Page 1
3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
Electroscope S 1009964
Instruction Sheet
02/13 ALF
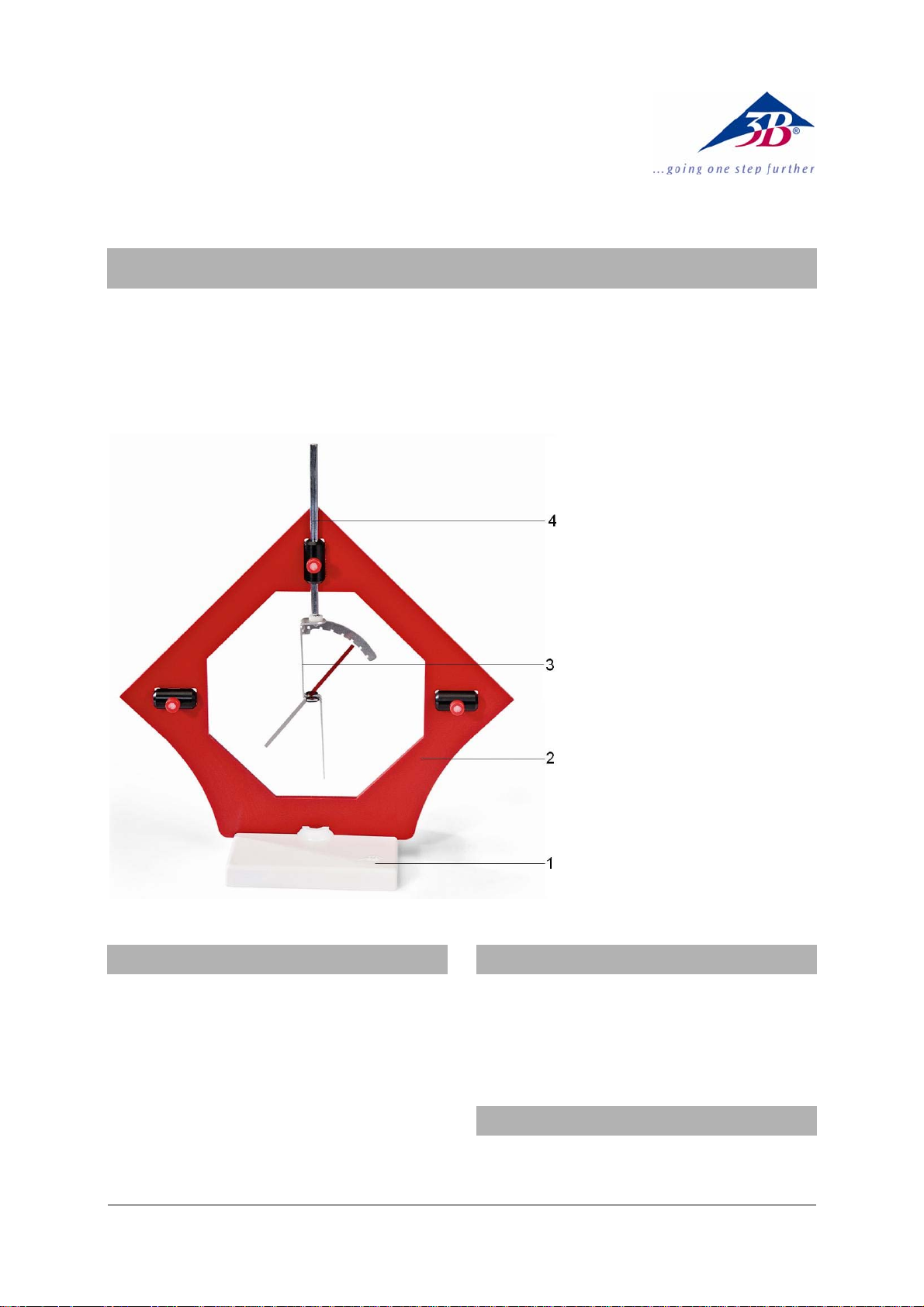
1 Stand base
2 Frame
3 Electroscope unit
4 Aluminium rod with magnet holder
1. Description
The electroscope S is used for the demonstration of electrical charges and voltages.
The electroscope features a plastic frame set on
a base. The actual electroscope unit, consisting
of a support and a pointer, is attached to an
aluminium rod with a magnetic holder which is
suspended within the frame.
2. Equipment supplied
1 Stand base
1 Frame
1 Electroscope unit
1 Aluminium rod with magnet holder
3. Technical Data
Dimensions: 280x80x280 mm3 approx.
Weight: 500 g approx.
1
Page 2

4. Operation
To perform experiments, the following equipment is also required:
Friction rods 1002709
Friction
rod
Rubbing material
Charge polarity
PVC Plastic foil +
Acrylic
glass
Plastic foil -
To indicate the charge polarity the following
equipment is recommended:
Charge Indicator 1009962
4.1 Electroscope set-up
• Insert the frame into the base.
• Slide the aluminium rod vertically into the
frame.
• Attach the electroscope unit to the magnetic
holder.
• Place the pointer needle in such a way that
it automatically points to zero.
4.2 Charging up the electroscope by touching it with a statically charged body
• Rub the friction rod with the suitable mate-
rial.
• Touch the aluminium rod with the charged
rod. The pointer deflects.
• Remove the friction rod, the pointer remains
deflected.
• Touch aluminium rod with your hand. The
pointer returns to normal.
• Repeat the experiment with the second fric-
tion rod.
• Determine the sign of the charge using the
charge indicator.
4.3 Using electrostatic induction to charge
up the electroscope
• Approach but do not touch the aluminium
rod with the statically charged friction rod.
The pointer deflects.
• Remove the friction rod. The pointer returns
to normal.
• Again approach the aluminium rod with the
statically charged friction rod. Once again
the pointer deflects.
• Briefly touch the aluminium rod with your
finger to discharge it. The pointer deflection
disappears and returns to normal.
• Now remove the friction rod. The pointer
again shows deflection.
Fig. 1 Charging the electroscope using a statically-
charged friction rod
Fig. 2 Charging the electroscope using electrostatic
induction
3B Scientific GmbH ▪ Rudorffweg 8 ▪ 21031 Hamburg ▪ Germany ▪ www.3bscientific.com
Subject to technical amendments
© Copyright 2013 3B Scientific GmbH
 Loading...
Loading...