
• Do not remove a component from its protective packaging until
you are ready to install it.
• Do not touch the component pins, leads, or circuitry.
• Components with a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) assembly should
always be laid with the assembly-side down.
• Wear a wrist grounding strap and attach it to a metal part of the
server before handling components. If a wrist strap is not
available, maintain contact with the server throughout any
procedure requiring ESD protection.
• Keep the work area free of nonconductive materials, such as
ordinary plastic assembly aids and foam packing.
Pre-installation instructions
Perform the steps below before you open the server or before you
remove or replace any component:
Warning! Failure to properly turn off the server before you start
installing components may cause serious damage. Do not attempt
the procedures described in the following sections unless you are
a qualified service technician.
1 Turn off the system and all the peripherals connected to it.
2 Unplug all cables from the power outlets.
3 Disconnect all telecommunication cables from their ports.
Page 43

25
4 Place the system unit on a flat, stable surface.
5 Open the system according to the instructions on page 34.
6 Follow the ESD precautions described in this section when
handling a server component.
Post-installation instructions
Perform the steps below after installing a server component.
1 See to it that all components are installed according to the
described step-by-step instructions.
2 Reinstall all components or cable that have been previously
removed.
3 Reinstall the top cover.
4 Reconnect the necessary cables.
5 Turn on the system.
Page 44

26
3 System upgrades
Opening the server
Caution! Before you proceed, make sure that you have turned off
the system and all peripherals connected to it. Read the “Preinstallation instructions” on page 24.
You need to open the server before you can install additional
components or access the system’s internal components. Refer to the
following sections for instructions.
Removing the top cover
Note: Observe the ESD precautions and pre-installation
instructions described on page 24.
1 Press and hold the two release buttons.
2 Slide the cover toward the rear of the chassis.
3 Lift the cover off the chassis.
4 Put the top cover aside for reinstallation later.
Installing the top cover
1 Perform the pre-installation instructions described on page 24.
Page 45

27
2 Install the top cover.
(1) Place the top cover on the chassis so that the tabs on the
cover align with the slots on the chassis.
(2) Slide the top cover toward the front of the chassis until it
is fully closed.
Page 46

28
3 System upgrades
Configuring the storage devices
The system supports up to four 3.5-inch hot-plug SAS/SATA hard disk
drives. An optional optical drive can also be added to the server.
Accessing the drive bays
Since SAS/SATA drives have hot-plug capability, you do not need to
access the inside of the chassis or power down the system to install or
replace SAS/SATA drives. Proceed to the next step for instructions.
Note: The operating system you use must have RAID support to
enable the hot-plug capability of the SATA drives.
Caution! When working around the SATA backplane, do not
touch the backplane with any metal objects and make sure no
cables touch the backplane. Also, regardless of how many SATA
drives are installed, all eight drive carriers must remain in the
chassis to maintain proper airflow.
Hard disk drive configuration guidelines
Observe these guidelines when replacing or installing a hard disk drive.
• Use only qualified SAS or SATA HDDs. To purchase a SAS or SATA
HDD, contact your local representative.
• Before removing a hard disk drive, make sure to back up all
important system files.
• Check hard disk drive status by checking the status LED indicators
on the HDD carrier.
• The hard disk drive carriers must be installed in the following
order:
Page 47

29
Determining drive status
Each HDD carrier features two status LED indicators (see page 3) to
display the hard drive status. If you are replacing a failed HDD,
determine which drive has failed by checking the hot-plug HDD status
indicators.
3.5” HDD
Description
Onboard SATA RAID
HDD present no access Off Off
HDD access Blink
R
AID add on card with SGPIO support
HDD present no access SAS: On
HDD access Blink
HDD failure On
HDD removal Off Off
HDD insertion and rebuilding Blink 1Hz
HDD locate Blink 4Hz
Blue
SATA: Off
Red
Off
Page 48
30
3 System upgrades
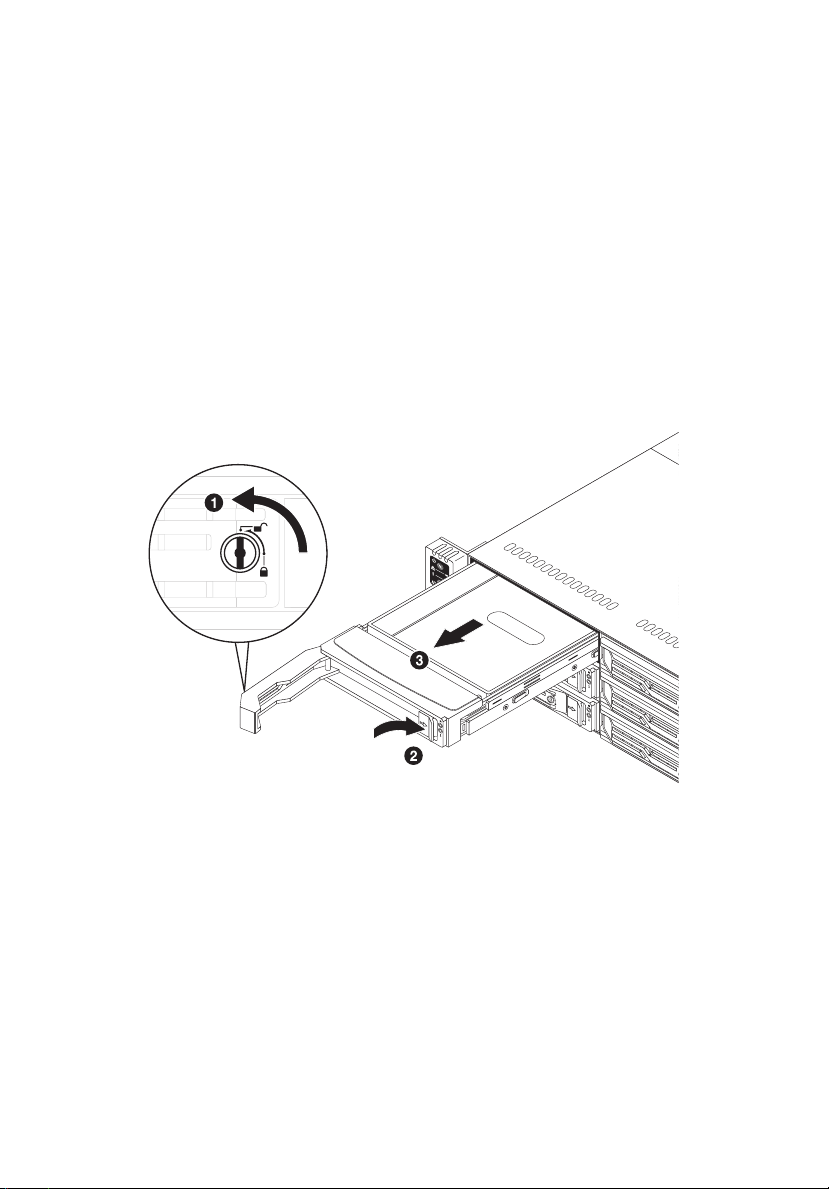
Removing and installing a 3.5” hard disk drive
Removing a 3.5” hard disk drive with carrier
1 Observe the ESD precautions described on page 24.
2 Remove the carrier with failed HDD.
3 Remove the HDD carrier.
(1) Unlock the HDD carrier latch.
(2) Slide the HDD carrier latch to release the lever.
(3) Pull the lever and slide the carrier from the chassis.
4 Observe the post-installation instructions described on page 25.
Installing a 3.5” hard disk drive with carrier
1 Slide the HDD carrier all the way into the drive bay.
2 Use the lever to push the HDD carrier until it locks into place, then
close the HDD carrier lever.
Page 49
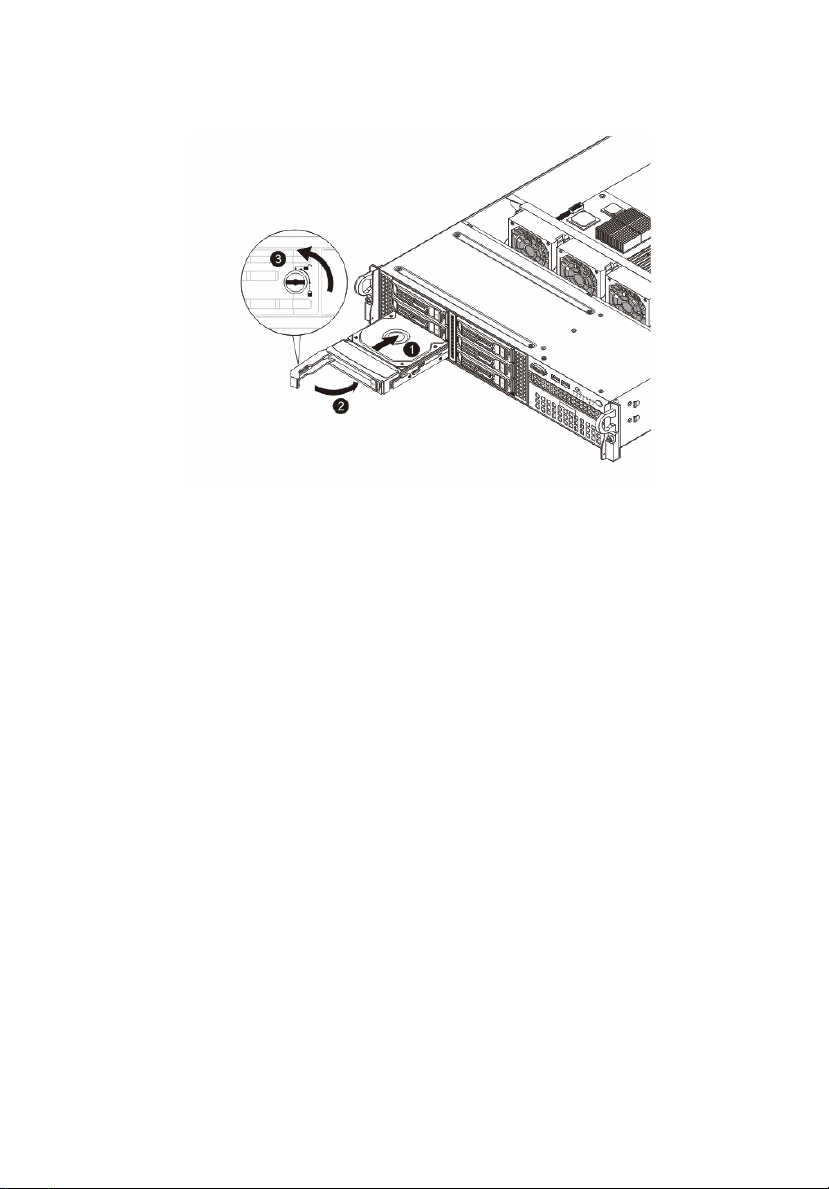
31
3 Lock the HDD carrier.
4 Observe the post-installation instructions described on page 25.
Page 50
32
3 System upgrades
Installing and removing the power supply
WARNING! To reduce the risk of personal injury or
damage to the equipment, the installation of power
supply modules should be referred to individuals who
are qualified to service server systems and are trained
to deal with equipment capable of generating
hazardous energy levels.
WARNING! To reduce the risk of personal injury from
hot surfaces, observe the thermal labels on each power
supply module. You can also consider wearing
protective gloves.
WARNING! To reduce the risk of personal injury from
electric shock hazards, do not open the power supply
modules. There are no serviceable parts inside the
module.
Caution! Electrostatic discharge can damage electronic
components. Make sure that you are properly
grounded before handling a power supply module.
Caution! Due to chassis airflow disruption, a power
supply bay should never be vacant for more than two
minutes when the server is powered on. Exceeding five
minutes might cause the system to exceed the
maximum acceptable temperature and possibly
damage the system components.
Caution! The power supply is only hot-pluggable if you
have a redundant system with two power supplies
installed. If you only have one power supply installed,
before removing or replacing the power supply, you
must first take the server out of service, turn off all
peripheral devices connected to the system, turn off
the system by pressing the power button, and unplug
the AC power cord from the system or wall outlet.
The server has a single 720-Watt power supply, capable of operating at
100 - 240 input volts.
Page 51
33
Power supply failure
If the power supply unit fails, the system will shut down and you will
need to replace the power supply unit. Replacement units can be
ordered directly from Acer.
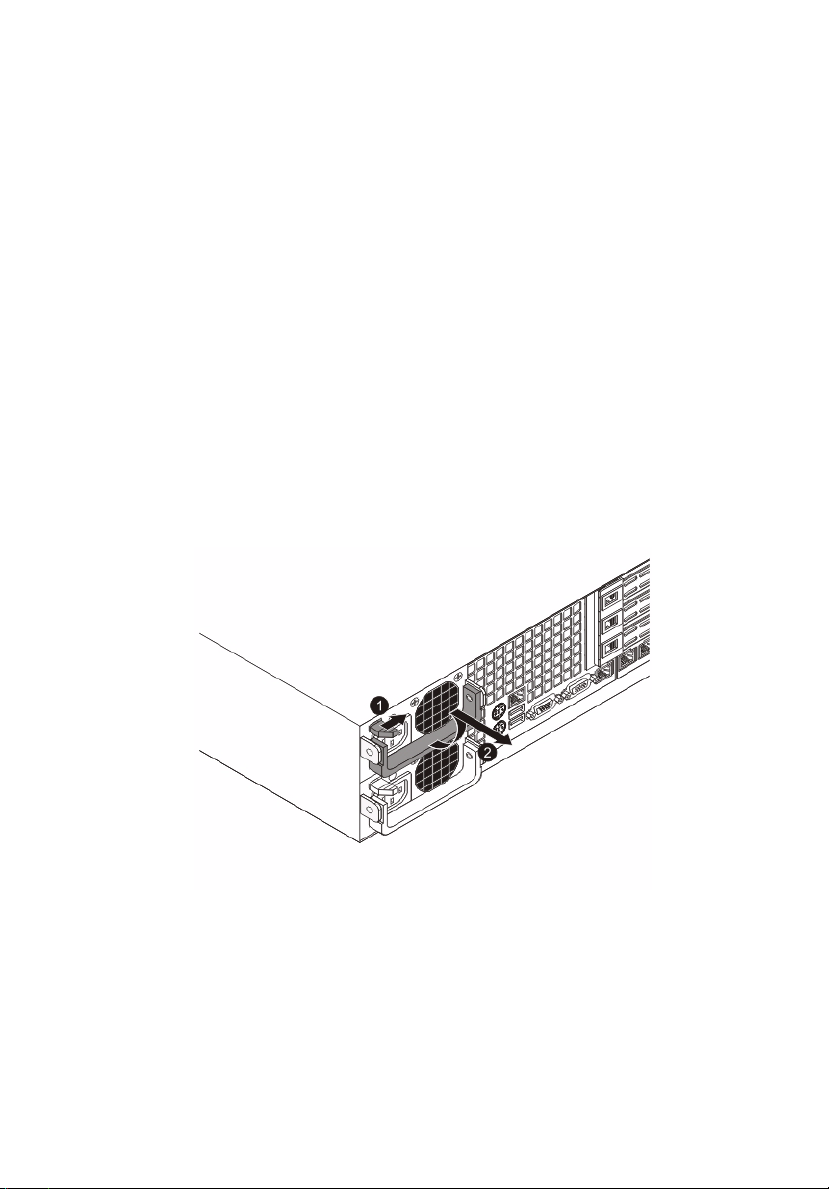
Replacing the power supply
Press the main power button on the front of the chassis and then
unplug the AC power cord to completely remove power from the
system before removing the power supply.
1 Remove the AC power cord from the power supply.
2 Remove the power supply module.
(1) Press the power supply release latch to release the power
supply module from the chassis.
(2) Use the handle to pull the failed power supply module
out of the server.
3 Install a new power supply module with the exact same model.
Page 52
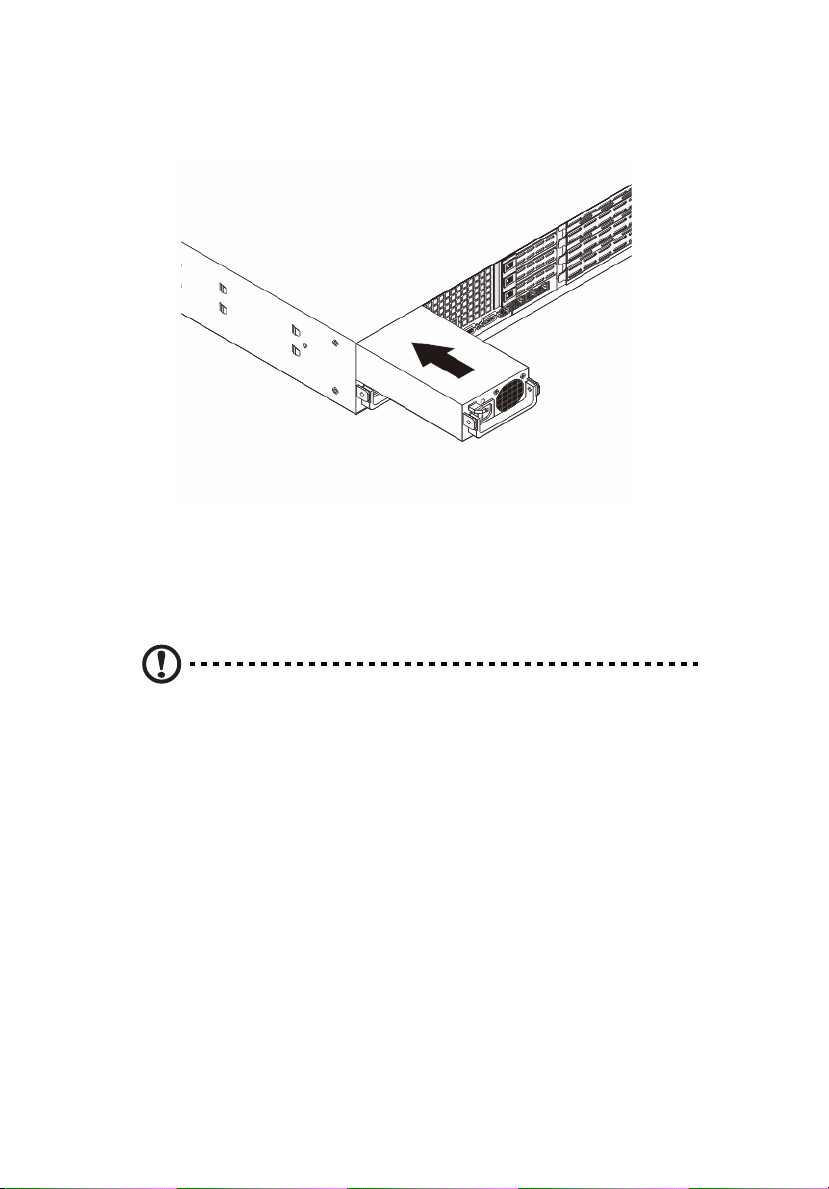
34
4 Push the new power supply module into the power bay until it
clicks into place.
5 Plug the AC power cord back into the module and power up the
server by pushing the power on button.
3 System upgrades
Removing and installing the air duct
Caution! Always operate your server with the air duct installed to
ensure reliable and continued operation.
You need to remove the air duct to perform the following procedures:
• Removing and installing a processor
• Removing and installing a memory module
Removing the air duct
1 Perform the pre-installation instructions described on page 24.
2 Lift the air duct from the chassis.
Installing the air duct
1 Perform the pre-installation instructions described on page 24.
Page 53

35
2 Place the air duct on the chassis so that the tabs on the air duct
align with the slots on the chassis.
Caution! Do not pinch or unplug cables that may be near or under
the air duct.
3 Observe the post-installation instructions described on page 25.
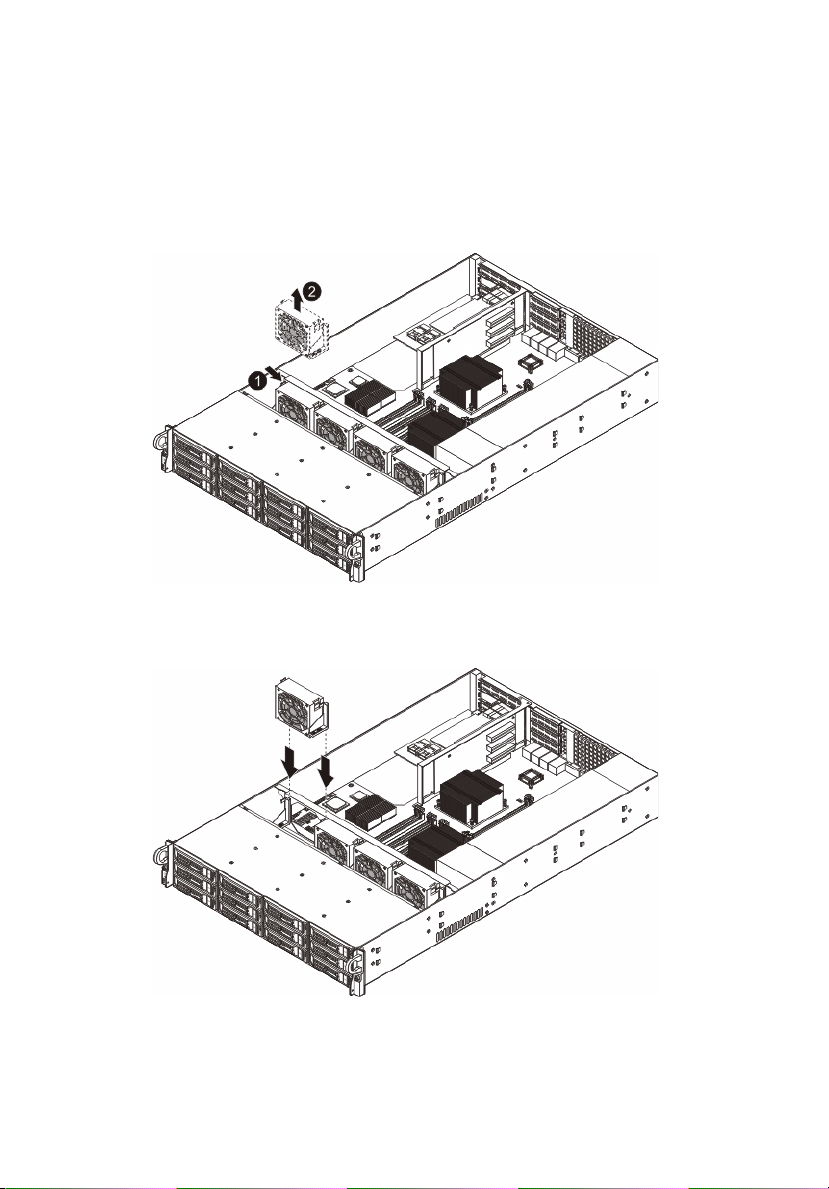
Replacing a system fan
The system has four high-performance PWM fans to provide the
cooling for the system. Fan speed may be controlled by a setting in
BIOS (see Chapter 4).
To replace a fan module:
1 Perform the pre-installation instructions described on page 24.
Warning! The system fan becomes very hot when the system is on.
Allow it to cool off first before handling.
Page 54
36
3 System upgrades
2 Remove the top chassis cover while the system is still running to
determine which of the fans has failed.
3 Remove the fan module.
(1) Push the fan clip handles inwards.
(2) Pull the fan up and away from the chassis.
4 Install the new fan module.
(1) Insert the new fan into the chassis.
(2) Push downwards until firmly seated.
5 Observe the post-installation instructions described on page 25.
Page 55
37
Replacing the processor and heatsink
Notes:
• Always connect the power cord last and always remove it before
adding, removing or changing any hardware components. Make
sure that you install the processor into the CPU socket before you
install the CPU heatsink.
• If you buy a CPU separately, make sure that you use an Intelcertified multidirectional heatsink and fan only.
• Make sure to install the serverboard into the chassis before you
install the CPU heatsinks.
• When receiving a serverboard without a processor pre-installed,
make sure that the plastic CPU socket cap is in place and none of
the socket pins is bent; otherwise, contact your retailer
immediately.
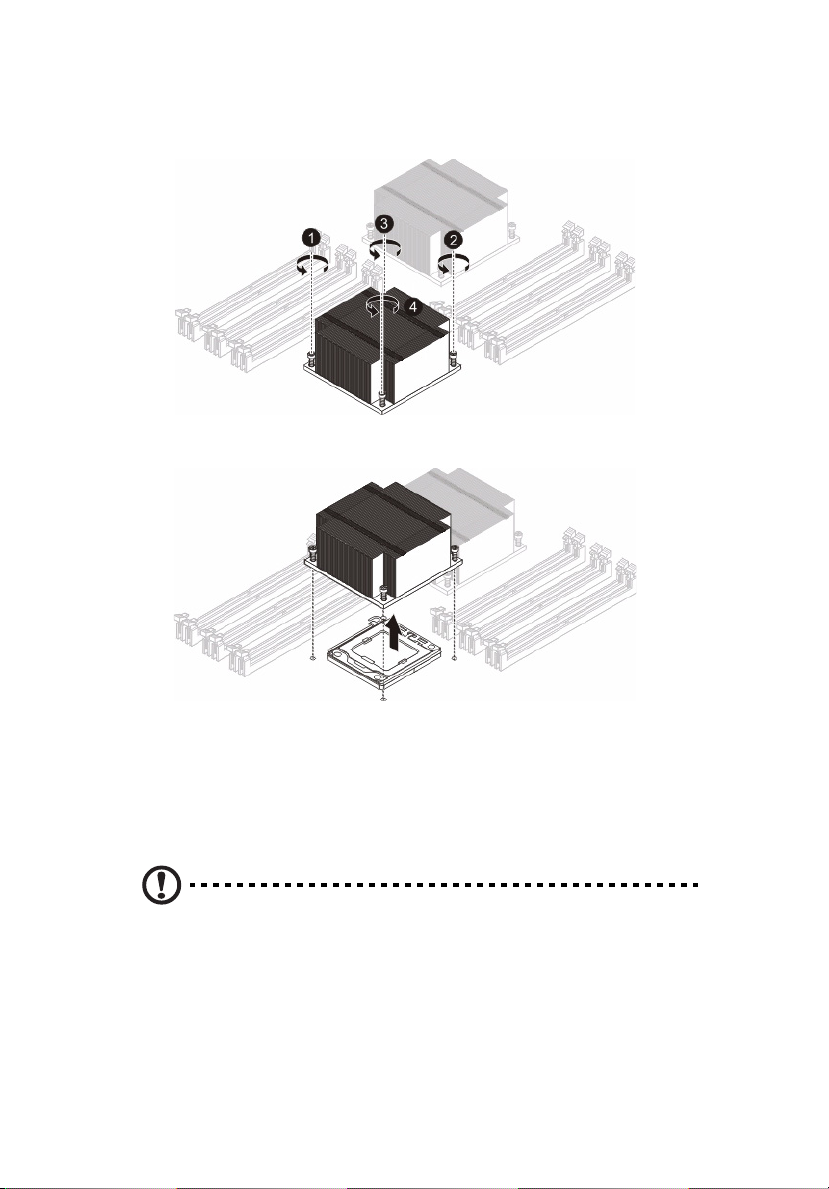
Removing the heatsink
Warning! We do not recommend that the CPU or the heatsink be
removed. However, if you do need to uninstall the heatsink,
please follow the instructions below to prevent damage to the
CPU or the CPU socket.
1 Remove power from the system and unplug the AC power cord
from the power supply.
2 Observe the pre-installation instructions on page 24.
3 Remove the air duct. See page 34.
4 Disconnect the heatsink fan wires from the CPU fan header.
Page 56
38
5 Using a screwdriver, loosen the heatsink screws from the
mainboard.
6 Lift the heat sink away from the processor.
3 System upgrades
7 Lay down the heat sink in an upright position — with the thermal
patch facing upward. Do not let the thermal patch touch the work
surface.
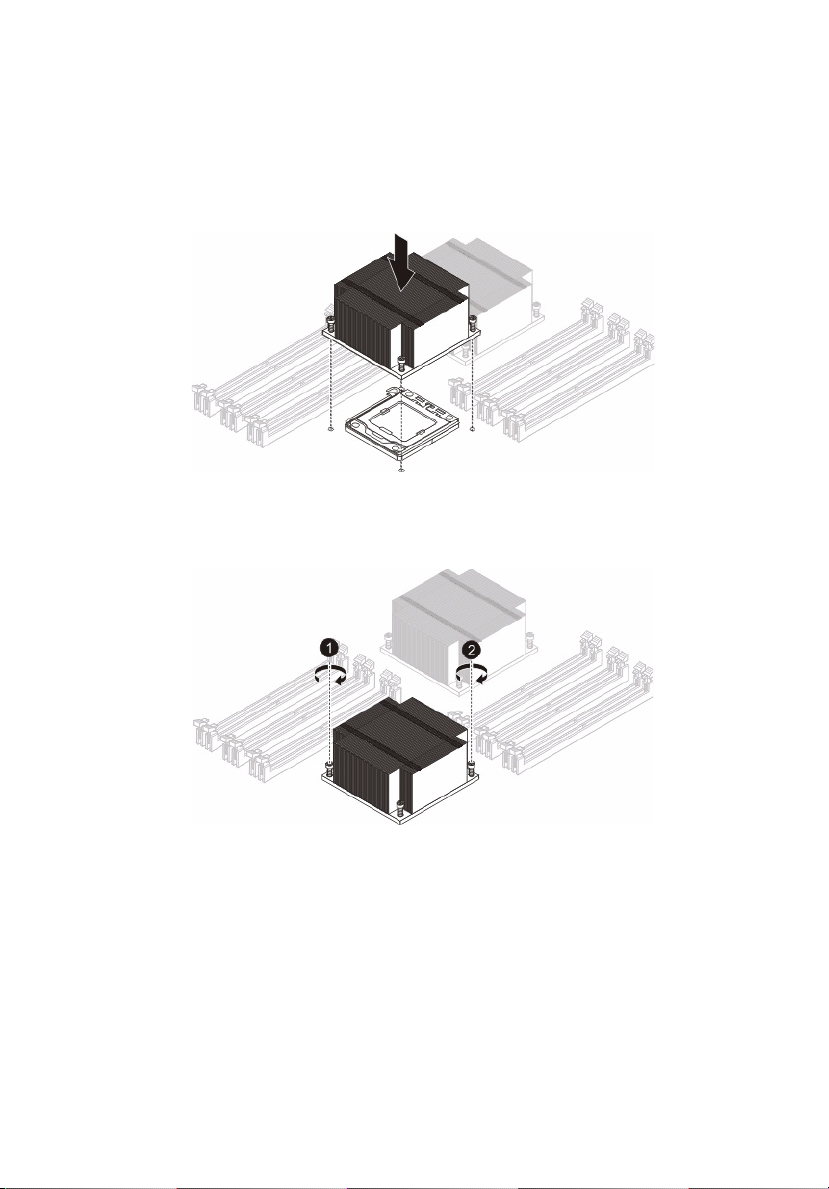
Installing a heatsink
Caution! The heat sink has a thermal interface material (TIM) on
the underside. Use caution so that you do not damage the TIM. If
a protective film is installed on the TIM, remove it.
1 Remove power from the system and unplug the AC power cord
from the power supply.
Page 57
39
2 Do not apply any thermal grease to the heatsink or the CPU die;
the required amount has already been applied.
3 Place the heatsink on top of the CPU so that the four mounting
holes are aligned with those on the (preinstalled) heatsink
retention mechanism.
4 Screw in two diagonal screws (i.e. the #1 and the #2 screws) until
just snug. Do not fully tighten the screws or you may damage the
CPU.)
5 Add the two remaining screws then finish the installation by fully
tightening all four screws.
6 Install the air duct. See page 34.
7 Observe the post-installation instructions on page 25.
Page 58

40
3 System upgrades
Upgrading the processor
Processor configuration guidelines
The server supports two LGA 1366 processor sockets supporting dualcore or quad-core Intel Xeon processors. The supplied processors may
be upgraded or additional processors installed.
Observe the following guidelines when replacing or installing a
processor.
• Processor 1 socket must always be populated. If no processor is
installed in this socket, the system will fail to boot.
• Before removing a processor, make sure to back up all important
system files.
• When installing a second processor, make sure it has same
stepping and frequency specifications as the default processor.
• Handle the processor and the heat sink carefully. Damage to either
may prevent the system from functioning properly.
Replacing the processor
Warning! The processor becomes very hot when the system is on.
Allow it to cool off first before handling.
1 Remove the heatsink (see “Removing the heatsink” on page 37).
2 Release then lift the load lever.
3 Open the retention plate to expose the socket body.
Page 59
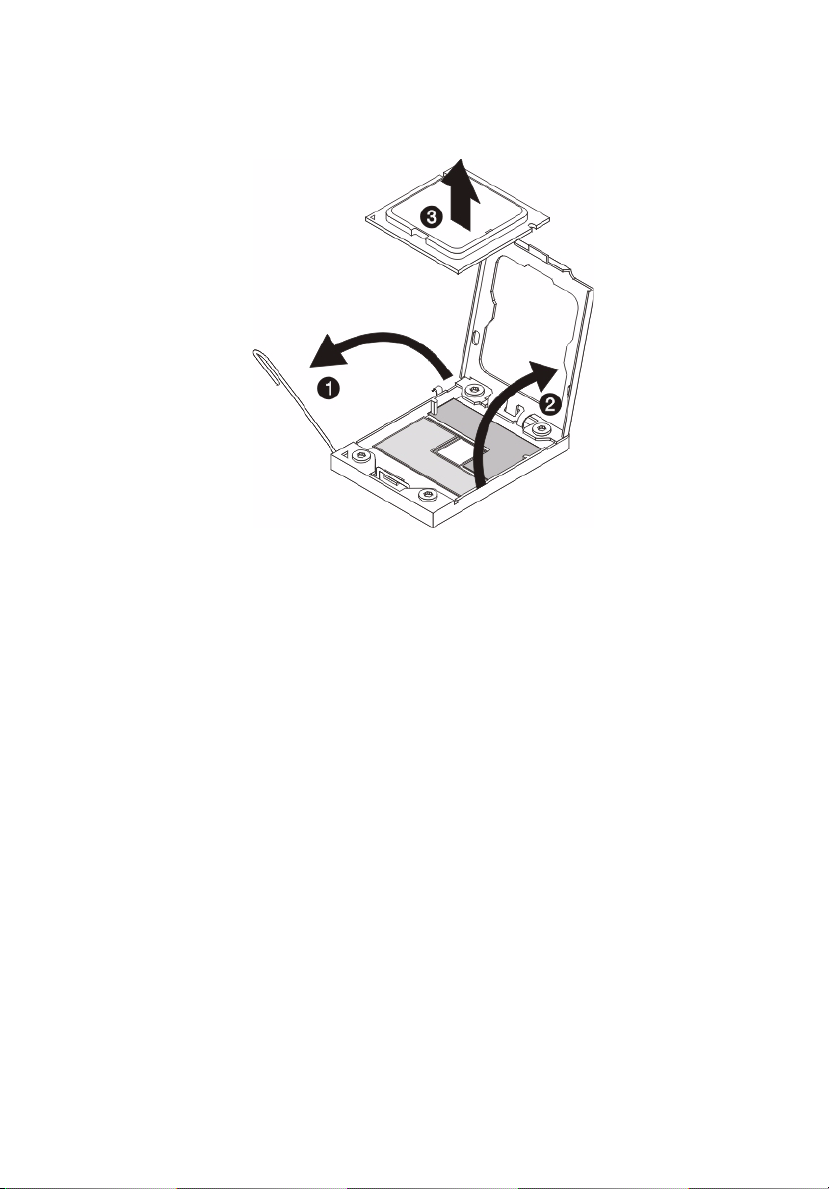
41
4 Grasp the installed processor by its edges and lift it out of its
socket.
5 Store the old processor inside an anti-static bag.
6 Remove the new processor from its protective packaging.
7 Install the new processor.
(1) Hold the processor by its edges. Make sure the alignment
tabs on the socket fit the two notch located on the edge
of the processor. The pins are keyed in such a way that
you cannot install the processor in the wrong orientation
without bending the pins.
(2) Insert the new processor in the socket.
(3) Close the retention plate.
Page 60

42
(4) Engage the load lever back into place.
8 Apply the thermal interface material.
(1) Use an alcohol pad to wipe off the old thermal grease
from both the heat sink and the processor socket
retention plate.
(2) Apply a thin layer of an approved thermal interface
material before installing the heat sink.
3 System upgrades
Make sure that only a very thin layer is applied so that
both contact surfaces are still visible.
9 Install the heatsink (see “Installing a heatsink” on page 38).
10 Observe the post-installation instructions described on page 25.
11 Repeat the steps above to replace the second processor.
Page 61

43
Upgrading the system memory
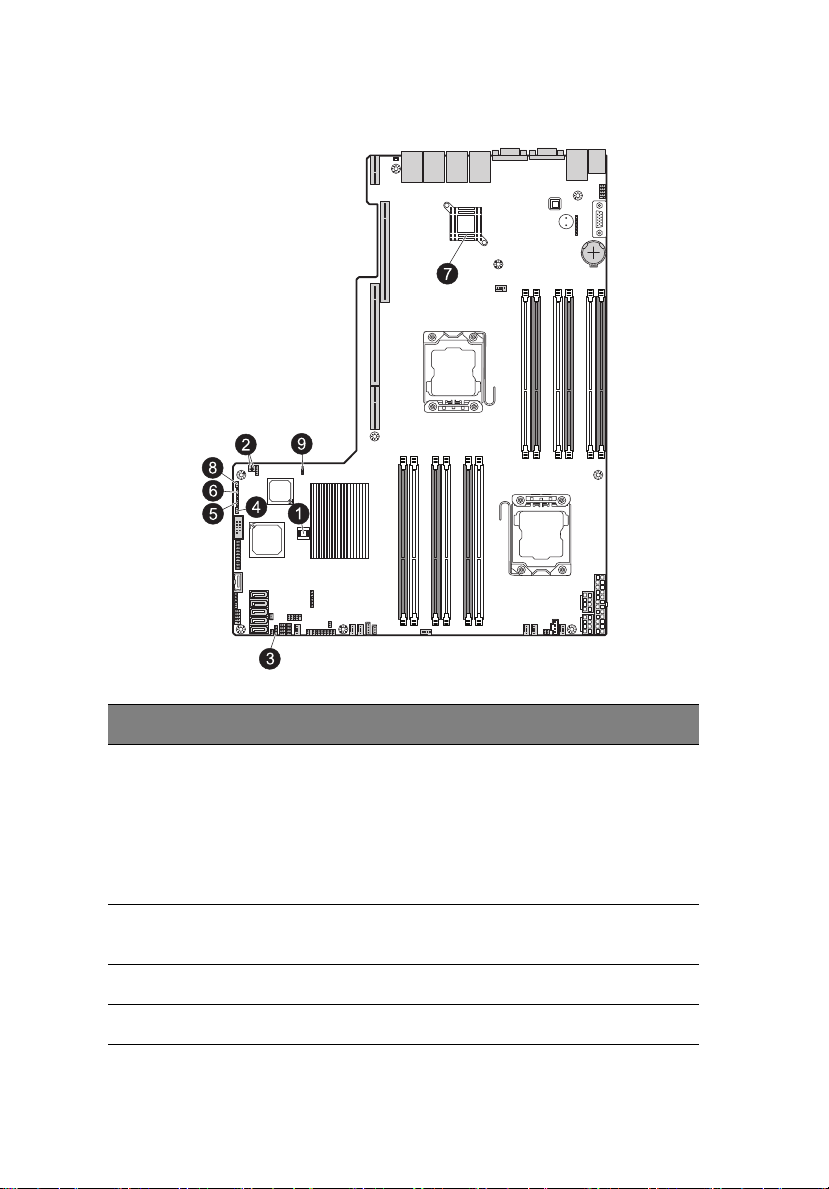
System memory interface
Each processor has three memory channels (1, 2 and 3 ) and each
channel has two slots - A (PxDIMM1A, 2A, 3A in blue) and B
(PxDIMM1B, 2B, 3B in black). So, the system has a total of twelve
memory slots. The memory slots support DDR3-1333 registered/
unbuffered ECC memory modules.
The folllowing illustration shows the processor 1 memory slots (1) and
processor 2 memory slots (2).
Independent mode
• For all memory modes, slot A in each channel should be populated
first and then slot B. If slot A is empty, then slot B cannot be used.
• For a single-processor server configuration, install the processor to
CPU1 socket and the memory modules in slots P1DIMM 1A to
P1DIMM 3B.
• If there is a processor installed in CPU2 socket, the system will
enable the slots P2DIMM 1A to P2DIMM 3B.
• It is recommended to install the DIMM modules in the following
sequence:
For single processor
• Populate slot 1A first, followed by slots 2A, 3A,1B, 2B and 3B.
• The memory slots for processor 2 are not available.
Page 62

44
3 System upgrades
For dual processors
• Populate DIMM slots 1A of each CPU first, followed by slots
2A, 3A,1B, 2B and 3B.
• Install DIMM modules of the same type, size, and manufacturer in
the same colored DIMM slots.
Memory population for independent mode
Single processor configuration
Single processor
Processor 1 P1DIMM slots
Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3
Configuration 1B 1A 2B 2A 3B 3A
AX
BXX
CXXX
DXXXX
E XXXXXX
Dual processor configuration
Dual processors
Processor 1 P1DIMM slots Processor 2 P2DIMM slots
Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3 Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3
Configuration 1B 1A 2B 2A 3B 3A 1B 1A 2B 2A 3B 3A
AX X
BXXX
CXX XX
D XXXXXX
E XXXX XXXX
F XXXXXX X X X
G XXXXXXXXXXXX
Notes: 1. Place DIMMs in “X” location.
2. DIMM population must correspond to the above tables.
3. DIMM modules support 1 GB, 2 GB, 4 GB and 8 GB
DIMMS.
4. The size of each DIMM must be the same across the
configuration.
5. Do not mix UDIMMs with RDIMMs.
Page 63

45
Mirroring mode
• In mirroring mode, the memory contains a primary image and a
copy of the primary image. Therefore, the effective size of
memory is redcued by at least one-half.
• Channel 3 has no function and cannot be populated in this mode.
• Follow the population rules described in independent mode.
• DIMM modules installed in channels 1 and 2 must be identical —
1A and 2A should be the same type, size and manufacturer. 1B and
2B memory should be the same type, size and manufacturer.
However, it is not necessary for slot A to have the same memory
module as slot B within a channel.
• The same rule applies to processor 2.
Memory population for lockstep mode
Single processor configuration
Single processor
Processor 1 P1DIMM slots
Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3
Configuration 1B 1A 2B 2A 3B 3A
AXXNANA
BXXXXNANA
Dual processor configuration
Dual processors
Processor 1 P1DIMM slots Processor 2 P2DIMM slots
Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3 Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3
Configuration 1B 1A 2B 2A 3B 3A 1B 1A 2B 2A 3B 3A
A X X NANA NANA
B X XNANA X XNANA
C X X X X NA NA X X NA NA
D X X X X NA NA X X X X NA NA
Notes: 1. Place DIMMs in “X” location.
2. DIMM population must correspond to the above tables.
3. DIMM modules support 1 GB, 2 GB, 4 GB and 8 GB
DIMMS.
4. The size of each DIMM must be the same across the
configuration.
5. Do not mix UDIMMs with RDIMMs.
Page 64
46
3 System upgrades
Lockstep mode
• In lockstep channel mode, each memory access is a 128-bit data
access that spans Channel 1 and Channel 2. This is done to support
SDDC for DRAM devices with 8-bit wide data ports. The same
address is used on both channels such that an address error on any
channel is detectable by ECC. Lockstep Channel mode is the only
RAS mode that supports x8 SDDC.
• Channel 3 has no function and cannot be populated in this mode.
• Follow the population rules described in independent mode.
• DIMM modules installed in channels 1 and 2 must be identical —
1A and 2A should be the same type, size and manufacturer. 1B and
2B memory should be the same type, size and manufacturer.
However, it is not necessary for slot A to have the same memory
module as slot B within a channel.
• The same rule applies to processor 2.
Memory population for lockstep mode
Single processor configuration
Single processor
Processor 1 P1DIMM slots
Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3
Configuration 1B 1A 2B 2A 3B 3A
AXXNANA
BXXXXNANA
Dual processor configuration
Dual processors
Processor 1 P1DIMM slots Processor 2 P2DIMM slots
Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3 Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3
Configuration 1B 1A 2B 2A 3B 3A 1B 1A 2B 2A 3B 3A
A X X NANA NANA
B X XNANA X XNANA
C X X X X NA NA X X NA NA
D X X X X NA NA X X X X NA NA
Notes: 1. Place DIMMs in “X” location.
2. DIMM population must correspond to the above tables.
3. DIMM modules support 1 GB, 2 GB, 4 GB and 8 GB
DIMMS.
Page 65
47
4. The size of each DIMM must be the same across the
configuration.
5. Do not mix UDIMMs with RDIMMs.
Sparing mode (only supported on Intel Xeon
Processor 5600 Series CPUs)
• In this mode, if the system detects degrading memory and did not
crash, the data in the failed channel will be copied to the spare
channel. The failed channel is then isolated and the spare channel
becomes active. However, any uncorrectable error that happens
before the isolation will still cause the system to stop normal
operation.
• Channel 3 is the spare channel. Therefore, the effective size will be
reduced by one-third.
• Follow the population rules described in the independent mode.
• Sparing mode requires that all three channels use identical DIMMs.
1A, 2A and 3A should be the same type, size and manufacturer,
likewise for 1B, 2B and 3B. The same rule applies to processor 2.
• Intel Xeon Processor 5500 Series CPU does NOT support the
memory sparing mode.
Memory population for sparing mode
Single processor configuration
Single processor
Processor 1 P1DIMM slots
Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3
Configuration 1B 1A 2B 2A 3B 3A
AXXX
B XXXXXX
Dual processor configuration
Dual processors
Processor 1 P1DIMM slots Processor 2 P2DIMM slots
Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3 Channel 1 Channel 2 Channel 3
Configuration 1B 1A 2B 2A 3B 3A 1B 1A 2B 2A 3B 3A
AXXX
B XXXXXX
C XXXXXX X X X
D XXXXXXXXXXXX
Page 66
48
Density
Rank
Bit Organization
Speed
3 System upgrades
Notes: 1. Place DIMMs in “X” location.
2. DIMM population must correspond to the above tables.
3. DIMM modules support 1 GB, 2 GB, 4 GB and 8 GB
DIMMS.
4. The size of each DIMM must be the same across the
configuration.
5. Do not mix UDIMMs with RDIMMs.
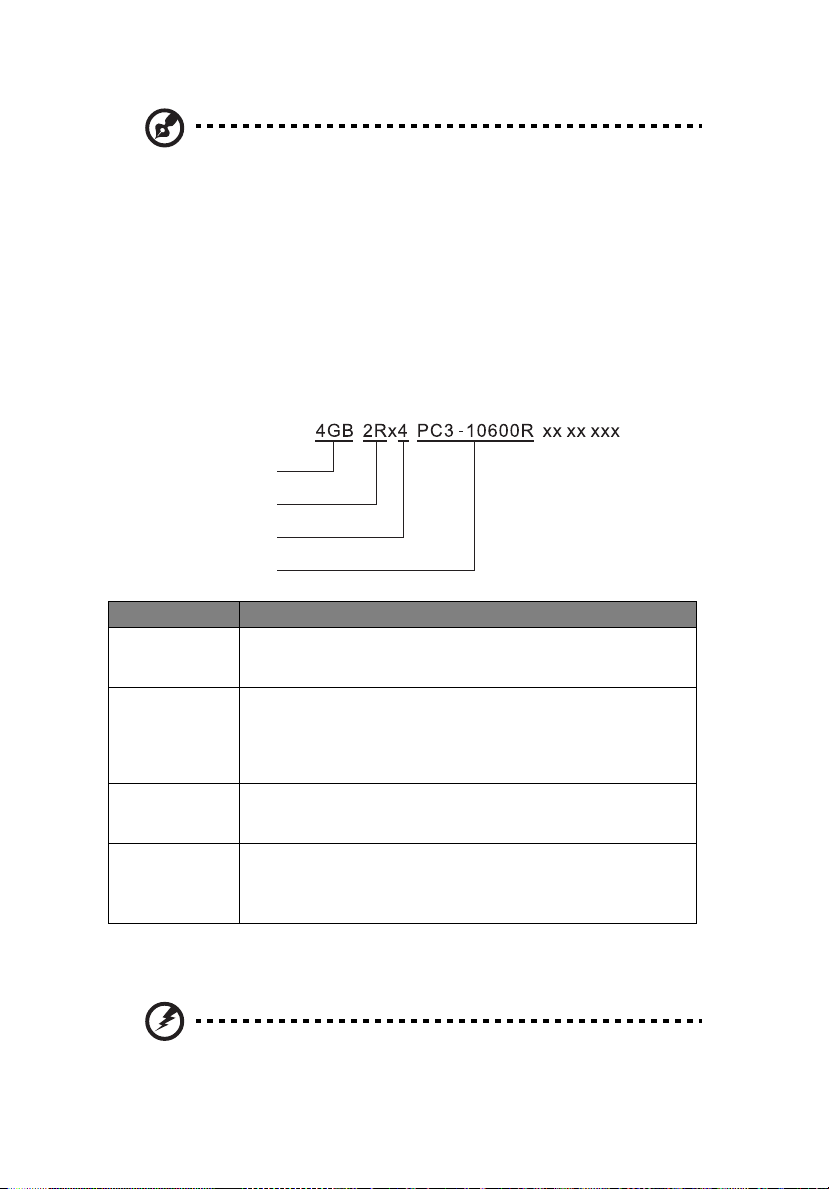
Memory identification
Generally, there is memory information printed on the label of each
DIMM module. Different vendors may have different formats but the
convention is as follows: :
Item Description
Density 1GB, 2GB,4GB,8GB.
Rank 1R = Single Rank
Bit
Organization
Speed PC3 - 6400 => DDR3- 800
Intel Xeon Processor 5500 Series CPU supports DIMM organized by
1Gb or 2Gb DRAM chips.
2R = Dual Rank
4R = Quad Rank
Note: If quad rank DIMM is used, a maximum of only two DIMMs
per channel can be supported.
This platform supports x4 and x8.
Note: It is not recommend to mix DIMMs with different bit
organizations in one system.
PC3 - 8500 => DDR3- 1066
PC3 - 10600 => DDR3- 1333
PC3 - 12800 => DDR3- 1600
Installing a memory module:
Warning! Memory of the identical size, speed, and organization
must be installed in the same colored DIMM slots.
Page 67
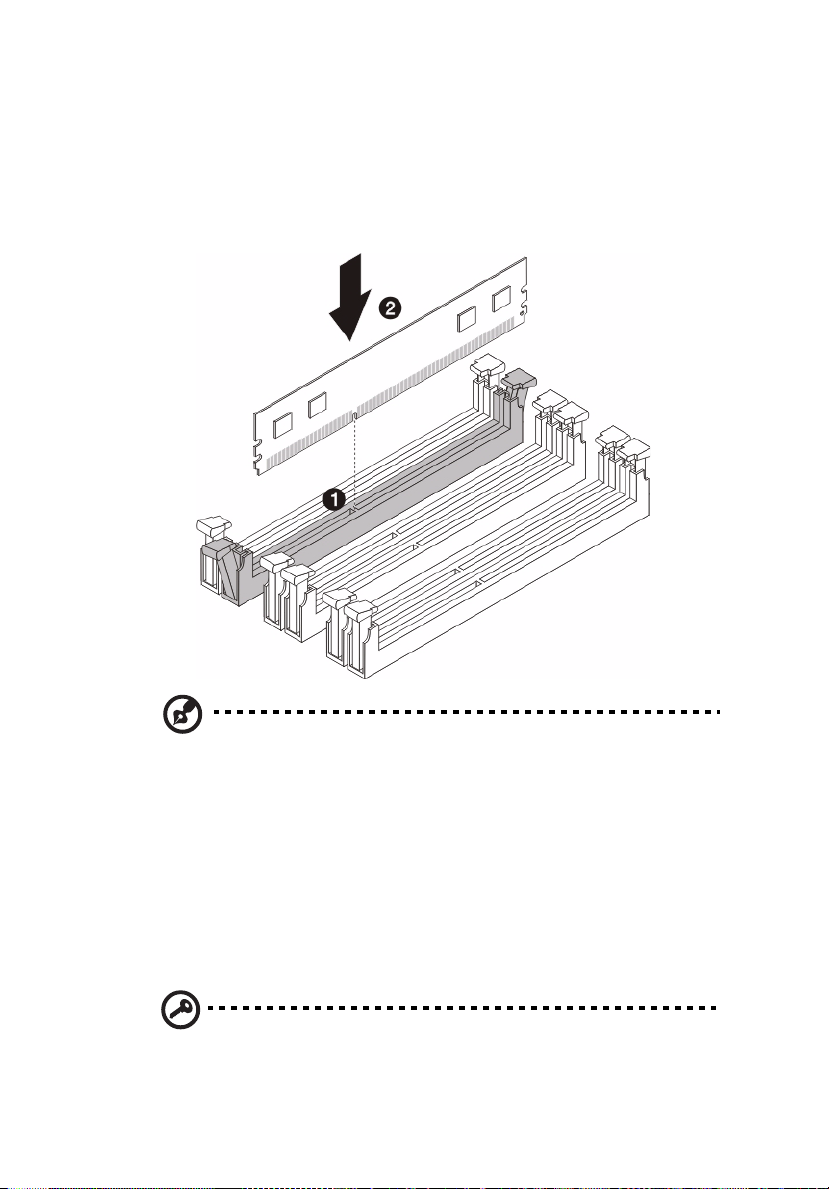
49
1 Observe the pre-installation instructions on page 24.
2 Locate the DIMM slot on the mainboard.
3 Install the memory module.
a Align then insert the DIMM into the socket (1).
b Push the DIMM to the socket until the retaining clips snap inward (2).
Note: The DIMM slot is slotted to ensure proper installation. If you
insert a DIMM but it does not fit easily into the socket, you may
have inserted it incorrectly. Reverse the orientation of the DIMM
and insert it again.
4 Observe the post-installation instructions described on page 25.
5 Reconfigure the system memory. See “To reconfigure the system
memory” section on page 50 for more information.
Removing a memory module:
Important: Before removing any DIMM from the mainboard,
make sure to create a backup file of all important data.
Page 68
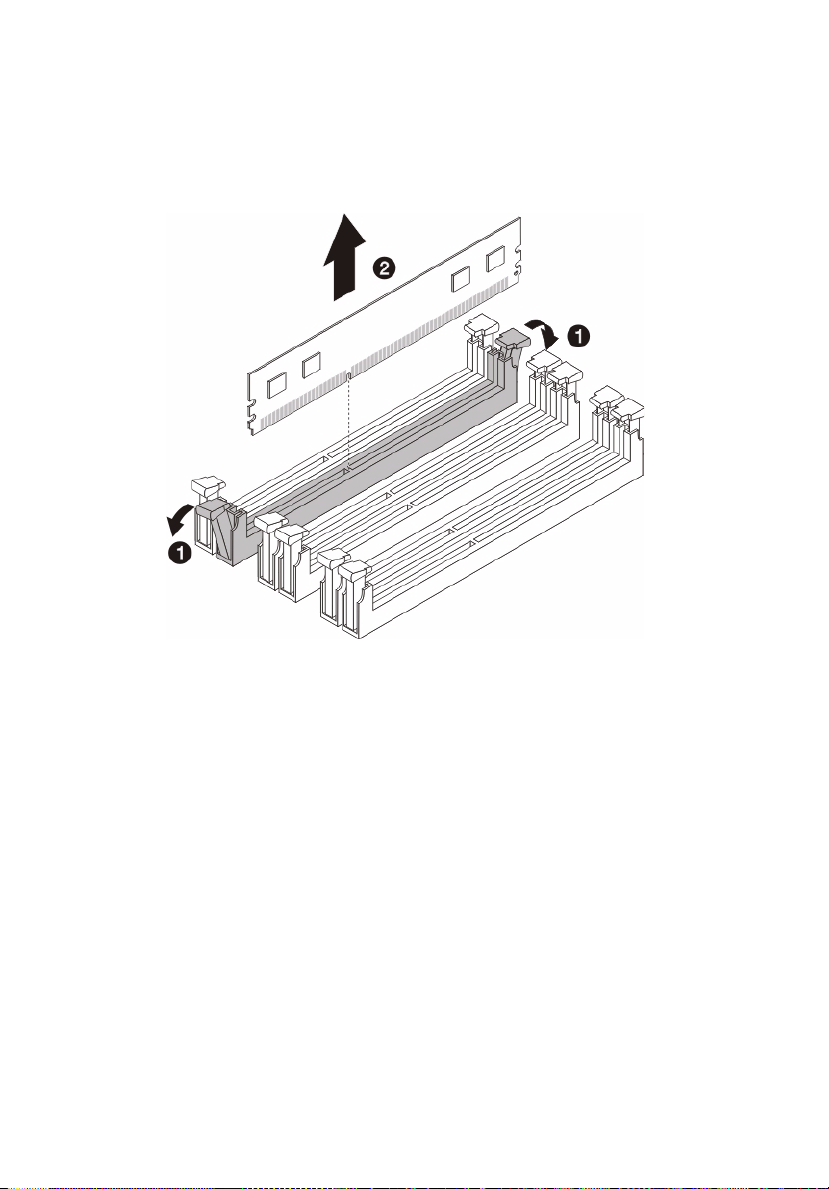
50
3 System upgrades
1 Remove the memory module.
a Press the holding clips on both sides of the DIMM slot outward to
release the DIMM (1).
b Gently pull the DIMM upward to remove it from the DIMM slot (2).
2 If you intend to install a new memory module, refer to the
previous section.
To reconfigure the system memory:
The system automatically detects the amount of memory installed. Run
the BIOS setup to view the new value for total system memory and
make a note of it.
Page 69
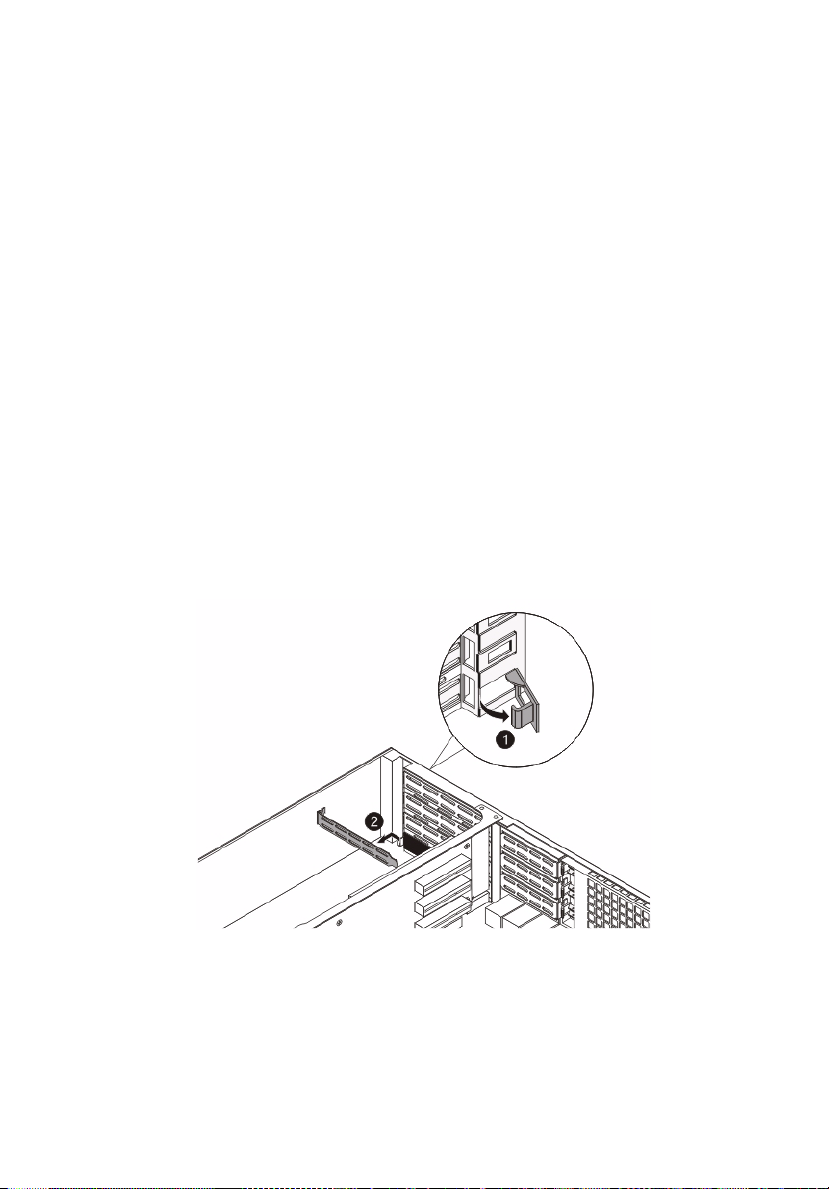
51
Installing an expansion card
Your server has a preinstalled riser card designed specifically for use in
the 2U rackmount chassis. Depending on the type of riser card
installed, you can install the following expansion cards:
• Left-side riser for 2U server (default in barebone)
• 8-port 3Gb/s SAS RAID
• Flex I/O Adapter
• Full height 1 x PCI-E x16 connector (w/ Gen2 x8 link)
• 2 x Full height 2 PCI-E x8 connector (w/ Gen2 x4 link)
• Right-side riser for 2U server (length under 5.6 inches)
• Low profile 3 PCI-E x8 connectors (w/ Gen2 x4 link)
Installing a SAS card
1 Observe the pre-installation instructions on page 24.
2 Unclip the restraining latch and open in the direction shown
below (1).
3 Remove the slot shield (2).
Page 70
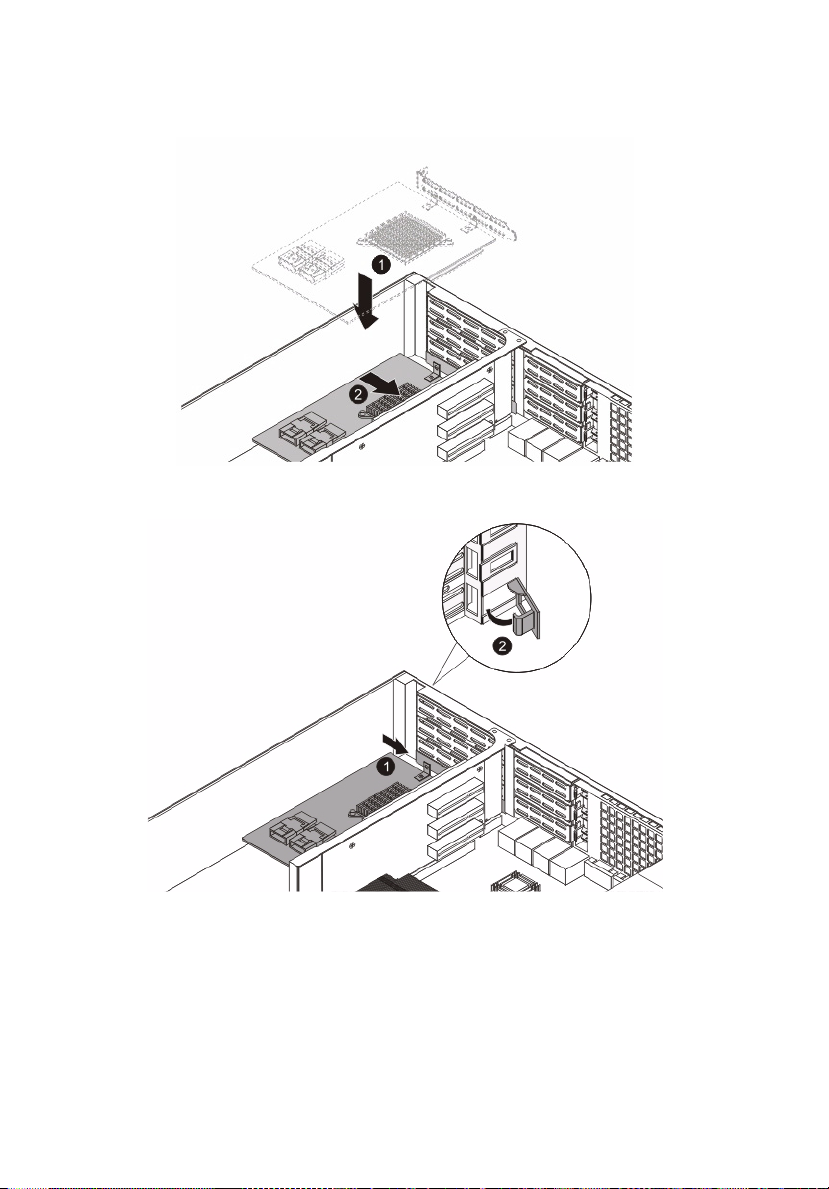
52
4 Insert the card.
5 Close the restraining latch.
3 System upgrades
6 Connect the appropriate cables to the card.
7 Observe the post-installation instructions on page 25.
Installing the rear SAS card
1 Observe the pre-installation instructions on page 24.
Page 71
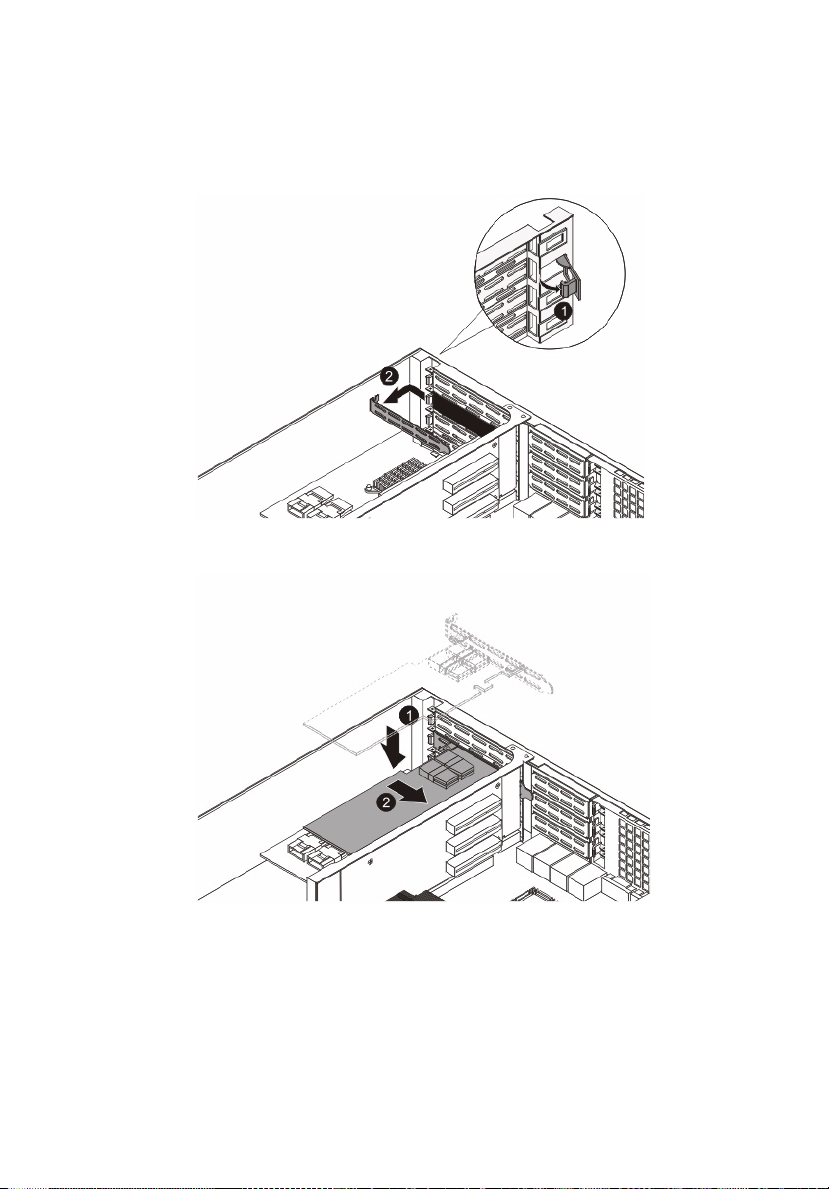
53
2 Unclip the restraining latch and open in the direction shown
below (1).
3 Remove the slot shield (2).
4 Insert the card.
Page 72
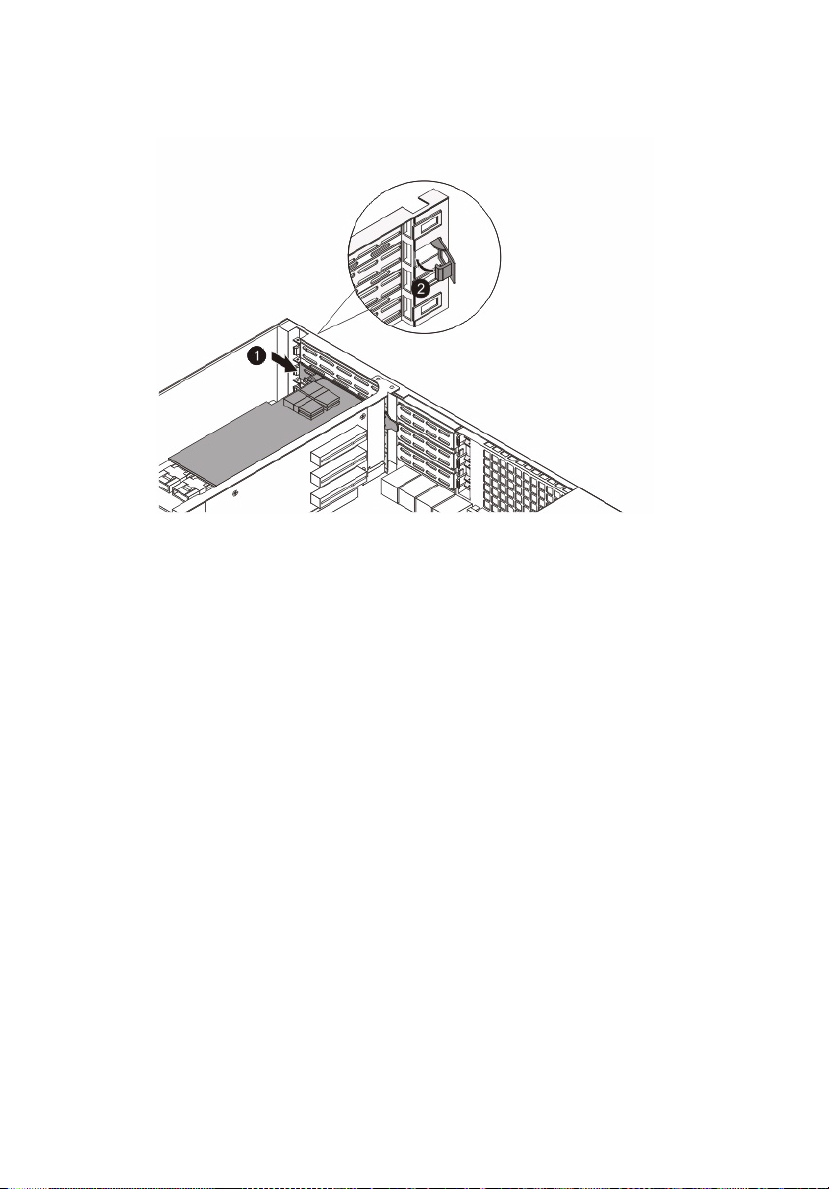
54
5 Close the restraining latch.
6 Connect the appropriate cables to the card.
7 Observe the post-installation instructions on page 25.
3 System upgrades
Installing the right riser card
Perform the following steps:
1 Observe the pre-installation instructions on page 24.
2 Unclip the restraining latch and open in the direction shown
below.
Page 73
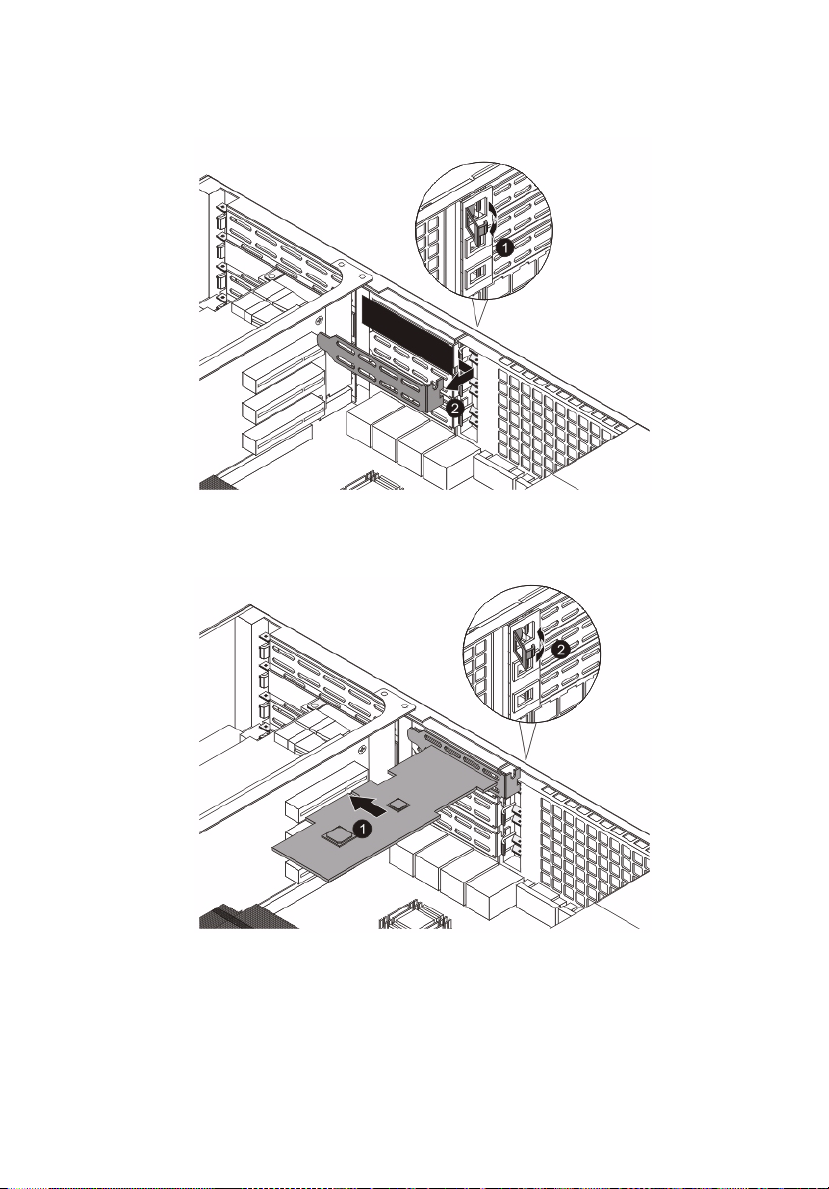
55
3 Remove the PCI slot shield.
4 Insert the add-on card into the riser card.
5 Close the restraining latch.
6 Connect the appropriate cables to the card.
7 Observe the post-installation instructions on page 25.
Page 74

56
3 System upgrades
Page 75

4 System
BIOS
Page 76

58
4 System BIOS
Introduction
This chapter describes the BIOS Setup Utility for your server. The AMI
ROM BIOS is stored in a Flash EEPROM and can be easily updated.
This chapter describes the basic navigation of the BIOS Setup Utility
setup screens.
The BIOS setup utility
To enter the BIOS Setup Utility, press the <F2> key while the system is
booting up.
Each main BIOS menu option is described in this manual. The Main
BIOS setup menu screen has two main frames. The left frame displays
all the options that can be configured. Grayed-out options cannot be
configured. Options in blue can be configured by you.
The right frame displays the key legend. Above the key legend is an
area reserved for a text message. When an option is selected in the left
frame, it is highlighted in white. Often a text message will accompany
it.
Note: the BIOS has default text messages built in. Acer retains the
option to include, omit or change any of these text messages.
The BIOS setup utility uses a key-based navigation system called
hotkeys. Most of the BIOS setup utility hotkeys can be used at any time
during the setup navigation process. These keys include <F1>, <F10>,
<Enter>, <Esc> and arrow keys.
Changing configuration data
The configuration data that determines the system parameters may be
changed by entering the BIOS setup utility. This setup utility can be
accessed by pressing <F2> at the appropriate time during system boot.
Starting the setup utility normally, the only visible Power-On Self-Test
(POST) routine is the memory test. As the memory is being tested, press
the <F2> key to enter the BIOS setup utility main menu. From the main
menu, you can access the other setup screens. A BIOS identification
string is displayed at the left bottom corner of the screen below the
copyright message.
Page 77

59
Warning! Do not upgrade the BIOS unless your system has a BIOSrelated issue. Flashing the wrong BIOS can cause irreparable
damage to the system. In no event shall Acer be liable for direct,
indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages arising
from a BIOS update. If you have to update the BIOS, do not shut
down or reset the system while the BIOS is updating. This is to
avoid possible boot failure.
Page 78

60
4 System BIOS
Main setup
When you first enter the BIOS setup utility, you will enter the main
setup screen. You can always return to the main setup screen by
selecting the main tab on the top of the screen. The main BIOS setup
screen is shown below.
System Overview
System Time/System Date
Use this option to change the system time and date. Highlight System
Time or System Date using the arrow keys. Enter new values using the
keyboard. Press the <Tab> key or the arrow keys to move between
fields. The date must be entered in MM/DD/YY format. The time is
entered in HH:MM:SS format. (Note: The time is in the 24-hour format.
For example, 5:30 P.M. appears as 17:30:00.)
BIOS Build Ver: This item displays the BIOS revision used in your system.
BIOS Build Date: This item displays the date this BIOS was completed.
Processor
The BIOS will automatically display the status of the processor used in
your system and indicate the CPU type used.
Speed: This item displays the speed of the CPU detected by the BIOS.
Physical Count: This item displays the number of processors installed in
your system as detected by the BIOS.
Page 79

61
Logical Count: This item displays the number of CPU cores installed in
your system as detected by the BIOS.
System Memory
This displays the size of memory available in the system as detected by
the BIOS.
Populated Size
Displays the size of the memory modules installed in the system as
detected by the BIOS.
Available Size
Displays the memory available for use.
Page 80

62
4 System BIOS
Advanced Settings
Use the arrow keys to select Boot Setup and press <Enter> to access the
submenu items:
Boot Features
Quick Boot: Skip certain tests during POST to reduce the time needed
for system boot.
Quiet Boot: Allows the bootup screen options to be modified between
POST messages or the OEM logo. Select Disabled to display the POST
messages. Select Enabled to display the OEM logo instead of the
normal POST messages.
AddOn ROM Display Mode: Sets the display mode for Option ROM.
Page 81

63
Bootup Num-Lock: Selects the Power-on state for Numlock key.
Wait For 'F1' If Error: Forces the system to wait until the <F1> key is
pressed if an error occurs.
Interrupt 19 Capture: Interrupt 19 is the software interrupt that
handles the boot disk function. When this item is set to Enabled, the
ROM BIOS of the host adaptors will capture Interrupt 19 at boot and
allow the drives that are attached to these host adaptors to function as
bootable disks. If this item is set to Disabled, the ROM BIOS of the host
adaptors will not capture Interrupt 19, and the drives attached to these
adaptors will not function as bootable devices.
Power Button Function: If set to Instant_Off, the system will power off
immediately when you press the power button. If set to
4_Second_Override, the system will power off when you press the
power button for four seconds or longer.
Restore on AC Power Loss: Use this feature to set the power state after
a power outage. Select Power-Off for the system power to remain off
after a power loss. Select Power-On for the system power to be turned
on after a power loss. Select Last State to allow the system to resume
its last state before a power loss.
Watch Dog Function: If Enabled, the Watch Dog Timer will allow the
system to reboot when it is inactive for more than five minutes.
Page 82

64
4 System BIOS
Processor & Clock Options
This submenu displays the status of the processor as detected by the
BIOS, including items such as the processor manufacturer, type,
frequency, CPUID, Microcode Revision, Cache L1/L2/L3, Ratio Status,
and Ratio Actual Value. The submenu also allows you to configure the
processor and clock settings.
Ratio to CMOS Setting: Select Manual to manually configure the CPU
Ratio. Select Auto to allow the BIOS to automatically configure the
CPU Ratio based on the processor installed on the motherboard.
C1E Support: Select Enabled to use the feature of Enhanced Halt State.
C1E significantly reduces the CPU's power consumption by reducing
the CPU's clock cycle and voltage during a Halt State.
Page 83
65
Important: The following feature is only available if supported by
the processor and/or operating system.
Hardware Prefetcher: If set to Enabled, the hardware prefetcher will
prefetch streams of data and instructions from the main memory to
the L2 cache in the forward or backward manner to improve CPU
performance.
Important: The following feature is only available if supported by
the processor and/or operating system.
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch: The CPU fetches the cache line for 64
bytes if this option is set to Disabled. The CPU fetches both cache lines
for 128 bytes as comprised if Enabled.
MPS and ACPI MADT Ordering: Allows you to configure the MPS
(Multi-Processor Specifi cations) and ACPI settings for your
motherboard. Select Modern Ordering if Windows XP or newer is used.
Select Legacy Ordering if Windows 2000 or earlier is used.
Important: The following feature is only available if supported by
the processor and/or operating system.
Intel (R) Virtualization Technology: Select Enabled to use Virtualization
Technology to allow one platform to run multiple operating systems
and applications in independent partitions, creating multiple virtual
systems in one physical computer.
Important: The following feature is only available if supported by
the processor and/or operating system.
Execute-Disable Bit Capability: Set to Enabled to enable the Execute
Disable Bit which will allow the processor to designate areas in the
system memory where an application code can execute and where it
cannot, thus preventing a worm or a virus from flooding illegal codes
to overwhelm the processor or damage the system during an attack.
Page 84

66
Important: The following feature is only available if supported by
the processor and/or operating system.
4 System BIOS
Simultaneous Multi-Threading: Set to Enabled to use simultaneous
multi-threading technology, which will result in increased CPU
performance.
Active Processor Cores: Set to Enabled to use a processor's second core
and beyond. The options are All, 1 and 2.
Intel EIST Technology: EIST (Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology)
allows the system to automatically adjust processor voltage and core
frequency in an effort to reduce power consumption and heat
dissipation. Please refer to Intel’s web site for detailed information.
The options are Disable (Disable GV3) and Enable (Enable GV3).
Intel C-STATE Tech: If Enabled, C-State is set by the system
automatically to either C2, C3 or C4.
C-State package limit setting: If set to Auto, the BIOS will automatically
set the limit on the C-State package register.
C1 Auto Demotion: When Enabled, the CPU will conditionally demote
C3, C6 or C7 requests to C1 based on un-core auto-demote
information.
C3 Auto Demotion: When Enabled, the CPU will conditionally demote
C6 or C7 requests to C3 based on un-core auto-demote information.
Clock Spread Spectrum: Select Enable to use the feature of Clock
Spectrum, which will allow the BIOS to monitor and attempt to reduce
the level of Electromagnetic Interference caused by the components
whenever needed.
DCA Technology: Uses Intel's DCA (Direct Cache Access) Technology to
enhance data transfer effi ciency.
DCA Prefetch Delay: Used with TOE components to prefetch data in
order to shorten execution cycles and maximize data processing effi
ciency. Prefetching too frequently can saturate the cache directory and
delay necessary cache accesses. This feature reduces or increases the
frequency the system prefetches data.
Clock Spread Spectrum: Select Enable to use the Clock Spectrum
feature, which allows BIOS to monitor and attempt to reduce the level
of Electromagnetic Interference caused by the components.
Page 85

67
Advanced Chipset Control
The items included in the Advanced Chipset Settings submenu are
listed below:
CPU Bridge Configuration
QPI Links Speed: This feature selects QPI data transfer speed.
Important: The following feature is only available when QPI Links
Speed is set to Full Speed.
QPI Frequency: This selects the desired QPI frequency.
QPI L0s and L1: This enables the QPI power state to low power. L0s and
L1 are automatically selected by the motherboard.
Page 86

68
4 System BIOS
Memory Frequency: This feature enables you to force a DDR3
frequency slower than what the system has detected.
Memory Mode: Set the memory mode.
• Independent - All DIMMs are available to the operating system.
• Channel Mirror - The motherboard maintains two identical copies
of all data in memory for redundancy.
• Lockstep - The motherboard uses two areas of memory to run the
same set of operations in parallel.
Demand Scrubbing: A memory error-correction scheme where the
processor writes corrected data back into the memory block from
where it was read by the processor.
Patrol Scrubbing: A memory error-correction scheme that works in the
background looking for and correcting resident errors.
Throttling - Closed Loop/Throttling - Open Loop: Throttling improves
reliability and reduces power in the processor by automatic voltage
control during processor idle states. If Enabled, the following items will
appear:
• Hysteresis Temperature (For Closed Loop only) - Temperature
Hysteresis is the temperature lag (in degrees Celsius) after the set
DIMM temperature threshold is reached before Closed Loop
Throttling begins.
• Guardband Temperature (For the Closed Loop only) - This is the
temperature which applies to the DIMM temperature threshold.
Steps are in 0.5 °C increments. The default is [006]. Press "+" or "-"
on your keyboard to change this value.
• Inlet Temperature - This is the temperature detected at the chassis
inlet. Steps are in 0.5 °C increments. The default is [070]. Press "+"
or "-" on your keyboard to change this value.
• Temperature Rise - This is the temperature rise to the DIMM
thermal zone. Steps are in 0.5 °C increments. The default is [020].
Press "+" or "-" on your keyboard to change this value.
• Air Flow - This is the air flow speed to the DIMM modules. Each
step is one mm/sec. The default is [1500]. Press "+" or "-" on your
keyboard to change this value.
• Altitude - This feature defines how many meters above or below
sea level the system is located.
• DIMM Pitch - This is the physical space between each DIMM
module. Each step is 1/1000 of an inch. The default is [400]. Press
Page 87
69
"+" or "-" on your keyboard to change this value.
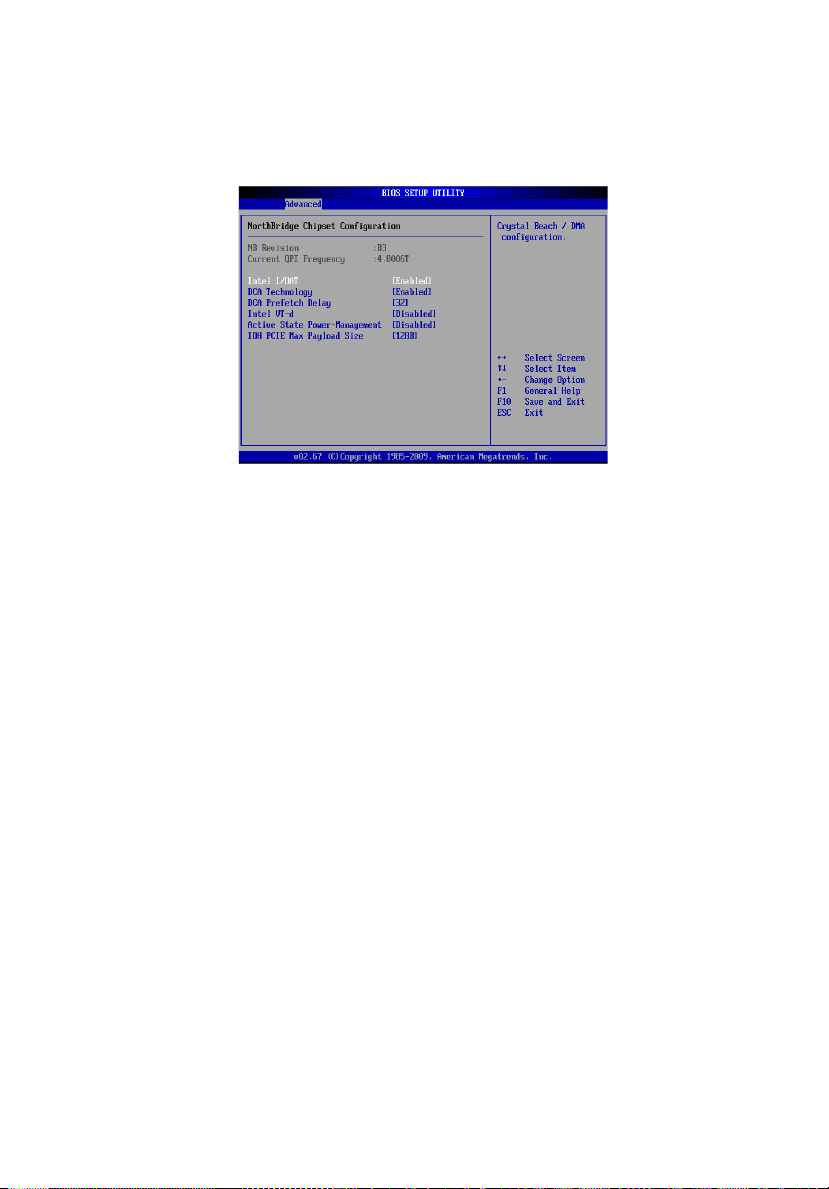
NorthBridge Chipset Configuration
Intel I/OAT: Significantly reduces CPU overhead by leveraging CPU
architectural improvements, freeing resources for other tasks.
DCA Technology: Select Enabled to use Intel's DCA (Direct Cache
Access) Technology to improve data transfer effi ciency.
DCA Prefetch Delay: A DCA Prefetch is used with TOE components to
prefetch data in order to shorten execution cycles and maximize data
processing effi ciency. A TOE device is a specialized, dedicated
processor that is installed on an add-on card or a network card to
handle some or all packet processing of this add-on card. Prefetching
too frequently can saturate the cache directory and delay necessary
cache accesses. This feature reduces or increases the frequency the
system prefetches data. The options are [8], [16], [32], [40], [48], [56],
[64], [72], [80], [88], [96], [104], [112], and [120].
Intel VT-d: Select Enabled to enable Intel Virtualization Technology
support for Direct I/O VT-d by reporting the I/O device assignments to
VMM through the DMAR ACPI Tables. This feature offers fullyprotected I/O resource-sharing across the Intel platforms, providing
you with greater reliability, security and availability in networking and
data-sharing.
Active State Power-Management: Uses power management for signal
transactions between the PCI Express L0 and L1 Links. Select Enabled to
configure PCI Express L0 and L1 Link power states.
IOH PCIE Max Payload Size: Some add-on cards perform faster with the
coalesce feature, which limits the payload size to 128 MB. Others
Page 88

70
4 System BIOS
perform better with a payload size of 256 MB, which inhibits the
coalesce feature.
Please refer to your add-on card user guide for the desired setting.
SouthBridge configuration
This feature allows you to configure the settings for the Intel ICH South
Bridge chipset.
USB Functions: This feature allows you to decide how many onboard
USB ports to enable.
Legacy USB Support: Select Enabled to use Legacy USB devices. If set to
Auto, legacy USB support will be automatically enabled if a legacy USB
device is installed on the motherboard.
Note: Only available when USB Functions is set to Enabled.
USB 2.0 Controller: Select Enabled to activate the onboard USB 2.0
controller.
Note: Only available when USB Functions is set to Disabled.
Otherwise, this item will be set to Enabled by the BIOS.
USB 2.0 Controller Mode: This setting allows you to select the USB 2.0
Controller mode.
Page 89

71
BIOS EHCI Hand-Off: Enable or disable BIOS Enhanced Host Controller
Interface support to provide a workaround solution for an operating
system that does not have EHCI Hand-Off support. When enabled, the
EHCI Interface will be changed from BIOS-controlled to OS-controlled.
IDE/SATA configuration
When this submenu is selected, the BIOS automatically detects the
presence of the IDE devices and displays the following items:
SATA#1 configuration: If Compatible is selected, it sets SATA#1 to
legacy compatibility mode, while selecting Enhanced sets SATA#1 to
native SATA mode.
• Configure SATA#1 as - This feature allows you to select the drive
type for SATA#1. The options are IDE, RAID and AHCI.
• ICH RAID Code Base - Select Intel or Adaptec to launch the
appropriate SATA RAID firmware to configure SATA RAID.
Note: Only available when RAID is selected in Configure SATA#1
as.
SATA#2 configuration: Selecting Enhanced will set SATA#2 to native
SATA mode.
Note: Only available when IDE is selected in Configure SATA#1 as.
Page 90

72
4 System BIOS
Primary IDE Master/Slave, Secondary IDE Master/Slave, Third IDE
Master, and Fourth IDE Master: These settings allow you to set the
parameters of the IDE slots. Press <Enter> to activate the submenu
screen for detailed options of these items. Set the configurations
accordingly. Items included in the submenu are:
• Type - Select the type of device connected to the system.
• LBA/Large Mode - LBA (Logical Block Addressing) is a method of
addressing data on a disk drive. In the LBA mode, the maximum
drive capacity is 137 GB. For drive capacities over 137 GB, your
system must be equipped with a 48-bit LBA mode addressing. If
not, contact your manufacturer or install an ATA/133 IDE
controller card that supports 48-bit LBA mode.
• Block (Multi-Sector Transfer) - Block Mode boosts the IDE drive
performance by increasing the amount of data transferred. Only
512 bytes of data can be transferred per interrupt if Block Mode is
not used. Block Mode allows transfers of up to 64 KB per interrupt.
Select Disabled to allow data to be transferred from and to the
device one sector at a time. Select Auto to allow data transfer
from and to the device occur multiple sectors at a time if the
device supports it.
• PIO Mode - The IDE PIO (Programmable I/O) Mode programs
timing cycles between the IDE drive and the programmable IDE
controller. As the PIO mode increases, the cycle time decreases.
Select Description
Auto Automatically detect the PIO mode. Use this value if the
IDE disk drive support cannot be determined.
0 Use PIO mode 0. It has a data transfer rate of 3.3 MBs.
1 Use PIO mode 1. It has a data transfer rate of 5.2 MBs.
2 Use PIO mode 2. It has a data transfer rate of 8.3 MBs.
3 Use PIO mode 3. It has a data transfer rate of 11.1 MBs.
4 Use PIO mode 4. It has a data transfer bandwidth of 32
bits. Select Enabled to enable 32-bit data transfer.
Page 91

73
•DMA Mode
Select Description
Auto Automatically detect IDE DMA mode when the IDE disk
drive support cannot be determined.
SWDMA0 Use Single Word DMA mode 0. It has a data transfer
rate of 2.1 MBs.
SWDMA2 Use Single Word DMA mode 2. It has a data transfer
rate of 8.3 MBs.
MWDMA0 Use Multi Word DMA mode 0. It has a data transfer rate
of 4.2 MBs.
MWDMA1 Use Multi Word DMA mode 1. It has a data transfer rate
of 13.3 MBs.
MWDMA2 Use Multi-Word DMA mode 2. It has a data transfer rate
of 16.6 MBs.
UDMA0 Use Ultra DMA mode 0. It has a data transfer rate of
16.6 MBs. It has the same transfer rate as PIO mode 4
and Multi Word DMA mode 2.
UDMA1 Use Ultra DMA mode 1. It has a data transfer rate of 25
MBs.
UDMA2 Use Ultra DMA mode 2. It has a data transfer rate of
33.3 MBs.
UDMA3 Use Ultra DMA mode 3. It has a data transfer rate of
66.6 MBs.
UDMA4 Use Ultra DMA mode 4. It has a data transfer rate of
100 MBs.
• S.M.A.R.T. For Hard disk drives - Self-Monitoring Analysis and
Reporting Technology (SMART) can help predict impending drive
failures. Select Auto to allow the BIOS to automatically detect hard
disk drive support.
• 32Bit Data Transfer - Select Enable to enable the function of 32-bit
IDE data transfer.
IDE Detect Timeout (Sec): Use this feature to set the time-out value for
the BIOS to detect the ATA, ATAPI devices installed in the system.
Page 92

74
4 System BIOS
PCI/PnP configuration
Clear NVRAM: This feature clears the NVRAM during system boot. The
options are No and Yes.
Plug & Play OS: Yes allows the OS to configure Plug & Play devices.
(This is not required for system boot if your system has an oerating
syste that supports Plug & Play.) Select No to allow the BIOS to
configure all devices in the system.
PCI Latency Timer: This feature sets the latency timer of each PCI device
installed on a PCI bus.
PCI IDE BusMaster: When Enabled, the BIOS uses PCI bus mastering for
reading/writing to IDE drives.
SR-IOV Supported: Select Enabled to enable Single-Root I/O
Virtualization (SR-IOV) support, which works in conjunction with Intel
Virtualization Technology to allow multiple operating systems to run
simultaneously within a single computer via natively-shared PCI Express
devices in order to enhance network connectivity and performance.
The options are Enabled and Disabled.
PCI-E Slot1 OPROM: Select Enabled to enable PCI Express slot SXB1.
You can also enable Option ROMs to boot the computer using a
network interface from these slots.
Load Onboard LAN1 Option ROM/Load Onboard LAN2 Option ROM:
Select Enabled to enable the onboard LAN1 or LAN2 Option ROM. This
is to boot computer using a network interface.
Page 93

75
Onboard LAN Option ROM Select: Select iSCSI to use the iSCSI Option
ROM to boot the computing using a network device. Select PXE to use
the PXE Option ROM to boot the computer using a network device.
Boots Graphic Adapter Boot Priority: This feature allows you to select
the graphics adapter to be used as the primary boot device.
Super IO Configuration
Serial Port1 Address/ Serial Port2 Address: This option specifies the
base I/O port address and the Interrupt Request address of Serial Port 1
and Serial Port 2. Select Disabled to prevent the serial port from
accessing any system resources. When this option is set to Disabled, the
serial port physically becomes unavailable. Select 3F8/IRQ4 to allow the
serial port to use 3F8 as its I/O port address and IRQ 4 for the interrupt
address.
Serial Port 2 Attribute: Select COM to configure the onboard COM2
port as a normal serial port. Select SOL (Serial Over_LAN) to configure
the onboard COM2 port as a virtual COM port for SOL use.
Page 94
76
4 System BIOS
Hardware Health Configuration
This feature allows you to monitor system health and review the status
of each item as displayed.
CPU Overheat Alarm: This option allows you to select the CPU
Overheat Alarm setting which determines when the CPU OH alarm will
be activated to provide warning of possible CPU overheat.
Warning: Any temperature that exceeds the CPU threshold
temperature predefined by the CPU manufacturer may result in
CPU overheat or system instability. When the CPU temperature
reaches this predefined threshold, the CPU and system cooling
fans will run at full speed.
The options are:
• The Early Alarm - Select this setting if you want the CPU overheat
alarm (including the LED and the buzzer) to be triggered as soon
as the CPU temperature reaches the CPU overheat threshold as
predefined by the CPU manufacturer.
• The Default Alarm - Select this setting if you want the CPU
overheat alarm (including the LED and the buzzer) to be triggered
when the CPU temperature reaches about 5 °C above the
threshold temperature as predefined by the CPU manufacturer to
give the CPU and system fans additional time needed for CPU and
system cooling.
Page 95

77
CPU Temperature/System Temperature: This feature displays current
temperature readings for the CPU and the System. The following items
will be displayed for your reference only:
CPU Temperature: The CPU thermal technology that reports absolute
temperatures (Celsius/Fahrenheit) has been upgraded to a more
advanced feature by Intel in its newer processors. The basic concept is
each CPU is embedded by unique temperature information that the
motherboard can read. This Temperature Threshold or Temperature
Tolerance has been assigned at the factory and is the baseline on
which the motherboard takes action during different CPU temperature
conditions (i.e., by increasing CPU fan speed, triggering the Overheat
Alarm, etc). Since CPUs can have different Temperature Tolerances’,
the installed CPU can now send information to the motherboard what
its Temperature Tolerance is, and not the other way around. This
results in better CPU thermal management.
Acer has leveraged this feature by assigning a temperature status to
certain thermal conditions in the processor (Low, Medium and High).
This makes it easier for you to understand the CPU’s temperature
status, rather than by just simply seeing a temperature reading (i.e., 25
°C). The CPU Temperature feature will display the CPU temperature
status as detected by the BIOS:
• Low – This level is considered as the normal operating state. The
CPU temperature is well below the CPU Temperature Tolerance.
The motherboard fans and CPU will run normally as configured in
the BIOS (Fan Speed Control).
User intervention: No action required.
• Medium – The processor is running warmer. This is a precautionary
level and generally means that there may be factors contributing
to this condition, but the CPU is still within its normal operating
state and below the CPU Temperature Tolerance. The
motherboard fans and CPU will run normally as configured in the
BIOS. The fans may adjust to a faster speed depending on the Fan
Speed Control settings.
User intervention: No action is required. However, consider
checking the CPU fans and the chassis ventilation for blockage.
• High – The processor is running hot. This is a caution level since the
CPU’s Temperature Tolerance has been reached (or has been
exceeded) and may activate an overheat alarm.
User intervention: If the system buzzer and Overheat LED has
activated, take action immediately by checking the system fans,
chassis ventilation and room temperature to correct any problems.
Page 96

78
Note: The system may shut down if it continues for a long period
to prevent damage to the CPU. The information provided above is
for your reference only. For more information on thermal
management, please refer to Intel’s Web site at www.intel.com.
4 System BIOS
System Temperature: The system temperature will be displayed (in
degrees in Celsius and Fahrenheit) as it is detected by the BIOS.
Fan1 to Fan 8 Reading: This feature displays the fan speed readings
from fan interfaces Fan1 through Fan8.
Fan Speed Control Modes: This feature allows you to decide how the
system controls the speeds of the onboard fans. The CPU temperature
and the fan speed are correlated. When the CPU on-die temperature
increases, the fan speed will also increase for effective system cooling.
Select Full Speed/FS to allow the onboard fans to run at full speed for
maximum cooling. The FS setting is recommended for special system
configuration or debugging. Select Performance/PF for better system
cooling. The PF setting is recommended for high-power-consuming
and high-density systems.
Select Balanced/BL for the onboard fans to run at a speed that will
balance the needs between system cooling and power saving. The BL
setting is recommended for regular systems with normal hardware
confi gurations. Select Energy Saving/ES for best power effi ciency and
maximum quietness.
Voltage Monitoring: Indicates CPU1 Vcore, CPU2 Vcore, 1.5V, 5V, 5VSB,
12V, -12V, 3.3Vcc, 3.3VSB, VBAT and Vtt readings.
Page 97

79
ACPI configuration
Use this feature to configure Advanced configuration and Power
Interface (ACPI) power management settings for your system.
ACPI Aware O/S:
ACPI Version Features: The options are ACPI v1.0, ACPI v2.0 and ACPI
v3.0. Please refer to ACPI's website for further explanation: http://
www.acpi.info/.
ACPI APIC Support: Select Enabled to include the ACPI APIC Table
Pointer in the RSDT pointer list.
Note: Only available when ACPI is enabled on an ACPI-aware
operating system.
APIC ACPI SCI IRQ: When this item is set to Enabled, APIC ACPI SCI IRQ
is supported by the system.
Headless Mode: Enables the system to function without a keyboard,
monitor, or mouse attached.
Note: Only available when ACPI is enabled on an ACPI-aware
operating system.
NUMA Support: Uses Non-Uniform Memory Access to improve CPU
performance.
Page 98

80
4 System BIOS
High Performance Event Timer: Select Enabled to activate the highperformance event timer to produce periodic interrupts at a much
higher frequency than a real-time clock does when synchronizing
multimedia streams, providing smooth playback and reducing the
dependency on other timestamp calculation devices, such as an x86
RDTSC Instruction embedded in the CPU. The high-performance event
timer is used to replace the 8254 programmable interval timer.
WHEA Support: Select Enabled to enable Windows Hardware Error
Architecture (WHEA) support, which will provide a common
infrastructure for handling hardware errors on Windows platforms in
order to reduce system crashes due to hardware errors and to improve
system recovery and health monitoring.
Page 99

81
Security Settings
The BIOS provides a Supervisor and a User password. If you use both
passwords, the Supervisor password must be set first.
Supervisor Password: This item indicates if a supervisor password has
been entered for the system.
not been used.
User Password: This item indicates if a user password has been entered
for the system.
Not installed
Not installed
means such a password has not been used.
means such a password has
Change Supervisor Password: Select this feature and press <Enter> to
access the submenu, and then type in a new Supervisor Password.
The Security screen then appears as follows:
Page 100

82
4 System BIOS
User Access Level: (Available when Supervisor Password is set as above)
Available options are:
• Full Access - grants full User read and write access to the Setup
Utility.
• View Only - allows access to the Setup Utility but the fields cannot
be changed.
• Limited - allows only limited .elfis to be changed such as Date and
Time
• No Access - prevents User access to the Setup Utility.
Change User Password: Select this feature and press <Enter> to access
the submenu , and then type in a new User Password.
The Security screen then appears as follows with both passwords set:
The Security screen appears as follows with only the User Password set:
 Loading...
Loading...