Page 1

Default Login Details
User’s Guide
NBG6604
AC1200 Dual-Band Wireless Router
LAN IP Address http://myrouter
Password 1234
Version 1.00 Edition 1, 08/2017
Copyright © 2017 Zyxel Communications Corporation
Page 2

IMPORTANT!
READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE.
KEEP THIS GUIDE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
Screenshots and graphics in this book may differ slightly from your product due to differences in your
product firmware or your computer operating system. Every effort has been made to ensure that the
information in this manual is accurate.
Related Documentation
•Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guide shows how to connect the NBG6604 and access the Web Configurator wizards.
It contains information on setting up your network and configuring for Internet access.
•More Information
Go to support.zyxel.com to find other information on the NBG6604.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
2
Page 3
Document Conventions
Document Conventions
Warnings and Notes
These are how warnings and notes are shown in this guide.
Warnings tell you about things that could harm you or your device.
Note: Notes tell you other important information (for example, other things you may need to
configure or helpful tips) or recommendations.
Syntax Conventions
• The NBG6604 may be referred to as the “NBG6604” or the “device” in this guide.
• Product labels, screen names, field labels and field choices are all in bold font.
• A right angle bracket ( > ) within a screen name denotes a mouse click. For example, WAN > Internet
Connection: IPoE Encapsulation means you first click WAN in the navigation panel, then the Internet
Connection sub menu and finally select the IPoE Encapsulation option to get to that screen.
Icons Used in Figures
Figures in this user guide may use the following generic icons. The NBG6604 icon is not an exact
representation of your device.
NBG6604 Generic Router or Modem Wireless Signal
Switch Firewall Printer
Server
NBG6604 User’s Guide
3
Page 4

Contents Overview
Contents Overview
Introduction ............................................................................................................................................. 9
Introducing the Web Configurator ..................................................................................................... 14
eaZy 123 Wizard .................................................................................................................................... 17
Operating Modes ................................................................................................................................. 25
Router Mode ......................................................................................................................................... 26
Access Point Mode .............................................................................................................................. 31
Tutorials .................................................................................................................................................. 38
Status ...................................................................................................................................................... 48
WAN ....................................................................................................................................................... 50
Wireless LAN .......................................................................................................................................... 63
LAN ......................................................................................................................................................... 80
Applications .......................................................................................................................................... 84
Security .................................................................................................................................................. 87
Maintenance ........................................................................................................................................ 91
Troubleshooting .................................................................................................................................. 101
NBG6604 User’s Guide
4
Page 5

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Document Conventions ............................................ ............................................ .... ..........................3
Contents Overview .............................................................................................................................4
Table of Contents.................................................................................................................................5
Chapter 1
Introduction ..........................................................................................................................................9
1.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................... 9
1.2 Applications ...................................................................................................................................... 9
1.3 Ways to Manage the NBG6604 ...................................................................................................... 9
1.4 Good Habits for Managing the NBG6604 ..................................................................................... 9
1.5 Resetting the NBG6604 .................................................................................................................. 10
1.5.1 How to Use the RESET Button ................................................................................................ 10
1.6 The WPS Button ............................................................................................................................... 10
1.7 LEDs .................................................................................................................................................. 11
1.8 Wall Mounting ................................................................................................................................. 13
Chapter 2
Introducing the Web Configurator ........................................................ .... ... .... .... ............................14
2.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 14
2.2 Accessing the Web Configurator ................................................................................................. 14
2.2.1 Login Screen .......................................................................................................................... 15
2.2.2 Change Default Password Screen ...................................................................................... 15
Chapter 3
eaZy 123 Wizard.................................................................................................................................17
3.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 17
3.2 Accessing the eaZy 123 Wizard .................................................................................................... 17
3.3 Internet Type ................................................................................................................................... 20
3.3.1 WAN Selection Type: Automatic - DHCP ........................................................................... 20
3.3.2 WAN Selection Type: PPPoE ................................................................................................. 20
3.3.3 WAN Selection Type: Static .................................................................................................. 21
3.4 Wireless Network ............................................................................................................................. 22
Chapter 4
Operating Modes...............................................................................................................................25
4.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 25
4.1.1 Operating Modes .................................................................................................................. 25
NBG6604 User’s Guide
5
Page 6

Table of Contents
Chapter 5
Router Mode.......................................................................................................................................26
5.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 26
5.2 Router Mode Status Screen ........................................................................................................... 26
5.2.1 Navigation Panel .................................................................................................................. 28
Chapter 6
Access Point Mode............................................................................................................................31
6.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 31
6.2 What You Can Do .......................................................................................................................... 31
6.3 What You Need to Know ............................................................................................................... 31
6.3.1 Setting your NBG6604 to AP Mode ..................................................................................... 32
6.3.2 Accessing the Web Configurator in Access Point Mode ................................................. 32
6.3.3 Configuring your WLAN and Maintenance Settings ......................................................... 33
6.4 AP Mode Status Screen ................................................................................................................. 34
6.4.1 Navigation Panel .................................................................................................................. 36
6.5 LAN Screen ...................................................................................................................................... 36
Chapter 7
Tutorials...............................................................................................................................................38
7.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 38
7.2 Set Up a Wireless Network Using WPS ........................................................................................... 38
7.2.1 Push Button Configuration (PBC) ........................................................................................ 38
7.2.2 PIN Configuration .................................................................................................................. 39
7.3 Connect to NBG6604 Wireless Network without WPS ................................................................. 40
7.3.1 Configure Your Notebook .................................................................................................... 42
7.4 Using Guest SSIDs on the NBG6604 ............................................................................................... 44
7.4.1 Configuring Security Settings of Guest SSIDs ...................................................................... 45
Chapter 8
Status...................................................................................................................................................48
8.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 48
8.1.1 What You Can Do ................................................................................................................. 48
8.2 Client Tables Screen ....................................................................................................................... 48
Chapter 9
WAN ....................................................................................................................................................50
9.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 50
9.2 What You Can Do .......................................................................................................................... 50
9.3 What You Need To Know .............................................................................................................. 51
9.3.1 Configuring Your Internet Connection ............................................................................... 51
9.4 Internet Connection Screen .......................................................................................................... 53
9.4.1 IPoE Encapsulation ................................................................................................................ 53
NBG6604 User’s Guide
6
Page 7

Table of Contents
9.4.2 PPPoE Encapsulation ............................................................................................................ 55
9.5 NAT ................................................................................................................................................... 58
9.5.1 General Screen ..................................................................................................................... 58
9.5.2 Port Trigger Screen ................................................................................................................ 59
9.5.3 Passthrough Screen .............................................................................................................. 60
9.6 Dynamic DNS Screen ..................................................................................................................... 61
Chapter 10
Wireless LAN .......................................................................................................................................63
10.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 63
10.1.1 What You Can Do ............................................................................................................... 64
10.1.2 What You Should Know ...................................................................................................... 64
10.2 Wireless Screen ............................................................................................................................ 68
10.3 Wireless Security ............................................................................................................................ 70
10.3.1 No Security ........................................................................................................................... 70
10.3.2 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK ............................................................................................................ 71
10.4 Guest Wireless Screen .................................................................................................................. 72
10.4.1 Guest Wireless Edit .............................................................................................................. 73
10.5 MAC Filter Screen ........................................................................................................................ 75
10.6 Advanced Screen ........................................................................................................................ 76
10.7 WPS Screen ................................................................................................................................... 77
10.8 Scheduling Screen ....................................................................................................................... 78
Chapter 11
LAN......................................................................................................................................................80
11.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 80
11.2 What You Can Do ........................................................................................................................ 80
11.3 What You Need To Know ............................................................................................................ 81
11.4 LAN IP Screen ................................................................................................................................ 81
11.5 Static DHCP Screen ...................................................................................................................... 82
11.6 IPv6 LAN Screen ............................................................................................................................ 83
Chapter 12
Applications .......................................................................................................................................84
12.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 84
12.1.1 What You Can Do ............................................................................................................... 84
12.2 UPnP Screen .................................................................................................................................. 84
12.3 ONE Connect Screen ................................................................................................................... 85
12.4 Technical Reference .................................................................................................................... 86
Chapter 13
Security ...............................................................................................................................................87
13.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 87
NBG6604 User’s Guide
7
Page 8

Table of Contents
13.1.1 What You Can Do ............................................................................................................... 87
13.1.2 What You Need To Know ...................................................................................................88
13.2 IPv4 Firewall Screen ..................................................................................................................... 89
Chapter 14
Maintenance......................................................................................................................................91
14.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 91
14.2 What You Can Do ........................................................................................................................ 91
14.3 General Screen ............................................................................................................................. 91
14.4 Password Screen ........................................................................................................................... 92
14.5 Time Screen ................................................................................................................................... 93
14.6 Firmware Upgrade Screen .......................................................................................................... 94
14.7 Backup/Restore Screen ............................................................................................................... 95
14.8 Restart Screen ............................................................................................................................... 96
14.9 Remote Management ................................................................................................................. 97
14.9.1 Remote Access ................................................................................................................... 97
14.10 Log Screen .................................................................................................................................. 98
14.11 System Operation Mode Overview .......................................................................................... 98
14.12 Operation Mode Screen ........................................................................................................... 99
Chapter 15
Troubleshooting................................................................................................................................101
15.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 101
15.2 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs ............................................................................... 101
15.3 NBG6604 Access and Login ...................................................................................................... 102
15.4 Internet Access ........................................................................................................................... 103
15.5 Resetting the NBG6604 to Its Factory Defaults ........................................................................ 105
15.6 Wireless Connections ................................................................................................................. 105
Appendix A Customer Support ..................................................................................................... 107
Appendix B Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address................................................................... 113
Appendix C Common Services .....................................................................................................139
Appendix D Legal Information ...................................................................................................... 142
Index.................................................................................................................................................149
NBG6604 User’s Guide
8
Page 9

1.1 Overview
This chapter introduces the main features and applications of the NBG6604.
The NBG6604 extends the range of your existing wired network without additional wiring, providing easy
network access to mobile users. You can set up a wireless network with other IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac
compatible devices. The NBG6604 is able to function both 2.4GHz and 5GHz networks at the same time.
A range of services such as a firewall are also available for secure Internet computing.
1.2 Applications
CHAPTER 1
Introduction
You can have the following networks with the NBG6604:
• Wired. You can connect network devices via the Ethernet ports of the NBG6604 so that they can
communicate with each other and access the Internet.
• Wireless. Wireless clients can connect to the NBG6604 to access network resources. You can use WPS
(Wi-Fi Protected Setup) to create an instant network connection with another WPS-compatible
device.
• WAN. Connect to a broadband modem/router for Internet access.
1.3 Ways to Manage the NBG6604
Use any of the following methods to manage the NBG6604:
• WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup). You can use the WPS button or the WPS section of the Web Configurator
to set up a wireless network with your NBG6604.
• Web Configurator. This is recommended for everyday management of the NBG6604 using a
(supported) web browser.
• Zyxel ONE Connect App. See Section 12.3 on page 85.
1.4 Good Habits for Managing the NBG6604
Do the following things regularly to make the NBG6604 more secure and to manage the NBG6604 more
effectively.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
9
Page 10

Chapter 1 Introduction
• Change the password. Use a password that’s not easy to guess and that consists of different types of
characters, such as numbers and letters.
• Write down the password and put it in a safe place.
• Back up the configuration (and make sure you know how to restore it). Restoring an earlier working
configuration may be useful if the device becomes unstable or even crashes. If you forget your
password, you will have to reset the NBG6604 to its factory default settings. If you backed up an
earlier configuration file, you would not have to totally re-configure the NBG6604. You could simply
restore your last configuration.
1.5 Resetting the NBG6604
If you forget your password or IP address, or you cannot access the Web Configurator, you will need to
use the RESET button at the back of the NBG6604 to reload the factory-default configuration file. This
means that you will lose all configurations that you had previously saved, the password will be reset to
“1234” and the IP address will be reset to “192.168.1.1”.
1.5.1 How to Use the RESET Button
1 Make sure the power LED is on.
2 Press the RESET button for one to four seconds to restart/reboot the NBG6604.
3 Press the RESET button for longer than five seconds to set the NBG6604 back to its factory-default
configurations.
1.6 The WPS Button
Your NBG6604 supports Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS), which is an easy way to set up a secure wireless
network. WPS is an industry standard specification, defined by the Wi-Fi Alliance.
WPS allows you to quickly set up a wireless network with strong security, without having to configure
security settings manually. Each WPS connection works between two devices. Both devices must
support WPS (check each device’s documentation to make sure).
Depending on the devices you have, you can either press a button (on the device itself, or in its
configuration utility) or enter a PIN (a unique Personal Identification Number that allows one device to
authenticate the other) in each of the two devices. When WPS is activated on a device, it has two
minutes to find another device that also has WPS activated. Then, the two devices connect and set up
a secure network by themselves.
You can use the WPS button ( ) on the top panel of the NBG6604 to activate WPS in order to
quickly set up a wireless network with strong security.
1 Make sure the power LED is on (not blinking).
2 Press the WPS button for more than three seconds and release it. Press the WPS button on another WPS-
enabled device within range of the NBG6604.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
10
Page 11
Note: You must activate WPS in the NBG6604 and in another wireless device within two
WLAN 5GHz
WPS
2.4G
5G
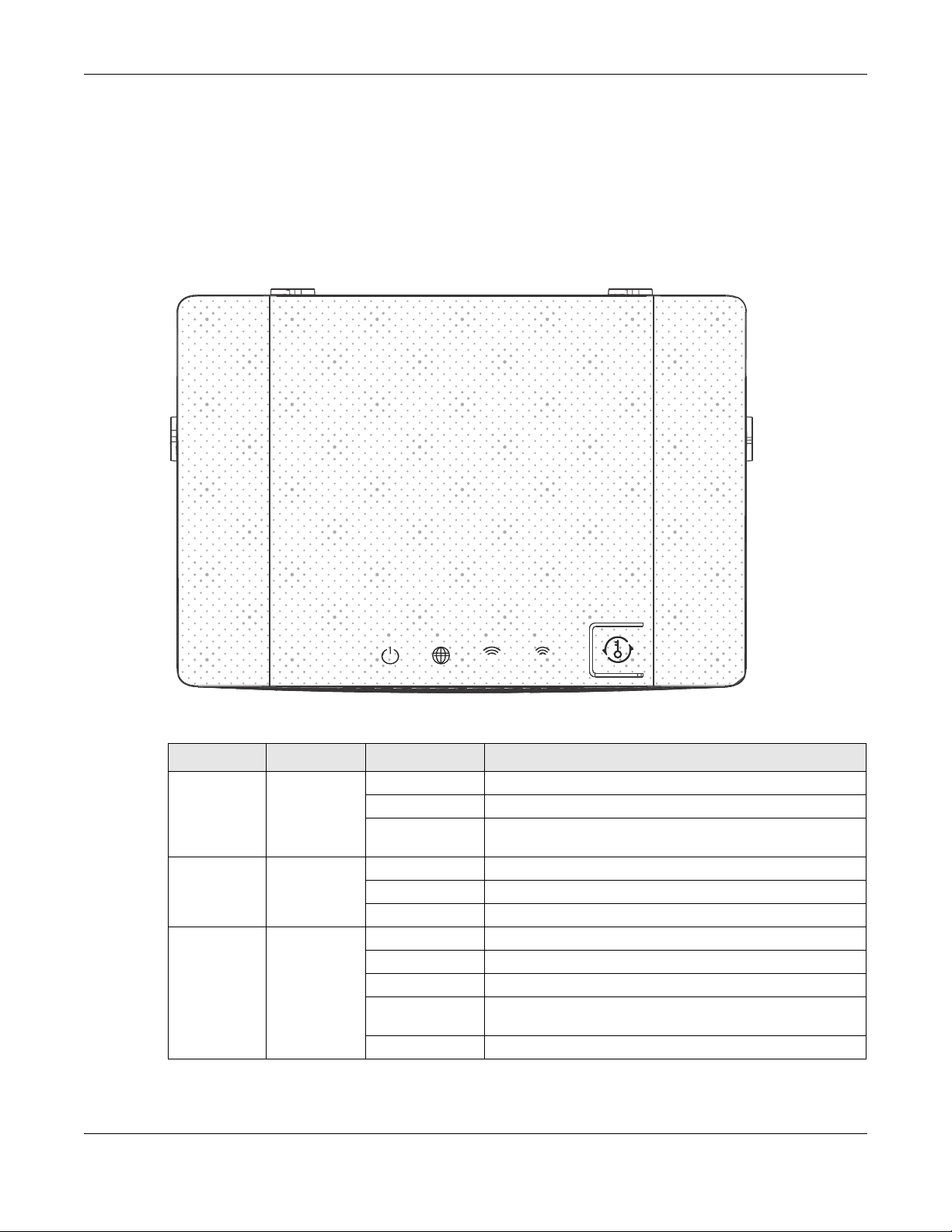
1.7 LEDs
Figure 1 Top Panel
Chapter 1 Introduction
minutes of each other.
Table 1 Top Panel LEDs
FUNCTION COLOR STATUS BEHAVIOR
Power/SYS
Internet White On The IP connection is available but no traffic.
WLAN 5G White Amber On The WLAN interface is enabled.
White
On The NBG6604 is ready.
Off The NBG6604 is powered off.
Blinking The firmware is being updated and restored. System is
booting.
Off The IP connection is not available.
Blinking The NBG6604 is transmitting/Receiving traffic.
Off The WLAN interface is disabled.
White blinking The NBG6604 is transmitting/receiving data.
Amber blinking The WPS process is in progress (at the same time, disable the
white LED).
Amber steady off The WPS process is inactive.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
11
Page 12
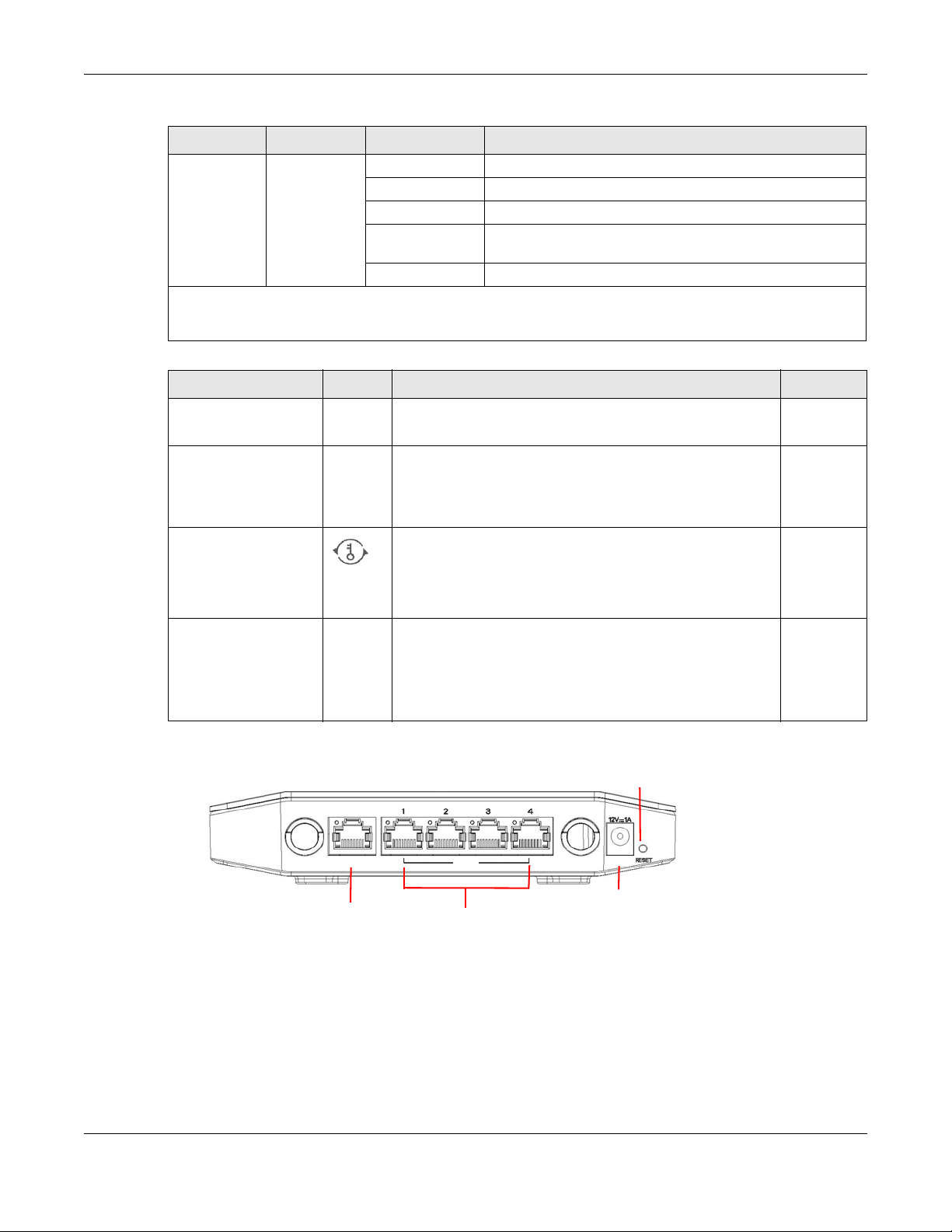
Chapter 1 Introduction
LAN Ports 1-4
WAN Port
Power Input
Reset Button
WAN
LAN
DC IN
Table 1 Top Panel LEDs (continued)
FUNCTION COLOR STATUS BEHAVIOR
WLAN 2.4G White Amber On The WLAN interface is enabled.
Off The WLAN interface is disabled.
White blinking The NBG6604 is transmitting/receiving data.
Amber blinking The WPS process is in progress (at the same time, disable the
white LED).
Amber steady off The WPS process is inactive.
Note: When you connect the power, only the power/sys LED blinks. Others are off -> system ready ->
all LEDs follow their behavior described in this table.
Table 2 Buttons and Interface Behavior
FUNCTION LABEL DESCRIPTION/BEHAVIOR LOCATION
Power Jack DV IN
12v 1A
Reset/Restore Button Reset - Press the button for 5 or less than 5 seconds, system will
WPS Button - WPS button can trigger both 2.4G and 5G.
Ethernet LAN LAN
WAN
Connect the included power adapter. Rear
reboot.
- Press the button for more than 5 seconds, system will reset
configuration.
- WPS can work with 2.4G and 5G at the same time.
- WPS LED will be off while the device is connected to clients
(2.4G client or 5G client or both 2.4G/5G clients).
WAN x1:
- RJ45 Connector
Rear
Top
Rear
Figure 2 Rear Panel
LAN x4:
- RJ45 Connector
NBG6604 User’s Guide
12
Page 13
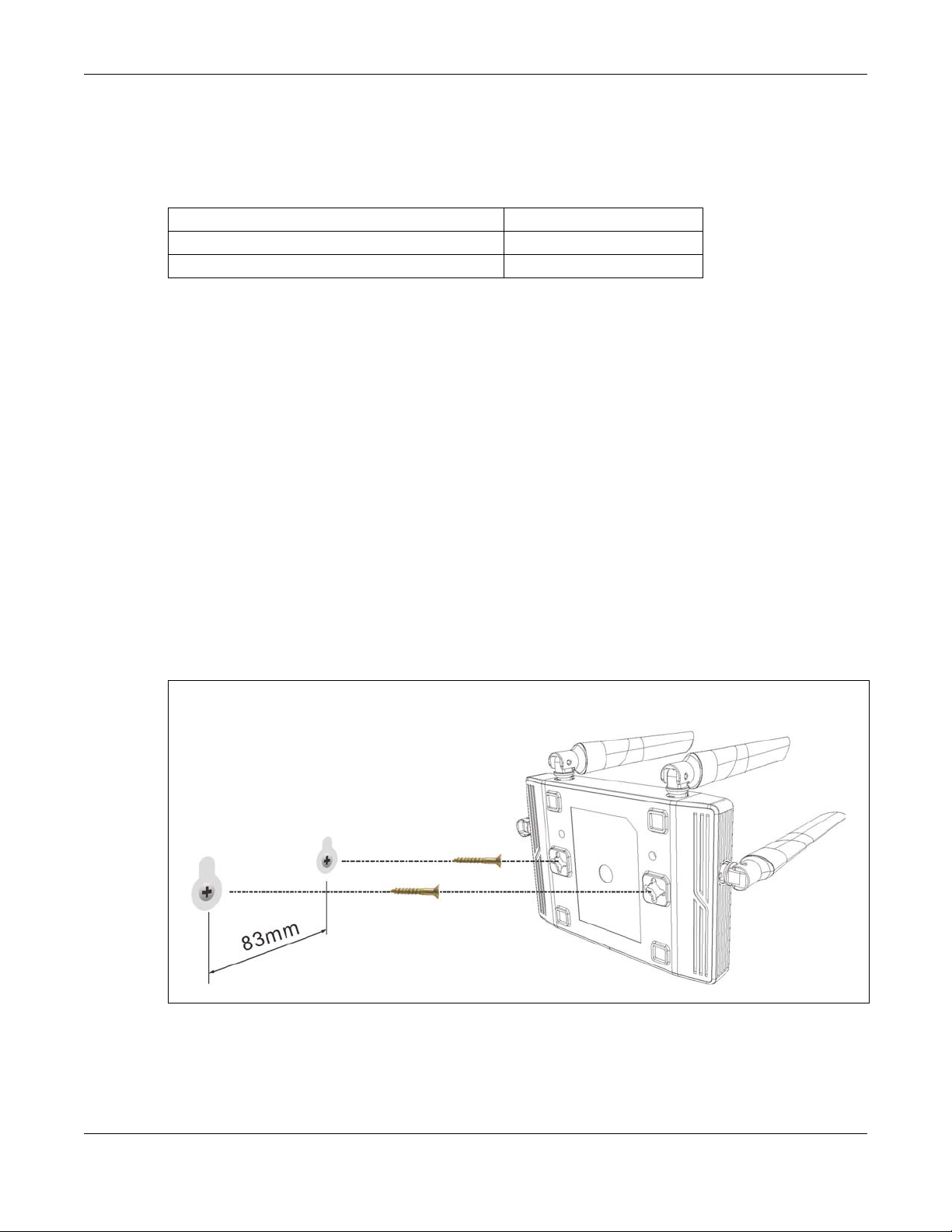
1.8 Wall Mounting
You may need screw anchors if mounting on a concrete or brick wall.
Table 3 Wall Mounting Information
Distance between holes 83 mm
M4 Screws Two
Screw anchors (optional) Two
1 Select a position free of obstructions on a wall strong enough to hold the weight of the device.
2 Mark two holes on the wall at the appropriate distance apart for the screws.
Be careful to avoid damaging pipes or cables located inside the wall
when drilling holes for the screws.
3 If using screw anchors, drill two holes for the screw anchors into the wall. Push the anchors into the full
depth of the holes, then insert the screws into the anchors. Do not insert the screws all the way in - leave
a small gap of about 0.5 cm.
If not using screw anchors, use a screwdriver to insert the screws into the wall. Do not insert the screws all
the way in - leave a gap of about 0.5 cm.
Chapter 1 Introduction
4 Make sure the screws are fastened well enough to hold the weight of the NBG6604 with the connection
cables.
5 Align the holes on the back of the NBG6604 with the screws on the wall. Hang the NBG6604 on the
screws.
Figure 3 Wall Mounting Example
NBG6604 User’s Guide
13
Page 14

2.1 Overview
This chapter describes how to access the NBG6604 Web Configurator and provides an overview of its
screens.
The Web Configurator is an HTML-based management interface that allows easy setup and
management of the NBG6604 via Internet browser. Use a browser that supports HTML5, such asInternet
Explorer 11.0 and later versions, Mozilla Firefox 50 and later versions, Safari 10.0 and later versions, Edge
14 and later versions or Google Chrome 54 and later versions. The recommended screen resolution is
1024 by 768 pixels.
CHAPTER 2
Introducing the Web
Configurator
In order to use the Web Configurator you need to allow:
• JavaScript (enabled by default).
• Java permissions (enabled by default).
Refer to the Troubleshooting chapter (Chapter 15 on page 101) to see how to make sure these functions
are allowed in Internet Explorer.
2.2 Accessing the Web Configurator
1 Make sure your NBG6604 hardware is properly connected and prepare your computer or computer
network to connect to the NBG6604 (refer to the Quick Start Guide).
2 Launch your web browser.
3 The NBG6604 is in router mode by default. Type "http://myrouter" as the website address. If the NBG6604
obtains a WAN IP address or a DNS server IP address in the same subnet as the LAN IP address
192.168.1.1, the default LAN IP address will be changed to 10.0.0.1 automatically. See
on page 52 for more information.
If the NBG6604 is in access point mode, the IP address will be 192.168.1.2. See Chapter 4 on page 25 for
more information about the modes of the NBG6604.
Auto-IP Change
Your computer must be in the same subnet in order to access this website address.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
14
Page 15
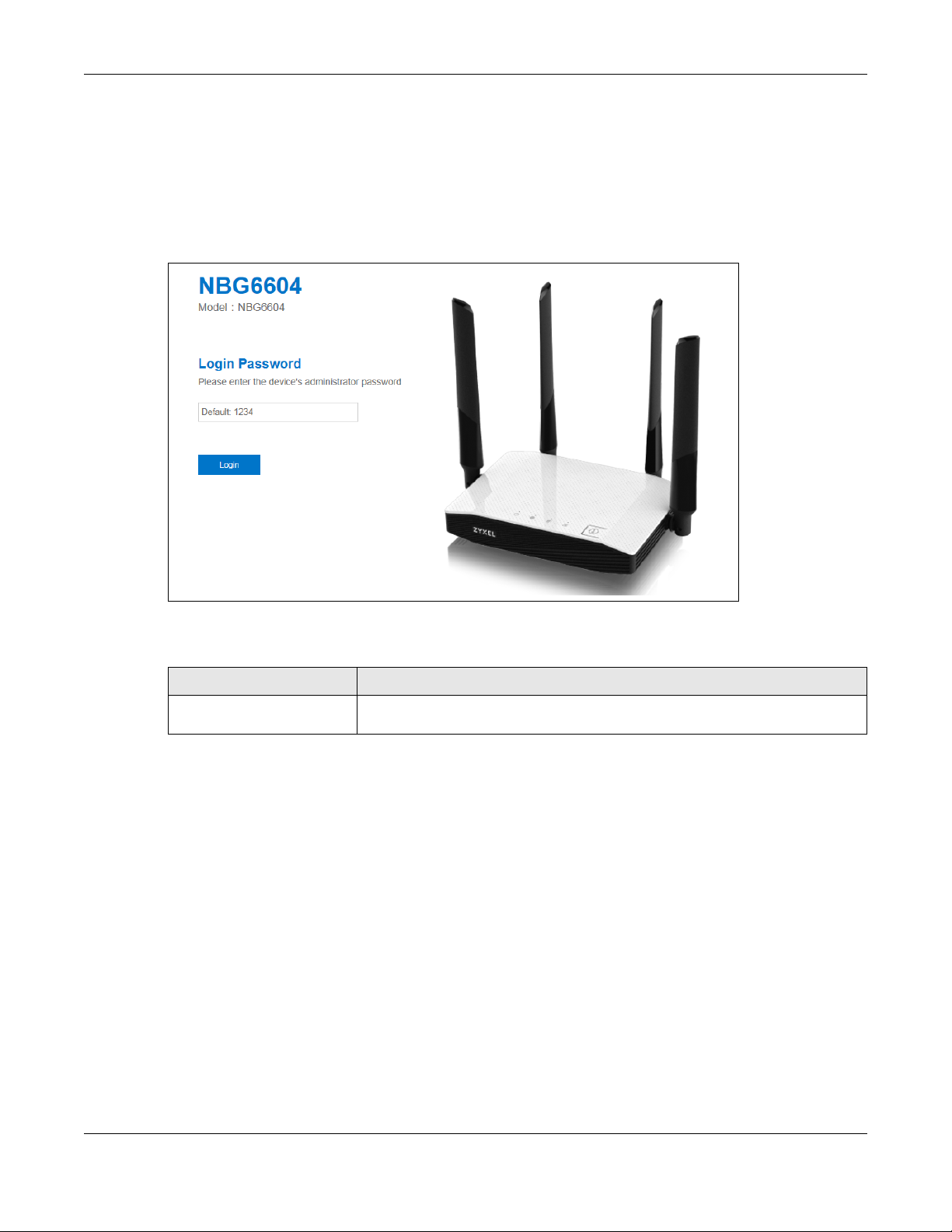
2.2.1 Login Screen
Note: If this is the first time you are accessing the Web Configurator, you may be redirected to
the eaZy123 wizard. Refer to Chapter 3 on page 17 for the eaZy123 setup screens.
The Web Configurator initially displays the following login screen.
Figure 4 Login Screen
Chapter 2 Introducing the Web Configurator
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 4 Login Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Please enter the device’s
administrator password
Type "1234" (default) as the password. Click Login.
2.2.2 Change Default Password Screen
You should see a screen asking you to change your password (highly recommended) as shown next.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
15
Page 16
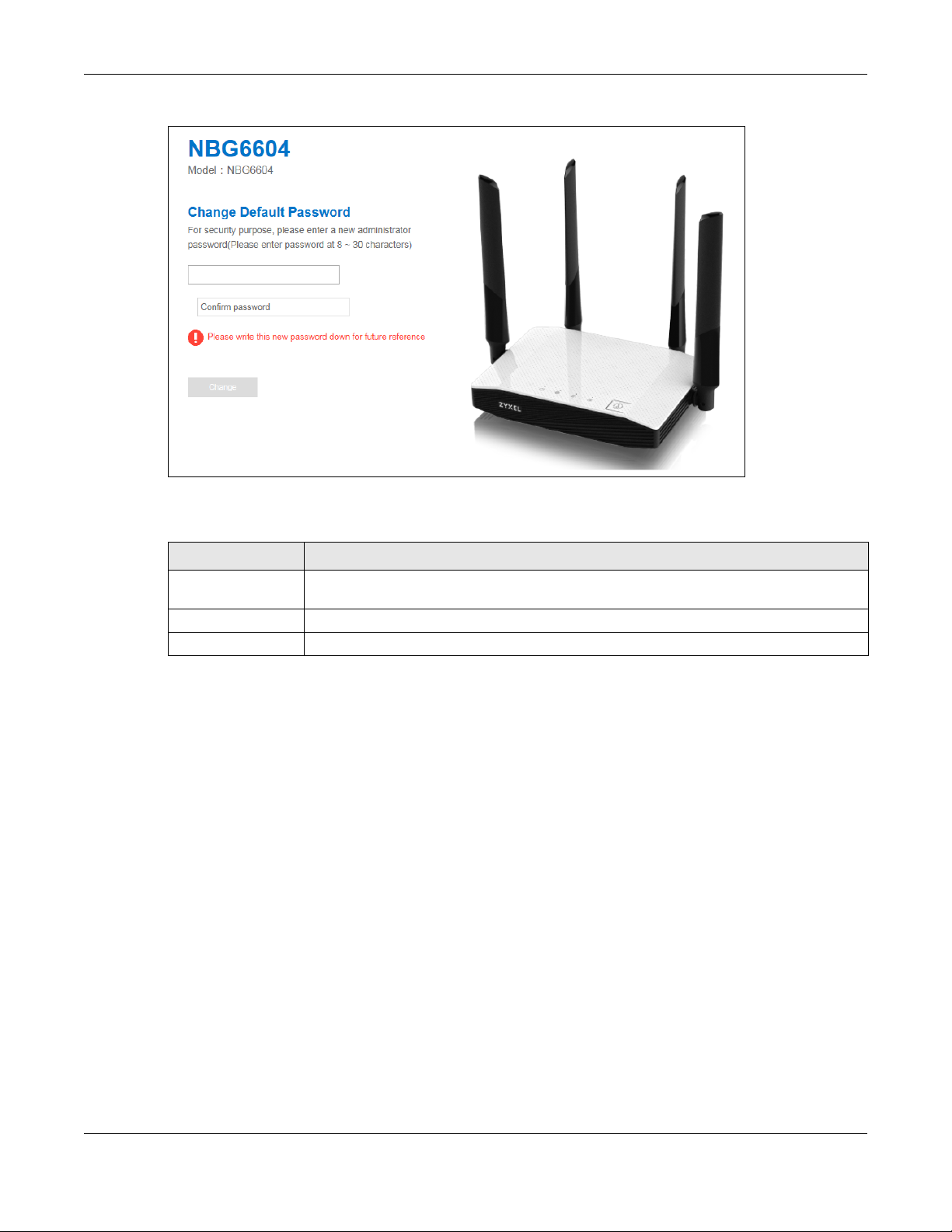
Chapter 2 Introducing the Web Configurator
Figure 5 Change Default Password Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 5 Change Default Password Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enter your new
password here
Confirm password Retype the password for confirmation.
Change Click Change to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Type a new password.
Note: The management session automatically times out when the time period set in the
Administrator Inactivity Timer field expires (default five minutes; go to Chapter 14 on
page 91 to change this). Simply log back into the NBG6604 if this happens.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
16
Page 17

eaZy 123 Wizard
3.1 Overview
This chapter provides information on the eaZy 123 setup screens in the Web Configurator.
The Web Configurator’s eaZy 123 setup wizard helps you configure your device to access the Internet.
Refer to your ISP for your Internet account information. Leave a field blank if you don’t have that
information.
3.2 Accessing the eaZy 123 Wizard
Launch your web browser and type "http://myrouter" as the website address. Type "1234" (default) as
the password and click Login.
CHAPTER 3
Note: The eaZy 123 wizard appears automatically when the NBG6604 is accessed for the first
time or when you reset the NBG6604 to its default factory settings. If you didn’t
configure the wizard screens, you will be redirected to the login page when you
connect to the Internet.
If you have already configured the wizard screens and want to open it again, click on the upper
right corner of any Web Configurator screen. The eaZy 123 wizard attempts to detect which WAN
connection type you are using.
If the eaZy 123 wizard does not detect a connection type, you must select one from the drop-down list
box. Check with your ISP to make sure you use the correct type.
If you do not have the Internet connection, the following screen opens.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
17
Page 18
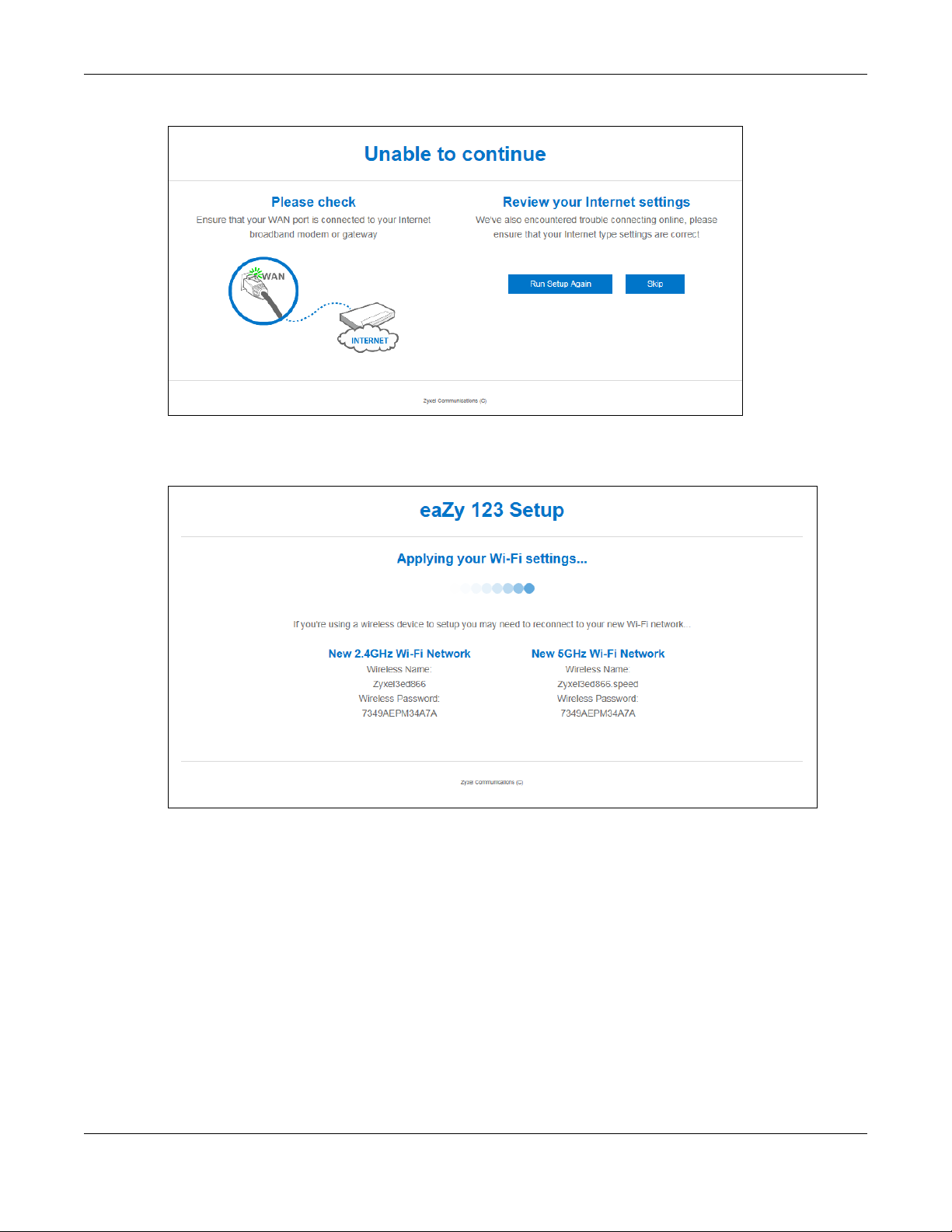
Chapter 3 eaZy 123 Wizard
Figure 6 Unable to continue: WAN
Figure 7 Detecting your Internet Connection Type
NBG6604 User’s Guide
18
Page 19

Figure 8 eaZy 123 Setup
Chapter 3 eaZy 123 Wizard
NBG6604 User’s Guide
19
Page 20
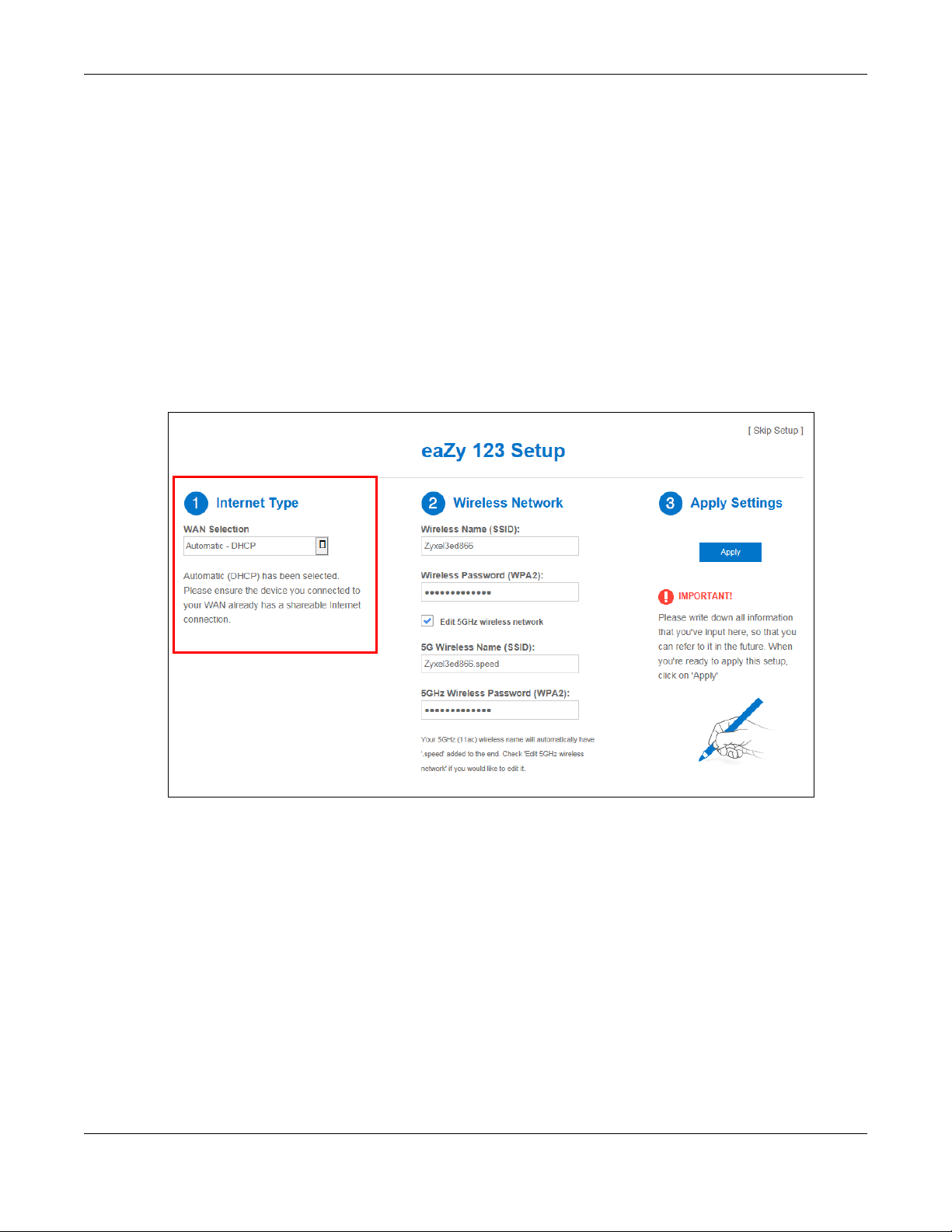
Chapter 3 eaZy 123 Wizard
3.3 Internet Type
The NBG6604 offers three WAN selection types. They are : Automatic - DHCP, PPPoE, and Static.
Configure the Internet type settings on your NBG6604 in the first part. The following screen depends on
your Internet connection type. Enter the details provided by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) in the
fields (if any).
Check with your ISP to make sure you use the correct type. This wizard screen varies according to the
connection type that you select.
3.3.1 WAN Selection Type: Automatic - DHCP
Select the Automatic - DHCP option if your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address.
Figure 9 WAN Selection Type: Automatic - DHCP
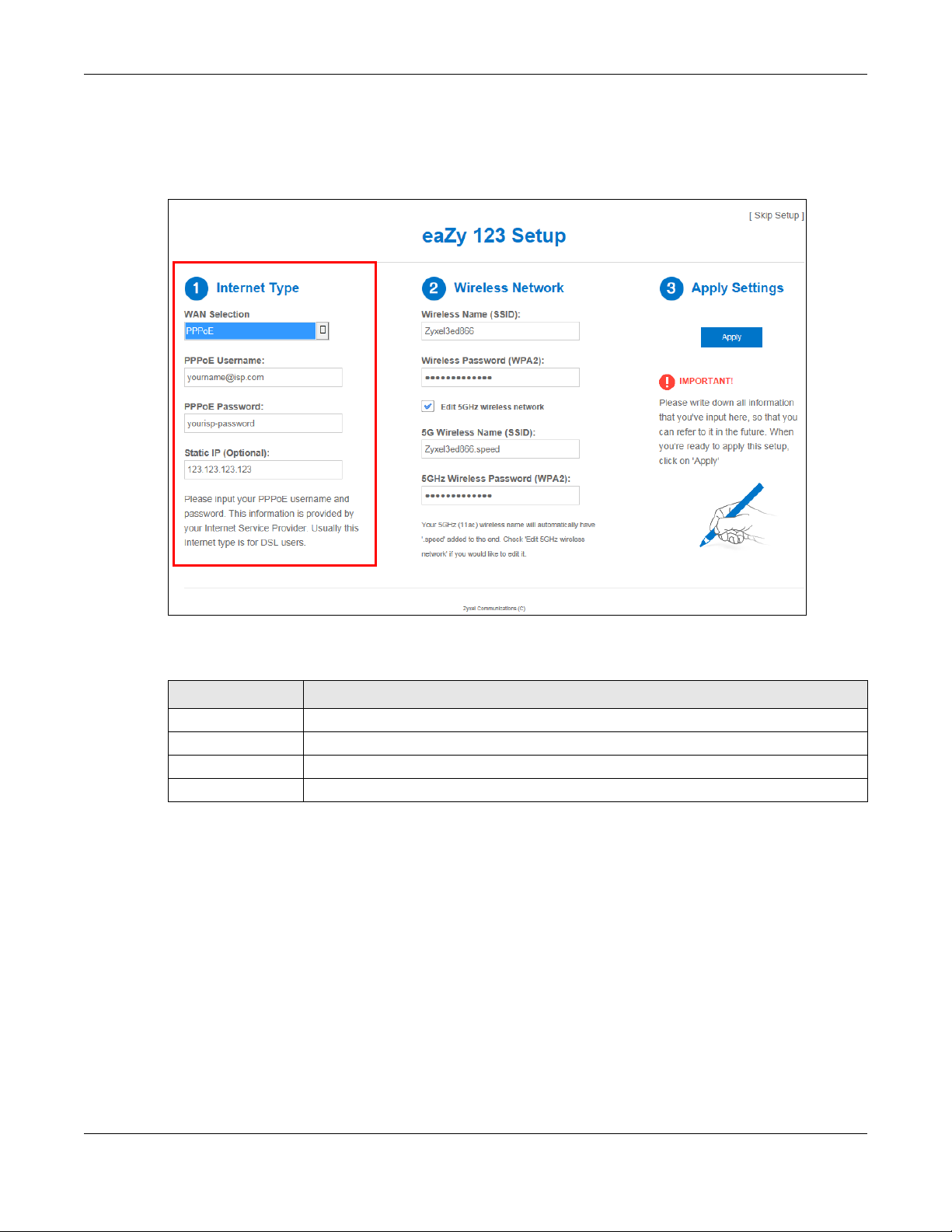
3.3.2 WAN Selection Type: PPPoE
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) functions as a dial-up connection. PPPoE is an IETF (Internet
Engineering Task Force) standard specifying how a host personal computer interacts with a broadband
modem (for example DSL, cable, wireless, etc.) to achieve access to high-speed data networks.
For the service provider, PPPoE offers an access and authentication method that works with existing
access control systems (for instance, RADIUS).
One of the benefits of PPPoE is the ability to let end users access one of multiple network services, a
function known as dynamic service selection. This enables the service provider to easily create and offer
new IP services for specific users.
Operationally, PPPoE saves significant effort for both the subscriber and the ISP/carrier, as it requires no
specific configuration of the broadband modem at the subscriber's site.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
20
Page 21
Chapter 3 eaZy 123 Wizard
By implementing PPPoE directly on the NBG6604 (rather than individual computers), the computers on
the LAN do not need PPPoE software installed, since the NBG6604 does that part of the task.
Furthermore, with NAT, all of the LAN's computers will have Internet access.
Figure 10 WAN Selection Type: PPPoE
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 6 WAN Selection Type: PPPoE
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WAN Selection Select the PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) option for a dial-up connection.
PPPoE Username Type the user name given to you by your ISP.
PPPoE Password Type the password associated with the user name above.
Static IP (Optional) Enter the WAN IP address assigned by your ISP.
Note: If you get an error message, make sure you have entered the correct information
provided by your ISP.
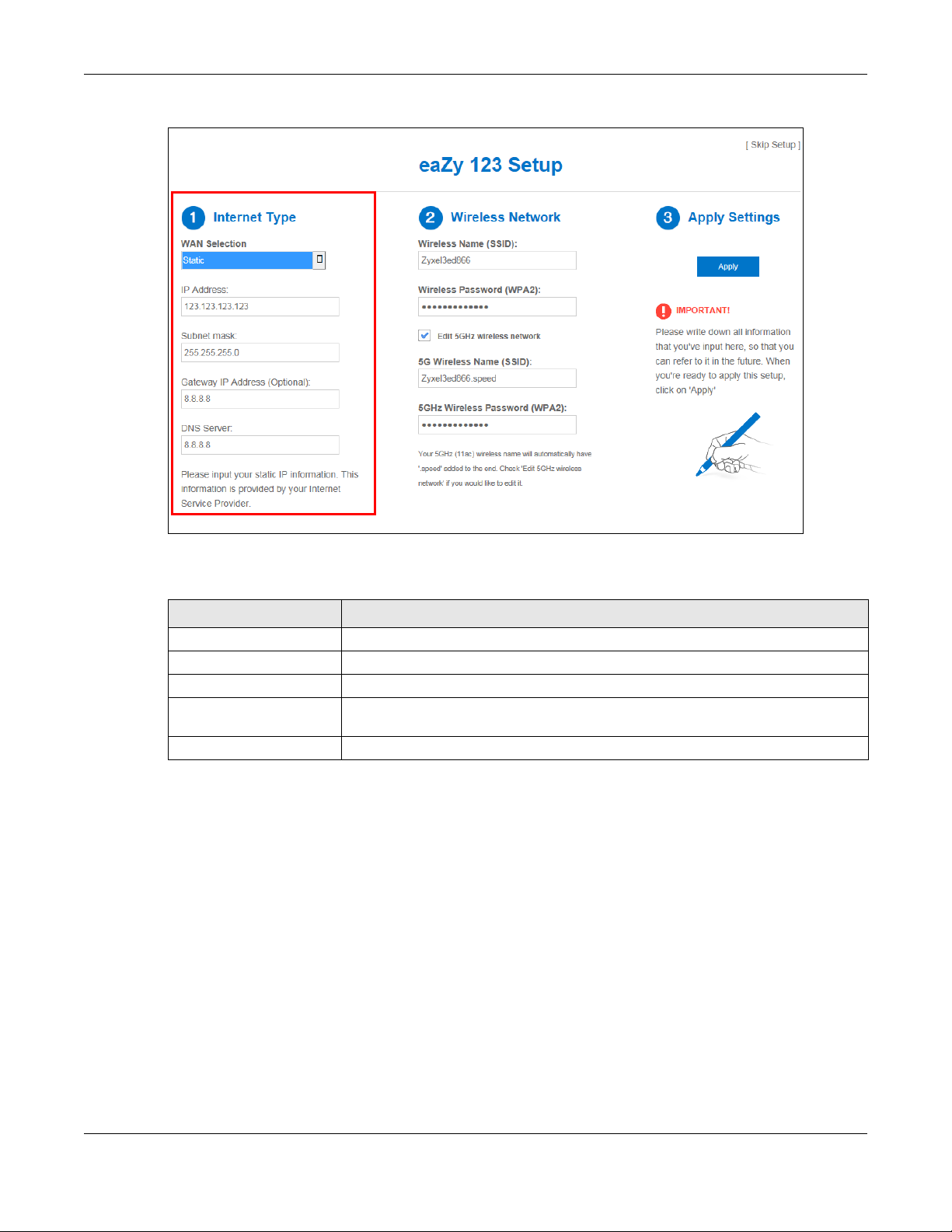
3.3.3 WAN Selection Type: Static
Choose Static as the WAN Selection Type when the WAN port is used as a regular Ethernet. Click Next.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
21
Page 22
Chapter 3 eaZy 123 Wizard
Figure 11 WAN Selection Type: Static
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 7 WAN Selection Type: Static
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WAN Selection Select the Static option when the WAN port is using a fixed IP address.
IP Address Enter the IP address provided by your ISP.
Subnet Mask Enter the IP subnet mask in this field.
Gateway IP Address
(Optional)
DNS Server Enter the DNS server in this field.
Enter the gateway IP address in this field.
Note: If you get an error screen, make sure your Internet connection is working and select the
right WAN Selection Type. Contact your ISP if you are not sure of your Internet
Connection type.
3.4 Wireless Network
Configure the wireless network settings on your NBG6604 in the second part. The default wireless security
setting is WPA2-PSK.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
22
Page 23

Figure 12 Wireless Network
Chapter 3 eaZy 123 Wizard
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 8 Wireless Network
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless Name
(SSID)
Enter a descriptive name for the wireless LAN.
Note: The setting here applies to 2.4 GHz wireless radios.
If you change this field on the NBG6604, make sure all wireless stations use the same SSID in order
to access the network.
Wireless
Password
(WPA2)
Edit 5GHz
wireless network
5GHz Wireless
Name (SSID)
5GHz Wireless
Password
(WPA2)
Type from 8 to 63 case-sensitive ASCII characters. You can set up the most secure wireless
connection by configuring WPA in the wireless LAN screens.
Select this check box to configure different SSID and wireless security settings for the NBG6604’s 5
GHz wireless network.
If you do not select this option, the NBG6604 uses the same SSID and Wi-Fi key (you configured
above) for the 5 GHz wireless network.
Enter a descriptive name for the wireless LAN.
If you change this field on the NBG6604, make sure all wireless stations use the same SSID in order
to access the network.
Type from 8 to 63 case-sensitive ASCII characters. You can set up the most secure wireless
connection by configuring WPA in the wireless LAN screens.
Click the Apply button in the third part to save your settings.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
23
Page 24
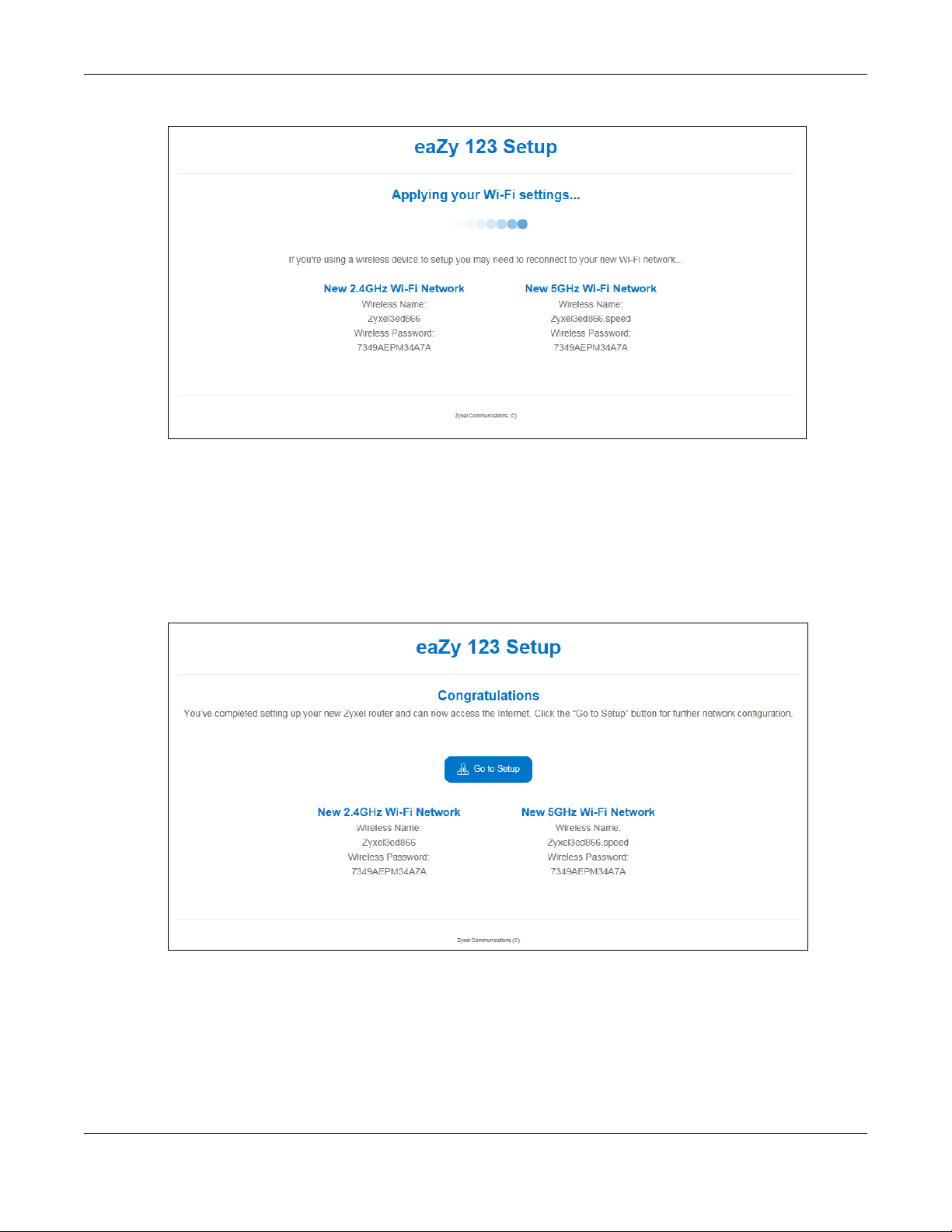
Chapter 3 eaZy 123 Wizard
Figure 13 Apply your Wi-Fi settings
Congratulations! Open a web browser, such as Internet Explorer, to visit your favorite website.
Note: If you cannot access the Internet when your computer is connected to one of the
NBG6604’s LAN ports, check your connections. Then turn the NBG6604 off, wait for a
few seconds then turn it back on. If that does not work, log in to the web configurator
again and check you have typed all information correctly. See the User’s Guide for
more suggestions.
Figure 14 Congratulations
You have successfully set up your NBG6604 to operate on your network and access the Internet.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
24
Page 25

4.1 Overview
This chapter introduces the different operating modes of your NBG6604, or simply how the NBG6604 is
being used in the network.
4.1.1 Operating Modes
This refers to the operating mode of the NBG6604, which can act as a:
• Router: This is the default operating mode of the NBG6604. Use this mode to connect the local
network to another network, like the Internet. Go to
in this mode.
• Access Point: Use this mode if you want to extend your network by allowing network devices to
connect to the NBG6604 wirelessly. Go to Section 6.4 on page 34 to view the Status screen in this
mode.
CHAPTER 4
Operating Modes
Section 5.2 on page 26 to view the Status screen
For more information on these modes and to change the mode of your NBG6604, refer to Chapter 14 on
page 99.
Note: Choose your operating mode carefully to avoid having to change it later.
When changing to another mode, the IP address of the NBG6604 changes. The running applications
and services of the network devices connected to the NBG6604 can be interrupted.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
25
Page 26
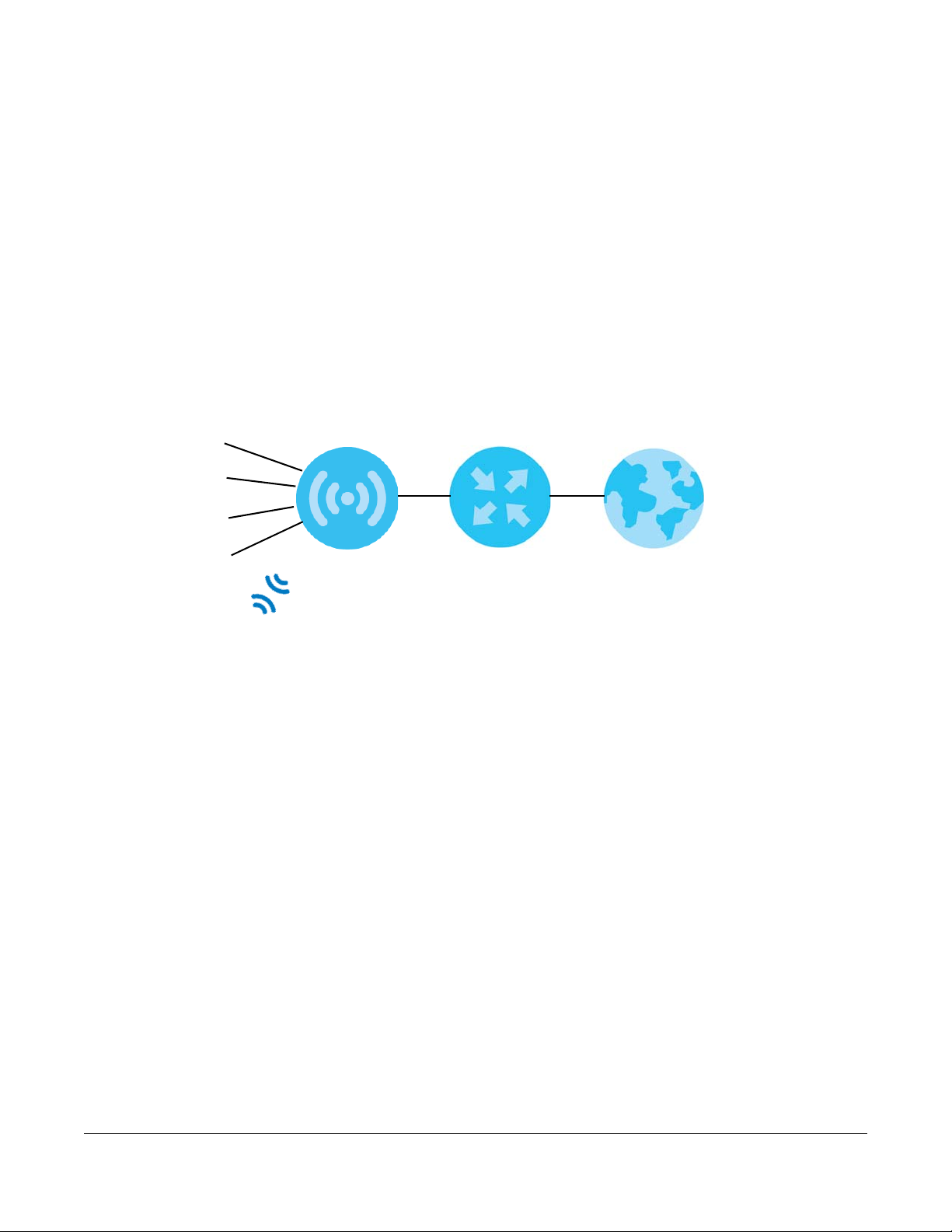
5.1 Overview
LAN1
LAN2
LAN3
LAN4
WLAN
WAN
Internet
MODEM
The NBG6604 is set to router mode by default. Routers are used to connect the local network to another
network (for example, the Internet). In the figure below, the NBG6604 connects the local network (LAN1
~ LAN4) to the Internet.
Figure 15 NBG6604 Network
CHAPTER 5
Router Mode
5.2 Router Mode Status Screen
Click Status > System Status to open the status screen.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
26
Page 27
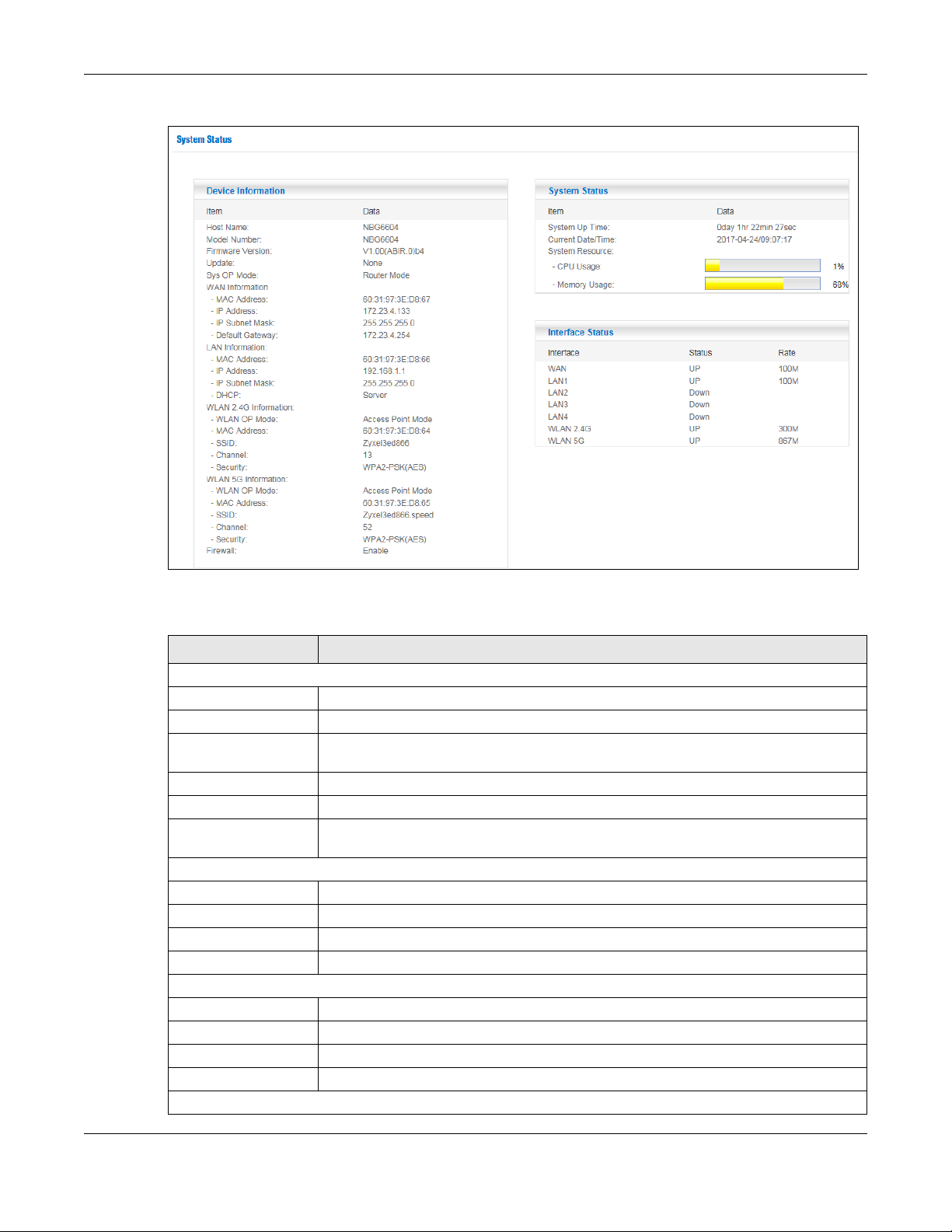
Chapter 5 Router Mode
Figure 16 Status > System Status: Router Mode
The following table describes the labels shown in the Status screen.
Table 9 Status > System Status: Router Mode
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Device Information
Item This column shows the type of data the NBG6604 is recording.
Data This column shows the actual data recorded by the NBG6604.
Host Name This is the System Name you enter in the Maintenance > General screen. It is for
Model Number This is the model name of your device.
Firmware Version This is the firmware version.
Sys OP Mode This is the device mode (Section 4.1.1 on page 25) to which the NBG6604 is set - Router
WAN Information
MAC Address This shows the WAN Ethernet adapter MAC Address of your device.
IP Address This shows the WAN port’s IP address.
IP Subnet Mask This shows the WAN port’s subnet mask.
Default Gateway This shows the WAN port’s gateway IP address.
LAN Information
MAC Address This shows the LAN Ethernet adapter MAC Address of your device.
IP Address This shows the LAN port’s IP address.
IP Subnet Mask This shows the LAN port’s subnet mask.
DHCP This shows the LAN port’s DHCP role - Server or Disable.
WLAN 2.4G Information
identification purposes.
Mode.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
27
Page 28
Chapter 5 Router Mode
Table 9 Status > System Status: Router Mode (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WLAN OP Mode This is the device mode (Section 4.1.1 on page 25) to which the NBG6604’s wireless LAN is
set - Access Point Mode.
MAC Address This shows the 2.4GHz wireless adapter MAC Address of your device.
SSID This shows a descriptive name used to identify the NBG6604 in the 2.4GHz wireless LAN.
Channel This shows the channel number which you select manually.
Security This shows the level of wireless security the NBG6604 is using.
WLAN 5G Information
WLAN OP Mode This is the device mode (Section 4.1.1 on page 25) to which the NBG6604’s wireless LAN is
set - Access Point Mode.
MAC Address This shows the 5GHz wireless adapter MAC Address of your device.
SSID This shows a descriptive name used to identify the NBG6604 in the 5GHz wireless LAN.
Channel This shows the channel number which you select manually.
Security This shows the level of wireless security the NBG6604 is using.
Firewall This shows whether the firewall is enabled or not.
System Status
System Up Time This is the total time the NBG6604 has been on.
Current Date/Time This field displays your NBG6604’s present date and time.
System Resource
- CPU Usage This displays what percentage of the NBG6604’s processing ability is currently used. When
this percentage is close to 100%, the NBG6604 is running at full load, and the throughput is
not going to improve anymore. If you want some applications to have more throughput,
you should turn off other applications.
- Memory Usage This shows what percentage of the heap memory the NBG6604 is using.
Interface Status
Interface This displays the NBG6604 port types. The port types are: WAN, LAN, and WLAN.
Status For the LAN and WAN ports, this field displays Down (line is down) or Up (line is up or
connected).
For the 2.4GHz/5GHz WLAN, it displays Up when the 2.4GHz/5GHz WLAN is enabled or
Down when the 2.4G/5G WLAN is disabled.
Rate For the LAN ports, this displays the port speed and duplex setting or is left blank when the
line is disconnected.
5.2.1 Navigation Panel
Use the sub-menus on the navigation panel to go to Web Configurator screens.
For the WAN port, it displays the port speed and duplex setting if you’re using Ethernet
encapsulation. This field displays N/A when the line is disconnected.
For the 2.4GHz/5GHz WLAN, it displays the maximum transmission rate when the 2.4GHz/
5GHz WLAN is enabled and N/A when the WLAN is disabled.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
28
Page 29

Chapter 5 Router Mode
Figure 17 Navigation Panel: Router Mode
The following table describes the sub-menus.
Table 10 Navigation Panel: Router Mode
LINK FUNCTION
Status
System Status This screen shows the NBG6604’s general device, system and interface status information. Use
this screen to access the wizard, and summary statistics tables.
Client Tables Use this screen to view current DHCP client information.
WAN
Internet
Connection
NAT Use this screen to enable NAT.
Dynamic DNS Use this screen to set up dynamic DNS.
Wireless
Wireless Use this screen to enable the wireless LAN and configure wireless LAN and wireless security
Guest Wireless Use this screen to configure multiple BSSs on the NBG6604.
MAC Filter Use the MAC filter screen to configure the NBG6604 to block access to devices or block the
Advanced This screen allows you to configure advanced wireless settings.
WPS Use this screen to configure WPS.
Scheduling Use this screen to schedule the times the Wireless LAN is enabled.
LAN
LAN IP Use this screen to configure LAN IP address and subnet mask.
This screen allows you to configure ISP parameters, WAN IP address assignment, DNS servers
and the WAN MAC address.
Use this screen to configure servers behind the NBG6604 and forward incoming service
requests to the server(s) on your local network.
Use this screen to change your NBG6604’s port triggering settings.
Use this screen to configure VPN pass-through settings.
settings.
devices from accessing the NBG6604.
Use this screen to enable the NBG6604’s DHCP server.
Static DHCP This screen allows you to assign IP addresses on the LAN to specific individual computers based
Applications
UPnP Use this screen to enable UPnP on the NBG6604.
One Connect Use this screen to enable or disable Wi-Fi auto-configuration.
Security
on their MAC addresses.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
29
Page 30
Chapter 5 Router Mode
Table 10 Navigation Panel: Router Mode (continued)
LINK FUNCTION
IPv4 Firewall Use this screen to configure IPv4 firewall rules.
Maintenance
General Use this screen to view and change administrative settings such as system and domain names.
Password Use this screen to change the password of your NBG6604.
Time Use this screen to change your NBG6604’s time and date.
Firmware
Upgrade
Backup/Restore Use this screen to backup and restore the configuration or reset the factory defaults to your
Restart This screen allows you to reboot the NBG6604 without turning the power off.
Remote
Management
Log Use this screen to view the list of activities recorded by your NBG6604.
Operation Mode This screen allows you to select whether your device acts as a router, or an access point.
Use this screen to upload firmware to your NBG6604.
NBG6604.
Use this screen to configure through which interface(s) and from which IP address(es) users can
use Telnet and HTTP/HTTPS to manage the NBG6604.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
30
Page 31

6.1 Overview
WLAN
LAN
Internet
Use your NBG6604 as an Access Point (AP) if you already have a router or gateway on your network. In
this mode your NBG6604 bridges a wired network (LAN) and wireless LAN (WLAN) in the same subnet.
See the figure below for an example.
Figure 18 Wireless Internet Access in Access Point Mode
CHAPTER 6
Access Point Mode
Many screens that are available in Router Mode are not available in Access Point Mode, such as firewall.
6.2 What You Can Do
• Use the Status screen to view read-only information about your NBG6604 (Section 6.4 on page 34).
• Use the LAN screen to set the IP address for your NBG6604 acting as an access point (Section 6.5 on
page 36).
6.3 What You Need to Know
See Chapter 7 on page 38 for a tutorial on setting up a network with the NBG6604 as an access point.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
31
Page 32

Chapter 6 Access Point Mode
6.3.1 Setting your NBG6604 to AP Mode
1 Log into the Web Configurator if you haven’t already. See the Quick start Guide for instructions on how
to do this.
2 To use your NBG6604 as an access point, go to Maintenance > Operation Mode and select Access Point
Mode.
Figure 19 Changing to Access Point Mode
Note: You have to log in to the Web Configurator again when you change modes. As soon as
you do, your NBG6604 is already in Access Point mode.
3 When you select Access Point Mode, the following pop-up message window appears:
Figure 20 Pop up for Access Point Mode
Click OK. Then click Apply. The Web Configurator refreshes once the change to Access Point mode is
successful.
6.3.2 Accessing the Web Configurator in Access Point Mode
Log in to the Web Configurator in Access Point mode, do the following:
1 Connect your computer to the LAN port of the NBG6604.
2 The default IP address of the NBG6604 is “192.168.1.2”. In this case, your computer must have an IP
address in the range between “192.168.1.3” and “192.168.1.254”.
3 Click Start > Run on your computer in Windows. Type “cmd” in the dialog box. Enter “ipconfig” to show
your computer’s IP address. If your computer’s IP address is not in the correct range then see
B on page 113 for information on changing your computer’s IP address.
4 After you’ve set your computer’s IP address, open a web browser such as Internet Explorer and type
“192.168.1.2” as the web address in your web browser.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
Appendix
32
Page 33

Chapter 6 Access Point Mode
6.3.3 Configuring your WLAN and Maintenance Settings
The configuration of wireless and maintenance settings in Access Point Mode is the same as for Router
Mode.
•See Chapter 10 on page 63 for information on the configuring your wireless network.
•See Chapter 14 on page 91 for information on configuring your maintenance settings.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
33
Page 34

Chapter 6 Access Point Mode
6.4 AP Mode Status Screen
Click Status to open the Status screen.
Figure 21 Status > System Status: Access Point Mode
The following table describes the labels shown in the Status screen.
Table 11 Status > System Status: Access Point Mode
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Device Information
Host Name This is the System Name you enter in the Maintenance > General screen. It is for
Model Number This is the model name of your device.
Firmware Version This is the firmware version and the date created.
Sys OP Mode This is the device mode (Section 4.1.1 on page 25) to which the NBG6604 is set - AP
LAN Information
MAC Address This shows the LAN Ethernet adapter MAC Address of your device.
IP Address This shows the LAN port’s IP address.
IP Subnet Mask This shows the LAN port’s subnet mask.
DHCP This shows the LAN port’s DHCP role - Client or None.
WLAN 2.4G Information
WLAN OP Mode This is the device mode (Section 4.1.1 on page 25) to which the NBG6604’s wireless LAN is
MAC Address This shows the 2.4GHz wireless adapter MAC Address of your device.
SSID This shows a descriptive name used to identify the NBG6604 in the 2.4GHz wireless LAN.
Channel This shows the channel number which you select manually.
Security This shows the level of wireless security the NBG6604 is using.
identification purposes.
Mode.
set - Access Point Mode.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
34
Page 35

Chapter 6 Access Point Mode
Table 11 Status > System Status: Access Point Mode (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WLAN 5G Information
WLAN OP Mode This is the device mode (Section 4.1.1 on page 25) to which the NBG6604’s wireless LAN is
set - Access Point Mode.
MAC Address This shows the 5GHz wireless adapter MAC Address of your device.
SSID This shows a descriptive name used to identify the NBG6604 in the 5GHz wireless LAN.
Channel This shows the channel number which you select manually.
Security This shows the level of wireless security the NBG6604 is using.
System Status
Item This column shows the type of data the NBG6604 is recording.
Data This column shows the actual data recorded by the NBG6604.
System Up Time This is the total time the NBG6604 has been on.
Current Date/Time This field displays your NBG6604’s present date and time.
System Resource
- CPU Usage This displays what percentage of the NBG6604’s processing ability is currently used. When
this percentage is close to 100%, the NBG6604 is running at full load, and the throughput
is not going to improve anymore. If you want some applications to have more
throughput, you should turn off other applications.
- Memory Usage This shows what percentage of the heap memory the NBG6604 is using.
Interface Status
Interface This displays the NBG6604 port types. The port types are: LAN and WLAN.
Status For the LAN ports, this field displays Down (line is down) or Up (line is up or connected).
For the 2.4GHz/5GHz WLAN, it displays Up when the 2.4GHz/5GHz WLAN is enabled or
Down when the 2.4G/5G WLAN is disabled.
Rate For the LAN ports, this displays the port speed and duplex setting or is left blank when the
line is disconnected.
For the 2.4GHz/5GHz WLAN, it displays the maximum transmission rate when the 2.4GHz/
5GHz WLAN is enabled and N/A when the WLAN is disabled.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
35
Page 36

6.4.1 Navigation Panel
Use the menu in the navigation panel to configure NBG6604 features in Access Point Mode.
Figure 22 Navigation Panel: Access Point Mode
Refer to Table 10 on page 29 for descriptions of the labels shown in the navigation panel.
Chapter 6 Access Point Mode
6.5 LAN Screen
Use this section to configure your LAN settings while in Access Point Mode.
Click LAN to see the screen below.
Note: If you change the IP address of the NBG6604 in the screen below, you will need to log
into the NBG6604 again using the new IP address.
Figure 23 LAN > LAN IP
NBG6604 User’s Guide
36
Page 37

Chapter 6 Access Point Mode
The table below describes the labels in the screen.
Table 12 LAN > LAN IP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Address
Obtain an IP Address
Automatically
Static IP Address Click this if you want to specify the IP address of your NBG6604. Or if your ISP or network
IP Address Type the IP address in dotted decimal notation. The default setting is 192.168.1.2. If you
Subnet Mask The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. Your NBG6604
Default Gateway Enter a Default Gateway’s IP address (if your ISP or network administrator gave you one)
DNS Server
First DNS Server
Second DNS Server
Third DNS Server
Apply Click Apply to save your changes to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
When you enable this, the NBG6604 gets its IP address from the network’s DHCP server
(for example, your ISP). Users connected to the NBG6604 can now access the network
(i.e., the Internet if the IP address is given by the ISP).
The Web Configurator may no longer be accessible unless you know the IP address
assigned by the DHCP server to the NBG6604. You need to reset the NBG6604 to be
able to access the Web Configurator again (see
how to reset the NBG6604).
Also when you select this, you cannot enter an IP address for your NBG6604 in the field
below.
administrator gave you a static IP address to access the network or the Internet.
change the IP address you will have to log in again with the new IP address.
will automatically calculate the subnet mask based on the IP address that you assign.
Unless you are implementing subnetting, use the subnet mask computed by the
NBG6604.
in this field.
Select Obtained From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server information (and the
NBG6604's WAN IP address). The field to the right displays the (read-only) DNS server IP
address that the ISP assigns.
Select User-Defined if you have the IP address of a DNS server. Enter the DNS server's IP
address in the field to the right. If you chose User-Defined, but leave the IP address set to
0.0.0.0, User-Defined changes to None after you click Apply. If you set a second choice
to User-Defined, and enter the same IP address, the second User-Defined changes to
None after you click Apply.
Select None if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do not configure a DNS
server, you must know the IP address of a computer in order to access it.
Section 14.7 on page 95 for details on
NBG6604 User’s Guide
37
Page 38

CHAPTER 7
7.1 Overview
This chapter provides tutorials for setting up your NBG6604.
• Set Up a Wireless Network Using WPS
• Connect to NBG6604 Wireless Network without WPS
• Using Guest SSIDs on the NBG6604
7.2 Set Up a Wireless Network Using WPS
This section gives you an example of how to set up wireless network using WPS. This example uses the
NBG6604 as the AP and NWD210N as the wireless client which connects to a notebook.
Tutorials
The wireless client must be a WPS-aware device. There are two WPS methods for creating a secure
connection via the web configurator or utility. This tutorial shows you how to do both.
• Push Button Configuration (PBC) - create a secure wireless network simply by pressing a button. See
Section 7.2.1 on page 38. This is the easier method.
• PIN Configuration - create a secure wireless network simply by entering a wireless client's PIN (Personal
Identification Number) in the NBG6604’s interface. See Section 7.2.2 on page 39. This is the more
secure method, since one device can authenticate the other.
7.2.1 Push Button Configuration (PBC)
1 Make sure that your NBG6604 is turned on. and that the device is placed within range of your notebook.
2 Make sure that you have installed the wireless client (this example uses the NWD210N) driver and utility in
your notebook.
3 In the wireless client utility, find the WPS settings. Enable WPS and press the WPS button (Start or WPS
button)
4 Log into NBG6604’s Web Configurator and press the Push Button in the Wireless > WPS screen.
Note: Your NBG6604 has a WPS button located on its top panel, as well as a WPS button in its
configuration utility. Both buttons have exactly the same function; you can use one or
the other.
Note: It doesn’t matter which button is pressed first. You must press the second button within
two minutes of pressing the first one.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
38
Page 39

Chapter 7 Tutorials
2.4G
5G
Wireless Client
Access Point
SECURITY INFO
COMMUNICATION
WITHIN 2 MINUTES
WPS
The NBG6604 sends the proper configuration settings to the wireless client. This may take up to two
minutes. Then the wireless client is able to communicate with the NBG6604 securely.
The following figure shows you an example to set up wireless network and security by pressing a button
on both NBG6604 and wireless client (the NWD210N in this example).
Figure 24 Example WPS Process: PBC Method
7.2.2 PIN Configuration
When you use the PIN configuration method, you need to use both NBG6604’s configuration interface
and the client’s utilities.
1 Launch your wireless client’s configuration utility. Go to the WPS settings and select the PIN method to
get a PIN number.
2 Enter the PIN number to the PIN field in the Wireless > WPS screen on the NBG6604.
3 Click Start buttons (or button next to the PIN field) on both the wireless client utility screen and the
NBG6604’s WPS screen within two minutes.
The NBG6604 authenticates the wireless client and sends the proper configuration settings to the wireless
client. This may take up to two minutes. Then the wireless client is able to communicate with the
NBG6604 securely.
The following figure shows you the example to set up wireless network and security on NBG6604 and
wireless client (ex. NWD210N in this example) by using PIN method.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
39
Page 40

Chapter 7 Tutorials
WITHIN 2 MINUTES
Wireless Client
Access Point
Figure 25 Example WPS Process: PIN Method
7.3 Connect to NBG6604 Wireless Network without WPS
This example shows you how to configure wireless security settings with the following parameters on your
NBG6604 and connect your computer to the NBG6604 wireless network.
Band 2.4GHz
SSID SSID_Example3
Channel 6
Security WPA2-PSK
(Pre-Shared Key: ThisismyWPA-PSKpre-sharedkey)
NBG6604 User’s Guide
40
Page 41

Chapter 7 Tutorials
Follow the steps below to configure the wireless settings on your NBG6604.
The instructions require that your hardware is connected (see the Quick Start Guide) and you are
logged into the Web Configurator through your LAN connection (see
1 Make sure the WIFI switch (at the rear panel of the NBG6604) is set to ON.
2 Open the Wireless > Wireless screen in the AP’s Web Configurator.
3 Confirm that the wireless LAN is enabled on the NBG6604.
4 Select to configure the wireless settings for the 2.4GHz wireless radio.
5 Enter SSID_Example3 as the SSID and select Channel-06 as the channel. Set security mode to WPA2-PSK
and enter ThisismyWPA-PSKpre-sharedkey in the Pre-Shared Key field. Click Apply.
Section 2.2 on page 14).
NBG6604 User’s Guide
41
Page 42

Chapter 7 Tutorials
6 Click Status to open the Status screen. Verify your wireless and wireless security settings under Device
Information and check if the WLAN connection is up under Interface Status.
7.3.1 Configure Your Notebook
Note: In this example, we use the Zyxel NWD6505 wireless adapter as the wireless client and
use the Windows built-in utility (Windows Zero Configuration (WZC)) to connect to the
wireless netwok.
1 The NBG6604 supports IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11n, and IEEE 802.11ac wireless
clients. Make sure that your notebook or computer’s wireless adapter supports one of these standards.
2 Wireless adapters come with software sometimes called a “utility” that you install on your computer. See
your wireless adapter’s User’s Guide for information on how to do that.
3 The Wireless Network Connection screen displays. Click Refresh network list to view the available wireless
APs within range.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
42
Page 43

Chapter 7 Tutorials
4 Select SSID_Example3 and click Connect.
5 Type the security key in the following screen. Click Connect.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
43
Page 44

Chapter 7 Tutorials
6 Check the status of your wireless connection in the screen below.
7 If the wireless client keeps trying to connect to or acquiring an IP address from the NBG6604, make sure
you entered the correct security key.
If the connection has limited or no connectivity, make sure the DHCP server is enabled on the NBG6604.
If your connection is successful, open your Internet browser and enter http://www.zyxel.com or the URL
of any other web site in the address bar. If you are able to access the web site, your wireless connection
is successfully configured.
7.4 Using Guest SSIDs on the NBG6604
You can configure more than one guest SSID on a NBG6604. See Section 10.4 on page 72.
This allows you to configure multiple independent wireless networks on the NBG6604 as if there were
multiple APs (virtual APs). Each guest SSID has its own wireless security type. That is, each SSID on the
NBG6604 represents a different access point/wireless network to wireless clients in the network.
Clients can associate only with the SSIDs for which they have the correct security settings. Clients using
different SSIDs can access the Internet and the wired network behind the NBG6604 (such as a printer).
NBG6604 User’s Guide
44
Page 45

Chapter 7 Tutorials
A
SSID_Worker
B
SSID_Guest
C
SSID_VoIP
Internet
M
ODEM
For example, you may set up three wireless networks (A, B, and C) in your office. A is for workers, B is for
guests, and C is specific to a VoIP device in the meeting room.
7.4.1 Configuring Security Settings of Guest SSIDs
The NBG6604 is in router mode by default.
This example shows you how to configure the SSIDs with the following parameters on your NBG6604 (in
router mode).
SSID SECURITY TYPE KEY
SSID_Worker WPA2-PSK
WPA Compatible
SSID_VoIP WPA-PSK VoIPOnly12345678
SSID_Guest WPA-PSK keyexample123
DoNotStealMyWirelessNetwork
Note: This tutorial assumes that you have disabled WPS in Wireless > WPS. Otherwise, the
“WPA-PSK” security type is not available to configure.
1 Connect your computer to the LAN port of the NBG6604 using an Ethernet cable.
2 The default IP address of the NBG6604 in router mode is “192.168.1.1”. In this case, your computer must
have an IP address in the range between “192.168.1.2” and “192.168.1.254”.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
45
Page 46

Chapter 7 Tutorials
3 Click Start > Run on your computer in Windows. Type “cmd” in the dialog box. Enter “ipconfig” to show
your computer’s IP address. If your computer’s IP address is not in the correct range then see
B on page 113 for information on changing your computer’s IP address.
4 After you’ve set your computer’s IP address, open a web browser such as Internet Explorer and type
“http://192.168.1.1” as the web address in your web browser.
5 Enter “1234” (default) as the password and click Login.
6 Type a new password and retype it to confirm, then click Apply. Otherwise, click Ignore.
7 The Easy Mode appears. Go to Wireless > Guest Wireless. Click the Edit icon of the first entry to configure
wireless and security settings for SSID_Worker.
Appendix
8 Configure the screen as follows. In this example, you enable Intra-BSS Traffic for SSID_Worker to allow
wireless clients in the same wireless network to communicate with each other. Click Apply.
9 Click the Edit icon of the second entry to configure wireless and security settings for SSID_VoIP.
10 Configure the screen as follows. You do not enable Intra-BSS Traffic for SSID_VoIP. Click Apply.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
46
Page 47

Chapter 7 Tutorials
11 Click the Edit icon of the third entry to configure wireless and security settings for SSID_Guest.
12 Configure the screen as follows. In this example, you enable Intra-BSS Traffic for SSID_Guest to allow
wireless clients in the same wireless network to communicate with each other. Select Enable Guest
WLAN to allow clients to access the Internet only. Click Apply.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
47
Page 48

8.1 Overview
This chapter discusses read-only information related to the device state of the NBG6604.
8.1.1 What You Can Do
• Use the Client Tables screen to view the current DHCP client information (Section 8.2 on page 48).
8.2 Client Tables Screen
You can configure the NBG6604’s LAN as a DHCP server or disable it. When configured as a server, the
NBG6604 assigns IP addresses to the clients. If DHCP service is disabled, you must have another DHCP
server on that network, or else the computer must be manually configured.
CHAPTER 8
Status
Use this screen to view current DHCP client information (including MAC Address, and IP Address) of all
network clients using the NBG6604’s DHCP server.
Click Status > Client Tables to open the Client Tables screen.
Figure 26 Status > Client Tables
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 13 Status > Client Tables
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Interface Select the interface from the drop-down list box to display current DHCP client information.
# This is the index number of the host computer.
Online This field displays whether the connection to the host computer is up (a yellow bulb) or down (a
gray bulb).
Host Name This field displays the computer host name.
IP Address This field displays the IP address relative to the # field listed above.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
48
Page 49

Chapter 8 Status
Table 13 Status > Client Tables
LABEL DESCRIPTION
MAC Address This field shows the MAC address of the computer with the name in the Host Name field.
Every Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address which uniquely
identifies a device. The MAC address is assigned at the factory and consists of six pairs of
hexadecimal characters, for example, 00:A0:C5:00:00:02.
Interface/Rssi This field displays the device’s interface type or received signal strength indicator (RSSI) that is
currently connected to the NBG6604.
Lease time This field displays the amount of time that the IP address is valid.
Reserve Select this if you want to reserve the IP address for this specific MAC address.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
49
Page 50

9.1 Overview
LAN WAN
Internet
This chapter discusses the NBG6604’s WAN screens. Use these screens to configure your NBG6604 for
Internet access.
A WAN (Wide Area Network) connection is an outside connection to another network or the Internet. It
connects your private networks such as a LAN (Local Area Network) and other networks, so that a
computer in one location can communicate with computers in other locations.
Figure 27 LAN and WAN
CHAPTER 9
WAN
9.2 What You Can Do
• Use the Internet Connection screen to enter your ISP information and set how the computer acquires
its IP, DNS and WAN MAC addresses (
• Use the NAT > General screen to enable NAT, set a default server and change your NBG6604’s port
forwarding settings (
• Use the NAT > Port Trigger screen to configure your NBG6604’s trigger port settings (Section 9.5.2 on
page 59).
• Use the NAT > Passthrough screen to configure your NBG6604’s VPN pass-through settings (Section
9.5.3 on page 60).
• Use the Dynamic DNS screen to change your NBG6604’s DDNS settings (Section 9.6 on page 61).
Section 9.5.1 on page 58).
Section 9.4 on page 53).
NBG6604 User’s Guide
50
Page 51

Chapter 9 WAN
9.3 What You Need To Know
The information in this section can help you configure the screens for your WAN connection, as well as
enable/disable some advanced features of your NBG6604.
9.3.1 Configuring Your Internet Connection
Encapsulation Method
Encapsulation is used to include data from an upper layer protocol into a lower layer protocol. To set up
a WAN connection to the Internet, you need to use the same encapsulation method used by your ISP
(Internet Service Provider). If your ISP offers a dial-up Internet connection using PPPoE (PPP over
Ethernet) or PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol), they should also provide a username and password
(and service name) for user authentication.
WAN IP Address
The WAN IP address is an IP address for the NBG6604, which makes it accessible from an outside
network. It is used by the NBG6604 to communicate with other devices in other networks. It can be static
(fixed) or dynamically assigned by the ISP each time the NBG6604 tries to access the Internet.
If your ISP assigns you a static WAN IP address, they should also assign you the subnet mask and DNS
server IP address(es) (and a gateway IP address if you use the Ethernet or ENET ENCAP encapsulation
method).
DNS Server Address Assignment
Use Domain Name System (DNS) to map a domain name to its corresponding IP address and vice versa,
for instance, the IP address of www.zyxel.com is 204.217.0.2. The DNS server is extremely important
because without it, you must know the IP address of a computer before you can access it.
The NBG6604 can get the DNS server addresses in the following ways:
1 The ISP tells you the DNS server addresses, usually in the form of an information sheet, when you sign up.
If your ISP gives you DNS server addresses, manually enter them in the DNS server fields.
2 If your ISP dynamically assigns the DNS server IP addresses (along with the NBG6604’s WAN IP address),
set the DNS server fields to get the DNS server address from the ISP.
WAN MAC Address
The MAC address screen allows users to configure the WAN port's MAC address by either using the
factory default or cloning the MAC address from a computer on your LAN. Choose Factory Default to
select the factory assigned default MAC Address.
Otherwise, click Clone the computer's MAC address - IP Address and enter the IP address of the
computer on the LAN whose MAC you are cloning. Once it is successfully configured, the address will be
copied to configuration file. It is recommended that you clone the MAC address prior to hooking up the
WAN Port.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
51
Page 52

Chapter 9 WAN
Server
A
B
C
D
Multicast
Traditionally, IP packets are transmitted in one of either two ways - Unicast (1 sender - 1 recipient) or
Broadcast (1 sender - everybody on the network). Multicast delivers IP packets to a group of hosts on
the network - not everybody and not just 1.
Figure 28 Multicast Example
In the multicast example above, systems A and D comprise one multicast group. In multicasting, the
server only needs to send one data stream and this is delivered to systems A and D.
IGMP (Internet Group Multicast Protocol) is a network-layer protocol used to establish membership in a
multicast group - it is not used to carry user data. The NBG6604 supports both IGMP version 1 (IGMP-v1)
and IGMP version 2 (IGMP-v2).
At start up, the NBG6604 queries all directly connected networks to gather group membership. After
that, the NBG6604 periodically updates this information. IP multicasting can be enabled/disabled on the
NBG6604 WAN interface in the Web Configurator (WAN). Select None to disable IP multicasting on these
interfaces.
Auto-IP Change
When the NBG6604 gets a WAN IP address or a DNS server IP address which is in the same subnet as the
LAN IP address 192.168.1.1, Auto-IP-Change allows the NBG6604 to change its LAN IP address to 10.0.0.1
automatically. If the NBG6604’s original LAN IP address is 10.0.0.1 and the WAN IP address is in the same
subnet, such as 10.0.0.3, the NBG6604 switches to use 192.168.1.1 as its LAN IP address.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
52
Page 53

Chapter 9 WAN
LAN WAN
192.168.1.1 192.168.1.23
10.0.0.1
Internet
Figure 29 Auto-IP-Change Example
Auto-IP-Change only works under the following conditions:
• The NBG6604 must be in Router Mode (see Section 14.11 on page 98 for more information) for Auto-IP-
Change to become active.
• The NBG6604 is set to receive a dynamic WAN IP address.
9.4 Internet Connection Screen
Use this screen to change your NBG6604’s Internet access settings. Click WAN > Internet Connection.
9.4.1 IPoE Encapsulation
This screen displays when you select IPoE encapsulation.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
53
Page 54

Chapter 9 WAN
Figure 30 WAN > Internet Connection: IPoE Encapsulation (IPv4 Only)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 14 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: IPoE Encapsulation
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ISP Parameters for Internet Access
Encapsulation You must choose the IPoE option when the WAN port is used as a regular Ethernet.
IPv4 Select IPv4 Only if you want the NBG6604 to run IPv4 only.
Select Dual Stack to allow the NBG6604 to run IPv4.
IP Address
Obtain an IP Address
Automatically (DHCP)
Static IP Address Select this option if the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
IP Address Enter your WAN IP address in this field if you selected Static IP Address.
Subnet Mask Enter the Subnet Mask in this field.
Default Gateway Enter a gateway IP address (if your ISP gave you one) in this field.
MTU Size Enter the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) size for each packet. If a larger packet arrives,
DNS Server
Select this option if your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address. This is the default
selection.
the NBG6604 divides it into smaller fragments.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
54
Page 55

Chapter 9 WAN
Table 14 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: IPoE Encapsulation (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
First DNS Server
Second DNS Server
Third DNS Server
WAN MAC Address
Once the WAN MAC address is successfully configured, the address will be copied to the configuration file. It will
not change unless you change the setting or upload a different configuration file.
Factory default Select this option to have the WAN interface use the factory assigned default MAC
Clone the computer's
MAC address - IP
Address
Set WAN MAC
Address
Automatically
configured by DHCPC
Manually Configured Select this if you have the IPv4 address of the relay server.
Border Relay IPv4
Address
IPv4 mask length Enter the subnet mask number (1~32) for the IPv4 network.
Relay Server IPv4
Address
Remote IPv4 Address Enter the IPv4 address of the remote gateway to which this interface tunnels traffic.
Auto-Subnet Configuration
Enable Auto-IPChange Mode
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Select Obtained From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server information (and the
NBG6604's WAN IP address). The field to the right displays the (read-only) DNS server IP
address that the ISP assigns.
Select User-Defined if you have the IP address of a DNS server. Enter the DNS server's IP
address in the field to the right.
Select None if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do not configure a DNS
server, you must know the IP address of a computer in order to access it.
address. By default, the NBG6604 uses the factory assigned MAC address to identify itself.
Select this option to have the WAN interface use a different MAC address by cloning the
MAC address of another device or computer. Enter the IP address of the device or
computer whose MAC you are cloning.
Select this option to have the WAN interface use a manually specified MAC address. Enter
the MAC address in the fields.
Select this to have the NBG6604 detect the relay server’s IP address automatically through
DHCP.
Specify the relay server’s IPv4 address.
Enter the IPv4 address of a 6to4 relay server which helps forward packets between 6to4
networks and native IPv6 networks.
Select this option to have the NBG6604 change its LAN IP address to 10.0.0.1 or 192.168.1.1
accordingly when the NBG6604 gets a dynamic WAN IP address in the same subnet as the
LAN IP address.
Select this option to have the NBG6604 change its LAN IP address to 10.0.0.1 or 192.168.1.1
accordingly when the NBG6604 gets a DNS server IP address in the same subnet as the
LAN IP address.
The NAT, DHCP server and firewall functions on the NBG6604 are still available in this mode.
9.4.2 PPPoE Encapsulation
The NBG6604 supports PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet). PPPoE is an IETF standard (RFC 2516)
specifying how a personal computer (PC) interacts with a broadband modem (DSL, cable, wireless,
etc.) connection. The PPP over Ethernet option is for a dial-up connection using PPPoE.
For the service provider, PPPoE offers an access and authentication method that works with existing
access control systems (for example Radius).
NBG6604 User’s Guide
55
Page 56

Chapter 9 WAN
One of the benefits of PPPoE is the ability to let you access one of multiple network services, a function
known as dynamic service selection. This enables the service provider to easily create and offer new IP
services for individuals.
Operationally, PPPoE saves significant effort for both you and the ISP or carrier, as it requires no specific
configuration of the broadband modem at the customer site.
By implementing PPPoE directly on the NBG6604 (rather than individual computers), the computers on
the LAN do not need PPPoE software installed, since the NBG6604 does that part of the task.
Furthermore, with NAT, all of the LANs’ computers will have access.
This screen displays when you select PPPoE encapsulation.
Figure 31 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPPoE Encapsulation (IPv4 Only)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 15 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPPoE Encapsulation
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ISP Parameters for Internet Access
Encapsulation Select PPPoE if you connect to your Internet via dial-up.
IPv4 Select IPv4 Only if you want the NBG6604 to run IPv4 only.
Select Dual Stack to allow the NBG6604 to run IPv4.
PPP Information
NBG6604 User’s Guide
56
Page 57

Chapter 9 WAN
Table 15 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPPoE Encapsulation (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
PPP Username Type the user name given to you by your ISP.
PPP Password Type the password associated with the user name above.
MTU Size Enter the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) or the largest packet size per frame that your
NBG6604 can receive and process.
PPP Auto Connect Select this option if you do not want the connection to time out.
IDLE Timeout
(second)
PPPoE Service
Name
WAN IP Address Assignment
Get automatically
from ISP
Use Fixed IP Address Select this option and enter your WAN IP address if the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
DNS Server
First DNS Server
Second DNS Server
Third DNS Server
WAN MAC Address
The MAC address section allows users to configure the WAN port's MAC address by using the NBG6604’s MAC
address, copying the MAC address from a computer on your LAN or manually entering a MAC address.
Factory default Select Factory default to use the factory assigned default MAC Address.
Clone the
computer’s MAC
address - IP Address
Set WAN MAC
Address
Automatically
configured by
DHCPC
Manually
Configured
Border Relay IPv4
Address
IPv4 mask length Enter the subnet mask number (1~32) for the IPv4 network.
Remote IPv4
Address
Multicast Setup
Multicast Setup Select IGMPv1/v2 to enable multicasting. This applies to traffic routed from the WAN to the
Auto-Subnet Configuration
This value specifies the time in minutes that elapses before the router automatically
disconnects from the PPPoE server.
Enter the PPPoE service name specified in the ISP account.
Select this option if your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address. This is the default selection.
Select Obtained From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server information (and the
NBG6604's WAN IP address). The field to the right displays the (read-only) DNS server IP
address that the ISP assigns.
Select User-Defined if you have the IP address of a DNS server. Enter the DNS server's IP
address in the field to the right.
Select None if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do not configure a DNS server,
you must know the IP address of a computer in order to access it.
Select Clone the computer's MAC address - IP Address and enter the IP address of the
computer on the LAN whose MAC you are cloning.
Select this option and enter the MAC address you want to use.
Select this to have the NBG6604 detect the relay server’s IP address automatically through
DHCP.
Select this if you have the IPv4 address of the relay server.
Specify the relay server’s IPv4 address.
Enter the IPv4 address of the remote gateway to which this interface tunnels traffic.
LAN.
Select None to disable this feature. This may cause incoming traffic to be dropped or sent to
all connected network devices.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
57
Page 58

Table 15 Network > WAN > Internet Connection: PPPoE Encapsulation (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable Auto-IPChange Mode
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
9.5 NAT
Use this screen to change your NBG6604’s NAT (Network Address Translation) settings. Click WAN > NAT.
9.5.1 General Screen
Chapter 9 WAN
Select this option to have the NBG6604 change its LAN IP address to 10.0.0.1 or 192.168.1.1
accordingly when the NBG6604 gets a dynamic WAN IP address in the same subnet as the
LAN IP address.
Select this option to have the NBG6604 change its LAN IP address to 10.0.0.1 or 192.168.1.1
accordingly when the NBG6604 gets a DNS server IP address in the same subnet as the LAN IP
address.
The NAT, DHCP server and firewall functions on the NBG6604 are still available in this mode.
Use this screen to enable NAT, set a default server and configure your NBG6604’s port forwarding
settings to forward incoming service requests to the server(s) on your local network. Click WAN > NAT >
General.
Figure 32 WAN > NAT > General
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 16 WAN > NAT > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General
Network Address
Translation (NAT)
Default Server Setup
Network Address Translation (NAT) allows the translation of an Internet protocol address used
within one network (for example a private IP address used in a local network) to a different IP
address known within another network (for example a public IP address used on the
Internet).
Select Enable to activate NAT. Select Disable to turn it off.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
58
Page 59

Chapter 9 WAN
Table 16 WAN > NAT > General (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Default Server You can decide whether you want to use the default server or specify a server manually. In
addition to the servers for specified services, NAT supports a default server. A default server
receives packets from ports that are not specified in the port forwarding summary table
below.
Select this to use the default server.
Change To Server Select this and manually enter the server’s IP address.
Port Forwarding (Max. Limit : 32)
# This is the number of an individual port forwarding server entry.
Name Select a pre-defined service from the drop-down list box. The pre-defined service port
Protocol Select the transport layer protocol supported by this virtual server. Choices are TCP, UDP, or
Local Port This shows the port number(s) that identifies the service if you select a pre-defined service. If
Server IP Address Select User define to manually enter the inside IP address of the virtual server here.
Port This shows the port number(s) that identifies the service if you select a pre-defined service. If
Name This field displays a name to identify this rule.
Protocol This is the transport layer protocol used for the service.
Local Port This field displays the port number(s).
Server IP Address This field displays the inside IP address of the server.
Port This field displays the port number(s).
Add Click to add the rule in the port forwarding summary table.
Delete Click to remove a rule.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
number(s) and protocol will be displayed in the port forwarding summary table. Otherwise,
select User define to manually enter the Port number(s) and select the Protocol.
TCP_UDP.
If you have chosen a pre-defined service in the Name field, the protocol will be configured
automatically.
you select User define in the Name field, enter the port number(s) manually.
you select User define in the Name field, enter the port number(s) manually.
9.5.2 Port Trigger Screen
To change your NBG6604’s trigger port settings, click WAN > NAT > Port Trigger. The screen appears as
shown.
Note: Only one LAN computer can use a trigger port (range) at a time.
Figure 33 WAN > NAT > Port Trigger
NBG6604 User’s Guide
59
Page 60

Chapter 9 WAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 17 WAN > NAT > Port Trigger
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port Trigger Rules (Max. Limit : 32)
# This is the rule index number (read-only).
Name Type a unique name (up to 15 characters) for identification purposes. All characters are
Incoming Port Incoming is a port (or a range of ports) that a server on the WAN uses when it sends out a
End Port Type a port number or the ending port number in a range of port numbers.
Trigger Port The trigger port is a port (or a range of ports) that causes (or triggers) the NBG6604 to record
End Port Type a port number or the ending port number in a range of port numbers.
Add Click to add the rule in the port trigger summary table.
Delete Click to remove a rule.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
permitted - including spaces.
particular service. The NBG6604 forwards the traffic with this port (or range of ports) to the
client computer on the LAN that requested the service.
Type a port number or the starting port number in a range of port numbers.
the IP address of the LAN computer that sent the traffic to a server on the WAN.
Type a port number or the starting port number in a range of port numbers.
9.5.3 Passthrough Screen
ALG Overview
Application Layer Gateway (ALG) allows VPN traffic to operate properly through the NBG6604’s NAT.
The ALG feature is only needed for traffic that goes through the NBG6604’s NAT.
To change your NBG6604’s VPN pass-through settings, click WAN > NAT > Passthrough. The screen
appears as shown.
Figure 34 WAN > NAT > Passthrough
NBG6604 User’s Guide
60
Page 61

Chapter 9 WAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 18 WAN > NAT > Passthrough
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VPN Passthrough
PPTP Select Enable to allow VPN clients to make outbound PPTP connections. It is required in order
L2TP Select Enable to allow VPN clients to make outbound L2TP connections. It is required in order
IPSEC Select Enable to allow VPN clients to make outbound IPSec connections. It is required in
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
to connect to a PPTP VPN account. If PPTP is disabled, then when a client sends a request to
a VPN server, the server will reply to the NBG6604 and the NBG6604 will drop the request.
When PPTP is enabled, the NBG6604 will forward the reply from the VPN server to the client
that initiated the request, and the connection will establish successfully.
to connect to a L2TP VPN account. If L2TP is disabled, then when a client sends a request to a
VPN server, the server will reply to the NBG6604 and the NBG6604 will drop the request. When
L2TP is enabled, the NBG6604 will forward the reply from the VPN server to the client that
initiated the request, and the connection will establish successfully.
order to connect to a IPSec VPN account. If IPSEC is disabled, then when a client sends a
request to a VPN server, the server will reply to the NBG6604 and the NBG6604 will drop the
request. When IPSEC is enabled, the NBG6604 will forward the reply from the VPN server to
the client that initiated the request, and the connection will establish successfully.
9.6 Dynamic DNS Screen
To change your NBG6604’s DDNS, click WAN > Dynamic DNS. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 35 WAN > Dynamic DNS
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 19 WAN > Dynamic DNS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Dynamic DNS Setup
Dynamic DNS Select Enable to use dynamic DNS. Select Disable to turn this feature off.
Service Provider Select the name of your Dynamic DNS service provider.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
61
Page 62

Chapter 9 WAN
Table 19 WAN > Dynamic DNS (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Host Name Enter a host names in the field provided. You can specify up to two host names in the
field separated by a comma (",").
Username Enter your user name.
Password Enter the password assigned to you.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
62
Page 63

10.1 Overview
AB
AP
This chapter discusses how to configure the wireless network settings in your NBG6604. The NBG6604 is
able to function both 2.4GHz and 5GHz network at the same time. You can have different wireless and
wireless security settings for 2.4GHz and 5GHz wireless LANs. Click Wireless to configure wireless LAN 2.4G
or wireless LAN 5G.
See the appendices for more detailed information about wireless networks.
The following figure provides an example of a wireless network.
Figure 36 Example of a Wireless Network
CHAPTER 10
Wireless LAN
The wireless network is the part in the blue circle. In this wireless network, devices A and B are called
wireless clients. The wireless clients use the Access Point (AP) to interact with other devices (such as the
printer) or with the Internet. Your NBG6604 is the AP.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
63
Page 64

10.1.1 What You Can Do
• Use the Wireless screen to enable or disable the 2.4GHz or 5GHz wireless LAN, set up wireless security
between the NBG6604 and the wireless clients, and make other basic configuration changes (Section
10.2 on page 68).
• Use the Guest Wireless screen to set up multiple wireless networks on your NBG6604 (Section 10.4 on
page 72).
• Use the MAC Filter screen to allow or deny wireless stations based on their MAC addresses from
connecting to the NBG6604 (
• Use the Advanced screen to allow intra-BSS networking and set the RTS/CTS Threshold (Section 10.6 on
page 76).
• Use the WPS screen to quickly set up a wireless network with strong security, without having to
configure security settings manually (
• Use the Scheduling screen to set the times your wireless LAN is turned on and off (Section 10.8 on
page 78).
Section 10.5 on page 75).
10.1.2 What You Should Know
Every wireless network must follow these basic guidelines.
Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
Section 10.7 on page 77).
• Every wireless client in the same wireless network must use the same SSID.
The SSID is the name of the wireless network. It stands for Service Set IDentity.
• If two wireless networks overlap, they should use different channels.
Like radio stations or television channels, each wireless network uses a specific channel, or frequency,
to send and receive information.
• Every wireless client in the same wireless network must use security compatible with the AP.
Security stops unauthorized devices from using the wireless network. It can also protect the
information that is sent in the wireless network.
Wireless Security Overview
The following sections introduce different types of wireless security you can set up in the wireless
network.
SSID
Normally, the AP acts like a beacon and regularly broadcasts the SSID in the area. You can hide the
SSID instead, in which case the AP does not broadcast the SSID. In addition, you should change the
default SSID to something that is difficult to guess.
This type of security is fairly weak, however, because there are ways for unauthorized devices to get the
SSID. In addition, unauthorized devices can still see the information that is sent in the wireless network.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
64
Page 65

Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
MAC Address Filter
Every wireless client has a unique identification number, called a MAC address.1 A MAC address is
usually written using twelve hexadecimal characters2; for example, 00A0C5000002 or 00:A0:C5:00:00:02.
To get the MAC address for each wireless client, see the appropriate User’s Guide or other
documentation.
You can use the MAC address filter to tell the AP which wireless clients are allowed or not allowed to use
the wireless network. If a wireless client is allowed to use the wireless network, it still has to have the
correct settings (SSID, channel, and security). If a wireless client is not allowed to use the wireless
network, it does not matter if it has the correct settings.
This type of security does not protect the information that is sent in the wireless network. Furthermore,
there are ways for unauthorized devices to get the MAC address of an authorized wireless client. Then,
they can use that MAC address to use the wireless network.
User Authentication
You can make every user log in to the wireless network before they can use it. This is called user
authentication. However, every wireless client in the wireless network has to support IEEE 802.1x to do
this.
For wireless networks, there are two typical places to store the user names and passwords for each user.
• In the AP: this feature is called a local user database or a local database.
• In a RADIUS server: this is a server used in businesses more than in homes.
If your AP does not provide a local user database and if you do not have a RADIUS server, you cannot
set up user names and passwords for your users.
Unauthorized devices can still see the information that is sent in the wireless network, even if they cannot
use the wireless network. Furthermore, there are ways for unauthorized wireless users to get a valid user
name and password. Then, they can use that user name and password to use the wireless network.
Local user databases also have an additional limitation that is explained in the next section.
Encryption
Wireless networks can use encryption to protect the information that is sent in the wireless network.
Encryption is like a secret code. If you do not know the secret code, you cannot understand the
message.
1. Some wireless devices, such as scanners, can detect wireless networks but cannot use wireless networks. These
kinds of wireless devices might not have MAC addresses.
2. Hexadecimal characters are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, and F.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
65
Page 66

Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
The types of encryption you can choose depend on the type of user authentication. (See page 65 for
information about this.)
Table 20 Types of Encryption for Each Type of Authentication
NO AUTHENTICATION RADIUS SERVER
Weakest No Security WPA
WPA-PSK
Strongest WPA2-PSK WPA2
For example, if the wireless network has a RADIUS server, you can choose WPA or WPA2. If users do not
log in to the wireless network, you can choose no encryption, WPA-PSK, or WPA2-PSK.
Usually, you should set up the strongest encryption that every wireless client in the wireless network
supports. For example, suppose the AP does not have a local user database, and you do not have a
RADIUS server. Therefore, there is no user authentication. Suppose the wireless network has two wireless
clients. Device A only supports WPA, and device B supports WPA and WPA2. Therefore, you should set
up WPA or WPA-PSK in the wireless network.
Note: It is recommended that wireless networks use WPA-PSK, WPA, or stronger encryption.
IEEE 802.1x and WEP encryption are better than none at all, but it is still possible for
unauthorized devices to figure out the original information pretty quickly.
Note: It is not possible to use WPA-PSK, WPA or stronger encryption with a local user database.
In this case, it is better to set up stronger encryption with no authentication than to set
up weaker encryption with the local user database.
When you select WPA2 or WPA2-PSK in your NBG6604, you can also select an option (WPA/WPA-PSK
Compatible) to support WPA/WPA-PSK as well. In this case, if some wireless clients support WPA and
some support WPA2, you should set up WPA2-PSK or WPA2 (depending on the type of wireless network
login) and select the WPA/WPA-PSK Compatible option in the NBG6604.
Many types of encryption use a key to protect the information in the wireless network. The longer the
key, the stronger the encryption. Every wireless client in the wireless network must have the same key.
Guest WLAN
Guest WLAN allows you to set up a wireless network where users can access to Internet via the NBG6604
(Z), but not other networks connected to the Z. In the following figure, a guest user can access the
Internet from the guest wireless network A via Z but not the home or company network N.
Note: The home or company network N and Guest WLAN network are independent networks.
Note: Only Router mode supports guest WLAN.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
66
Page 67

Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
A
N
Z
Internet
A
N
600 kbps
300 kbps
100 kbps
Internet
Figure 37 Guest Wireless LAN Network
Guest WLAN Bandwidth
The Guest WLAN Bandwidth function allows you to restrict the maximum bandwidth for the guest
wireless network. Additionally, you can also define bandwidth for your home or office network. An
example is shown next to define maximum bandwidth for your networks (A is Guest WLAN and N is home
or company network.)
Figure 38 Example: Bandwidth for Different Networks
NBG6604 User’s Guide
67
Page 68

WPS
WiFi Protected Setup (WPS) is an industry standard specification, defined by the WiFi Alliance. WPS
allows you to quickly set up a wireless network with strong security, without having to configure security
settings manually. Depending on the devices in your network, you can either press a button (on the
device itself, or in its configuration utility) or enter a PIN (Personal Identification Number) in the devices.
Then, they connect and set up a secure network by themselves. See how to set up a secure wireless
network using WPS in the
Section 7.2 on page 38.
10.2 Wireless Screen
Use this screen to configure the SSID and wireless security of the NBG6604’s default wireless LAN.
Note: If you are configuring the NBG6604 from a computer connected to the wireless LAN
and you change the NBG6604’s SSID, channel or security settings, you will lose your
wireless connection when you press Apply to confirm. You must then change the
wireless settings of your computer to match the NBG6604’s new settings.
Click Wireless.
Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
Figure 39 Wireless
The following table describes the general wireless LAN labels in this screen.
Table 21 Wireless
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless Setup
Band Select the frequency band to set whether you want to apply the wireless and security settings
to the default 2.4GHz or 5GHz wireless LAN.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
68
Page 69

Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
Table 21 Wireless (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless LAN Select Enable to activate the 2.4GHz and/or 5GHz wireless LAN. Select Disable to turn it off.
Name (SSID) The SSID (Service Set IDentity) identifies the Service Set with which a wireless client is
Hide SSID Select this check box to hide the SSID in the outgoing beacon frame so a station cannot
Channel Selection Select a channel from the drop-down list box. The options vary depending on the frequency
Operating
Channel
Channel Width Select the wireless channel width used by NBG6604.
802.11 Mode If you set Band to 2.4GHz, you can select from the following:
associated. Enter a descriptive name (up to 32 printable characters found on a typical English
language keyboard) for the wireless LAN.
obtain the SSID through scanning using a site survey tool.
band and the country you are in.
This option is only available if Auto Channel Selection is disabled.
This displays the channel the NBG6604 is currently using.
A standard 20MHz channel offers transfer speeds of up to 144Mbps (2.4GHz) or 217Mbps
(5GHZ) whereas a 40MHz channel uses two standard channels and offers speeds of up to
300Mbps (2.4GHz) or 450Mbps (5GHz).
Because not all devices support 40 MHz channels, select Auto 20/40MHz to allow the NBG6604
to adjust the channel bandwidth automatically.
40MHz (channel bonding or dual channel) bonds two adjacent radio channels to increase
throughput. The wireless clients must also support 40 MHz. It is often better to use the 20 MHz
setting in a location where the environment hinders the wireless signal.
Select 20MHz if you want to lessen radio interference with other wireless devices in your
neighborhood or the wireless clients do not support channel bonding.
• 802.11b: allows either IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11g compliant WLAN devices to associate
with the NBG6604. In this mode, all wireless devices can only transmit at the data rates
supported by IEEE 802.11b.
• 802.11g: allows IEEE 802.11g compliant WLAN devices to associate with the Device. IEEE
802.11b compliant WLAN devices can associate with the NBG6604 only when they use the
short preamble type.
• 802.11bg: allows either IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11g compliant WLAN devices to associate
with the NBG6604. The NBG6604 adjusts the transmission rate automatically according to
the wireless standard supported by the wireless devices.
• 802.11n: allows IEEE 802.11n compliant WLAN devices to associate with the NBG6604. This
can increase transmission rates, although IEEE 802.11b or IEEE 802.11g clients will not be
able to connect to the NBG6604.
• 802.11gn: allows either IEEE 802.11g or IEEE 802.11n compliant WLAN devices to associate
with the NBG6604. The transmission rate of your NBG6604 might be reduced.
• 802.11 bgn: allows IEEE802.11b, IEEE802.11g and IEEE802.11n compliant WLAN devices to
associate with the NBG6604. The transmission rate of your NBG6604 might be reduced.
If you set Band to 5GHz, you can select from the following:
Security
• 802.11a: allows only IEEE 802.11a compliant WLAN devices to associate with the NBG6604.
• 802.11a/an: allows both IEEE802.11n and IEEE802.11a compliant WLAN devices to
associate with the NBG6604. The transmission rate of your NBG6604 might be reduced.
• 802.11a/an/ac: allows IEEE802.11n, IEEE802.11a and IEEE 802.11c compliant WLAN devices
to associate with the NBG6604.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
69
Page 70

Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
Table 21 Wireless (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Security Mode Select WPA2-PSK to add security on this wireless network. The wireless clients which want to
associate to this network must have same wireless security settings as this device. After you
select to use a security, additional options appears in this screen. See
for detailed information on different security modes. Or you can select No Security to allow
any client to associate this network without authentication.
Section 10.3 on page 70
Note: If the WPS function is enabled (default), only No Security and WPA2-PSK are
available in this field.
WPA-PSK
Compatible
PMF Protected Management Frames (PMF) is a protection mechanism of action management
Pre-Shared Key WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK uses a simple common password for authentication.
Group Key Update
Timer
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
This field appears when you choose WPA2-PSK as the Security Mode.
Select this to allow wireless devices using WPA-PSK security mode to connect to your
NBG6604.
frames.
Select this to allow wireless devices using the PMF protection mechanism to connect to your
NBG6604.
Type a pre-shared key from 8 to 63 case-sensitive keyboard characters.
The Group Key Update Timer is the rate at which the AP sends a new group key out to all
clients.
The default is 3600 seconds (60 minutes).
See the rest of this chapter for information on the other labels in this screen.
10.3 Wireless Security
The screen varies depending on what you select in the Security Mode field.
10.3.1 No Security
Select No Security to allow wireless clients to communicate with the access points without any data
encryption.
Note: If you do not enable any wireless security on your NBG6604, your network is accessible
to any wireless networking device that is within range.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
70
Page 71

Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
Figure 40 Wireless > Security Mode: No Security
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 22 Wireless > Security Mode: No Security
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Security Mode Choose No Security from the drop-down list box.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
10.3.2 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
Select WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK from the Security Mode list.
Note: WPA-PSK is not available if you enable WPS before you configure WPA-PSK in the
Wireless > Wireless screen.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
71
Page 72

Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
Figure 41 Wireless > Security Mode: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 23 Wireless > Security Mode: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Security Mode Select WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK to enable data encryption.
WPA-PSK
Compatible
PMF Protected Management Frames (PMF) is a protection mechanism of action management
Pre-Shared Key WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK uses a simple common password for authentication.
Group Key Update
Timer
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
This field appears when you choose WPA2-PSK as the Security Mode.
Check this field to allow wireless devices using WPA-PSK security mode to connect to your
NBG6604.
frames.
Check this field to allow wireless devices using the PMF protection mechanism to connect to
your NBG6604.
Type a pre-shared key from 8 to 63 case-sensitive keyboard characters.
The Group Key Update Timer is the rate at which the AP sends a new group key out to all
clients.
The default is 3600 seconds (60 minutes).
10.4 Guest Wireless Screen
This screen allows you to enable and configure multiple guest wireless network settings on the NBG6604.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
72
Page 73

Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
You can configure up to four SSIDs to enable multiple BSSs (Basic Service Sets) on the NBG6604. This
allows you to use one access point to provide several BSSs simultaneously. You can then assign varying
security types to different SSIDs. Wireless clients can use different SSIDs to associate with the same access
point.
Click Wireless > Guest Wireless. The following screen displays.
Figure 42 Wireless > Guest Wireless
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 24 Wireless > Guest Wireless
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Band Use 2.4GHz or 5GHz to set up the NBG6604’s guest Wi-Fi network.
# This is the index number of each SSID profile.
Status This shows whether the SSID profile is active (a yellow bulb) or not (a gray bulb).
SSID An SSID profile is the set of parameters relating to one of the NBG6604’s BSSs. The SSID (Service
Set IDentifier) identifies the Service Set with which a wireless device is associated.
This field displays the name of the wireless profile on the network. When a wireless client scans
for an AP to associate with, this is the name that is broadcast and seen in the wireless client
utility.
Security This field indicates the security mode of the SSID profile.
Remaining time If the user is currently not permitted to access the Internet, you can click the Set to allow access
for a specified period of time. A screen then displays allowing you to set how long (in hours) the
user is allowed to access the Internet.
This field displays the amount of Internet access time that remains for each user before the
NBG6604 blocks the user from accessing the Internet.0:0:0 means there is no extra Internet
access time.
Edit Click the Edit icon to configure the SSID profile.
10.4.1 Guest Wireless Edit
Use this screen to edit an SSID profile. Click the Edit icon next to an SSID in the Guest Wireless screen. The
following screen displays.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
73
Page 74

Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
Figure 43 Wireless > Guest Wireless > Guest Wireless Setup: Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 25 Wireless > Guest Wireless > Guest Wireless Setup: Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active Select this to activate the SSID profile.
Name (SSID) The SSID (Service Set IDentity) identifies the Service Set with which a wireless client is associated.
Enter a descriptive name (up to 32 printable characters found on a typical English language
keyboard) for the wireless LAN.
Hide SSID Select this check box to hide the SSID in the outgoing beacon frame so a station cannot obtain
Intra-BSS Traffic
Blocking
WMM QoS Check this to have the NBG6604 automatically give a service a priority level according to the
the SSID through scanning using a site survey tool.
A Basic Service Set (BSS) exists when all communications between wireless clients or between a
wireless client and a wired network client go through one access point (AP).
Intra-BSS traffic is traffic between wireless clients in the BSS. When Intra-BSS is enabled, wireless
clients can access the wired network and communicate with each other. When Intra-BSS is
disabled, wireless clients can still access the wired network but cannot communicate with each
other.
ToS value in the IP header of packets it sends.
WMM QoS (Wifi MultiMedia Quality of Service) gives high priority to voice and video, which
makes them run more smoothly.
Maximum
Bandwidth
Security Mode Select WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK to add security on this wireless network. The wireless clients which
Enter a number to specify maximum bandwidth the Guest Wi-Fi network can use.
want to associate to this network must have same wireless security settings as this device. After
you select to use a security, additional options appears in this screen. See
70 for detailed information on different security modes. Or you can select No Security to allow
any client to associate this network without authentication.
Section 10.3 on page
Note: If the WPS function is enabled (default), only No Security and WPA2-PSK are
available in this field.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
74
Page 75

10.5 MAC Filter Screen
The MAC filter screen allows you to configure the NBG6604 to give exclusive access to devices (Allow) or
exclude devices from accessing the NBG6604 (Deny). Every Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media
Access Control) address. The MAC address is assigned at the factory and consists of six pairs of
hexadecimal characters, for example, 00:A0:C5:00:00:02. You need to know the MAC address of the
devices to configure this screen.
To change your NBG6604’s MAC filter settings, click Wireless > MAC Filter. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 44 Wireless > MAC Filter
Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the labels in this menu.
Table 26 Wireless > MAC Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Band Select the frequency band to set whether you want to apply the wireless and security settings to
SSID Select This shows the SSID for which you are configuring MAC filtering.
MAC Address
Filter
Filter Action Define the filter action for the list of MAC addresses in the MAC Filter Summary table.
MAC Filter Summary (Max Limit : 64)
# This is the index number of the MAC address. Select Auto Detection to automatically detect the
MAC Address This field displays the MAC address of the wireless station. If you select User define in the # field,
Add/Delete Click to add the rule in the MAC filter summary table.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
the default 2.4GHz or 5GHz wireless LAN.
Select to turn on (Enable) or off (Disable) MAC address filtering.
Select Allow to permit access to the NBG6604, MAC addresses not listed will be denied access to
the NBG6604.
Select Deny to block access to the NBG6604, MAC addresses not listed will be allowed to access
the NBG6604.
MAC address of the wireless station that are allowed or denied access to the NBG6604.
Otherwise, select User define to enter the MAC address of the wireless station in the MAC Address
field that are allowed or denied access to the NBG6604.
enter the MAC address(es) manually.
Click to remove a rule.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
75
Page 76

10.6 Advanced Screen
Use this screen to allow wireless advanced features, such as the output power, RTS/CTS Threshold
settings.
Click Wireless > Advanced. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 45 Wireless > Advanced
Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 27 Wireless > Advanced
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless Advanced Setup
Band Select the frequency band to set whether you want to apply the wireless and security settings
to the default 2.4GHz or 5GHz wireless LAN.
RTS/CTS Threshold Data with its frame size larger than this value will perform the RTS (Request To Send)/CTS (Clear
To Send) handshake.
This field is not configurable and the NBG6604 automatically changes to use the maximum
value if you select 802.11n, 802.11an, 802.11gn, or 802.11bgn in the
Fragmentation
Threshold
Intra-BSS Traffic A Basic Service Set (BSS) exists when all communications between wireless clients or between
Tx Power Set the output power of the NBG6604 in this field. If there is a high density of APs in an area,
QoS Setup
The threshold (number of bytes) for the fragmentation boundary for directed messages. It is
the maximum data fragment size that can be sent.
This field is not configurable and the NBG6604 automatically changes to use the maximum
value if you select 802.11n, 802.11an, 802.11gn, or 802.11bgn in the
a wireless client and a wired network client go through one access point (AP).
Intra-BSS traffic is traffic between wireless clients in the BSS. When you Enable Intra-BSS, wireless
clients can access the wired network and communicate with each other. When you Disable
Intra-BSS, wireless clients can still access the wired network but cannot communicate with
each other.
decrease the output power of the NBG6604 to reduce interference with other APs. Select one
of the following 100%, 90%, 75%, 50%, 25%, or 10%.
Wireless screen.
Wireless screen.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
76
Page 77

Table 27 Wireless > Advanced (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WMM QoS Select Enable to have the NBG6604 automatically give a service a priority level according to
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
10.7 WPS Screen
Use this screen to enable/disable WPS, view or generate a new PIN number and check current WPS
status. To open this screen, click Wireless > WPS.
Note: With WPS, wireless clients can only connect to the wireless network using the first SSID on
the NBG6604.
Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
the ToS value in the IP header of packets it sends. WMM QoS (Wifi MultiMedia Quality of
Service) gives high priority to voice and video, which makes them run more smoothly.
This field is not configurable and the NBG6604 automatically enables WMM QoS if you select
802.11n, 802.11an, 802.11gn, or 802.11bgn in the Wireless screen.
Figure 46 Wireless > WPS
NBG6604 User’s Guide
77
Page 78

Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 28 Wireless > WPS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WPS Setup
Band Select the frequency band to set whether you want to apply the wireless and security
WPS Select Enable to turn on the WPS feature. Otherwise, select Disable.
PIN Code Select Enable and click Apply to allow the PIN Configuration method. If you select Disable,
PIN Number This is the WPS PIN (Personal Identification Number) of the NBG6604. Enter this PIN in the
Push Button Use this button when you use the PBC (Push Button Configuration) method to configure
Or input station’s PIN
number
WPS Status
Status This displays Configured when the NBG6604 has connected to a wireless network using WPS
settings to the default 2.4GHz or 5GHz wireless LAN.
you cannot create a new PIN number.
configuration utility of the device you want to connect to the NBG6604 using WPS.
The PIN is not necessary when you use WPS push-button method.
Click Generate to generate a new PIN number.
wireless stations’s wireless settings.
Click this to start WPS-aware wireless station scanning and the wireless security information
synchronization.
Use this button when you use the PIN Configuration method to configure wireless station’s
wireless settings.
Type the same PIN number generated in the wireless station’s utility. Then click Start to
associate to each other and perform the wireless security information synchronization.
or when WPS Enable is selected and wireless or wireless security settings have been
changed. The current wireless and wireless security settings also appear in the screen.
This displays Unconfigured if WPS is disabled and there are no wireless or wireless security
changes on the NBG6604 or you click Release Configuration to remove the configured
wireless and wireless security settings.
Release
Configuration
802.11 Mode This is the 802.11 mode used. Only compliant WLAN devices can associate with the
SSID This is the name of the wireless network (the NBG6604’s first SSID).
Security This is the type of wireless security employed by the network.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
This button is only available when the WPS status displays Configured.
Click this button to remove all configured wireless and wireless security settings for WPS
connections on the NBG6604.
NBG6604.
10.8 Scheduling Screen
Use this screen to set the times your wireless LAN is turned on and off. Wireless LAN scheduling is disabled
by default. The wireless LAN can be scheduled to turn on or off on certain days and at certain times. To
open this screen, click Wireless > Scheduling.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
78
Page 79

Chapter 10 Wireless LAN
Figure 47 Wireless > Scheduling
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 29 Wireless > Scheduling
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Band Select the frequency band to set whether you want to apply the wireless and security
settings to the default 2.4GHz or 5GHz wireless LAN.
Wireless LAN
Scheduling
Internet Access
Schedule
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Select Enable to activate the wireless LAN scheduling feature. Select Disable to turn it off.
The y-axis shows the time period in days. The x-axis shows the time period in hours.
Click Select All or click gray blocks to specify days and times to turn the Wireless LAN on or
off. If you click Select All you can not select any specific days and times. Click Clean All to
remove all the wireless LAN scheduling.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
79
Page 80

11.1 Overview
WLAN
LAN
Internet
This chapter describes how to configure LAN settings.
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a shared communication system to which many computers are
attached. A LAN is a computer network limited to the immediate area, usually the same building or floor
of a building.
Figure 48 LAN Example
CHAPTER 11
LAN
The LAN screens can help you configure a manage IP address, and partition your physical network into
logical networks.
11.2 What You Can Do
• Use the LAN IP screen to configure the IPv4 address for your NBG6604 on the LAN (Section 11.4 on
page 81).
• Use the Static DHCP screen to assign IP addresses on the LAN to specific individual computers based
on their MAC Addresses (Section 11.5 on page 82).
NBG6604 User’s Guide
80
Page 81

Chapter 11 LAN
LAN WAN
Internet
11.3 What You Need To Know
The actual physical connection determines whether the NBG6604 ports are LAN or WAN ports. There are
two separate IP networks, one inside the LAN network and the other outside the WAN network as shown
next.
Figure 49 LAN and WAN IP Addresses
The LAN parameters of the NBG6604 are preset in the factory with the following values:
• IPv4 address of 192.168.1.1 with subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 (24 bits)
• DHCP server enabled with 32 client IPv4 addresses starting from 192.168.1.33.
These parameters should work for the majority of installations.
11.4 LAN IP Screen
Use this screen to change the IP address for your NBG6604. Click LAN > LAN IP.
Figure 50 LAN > LAN IP
NBG6604 User’s Guide
81
Page 82

Chapter 11 LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 30 LAN > LAN IP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Address Type the IP address of your NBG6604 in dotted decimal notation.
IP Subnet Mask The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. Your NBG6604 will
DHCP Server Select Enable to activate DHCP for LAN.
IP Pool Starting
Address
Pool Size This field specifies the size, or count of the IP address pool for LAN.
Lease Time Specify for how many hours each DHCP client device can use the DHCP information
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
automatically calculate the subnet mask based on the IP address that you assign. Unless
you are implementing subnetting, use the subnet mask computed by the NBG6604.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, RFC 2131 and RFC 2132) allows
individual clients (computers) to obtain TCP/IP configuration at startup from a server.
Enable the DHCP server unless your ISP instructs you to do otherwise. Select Disable to stop
the NBG6604 acting as a DHCP server. When configured as a server, the
NBG6604 provides TCP/IP configuration for the clients. If not, DHCP service is
disabled and you must have another DHCP server on your LAN, or else the computers
must be manually configured. When set as a server, fill in the following four fields.
This field specifies the first of the contiguous addresses in the IP address pool for LAN.
(especially the IP address) before it has to request the information again.
11.5 Static DHCP Screen
This screen allows you to assign IP addresses on the LAN to specific individual computers based on
their MAC addresses.
To change your NBG6604’s static DHCP settings, click LAN > Static DHCP.
Figure 51 LAN > Static DHCP
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
Table 31 LAN > Static DHCP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the index number of the static IP table entry (row). Select Auto Detection to automatically
detect the MAC address of a computer on your LAN. Otherwise, select User define to enter the
MAC address of a computer on your LAN in the MAC Address field.
MAC Address This field displays the MAC address of a computer on your LAN. If you select User define in the #
field, enter the MAC address(es) manually.
IP Address This field displays the LAN IP address of a computer on your LAN. If you select User define in the #
field, enter the IP address(es) manually.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
82
Page 83

Table 31 LAN > Static DHCP (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Add/Delete Click to add the rule in the MAC filter summary table.
Click to remove a rule.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes with the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
11.6 IPv6 LAN Screen
Use this screen to configure the IP address for your NBG6604 on the LAN. Click LAN > IPv6 LAN.
Figure 52 LAN > IPv6 LAN
Chapter 11 LAN
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
83
Page 84

12.1 Overview
This chapter shows you how to configure UPnP and One Connect.
12.1.1 What You Can Do
• Use the UPnP screen to enable UPnP on your NBG6604 (Section 12.2 on page 84).
• Use the One Connect screen to enable or disable Wi-Fi auto-configuration (Section 12.3 on page 85).
12.2 UPnP Screen
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) is a distributed, open networking standard that uses TCP/IP for simple
peer-to-peer network connectivity between devices. A UPnP device can dynamically join a network,
obtain an IP address, convey its capabilities and learn about other devices on the network. In turn, a
device can leave a network smoothly and automatically when it is no longer in use.
CHAPTER 12
Applications
Use this screen to enable UPnP on your NBG6604.
Click Applications > UPnP to open the following screen.
Figure 53 Applications > UPnP
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 32 Applications > UPnP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
UPnP Select Enable to activate UPnP. Be aware that anyone could use a UPnP application to
open the web configurator's login screen without entering the NBG6604's IP address
(although you must still enter the password to access the web configurator).
Apply Click Apply to save the setting to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to return to the previously saved settings.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
84
Page 85

Chapter 12 Applications
12.3 ONE Connect Screen
One Connect is a Zyxel-proprietary feature. It complies with the IEEE 1905.1 standard and allows autodetection and auto-configuration.
If your wireless router supports Zyxel One Connect, NBG6604 for example, you can download and install
the Zyxel One Connect App in your mobile device to check the connection status, do speed test, turn
on or turn off the devices in your network, block or allow a device’s access and set up a guest Wi-Fi
network from the mobile device. You can even use the App to access the NBG6604’s web configurator.
The mobile device with the App installed must be connected to the NBG6604 wirelessly.
Figure 54 Zyxel ONE Connect App
Use this screen to enable or disable Wi-Fi auto-configuration on the NBG6604.
Click Applications > ONE Connect to open the following screen.
Figure 55 Applications > ONE Connect
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 33 Applications > ONE Connect
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ONE Connect
QR Code Scan the QR code and go to a website to download the Zyxel One Connect App in your
mobile device. One is for the iTunes App Store, and the other is for Google Play.
One Connect Compatible Devices
NBG6604 User’s Guide
85
Page 86

Chapter 12 Applications
Table 33 Applications > ONE Connect (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Automatically
Update AP/
Repeater Wi-Fi
Settings
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Select Enable to allow the NBG6604 to automatically update the wireless settings on the APs
or wireless repeaters (which also support Zyxel One Connect) in its network.
Select Disable to turn this feature off if you want to have the APs or repeaters in the network
use different wireless settings.
12.4 Technical Reference
The following section contains additional technical information about the NBG6604 features described
in this chapter.
NAT Traversal
UPnP NAT traversal automates the process of allowing an application to operate through NAT. UPnP
network devices can automatically configure network addressing, announce their presence in the
network to other UPnP devices and enable exchange of simple product and service descriptions. NAT
traversal allows the following:
• Dynamic port mapping
• Learning public IP addresses
• Assigning lease times to mappings
Windows Messenger is an example of an application that supports NAT traversal and UPnP.
See the NAT chapter for more information on NAT.
Cautions with UPnP
The automated nature of NAT traversal applications in establishing their own services and opening
firewall ports may present network security issues. Network information and configuration may also be
obtained and modified by users in some network environments.
When a UPnP device joins a network, it announces its presence with a multicast message. For security
reasons, the NBG6604 allows multicast messages on the LAN only.
All UPnP-enabled devices may communicate freely with each other without additional configuration.
Disable UPnP if this is not your intention.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
86
Page 87

13.1 Overview
1
2
3
4
LAN WAN
Internet
Use these screens to enable and configure the firewall that protects your NBG6604 and your LAN from
unwanted or malicious traffic.
Enable the firewall to protect your LAN computers from attacks by hackers on the Internet and control
access between the LAN and WAN. By default the firewall:
• Allows traffic that originates from your LAN computers to go to all of the networks.
• Blocks traffic that originates on the other networks from going to the LAN.
The following figure illustrates the default firewall action. User A can initiate an IM (Instant Messaging)
session from the LAN to the WAN (1). Return traffic for this session is also allowed (2). However other traffic
initiated from the WAN is blocked (3 and 4).
CHAPTER 13
Security
Figure 56 Default Firewall Action
13.1.1 What You Can Do
• Use the IPv4 Firewall screen to enable or disable the NBG6604’s IPv4 firewall (Section 13.2 on page
89).
NBG6604 User’s Guide
87
Page 88

13.1.2 What You Need To Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read through this chapter.
About the NBG6604 Firewall
The NBG6604’s firewall feature physically separates the LAN and the WAN and acts as a secure
gateway for all data passing between the networks.
It is a stateful inspection firewall and is designed to protect against Denial of Service attacks when
activated (click the IPv4 Firewall tab under Security and then click the Enable Firewall check box). The
NBG6604's purpose is to allow a private Local Area Network (LAN) to be securely connected to the
Internet. The NBG6604 can be used to prevent theft, destruction and modification of data, as well as log
events, which may be important to the security of your network.
The NBG6604 is installed between the LAN and a broadband modem connecting to the Internet. This
allows it to act as a secure gateway for all data passing between the Internet and the LAN.
The NBG6604 has one Ethernet WAN port and four Ethernet LAN ports, which are used to physically
separate the network into two areas. The WAN (Wide Area Network) port attaches to the broadband
(cable or DSL) modem to the Internet.
Chapter 13 Security
The Local Area Network (LAN) port attaches to a network of computers, which needs security from the
outside world. These computers will have access to Internet services such as e-mail, FTP and the World
Wide Web. However, "inbound access" is not allowed (by default) unless the remote host is authorized to
use a specific service.
Guidelines For Enhancing Security With Your Firewall
1 Change the default password via Web Configurator.
2 Think about access control before you connect to the network in any way, including attaching a
modem to the port.
3 Limit who can access your router.
4 Don't enable any local service (such as NTP) that you don't use. Any enabled service could present a
potential security risk. A determined hacker might be able to find creative ways to misuse the enabled
services to access the firewall or the network.
5 For local services that are enabled, protect against misuse. Protect by configuring the services to
communicate only with specific peers, and protect by configuring rules to block packets for the services
at specific interfaces.
6 Protect against IP spoofing by making sure the firewall is active.
7 Keep the firewall in a secured (locked) room.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
88
Page 89

Chapter 13 Security
13.2 IPv4 Firewall Screen
Use this screen to enable or disable the NBG6604’s IPv4 firewall, and set up firewall logs. Click Security >
IPv4 Firewall to open the firewall setup screen.
Figure 57 Security > IPv4 Firewall
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 34 Security > IPv4 Firewall
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol is a message control and error-reporting protocol between
a host server and a gateway to the Internet. ICMP uses Internet Protocol (IP) datagrams, but
the messages are processed by the TCP/IP software and directly apparent to the application
user.
Respond to Ping onThe NBG6604 will not respond to any incoming Ping requests when Disable is selected. Select
LAN to reply to incoming LAN Ping requests. Select WAN to reply to incoming WAN Ping
requests. Otherwise select LAN&WAN to reply to all incoming LAN and WAN Ping requests.
Firewall Setup
Enable Firewall Select this check box to activate the firewall. The NBG6604 performs access control and
Enable Firewall Rule
Enable Firewall
Rule
Filter table type Select DROP to silently discard the packets which meet the firewall rules. The others are
Add Firewall Rule
Service Name Enter a name that identifies or describes the firewall rule.
MAC Address Enter the MAC address of the computer for which the firewall rule applies.
Dest IP Address Enter the IP address of the computer to which traffic for the application or service is entering.
Source IP Address Enter the IP address of the computer that initializes traffic for the application or service.
Protocol Select the protocol (TCP, UDP, or ICMP) used to transport the packets for which you want to
Dest Port Range This is the port number/range of the destination that define the traffic type, for example TCP
Source Port Range This is the port number/range of the source that define the traffic type, for example TCP port
Add Rule Click Add Rule to save the firewall rule.
Firewall Rule
protects against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks when the firewall is activated.
Select this check box to activate the firewall rules that you define (see Add Firewall Rule
below).
accepted.Select ACCEPT to allow the passage of the packets which meet the firewall rules.
The others are blocked.
The NBG6604 applies the firewall rule to traffic initiating from this computer.
The NBG6604 applies the firewall rule to traffic initiating from this computer.
apply the firewall rule.
port 80 defines web traffic.
80 defines web traffic.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
89
Page 90

Chapter 13 Security
Table 34 Security > IPv4 Firewall (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is your firewall rule number. The ordering of your rules is important as rules are applied in
turn.
Service Name This is a name that identifies or describes the firewall rule.
MAC address This is the MAC address of the computer for which the firewall rule applies.
Dest IP This is the IP address of the computer to which traffic for the application or service is entering.
Source IP This is the IP address of the computer from which traffic for the application or service is
initialized.
Protocol This is the protocol (TCP, UDP or ICMP) used to transport the packets for which you want to
Dest Port Range This is the port number/range of the destination that define the traffic type, for example TCP
Source Port Range This is the port number/range of the source that define the traffic type, for example TCP port
Apply Click Apply to save the settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to start configuring this screen again.
apply the firewall rule.
port 80 defines web traffic.
80 defines web traffic.
Click to remove the firewall rule.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
90
Page 91

14.1 Overview
This chapter provides information on the Maintenance screens.
14.2 What You Can Do
• Use the General screen to set the timeout period of the management session (Section 14.3 on page
91).
• Use the Password screen to change your NBG6604’s system password (Section 14.4 on page 92).
• Use the Time screen to change your NBG6604’s time and date (Section 14.5 on page 93).
• Use the Firmware Upgrade screen to upload firmware to your NBG6604 (Section 14.6 on page 94).
• Use the Backup/Restore screen to view information related to factory defaults, backup configuration,
and restoring configuration (Section 14.7 on page 95).
• Use the Restart screen to reboot the NBG6604 without turning the power off (Section 14.8 on page 96).
• Use the Remote Management screen to configure the interface/s from which the NBG6604 can be
managed remotely and specify a secure client that can manage the NBG6604
page 97).
• Use the Log screen to see the logs for the activity on the NBG6604 (Section 14.10 on page 98).
• Use the Operation Mode screen to select how you want to use your NBG6604 (Section 14.12 on page
99).
CHAPTER 14
Maintenance
. (Section 14.9.1 on
14.3 General Screen
Use this screen to set the management session timeout period. Click Maintenance > General. The
following screen displays.
Figure 58 Maintenance > General
NBG6604 User’s Guide
91
Page 92

The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 35 Maintenance > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
System Name System Name is a unique name to identify the NBG6604 in an Ethernet network.
Domain Name Enter the domain name you want to give to the NBG6604.
Administrator
Inactivity Timer
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Type how many minutes a management session can be left idle before the session times out.
The default is 5 minutes. After it times out you have to log in with your password again. Very
long idle timeouts may have security risks. A value of "0" means a management session
never times out, no matter how long it has been left idle (not recommended).
14.4 Password Screen
It is strongly recommended that you change your NBG6604's password.
If you forget your NBG6604's password (or IP address), you will need to reset the device. See Section 14.8
on page 96 for details.
Chapter 14 Maintenance
Click Maintenance > Password. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 59 Maintenance > Password
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 36 Maintenance > Password
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Old Password Type the default password or the existing password you use to access the system in this
field.
New Password Type your new system password (up to 30 characters). Note that as you type a password,
Retype to Confirm Type the new password again in this field.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
the screen displays an asterisk (*) for each character you type.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
92
Page 93

14.5 Time Screen
Use this screen to configure the NBG6604’s time based on your local time zone. To change your
NBG6604’s time and date, click Maintenance > Time. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 60 Maintenance > Time
Chapter 14 Maintenance
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 37 Maintenance > Time
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Current Time and Date
Current Time This field displays the time of your NBG6604.
Each time you reload this page, the NBG6604 synchronizes the time with the time server.
Current Date This field displays the date of your NBG6604.
Each time you reload this page, the NBG6604 synchronizes the date with the time server.
Time and Date Setup
Manual Select this radio button to enter the time and date manually. If you configure a new time
and date, Time Zone and Daylight Saving at the same time, the new time and date you
entered has priority and the Time Zone and Daylight Saving settings do not affect it.
New Time
(hh:mm:ss)
New Date
(yyyy/mm/dd)
Get from Time Server Select this radio button to have the NBG6604 get the time and date from the time server
User Defined Time
Server Address
Time Zone Setup
Time Zone Choose the time zone of your location. This will set the time difference between your time
This field displays the last updated time from the time server or the last time configured
manually.
When you select Manual, enter the new time in this field and then click Apply.
This field displays the last updated date from the time server or the last date configured
manually.
When you select Manual, enter the new date in this field and then click Apply.
you specified below.
Select User Defined Time Server Address and enter the IP address or URL (up to 20 extended
ASCII characters in length) of your time server. Check with your ISP/network administrator if
you are unsure of this information.
zone and Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
NBG6604 User’s Guide
93
Page 94

Chapter 14 Maintenance
Table 37 Maintenance > Time (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
14.6 Firmware Upgrade Screen
Find firmware at www.zyxel.com in a file that uses the version number and project code with a “*.bin”
extension, e.g., “V1.00(AARO.0).bin”. The upload process uses HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and
may take up to two minutes. After a successful upload, the system will reboot.
Click Maintenance > Firmware Upgrade. Follow the instructions in this screen to upload firmware to your
NBG6604.
Figure 61 Maintenance > Firmware Upgrade
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 38 Maintenance > Firmware Upgrade
LABEL DESCRIPTION
File Path Click Choose File to find the location of the file you want to upload in this field.
Choose File Click Choose File to find the .bin file you want to upload. Remember that you must decompress
Upload Click Upload to begin the upload process. This process may take up to two minutes.
Check for Latest
Firmware Now
compressed (.zip) files before you can upload them.
Click this to check for the latest updated firmware.
Note: Do not turn off the NBG6604 while firmware upload is in progress!
After you see the Firmware Upload In Process screen, wait two minutes before logging into the NBG6604
again.
The NBG6604 automatically restarts in this time causing a temporary network disconnect. In some
operating systems, you may see the following icon on your desktop.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
94
Page 95

Chapter 14 Maintenance
Figure 62 Network Temporarily Disconnected
After two minutes, log in again and check your new firmware version in the Status screen.
If the upload was not successful, an error message appears. Click Return to go back to the Firmware
Upgrade screen.
14.7 Backup/Restore Screen
Backup configuration allows you to back up (save) the NBG6604’s current configuration to a file on your
computer. Once your NBG6604 is configured and functioning properly, it is highly recommended that
you back up your configuration file before making configuration changes. The backup configuration file
will be useful in case you need to return to your previous settings.
Restore configuration allows you to upload a new or previously saved configuration file from your
computer to your NBG6604.
Click Maintenance > Backup/Restore. Information related to factory defaults, backup configuration,
and restoring configuration appears as shown next.
Figure 63 Maintenance > Backup/Restore
NBG6604 User’s Guide
95
Page 96

Chapter 14 Maintenance
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 39 Maintenance > Backup/Restore
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Backup Configuration
Backup Click Backup to save the NBG6604’s current configuration to your computer.
Restore Configuration
File Path Click Choose File to find the location of the file you want to upload in this field.
Choose File Click Choose File to find the file you want to upload. Remember that you must decompress
Upload Click Upload to begin the upload process.
Back to Factory Defaults
Reset Pressing the Reset button in this section clears all user-entered configuration information and
compressed (.ZIP) files before you can upload them.
Note: Do not turn off the NBG6604 while configuration file upload is in progress.
After you see a “configuration upload successful” screen, you must then wait one minute
before logging into the NBG6604 again. The NBG6604 automatically restarts in this time causing
a temporary network disconnect.
If you see an error screen, click Back to return to the Backup/Restore screen.
returns the NBG6604 to its factory defaults.
You can also press the RESET button on the rear panel to reset the factory defaults of your
NBG6604. Refer to the chapter about introducing the Web Configurator for more information
on the RESET button.
Note: If you uploaded the default configuration file you may need to change the IP address
of your computer to be in the same subnet as that of the default NBG6604 IP address
(192.168.1.1). See Appendix B on page 113 for details on how to set up your computer’s
IP address.
14.8 Restart Screen
System restart allows you to reboot the NBG6604 without turning the power off.
Click Maintenance > Restart to open the following screen.
Figure 64 Maintenance > Restart
Click Restart to have the NBG6604 reboot. This does not affect the NBG6604's configuration.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
96
Page 97

Chapter 14 Maintenance
14.9 Remote Management
Remote Management allows you to manage your NBG6604 from a remote location through the LAN/
WLAN or WAN interface.
14.9.1 Remote Access
Use this screen to change your NBG6604’s remote management settings. You can use Telnet, HTTP or
HTTPS to access and manage the NBG6604.
Click Maintenance > Remote Management > Remote Access to open the following screen.
Figure 65 Maintenance > Remote Management > Remote Access
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 40 Maintenance > Remote Management > WAN Access
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WWW
Port You may change the server port number for a service if needed; however you must use the
same port number in order to use that service for remote management.
Access Status Select the interfaces through which a computer may access the NBG6604 using this service.
Secured Client IP
Address
Telnet
Telnet Select this to allow Telnet access.
Port You may change the server port number for a service if needed; however you must use the
Access Status Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the NBG6604 using this service.
Select All to allow all computes to access the NBG6604.
Otherwise, check Selected and specify the IP address of the computer that can access the
NBG6604.
same port number in order to use that service for remote management.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
97
Page 98

Table 40 Maintenance > Remote Management > WAN Access
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Secured Client IP
Address
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the NBG6604.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Select All to allow all computes to access the NBG6604.
Otherwise, check Selected and specify the IP address of the computer that can access the
NBG6604.
14.10 Log Screen
The Web Configurator allows you to look at all of the NBG6604’s logs in one location.
You can configure which logs to display in the Log screen. Select the logs you wish to display. Click
Apply to save your settings. Click Cancel to start the screen afresh.
Use this screen to see the logged messages for the NBG6604. The log wraps around and deletes the old
entries after it fills. Select the logs you want to see from the Display drop list. The log choices depend on
your settings above this screen. Click Refresh to renew the log screen. Click Clear Log to delete all the
logs.
Chapter 14 Maintenance
Figure 66 Maintenance > Log
14.11 System Operation Mode Overview
The Sys OP Mode (System Operation Mode) function lets you configure your NBG6604 as a router or
access point. You can choose between Router Mode and Access Point Mode depending on your
network topology and the features you require from your device.
The following describes the device modes available in your NBG6604.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
98
Page 99

Chapter 14 Maintenance
LAN IP WAN IP
LAN WAN
Internet
1 IP
LAN
Internet
Router
A router connects your local network with another network, such as the Internet. The router has two IP
addresses, the LAN IP address and the WAN IP address.
Figure 67 LAN and WAN IP Addresses in Router Mode
Access Point
An access point enables all ethernet ports to be bridged together and to be in the same subnet. To
connect to the Internet, another device, such as a router, is required.
Figure 68 Access Point Mode
14.12 Operation Mode Screen
Use this screen to select how you want to use your NBG6604.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
99
Page 100

Chapter 14 Maintenance
Figure 69 Maintenance > Operation Mode
The following table describes the labels in the Operation Mode screen.
Table 41 Maintenance > Operation Mode
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Configuration Mode
Router Mode Select Router Mode if your device routes traffic between a local network and another
Access Point Mode Select Access Point Mode if your device bridges traffic between clients on the same
Apply Click Apply to save your settings.
Cancel Click Cancel to return your settings to the default (Router).
network such as the Internet. This mode offers services such as a firewall.
You can configure the IP address settings on your WAN port. Contact your ISP or system
administrator for more information on appropriate settings.
network.
•In Access Point Mode, all Ethernet ports have the same IP address.
• All ports on the rear panel of the device are LAN ports, including the port labeled WAN.
There is no WAN port.
• The DHCP server on your device is disabled.
• Router functions (such as NAT, remote management, firewall and so on) are not
available when the NBG6604 is in Access Point Mode.
• The IP address of the device on the local network is set to 192.168.1.2.
Note: If you select the incorrect system operation Mode you may not be able to connect to
the Internet.
NBG6604 User’s Guide
100
 Loading...
Loading...