ZyXEL P-660HNU-Tx Support Notes

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
1
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
P-660HNU-Tx
Wireless N ADSL2+ 4-port Gateway with USB
Support Notes
Version 1.02
Aug. 2011

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
2
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
FAQ ................................................................................................................. 6
System FAQ ................................................................................................ 6
1. What‟s the Embedded Web Configurator?............................................ 6
2. How do I access the P-660HNU-Tx Command Line Interface (CLI)? ... 6
3. How do I update the firmware and configuration file? ........................... 6
4. How do I upgrade the firmware by using Web configurator? ................ 6
5. How do I restore/backup P-660HNU-Tx configurations by using Web
Configurator? ............................................................................................ 7
6. What should I do if I forget the system password? ............................... 8
7. How to use the Reset button? ............................................................... 8
8. What is SUA? When should I use SUA? .............................................. 8
9. Is it possible to access a server running behind SUA from the outside
Internet? How can I do it? ................................................................ ......... 9
10. How can I protect against IP spoofing attacks? .................................. 9
Product FAQ ............................................................................................. 11
1. How can I manage P-660HNU-Tx? .................................................... 11
2. What is the default password for Web Configurator? .......................... 11
3. How do I know the P-660HNU-Tx's WAN IP address assigned by the
ISP? ........................................................................................................ 11
4. What is the micro filter or splitter used for? ......................................... 11
5. The P-660HNU-Tx supports Bridge and Router mode, what's the
difference between them? ...................................................................... 11
6. How do I know I am using PPPoE? .................................................... 12
7. Why does my provider use PPPoE? ................................................... 12
8. What is DDNS? ................................................................................... 12
9. When do I need DDNS service? ......................................................... 13
10. What is DDNS wildcard? Does the P-660HNU-Tx support DDNS
wildcard?................................................................................................. 13
11. What is Traffic Shaping? ................................................................... 13
12. Why do we perform traffic shaping in the P-660HNU-Tx? ................ 13
13. What do the parameters (PCR, SCR, MBS) mean? ......................... 14
14. What do the ATM QoS Types (CBR, UBR, VBR-nRT, VBR-RT) mean?
................................................................................................................ 14
ADSL FAQ ................................ ................................ ................................ . 15
1. How does ADSL compare to Cable modems? .................................... 15
2. What is the expected throughput? ................................ ...................... 15
3. What is the microfilter used for? ......................................................... 15
4. How do I know the ADSL line is up? ................................................... 15
5. How does the P-660HNU-Tx work on a noisy ADSL? ........................ 15
6. Does the VC-based multiplexing perform better than the LLC-based
multiplexing? ........................................................................................... 16
7. How do I know the details of my ADSL line statistics? ........................ 16
8. What are the signaling pins of the ADSL connector? .......................... 16
9. What is port binding? .......................................................................... 16

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
3
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Firewall FAQ ............................................................................................. 18
General .................................................................................................. 18
1. What is a network firewall? ................................................................. 18
2. What makes P-660HNU-Tx secure? ................................................... 18
3. What are the basic types of firewalls? ................................................ 18
4. Why do you need a firewall when your router has packet filtering and
NAT built-in? ........................................................................................... 19
5. What is Denials of Service (DoS) attack? ........................................... 19
6. What is Ping of Death attack? ............................................................. 19
7. What is Teardrop attack? .................................................................... 19
8. What is SYN Flood attack? ................................................................. 20
9. What is LAND attack? ......................................................................... 20
10 What is Brute-force attack? ................................................................ 20
11. What is IP Spoofing attack? .............................................................. 20
12. What are the default ACL firewall rules in P-660HNU-Tx?................ 21
Configuration .......................................................................................... 21
1. How do I active the firewall? ............................................................... 21
2. How do I prevent others from configuring my firewall? ....................... 21
3. Why can't I access my P-660HNU-Tx using Web Configurator/Telnet
over WAN? ............................................................................................. 21
Wireless FAQ ............................................................................................ 23
General FAQ .......................................................................................... 23
1. What is a Wireless LAN? .................................................................... 23
2. What are the advantages of Wireless LAN? ....................................... 23
3. What is the disadvantage of Wireless LAN? ....................................... 23
4. Where can you find 802.11 wireless networks? .................................. 24
5. What is an Access Point? ................................................................... 24
6. Is it possible to use wireless products from a variety of vendors? ...... 24
7. What is Wi-Fi? .................................................................................... 24
8. What types of devices use the 2.4GHz Band? .................................... 24
9. Does the 802.11 interfere with Bluetooth device? ............................... 25
10. Can radio signals pass through wall? ............................................... 25
11. What are potential factors that may causes interference among WLAN
products? ................................ ................................ ................................ 25
12. What's the difference between a WLAN and a WWAN? ................... 26
13. Can I manually swap the wireless module without damage any
hardware? ............................................................................................... 26
14. What wireless security mode does P-660HNU-Tx support? ............. 26
15. What Wireless standard does P-660HNU-Txsupport? ...................... 26
16. Does P-660HNU-Tx support WLAN MAC filtering? .......................... 26
17. Does P-660HNU-Tx support auto rate adaption? ............................. 26
Advanced FAQ ...................................................................................... 27
1. What is Ad Hoc mode? ....................................................................... 27
2. What is Infrastructure mode? .............................................................. 27

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
4
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
3. How many Access Points are required in a given area? ..................... 27
4. What is Direct-Sequence Spread Spectrum Technology – (DSSS)? .. 27
5. What is Frequency-hopping Spread Spectrum Technology – (FHSS)?
................................................................................................................ 27
6. Do I need the same kind of antenna on both sides of a link? ............. 28
7. Why the 2.4 GHZ Frequency range? .................................................. 28
8. What is Server Set ID (SSID)? ............................................................ 28
9. What is an ESSID? ............................................................................. 28
Security FAQ............................................................................................. 28
1. How do I secure the data across the P-660HNU-Tx Access Point's radio
link? ........................................................................................................ 28
2. What is WEP? ..................................................................................... 29
3. What is WPA-PSK? ............................................................................ 29
4. What is the difference between 40-bit and 64-bit WEP? ..................... 29
5. What is a WEP key? ........................................................................... 29
6. Will 128-bit WEP communicates with 64-bit WEP? ............................ 29
7. Can the SSID be encrypted? .............................................................. 29
8. By turning off the broadcast of SSID, can someone still sniff the SSID?
................................................................................................................ 30
9. What are Insertion Attacks? ................................................................ 30
10. What is Wireless Sniffer? .................................................................. 30
Application Notes ........................................................................................ 31
General Application Notes....................................................................... 31
1. Internet Access Using P-660HNU-Tx under Bridge mode .................. 31
2. Internet Access Using P-660HNU-Tx under Routing mode ................ 34
3. 3G backup .......................................................................................... 37
4. SUA Notes .......................................................................................... 42
5. Using the Dynamic DNS (DDNS) ........................................................ 49
6. QoS .................................................................................................... 50
7. Network Management Using SNMP ................................................... 52
8. SSH .................................................................................................... 55
9. Using IP Alias ..................................................................................... 55
10. Using IP Multicast ............................................................................. 56
11. How to configure filter rules on P-660HNU-Tx? ................................ 57
12. Change WAN MTU via WEB-GUI. .................................................... 60
13. Manage CPE via TR-069 ................................................................ .. 61
14. USB sharing ...................................................................................... 63
Wireless Application Notes ..................................................................... 67
1. Configure a Wireless Client to Ad hoc mode ...................................... 67
2. MAC Filter ........................................................................................... 73
3. Setup WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) .............................................. 76
4. Site Survey ......................................................................................... 80
5. Configure WPA(2)-PSK ...................................................................... 83
6. The WPS/WLAN Button ...................................................................... 87

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
5
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Support Tool................................................................................................. 88
1. Upgrading Firmware via Web GUI ...................................................... 88
2. Backing – up the Configuration ........................................................... 88
3. Uploading Configuration via Web GUI ................................................ 89

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
6
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
FAQ
System FAQ
1. What‟s the Embedded Web Configurator?
The web configurator is an HTML-based management interface that allows
easy device setup and management via Internet browser.
2. How do I access the P-660HNU-Tx Command Line Interface (CLI)?
The Command Line Interface is for the Administrator use only, and it could be
accessed via telnet session.
Note: It is protected by super password, admin/1234 by factory default.
3. How do I update the firmware and configuration file?
You can do this if you access the P-660HNU-Tx (x here stands for 1 or 3) as
Administrator. You can upload the firmware and configuration file to Prestige
from Web Configurator. Note: There may be firmware that could not be
upgraded from Web Configurator. In this case, ZyXEL will prepare
special Upload Software for you. Please read the firmware release note
carefully when you want to upload a new firmware.
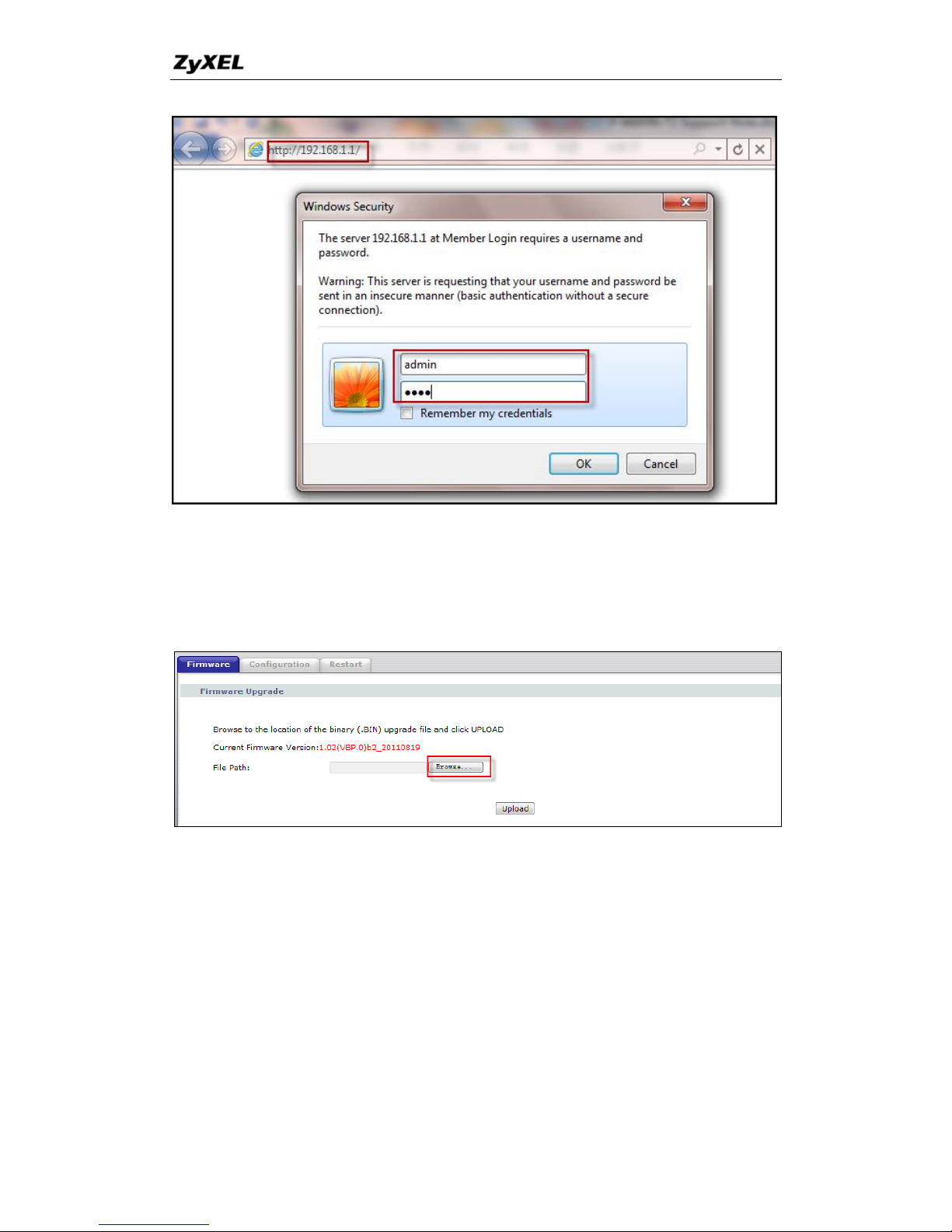
4. How do I upgrade the firmware by using Web configurator?
The P-660HNU-Tx allows you to transfer the firmware to P-660HNU-Tx using
Web Configurator. The procedure for uploading firmware via Web Configurator
is as follows.
a. Type „http://192.168.1.1‟ in the web browser URL box in your PC to
login to your P-660HNU-Tx.
Note: The factory default LAN IP is 192.168.1.1.
b. Login with the administrator account. admin/1234 by default.
P-660HNU Series Support Notes
7
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
c. To upgrade firmware, you can do it in Web Configurator, Advanced
Setup, Maintenance -> Tools -> Firmware. After data transfer is
finished, the P-660HNU-Tx will program the upgraded firmware into
FLASH ROM and reboot itself.
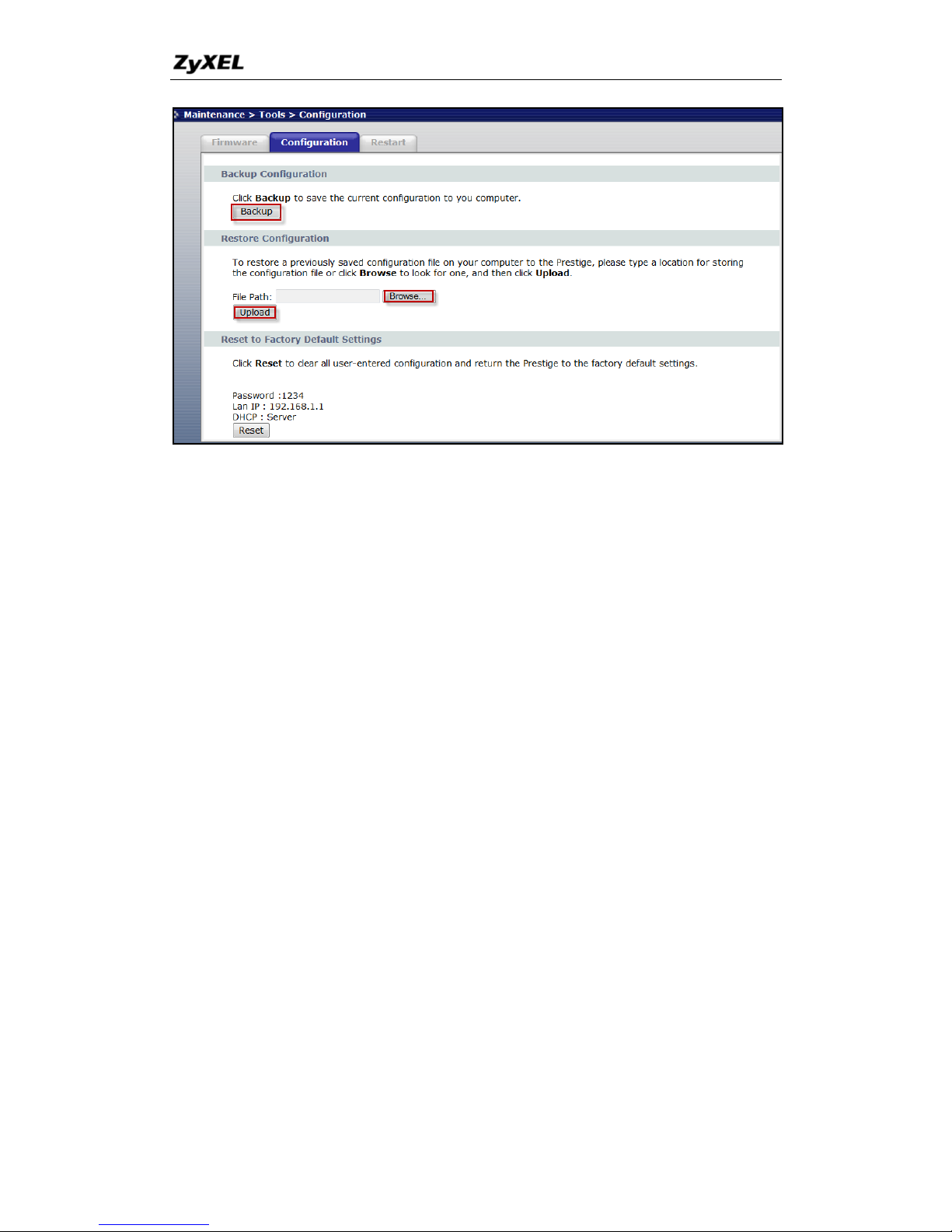
5. How do I restore/backup P-660HNU-Tx configurations by using Web
Configurator?
a. Log into your P-660HNU-Tx using Web Configurator. Please refer to the
step a & b above.
b. To backup the P-660HNU-Tx configurations, you can click Backup in
the page Maintenance -> Tools -> Configuration.
c. To restore the P-660HNU-Tx configurations, you can type the file path
or click Browser to look for one, and then click Upload.
P-660HNU Series Support Notes
8
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
6. What should I do if I forget the system password?
In case you forget the system password, you can erase the current
configuration and restore factory defaults this way:
Use the RESET button of P-660HNU-Tx to reset the router. After the router is
reset, the LAN IP address will be reset to '192.168.1.1', the common user
username will be reset to 'user', there is no password for common user
account, the Administrator username/password will be reset to „admin/1234‟.
7. How to use the Reset button?
a. Turn your P-660HNU-Tx on. Make sure the POWER led is on (not
blinking)
b. Press the RESET button for ten seconds and then release it. If the
POWER LED begins to blink, the default configuration has been
restored and the P-660HNU-Tx restarts.
8. What is SUA? When should I use SUA?
SUA (Single User Account) is a unique feature supported by Prestige router
which allows multiple people to access Internet concurrently for the cost of a
single user account.
When Prestige acting as SUA receives a packet from a local client destined for
the outside Internet, it replaces the source address in the IP packet header
with its own address and the source port in the TCP or UDP header with
another value chosen out of a local pool. It then recomputes the appropriate
header checksums and forwards the packet to the Internet as if it is originated

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
9
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
from Prestige using the IP address assigned by ISP. When reply packets from
the external Internet are received by Prestige, the original IP source address
and TCP/UDP source port numbers are written into the destination fields of the
packet (since it is now moving in the opposite direction), the checksums are
recomputed, and the packet is delivered to its true destination. This is because
SUA keeps a table of the IP addresses and port numbers of the local systems
currently using it.
By fatory default, the NAT is select as SUA in Web Configurator, Advanced
Setup, Network -> NAT -> General -> NAT Setup.
9. Is it possible to access a server running behind SUA from the outside
Internet? How can I do it?
Yes, it is possible because P-660HNU-Tx delivers the packet to the local
server by looking up to a SUA server table. Therefore, to make a local server
accessible to the outside users, the port number and the inside IP address of
the server must be configured. (You can configure it in Web Configurator,
Advanced Setup, Network -> NAT -> Port Forwarding).
10. How can I protect against IP spoofing attacks?
The P-660HNU-Tx's filter sets provide a means to protect against IP spoofing
attacks. The basic scheme is as follows:
For the input data filter:
Deny packets from the outside that claim to be from the inside
Allow everything that is not spoofing us
Filter rule setup: Filter type =TCP/IP Filter Rule
Active =Yes
Source IP Addr =a.b.c.d
Source IP Mask =w.x.y.z
Action Matched =Drop
Action Not Matched =Forward
Where a.b.c.d is an IP address on your local network and w.x.y.z is your
netmask:
For the output data filters:
Deny bounce back packet
Allow packets that originate from us

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
10
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Filter rule setup:
Filter Type =TCP/IP Filter Rule
Active =Yes
Destination IP Addr =a.b.c.d
Destination IP Mask =w.x.y.z
Action Matched =Drop
Action No Matched =Forward
Where a.b.c.d is an IP address on your local network and w.x.y.z is your
netmask.

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
11
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Product FAQ
1. How can I manage P-660HNU-Tx?
The Embedded Web GUI for Local and Remote management.
CLI (Command-line interface)
Telnet support (Administrator Password Protected ) for remote
configuration change and status monitoring
TR-069. This is an auto-configuration server used to remotely configure
your device.
2. What is the default password for Web Configurator?
There is account for P-660HNU-Tx Web Configurator: Administrator
Account.
By factory default the password for the admininistrator accounts is:
Administrator Account: admin/1234.
You can change the Administrator Account‟s password in
Maintenance>System>General page after you logging in the Web
Configurator.
Please record your new password whenever you change it. The system
will lock you out if you have forgotten your password.
3. How do I know the P-660HNU-Tx's WAN IP address assigned by the
ISP?
You can view "My WAN IP <from ISP> : x.x.x.x" shown in Web Configurator
„Status->Device Information ->WAN Information‟ to check this IP address.
4. What is the micro filter or splitter used for?
Generally, the voice band uses the lower frequency ranging from 0 to 4KHz,
while ADSL data transmission uses the higher frequency. The micro filter acts
as a low-pass filter for your telephone set to ensure that ADSL transmissions
do not interfere with your voice transmissions. For the details about how to
connect the micro filter please refer to the user's manual.
5. The P-660HNU-Tx supports Bridge and Router mode, what's the
difference between them?
When the ISP limits some specific computers to access Internet, that means
only the traffic to/from these computers will be forwarded and the other will be
filtered. In this case, we use bridge mode which works as an ADSL modem to
connect to the ISP. The ISP will generally give one Internet account and limit

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
12
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
only one computer to access the Internet.
For most Internet users having multiple computers want to share an Internet
account for Internet access, they have to add another Internet sharing device,
like a router. In this case, we use the router mode which works as a general
Router plus an ADSL Modem.
6. How do I know I am using PPPoE?
PPPoE requires a user account to login to the provider's server. If you need to
configure a user name and password on your computer to connect to the ISP
you are probably using PPPoE. If you are simply connected to the Internet
when you turn on your computer, you probably are not. You can also check
your ISP or the information sheet given by the ISP. Please choose PPPoE as
the encapsulation type in the P-660HNU-Tx if the ISP uses PPPoE.
7. Why does my provider use PPPoE?
PPPoE emulates a familiar Dial-Up connection. It allows your ISP to provide
services using their existing network configuration over the broadband
connections. Besides, PPPoE supports a broad range of existing applications
and service including authentication, accounting, secure access and
configuration management.
8. What is DDNS?
The Dynamic DNS service allows you to alias a dynamic IP address to a static
hostname, allowing your computer to be more easily accessed from various
locations on the Internet. To use the service, you must first apply an account
from several free Web servers such as http://www.dyndns.org/.
Without DDNS, we always tell the users to use the WAN IP of the
P-660HNU-Tx to reach our internal server. It is inconvenient for the users if this
IP is dynamic. With DDNS supported by the P-660HNU-Tx, you apply a DNS
name (e.g., www.zyxel.com.tw) for your server (e.g., Web server) from a
DDNS server. The outside users can always access the web server using the
www.zyxel.com.tw regardless of the WAN IP of the P-660HNU-Tx.
When the ISP assigns the P-660HNU-Tx a new IP, the P-660HNU-Tx updates
this IP to DDNS server so that the server can update its IP-to-DNS entry. Once
the IP-to-DNS table in the DDNS server is updated, the DNS name for your
web server (i.e., www.zyxel.com.tw) is still usable.

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
13
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
9. When do I need DDNS service?
When you want your internal server to be accessed by using DNS name rather
than using the dynamic IP address we can use the DDNS service. The DDNS
server allows to alias a dynamic IP address to a static hostname. Whenever
the ISP assigns you a new IP, the P-660HNU-Tx sends this IP to the DDNS
server for its updates.
10. What is DDNS wildcard? Does the P-660HNU-Tx support DDNS
wildcard?
Some DDNS servers support the wildcard feature which allows the hostname,
*.yourhost.dyndns.org, to be aliased to the same IP address as
yourhost.dyndns.org. This feature is useful when there are multiple servers
inside and you want users to be able to use things such as
www.yourhost.dyndns.org and still reach your hostname.
Yes, the P-660HNU-Tx supports DDNS wildcard that http://www.dyndns.org/
supports. When using wildcard, you simply enter yourhost.dyndns.org in the
Host field in Advanced> Dynamic DNS page.
11. What is Traffic Shaping?
Traffic Shaping allocates the bandwidth to WAN dynamically and aims at
boosting the efficiency of the bandwidth. If there are serveral VCs in the
P-660HNU-Tx but only one VC activated at one time, the P-660HNU-Tx
allocates all the Bandwidth to the VC and the VC gets full bandwidth. If another
VCs are activated later, the bandwidth is yield to other VCs afterward.
12. Why do we perform traffic shaping in the P-660HNU-Tx?
The P-660HNU-Tx must manage traffic fairly and provide bandwidth allocation
for different sorts of applications, such as voice, video, and data. All
applications have their own natural bit rate. Large data transactions have a
fluctuating natural bit rate. The P-660HNU-Tx is able to support variable traffic
among different virtual connections. Certain traffic may be discarded if the
virtual connection experiences congestion. Traffic shaping defines a set of
actions taken by the P-660HNU-Tx to avoid congestion; traffic shaping takes
measures to adapt to unpredictable fluctuations in traffic flows and other
problems among virtual connections.

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
14
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
13. What do the parameters (PCR, SCR, MBS) mean?
Traffic shaping parameters (PCR, SCR, MBS) can be set in Web Configurator,
Advanced Setup, Network -> WAN-> Remote Node -> Edit -> Advanced
Setup -> ATM QOS:
Peak Cell Rate(PCR): The maximum bandwidth allocated to this connection.
The VC connection throughput is limited by PCR.
Sustainable Cell Rate(SCR): The least guaranteed bandwidth of a VC.
When there are multi-VCs on the same line, the VC throughput is guaranteed
by SCR.
Maximum Burst Size(MBS): The amount of cells transmitted through this
VC at the Peak Cell Rate before yielding to other VCs. Total bandwidth of the
line is dedicated to single VC if there is only one VC on the line. However, as
the other VC asking the bandwidth, the MBS defines the maximum number of
cells transmitted via this VC with Peak Cell rate before yielding to other VCs.
The P-660HNU-Tx holds the parameters for shaping the traffic among its
virtual channels. If you do not need traffic shaping, please set SCR = 0, MBS =
0 and PCR as the maximum value according to the line rate (for example, 2.3
Mbps line rate will result PCR as 5424 cell/sec.)
14. What do the ATM QoS Types (CBR, UBR, VBR-nRT, VBR-RT) mean?
Constant bit rate(CBR): An ATM bandwidth-allocation service that requires
the user to determine a fixed bandwidth requirement at the time the connection
is set up so that the data can be sent in a steady stream. CBR service is often
used when transmitting fixed-rate uncompressed video.
Unspecified bit rate(UBR): An ATM bandwidth-allocation service that does
not guarantee any throughput levels and uses only available bandwidth. UBR
is often used when transmitting data that can tolerate delays, such as e-mail.
Variable bit rate(VBR): An ATM bandwidth-allocation service that allows
users to specify a throughput capacity (i.e., a peak rate) and a sustained rate
but data is not sent evenly. You can select VBR for bursty traffic and
bandwidth sharing with other applications. It contains two subclasses:
Variable bit rate nonreal time (VBR-nRT):
Variable bit rate real time (VBR-RT):

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
15
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
ADSL FAQ
1. How does ADSL compare to Cable modems?
ADSL provides a dedicated service over a single telephone line; cable
modems offer a dedicated service over a shared media. While cable modems
have greater downstream bandwidth capabilities (up to 24 Mbps), that
bandwidth is shared among all users on a line, and will therefore vary, perhaps
dramatically, as more users in a neighborhood get online at the same time.
Cable modem upstream traffic will in many cases be slower than ADSL, either
because the particular cable modem is inherently slower, or because of rate
reductions caused by contention for upstream bandwidth slots. The big
difference between ADSL and cable modems, however, is the number of lines
available to each. There are no more than 12 million homes passed today that
can support two-way cable modem transmissions, and while the figure also
grows steadily, it will not catch up with telephone lines for many years.
Additionally, many of the older cable networks are not capable of offering a
return channel; consequently, such networks will need significant upgrading
before they can offer high bandwidth services.
2. What is the expected throughput?
In our lab test environment, we can get about 2Mbps DSL data rate on 15Kft
using the 26AWG loop. The shorter the loop, the better the throughput is.
3. What is the microfilter used for?
Generally, the voice band uses the lower frequency ranging from 0 to 4KHz,
while ADSL data transmission uses the higher frequency. The micro filter acts
as a low-pass filter for your telephone set to ensure that ADSL transmissions
do not interfere with your voice transmissions. For the details about how to
connect the micro filter please refer to the user's manual.
4. How do I know the ADSL line is up?
You can see the DSL LED Green on the P-660HNU-Tx's front panel is on
when the ADSL physical layer is up.
5. How does the P-660HNU-Tx work on a noisy ADSL?
Depending on the line quality, the P-660HNU-Tx uses "Fall Back" and "Fall
Forward" to automatically adjust the date rate.
P-660HNU Series Support Notes
16
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
6. Does the VC-based multiplexing perform better than the LLC-based
multiplexing?
Though the LLC-based multiplexing can carry multiple protocols over a single
VC, it requires extra header information to identify the protocol being carried
on the virtual circuit (VC). The VC-based multiplexing needs a separate VC for
carrying each protocol but it does not need the extra headers. Therefore, the
VC-based multiplexing is more efficient.
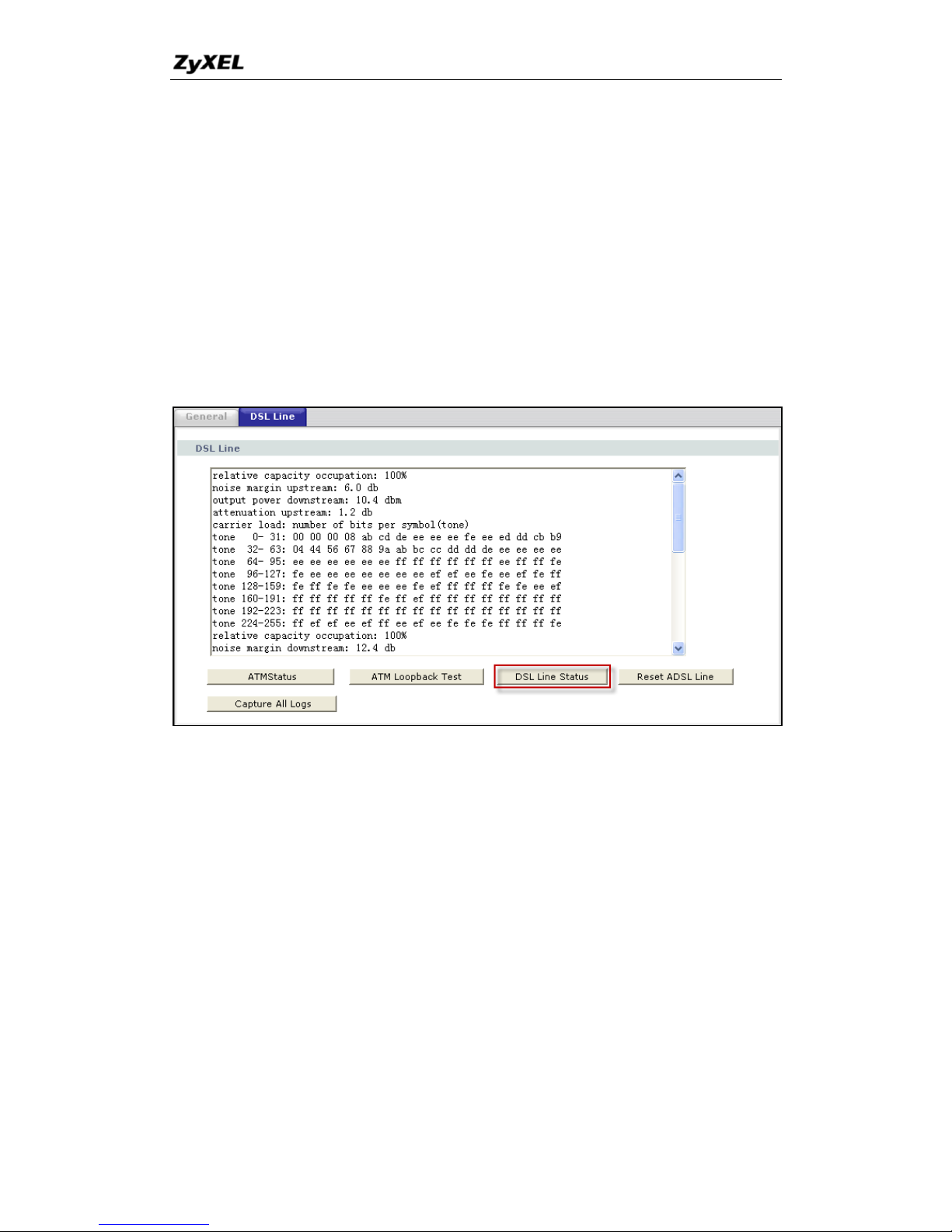
7. How do I know the details of my ADSL line statistics?
You can check it in Web Configurator, Advanced Setup,
Maintenance -> Diagnostic -> DSL Line -> DSL Status:
8. What are the signaling pins of the ADSL connector?
The signaling pins on the P-660HNU-Tx's ADSL connector are pin 3 and pin 4.
The middle two pins for a RJ11 cable.
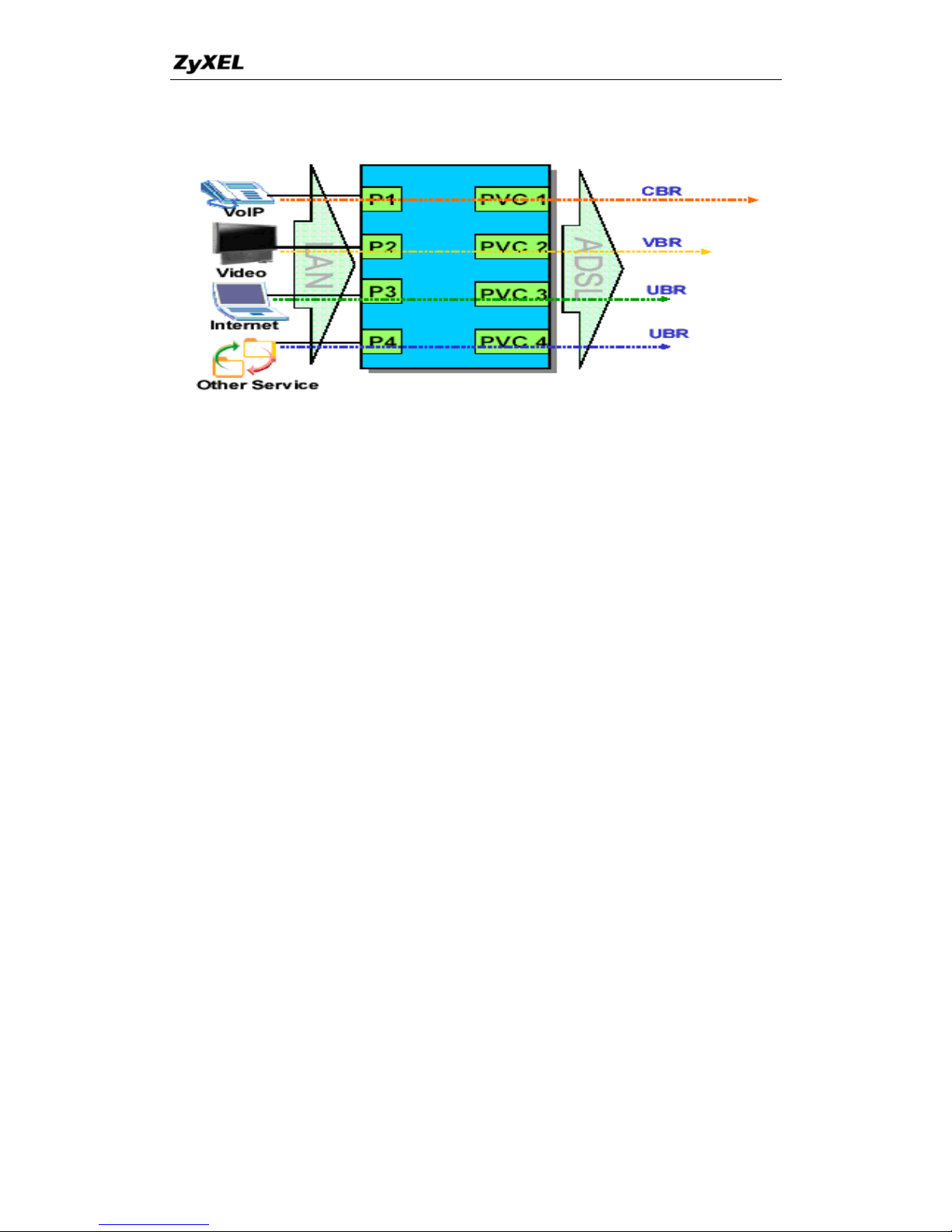
9. What is port binding?
More and more Telco/ISPs are providing three kinds of services (VoIP, Video
and Internet) over one existing ADSL connection.
The different services (such as video, VoIP and Internet access) require
different Qulity of Service.
The high priority is Voice (VoIP) data.
The Medium priority is Video (IPTV) data.
P-660HNU Series Support Notes
17
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
The low priority is internet access such as ftp etc …
Port binding is to bind different LAN ports to different PVCs, thus you can
configure each PVC separately to assign different QoS to different application.

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
18
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Firewall FAQ
General
1. What is a network firewall?
A firewall is a system or group of systems that enforces an access-control
policy between two networks. It may also be defined as a mechanism used to
protect a trusted network from an untrusted network. The firewall can be
thought of two mechanisms: One to block the traffic, and the other to permit
traffic.
2. What makes P-660HNU-Tx secure?
The P-660HNU-Tx is pre-configured to automatically detect and thwart Denial
of Service (DoS) attacks such as Ping of Death, SYN Flood, LAND attack etc.
It also uses stateful packet inspection to determine if an inbound connection is
allowed through the firewall to the private LAN. The P-660HNU-Tx supports
Network Address Translation (NAT), which translates the private local
addresses to one or multiple public addresses. This adds a level of security
since the clients on the private LAN are invisible to the Internet.
3. What are the basic types of firewalls?
Conceptually, there are three types of firewalls:
1. Packet Filtering Firewall
2. Application-level Firewall
3. Stateful Inspection Firewall
Packet Filtering Firewalls generally make their decisions based on the header
information in individual packets. These headers information include the
source, destination addresses and ports of the packets.
Application-level Firewalls generally are hosts running proxy servers, which
permit no traffic directly between networks, and which perform logging and
auditing of traffic passing through them. A proxy server is an application
gateway or circuit-level gateway that runs on top of general operating system
such as UNIX or Windows NT. It hides valuable data by requiring users to
communicate with secure systems by mean of a proxy. A key drawback of this
device is performance.
Stateful Inspection Firewalls restrict access by screening data packets against
defined access rules. They make access control decisions based on IP

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
19
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
address and protocol. They also 'inspect' the session data to assure the
integrity of the connection and to adapt to dynamic protocols. The flexible
nature of Stateful Inspection firewalls generally provides the best speed and
transparency, however, they may lack the granular application level access
control or caching that some proxies support.
4. Why do you need a firewall when your router has packet filtering and
NAT built-in?
With the spectacular growth of the Internet and online access, companies that
do business on the Internet face greater security threats. Although packet filter
and NAT restrict access to particular computers and networks, however, for
the other companies this security may be insufficient, because packets filters
typically cannot maintain session state. Thus, for greater security, a firewall is
considered.
5. What is Denials of Service (DoS) attack?
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks are aimed at devices and networks with a
connection to the Internet. Their goal is not to steal information, but to disable
a device or network so users no longer have access to network resources.
There are four types of DoS attacks:
1. Those that exploits bugs in a TCP/IP implementation such as Ping of
Death and Teardrop.
2. Those that exploits weaknesses in the TCP/IP specification such as
SYN Flood and LAND Attacks.
3. Brute-force attacks that flood a network with useless data such as
Smurf attack.
4. IP Spoofing
6. What is Ping of Death attack?
Ping of Death uses a 'PING' utility to create an IP packet that exceeds the
maximum 65535 bytes of data allowed by the IP specification. The oversize
packet is then sent to an unsuspecting system. Systems may crash, hang, or
reboot.
7. What is Teardrop attack?
Teardrop attack exploits weakness in the reassemble of the IP packet
fragments. As data is transmitted through a network, IP packets are often
broken up into smaller chunks. Each fragment looks like the original packet
except that it contains an offset field. The Teardrop program creates a series of

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
20
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
IP fragments with overlapping offset fields. When these fragments are
reassembled at the destination, some systems will crash, hang, or reboot.
8. What is SYN Flood attack?
SYN attack floods a targeted system with a series of SYN packets. Each
packet causes the targeted system to issue a SYN-ACK response, While the
targeted system waits for the ACK that follows the SYN-ACK, it queues up all
outstanding SYN-ACK responses on what is known as a backlog queue.
SYN-ACKs are moved off the queue only when an ACK comes back or when
an internal timer (which is set a relatively long intervals) terminates the TCP
three-way handshake. Once the queue is full, the system will ignore all
incoming SYN requests, making the system unavailable for legitimate users.
9. What is LAND attack?
In a LAN attack, hackers flood SYN packets to the network with a spoofed
source IP address of the targeted system. This makes it appear as if the host
computer sent the packets to itself, making the system unavailable while the
target system tries to respond to itself.
10 What is Brute-force attack?
A Brute-force attack, such as 'Smurf' attack, targets a feature in the IP
specification known as directed or subnet broadcasting, to quickly flood the
target network with useless data. A Smurf hacker flood a destination IP
address of each packet is the broadcast address of the network, the router will
broadcast the ICMP echo request packet to all hosts on the network. If there
are numerous hosts, this will create a large amount of ICMP echo request
packet, the resulting ICMP traffic will not only clog up the 'intermediary'
network, but will also congest the network of the spoofed source IP address,
known as the 'victim' network. This flood of broadcast traffic consumes all
available bandwidth, making communications impossible.
11. What is IP Spoofing attack?
Many DoS attacks also use IP Spoofing as part of their attack. IP Spoofing
may be used to break into systems, to hide the hacker's identity, or to magnify
the effect of the DoS attack. IP Spoofing is a technique used to gain
unauthorized access to computers by tricking a router or firewall into thinking
that the communications are coming from within the trusted network. To
engage in IP Spoofing, a hacker must modify the packet headers so that it
appears that the packets originate from a trusted host and should be allowed
through the router or firewall.
P-660HNU Series Support Notes
21
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
12. What are the default ACL firewall rules in P-660HNU-Tx?
There are two default ACLs pre-configured in the P-660HNU-Tx, one allows all
connections from LAN to WAN and the other blocks all connections from WAN
to LAN except of the DHCP packets.
Configuration
1. How do I active the firewall?
You can use the Web Configurator to active the firewall for P-660HNU-Tx. By
factory default, if you connect your PC to the LAN Interface of P-660HNU-Tx,
you can access Web Configurator via „http://192.168.1.1‟.
Note: Don‟t forget to type in the Administrator Password.
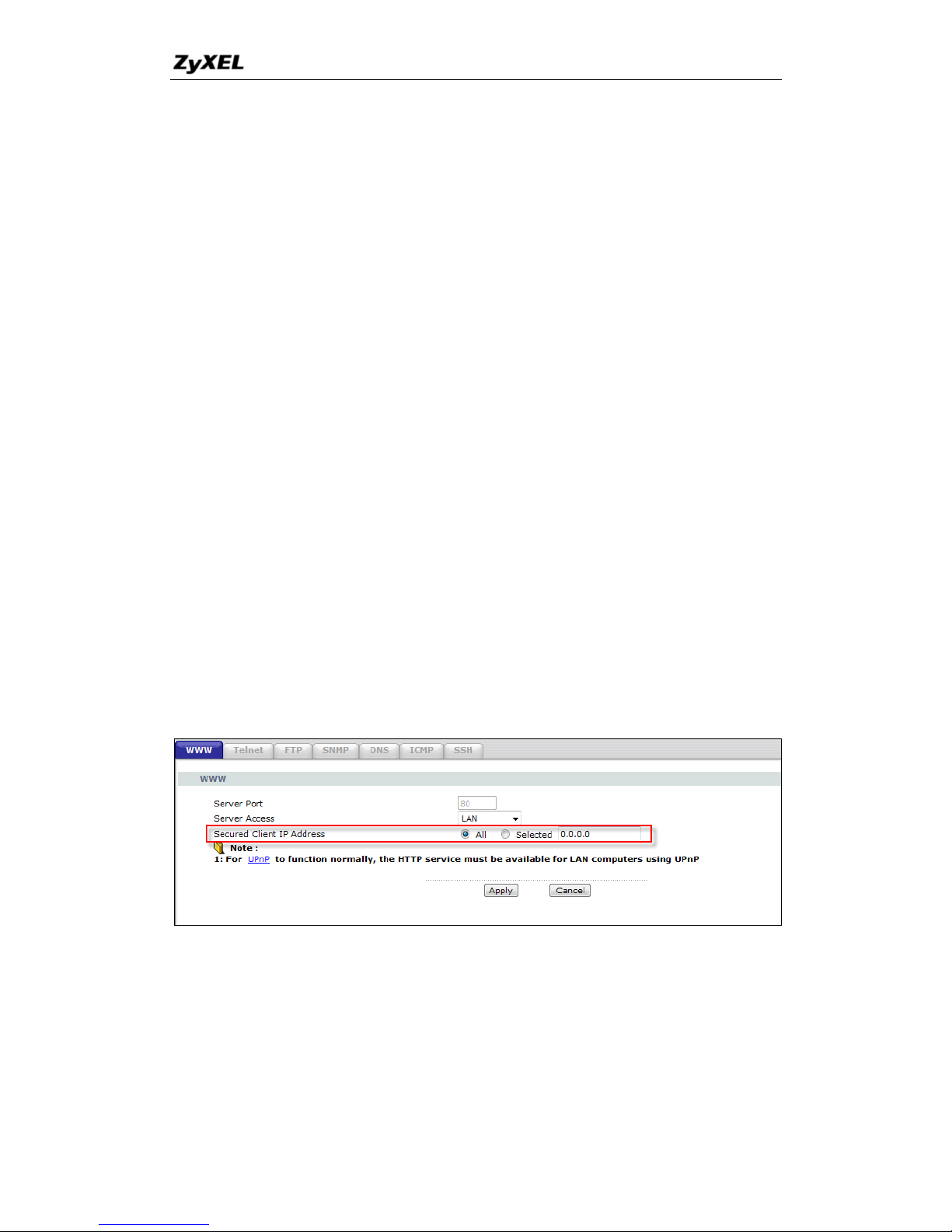
2. How do I prevent others from configuring my firewall?
There are several ways to protect others from touching the settings of your
firewall.
1. Change the default Administrator password since it is required when
setting up the firewall.
2. Limit who can access to your P-660HNU-Tx‟s Web Configurator. You
can enter the IP address of the secured LAN host in Web Configurator,
Advanced Setup, Advanced -> Remote MGNT ->Secured Client IP to
allow special access to your P-660HNU-Tx:
The default value in this field is 0.0.0.0, which means you do not care which
host is trying to telnet your P-660HNU-Tx or access the Web Configurator.
3. Why can't I access my P-660HNU-Tx using Web Configurator/Telnet
over WAN?
There are three reasons that WWW/Telnet from WAN is blocked.

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
22
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
(1) When the firewall is turned on, all connections from WAN to LAN are
blocked by the default ACL rule. To enable Telnet from WAN, you must turn
the firewall off.
(2)You have disabled WWW/Telnet service from WAN in Web Configurator,
Advanced setup, Advanced -> Remote MGNT. You need to enable
access from WAN.
(3) WWW/Telnet WAN access service is enabled but your host IP is not the
secured host entered in Web Configurator, Advanced setup, Advanced ->
Remote MGNT:

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
23
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Wireless FAQ
General FAQ
1. What is a Wireless LAN?
Wireless LANs provide all the functionality of wired LANs, without the need for
physical connections (wires). Data is modulated onto a radio frequency carrier
and transmitted through the air. Typical bit-rates are 11Mbps and 54Mbps,
although in practice data throughput is half of this. Wireless LANs can be
formed simply by equipping PC's with wireless NICs. If connectivity to a wired
LAN is required an Access Point (AP) is used as a bridging device. AP's are
typically located close to the centre of the wireless client population.
2. What are the advantages of Wireless LAN?
Mobility: Wireless LAN systems can provide LAN users with access to
real-time information anywhere in their organization. This mobility supports
productivity and service opportunities not possible with wired networks.
Installation Speed and Simplicity: Installing a wireless LAN system can be
fast and easy and can eliminate the need to pull cable through walls and
ceilings.
Installation Flexibility: Wireless technology allows the network to go where
wire cannot go.
Reduced Cost-of-Ownership: While the initial investment required for
wireless LAN hardware can be higher than the cost of wired LAN hardware,
overall installation expenses and life-cycle costs can be significantly lower.
Long-term cost benefits are greatest in dynamic environments requiring
frequent moves and changes.
Scalability: Wireless LAN systems can be configured in a variety of topologies
to meet the needs of specific applications and installations. Configurations are
easily changed and range from peer-to-peer networks suitable for a small
number of users to full infrastructure networks of thousands of users that
enable roaming over a broad area.
3. What is the disadvantage of Wireless LAN?

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
24
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
The speed of Wireless LAN is still relatively slower than wired LAN. The setup
cost of Wireless LAN is relative high because the equipment cost including
access point and PCMCIA Wireless LAN card is higher than hubs and CAT 5
cables.
4. Where can you find 802.11 wireless networks?
Airports, hotels, and even coffee shops like Starbucks are deploying 802.11
networks, so people can wirelessly surf the Internet with their laptops.
5. What is an Access Point?
The AP (access point also known as a base station) is the wireless server that
with an antenna and a wired Ethernet connection that broadcasts information
using radio signals. AP typically acts as a bridge for the clients. It can pass
information to wireless LAN cards that have been installed in computers or
laptops allowing those computers to connect to the campus network and the
Internet without wires.
6. Is it possible to use wireless products from a variety of vendors?
Yes. As long as the products comply to the same IEEE 802.11 standard. The
Wi-Fi logo is used to define 802.11b compatible products. Wi-Fi5 is a
compatibility standard for 802.11a products running in the 5GHz band.
7. What is Wi-Fi?
The Wi-Fi logo signifies that a product is interoperable with wireless
networking equipment from other vendors. A Wi-Fi logo product has been
tested and certified by the Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA).
The Socket Wireless LAN Card is Wi-Fi certified, and that means that it will
work (interoperate) with any brand of Access Point that is also Wi-Fi certified.
8. What types of devices use the 2.4GHz Band?
Various spread spectrum radio communication applications use the 2.4 GHz
band. This includes WLAN systems (not necessarily of the type IEEE

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
25
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
802.11b), cordless phones, wireless medical telemetry equipment and
Bluetooth™ short-range wireless applications, which include connecting
printers to computers and connecting modems or hands-free kits to mobile
phones.
9. Does the 802.11 interfere with Bluetooth device?
Any time devices are operated in the same frequency band, there is the
potential for interference.
Both the 802.11b/g and Bluetooth devices occupy the same2.4-to-2.483-GHz
unlicensed frequency range-the same band. But a Bluetooth device would not
interfere with other 802.11 devices much more than another 802.11 device
would interefere. While more collisions are possible with the introduction of a
Bluetooth device, they are also possible with the introduction of another 802.11
device, or a new 2.4 GHz cordless phone for that matter. But, BlueTooth
devices are usually low-power, so the effects that a Bluetooth device may have
on an 802.11 network, if any, aren't far-reaching.
10. Can radio signals pass through wall?
Transmitting through a wall is possible depending upon the material used in its
construction. In general, metals and substances with a high water content do
not allow radio waves to pass through. Metals reflect radio waves and concrete
attenuates radio waves. The amount of attenuation suffered in passing through
concrete will be a function of its thickness and amount of metal re-enforcement
used.
11. What are potential factors that may causes interference among WLAN
products?
Factors of interference:
(1) Obstacles: walls, ceilings, furniture… etc.
(2) Building Materials: metal door, aluminum studs.
(3) Electrical devices: microwaves, monitors, electric motors.
Solution:
(1) Minimizing the number of walls and ceilings
(2) Antenna is positioned for best reception
(3) Keep WLAN products away from electrical devices, eg: microwaves,
monitors, electric motors,…, etc.
(4) Add additional APs if necessary.

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
26
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
12. What's the difference between a WLAN and a WWAN?
WLANs are generally privately owned, wireless systems that are deployed in a
corporation, warehouse, hospital, or educational campus setting. Data rates
are high and there are no per-packet charges for data transmission.
WWANs are generally publicly shared data networks designed to provide
coverage in metropolitan areas and along traffic corridors. WWANs are owned
by a service provider or carrier. Data rates are low and charges are based on
usage. Specialized applications are characteristically designed around short,
burst messaging.
13. Can I manually swap the wireless module without damage any
hardware?
Yes, it will not harm the hardware, but the module will not be detected and
work after inserting to the slot. You need to reboot the router to initialize the
module.
14. What wireless security mode does P-660HNU-Tx support?
The wireless security modes supported on P-660HNU-Tx are: Static WEP,
WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK.
15. What Wireless standard does P-660HNU-Tx support?
It supports IEEE 802.11b/g/draft n standard. With an integrated 802.11n
Wireless Access Point, the router enables you to surf the Internet from
anywhere at home or in the office, delivering fast wireless speeds of up to
300Mbps.
16. Does P-660HNU-Tx support WLAN MAC filtering?
Yes, it supports up to 16 MAC Address filtering.
17. Does P-660HNU-Tx support auto rate adaption?
Yes, it means that the AP on P-660HNU-Tx will automatically decelerate when
devices move beyond the optimal range, or other interference is present. If the

P-660HNU Series Support Notes
27
All contents copyright © 2011 ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
device moves back within the range of a higher-speed transmission, the
connection will automatically speed up again. Rate shifting is a physical-layer
mechanism transparent to the user and the upper layers of the protocol stack.
Advanced FAQ
1. What is Ad Hoc mode?
A wireless network consists of a number of stations without using an access
point or any connection to a wired network.
2. What is Infrastructure mode?
Infrastructure mode implies connectivity to a wired communications
infrastructure. If such connectivity is required the Access Points must be used
to connect to the wired LAN backbone. Wireless clients have their
configurations set for "infrastructure mode" in order to utilise access points
relaying.
3. How many Access Points are required in a given area?
This depends on the surrounding terrain, the diameter of the client population,
and the number of clients. If an area is large with dispersed pockets of
populations then extension points can be used for extend coverage.
4. What is Direct-Sequence Spread Spectrum Technology – (DSSS)?
DSSS spreads its signal continuously over a wide frequency band. DSSS
maps the information bearing bit-pattern at the sending station into a higher
data rate bit sequence using a "chipping" code. The chipping code (also known
as processing gain) introduces redundancy which allows data recovery if
certain bit errors occur during transmission. The FCC rules the minimum
processing gain should be 10, typical systems use processing gains of 20.
IEEE 802.11b specifies the use of DSSS.
5. What is Frequency-hopping Spread Spectrum Technology – (FHSS)?
FHSS uses a narrowband carrier which hops through a predefined sequence
 Loading...
Loading...