Page 1

Chapter 11 Filters
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
151
1
1.4 IPv6 Filter
Use this screen to create and apply IPv6 filters. Click Security > Filter > IPv6
Filter. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 69 Security > Filter > IPv6 Filter
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 47 Security > Filter > IPv6 Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Rule Type
Rule Type selection Select White List to specify traffic to allow and Black List to
specify traffic to block.
IPv6 Filter Rule Editing
IPv6 Filter Rule Index Select the index number of the filter rule.
Active Use this field to enable or disable the filter rule.
Interface Select the PVC to which to apply the filter.
Page 2
Chapter 11 Filters
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
152
Direction Apply the filter to Incoming or Outgoing traffic direction.
Rule Type Use the IPv6 filter to block or allow traffic by IPv6 addresses.
Source IPv6 Address Enter the source IPv6 address of the packets you wish to filter.
This field is ignored if it is ::.
Source Prefix Length Enter the prefix length for the source IPv6 address
Destination IPv6
Address
Enter the destination IPv6 address of the packets you wish to
filter. This field is ignored if it is ::.
Destination Prefix
Length
Enter the prefix length for the destination IPv6 address.
ICMPv6 Type Select the ICMPv6 message type to filter. The following
message types can be selected:
1 / Destination Unreachable: 0 - no route to destination; 1 -
communication with destination administratively prohibited; 3 -
address unreachable; 4 - port unreachable
2 / Packet Too Big
3 / Time Exceeded: 0 - hop limit exceeded in transit; 1 -
fragment reassembly time exceeded
4 / Parameter Problem: 0 - erroneous header field
encountered; 1 - unrecognized Next Header type encountered;
2 - unrecognized IPv6 option encountered
128 / Echo Request
129 / Echo Response
130 / Listener Query - Multicast listener query
131 / Listener Report - Multicast listener report
132 / Listener Done - Multicast listener done
143 / Listener Reportv2 - Multicast listener report v2
133 / Router Solicitation
134 / Router Advertisement
135 / Neighbor Solicitation
136 / Neighbor Advertisement
137 / Redirect - Redirect message
Protocol This is the (upper layer) protocol that defines the service to
which this rule applies. By default it is ICMPv6.
IPv6 Filter Listing
IPv6 Filter Rule Index Select the index number of the filter set from the drop-down list
box.
# This is the index number of the rule in a filter set.
Active This field shows whether the rule is activated.
Interface This is the interface that the rule applies to.
Table 47 Security > Filter > IPv6 Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Page 3
Chapter 11 Filters
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
153
Direction The filter set applies to this traffic direction.
ICMPv6 Type The ICMPv6 message type to filter.
Src IP/PrefixLength This displays the source IPv6 address and prefix length.
Dest IP/PrefixLength This displays the destination IPv6 address and prefix length.
Protocol This is the (upper layer) protocol that defines the service to
which this rule applies. By default it is ICMPv6.
Apply Click this to apply your changes.
Delete Click this to remove the filter rule.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Table 47 Security > Filter > IPv6 Filter
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Page 4

Chapter 11 Filters
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
154
Page 5

P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
155
CHAPTER 12
Certificate
12.1 Overview
The ZyXEL Device can use certificates (also called digital IDs) to authenticate
users. Certificates are based on public-private key pairs. A certificate contains the
certificate owner’s identity and public key. Certificates provide a way to exchange
public keys for use in authentication.
12.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•The Trusted CA screen lets you save the certificates of trusted CAs to the
ZyXEL Device (
Section 12.3 on page 156).
1
2.2 What You Need to Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read through this chapter.
Certification Authority
A Certification Authority (CA) issues certificates and guarantees the identity of
each certificate owner. There are commercial certification authorities like
CyberTrust or VeriSign and government certification authorities. The certification
authority uses its private key to sign certificates. Anyone can then use the
certification authority's public key to verify the certificates. You can use the ZyXEL
Device to generate certification requests that contain identifying information and
public keys and then send the certification requests to a certification authority.
Certificate File Format
The certification authority certificate that you want to import has to be in one of
these file formats:
• PEM (Base-64) encoded X.509: This Privacy Enhanced Mail format uses 64
ASCII characters to convert a binary X.509 certificate into a printable form.
Page 6

Chapter 12 Certificate
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
156
1
2.3 The Trusted CA Screen
Click Security > Certificates to open the following screen. This screen displays a
summary list of certificates of the certification authorities that you have set the
ZyXEL Device to accept as trusted. The ZyXEL Device accepts any valid certificate
signed by a certification authority on this list as being trustworthy; thus you do
not need to import any certificate that is signed by one of these certification
authorities.
Figure 70 Trusted CA
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 48 Trusted CA
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name This field displays the name used to identify this certificate.
Subject This field displays information that identifies the owner of the
certificate, such as Common Name (CN), OU (Organizational Unit or
department), Organization (O), State (ST) and Country (C). It is
recommended that each certificate have unique subject information.
Type This field displays general information about the certificate. ca means
that a Certification Authority signed the certificate.
Action Click View to open a screen with an in-depth list of information about
the certificate.
Click Remove to delete the certificate.
Import
Certificate
Click this button to open a screen where you can save the certificate of
a certification authority that you trust to the ZyXEL Device.
Page 7

Chapter 12 Certificate
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
157
1
2.3.1 View Trusted CA Certificate
Click the View button in the Trusted CA screen to open the following screen. Use
this screen to view in-depth information about the certification authority’s
certificate.
Figure 71 Trusted CA: View
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 49 Trusted CA: View
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name This field displays the identifying name of this certificate.
Type This field displays general information about the certificate. ca means
that a Certification Authority signed the certificate.
Subject This field displays information that identifies the owner of the
certificate, such as Common Name (CN), Organizational Unit (OU),
Organization (O) and Country (C).
Certificate This read-only text box displays the certificate in Privacy Enhanced
Mail (PEM) format. PEM uses 64 ASCII characters to convert the binary
certificate into a printable form.
You can copy and paste the certificate into an e-mail to send to friends
or colleagues or you can copy and paste the certificate into a text
editor and save the file on a management computer for later
distribution (via floppy disk for example).
Back Click this button to return to the previous screen.
Page 8

Chapter 12 Certificate
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
158
1
2.3.2 Import Trusted CA Certificate
Click the Import Certificate button in the Trusted CA screen to open the
following screen. The ZyXEL Device trusts any valid certificate signed by any of
the imported trusted CA certificates.
Figure 72 Trusted CA: Import Certificate
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 50 Trusted CA: Import Certificate
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Browse Click this button to locate the certificate file on your computer.
Back Click this button to return to the previous screen.
Apply Click this button to save your changes back to the ZyXEL Device.
Page 9
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
159
CHAPTER 13
Static Route
13.1 Overview
The ZyXEL Device usually uses the default gateway to route outbound traffic from
computers on the LAN to the Internet. To have the ZyXEL Device send data to
devices not reachable through the default gateway, use static routes.
For example, the next figure shows a computer (A) connected to the ZyXEL
Device’s LAN interface. The ZyXEL Device routes most traffic from A to the
Internet through the ZyXEL Device’s default gateway (R1). You create one static
route to connect to services offered by your ISP behind router R2. You create
another static route to communicate with a separate network behind a router R3
connected to the LAN.
Figure 73 Example of Static Routing Topology
WAN
R1
R2
A
R3
LAN
Page 10
Chapter 13 Static Route
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
160
1
3.1.1 What You Can Do in the Static Route Screens
•Use the Static Route screens (
Section 13.2 on page 160) to view and configure
I
P static routes on the ZyXEL Device.
•Use the IPv6 Static Route screens (
Section 13.2.2 on page 162) to view and
configure IPv6 static routes on the ZyXEL Device.
13.2 The Static Route Screen
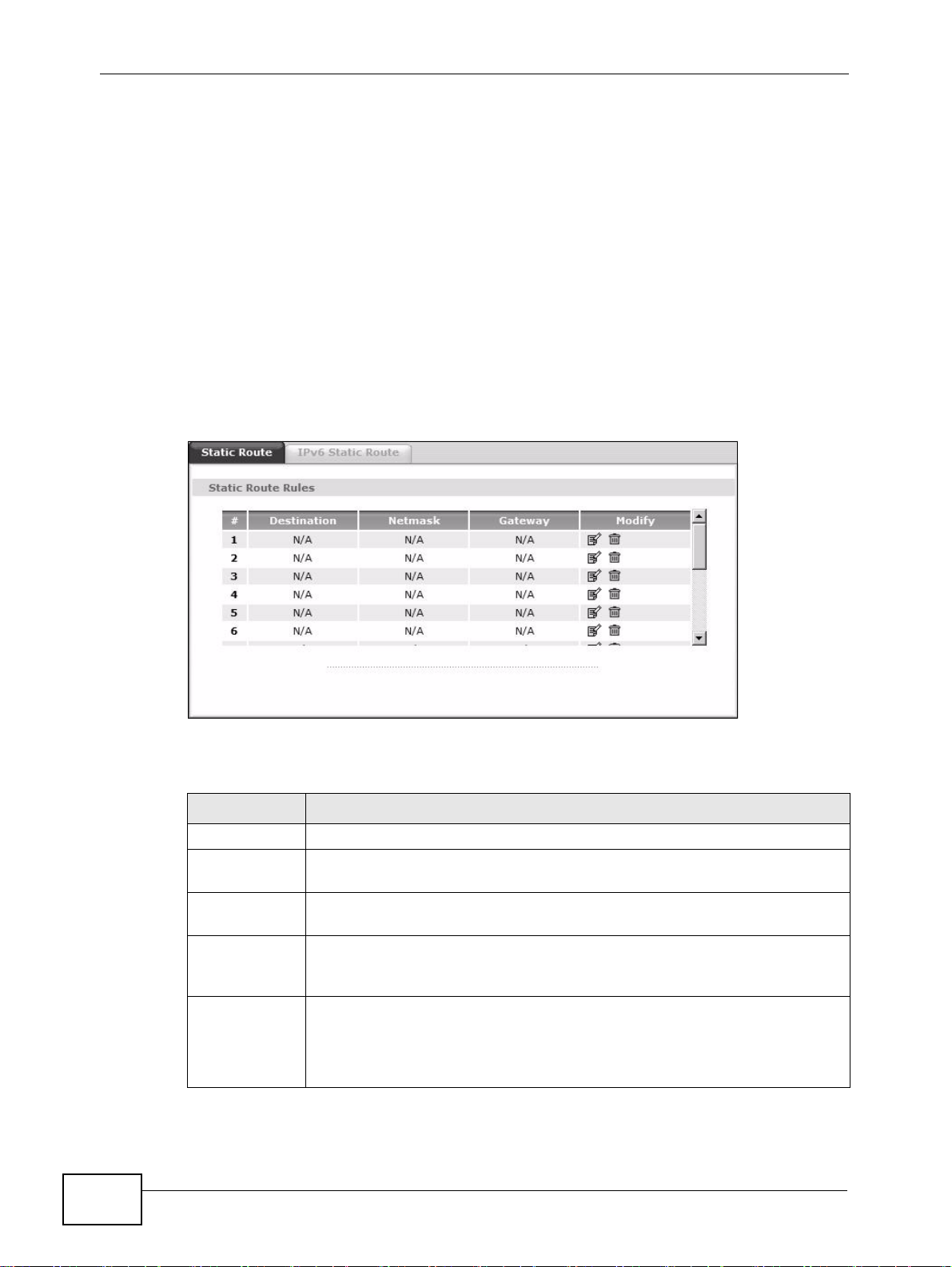
Use this screen to view the static route rules. Click Advanced > Static Route to
open the Static Route screen.
Figure 74 Advanced > Static Route
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 51 Advanced > Static Route
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the number of an individual static route.
Destination This parameter specifies the IP network address of the final destination.
Routing is always based on network number.
Netmask This parameter specifies the IP network subnet mask of the final
destination.
Gateway This is the IP address of the gateway. The gateway is a router or switch
on the same network segment as the device's LAN or WAN port. The
gateway helps forward packets to their destinations.
Modify Click the Edit icon to go to the screen where you can set up a static route
on the ZyXEL Device.
Click the Remove icon to remove a static route from the ZyXEL Device. A
window displays asking you to confirm that you want to delete the route.
Page 11

Chapter 13 Static Route
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
161
1
3.2.1 Static Route Edit
Use this screen to configure the required information for a static route. Select a
static route index number and click Edit. The screen shown next appears.
Figure 75 Advanced > Static Route: Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 52 Advanced > Static Route: Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Static Route Setup
Destination IP
Address
This parameter specifies the IP network address of the final destination.
Routing is always based on network number. If you need to specify a
route to a single host, use a subnet mask of 255.255.255.255 in the
subnet mask field to force the network number to be identical to the host
ID.
IP Subnet
Mask
Enter the IP subnet mask here.
Gateway IP
Address
Enter the IP address of the gateway. The gateway is a router or switch on
the same network segment as the device's LAN or WAN port. The
gateway helps forward packets to their destinations.
Back Click this to return to the previous screen without saving.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Page 12

Chapter 13 Static Route
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
162
1
3.2.2 IPv6 Static Route
Use this screen to view the IPv6 static route rules. Click Advanced > Static
Route > IPv6 Static Route to open the IPv6 Static Route screen.
Figure 76 Advanced > Static Route > IPv6 Static Route
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 53 Advanced > Static Route > IPv6 Static Route
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the number of an individual static route.
Destination This parameter specifies the IP network address of the final destination.
Routing is always based on network number.
Prefix Length An IPv6 prefix length specifies how many most significant bits (starting
from the left) in the address compose the network address. This field
displays the bit number of the IPv6 subnet mask.
Gateway This is the IP address of the gateway. The gateway is a router or switch
on the same network segment as the device's LAN or WAN port. The
gateway helps forward packets to their destinations.
Device This specifies the LAN or WAN PVC.
Modify Click the Edit icon to go to the screen where you can set up a static route
on the ZyXEL Device.
Click the Remove icon to remove a static route from the ZyXEL Device. A
window displays asking you to confirm that you want to delete the route.
Page 13

Chapter 13 Static Route
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
163
1
3.2.3 IPv6 Static Route Edit
Use this screen to configure the required information for an IPv6 static route.
Select an IPv6 static route index number and click Edit. The screen shown next
appears.
Figure 77 Advanced > Static Route > IPv6 Static Route: Edit
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 54 Advanced > Static Route > IPv6 Static Route: Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Static Route Setup
Destination
IPv6 Address
This parameter specifies the IP network address of the final destination.
Routing is always based on network number. If you need to specify a
route to a single host, use a prefix length of 128 in the prefix length field
to force the network number to be identical to the host ID.
IPv6 Prefix
Length
Enter the address prefix to specify how many most significant bits
compose the network address.
Gateway IPv6
Address
Enter the IP address of the gateway. The gateway is a router or switch on
the same network segment as the device's LAN or WAN port. The
gateway helps forward packets to their destinations.
PVC IPv6
Address
Select the interface through which the traffic is routed.
Back Click this to return to the previous screen without saving.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Page 14

Chapter 13 Static Route
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
164
Page 15

P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
165
CHAPTER 14
Quality of Service (QoS)
14.1 Overview
Use the QoS screen to set up your ZyXEL Device to use QoS for traffic
management.
Quality of Service (QoS) refers to both a network’s ability to deliver data with
minimum delay, and the networking methods used to control bandwidth. QoS
allows the ZyXEL Device to group and prioritize application traffic and fine-tune
network performance.
Without QoS, all traffic data are equally likely to be dropped when the network is
congested. This can cause a reduction in network performance and make the
network inadequate for time-critical applications such as video-on-demand.
The ZyXEL Device assigns each packet a priority and then queues the packet
accordingly. Packets assigned with a high priority are processed more quickly than
those with low priorities if there is congestion, allowing time-sensitive applications
to flow more smoothly. Time-sensitive applications include both those that require
a low level of latency (delay) and a low level of jitter (variations in delay) such as
Voice over IP (VoIP) or Internet gaming, and those for which jitter alone is a
problem such as Internet radio or streaming video.
In the following figure, your Internet connection has an upstream transmission
speed of 50 Mbps. You configure a classifier to assign the highest priority queue
(6) to VoIP traffic from the LAN interface, so that voice traffic would not get
delayed when there is network congestion. Traffic from the boss’s IP address
(192.168.1.23 for example) is mapped to queue 5. Traffic that does not match
Page 16

Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
166
t
hese two classes are assigned priority queue based on the internal QoS mapping
table on the ZyXEL Device.
Figure 78 QoS Example
14.1.1 What You Can Do in the QoS Screens
•Use the General screen (Section 14.2 on page 167) to enable QoS on the
Z
yXEL Device, and specify the type of scheduling.
•Use the QoS Summary List screen (
Section 14.2.1 on page 168) to check the
summary of QoS rules and actions you configured for the ZyXEL Device.
•Use the Queue Setup screen (Section 14.3 on page 168) to configure QoS
settings on the ZyXEL Device.
•Use the Class Setup screen (
Section 14.4 on page 170) to configure QoS
settings on the ZyXEL Device.
14.1.2 What You Need to Know About QoS
802.1p
QoS is used to prioritize source-to-destination traffic flows. All packets in the same
flow are given the same priority. 802.1p is a way of managing traffic in a network
by grouping similar types of traffic together and treating each type as a class. You
can use 802.1p to give different priorities to different packet types.
Tagging and Marking
In a QoS class, you can configure whether to add or change the DiffServ Code
Point (DSCP) value and IEEE 802.1p priority level in a matched packet. When the
packet passes through a compatible network, the networking device, such as a
backbone switch, can provide specific treatment or service based on the tag or
marker.
50 Mbps
DSL
VoIP: Queue 6
Boss: Queue 5
IP=192.168.1.23
Page 17

Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
167
F
inding Out More
See Section on page 171 for advanced technical information on QoS.
1
4.2 The General Screen
Use this screen to enable or disable QoS.
Click Advanced Setup > QoS to open the screen as shown next.
Figure 79 Advanced Setup > QoS
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 55 Advanced Setup > QoS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
QoS Use this field to turn on QoS to improve your network
performance.
You can give priority to traffic that the ZyXEL Device forwards out
through the WAN interface. Give high priority to voice and video
to make them run more smoothly. Similarly, give low priority to
many large file downloads so that they do not reduce the quality
of other applications.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Rule&Action
Summary
Click this to display a summary of configured rules and actions.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Page 18

Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
168
1
4.2.1 The QoS Summary List Screen
Use this screen to display a summary of rules and actions configured for the
ZyXEL Device. In the Advanced > QoS screen, click the Rule&Action Summary
button to open the following screen.
Figure 80 Advanced Setup > QoS > QoS Summary List
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
14.3 The Queue Setup Screen
Use this screen to configure QoS queue disciplines and priorities.
Table 56 Advanced Setup > QoS > QoS Summary List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the rule’s index number.
Active This shows whether the rule is enabled or disabled.
Physical Ports This is the physical port associated with the rule.
Classification
Criteria
This shows criteria specified in this rule, for example the interface
from which traffic of this class should come and the source MAC
address of traffic that matches this classifier.
Forward To This is the interface through which traffic that matches the rule is
forwarded out.
IPP/TOS (DSCP) This shows the IPP/TOS or DSCP settings.
802.1p This is the 802.1p priority level.
IPP/TOS (DSCP)
Remarking
The ZyXEL Device re-assigns the priority values specified in this field
to matched traffic.
802.1p Remarking The ZyXEL Device re-assigns the priority levels specified in this field
to matched traffic.
To Q u eu e The ZyXEL Device assigns the queue level specified in this field to
matched traffic.
Page 19

Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
169
C
lick Advanced Setup > QoS > Queue Setup to open the screen as shown
next.
Figure 81 Advanced Setup > QoS > Queue Setup
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 57 Advanced Setup > QoS > Queue Setup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Queue Editing
Queue Discipline Select weighted round-robin (WRR) scheduling to allow packets
of all priorities to transmit depending on their assigned relative
weight. Select Strict Priority to require traffic transmit in order
of priority.
Queue Index Specify the queue index.
Queue Enable Specify to enable or disable the queue.
Queue Weight If you selected WRR, specify the WRR weight for each queue
index. A higher weight indicates higher priority while a lower
weight indicates lower priority. For example, 15 is higher priority
than 1.
Queue Priority If you selected strict priority, specify the queue priority for each
queue index.
Add Click this to add the queue to the list.
Delete Click this to delete the specified queue index.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Queue List
Queue Index This is the specified queue index.
Active This specifies if the queue is enabled or disabled.
Priority This specifies the assigned priority.
Page 20
Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
170
1
4.4 The Class Setup Screen
Use this screen to set up QoS class rules and have the ZyXEL Device assign
priority levels to traffic according to the port range, IEEE 802.1p priority level and/
or IP precedence.
Click Advanced Setup > QoS > Class Setup to open the screen as shown next.
Figure 82 Advanced Setup > QoS > Class Setup
Page 21

Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
171
T
he following table describes the labels in this screen. QoS Technical Reference
Table 58 Advanced Setup > QoS > Class Setup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Class Rule
Rule Index Select the rule’s index number from the drop-down list box.
Rule Enable Use this field to enable or disable the rule.
Application Select an application from the drop-down list box. The Destination Port
Range and Protocol ID fields may change depending on the type of
applications you choose.
Physical Ports Select Enet1 to apply the rule to the Ethernet port.
Destination
MAC
Type a destination MAC address here. QoS is then applied to traffic
containing this destination MAC address. Leave it blank to apply the rule
to all MAC addresses.
Destination IP Enter a destination IP address in dotted decimal notation. QoS is then
applied to traffic containing this destination IP address. A blank
destination IP address means any destination IP address.
Destination
SubNet Mask
Enter a destination subnet mask here.
Destination
Port Range
Either use the default value set by the application you choose, or enter
the port number to which the rule should be applied.
Source MAC Type a source MAC address here. QoS is then applied to traffic containing
this source MAC address. Leave it blank to apply the rule to all MAC
addresses.
Source IP Enter a source IP address in dotted decimal notation. QoS is then applied
to traffic containing this source IP address. A blank source IP address
means any source IP address.
Source SubNet
Mask
Enter a source subnet mask here.
Source Port
Range
Enter the port number to which the rule should be applied. 0 means any
source port number. See Appendix F on page 305 for some common
services and port numbers.
Protocol ID Select an IP protocol type from the drop-down list box.
Vlan ID Range Enter the source VLAN ID in this field.
IPP/DS Field Select IPP/TOS to specify an IP precedence range and type of services.
Select DSCP to specify a DiffServ Code Point (DSCP) range.
IP Precedence
Range
Enter a range from 0 to 7 for IP precedence. Zero is the lowest priority
and seven is the highest.
Typ e of
Service
Select a type of service from the drop-down list box.
Available options are: Normal service, Minimize delay, Maximize
throughput, Maximize reliability and Minimize monetary cost.
DSCP Range Specify a DSCP number between 0 and 63 in this field.
802.1p Select a priority level (0 to 7) from the drop-down list box.
Action
Page 22

Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
172
1
4.5 QoS Technical Reference
This section provides some technical background information about the topics
covered in this chapter.
Forward To Select the interface through which traffic that matches the rule is
forwarded out. If you select Unchange, the ZyXEL Device forwards
traffic of this class according to the default routing table.
If traffic of this class comes from a WAN interface and is in a queue that
forwards traffic through the LAN/WLAN interface, the ZyXEL Device
ignores the setting here.
IPP/DS Field Select IPP/TOS to specify an IP precedence range and type of services.
Select DSCP to specify a DiffServ Code Point (DSCP) range.
IP Precedence
Remarking
Enter a range from 0 to 7 to re-assign IP precedence to matched traffic.
Zero is the lowest priority and seven is the highest.
Typ e of
Service
Remarking
Select a type of service to re-assign the priority level to matched traffic.
Available options are: Normal service, Minimize delay, Maximize
throughput, Maximize reliability and Minimize monetary cost.
DSCP
Remarking
Specify a DSCP number between 0 and 63 to re-assign the priority level
to matched traffic.
802.1p
Remarking
Select a priority level (0 to 7) to re-assign the priority level to matched
traffic.
Queue # Specify a queue tag to matched traffic. Traffic assigned to a higher queue
gets through faster while traffic in lower queues is dropped when there is
network congestion.
Add Click this to add the rule.
Delete Click this to remove the rule.
Cancel Click this to restore previously saved settings.
Table 58 Advanced Setup > QoS > Class Setup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Page 23
Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
173
1
4.5.1 IEEE 802.1p
IEEE 802.1p specifies the user priority field and defines up to eight separate traffic
types. The following table describes the traffic types defined in the IEEE 802.1d
standard (which incorporates the 802.1p).
14.5.2 IP Precedence
Similar to IEEE 802.1p prioritization at layer-2, you can use IP precedence to
prioritize packets in a layer-3 network. IP precedence uses three bits of the eightbit ToS (Type of Service) field in the IP header. There are eight classes of services
(ranging from zero to seven) in IP precedence. Zero is the lowest priority level and
seven is the highest.
14.5.3 Automatic Priority Queue Assignment
If you enable QoS on the ZyXEL Device, the ZyXEL Device can automatically base
on the IEEE 802.1p priority level, IP precedence and/or packet length to assign
priority to traffic which does not match a class.
The following table shows you the internal layer-2 and layer-3 QoS mapping on
the ZyXEL Device. On the ZyXEL Device, traffic assigned to higher priority queues
Table 59 IEEE 802.1p Priority Level and Traffic Type
PRIORITY
LEVEL
TRAFFIC TYPE
Level 7 Typically used for network control traffic such as router configuration
messages.
Level 6 Typically used for voice traffic that is especially sensitive to jitter (jitter is the
variations in delay).
Level 5 Typically used for video that consumes high bandwidth and is sensitive to
jitter.
Level 4 Typically used for controlled load, latency-sensitive traffic such as SNA
(Systems Network Architecture) transactions.
Level 3 Typically used for “excellent effort” or better than best effort and would
include important business traffic that can tolerate some delay.
Level 2 This is for “spare bandwidth”.
Level 1 This is typically used for non-critical “background” traffic such as bulk
transfers that are allowed but that should not affect other applications and
users.
Level 0 Typically used for best-effort traffic.
Page 24
Chapter 14 Quality of Service (QoS)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
174
ge
ts through faster while traffic in lower index queues is dropped if the network is
congested.
Table 60 Internal Layer2 and Layer3 QoS Mapping
PRIORITY
QUEUE
LAYER 2 LAYER 3
IEEE 802.1P
USER PRIORITY
(ETHERNET
PRIORITY)
TOS (IP
PRECEDENCE)
DSCP
IP PACKET
LENGTH (BYTE)
0 1 0 000000
12
2 0 0 000000 >1100
3 3 1 001110
001100
001010
001000
250~1100
4 4 2 010110
010100
010010
010000
5 5 3 011110
011100
011010
011000
<250
6 6 4 100110
100100
100010
100000
5 101110
101000
7 7 6 110000
111000
7
Page 25

P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
175
CHAPTER 15
Dynamic DNS Setup
15.1 Overview
Dynamic DNS allows you to update your current dynamic IP address with one or
many dynamic DNS services so that anyone can contact you (in NetMeeting, CUSeeMe, etc.). You can also access your FTP server or Web site on your own
computer using a domain name (for instance myhost.dhs.org, where myhost is a
name of your choice) that will never change instead of using an IP address that
changes each time you reconnect. Your friends or relatives will always be able to
call you even if they don't know your IP address.
First of all, you need to have registered a dynamic DNS account with
www.dyndns.org. This is for people with a dynamic IP from their ISP or DHCP
server that would still like to have a domain name. The Dynamic DNS service
provider will give you a password or key.
15.1.1 What You Can Do in the DDNS Screen
Use the Dynamic DNS screen (Section 15.2 on page 176) to enable DDNS and
c
onfigure the DDNS settings on the ZyXEL Device.
15.1.2 What You Need To Know About DDNS
DYNDNS Wildcard
Enabling the wildcard feature for your host causes *.yourhost.dyndns.org to be
aliased to the same IP address as yourhost.dyndns.org. This feature is useful if
you want to be able to use, for example, www.yourhost.dyndns.org and still reach
your hostname.
If you have a private WAN IP address, then you cannot use Dynamic DNS.
Page 26

Chapter 15 Dynamic DNS Setup
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
176
1
5.2 The Dynamic DNS Screen
Use this screen to change your ZyXEL Device’s DDNS. Click Advanced >
Dynamic DNS. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 83 Advanced > Dynamic DNS
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 61 Advanced > Dynamic DNS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Dynamic DNS Setup
Active
Dynamic DNS
Select this check box to use dynamic DNS.
Service
Provider
This is the name of your Dynamic DNS service provider.
Dynamic DNS
Typ e
Select the type of service that you are registered for from your Dynamic
DNS service provider.
Host Name Type the domain name assigned to your ZyXEL Device by your Dynamic
DNS provider.
You can specify up to two host names in the field separated by a comma
(",").
User Name Type your user name.
Password Type the password assigned to you.
Enable
Wildcard
Option
Select the check box to enable DynDNS Wildcard.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Page 27
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
177
CHAPTER 16
Remote Management
16.1 Overview
Remote management allows you to determine which services/protocols can access
which ZyXEL Device interface (if any) from which computers.
The following figure shows remote management of the ZyXEL Device coming in
from the WAN.
Figure 84 Remote Management From the WAN
Note: When you configure remote management to allow management from the WAN,
you still need to configure a IP filter rule to allow access.
You may manage your ZyXEL Device from a remote location via:
•Internet (WAN only)
•LAN only
•LAN and WAN
• None (Disable)
To disable remote management of a service, select Disable in the corresponding
Service Access field.
LAN
WAN
HTTP
Telnet
Page 28

Chapter 16 Remote Management
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
178
1
6.1.1 What You Can Do in the Remote Management Screens
•Use the WWW screen (
Section 16.2 on page 179) to configure through which
i
nterface(s) and from which IP address(es) users can use HTTP to manage the
ZyXEL Device.
•Use the Telnet screen (
Section 16.3 on page 180) to configure through which
interface(s) and from which IP address(es) users can use Telnet to manage the
ZyXEL Device.
•Use the FTP screen (
Section 16.4 on page 180) to configure through which
interface(s) and from which IP address(es) users can use FTP to access the
ZyXEL Device.
• Your ZyXEL Device can act as an SNMP agent, which allows a manager station to
manage and monitor the ZyXEL Device through the network. Use the SNMP
screen (see
Section 16.5 on page 181) to configure through which interface(s)
and from which IP address(es) users can use SNMP to access the ZyXEL Device.
•Use the ICMP screen (Section 16.6 on page 184) to set whether or not your
ZyXEL Device will respond to pings and probes for services that you have not
made available.
16.1.2 What You Need to Know About Remote Management
Remote Management Limitations
Remote management does not work when:
• You have not enabled that service on the interface in the corresponding remote
management screen.
• You have disabled that service in one of the remote management screens.
• The IP address in the Secured Client IP Address field does not match the
client IP address. If it does not match, the ZyXEL Device will disconnect the
session immediately.
• There is a firewall rule that blocks it.
Remote Management and NAT
When NAT is enabled:
• Use the ZyXEL Device’s WAN IP address when configuring from the WAN.
• Use the ZyXEL Device’s LAN IP address when configuring from the LAN.
Page 29

Chapter 16 Remote Management
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
179
1
6.2 The WWW Screen
Use this screen to specify how to connect to the ZyXEL Device from a web
browser, such as Internet Explorer.
16.2.1 Configuring the WWW Screen
Click Advanced > Remote MGMT to display the WWW screen.
Figure 85 Advanced > Remote MGMT > WWW
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 62 Advanced > Remote Management > WWW
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port You may change the server port number for a service, if needed.
However, you must use the same port number in order to use that
service for remote management.
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the ZyXEL
Device using this service.
Secured Client
IP Address
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to communicate
with the ZyXEL Device using this service.
Select All to allow any computer to access the ZyXEL Device using this
service.
Choose Selected to just allow the computer with the IP address that
you specify to access the ZyXEL Device using this service.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Page 30

Chapter 16 Remote Management
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
180
1
6.3 The Telnet Screen
You can use Telnet to access the ZyXEL Device’s command line interface. Specify
which interfaces allow Telnet access and from which IP address the access can
come.
Click Advanced > Remote MGMT > Telnet tab to display the screen as shown.
Figure 86 Advanced > Remote MGMT > Telnet
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
16.4 The FTP Screen
You can use FTP (File Transfer Protocol) to upload and download the ZyXEL
Device’s firmware and configuration files. Please see the User’s Guide chapter on
firmware and configuration file maintenance for details. To use this feature, your
computer must have an FTP client.
Table 63 Advanced > Remote Management > Telnet
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port You may change the server port number for a service if needed, however
you must use the same port number in order to use that service for
remote management.
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the ZyXEL
Device using this service.
Secured Client
IP Address
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to communicate
with the ZyXEL Device using this service.
Select All to allow any computer to access the ZyXEL Device using this
service.
Choose Selected to just allow the computer with the IP address that you
specify to access the ZyXEL Device using this service.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Page 31

Chapter 16 Remote Management
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
181
U
se this screen to specify which interfaces allow FTP access and from which IP
address the access can come. To change your ZyXEL Device’s FTP settings, click
Advanced > Remote MGMT > FTP. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 87 Advanced > Remote MGMT > FTP
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
16.5 The SNMP Screen
Simple Network Management Protocol is a protocol used for exchanging
management information between network devices. Your ZyXEL Device supports
SNMP agent functionality, which allows a manager station to manage and monitor
the ZyXEL Device through the network. The ZyXEL Device supports SNMP version
Table 64 Advanced > Remote MGMT > FTP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port You may change the server port number for a service, if needed.
However, you must use the same port number in order to use that
service for remote management.
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the ZyXEL
Device using this service.
Secured Client
IP Address
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to communicate
with the ZyXEL Device using this service.
Select All to allow any computer to access the ZyXEL Device using this
service.
Choose Selected to just allow the computer with the IP address that
you specify to access the ZyXEL Device using this service.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Page 32

Chapter 16 Remote Management
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
182
o
ne (SNMPv1) and version two (SNMPv2c). The next figure illustrates an SNMP
management operation.
Figure 88 SNMP Management Model
An SNMP managed network consists of two main types of component: agents and
a manager.
An agent is a management software module that resides in a managed device (the
ZyXEL Device). An agent translates the local management information from the
managed device into a form compatible with SNMP. The manager is the console
through which network administrators perform network management functions. It
executes applications that control and monitor managed devices.
The managed devices contain object variables/managed objects that define each
piece of information to be collected about a device. Examples of variables include
such as number of packets received, node port status etc. A Management
Information Base (MIB) is a collection of managed objects. SNMP allows a
manager and agents to communicate for the purpose of accessing these objects.
Page 33

Chapter 16 Remote Management
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
183
1
6.5.1 Configuring SNMP
To c ha n ge yo u r Z y XE L D evi ce’s SNMP settings, click Advanced > Remote MGMT
> SNMP tab. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 89 Advanced > Remote MGMT > SNMP
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 65 Advanced > Remote MGMT > SNMP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server Port The SNMP agent listens on port 161 by default. If you change the SNMP
server port to a different number on the ZyXEL Device, for example
8161, then you must notify people who need to access the ZyXEL Device
SNMP agent to use the same port.
Server Access Select the interface(s) through which a computer may access the ZyXEL
Device using this service.
Secured Client
IP Address
A secured client is a “trusted” computer that is allowed to access the
SNMP agent on the ZyXEL Device.
Select All to allow any computer to access the SNMP agent.
Choose Selected to just allow the computer with the IP address that you
specify to access the SNMP agent.
Get
Community
Enter the Get Community, which is the password for the incoming Get
and GetNext requests from the management station. The default is
public and allows all requests.
Set
Community
Enter the Set community, which is the password for incoming Set
requests from the management station. The default is public and allows
all requests.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the ZyXEL Device.
Cancel Click Cancel to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Page 34

Chapter 16 Remote Management
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
184
1
6.6 The ICMP Screen
To c ha n ge yo u r Z y XE L D ev i ce ’s security settings, click Advanced > Remote
MGMT > ICMP. The screen appears as shown.
If an outside user attempts to probe an unsupported port on your ZyXEL Device,
an ICMP response packet is automatically returned. This allows the outside user to
know the ZyXEL Device exists. Your ZyXEL Device supports anti-probing, which
prevents the ICMP response packet from being sent. This keeps outsiders from
discovering your ZyXEL Device when unsupported ports are probed.
Note: If you want your device to respond to pings and requests for unauthorized
services, you will also need to configure the firewall accordingly by disabling
SPI.
Figure 90 Advanced > Remote Management > ICMP
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 66 Advanced > Remote Management > ICMP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol is a message control and error-
reporting protocol between a host server and a gateway to the Internet.
ICMP uses Internet Protocol (IP) datagrams, but the messages are
processed by the TCP/IP software and directly apparent to the
application user.
Respond to
Ping on
The ZyXEL Device will not respond to any incoming Ping requests when
Disable is selected. Select LAN to reply to incoming LAN Ping requests.
Select WAN to reply to incoming WAN Ping requests. Otherwise select
LAN & WAN to reply to both incoming LAN and WAN Ping requests.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Page 35

Chapter 17 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
185
CHAPTER 17
Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
17.1 Overview
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) is a distributed, open networking standard that
uses TCP/IP for simple peer-to-peer network connectivity between devices. A
UPnP device can dynamically join a network, obtain an IP address, convey its
capabilities and learn about other devices on the network. In turn, a device can
leave a network smoothly and automatically when it is no longer in use.
17.1.1 What You Can Do in the UPnP Screen
Use the UPnP screen (Section 17.2 on page 187) to enable UPnP on the ZyXEL
D
evice and allow UPnP-enabled applications to automatically configure the ZyXEL
Device.
17.1.2 What You Need to Know About UPnP
Identifying UPnP Devices
UPnP hardware is identified as an icon in the Network Connections folder
(Windows XP). Each UPnP compatible device installed on your network will appear
as a separate icon. Selecting the icon of a UPnP device will allow you to access the
information and properties of that device.
NAT Traversal
UPnP NAT traversal automates the process of allowing an application to operate
through NAT. UPnP network devices can automatically configure network
addressing, announce their presence in the network to other UPnP devices and
enable exchange of simple product and service descriptions. NAT traversal allows
the following:
• Dynamic port mapping
• Learning public IP addresses
Page 36

Chapter 17 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
186
•
Assigning lease times to mappings
Windows Messenger is an example of an application that supports NAT traversal
and UPnP.
See the NAT chapter for more information on NAT.
Cautions with UPnP
The automated nature of NAT traversal applications in establishing their own
services and opening firewall ports may present network security issues. Network
information and configuration may also be obtained and modified by users in some
network environments.
When a UPnP device joins a network, it announces its presence with a multicast
message. For security reasons, the ZyXEL Device allows multicast messages on
the LAN only.
All UPnP-enabled devices may communicate freely with each other without
additional configuration. Disable UPnP if this is not your intention.
UPnP and ZyXEL
ZyXEL has achieved UPnP certification from the Universal Plug and Play Forum
UPnP™ Implementers Corp. (UIC). ZyXEL's UPnP implementation supports
Internet Gateway Device (IGD) 1.0.
See the following sections for examples of installing and using UPnP.
Page 37

P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
187
1
7.2 The UPnP Screen
Use the following screen to configure the UPnP settings on your ZyXEL Device.
Click Advanced > UPnP to display the screen shown next.
See Section 17.1 on page 185 for more information.
F
igure 91 Advanced > UPnP > General
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 67 Advanced > UPnP > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active the Universal Plug
and Play (UPnP) Feature
Select this check box to activate UPnP. Be aware that anyone
could use a UPnP application to open the web configurator's
login screen without entering the ZyXEL Device's IP address
(although you must still enter the password to access the web
configurator).
Allow users to make
configuration changes
through UPnP
Select this check box to allow UPnP-enabled applications to
automatically configure the ZyXEL Device so that they can
communicate through the ZyXEL Device, for example by using
NAT traversal, UPnP applications automatically reserve a NAT
forwarding port in order to communicate with another UPnP
enabled device; this eliminates the need to manually configure
port forwarding for the UPnP enabled application.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Page 38

Chapter 17 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
188
1
7.3 Installing UPnP in Windows Example
This section shows how to install UPnP in Windows Me and Windows XP.
Installing UPnP in Windows Me
Follow the steps below to install the UPnP in Windows Me.
1 Click Start and Control Panel. Double-click Add/Remove Programs.
2 Click on the Windows Setup tab and select Communication in the
Components selection box. Click Details.
Add/Remove Programs: Windows Setup: Communication
Page 39

Chapter 17 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
189
3 I
n the Communications window, select the Universal Plug and Play check box
in the Components selection box.
Add/Remove Programs: Windows Setup: Communication: Components
4 C
lick OK to go back to the Add/Remove Programs Properties window and click
Next.
5 Restart the computer when prompted.
Installing UPnP in Windows XP
Follow the steps below to install the UPnP in Windows XP.
1 Click Start and Control Panel.
2 Double-click Network Connections.
Page 40

Chapter 17 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
190
3 I
n the Network Connections window, click Advanced in the main menu and
select Optional Networking Components ….
Network Connections
4 T
he Windows Optional Networking Components Wizard window displays.
Select Networking Service in the Components selection box and click Details.
Windows Optional Networking Components Wizard
Page 41

Chapter 17 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
191
5 I
n the Networking Services window, select the Universal Plug and Play check
box.
Networking Services
6 C
lick OK to go back to the Windows Optional Networking Component Wizard
window and click Next.
17.4 Using UPnP in Windows XP Example
This section shows you how to use the UPnP feature in Windows XP. You must
already have UPnP installed in Windows XP and UPnP activated on the ZyXEL
Device.
Make sure the computer is connected to a LAN port of the ZyXEL Device. Turn on
your computer and the ZyXEL Device.
Auto-discover Your UPnP-enabled Network Device
1 Click Start and Control Panel. Double-click Network Connections. An icon
displays under Internet Gateway.
Page 42

Chapter 17 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
192
2 R
ight-click the icon and select Properties.
Network Connections
3 I
n the Internet Connection Properties window, click Settings to see the port
mappings there were automatically created.
Internet Connection Properties
Page 43

Chapter 17 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
193
4 Y
ou may edit or delete the port mappings or click Add to manually add port
mappings.
Internet Connection Properties: Advance d Settings
In
ternet Connection Properties: Advanced Set tings: Add
5 When the UPnP-enabled device is disconnected from your computer, all port
mappings will be deleted automatically.
Page 44

Chapter 17 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
194
6 S
elect Show icon in notification area when connected option and click OK.
An icon displays in the system tray.
System Tray Icon
7 D
ouble-click on the icon to display your current Internet connection status.
Internet Connection Status
Web Configurator Easy Access
With UPnP, you can access the web-based configurator on the ZyXEL Device
without finding out the IP address of the ZyXEL Device first. This comes helpful if
you do not know the IP address of the ZyXEL Device.
Follow the steps below to access the web configurator.
1 Click Start and then Control Panel.
2 Double-click Network Connections.
Page 45

Chapter 17 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
195
3 S
elect My Network Places under Other Places.
Network Connections
4 A
n icon with the description for each UPnP-enabled device displays under Local
Network.
Page 46

Chapter 17 Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
196
5 R
ight-click on the icon for your ZyXEL Device and select Invoke. The web
configurator login screen displays.
Network Connections: M y Network Places
6 R
ight-click on the icon for your ZyXEL Device and select Properties. A properties
window displays with basic information about the ZyXEL Device.
Network Connections: M y Network Places: P roperties: Example
Page 47

P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
197
CHAPTER 18
CWMP
18.1 Overview
The ZyXEL Device supports TR-069 Amendment 1 (CPE WAN Management
Protocol Release 2.0) and TR-069 Amendment 2 (CPE WAN Management Protocol
v1.1, Release 3.0).
TR-069 is a protocol that defines how your ZyXEL Device (ZD) can be managed
via a management server (MS) such as ZyXEL’s Vantage Access.
Figure 92 LAN and WAN
An administrator can use a management server to remotely set up the ZyXEL
device, modify settings, perform firmware upgrades as well as monitor and
diagnose the ZyXEL device.
In order to use CWMP, you need to configure the following steps:
1 Activate CWMP
2 Specify the URL, username and password.
3 Activate periodic inform and specify an interval value.
MSZD
Page 48

Chapter 18 CWMP
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
198
1
8.2 The CWMP Setup Screen
Use this screen to configure your ZyXEL Device to be managed by a management
server. Click Advanced> CWMP to display the following screen.
Figure 93 Advanced > CWMP
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 68 Advanced > CWMP
LINK DESCRIPTION
CWMP Setup
CWMP Select Activated to allow the ZyXEL Device to be managed by a
management server or select Deactivated to not allow the ZyXEL Device
to be managed by a management server.
Login ACS Configure this part of the screen to log into the management server.
URL Type the IP address or domain name of the management server. If the
ZyXEL Device is behind a NAT router that assigns it a private IP address,
you will have to configure a NAT port forwarding rule on the NAT router.
Page 49

Chapter 18 CWMP
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
199
U
ser Name The user name is used to authenticate the ZyXEL Device when making a
connection to the management server. This user name on the management
server and the ZyXEL Device must be the same. Type a user name of up to
255 printable characters found on an English-language keyboard. Spaces
and characters such as @#$%^&*()_+ are allowed.
Password The password is used to authenticate the ZyXEL Device when making a
connection to the management server. This password on the management
server and the ZyXEL Device must be the same. Type a password of up to
255 printable characters found on an English-language keyboard.
Connection
Request
Use this part of the screen to allow the management server to connect to
the ZyXEL Device after a successful login.
Path Type the IP address or domain name of the ZyXEL Device. The
management server uses this path to verify the ZyXEL Device.
Port The default port for access to the ZyXEL Device from the management
server is port 7547. If you change it, make sure it does not conflict with
another port on your network and it is recommended to use a port number
above 1024 (not a commonly used port). The management server should
use this port to connect to the ZyXEL Device. You may need to alter your
NAT port forwarding rules if they were already configured.
UserName The user name is used to authenticate the management server when
connecting to the ZyXEL Device. Type a user name of up to 255 printable
characters found on an English-language keyboard. Spaces and characters
such as @#$%^&*()_+ are allowed.
Password The password is used to authenticate the management server when
connecting to the ZyXEL Device. Type a password of up to 255 printable
characters found on an English-language keyboard. Spaces are not
allowed.
Periodic
Inform
Select Activated to have the ZyXEL Device periodically send information to
the management server (recommended if CWMP is enabled) or select
Deactivated to not have the ZyXEL Device periodically send information to
the management server
Interval The interval is the duration in seconds for which the ZyXEL Device must
attempt to connect with the management server to send information and
check for configuration updates. Enter a value between 1 and 86400
seconds.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Table 68 Advanced > CWMP (continued)
LINK DESCRIPTION
Page 50

Chapter 18 CWMP
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
200
Page 51

P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
201
CHAPTER 19
System Settings
19.1 Overview
This chapter shows you how to configure system related settings, such as system
time, password, name, the domain name and the inactivity timeout interval.
19.1.1 What You Can Do in the System Settings Screens
•Use the General screen (Section 19.2 on page 201) to configure system
settings.
•Use the Time Setting screen (
Section 19.3 on page 202) to set the system
time.
19.2 The General Screen
Use this screen to configure system admin password.
Click Maintenance > System to open the General screen.
Figure 94 Maintenance > System > General
Page 52

Chapter 19 System Settings
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
202
T
he following table describes the labels in this screen.
19.3 The Time Setting Screen
Use this screen to configure the ZyXEL Device’s time based on your local time
zone. To change your ZyXEL Device’s time and date, click Maintenance >
System > Time Setting. The screen appears as shown.
Figure 95 Maintenance > System > Time Setting
Table 69 Maintenance > System > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Password
Admin
Password
Old
Password
Type the default password or the existing password you use to access the
system in this field.
New
Password
Type your new system password (up to 30 characters). Note that as you
type a password, the screen displays a (*) for each character you type.
After you change the password, use the new password to access the
ZyXEL Device.
Retype to
confirm
Type the new password again for confirmation.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Page 53

Chapter 19 System Settings
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
203
T
he following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 70 Maintenance > System > Time Setting
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Current Time and Date
Current Time This field displays the time and date of your ZyXEL Device.
Each time you reload this page, the ZyXEL Device synchronizes the
time and date with the time server.
Time and Date Setup
Manual Select this radio button to enter the time and date manually. If you
configure a new time and date, Time Zone and Daylight Saving at the
same time, the new time and date you entered has priority and the
Time Zone and Daylight Saving settings do not affect it.
New Time
(hh:mm:ss)
This field displays the last updated time from the time server or the last
time configured manually.
When you set Time and Date Setup to Manual, enter the new time in
this field and then click Apply.
New Date
(yyyy/mm/dd)
This field displays the last updated date from the time server or the last
date configured manually.
When you set Time and Date Setup to Manual, enter the new date in
this field and then click Apply.
Get from Time
Server
Select this radio button to have the ZyXEL Device get the time and date
from the time server you specified below.
Time Server
Address
Enter the IP address or URL (up to 20 extended ASCII characters in
length) of your time server. Check with your ISP/network administrator
if you are unsure of this information.
Time Zone Setup
Time Zone Choose the time zone of your location. This will set the time difference
between your time zone and Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
Daylight
Savings
Daylight saving is a period from late spring to early fall when many
countries set their clocks ahead of normal local time by one hour to
give more daytime light in the evening.
Select this option if you use Daylight Saving Time.
Start Date Configure the day and time when Daylight Saving Time starts if you
selected Enable Daylight Saving. The o'clock field uses the 24 hour
format. Here are a couple of examples:
Daylight Saving Time starts in most parts of the United States on the
second Sunday of March. Each time zone in the United States starts
using Daylight Saving Time at 2 A.M. local time. So in the United States
you would select Second, Sunday, March and type 2 in the o'clock
field.
Daylight Saving Time starts in the European Union on the last Sunday
of March. All of the time zones in the European Union start using
Daylight Saving Time at the same moment (1 A.M. GMT or UTC). So in
the European Union you would select Last, Sunday, March. The time
you type in the o'clock field depends on your time zone. In Germany
for instance, you would type 2 because Germany's time zone is one
hour ahead of GMT or UTC (GMT+1).
Page 54

Chapter 19 System Settings
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
204
End Date Configure the day and time when Daylight Saving Time ends if you
selected Enable Daylight Saving. The o'clock field uses the 24 hour
format. Here are a couple of examples:
Daylight Saving Time ends in the United States on the first Sunday of
November. Each time zone in the United States stops using Daylight
Saving Time at 2 A.M. local time. So in the United States you would
select First, Sunday, November and type 2 in the o'clock field.
Daylight Saving Time ends in the European Union on the last Sunday of
October. All of the time zones in the European Union stop using
Daylight Saving Time at the same moment (1 A.M. GMT or UTC). So in
the European Union you would select Last, Sunday, October. The
time you type in the o'clock field depends on your time zone. In
Germany for instance, you would type 2 because Germany's time zone
is one hour ahead of GMT or UTC (GMT+1).
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Cancel Click this to restore your previously saved settings.
Table 70 Maintenance > System > Time Setting (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Page 55

P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
205
CHAPTER 20
Logs
20.1 Overview
This chapter contains information about viewing the ZyXEL Device’s logs.
The web configurator allows you to choose which types of events and/or alerts to
have the ZyXEL Device log and then display the logs.
20.1.1 What You Need To Know About Logs
Alerts
An alert is a message that is enabled as soon as the event occurs. They include
system errors, attacks (access control) and attempted access to blocked web
sites. Some categories such as System Errors consist of both logs and alerts. You
may differentiate them by their color in the View Log screen. Alerts display in red
and logs display in black.
Logs
A log is a message about an event that occurred on your ZyXEL Device. For
example, when someone logs in to the ZyXEL Device, you can set a schedule for
how often logs should be enabled, or sent to a syslog server.
20.2 The View Log Screen
Use the View Log screen to view logs.
Page 56

Chapter 20 Logs
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
206
T
o view your ZyXEL Device’s logs, click Maintenance > Logs > View Log. The
screen appears as shown.
Figure 96 Maintenance > System Logs
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
20.3 The Log Settings Screen
Use the Log Settings screen to configure to where the ZyXEL Device is to send
logs and which logs and/or immediate alerts the ZyXEL Device is to record and
display.
To change your ZyXEL Device’s log settings, click Maintenance > Logs > Log
Settings. The screen appears as shown.
Maintenance > Logs > Log Settings
LABEL DESCRIPTION
System Log
Refresh Click this to refresh to log display.
Page 57

Chapter 20 Logs
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
207
F
igure 97 Maintenance > System Logs > Log Settings
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 71 Maintenance > Logs > Log Settings
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active Select to enable or disable system logging.
Mode Select Local File to record the logs and store them in the local memory
of the ZyXEL Device only.
Select Local File and Remote to record the logs and store them in the
local memory and also send logs to the log server.
Syslog Server
IP Address
Enter the server name or the IP address of the log server.
Syslog Server
UDP Port
Enter the UDP port of the log server.
Apply Click Apply to save your customized settings.
Page 58

Chapter 20 Logs
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
208
Page 59

P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
209
CHAPTER 21
Tools
21.1 Overview
This chapter explains how to upload new firmware, manage configuration files and
restart your ZyXEL Device.
Use the instructions in this chapter to change the device’s configuration file or
upgrade its firmware. After you configure your device, you can backup the
configuration file to a computer. That way if you later misconfigure the device, you
can upload the backed up configuration file to return to your previous settings.
You can alternately upload the factory default configuration file if you want to
return the device to the original default settings. The firmware determines the
device’s available features and functionality. You can download new firmware
releases from your nearest ZyXEL FTP site (or www.zyxel.com) to use to upgrade
your device’s performance.
Only use firmware for your device’
s specific model. Refer to the
label on the bottom of your ZyXEL Device.
21.1.1 What You Can Do in the Tool Screens
•Use the Firmware Upgrade screen (
Section 21.2 on page 209) to upload
firmware to your device.
•Use the Configuration screen (Section 21.3 on page 212) to backup and
restore device configurations. You can also reset your device settings back to
the factory default.
•Use the Restart screen (
Section 21.4 on page 215) to restart your ZyXEL
device.
21.2 The Firmware Screen
Click Maintenance > Tools to open the Firmware screen. Follow the
instructions in this screen to upload firmware to your ZyXEL Device. The upload
process uses HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and may take up to two minutes.
After a successful upload, the system will reboot.
Page 60

Chapter 21 Tools
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
210
Do NOT turn off the ZyXEL Device while firmware upload is in
progress!
Figure 98 Maintenance > Tools > Firmware
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
After you see the Firmware Upload in Progress screen, wait two minutes
before logging into the ZyXEL Device again.
Figure 99 Firmware Upload In Progress
Table 72 Maintenance > Tools > Firmware
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Current
Firmware
Version
This is the present Firmware version and the date created.
File Path Type in the location of the file you want to upload in this field or click
Browse ... to find it.
Browse... Click this to find the .bin file you want to upload. Remember that you
must decompress compressed (.zip) files before you can upload them.
Upload Click this to begin the upload process. This process may take up to two
minutes.
Page 61

Chapter 21 Tools
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
211
T
he ZyXEL Device automatically restarts in this time causing a temporary network
disconnect. In some operating systems, you may see the following icon on your
desktop.
Figure 100 Network Temporarily Disconnected
After two minutes, log in again and check your new firmware version in the
Status screen.
If the upload was not successful, the following screen will appear. Click Return to
go back to the Firmware screen.
Figure 101 Error Message
Page 62

Chapter 21 Tools
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
212
2
1.3 The Configuration Screen
Click Maintenance > Tools > Configuration. Information related to factory
defaults, backup configuration, and restoring configuration appears in this screen,
as shown next.
Figure 102 Maintenance > Tools > Configuration
Backup Configuration
Backup Configuration allows you to back up (save) the ZyXEL Device’s current
configuration to a file on your computer. Once your ZyXEL Device is configured
and functioning properly, it is highly recommended that you back up your
configuration file before making configuration changes. The backup configuration
file will be useful in case you need to return to your previous settings.
Click Backup to save the ZyXEL Device’s current configuration to your computer.
Page 63

Chapter 21 Tools
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
213
R
estore Configuration
Restore Configuration allows you to upload a new or previously saved
configuration file from your computer to your ZyXEL Device.
Do not turn off the ZyXEL Device whi
le configuration file upload is
in progress.
After you see a “restore configuration successful” screen, you must then wait one
minute before logging into the ZyXEL Device again.
Figure 103 Configuration Upload Successful
The ZyXEL Device automatically restarts in this time causing a temporary network
disconnect. In some operating systems, you may see the following icon on your
desktop.
Figure 104 Network Temporarily Disconnected
If you uploaded the default configuration file you may need to change the IP
address of your computer to be in the same subnet as that of the default device IP
address (192.168.1.1). See Appendix A on page 235 for details on how to set up
your computer’s IP address.
Table 73 Restore Configuration
LABEL DESCRIPTION
File Path Type in the location of the file you want to upload in this field or click
Browse ... to find it.
Browse... Click this to find the file you want to upload. Remember that you must
decompress compressed (.ZIP) files before you can upload them.
Upload Click this to begin the upload process.
Page 64

Chapter 21 Tools
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
214
I
f the upload was not successful, the following screen will appear. Click Return to
go back to the Configuration screen.
Figure 105 Configuration Upload Error
Reset to Factory Defaults
Click the Reset button to clear all user-entered configuration information and
return the ZyXEL Device to its factory defaults. The following warning screen
appears.
Figure 106 Reset Warning Message
Figure 107 Reset In Process Message
You can also press the RESET button on the rear panel to reset the factory
defaults of your ZyXEL Device. Refer to
Section 1.7 on page 27 for more
i
nformation on the RESET button.
Page 65

Chapter 21 Tools
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
215
2
1.4 The Restart Screen
System restart allows you to reboot the ZyXEL Device remotely without turning
the power off. You may need to do this if the ZyXEL Device hangs, for example.
Click Maintenance > Tools > Restart. Click Restart to have the ZyXEL Device
reboot. This does not affect the ZyXEL Device's configuration.
Figure 108 Maintenance > Tools >Restart
Page 66

Chapter 21 Tools
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
216
Page 67

P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
217
CHAPTER 22
Diagnostic
22.1 Overview
These read-only screens display information to help you identify problems with the
ZyXEL Device.
22.1.1 What You Can Do in the Diagnostic Screens
•Use the General screen (Section 22.2 on page 217) to ping an IP address.
•Use the DSL Line screen (
Section 22.3 on page 218) to view the DSL line
statistics and reset the ADSL line.
22.2 The General Screen
Use this screen to ping an IP address. Click Maintenance > Diagnostic to open
the screen shown next.
Figure 109 Maintenance > Diagnostic > General
Page 68

Chapter 22 Diagnostic
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
218
T
he following table describes the fields in this screen.
22.3 The DSL Line Screen
Use this screen to view the DSL line statistics and reset the ADSL line. Click
Maintenance > Diagnostic > DSL Line to open the screen shown next.
Figure 110 Maintenance > Diagnostic > DSL Line
Table 74 Maintenance > Diagnostic > General
LABEL DESCRIPTION
TCP/IP
Address
Type the IP address of a computer that you want to ping in order to test a
connection.
Ping Click this to ping the IP address that you entered.
PingV6 Click this to ping the IPv6 address that you entered.
Page 69

Chapter 22 Diagnostic
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
219
T
he following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 75 Maintenance > Diagnostic > DSL Line
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ATM Status Click this to view your DSL connection’s Asynchronous Transfer Mode
(ATM) statistics. ATM is a networking technology that provides highspeed data transfer. ATM uses fixed-size packets of information called
cells. With ATM, a high QoS (Quality of Service) can be guaranteed.
The (Segmentation and Reassembly) SAR driver translates packets into
ATM cells. It also receives ATM cells and reassembles them into packets.
These counters are set back to zero whenever the device starts up.
inPkts is the number of good ATM cells that have been received.
inDiscards is the number of received ATM cells that were rejected.
outPkts is the number of ATM cells that have been sent.
outDiscards is the number of ATM cells sent that were rejected.
inF4Pkts is the number of ATM Operations, Administration, and
Management (OAM) F4 cells that have been received. See ITU
recommendation I.610 for more on OAM for ATM.
outF4Pkts is the number of ATM OAM F4 cells that have been sent.
inF5Pkts is the number of ATM OAM F5 cells that have been received.
outF5Pkts is the number of ATM OAM F5 cells that have been sent.
openChan is the number of times that the ZyXEL Device has opened a
logical DSL channel.
closeChan is the number of times that the ZyXEL Device has closed a
logical DSL channel.
txRate is the number of bytes transmitted per second.
rxRate is the number of bytes received per second.
ATM Loopback
Te st
Click this to start the ATM loopback test. Make sure you have configured
at least one PVC with proper VPIs/VCIs before you begin this test. The
ZyXEL Device sends an OAM F5 packet to the DSLAM/ATM switch and
then returns it (loops it back) to the ZyXEL Device. The ATM loopback
test is useful for troubleshooting problems with the DSLAM and ATM
network.
Page 70

Chapter 22 Diagnostic
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
220
DSL Line
Status
Click this to view statistics about the DSL connections.
noise margin downstream is the signal to noise ratio for the
downstream part of the connection (coming into the ZyXEL Device from
the ISP). It is measured in decibels. The higher the number the more
signal and less noise there is.
output power upstream is the amount of power (in decibels) that the
ZyXEL Device is using to transmit to the ISP.
attenuation downstream is the reduction in amplitude (in decibels) of
the DSL signal coming into the ZyXEL Device from the ISP.
Discrete Multi-Tone (DMT) modulation divides up a line’s bandwidth into
sub-carriers (sub-channels) of 4.3125 KHz each called tones. The rest of
the display is the line’s bit allocation. This is displayed as the number (in
hexadecimal format) of bits transmitted for each tone. This can be used
to determine the quality of the connection, whether a given sub-carrier
loop has sufficient margins to support certain ADSL transmission rates,
and possibly to determine whether particular specific types of
interference or line attenuation exist. Refer to the ITU-T G.992.1
recommendation for more information on DMT.
The better (or shorter) the line, the higher the number of bits transmitted
for a DMT tone. The maximum number of bits that can be transmitted per
DMT tone is 15. There will be some tones without any bits as there has to
be space between the upstream and downstream channels.
Reset ADSL
Line
Click this to reinitialize the ADSL line. The large text box above then
displays the progress and results of this operation, for example:
"Start to reset ADSL
Loading ADSL modem F/W...
Reset ADSL Line Successfully!"
Capture All
Logs
Click this to display information and statistics about your ZyXEL Device’s
ATM statistics, DSL connection statistics, DHCP settings, firmware
version, WAN and gateway IP address, VPI/VCI and LAN IP address.
Table 75 Maintenance > Diagnostic > DSL Line (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Page 71

P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
221
CHAPTER 23
Troubleshooting
This chapter offers some suggestions to solve problems you might encounter. The
potential problems are divided into the following categories.
• Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
• ZyXEL Device Access and Login
• Internet Access
23.1 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs
The ZyXEL Device does not turn on. None of the LEDs turn on.
1 Make sure the ZyXEL Device is turned on.
2 Make sure you are using the power adaptor or cord included with the ZyXEL
Device.
3 Make sure the power adaptor or cord is connected to the ZyXEL Device and
plugged in to an appropriate power source. Make sure the power source is turned
on.
4 Turn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
5 If the problem continues, contact the vendor.
One of the LEDs does not behave as expected.
1 Make sure you understand the normal behavior of the LED. See Section 1.6 on
page 26
.
Page 72

Chapter 23 Troubleshooting
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
222
2 C
heck the hardware connections.
3 Inspect your cables for damage. Contact the vendor to replace any damaged
cables.
4 Turn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
5 If the problem continues, contact the vendor.
23.2 ZyXEL Device Access and Login
I forgot the IP address for the ZyXEL Device.
1 The default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
2 If you changed the IP address and have forgotten it, you might get the IP address
of the ZyXEL Device by looking up the IP address of the default gateway for your
computer. To do this in most Windows computers, click Start > Run, enter cmd,
and then enter ipconfig. The IP address of the Default Gateway might be the IP
address of the ZyXEL Device (it depends on the network), so enter this IP address
in your Internet browser.
3 If this does not work, you have to reset the device to its factory defaults. See
Section 1.7 on page 27.
I forgot the password.
1 The default admin user name and password can be found on the cover of this
User’s Guide.
2 If this does not work, you have to reset the device to its factory defaults. See
Section 1.7 on page 27.
I cannot see or access the Login screen for the web configurator.
1 Make sure you are using the correct IP address.
Page 73

Chapter 23 Troubleshooting
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
223
•
The default IP address is 192.168.1.1.
•
If you changed the IP address (Section 7.2 on page 91), use the new IP
address.
• If you changed the IP address and have forgotten it, see the troubleshooting
suggestions for
I forgot the IP address for the ZyXEL Device.
2 Check the hardware connections, and make sure the LEDs are behaving as
expected. See the Quick Start Guide.
3 Make sure your Internet browser does not block pop-up windows and has
JavaScripts and Java enabled. See
Appendix C on page 269.
4 R
eset the device to its factory defaults, and try to access the ZyXEL Device with
the default IP address. See Section 1.7 on page 27.
5 If the problem continues, contact the network administrator or vendor, or try one
of the advanced suggestions.
Advanced Suggestions
• Try to access the ZyXEL Device using another service, such as Telnet. If you can
access the ZyXEL Device, check the remote management settings and firewall
rules to find out why the ZyXEL Device does not respond to HTTP.
• If your computer is connected to the WAN port or is connected wirelessly, use a
computer that is connected to a ETHERNET port.
I can see the Login screen, but I cannot log in to the ZyXEL Device.
1 Make sure you have entered the password correctly. The default user and default
admin password can be found on the cover page of this User’s Guide. The field is
case-sensitive, so make sure [Caps Lock] is not on.
2 You cannot log in to the web configurator while someone is using Telnet to access
the ZyXEL Device. Log out of the ZyXEL Device in the other session, or ask the
person who is logged in to log out.
3 Turn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
4 If this does not work, you have to reset the device to its factory defaults. See
Section 23.1 on page 221.
I cannot Telnet to the ZyXEL Device.
Page 74

Chapter 23 Troubleshooting
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
224
S
ee the troubleshooting suggestions for I cannot see or access the Login screen
f
or the web configurator.
Ignore the suggestions about your browser.
I cannot use FTP to upload / download the configuration file. / I cannot use FTP to
upload new firmware.
See the troubleshooting suggestions for I cannot see or access the Login screen
for the web configurator.
Ignore the suggestions about your browser.
23.3 Internet Access
I cannot access the Internet.
1 Check the hardware connections, and make sure the LEDs are behaving as
expected. See the Quick Start Guide and
Section 1.6 on page 26.
2 Make sure you entered your ISP account information correctly in the wizard. These
fields are case-sensitive, so make sure [Caps Lock] is not on.
3 If you are trying to access the Internet wirelessly, make sure the wireless settings
in the wireless client are the same as the settings in the AP.
4 If you are trying to access the Internet wirelessly, make sure you enabled the
wireless LAN and have selected the correct country and channel in which your
ZyXEL Device operates in the Wireless LAN > AP screen.
5 Disconnect all the cables from your device, and follow the directions in the Quick
Start Guide again.
6 If the problem continues, contact your ISP.
I cannot access the Internet anymore. I had access to the Internet (with the ZyXEL
Device), but my Internet connection is not available anymore.
1 Check the hardware connections, and make sure the LEDs are behaving as
expected. See the Quick Start Guide and
Section 1.6 on page 26.
Page 75

Chapter 23 Troubleshooting
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
225
2 T
urn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
3 If the problem continues, contact your ISP.
The Internet connection is slow or intermittent.
1 There might be a lot of traffic on the network. Look at the LEDs, and check Section
1.6 on page 26
. If the ZyXEL Device is sending or receiving a lot of information,
try closing some programs that use the Internet, especially peer-to-peer
applications.
2 Check the signal strength. If the signal strength is low, try moving your computer
closer to the ZyXEL Device if possible, and look around to see if there are any
devices that might be interfering with the wireless network (for example,
microwaves, other wireless networks, and so on).
3 Turn the ZyXEL Device off and on.
4 If the problem continues, contact the network administrator or vendor, or try one
of the advanced suggestions.
Advanced Suggestions
• Check the settings for QoS. If it is disabled, you might consider activating it. If it
is enabled, you might consider raising or lowering the priority for some
applications.
Page 76

Chapter 23 Troubleshooting
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
226
Page 77

P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
227
CHAPTER 24
Product Specifications
The following tables summarize the ZyXEL Device’s hardware and firmware
features.
24.1 Hardware Specifications
24.2 Firmware Specifications
Table 76 Hardware Specifications
Dimensions 133 x 61 x 163 mm
Weight 215g
Power Specification 12V 0.5A or 12V 1A
Built-in Switch Four auto-negotiating, auto MDI/MDI-X 10/100 Mbps RJ-45
Ethernet ports
ADSL Port 1 RJ-11 FXS POTS port
RESET Button Restores factory defaults
Antenna 2 internal antenna, 2dBi
WPS Button Press for over 5 seconds to turn on or off WLAN
Press for 1-5 seconds to enable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup)
Operation
Tem p er a tu r e
0º C ~ 40º C
Storage Temperature -25º ~ 60º C
Operation Humidity 20% ~ 90% RH
Storage Humidity 20% ~ 90% RH
Table 77 Firmware Specifications
Default IP Address 192.168.1.1
Default Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 (24 bits)
Page 78

Chapter 24 Product Specifications
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
228
Default user admin
Default Admin
Password
1234
DHCP Server IP Pool 192.168.1.32 to 192.168.1.64
Static DHCP
Addresses
10
Static Routes 16
Device Management Use the web configurator to easily configure the rich range of
features on the ZyXEL Device.
Wireless
Functionality
(wireless devices
only)
Allow the IEEE 802.11b/g/n wireless clients to connect to the
ZyXEL Device wirelessly. Enable wireless security (WEP, WPA(2),
WPA(2)-PSK) and/or MAC filtering to protect your wireless
network.
Firmware Upgrade Download new firmware (when available) from the ZyXEL web site
and use the web configurator to put it on the ZyXEL Device.
Note: Only upload firmware for your specific model!
Configuration Backup
& Restoration
Make a copy of the ZyXEL Device’s configuration. You can put it
back on the ZyXEL Device later if you decide to revert back to an
earlier configuration.
Ne
twork Address
Translation (NAT)
Each computer on your network must have its own unique IP
address. Use NAT to convert your public IP address(es) to multiple
private IP addresses for the computers on your network.
Port Forwarding If you have a server (mail or web server for example) on your
network, you can use this feature to let people access it from the
Internet.
DHCP (Dynamic Host
Configuration
Protocol)
Use this feature to have the ZyXEL Device assign IP addresses, an
IP default gateway and DNS servers to computers on your
network. Your device can also act as a surrogate DHCP server
(DHCP Relay) where it relays IP address assignment from the
actual real DHCP server to the clients.
DHCPv6 Use this feature to have the ZyXEL Device assign IPv6 addresses,
an IPv6 default gateway and IPv6 DNS servers to computers on
your network.
Dynamic DNS
Support
With Dynamic DNS (Domain Name System) support, you can use
a fixed URL, www.zyxel.com for example, with a dynamic IP
address. You must register for this service with a Dynamic DNS
service provider.
IP Multicast IP multicast is used to send traffic to a specific group of
computers. The ZyXEL Device supports versions 1 and 2 of IGMP
(Internet Group Management Protocol) used to join multicast
groups (see RFC 2236).
IPv6 Multicast IPv6 multicast is used to send traffic to a specific group of
computers. The ZyXEL Device supports MLD (Multicast Listener
Discovery) used to join IPv6 multicast groups (see RFC 2236).
Time and Date Get the current time and date from an external server when you
turn on your ZyXEL Device. You can also set the time manually.
These dates and times are then used in logs.
Table 77 Firmware Specifications (continued)
Page 79

Chapter 24 Product Specifications
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
229
L
ogs Use logs for troubleshooting. You can send logs from the ZyXEL
Device to an external syslog server.
Universal Plug and
Play (UPnP)
A UPnP-enabled device can dynamically join a network, obtain an
IP address and convey its capabilities to other devices on the
network.
Firewall Your device has a stateful inspection firewall with DoS (Denial of
Service) protection. By default, when the firewall is activated, all
incoming traffic from the WAN to the LAN is blocked unless it is
initiated from the LAN. The firewall supports TCP/UDP inspection,
DoS detection and prevention, real time alerts, reports and logs.
URL Filtering URL filtering allows you to block access to Internet web sites of
certain URL that you specify.
IP and IPv6 Filtering IP/MAC and IPv6 filtering allows you to block traffic by IP
addresses, MAC addresses and IPv6 addresses.
QoS (Quality of
Service)
You can efficiently manage traffic on your network by reserving
bandwidth and giving priority to certain types of traffic and/or to
particular computers.
Remote Management This allows you to decide whether a service (HTTP or FTP traffic for
example) from a computer on a network (LAN or WAN for
example) can access the ZyXEL Device.
PPPoE Support
(RFC2516)
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) emulates a dial-up
connection. It allows your ISP to use their existing network
configuration with newer broadband technologies such as ADSL.
The PPPoE driver on your device is transparent to the computers
on the LAN, which see only Ethernet and are not aware of PPPoE
thus saving you from having to manage PPPoE clients on individual
computers.
Other PPPoE Features PPPoE idle time out
PPPoE dial on demand
Multiple PVC
(Permanent Virtual
Circuits) Support
Your device supports up to 8 Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs).
IP Alias IP alias allows you to partition a physical network into logical
networks over the same Ethernet interface. Your device supports
three logical LAN interfaces via its single physical Ethernet
interface with the your device itself as the gateway for each LAN
network.
Packet Filters Your device’s packet filtering function allows added network
security and management.
Table 77 Firmware Specifications (continued)
Page 80

Chapter 24 Product Specifications
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
230
ADSL Standards Support Multi-Mode standard (ANSI T1.413, Issue 2; G.dmt
(G.992.1); G.lite (G992.2))
EOC specified in ITU-T G.992.1
ADSL2 G.dmt.bis (G.992.3)
ADSL2 G.lite.bis (G.992.4)
ADSL2+ (G.992.5)
Reach Extended ADSL (RE ADSL)
SRA (Seamless Rate Adaptation)
Auto-negotiating rate adaptation
ADSL physical connection ATM AAL5 (ATM Adaptation Layer type
5)
Support multi-protocol over AAL5 (RFC2684/1483)
Support PPP over ATM AAL5 (RFC2364)
PPP over Ethernet support for DSL connection (RFC 2516)
Support VC-based and LLC-based multiplexing
Support up to 8 PVCs
I.610 F4/F5 OAM
TR-067/TR-100 supported
Table 77 Firmware Specifications (continued)
Page 81

Chapter 24 Product Specifications
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
231
2
4.3 Wireless Features
Other Protocol
Support
SIP pass-through
DNS Proxy
Dynamic DNS (www.dyndns.org)
IP Alias
DHCP client/server/relay
RIP I/ RIP II supported
Support 16 IP Static routes and 16 IPv6 Static routes by Gateway
IGMP v1 and v2
IP Policy Routing
UPnP support
Transparent bridging, VLAN-tagging pass-through bridge mode
Static DHCP
Management Embedded Web Configurator(remove webhelp)
SNMP v1 & v2c with MIB II
Remote Management Control: Telnet, FTP, and Web.
TR-069 HTTPS
MTU adjustable on WebGUI
SMT
Table 77 Firmware Specifications (continued)
Table 78 Wireless Features
Internal Antenna The ZyXEL Device is equipped with two internal antenna to
provide a clear radio signal between the wireless stations and
the access points.
Wireless LAN MAC Address
Filtering
Your device can check the MAC addresses of wireless stations
against a list of allowed or denied MAC addresses.
WEP Encryption WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) encrypts data frames before
transmitting over the wireless network to help keep network
communications private.
Wi-Fi Protected Access Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a subset of the IEEE 802.11i
security standard. Key difference between WPA-PSK and WEP
is improved data encryption.
WPA2-PSK WPA2-PSK is a wireless security standard that defines
stronger encryption, authentication and key management
than WPA-PSK.
Page 82

Chapter 24 Product Specifications
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
232
T
he following list, which is not exhaustive, illustrates the standards supported in
the ZyXEL Device.
WMM QoS WMM (Wi-Fi MultiMedia) QoS (Quality of Service) allows you
to prioritize wireless traffic according to the delivery
requirements of individual services.
Other Wireless Features WDS(wireless client: G-570S v2)
IEEE 802.11n Compliance
Frequency Range:2.4 GHz
Advanced Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
(OFDM)
2x2 Wireless Configuration
Data Rates:300Mbps and Auto Fallback
EIRP: 22dBm
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) Data Encryption 64/128
WLAN bridge to LAN
16 MAC Address filter
WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK
WPS
IEEE 802.1x (EAP-MD5, TLS and TTLS)
WMM
Multi BSSID (4 BSSIDs)
Table 79 Standards Supported
STANDARD DESCRIPTION
RFC 867 Daytime Protocol
RFC 868 Time Protocol
RFC 1058 RIP-1 (Routing Information Protocol)
RFC 1112 IGMP v1
RFC 1305 Network Time Protocol (NTP version 3)
RFC 1483 Multiprotocol Encapsulation over ATM Adaptation Layer 5
RFC 1631 IP Network Address Translator (NAT)
RFC 1661 The Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
RFC 1723 RIP-2 (Routing Information Protocol)
RFC 1981 Path MTU Discovery for IPv6
RFC 2236 IGMP v2
RFC 2364 PPP over AAL5 (PPP over ATM over ADSL)
RFC 2408 Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol
(ISAKMP)
Table 78 Wireless Features
Page 83

Chapter 24 Product Specifications
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
233
R
FC 2460 IPv6 Specification
RFC 2516 A Method for Transmitting PPP Over Ethernet (PPPoE)
RFC 2684 Multiprotocol Encapsulation over ATM Adaptation Layer 5.
RFC 2766 Network Address Translation - Protocol
RFC 3484 Default Address Selection for IPv6
RFC 4291 IPv6 Addressing Architecture
RFC 4443 ICMPv6
RFC 4861 Neighbor Discovery for IPv6
RFC 4862 IPv6 Stateless Address Autoconfiguration
IEEE 802.11 Also known by the brand Wi-Fi, denotes a set of Wireless LAN/
WLAN standards developed by working group 11 of the IEEE
LAN/MAN Standards Committee (IEEE 802).
IEEE 802.11b Uses the 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) band
IEEE 802.11g Uses the 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) band
IEEE 802.11n Uses the 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) band
IEEE 802.11g+ Turbo and Super G modes
IEEE 802.11d Standard for Local and Metropolitan Area Networks: Media
Access Control (MAC) Bridges
IEEE 802.11x Port Based Network Access Control.
IEEE 802.11e QoS IEEE 802.11 e Wireless LAN for Quality of Service
ANSI T1.413, Issue 2 Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) standard.
G dmt(G.992.1) G.992.1 Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL)
Transceivers
ITU G.992.1 (G.DMT) ITU standard for ADSL using discrete multitone modulation.
ITU G.992.2 (G. Lite) ITU standard for ADSL using discrete multitone modulation.
ITU G.992.3
(G.dmt.bis)
ITU standard (also referred to as ADSL2) that extends the
capability of basic ADSL in data rates.
ITU G.992.4
(G.lite.bis)
ITU standard (also referred to as ADSL2) that extends the
capability of basic ADSL in data rates.
ITU G.992.5 (ADSL2+) ITU standard (also referred to as ADSL2+) that extends the
capability of basic ADSL by doubling the number of downstream
bits.
Microsoft PPTP MS PPTP (Microsoft's implementation of Point to Point Tunneling
Protocol)
MBM v2 Media Bandwidth Management v2
RFC 2383 ST2+ over ATM Protocol Specification - UNI 3.1 Version
TR-069 TR-069 DSL Forum Standard for CPE Wan Management.
1.363.5 Compliant AAL5 SAR (Segmentation And Re-assembly)
Table 79 Standards Supported (continued)
STANDARD DESCRIPTION
Page 84

Chapter 24 Product Specifications
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
234
2
4.4 Power Adaptor Specifications
Table 80 ZyXEL Device Series Power Adaptor Specifications
AC POWER ADAPTER
MODEL
12V 0.5A SWITCHING PA
Input Power 100~240V-50/60HZ
Output Power DC 12Volts/0.5A
Power Consumption 7Watt max
Safety Standards EN 60950-1:2006/A11:2009
AC POWER ADAPTER
MODEL
12V 1A SWITCHING PA
Input Power 100~240V-50/60HZ
Output Power DC 12Volts/1A
Power Consumption 7Watt max
Safety Standards EN 60950-1:2006/A11:2009
Page 85

P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
235
APPENDIX A
Setting up Your Computer’s IP
Address
All computers must have a 10M or 100M Ethernet adapter card and TCP/IP
installed.
Windows 95/98/Me/NT/2000/XP/Vista, Macintosh OS 7 and later operating
systems and all versions of UNIX/LINUX include the software components you
need to install and use TCP/IP on your computer. Windows 3.1 requires the
purchase of a third-party TCP/IP application package.
TCP/IP should already be installed on computers using Windows NT/2000/XP,
Macintosh OS 7 and later operating systems.
After the appropriate TCP/IP components are installed, configure the TCP/IP
settings in order to "communicate" with your network.
If you manually assign IP information instead of using dynamic assignment, make
sure that your computers have IP addresses that place them in the same subnet
as the ZyXEL Device’s LAN port.
Page 86

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
236
W
indows 95/98/Me
Click Start, Settings, Control Panel and double-click the Network icon to open
the Network window.
Figure 111 WIndows 95/98/Me: Network: Configuration
Installing Components
The Network window Configuration tab displays a list of installed components.
You need a network adapter, the TCP/IP protocol and Client for Microsoft
Networks.
If you need the adapter:
1 In the Network window, click Add.
2 Select Adapter and then click Add.
3 Select the manufacturer and model of your network adapter and then click OK.
If you need TCP/IP:
1 In the Network window, click Add.
2 Select Protocol and then click Add.
Page 87

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
237
3 S
elect Microsoft from the list of manufacturers.
4 Select TCP/IP from the list of network protocols and then click OK.
If you need Client for Microsoft Networks:
1 Click Add.
2 Select Client and then click Add.
3 Select Microsoft from the list of manufacturers.
4 Select Client for Microsoft Networks from the list of network clients and then
click OK.
5 Restart your computer so the changes you made take effect.
Configuring
1 In the Network window Configuration tab, select your network adapter's TCP/IP
entry and click Properties
2 Click the IP Address tab.
• If your IP address is dynamic, select Obtain an IP address automatically.
• If you have a static IP address, select Specify an IP address and type your
information into the IP Address and Subnet Mask fields.
Figure 112 Windows 95/98/Me: TCP/IP Properties: IP Address
Page 88

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
238
3 C
lick the DNS Configuration tab.
• If you do not know your DNS information, select Disable DNS.
• If you know your DNS information, select Enable DNS and type the
information in the fields below (you may not need to fill them all in).
Figure 113 Windows 95/98/Me: TCP/IP Properties: DNS Configuration
4 Click the Gateway tab.
• If you do not know your gateway’s IP address, remove previously installed
gateways.
• If you have a gateway IP address, type it in the New gateway field and click
Add.
5 Click OK to save and close the TCP/IP Properties window.
6 Click OK to close the Network window. Insert the Windows CD if prompted.
7 Turn on your ZyXEL Device and restart your computer when prompted.
Verifying Settings
1 Click Start and then Run.
2 In the Run window, type "winipcfg" and then click OK to open the IP
Configuration window.
3 Select your network adapter. You should see your computer's IP address, subnet
mask and default gateway.
Page 89

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
239
W
indows 2000/NT/XP
The following example figures use the default Windows XP GUI theme.
1 Click start (Start in Windows 2000/NT), Settings, Control Panel.
Figure 114 Windows XP: Start Menu
2 In the Control Panel, double-click Network Connections (Network and Dial-
up Connections in Windows 2000/NT).
Figure 115 Windows XP: Control Panel
Page 90

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
240
3 R
ight-click Local Area Connection and then click Properties.
Figure 116 Windows XP: Control Panel: Network Connections: Properties
4 Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) (under the General tab in Win XP) and then
click Properties.
Figure 117 Windows XP: Local Area Connection Properties
5 The Internet Protocol TCP/IP Properties window opens (the General tab in
Windows XP).
Page 91

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
241
•
If you have a dynamic IP address click Obtain an IP address
automatically.
• If you have a static IP address click Use the following IP Address and fill in
the IP address, Subnet mask, and Default gateway fields.
•Click Advanced.
Figure 118 Windows XP: Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties
6 If you do not know your gateway's IP address, remove any previously installed
gateways in the IP Settings tab and click OK.
Do one or more of the following if you want to configure additional IP addresses:
•In the IP Settings tab, in IP addresses, click Add.
•In TCP/IP Address, type an IP address in IP address and a subnet mask in
Subnet mask, and then click Add.
• Repeat the above two steps for each IP address you want to add.
• Configure additional default gateways in the IP Settings tab by clicking Add
in Default gateways.
•In TCP/IP Gateway Address, type the IP address of the default gateway in
Gateway. To manually configure a default metric (the number of transmission
hops), clear the Automatic metric check box and type a metric in Metric.
•Click Add.
• Repeat the previous three steps for each default gateway you want to add.
Page 92

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
242
•
Click OK when finished.
Figure 119 Windows XP: Advanced TCP/IP Properties
7 In the Internet Protocol TCP/IP Properties window (the General tab in
Windows XP):
•Click Obtain DNS server address automatically if you do not know your
DNS server IP address(es).
• If you know your DNS server IP address(es), click Use the following DNS
server addresses, and type them in the Preferred DNS server and
Alternate DNS server fields.
Page 93

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
243
I
f you have previously configured DNS servers, click Advanced and then the
DNS tab to order them.
Figure 120 Windows XP: Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties
8 Click OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window.
9 Click Close (OK in Windows 2000/NT) to close the Local Area Connection
Properties window.
10 Close the Network Connections window (Network and Dial-up Connections
in Windows 2000/NT).
11 Turn on your ZyXEL Device and restart your computer (if prompted).
Verifying Settings
1 Click Start, All Programs, Accessories and then Command Prompt.
2 In the Command Prompt window, type "ipconfig" and then press [ENTER]. You
can also open Network Connections, right-click a network connection, click
Status and then click the Support tab.
Windows Vista
This section shows screens from Windows Vista Enterprise Version 6.0.
Page 94

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
244
1 C
lick the Start icon, Control Panel.
Figure 121 Windows Vista: Start Menu
2 In the Control Panel, double-click Network and Internet.
Figure 122 Windows Vista: Control Panel
3 Click Network and Sharing Center.
Figure 123 Windows Vista: Network And Internet
Page 95

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
245
4 C
lick Manage network connections.
Figure 124 Windows Vista: Network and Sharing Center
5 Right-click Local Area Connection and then click Properties.
Note: During this procedure, click Continue whenever Windows displays a screen
saying that it needs your permission to continue.
Figure 125 Windows Vista: Network and Sharing Center
Page 96

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
246
6 S
elect Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties.
Figure 126 Windows Vista: Local Area Connection Properties
7 The Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties window opens (the
General tab).
• If you have a dynamic IP address click Obtain an IP address
automatically.
• If you have a static IP address click Use the following IP address and fill in
the IP address, Subnet mask, and Default gateway fields.
Page 97

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
247
•
Click Advanced.
Figure 127 Windows Vista: Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties
8 If you do not know your gateway's IP address, remove any previously installed
gateways in the IP Settings tab and click OK.
Do one or more of the following if you want to configure additional IP addresses:
•In the IP Settings tab, in IP addresses, click Add.
•In TCP/IP Address, type an IP address in IP address and a subnet mask in
Subnet mask, and then click Add.
• Repeat the above two steps for each IP address you want to add.
• Configure additional default gateways in the IP Settings tab by clicking Add
in Default gateways.
•In TCP/IP Gateway Address, type the IP address of the default gateway in
Gateway. To manually configure a default metric (the number of transmission
hops), clear the Automatic metric check box and type a metric in Metric.
•Click Add.
• Repeat the previous three steps for each default gateway you want to add.
Page 98

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
248
•
Click OK when finished.
Figure 128 Windows Vista: Advanced TCP/IP Properties
9 In the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties window, (the
General tab):
•Click Obtain DNS server address automatically if you do not know your
DNS server IP address(es).
• If you know your DNS server IP address(es), click Use the following DNS
server addresses, and type them in the Preferred DNS server and
Alternate DNS server fields.
Page 99

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
249
I
f you have previously configured DNS servers, click Advanced and then the
DNS tab to order them.
Figure 129 Windows Vista: Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties
10 Click OK to close the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties
window.
11 Click Close to close the Local Area Connection Properties window.
12 Close the Network Connections window.
13 Turn on your ZyXEL Device and restart your computer (if prompted).
Verifying Settings
1 Click Start, All Programs, Accessories and then Command Prompt.
2 In the Command Prompt window, type "ipconfig" and then press [ENTER]. You
can also open Network Connections, right-click a network connection, click
Status and then click the Support tab.
Page 100

Appendix A Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address
P-660HN-Tx User’s Guide
250
Ma
cintosh OS 8/9
1 Click the Apple menu, Control Panel and double-click TCP/IP to open the TCP/
IP Control Panel.
Figure 130 Macintosh OS 8/9: Apple Menu
 Loading...
Loading...