ZyXEL P870HW51AV2 Installation guide

Chapter 17 Tools
Figure 89 Firmware Upload In Progress
The ZyXEL Device automatically restarts in this time causing a temporary network
disconnect. In some operating systems, you may see the following icon on your desktop.
Figure 90 Network Temporarily Disconnected
After two minutes, log in again and check your new firmware version in the Status screen.
If the upload was not successful, the following screen will appear. Click Tools to go back to
the Firmware screen.
Figure 91 Error Message
17.3 The Configuration Screen
Click Maintenance > Tools > Configuration. Information related to facto ry defaults, backup
configuration, and restoring configuration appears in this screen , as shown next.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
151

Chapter 17 Tools
Figure 92 Maintenance > Tools > Configuration
Backup Configuration
Backup Configuration allows you to back up (save) the ZyXEL Device’ s current configuration
to a file on your computer. Once your ZyXEL Device is configured and functioning properly,
it is highly recommended that you back up your configuration file before mak i ng
configuration changes. The backup configuration file will be useful in case you need to return
to your previous settings.
Click Backup to save the ZyXEL Device’s current configuration to your computer.
Restore Configuration
Restore Configuration allows you to upload a new or previously saved configuration file from
your computer to your ZyXEL Device.
Table 51 Restore Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
File Path Type in the location of the file you want to upload in this field or click Browse ... to find it.
Browse... Click Browse... to find the file you want to upload. Remember that you must
Upload Click Upload to begin the upload process.
decompress compressed (.ZIP) files before you can upload them.
1 Do not turn off the ZyXEL Device while configuration file upload is in progress.
152
After you see a “restore configuration successful” screen, you must then wait one minute
before logging into the ZyXEL Device again.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide

Chapter 17 Tools
Figure 93 Configuration Upload Successful
The ZyXEL Device automatically restarts in this time causing a temporary network
disconnect. In some operating systems, you may see the following icon on your desktop.
Figure 94 Network Temporarily Disconnected
If you uploaded the default configuration file you may need to change the IP addre ss of your
computer to be in the same subnet as that of the default device IP address (192.168.1.1). See
Appendix A on page 173 for details on how to set up your computer’s IP address.
If the upload was not successful, the following screen will appear. Click Tools >
Configuration to go back to the Configuration screen.
Figure 95 Configuration Upload Error
Reset to Factory Defaults
Click the Reset button to clear all user-entered configuration information and return the
ZyXEL Device to its factory defaults. The following warning screen appears.
Figure 96 Reset Warning Message
You can also press the RESET button on the rear panel to reset the factory defaults of your
ZyXEL Device. Refer to Section 1.6 on page 28 for more information on the RESET button.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
153
Chapter 17 Tools
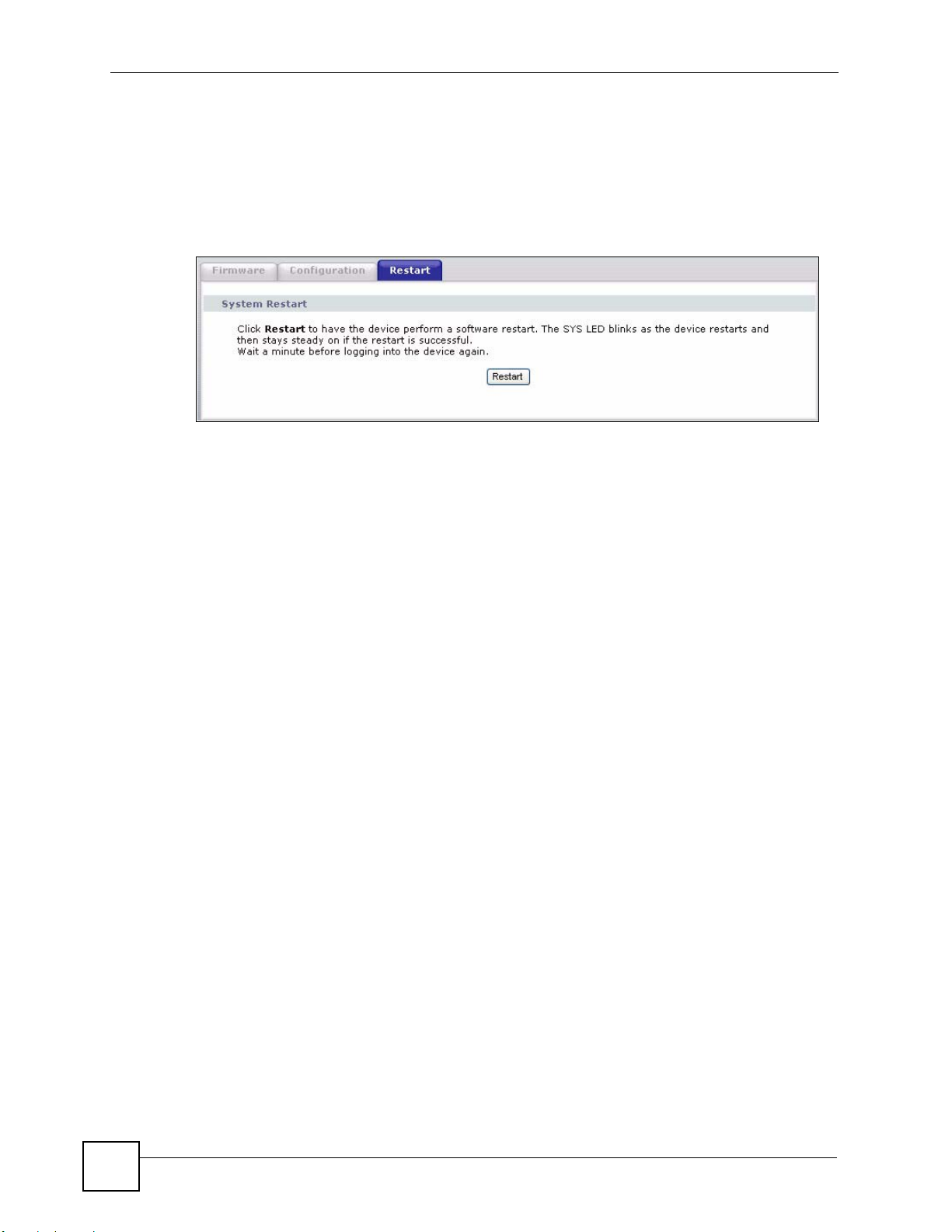
17.4 The Restart Screen
System restart allows you to reboot the ZyXEL Device without turning the power off.
Click Maintenance > Tools > Restart. Click Restart to have the ZyXEL Device reboot. This
does not affect the ZyXEL Device's configuration.
Figure 97 Maintenance > Tools >Restart
154
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide

CHAPTER 18
Diagnostic
18.1 Overview
The route between a CO VDSL switch and one of its CPE may go through switches owned by
independent organizations. A connectivity fault point generally takes time to discover and
impacts subscriber’s network access. In order to eliminate the management and maintenance
efforts, IEEE 802.1ag is a Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) specification which allows
network administrators to identify and manage connection faults. Through discovery and
verification of the path, CFM can detect, analyze and isolate connectivity faults in bridged
LANs.
18.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
The 802.1ag screen lets perform CFM actions (Section 18.3 on page 156).
18.2 What You Need to Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read through this chapter.
How CFM Works
A Maintenance Association (MA) defines a VLAN and associated Maintenance End Point
(MEP) ports on the device under a Maintenance Domain (MD) level. An MEP port has the
ability to send Connectivity Check Messages (CCMs) and get other MEP ports information
from neighbor devices’ CCMs within an MA.
CFM provides two tests to discover connectivity faults.
• Loopback test - checks if the MEP port receives its Loop Back Response (LBR) from its
target after it sends the Loop Back Message (LBM). If no response is received, there might
be a connectivity fault between them.
• Link trace test - provides additional connectivity fault analysis to get more information on
where the fault is. If an MEP port does not respond to the source MEP, this may indicate a
fault. Administrators can take further action to check and resume services from the fault
according to the line connectivity status report.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
155
Chapter 18 Diagnostic
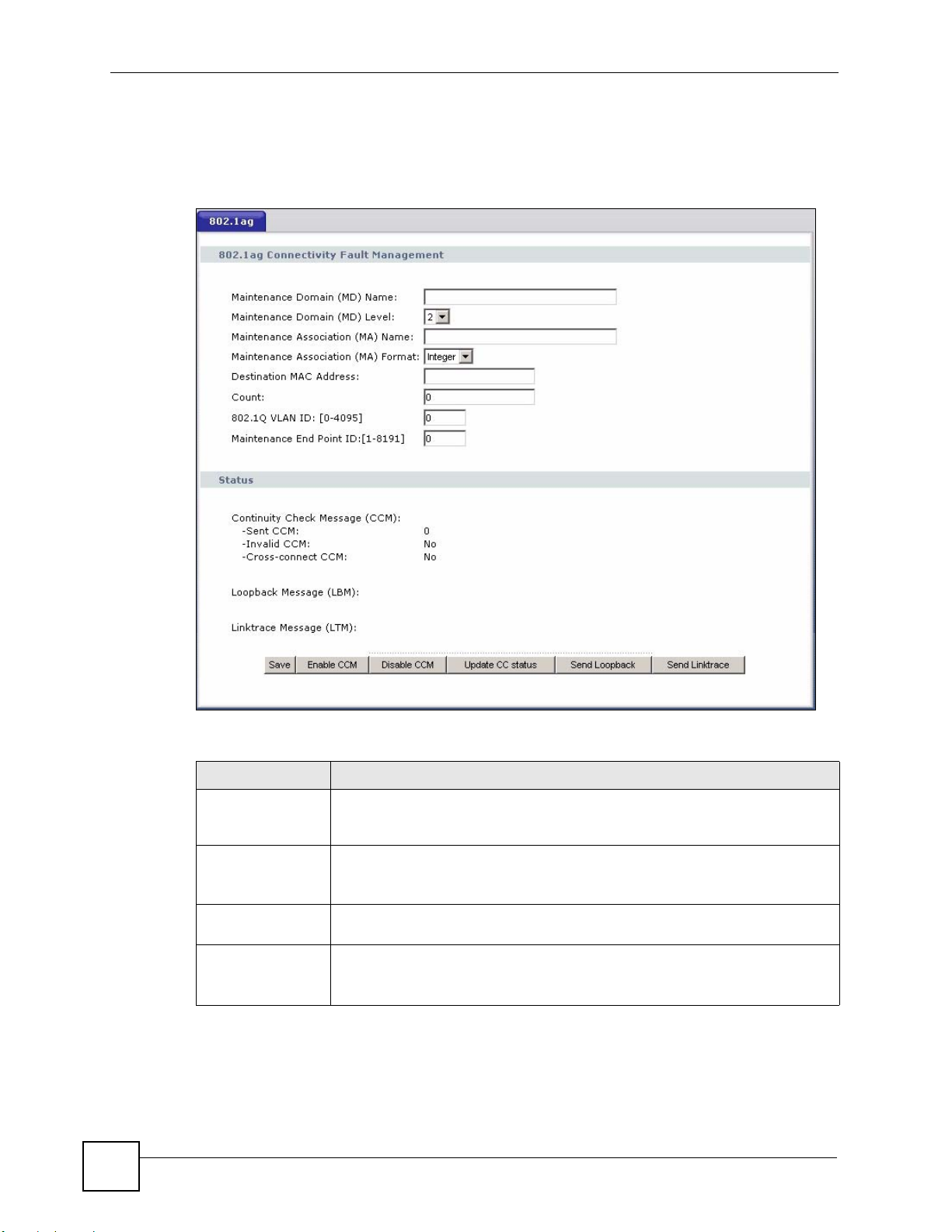
18.3 The 802.1ag Screen
Click Diagnostic to open the following screen. Use this screen to perform CFM actions.
Figure 98 802.1ag
156
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 52 802.1ag
LABEL DESCRIPTION
802.1ag
Connectivity Fault
Management
Maintenance
Domain (MD)
Name
Maintenance
Domain (MD) Level
Maintenance
Association (MA)
Name
Type a name of up to 39 pr in table English keyboard characters for this MD.
The combined length of the MD Name and MA name must be less or equal to
44bytes.
Select a level (0-7) under which you want to create an MA.
Type a name of up to 39 pr in table English keyboard characters for this MA.
The combined length of the MD Name and MA name must be less or equal to
44bytes.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide

Chapter 18 Diagnostic
Table 52 802.1ag (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Maintenance
Association (MA)
Format
Select the format which the ZyXEL Device uses to send this MA information in
the domain (MD). Options are VID, String and Integer.
If you select VID or Integer, the ZyXEL Device adds the VLAN ID you specified
for an MA in the CCM.
If you select String, the ZyXEL Device adds the MA name you specified above in
the CCM.
Note: The MEPs in the same MA shoule use the same MA format.
Destination MAC
Address
Count Set how many times the ZyXEL Device send loopback messages (LBMs).
802.1Q VLAN ID Type a VLAN ID (0-4095) for this MA.
Maintenance End
Point ID
Status
Continuity Check
Message (CCM)
Loopback Message
(LBM)
Linktrace Message
(LTM)
Enable CCM Click this button to have the selected MEP send Connectivity Check Messages
Disable CCM Click this button to disallow the selected MEP to send Connectivity Check
Update CC status Click this button to reload the test result.
Send Loopback Click this button to have the selected MEP send the LBM (Loop Back Message)
Send Linktrace Click this button to have the selected MEP send the LTMs (Link Trace
Enter the target device’s MAC address to which the ZyXEL Device performs a
CFM loopback test.
Enter an ID number (1-8191) for this MEP port. Each MEP port needs a unique
ID number within an MD. The MEP ID is to identify an MEP port used when you
perform a CFM action
This shows how many Connectivity Check Messages (CCMs) are sent and if
there is any invalid CCM or cross-connect CCM.
This shows how many Loop Back Messages (LBMs) are sent and if there is any
inorder or outorder Loop Back Response (LBR) received from a remote MEP.
This shows the Time-to-Live (TTL) value and destination MAC address in the
Link Trace Response (L TR).
(CCMs) to other MEPs.
Messages (CCMs) to other MEPs.
to a specified remote end point.
Messages) to a specified remote end point.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
157

Chapter 18 Diagnostic
158
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide

CHAPTER 19
Troubleshooting
This chapter offers some suggestions to solve problems you might encounter. The potential
problems are divided into the following categories.
• Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
• ZyXEL Device Access and Login
• Internet Access
19.1 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
V The ZyXEL Device does not turn on. None of the LEDs turn on.
1 Make sure the ZyXEL Device is turned on.
2 Make sure you are using the power adaptor or cord included with the ZyXEL Device.
3 Make sure the power adaptor or cord is connected to the ZyXEL Device and plugged in
to an appropriate power source. Make sure the power source is turned on.
4 Turn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
5 If the problem continues, contact the vendor.
V One of the LEDs does not behave as expected.
1 Make sure you understand the normal behavior of the LED. See Section 1.5 on page 26.
2 Check the hardware connections. See the Quick Start Guide.
3 Inspect your cables for damage. Contact the vendor to replace any damaged cables.
4 Turn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
5 If the problem continues, contact the vendor.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
159
Chapter 19 Troubleshooting
19.2 ZyXEL Device Access and Login
V I forgot the IP address for the ZyXEL Device.
1 The default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
2 If you changed the IP address and have forgotten it, you might get the IP address of the
ZyXEL Device by looking up the IP address of the default gateway for your computer.
To do this in most Windows computers, click Star t > Run, enter cmd, and then enter
ipconfig. The IP address of the Default Gateway might be the IP address of the ZyXEL
Device (it depends on the network), so enter this IP address in your Internet browser.
3 If this does not work, you have to reset the device to its factory defaults. See Section 1.6
on page 28.
V I forgot the password.
1 The default password is 1234.
2 If this does not work, you have to reset the device to its factory defaults. See Section 1.6
on page 28.
V I cannot see or access the Login screen in the web configurator.
1 Make sure you are using the correct IP address.
• The default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
• If you changed the IP address (Section on page 72), use the new IP address.
• If you changed the IP address and have forgotten it, see the troubleshooting
suggestions for I forgot the IP address for the ZyXEL Device.
2 Check the hardware connections, and make sure the LEDs are behaving as expected. See
the Quick Start Guide.
3 Make sure your Internet browser does not block pop-up windows and has JavaScripts
and Java enabled. See Appendix B on page 197.
4 Reset the device to its factory defaults, and try to access the ZyXEL Device with the
default IP address. See Section 1.6 on page 28.
5 If the problem continues, contact the network administrator or vendor, or try one of the
advanced suggestions.
160
Advanced Suggestions
• If your computer is connected wirelessly, use a computer that is connected to a
ETHERNET port.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Chapter 19 Troubleshooting
V I can see the Login screen, but I cannot log in to the ZyXEL Device.
1 Make sure you have entered the user name and password correctly . The default password
is 1234. These fields are case-sensitive, so make sure [Caps Lock] is not on.
2 Turn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
3 If this does not work, you have to reset the device to its factory defaults. See Section
19.1 on page 159.
19.3 Internet Access
V I cannot access the Internet.
1 Check the hardware connections, and make sure the LEDs are behaving as expected. See
the Quick Start Guide and Section 1.5 on page 26.
2 Make sure you entered your ISP account information correctly in the WAN screens.
These fields are case-sensitive, so make sure [Caps Lock] is not on.
3 If you are trying to access the Internet wirelessly, make sure the wireless settings in the
wireless client are the same as the settings in the AP.
4 Disconnect all the cables from your device, and follow the directions in the Quick Start
Guide again.
5 If the problem continues, contact your ISP.
V I cannot access the Internet anymore. I had access to the Internet (with the
ZyXEL Device), but my Internet connection is not available anymore.
1 Check the hardware connections, and make sure the LEDs are behaving as expected. See
the Quick Start Guide and Section 1.5 on page 26.
2 Turn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
3 If the problem continues, contact your ISP.
V The Internet connection is slow or intermittent.
1 There might be a lot of traffic on the network. Look at the LEDs, and check Section 1.5
on page 26. If the ZyXEL Device is sending or receiving a lot of information, try closing
some programs that use the Internet, especially peer-to-peer applications.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
161

Chapter 19 Troubleshooting
2 Check the signal strength. If the signal strength is low, try moving your computer closer
to the ZyXEL Device if possible, and look around to see if there are any devices that
might be interfering with the wireless network (for example, microwaves, other wireless
networks, and so on).
3 Turn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
4 If the problem continues, contact the network administrator or vendor, or try one of the
advanced suggestions.
Advanced Suggestions
• Check the settings for QoS. If it is disabled, you might consider activating it. If it is
enabled, you might consider raising or lowering the priority for some applications.
162
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide

Chapter 19 Troubleshooting
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
163

Chapter 19 Troubleshooting
164
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
CHAPTER 20
Product Specifications
The following tables summarize the ZyXEL Device’s hardware and firmware features.
20.1 Hardware Specifications
Table 53 Hardware Specifications
Dimensions (220 W) x (150 D) x (40 H) mm
Weight 485 g
Power Specification 18VDC 1A
Built-in Switch Four auto-negotiating, auto MDI/MDI-X 10/100 Mbps RJ-45 Ethernet ports
RESET Button Restores factory defaults
Antenna One attached external dipole antenna, 3dBi
WPS Button 1 second: turn on or off WLAN
5 seconds: enable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup)
Operation Temperature 0º C ~ 40º C
Storage Temperature -20º ~ 60º C
Operation Humidity 20% ~ 85% RH
Storage Humidity 20% ~ 90% RH
20.2 Firmware Specifications
Table 54 Firmware Specifications
Default IP Address 192.168.1.1
Default Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 (24 bits)
Default Password 1234
DHCP Server IP Pool 192.168.1.33 to 192.168.1.254
Static DHCP Addresses 10
Static Routes 16
Device Management Use the web configurator to easi ly configure the rich range of features on
the ZyXEL Device.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
165
Chapter 20 Product Specifications
Table 54 Firmware Specifications (continued)
Wireless Functionality
(wireless devices only)
Firmware Upgrade Download new firmware (when available) from the ZyXEL web site and use
Configuration Backup &
Restoration
Port Forwarding If you have a server (mail or web server for example) on your network, you
DHCP (Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol)
Dynamic DNS Support With Dynamic DNS (Domain Name System) support, you can use a fixed
IP Multicast IP multicast is used to send traffic to a specific group of computers. The
Time and Date Get the current time and date from an external server when you turn on your
Logs Use logs for troubleshooting. You can send logs from the ZyXEL Device to
Universal Plug and Play
(UPnP)
QoS (Quality of Service) You can efficiently manage traffic on your network by reserving bandwidth
Remote Management This allows you to decide whether a service (HTTP or FTP traffic for
PPPoE Support
(RFC2516)
Other PPPoE Features PPPoE idle time out
Multiple PVC
(Permanent Virtual
Circuits) Support
IP Alias IP alias allows you to partition a physical network into logical networks over
Packet Filters Your device’s packet filtering function allows added network security and
Allow the IEEE 802.11b and/or IEEE 802.11g wireless clients to connect to
the ZyXEL Device wirelessly. Enable wireless security (WEP, WPA(2),
WPA(2)-PSK) and/or MAC filtering to protect your wireless network.
the web configurator to put it on the ZyXEL Device.
Note: Only upload firmware for your specific model!
Make a copy of the ZyXEL Device’s configuration. Y ou can put it back on the
ZyXEL Device later if you decide to revert back to an earlier configuration.
can use this feature to let people access it from the Internet.
Use this feature to have the ZyXEL Device assign IP addresses, an IP
default gateway and DNS servers to computers on your network. Your
device can also act as a surrogate DHCP server (DHCP Relay) where it
relays IP address assignment from the actual real DHCP server to the
clients.
URL, www.zyxel.com for example, with a dynamic IP address. You must
register for this service with a Dynamic DNS service provider.
ZyXEL Device supports versions 1 and 2 of IGMP (Internet Group
Management Protocol) used to join multicast groups (see RFC 2236).
ZyXEL Device. You can also set the time manually. These dates and times
are then used in logs.
an external syslog server.
A UPnP-enabled device can dynamically join a network, obtain an IP
address and convey its capabilities to other devices on the network.
and giving priority to certain types of traffic and/or to particular computers.
example) from a computer on a network (LAN or WAN for example) can
access the ZyXEL Device.
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) emulates a dial-up
connection. It allows your ISP to use their existing network configuration
with newer broadband technologies such as ADSL. The PPPoE driver on
your device is transparent to the computers on the LAN, which see only
Ethernet and are not aware of PPPoE thus saving you from having to
manage PPPoE clients on individual computers.
PPPoE dial on demand
Your device supports up to 8 Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs).
the same Ethernet interface. Your device supports three logical LAN
interfaces via its single physical Ethernet interface with the your device itself
as the gateway for each LAN network.
management.
166
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Chapter 20 Product Specifications
Table 54 Firmware Specifications (continued)
ADSL Standards Support ITU G.992.1 G.dmt (Annex B, U-R2)
EOC specified in ITU-T G.992.1
ADSL2 G.dmt.bis (G.992.3)
ADSL2 G.lite.bis (G.992.4)
ADSL 2/2+ AnnexM
ADSL2+ (G.992.5)
Reach-Extended ADSL (RE ADSL)
SRA (Seamless Rate Adaptation)
Auto-negotiating rate adaptation
ADSL physical connection ATM AAL5 (ATM Adaptation Layer type 5)
Multi-protocol over AAL5 (RFC 2684/1483)
PPP over ATM AAL5 (RFC 2364)
PPP over Ethernet (RFC 2516)
Multiple PPPoE
VC-based and LLC-based multiplexing
Up to 8 PVCs (Permanent Virtual Circuits)
I.610 F4/F5 OAM
Zero configuration
Other Protocol Support PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) link layer protocol
Transparent bridging for unsupported network layer protocols
RIP I/RIP II
ICMP
ATM QoS
SNMP v1 and v2c with MIB II support (RFC 1213)
IP Multicasting IGMP v1 and v2
IGMP Proxy
Management Embedded Web Configurator
Remote Firmware Upgrade
Syslog
TR-069
20.3 Wireless Features
Table 55 Wireless Features
External Antenna The ZyXEL Device is equipped with an attached antenna to provide a
Wireless LAN MAC Address
Filtering
WEP Encryption WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encrypts data frames before
Wi-Fi Protected Access Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a subset of the IEEE 802.11i
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
clear radio signal between the wireless stations and the access
points.
Your device can check the MAC addresses of wireless stations
against a list of allowed or denied MAC addresses.
transmitting over the wireless network to help keep network
communications private.
security standard. Key differences between WPA and WEP are user
authentication and improved data encryption.
167
Chapter 20 Product Specifications
Table 55 Wireless Features
WPA2 WPA 2 is a wireless security standard that defines stronger
Other Wireless Features IEEE 802.11g Compliance
The following list, which is not exhaustive, illustrates the standards supported in the ZyXEL
Device.
Table 56 Standards Supported
STANDARD DESCRIPTION
RFC 867 Daytime Protocol
RFC 868 Time Protocol.
RFC 1058 RIP-1 (Routing Information Protocol)
RFC 1112 IGMP v1
RFC 1157 SNMPv1: Simple Network Management Protocol version 1
RFC 1305 Network Time Protocol (NTP version 3)
RFC 1441 SNMPv2 Simple Network Management Protocol version 2
RFC 1483 Multiprotocol Encapsulation over ATM Adaptation Layer 5
RFC 1631 IP Network Address Translator (NAT)
RFC 1661 The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
RFC 1723 RIP-2 (Routing Information Protocol)
RFC 1901 SNMPv2c Simple Network Management Protocol version 2c
RFC 2236 Internet Group Management Protocol, Version 2.
RFC 2364 PPP over AAL5 (PPP over ATM over ADSL)
RFC 2408 Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP)
RFC 2516 A Method for Transmitting PPP Over Ethernet (PPPoE)
RFC 2684 Multiprotocol Encapsulation over ATM Adaptation Layer 5.
RFC 2766 Network Address Translation - Protocol
IEEE 802.11 Also known by the brand Wi-Fi, denotes a set of Wireless LAN/WLAN
IEEE 802.11b Uses the 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) band
encryption, authentication and key management than WPA.
Frequency Range: 2.4 GHz ISM Band
Advanced Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
Data Rates: 54Mbps, 11Mbps, 5.5Mbps, 2Mbps, and 1 Mbps Auto
Fallback
WPA2
WMM
IEEE 802.11i
IEEE 802.11e
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) Data Encryption 64/128/256 bit.
WLAN bridge to LAN
Up to 32 MAC Address filters
IEEE 802.1x
Store up to 32 built-in user profiles using EAP-MD5 (Local User
Database)
External RADIUS server using EAP-MD5, TLS, TTLS
standards developed by working group 11 of the IEEE LAN/MAN
Standards Committee (IEEE 802).
168
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Chapter 20 Product Specifications
Table 56 Standards Supported (continued)
STANDARD DESCRIPTION
IEEE 802.11g Uses the 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) band
IEEE 802.11g+ Turbo and Super G modes
IEEE 802.11d S tandard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks: Media Access Control
(MAC) Bridges
IEEE 802.11x Port Based Network Access Control.
IEEE 802.11e QoS IEEE 802.11 e Wireless LAN for Quality of Service
ANSI T1.413, Issue 2 Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) standard.
G dmt(G.992.1) G.992.1 Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) Transceivers
ITU G.992.1 (G.DMT) ITU standard for ADSL using discrete multitone modulation.
ITU G.992.2 (G. Lite) ITU standard for ADSL using discrete multitone modulation.
ITU G.992.3 (G.dmt.bis) ITU standard (also referred to as ADSL2) that extends the capability of
basic ADSL in data rates.
ITU G.992.4 (G.lite.bis) ITU standard (also referred to as ADSL2) that extends the capability of
basic ADSL in data rates.
ITU G.992.5 (ADSL2+) ITU standard (also referred to as ADSL2+) that extends the capability of
Microsoft PPTP MS PPTP (Microsoft's implementation of Point to Point Tunneling Protocol)
MBM v2 Media Bandwidth Management v2
RFC 2383 ST2+ over ATM Protocol Specification - UNI 3.1 Version
TR-069 TR-069 DSL Forum Standard for CPE Wan Management.
1.363.5 Compliant AAL5 SAR (Segmentation And Re-assembly)
basic ADSL by doubling the number of downstream bits.
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
169

Chapter 20 Product Specifications
170
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
PART VI
Appendices and
Index
" The appendices provide general information. Some details may not apply to
your ZyXEL Device.
Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address (173)
Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions (197)
IP Addresses and Subnetting (205)
Wireless LANs (215)
Common Services (229)
Legal Information (233)
Customer Support (237)
Index (243)
171

172
APPENDIX A
Setting Up Your Computer’s IP
Address
" Your specific ZyXEL device may not support all of the operating systems
described in this appendix. See the product specifications for more information
about which operating systems are supported.
This appendix shows you how to configure the IP settings on your computer in order for it to
be able to communicate with the other devices on your network. Windows Vista/XP/2000,
Mac OS 9/OS X, and all versions of UNIX/LINUX include the software components you need
to use TCP/IP on your computer.
If you manually assign IP information instead of using a dynamic IP, make sure that your
network’s computers have IP addresses that place them in the same subnet.
In this appendix, you can set up an IP address for:
• Windows XP/NT/2000 on page 174
• Windows Vista on page 177
• Mac OS X: 10.3 and 10.4 on page 181
• Mac OS X: 10.5 on page 184
• Linux: Ubuntu 8 (GNOME) on page 187
• Linux: openSUSE 10.3 (KDE) on page 191
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
173
Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
Windows XP/NT/2000
The following example uses the default Windows XP display theme but can also apply to
Windows 2000 and Windows NT.
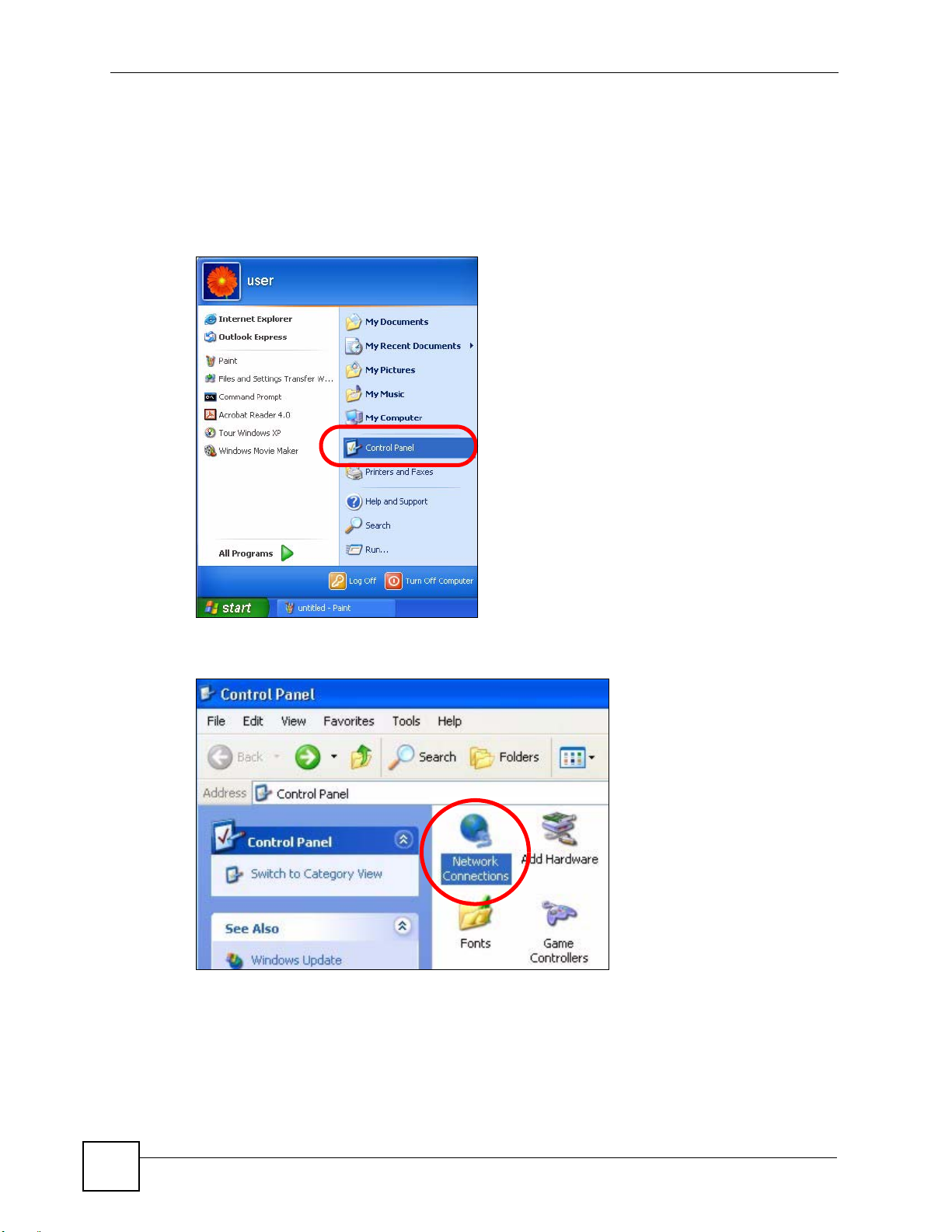
1 Click Start > Control Panel.
Figure 99 Windows XP: Start Menu
2 In the Control Panel, click the Network Connections icon.
Figure 100 Windows XP: Control Panel
174
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
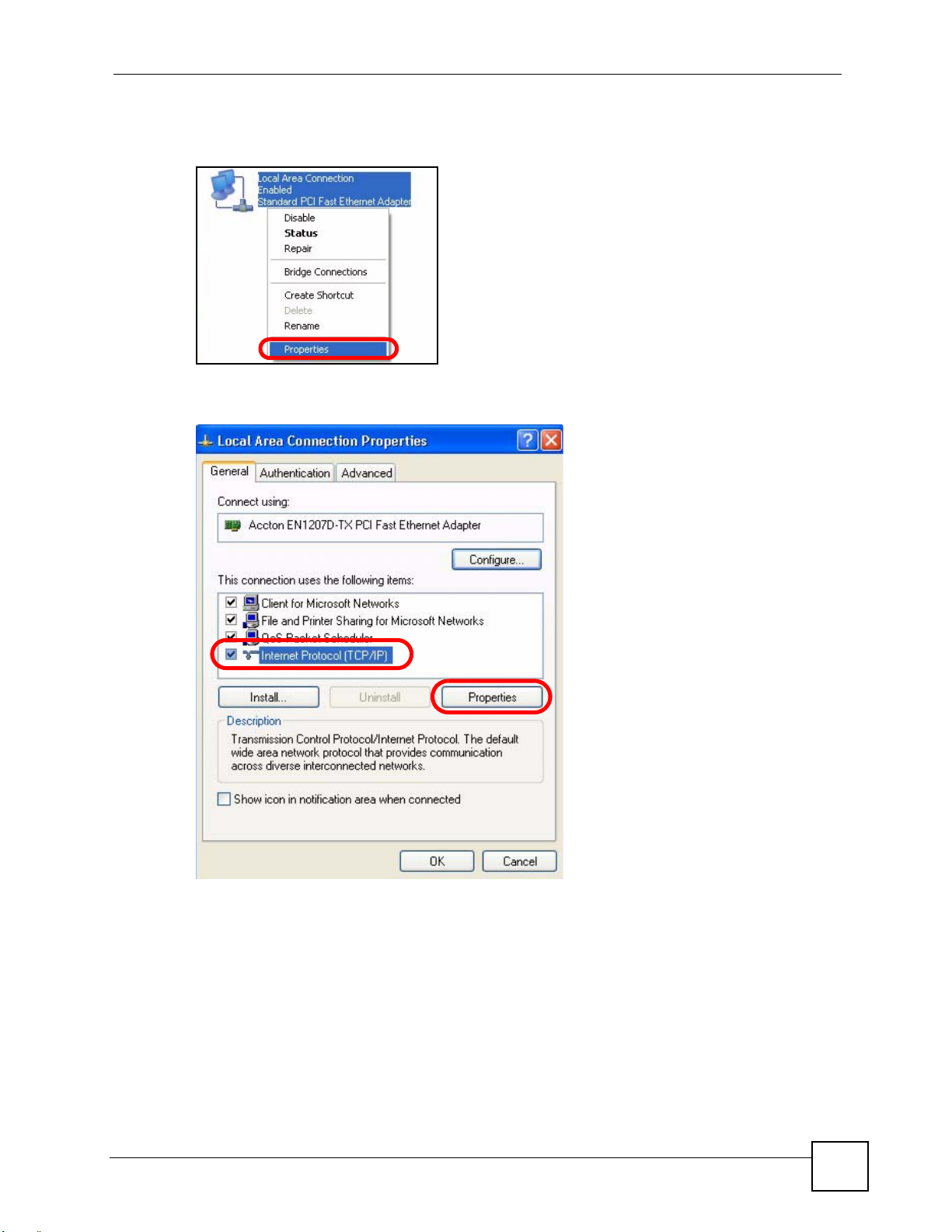
3 Right-click Local Area Connection and then select Properties.
Figure 101 Windows XP: Control Panel > Network Connections > Properties
4 On the General tab, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and then click Properties.
Figure 102 Windows XP: Local Area Connection Properties
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
175
Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
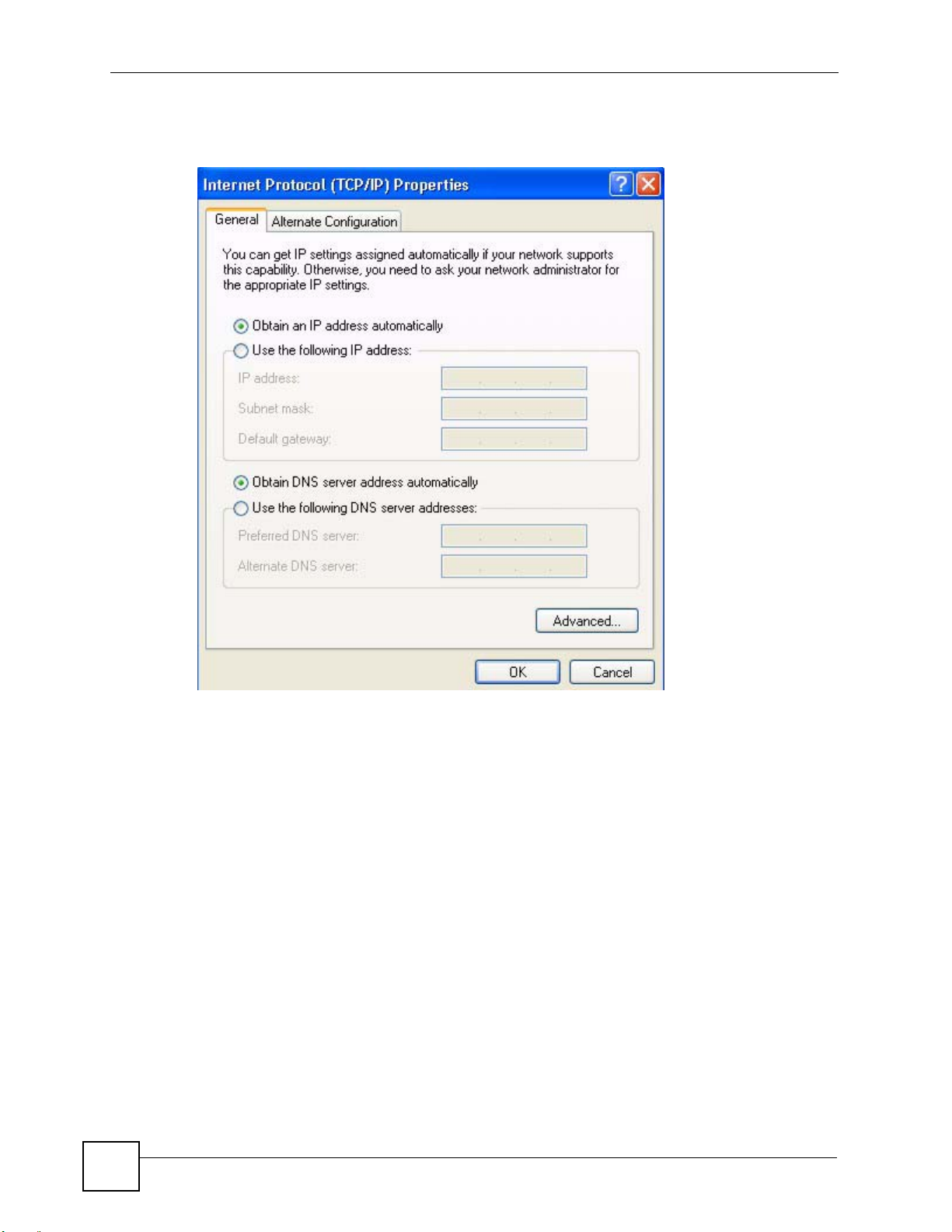
5 The Internet Protocol TCP/IP Properties window opens.
Figure 103 Windows XP: Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties
6 Select Obtain an IP address automatically if your network administrator or ISP
assigns your IP address dynamically.
Select Use the following IP Address and fill in the IP address , Subnet mask, and
Default gateway fields if you have a static IP address that was assigned to you by your
network administrator or ISP. You may also have to enter a Preferred DNS server and
an Alternate DNS server, if that information was provided.
7 Click OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
8 Click OK to close the Local Area Connection Properties window.
Verifying Settings
1 Click Start > All Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt.
2 In the Command Prompt window, type "ipconfig" and then press [ENTER].
You can also go to Start > Control Panel > Network Connections, right-click a
network connection, click Status and then click the Support tab to view your IP address
and connection information.
176
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Windows Vista
This section shows screens from Windows Vista Professional.
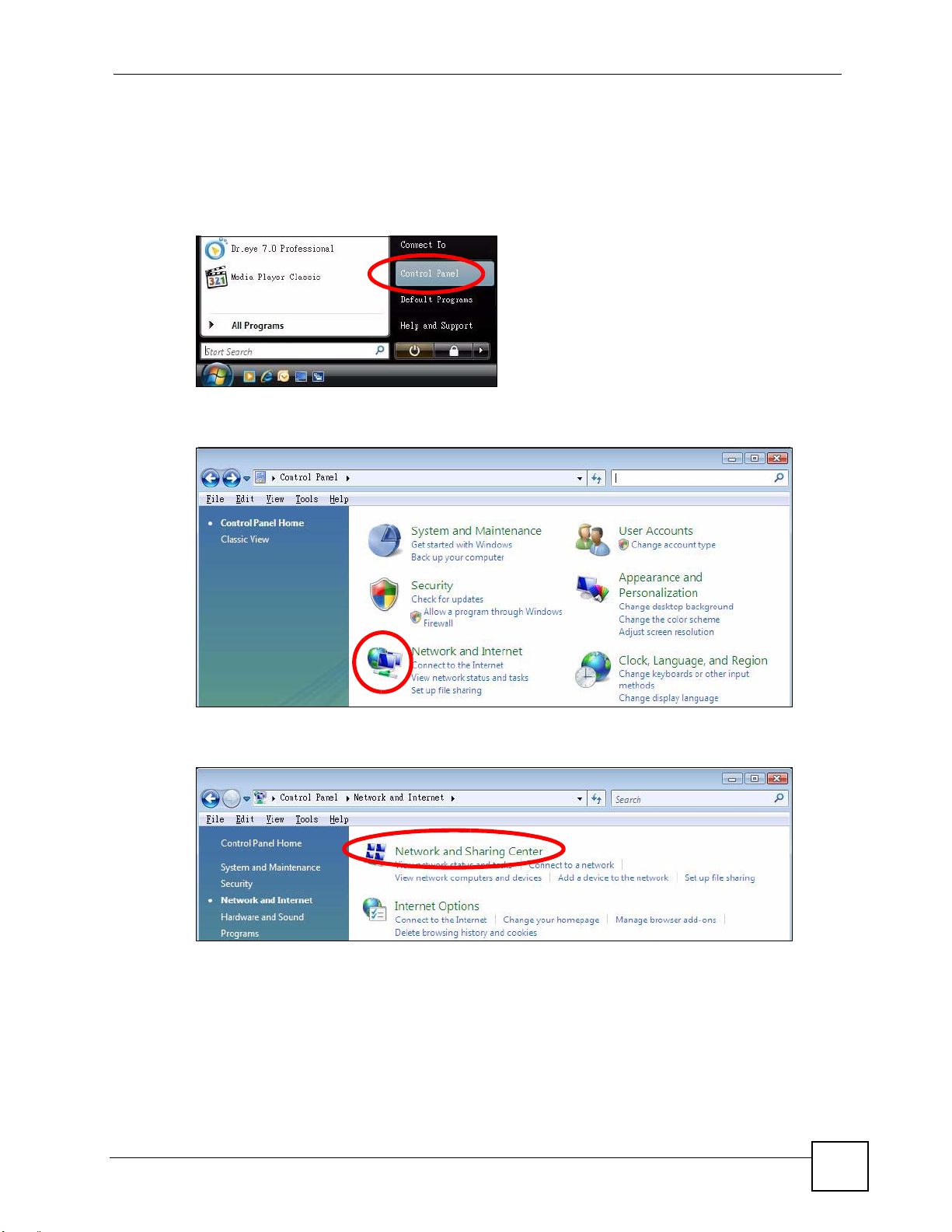
1 Click Start > Control Panel.
Figure 104 Windows Vista: Start Menu
2 In the Control Panel, click the Network and Internet icon.
Figure 105 Windows Vista: Control Panel
Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
3 Click the Network and Sharing Center icon.
Figure 106 Windows Vista: Network And Internet
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
177
Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
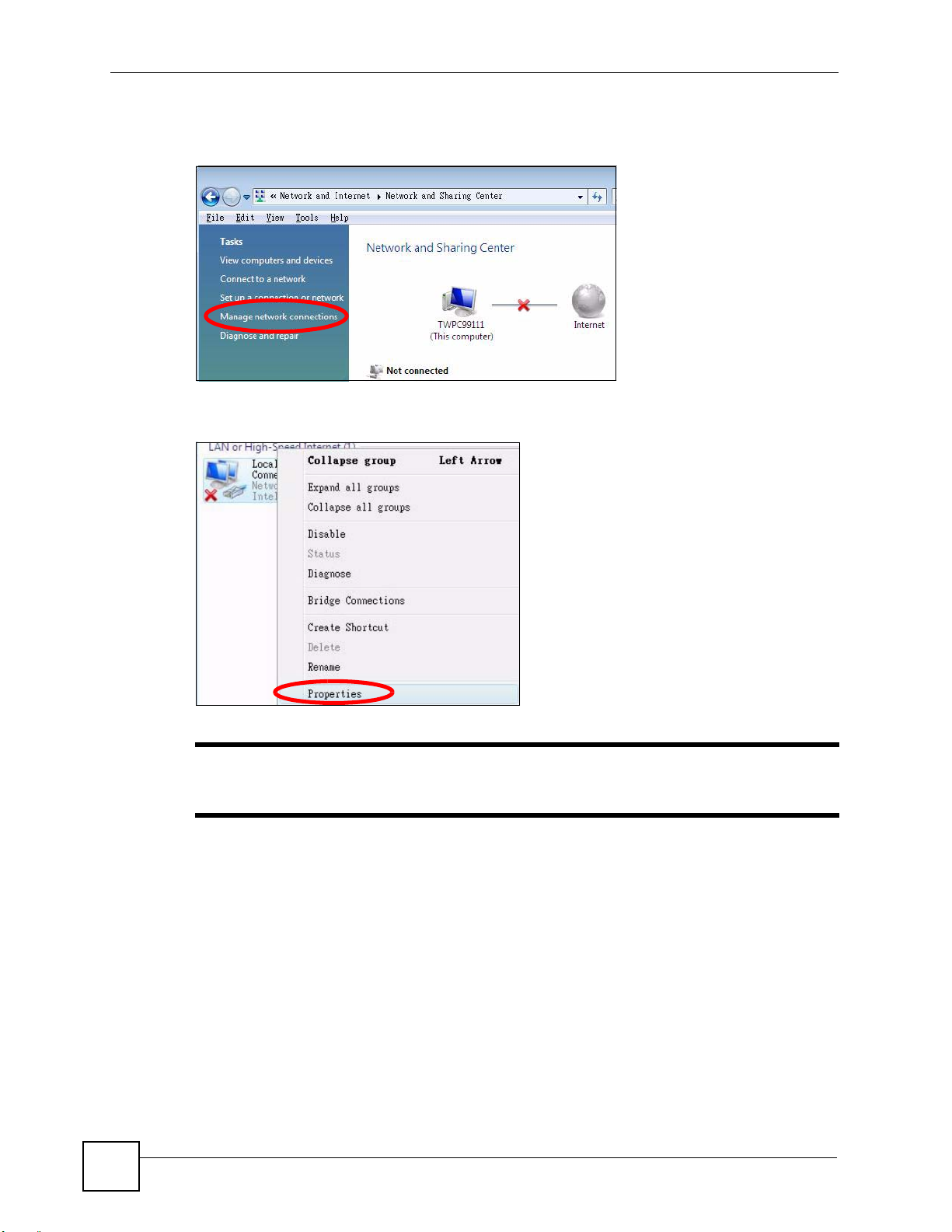
4 Click Manage network connections.
Figure 107 Windows Vista: Network and Sharing Center
5 Right-click Local Area Connection and then select Properties.
Figure 108 Windows Vista: Network and Sharing Center
" During this procedure, click Continue whenever Windows displays a screen
saying that it needs your permission to continue.
178
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
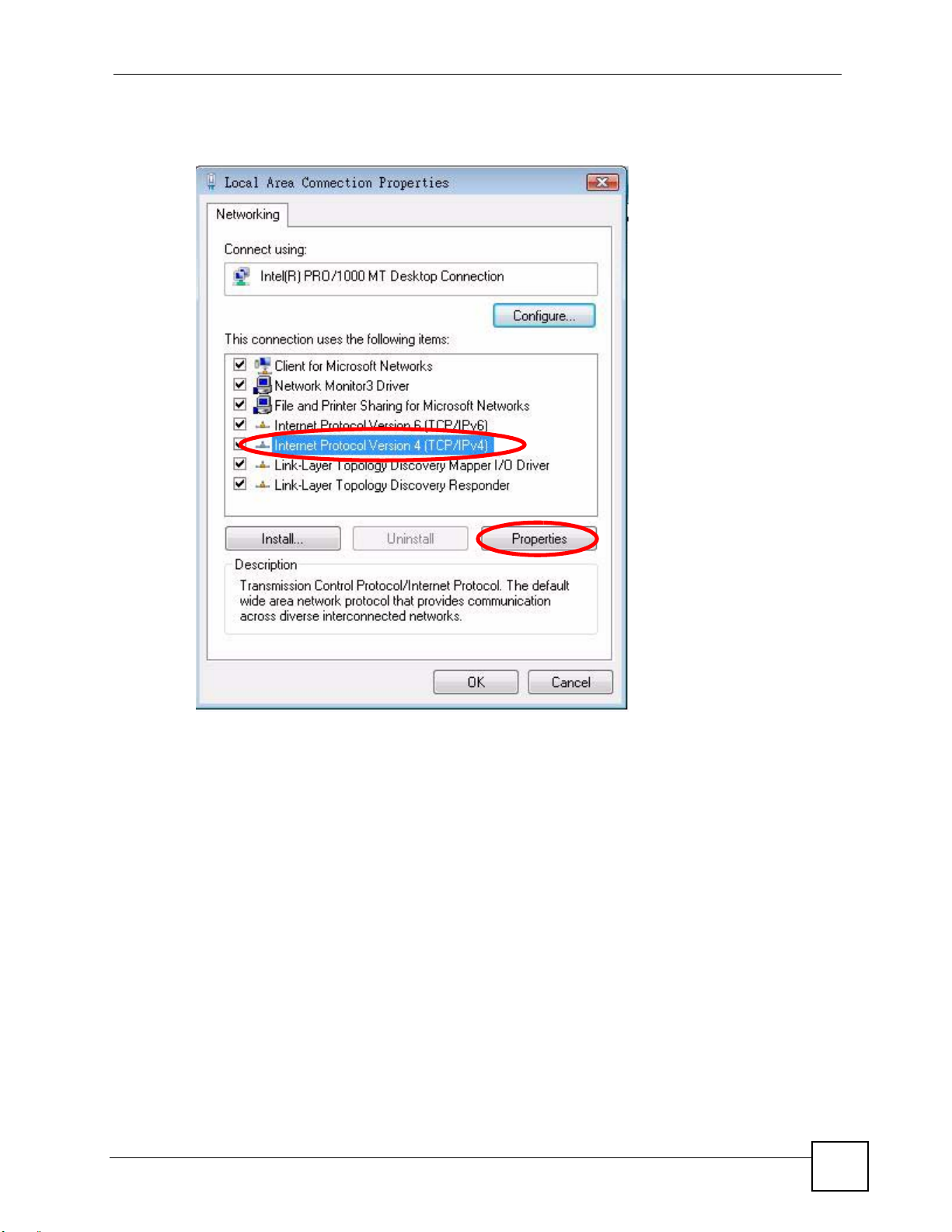
6 Select Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and then select Properties.
Figure 109 Windows Vista: Local Area Connection Properties
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
179
Appendix A Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
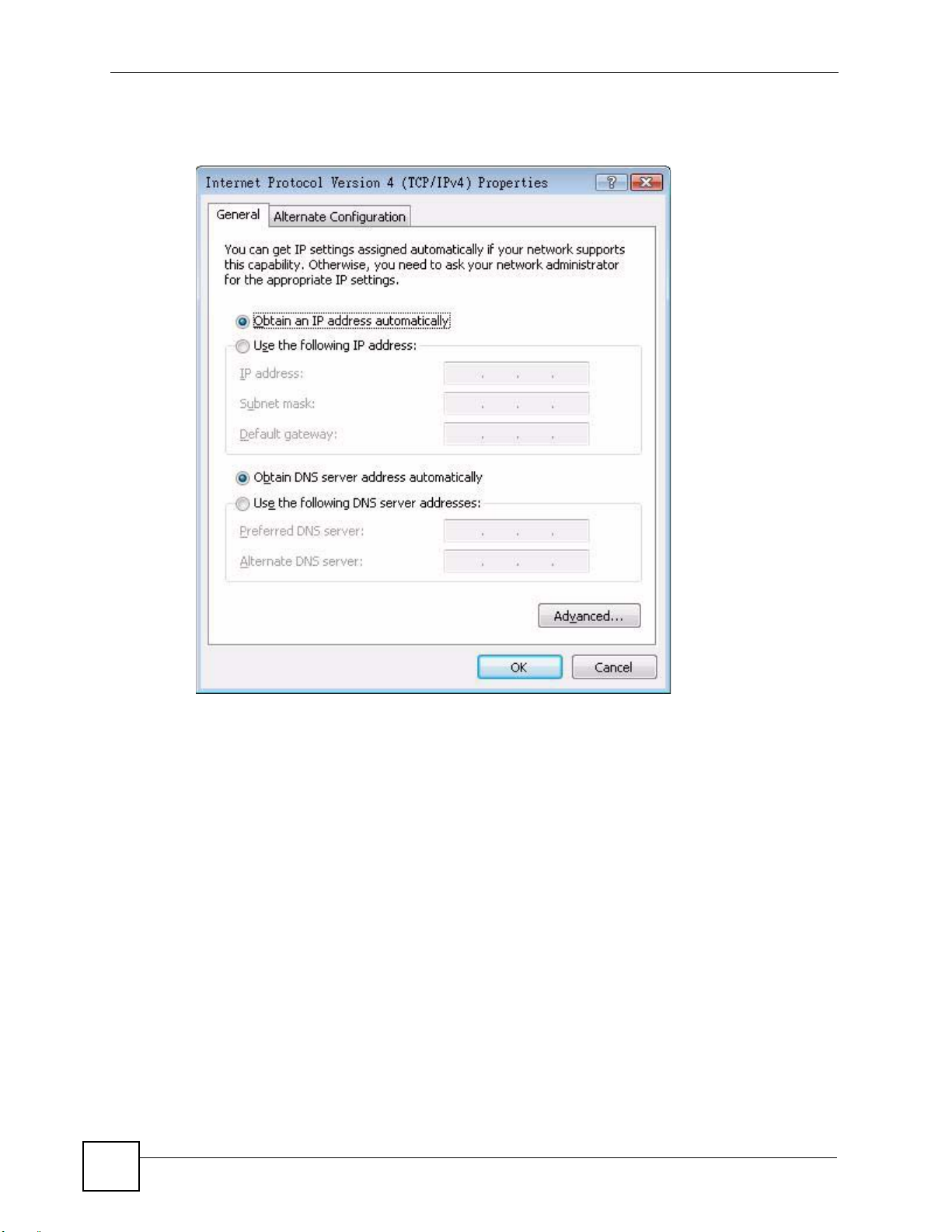
7 The Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties window opens.
Figure 110 Windows Vista: Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties
8 Select Obtain an IP address automatically if your network administrator or ISP
assigns your IP address dynamically.
Select Use the following IP Address and fill in the IP address , Subnet mask, and
Default gateway fields if you have a static IP address that was assigned to you by your
network administrator or ISP. You may also have to enter a Preferred DNS server and
an Alternate DNS server, if that information was provided.Click Advanced.
9 Click OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
10Click OK to clos e the Local Area Connection Properties window.
Verifying Settings
1 Click Start > All Programs > Accessories > Command Prompt.
2 In the Command Prompt window, type "ipconfig" and then press [ENTER].
You can also go to Start > Control Panel > Network Connections, right-click a
network connection, click Status and then click the Support tab to view your IP address
and connection information.
180
P-870HW-51a v2 User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...