Page 1

NBG-419N v2
Wireless N NetUSB Router
Default Login Details
LAN IP
Address
Password 1234
Version 1.00
Edition 2, 03/2012
www.zyxel.com
http://192.168.1.1
www.zyxel.com
IMPORTANT!
READ CAREFULL Y
BEFORE USE.
KEEP THIS GUIDE
FOR FUTURE
REFERENCE.
Copyright © 2012
ZyXEL Communications Corporation
Page 2

IMPORTANT!
READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE.
KEEP THIS GUIDE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
Graphics in this book may differ slightly from the product due to differences in operating systems,
operating system versions, or if you installed updated firmware/software for your device. Every
effort has been made to ensure that the information in this manual is accurate.
Related Documentation
•Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guid shows how to connect the NBG-419N v2 and access the Web Configurator .
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide2
Page 3

Contents Overview
Contents Overview
User’s Guide .......................................................................................................................................13
Getting to Know Your Router ..................................................................................................................15
The WPS Button .....................................................................................................................................20
ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility .......................................................................................................21
Connection Wizard ....... ... ................................................ .... ... .................................................................29
Introducing the Web Configurator ...........................................................................................................39
Monitor ....................................................................................................................................................45
Router Modes ..........................................................................................................................................51
Easy Mode ..............................................................................................................................................53
Router Mode ...........................................................................................................................................64
Access Point Mode .................................................................................................................................71
WISP Mode .............................................................................................................................................78
Tutorials ..................................................................................................................................................89
Technical Reference ........................................................................................................................101
Wireless LAN .................. ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ............................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ............................103
WAN ....................................................... ...................................................... .........................................119
LAN .......................................................................................................................................................133
DHCP Server ........................................................................................................................................137
Network Address Translation (NAT) .......................................... .................................... ........................141
Dynamic DNS ........................................................................................................................................147
Static Route ...........................................................................................................................................149
RIP ........................................................................................................................................................153
Firewall ...................................... ................................ ................................... .........................................155
Content Filter .........................................................................................................................................159
Bandwidth Management ................. ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ............................................................163
Remote Management ............................................................................................................................170
Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP) ...........................................................................................................173
Maintenance .................................... ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ... ...... ............................181
Troubleshooting ....................................................................................................................................191
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
3
Page 4

Contents Overview
4
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 5

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Contents Overview ..............................................................................................................................3
Table of Contents .................................................................................................................................5
Part I: User’s Guide .........................................................................................13
Chapter 1
Getting to Know Your Router.............................................................................................................15
1.1 Overview ................................................ ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .... ..........................15
1.2 Applications ............................................ ... ... .... ... ... ... .............................................. ..........................15
1.3 Ways to Manage the Router ............ ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .............................................. ... ... ... ... ..............15
1.4 Good Habits for Managing the Router ..............................................................................................16
1.5 LEDs ............... ... .... ... ... ... .............................................. ... ... ... ...........................................................17
1.6 Wall-mounting Instructions ........................................ .... ... ... ... ...........................................................18
Chapter 2
The WPS Button..................................................................................................................................20
2.1 Overview ................................................ ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .... ..........................20
Chapter 3
ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility..................................................................................................21
3.1 Overview ................................................ ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .... ..........................21
3.1.1 Quick Setup ......................................................... ... ... ... .... ... ....................................................21
3.1.2 Installing ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility .........................................................................21
3.2 The ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility ..........................................................................................22
3.2.1 The Menus ................. ... ... ... .............................................. ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .......................23
3.2.2 The ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Configuration Window ......................................................25
3.2.3 The Auto-Connect Printer List Window ...................................................................................25
3.2.4 Exit the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility ....... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ..............................................26
Chapter 4
Connection Wizard.............................................................................................................................29
4.1 Overview ................................................ ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .... ..........................29
4.2 Accessing the Wizard ........................................................................................................................29
4.3 Connect to Internet ........................... ... ... ... ... .............................................. ... ... ... .... ... .......................30
4.3.1 Connection Type: DHCP .........................................................................................................31
4.3.2 Connection Type: Static IP ......................................................................................................31
4.3.3 Connection Type: PPPoE ........................................................................................................32
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
5
Page 6

Table of Contents
4.3.4 Connection Type: PPTP ..........................................................................................................33
4.3.5 Connection Type: L2TP ...........................................................................................................34
4.4 Router Password .................................... ... ... .... ... ... ...........................................................................36
4.5 Wireless Security ................ ... ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ..........................36
4.5.1 Wireless Security: No Security ................................................................................................36
4.5.2 Wireless Security: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK .............................................................. ... .... ... ... ... .37
Chapter 5
Introducing the Web Configurator ....................................................................................................39
5.1 Overview ................................................ ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .... ..........................39
5.2 Accessing the Web Configurator .......................................................................................................39
5.2.1 Login Screen ............................................. ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .................39
5.2.2 Password Screen ................................................................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... ... ...........40
5.2.3 Home Screen ............. ............................................. ... ... .... ... ... .................................................41
5.3 Resetting the Router .............................................. ... .... ............................................. ... . ...................43
5.3.1 Procedure to Use the Reset Button .........................................................................................43
Chapter 6
Monitor.................................................................................................................................................45
6.1 Overview ................................................ ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .... ..........................45
6.2 What You Can Do ........... .... ... ................................................ .... ... ....................................................45
6.3 The Log Screen .................................................................................................................................45
6.3.1 View Log ....................... ... ... .... ... ... ............................................. ... .... ... ... .................................45
6.4 BW MGMT Monitor ................... ... .... ... ... ... ................................................. ... ... .................................47
6.5 DHCP Table ...................................................................................................................................47
6.6 Packet Statistics .............................................................................................................................48
6.7 WLAN Station Status .....................................................................................................................49
Chapter 7
Router Modes......................................................................................................................................51
7.1 Overview ................................................ ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .... ..........................51
7.1.1 Web Configurator Modes .........................................................................................................51
7.1.2 Device Modes ............................ ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..............................................................51
Chapter 8
Easy Mode...........................................................................................................................................53
8.1 Overview ................................................ ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .... ..........................53
8.2 What You Can Do ........... .... ... ................................................ .... ... ....................................................54
8.3 What You Need to Know . .... ... ... ... .... .................................................................................................54
8.4 Navigation Panel ....................... ... .... ... ... ... ........................................................................................55
8.5 Network Map ................ ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ..............................................................................................55
8.6 Control Panel ......................... ... ... .... ............................................. ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ..........................56
8.6.1 Game Engine ............. ............................................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ..............................................57
6
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 7

Table of Contents
8.6.2 Power Saving ............................................ ... ... .... ............................................. ... ... .................57
8.6.3 Content Filter ............................................................. ... .... ... ....................................................59
8.6.4 Bandwidth MGMT ......................... ... ........................................................................................59
8.6.5 Firewall ................................................................... ... ... .... .......................................................60
8.6.6 Wireless Security ....................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ........................................................................60
8.6.7 WPS ............................................. ............................................. ... .... ... ....................................62
8.7 Status Screen in Easy Mode .............................................................................................................63
Chapter 9
Router Mode........................................................................................................................................64
9.1 Overview ................................................ ... ............................................. .... ... ... ... .... ..........................64
9.2 What You Can Do ........... .... ... ................................................ .... ... ....................................................64
9.3 Status Screen ............................ ... .... ... ... ... ... .............................................. ... ... ... .... ... .......................65
9.3.1 Navigation Panel ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... .................................................................................68
Chapter 10
Access Point Mode.............................................................................................................................71
10.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................71
10.2 What You Can Do ...........................................................................................................................71
10.3 What You Need to Know .................................................................................................................71
10.3.1 Setting your Router to AP Mode ............................................................................................72
10.3.2 Accessing the Web Configurator in Access Point Mode ........................................................72
10.3.3 Configuring your WLAN, Bandwidth Management and Maintenance Settings ......................73
10.4 AP Mode Status Screen ..................................................................................................................74
10.5 LAN Screen .....................................................................................................................................76
Chapter 11
WISP Mode ..........................................................................................................................................78
11.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................78
11.2 What Y ou Can Do ............................................................................................................................78
11.3 What You Need to Know .................................................................................................................78
11.3.1 Setting your Router to WISP Mode ........................................................................................79
11.3.2 Accessing the Web Configurator in WISP Mode ...................................................................79
11.4 WISP Mode Status Screen ..............................................................................................................80
11.5 Wireless LAN General Screen ........................................................................................................82
11.5.1 Static WEP .............................................................................................................................84
11.5.2 WPA(2)-PSK ...................................................... ....................................................................85
11.5.3 Advance Screen .....................................................................................................................86
11.5.4 Site Survey Screen ................................................................................................................87
Chapter 12
Tutorials...............................................................................................................................................89
12.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................89
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
7
Page 8

Table of Contents
12.2 Connecting to the Internet from an Access Point ..................... ................................... ....................89
12.3 Configuring Wireless Security Using WPS ......................................................................................89
12.3.1 Push Button Configuration (PBC) ..........................................................................................90
12.3.2 PIN Configuration ..................................................................................................................91
12.4 Enabling and Configuring Wireless Security (No WPS) ........... ...................................... ................. 93
12.4.1 Configure Your Notebook ......................................................................................................94
12.5 Connecting to USB Storage with the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility .....................................96
12.5.1 Multiple Connections to the USB Device ........................... ... ................................................ .96
12.6 Automatically Connecting to a USB Printer .....................................................................................98
Part II: Technical Reference..........................................................................101
Chapter 13
Wireless LAN.....................................................................................................................................103
13.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................103
13.2 What You Can Do .........................................................................................................................103
13.3 What You Should Know ................................................................................................................104
13.3.1 Wireless Security Overview ........................ ....................................................... ..................104
13.4 General Wireless LAN Screen .....................................................................................................106
13.4.1 No Security ..........................................................................................................................107
13.4.2 WEP Encryption ..................................................................................................................108
13.4.3 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK .........................................................................................................110
13.5 MAC Filter .....................................................................................................................................110
13.6 Wireless LAN Advanced Screen ................................................................................................... 111
13.7 Quality of Service (QoS) Screen ...................................................................................................113
13.8 WPS Screen ..................................................................................................................................114
13.9 WPS Station Screen ......................................................................................................................115
13.10 Scheduling Screen ......................................................................................................................116
13.11 WDS Screen ................ .... ... ... ... .... ...............................................................................................117
Chapter 14
WAN ...................................................................................................................................................119
14.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................1 19
14.2 What You Can Do .........................................................................................................................119
14.3 What You Need To Know ..............................................................................................................119
14.3.1 Configuring Your Internet Connection ..................................................................................120
14.3.2 Multicast ..............................................................................................................................121
14.4 Internet Connection .......................................................................................................................121
14.4.1 Ethernet Encapsulation .......................................................................................................121
14.4.2 PPPoE Encapsulation .........................................................................................................123
14.4.3 PPTP Encapsulation ............................................................................................................125
8
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 9

Table of Contents
14.4.4 L2TP Encapsulation ............................................................................................................128
14.5 Advanced WAN Screen ................................................................................................................130
14.6 IGMP Blocking Screen ..................................................................................................................131
Chapter 15
LAN ....................................................................................................................................................133
15.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................133
15.2 What You Can Do .........................................................................................................................133
15.3 What You Need To Know ..............................................................................................................134
15.3.1 IP Pool Setup .......................................................................................................................134
15.3.2 LAN TCP/IP .........................................................................................................................134
15.3.3 IP Alias ................................................................................................................................134
15.4 LAN IP Screen ..............................................................................................................................135
15.5 IP Alias Screen ..............................................................................................................................135
Chapter 16
DHCP Server .....................................................................................................................................137
16.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................137
16.2 What You Can Do .........................................................................................................................137
16.3 General Screen .............................................................................................................................137
16.4 Advanced Screen .......................................................................................................................138
Chapter 17
Network Address Translation (NAT)................................................................................................141
17.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................141
17.2 What You Can Do .........................................................................................................................141
17.3 General NAT Screen .....................................................................................................................142
17.4 NAT Application Screen ..............................................................................................................142
17.5 NAT Advanced Screen ..................................................................................................................144
17.5.1 Trigger Port Forwarding Example ........................................................................................146
17.5.2 Two Point s To Remember About Trigger Ports ...................................................................146
Chapter 18
Dynamic DNS ....................................................................................................................................147
18.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................147
18.2 What You Can Do .........................................................................................................................147
18.3 What You Need To Know ..............................................................................................................147
18.4 Dynamic DNS Screen .................................................................................................................147
Chapter 19
Static Route.......................................................................................................................................149
19.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................149
19.2 What You Can Do .........................................................................................................................149
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
9
Page 10

Table of Contents
19.3 IP Static Route Screen .................................................................................................................150
Chapter 20
RIP......................................................................................................................................................153
20.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................153
20.2 What You Can Do .........................................................................................................................153
20.3 RIP Screen ..................................................................................................................................153
Chapter 21
Firewall ..............................................................................................................................................155
21.1 Overview .....................................................................................................................................155
21.2 What You Can Do .........................................................................................................................155
21.3 What You Need To Know ..............................................................................................................156
21.4 General Firewall Screen .............................................................................................................156
21.5 Services Screen .........................................................................................................................157
Chapter 22
Content Filter ....................................................................................................................................159
22.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................159
22.2 What You Can Do .........................................................................................................................159
22.3 What You Need To Know ..............................................................................................................159
22.3.1 Content Filtering Profiles .....................................................................................................159
22.4 Content Filter Screen ....................................................................................................................160
Chapter 23
Bandwidth Management...................................................................................................................163
23.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................163
23.2 What You Can Do .........................................................................................................................163
23.3 What You Need To Know ..............................................................................................................164
23.4 General Screen ............................................................................................................................164
23.5 Advanced Screen .........................................................................................................................164
23.5.1 Rule Configuration: Application Rule Configuration .........................................................166
23.5.2 Rule Configuration: User Defined Service Rule Configuration .........................................167
23.6 Monitor Screen ..............................................................................................................................168
23.6.1 Predefined Bandwidth Management Services .....................................................................169
Chapter 24
Remote Management........................................................................................................................170
24.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................170
24.2 What You Can Do .........................................................................................................................170
24.3 What You Need to Know ...............................................................................................................170
24.3.1 Remote Management and NAT ...........................................................................................170
24.3.2 System Timeout ..................................................................................................................171
10
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 11

Table of Contents
24.4 WWW Screen .............................................................................................................................171
Chapter 25
Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)......................................................................................................173
25.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................173
25.2 What You Can Do .........................................................................................................................173
25.3 What You Need to Know ...............................................................................................................173
25.3.1 NAT Traversal ......................................................................................................................173
25.3.2 Cautions with UPnP .............................................................................................................174
25.4 UPnP Screen ...................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ...................................................................................174
25.5 Technical Refereance ........................................... ... .... ... ... ... .... .....................................................174
25.5.1 Using UPnP in Windows XP Example .................................................................................174
25.5.2 Web Configurator Easy Access ......................................... .................................................. 177
Chapter 26
Maintenance......................................................................................................................................181
26.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................181
26.2 What You Can Do .........................................................................................................................181
26.3 General Screen .............................................................................................................................181
26.4 Password Screen ..........................................................................................................................182
26.5 Time Setting Screen ......................................................................................................................183
26.6 Firmware Upgrade Screen ................................................................ ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..................184
26.7 Configuration Backup/Restore Screen ..........................................................................................186
26.8 Reset/Restart Screen ....................................................................................................................187
26.9 System Operation Mode Overview ...............................................................................................187
26.10 Sys OP Mode Screen ..................................................................................................................189
Chapter 27
Troubleshooting................................................................................................................................191
27.1 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs ........................ ... .... ... ... ... ............................................191
27.2 Router Access and Login ........................ ... .... ................................................ ... .... ... ... ... ...............192
27.3 Internet Access .............................................................................................................................193
27.4 Resetting the Router to Its Factory Defaults .................................................................................195
27.5 Wireless Router/AP Troubleshooting ............................................................................................195
27.6 ZyXEL Share Center Utility Problems ...........................................................................................196
Appendix A Pop-up Windows, JavaScript and Java Permissions...................................................199
Appendix B IP Addresses and Subnetting.......................................................................................211
Appendix C Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address......................................................................221
Appendix D Wireless LANs..............................................................................................................249
Appendix E Common Services........................................................................................................263
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
11
Page 12

Table of Contents
Appendix F Legal Information..........................................................................................................267
Index ..................................................................................................................................................275
12
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 13

PART I
User’s Guide
13
Page 14

14
Page 15

1.1 Overview
This chapter introduces the main features and applications of the Router.
The Router extends the range of your existing wired network without additional wiring, providing
easy network access to mobile users. You can set up a wireless network with other IEEE 802.11b/g/
n compatible devices.
A range of services such as a firewall and content filtering are also available for secure Internet
computing. You can use media bandwidth management to efficiently manage traffic on your
network. Bandwidth management features allow you to prioritize time-sensitive or highly important
applications such as Voice over the Internet (VoIP).
There is one USB 2.0 port on your Router. You can connect a USB (version 2.0 or lower) memory
stick, USB hard drive, or USB device for file sharing. The Router automatically detects the USB
device.
CHAPTER 1
Getting to Know Your Router
Note: For the USB function, it is strongly recommended to use version 2.0 or lower USB
storage devices (such as memory sticks, USB hard drives) and/or USB devices
(such as USB printers). Other USB products are not guaranteed to function properly
with the Router.
Note: Be sure to install the ZyXEL NetUSB
functionality) from the included disc, or download the latest version from the
zyxel.com website.
1.2 Applications
Your can create the following networks using the Router:
• Wired. You can connect network devices via the Ethernet ports of the Router so that they can
communicate with each other and access the Internet.
• Wireless. Wireless clients can connect to the Router to access network resources.
• WAN. Connect to a broadband modem/router for Internet access.
1.3 Ways to Manage the Router
TM
Share Center Utility (for NetUSB
Use any of the following methods to manage the Router.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide 15
Page 16

Chapter 1 Getti ng to Know Your Router
• Web Configurator. This is recommended for everyday management of the Router using a
(supported) web browser.
• Wireless switch. You can use the built-in switch of the Router to turn the wireless function on and
off without opening the Web Configurator.
• WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) button. You can use the WPS button or the WPS section of the Web
Configurator to set up a wireless network with your Router.
1.4 Good Habits for Managing the Router
Do the following things regularly to make the Router more secure and to manage the Router more
effectively.
• Change the password. Use a password that’s not easy to guess and that consists of different
types of characters, such as numbers and letters.
• Write down the password and put it in a safe place.
• Back up the configuration (and make sure you know how to restore it). Restoring an earlier
working configuration may be useful if the device becomes unstable or even crashes. If you
forget your password, you will have to reset the Router to its factory default settings. If you
backed up an earlier configuration file, you would not have to totally re-configure the Router. You
could simply restore your last configuration.
16
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 17
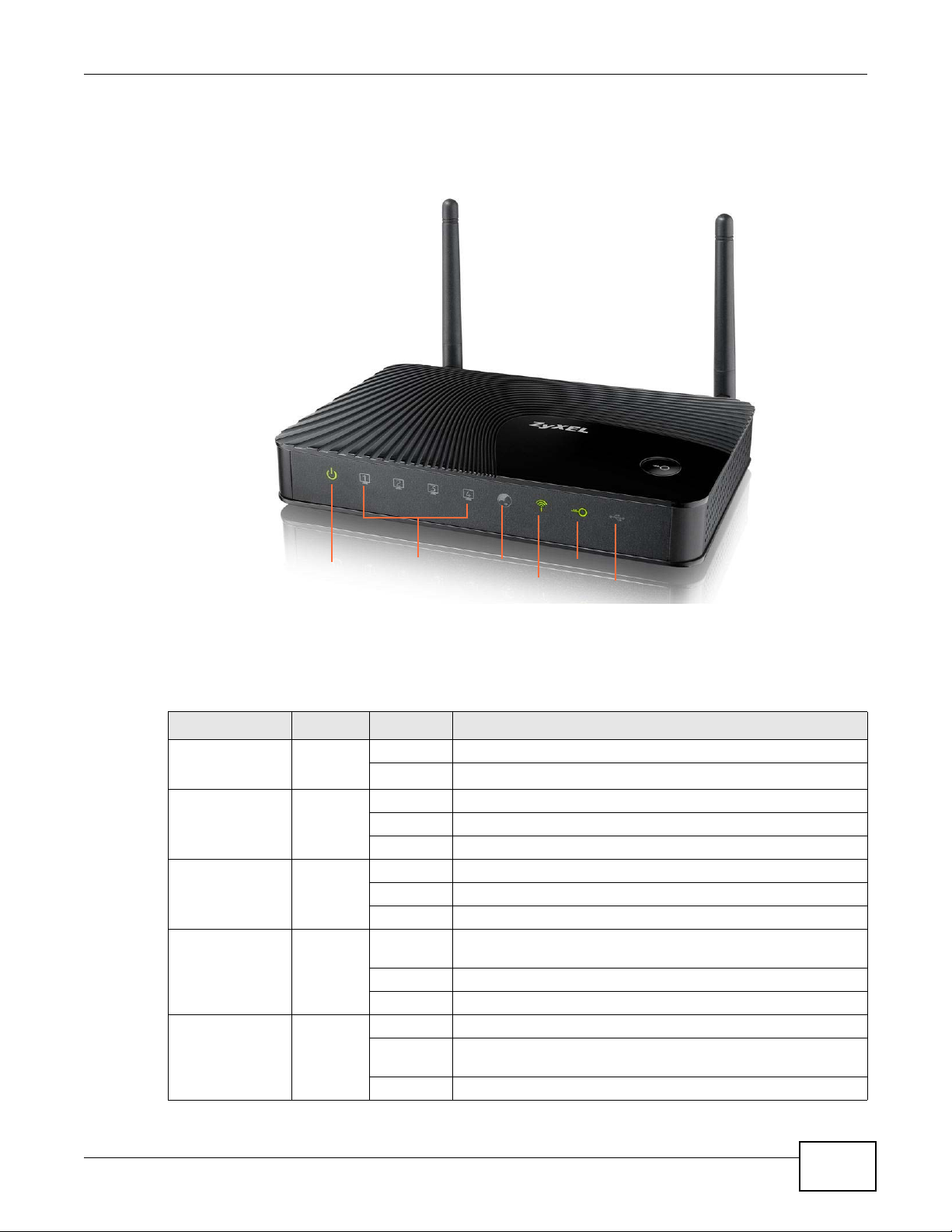
1.5 LEDs
Power
LAN 1-4
WAN
WLAN
USB
WPS
Figure 1 Front Panel
Chapter 1 Gettin g to Know Your Router
The following table describes the LEDs and the WPS button.
Table 1 Front Panel LEDs and WPS Button
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
POWER Green On The Router is receiving power and functioning properly.
Off The Router is not receiving power.
LAN 1-4 Green On The Router has a successful 10/100MB Ethernet connection.
Blinking The Router is sending/receiving data through the LAN.
Off The LAN is not connected.
WAN Green On The Router has a successful 10/100MB WAN connection.
Blinking The Router is sending/receiving data through the WAN.
Off The WAN connection is not ready, or has failed.
WLAN Green On The Router is ready, but is not sending/receiving data through
the wireless LAN.
Blinking The Router is sending/receiving data through the wireless LAN.
Off The wireless LAN is not ready or has failed.
WPS Green On WPS is enabled.
Blinking The Router is negotiating a WPS connection with a wireless
client.
Off The wireless LAN is not ready or has failed.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
17
Page 18
Chapter 1 Getti ng to Know Your Router
Table 1 Front Panel LEDs and WPS Button (continued)
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
USB Green On The Router has a USB device installed.
Blinking The Router is transmitting and/or receiving data from routers
through an installed USB device.
Off There is no USB device connected to the Router.
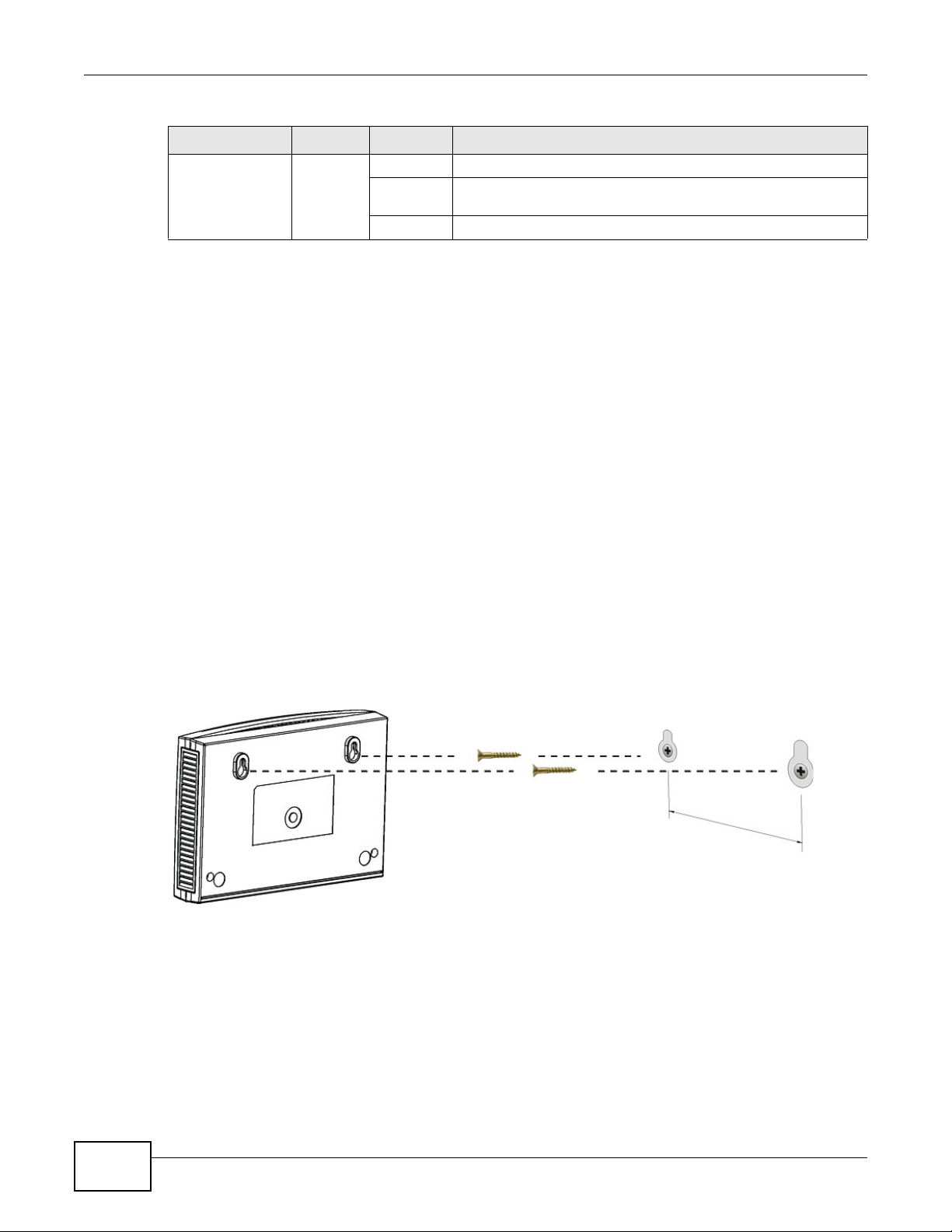
1.6 Wall-mounting Instructions
Complete the following steps to hang your Router on a wall.
1 Select a position free of obstructions on a sturdy wall.
2 Drill two holes for the screws.
Be careful to avoid damaging pipes or cables located inside the wall
when drilling holes for the screws.
3 Do not insert the screws all the way into the wall. Leave a small gap of about 0.5 cm between the
heads of the screws and the wall.
4 Make sure the screws are snugly fastened to the wall. They need to hold the weight of the Router
with the connection cables.
5 Align the holes on the back of the Router with the screws on the wall. Hang the Router on the
screws.
Figure 2 Wall-mounting Example
18
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 19

Chapter 1 Gettin g to Know Your Router
The following are dimensions of an M4 tap screw and masonry plug used for wall mounting. All
measurements are in millimeters (mm).
Figure 3 Masonry Plug and M4 Tap Screw
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
19
Page 20

2.1 Overview
Your Router supports WiFi Protected Setup (WPS), which is an easy way to set up a secure wireless
network. WPS is an industry standard specification, defined by the WiFi Alliance.
WPS allows you to quickly set up a wireless network with strong security, without having to
configure security settings manually. Each WPS connection works between two devices. Both
devices must support WPS (check each device’s documentation to make sure).
Depending on the devices you have, you can either press a button (on the device itself, or in its
configuration utility) or enter a PIN (a unique Personal Identification Number that allows one device
to authenticate the other) in each of the two devices. When WPS is activated on a device, it has two
minutes to find another device that also has WPS activated. Then, the two devices connect and set
up a secure network by themselves.
CHAPTER 2
The WPS Button
For more information on using WPS, see Section 12.3 on page 89.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide 20
Page 21

ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility
3.1 Overview
The ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility allows you to work with the USB devices that are connected
directly to the Router as if they are connected directly to your computer. This allows you to easily
share USB-based devices such as printers, scanners, portable hard disks, MP3 players, faxes, and
digital cameras (to name a few) with all the other people in your home or office as long as they are
connected to the Router and have the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility installed.
Note: Be sure to install the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility (for NetUSB functionality)
from the included disc, or download the latest version from the zyxel.com website.
3.1.1 Quick Setup
This section shows you how to get started using the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility.
CHAPTER 3
1 Install the ZyXEL NetUSB
2 Connect a USB device to the USB port on the Router.
Note: If you are connecting multiple devices to the Router, first connect a USB hub to the
Router then connect your other USB devices to it.
3 Run the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility to display a list of all connected USB devices, then use
it to connect your computer to them.
Share Center Utility on each computer connected to the Router.
3.1.2 Installing ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility
Before you can access USB devices connected to the Router, you must first install the ZyXEL
NetUSB
these devices.
Note: In order to properly use the utility with your Router, ensure that the Router
To install the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility:
1 Insert the disc that came with your Router into your computer’s disc drive.
Share Center Utility on any computer on your LAN to which you want to allow access to
firmware is version v1.00(BWQ.0) or higher. See Chapter 26 on page 184 for
information on updating your device’s firmware.
2 Run the Setup program by double-clicking it and then follow the on-screen instructions for
installing it on your computer.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide 21
Page 22
Chapter 3 ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility
Note: The following operating systems are supported: Windows XP/Vista/7 (32 and 64-bit
versions), and Mac OS X 10.6.
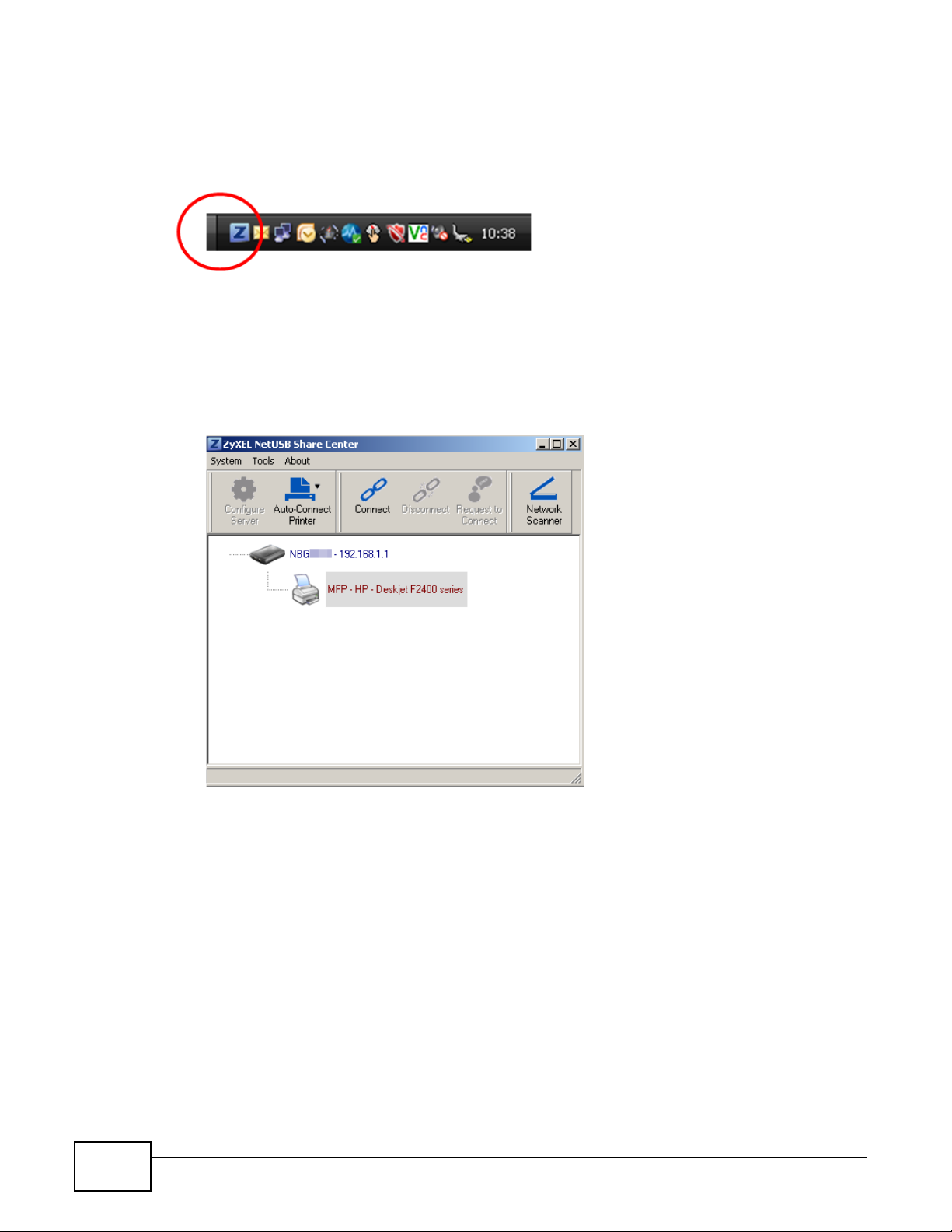
3 To open the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility, double-click its system tray icon.
3.2 The ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility
This section describes the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility main window.
Figure 4 ZyXEL NetUSB
Share Center Utility Main Window
22
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 23
Chapter 3 ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility
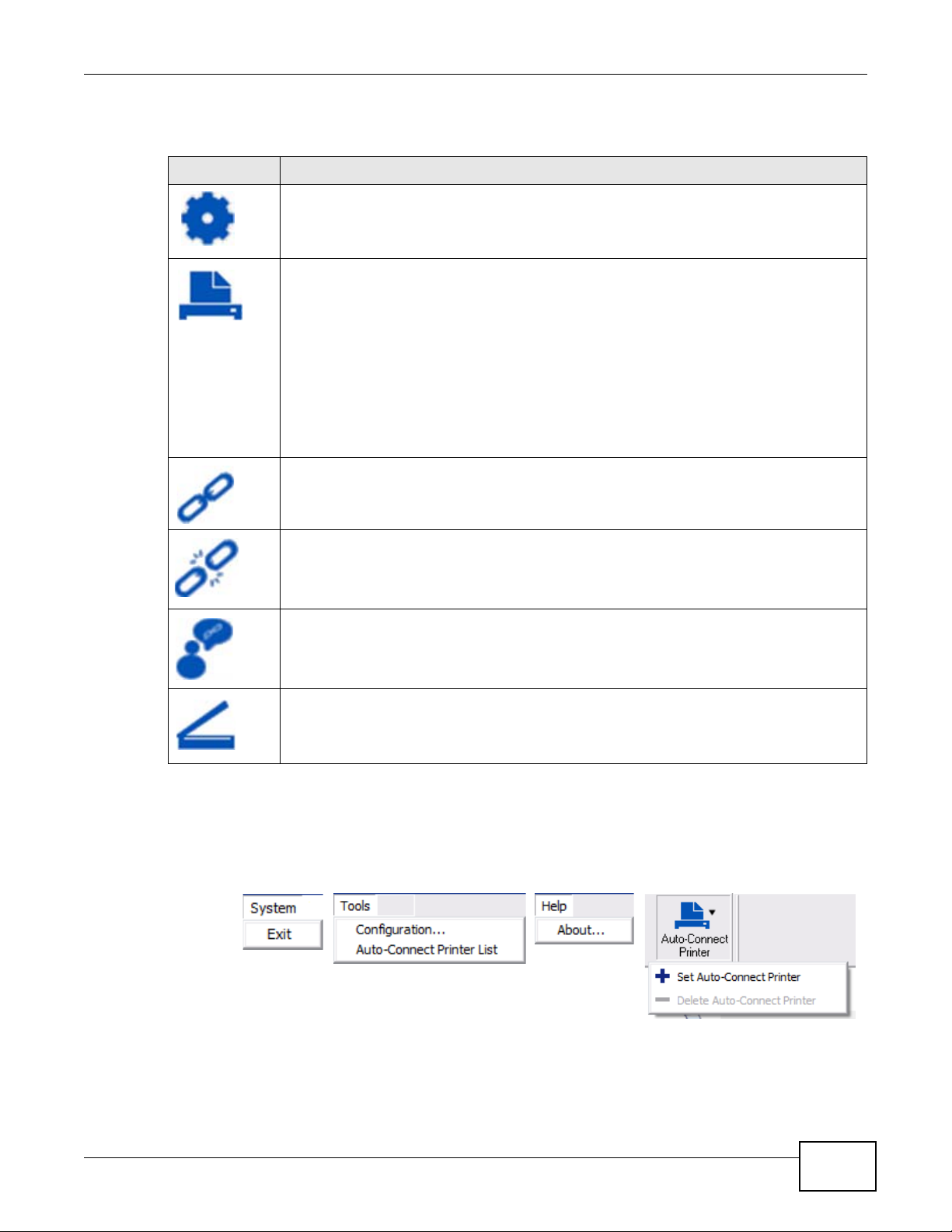
The following table describes the icons in this window.
Table 2 ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility Main Window Icons
ICON DESCRIPTION
Configure Server
Click to open the Router’s built-in Web Configurator, which you can use to set up the Router
(see Chapter 5 on page 39 for details).
Auto-Connect Printer
You can set the selected printer to ‘auto-connect’ after you have connected it to your
computer during inital connection. If the printer is auto-connected to your computer, they
will always be connected over the network. You do not need to configure it manually each
time.
Note: If the computer is connecting to the shared USB printer for the first time, you need to
click Connect and setup the printer before you can use the Auto-Connect Printer
function. See Chapter 12 on page 89 for more details.
Note: You first must install the appropriate drivers for the printer that you intend to use.
Connect
Select a USB device and then click this button to connect to it. Your computer can connect
to as many USB devices as are connected to the Router.
3.2.1 The Menus
This section describes the utility’s menus.
Figure 5 ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility Menus
Disconnect
Select a device to which your computer is connected and then click this button to disconnect
from it.
Request to Connect
Some USB devices may not allow automatic connections over the network. If so, select the
device in question and click this button to issue a request to connect to it.
Network Scanner
Click this to open the scanner options on your computer for working with a scanner
connected to the network.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
23
Page 24
Chapter 3 ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility
The following table describes the menus in this screen.
Table 3 ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility Main Screen Menus
MENU ITEM DESCRIPTION
System Exit This closes the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility.
Tools Configuration This opens the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility
Auto-Connect Printer List This opens the list window that displays all of the
Help About This opens the about window, which provides
Auto-Connect
Printer
Set Auto-Connect Printer You can set the selected printer to ‘auto-connect’
configuration window.
printing devices connected to the Router.
information of the utility software and driver versions.
after you have connected it to your computer during
inital connection. If the printer is auto-connected to
your computer, they will always be connected over
the network. You do not need to configure it manually
each time.
Click this to show your installed printer list and select
the one you want to set as auto-connected.
Note: If the computer is connecting to the shared USB
printer for the first time, you need to click
Connect and setup the printer before you can
use the Auto-Connect Printer function. See
Chapter 12 on page 89 for more details.
Note: You first must install the appropriate drivers for
the printer that you intend to use.
Delete Auto-Connect Printer This removes the auto-connect option from the
selected printer.
24
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 25

Chapter 3 ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility
3.2.2 The ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Configuration Window
This section describes the utility’s configuration window, which allows you to set certain options for
the utility. These options do not apply to the USB devices connected to the Router.
You can open it by clicking the Tools > Configuration menu command.
Figure 6 ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility Configuration Window
The following table describes the labels in this window.
Table 4 ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility Configuration Window
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Basic Select this to run the utility automatically when you log into or start up Windows.
Language Select a language for the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility. You must restart the utility for
the change to take effect.
OK Click this to save your changes and close the window.
Cancel Click this cancel to close the window without saving.
Apply Click this to save your changes without closing the window.
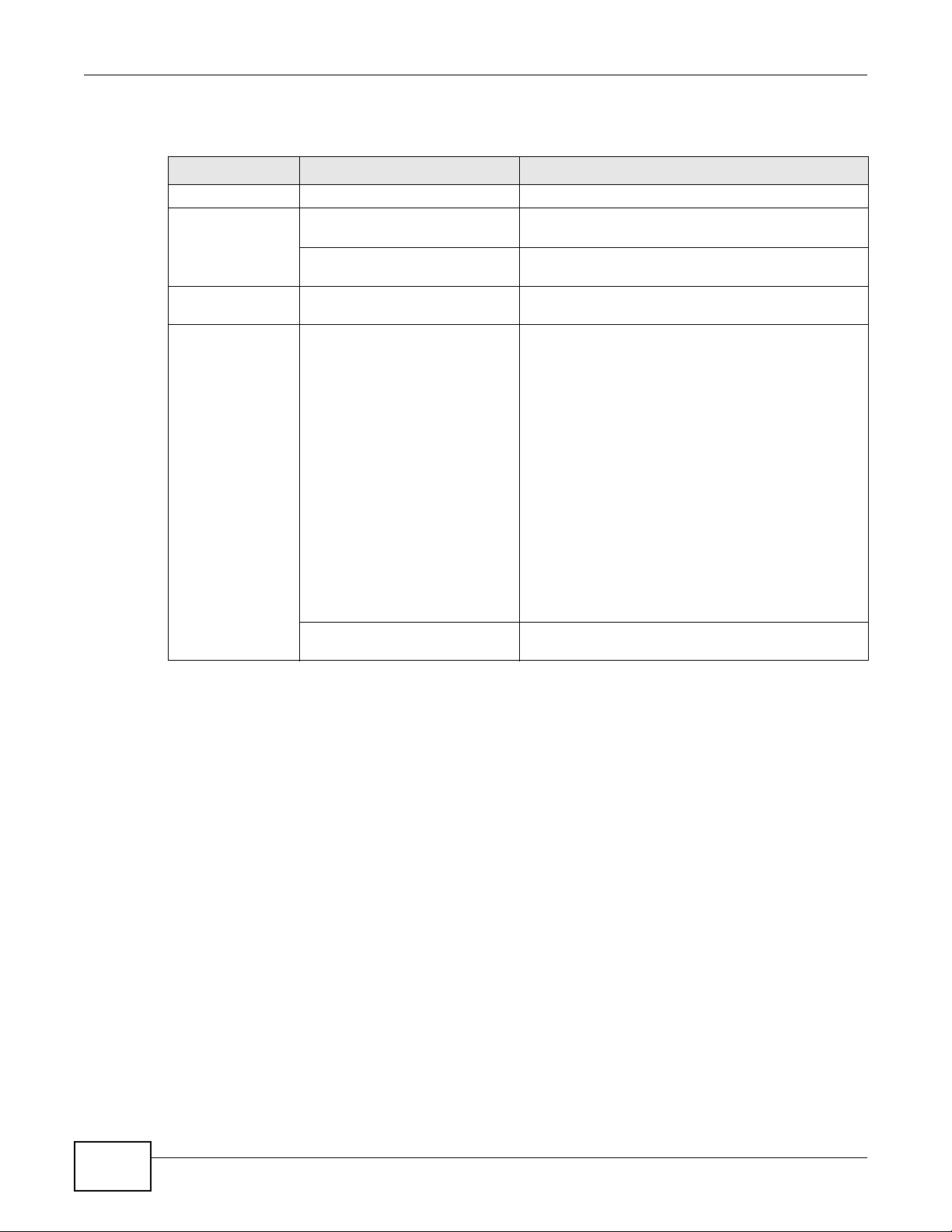
3.2.3 The Auto-Connect Printer List Window
This section describes the utility’s auto-connect printer list window. You can open it by clicking the
Tools > Auto-Connect Printer List menu command.
Note: If the computer is connecting to the shared USB printer for the first time, you need
to click Connect and setup the printer before you can use the Auto-Connect
Printer function. See Chapter 12 on page 89 for more details.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
25
Page 26
Chapter 3 ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility
Figure 7 ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility Auto-Connect Printer List Window
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 5 ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility Auto-Connect Printer List Window
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server IP &
Printer Name
Windows
Printer Name
Delete Select an printer from the list and click this to remove it.
Close Click this to close the window.
Displays a list of print server IPs and printer names connected to this Router.
Displays a corresponding list of Windows printer names connected to this devices listed in
the other list.
3.2.4 Exit the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility
If you want to exit the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility when your computer is not connected to
any USB device, follow the steps below:
1 Click System > Exit on the Utility screen. The Utility will automatically close.
Or you can close the Utlity screen first, then exit:
26
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 27
Chapter 3 ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility
1 Click the X on the upper-right corner of the Utility:
2 This will close the Utility screen to an icon at the system tray of your computer. Right-click on the
Utility’s icon and click Exit.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
27
Page 28

Chapter 3 ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility
28
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 29
4.1 Overview
This chapter provides information on the wizard setup screens in the Web Configurator.
The Web Configurator’s wizard setup helps you configure your device to access the Internet. Refer
to your ISP for your Internet account information. Leave a field blank if you don’t have that
information.
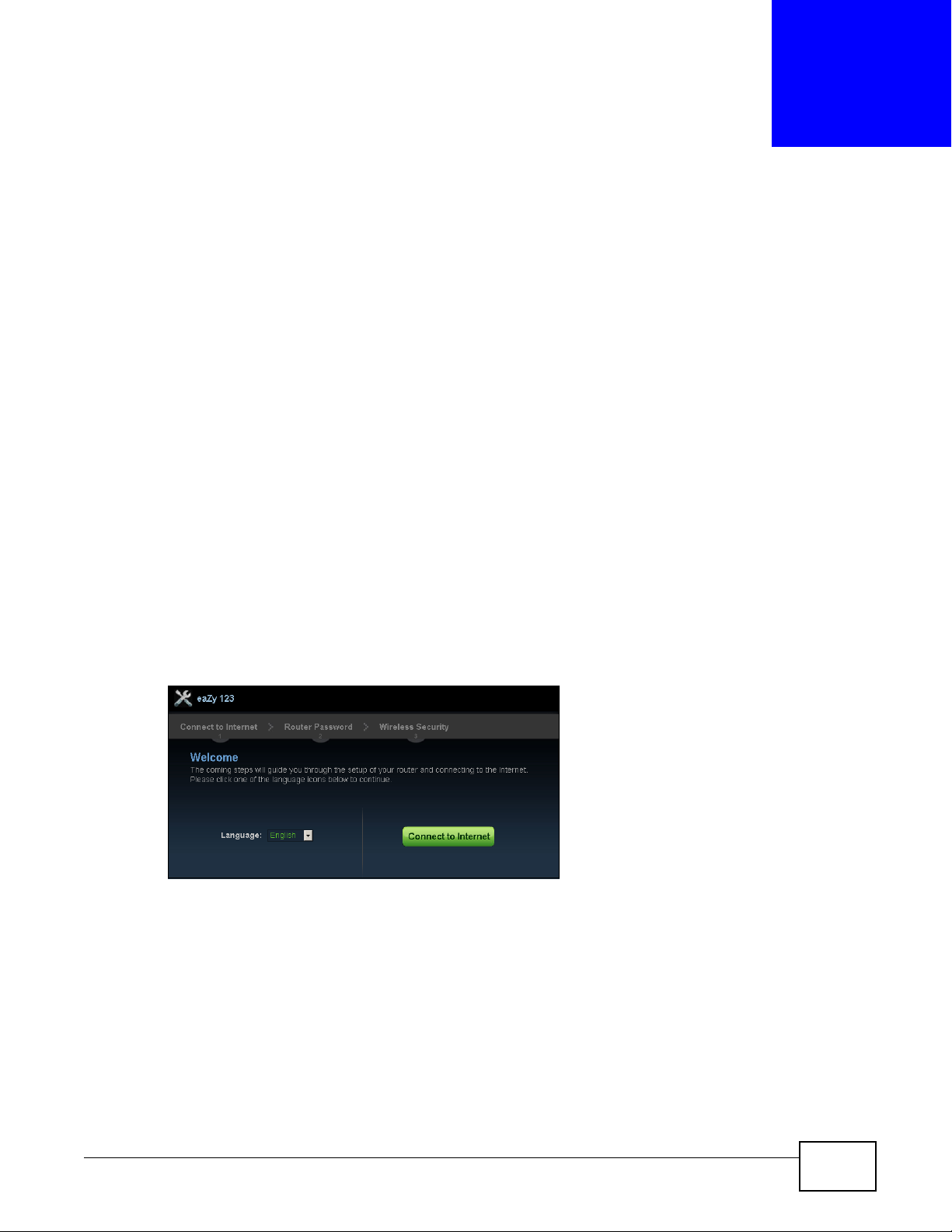
4.2 Accessing the Wizard
Launch your web browser and type "http://192.168.1.1" as the website address. Type "1234"
(default) as the password and click Login.
CHAPTER 4
Connection Wizard
Note: The Wizard appears when the Router is accessed for the first time or when you
reset the Router to its default factory settings.
The Wizard screen opens. Choose your Language and click Connect to Internet .
Figure 8 Welcome
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide 29
Page 30
Chapter 4 Connection Wizard
4.3 Connect to Internet
The Router offers five Internet connection types. They are Static IP, DHCP, PPPoE, PPTP or
L2TP. The wizard attempts to detect which WAN connection type you are using.
Figure 9 Detecting your Internet Connection Type
If the wizard does not detect a connection type, you must select one from the drop-down list box.
Check with your ISP to make sure you use the correct type.
Note: If you get an error message, check your hardware connections. Make sure your
Internet connection is up and running.
The following screen depends on your Internet connection type. Enter the details provided by your
Internet Service Provider (ISP) in the fields (if any).
Figure 10 Internet Connection Type
Your Router detects the following Internet Connection type.
Table 6 Internet Connection Type
CONNECTION
TYPE
Static IP Select the Static IP if an administrator assigns the IP address of your computer.
DHCP Select the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) option when the WAN port is used
PPPoE
PPTP Select the PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) option for a dial-up connection, and
L2TP Select the L2TP (Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol) if you are connecting to another device over
DESCRIPTION
as a regular Ethernet.
Select the PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) option for a dial-up connection.
your ISP gave you an IP address and/or subnet mask.
another network (like the Internet or VPN).
30
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 31

4.3.1 Connection Type: DHCP
Choose DHCP as the Internet Connection Type when the WAN port is used as a regular
Ethernet. Click Next.
Figure 11 Internet Connection Type: DHCP
Note: If you get an error screen after clicking Next, you might have selected the wrong
Internet Connection type. Click Back, make sure your Internet connection is
working and select the right Connection Type. Contact your ISP if you are not sure
of your Internet Connection type.
Chapter 4 Connection Wizard
4.3.2 Connection Type: Static IP
Choose Static IP as the Internet Connection Type if your ISP assigned an IP address for your
Internet connection. Click Next.
Figure 12 Internet Connection Type: Static IP
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 7 Internet Connection Type: Static IP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Internet
Connection
Type
IP Address Enter the IP address provided by your ISP.
Select the Static IP option.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
31
Page 32

Chapter 4 Connection Wizard
Table 7 Internet Connection Type: Static IP (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Subnet Mask Enter the IP subnet mask in this field.
Default
Gateway
Primary DNS DNS (Domain Name System) is for mapping a domain name to its corresponding IP address
Secondary DNS Enter the secondary DNS server's IP address in the fields provided.
Exit Click this to close the wizard screen without saving.
Back Click this to return to the previous screen.
Next Click this to continue.
Enter the gateway IP address in this field.
and vice versa. The DNS server is extremely important because without it, you must know
the IP address of a computer before you can access it. The Router uses a system DNS
server (in the order you specify here) to resolve domain names for DDNS and the time
server.
Enter the primary DNS server's IP address in the fields provided.
4.3.3 Connection Type: PPPoE
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) functions as a dial-up connection. PPPoE is an IETF
(Internet Engineering Task Force) standard specifying how a host personal computer interacts with
a broadband modem (for example DSL, cable, wireless, etc.) to achieve access to high-speed data
networks.
For the service provider, PPPoE offers an access and authentication method that works with existing
access control systems (for instance, RADIUS).
One of the benefits of PPPoE is the ability to let end users access one of multiple network services,
a function known as dynamic service selection. This enables the service provider to easily create
and offer new IP services for specific users.
Operationally, PPPoE saves significant effort for both the subscriber and the ISP/carrier, as it
requires no specific configuration of the broadband modem at the subscriber's site.
By implementing PPPoE directly on the Router (rather than individual computers), the computers on
the LAN do not need PPPoE software installed, since the Router does that part of the task.
Furthermore, with NAT, all of the LAN's computers will have Internet access.
Figure 13 Internet Connection Type: PPPoE
32
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 33

The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 8 Internet Connection Type: PPPoE
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Internet
Connection
Type
Dynamic IP Select this radio button if your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address.
Static IP Select this radio button, provided by your ISP to give the Router a fixed, unique IP address.
IP Address Type the name of your service provider.
User Name Type the user name given to you by your ISP.
Password Type the password associated with the user name above.
Exit Click this to close the wizard screen without saving.
Back Click this to return to the previous screen.
Next Click this to continue.
Select the PPPoE option for a dial-up connection.
4.3.4 Connection Type: PPTP
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a network protocol that enables transfers of data from a
remote client to a private server, creating a Virtual Private Network (VPN) using TCP/IP-based
networks.
Chapter 4 Connection Wizard
PPTP supports on-demand, multi-protocol, and virtual private networking over public networks,
such as the Internet.
Refer to the appendix for more information on PPTP.
The Router supports one PPTP server connection at any given time.
Figure 14 Internet Connection Type: PPTP
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
33
Page 34

Chapter 4 Connection Wizard
The following table describes the fields in this screen
Table 9 Internet Connection Type: PPTP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Internet
Connection
Type
Dynamic IP Select this radio button if your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address.
Static IP Select this radio button, provided by your ISP to give the Router a fixed, unique IP address.
PPTP Address Type the (static) IP address assigned to you by your ISP.
PPTP Subnet
Mask
PPTP Gateway
IP Address
PPTP Server IP
Address
User Name Type the user name given to you by your ISP.
Password Type the password associated with the User Name above.
Exit Click this to close the wizard screen without saving.
Back Click this to return to the previous screen.
Next Click this to continue.
Select PPTP from the drop-down list box. To configure a PPTP client, you must configure the
User Name and Password fields for a PPP connection and the PPTP parameters for a PPTP
connection.
Type the subnet mask assigned to you by your ISP (if given).
Type the gateway IP address of the PPTP server.
Type the server IP address of the PPTP server.
4.3.5 Connection Type: L2TP
The Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) works at layer 2 (the data link layer) to tunnel network traffic
between two peer devices over another network (like the Internet).
Figure 15 Internet Connection Type: L2TP
The following table describes the fields in this screen
Table 10 Internet Connection Type: L2TP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Internet
Connection
Type
Dynamic IP Select this radio button if your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address.
Select L2TP from the drop-down list box.
34
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 35

Chapter 4 Connection Wizard
Table 10 Internet Connection Type: L2TP (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Static IP Select this radio button, provided by your ISP to give the Router a fixed, unique IP address.
L2TP Address Type the (static) IP address assigned to you by your ISP.
L2TP Subnet
Mask
L2TP Gateway
IP Address
L2TP Server IP
Address
User Name Type the user name given to you by your ISP.
Password Type the password associated with the User Name above.
Exit Click this to close the wizard screen without saving.
Back Click this to return to the previous screen.
Next Click this to continue.
Type the subnet mask assigned to you by your ISP (if given).
Type the gateway IP address of the L2TP server.
Type the server IP address of the L2TP server.
The Router connects to the Internet.
Figure 16 Connecting to the Internet
Note: If the Wizard successfully connects to the Internet, it proceeds to the next step. If
you get an error message, go back to the previous screen and make sure you have
entered the correct information provided by your ISP.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
35
Page 36

Chapter 4 Connection Wizard
4.4 Router Password
Change the login password in the following screen. Enter the new password and retype it to
confirm. Click Next to proceed with the Wireless Security screen.
Figure 17 Router Password
4.5 Wireless Security
Configure Wireless Settings. Configure the wireless network settings on your Router in the following
screen. The fields that show up depend on the kind of security you select.
4.5.1 Wireless Security: No Security
Choose No Security in the Wireless Security screen to let wireless devices within range access
your wireless network.
Figure 18 Wireless Security: No Security
36
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 37

The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 11 Wireless Security: No Security
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless
Network Name
(SSID)
Security mode Select a Security level from the drop-down list box.
Exit Click this to close the wizard screen without saving.
Back Click this to return to the previous screen.
Next Click this to continue.
Enter a descriptive name (up to 32 printable 7-bit ASCII characters) for the wireless LAN.
If you change this field on the Router, make sure all wireless stations use the same SSID in
order to access the network.
Choose None to have no wireless LAN security configured. If you do not enable any wireless
security on your Router, your network is accessible to any wireless networking device that is
within range.
4.5.2 Wireless Security: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
Choose WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK security in the Wireless Security screen to set up a password for
your wireless network.
Chapter 4 Connection Wizard
Figure 19 Wireless Security: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 12 Wireless Security: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless
Network Name
(SSID)
Security mode Select a Security level from the drop-down list box.
Wireless
password
Verify Password Retype the password to confirm.
Exit Click this to close the wizard screen without saving.
Enter a descriptive name (up to 32 printable 7-bit ASCII characters) for the wireless LAN.
If you change this field on the Router, make sure all wireless stations use the same SSID in
order to access the network.
Choose WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK security to configure a Pre-Shared Key. Choose this
option only if your wireless clients support WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK respectively.
Type from 8 to 63 case-sensitive ASCII characters. You can set up the most secure wireless
connection by configuring WPA in the wireless LAN screens.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
37
Page 38

Chapter 4 Connection Wizard
Table 12 Wireless Security: WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Back Click this to return to the previous screen.
Next Click this to continue.
Congratulations! Open a web browser, such as Internet Explorer, to visit your favorite website.
Note: If you cannot access the Internet when your computer is connected to one of the
Router’s LAN ports, check your connections. Then turn the Router off, wait for a few
seconds then turn it back on. If that does not work, log in to the web configurator
again and check you have typed all information correctly. See the User’s Guide for
more suggestions.
Figure 20 Congratulations
You can also click ZyGO to open the Easy Mode Web Configurator of your Router.
You have successfully set up your Router to operate on your network and access the Internet. You
are now ready to connect wirelessly to your Router and access the Internet.
38
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 39

5.1 Overview
This chapter describes how to access the Router Web Configurator and provides an overview of its
screens.
The Web Configurator is an HTML-based management interface that allows easy setup and
management of the Router via Internet browser. Use Internet Explorer 6.0 and later or Netscape
Navigator 7.0 and later versions or Safari 2.0 or later versions. The recommended screen resolution
is 1024 by 768 pixels.
In order to use the Web Configurator you need to allow:
• Web browser pop-up windows from your device. Web pop-up blocking is enabled by default in
Windows XP SP (Service Pack) 2.
• JavaScript (enabled by default).
• Java permissions (enabled by default).
CHAPTER 5
Introducing the Web Configurator
Refer to the Troubleshooting chapter (Chapter 27 on page 191) to see how to make sure these
functions are allowed in Internet Explorer.
5.2 Accessing the Web Configurator
1 Make sure your Router hardware is properly connected and prepare your computer or computer
network to connect to the Router (refer to the Quick Start Guide).
2 Launch your web browser.
3 Type "http://192.168.1.1" as the website address.
Your computer must be in the same subnet in order to access this website address.
5.2.1 Login Screen
Note: If this is the first time you are accessing the Web Configurator, you may be
redirected to the Wizard. Refer to Chapter 4 on page 29 for the Connection Wizard
screens.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide 39
Page 40

Chapter 5 Introdu cing the Web Configurator
The Web Configurator initially displays the following login screen.
Figure 21 Login screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 13 Login screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Password Type "1234" (default) as the password.
Language Select the language you want to use to configure the Web Configurator. Click Login.
This shows the current weather, either in celsius or fahrenheit, of the city you specify in
Section 5.2.3.1 on page 42.
This shows the time (hh:mm:ss) and date (yyyy:mm:dd) of the timezone you select in
Section 5.2.3.2 on page 42 or Section 26.5 on page 183. The time is in 24-hour format, for
example 15:00 is 3:00 PM.
5.2.2 Password Screen
You should see a screen asking you to change your password (highly recommended) as shown
next.
Figure 22 Change Password Screen
40
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 41

The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 14 Change Password Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
New Password Type a new password.
Retype to Confirm Retype the password for confirmation.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Router.
Ignore Click Ignore if you do not want to change the password this time.
Note: The management session automatically times out when the time period set in the
Administrator Inactivity Timer field expires (default five minutes; go to Chapter
26 on page 181 to change this). Simply log back into the Router if this happens.
5.2.3 Home Screen
If you have previously logged into the Web Configurator but did not click Logout, you may be
redirected to the Home screen.
You can also open this screen by clicking Home ( or ) in the Easy Mode or Expert
mode screens.
Chapter 5 Introducing the Web Configurator
The Home screen displays as follows.
Figure 23 Home Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 15 Home Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Go Click this to open the Easy mode Web Configurator.
Language Select a language to go to the Easy mode Web Configurator in that language and click
Login.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
41
Page 42

Chapter 5 Introdu cing the Web Configurator
Table 15 Home Screen (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
(This is just an example). This shows the current weather, either in celsius or fahrenheit, of
the city you specify in Section 5.2.3.1 on page 42.
(This is just an example). This shows the time (hh:mm:ss) and date (yyyy:mm:dd) of the
timezone you select in Section 5.2.3.2 on page 42 or Section 26.5 on page 183.
5.2.3.1 Weather Edit
You can change the temperature unit and select the location for which you want to know the
weather.
Click the icon to change the Weather display.
Figure 24 Change Weather
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 16 Change Weather
LABEL DESCRIPTION
o
C or oF Choose which temperature unit you want the Router to display.
Change
Location
Finish Click this to apply the settings and refresh the date and time display.
5.2.3.2 Time/Date Edit
One timezone can cover more than one country. You can choose a particular country in which the
Router is located and have the Router display and use the current time and date for its logs.
Click the icon to change the Weather display.
Figure 25 Change Password Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 17 Change Password Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Change time
zone
Finish Click this to apply the settings and refresh the weather display.
Select the location for which you want to know the weather. If the city you want is not listed,
choose one that is closest to it.
Select the specific country whose current time and date you want the Router to display.
42
Note: You can also edit the timezone in Section 26.5 on page 183.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 43

5.3 Resetting the Router
If you forget your password or IP address, or you cannot access the Web Configurator, you will need
to use the RESET button at the back of the Router to reload the factory-default configuration file.
This means that you will lose all configurations that you had previously saved, the password will be
reset to “1234” and the IP address will be reset to “192.168.1.1”.
5.3.1 Procedure to Use the Reset Button
1 Make sure the power LED is on.
2 Press the RESET button for longer than 1 second to restart/reboot the Router.
3 Press the RESET button for longer than five seconds to set the Router back to its factory-default
configurations.
Chapter 5 Introducing the Web Configurator
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
43
Page 44

Chapter 5 Introdu cing the Web Configurator
44
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 45

6.1 Overview
This chapter discusses read-only information related to the device state of the Router.
Note: To access the Monitor screens, you can also click the links in the Summary table of
the Status screen to view the bandwidth consumed, packets sent/received as well
as the status of clients connected to the Router.
6.2 What You Can Do
•Use the Log (Section 6.3 on page 45) screen to see the logs for the activity on the Router.
•Use the BW MGMT Monitor screen (Section 6.4 on page 47) to view the amount of network
bandwidth that applications running in the network are using.
•Use the DHCP Table screen (Section 6.5 on page 47) to view information related to your DHCP
status.
•use the Packet Statistics screen (Section 6.6 on page 48) to view port status, packet specific
statistics, the "system up time" and so on.
•Use the WLAN Station Status screen (Section 6.7 on page 49) to view the wireless stations
that are currently associated to the Router.
CHAPTER 6
Monitor
6.3 The Log Screen
The Web Configurator allows you to look at all of the Router’s logs in one location.
6.3.1 View Log
Use the View Log screen to see the logged messages for the Router. The log wraps around and
deletes the old entries after it fills. Select what logs you want to see from the Display drop list. The
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide 45
Page 46

Chapter 6 Monitor
log choices depend on your settings in the Log Settings screen. Click Refresh to renew the log
screen. Click Clear to delete all the logs.
Figure 26 View Log
You can configure which logs to display in the View Log screen. Go to the Log Settings screen
and select the logs you wish to display. Click Apply to save your settings. Click Refresh to start the
screen afresh.
Figure 27 Log Settings
46
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 47

6.4 BW MGMT Monitor
The Bandwidth Management (BW MGMT) Monitor allows you to view the amount of network
bandwidth that applications running in the network are using.
The bandwidth is measured in kilobits per second (kbps).
The monitor shows what kinds of applications are running in the network, the maximum kbps that
each application can use, as well as the percentage of bandwidth it is using.
Figure 28 Summary: BW MGMT Monitor
Chapter 6 Monitor
6.5 DHCP Table
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, RFC 2131 and RFC 2132) allows individual clients to
obtain TCP/IP configuration at start-up from a server. You can configure the Router’s LAN as a DHCP
server or disable it. When configured as a server, the Router provides the TCP/IP configuration for
the clients. If DHCP service is disabled, you must have another DHCP server on that network, or
else the computer must be manually configured.
Click the DHCP Table (Details...) hyperlink in the Status screen. Read-only information here
relates to your DHCP status. The DHCP table shows current DHCP client information (including IP
Address, Host Name and MAC Address) of all network clients using the Router’s DHCP server.
Figure 29 Summary: DHCP Table
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
47
Page 48

Chapter 6 Monitor
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 18 Summary: DHCP Table
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the index number of the host computer.
MAC Address This field shows the MAC address of the computer with the name in the Host Name field.
Every Ethernet device has a unique MAC (Media Access Control) address which uniquely
identifies a device. The MAC address is assigned at the factory and consists of six pairs of
hexadecimal characters, for example, 00:A0:C5:00:00:02.
IP Address This field displays the IP address relative to the # field listed above.
Expires in This field displays the time when the IP address and MAC address association ends.
Refresh Click Refresh to renew the screen.
6.6 Packet Statistics
Click the Packet Statistics (Details...) hyperlink in the Status screen. Read-only information
here includes port status, packet specific statistics and the "system up time". The Poll Interval(s)
field is configurable and is used for refreshing the screen.
Figure 30 Summary: Packet Statistics
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 19 Summary: Packet Statistics
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port This is the Router’s port type.
Status For the LAN ports, this displays the port speed and duplex setting or Down when the line is
TxPkts This is the number of transmitted packets on this port.
RxPkts This is the number of received packets on this port.
disconnected.
For the WAN port, it displays the port speed and duplex setting if you’re using Ethernet
encapsulation and Idle (line (ppp) idle), Dial (starting to trigger a call) and Drop (dropping
a call) if you're using PPPoE or PPTP encapsulation. This field displays Down when the line is
disconnected.
For the WLAN, it displays the maximum transmission rate when the WLAN is enabled and
Down when the WLAN is disabled.
48
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 49

Table 19 Summary: Packet Statistics (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Collisions This is the number of collisions on this port.
Tx B/s This displays the transmission speed in bytes per second on this port.
Rx B/s This displays the reception speed in bytes per second on this port.
Up Time This is the total time the Router has been for each session.
System Up
Time
Poll Interval(s) Enter the time interval in seconds for refreshing statistics in this field.
Set Interval Click this button to apply the new poll interval you entered in the Poll Interval(s) field.
Stop Click Stop to stop refreshing statistics.
This is the total time the Router has been on.
6.7 WLAN Station Status
Click the WLAN Station Status (Details...) hyperlink in the Status screen. View the wireless
stations that are currently associated to the Router in the Association List. Association means
that a wireless client (for example, your network or computer with a wireless network card) has
connected successfully to the AP (or wireless router) using the same SSID, channel and security
settings.
Chapter 6 Monitor
Figure 31 Summary: Wireless Association List
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 20 Summary: Wireless Association List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the index number of an associated wireless station.
MAC Address This field displays the MAC address of an associated wireless station.
Association
Time
Refresh Click Refresh to reload the list.
This field displays the time a wireless station first associated with the Router’s WLAN
network.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
49
Page 50

Chapter 6 Monitor
50
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 51

7.1 Overview
This chapter introduces the different modes available on your Router. First, the term “mode” refers
to two things in this User’s Guide.
• Web Configurator mode. This refers to the Web Configurator interface you want to use for
editing Router features.
• Device mode. This is the operating mode of your Router, or simply how the Router is being used
in the network.
7.1.1 Web Configurator Modes
This refers to the configuration interface of the Web Configurator, which has two modes:
CHAPTER 7
Router Modes
• Easy. The Web Configurator shows this mode by default. Refer to Chapter 8 on page 53 for more
information on the screens in this mode. This interface may be sufficient for users who just want
to use the device.
• Expert. Advanced users can change to this mode to customize all the functions of the Router.
Click Expert Mode after logging into the Web Configurator. The User’s Guide Chapter 5 on page
39 through Chapter 26 on page 181 discusses the screens in this mode.
7.1.2 Device Modes
This refers to the operating mode of the Router, which can act as a:
• Router. This is the default device mode of the Router. Use this mode to connect the local
network to another network, like the Internet. Go to Section 9.3 on page 65 to view the Status
screen in this mode.
• Access Point. Use this mode if you want to extend your network by allowing network devices to
connect to the Router wirelessly. Go to Section 10.4 on page 74 view the Status screen in this
mode.
• WISP mode. Use this mode if there is an existing wireless router or access point in the network
to which you want to connect your local network. Go to Section 11.4 on page 80 to view the
Status screen in this mode.
For more information on these modes and to change the mode of your Router, refer to Section
26.10 on page 189.
The menu for changing device modes is available in Expert mode only.
Note: Choose your Device Mode carefully to avoid having to change it later.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide 51
Page 52

Chapter 7 Router Modes
When changing to another mode, the IP address of the Router changes. The running applications
and services of the network devices connected to the Router can be interrupted.
In WISP mode, you should know the SSID and wireless security details of the access point to which
you want to connect.
52
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 53

8.1 Overview
Network Map
Control Panel
Go to
Status
Screen
Navigation Panel
The Web Configurator is set to Easy Mode by default. You can configure several key features of the
Router in this mode. This mode is useful to users who are not fully familiar with some features that
are usually intended for network administrators.
When you log in to the Web Configurator, the following screen opens.
Figure 32 Easy Mode: Network Map
CHAPTER 8
Easy Mode
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide 53
Page 54

Chapter 8 Easy Mode
Control Panel
Status Screen
Go to
Network
Map
Screen
Navigation Panel
Click Status to open the following screen screen.
Figure 33 Easy Mode: Status Screen
8.2 What You Can Do
You can do the following in this mode:
•Use this Navigation Panel (Section 8.4 on page 55) to opt out of the Easy mode.
•Use the Network Map screen (Section 8.5 on page 55) to check if your Router can ping the
gateway and whether it is connected to the Internet.
•Use the Control Panel (Section 8.6 on page 56) to configure and enable Router features,
including wireless security, wireless scheduling and bandwidth management and so on.
•Use the Status Screen screen (Section 8.7 on page 63) to view read-only information about the
Router, including the WAN IP, MAC Address of the Router and the firmware version.
8.3 What You Need to Know
Between the different device modes, the Control Panel (Section 8.6 on page 56) changes depending
on which features are applicable to the mode:
• Router Mode: All Control Panel features are available.
• Access Point Mode: Only Power Saving and Wireless Security are available.
• WISP Mode: The available features for this mode are Game Console, Content Filter,
Bandwidth MGMT, and Firewall.
54
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 55

8.4 Navigation Panel
Use this navigation panel to opt out of the Easy mode.
Figure 34 Control Panel
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 21 Control Panel
ITEM DESCRIPTION
Home Click this to go to the Login page.
Expert Mode Click this to change to Expert mode and customize features of the Router.
Logout Click this to end the Web Configurator session.
8.5 Network Map
Chapter 8 Easy Mode
Note: The Network MAP is viewable by Windows XP (need to install patch), Windows
Vista and Windows 7 users only. For Windows XP (Service Pack 2) users, you can
see the network devices connected to the Router by downloading the LLTD (Link
Layer Topology Discovery) patch from the Microsoft Website.
Note: Don’t worry if the Network Map does not display in your web browser. This feature
may not be supported by your system. You can still configure the Control Panel
(Section 8.6 on page 56) in the Easy Mode and the Router features that you want to
use in the Expert Mode.
When you log into the Network Configurator, the Network Map is shown as follows.
Figure 35 Network Map
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
55
Page 56

Chapter 8 Easy Mode
The line connecting the Router to the gateway becomes green when the Router is able to ping the
gateway. It becomes red when the ping initiating from the Router does not get a response from the
gateway. The same rule applies to the line connecting the gateway to the Internet.
You can also view the devices (represented by icons indicating the kind of network device)
connected to the Router, including those connecting wirelessly. Right-click on the Router icon to
refresh the network map and go to the Wizard. Right click on the other icons to view information
about the device.
8.6 Control Panel
The features configurable in Easy Mode are shown in the Control Panel.
Figure 36 Control Panel
Switch ON to enable the feature. Otherwise, switch OFF. If the feature is turned on, the green light
flashes. If it is turned off, the red light flashes.
Additionally, click the feature to open a screen where you can edit its settings.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 22 Control Panel
ITEM DESCRIPTION
Game Engine Switch ON to maximize bandwidth for gaming traffic in your network. Otherwise, switch
OFF.
Refer to Section 8.6.1 on page 57 to see this screen.
Power Saving Click this to schedule the wireless feature of the Router.
Disabling the wireless function helps lower the energy consumption of the Router.
Switch ON to apply wireless scheduling. Otherwise, switch OFF.
Refer to Section 8.6.2 on page 57 to see this screen.
Content Filter Click this to restrict access to certain websites, based on keywords contained in URLs, to
which you do not want users in your network to open.
Switch ON to apply website filtering. Otherwise, switch OFF.
Refer to Section 8.6.3 on page 59 to see this screen.
Bandwidth
MGMT
Click this to edit bandwidth management for predefined applications.
Switch ON to have the Router management bandwidth for uplink and downlink traffic
according to an application or service. Otherwise, switch OFF.
Refer to Section 8.6.4 on page 59 to see this screen.
56
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 57

Table 22 Control Panel (continued)
ITEM DESCRIPTION
Firewall Switch ON to ensure that your network is protected from Denial of Service (DoS) attacks.
Wireless
Security
8.6.1 Game Engine
When this feature is enabled, the Router maximizes the bandwidth for gaming traffic that it
forwards out through an interface.
Figure 37 Game Engine
Chapter 8 Easy Mode
Otherwise, switch OFF.
Refer to Section 8.6.5 on page 60 to see this screen.
Click this to configure the wireless security, such as SSID, security mode and WPS key on
your Router.
Refer to Section 8.6.6 on page 60 to see this screen.
Note: When this is switched on, the Game Console tab in the Bandwidth MGMT screen
is automatically positioned on top.
Turn this off if your network is not using gaming.
Click OK to close this screen.
8.6.2 Power Saving
Use this screen to set the day of the week and time of the day when your wireless LAN is turned on
and off. Wireless LAN scheduling is disabled by default.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
57
Page 58

Chapter 8 Easy Mode
Disabling the wireless capability lowers the energy consumption of the of the Router.
Figure 38 Power Saving
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 23 Power Saving
LABEL DESCRIPTION
WLAN Status Select On or Off to specify whether the Wireless LAN is turned on or off (depending on
what you selected in the WLAN Status field). This field works in conjunction with the
Day and Except for the following times fields.
Day Select Everyday or the specific days to turn the Wireless LAN on or off.
If you select Everyday you can not select any specific days. This field works in
conjunction with the Except for the following times field.
For the following
times (24-Hour
Format)
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Router.
Reset Click Reset to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Select a begin time using the first set of hour and minute (min) drop down boxes and
select an end time using the second set of hour and minute (min) drop down boxes. If
you have chosen On earlier for the WLAN Status the Wireless LAN will turn on between
the two times you enter in these fields. If you have chosen Off earlier for the WLAN
Status the Wireless LAN will turn off between the two times you enter in these fields.
In this time format, midnight is 00:00 and progresses up to 24:00. For example, 6:00 PM
is 18:00.
58
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 59

8.6.3 Content Filter
Use this screen to restrict access to certain websites, based on keywords contained in URLs, to
which you do not want users in your network to open.
Figure 39 Content Filter
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 24 Content Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Add Click Add after you have typed a keyword.
Chapter 8 Easy Mode
Repeat this procedure to add other keywords. Up to 64 keywords are allowed.
Note: The Router does not recognize wildcard characters as keywords.
When you try to access a web page containing a keyword, you will get a message telling you
that the content filter is blocking this request.
Delete Highlight a keyword in the text box and click Delete to remove it. The keyword disappears
from the text box after you click Apply.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to close this screen without saving any changes.
8.6.4 Bandwidth MGMT
Use this screen to set bandwidth allocation to pre-defined services and applications for bandwidth
allocation.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
59
Page 60

Chapter 8 Easy Mode
Use your mouse
to drag the items
according to how
you want to
prioritze them.
Left-click and
slide up or down.
The Router uses bandwidth management for incoming and outgoing traffic. Rank the services and
applications by dragging them accordingly from High to Low and click Apply . Click Cancel to close
the screen.
Figure 40 Bandwidth MGNT
8.6.5 Firewall
Enable this feature to protect the network from Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. The Router blocks
repetitive pings from the WAN that can otherwise cause systems to slow down or hang.
Figure 41 Firewall
Click OK to close this screen.
8.6.6 Wireless Security
Use this screen to configure security for your the Wireless LAN. You can enter the SSID and select
the wireless security mode in the following screen.
60
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 61

Chapter 8 Easy Mode
Note: You can enable the Wireless function of your Router by first turning on the switch in
the back panel.
Figure 42 Wireless Security
The following table describes the general wireless LAN labels in this screen.
Table 25 Wireless Security
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless
Network Name
(SSID)
Security mode Select WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK to add security on this wireless network. The wireless
Wireless
password
Verify password Type the password again to confirm.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Router.
Cancel Click Cancel to close this screen.
WPS Click this to configure the WPS screen.
(Service Set IDentity) The SSID identifies the Service Set with which a wireless station is
associated. Wireless stations associating to the access point (AP) must have the same SSID.
Enter a descriptive name (up to 32 keyboard characters) for the wireless LAN.
clients which want to associate to this network must have same wireless security settings as
this device. After you select to use a security, additional options appears in this screen.
Select No Security to allow any client to connect to this network without authentication.
This field appears when you choose wither WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK as the security mode.
Type a pre-shared key from 8 to 63 case-sensitive keyboard characters.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
You can transfer the wireless settings configured here (Wireless Security screen) to
another wireless device that supports WPS.
61
Page 62

Chapter 8 Easy Mode
8.6.7 WPS
Use this screen to add a wireless station to the network using WPS. Click WPS in the Wireless
Security to open the following screen.
Figure 43 Wireless Security: WPS
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 26 Wireless Security: WPS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless
Security
WPS Create a secure wireless network simply by pressing a button.
Click this to go back to the Wireless Security screen.
The Router scans for a WPS-enabled device within the range and performs wireless security
information synchronization.
Note: After you click the WPS button on this screen, you have to press a similar button in the
wireless station utility within 2 minutes. To add the second wireless station, you have
to press these buttons on both device and the wireless station again after the first 2
minutes.
Register Create a secure wireless network simply by entering a wireless client's PIN (Personal
Identification Number) in the Router’s interface and pushing this button.
Type the same PIN number generated in the wireless station’s utility. Then click Register to
associate to each other and perform the wireless security information synchronization.
Exit Click Exit to close this screen.
62
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 63

8.7 Status Screen in Easy Mode
In the Network Map screen, click Status to view read-only information about the Router.
Figure 44 Status Screen in Easy Mode
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 27 Status Screen in Easy Mode
ITEM DESCRIPTION
Name This is the name of the Router in the network. You can change this in the Maintenance >
General screen in Section 26.3 on page 181.
Time This is the current system date and time.
The date is in YYYY:MM:DD (Year-Month-Day) format. The time is in HH:MM:SS
(Hour:Minutes:Seconds) format.
WAN IP This is the IP address of the WAN port.
MAC Address This is the MAC address of the Router.
Firmware
Version
Wireless
Network Name
Security This shows the wireless security used by the Router.
This shows the firmware version of the Router.
The firmware version format shows the trunk version, model code and release number.
This shows the SSID of the wireless network. You can configure this in the Wireless Security
screen (Section 8.6.6 on page 60; Section 13.3.1.1 on page 104).
Chapter 8 Easy Mode
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
63
Page 64

9.1 Overview
Modem
Router
The Router is set to router mode by default. Routers are used to connect the local network to
another network (for example, the Internet). In the figure below, the Router connects the local
network (LAN1 ~ LAN4) to the Internet.
Figure 45 Router Network
CHAPTER 9
Router Mode
Note: The Status screen is shown after changing to the Expert mode of the Web
Configurator. It varies depending on the device mode of your Router.
9.2 What You Can Do
Use the Status screen (Section 9.3 on page 65) to view read-only information about your Router.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide 64
Page 65

9.3 Status Screen
Click to open the status screen.
Figure 46 Status Screen: Router Mode
Chapter 9 Router Mode
The following table describes the icons shown in the Status screen.
Table 28 Status Screen Icon Key: Router Mode
ICON DESCRIPTION
Click this icon to view copyright and a link for related product information.
Click this icon to go to Easy Mode. See Chapter 8 on page 53.
Click this to go to the Home page. See Chapter 6 on page 45.
Select a number of seconds or None from the drop-down list box to refresh all screen statistics
automatically at the end of every time interval or to not refresh the screen statistics.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
65
Page 66

Chapter 9 Router Mode
Table 28 Status Screen Icon Key: Router Mode (continued)
ICON DESCRIPTION
Click this button to refresh the status screen statistics.
Click this icon to see the Status page. The information in this screen depends on the device
mode you select.
Click this icon to see the Monitor navigation menu.
Click this icon to see the Configuration navigation menu.
Click this icon to see the Maintenance navigation menu.
The following table describes the labels shown in the Status screen.
Table 29 Status Screen: Router Mode
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Logout Click this at any time to exit the Web Configurator.
Device Information
Host Name This is the System Name you enter in the Maintenance > General screen. It is for
Firmware Version This is the firmware version and the date created.
Sys OP Mode This is the device mode (Section 7.1.2 on page 51) to which the Router is set - Router
WAN Information
- MAC Address This shows the WAN Ethernet adapter MAC Address of your device.
- IP Address This shows the WAN port’s IP address.
- IP Subnet Mask This shows the WAN port’s subnet mask.
- Default Gateway This shows the WAN port’s gateway IP address.
- DHCP This shows the LAN port’s DHCP role - Client or Server.
LAN Information
- MAC Address This shows the LAN Ethernet adapter MAC Address of your device.
- IP Address This shows the LAN port’s IP address.
- IP Subnet Mask This shows the LAN port’s subnet mask.
- DHCP This shows the LAN port’s DHCP role - Server or None.
WLAN Information
- WLAN OP Mode This is the device mode (Section 7.1.2 on page 51) to which the Router’s wireless LAN is set
- MAC Address This shows the wireless adapter MAC Address of your device.
- Status This shows the current status of the Wireless LAN - ON or OFF.
- Name (SSID) This shows a descriptive name used to identify the Router in the wireless LAN.
- Channel This shows the channel number which you select manually.
- Operating Channel This shows the channel number which the Router is currently using over the wireless LAN.
- Security Mode This shows the level of wireless security the Router is using.
- 802.11 Mode This shows the wireless standard.
identification purposes.
Mode.
- Access Point Mode.
66
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 67

Chapter 9 Router Mode
Table 29 Status Screen: Router Mode (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
- WPS This displays Configured when the WPS has been set up.
This displays Unconfigured if the WPS has not been set up.
Click the status to display Network > Wireless LAN > WPS screen.
System Status
Item This column shows the type of data the Router is recording.
Data This column shows the actual data recorded by the Router.
System Up Time This is the total time the Router has been on.
Current Date/Time This field displays your Router’s present date and time.
System Resource
- CPU Usage This displays what percentage of the Router’s processing ability is currently used. When this
percentage is close to 100%, the Router is running at full load, and the throughput is not
going to improve anymore. If you want some applications to have more throughput, you
should turn off other applications (for example, using bandwidth management.)
- Memory Usage This shows what percentage of the heap memory the Router is using.
System Setting
- Firewall This shows whether the firewall is enabled or not.
- Bandwidth
Management
- UPnP This shows whether UPnP is enabled or not.
- Configuration Mode This shows the web configurator mode you are viewing - Expert.
Interface Status
Interface This displays the Router port types. The port types are: WAN, LAN and WLAN.
Status For the LAN and WAN ports, this field displays Down (line is down) or Up (line is up or
This shows whether the bandwidth management is enabled or not.
connected).
For the WLAN, it displays Up when the WLAN is enabled or Down when the WLAN is
disabled.
Rate For the LAN ports, this displays the port speed and duplex setting or N/A when the line is
disconnected.
For the WAN port, it displays the port speed and duplex setting if you’re using Ethernet
encapsulation and Idle (line (ppp) idle), Dial (starting to trigger a call) and Drop (dropping
a call) if you're using PPPoE or PPTP encapsulation. This field displays N/A when the line is
disconnected.
For the WLAN, it displays the maximum transmission rate when the WLAN is enabled and N/
A when the WLAN is disabled.
Summary
BW MGMT Monitor Click Details... to go to the Monitor > BW MGMT Monitor screen (Section 6.4 on page
47). Use this screen to view the amount of network bandwidth that applications running in
the network are using.
DHCP Table Click Details... to go to the Monitor > DHCP Table screen (Section 6.5 on page 47
this screen to view current DHCP client information.
Packet Statistics Click Details... to go to the Monitor > Packet Statistics screen (Section 6.6 on page 48).
Use this screen to view port status and packet specific statistics.
WLAN Station Status Click Details... to go to the Monitor > WLAN Station Status screen (Section 6.7 on page
49). Use this screen to view the wireless stations that are currently associated to the Router.
). Use
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
67
Page 68

Chapter 9 Router Mode
9.3.1 Navigation Panel
Use the sub-menus on the navigation panel to configure Router features.
Figure 47 Navigation Panel: Router Mode
The following table describes the sub-menus.
Table 30 Navigation Panel: Router Mode
LINK TAB FUNCTION
Status This screen shows the Router’s general device, system and interface status
MONITOR
Log Use this screen to view the list of activities recorded by your Router.
BW MGMT Use this screen to view the amount of network bandwidth that applications
DHCP Table Use this screen to view current DHCP client information.
Packet Statistics Use this screen to view port status and packet specific statistics.
WLAN Station
Status
CONFIGURATION
Network
information. Use this screen to access the wizard, and summary statistics
tables.
running in the network are using.
Use this screen to view the wireless stations that are currently associated
to the Router.
68
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 69

Chapter 9 Router Mode
Table 30 Navigation Panel: Router Mode (continued)
LINK TAB FUNCTION
Wireless LAN General Use this screen to configure wireless LAN.
MAC Filter Use the MAC filter screen to configure the Router to block access to devices
or block the devices from accessing the Router.
Advanced This screen allows you to configure advanced wireless settings.
QoS Use this screen to configure Wi-Fi Multimedia Quality of Service (WMM
QoS). WMM QoS allows you to prioritize wireless traffic according to the
delivery requirements of individual services.
WPS Use this screen to configure WPS.
WPS Station Use this screen to add a wireless station using WPS.
Scheduling Use this screen to schedule the times the Wireless LAN is enabled.
WDS Use this screen to set up Wireless Distribution System (WDS) on your
Router.
WAN Internet
Connection
Advanced Use this screen to configure other advanced properties.
IGMP
Snooping
LAN IP Use this screen to configure LAN IP address and subnet mask.
IP Alias Use this screen to have the Router apply IP alias to create LAN subnets.
DHCP Server General Use this screen to enable the Router’s DHCP server.
Advanced Use this screen to assign IP addresses to specific individual computers
NAT General Use this screen to enable NAT.
Application Use this screen to configure servers behind the Router.
Advanced Use this screen to change your Router’s port triggering settings.
DDNS General Use this screen to set up dynamic DNS.
Static Route IP Static
Route
RIP Use this screen to enable RIPv1 or RIPv2, which are LAN broadcast
Security
Firewall General Use this screen to activate/deactivate the firewall.
Services This screen shows a summary of the firewall rules, and allows you to edit/
Content Filter Use this screen to block certain web features and sites containing certain
Management
Bandwidth
Management
Remote
Management
UPnP General Use this screen to enable UPnP on the Router.
General Use this screen to enable bandwidth management.
Advanced Use this screen to set the upstream bandwidth and edit a bandwidth
Monitor Use this screen to view the amount of network bandwidth that applications
WWW Use this screen to be able to access the Router from the LAN, WAN or both.
This screen allows you to configure ISP parameters, WAN IP address
assignment, DNS servers and the WAN MAC address.
Use this screen to enable IGMP snooping if you have LAN users that
subscribe to multicast services.
based on their MAC addresses and to have DNS servers assigned by the
DHCP server.
Use this screen to configure IP static routes.
protocols.
add a firewall rule.
keywords in the URL.
management rule.
running in the network are using.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
69
Page 70

Chapter 9 Router Mode
Table 30 Navigation Panel: Router Mode (continued)
LINK TAB FUNCTION
MAINTENANCE
General Use this screen to view and change administrative settings such as system
Password Password
Time Time Setting Use this screen to change your Router’s time and date.
Remote
Management
Firmware
Upgrade
Backup/
Restore
Reset/
Restart
Sys OP Mode This screen allows you to select whether your device acts as a Router or a
and domain names.
Use this screen to change the password of your Router.
Setup
WWW Use this screen to configure through which interface(s) and from which IP
address(es) users can use HTTP to manage the Router.
Use this screen to upload firmware to your Router.
Use this screen to backup and restore the configuration or reset the factory
defaults to your Router.
Restart This screen allows you to reboot the Router without turning the power off.
Access Point.
70
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 71

10.1 Overview
Router
Use your Router as an access point (AP) if you already have a router or gateway on your network.
In this mode your Router bridges a wired network (LAN) and wireless LAN (WLAN) in the same
subnet. See the figure below for an example.
Figure 48 Wireless Internet Access in Access Point Mode
CHAPTER 10
Access Point Mode
Many screens that are available in Router mode are not available in Access Point mode, such as
bandwidth management and firewall.
Note: See Chapter 12 on page 89 for an example of setting up a wireless network in
Access Point mode.
10.2 What You Can Do
•Use the Status screen (Section 10.4 on page 74) to view read-only information about your
Router.
•Use the LAN screen (Section 10.5 on page 76) to set the IP address for your Router acting as an
access point.
10.3 What You Need to Know
See Chapter 12 on page 89 for a tutorial on setting up a network with the Router as an access
point.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide 71
Page 72

Chapter 10 Access Point Mode
10.3.1 Setting your Router to AP Mode
1 Log into the Web Configurator if you haven’t already. See the Quick start Guide for instructions on
how to do this.
2 To use your Router as an access point, go to Maintenance > Sys OP Mode > General and select
Access Point mode.
Figure 49 Changing to Access Point mode
Note: You have to log in to the Web Configurator again when you change modes. As soon
as you do, your Router is already in Access Point mode.
3 When you select Access Point Mode, the following pop-up message window appears.
Figure 50 Pop up for Access Point mode
Click OK. The Web Configurator refreshes once the change to Access Point mode is successful.
10.3.2 Accessing the Web Configurator in Access Point Mode
Log in to the Web Configurator in Access Point mode, do the following:
1 Connect your computer to the LAN port of the Router.
2 The default IP address of the Router is “192.168.1.2”. In this case, your computer must have an IP
address in the range between “192.168.1.3” and “192.168.1.254”.
3 Click Start > Run on your computer in Windows. Type “cmd” in the dialog box. Enter “ipconfig” to
show your computer’s IP address. If your computer’s IP address is not in the correct range then see
Appendix C on page 221 for information on changing your computer’s IP address.
72
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 73

Chapter 10 Access Point Mode
4 After you’ve set your computer’s IP address, open a web browser such as Internet Explorer and
type “192.168.1.2” as the web address in your web browser.
Note: After clicking Login, the Easy mode appears. Refer to page 53 for the Easy mode
screens. Change to Expert mode to see the screens described in the sections
following this.
10.3.3 Configuring your WLAN, Bandwidth Management and Maintenance
Settings
The configuration of wireless, bandwidth management and maintenance settings in Access Point
mode is the same as for Router Mode.
•See Chapter 13 on page 103 for information on the configuring your wireless network.
•See Chapter 23 on page 163 for information on configuring your Bandwidth Management screen.
•See Chapter 26 on page 181 to Chapter 26 on page 181 for information on configuring your
Maintenance settings.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
73
Page 74

Chapter 10 Access Point Mode
10.4 AP Mode Status Screen
Click to open the Status screen.
Figure 51 Status Screen: Access Point Mode
The following table describes the labels shown in the Status screen.
Table 31 Status Screen: Access Point Mode
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Logout Click this at any time to exit the Web Configurator.
Device Information
Host Name This is the System Name you enter in the Maintenance > General screen. It is for
identification purposes.
Firmware Version This is the firmware version and the date created.
Sys OP Mode This is the device mode (Section 7.1.2 on page 51) to which the Router is set - Access
Point Mode.
LAN Information
- MAC Address This shows the LAN Ethernet adapter MAC Address of your device.
- IP Address This shows the LAN port’s IP address.
- IP Subnet Mask This shows the LAN port’s subnet mask.
- DHCP This shows the LAN port’s DHCP role - Server, Client or None.
WLAN Information
74
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 75

Chapter 10 Access Point Mode
Table 31 Status Screen: Access Point Mode (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
- WLAN OP Mode This is the device mode (Section 7.1.2 on page 51) to which the Router’s wireless LAN is set
- Access Point Mode.
- MAC Address This shows the wireless adapter MAC Address of your device.
- Status This shows the current status of the Wireless LAN - ON or OFF.
- Name (SSID) This shows a descriptive name used to identify the Router in the wireless LAN.
- Channel This shows the channel number which you select manually.
- Operating Channel This shows the channel number which the Router is currently using over the wireless LAN.
- Security Mode This shows the level of wireless security the Router is using.
- 802.11 Mode This shows the wireless standard.
- WPS This displays Configured when the WPS has been set up.
This displays Unconfigured if the WPS has not been set up.
Click the status to display Network > Wireless LAN > WPS screen.
System Status
Item This column shows the type of data the Router is recording.
Data This column shows the actual data recorded by the Router.
System Up Time This is the total time the Router has been on.
Current Date/Time This field displays your Router’s present date and time.
System Resource
- CPU Usage This displays what percentage of the Router’s processing ability is currently used. When this
percentage is close to 100%, the Router is running at full load, and the throughput is not
going to improve anymore. If you want some applications to have more throughput, you
should turn off other applications (for example, using bandwidth management.
- Memory Usage This shows what percentage of the heap memory the Router is using.
System Setting
- Configuration Mode This shows the web configurator mode you are viewing - Expert.
Interface Status
Interface This displays the Router port types. The port types are: LAN and WLAN.
Status For the LAN and WAN ports, this field displays Down (line is down) or Up (line is up or
connected).
For the WLAN, it displays Up when the WLAN is enabled or Down when the WLAN is
disabled.
Rate For the LAN ports, this displays the port speed and duplex setting or N/A when the line is
disconnected.
For the WAN port, it displays the port speed and duplex setting if you’re using Ethernet
encapsulation and Idle (line (ppp) idle), Dial (starting to trigger a call) and Drop (dropping
a call) if you're using PPPoE or PPTP encapsulation. This field displays N/A when the line is
disconnected.
For the WLAN, it displays the maximum transmission rate when the WLAN is enabled and N/
A when the WLAN is disabled.
Summary
Packet Statistics Click Details... to go to the Monitor > Packet Statistics screen (Section 6.6 on page 48
Use this screen to view port status and packet specific statistics.
WLAN Station Status Click Details... to go to the Monitor > WLAN Station Status screen (Section 6.7 on page
49). Use this screen to view the wireless stations that are currently associated to the Router.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
).
75
Page 76

Chapter 10 Access Point Mode
10.4.0.1 Navigation Panel
Use the menu in the navigation panel to configure Router features in Access Point mode.
The following screen and table show the features you can configure in Access Point mode.
Figure 52 Menu: Access Point Mode
Refer to Table 30 on page 68 for descriptions of the labels shown in the Navigation panel.
10.5 LAN Screen
Use this section to configure your LAN settings while in Access Point mode.
Click Network > LAN to see the screen below.
Note: If you change the IP address of the Router in the screen below, you will need to log
into the Router again using the new IP address.
Figure 53 Network > LAN > IP
76
The table below describes the labels in the screen.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 77

Chapter 10 Access Point Mode
Table 32 Network > LAN > IP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Get from DHCP
Server
Use Defined
LAN IP Address
IP Address Type the IP address in dotted decimal notation. The default setting is 192.168.1.2. If you
IP Subnet Mask The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. Your Router will
Gateway IP
Address
DNS Assignment
First DNS
Server
Second DNS
Server
Click this to deploy the Router as an access point in the network.
When you enable this, the Router gets its IP address from the network’s DHCP server (for
example, your ISP). Users connected to the Router can now access the network (i.e., the
Internet if the IP address is given by the ISP).
The Web Configurator may no longer be accessible unless you know the IP address assigned
by the DHCP server to the Router. You need to reset the Router to be able to access the Web
Configurator again (see Section 26.7 on page 186 for details on how to reset the Router).
Also when you select this, you cannot enter an IP address for your Router in the field below.
Click this if you want to specify the IP address of your Router. Or if your ISP or network
administrator gave you a static IP address to access the network or the Internet.
change the IP address you will have to log in again with the new IP address.
automatically calculate the subnet mask based on the IP address that you assign. Unless
you are implementing subnetting, use the subnet mask computed by the Router.
Enter a Gateway IP Address (if your ISP or network administrator gave you one) in this
field.
Select From ISP if your ISP dynamically assigns DNS server information (and the Router's
WAN IP address). The field to the right displays the (read-only) DNS server IP address that
the ISP assigns.
Select User-Defined if you have the IP address of a DNS server. Enter the DNS server's IP
address in the field to the right. If you chose User-Defined, but leave the IP address set to
0.0.0.0, User-Defined changes to None after you click Apply. If you set a second choice to
User-Defined, and enter the same IP address, the second User-Defined changes to None
after you click Apply.
Select None if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do not configure a DNS
server, you must know the IP address of a computer in order to access it.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes to the Router.
Reset Click Reset to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
77
Page 78

11.1 Overview
built-in
firewall
Access
Point
WISP
Your Router can act as a wireless client. In wireless client mode, it can connect to an existing
network via an access point. Use this mode if you already have an access point or router in your
network.
In the example below, one Router (A) is configured as a wireless client and another is used as an
access point (B). The wireless client has two clients that need to connect to the Internet. The
Router wirelessly connects to the available access point (B).
Figure 54 Wireless Client Mode
CHAPTER 11
WISP Mode
After the Router and the access point connect, the Router acquires its WAN IP address from the
access point. The clients of the Router can now surf the Internet.
11.2 What You Can Do
•Use the Status screen (Section 11.4 on page 80) to view read-only information about your
Router.
•Use the LAN screen (Chapter 15 on page 133) to set the IP address for your Router acting as an
access point.
•Use the Wireless LAN screen (Section 11.5 on page 82) to associate your Router (acting as a
wireless client) with an existing access point.
11.3 What You Need to Know
With the exception of the LAN screen, the Monitor, Configuration and Maintainance screens in
WISP mode are similar to the ones in Router Mode. See Chapter 13 on page 103 through Chapter
26 on page 189 of this User’s Guide.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide 78
Page 79

11.3.1 Setting your Router to WISP Mode
1 Log into the Web Configurator if you haven’t already. See the Quick start Guide for instructions on
how to do this.
2 To set your Router to AP Mode, go to Maintenance > Sys OP Mode > General and select WISP
Mode.
Figure 55 Changing to WISP mode
Chapter 11 WISP Mode
Note: You have to log in to the Web Configurator again when you change modes.As soon
as you do, your Router is already in WISP mode.
3 When you select WISP Mode, the following pop-up message window appears.
Figure 56 Pop up window for WISP mode
Click OK. The Web Configurator refreshes once the change to WISP mode is successful.
11.3.2 Accessing the Web Configurator in WISP Mode
To login to Web Configurator in WISP mode, do the following:
1 Connect your computer to the LAN port of the Router.
2 The default IP address of the Router is “192.168.1.1”. If you did not change this, you can use the
same IP address in WISP mode. Open a web browser such as Internet Explorer and type
“192.168.1.1” as the web address in your web browser.
If you changed the IP address of your Router while in Router Mode, use this IP address in WISP
mode. The WISP mode IP address is always the same as the Router mode IP adderss.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
79
Page 80

Chapter 11 WISP Mode
Note: After clicking Login, the Easy mode appears. Refer to Section on page 53 for the
Easy mode screens. Click Expert mode to see the screens described in the sections
following this.
11.4 WISP Mode Status Screen
Click to open the status screen.
Figure 57 Status: WISP Mode
The following table describes the labels shown in the Status screen.
Table 33 Status Screen: WISP Mode
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Logout Click this at any time to exit the Web Configurator.
Device Information
Host Name This is the System Name you enter in the Maintenance > General screen. It is for
identification purposes.
Firmware Version This is the firmware version and the date created.
Sys OP Mode This is the device mode (Section 7.1.2 on page 51) to which the Router is set - WISP Mode.
WAN Information
80
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 81

Chapter 11 WISP Mode
Table 33 Status Screen: WISP Mode (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
- MAC Address This shows the WAN Ethernet adapter MAC Address of your device.
- IP Address This shows the WAN port’s IP address.
- IP Subnet Mask This shows the WAN port’s subnet mask.
- Default Gateway This shows the WAN port’s gateway IP address.
- DHCP This shows the LAN port’s DHCP role - Client or Server.
LAN Information
- MAC Address This shows the LAN Ethernet adapter MAC Address of your device.
- IP Address This shows the LAN port’s IP address.
- IP Subnet Mask This shows the LAN port’s subnet mask.
- DHCP This shows the LAN port’s DHCP role - Server or None.
WLAN Information
- WLAN OP Mode This is the device mode (Section 7.1.2 on page 51) to which the Router’s wireless LAN is set
- Access Point Mode.
- MAC Address This shows the wireless adapter MAC Address of your device.
- Status This shows the current status of the Wireless LAN - ON or OFF.
- Name (SSID) This shows a descriptive name used to identify the Router in the wireless LAN.
- Connect Status This shows whether or not the Router has successfully associated with an access point Connected or Disassociated.
- Security Mode This shows the level of wireless security the Router is using.
- 802.11 Mode This shows the wireless standard.
System Status
Item This column shows the type of data the Router is recording.
Data This column shows the actual data recorded by the Router.
System Up Time This is the total time the Router has been on.
Current Date/Time This field displays your Router’s present date and time.
System Resource
- CPU Usage This displays what percentage of the Router’s processing ability is currently used. When this
percentage is close to 100%, the Router is running at full load, and the throughput is not
going to improve anymore. If you want some applications to have more throughput, you
should turn off other applications (for example, using bandwidth management.
- Memory Usage This shows what percentage of the heap memory the Router is using.
System Setting
- Firewall This shows whether the firewall is enabled or not.
- Bandwidth
Management
- UPnP This shows whether UPnP is enabled or not.
- Configuration Mode This shows the web configurator mode you are viewing - Expert.
Interface Status
Interface This displays the Router port types. The port types are: LAN and WLAN.
Status For the LAN and WAN ports, this field displays Down (line is down) or Up (line is up or
This shows whether the bandwidth management is enabled or not.
connected).
For the WLAN, it displays Up when the WLAN is enabled or Down when the WLAN is
disabled.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
81
Page 82

Chapter 11 WISP Mode
Table 33 Status Screen: WISP Mode (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Rate For the LAN ports, this displays the port speed and duplex setting or N/A when the line is
disconnected.
For the WAN port, it displays the port speed and duplex setting if you’re using Ethernet
encapsulation and Idle (line (ppp) idle), Dial (starting to trigger a call) and Drop (dropping
a call) if you're using PPPoE or PPTP encapsulation. This field displays N/A when the line is
disconnected.
For the WLAN, it displays the maximum transmission rate when the WLAN is enabled and N/
A when the WLAN is disabled.
Summary
BW MGMT Monitor Click Details... to go to the Monitor > BW MGMT Monitor screen (Section 6.4 on page
47). Use this screen to view the amount of network bandwidth that applications running in
the network are using.
DHCP Table Click Details... to go to the Monitor > DHCP Table screen (Section 6.5 on page 47). Use
Packet Statistics Click Details... to go to the Monitor > Packet Statistics screen (Section 6.6 on page 48).
this screen to view current DHCP client information.
Use this screen to view port status and packet specific statistics.
11.5 Wireless LAN General Screen
Use this screen to configure the wireless LAN settings of your Router. Go to Configuration >
Wireless LAN > General to open the following screen.
Figure 58 WISP Mode: LAN > General Screen
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 34 WISP Mode: LAN > General Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless Setup
Network Name
(SSID)
Security
Security Mode Select the security mode of the access point to which you want to connect.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Router.
Reset Click Reset to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Enter the name of the access point to which you are connecting.
82
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 83

11 .5.0.1 No Security
Use this screen if the access point to which you want to connect does not use encryption.
Figure 59 No Security (WISP)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 35 No Security (WISP)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless Setup
Network Name
(SSID)
Security
Security Mode Select No Security in this field.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Router.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Chapter 11 WISP Mode
Enter the name of the access point to which you are connecting.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
83
Page 84

Chapter 11 WISP Mode
11.5.1 Static WEP
Use this screen if the access point to which you want to connect to uses WEP security mode.
Figure 60 WEP (WISP)
The following table describes the labels in this screen..
Table 36 WEP (WISP)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless Setup
Network Name
(SSID)
Security
Security Mode Select Static WEP to enable data encryption.
PassPhrase Enter a Passphrase (up to 26 printable characters) and click Generate.
WEP Encryption Select 64-bit WEP or 128-bit WEP.
Authentication
Method
ASCII Select this option in order to enter ASCII characters as WEP key.
Enter the name of the access point to which you are connecting.
A passphrase functions like a password. In WEP security mode, it is further converted by
the Router into a complicated string that is referred to as the “key”. This key is requested
from all devices wishing to connect to a wireless network.
This dictates the length of the security key that the network is going to use.
Select Auto or Shared Key from the drop-down list box.
This field specifies whether the wireless clients have to provide the WEP key to login to the
wireless client. Keep this setting at Auto unless you want to force a key verification before
communication between the wireless client and the Router occurs.
Select Shared Key to force the clients to provide the WEP key prior to communication.
84
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 85

Table 36 WEP (WISP) (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Hex Select this option in order to enter hexadecimal characters as a WEP key.
Key 1 to Key 4 The WEP keys are used to encrypt data. Both the Router and the wireless stations must
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Router.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
11.5.2 WPA(2)-PSK
Use this screen if the access point to which you want to connect uses WPA(2)-PSK security mode.
Chapter 11 WISP Mode
The preceding "0x", that identifies a hexadecimal key, is entered automatically.
use the same WEP key for data transmission.
If you chose 64-bit WEP , then enter any 5 ASCII characters or 10 hexadecimal characters
("0-9", "A-F").
If you chose 128-bit WEP, then enter 13 ASCII characters or 26 hexadecimal characters
("0-9", "A-F").
You must configure at least one key, only one key can be activated at any one time. The
default key is key 1.
Figure 61 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK (WISP)
The following table describes the labels in this screen. .
Table 37 WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK (WISP)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Wireless Setup
Network Name
(SSID)
Security
Encryption Type Select the type of wireless encryption employed by the access point to which you want to
Pre-Shared Key WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK uses a simple common password for authentication.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Router.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Enter the name of the access point to which you are connecting.
connect.
Type the pre-shared key employed by the access point to which you want to connect.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
85
Page 86

Chapter 11 WISP Mode
11.5.3 Advance Screen
Use this screen to enable the power saving mode of your Router. Go to Configuration > Wireless
LAN to open the following screen.
Figure 62 Configuration > Wireless LAN > Advance Screen (WISP)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 38 Configuration > Wireless LAN > Advance Screen (WISP)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Power Saving
Mode
RTS Threshold This is the maximum data fragment size that can be sent in a wireless network before the
Fragment
Threshold
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the Router.
Cancel Click Cancel to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Select CAM (Constantly Awake Mode) if you do not want your Router to go to “sleep”
when no wireless activity is detected in the Wireless LAN.
Select Power Saving Mode if you want the Router to go to sleep when no wireless
connection is needed for a period of time. This means the Router consumes less electrical
power.
AP fragments the packet into smaller data frames.
This value controls how often wireless clients must get permission to send information to
the AP. The lower the value, the more often the wireless clients must get permission. If this
value is greater than the fragmentation threshold value, then wireless clients never have to
get permission to send information to the AP.
86
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 87

11.5.4 Site Survey Screen
Use this screen to scan for and connect to a wireless network automatically. Go to Configuration >
Site Survey to open the following screen.
Figure 63 Configuration > Wireless LAN > Site Survey (WISP)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Chapter 11 WISP Mode
Table 39 Configuration > Wireless LAN > Site Survey (WISP)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Station Site Survey
# Select a wireless device and click Add Profile to open a configuration screen where you
can add the selected wireless device to a profile and then enable it.
SSID This displays the SSID of the wireless device.
indicates the wireless device is added to an activated profile and the Router is
connecting to it.
BSSID This displays the MAC address of the wireless device.
Signal Strength This displays the strength of the wireless signal. The signal strength mainly depends on the
antenna output power and the distance between your Router and this device.
Channel This displays the channel number used by this wireless device.
station encryp This displays the data encryption method used by this wireless device.
station auth This displays the authentication method used by this wireless device.
Network Type This displays the network type (In (Infrastructure) or Ad (Ad Hoc) of this wireless device.
Rescan Click this button to search for available wireless devices within transmission range and
Setting Select a wireless device and click this button to add it to a profile.
update this table.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
87
Page 88

Chapter 11 WISP Mode
88
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 89

CHAPTER 12
Tutorials
12.1 Overview
This chapter provides tutorials for your Router as follows:
• Connecting to the Internet from an Access Point
• Configuring Wireless Security Using WPS
• Enabling and Configuring Wireless Security (No WPS)
• Connecting to USB Storage with the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility
• Automatically Connecting to a USB Printer
12.2 Connecting to the Internet from an Access Point
This section gives you an example of how to set up an access point (AP) and wireless client (a
notebook (B), in this example) for wireless communication. B can access the Internet through the
access point wirelessly.
Figure 64 Wireless Access Point Connection to the Internet
12.3 Configuring Wireless Security Using WPS
This section gives you an example of how to set up wireless network using WPS. This example uses
the Router as the AP and NWD210N as the wireless client which connects to a notebook.
Note: The wireless client must be a WPS-aware device (for example, a WPS USB adapter
or PCI card).
There are two WPS methods for creating a secure connection. This tutorial shows you how to do
both.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide 89
Page 90

Chapter 12 Tutorials
• Push Button Configuration (PBC) - create a secure wireless network simply by pressing a
button. See Section 12.3.1 on page 90.This is the easier method.
• PIN Configuration - create a secure wireless network simply by entering a wireless client's PIN
(Personal Identification Number) in the Router’s interface. See Section 12.3.2 on page 91. This is
the more secure method, since one device can authenticate the other.
12.3.1 Push Button Configuration (PBC)
1 Make sure that your Router is turned on and that it is within range of your computer.
2 Make sure that you have installed the wireless client (this example uses the NWD210N) driver and
utility in your notebook.
3 In the wireless client utility, find the WPS settings. Enable WPS and press the WPS button (Start or
WPS button)
4 Log into Router’s Web Configurator and press the Push Button button in the Network > Wireless
Client > WPS Station screen.
Note: Your Router has a WPS button located on its panel, as well as a WPS button in its
configuration utility. Both buttons have exactly the same function; you can use one
or the other.
Note: It doesn’t matter which button is pressed first. You must press the second button
within two minutes of pressing the first one.
The Router sends the proper configuration settings to the wireless client. This may take up to two
minutes. Then the wireless client is able to communicate with the Router securely.
90
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 91

Chapter 12 Tutorials
Wireless Client
NBG-419N v2
SECURITY INFO
COMMUNICATION
WITHIN 2 MINUTES
The following figure shows you an example to set up wireless network and security by pressing a
button on both Router and wireless client (the NWD210N in this example).
Figure 65 Example WPS Process: PBC Method
12.3.2 PIN Configuration
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
When you use the PIN configuration method, you need to use both Router’s configuration interface
and the client’s utilities.
1 Launch your wireless client’s configuration utility. Go to the WPS settings and select the PIN method
to get a PIN number.
2 Enter the PIN number to the PIN field in the Network > Wireless LAN > WPS Station screen on
the Router.
3 Click Start buttons (or button next to the PIN field) on both the wireless client utility screen and the
Router’s WPS Station screen within two minutes.
The Router authenticates the wireless client and sends the proper configuration settings to the
wireless client. This may take up to two minutes. Then the wireless client is able to communicate
with the Router securely.
91
Page 92

Chapter 12 Tutorials
Authentication by PIN
SECURITY INFO
WITHIN 2 MINUTES
Wireless Client
NBG-419N v2
COMMUNICATION
The following figure shows you the example to set up wireless network and security on Router and
wireless client (ex. NWD210N in this example) by using PIN method.
Figure 66 Example WPS Process: PIN Method
92
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 93

Chapter 12 Tutorials
12.4 Enabling and Configuring Wireless Security (No WPS)
This example shows you how to configure wireless security settings with the following parameters
on your Router.
SSID SSID_Example3
Channel 6
Security WPA-PSK
(Pre-Shared Key: ThisismyWPA-PSKpre-sharedkey)
Follow the steps below to configure the wireless settings on your Router.
The instructions require that your hardware is connected (see the Quick Start Guide) and you are
logged into the Web Configurator through your LAN connection (see Section 5.2 on page 39).
1 Open the Wireless LAN > General screen in the AP’s Web Configurator.
2 Make sure the Enable Wireless LAN check box is selected.
3 Enter SSID_Example3 as the SSID and select a channel.
4 Set security mode to WPA-PSK and enter ThisismyWPA-PSKpre-sharedkey in the Pre-Shared
Key field. Click Apply.
Figure 67 Tutorial: Network > Wireless LAN > General
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
93
Page 94

Chapter 12 Tutorials
5 Open the Status screen. Verify your wireless and wireless security settings under Device
Information and check if the WLAN connection is up under Interface Status.
Figure 68 Tutorial: Checking Wireless Settings
12.4.1 Configure Your Notebook
Note: We use the ZyXEL M-302 wireless adapter utility screens as an example for the
wireless client. The screens may vary for different models.
1 The Router supports IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g and IEEE 802.11n wireless clients. Make sure that
your notebook or computer’s wireless adapter supports one of these standards.
2 Wireless adapters come with software sometimes called a “utility” that you install on your
computer. See your wireless adapter’s User’s Guide for information on how to do that.
3 After you’ve installed the utility, open it. If you cannot see your utility’s icon on your screen, go to
Start > Programs and click on your utility in the list of programs that appears. The utility displays
a list of APs within range, as shown in the example screen below.
4 Select SSID_Example3 and click Connect.
Figure 69 Connecting a Wireless Client to a Wireless Network t
94
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 95

Chapter 12 Tutorials
5 Select WPA-PSK and type the security key in the following screen. Click Next.
Figure 70 Security Settings
6 The Confirm Save window appears. Check your settings and click Save to continue.
Figure 71 Confirm Save
7 Check the status of your wireless connection in the screen below. If your wireless connection is
weak or you have no connection, see the Troubleshooting section of this User’s Guide.
Figure 72 Link Status
If your connection is successful, open your Internet browser and enter http://www.zyxel.com or the
URL of any other web site in the address bar. If you are able to access the web site, your wireless
connection is successfully configured.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
95
Page 96

Chapter 12 Tutorials
12.5 Connecting to USB Storage with the ZyXEL NetUSB
Share Center Utility
This tutorial shows you how to connect to a USB device over your Router network by using the
ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility.
1 Install the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility on the computer to which you want to connect the
USB device. See Chapter 3 on page 21 for details on the installation.
2 Connect a USB device to one of the USB ports of the Router.
3 Open the ZyXEL NetUSB Sharing Center Utility on your computer. The name of the USB device
automatically shows in the Utility screen.
4 Click on the USB device’s name. Then click Connect.
5 The device mounts on your system.
12.5.1 Multiple Connections to the USB Device
The Utility supports one connection to the Router’s USB device at a time. If more than one
computer want to connect to the USB device, follow the steps below:
96
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 97

Chapter 12 Tutorials
1 After the first computer (A) finishes using the USB device, click Disconnect on the Utilty to
unmount it.
2 Click Connect on the Utility of the second computer (B) to mount the USB device on B.
3 If A does not disconnect from the USB device, B cannot use it. B can click the Request to Connect
button to request A to disconnect. B will see the following message on its Utility:
4 A will receive the following message on its Utility screen.
5 A should click Accept to disconnect to the USB device.
6 After A is disconnected from USB device, B will see the following message on its Utility. Now B can
access the USB device.
Note: If your computer is connected to a USB device, you must disconnect it and use Exit
to close the Utility. If you use the X on the Utility screen, it only closes the Utility
window. The Utility is still connected. Do not exit the Utility until the USB device is
disconnected via the Utility or until you receive a request to disconnect. See
Chapter 3 on page 21 for details on how to exit the Utility.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
97
Page 98

Chapter 12 Tutorials
12.6 Automatically Connecting to a USB Printer
Your computer can connect to a shared USB printer by using the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center
Utility. This tutorial shows you how to set your computer to automatically connect to a shared USB
printer over your Router network each time you log into your computer.
1 Install the ZyXEL NetUSB Share Center Utility to your computer. See Chapter 3 on page 21 for
details on the installation.
2 Connect a USB printer to one of the USB ports of the Router.
3 Open the ZyXEL NetUSB Sharing Center Utility on your computer. The name of the USB printer
automatically shows in the Utility screen.
4 Click on the printer name. Then click Connect. Your computer will search for the printer driver. You
may be prompted to install the driver. Follow the driver’s installation steps to finish installing.
5 Click the Auto-Connect Printer menu and select Set Auto-Connect Printer from the menu.
98
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
Page 99

Chapter 12 Tutorials
6 Select the USB printer you want to connect to and click Apply.
7 Now your computer can automatically connect to this shared USB printer over your Router network
each time you log into your computer. The printer will be automatically added to your printer list.
8 The Utility supports one connection to the Router’s USB device at a time. If more than one
computer is using the printer and are all auto-connected to the USB device, the second computer
automatically starts printing after the first computer finishes its printing task.
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
99
Page 100

Chapter 12 Tutorials
100
NBG-419N v2 User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...