Zyxel WAX640S-6E, WAX655E, WAX650S, WAC500H, WAX620D-6E User's Guide
...
Default Login Details
User’s Guide
NWA/WAC/WAX Series
802.11 a/b/g/n/ac/ax Access Point
Management IP
Address
User Name admin
Password 1234
http://DHCP-assigned IP
OR
http://192.168.1.2
Version 6.55 Edition 1, 04/2023
Copyright © 2023 Zyxel and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.

IMPORTANT!
READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE.
KEEP THIS GUIDE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
This is a User’s Guide for a series of products. Not all products support all firmware features. Screenshots
and graphics in this book may differ slightly from your product due to differences in your product
hardware, firmware, or your computer operating system. Every effort has been made to ensure that the
information in this manual is accurate.
Some screens or options in this book may not be available for your product (see the product feature
tables in Section 1.2 on page 13).
Related Documentation
•Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guide shows how to connect the Zyxel Device and access the Web Configurator.
•CLI Reference Guide
The CLI Reference Guide explains how to use the Command-Line Interface (CLI) and CLI commands
to configure the Zyxel Device.
Note: It is recommended you use the Web Configurator to configure the Zyxel Device.
• Web Configurator Online Help
Click the help icon in any screen for help in configuring that screen and supplementary information.
• Nebula Control Center User’s Guide
This User’s Guide shows how to manage the Zyxel Device remotely. The features of these devices can
be managed through Nebula Control Center. It also offers features that are not available when the
Zyxel Device is in standalone mode (see Section 2.1.2 on page 27).
• AC (AP Controller) User’s Guide
See the ZyWALL ATP, ZyWALL VPN, USG FLEX, or NXC User’s Guide for instructions on using the
gateways or NXC as an AP Controller (AC) for the Zyxel Device. This is used when the Zyxel Device is
set to be managed by a Zyxel AC.
•More Information
Go to support.zyxel.com to find other information on the Zyxel Device
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
.
2
Document Conventions
Document Conventions
Warnings and Notes
These are how warnings and notes are shown in this guide.
Warnings tell you about things that could harm you or your device.
Note: Notes tell you other important information (for example, other things you may need to
configure or helpful tips) or recommendations.
Syntax Conventions
• All models in this series may be referred to as the “Zyxel Device” in this guide.
• Product labels, screen names, field labels and field choices are all in bold font.
• A right angle bracket ( > ) within a screen name denotes a mouse click. For example, Configuration >
Network > IP Setting means you first click Configuration in the navigation panel, then the Network sub
menu and finally the IP Setting tab to get to that screen.
Icons Used in Figures
Figures in this guide may use the following generic icons. The Zyxel Device icon is not an exact
representation of your device.
Zyxel Device Router Switch Internet
Server Desktop Laptop IP Phone
Printer Smart T.V.
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
3

Contents Overview
Contents Overview
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................... 12
AP Management .................................................................................................................................. 26
Hardware ............................................................................................................................................... 36
Web Configurator ................................................................................................................................. 42
Standalone Configuration ................................................................................................................54
Standalone Configuration ................................................................................................................... 55
Dashboard ............................................................................................................................................ 57
Setup Wizard ......................................................................................................................................... 63
Monitor ................................................................................................................................................... 70
Network ................................................................................................................................................. 82
Wireless ................................................................................................................................................... 95
Bluetooth ............................................................................................................................................. 111
User ....................................................................................................................................................... 114
AP Profile .............................................................................................................................................. 121
WDS Profile ........................................................................................................................................... 165
Certificates .......................................................................................................................................... 167
System .................................................................................................................................................. 183
Log and Report ................................................................................................................................... 205
File Manager ....................................................................................................................................... 217
Diagnostics .......................................................................................................................................... 229
LEDs ...................................................................................................................................................... 232
Antenna Switch .................................................................................................................................. 235
Reboot ................................................................................................................................................. 237
Local Configuration in Cloud Mode ..............................................................................................238
Cloud Mode ........................................................................................................................................ 239
Network ............................................................................................................................................... 242
Maintenance ...................................................................................................................................... 245
Appendices and Troubleshooting .................................................................................................251
Troubleshooting .................................................................................................................................. 252
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
4

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Document Conventions ... .... .... ................................................... .... ....................................................3
Contents Overview .............................................................................................................................4
Table of Contents.................................................................................................................................5
Chapter 1
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................12
1.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 12
1.2 Zyxel Device Product Feature Comparison ................................................................................ 13
1.3 Zyxel Device Roles .......................................................................................................................... 18
1.3.1 Root AP ................................................................................................................................... 21
1.3.2 Wireless Repeater .................................................................................................................. 21
1.3.3 Radio Frequency (RF) Monitor .............................................................................................23
1.4 Sample Feature Applications ........................................................................................................ 23
1.4.1 MBSSID .................................................................................................................................... 23
1.4.2 Dual-Radio/Triple-Radio and BandFlex .............................................................................. 24
Chapter 2
AP Management................................................................................................................................26
2.1 Management Mode ...................................................................................................................... 26
2.1.1 Standalone ............................................................................................................................ 26
2.1.2 Nebula Control Center ......................................................................................................... 27
2.1.3 AP Controller (AC) ................................................................................................................ 28
2.2 Switching Management Modes ................................................................................................... 29
2.3 Zyxel One Network (ZON) Utility .................................................................................................... 30
2.3.1 Requirements ......................................................................................................................... 30
2.3.2 Run the ZON Utility ................................................................................................................. 30
2.4 Ways to Access the Zyxel Device ................................................................................................. 34
2.5 Good Habits for Managing the Zyxel Device ............................................................................. 35
Chapter 3
Hardware............................................................................................................................................36
3.1 Grounding (WAC6552D-S, WAC6553D-E and WAX655E) .......................................................... 36
3.2 Zyxel Device Models With Single LEDs .......................................................................................... 37
3.3 Zyxel Device LED ............................................................................................................................. 37
Chapter 4
Web Configurator...............................................................................................................................42
4.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 42
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
5

Table of Contents
4.2 Accessing the Web Configurator ................................................................................................. 42
4.3 Navigating the Web Configurator ............................................................................................... 45
4.3.1 Title Bar ................................................................................................................................... 46
4.3.2 Navigation Panel .................................................................................................................. 47
4.3.3 Standalone Mode Navigation Panel Menus ..................................................................... 48
4.3.4 Cloud Mode Navigation Panel Menus ............................................................................... 50
4.3.5 Tables and Lists ...................................................................................................................... 51
Part I: Standalone Configuration...................................................................54
Chapter 5
Standalone Configuration.................................................................................................................55
5.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 55
5.2 Starting and Stopping the Zyxel Device ...................................................................................... 55
Chapter 6
Dashboard..........................................................................................................................................57
6.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 57
6.1.1 CPU Usage ............................................................................................................................. 61
6.1.2 Memory Usage ...................................................................................................................... 62
Chapter 7
Setup Wizard.......................................................................................................................................63
7.1 Accessing the Wizard ..................................................................................................................... 63
7.2 Using the Wizard ............................................................................................................................. 63
7.2.1 Step 1 Time Settings .............................................................................................................. 63
7.2.2 Step 2 Password and Uplink Connection ........................................................................... 64
7.2.3 Step 3 SSID .............................................................................................................................. 65
7.2.4 Step 4 Radio .......................................................................................................................... 67
7.2.5 Summary ................................................................................................................................ 68
Chapter 8
Monitor................................................................................................................................................70
8.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 70
8.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ....................................................................................... 70
8.2 What You Need to Know ............................................................................................................... 70
8.3 Network Status ................................................................................................................................ 71
8.3.1 Port Statistics Graph .............................................................................................................. 72
8.4 Radio List .......................................................................................................................................... 73
8.4.1 AP Mode Radio Information ................................................................................................74
8.5 Station List ........................................................................................................................................ 76
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
6

Table of Contents
8.6 WDS Link Info ................................................................................................................................... 77
8.7 Detected Device ............................................................................................................................ 78
8.8 View Log .......................................................................................................................................... 80
Chapter 9
Network...............................................................................................................................................82
9.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................... 82
9.1.1 AP Controller Management ................................................................................................ 82
9.1.2 What You Can Do in this Chapter ....................................................................................... 84
9.2 IP Setting .......................................................................................................................................... 85
9.3 VLAN ................................................................................................................................................ 86
9.4 Storm Control .................................................................................................................................. 91
9.5 AC (AP Controller) Discovery ........................................................................................................ 92
9.6 NCC Discovery ................................................................................................................................ 93
Chapter 10
Wireless...............................................................................................................................................95
10.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 95
10.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ..................................................................................... 95
10.1.2 What You Need to Know ...................................................................................................96
10.2 AP Management .......................................................................................................................... 96
10.3 Rogue AP ..................................................................................................................................... 102
10.3.1 Add/Edit Rogue/Friendly List ............................................................................................105
10.4 Load Balancing .......................................................................................................................... 106
10.4.1 Disassociating and Delaying Connections .................................................................... 107
10.5 DCS ............................................................................................................................................... 108
10.6 Technical Reference .................................................................................................................. 109
Chapter 11
Bluetooth...........................................................................................................................................111
11.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 111
11.1.1 What You Need To Know ................................................................................................. 111
11.2 Bluetooth Advertising Settings ................................................................................................... 111
11.2.1 Edit Advertising Settings .................................................................................................... 112
Chapter 12
User....................................................................................................................................................114
12.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 114
12.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 114
12.1.2 What You Need To Know ................................................................................................. 114
12.2 User Summary .............................................................................................................................. 115
12.2.1 Add/Edit User ..................................................................................................................... 115
12.3 Setting .......................................................................................................................................... 117
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
7

Table of Contents
12.3.1 Edit User Authentication Timeout Settings ...................................................................... 119
Chapter 13
AP Profile...........................................................................................................................................121
13.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 121
13.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 121
13.1.2 What You Need To Know ................................................................................................. 121
13.2 Radio ............................................................................................................................................ 124
13.2.1 Add/Edit Radio Profile ...................................................................................................... 125
13.3 SSID ............................................................................................................................................... 132
13.3.1 SSID List ............................................................................................................................... 132
13.3.2 Add/Edit SSID Profile ......................................................................................................... 133
13.3.3 Setting Up General and Guest WiFi Networks on Both Radios .................................... 136
13.4 Security List .................................................................................................................................. 141
13.4.1 Add/Edit Security Profile ................................................................................................... 142
13.4.2 Creating a Security Profile ............................................................................................... 158
13.5 MAC Filter List .............................................................................................................................. 159
13.5.1 Add/Edit MAC Filter Profile ............................................................................................... 160
13.6 Layer-2 Isolation List .................................................................................................................... 161
13.6.1 Add/Edit Layer-2 Isolation Profile .................................................................................... 163
Chapter 14
WDS Profile........................................................................................................................................165
14.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 165
14.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 165
14.2 WDS Profile ................................................................................................................................... 165
14.2.1 Add/Edit WDS Profile ........................................................................................................ 166
Chapter 15
Certificates .......................................................................................................................................167
15.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 167
15.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 167
15.1.2 What You Need to Know ................................................................................................. 167
15.1.3 Verifying a Certificate ...................................................................................................... 169
15.2 My Certificates ............................................................................................................................ 170
15.2.1 Add My Certificates .......................................................................................................... 171
15.2.2 Edit My Certificates ........................................................................................................... 173
15.2.3 Import Certificates ............................................................................................................ 176
15.3 Trusted Certificates ..................................................................................................................... 177
15.3.1 Edit Trusted Certificates .................................................................................................... 178
15.3.2 Import Trusted Certificates ............................................................................................... 181
15.4 Technical Reference .................................................................................................................. 182
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
8

Table of Contents
Chapter 16
System...............................................................................................................................................183
16.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 183
16.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 183
16.2 Host Name ................................................................................................................................... 183
16.3 Power Mode ................................................................................................................................ 184
16.4 Date and Time ............................................................................................................................ 185
16.4.1 Pre-defined NTP Time Servers List ..................................................................................... 187
16.4.2 Time Server Synchronization ............................................................................................ 187
16.5 WWW Overview .......................................................................................................................... 188
16.5.1 Service Access Limitations ............................................................................................... 188
16.5.2 System Timeout .................................................................................................................. 188
16.5.3 HTTPS ................................................................................................................................... 189
16.5.4 Configuring WWW Service Control ................................................................................. 189
16.5.5 HTTPS Example ................................................................................................................... 191
16.6 SSH ................................................................................................................................................ 196
16.6.1 How SSH Works .................................................................................................................. 197
16.6.2 SSH Implementation on the Zyxel Device ...................................................................... 198
16.6.3 Requirements for Using SSH ..............................................................................................198
16.6.4 Configuring SSH ................................................................................................................. 198
16.6.5 Examples of Secure Telnet Using SSH .............................................................................. 199
16.7 FTP ................................................................................................................................................. 200
16.8 SNMP ............................................................................................................................................ 201
16.8.1 Supported MIBs ................................................................................................................. 202
16.8.2 SNMP Traps ......................................................................................................................... 202
16.8.3 Configuring SNMP ............................................................................................................. 202
16.8.4 Adding or Editing an SNMPv3 User Profile ...................................................................... 203
Chapter 17
Log and Report....... .... ... .................................................... ...............................................................205
17.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 205
17.1.1 What You Can Do In this Chapter .................................................................................. 205
17.2 Email Daily Report ....................................................................................................................... 205
17.3 Log Setting ................................................................................................................................... 207
17.3.1 Log Setting Screen ............................................................................................................ 207
17.3.2 Edit System Log Settings ................................................................................................... 208
17.3.3 Edit Remote Server ............................................................................................................ 212
17.3.4 Active Log Summary ........................................................................................................ 213
Chapter 18
File Manager ....................................................................................................................................217
18.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 217
18.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 217
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
9

Table of Contents
18.1.2 What you Need to Know .................................................................................................. 217
18.2 Configuration File ....................................................................................................................... 219
18.2.1 Example of Configuration File Download Using FTP ...................................................... 223
18.3 Firmware Package ..................................................................................................................... 224
18.3.1 Example of Firmware Upload Using FTP .......................................................................... 226
18.4 Shell Script .................................................................................................................................... 227
Chapter 19
Diagnostics.......................................................................................................................................229
19.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 229
19.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 229
19.2 Diagnostics .................................................................................................................................. 229
19.3 Remote Capture ........................................................................................................................ 230
Chapter 20
LEDs ...................................................................................................................................................232
20.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 232
20.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 232
20.2 Suppression Screen .................................................................................................................... 232
20.3 Locator Screen ........................................................................................................................... 233
Chapter 21
Antenna Switch................................................................................................................................235
21.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 235
21.1.1 What You Need To Know ................................................................................................. 235
21.2 Antenna Switch Screen ............................................................................................................. 235
Chapter 22
Reboot...............................................................................................................................................237
22.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 237
22.1.1 What You Need To Know ................................................................................................. 237
22.2 Reboot ......................................................................................................................................... 237
Part II: Local Configuration in Cloud Mode................................................238
Chapter 23
Cloud Mode .....................................................................................................................................239
23.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 239
23.2 Cloud Mode Web Configurator Screens ................................................................................. 239
23.3 Dashboard .................................................................................................................................. 240
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
10

Table of Contents
Chapter 24
Network.............................................................................................................................................242
24.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 242
24.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 242
24.2 IP Setting ...................................................................................................................................... 242
24.3 VLAN ............................................................................................................................................ 244
Chapter 25
Maintenance....................................................................................................................................245
25.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 245
25.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ................................................................................... 245
25.2 Shell Script .................................................................................................................................... 245
25.3 Diagnostics .................................................................................................................................. 246
25.4 Remote Capture ........................................................................................................................ 247
25.5 View Log ...................................................................................................................................... 248
Part III: Appendices and Troubleshooting.................................................. 251
Chapter 26
Troubleshooting................................................................................................................................252
26.1 Overview ..................................................................................................................................... 252
26.2 Power, Hardware Connections, and LED ................................................................................ 252
26.3 Zyxel Device Management, Access, and Login ..................................................................... 253
26.4 Internet Access ........................................................................................................................... 257
26.5 WiFi Network ................................................................................................................................ 258
26.6 Resetting the Zyxel Device ........................................................................................................ 261
26.7 Getting More Troubleshooting Help .........................................................................................261
Appendix A Importing Certificates ............................................................................................... 262
Appendix B IPv6............................................................................................................................... 286
Appendix C Customer Support ..................................................................................................... 294
Appendix D Legal Information ...................................................................................................... 299
Index.................................................................................................................................................310
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
11

1.1 Overview
This User’s Guide covers the models listed in the following table. They can be managed in one of the
following methods: remote management through Nebula Control Center (NCC) or an AP Controller
(AC) such as the ZyWALL ATP, or local management in Standalone Mode. Each Zyxel Device runs in
standalone mode by default, but it is recommended to use NCC management if it is available for your
device.
NCC, AC or Standalone (NebulaFlex PRO) NCC or Standalone (NebulaFlex)
• WAC500 • NWA110AX
• WAC500H • NWA210AX
• WAX510D • NWA220AX-6E
• WAX610D • NWA1123ACv3
• WAX620D-6E
• WAX630S
• WAX640S-6E
• WAX650S
• WAX655E
CHAPTER 1
Introduction
For more information about Access Point (AP) management, see Section 2.1 on page 26.
When two or more APs are interconnected, this network is called a Wireless Distribution System (WDS).
See Section 1.3.2 on page 21 for more information on root and repeater APs and how to set them up.
The screens you see in the web configurator may be different depending on the Zyxel Device model
you’re using.
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
12

Chapter 1 Introduction
1.2 Zyxel Device Product Feature Comparison
The following tables show the differences between each Zyxel Device model. You can find the feature
introductions in the later sections.
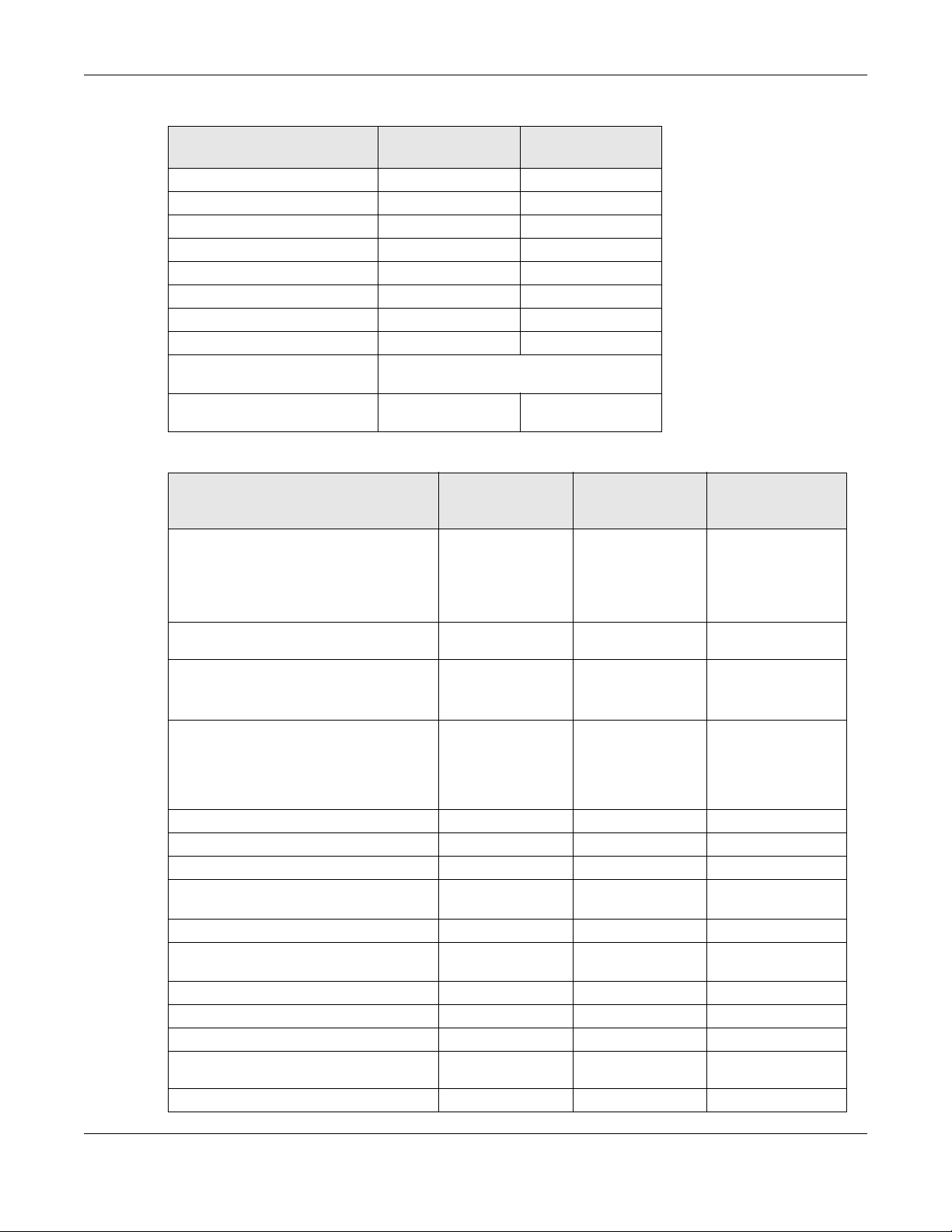
Table 1 500/1000 Models Comparison Table
FEATURES
Supported WiFi Standards IEEE 802.11a
Supported Frequency Bands 2.4 GHz
Supported Channel Width 2.4G: 20/40 MHz
Available Security Modes None
Number of SSID Profiles 64 64
Number of WiFi Radios 2 2
Security Profile Radius Settings Yes Yes
Security Profile Enterprise
Authentication Settings
Rogue AP Detection Yes Yes
WDS (Wireless Distribution
System) - Root AP & Repeater
Modes
Wireless Bridge No No
Tunnel Forwarding Mode Yes No
Layer-2 Isolation Yes Yes
Supported PoE Standards IEEE 802.3af
Power Detection No No
External Antennas No No
Internal Antennas Yes Yes
Antenna Switch No No
Smart Antenna Yes Yes
Console Port 4-Pin Serial 4-Pin Serial
Reset Button Yes Yes
LED Locator Yes Yes
LED Suppression Yes Yes
AC (AP Controller) Discovery Yes No
NebulaFlex PRO Yes No
NCC Discovery Yes Yes
802.11r Fast Roaming Support Yes Yes
802.11k/v Assisted Roaming Yes Yes
WAC500/
WAC500H
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
5 GHz
5G: 20/40/80 MHz
Enhanced-open
WEP
WPA2-MIX / WPA3 -
Personal & Enterprise
Yes Yes
Yes Yes
IEEE 802.3at
NWA1123-ACV3
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
2.4G: 20/40 MHz
5G: 20/40/80 MHz
None
Enhanced-open
WEP
WPA2-MIX / WPA3 -
Personal & Enterprise
IEEE 802.3af
IEEE 802.3at
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
13
Chapter 1 Introduction
Table 1 500/1000 Models Comparison Table (continued)
FEATURES
Proxy ARP Yes Yes
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) No No
Load Balancing Yes Yes
Ethernet Storm Control Yes Yes
Wireless Remote Capture Yes Yes
SNMP Yes Yes
Grounding No No
Power Jack Yes Yes
Maximum number of log
messages
Latest Firmware Version
Supported
WAC500/
WAC500H
512 event logs
6.55 6.55
NWA1123-ACV3
Table 2 WiFi 6 Models Comparison Table
NWA110AX
FEATURES WAX630S WAX650S
NWA210AX
Supported WiFi Standards IEEE 802.11a
Supported Frequency Bands 2.4 GHz
Supported Channel Width
Available Security Modes None
Number of SSID Profiles 64 64 64
Number of WiFi Radios 2 2 2
Security Profile Radius Settings Yes Yes Yes
Security Profile Enterprise Authentication
Settings
Rogue AP Detection Yes Yes Yes
WDS (Wireless Distribution System) - Root AP
& Repeater Modes
Wireless Bridge Yes Yes No
Tunnel Forwarding Mode Yes Yes No
Layer-2 Isolation Yes Yes Yes
Supported PoE Standards IEEE 802.3af
Power Detection Yes Yes Yes
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
IEEE 802.11ax
5 GHz
2.4G: 20/40 MHz
5G: 20/40/80/160
MHz
Enhanced-open
WEP
WPA2-MIX / WPA3 -
Personal &
Enterprise
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
IEEE 802.3at
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
IEEE 802.11ax
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
2.4G: 20/40 MHz
5G: 20/40/80/160
MHz
None
Enhanced-open
WEP
WPA2-MIX / WPA3 -
Personal &
Enterprise
IEEE 802.3at
IEEE 802.3bt
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
IEEE 802.11ax
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
2.4G: 20/40 MHz
5G: 20/40/80 MHz
(NWA210AX supports
160 MHz)
None
Enhanced-open
WPA2-MIX / WPA3 -
Personal & Enterprise
IEEE 802.3af
IEEE 802.3at
WEP
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
14
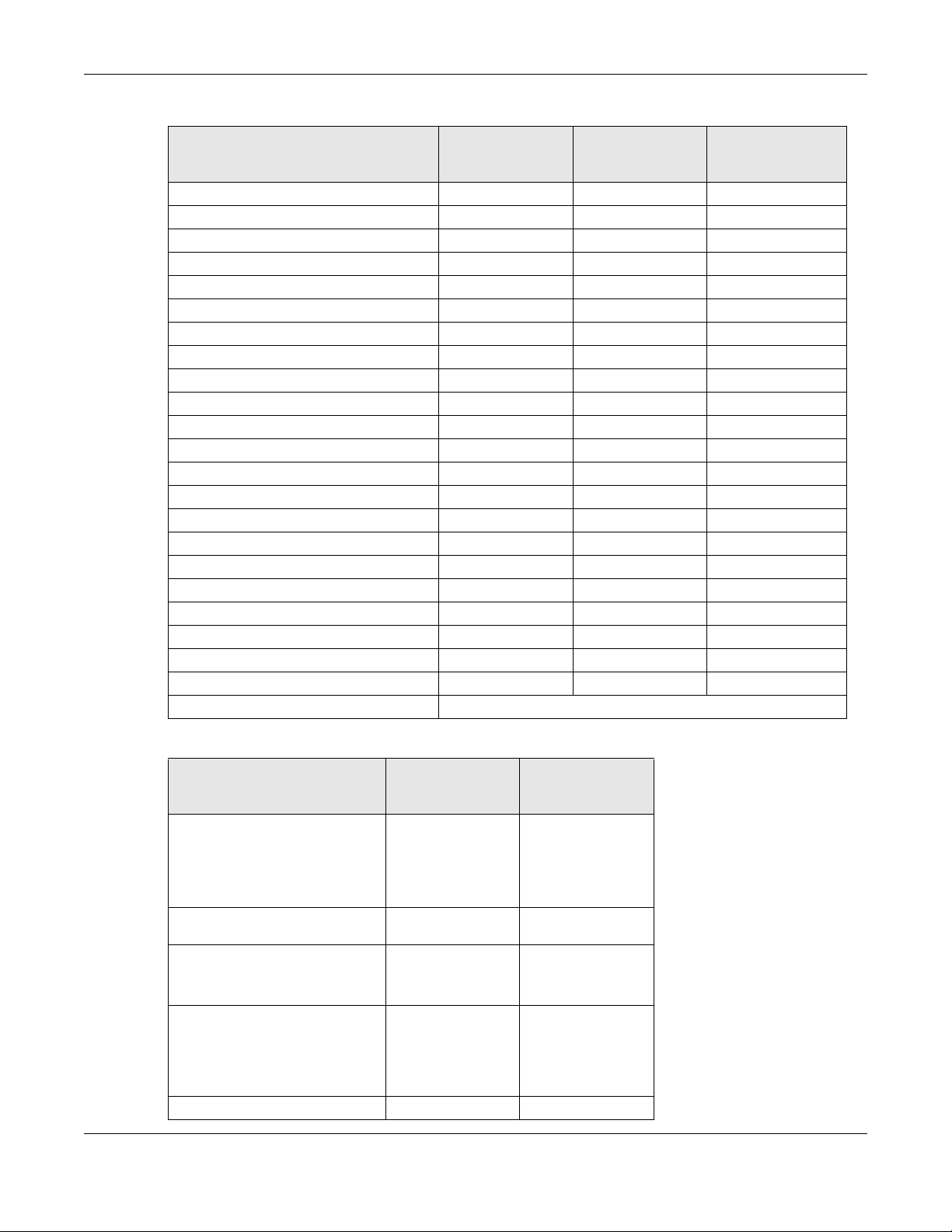
Chapter 1 Introduction
Table 2 WiFi 6 Models Comparison Table (continued)
NWA110AX
FEATURES WAX630S WAX650S
NWA210AX
External Antennas No No No
Internal Antennas Yes Yes Yes
Antenna Switch No No No
Smart Antenna Yes Yes No
Console Port 4-Pin Serial 4-Pin Serial 4-Pin Serial
Reset Button Yes Yes Yes
LED Locator Yes Yes Yes
LED Suppression Yes Yes Yes
AC (AP Controller) Discovery Yes Yes No
NebulaFlex PRO Yes Yes No
NCC Discovery Yes Yes Yes
802.11r Fast Roaming Support Yes Yes Yes
802.11k/v Assisted Roaming Yes Yes Yes
Proxy ARP Yes Yes Yes
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) No Yes No
Load Balancing Yes Yes Yes
Ethernet Storm Control Yes Yes Yes
Wireless Remote Capture Yes Yes Yes
SNMP Yes Yes Yes
Grounding Yes Yes Yes
Power Jack Yes Yes Yes
Latest Firmware Version Supported 6.55 6.55 6.55
Maximum number of log messages 512 event logs
Table 3 WiFi 6 Models Comparison Table
WAX510D
FEATURES WAX655E
WAX610D
Supported WiFi Standards IEEE 802.11a
Supported Frequency Bands 2.4 GHz
Supported Channel Width
Available Security Modes None
Number of SSID Profiles 64 64
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
IEEE 802.11ax
5 GHz
2.4G: 20/40 MHz
5G: 20/40/80/160
MHz
Enhanced-open
WEP
WPA2-MIX / WPA3 -
Personal &
Enterprise
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
IEEE 802.11ax
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
2.4G: 20/40 MHz
5G: 20/40/80 MHz
(WAX610D supports
160 MHz)
Enhanced-open
WPA2-MIX / WPA3 -
Personal &
Enterprise
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
15
None
WEP
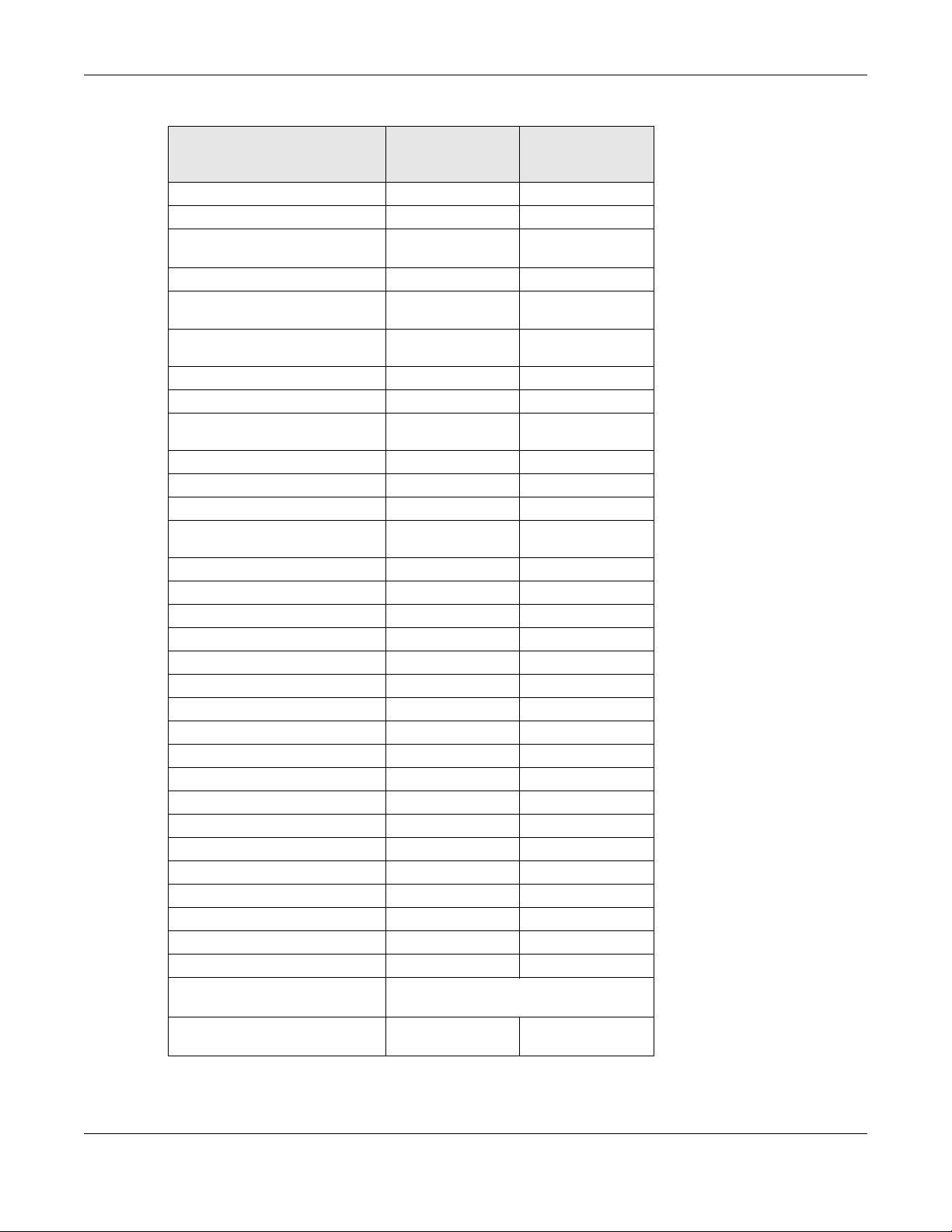
Chapter 1 Introduction
Table 3 WiFi 6 Models Comparison Table (continued)
WAX510D
FEATURES WAX655E
WAX610D
Number of WiFi Radios 2 2
Security Profile Radius Settings Yes Yes
Security Profile Enterprise
Authentication Settings
Rogue AP Detection Yes Yes
WDS (Wireless Distribution System)
- Root AP & Repeater Modes
Wireless Bridge
Tunnel Forwarding Mode Yes Yes
Layer-2 Isolation Yes Yes
Supported PoE Standards IEEE 802.3af
Power Detection Yes Yes
External Antennas Yes No
Internal Antennas No Yes
Antenna Switch
Smart Antenna No No
Console Port 4-Pin Serial 4-Pin Serial
Reset Button Yes Yes
LED Locator Yes Yes
LED Suppression Yes Yes
AC (AP Controller) Discovery Yes Yes
NebulaFlex PRO Yes Yes
NCC Discovery Yes Yes
802.11r Fast Roaming Support Yes Yes
802.11k/v Assisted Roaming Yes Yes
Proxy ARP Yes Yes
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) No No
Load Balancing Yes Yes
Ethernet Storm Control Yes Yes
Wireless Remote Capture Yes Yes
SNMP Yes Yes
Grounding Yes Yes
Power Jack Yes Yes
Maximum number of log
messages
Latest Firmware Version
Supported
Yes Yes
Yes Yes
Yes
IEEE 802.3at
No
512 event logs
6.55 6.55
WAX510D: No
WAX610D: Yes
IEEE 802.3af
IEEE 802.3at
Yes
(per AP)
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
16
Chapter 1 Introduction
Table 4 WiFi 6E Models Comparison Table
FEATURES WAX620D-6E WAX640S-6E NWA220AX-6E
Supported WiFi Standards IEEE 802.11a
Supported Frequency Bands 2.4 GHz
BandFlex (5 GHz/6 GHz) Yes No Yes
Supported Channel Width 2.4G: 20/40 MHz
Available Security Modes None
Number of SSID Profiles 64 64 64
Number of WiFi Radios 2 3 2
Security Profile Radius Settings Yes Yes Yes
Security Profile Enterprise
Authentication Settings
Rogue AP Detection Yes Yes Yes
WDS (Wireless Distribution
System) - Root AP & Repeater
Modes
Wireless Bridge Yes Yes No
Tunnel Forwarding Mode Yes Yes No
Layer-2 Isolation Yes Yes Yes
Supported PoE Standards IEEE 802.3af
Power Detection Yes Yes Yes
External Antennas No No No
Internal Antennas Yes Yes Yes
Antenna Switch Yes
Smart Antenna No Yes No
Console Port 4-Pin Serial 4-Pin Serial 4-Pin Serial
Reset Button Yes Yes Yes
LED Locator Yes Yes Yes
LED Suppression Yes Yes Yes
AC (AP Controller) Discovery Yes Yes No
NebulaFlex PRO Yes Yes No
NCC Discovery Yes Yes Yes
802.11r Fast Roaming Support Yes Yes Yes
802.11k/v Assisted Roaming Yes Yes Yes
Proxy ARP Yes Yes Yes
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
IEEE 802.11ax
5 GHz
6 GHz
5G: 20/40/80/160 MHz
6G: 20/40/80/160 MHz
Enhanced-open WEP
WPA2-MIX / WPA3 -
Personal & Enterprise
Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes
IEEE 802.3at
(per AP)
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
IEEE 802.11ax
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
6 GHz
2.4G: 20/40 MHz
5G: 20/40/80/160 MHz
6G: 20/40/80/160 MHz
Enhanced-open WEP
Personal & Enterprise
None
WPA2-MIX / WPA3 -
IEEE 802.3at
IEEE 802.3bt
No No
IEEE 802.11a
IEEE 802.11b
IEEE 802.11g
IEEE 802.11n
IEEE 802.11ac
IEEE 802.11ax
2.4 GHz
5 GHz
6 GHz
2.4G: 20/40 MHz
5G: 20/40/80/160 MHz
6G: 20/40/80/160 MHz
None
Enhanced-open WEP
WPA2-MIX / WPA3 -
Personal & Enterprise
IEEE 802.3af
IEEE 802.3at
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
17
Table 4 WiFi 6E Models Comparison Table (continued)
FEATURES WAX620D-6E WAX640S-6E NWA220AX-6E
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) No Yes No
Load Balancing Yes Yes Yes
Ethernet Storm Control Yes Yes Yes
Wireless Remote Capture Yes Yes Yes
SNMP Yes Yes Yes
Grounding No Yes No
Power Jack Yes Yes Yes
Maximum number of log
messages
Latest Firmware Version
Supported
1.3 Zyxel Device Roles
This section describes some of the different roles that your Zyxel Device can take up within a network.
Not all roles are supported by all models (see Section 1.2 on page 13). The Zyxel Device can serve as a:
Chapter 1 Introduction
512 event logs
6.55 6.55 6.55
• Access Point (AP) - This is used to allow WiFi clients to connect to the Internet.
• Radio Frequency (RF) monitor - If your Zyxel Device supports rogue APs detection, it can serve as an
RF monitor and searches for rogue APs to help eliminate network threats. An RF monitor can simultaneously act as an AP.
• Root AP - A root AP connects to the gateway or switch through a wired Ethernet connection and
has wireless repeaters connected to it to extend its range.
• Wireless repeater - A wireless repeater wirelessly connects to a root AP and extends the network’s
wireless range. A wireless repeater can also be a wireless bridge that connects to a root AP and
extends the network to wired client devices.
If a client (D) tries to set up his own AP (R) with weak security settings, the network becomes exposed to
threats. The RF monitor (M) scans the area to detect all APs, which can help the network administrator
discover these rogue APs and remove them.
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
18

Chapter 1 Introduction
Figure 1 Zyxel Device Application in a Network
Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
Wireless Distribution System (WDS) is a network system that allows you to distribute the network to areas
that require Internet connections. You can extend your network to unreachable areas with wireless
repeaters.
The following figure shows you how to create a secure WDS with two wireless repeaters. The root AP (Y) is
connected to a network with Internet access and has wireless repeaters (X and Z) connected to it to
expand the WiFi network’s range. Clients (A and B) can access the wired network through the wireless
repeaters (X and Z) and/or root AP.
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
19
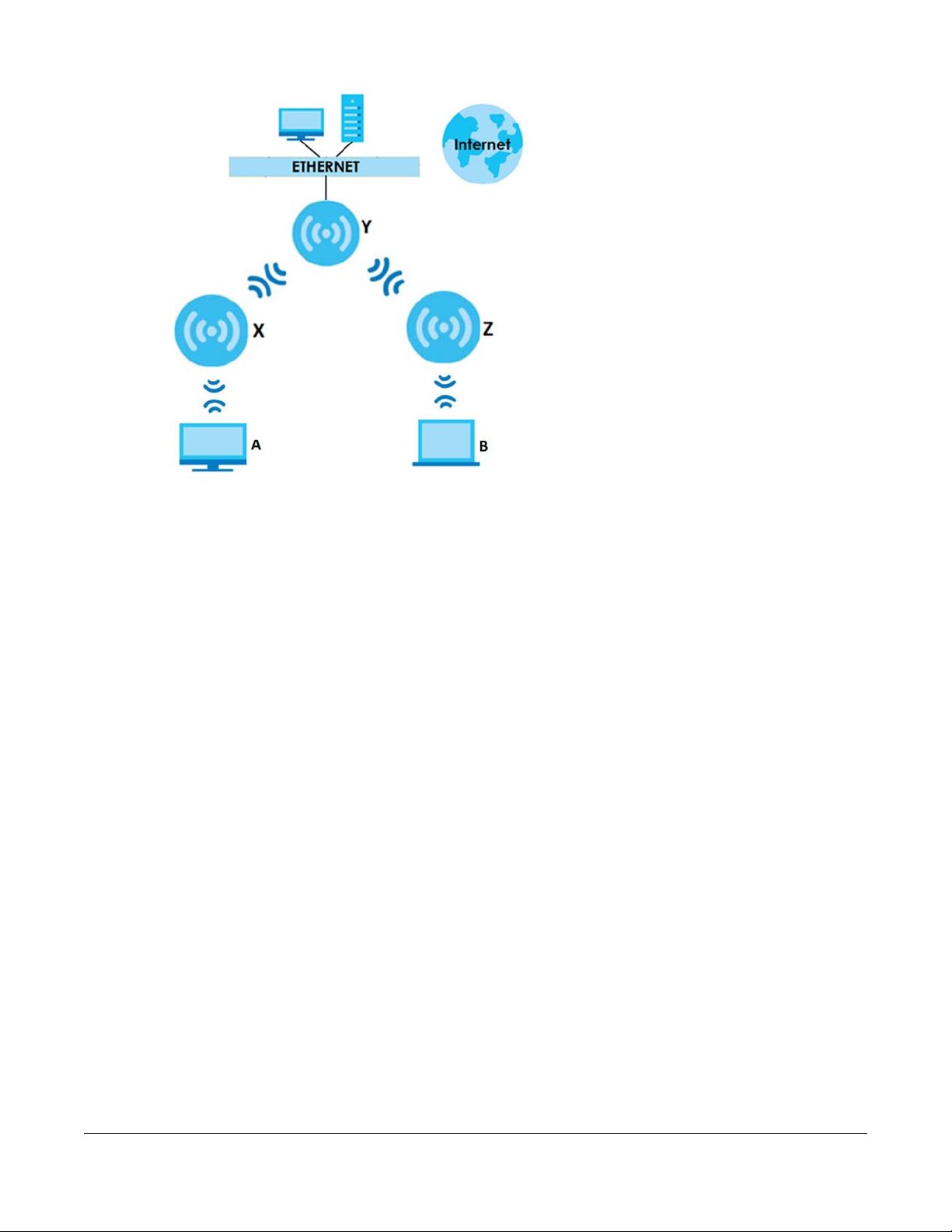
Figure 2 Wireless Distribution System Network Example
The Zyxel Device can also serve as a wireless bridge in Repeater mode. A wireless bridge connects two
wired networks through a wireless connection. When the Zyxel Device is connected to a root AP, enable
wireless bridge to allow traffic through the Ethernet port on the Zyxel Device to a wired network. Check
Section 1.2 on page 13 for models that support wireless bridge.
The following figure shows an example of a WDS with a repeater acting as a wireless bridge. The root AP
(X) is connected to a network with Internet access. The wireless repeater (Y) is connected to the root AP
(X) to expand the network. Clients (A and B) are connected to the wireless repeater through the switch/
gateway/router (G). They can access the network with the extended wired network the wireless bridge
(wireless repeater) provides.
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
20
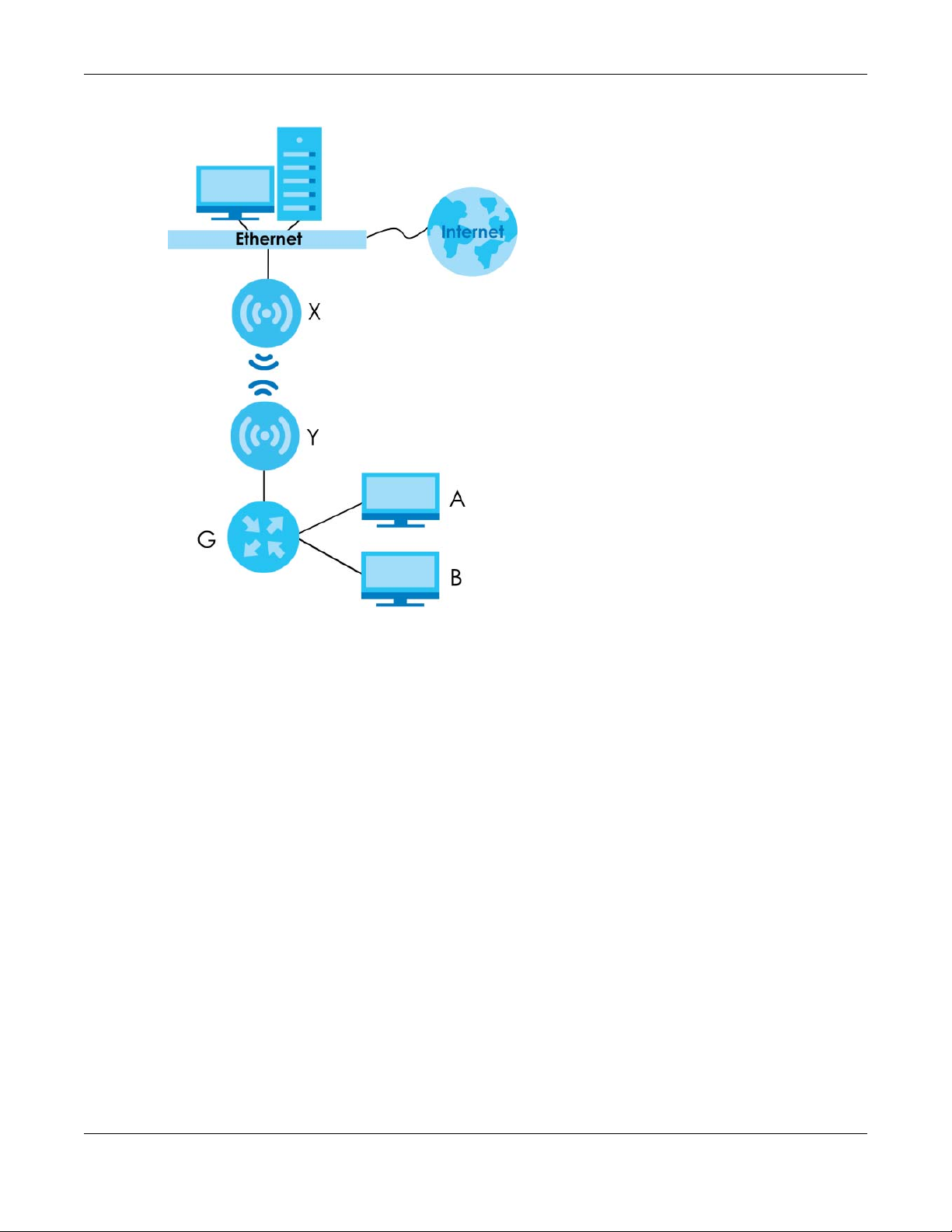
Chapter 1 Introduction
Figure 3 Wireless Bridge Network Example
1.3.1 Root AP
In Root AP mode, you can have multiple SSIDs active for regular WiFi connections and one SSID (WDS
SSID) for the connection with a repeater. WiFi clients can use either SSID to associate with the Zyxel
Device in Root AP mode. A repeater must use the repeater SSID to connect to the Zyxel Device in Root
AP mode. See Section 14.1 on page 165 for more details.
When the Zyxel Device is in Root AP mode, repeater security between the Zyxel Device and other
repeaters is independent of the security between the WiFi clients and the AP or repeater. When
repeater security is enabled, both APs and repeaters must use the same pre-shared key. See Section
10.2 on page 96 and Section 14.2 on page 165 for more details.
Unless specified, the term “security settings” refers to the traffic between the WiFi clients and the AP. At
the time of writing, repeater security is compatible with the Zyxel Device only.
1.3.2 Wireless Repeater
Using Repeater mode, your Zyxel Device can extend the range of the WLAN. In the figure below, the
Zyxel Device in Repeater mode (Z) has a wireless connection to the Zyxel Device in Root AP mode (X)
which is connected to a wired network and also has a wireless connection to another Zyxel Device in
Repeater mode (Y) at the same time. Z acts as a repeater that forwards traffic between associated WiFi
clients and the wired LAN. Y acts as a wireless bridge (repeater with WDS wireless bridging enabled) that
forwards traffic between wired clients and the wired LAN. Clients A and B access the AP and the wired
network behind the AP through repeaters Z and Y.
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
21
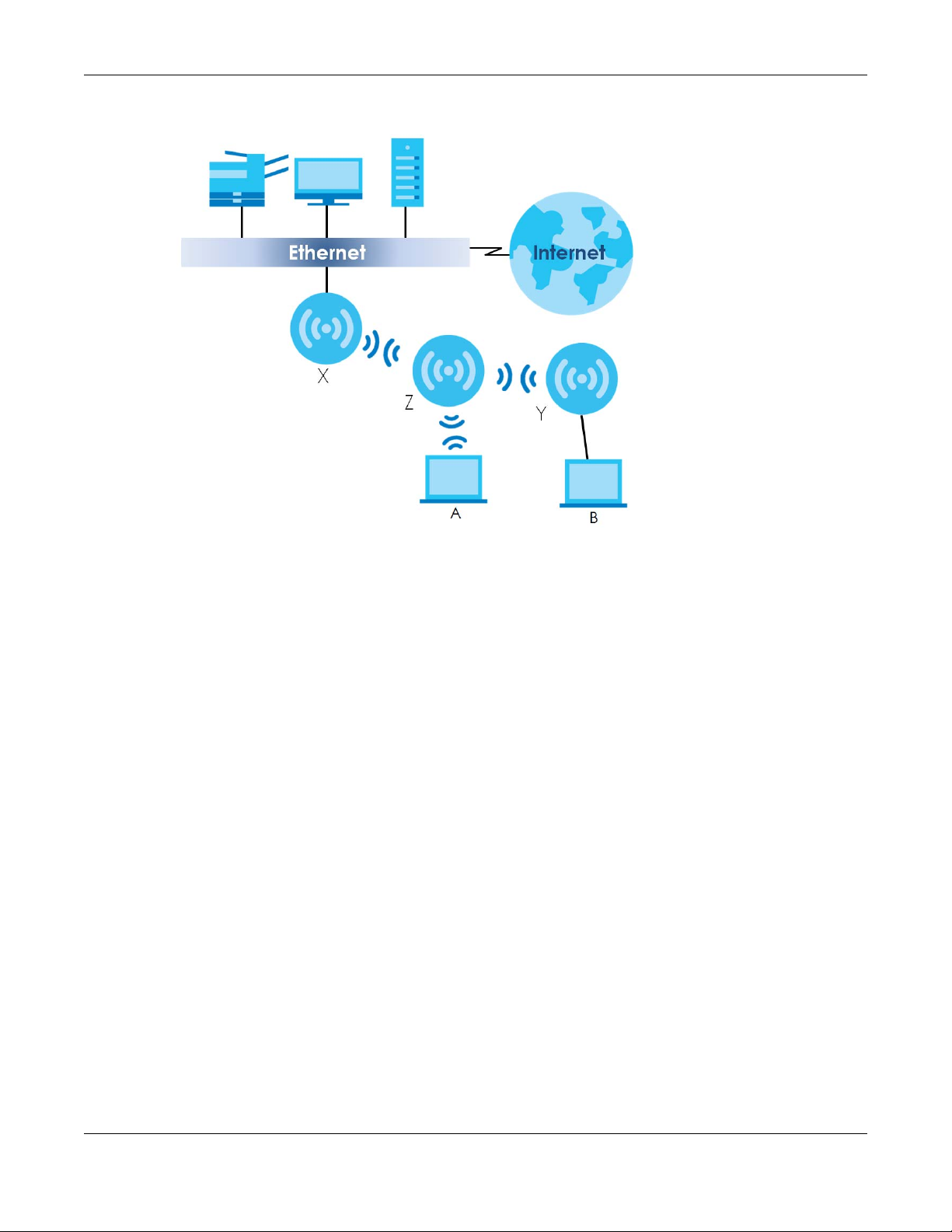
Figure 4 Repeater Application
Chapter 1 Introduction
When the Zyxel Device is in Repeater mode, repeater security between the Zyxel Device and other
repeater is independent of the security between the WiFi clients and the AP or repeater. When repeater
security is enabled, both APs and repeaters must use the same pre-shared key. See Section 10.2 on
page 96 and Section 14.2 on page 165 for more details.
For NCC managed devices, you only need to enable AP Smart Mesh to automatically create wireless
links between APs. See the NCC User’s Guide for more details.
To set up a WDS in standalone mode APs, do the following steps. You should already have the root AP
set up (see the Quick Start Guide for hardware connections).
1 Go to Configuration > Object > WDS Profile in your root AP Web Configurator and click Add.
2 Enter a profile name, a WDS SSID, and a pre-shared key.
3 Go to Configuration > Wireless > AP Management, select the Radio WDS Profile of the radio on which
you are setting the WDS connection to use the WDS profile you set, and click Apply.
4 Do steps 1 and 3 for the wireless repeater using the same WDS SSID and pre-shared key.
5 Once the security settings of peer sides match one another, the connection between the root and
repeater Zyxel Devices is made.
(Optional) If your Zyxel Device supports wireless bridging, you can extend a wired network from the port
on the wireless repeater, do the following steps:
6 Go to Configuration > Wireless > AP Management, select Setup WDS Wire less Bridging to enable wireless
bridge on the wireless repeater.
7 Connect the client device to the Zyxel Device’s port with an Ethernet cable.
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
22

Chapter 1 Introduction
Note: Make sure the VLAN settings on both the root AP and the wireless repeater are exactly
the same so they can communicate.
Note: When wireless bridge is enabled, wireless interfaces for client devices will be disabled.
You can only transmit data through the wireless repeater’s ports.
To set up a WDS in AC (AP Controller)-managed Zyxel Devices, see the ZyWALL ATP, ZyWALL VPN, USG
FLEX, or NXC User’s Guide.
1.3.3 Radio Frequency (RF) Monitor
The Zyxel Device supports Rogue AP Detection (see Section 10.3 on page 102). Rogue AP Detection
allows the Zyxel Device to be set to work as an RF monitor to discover nearby Access Points. The
information it obtains from other APs is used to tag possible rogue APs and friendly APs. The Zyxel Device
can still work as an AP while it scans the environment for wireless signals.
1.4 Sample Feature Applications
This section describes some possible scenarios and topologies that you can set up using your Zyxel
Device.
1.4.1 MBSSID
A Basic Service Set (BSS) is the set of devices forming a single WiFi network (usually an access point and
one or more WiFi clients). The Service Set IDentifier (SSID) is the name of a BSS. In Multiple BSS (MBSSID)
mode, the Zyxel Device provides multiple virtual APs, each forming its own BSS and using its own
individual SSID profile.
You can configure multiple SSID profiles, and have all of them active at any one time.
You can assign different wireless and security settings to each SSID profile. This allows you to
compartmentalize groups of users, set varying access privileges, and prioritize network traffic to and
from certain BSSs.
To the WiFi clients in the network, each SSID appears to be a different access point. As in any WiFi
network, clients can associate only with the SSIDs for which they have the correct security settings.
For example, you might want to set up a WiFi network in your office where Internet telephony (VoIP)
users have priority. You also want a regular WiFi network for standard users, as well as a ‘guest’ WiFi
network for visitors. In the following figure, VoIP_SSID users have QoS priority, SSID01 is the WiFi network for
standard users, and Guest_SSID is the WiFi network for guest users. In this example, the guest user is
forbidden access to the wired Local Area Network (LAN) behind the AP and can access only the
Internet.
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
23

Figure 5 Multiple BSSs
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.4.2 Dual-Radio/Triple-Radio and BandFlex
The Zyxel Device models are equipped with two or even three WiFi radios. The Zyxel Device uses the WiFi
radios to transmit WiFi signals. This means you can configure two to three different WiFi networks to
operate simultaneously.
BandFlex allows you to select the frequency bands operating on the radios by configuration. A
frequency band is a range of frequency divided into channels which carry the WiFi signals for data
transmission. If your Zyxel Device supports BandFlex, you can configure the second radio on the Zyxel
Device to use the 5 GHz or 6 GHz bands, while the first radio is always set to use the 2.4 GHz band. The 6
GHz band provides less coverage but has the highest amount of channels among the three frequency
bands. Use the 6 GHz band for the most congestion-free transmission if your client devices supports WiFi
6E (see Section 13.1.2 on page 121).
Note: Due to each country’s regulations on frequency band usage, the available radio
bands (2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz) may differ by countries or markets the Zyxel Device
products are sold to.
Note: A different channel should be configured for each WLAN interface to reduce the
effects of radio interference.
You could use the 2.4 GHz band for regular Internet surfing and downloading while using the 5 GHz or 6
GHz band for time sensitive traffic like high-definition video, music, and gaming.
See Section 1.2 on page 13 for the supported number of radios, frequency bands, and see if your Zyxel
Device supports BandFlex.
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
24
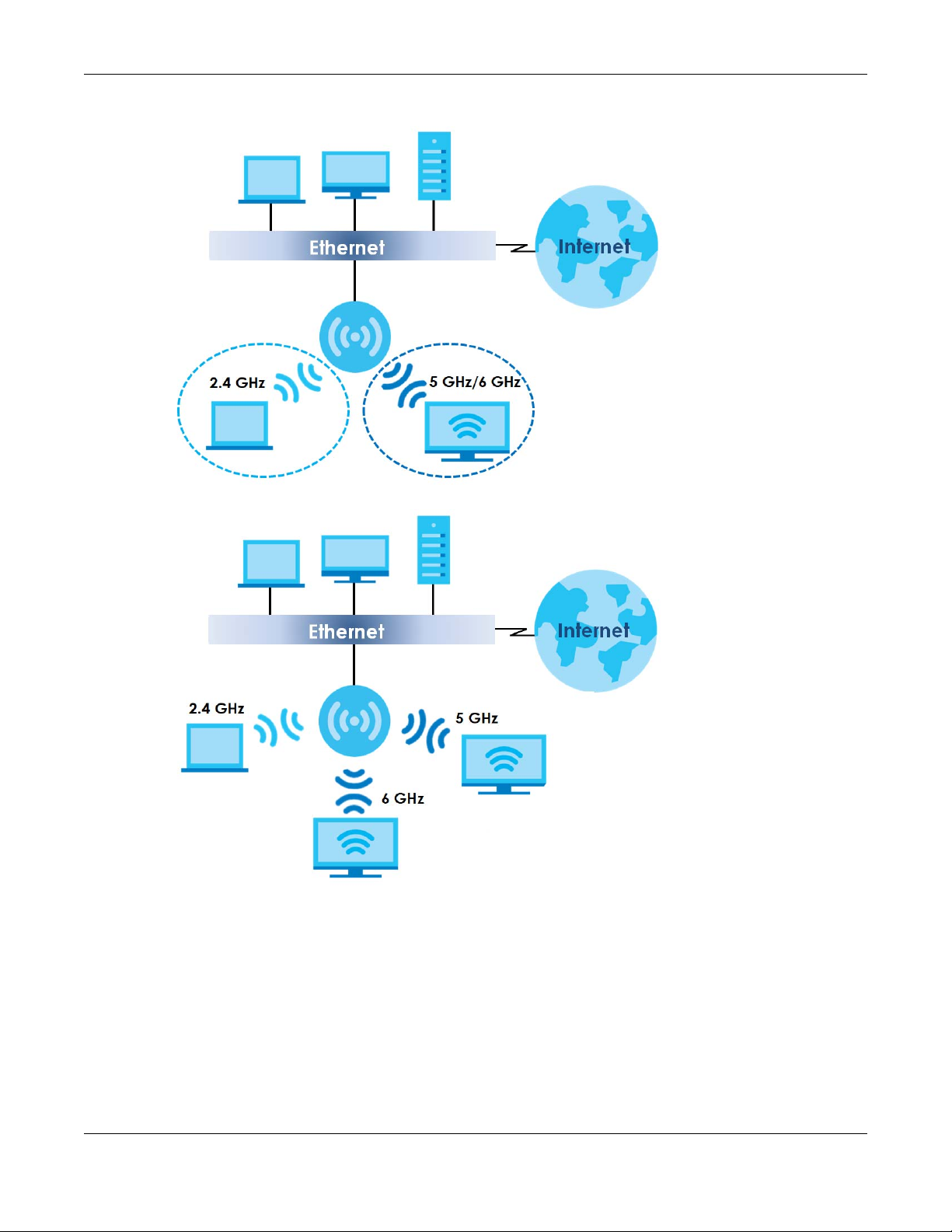
Figure 6 Dual-Radio Application
Figure 7 Triple-Radio Application
Chapter 1 Introduction
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
25
Chapter 2 AP Management
2.1 Management Mode
The Zyxel Device is a unified AP and can be managed by the NCC or an AP controller (AC), or work as a
standalone device. We recommend you use NCC to manage multiple APs (see the NCC User’s Guide).
An AP Controller, such as the ZyWALL ATP/VPN, USG FLEX, or NXC, can only manage multiple APs in the
same location.
Note: Not all models can be managed by NCC or an AC. See Section 1.2 on page 13 to
check whether your product supports these.
CHAPTER 2
AP Management
The following table shows the default IP addresses and firmware upload methods for different
management modes.
Table 5 Zyxel Device Management Mode Comparison
MANAGEMENT MODE DEFAULT IP ADDRESS UPLOAD FIRMWARE VIA
Nebula Control Center Dynamic NCC Portal
AP Controller Dynamic AP Controller using CAPWAP
Standalone Dynamic or
When the Zyxel Device is in standalone mode and connects to a DHCP server, it uses the IP address
assigned by the DHCP server. Otherwise, the Zyxel Device uses the default static management IP
address (192.168.1.2). You can use the NCC Discovery or AC Discovery screen to allow the Zyxel Device
to be managed by the NCC or an AC, respectively.
When the Zyxel Device is managed by the NCC or an AC, it acts as a DHCP client and obtains an IP
address from the NCC/AC. It can be configured ONLY by the NCC/AC. To change the Zyxel Device
back to standalone mode, use the Reset button to restore the default configuration. Alternatively, you
need to check the NCC/AC for the Zyxel Device’s IP address and use FTP to upload the default
configuration file at conf/system-default.conf to the Zyxel Device and reboot the device.
2.1.1 Standalone
Static (192.168.1.2)
Built-in Web Configurator
When working in standalone mode, the Zyxel Device is configured mainly with its built-in Web
Configurator. You can only connect to and set up one Zyxel Device at a time in this mode.
See Chapter 5 on page 55 for detailed information about the standalone Web Configurator screens.
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
26

2.1.2 Nebula Control Center
In this mode, which is also called cloud mode, you can manage and monitor the Zyxel Device through
the Zyxel Nebula cloud-based network management system. This means you can manage devices
remotely without the need of connecting to each device directly. It offers many features to better
manage and monitor not just the Zyxel Device, but your network as a whole, including supported
switches and gateways. Your network can also be managed through your smartphone using the
Nebula Mobile app. See Section on page 239 for an example NCC managed network topology.
NCC allows different levels of management. You can configure each device on its own or configure a
set of devices together as a site. You can also monitor groups of sites called organizations, as shown
below.
Table 6 NCC Management Levels
Device A-1 Device A-2 Device B-1 Device B-2
It graphically presents your device/network statistics and shows an overview of your network topology,
as shown in the following figure. It also sends reports, alerts, and notifications for events, such as when a
site goes offline.
Chapter 2 AP Management
Organization
Site A Site B
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
27

Chapter 2 AP Management
Figure 8 Traffic Monitoring Graph From NCC
See the NCC (Nebula Control Center) User’s Guide for how to configure Nebula managed devices. See
Chapter 24 on page 242 if you want to change the Zyxel Device’s VLAN setting or manually set its IP
address.
Note: Make sure your network firewall allows TCP ports 443, 4335, and 6667 as well as UDP port
123 so the device can connect to and sync with the NCC.
2.1.3 AP Controller (AC)
If the Zyxel Device supports management using an AC (see Section 9.1.1 on page 82) such as the
ZyWALL ATP, ZyWALL VPN, USG FLEX, and the NXC series, and you have this AC in the same subnet, it will
be managed by the controller automatically. To set the Zyxel Device to be managed by an AC in a
different subnet or change between management modes, use the AC Discovery screen (see Section
9.5 on page 92 and Section 9.1.1 on page 82). You can use the AC to manage multiple Zyxel Devices.
See Section 9.1.1 on page 82 for an example AC managed network topology.
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
28

Chapter 2 AP Management
Note: If the Zyxel Device is already registered to NCC, the controller will be unable to manage
it.
An AC uses Control And Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP, see RFC 5415) to discover and
configure multiple managed APs.
2.2 Switching Management Modes
The Zyxel Device is in standalone mode by default, with NCC and/or AC discovery enabled.
Standalone-to-NCC
Register the Zyxel Device at the NCC website and then turn on the Zyxel Device. Make sure that NCC
Discovery is enabled (see Section 9.6 on page 93). The NCC manages the Zyxel Device automatically
when it is discovered. Settings on the Zyxel Device will be overwritten with what you have configured on
the NCC website.
Standalone-to-AC
By default, the Zyxel Device must be in the same subnet as the AC. See Section 9.1.1 on page 82 for
setting it up in a different subnet. Make sure AC Discovery is enabled (see Section 9.5 on page 92). The
AC manages the Zyxel Device automatically when it is discovered.
AC-to-NCC
Register the Zyxel Device at the NCC website. Make sure that NCC Discovery is enabled on your Zyxel
Device (see Section 9.6 on page 93). In the AC Web Configurator, select the Zyxel Device and press the
Nebula button. The NCC manages the Zyxel Device automatically when it is discovered.
NCC-to-AC
Unregister the Zyxel Device at the NCC portal. By default, the Zyxel Device must be in the same subnet
as the AC. See Section 9.1.1 on page 82 for setting it up in a different subnet. Make sure AC Discovery is
enabled (see Section 9.5 on page 92). The AC manages the Zyxel Device automatically when it is
discovered.
NCC-to-Standalone
Unregister the Zyxel Device from the NCC organization/site. The Zyxel Device will automatically reset to
its factory defaults and return to standalone mode.
AC-to-Standalone
Use the Reset button to return the Zyxel Device to its factory default settings (see Section 26.6 on page
261).
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
29

Chapter 2 AP Management
2.3 Zyxel One Network (ZON) Utility
ZON Utility is a program designed to help you deploy and manage a network more efficiently. It detects
devices automatically and allows you to do basic settings on devices in the network without having to
be near it.
The ZON Utility issues requests via Zyxel Discovery Protocol (ZDP) and in response to the query, the device
responds back with basic information including IP address, firmware version, location, system and model
name in the same broadcast domain. The information is then displayed in the ZON Utility screen and you
can perform tasks like basic configuration of the devices and batch firmware upgrade in it. You can
download the ZON Utility at www.zyxel.com and install it on your computer (Windows operating system).
2.3.1 Requirements
Before installing the ZON Utility on your PC, please make sure it meets the requirements listed below.
Operating System
At the time of writing, the ZON Utility is compatible with:
• Windows 7 (both 32-bit / 64-bit versions)
• Windows 8 (both 32-bit / 64-bit versions)
• Windows 8.1 (both 32-bit / 64-bit versions)
• Window 10 (both 32-bit / 64-bit versions)
Note: To check for your Windows operating system version, right-click on My Computer >
Properties on your computer. You should see this information in the General tab.
Note: It is suggested that you install Npcap, the packet capture library for Windows operating
systems, and remove WinPcap or any other installed packet capture tools before you
install the ZON utility.
Hardware
Here are the minimum hardware requirements to use the ZON Utility on your PC.
• Core i3 processor
•2 GB RAM
• 100 MB free hard disk
• WXGA (Wide XGA 1280x800)
2.3.2 Run the ZON Utility
1 Double-click the ZON Utility to run it.
2 The first time you run the ZON Utility, you will see if your device and firmware version support the ZON
Utility. Click the OK button to close this screen.
NWA/WAC/WAX Series User’s Guide
30
 Loading...
Loading...