Page 1
Operation and
Maintenance
Manual
SEBU6251-06
April 1999
Caterpillar Commercial Diesel Engine
Fluids Recommendations
For All Commercial Diesel Engines Except 3600 Series Engines
Page 2

i01097883
Important Safety Information
Most accidents that involve product operation, maintenance and repair are caused by failure to
observe basic safety rules or precautions. An accident can often be avoided by recognizing potentially
hazardous situations before an accident occurs. A person must be alert to potential hazards. This
person should also have the necessary training, skills and tools to perform these functions properly.
Improper operation, lubrication, maintenance or repair of this product can be dangerous and
could result in injury or death.
Do not operate or perform any lubrication, maintenance or repair on this product, until you have
read and understood the operation, lubrication, maintenance and repair information.
Safety precautions and warnings are provided in this manual and on the product. If these hazard
warnings are not heeded, bodily injury or death could occur to you or to other persons.
The hazards are identified by the “Safety Alert Symbol” and followed by a “Signal Word” such as
“DANGER”, “WARNING” or “CAUTION”. The Safety Alert “WARNING” label is shown below.
The meaning of this safety alert symbol is as follows:
Attention! Become Alert! Your Safety is Involved.
The message that appears under the warning explains the hazard and can be either written or
pictorially presented.
Operations that may cause product damage are identified by “NOTICE” labels on the product and in
this publication.
Caterpillar cannot anticipate every possible circumstance that might involve a potential hazard. The
warnings in this publication and on the product are, therefore, not all inclusive. If a tool, procedure,
work method or operating technique that is not specifically recommended by Caterpillar is used,
you must satisfy yourself that it is safe for you and for others. You should also ensure that the
product will not be damaged or be made unsafe by the operation, lubrication, maintenance or
repair procedures that you choose.
The information, specifications, and illustrations in this publication are on the basis of information that
was available at the time that the publication was written. The specifications, torques, pressures,
measurements, adjustments, illustrations, and other items can change at any time. These changes can
affect the service that is given to the product. Obtain the complete and most current information before
you start any job. Caterpillar dealers have the most current information available. For a list of the most
current publication form numbers available, see the Service Manual Contents Microfiche, REG1139F.
When replacement parts are required for this
product Caterpillar recommends using Caterpillar replacement parts or parts with equivalent
specifications including, but not limited to, physical dimensions, type, strength and material.
Failure to heed this warning can lead to premature failures, product damage, personal injury or
death.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Foreword ............................................................... 4
Maintenance Section
Lubricant Specifications ........................................ 5
Fuel Specifications ................................................ 17
Cooling System Specifications ............................. 24
Reference Information Section
Reference Materials .............................................. 37
Index Section
Index ..................................................................... 39
3
Table of Contents
Page 4

4
Foreword
Foreword
Literature Information
This manual should be stored in the literature
storage area.
The information contained in this document is the
most current information available for coolants,
fuels, and lubricants. Refer to the Operation and
Maintenance Manual for any special lubrication
requirements for your engine.
Whenever a question arises regarding the engine,
this publication, or the Operation and Maintenance
Manual, please consult any Caterpillar dealer for
the latest available information.
Safety
Refer to the Operation and Maintenance Manual
for your engine for all safety information. Read and
understand the basic safety precautions listed in
the Safety Section. In addition to safety precautions,
this section identifies the text and locations of safety
signs used on the engine.
Read and understand the basic precautions listed
in the Safety Section before operating or performing
lubrication, maintenance and repair on this engine.
Maintenance
Refer to the Operation and Maintenance Manual
for your engine to determine all maintenance
requirements.
Maintenance Intervals
Use the Maintenance Interval Schedule in the
Operation and Maintenance Manual for your
engine to determine servicing intervals. The actual
operating environment of the engine also governs
the maintenance interval schedule. Therefore,
under extremely severe, dusty, wet or freezing cold
operating conditions, more frequent lubrication and
maintenance than is specified in the Maintenance
Interval Schedule may be necessary.
Page 5
Maintenance Section
Lubricant Specifications
5
Maintenance Section
Lubricant Specifications
i01111306
Lubricant Information
SMCS Code: 1000; 1300; 7581
General Information
Because of government regulations regarding
the certification of engine exhaust emissions, the
lubricant recommendations must be followed.
Engine Manufacturers Association
(EMA) Oils
The “Engine Manufacturers Association
Recommended Guideline on Diesel Engine Oil” is
recognized by Caterpillar. For detailed information
about this guideline, see the latest edition of EMA
publication, “EMA LRG-1”.
API Oils
The Engine Oil Licensing and Certification System
by the American Petroleum Institute (API) is
recognized by Caterpillar. For detailed information
about this system, see the latest edition of the “API
publication No. 1509”. Engine oils that bear the API
symbol are authorized by API.
Ta bl e 1
API Classifications
Current Obsolete
CF-4, CG-4, CH-4 CE
CF CC, CD
(1)
CF-2
(1)
CD-2 and API CF-2 are classifications for two-cycle diesel
engines. Caterpillar does not sell engines that utilize CD-2 and
API CF-2 oils.
Note: API CF is not the same classification as
API CF-4. API CF oils are only recommended
for Caterpillar 3600 Series Diesel Engines and
Caterpillar engines with precombustion chamber
(PC) fuel systems.
CD-2
(1)
Grease
The classifications of grease are based on the
“ASTM D217” worked penetration characteristics.
These characteristics for grease are given a defined
consistency number.
Terminology
Certain abbreviations follow the nomenclature of
“SAE J754”. Some classifications follow “SAE J183”
abbreviations, and some classifications follow the
“EMA Recommended Guideline on Diesel Engine
Oil”. In addition to Caterpillar definitions, there
are other definitions that will be of assistance in
purchasing lubricants. Recommended oil viscosities
can be found in this publication, “Engine Oil” topic
(Maintenance Section).
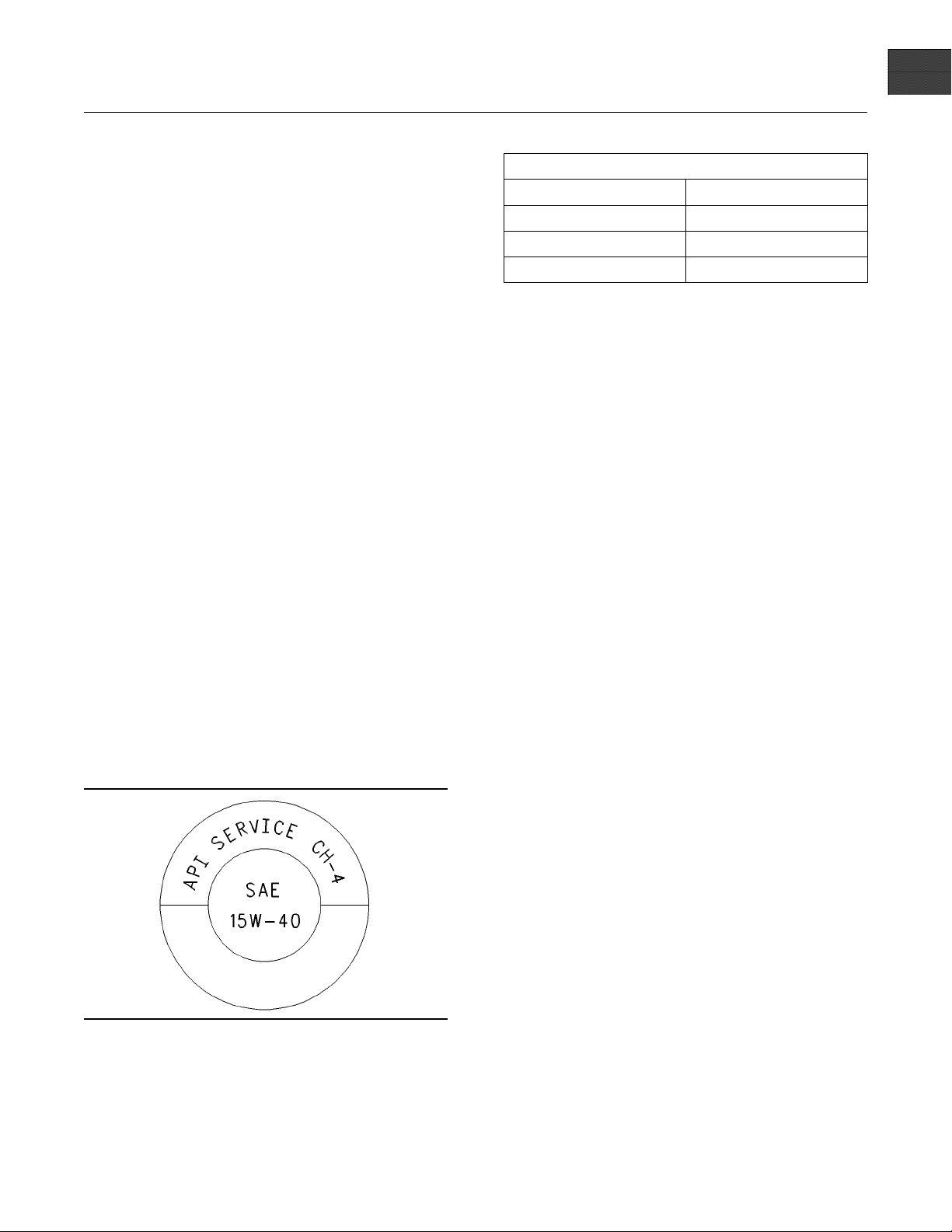
Illustration 1
Typical API symbol
Diesel engine oils CC, CD, CD-2, and CE have
not been API authorized classifications since 1
January 1996. Table 1 summarizes the status of the
classifications.
g00546535
i01072547
Engine Oil
SMCS Code: 1348
Caterpillar Diesel Engine Oil
Caterpillar Oils have been developed and tested in
order to provide the full performance and service
life that has been designed and built into Caterpillar
Engines. Caterpillar Oils are currently used to fill
diesel engines at the factory. These oils are offered
by Caterpillar dealers for continued use when the
engine oil is changed. Consult your Caterpillar
dealer for more information on these oils.
Due to significant variations in the quality and in
the performance of commercially available oils,
Caterpillar makes the following recommendations:
Caterpillar Diesel Engine Oil (10W30)
•
Page 6

6
Maintenance Section
Lubricant Specifications
Caterpillar Diesel Engine Oil (15W40)
•
Caterpillar multigrade Diesel Engine Oil is
formulated with the correct amounts of detergents,
dispersants, and alkalinity in order to provide
superior performance in Caterpillar Diesel Engines.
Caterpillar multigrade Diesel Engine Oil is available
in two viscosity grades (10W30 and 15W40).
For direct injection engines, see Table 2 in order
to choose the correct viscosity grade for the
ambient temperature. Multigrade oils provide the
correct viscosity for a broad range of operating
temperatures.
Multigrade oils are effective in maintaining low oil
consumption and low levels of piston deposits.
Caterpillar multigrade Diesel Engine Oil can be
used in other diesel engines and in gasoline
engines. See the engine manufacturer’s guide for
the recommended specifications. Compare the
specifications to the specifications of Caterpillar
multigrade Diesel Engine Oil. The current industry
standards for Caterpillar Diesel Engine Oil are listed
on the product label and on the data sheets for the
product.
Consult your Caterpillar dealer for part numbers
and for available sizes of containers.
Commercial Oils
The performance of commercial diesel engine
oils is based on American Petroleum Institute
(API) classifications. These API classifications are
developed in order to provide commercial lubricants
for a broad range of diesel engines that operate at
various conditions.
If Caterpillar multigrade Diesel Engine Oil is not
used, only use commercial oils that meet the
following classifications:
EMA LRG-1 multigrade oil (preferred oil)
•
API CH-4 multigrade oil (preferred oil)
•
API CG-4 multigrade oil (preferred oil)
•
API CF-4 multigrade oil (acceptable oil)
•
In order to make the proper choice of a commercial
oil, refer to the following explanations:
EMA LRG-1 – The Engine Manufacturers
Association (EMA) has developed lubricant
recommendations as an alternative to the API oil
classification system. LRG-1 is a Recommended
Guideline that defines a level of oil performance
for these types of diesel engines: high speed, four
stroke cycle, heavy-duty, and light duty. LRG-1 oils
may be used in Caterpillar engines when API CH-4,
API CG-4, and API CF-4 oils are recommended.
LRG-1 oils are intended to provide superior
performance in comparison to API CG-4 and API
CF-4.
LRG-1 oils will meet the needs of high performance
Caterpillar diesel engines that are operating in
many applications. The tests and the test limits that
are used to define LRG-1 are similar to the new
API CH-4 classification. Therefore, these oils will
also meet the requirements of the low emissions
diesel engines. LRG-1 oils are designed to control
the harmful effects of soot with improved wear
resistance and improved resistance to oil filter
plugging. These oils will also provide superior piston
deposit control for engines with either two-piece
steel pistons or aluminum pistons.
All LRG-1 oils must complete a full test program
with the base stock and with the viscosity grade of
the finished commercial oil. The use of “API Base
Oil Interchange Guidelines” are not appropriate for
LRG-1 oils. This feature reduces the variation in
performance that can occur when base stocks are
changed in commercial oil formulations.
LRG-1 oils are recommended for use in extended
oil change interval programs that optimize oil life.
These oil change interval programs are based
on oil analysis. LRG-1 oils are recommended
for conditions that demand a premium oil. Your
Caterpillar dealer has the specific guidelines for
optimizing oil change intervals.
API CH-4 – API CH-4 oils were developed in
order to meet the requirements of the new high
performance diesel engines. Also, the oil was
designed to meet the requirements of the low
emissions diesel engines. API CH-4 oils are also
acceptable for use in older diesel engines and in
diesel engines that use high sulfur diesel fuel. API
CH-4 oils may be used in Caterpillar engines that
use API CG-4 and API CF-4 oils. API CH-4 oils will
generally exceed the performance of API CG-4 oils
in the following criteria: deposits on pistons, control
of oil consumption, wear of piston rings, valve train
wear, viscosity control, and corrosion.
Page 7
Maintenance Section
Lubricant Specifications
7
Three new engine tests were developed for the
API CH-4 oil. The first test specifically evaluates
deposits on pistons for engines with the two-piece
steel piston. This test (piston deposit) also measures
the control of oil consumption. A second test is
conducted with moderate oil soot. The second
test measures the following criteria: wear of piston
rings, wear of cylinder liners, and resistance to
corrosion. A third new test measures the following
characteristics with high levels of soot in the oil:
wear of the valve train, resistance of the oil in
plugging the oil filter, and control of sludge.
In addition to the new tests, API CH-4 oils have
tougher limits for viscosity control in applications
that generate high soot. The oils also have improved
oxidation resistance. API CH-4 oils must pass an
additional test (piston deposit) for engines that use
aluminum pistons (single piece). Oil performance is
also established for engines that operate in areas
with high sulfur diesel fuel.
All of these improvements allow the API CH-4 oil
to achieve optimum oil change intervals. API CH-4
oils are recommended for use in extended oil
change intervals. API CH-4 oils are recommended
for conditions that demand a premium oil. Your
Caterpillar dealer has specific guidelines for
optimizing oil change intervals.
Some commercial oils that meet the API
classifications may require reduced oil change
intervals. To determine the oil change interval,
closely monitor the condition of the oil and perform a
wear metal analysis. Caterpillar’sS·O·S oil analysis
program is the preferred method.
NOTICE
Failure to follow these oil recommendations can cause
shortened engine service life due to deposits and/or
excessive wear.
Total Base Number (TBN) and Fuel
Sulfur Levels for Direct Injection
(DI) Diesel Engines
The Total Base Number (TBN) for an oil depends on
the fuel sulfur level. For direct injection engines that
use distillate fuel, the minimum TBN of the new oil
must be 10 times the fuel sulfur level. The TBN is
defined by “ASTM D2896”. The minimum TBN of
the oil is 5 regardless of fuel sulfur level. Illustration
2 demonstrates the TBN.
API CG-4 – API CG-4 oils were developed primarily
for diesel engines that use a 0.05 percent level of
fuel sulfur. However, API CG-4 oils can be used
with higher sulfur fuels. The TBN of the new oil
determines the maximum fuel sulfur level for API
CG-4 and API CF-4 oils. See Illustration 2.
API CG-4 oils are the first oils that are required to
pass industry standard tests for foam control and
viscosity shear loss. API CG-4 oils must also pass
tests that were developed for corrosion, wear and
oxidation.
API CF-4 – These oils service a wide variety of
modern diesel engines. API CF-4 oils provide more
stable oil control and reduced piston deposits in
comparison to API CF and the obsolete CE and CD
classifications of oil. API CF-4 oils provide improved
soot dispersancy in comparison to API CF and
obsolete CD oils. The API CF-4 classification was
developed with a 0.40 percent sulfur diesel fuel.
This represents the type of diesel fuels that are
commonly available worldwide.
Note: Do not use single grade API CF oils or
multigrade API CF oils in Caterpillar Direct Injection
(DI) Commercial Diesel Engines.
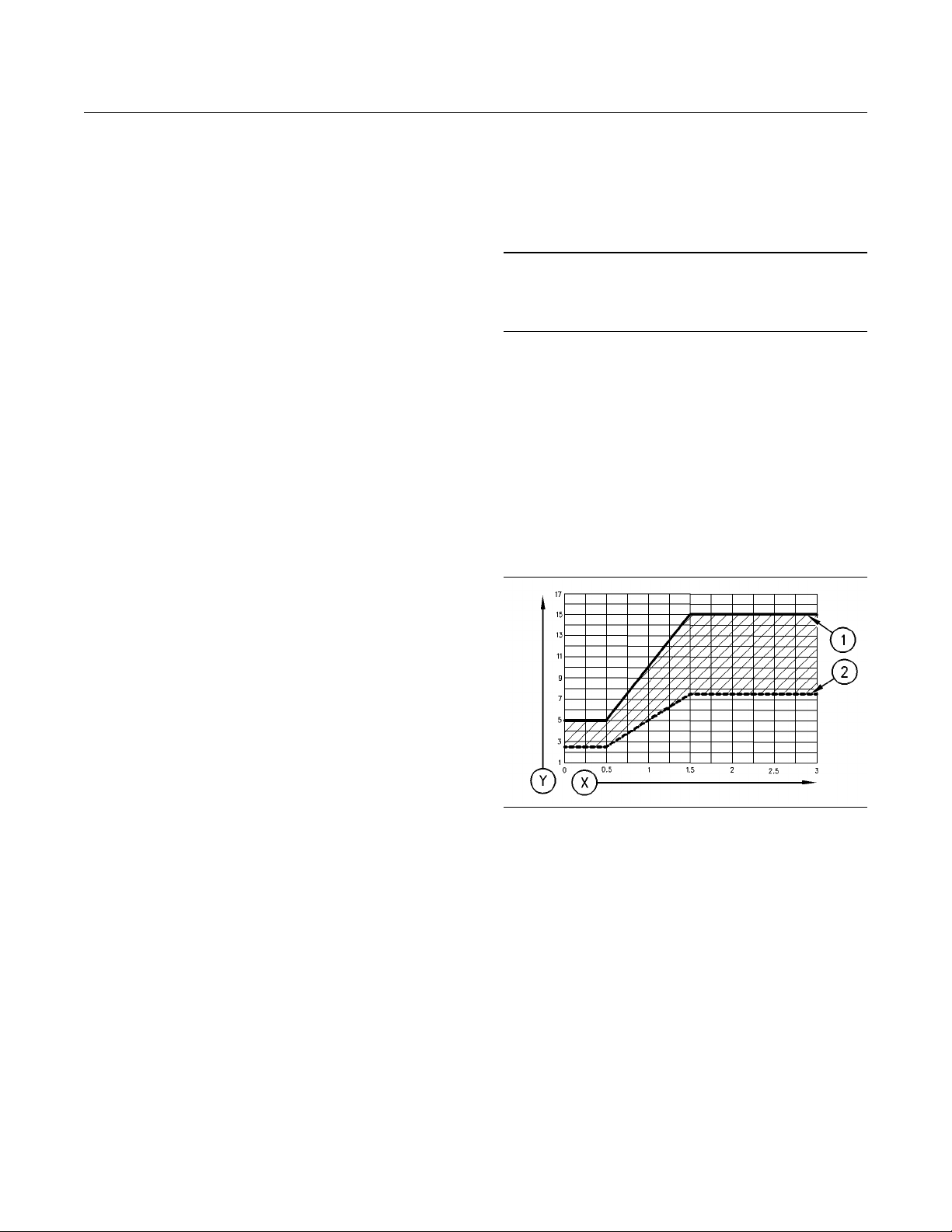
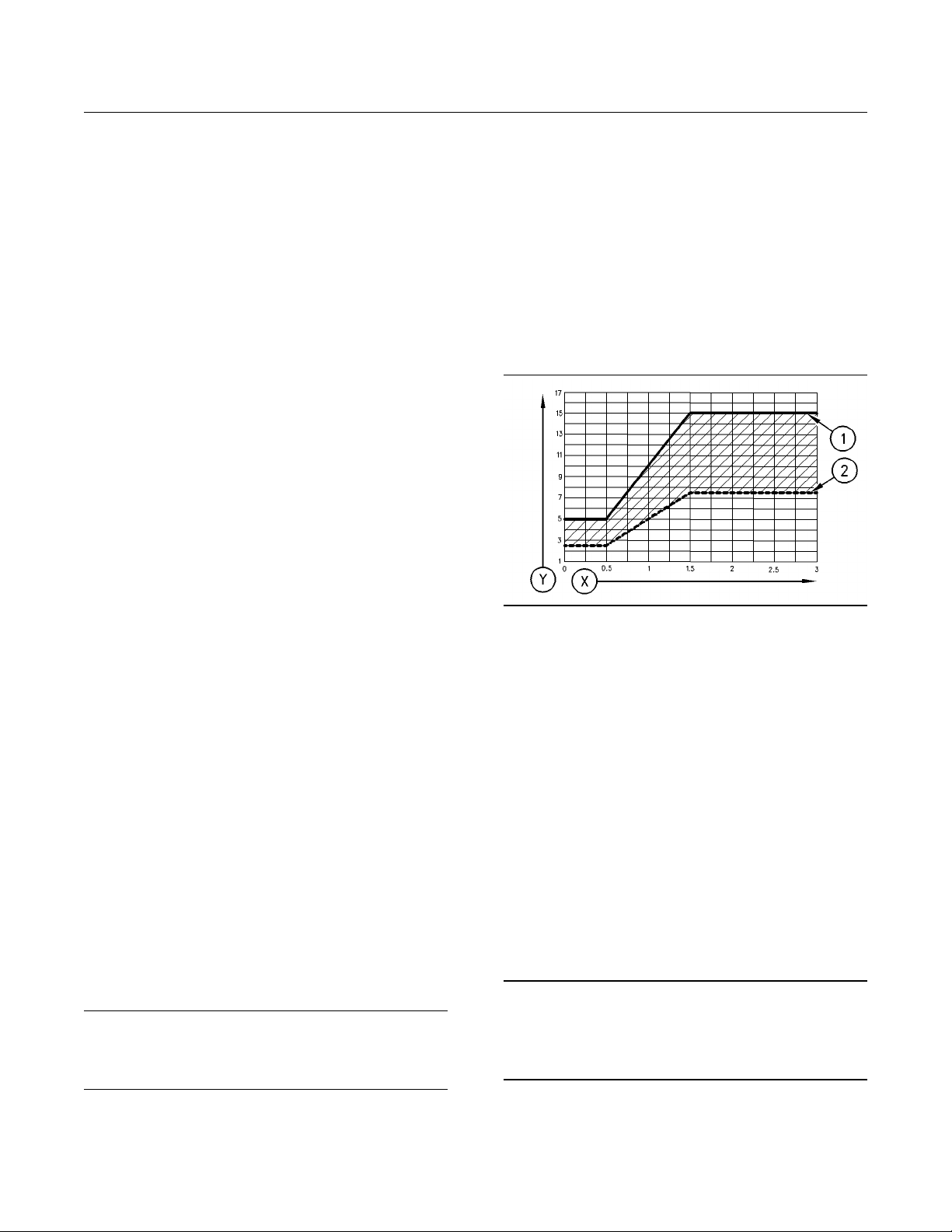
Illustration 2
(Y) TBN by “ASTM D2896”
(X) Percentage of fuel sulfur by weight
(1) TBN of new oil
(2) Change the oil when the TBN deteriorates to 50 percent of
the original TBN.
Use the following guidelines for fuel sulfur levels
that exceed 1.5 percent:
Choose an oil with the highest TBN that meets
•
one of these classifications: EMA LRG-1, API
CH-4, API CG-4, and API CF-4.
Reduce the oil change interval. Base the oil
•
change interval on the oil analysis. Ensure that
the oil analysis includes the condition of the oil
and a wear metal analysis.
g00104890
Excessive piston deposits can be produced by an
oil with a high TBN. These deposits can lead to a
loss of control of the oil consumption and to the
polishing of the cylinder bore.
Page 8
8
Maintenance Section
Lubricant Specifications
NOTICE
Operating Direct Injected (DI) diesel engines with fuel
sulfur levels over 1.0 percent may require shortened
oil change intervals in order to help maintain adequate
wear protection.
i01111341
Engine Oil (3116 and 3126
Marine Engines)
SMCS Code: 1348
Lubricant Viscosity Recommendations
for Direct Injection (DI) Diesel Engines
The proper SAE viscosity grade of oil is determined
by the minimum ambient temperature during
cold engine start-up, and the maximum ambient
temperature during engine operation.
Refer to Table 2 (minimum temperature) in order
to determine the required oil viscosity for starting
a cold engine.
Refer to Table 2 (maximum temperature) in order to
select the oil viscosity for engine operation at the
highest ambient temperature that is anticipated.
Generally, use the highest oil viscosity that
is available to meet the requirement for the
temperature at start-up.
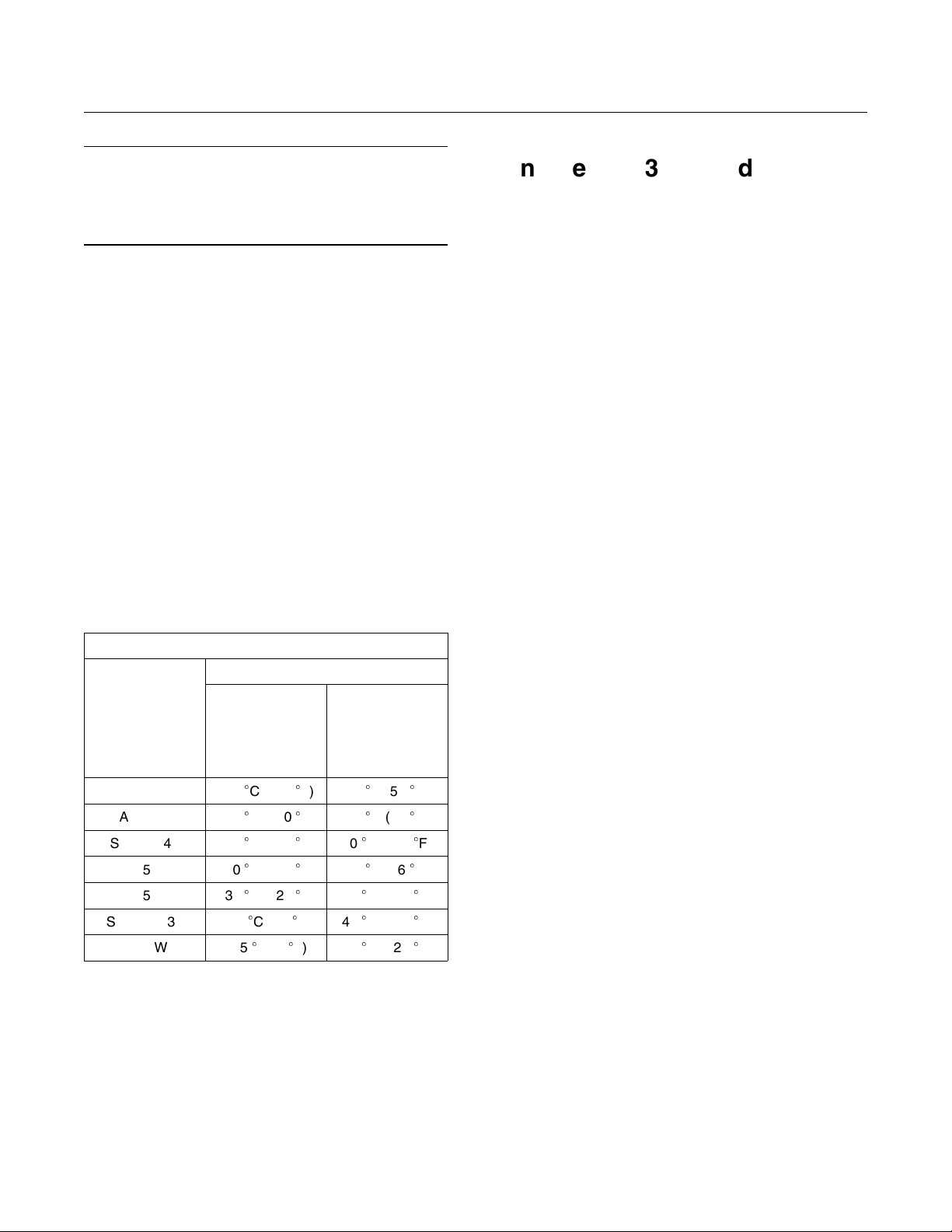
Ta bl e 2
Engine Oil Viscosity
Ambient TemperatureCaterpillar DEO
Multigrade
EMA LRG-1
API CH-4
API CG-4 and
API CF-4
Viscosity Grade
SAE 0W20
SAE 0W30
SAE 0W40
SAE 5W30 −30C(−22F) 30C (86F)
SAE 5W40 −30C(−22F) 40C (104F)
SAE 10W30 −20C(−4F) 40C (104F)
SAE 15W40 −15C(5
Minimum Maximum
−40C(−40
−40
C(−40F)
−40C(−40
F)
F)
F)
10
C (50F)
30
C (86F)
40C (104
50C (122
F)
F)
Recommendations
Caterpillar does not recommend the use of
multigrade oils in the 3116 and 3126 Marine Diesel
Engines with mechanical unit injection.
Multigrade oils use high molecular weight polymers
as viscosity index improvers.
When the crankcase blowby flows through the
turbocharger and the aftercooler, the viscosity
index improvers in the oil vapor can adhere to the
turbocharger compressor and aftercooler core.
The fouling of the turbocharger and aftercooler can
cause reduced air flow, loss of power, and increased
black smoke. The emission of black smoke results
in buildup of soot on the transom of the boat.
Note: Caterpillar recommends the use of single
grade oils with the API CF-4 classification for all
3116 and 3126 Marine Engines unless crankcase
blowby has been routed completely away from the
air cleaner inlet.
Caterpillar Special Application Engine
Oil (SAEO)
Note: Special Application Engine Oil is for use in
Caterpillar 3116 and 3126 Marine Diesel Engines
with mechanical unit injection. This includes all 3116
and 3126 Marine Diesel Engines that begin with the
following serial number prefixes: (S/N: 4KG), (S/N:
1SK), (S/N: 8NM), and (S/N: 6SR).
The factory fill in 3116 and 3126 Marine Engines is
Caterpillar Special Application Engine Oil (SAEO).
The oil that is used for the factory fill has the
following properties:
API CF-4 classification
•
Viscosity of SAE 30
•
For maximum performance in 3116 and 3126 Marine
Diesel Engines with mechanical unit injection,
Caterpillar recommends the following engine oil:
Caterpillar Special Application Engine Oil (SAEO)
•
with a viscosity of SAE 30
Caterpillar Special Application Engine Oil (SAEO)
•
with a viscosity of SAE 40
Page 9
Maintenance Section
Lubricant Specifications
9
Commercial Oils (3116 and 3126
Marine Engines)
The performance of commercial diesel engine
oil is based on American Petroleum Institute
(API) classifications. These API classifications are
developed in order to provide commercial lubricants
for a broad range of diesel engines that operate at
various conditions.
When a Caterpillar Special Application Engine Oil
(SAEO) is not used, use the following commercial
oils:
Single grade oil with a viscosity of SAE 30 or SAE
•
40 with an API CF-4 classification is preferred.
Single grade oil with a viscosity of SAE 30 or
•
SAE 40 with a CF-4 or CG-4 additive package
that does NOT contain viscosity improvers is an
acceptable oil.
For an acceptable commercial single grade oil,
contact your oil supplier or Caterpillar Customer
Service:
Total Base Number (TBN) and Fuel
Sulfur Levels for Direct Injection
(DI) Diesel Engines (3116 and 3126
Marine Engines)
The Total Base Number (TBN) for an oil depends
on the fuel sulfur level. For direct injection engines
that use distillate fuel, the minimum TBN must be 10
times the fuel sulfur level. The TBN is determined by
the “ASTM D2896” procedure. The minimum TBN
of the oil is 5 regardless of a low fuel sulfur level.
Illustration 3 demonstrates the TBN.
1-800-447-4986
The following explanation of the API CF-4
classification can be used to make the proper
choice when a commercial single grade oil with API
CF-4 classification is chosen.
API CF-4 – These oils service a wide variety of
modern diesel engines. API CF-4 oils provide more
stable oil control and reduced piston deposits in
comparison to API CF and the obsolete CE and CD
classifications of oil. API CF-4 oils provide improved
soot dispersancy in comparison to API CF and
obsolete CD oils. The API CF-4 classification was
developed with a 0.40 percent sulfur diesel fuel.
This represents the type of diesel fuels that are
commonly available worldwide.
Some commercial oils that meet the API CF-4
classifications may require reduced oil change
intervals. To determine the oil change interval,
closely monitor the condition of the oil and perform a
wear metal analysis. Caterpillar’sS·O·S oil analysis
program is the preferred method.
NOTICE
Failure to follow these oil recommendations can cause
shortened engine service life due to deposits and/or
excessive wear.
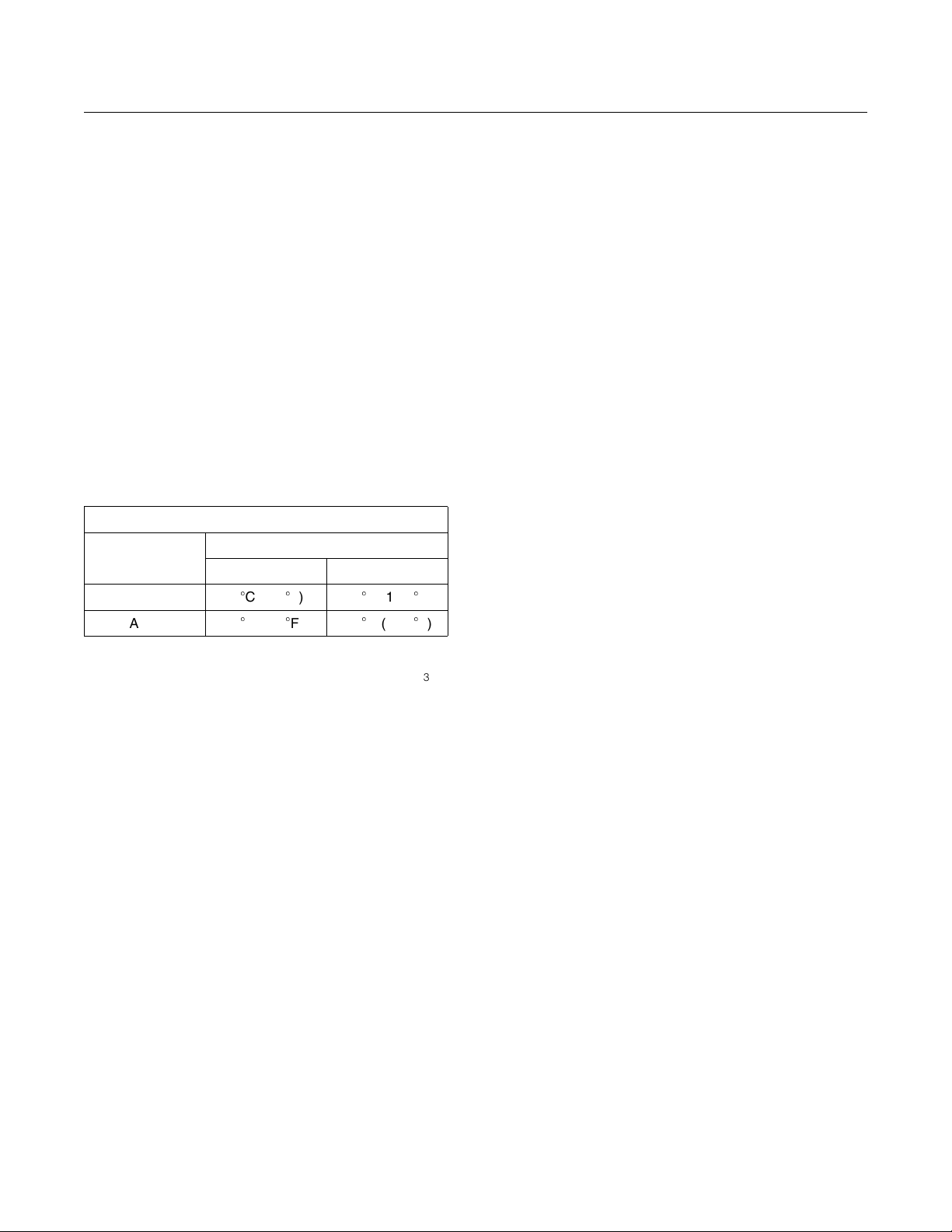
Illustration 3
(Y) TBN by “ASTM D2896”
(X) Percentage of fuel sulfur by weight
(1) TBN of new oil
(2) Change the used oil when the TBN reaches this level.
Use the following guidelines for fuel sulfur levels
that exceed 1.5 percent:
Choose an oil with the highest TBN within the
•
API CF-4 classification.
Reduce the oil change interval. Base the oil
•
change interval on the oil analysis. Ensure that
the oil analysis includes the condition of the oil
and a wear metal analysis.
Excessive piston deposits can be produced by an
oil with a high TBN. These deposits can lead to a
loss of control of the oil consumption and to the
polishing of the cylinder bore.
NOTICE
Operating Direct Injected (DI) diesel engines with fuel
sulfur levels over 1.0 percent may require shortened
oil change intervals in order to help maintain adequate
wear protection.
g00104890
Page 10
10
Maintenance Section
Lubricant Specifications
Lubricant Viscosity
Recommendations (3116 and
3126 Marine Engines)
The proper SAE viscosity grade of oil is determined
by the minimum ambient temperature during
cold engine start-up, and the maximum ambient
temperature during engine operation.
Refer to Table 3 (minimum temperature) in order
to determine the required oil viscosity for starting
a cold engine.
Refer to Table 3 (maximum temperature) in order to
select the oil viscosity for engine operation at the
highest ambient temperature that is anticipated.
Generally, use the highest oil viscosity that is
allowed for the ambient temperature at start-up.
Ta bl e 3
Engine Oil Viscosity
API CF-4 Oil
Viscosity Grade
SAE 30 0C (32F) 40C (104
SAE 40 5
Ambient Temperature
Minimum Maximum
C (41F)
50
C (122F)
i01123508
F)
Caterpillar multigrade Diesel Engine Oil is available
in two viscosity grades (10W30 and 15W40). For
precombustion chamber engines, see Table 4 in
order to choose the correct viscosity grade for the
ambient temperature. Multigrade oils provide the
correct viscosity for a broad range of operating
temperatures.
Multigrade oils are effective in maintaining low oil
consumption and low levels of piston deposits.
Caterpillar multigrade Diesel Engine Oil can be
used in other diesel engines and in gasoline
engines. See the engine manufacturer’s guide for
the recommended specifications. Compare the
specifications to the specifications of Caterpillar
multigrade Diesel Engine Oil. The current industry
standards for Caterpillar Diesel Engine Oil are listed
on the product label and on the data sheets for the
product.
Consult your Caterpillar dealer for part numbers
and for available sizes of containers.
Commercial Oils
The performance of commercial diesel engine
oils is based on American Petroleum Institute
(API) classifications. These API classifications are
developed in order to provide commercial lubricants
for a broad range of diesel engines that operate at
various conditions.
Engine Oil for Precombustion
Chamber (PC) Diesel Engines
SMCS Code: 1348
Caterpillar Diesel Engine Oil
Caterpillar Oils have been developed and tested in
order to provide the full performance and service
life that has been designed and built into Caterpillar
Engines. Caterpillar Oils are currently used to fill
diesel engines at the factory. These oils are offered
by Caterpillar dealers for continued use when the
engine oil is changed. Consult your Caterpillar
dealer for more information on these oils.
Due to significant variations in the quality and in
the performance of commercially available oils,
Caterpillar makes the following recommendations:
Caterpillar Diesel Engine Oil (10W30)
•
Caterpillar Diesel Engine Oil (15W40)
•
Caterpillar multigrade Diesel Engine Oil is
formulated with the correct amounts of detergents,
dispersants, and alkalinity in order to provide
superior performance in Caterpillar Diesel Engines.
If Caterpillar multigrade Diesel Engine Oil is not
used, only use commercial oils that meet the
following classifications:
EMA LRG-1 multigrade oil (preferred oil)
•
API CH-4 multigrade oil (preferred oil)
•
API CG-4 multigrade oil (preferred oil)
•
API CF-4 multigrade oil (acceptable oil)
•
API CF oil (acceptable oil for PC engines)
•
In order to make the proper choice of a commercial
oil, refer to the following explanations:
Page 11

11
Maintenance Section
Lubricant Specifications
EMA LRG-1 – The Engine Manufacturers
Association (EMA) has developed lubricant
recommendations as an alternative to the API oil
classification system. LRG-1 is a Recommended
Guideline that defines a level of oil performance
for these types of diesel engines: high speed, four
stroke cycle, heavy-duty, and light duty. LRG-1 oils
may be used in Caterpillar engines when API CH-4,
API CG-4, and API CF-4 oils are recommended.
LRG-1 oils are intended to provide superior
performance in comparison to API CG-4 and API
CF-4.
LRG-1 oils will meet the needs of high performance
Caterpillar diesel engines that are operating in
many applications. The tests and the test limits that
are used to define LRG-1 are similar to the new
API CH-4 classification. Therefore, these oils will
also meet the requirements of the low emissions
diesel engines. LRG-1 oils are designed to control
the harmful effects of soot with improved wear
resistance and improved resistance to oil filter
plugging. These oils will also provide superior piston
deposit control for engines with either two-piece
steel pistons or aluminum pistons.
All LRG-1 oils must complete a full test program
with the base stock and with the viscosity grade of
the finished commercial oil. The use of “API Base
Oil Interchange Guidelines” are not appropriate for
LRG-1 oils. This feature reduces the variation in
performance that can occur when base stocks are
changed in commercial oil formulations.
LRG-1 oils are recommended for use in extended
oil change interval programs that optimize oil life.
These oil change interval programs are based
on oil analysis. LRG-1 oils are recommended
for conditions that demand a premium oil. Your
Caterpillar dealer has the specific guidelines for
optimizing oil change intervals.
API CH-4 – API CH-4 oils were developed in
order to meet the requirements of the new high
performance diesel engines. Also, the oil was
designed to meet the requirements of the low
emissions diesel engines. API CH-4 oils are also
acceptable for use in older diesel engines and in
diesel engines that use high sulfur diesel fuel. API
CH-4 oils may be used in Caterpillar engines that
use API CG-4 and API CF-4 oils. API CH-4 oils will
generally exceed the performance of API CG-4 oils
in the following criteria: deposits on pistons, control
of oil consumption, wear of piston rings, valve train
wear, viscosity control, and corrosion.
Three new engine tests were developed for the
API CH-4 oil. The first test specifically evaluates
deposits on pistons for engines with the two-piece
steel piston. This test (piston deposit) also measures
the control of oil consumption. A second test is
conducted with moderate oil soot. The second
test measures the following criteria: wear of piston
rings, wear of cylinder liners, and resistance to
corrosion. A third new test measures the following
characteristics with high levels of soot in the oil:
wear of the valve train, resistance of the oil in
plugging the oil filter, and control of sludge.
In addition to the new tests, API CH-4 oils have
tougher limits for viscosity control in applications
that generate high soot. The oils also have improved
oxidation resistance. API CH-4 oils must pass an
additional test (piston deposit) for engines that use
aluminum pistons (single piece). Oil performance is
also established for engines that operate in areas
with high sulfur diesel fuel.
All of these improvements allow the API CH-4 oil
to achieve optimum oil change intervals. API CH-4
oils are recommended for use in extended oil
change intervals. API CH-4 oils are recommended
for conditions that demand a premium oil. Your
Caterpillar dealer has specific guidelines for
optimizing oil change intervals.
API CG-4 – API CG-4 oils were developed primarily
for diesel engines that use a 0.05 percent level of
fuel sulfur. However, API CG-4 oils can be used
with higher sulfur fuels. The TBN of the new oil
determines the maximum fuel sulfur level for API
CG-4 and API CF-4 oils. See Illustration 4.
API CG-4 oils are the first oils that are required to
pass industry standard tests for foam control and
viscosity shear loss. API CG-4 oils must also pass
tests that were developed for corrosion, wear and
oxidation.
API CF-4 – These oils service a wide variety of
modern diesel engines. API CF-4 oils provide more
stable oil control and reduced piston deposits in
comparison to API CF and the obsolete CE and CD
classifications of oil. API CF-4 oils provide improved
soot dispersancy in comparison to API CF and
obsolete CD oils. The API CF-4 classification was
developed with a 0.40 percent sulfur diesel fuel.
This represents the type of diesel fuels that are
commonly available worldwide.
Some commercial oils that meet the API
classifications may require reduced oil change
intervals. To determine the oil change interval,
closely monitor the condition of the oil and perform a
wear metal analysis. Caterpillar’sS·O·S oil analysis
program is the preferred method.
Page 12
12
Maintenance Section
Lubricant Specifications
NOTICE
Failure to follow these oil recommendations can cause
shortened engine service life due to deposits and/or
excessive wear.
Total Base Number (TBN) and Fuel
Sulfur Levels for Precombustion
Chamber (PC) Diesel Engines
The TBN for a new oil depends on the fuel sulfur
level of the fuel that is used. The minimum TBN of
the oil that is used in PC engines must be 20 times
the fuel sulfur level. The TBN is defined in “ASTM
D2896”. Regardless of fuel sulfur level, the minimum
TBN of new oil is five. Refer to illustration 4.
Lubricant Viscosity Recommendations
for Precombustion Chamber (PC) Diesel
Engines
The proper SAE viscosity grade of oil is determined
by the minimum ambient temperature during
cold engine start-up, and the maximum ambient
temperature during engine operation.
Refer to Table 4 (minimum temperature) in order
to determine the required oil viscosity for starting
a cold engine.
Refer to Table 4 (maximum temperature) in order to
select the oil viscosity for engine operation at the
highest ambient temperature that is anticipated.
Generally, use the highest oil viscosity that
is available to meet the requirement for the
temperature at start-up.
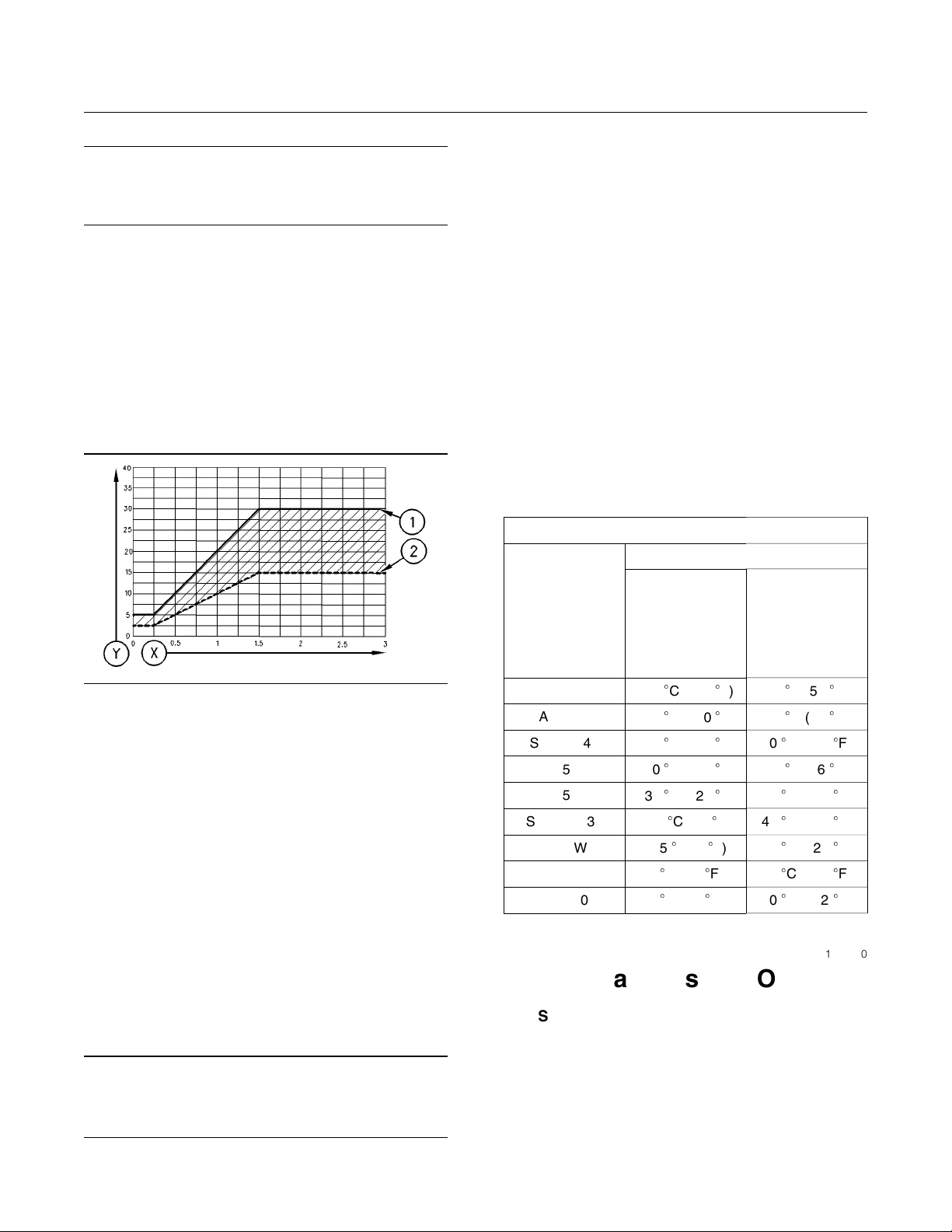
Illustration 4
(Y) The TBN that is shown by “ASTM D2896”
(X) Percentages of fuel sulfur by weight
(1) TBN of new oil
(2) Change the oil when the TBN deteriorates to 50 percent of
the original TBN.
g00274867
Whenever the fuel sulfur exceeds 1.5 percent, do
the following tasks.
Choose an oil with the highest TBN that meets
•
one of these classifications: EMA LRG-1, API CF,
API CF-4, API CG-4, and API CH-4.
Shorten the oil change interval if the oil analysis
•
dictates.
Ta bl e 4
Engine Oil Viscosity
Caterpillar DEO
Multigrade
EMA LRG-1
API CH-4
API CG-4
API CF-4 and
API CF
Viscosity Grade
SAE 0W20 −40C(−40F) 10C (50F)
SAE 0W30
SAE 0W40
SAE 5W30
SAE 5W40
SAE 10W30 −20C(−4F) 40C (104F)
SAE 15W40 −15C(5F) 50C (122F)
SAE 30 0C (32F) 40C (104F)
SAE 40 5C (41F) 50C (122F)
Ambient Temperature
Minimum Maximum
−40C(−40F) 30C (86F)
−40C(−40F) 40C (104F)
−30C(−22F) 30C (86F)
−30C(−22F) 40C (104F)
i01098470
Excessive piston deposits can be produced by an
oil with a high TBN. These deposits can lead to a
loss of control of the oil consumption and to the
polishing of the cylinder bore.
NOTICE
Operating PC engines at fuel sulfur levels over 1.0
percent may require shortened oil change intervals to
maintain adequate wear protection.
Marine Transmission Oil
SMCS Code: 3080; 3300
Caterpillar Transmission/Drive Train Oil (TDTO)
is balanced in order to give maximum frictional
material service life in Caterpillar transmissions.
TDTO exceeds the requirements for the Caterpillar
TO-4 oil specification which includes the frictional
requirements and gear wear requirements. TDTO
is offered in different lubricant viscosity grades
for maximum service life of components at high
ambient temperatures and heavy duty cycles.
Page 13
For maximum transmission service life and
performance, Caterpillar recommends Caterpillar
Transmission/Drive Train Oil (TDTO).
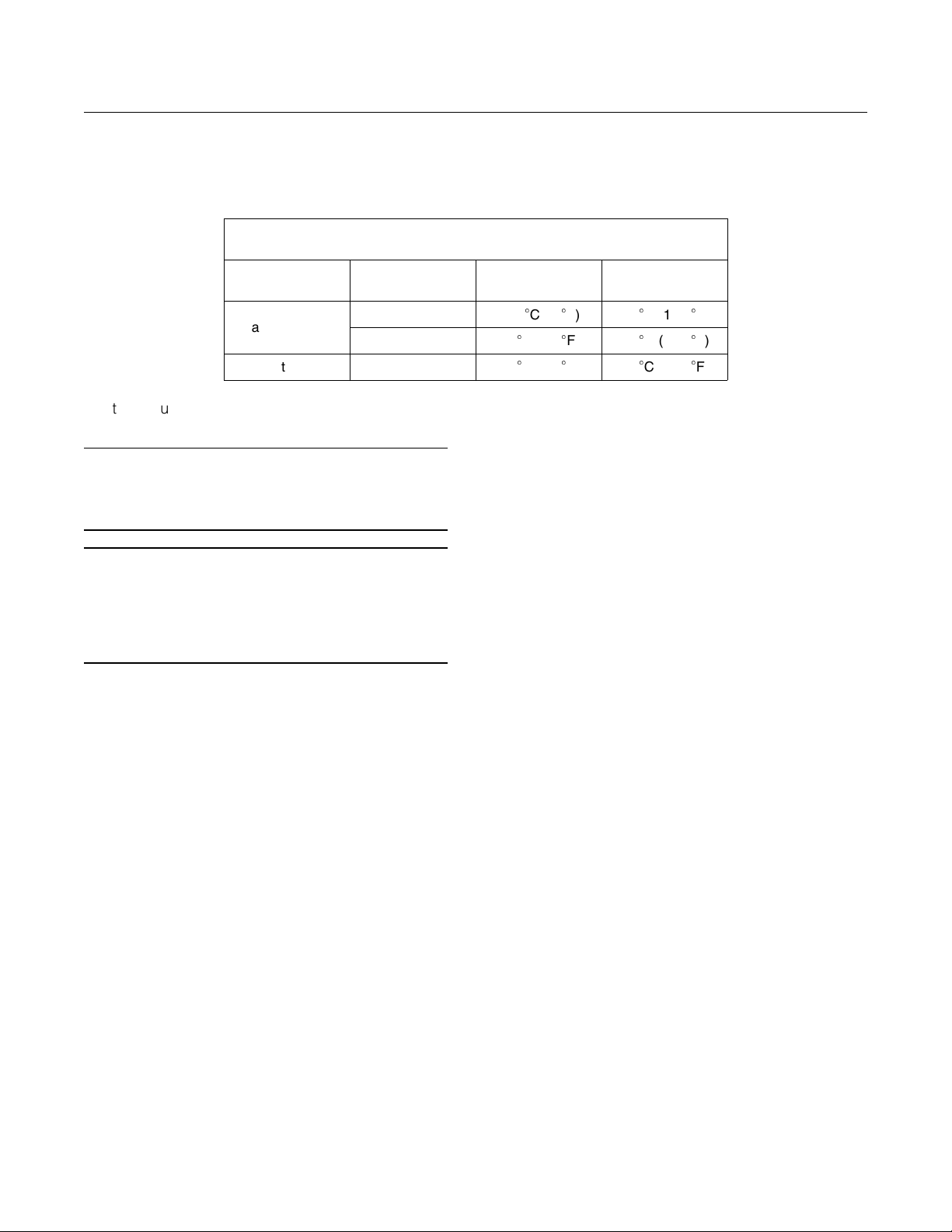
Ta bl e 5
Lubricant Viscosities For Operating Temperatures
Cooling of
Transmission
Raw/Seawater
Jacket Water SAE 50 −5
Oil Viscosities
SAE 30
SAE 50
Caterpillar TDTO
Minimum
Temperature
−15C(5
−5C (23
C (23
13
Maintenance Section
Lubricant Specifications
Maximum
Temperature
F)
F)
F)
80
C (176F)
95C (203
95
C (203
F)
F)
Contact your Caterpillar dealer for part numbers
and for sizes of available containers.
NOTICE
This oil is formulated for transmissions and drive trains
only, and should not be used in engines. Shortened
engine life will result.
NOTICE
Caterpillar Gear Oil (GO) is not the same as
Caterpillar Transmission/Drive Train Oil, and does
not meet Caterpillar’s specifications for TO-4 oil.
Caterpillar GO or commercial gear oils should not be
used in compartments which specify TO-4 oil.
Caterpillar Transmission/Drive
Train Oils
If Caterpillar Transmission/Drive Train Oil is not
used, commercial oils meeting the Caterpillar TO-4
specification must be used in Caterpillar marine
transmissions. Use TO-4 Specification Oils that are
single grade only.
Commercial Marine Transmissions
For marine transmissions which are not
manufactured by Caterpillar, refer to the lubrication
recommendation of the OEM for the marine
transmission or the vessel.
i01111406
Synthetic base oils generally perform better than
conventional oils in the following two areas:
Synthetic base oils have improved flow at low
•
temperatures especially in arctic conditions.
Synthetic base oils have improved oxidation
•
stability especially at high operating temperatures.
Some synthetic base oils have performance
characteristics that enhance the service life of the
oil. However, Caterpillar does not recommend the
automatic extension of oil change intervals for
any type of oil. Oil change intervals for Caterpillar
engines can only be adjusted after an oil analysis
program that contains the following tests: oil
condition and wear metal analysis (Caterpillar’s
S·O·S oil analysis), trend analysis, fuel consumption,
and oil consumption.
i01111412
Re-refined Base Stock Oils
SMCS Code: 1300; 1348; 7581
Re-refined base stock oils are acceptable for
use in Caterpillar engines if these oils meet the
performance requirements that are specified by
Caterpillar. Re-refined base stock oils can be used
exclusively in finished oil or in a combination with
new base stock oils. The US military specifications
and the specifications of other heavy equipment
manufacturers also allow the use of re-refined base
stock oils that meet the same criteria.
Synthetic Base Stock Oils
SMCS Code: 1300; 1348; 7581
Synthetic base oils are acceptable for use
in Caterpillar engines if these oils meet the
performance requirements that are specified for the
engine compartment.
The process that is used to make re-refined base
stock oil should adequately remove all wear metals
that are in the used oil and all additives that are
in the used oil. The process that is used to make
re-refined base stock oil generally involves the
processes of vacuum distillation and hydrotreating
the used oil. Filtering is inadequate for the
production of high quality re-refined base stock oils
from used oil.
Page 14

14
Maintenance Section
Lubricant Specifications
i01123104
Aftermarket Oil Additives
SMCS Code: 1300; 1348; 7581
Caterpillar does not recommend the use of
aftermarket additives in oil. It is not necessary to
use aftermarket additives in order to achieve the
engine’s maximum service life or rated performance.
Fully formulated, finished oils consist of base oils
and of commercial additive packages. These
additive packages are blended into the base oils
at precise percentages in order to help provide
finished oils with performance characteristics that
meet industry standards.
There are no industry standard tests that evaluate
the performance or the compatibility of aftermarket
additives in finished oil. Aftermarket additives may
not be compatible with the finished oil’s additive
package, which could lower the performance of the
finished oil. The aftermarket additive could fail to
mix with the finished oil. This could produce sludge
in the crankcase. Caterpillar discourages the use of
aftermarket additives in finished oils.
To achieve the best performance from a Caterpillar
engine, conform to the following guidelines:
When an engine is started and operated in ambient
temperatures below −30
C(−22
F), use a synthetic
base stock multigrade oil with a 0W viscosity grade
or with a 5W viscosity grade. Use an oil with a pour
point that is lower than −50
C(−58
F).
The number of acceptable lubricants is limited in
cold weather conditions. Caterpillar recommends
the following lubricants for use in cold weather
conditions:
First Choice – use an oil with an EMA LRG-1
Recommended Guideline or use a CH-4 oil that is
API licensed with an SAE 0W20, SAE 0W30, SAE
0W40, SAE 5W30, or SAE 5W40 lubricant viscosity
grade. A CG-4 oil that is API licensed with an SAE
0W20, SAE 0W30, SAE 0W40, SAE 5W30, or SAE
5W40 lubricant viscosity grade may also be used.
A CF-4 oil that is API licensed with an SAE 0W20,
SAE 0W30, SAE 0W40, SAE 5W30, or SAE 5W40
lubricant viscosity grade may also be used.
Second Choice – use an oil that contains the CH-4,
CG-4, or CF-4 additive package although the oil
has not been tested for the requirements of the
API license. The oil must have an SAE 0W20,
SAE 0W30, SAE 0W40, SAE 5W30, or SAE 5W40
lubricant viscosity grade.
Select the proper Caterpillar oil or a commercial
•
oil that meets the “EMA Recommended Guideline
on Diesel Engine Oil” or the recommended API
classification.
See the appropriate “Lubricant Viscosities” table
•
in order to find the correct oil viscosity grade for
your engine.
At the specified interval, service the engine
•
compartment. Use new oil and install a new oil
filter.
Perform maintenance at the intervals that are
•
specified in the Operation and Maintenance
Manual, “Maintenance Interval Schedule”.
i01113213
Cold Weather Lubricants
SMCS Code: 1300; 1348; 7581
When an engine is started and an engine is
operated in ambient temperatures below −20
(−4
F), use multigrade oils that are capable of
flowing in low temperatures.
NOTICE
Shortened engine service life could result if second
choice oils are used.
i01111438
Lubricating Grease
SMCS Code: 1000; 7581
Caterpillar provides greases in order to cover a
variety of applications and extreme temperature
conditions. Consult your Caterpillar dealer for part
numbers and for available sizes of containers.
Note: Some greases may not be used with other
greases. When a commercial grease is used,
ensure that the grease is compatible with the
grease that is currently used in the system. If the
commercial grease is not compatible, the system
must be purged. If any questions arise concerning
the compatibility of a grease, consult the supplier.
C
These oils have lubricant viscosity grades of SAE
0W or SAE 5W.
Page 15

15
Maintenance Section
Lubricant Specifications
Multipurpose Greases
Multipurpose Lithium Complex Grease
(MPGL)
Multipurpose Lithium Complex Grease (MPGL)
is a general purpose lithium complex grease for
medium-duty applications. This product has good
characteristics at high temperatures such as a
dropping point of 260
unleaded extreme pressure additives, antiwear
inhibitors, and corrosion inhibitors that provide extra
protection in the following applications:
Construction
•
Agricultural
•
Automotive
•
MPGL meets the requirements for extended service
intervals of automotive chassis points. MPGL also
meets the requirements for extended service
intervals of wheel bearings with disc brakes in
automobiles, in vans and in light trucks. This
product meets the NLGI certification of “GC-LB”.
MPGL is also available in a NGLI No. 2 grade.
Normal operating temperatures for this product are
−28 to 149
available as a white lithium complex grease.
C(−18 to 300
Multipurpose Lithium Complex Grease
with Molybdenum (MPGM)
Multipurpose Lithium Complex Grease with
Molybdenum (MPGM) is a general purpose
lithium complex grease that is used for light-duty
applications and for medium-duty applications. The
MPGM is available in the following grades: NLGI
No. 2 and NLGI No. 0. The MPGM is strengthened
with a molybdenum disulfide and a polymer for
extra lubrication and protection. MPGM contains
unleaded additives. MPGM also contains antiwear
inhibitors, rust inhibitors, and corrosion inhibitors
that are for protection and lubrication in many
environments. The MPGM is formulated with a base
fluid that has high viscosity.
The MPGM has the following features:
Increased protection against water washout
•
Increased retention
•
Resistance to heavy loads
•
C (500
F). MPGL contains
F). This product is also
This product is recommended for heavily loaded pin
joints and for journal bearings. This product meets
the certification of “GC-LB”. Normal operating
temperatures for this product are −28 to 149
(−18 to 300
temperatures for this product are −18 to 149
(0 to 300
Note: If MPGM is not available, use a multipurpose
type grease which contains three to five percent
molybdenum.
F) for the NLGI No. 0. Normal operating
F) for the NLGI No. 2.
C
C
Special Purpose Grease (SPG)
Bearing Lubrication (SPG)
Bearing Lubricant (SPG) is available in a NLGI
No. 2 grade with a polyurea thickener. This
grease is recommended for high temperature
antifriction bearings in the following applications:
electric starting motors, alternators, fan drives,
and generators. The Bearing Lubricant (SPG) has
an effective operating range of −29 to 177
(−20 to 350
F).
Water and Temperature Resistant Grease
(WTR)
The Water and Temperature Resistant Grease is
designed for use whenever the following conditions
are a concern: water washout, severe corrosion,
and high operating temperatures. The Water and
Temperature Resistant Grease provides extreme
pressure protection, antiwear protection, rust
protection and corrosion protection. The Water and
Temperature Resistant Grease is an environmentally
friendly grease which does not contain the following
materials: antimony, sulfur, barium, zinc, lead, and
phosphorous materials. The Water and Temperature
Resistant Grease has excellent shear stability. Water
and Temperature Resistant Grease can also resist
breakdown in the presence of water. The Water
and Temperature Resistant Grease works well in
the following applications:
Construction
•
Agricultural
•
Automotive
•
Industrial
•
Marine
•
This product meets the NLGI certification of
“GC-LB”. Normal operating temperatures for this
product are −40 to 204
C(−40 to 400F).
C
Page 16

16
Maintenance Section
Lubricant Specifications
Caterpillar Premium Grease (CPG)
Desert Gold (CPG)
Desert Gold is a heavy-duty, premium synthetic
grease that is developed for the most extreme
operating environments. This grease is formulated
with the following characteristics: high viscosity
synthetic base fluid, polymers, molybdenum
disulfide, high viscosity index, and high dropping
point.
Desert Gold will protect equipment against
heavy shock loads. Desert Gold protects against
corrosion in extreme heat, in moist conditions, or
in dusty conditions. This product has excellent
characteristics of adhesion and of stability.
Desert Gold provides longer protection than other
greases. Desert Gold is an environmentally friendly
grease which does not contain the following
materials: antimony, sulfur, barium, zinc, lead,
and phosphorous materials. Normal operating
temperatures are
−6 to 230
Gold can operate at higher temperatures for short
time periods. Desert Gold has additional extreme
pressure protection for highly loaded pin joints.
Arctic Platinum (CPG)
Arctic Platinum is a super-premium extreme
pressure lubricating grease that is developed for
lubrication in temperatures that are below zero to
moderate operating temperatures. Arctic Platinum
is available in grades 000, 00, 0, 1, and 2. These
grades ensure pumpability in central lube systems in
a variety of ambient temperatures from −60 to 18
(−76 to 65
point. Arctic Platinum contains a five percent
concentrate of molybdenum disulfide for protection
against extra heavy loads. Arctic Platinum provides
excellent corrosion protection and rust protection.
Arctic Platinum is an environmentally friendly grease
which does not contain the following materials:
antimony, sulfur, barium, zinc, and phosphorous.
Arctic Platinum is designed for long life lubrication
of the following components: horizontal pivot
bearings, lower link bearings, steering cylinders,
kingbolt bearings, upper hitch link bearings, and
ejector carrier roller bearings. This grease is extra
tacky for retention on excavator carbody bearings.
Arctic Platinum has additional extreme pressure
protection for highly loaded pin joints.
F). Arctic Platinum has a high dropping
C (21 to 450
F). Desert
i01065849
S·O·S Oil Analysis
SMCS Code: 1000; 7542
Caterpillar recommends the use of the S·O·S
oil analysis program in order to monitor the
condition and the maintenance requirements of
the equipment. The S·O·S oil analysis program will
complement the preventive maintenance program.
The S·O·S oil analysis is a diagnostic tool that is
used to determine oil performance and component
wear rates. Contamination can be identified and
measured through the use of the S·O·S oil analysis.
The S·O·S oil analysis includes the following tests:
The Wear Rate Analysis monitors the wear of the
•
engine’s metals. The amount of wear metal and
type of wear metal that is in the oil is analyzed.
The increase in the rate of engine wear metal in
the oil is as important as the quantity of engine
wear metal in the oil. For this reason, regular
sampling at specified intervals is necessary
in order to establish wear rates. Intermittent
sampling does not allow wear rate trend lines
to be established. Engine wear metals in the oil
sample are compared to established Caterpillar
norms in order to determine acceptability.
Tests are conducted in order to detect
•
contamination of the oil by water, glycol or fuel.
The Oil Condition Analysis determines the loss
•
C
of the oil’s lubricating properties. An infrared
analysis is used to compare the properties of
new oil to the properties of the used oil sample.
This analysis allows technicians to determine
the amount of deterioration of the oil during use.
This analysis also allows technicians to verify
the performance of the oil according to the
specification during the entire oil change interval.
The test results of the oil samples will then be used
as a basis for determining the oil change interval
for the engine. The results of the S·O·S oil analysis
may allow the engine to operate longer between oil
changes without the risk of engine damage.
Ta bl e 6
S·O·S Oil Analysis Interval
Compartment
Engine crankcase Every 250 Service Hours
Interval
For more information, see Special Publication,
PEDP7036, “S·O·S Fluid Analysis”. Consult your
Caterpillar dealer for complete information and
assistance about the program.
Page 17

17
Maintenance Section
Fuel Specifications
Fuel Specifications
i01060086
General Fuel Information
SMCS Code: 1250; 1280
Purchase fuel from a reputable supplier.
•
Use fuel that meets the minimum Caterpillar
•
specifications for diesel fuel. The specifications
are included in the table Caterpillar Specifications
for Distillate Fuel. This table is included in the
recommendations for diesel fuel. These fuels
have a minimum lubricity level of 3100 g. This
result is obtained by conducting the Scuffing
Load Wear Test (SBOCLE). If a High Frequency
Reciprocating Rig (HFRR) is used for testing,
the maximum allowable wear scar is .45 mm
(0.018 inch) at 60
allowable wear scar is .38 mm (0.0150 inch) at
25
Keep the fuel storage tank clean of water, debris
•
and sediment.
Drain water and sediment from the fuel storage
•
tank weekly. Drain water and sediment before the
tank is refilled.
C (77
F).
C (140F). The maximum
i01096371
Fuel Information for Diesel
Engines
SMCS Code: 1250; 1280
The two basic types of diesel fuel are No. 2 diesel
fuel and No. 1 diesel fuel. No. 2 diesel fuel is a
heavier diesel fuel than No. 1 diesel fuel. Heavier
fuels can cause problems with fuel filters, fuel
lines, fuel tanks, and fuel storage in cold weather.
Heavier diesel fuels such as No. 2 diesel fuel can
be used in diesel engines that operate in cold
temperatures with a minimum amount of pour point
depressant additive. For more information on fuels
which include blends of No. 1 and No. 2 diesel fuel,
consult your fuel supplier.
When you use No. 2 diesel fuel or other heavier
fuels, some of the fuel’s qualities may interfere
with successful cold weather operation. Additional
information about the characteristics of diesel fuel
is available. This information contains a discussion
on the modification to the characteristics of diesel
fuel. There are several possible methods that can
be used to compensate for the fuel qualities that
may interfere with cold weather operation. These
methods include the use of starting aids, engine
coolant heaters, fuel heaters, and de-icers.
Keep the area around the fuel tank filler neck
•
clean of debris in order to prevent contamination
of the fuel tank.
As required, clean the inside of the engine’s fuel
•
tank.
Drain water and sediment from the engine’s fuel
•
tank daily. Drain the tank at the start of a shift.
After the fuel tank has been filled, allow the fuel
to settle for ten minutes. This will allow the water
and sediment to separate from the fuel. Then,
drain the water and sediment from the tank.
Install water separators.
•
Drain the water from the water separator daily.
•
For some applications, Caterpillar high efficiency
•
fuel filters are required in order to provide
maximum life to the fuel system.
Change fuel filters at the scheduled interval.
•
Never fill the new fuel filter with fuel before
installation. Use the fuel priming pump to remove
air from the system.
Install breather filters on the fuel tanks.
•
Starting Aids
The use of a starting aid is a conventional method
of assistance for cold starts in low temperature
conditions. A variety of starting aids are available
for Caterpillar engines. Follow the recommendations
that are provided by the manufacturer of the starting
aid.
Engine Coolant Heaters
These heaters heat the engine coolant. The heated
coolant flows through the cylinder block. The flow
of heated coolant keeps the engine warm. A warm
engine is easier to start in cold weather. Most
coolant heaters use electrical power. A source of
electricity is necessary for this type of heater. Other
heaters that burn fuel are available as a source of
heat. These heaters may be used in place of the
electrical heaters.
With either type of heater, starting aids and/or fuels
with higher cetane numbers are less important
because the engine is warm. Problems with fuel
cloud point can cause the plugging of fuel filters.
Problems with fuel cloud point cannot be corrected
by engine coolant heaters. This is especially true
for fuel filters that are cooled by air flow during
operation.
Page 18

18
Maintenance Section
Fuel Specifications
Fuel Heaters
The fuel cloud point is related to problems with
fuel filters. The heater heats the fuel above the
cloud point before the fuel enters the fuel filter. This
prevents wax from blocking the filter. Fuel can flow
through pumps and lines at temperatures below the
cloud point. The cloud point is often above the pour
point of a fuel. While the fuel can flow through these
lines, the wax in the fuel can still plug the fuel filter.
In some engine installations, small modifications
can prevent problems that are caused by the cloud
point. One of the following changes can prevent
problems in many conditions: a change in the
location of fuel filters and/or supply lines and the
addition of insulation. In extreme temperatures,
heating of the fuel may be required to prevent the
filters from plugging. There are several types of fuel
heaters that are available. The heaters use either
engine coolant or exhaust gas as a heat source.
These systems may prevent filter waxing problems
without the use of de-icers. These systems may be
ineffective when the fuel contains a large amount
of dirt or of water. Use of a fuel heater can help
eliminate some cold weather problems. A fuel
heater should be installed so that the fuel is heated
before flowing into the fuel filter.
Note: Only use fuel heaters that are controlled
by thermostats or use fuel heaters that are
self-regulated. Do not use fuel heaters in warm
temperatures.
Select a fuel heater that is mechanically simple, yet
adequate for the application. The fuel heater should
also prevent overheating of the fuel. Disconnect the
fuel heater or deactivate the fuel heater in warm
weather. An unacceptable loss of fuel viscosity
and engine power will occur if the fuel supply
temperature is allowed to become too hot.
For additional information on fuel heaters, see your
Caterpillar dealer.
De-Icers
De-icers lower the freezing point of the moisture in
the fuel. De-icers are not generally needed when
fuel heaters are used. If you experience trouble,
consult your fuel supplier for recommendations of
a compatible commercial de-icer.
i01111474
Fuel Recommendations
SMCS Code: 1250; 1280
Diesel engines have the ability to burn a wide
variety of fuels. These fuels are divided into two
general groups. The two groups are called the
preferred fuels and the permissible fuels.
The preferred fuels provide maximum engine
service life and performance. The preferred fuels
are distillate fuels. These fuels are commonly called
diesel fuel, furnace fuel, gas oil, or kerosene.
The permissible fuels are crude oils or blended
fuels. Use of these fuels can result in higher
maintenance costs and in reduced engine service
life.
Diesel fuels that meet the specifications in Table 7
will help to provide maximum engine service life
and performance. In North America, diesel fuel that
is identified as No. 1-D or No. 2-D in “ASTM D975”
generally meet the specifications. Table 7 is for
diesel fuels that are distilled from crude oil. Diesel
fuels from other sources could exhibit detrimental
properties that are not defined or controlled by this
specification.
Ta bl e 7
Caterpillar Specifications for Distillate Diesel Fuel
Specifications
Aromatics 35% maximum “D1319”
Ash 0.02% maximum (weight) “D482”
Carbon Residue
on 10% Bottoms
Cetane Number
Cloud Point
Copper Strip
Corrosion
Distillation
Flash Point legal limit “D93”
Requirements
0.35% maximum (weight) “D524”
40 minimum (DI engines)
35 minimum (PC engines)
The cloud point must
not exceed the lowest
expected ambient
temperature.
No. 3 maximum “D130”
10% at 282C (540F)
maximum
90% at 360C (680F)
maximum
ASTM
Test
“D613”
-
“D86”
(continued)
Page 19

19
Maintenance Section
Fuel Specifications
(Table 7, contd)
Caterpillar Specifications for Distillate Diesel Fuel
Specifications
Requirements
ASTM
Test
30 minimum
“D287”
API Gravity
45 maximum
Pour Point
6
F) minimum
C (10
below ambient
“D97”
temperature
3% maximum “D3605”
(1)
Sulfur
or
“D1552”
Kinematic
Viscosity
Water and
1.4 cSt minimum and 20.0
(2)
cSt maximum at 40
(104
F)
C
0.1% maximum “D1796”
“D445”
Sediment
Water 0.1% maximum “D1744”
Sediment 0.05% maximum (weight) “D473”
Gums and
(3)
Resins
10 mg per 100 mL
maximum
“D381”
3100 g minimum “D6708”
Lubricity
(4)
0.45 mm (0.018 inch)
maximum at 60
C (140
F)
“D6079”
0.38 mm (0.015 inch)
maximum at 25
(1)
Caterpillar fuel systems and engine components can
operate on high sulfur fuels. Fuel sulfur levels affect exhaust
emissions. High sulfur fuels also increase the potential for
corrosion of internal components. Fuel sulfur levels above 1.0
percent may significantly shorten the oil change interval. For
additional information, see this publication, “Engine Oil” topic
(Maintenance Section).
(2)
The values of the fuel viscosity are the values as the fuel
is delivered to the fuel injection pumps. If a fuel with a low
viscosity is used, cooling of the fuel may be required to maintain
a 1.4 cSt viscosity at the fuel injection pump. Fuels with a high
viscosity might require fuel heaters in order to bring down the
viscosity to a 20 cSt viscosity. For additional information, see
Special Publication, SEBD0717, “Diesel Fuel and Your Engine”.
(3)
Follow the test conditions and procedures for gasoline (motor).
(4)
The lubricity of a fuel is a concern with low sulfur fuel. To
determine the lubricity of the fuel, use either the “ASTM D6708
Scuffing Load Wear Test (SBOCLE)” or the “ASTM D6079 High
Frequency Reciprocating Rig (HFRR)” test. If the lubricity of a
fuel does not meet the minimum requirements, consult your
fuel supplier. Do not treat the fuel without consulting the fuel
supplier. Some additives are not compatible. These additives
can cause problems in the fuel system.
C (77
F)
NOTICE
Operating with fuels that do not meet Caterpillar’s recommendations can cause the following effects: starting difficulty, poor combustion, deposits in the fuel injectors, reduced service life of the fuel system, deposits in the combustion chamber, and reduced service life of the engine.
In the USA, 0.05 percent diesel fuels have been
used in all on-highway truck engines since 1
January 1994. This low sulfur diesel fuel was
mandated as a means of directly reducing
particulate emissions from diesel truck engines.
This low sulfur fuel will also be used in Caterpillar
commercial diesel engines when low emissions are
required or when the fuel supply sources provide
this type of fuel. Caterpillar has not seen any
detrimental effects with 0.05 percent sulfur fuel in
Caterpillar diesel engines.
NOTICE
Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO), Residual fuel, or Blended fuel
must NOT be used in Caterpillar diesel engines (except in 3600 Series HFOengines). Severe component
wear and component failures will result if HFO type fuels are used in engines that are configured to use distillate fuel.
In extreme cold ambient conditions, you may
use the distillate fuels that are specified in Table
8. However, the fuel that is selected must meet
the requirements that are specified in Table 7.
These fuels are intended to be used in operating
temperatures that are down to
Ta bl e 8
Distillate Fuels
Specification Grade
“MIL-T-5624R” JP-5
“ASTM D1655” Jet-A-1
“MIL-T-83133D” JP-8
(1)
The fuels that are listed in this Table may not meet the
requirements that are specified in the “Caterpillar Specifications
for Distillate Diesel Fuel” Table. Consult the supplier for the
recommended additives in order to maintain the proper fuel
lubricity.
−54
(1)
C(−65
F).
These fuels are lighter than the No. 2 grades of fuel.
The cetane number of the fuels in Table 8 must be
at least 40. If the viscosity is below 1.4 cSt at 38
(100
F), use the fuel only in temperatures below
C (32F). Do not use any fuels with a viscosity
0
of less than 1.2 cSt at 38
C (100
F). Fuel cooling
C
may be required in order to maintain the minimum
viscosity of 1.4 cSt at the fuel injection pump.
There are many other diesel fuel specifications that
are published by governments and by technological
societies. Usually, those specifications do not
review all the requirements that are addressed
in this specification. To ensure optimum engine
performance, a complete fuel analysis should be
obtained before engine operation. The fuel analysis
should include all of the properties that are listed
in Table 7.
Page 20

20
Maintenance Section
Fuel Specifications
i01111650
Characteristics of Diesel Fuel
SMCS Code: 1250; 1280
The primary characteristics that affect engine
operation and performance in cold temperatures
are the following characteristics: Lubricity, Viscosity,
Cetane Number, Cloud Point, Pour Point, and
Moisture Content.
Refer to Special Publication, SEBD0717, “Diesel
Fuels and Your Engine” for information about the
following fuel properties: ignition quality, gravity
(density), viscosity, cloud point, pour point, and
sulfur content.
Lubricity and Low Sulfur Fuel
Note: The fuel lubricity is important. You should
consider the fuel’s lubricity whenever you operate
the equipment in arctic weather. Also, you should
consider the fuel’s lubricity whenever you use
fuels that are lower in viscosity. There are many
aftermarket additives that are available to treat fuel.
If the fuel’s lubricity is an issue, consult your fuel
supplier for proper recommendations regarding fuel
additives.
In the USA, a 0.05 percent limit on the amount of
fuel sulfur in diesel fuel was mandated in January
of 1994 for on-highway trucks. The removal of
sulfur from diesel fuel helps to reduce particulate
emissions from diesel engines. While limits for
fuel sulfur have not generally been mandated for
off-highway use, some local governments have
regulations that include off-highway use. There
is frequently no difference in the fuel that is
sold for different applications. The same fuel is
often used for both on-highway applications and
off-highway applications. Other areas of the world
are mandating similar limits. Regulations continue to
become more stringent. Lower sulfur limits can be
expected in the future.
The fluid’s lubricity describes the ability of the fluid
to reduce the friction between surfaces that are
under load. This ability reduces the damage that
is caused by friction. Fuel injection systems rely
on the lubricating properties of the fuel. Until fuel
sulfur limits were mandated, the fuel’s lubricity was
generally believed to be a function of fuel viscosity.
The process that is most commonly used to remove
sulfur from fuel is called hydro-treatment. This
process is also the most economical process. Each
source of crude oil contains different amounts
of sulfur. Crude oils with low sulfur require little
hydro-treatment to obtain the 0.05 percent limit.
Crude oils with high sulfur require a more severe
treatment.
The Hydro-treatment removes the fuel’s sulfur as
well as other components. The treatment removes
nitrogen compounds, polar materials, bicyclic
aromatics, polycyclic aromatics, and oxygen
compounds. While the removal of sulfur has shown
no detrimental effects to the engine, the removal of
other compounds have lowered the lubricity of the
fuel. As a result of the lowered lubricity, the fuel is
less tolerant of contamination by water and dirt. The
lower fuel lubricity can be seen as abrasive wear
of fuel system components. Fuels that have a low
lubricity may not provide adequate lubrication to
plungers, to barrels, and to injectors. This problem
may be compounded in areas that require winter
blends of fuel. The lighter winter fuel blend has
the following characteristics: lower viscosity, lower
cloud point, and lower pour point.
All low sulfur fuels do not have a low lubricity. The
fuel’s lubricity may be enhanced with additives.
Many fuel suppliers treat the fuel with these
additives. Do not use a fuel lubricity additive before
you consult the fuel’s supplier. Some aftermarket
additives may not be compatible with the additives
that are already in the fuel. Some additive packages
that are supplied by the aftermarket manufacturer
may not be compatible with the seals that are used
in fuel systems of some diesel engines. Other
additive packages that are supplied by aftermarket
manufacturers cannot provide proper performance
in high temperature conditions. These additives may
leave deposits because of the high temperatures
that exist in the fuel systems of diesel engines.
Maximum life of the fuel system can be achieved by
performing the following tasks: using a reliable fuel
supplier, performing proper maintenance of the fuel
system, and installing Caterpillar high efficiency fuel
filters in the fuel system.
Note: Lighter fuels are frequently used in arctic
temperatures. Lighter fuels may include the following
fuels: Jet A-1, JP-8, JP-5, and kerosene. The fuel
lubricity is not a requirement of the specifications
for these fuels. Do not assume that a fuel meets
the minimum Caterpillar specification. Contact the
fuel supplier for proper recommendations on fuel
lubricity additives.
Viscosity
The viscosity of the fuel is significant because
the fuel serves as a lubricant for fuel system
components. Arctic fuels need to have sufficient
viscosity. The fuel must lubricate the fuel system at
a temperature of 0
kinematic viscosity of the fuel is lower than 1.4 cSt
as supplied to the fuel injection pump or to the unit
injectors, excessive scuffing and seizure can occur.
C (32F) or below freezing. If the
Page 21

21
Maintenance Section
Fuel Specifications
Cetane Number
The cetane number of the fuel has an effect on
the ability of the engine to start. Also, the cetane
number has an effect on the interval of time before
the engine runs smoothly. Generally, an increase
of ten in the cetane number will allow the engine
to be started at a lower temperature. The starting
temperature can be improved approximately
7to8
the cetane number. After the engine reaches the
normal operating temperature, a change in the
cetane from 40 to 50 will have a minimal effect on
engine performance.
Most fuels that have a cetane number above 40 will
permit acceptable engine starts in warmer outside
temperatures. The engine will start satisfactorily with
this fuel when the engine is kept warm. The engine
can be kept warm by using either a heated room
or a coolant heater.
During average starting conditions, direct injection
engines require a minimum cetane number of 40. A
higher cetane value may be required for operation
in high altitudes or for cold weather operation. The
minimum fuel cetane number that is required for the
precombustion engine is 35.
C (12 to 15
Modifying the Cetane Number
The cetane number of a fuel can be changed if
the fuel is mixed with a fuel that has a different
cetane number. Generally, the cetane number of
the mixture will be in direct relation to the ratio of
the fuels that were mixed. Your fuel supplier can
provide the information about the cetane number
of a particular fuel.
Additives can also be used to improve the cetane
number of a fuel. Additives are evaluated through
testing in special engines. However, the fuel
characteristics of additives are not identical to a
natural product. While both fuels may be rated as
having the same cetane number, starting may be
different.
F) for every increase of ten in
Cloud Point
It is important to understand that the cloud point of
a fuel is different from the pour point. There is no
relationship between cloud point and the pour point.
The cloud point is the temperature that allows some
of the heavier components in the wax to solidify in
the fuel. This wax is not a contaminant in the fuel.
The wax is an important element of No. 2 diesel
fuel. The wax has a high fuel energy content and
the wax has a very high cetane value. Removal of
the heavier wax lowers the cloud point of the fuel.
Removal of the wax also increases the cost because
less fuel can be made from the same amount of
crude oil. Basically, a No. 1 diesel fuel is formulated
by removing the wax from a No. 2 diesel fuel.
The cloud point of the fuel is important because
the cloud point can limit the performance of the
fuel filter. The wax can alter the fuel characteristics
in cold weather. Solid wax can fill the fuel filters.
The solidified wax will stop the flow of fuel. Fuel
filters are necessary in order to remove dirt from
the fuel. The filters block foreign material, and the
filters protect the parts for the fuel injection system.
Since fuel must flow through the filters, installing
a fuel heater is the most practical way to prevent
the problem. A fuel heater will keep the fuel above
the cloud point as the fuel flows through the fuel
system. The fuel heater will permit the wax to flow
through the filters with the fuel.
Modifying the Cloud Point
You can lower the cloud point of a diesel fuel by
mixing the diesel fuel with a different fuel that has a
lower cloud point. No. 1 diesel fuel or kerosene may
be used to lower the cloud point of a diesel fuel. The
efficiency of this method is not good, because the
ratio of the mixture does not have a direct relation
to the improvement in cloud point. The amount of
fuel with low cloud point that is required makes the
process less preferable to use.
The following illustration contains a table that can be
used to find the necessary mixture for two fuels with
different cloud points. In order to use the table, you
must know the exact fuel cloud point of each fuel.
This specification can change from one purchase of
fuel to the next purchase of fuel. This specification
is normally available from personnel at the source of
the fuel supply. When fuels that have a lower cloud
point are not available, this method cannot be used.
The manufacturer of the fuel can add cold flow
improvers to the fuel. Cold flow improvers modify the
wax crystals in the fuels. The cold flow improvers
do not change the fuel’s cloud point. However, the
cold flow improvers keep the wax crystals small
enough to pass through standard fuel filters. For
mixing precautions, see the topic “Pour Point”.
Page 22

22
Maintenance Section
Fuel Specifications
Modifying the Pour Point
You can lower the fuel’s pour point by using
additives. You can also lower the pour point by
mixing the fuel with a fuel that has a lower pour
point. See the topic “Cloud Point” for the procedure.
This procedure is not the best procedure to use.
The same table that was use for cloud point can
be used for an estimate of pour points. This is true
only if the fuels do not have additives which change
the pour point.
Illustration 5
Cloud point of fuel mixtures
Generally, the most practical method that is used to prevent
problems that are caused by fuel cloud point at low temperatures
is the use of fuel heaters. In most applications, fuel heaters can
be used at a lower cost than fuel mixtures.
g00592741
Pour Point
The fuel’s pour point is a temperature below the
fuel’s cloud point. Fuel stops flowing below the pour
point. The pour point is the temperature which limits
movement of the fuel with pumps.
To measure the pour point, the fuel temperature
is lowered below the cloud point in steps of 3
(5
F) at a time. The temperature is lowered until
the fuel does not flow. The pour point is the last
temperature that is shown before the flow stops.
At the pour point, the wax has solidified out of the
fuel. This makes the fuel more solid than liquid. The
pour point of the fuel can be improved. This does
not require the removal of important elements. This
process is the same process that is used to improve
the cloud point of a fuel.
A fuel’s pour point should be at least 6
below the lowest ambient temperature that is
required for engine start-up and for engine
operation. To operate the engine in extremely cold
weather, No. 1 fuel or No. 1-D fuel may be necessary
because of these fuels’ lower pour points.
C (10F)
C
Illustration 6
Cloud point of fuel mixtures
g00592741
In order to calculate the amount of lighter fuel that
is required to be blended with the heavier fuel,
perform the following steps:
1. Obtain the specification for fuel cloud point of
both fuels from your fuel supplier.
2. Locate the cloud point of the heavier fuel on the
left side of the table. Mark the point on the table.
3. Locate the cloud point of the lighter fuel on the
right side of the table. Mark the point on the
table.
4. Draw a line between the two points that were
established. Label this line “A”.
Page 23

23
Maintenance Section
Fuel Specifications
5. Determine the lowest outside temperature
for machine operation. Find this point on the
left side of the table. Mark this point. Draw a
horizontal line from this point. Stop the line at the
intersection of line “A”. Label this new line “C”.
6. Line “C” and line “A” intersect. Mark this point.
Draw a vertical line from this point. Stop the
line at the bottom of the table. Label this line
“B”. The point at the bottom of line “B” reveals
the percentage of lighter fuel that is required to
modify the pour point.
The above example shows that the blending will
require a thirty percent mixture of lighter fuel.
Additives are a good method to use in order to
lower the pour point of a fuel. These additives are
known by the following names: pour depressants,
cold flow improvers, and wax modifiers. When the
additives are used in a low concentration, the fuel
will flow through pumps, lines, and hoses. These
additives must be thoroughly mixed into the fuel at
temperatures that are above the cloud point. The
fuel supplier should be contacted in order to blend
the fuel with the additives. The blended fuel can be
delivered to your fuel tanks.
Moisture Content
Problems with fuel filters can occur at any time. The
cause of the problem can be water in the fuel or
moisture in the fuel. At low temperatures, moisture
causes special problems. There are three types of
moisture in fuel: dissolved moisture (moisture in
solution), free and dispersed moisture in the fuel,
and free and settled at the bottom of the tank.
Most diesel fuels have some dissolved moisture.
Just as the moisture in air, the fuel can only contain
a specific maximum amount of moisture at any one
temperature. The amount becomes less as the
temperature is lowered. For example, a fuel could
contain 100 ppm (0.010 percent) of water in solution
C (65F). This same fuel can possibly hold
at 18
only 30 ppm (0.003 percent) at 4
C (40F).
The small drops of water cause a cloudy
appearance in the fuel. If the change in temperature
is slow, the small drops of water can settle to the
bottom of the tank. When the fuel temperature
is lowered rapidly to freezing temperature, the
moisture that comes out-of-solution changes to very
fine particles of ice instead of small drops of water.
The particles of ice are lighter than the fuel, and
the particles of ice will not settle to the bottom of
the tank. When this type of moisture is mixed in
the fuel, this moisture will fill the fuel filters. The ice
crystals will plug the fuel filters in the same way as
wax plugs the fuel filters.
If a filter is plugged and fuel flow is stopped,
perform the following procedure to determine the
cause:
1. Remove the fuel filters.
2. Cut the fuel filters open.
3. Inspect the fuel filter before the filter warms. This
inspection will show that the filter is filled with
particles of either ice or wax.
The moisture which is free and settled at the bottom
of the tank can become mixed with the fuel. The
force of any pumping action will mix the moisture
with the fuel whenever fuel is transferred. This
moisture then becomes free and dispersed water.
This moisture can cause ice in the filters. This
moisture can cause other problems with filters at
any temperature. Generally, the same force that
mixes the water into the fuel will also mix dirt and
rust from the bottom of the tank with the water. The
result is a dirty mixture of fuel and water which can
also fill the filters and stop fuel flow.
After the fuel has absorbed the maximum possible
amount of water, the additional water will be free
and dispersed. Free and dispersed moisture is
fine droplets of water that is suspended in the fuel.
Since the water is heavier than the fuel, the water
will slowly become free and settled at the bottom
of the tank. In the above example, when the fuel
temperature was lowered from 18
(40
F), 70 ppm of water became free and dispersed
C (65F) to 4C
in the fuel.
Page 24

24
Maintenance Section
Cooling System Specifications
Cooling System
Specifications
i01111669
General Coolant Information
SMCS Code: 1350; 1395
NOTICE
Never add coolant to an overheated engine. Engine
damage could result. Allow the engine to cool first.
NOTICE
If the engine is to be stored in, or shipped to an area
with below freezing temperatures, the cooling system
must be either protected to the lowest outside temperature or drained completely to prevent damage.
NOTICE
In cold weather, frequently check the specific gravity
of the coolant solution to ensure adequate protection.
Clean the cooling system for the following reasons:
Contamination of the cooling system
•
Many engine failures are related to the cooling
system. The following problems are related to
cooling system failures: overheating, leakage of the
water pump, plugged radiators or heat exchangers,
and pitting of the cylinder liners.
These failures can be avoided with proper cooling
system maintenance. Cooling system maintenance
is as important as maintenance of the fuel system
and the lubrication system. Quality of the coolant
is as important as the quality of the fuel and the
lubricating oil.
Coolant is normally composed of three elements:
water, additives, and glycol.
Water
NOTICE
All Caterpillar diesel engines equipped with air-to-air
aftercooling (ATAAC) require a minimum of 30 percent
glycol to prevent water pump cavitation.
NOTICE
Never use water alone without Supplemental Coolant
Additives (SCA) or without inhibited coolant. Water
alone is corrosive at engine operating temperatures.
Water alone does not provide adequate protection
against boiling or freezing.
Overheating of the engine
•
Foaming of the coolant
•
Note: Air pockets can form in the cooling system if
the cooling system is filled at a rate that is greater
than 20 L (5 US gal) per minute.
After you drain the cooling system and after you
refill the cooling system, operate the engine.
Operate the engine without the filler cap until the
coolant reaches normal operating temperature and
the coolant level stabilizes. Ensure that the coolant
is maintained to the proper level.
NOTICE
Never operate an engine without water temperature
regulators in the cooling system. Water temperature
regulators help to maintain the engine coolant at the
proper operating temperature. Cooling system problems can develop without water temperature regulators.
Refer to Special Instruction, SEBD0518, “Know
Your Cooling System” and Special Instruction,
SEBD0970, “Coolant and Your Engine” for more
detailed information.
Water is used in the cooling system in order to
transfer heat.
Distilled water or deionized water is
recommended for use in engine cooling systems.
DO NOT use the following types of water in cooling
systems: hard water, softened water that has been
conditioned with salt, and sea water.
If distilled water or deionized water is not available,
use water with the properties that are listed in Table
9.
Page 25

25
Maintenance Section
Cooling System Specifications
Ta bl e 9
Caterpillar Minimum Acceptable Water Requirements
Property Maximum Limit ASTM Test
Chloride (Cl)
Sulfate (SO
Total Hardness
Total Solids
Acidity pH of 5.5 to 9.0 “D1293”
)
4
40 mg/L
(2.4 grains/US gal)
100 mg/L
(5.9 grains/US gal)
170 mg/L
(10 grains/US gal)
340 mg/L
(20 grain/US gal)
“D512”,
“D4327”
“D516”
“D1126”
“D1888”
For a water analysis, consult one of the following
sources:
Caterpillar dealer
•
Local water utility company
•
Agricultural agent
•
Independent laboratory
•
Reduction of heat transfer
•
Leakage of the water pump seal
•
Plugging of radiators, coolers, and small
•
passages
Glycol
Glycol in the coolant helps to provide protection
against the following conditions:
Boiling
•
Freezing
•
Cavitation of the water pump and the cylinder liner
•
For optimum performance, Caterpillar recommends
a 1:1 mixture of a water/glycol solution.
NOTICE
All Caterpillar diesel engines equipped with air-to-air
aftercooling (ATAAC) require a minimum of 30 percent
glycol to prevent water pump cavitation.
Additives
Additives help to protect the metal surfaces of
the cooling system. A lack of coolant additives
or insufficient amounts of additives enable the
following conditions to occur:
Corrosion
•
Formation of mineral deposits
•
Rust
•
Scale
•
Pitting and erosion from cavitation of the cylinder
•
liner
Foaming of the coolant
•
Many additives are depleted during engine
operation. These additives must be replaced
periodically. This can be done by adding
Supplemental Coolant Additives (SCA) to Diesel
Engine Antifreeze/Coolant (DEAC) or by adding
ELC Extender to Extended Life Coolant (ELC).
Additives must be added at the proper
concentration. Overconcentration of additives can
cause the inhibitors to drop out-of-solution. The
deposits can enable the following problems to
occur:
Note: Use a mixture that will provide protection
against the lowest ambient temperature.
Note: 100 percent pure glycol will freeze at a
temperature of −23
C(−9
F).
Most conventional heavy-duty coolant/antifreezes
use ethylene glycol. Propylene glycol may also be
used. In a 1:1 mixture with water, ethylene and
propylene glycol provide similar protection against
freezing and boiling. See Tables 10 and 11.
Ta bl e 1 0
Ethylene Glycol
Concentration
50 Percent
60 Percent
Freeze
Protection
−36C(−33F) 106C (223
−51C(−60
F)
Boil
Protection
111C (232
F)
F)
NOTICE
Do not use propylene glycol in concentrations that exceed 50 percent glycol because of propylene glycol’s
reduced heat transfer capability. Use ethylene glycol
in conditions that require additional protection against
boiling or freezing.
Formation of gel compounds
•
Page 26

26
Maintenance Section
Cooling System Specifications
Ta bl e 1 1
Propylene Glycol
Concentration
50 Percent −29C(−20
Freeze
Protection
F)
Anti-Boil
Protection
106
C (223F)
To check the concentration of glycol, use the
1U-7298 Coolant/Battery Tester (Celsius) or use
the 1U-7297 Coolant/Battery Tester (Fahrenheit).
The testers give readings that are immediate and
accurate. The testers can be used with ethylene
or propylene glycol.
i01096597
Coolant Recommendations
SMCS Code: 1350; 1352; 1395
The following two coolants are used in Caterpillar
diesel engines:
Preferred – Caterpillar Extended Life Coolant (ELC)
or a commercial extended life coolant that meets
the Caterpillar EC-1 specification
NOTICE
All Caterpillar diesel engines equipped with air-to-air
aftercooling (ATAAC) require a minimum of 30 percent
glycol to prevent water pump cavitation.
Ta bl e 1 2
Coolant Service Life
Coolant Type Service Life
Caterpillar ELC
Caterpillar DEAC
Commercial Heavy-Duty
Coolant/Antifreeze that
meets “ASTM D5345”
Commercial Heavy-Duty
Coolant/Antifreeze that
meets “ASTM D4985”
Caterpillar SCA and
Water
Commercial SCA and
Water
6000 Service Hours or
Six Years
3000 Service Hours or
Three Years
3000 Service Hours or
Two Years
3000 Service Hours or
One Year
3000 Service Hours or
Two Years
3000 Service Hours or
One Year
Acceptable – A Caterpillar Diesel Engine
Antifreeze/Coolant (DEAC) or a commercial
heavy-duty coolant/antifreeze that meets “ASTM
D4985” or “ASTM D5345” specifications
NOTICE
Do not use a commercial coolant/antifreeze that only
meets the ASTM D3306 or D4656 specification. This
type of coolant/antifreeze is made for light duty automotive applications.
Caterpillar recommends a 1:1 mixture of water
and glycol. This mixture of water and glycol will
provide optimum heavy-duty performance as a
coolant/antifreeze.
Note: Caterpillar DEAC DOES NOT require a
treatment with an SCA at the initial fill. Commercial
heavy-duty coolant/antifreeze that meets “ASTM
D4985” or “ASTM D5345” specifications MAY
require a treatment with an SCA at the initial fill.
Read the label or the instructions that are provided
by the OEM of the product.
In stationary engine applications and marine engine
applications that do not require anti-boil protection
or freeze protection, a mixture of SCA and water is
acceptable. Caterpillar recommends a six percent
to eight percent concentration of SCA in those
cooling systems. Distilled water or deionized water
is preferred. Water which has the recommended
properties may be used.
i01096605
Extended Life Coolant (ELC)
SMCS Code: 1350; 1352; 1395
Caterpillar provides Extended Life Coolant (ELC) for
use in the following applications:
Heavy-duty spark ignited gas engines
•
Heavy-duty diesel engines
•
Automotive applications
•
The anti-corrosion package for Caterpillar ELC is
different from the anti-corrosion package for other
coolants. Caterpillar ELC is an ethylene glycol
base coolant. However, Caterpillar ELC contains
organic corrosion inhibitors and antifoam agents
with low amounts of nitrite. Caterpillar ELC has
been formulated with the correct amount of these
additives in order to provide superior corrosion
protection for all metals in engine cooling systems.
ELC extends the service life of the coolant to 6000
service hours or six years. ELC does not require
a frequent addition of a Supplemental Coolant
Additive (SCA). An Extender is the only additional
maintenance that is needed at 3000 service hours
or one half of the ELC service life.
Page 27

ELC is available in a 1:1 premixed cooling solution
with distilled water. The Premixed ELC provides
freeze protection to −36
C(−33
F). The Premixed
ELC is recommended for the initial fill of the cooling
system. The Premixed ELC is also recommended
for topping off the cooling system.
ELC Concentrate is also available. ELC Concentrate
can be used to lower the freezing point to −51
F) for arctic conditions.
(−60
C
Containers of several sizes are available. Consult
your Caterpillar dealer for the part numbers.
Note: Caterpillar developed the EC-1 specification.
The EC-1 specification is an industry standard. The
EC-1 specification defines all of the performance
requirements that are needed for an engine coolant
to be sold as an extended life coolant for Caterpillar
engines. ELC can be used in most OEM engines of
the following types: diesel, gasoline, and natural
gas. ELC meets the performance requirements of
“ASTM D4985” and “ASTM D5345” for heavy-duty
low silicate antifreeze/coolants. ELC also meets the
performance requirements of “ASTM D3306” and
“ASTM D4656” for automotive applications.
i01111712
Extended Life Coolant (ELC)
Cooling System Maintenance
SMCS Code: 1350; 1352; 1395
Proper additions to the Extended
Life Coolant
NOTICE
Use only Caterpillar products or commercial products
that have passed Caterpillar’s EC-1 specification for
pre-mixed or concentrated coolants.
Use only Caterpillar Extender with Extended Life
Coolant.
Mixing Extended Life Coolant with other products reduces the Extended LifeCoolant service life. Failure to
follow the recommendations can reduce cooling system components life unless appropriate corrective action is performed.
27
Maintenance Section
Cooling System Specifications
NOTICE
Do not use a conventional coolant to top-off a cooling
system that is filled with Extended Life Coolant (ELC).
Do not use standard supplemental coolant additive
(SCA). Only use ELC Extender in cooling systems that
are filled with ELC.
Caterpillar ELC Extender
Caterpillar ELC Extender is added to the cooling
system halfway through the ELC service life. Treat
the cooling system with ELC Extender at 3000 hours
or one half of the coolant service life. Use Table 13
in order to determine the proper amount of ELC
Extender that is required.
Containers of several sizes are available. Consult
your Caterpillar dealer for the part numbers.
Ta bl e 1 3
Caterpillar ELC Extender Additions by
Cooling System Capacity
Cooling System Capacity
22 to 30 L (6 to 8 US gal) 0.57 L (20 fl oz)
31 to 38 L (9 to 10 US gal) 0.71 L (24 fl oz)
39 to 49 L (11 to 13 US gal) 0.95 L (32 fl oz)
50 to 64 L (14 to 17 US gal) 1.18 L (40 fl oz)
65 to 83 L (18 to 22 US gal) 1.60 L (54 fl oz)
84 to 114 L (23 to 30 US gal) 2.15 L (72 fl oz)
115 to 163 L (31 to 43 US gal) 3.00 L (100 fl oz)
164 to 242 L (44 to 64 US gal) 4.40 L (148 fl oz)
For cooling system capacities that exceed the
capacities that are specified in Table 13, use the
equation that is in Table 14 in order to determine
the proper amount of ELC Extender that is required.
Ta bl e 1 4
Equation For Adding ELC Extender To ELC
V × 0.02 = X
V is the total volume of the cooling system.
X is the amount of ELC Extender that is required.
Addition of ELC
Extender
In order to maintain the correct balance between
the antifreeze and the additives, you must maintain
the recommended concentration of Extended Life
Coolant (ELC). Lowering the proportion of antifreeze
lowers the proportion of additive. This will lower
the ability of the coolant to protect the system from
pitting, from cavitation, from erosion, and from
deposits.
Table 15 is an example for using the equation that
is in Table 14.
Page 28

28
Maintenance Section
Cooling System Specifications
Ta bl e 1 5
Example Of The Equation For Adding ELC
Total Volume
of the Cooling
System (V)
946 L
(250 US gal)
Extender To ELC
Multiplication
Factor
× 0.02
Amount of ELC
Extender that is
Required (X)
19 L
(5 US gal)
NOTICE
When using Caterpillar ELC, do not use standard
SCA’s or SCA filters. To avoid SCA contamination of
an ELC system, remove the SCA filter base and plug
off or by-pass the coolant lines.
NOTICE
Care mustbe taken to ensure that fluids are contained
during performance of inspection, maintenance, testing, adjusting and repair of the product. Be prepared to
collect the fluid with suitable containers before opening any compartment or disassembling any component containing fluids.
Refer to Special Publication, NENG2500, “Caterpillar
Tools and Shop Products Guide” for tools and supplies
suitable to collect and contain fluids on Caterpillar
products.
Dispose of all fluids according to local regulations and
mandates.
ELC Cooling System Cleaning
Note: If the cooling system is already using ELC,
cleaning agents are not required to be used at
the specified coolant change interval. Cleaning
agents are only required if the system has been
contaminated by the addition of some other type of
coolant or by cooling system damage.
Clean water is the only cleaning agent that is
required when ELC is drained from the cooling
system.
ELC can be recycled. The drained coolant mixture
can be distilled in order to remove the ethylene
glycol and the water. The ethylene glycol and the
water can be reused. Consult your Caterpillar dealer
for more information.
After the cooling system is drained and after the
cooling system is refilled, operate the engine while
the cooling system filler cap is removed. Operate
the engine until the coolant level reaches the normal
operating temperature and until the coolant level
stabilizes. As needed, add the coolant mixture in
order to fill the system to the proper level.
1. Drain the coolant into a suitable container.
2. Dispose of the coolant according to local
regulations.
NOTICE
Do not leave an empty SCA filter on an ELC system.
The filter housing may corrode and leak causing an
engine failure.
Remove the SCA filter base and plug off or by-pass
the coolant lines.
3. Remove the empty SCA filter and remove the
filter base. Plug the coolant lines or bypass the
coolant lines.
4. Flush the system with clean water in order to
remove any debris.
5. Use Caterpillar cleaner to clean the system.
Follow the instruction on the label.
6. Drain the cleaner into a suitable container. Flush
the cooling system with clean water.
Changing to Caterpillar ELC
To change from heavy-duty coolant/antifreeze to the
Caterpillar ELC, perform the following steps:
7. Fill the cooling system with clean water and
operate the engine until the engine is warmed to
to 66C (120to 150
49
F).
NOTICE
Improper or incomplete rinsing of the cooling system
can result in damage to copper and other metal components.
To avoid damage to the cooling system, make sure
to completely flush the cooling system with clear water. Continue to flush the system until all signs of the
cleaning agent are gone.
Page 29

29
Maintenance Section
Cooling System Specifications
8. Drain the cooling system into a suitable container
and flush the cooling system with clean water.
Note: The cooling system cleaner must be
thoroughly flushed from the cooling system. Cooling
system cleaner that is left in the system will
contaminate the coolant. The cleaner may also
corrode the cooling system.
9. Repeat Steps 7 and 8 until the system is
completely clean.
10. Fill the cooling system with the Caterpillar
premixed ELC.
11. Attach the Special Publication, PEEP5027,
“Label” to the cooling system filler for the engine
in order to indicate the use of Caterpillar ELC.
ELC Cooling System
Contamination
NOTICE
Mixing ELC with other products reduces the effectiveness of the ELC and shortens the ELC service life.
Use only Caterpillar products or commercial products
that have passed the Caterpillar EC-1 specification for
premixed or concentrate coolants. Use only Caterpillar
ELC Extender with Caterpillar ELC. Failure to follow
these recommendations can result in shortened cooling system component life.
Commercial ELC
If Caterpillar ELC is not used, then select a
commercial ELC that meets the Caterpillar
specification of EC-1 and either the “ASTM D5345”
specification or the “ASTM D4985” specification. Do
not use an extended life coolant that does not meet
the EC-1 specification. Follow the maintenance
guide for the coolant from the supplier of the
commercial ELC. Follow the Caterpillar guidelines
for the quality of water and the specified coolant
change interval.
i01111753
Diesel Engine Antifreeze/
Coolant (DEAC)
SMCS Code: 1350; 1352; 1395
Caterpillar recommends using Caterpillar
Diesel Engine Antifreeze/Coolant (DEAC) for
cooling systems that require a heavy-duty
coolant/antifreeze. Caterpillar DEAC is an alkaline
single-phase ethylene glycol type antifreeze that
contains corrosion inhibitors and antifoam agents.
Caterpillar DEAC is formulated with the correct
amount of Caterpillar Supplemental Coolant Additive
(SCA). Do no use SCA at the initial fill when DEAC
is used.
ELC cooling systems can withstand contamination
to a maximum of ten percent of conventional
heavy-duty coolant/antifreeze or SCA. If the
contamination exceeds ten percent of the total
system capacity, perform ONE of the following
procedures:
Drain the cooling system into a suitable container.
•
Dispose of the coolant according to local
regulations. Flush the system with clean water. Fill
the system with the Caterpillar ELC.
Drain a portion of the cooling system into a
•
suitable container according to local regulations.
Then, fill the cooling system with premixed ELC.
This should lower the contamination to less than
10 percent.
Maintain the system as a conventional Diesel
•
Engine Antifreeze/Coolant (DEAC). Treat the
system with an SCA. Change the coolant at the
interval that is recommended for the conventional
Diesel Engine Antifreeze/Coolant (DEAC).
Containers of several sizes are available. Consult
your Caterpillar dealer for the part numbers.
If concentrated DEAC is used, Caterpillar
recommends mixing the concentrate with distilled
water or with deionized water. If distilled water is
not available or deionized water is not available,
use water which has the required properties. For
the water properties, see this publication, “General
Coolant Information” topic (Maintenance Section).
i01069295
Supplemental Coolant Additive
(SCA)
SMCS Code: 1350; 1352; 1395
The use of SCA helps to prevent the following
conditions from occurring:
Corrosion
•
Formation of mineral deposits
•
Cavitation erosion of the cylinder liners
•
Foaming of the coolant
•
Page 30

30
Maintenance Section
Cooling System Specifications
Caterpillar Diesel Engine Antifreeze/Coolant (DEAC)
is formulated with the correct level of Caterpillar
SCA. When the cooling system is initially filled with
DEAC, adding more SCA is not necessary until the
concentration of SCA has been depleted. To ensure
that the correct amount of SCA is in the cooling
system, the concentration of SCA must be tested
on a scheduled basis. Refer to the specific engine’s
Operation and Maintenance Manual, “Maintenance
Interval Schedule”.
Containers of SCA are available in several sizes.
Consult your Caterpillar dealer for the part numbers.
i01111872
Conventional Coolant/
Antifreeze Cooling System
Maintenance
SMCS Code: 1350; 1352; 1395
NOTICE
Never operate an engine without water temperature
regulators in the cooling system. Water temperature
regulators help to maintain the engine coolant at the
proper operating temperature. Cooling system problems can develop without water temperature regulators.
Table 16 also lists additions of SCA for liquid
and for maintenance elements at 250 hours. The
additions are required for Caterpillar DEAC and for
commercial coolant/antifreezes.
Check the coolant/antifreeze (glycol concentration)
in order to ensure adequate protection against
boiling or freezing. Caterpillar recommends the
use of a refractometer for checking the glycol
concentration. Use the 1U-7298 Coolant/Battery
Tester (Celsius) or use the 1U-7297 Coolant/Battery
Tester (Fahrenheit). The testers give readings that
are immediate and accurate. The testers can be
used with ethylene or with propylene glycol.
Caterpillar engine cooling systems should be
tested at 250 hour intervals for the concentration of
Supplemental Coolant Additive (SCA). SCA test kits
are available from your Caterpillar dealer. Test the
concentration of SCA or submit a coolant sample to
your Caterpillar dealer at 250 hour intervals. Refer
to S·O·S Coolant Analysis for more information on
this topic.
Additions of SCA are based on the results of the
test or based on the results of the coolant analysis.
An SCA that is liquid or a maintenance element for
an SCA (if equipped) may be needed at 250 hour
intervals.
Table 16 lists the amount of Caterpillar SCA
that is needed at the initial fill in order to treat
coolant/antifreeze. These amounts of SCA are for
systems that use heavy-duty coolant/antifreeze.
Page 31

Ta bl e 1 6
Caterpillar SCA Requirements for Heavy-Duty Coolant/Antifreeze
Cooling System
Capacity
22 to 30 L
(6 to 8 US gal)
31 to 38 L
(9 to 10 US gal)
39 to 49 L
(11 to 13 US gal)
50 to 64 L
(14 to 17 US gal)
65 to 83 L
(18 to 22 US gal)
84 to 114 L
(23 to 30 US gal)
115 to 163 L
(31 to 43 US gal)
164 to 242 L
(44 to 64 US gal)
(1)
When the coolant system is first filled, the SCA is not required to be used with
Caterpillar DEAC.
(2)
Do not exceed the six percent maximum concentration. Check the concentration
of SCA with a SCA test kit.
(3)
Do not use the maintenance element for the SCA and the liquid for the SCA at the
same time.
Initial Fill
0.95 L (32 fl oz) 0.24 L (8 fl oz) 111-2370 (1)
1.18 L (40 fl oz) 0.36 L (12 fl oz) 111-2369 (1)
1.42 L (48 fl oz) 0.36 L (12 fl oz) 111-2369 (1)
1.90 L (64 fl oz) 0.47 L (16 fl oz) 9N-3368 (1)
2.37 L (80 fl oz) 0.60 L (20 fl oz) 111-2371 (1)
3.32 L (112 fl oz) 0.95 L (32 fl oz) 9N-3718 (1)
4.75 L (160 fl oz) 1.18 L (40 fl oz) 111-2371 (2)
7.60 L (256 fl oz) 1.90 L (64 fl oz) 9N-3718 (2)
(1)
250 Service
Hour
Maintenance
(2)
Spin-on
Element at 250
Service Hour
Maintenance
31
Maintenance Section
Cooling System Specifications
(3)
Note: Specific engine applications may require
maintenance practices to be periodically evaluated
in order to properly maintain the engine’s cooling
system.
Refer to Table 17 for part numbers and for quantities
of SCA.
Ta bl e 1 7
Caterpillar Liquid SCA
Part Number
6V-3542 0.24 L (8 oz)
111-2372 0.36 L (12 oz)
8T-1589 0.47 L (16 oz)
3P-2044 0.94 L (32 oz)
8C-3680 19 L (5 US gal)
5P-2907 208 L (55 US gal)
Quantity
Cooling Systems with Larger
Capacities
Adding the SCA to Conventional
Coolant/Antifreeze at the Initial Fill
Note: Caterpillar DEAC DOES NOT require an
addition of SCA when the cooling system is initially
filled.
Commercial heavy duty coolant/antifreeze that meet
“ASTM D4985” or “ASTM D5345” specifications
MAY require an addition of SCA at the initial fill.
Read the label or the instructions that are provided
by the OEM of the product.
Use the equation that is in Table 18 to determine
the amount of Caterpillar SCA that is required when
the cooling system is initially filled with the following
fluids:
“ASTM D4985”
•
“ASTM D5345”
•
Page 32

32
Maintenance Section
Cooling System Specifications
Ta bl e 1 8
Equation For Adding The SCA To Conventional
Coolant/Antifreeze At The Initial Fill
V × 0.045 = X
V is the total volume of the cooling system.
X is the amount of SCA that is required.
Table 19 is an example for using the equation that
is in Table 18.
Ta bl e 1 9
Example Of The Equation For Adding The SCA To
Conventional Coolant/Antifreeze At The Initial Fill
Total Volume
of the Cooling
System (V)
946 L
(250 US gal)
Multiplication
Factor
× 0.045
Amount of SCA
that is Required
(X)
43 L
(11 US gal)
Adding the SCA to Conventional
Coolant/Antifreeze For Maintenance
Heavy duty coolant/antifreeze of all types REQUIRE
periodic additions of an SCA.
Test the coolant/antifreeze periodically for the
concentration of SCA. For the interval, see the
Operation and Maintenance Manual, “Maintenance
Interval Schedule” (Maintenance Section). SCA
test kits are available from your Caterpillar
dealer. Test the concentration of SCA or submit
a coolant sample to your Caterpillar dealer. See
this publication, “S·O·S Coolant Analysis” topic
(Maintenance Section).
Ta bl e 2 1
Example Of The Equation For Adding The SCA To
Conventional Coolant/Antifreeze For Maintenance
Total Volume
of the Cooling
System (V)
946 L
(250 US gal)
Multiplication
Factor
× 0.014
Amount of SCA
that is Required
(X)
9L
(4 US gal)
Note: Specific engine applications may require
maintenance practices to be periodically evaluated
in order to properly maintain the engine’s cooling
system.
Table 17 lists part numbers and quantities of SCA
that is available from your Caterpillar dealer.
Cleaning the System of Heavy-Duty
Coolant/Antifreeze
Caterpillar cooling system cleaners are designed
to clean the cooling system of harmful scale and
corrosion. Caterpillar cooling system cleaners
dissolve mineral scale, corrosion products, light oil
contamination and sludge.
Clean the cooling system after used coolant is
•
drained or before the cooling system is filled with
new coolant.
Clean the cooling system whenever the coolant is
•
contaminated or whenever the coolant is foaming.
For the recommended service interval, refer
•
to the Operation and Maintenance Manual,
“Maintenance Interval Schedule” for your engine.
Additions of SCA are based on the results of the
test or based on the results of the coolant analysis.
The size of the cooling system determines the
amount of SCA that is needed.
Use the equation that is in Table 20 to determine
the amount of Caterpillar SCA that is required, if
necessary:
Ta bl e 2 0
Equation For Adding The SCA To Conventional
Coolant/Antifreeze For Maintenance
V × 0.014 = X
V is the total volume of the cooling system.
X is the amount of SCA that is required.
Table 21 is an example for using the equation that
is in Table 20.
i01111887
Commercial Heavy-Duty
Coolant/Antifreeze and SCA
SMCS Code: 1350; 1352; 1395
If Caterpillar DEAC is not used, select a
coolant/antifreeze with low silicate content for
heavy-duty applications that meets “ASTM D5345”
or “ASTM D4985” specifications.
Note: When you are not using Caterpillar DEAC the
cooling system must be drained one time during
every year. The cooling system must be flushed at
this time as well.
Page 33

33
Maintenance Section
Cooling System Specifications
When a heavy-duty coolant/antifreeze is used,
treat the cooling system with three to six
percent Caterpillar SCA by volume. For more
information, see this publication, “Conventional
Coolant/Antifreeze Cooling System Maintenance”
topic (Maintenance Section).
If Caterpillar SCA is not used, select a commercial
SCA. The commercial SCA must provide a minimum
of 1200 mg/L or 1200 ppm (70 grains/US gal) of
nitrates in the final coolant mixture.
Coolant/antifreeze that meets “ASTM D5345” or
“ASTM D4985” specifications MAY require treatment
with SCA at the initial fill. These coolants WILL
require treatment with SCA on a maintenance basis.
When concentrated coolant/antifreeze is mixed,
Caterpillar recommends mixing the concentrate with
distilled water or with deionized water. If distilled
water or deionized water is not available, water
which has the required properties may be used. For
the water properties, see this publication, “General
Coolant Information” topic (Maintenance Section).
i01096747
Water/Supplemental Coolant
Cavitation erosion of the cylinder liner
•
Foaming of the coolant
•
If Caterpillar SCA is not used, select a commercial
SCA. The commercial SCA must provide a minimum
of 2400 mg/L or 2400 ppm (140 grains/US gal) of
nitrates in the final coolant mixture.
The quality of the water is a very important factor
in this type of cooling system. Distilled water
or deionized water is recommended for use in
cooling systems. If distilled water or deionized
water is not available, use water that meets the
minimum requirements that are listed in the table for
recommended water properties in this publication,
“General Coolant Information” topic (Maintenance
Section).
A cooling system that uses a mixture of SCA
and water only needs more SCA than a cooling
system that uses a mixture of glycol and water. The
SCA concentration in a cooling system that uses
SCA and water should be six to eight percent by
volume. Refer to Table 22 for the amount of SCA
that is required for various capacities of the cooling
system.
Additive (SCA)
SMCS Code: 1350; 1352; 1395
NOTICE
All Caterpillar diesel engines equipped with air-to-air
aftercooling (ATAAC) require a minimum of 30 percent
glycol to prevent water pump cavitation.
NOTICE
Never use water alone without Supplemental Coolant
Additives (SCA) or without inhibited coolant. Water
alone is corrosive at engine operating temperatures.
Water alone does not provide adequate protection
against boiling or freezing.
Note: Premix the coolant solution in order to provide
protection to the lowest ambient temperature that
is expected.
Note: Pure undiluted antifreeze freezes at −23
(−9
F).
In engine cooling systems that use Supplemental
Coolant Additive (SCA) and water alone, Caterpillar
recommends the use of SCA. SCA helps to prevent
the following conditions from occurring:
C
Corrosion
•
Formation of mineral deposits
•
Page 34

34
Maintenance Section
Cooling System Specifications
Ta bl e 2 2
Caterpillar SCA Requirements for SCA and
Cooling System
Capacity
22 to 30 L
(6 to 8 US gal)
31 to 38 L
(9 to 10 US gal)
39 to 49 L
(11 to 13 US gal)
50 to 64 L
(14 to 17 US gal)
65 to 83 L
(18 to 22 US gal)
84 to 110 L
(23 to 29 US gal)
111 to 145 L
(30 to 38 US gal)
146 to 190 L
(39 to 50 US gal)
191 to 250 L
(51 to 66 US gal)
Water Cooling Systems
Caterpillar SCA
at Initial Fill
1.75 L (64 fl oz) 0.44 L (15 fl oz)
2.30 L (80 fl oz) 0.57 L (20 fl oz)
3.00 L (100 fl oz) 0.75 L (25 fl oz)
3.90 L (128 fl oz) 0.95 L (32 fl oz)
5.00 L (168 fl oz) 1.25 L (42 fl oz)
6.60 L (224 fl oz) 1.65 L (56 fl oz)
8.75 L (296 fl oz) 2.19 L (74 fl oz)
11.50 L
(392 fl oz)
15.00 L
(512 fl oz)
Caterpillar SCA
at 250 Hours
2.88 L (98 fl oz)
3.75 L (128 fl oz)
Refer to Table 23 for part numbers and for quantities
of SCA.
Ta bl e 2 3
Caterpillar Liquid SCA
Part Number
6V-3542 0.24 L (8 oz)
111-2372 0.36 L (12 oz)
8T-1589 0.47 L (16 oz)
3P-2044 0.94 L (32 oz)
8C-3680 19 L (5 US gal)
5P-2907 208 L (55 US gal)
Quantity
Maintain the SCA in the same way as you would
maintain a cooling system that uses heavy-duty
coolant/antifreeze. Adjust the maintenance for the
amount of SCA additions. See Table 22 for the
amount of SCA that is required.
Cooling Systems with Larger
Capacities
Adding the SCA to Water at the Initial Fill
Use the equation that is in Table 24 to determine
the amount of Caterpillar SCA that is required at
the initial fill. This equation is for a mixture of only
SCA and water.
Ta bl e 2 4
Equation For Adding The SCA To Water
V is the total volume of the cooling system.
X is the amount of SCA that is required.
Table 25 is an example for using the equation that
is in Table 24.
Ta bl e 2 5
Example Of The Equation For Adding The SCA
Total Volume
of the Cooling
System (V)
946 L
(250 US gal)
Adding the SCA to Water for Maintenance
For the recommended service interval, refer to the
Operation and Maintenance Manual, “Maintenance
Interval Schedule” for your engine.
Use the 8T-5296 Coolant Conditioner Test Kit to
test the concentration of SCA. Make the following
modifications to Steps 3 and 5 of the 8T-5296
Coolant Conditioner Test Kit instructions:
STEP 3 – Add tap water to the vial up to the “20
ml” mark.
STEP 5 – When the defined procedure is used,
a concentration of six to eight percent will yield
between 20 drops and 27 drops. If the number of
drops is below 20 drops, the concentration of SCA
is low. If the number of drops is above 27 drops, the
concentration of SCA is high. Make the appropriate
adjustments to the concentration of SCA.
At The Initial Fill
V × 0.07 = X
To Water At The Initial Fill
Multiplication
Factor
× 0.07 66 L
Amount of SCA
that is Required
(X)
(18 US gal)
Test the concentration of SCA or submit a
coolant sample to your Caterpillar dealer. See
this publication, “S·O·S Coolant Analysis” topic
(Maintenance Section).
Page 35

Additions of SCA are based on the results of the
test or based on the results of the coolant analysis.
The size of the cooling system determines the
amount of SCA that is required.
Use the equation that is in Table 24 to determine
the amount of Caterpillar SCA that is required for
maintenance, if necessary:
Ta bl e 2 6
SCA To Water Addition Equation For Maintenance
V × 0.023 = X
V is the total volume of the cooling system.
X is the amount of SCA that is required.
35
Maintenance Section
Cooling System Specifications
NOTICE
Do not use the same vacuum sampling pump for extracting oil samples that is used for extracting coolant
samples.
A small residue of either type sample may remain in
the pump and may cause a false positive analysis for
the sample being taken.
Always use a designated pump for oil sampling and a
designated pump for coolant sampling.
Failure to do so may cause a false analysis which
could lead to customer and dealer concerns.
Table 27 is an example for using the equation that
is in Table 24.
Ta bl e 2 7
SCA To Water Addition Equation Example
Total Volume
of the Cooling
System (V)
946 L
(250 US gal)
Note: Specific engine applications may require
maintenance practices to be periodically evaluated
in order to properly maintain the engine’s cooling
system.
Table 23 lists part numbers and quantities of SCA
that is available from your Caterpillar dealer.
For Maintenance
Multiplication
Factor
× 0.023
Amount of SCA
that is Required
(X)
22 L
(6 US gal)
i01053475
S·O·S Coolant Analysis
SMCS Code: 1350; 1352; 1395; 7542-008; 7542
Testing the engine coolant is important to ensure
that the engine is protected from internal cavitation
and from corrosion. The analysis also tests the
ability of the coolant to protect the engine from
boiling and from freezing. The S·O·S Coolant
Analysis can be done at your Caterpillar dealer.
Caterpillar S·O·S Coolant Analysis is the best
way to monitor the condition of your coolant and
your cooling system. S·O·S Coolant Analysis is a
program that is based on periodic samples.
Recommended Interval for S·O·S
Coolant Sample
Ta bl e 2 8
Recommended Interval
Type of Coolant Level 1 Level 2
DEAC Every 250 Hours Yearly
ELC Not Required Yearly
Converted Systems
Perform a coolant analysis (Level 2) at 500 service
hours for new systems or for converted systems
that use ELC or use DEAC. This 500 hour check will
also check for any residual cleaner that may have
contaminated the system.
S·O·S Coolant Analysis (Level 1)
A coolant analysis (Level 1) is a test of the
properties of the coolant.
The following properties of the coolant are tested:
Glycol Concentration for freeze protection
•
Ability to protect from erosion and corrosion
•
pH
•
Conductivity
•
Water hardness
•
Visual analysis
•
Odor analysis
•
The results are reported, and appropriate
recommendations are made.
Page 36

36
Maintenance Section
Cooling System Specifications
S·O·S Coolant Analysis (Level 2)
Level 2 coolant analysis is a comprehensive
chemical evaluation of the coolant. This analysis is
also a check of the overall condition of the inside of
the cooling system.
The S·O·S Coolant Analysis has the following five
features:
Full analysis of Level 1
•
Identification of the source of metal corrosion and
•
of contaminants
Identification of buildup of the impurities that
•
cause corrosion
Identification of buildup of the impurities that
•
cause scaling
Determination of possible electrolysis within the
•
engines’ cooling system
The results are reported, and appropriate
recommendations are made.
For more information on S·O·S Coolant Analysis,
consult your Caterpillar dealer.
Page 37

Reference Information
Section
Reference Materials
i01123492
Reference Material
SMCS Code: 1000
The following literature can be obtained through any
Caterpillar dealer.
Coolants
Special Publication, SEBD0970, “Coolant and
•
Your Engine”
Reference Information Section
Reference Materials
Special Publication, NEDG6022, “Data Sheet -
•
Multipurpose Lithium Complex Grease (MPG)”
Special Publication, PEHP0002, “Data Sheet
•
- Multipurpose Lithium Complex Grease with
Molybdenum (MPGM)”
Special Publication, PEHP0017, “Data Sheet -
•
Special Purpose Grease (SPG) Bearing Lubricant”
Special Publication, NEHP5621, “How To Select
•
The Right Grease For Any Job”
Special Publication, PEHP6001, “How To Take A
•
Good Oil Sample”
Special Publication, SEBD0640, “Oil and Your
•
Engine”
Special Publications, PEDP7036, “S·O·S Fluids
•
Analysis Cornerstone”
37
Special Publication, PEHP4036, “Data Sheet-
•
Extended Life Coolant”
Special Publication, SEBD0518, “Know Your
•
Cooling System”
Special Publication, PEEP5027, “Label - ELC
•
Radiator Label”
Special Publication, PEHP7057, “S·O·S Coolant
•
Analysis”
Fuels
Special Publication, SEBD0717, “Diesel Fuels and
•
Your Engine”
Lubricants
Special Publication, PEHP8038, “Data Sheet -
•
Caterpillar Diesel Engine Oils (DEO) (CH-4, CG-4,
CF-4) (North America and Australia)”
Special Publication, PEHP7041, “Product Data
•
Sheet for Caterpillar Diesel Engine Oils (DEO)”
CG-4 engine oils (International markets)
Miscellaneous
Special Publication, PECP6026, “One Safe Source”
English language for use in NACD
Special Publication, PECP6027, “One Safe Source”
English language for use in COSA
Special Publication, PECP6028, “One Safe Source”
English language for use in non NACD and non
COSA
i01109461
Additional Reference Material
SMCS Code: 1000
The “EMA Lubricating Oils Data Book” can
be obtained from the following locations: local
technological society, local library, and local college.
If necessary, consult EMA at the following address:
Engine Manufacturers Associaton
401 N. Michigan Ave.
Chicago, IL, USA 60611
Telephone: (312) 644-6610 ext. 3626
Special Publication, PEHP9516, “Product Data
•
Sheet for Special Application Engine Oil For
Caterpillar 3116 and 3126 Marine Diesel Engines
with Mechanical Unit Injectors”
Special Publication, PEWP3014, “Cat Fluids
•
Selector Dial (International)”
Special Publication, PEWP9733, “Cat Fluids
•
Selector Dial (North America)”
The “Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE)
Specifications” can be found in your SAE handbook.
This publication can also be obtained from the
following locations: local technological society, local
library, and local college. If necessary, consult SAE
at the following address:
SAE International
400 Commonwealth Drive
Warrendale, PA, USA 15096-0001
Telephone: (724) 776-4841
Page 38

38
Reference Information Section
Reference Materials
The “American Petroleum Institute Publication No.
1509” can be obtained from the following locations:
local technological society, local library, and local
college. If necessary, consult API at the following
address:
American Petroleum Institute
1220 L St. N.W.
Washington, DC, USA 20005
Telephone: (202) 682-8000
The International Organization for Standardization
(ISO) offers information and customer service
regarding international standards and standardizing
activities. ISO can also supply information on the
following subjects that are not controlled by ISO:
national standards, regional standards, regulations,
certification, and related activities. Consult the
member of ISO in your country.
International Organization for Standardization
(ISO)
1, rue de Varembé
Case postale 56
CH-1211 Genève 20
Switzerland
Telephone: +41 22 749 01 11
Facsimile: +41 22 733 34 30
E-mail: central@iso.ch
Web site: http://www.iso.ch
European classifications are established by the
Counseil International Des Machines a Combustion
(CIMAC) (International Council on Combustion
Engines).
CIMAC Central Secretariat
Lyoner Strasse 18
60528 Frankfurt
Germany
Telephone: +49 69 6603 1567
Facsimile: +49 69 6603 1566
Page 39

Index
39
Index Section
A
Additional Reference Material ............................... 37
Aftermarket Oil Additives....................................... 14
C
Characteristics of Diesel Fuel................................ 20
Cetane Number.................................................. 21
Cloud Point ........................................................ 21
Lubricity and Low Sulfur Fuel............................. 20
Moisture Content................................................ 23
Pour Point .......................................................... 22
Viscosity............................................................. 20
Cold Weather Lubricants....................................... 14
Commercial Heavy-Duty Coolant/Antifreeze and
SCA ..................................................................... 32
Conventional Coolant/Antifreeze Cooling System
Maintenance ........................................................ 30
Cleaning the System of Heavy-Duty
Coolant/Antifreeze ........................................... 32
Cooling Systems with Larger Capacities ........... 31
Coolant Recommendations ................................... 26
Cooling System Specifications .............................. 24
D
Diesel Engine Antifreeze/Coolant (DEAC) ............ 29
Extended Life Coolant (ELC) Cooling System
Maintenance ........................................................ 27
Caterpillar ELC Extender .................................. 27
Changing to Caterpillar ELC .............................. 28
Commercial ELC................................................ 29
ELC Cooling System Cleaning........................... 28
ELC Cooling System Contamination.................. 29
Proper additions to the Extended Life Coolant .. 27
F
Foreword................................................................ 4
Literature Information......................................... 4
Maintenance ...................................................... 4
Safety................................................................. 4
Fuel Information for Diesel Engines ...................... 17
Starting Aids ...................................................... 17
Fuel Recommendations......................................... 18
Fuel Specifications ................................................ 17
G
General Coolant Information ................................. 24
Additives ............................................................ 25
Glycol................................................................. 25
Water ................................................................. 24
General Fuel Information....................................... 17
E
Engine Oil.............................................................. 5
Caterpillar Diesel Engine Oil.............................. 5
Commercial Oils................................................. 6
Total Base Number (TBN) and Fuel Sulfur Levels
for Direct Injection (DI) Diesel Engines ............ 7
Engine Oil (3116 and 3126 Marine Engines) ........ 8
Commercial Oils (3116 and 3126 Marine
Engines)........................................................... 9
Lubricant Viscosity Recommendations (3116 and
3126 Marine Engines)...................................... 10
Recommendations............................................. 8
Total Base Number (TBN) and Fuel Sulfur Levels
for Direct Injection (DI) Diesel Engines (3116 and
3126 Marine Engines)...................................... 9
Engine Oil for Precombustion Chamber (PC) Diesel
Engines................................................................ 10
Caterpillar Diesel Engine Oil.............................. 10
Commercial Oils................................................. 10
Total Base Number (TBN) and Fuel Sulfur
Levels for Precombustion Chamber (PC) Diesel
Engines ............................................................ 12
Extended Life Coolant (ELC)................................. 26
I
Important Safety Information ................................. 2
L
Lubricant Information............................................. 5
API Oils.............................................................. 5
Engine Manufacturers Association (EMA) Oils.. 5
General Information ........................................... 5
Lubricant Specifications ........................................ 5
Lubricating Grease ................................................ 14
Caterpillar Premium Grease (CPG) ................... 16
Multipurpose Greases........................................ 15
Special Purpose Grease (SPG)......................... 15
M
Maintenance Section............................................. 5
Marine Transmission Oil ........................................ 12
Caterpillar Transmission/Drive Train Oils ........... 13
Commercial Marine Transmissions.................... 13
Page 40

40
Index Section
R
Re-refined Base Stock Oils ................................... 13
Reference Information Section.............................. 37
Reference Material ................................................ 37
Coolants............................................................. 37
Fuels .................................................................. 37
Lubricants .......................................................... 37
Miscellaneous .................................................... 37
Reference Materials .............................................. 37
S
S·O·S Coolant Analysis ......................................... 35
Recommended Interval for S·O·S Coolant
Sample............................................................. 35
S·O·S Coolant Analysis (Level 1)....................... 35
S·O·S Coolant Analysis (Level 2)....................... 36
S·O·S Oil Analysis ................................................. 16
Supplemental Coolant Additive (SCA)................... 29
Synthetic Base Stock Oils ..................................... 13
T
Table of Contents................................................... 3
W
Water/Supplemental Coolant Additive (SCA)........ 33
Cooling Systems with Larger Capacities ........... 34
Page 41

Product and Dealer Information
Note: For product identification plate locations, see the section “Product Identification Information” in the
Operation and Maintenance Manual.
Delivery Date:
Product Information
Model:
Product Identification Number:
Engine Serial Number:
Transmission Serial Number:
Generator Serial Number:
Attachment Serial Numbers:
Attachment Information:
Customer Equipment Number:
Dealer Equipment Number:
Dealer Information
Name: Branch:
Address:
Dealer Contact Phone Number Hours
Sales:
Parts:
Service:
Page 42

©1999 Caterpillar
All Rights Reserved Printed in U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...