Page 1

MAINTENANCE MANUAL FOR
ROUGH TERRAIN CRANE
Address:Quantang Indust=rial Park, 2nd Yuanda Road,
Changsha Economic and Technological Development
Zone, Hunan Province, China
Postcode: 410131
Website: www.zoomlion.com
Page 2

MAINTENANCE
MANUAL
Edition 1
Dec 2013
Page 3

Dec 2013
Page 4

(Thank you letter)
Owners, Users and Operators:
Zoomlion Cranes appreciates your selection of the ZOOMLION Rough Terrain Crane for your
application.
No one should do the maintenance/service tasks to the crane unless they read and know the
data in this manual and the other technical documents supplied with the crane.
The Maintenance and Service Manual provides periodic inspections, maintenance and service
procedures that are necessary to make sure the performance, safety and reliability are at the
highest level. They can also increase the service life of the crane.
When you follow the instructions in this manual, your crane can operate at MAXIMUM
EFFICIENCY.
To look after your rights & interests and safety, you must obey all safety data in the
Maintenance and Service Manual. Only approved personnel can disassemble and adjust
hydraulic system components during maintenance. When a hydraulic component malfunctions
or is damaged, tell the local repair facility.
You do not have to keep the Maintenance & Service Manual in the cab of the crane. The
Maintenance & Service Manual must be with the crane if it is sold.
If there is something in the manual that you do not understand, speak with us. We (Zoomlion
Cranes) are NOT responsible for damages from an operator or service technician who does not
obey the instructions in the Maintenance and Service Manual.
THANK YOU!
Mobile Crane Branch Company of ZOOMLION Heavy Industry Science and Technology Co.,
Ltd
Copyright
Under the copyright laws, this manual cannot be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated, or reduced to any electronic medium
or machine readable form, in whole or part, without the prior written consent of Zoomlion Heavy Industry Science and Technology
Co., Ltd.
Copyright © 20XX, Zoomlion Heavy Industry Science and Technology Co., Ltd.
All rights reserved. Printed in the United States
Edition 2 Page i
Dec/2013
Page 5

Edition 2 Page ii
Dec/2013
Page 6

Contents
(Thank you letter) ......................................................................................................................... i
Contents .................................................................................................................................... iii
About This Manual ...................................................................................................................... v
Safety ....................................................................................................................................... vii
Introduction ............................................................................................................................ 1
1.1 INTRODUCTION ....................................................................................................... 1
1.2 OPERATOR OBSERVATION .................................................................................... 1
1.3 WIRE-ROPE INSPECTION RECORD ....................................................................... 3
1.4 ENGINE MAINTENANCE .......................................................................................... 4
1.5 ENGINE RADIATOR MAINTENANCE ....................................................................... 7
1.6 TRANSMISSION MAINTENANCE ............................................................................ 8
1.7 AXLE MAINTENANCE CHECK ............................................................................... 10
1.8 TIRE MAINTENANCE CHECK ................................................................................ 11
1.9 BRAKE SYSTEM MAINTENANCE .......................................................................... 14
1.10 AIR SYSTEM MAINTENANCE ................................................................................ 15
1.11 BATTERY MAINTENANCE ..................................................................................... 15
1.12 FUEL, COOLANT AND TORQUE CONVERTER HYDRAULIC TRANSMISSION
OIL .......................................................................................................................... 16
1.13 LUBRICATION ........................................................................................................ 17
1.14 HYDRAULIC OIL ..................................................................................................... 24
1.15 GEAR OIL ............................................................................................................... 28
1.16 LUBRICATING GREASE......................................................................................... 30
1.17 LUBRICATING POINTS .......................................................................................... 31
1.18 ADJUST, CLEAN AND REPLACE THE PARTS ...................................................... 33
1.19 BATTERY MAINTENANCE AND SERVICE ............................................................ 50
1.20 BATTERY MAINTENANCE – WINTER ................................................................... 51
1.21 OPERATION IN WINTER ........................................................................................ 52
1.22 OPERATION IN SUMMER ...................................................................................... 53
Troubleshooting .......................................................................................................................... 1
Edition 2 Page iii
Dec/2013
Page 7

2.1 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM ............................................................................................. 1
2.2 HYDRAULIC SYSTEM ............................................................................................ 12
2.3 EXTEND / RETRACT SYSTEM............................................................................... 13
2.4 DERRICKING MECHANISM ................................................................................... 14
2.5 SWING MECHANISM ............................................................................................. 15
2.6 HOIST MECHANISM ............................................................................................... 16
2.7 OUTRIGGERS ........................................................................................................ 17
2.8 TRANSMISSION ..................................................................................................... 18
2.9 BRAKE SYSTEM .................................................................................................... 21
2.10 STEERING SYSTEM .............................................................................................. 22
2.11 FRONT / REAR AXLES ........................................................................................... 25
2.12 DRIVE SHAFT ......................................................................................................... 27
2.13 TIRES...................................................................................................................... 28
2.14 ENGINE ERROR CODE.......................................................................................... 30
2.15 TRANSMISSION ERROR CODE ........................................................................... 40
Inspection ................................................................................................................................. 84
3.1 PRE-START INSPECTION ..................................................................................... 84
3.2 NEW CRANE SPECIAL BREAK-IN REQUIREMENTS ........................................... 88
3.3 PERIODIC INSPECTIONS AND SERVICE ............................................................. 88
3.4 PERIODIC CRANE INSPECTIONS ......................................................................... 96
3.5 INSPECTIONS AND MAINTENANCES DURING BREAK-IN PERIOD .................. 103
3.6 FILTER ELEMENTS LISTS ................................................................................... 104
3.7 FLUID VOLUME REQUIREMENTS ...................................................................... 106
Edition 2 Page iv
Dec/2013
Page 8

About This Manual
General
The data (data, specifications, illustrations) in this manual is for cranes in production at the time of this
manuals publication. We reserve the right to make changes to this manual at any time, without obligation.
This manual is for maintaining and servicing the RT Crane in the field. Follow the operation and
maintenance procedures to make sure that your machine operates at MAXIMUM EFFICIENCY. Use the
CRANE PERIODIC INSPECTION CHECKLIST. Keep a maintenance log to monitor all maintenance
work on the machine.
An example of a Maintenance Log and Crane Periodic Inspection Checklist is at the end of this section.
Again, we at ZOOMLION appreciate your selection of our crane. User safety is most important. To
complete on-site tasks safely, operators and service technicians must be responsible. Obey the
instructions that follow:
• Comply - with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), Federal,
State and Local Regulations.
• Read, Understand and Follow - the instructions in this and other manuals and
documents that come with the crane.
• Use Good, Safe Work Practices - in a common sense way.
• Only have trained operators and service technicians - directed by informed
and knowledgeable job-site supervisors.
• Do not use this crane - before the portable fire extinguisher, installed in the cab,
agrees with local fire protection rules.
Edition 2 Page v
Dec /2013
Page 9

OSHA prohibits the alteration or modification of this crane without written
manufacturer’s approval. Use only the factory approved parts to service or repair
the crane.
If you make modifications/additions which affect the safe operation of the
equipment to the crane before you use it, the crane owner must make sure that the
modifications/additions agree with OSHA 1926:1412.
Speak with us if special data is necessary for the maintenance or operation of your RT Crane. Send your
machine model and a serial number to make sure that you receive the correct data.
If there is anything in this manual that is not clear or which you think is necessary, write to the address
that follows:
Rough Terrain Crane R & D Institute
Zoomlion Mobile Crane Branch Company
Quantang Industrial Park, 2nd Yuanda Road,
Economic and Technological Development Zone,
Changsha, Hunan Province, China, 410131
You can also speak to us by telephone at 0086-84671997 (international), 0731-84671997 (in China).
Thank You!
Edition 2 Page vi
Dec /2013
Page 10

Safety
The safety symbol, used on the Danger, Warning and Caution labels, tells personnel of possible death,
injury, or property damage. Obey all safety data that follows this symbol to prevent dangerous conditions.
HAZARD CLASSIFICATION
Hazard classification is a system to show different classes of possible injury levels. A safety symbol and
a signal word show how dangerous the level of possible injury can be.
A signal word without a safety symbol refers to property damage, protection devices, or important data.
You will find this system used in this manual and on signs on the crane to help find and prevent
dangerous situations.
HAZARD INDICATORS
DANGER, WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE labels are on signs and decals and as you read this manual
to show important instructions. In this manual, DANGER, WARNING and CAUTION labels are before the
paragraph or item to which they apply. NOTEs follow the paragraph or item they apply to. The labels are
as follows:
Refers to a dangerous situation which, if you do not prevent, will cause death or injury.
Refers to a possible dangerous situation which, if you do not prevent, could cause death or injury.
Refers to a possible dangerous situation which, if you do not prevent, may cause light or moderate injury.
Refers to a tip or hint in the instructions.
INTENDED USE
Edition 2 Page vii
Dec /2013
Page 11

Scope
The owner of this crane must know federal, state and local rules. When your equipment is in operation, the
area must be safe for employees and non-employees. Do not cause damage to other equipment or local
structures while you operate this crane. Rules change by location and this manual does not give that data.
ZOOMLION makes manuals for different construction and industrial equipment. It is policy to include
applicable national consensus, industry standards and safety data with the manuals. Use this data to give
applicable training to personnel who are to operate, do the maintenance and supervise the equipment
correctly and safely.
We make equipment for heavy-duty labor. Do periodic inspections regularly because the equipment wears
during operation. This prevents accidents, decreases downtime and helps equipment work satisfactorily. The
goal of these inspections is to find worn, cracked, damaged parts and loose or missing fasteners before they
cause a problem.
Correct training and inspection procedures are necessary to prevent injury to persons, property damage and
high maintenance costs.
Read and understand the data that comes with this crane. Help is available from the distributors of your
ZOOMLION crane and from the ZOOMLION manufacturing facility.
This manual contains the instructions and data on the operation, maintenance, lubrication and adjustments of
the Rough Terrain Crane. Do not operate or service the crane before you understand the data in this manual.
Edition 2 Page viii
Dec /2013
Page 12
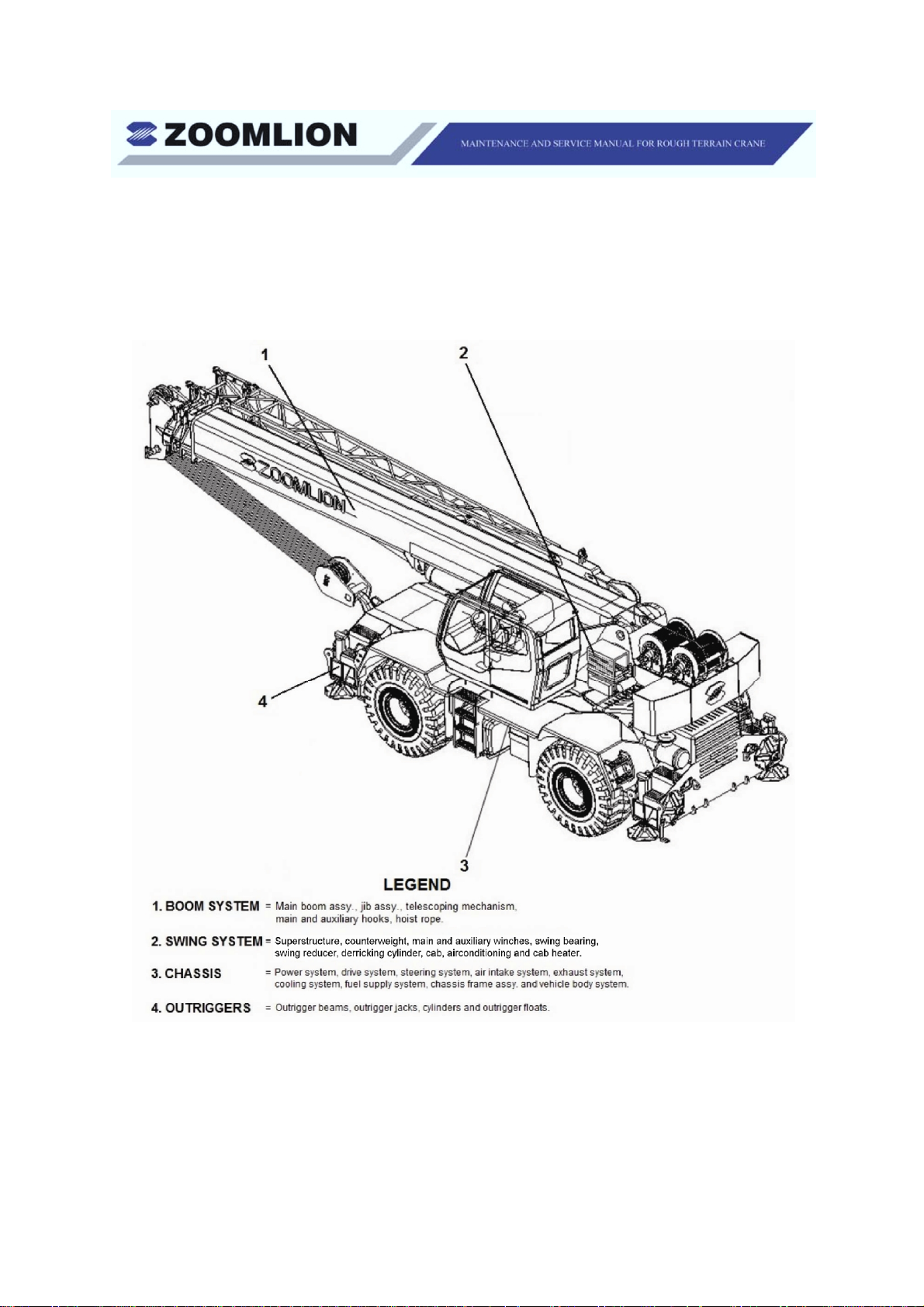
Nomenclature
To help you understand the contents of this manual, refer to the figure below. Each numbered term can
represent several components of the same main part.
Edition 2 Page ix
Dec /2013
Page 13
CRANE PERIODIC INSPECTION CHECKLIST
This inspection checklist provides supplementary data to facilitate the correct operation and maintenance
of the crane.
Component
Inspected
Interval
Function
Adjusting
Condition
Maintenance
Condition
Component
Inspected
Inspection
Code Function
Adjusting
Condition
Maintenance
Condition
Edition 2 Page x
Dec /2013
Page 14

MAINTENANCE LOG
Item
Adjusting Condition
Date
Edition 2 Page xi
Dec /2013
Page 15

Edition 2 Page xii
Dec /2013
Page 16

MAINTENANCE AND SERVICE MANUAL FOR ROUGH TERRAIN CRANE
Chapter 1 Maintenance and Service
Page 17

Page 18

1.1 INTRODUCTION
A set of preventive maintenance tasks is necessary to extend the serviceable life of
the crane. The tasks can help to maximize efficient service and decrease the time
the crane is at the repair facility. This section has checks and procedures which you
are to do on daily, weekly, monthly and semi-annual intervals. These intervals are
specified in conditions of calendar and hours of operation.
The checks for long intervals include all the checks that you do in the shorter
intervals. Thus, the weekly check includes all items in the daily check. The monthly
check includes the weekly and the daily checks. The semi-annual check includes the
quarterly, monthly, weekly and daily checks.
The chart makes it possible for you to record the preventive maintenance tasks that
you complete. It also supplies you with a tool to find the problem areas and to
examine the value of the maintenance tasks. The items in each check interval on the
chart are assembled by their applicable headings and explained in this chapter.
This maintenance schedule is a procedure to make sure that basic preventive
maintenance tasks are completed in the usual conditions that you operate. The
conditions which increase wear, loads or strain on the crane, usually make it
necessary to decrease the interval time. Before you change the maintenance
schedule, examine your operation and the maintenance records of the crane. Think
about all the factors involved and make a new schedule that is sufficient to align the
usual maintenance tasks.
Introduction
As a part of each preventive maintenance check, refer to the Engine Manufacturer’s
Manual for engine maintenance tasks. When you do the servicing of the engine, use
the data in the engine manual if this chapter has data that is different.
1.2 OPERATOR OBSERVATION
A. Do a visual inspection for:
(1) Unusual conditions
(2) Hydraulic system leaks or damage.
B. Examine the area around the engine for:
(1) Belts (tension and wear)
(2) Coolant level
(3) Engine oil level
(4) Hydraulic transmission oil level
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-1
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 19

(5) Air cleaner vacuum actuated indicator
(6) Air inlet
(7) Silencer and exhaust device.
C. Examine the condition of each battery.
D. Examine the boom for:
(1) Sheave (wear or damage)
(2) The function of the anti-two block system
(3) Wire-rope on the winches (wear and breaks)
(4) Wear of the cylinder pin.
E. Tires, axles and drivelines (wear or damage).
F. Examine the cab for:
(1) Gauge and indicator functions
(2) Function of the switches and joysticks
(3) Clear windows
(4) Safety device in position
(5) Each light operates
(6) Cleanliness: free from dirt, mud and waste material.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-2
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 20

WIRE
-
ROPE INSPECTION RECORD
________________________________
________________________________
_________
1.3 WIRE-ROPE INSPECTION RECORD
(See pages 1-37 and 1-38)
Place of inspection ________________________ Date _______________
DESCRIPTION OF CRANE
Make _____________________________ Model _________ Serial No. ___________
Type and Arrangement of Attachments ___________________________________________
Date of Last Rope Inspection __________________________________________________
Hours and Time of Service Since Last Inspection ___________________________________
RESULT OF INSPECTION
Rope Inspected Type and Size Conditions noted Recommendations
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
___________________ Inspector:
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-3
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 21
1.4 ENGINE MAINTENANCE
For Cummins engine maintenance, refer to the EngineManufacturer’s Manual.
Engine productivity, longevity and low-cost performance depend on a regular
program of periodic maintenance. The materials presented here are listed in
accordance with the EngineManufacturer’s Manual. Consideration may dictate a
revision in scheduling for the periodic checks.
A good periodic preventive maintenance program can increase the productivity,
longevity and low-cost performance of the engine. The data, in this section of the
manual, is from the data in the EngineManufacturer’s Manual. You can change the
interval or schedule of the preventive maintenance program because of the area and
the types of operations you do.
A. Daily Inspections:
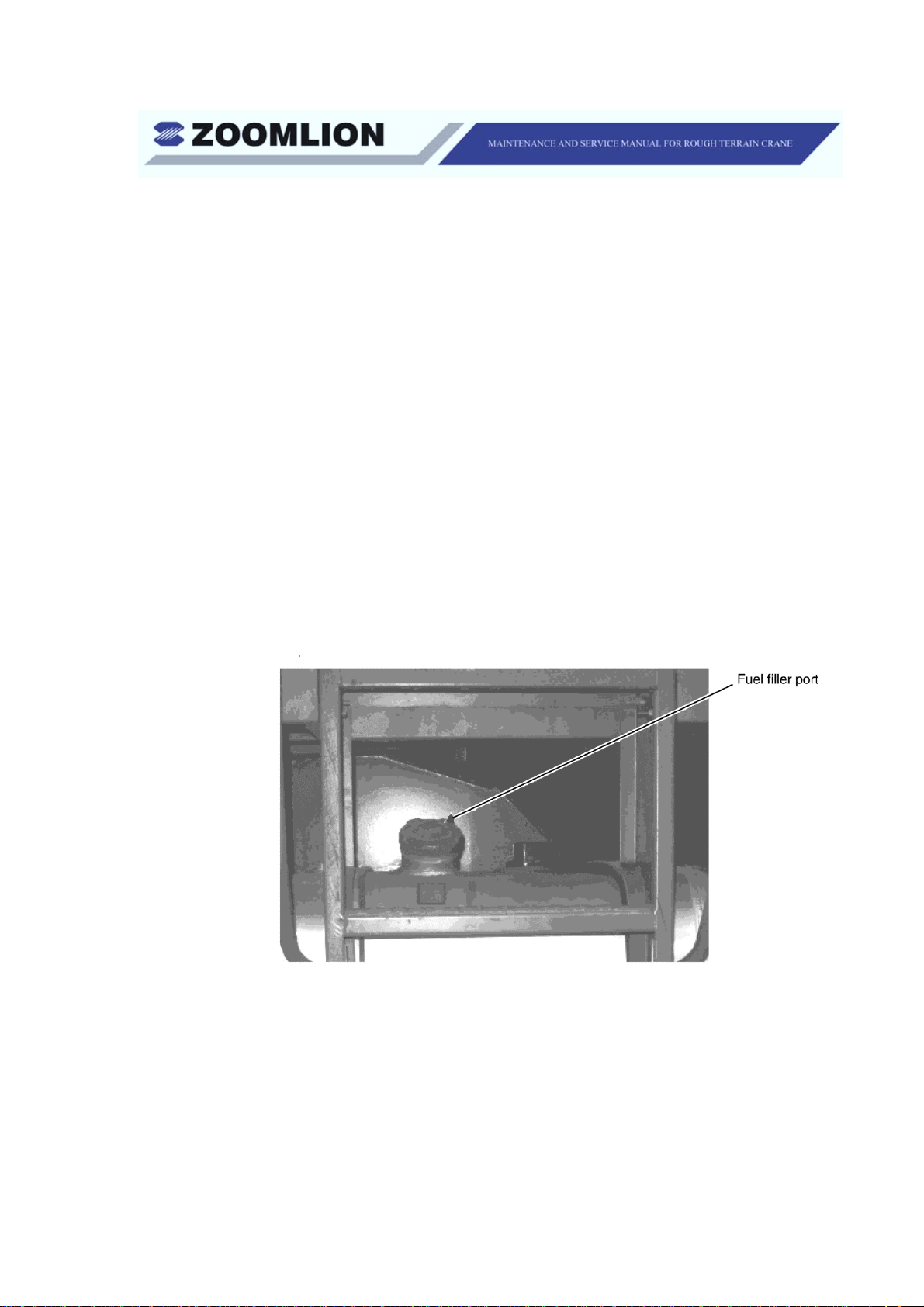
(1) Fuel Level
(a) You can find the fuel tank on the left side of the crane (Figure 1-1). If
you keep the tank full of fuel, in cold weather, you can decrease the
quantity of condensation.
Figure 1-1 Fuel Tank Cap
(b) Use a good grade of diesel fuel. The tank capacity is 79 gal. (300 l).
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-4
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 22
(2) Engine Oil Level
(a) You can measure the level of oil in the engine by a dipstick. The
dipstick is on the right side of the engine (aft end of the crane). The
engine must be OFF and sit for a short time before you can
measure the oil level. Wait for 15 minutes, after you stop the engine,
to measure the level. Adjust the level of oil to the full mark.
(b) Do not overfill!
Do not operate the crane if the level of engine oil is too low or too high.
(3) Water Separator
(a) The fuel line contains a water separator. It removes the
condensation and contamination from the fuel before it goes into the
engine. You must examine the water separator before you operate
the crane to drain the condensation and contamination.
(b) Do not let the water separator fill more than 1/2 full.
(4) Air Filter
(a) Examine the air filter and its connections for leaks, dents and
damage (See Figure 1-2).
Figure 1-2 Air Filter
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-5
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 23
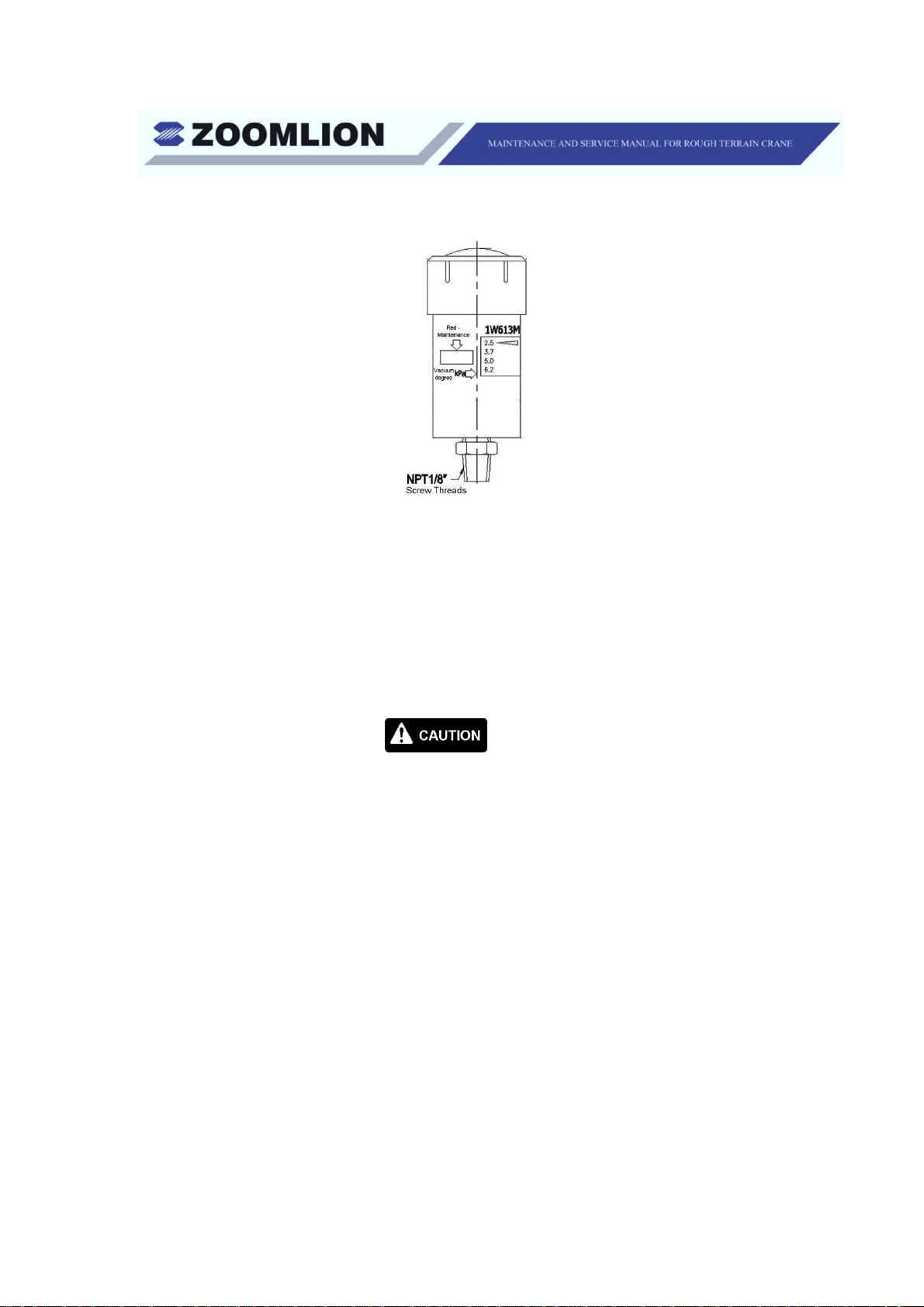
Figure 1-3 Indicator
(b) A vacuum actuated indicator (See Figure 1-3) is attached on the
side of the air filter assembly. Its gives you an indication of restricted
airflow through the air filter. The quantity of airflow shows on the
indicator at three different levels. When the light is in the green area,
the air filter is good. If the light is in the yellow area, you need to
clean or replace the filter cartridge. If the light is in red area, do not
operate the engine. Replace or clean the filter cartridge. Examine
the intake screen and cartridge area.Make sure that they are clean.
When you use a degreasing agent to clean the engine, make sure that
you put a protective material around the vacuum actuated indicator
(filter minder). The polycarbonate base of the engine degreasing
solvents can damage or destroy the indicator.
(c) Reset the air cleaner indicator each time after the filter element is
replaced to assure proper function.
(d) After you do the servicing on the air filter assembly, reset the
indicator.
(5) Engine Belts
(a) Examine the engine belts for condition and correct adjustment.
Refer to the Engine Manufacturer’s Manual for the belt tension and
the correct procedure to make the belts tight.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-6
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 24

B. Quarterly Inspection
(1) Fuel Tank
(a) Drain the collected water and sediment from the fuel tank.
• Remove the drain plug and let the tank drain.
• Stop the flow when the fuel is clear of water and sediment.
(b) If the tank has a large quantity of sediment, do the task that follows:
• Fully drain the tank.
• Flush the tank with kerosene until you remove all the sediment.
• Fully drain the kerosene and refuel the tank.
C. Semi-Annually Inspection
(1) Crankcase Breather
To do servicing on the crankcase breather, follow the procedure in the
Engine Manufacturer’s Manual.
1.5 ENGINE RADIATOR MAINTENANCE
A. Daily / 8 Hours:
(1) Coolant Level
(a) Insert the engine radiator coolant level and add coolant to adjust the
level. You can see the level of coolant in the sight gauge near the
top of the radiator tank. A solution of 50% ethylene glycol by volume
is the recommended year-round coolant mixture. If necessary, refill
the corrosion inhibitor. Refer to the engine manual or the servicing
facility to pick the correct coolant and corrosion inhibitor.
(b) If you operate in an area that does not freeze, use a solution of
clean water with a corrosion inhibitor. This gives you the best
performance.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-7
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 25

B. Monthly / 160 Hours:
(1) Radiator Exterior
Clean the radiator fins and through-core cooling passages. Use
compressed air and water in the opposite direction of usual air flow to
push the unwanted material out of the radiator core.
C. Quarterly:
(1) Corrosion Inhibitor
Adjust the cooling system corrosion inhibitor to the correct level after 500
hours of operation.
Do not use a chromate based corrosion inhibitor when the coolant in
the system contains ethylene glycol. Only use non-chromate based
inhibitors. The chromate base inhibitorreacts with ethylene glycol to
make hydroxide. This you know as Green Slime. The slime decreases
the heat movement rate and can cause the engine to be too hot.
D. Semi-Annually:
(1) Cooling System
Clean the cooling systemat 1000 hours or semi-annually whichevercomes
first. Use a radiator cleaning compound and follow the instructions on the
container. Flush the system with clean water and fill it with an ethylene
glycol solution of 50% by volume.
1.6 TRANSMISSION MAINTENANCE
A. Daily Maintenance Check
(1) Before you move the crane, make sure that the level of oil in the
transmission is correct.
(2) Start the engine and let it idle at 1000 to 1500 rpm until the transmission
increases to a temperature of 180° F to 200° F (82.2° C to 93.3° C).
When the engine is at the correct temperature, slowly move the shift lever
through all the gear positions. This moves oil to all parts of the system.
Set the shift lever to the neutral position and set the engine speed at idle
rpm.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-8
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 26
B. Service the Transmission After Overhaul
When you service the crane for the first time after vehicle installation and / or
after repair, fill the unit as follows:
(1) Fill the transmission with recommended lubricant.
(2) Start the engine and set the speed at idle to let oil fill the torque converter
and lines. Stop the engine after 3 minutes.
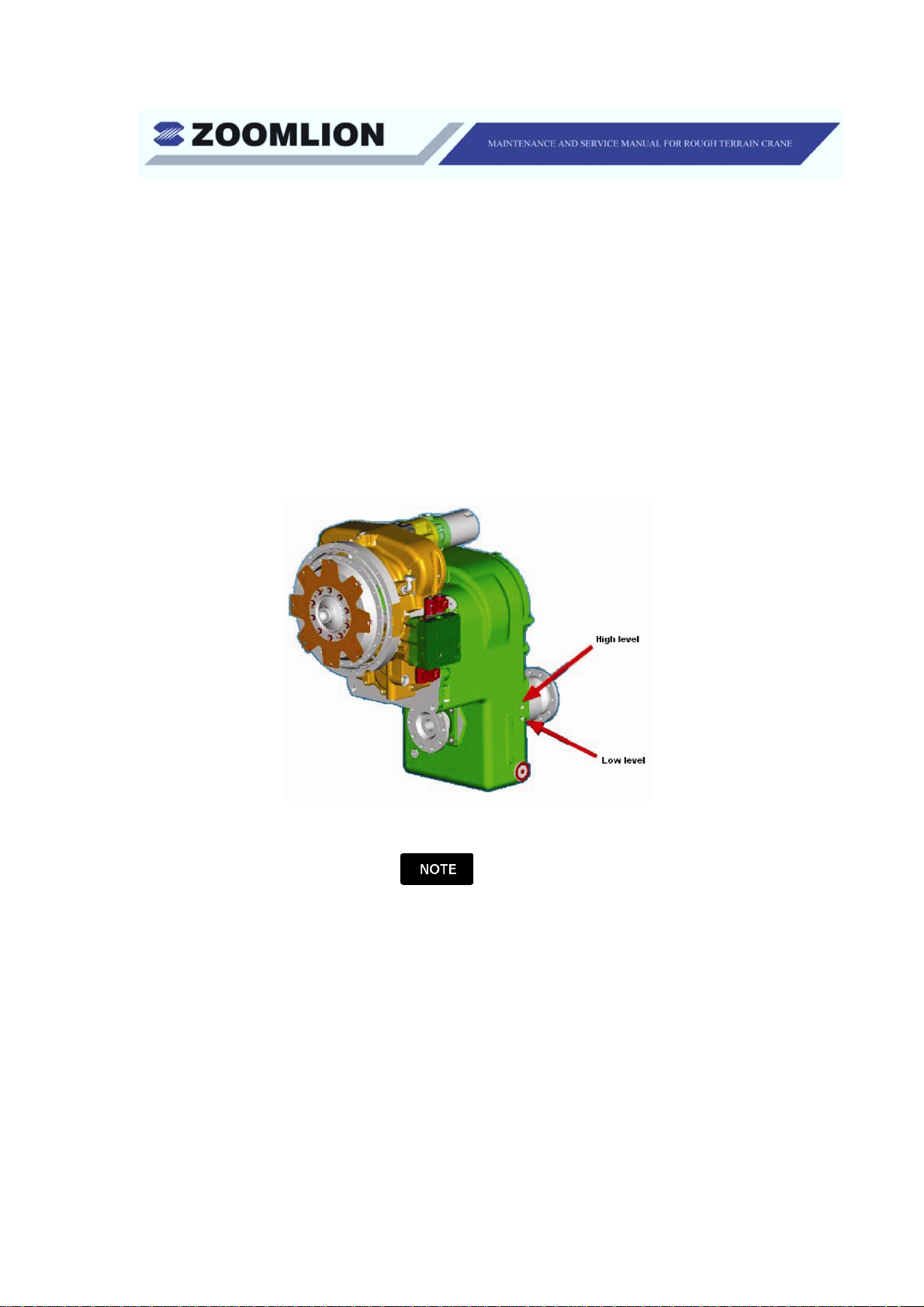
(3) Adjust the level of transmission oil as follows:
(a) Find and remove the oil level plugs on the lower part of the
transmission case on the right side of the crane.
Figure 1-4 Low and High Level Plugs
There are two taper pipe thread oil level holes. One is the low level plug
and the other one is the full level plug.
(b) Add the transmission oil until it flows out of the low level plug hole.
(c) Start the engine at idle speed to let the oil flow through the torque
converter, oil cooler and lines. Check the oil level. Add transmission
oil until it flows out of the low level plug. Install the low level plug.
(d) Let the oil temperature increase to between 180° F and 200° F (82.2°
C and 93.3° C). Add oil until it flows out of the full level plug. Install
the full level plug.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-9
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 27
(e) Always do the transmission oil level checks with the speed of the
engine at idle. The transmission must be in the neutral position and
the transmission temperature between 180° F and 200° F (82.2° C
and 93.3° C).
(4) Do not put too much fluid in the transmission!
C. Lubricant and Filter Change Interval
(1) Refer to Section 1.13 for the lubrication schedule.
(2) Use the Dana-Clark Filter.
(3) Change the hydraulic transmission oil and filter after the first 50 hours of
transmission operation. After the first transmission oil and filter change,
the change interval is 500 hours or 3 months of operation. Change the
lubricant at the 1000 hours or 6 months of operation point.
When you operate in cold weather areas or at the initial startup, the
transmission oil is cold and thick. This can cause the oil to intermittently
bypass the filter.
1.7 AXLE MAINTENANCE CHECK
A. Monthly
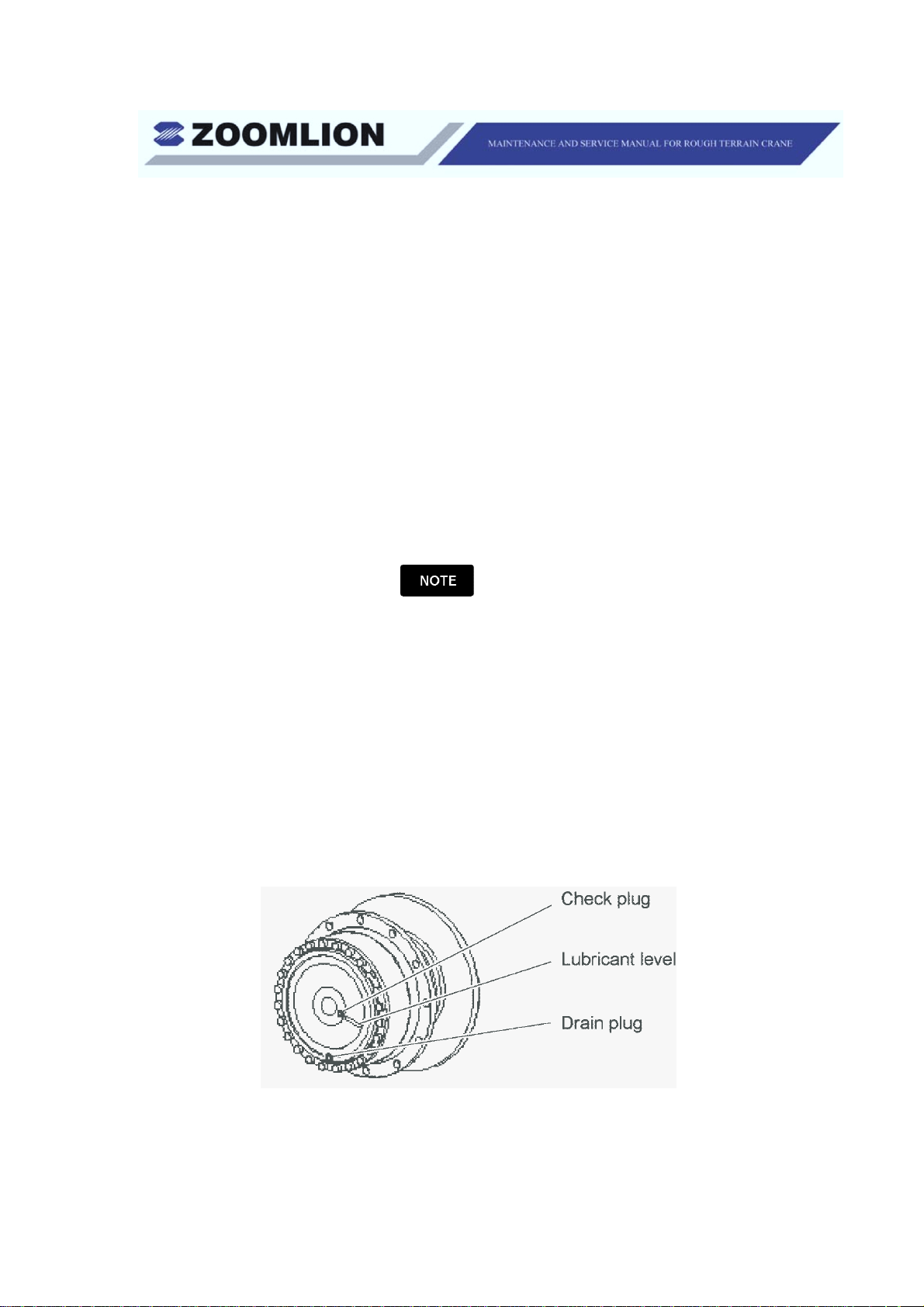
(1) Examine the wheel end oil level as follows:
(a) Move each wheel until the planet gear cover is at the position in
Figure 1-5. The arrow on the planet gear cover points horizontally
when the cover is at the correct position. Make sure that the oil is at
the correct level.
Figure 1-5 Wheel End
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-10
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 28
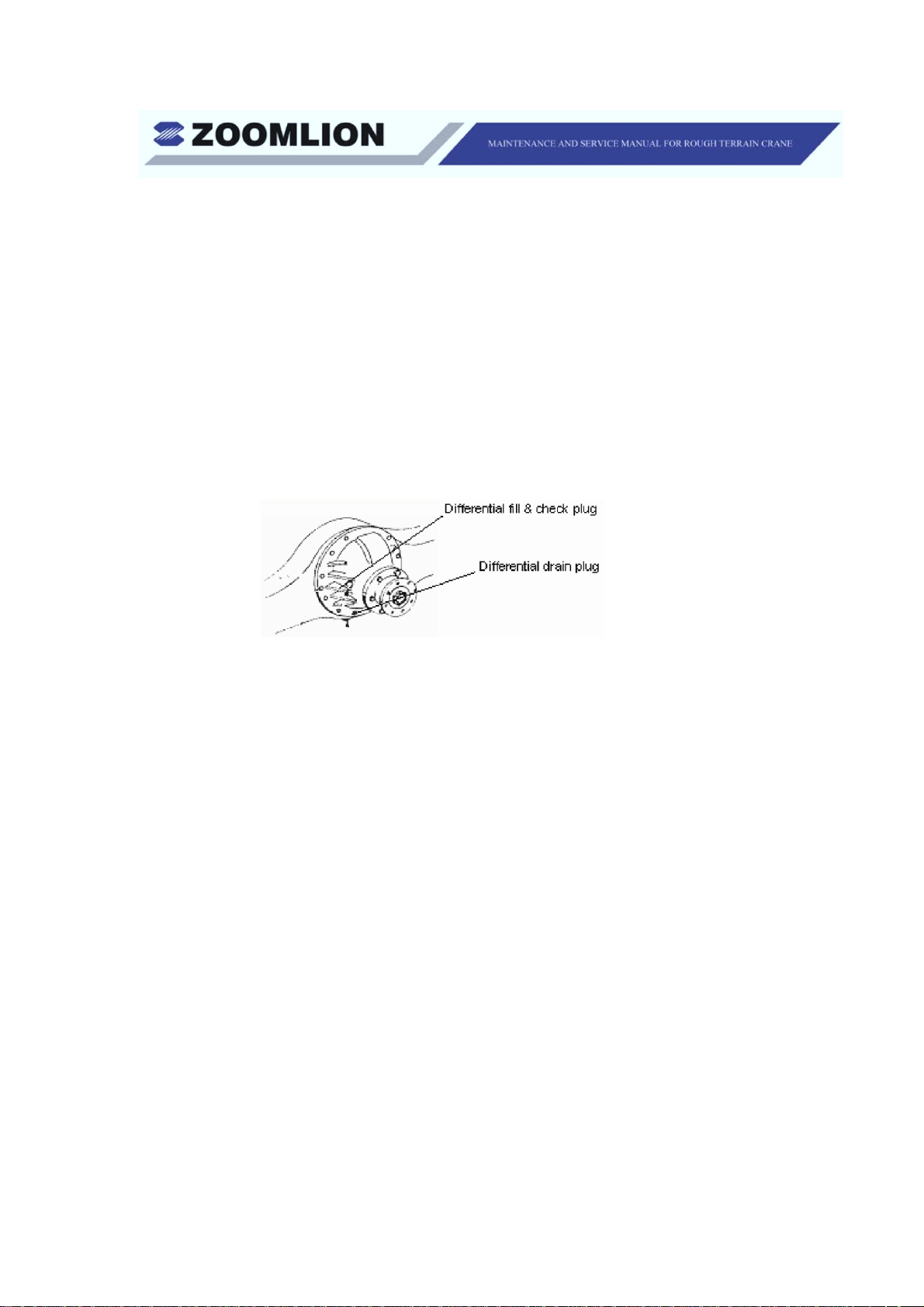
(b) Check the differential oil level by removing the filler and check plug
indicated in Figure 1-6. Add oil as necessary to bring the oil level to
the bottom of the hole.
(2) Do a check of the level of differential oil as follows:
(a) Remove the fill plug.
(b) Make sure that you can see oil at the bottom of the plug hole.
(c) If necessary, add oil until it comes out of the fill plug hole.
(d) Install the fill plug.
Figure 1-6 Differential Plugs
B. Annually
(1) Remove and replace the oil in the differential as follows:
(a) Remove the fill plug and the check plug to drain the oil. Refer to
Figure 1-6.
(b) Make sure that you can see oil at the bottom of the plug hole.
(c) If necessary, add oil until it comes out of the fill plug hole.
(d) Install the fill plug.
1.8 TIRE MAINTENANCE CHECK
A. Weekly
(1) Examine the tires and rims for the items that follow:
(a) Damage
(b) Cuts and bruises
(c) Cracks
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-11
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 29

(d) Punctures
(e) Abrasion.
(2) If necessary, make sure that you repair these items.
(3) Replace or repair the wheels if they are bent, contain a crack or are loose.
(4) Make sure that the wheel nuts are correctly tightened.
B. Tire Pressures
(1) Always keep the correct tire pressure in all the tires.
(2) Friction makes heat that increases the pressure in the tires when you
move the crane. Movement at high speeds also increases the pressures
in the tires. Do not deflate the tires if these conditions occur. Decrease
your speed or stop until the pressure decreases.
(3) Always use an accurate tire pressure gauge. You must measure the tire
pressure when the tires are cool. Do a check of the pressures at regular
intervals.
Because of the explosive nature (high temperature and high pressure)
of the tire and rim it is dangerous to change a tire if you are not trained.
Death or personal injury can occur while you touch or do the
maintenance work on these tires. You must follow special procedures
and use special tools to safely change the tires. If it is possible, let your
repair company do this work. If you must change a tire, follow the step
by step instructions in a Tire Repair Manual. If you must add air
because of low pressure, do not be adjacent to the tire tread. Use a long
extension hose to be behind the tire tread. Always use a tire cage or
equivalent protection when you add air.
(4) Do not deflate air from a hot tire. The pressure lowers but the
temperature increases when the tire continues to move. This increase in
temperature causes the tire to malfunction.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-12
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 30
(5) Under Inflation
The tires that do not have a sufficient quantity of pressure in them cause
them to wipe and scuff over the road. Strain on the tire increases the
chance to bruise.
(6) Correct Inflation
When the tires have the correct pressure in them, they do not wear too
quickly.
(7) Over Inflation
When the tires have too much pressure in them, they do not touch the
surface of the ground correctly. When this occurs, the tires touch the
ground on the crown of the tires and quickly wear in the middle.
Figure 1-7 Correct Way
Figure 1-8 Wrong Way
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-13
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 31

C. Tire Change Safety Precautions
When you must make the repair on a wheel (demount and mount the rim and
tire), follow these precautions:
DO:
(1) Follow the procedures (assemble and disassemble) that you find in the
tire change safety guidelines or other instruction manual.
(2) Before you start to disassemble the wheel, fully deflate the tire.
(3) Replace the parts with damage, cracks, signs of wear and corrosion.
(4) Before you inflate the tire, make sure that you examine the removable
ring. It must be seated correctly.
(5) Examine the side ring and make sure that it is not too loose. This is an
indication of parts that do not match correctly.
(6) Do not inflate the tire until the safety cage is in position.
(7) After you inflate the tire, make sure that the rim ring clearance is between
0.06 in. to 0.25 in. (1.6 mm to 6.3 mm).
(8) After you complete the repair, examine the wheel nuts and rim clamps for
wear, corrosion, proper centering and the correct torque.
DO NOT:
(1) Mix the parts. This is a dangerous condition. Make sure that the side ring
and lock ring agree with the identification marks on the base.
(2) Lift a load or move a load that is above the capacity of the crane.
(3) Inflate a tire if it is fully flat or near flat. You must first disassemble and
examine the tire and rim assembly.
(4) Use a tire and rim configuration that is not approved by the Tire & Rim
Association (TRA).
1.9 BRAKE SYSTEM MAINTENANCE
A. Brake Pedal
(1) Routine Maintenance
(a) Usually the brake pedal is a maintenance free part.
(b) Make sure that the brake pedal moves freely before you move the
crane.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-14
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 32

(c) Examine the brake pedal annually and replace the parts that show
wear or damage.
If you push the service brake pedal and the distance to stop is more than
usual, the system can have a malfunction. When the service brake indicator
illuminates, the pressure in the system can be low. In that condition, do the
necessary steps to correct the condition or send the crane to the repair facility.
Do not move the crane if the indicator stays illuminated.
B. Park Brake
(1) Routine Maintenance
Usually the park pedal is a maintenance free part.
1.10 AIR SYSTEM MAINTENANCE
When the air system does not supply the usual quantity of air, look at the items that
follow to correct the condition:
• Defective components
• System leak
• Blocked lines
• Moisture and sediment in the system.
A good preventive maintenance program is a necessary part of the air system
operation. Refer to the maintenance schedule in this manual. You can change the
interval between checks if the conditions and weather are hard on the equipment.
1.11 BATTERY MAINTENANCE
A. Examine the batteries and the area around the batteries as follows:
(1) Make sure that the terminal connections are tight.
(2) Remove dirt and corrosion from the wires and terminals.
(3) Clean the battery area with soda water or pure water. When the terminals
dry, apply Vaseline to them.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-15
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 33

Figure 1-9 Battery
1.12 FUEL, COOLANT AND TORQUE CONVERTER HYDRAULIC TRANSMISSION OIL
A. Fuel Selection
(1) Always use the correct light diesel fuel and engine oil. Make your
selection on the lowest ambient temperature where you are to do the
work.
(2) Refer to the Operator’s Manual for the fuel sulfur content standards.
(3) Refer to the Service and Maintenance Manual for the Engine when it is
necessary to put oil into the engine.
Do not use fuel which is mixed with lubricant or other chemicals.
Make sure that the fuel you use in the crane has the correct thickness.
Make your selection on the lowest temperature you operate in.
Make sure that the fuel tank is full. Condensation, rust and sediment
can freeze and cause a blockage in the flow of fuel. The engine cannot
start if the fuel does not flow or flows too slowly.
B. Coolant Selection
We recommend that you use ethylene glycol coolant. It is all-season, allpurpose and continues to cool for long intervals of time. You can use other
types of antifreeze if it continues to cool for long intervals of time and has:
• High boiling point
• Low freezing point
• Correct PH-value.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-16
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 34

C. Torque Converter Hydraulic Transmission Oil Selection
For torque converter hydraulic transmission oil selection and change
interval, refer to the Operating Instructions for the Torque Converter.
1.13 LUBRICATION
You can increase the service life of the crane if you obey the preventive maintenance
schedule and use the correct lubricants. When you decrease the effects of friction on
the parts that move, you can prevent unusual malfunctions. Refer to Figure 1-10.
A. Chassis Lubrication
Make sure that you obey the lubrication types and intervals in Table 1-1.
Lubrication method: grease or inject with grease pump.
Figure 1-10 Crane Chassis Lubrication Points
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-17
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 35

Number of
3106 miles
6213 miles
Change the
Steering knuckle
Tie-rod ball pin of
Intermediate
Sliding fork for
6213 miles
31065 miles
Change the
Sliding fork for
3106 miles
Inject with
ZL-2 lithium
3106 miles
6213 miles
Change the
3106 miles
6213 miles
Change the
Change the
Sliding fork for
3106 miles
Inject with
ZL-2 lithium
3106 miles
(5000 km)
6213 miles
Change the
Table 1-1 Lubrication
Ser.
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6 Transmission 1
7
Description
Central reducer
for front axle
of front and rear
axles
front and rear
axles
bearing for drive
lines
intermediate drive
lines
rear drive lines
Lubricating
Point
1
4
4
1
2
1
Lubricating
Intervals
(5000 km)
(10000 km)
3106 miles
(5000 km)
3106 miles
(5000 km)
932 miles
(1500 km)
3106 miles
(5000 km)
(10000 km)
(50000 km)
(5000 km)
Lubricating
Method
Add grease
grease
Inject with
grease pump
Inject with
grease pump
Inject with
grease pump
Inject with
grease pump
Add grease
grease
grease pump
Lubricating
Grease Type
GL-5 80W/90
ZL-2 lithium
base grease
ZL-2 lithium
base grease
ZL-2 lithium
base grease
ZL-2 lithium
base grease
Great Wall # 8
hydraulic
transmission oil
base grease
Wheel ends for
8
rear axle
Central reducer
9
for rear axle
Engine oil
10
underpan
11
front drive lines
Wheel ends for
12
front axle
2
1
1
1
2
(5000 km)
(10000 km)
(5000 km)
(10000 km)
250 hours Add grease
500 hours
(5000 km)
(10000 km)
Add grease
grease
Add grease
grease
grease
grease pump
Add grease
grease
GL-5 80W/90
GL-5 80W/90
10W/40 CH-4
engine oil
base grease
GL-5 80W/90
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-18
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 36

The engine oil add or change interval (in your preventive maintenance
schedule) cannot be more than the interval you find in the diesel engine
maintenance specifications in the Engine Manufacturer’s Manual.
When you add or change grease, you must clean the grease off and
around the plug (grease nipple) and check for leaks.
B. Monthly Lubrication
(1) Do a check of the level of oil in the transmission.
(a) You can find the transmission oil change interval in Section 1.6. If
you do work in harsh conditions, you can decrease the interval
between oil changes.
(b) The oil changes can become more frequent if the crane operates in
rough conditions.
(2) Do a check of the gear oil level in the front and rear axles. Refer to Figure
1-11.
Figure 1-11 Front and Rear Axles
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-19
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 37

When you change the gear oil, only drain the remaining gear oil while it
is warm.
(3) The first time you replace the middle and rear axle gear oil (after the
break-in period) of a new crane:
(a) Drain the gear oil and add engine oil to the axle to the correct level.
(b) Lift the axles off the ground (support with jack stands). Start the
engine and set the transmission in gear.
(c) Allow the wheels to turn for five minutes and then drain the oil.
(d) Add new gear oil to the correct level.
(4) Add grease to the main reducer and wheel ends until the grease comes
out of the oil filler.
(5) Add grease to the oil cup.
When you add or change grease, you must clean the grease off and
around the plug (grease nipple) and check for leaks.
(6) Add grease to the drive lines. Refer to Figure 1-12.
Figure 1-12 Drive Line Lubrication Points
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-20
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 38

(7) Lubricate the rear suspension. Refer to Figure 1-13.
Figure 1-13 Rear Suspension Points
(8) Lubricate the steering system. Refer to Figure 1-14.
Figure 1-14 Steering System Lubrication Points
C. Lubrication – 500 Hours
(1) Change engine oil.
(a) On a warm engine, remove the oil pan drain plug and drain the oil
from the engine and oil filter assembly.
(b) Replace the oil filter.
Always replace the oil filter when you replace the engine oil.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-21
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 39

(c) Install the oil pan drain plug and add oil to the engine through the oil
filler port. Refer to Figure 1-15.
The weather in the area that you operate the crane determines what type of
oil to use in the engine. The oil viscosity decreases in areas of heat and
increases in areas of cold. As a result, incorrect engine oil can cause the
crane to be hard to start in a cold area. Use Table 1-2 to make a selection of
the correct type of oil for the engine.
(d) Install the oil filler cap.
(e) Operate the engine, without a load, for approximately three minutes.
Examine the area below the engine for leaks.
(f) Stop the engine and let it stand for 30 minutes. Measure the level of
oil with the dipstick. Add oil until it increases to the full mark on the
dipstick. Do not add too much oil in the engine.
Figure 1-15 Oil Fill Port
Table 1-2 Engine Oil Viscosity
Ambient Temperature Oil Viscosity
Above 104° F (40° C) 20W/40
104° F to 14° F (40° C to -10° C) 10W/40
Below 14° F (-10° C) 5W/30or 10W/30
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-22
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 40

• The service life of the engine decreases when you operate the engine at high
speeds or the operating load is high for long intervals.
• When the crane is new, change the engine oil after the engine operates
between 30-50 hours.
(2) Change gear oil in the transmission.
(a) When the transmission is warm, remove the drain plug.
(b) Clean the drain plug and install it onto the transmission.
(c) Add gear oil to the transmission.
When the crane is new, change the transmission gear oil after the crane
travels the first 1242-3106 miles (2000-5000 km).
D. Lubrication Every 3 Months
Do a check of the level of gear oil in the front and rear axles as follows:
(1) Remove the fill plug.
(2) Make sure that you can see oil at the bottom of the plug hole.
(3) If necessary, add oil until it comes out of the fill plug hole.
(4) Install the fill plug.
E. Lubrication Every 6 Months
Remove and replace the oil in the front and rear axles as follows:
Only do this procedure when the oil is warm.
(1) Remove the drain and fill plugs to drain the oil.
(2) Install the drain plug.
(3) Add oil (specified on the lubrication chart) until it comes out of the fill plug
hole.
(4) Replace the fill plug.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-23
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 41

When the crane is new, change the gear oil after the crane operates the first
250 hours.
1.14 HYDRAULIC OIL
When the crane comes out of the factory, the hydraulic tank is topped up with
hydraulic oil.
The controls on the crane are hydraulically operated.
The most important item for the usual operation of the crane is the quality
viscosity of the hydraulic oil used in the crane. Also important is how
clean you keep the oil.
A lack of knowledge of (ignorance to) the hydraulic oil replacement
schedule can cause different components to malfunction and greatly
decrease the service life of the crane.
Zoomlion cannot be legally responsible for the damage you cause when
you do not obey the data in this manual with reference to: oil and oil filter
change.
Figure 1-16 Filtering – Changing Intervals
A. Changing Steps
(1) Remove and replace the hydraulic oil in the hydraulic tank as follows:
(a) Remove the drain plug at the bottom of the tank.
(b) Remove the master oil return pipe.
(c) Carefully clean the oil tank and filter with a chemical cleaning agent
(solid particle pollution grade ≤ 18/15).
(d) After the tank is dry, clean the tank with new hydraulic oil (solid
particle pollution grade ≤ 18/15).
(e) Drain the oil used to clean the tank.
(f) Fill the tank with new hydraulic oil.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-24
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 42

≥ 40 µ
30
(g) Screw down the plug fitted on the brake disc to drain the hydraulic
oil in brake return lines every 6 months.
(2) Flush the expired (initial) oil out of the system as follows:
The function of this procedure is to remove all the initial oil out of the system.
(a) Start the engine and operate it at a low speed.
(b) Start the hydraulic system pump.
(c) Operate all the hydraulically controlled functions.
• Make sure that you fully move the items through the full travel
of operation.
• Make sure that you add new oil into the tank as the expired oil
flows out.
• Do not let the initial oil go back into to the oil tank.
• Do not stop the system pump until the new oil flows out of the
master oil return pipe.
(3) Connect master oil return pipe to the oil tank. Move all the hydraulically
controlled functions through the full travel and monitor the level of oil in
the tank. If necessary, add oil.
(4) You must monitor (interval set by management) the quality of the oil.
Change the oil when the number of particles is greater than the number in
the chart.
Change the oil when:
Particle Size Number of particles / ounce (milliliter)
≥ 10 µ 3000
≥ 20 µ 300
≥ 30 µ 100
≥ 50 µ 10
≥ 100 µ 1
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-25
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 43

Change the oil when the oil is found to be contaminated. Do not wait for the
scheduled service.
Always use the correct oil for the temperature the crane operates in.
You cannot mix oil of different brands (specifications) or types.
You must change the oil every 24 months.
Figure 1-17 Liquid Level Gauge
B. Hydraulic Oil Temperature
(1) Examine the hydraulic oil temperature through the liquid level gauge.
(2) When the crane is in operation, the oil temperature cannot be more than
176° F (80° C).
C. Hydraulic Oil Level
(1) When the crane travels between locations, monitor the level of hydraulic
oil through the liquid level gauge.
Retract cylinders when you do an oil level check.
(2) If the oil level is below the low mark, add oil to the tank until the oil level is
between the low and full marks.
D. Hydraulic Oil Performance and Type
The selection of the type of oil you use in the crane must align with the data
found in Table 1-3.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-26
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 44

Table 1-3 Hydraulic Oil Performance and Type
Ambient
Item
Reference standard GB11118.1-94 GB11118.1-94
Type L-HM L-HV L-HS
Viscosity grade 68 32 22 10
Min. flash point
(split) ° F (° C)
Kinematic viscosity at
104° F in²/s
(40° C mm²/s)
Max. temperature
when kinematic
viscosity at
59 in²/s ° F
(1500 mm²/s ° C)
Min. viscosity index 95 130 130
Max. pour point (° C)
Temperature
Above 104° F
(40° C)
356 (180) 320 (160) 284 (140) 198 (92)
61.2-74.8 28.8-35.2 19.8-24.2
-0.4 (-18) -22 (-30) -58 (-50)
15.8 (-9) -27 (-33) -49 (-45)
Ambient
Temperature
-4° F - 104° F
(-20° C - 40° C)
Ambient
Temperature-
22° F - -4° F
(-30° C - -20° C)
GB11118.1-94 SH 0358-95
Ambient
Temperature
Below -22° F
(-30° C)
Aviation
hydraulic oil
More than 10
at 50° C
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-27
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 45

1.15 GEAR OIL
Organic acid fat, phosphoric acid
A. Always use the correct gear oil (type and viscosity) in the crane.
B. When the crane comes out of the factory, the gear oil level is full. You must use
the data from Table 1-4 when you choose the type of oil for the crane.
Table 1-4 Gear Oil Performance
Kinematic viscosity at
212° F (100 °C)
mm²/s
56.3 (13.5) ~<24.0
Minimum flash
point (split)
° F (° C)
329 (165)
Ingredients
fat, silicic acid fat, fluorin oil, silicon
oil, polyphenylene oxide +
addictive
Figure 1-18 Changing Intervals
When there is contamination in the gear oil, change the oil immediately.
Monitor the oil level regularly and add oil if it is below the low mark.
You cannot mix oil of different brands (specifications) or types.
Always use the correct oil based on the temperature the crane operates in.
If you use the incorrect oil (type or viscosity) in the reducer mechanism,
you can damage it.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-28
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 46

C. Oil Change Parts
(1) Winch Reducer
Figure 1-19 Fill, Check and Drain Ports
Fill the gear oil to the top.
(2) Swing Reducer
(a) Fill oil after removing the plug of oil fill aperture.
Figure 1-20 Swing Reducer Fill and Drain Ports
Fill the gear oil to the top.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-29
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 47

1.16 LUBRICATING GREASE
Smooth inunctum
with the color from
Equal
inunctum
with the color from
When you lubricate the crane, use only ZL-2 or ZG-3 types of grease. There are two
procedures to lubricate the crane:
• Use a grease pump to put (inject) lubricant through a grease fitting (nipple).
• Apply the grease directly to the part by hand.
Figure 1-21 Grease Pump
Table 1-5 Types of Grease
Type of
Grease
ZL-2
ZG-3
Appearance
light yellow to brown.
light yellow to dark brown.
Parameters
Drop point
°F (°C)
347 (175) 1 ——
194 (90) 1 2.5
Cone
penetration
(in)
Maximum
moisture
(%)
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-30
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 48

1.17 LUBRICATING POINTS
Lubricant
A. You can use Table 1-6 and Figure 1-22.
Table 1-6 Lubrication Intervals and Points
No.
Upper pulley block (shaft) on
1
main boom
2 Slider pads of main boom 10 Days
Lower pulley block (shaft) on
3
main boom
Sliding surfaces of the main
4
boom
Upper articulated-point shaft
5
of derricking cylinder
Pulley block (shaft) on main /
6
auxiliary hook
7 Drive lines of oil pump Daily
Lower articulated-point shaft
8
of derricking cylinder
9 Outrigger slider pads 10 Days
Description Intervals Method
10 Days Grease ZL-2
10 Days
10 Days Grease ZL-2
Monthly
10 Days
Monthly
Grease or inject
with grease pump
Inject with grease
pump
Inject with grease
pump
Inject with grease
pump
Inject with grease
pump
Inject with grease
pump
Grease or inject
with grease
Type
ZL-2
ZL-2
ZL-2
ZG-3
ZL-2
ZL-2
ZL-2
10 Main / auxiliary winch Semi-annual Directly pour
11 Main boom main shaft Daily
12 Swing reducer Semi-annual Directly pour
13 Wire-rope 10 Days Grease ZG-3
14 Pulley block (shaft) on jib 10 Days
Grease or inject
with grease pump
Inject with grease
pump
90# industrial
gear oil
ZL-2
90# industrial
gear oil
ZL-2
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-31
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 49

Figure 1-22 Crane Lubrication Points
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-32
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 50

Semi
-
Before you put lubricant (grease) on a part by hand, clean the part then add
the lubricant.
Clean and lubricate all the sliding surface areas (bare metal, includes cylinder
pistons), not in the table, at a regular interval.
You cannot mix grease of different brands (specifications) or types.
When you inject lubricant (grease) with a grease pump, continue the
procedure until you see old grease come out of the joints.
1.18 ADJUST, CLEAN AND REPLACE THE PARTS
A. Adjustments
Table 1-7 Adjustments
Item Monthly Quarterly
Adjust the adjusting bolt under the brake
pedal to make sure that the free stroke
varies from 0.4 to 0.86 in. (10 to 22 mm).
Adjust the limit screw on the steering
knuckle of front axles to ensure that the limit
screws on steering axles reach their limit
position at the same time.
Adjust engine fan, air compressor and
generator belts to between 0.4 to 0.6 in. (10
to 15 mm).
•
Annual
Yearly
•
•
Figure 1-23 Adjustments
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-33
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 51

B. Clean the Chassis
Semi
-
(1) Intervals
Table 1-8 Intervals
Item Daily Monthly Quarterly
Drain brake system. Pull the draw
ring of manual water drain valve
downwards to drain water.
Clean the fuel filter.
Clean the water tank.
Clean the air cleaner filter
element with compressed air from
the inside.
Clean the air cleaner filter
element.
C. Clean the Diesel Fuel Filter
(1) Clean the diesel fuel filter as follows:
(a) Put a container below the fuel filter drain plug.
(b) Loosen the air relief cock and remove the drain plug to drain fuel
and unwanted material from the filter bowl.
(c) Remove the long central treaded bolt and washer from the fuel filter
assembly. Remove the parts that follow:
•
Annual
Yearly
•
•
•
•
• Fuel filter bowl
• Spring
• Spring seat
• Filter element
• Washer.
(d) Clean the parts from step (c) but do not clean the filter element.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-34
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 52

Do not wash the filter element!
(e) Examine the filter element. If it is dirty or full of contamination,
discard it. If this is a 1000 hours inspection, discard the element.
If you install a new filter element, replace the washer and O-ring.
(f) Assemble the fuel filter in sequence as follows (See Figure 1-24):
• Long central treaded bolt
• Washer (new)
• Fuel filter bowl
• Spring
• Spring seat
• Filter element (new)
• O-ring (new).
(g) Remove the air with manual oil pump.
(h) Examine the filter assembly for leaks.
Figure 1-24 Fuel Filter and Water Separator
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-35
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 53

D. Clean the Cooling System
Operate the engine until it increases to the usual temperature of 185° F (85° C).
If the water temperature is too low, the thermostat cannot open and the coolant
cannot flow through the radiator. Clean the cooling system as follows:
(1) Loosen the radiator drain cock to fully drain the engine coolant. Operate
the engine at idle speed (as you remove the engine coolant) for five
seconds.
(2) Close the radiator drain cock and remove the radiator cap. Fill the
radiator with a fluid to clean the engine coolant system and tap water.
Install the radiator cap.
(3) Operate the engine until it increases to the usual temperature 185° F
(85° C). Set the heater control to full heat and the blower to ON.
(4) Operate the engine for 30 minutes at idle speed with no load.
(5) Stop the engine and drain the coolant system.
(6) Add tap water and operate the engine to flow through the system, then
stop the engine and drain the coolant system. Do this step again 2 or 3
times.
(7) Add the correct quantity of antirust, antifreeze and tap water to fill the
system.
(8) Operate the engine until it increases to the usual temperature 185° F
(85° C). Remove the air from the system.
(9) Stop the engine and make sure that the level of fluid in the system is at
the correct level. If necessary, add tap water to fill the system.
E. Clean the Air Cleaner
Clean the air cleaner as follows:
(1) Remove the clamp from the air cleaner and remove the rear end cover.
(2) Remove the filter element.
(3) Clean the contaminations from the inner side of the air cleaner and cover.
Make sure that the air filter element is free of contamination. If necessary,
replace the element.
(4) Install the element and cover. Tighten the clamp.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-36
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 54

Every
Every 2
Every 4
F. Chassis Parts – Replacement Intervals
Table 1-9 Replacement Intervals
Item
Diaphragm and rubber parts of pressure
regulating valve of air dryer
Air cleaner filter element
Shims and rubber parts of service brake valve
Hose connecting the air compressor and
pressure regulating valve
Shim and rubber parts of the relay valve
Shims and rubber parts of quick release valve
Shims and rubber parts of park brake valve
Shims and rubber parts of tee clack
Air cleaner filter element
Diesel fuel hose inside the engine hood
Diesel fuel hose outside the engine hood
1 year
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
years
•
years
•
G. Wire-RopeMaintenance
When the wire-rope is on the crane for a long interval, it can become
weak and can cause a dangerous condition.
(1) Wire-Rope Inspection
Replace the wire-rope if you find one of the items that follow:
• Steel wire breaks: six on one rope layer or three on one rope strand.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-37
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 55

• Torsion resistant wire-rope breaks: two steel wires of rope diameter in
less than 0.2 in. (6 mm) or four steel wires of rope diameter in less than
1.2 in. (30 mm).
• A break in the wire-rope on the external rope layer at the core position
(causes rope core to extrude or in circle).
• The thickness (diameter) of one wire-rope on the external layer is less
than 2/3 of its usual thickness (diameter).
• Wire-rope that is not usual: distortion, flattened or broke wire nests etc.
• Wire-rope with an area of damage because of too much heat.
• If the wire-rope has an area that you think is not as thick as it must be,
you must replace the rope. Use the data that follows to examine the rope:
Inches Millimeters
Rope Thickness D Maximum Loss Rope Thickness D Maximum Loss
≤ 0.3 0.02 ≤ 8 0.4
0.4 to 0.5 0.03 9.5 to 13 0.8
0.6 to 0.7 0.05 14.5 to 19 1.2
0.9 to 1.1 0.06 22 to 29 1.6
1.3 to 1.5 0.09 32 to 38 2.4
• Wire strand breaks: two out of the rope connection or one at the rope
connection.
(2) Wire-Rope Replacement
(a) Make the crane level on a hard surface.
(b) Fully retract the boom.
(c) Lower the main hook and set it on the ground.
Figure 1-25 Hook on the Ground
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-38
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 56

Operate carefully to avoid the rope from disordering on the drum.
(d) Remove the press nipple from the boom (top section) or the main
hook.
1 Tools necessary: Wrench.
2 Set the parts to the side until they are necessary.
Figure 1-26 Main Hook and Nipple
(e) Remove the wire-rope from the press nipple.
1 Tools necessary: Steel rod (punch), hammer and wrench.
2 Set the parts to the side until they are necessary.
Figure 1-27 Wire-Rope Nipple
(f) Manually pull all the wire-rope from the drum.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-39
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 57

Figure 1-28 Pull Wire-Rope
The 3rd wrap warning alarm comes ON when only 3 hoist rope wraps are
left on the main winch. Push the bypass key switch until the wire-rope
stops.
(g) Remove the wire-rope from the main winch drum.
1 Tools necessary: Steel rod (punch) and hammer.
2 You must be careful when you remove the chock.
Figure 1-29 Wire-Rope Off the Drum
(h) Reeve the new wire-rope through the boom sheave.
1 Tools necessary: Thin steel wire or ethylene plastic strap.
Figure 1-30 The End of the New Wire-Rope
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-40
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 58

Put thin steel wire or ethylene plastic strap on the end of the wire-rope.
(i) Install the new wire-rope onto the main winch drum with the chock.
1 Tools necessary: Hammer.
Figure 1-31 New Wire-Rope on the Drum
• Make sure that the chock is in the correct position before you make the
wire-rope tight.
• Make sure that the end of the wire-rope does not go fully through the
drum. The wire-rope must extend more than the surface of the drum.
(j) Spool-up the wire-rope.
1 Tools necessary: Thin steel wire or ethylene plastic strap.
Figure 1-32 Monitor the Rope (Must Lay Flat and Evenly)
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-41
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 59

Do not spool-up the wire-rope too quickly. Make sure that the rope
collects on the drum correctly.
(k) Reeve the wire-rope through the top boom head sheave and hook
pulley block in the related line parts.
Make sure that you attach the wire-rope in the correct sequence.
Figure 1-33 Wire-Rope Wrap Sequence
(l) Install the becket and wedge onto the wire-rope.
1 Tools necessary: Wrench and hammer.
Figure 1-34 Becket and Wedge
Make sure that the tapered (beveled) end of the becket is in the same
direction as the end of the wire-rope.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-42
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 60

(m) Install the becket to the end of the boom or to the main hook.
1 Tools necessary: Wrench.
Figure 1-35 Becket Attachment
(n) Derrick the boom and fully extend the boom. Reel-off the wire-rope
from the main winch until the 3rd wrap alarm sounds.
Figure 1-36 Boom Extended and Elevated
Do not let the main hook hit the ground or move too quickly to prevent
rope damage or an accident.
(o) Attach a load to the main hook and spool-up the wire-rope. The load
must not be more than 30% of the maximum lift capacity for each
wire strand. For example:
1 Weight of the load: W = 0.3 x NP
2 Line parts: N
3 Max. permissible lift capacity per strand: P
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-43
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 61

Figure 1-37 Spool-Up Wire-Rope
Do not lift more than the lift capacity of the wire-rope.
(p) Remove the load from the main hook.
H. Hook Inspection
(1) Do an inspection on the hook. Replace the hook if you find one of the
items in the next step.
Do not weld the hooks to repair the disfigurements.
(a) A crack and crevasse on the surface of the hook.
(b) The split degree of the hook cannot be more than 10% of the usual
distance.
(c) An abrasion of the dangerous sectional plane cannot be more than
10% of the usual thickness.
(d) The wear extent of the sectional plane in point where wire-rope
suspended exceeds 10% of original height.
(e) The torsion and deformation of hook exceeds 10°.
(f) There is plastic deformation in dangerous sectional plane such as
the tail of hook, the screw threaded part and hook web.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-44
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 62

I. Replace the Return-Line Filter Element
The hydraulic tank (reservoir) has a return-line filter on the input connection
(return-line). The filter stops contamination of the hydraulic fluid, such as
particles of metal and rubber. Make sure that you are careful when you add
fluid to the system.
The filter element in the filter stops the particles that are more than 1 um in
dimension. It can decrease the number of magnetized and non-magnetized
particles. The filter increases the quality of the hydraulic fluid which increases
the service life of all the components in the system.
The texture of the filter is a non-woven chemical fabric which can stop the flow
of contamination and let a large quantity of fluid go through. The usual system
pressure does not decrease. Its filter precision is calibrated by the absolute
filter precision. Its filter ratio and efficiency align with the requirements of ISO.
To replace the filter, the top cover is the only part you must remove.
When the system is open (top cover off), the contamination that is caught by
the filter cannot go into the system because of the internal fluid openings.
Figure 1-38 Filter Change Interval
Do not replace the filter element if the hydraulic system is pressurized.
J. Filter Replacement
(1) Remove the four bolts and top cover.
Figure 1-39 Top Cover
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-45
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 63

(2) Remove the spring and the permanent magnetunit.
Figure 1-40 Disassemble
(3) Remove and replace the filter element.
Figure 1-41 Filter Element
(4) Install thepermanent magnetunit and spring.
Figure 1-42 Assemble
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-46
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 64

(5) Install the top cover with the four bolts.
Figure 1-43 Top Cover Assembly
K. Boom Extend / Retract
(1) Troubleshoot
Problem: The top boom section does not fully retract.
Cause: The boom extend / retract rope is not at the correct length.
Correction: Adjust the rope.
(2) Adjust the retract rope top section of the boom as follows:
(a) Remove the access panel on top boom section to get access to the
nut at the head of the boom retraction rope.
(b) Loosen the lock nut, then turn the adjustment nut to tighten the
extend rope. Make sure that the rope is not loose. Do not make the
rope too tight.
Tools necessary: Socket wrench.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-47
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 65

locking nut
Adjusting nut
top section
Figure 1-44 Adjust and Lock nuts
(3) Adjust the retract rope on the boom section 2 as follows:
Use the same procedure that you used to adjust the top section retract
rope. The adjustment nut is on the side of the boom head.
• Make sure that the crane is on a hard surface.
• The boom extend rope is not adjustable.
• Do not make the adjustment nut too tight. Make sure that the
lock nut is tight after you adjust the wire-rope.
L. Swing Bearing Bolts – Inspection and Torque
It is important to do an inspection on the swing bearing bolts. The interval of the
inspection is set to make sure that the crane operates in a safe manner.
Make sure that the bolts are tight with the specified torque.
After the break-in period, examine the bolts semi-annually or after 1000 hours.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-48
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 66

Torque sequence:
When you do a check of the torque on the bolts, follow the sequence in Figure
1-45.
(1) Tighten the bolts on the inner ring (chassis frame).
(2) Tighten the bolts on the outer ring (superstructure).
Figure 1-45 Torque Sequence
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-49
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 67

1.19 BATTERY MAINTENANCE AND SERVICE
The batteries in the crane align with national standard GB/T 5008.1 - 2005. If the
electrical system is free of malfunctions, keep the batteries fully charged. If the
batteries do not charge or cannot hold voltage, examine the generator and voltage
regulator for malfunction.
Do an inspection of the batteries and the battery storage area as follows:
A. When the batteries are fully charged, make sure that the acid level is between
0.4 and 0.6 in (10 and 15 mm) above the top edge of the battery plates.
B. Examine the battery cell caps as follows:
• The caps are tight and air vents are not blocked.
• The batteries and the storage area are dry.
C. Usual charge refers to the charge of battery after use. When you measure the
level of charge on a battery, the voltage on a usual charged battery is 1.2 - 1.5
times that of a discharged one. When you find a battery that is too low,
measure the voltage level of each cell. If you find a cell that has less than 1.75
volts, stop the check and charge the battery.
D. Charge a usual charged battery as follows:
(1) Make sure that the charger power is OFF and put the charger power plug
into the power socket. If the charger has a voltage selector switch, set it
to the correct voltage of the battery/batteries you charge. When you
charge two batteries (batteries in series) at the same time, set the voltage
selector switch to 24 V.
(2) Connect the positive (+) and negative (-) clips to the battery terminals.
Adjust the time to charge interval by the charger operating manual. Do
not do a rapid charge on the batteries.
(3) Set the charger power switch to ON and adjust the current selector
(below 20 A). When the battery electrolyte temperature increases to 113°
F (45° C), immediately stop charge.
(4) The battery charge can continue for approximately 5 - 10 hours. When
the battery/batteries are fully charged, use a voltmeter to measure the
voltage. The voltage in the battery must be > 15 volts or electric eye is in
good condition.
(5) Set the current rotary switch and the charger power switch to OFF.
(6) Disconnect the positive (+) and negative (-) clips from the battery
terminals.
(7) Remove the charger power plug.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-50
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 68

E. Do an equalizing charge procedure if one of the items that follows occurs:
• Monthly, when the crane operates in usual conditions.
• When the battery charge interval is too long or unusually high loss of power
in the battery.
• The battery voltage is too low or it fails to charge.
• If you find a battery cell with a voltage level of < 1 volt or three cells that are
< 1.5 volts.
(1) Equalizing charge procedure:
(a) When the battery has a usual charge do not move it for one hour.
(b) Charge the battery (at 10 amp setting) until the battery electrolyte
starts to bubble. Do not move it for one hour.
(c) Do step 2 again until the electrolyte starts to bubble. Make sure that
the level of electrolyte and the voltage are at the correct level.
F. If you do not operate the crane for a long time, remove the battery from the
crane and charge it. Do a usual charge two times each month. Do a full
discharge and charge four times each year.
G. Examine the batteries and the area around the batteries as follows:
• Make sure that the terminal connections are tight.
• Remove dirt and corrosion from the wires and terminals.
1.20 BATTERY MAINTENANCE – WINTER
When you operate the crane in cold conditions, you use more electricity more than in
other season. Battery maintenance before winter is very important for the battery and
crane operation.
A. Make sure that the acid level is between 0.4 and 0.6 in (10 and 15 mm) above
the top edge of the battery plates. If necessary, add distilled water.
B. Adjust the electrolyte ratio (acid to distilled water) determined by the area and
time of year.
C. Make sure that you install the fluid air plugs correctly. The vent holes must be
clean, dry and have no blockage.
D. Make sure that the battery terminals are clean (corrosion free), dry and
connected correctly and tight. Add a small quantity of Vaseline to prevent
corrosion.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-51
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 69

E. If you do not operate the crane for a long time, remove the battery from the
crane and make sure that it is charged at all times.
F. Before you start the engine, make sure that all items that use battery power are
in the OFF position.
G. If the engine does not start after 15 seconds, do not continue to apply power to
the starter. Wait for 2 minutes before you start the engine again.
H. When a battery is bad, replace it. Make sure that the new battery has the same
power capacity.
When the temperature is lower than 22°F (-30° C), make sure that you
protect the battery to prevent loss of heat.
1.21 OPERATION IN WINTER
When you operate the crane in the winter, the fluids in the crane become thick. Make
sure that all the fluids are the correct type for the area time of year. Good
maintenance and correct operations are very important for safety operation and can
prevent many crane malfunctions.
Make sure that you prepare the crane correctly when you operate the crane in cold
area. Decrease the speed of the crane when you move. If it is necessary, stop the
crane at a flat, dry and sunny area.
A. Chassis Maintenance
(1) The engine oil must be the correct grade to operate in cold weather.
When the temperature decreases, the viscosity of the oil decreases. If it
is too low, the oil cannot move to all the inner parts of the engine. You
can cause damage to the engine.
• Do not mix the engine oil of different brand and different type.
• Make sure that you always use the correct oil type and grade of oil. Multi-
grade oils let the engine to operate in a wide range of temperatures.
(2) Add / change the coolant. Clean the engine cooling system and add the
coolant. You can get the best system performance (all-seasons and allpurpose) when you use a long-acting coolant.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-52
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 70

If you find that the coolant is bad, make sure that you follow the
procedure(Clean the Cooling System).
(3) Always use the correct type of diesel fuel. For more data on the correct
fuel to use, refer to the Engine Manufacturer’sManual. The fuel must be
winterized when the crane operates in a cold area. Change the diesel fuel
filter at the interval in this manual.
(4) Replace the air cleaner filter element to increase the quantity and quality
of the air that goes into the engine. This can increase the fuel efficiency
and increase the power output of the engine.
(5) Check tires and their pressure. The road can be slippery in cold weather.
Tire pressures that are too high or too low cause dangerous conditions
(low temperature, fragile tire and low pressure of tire knead tire badly and
accelerate aging). Rotate the tires at the correct interval.
(6) Make sure that the fan operates correctly and that there are no leaks in
the heater lines.
Frequently clean the oil tank lines and brake lines so they do not freeze.
Drain the water and the contaminations from the air filter assembly and
the water in water separator before you park or move the crane.
1.22 OPERATION IN SUMMER
If the highest daily temperature is frequently higher than 95° F (35° C), the engine
can get too hot. To prevent this and make sure that the crane can operate safely and
satisfactorily, you must do the maintenance below on the chassis:
A. Make sure that the oil is the correct grade if the crane operates in a hot area.
Frequently make sure that the quantity and quality of lubricants used on the
crane are at the correct level. Replace the lubricant if it has contamination.
B. Make sure that the engine thermostat operates correctly. Replace the
thermostat if it does not open at the correct temperature.
C. Make sure that the coolant in the engine is at the correct level and mixture. If
necessary, add water and coolant.
D. Make sure that the engine cooling system functions correctly.
E. Keep the surface of the water tank clean so it can remove the heat.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-53
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 71

F. When you move the crane, make sure that the coolant temperature is not more
than 203° F (95° C). If the temperature is too high, stop the crane to decrease
the coolant temperature.
In special conditions, you can open the engine hood to help decrease
the temperature. Make sure that the air conditioner is in the OFF
position.
G. Do not stop the engine immediately when the coolant is too hot. Stop the crane
and keep the engine ON at idle speed. Open the engine hood fully to increase
air flow at the same time. After the coolant is cool, you can continue to move
the crane.
If the coolant boils, do not stop the engine immediately. Permanent
damage to the engine can occur.
Do not directly face the water fill port when you remove the water cap.
Hot water can spray from the port.
H. If there is antifreeze in the expansion tank, fill it with distilled or deionized water
(instead of tap water).
Damage to the engine occurs if you put cold water onto the engine
when the temperature is too high.
I. Monitor the tire temperature and pressure while you move.
Do not put water on or deflate the tire if the pressure or temperature is
too high. Stop the crane in a cool area to lower the temperature and
pressure naturally. If you must go through water, make sure that the tire
temperature is in the correct range before you go.
Edition 2 Chapter 1 Page 1-54
Dec /2013 Maintenance
Page 72

MANUAL FOR ROUGH TERRAIN CRANE
Chapter 2 Troubleshooting
Page 73

Page 74

2.1 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
Combination instruments do
Troubleshooting
Table 2-1
Part
Problem Cause Remedy
Work light does not
illuminate
Vehicle length indicator
does not illuminate
Interior light does
notilluminate
Instrument lights do not
illuminate
not illuminate
Electrical System
a) Bulb damaged
b) FU811 burnt out
c) Poor grounding
d) Conducting wire broke
e) Switch defective
f) Bulb damaged
g) Switch defective
h) Conducting wire broke
a) Bulb damaged
b) Switch defective
c) Conducting wire broke
d) FU85 burnt out
a) Bulb damaged
b) Switch defective
c) Conducting wire broke
d) FU811 burnt out
a) Conducting wire broke
b) FU66 burnt out
c) FU61 burnt out
d) Instruments damaged
Replace
Repair
Repair
Repair
Replace
Replace
Repair
Replace
Replace
Replace
Repair
Replace
Replace
Replace
Repair
Replace
Repair
Replace
Replace
Replace
Windshield wiper does not
operate
Horn does not operate
Anti-two block switch does
not operate
a) FU86 burnt out
b) Switch defective
c) Damage to the motor
a) FU87 burnt out
b) Switch defective
c) Relay defect
d) Conducting wire broke
e) Horn damaged
a) See the error codes that the
RCI display shows
b) Winding reel defective
c) Conducting wire broke
d) Anti-two block switch
defective
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Repair
Replace
Repair
Repair or replace
Repair
Replace
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-1
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 75

Indicator for Anti
-
two block
Part
Crane cannot move
RCI defective
switch / 3rd wrap activated
stays on
Problem Cause Remedy
e) Rope for counterweight
attached to the switch broke
f) Solenoid valve defective
g) Solenoid valve is not
grounded correctly
a) Inspect FU12, FU13 and
FU14
b) Controller burnt out
a) FU64 burnt out.
b) See the error codes that the
RCI display shows
a) Anti-two block switch / 3rd
wrap defective
Replace
Repair or replace
Repair
Replace or notify the
manufacturer
Replace the controller
Replace
Repair
Repair
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-2
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 76

A. Fuse
Electrical movement mechanisms are equipped with individual fuse which all been
placed in fuse terminal for convenient searching and maintenance. The fuse terminal
comprises of two parts: fuse terminal of chassis control ; fuse terminal of superstructure
control . Layout of fuse terminal demonstrates as follows:
-1FU2 -2FU2 -11FU1 -3FU2 - 3FU3 -3FU4 -11FU2
-1FU1: Fuse for control box light power supply
-2FU2: Fuse for engine ECU power supply
-11FU1:Fuse for hydraulic fan power supply
-3FU2: Fuse for engine ignitionpower supply
-3FU3: Fuse for desiccatorspower supply
-3FU4: Fuse for incline sensor power supply
-11FU2: Fuse for vehicle flexible valve power supply
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-3
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 77

-4FU1 -4FU2 -4FU3 -5FU1 -9FU1 -9FU2 -9FU3
-4FU1: Fuse forchassis controller CPU1 VBBS
-4FU2:Fuse forchassis controller CPU1 VBBO
-4FU3:Fuse forchassis controller CPU1 VBBR
-5FU1: Fuse for sensor power supply
-9FU1: Fuse forchassis controller CPU2 VBBS
-9FU2: Fuse forchassis controller CPU2 VBBO
-9FU3: Fuse forchassis controller CPU2 VBBR
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-4
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 78

-12FU1 -12FU2
-12FU1: Fuse one for Transmission controller power supply
-12FU2:Fuse two for Transmission controller power supply
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-5
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 79

-15FU3 -15FU7 -21FU1 -31FU1 -31FU6 -32FU4
-15FU1 -15FU5 -16FU2 -21FU3 -31FU4 -32FU2 -31FU2
-15FU2 -15FU6 -16FU3 -23FU1 -31FU5 -32FU3 -31FU7
-15FU4 -16FU1 -21FU2 -31FU3 -32FU1 -32FU5
-15FU1: Fuse for superstructure power supply
-15FU2:Fuse for COBO system power supply
-15FU3:Fuse for moment limiter power supply
-15FU4: Fuse for display power supply
-15FU5: Fuse for joystick power supply
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-6
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 80

-15FU6: Fuse for camera power supply
-15FU7: Fuse for air conditioner system
-16FU1:Fuse forsuperstructure controller CPU1 VBBS
-16FU2: Fuse forsuperstructure controller CPU1 VBBO
-16FU3: Fuse forsuperstructure controller CPU1 VBBR
-21FU1:Fuse forsuperstructure controller CPU2 VBBS
-21FU2: Fuse forsuperstructure controller CPU2 VBBO
-21FU3: Fuse forsuperstructure controller CPU2 VBBR
-23FU1: Fuse for inductive switch power supply
-31FU1: Fuse for fan of operation cabpower supply
-31FU3: Fuse for on-board battery (24V/12V)
-31FU4: Fuse for roof windshield wiperpower supply
-31FU5: Fuse for top light on operation cabpower supply
-31FU6: Fuse for syringepower supply
-32FU1: Fuse for horn power supply
-32FU2: Fuse for warning lamp power supply
-32FU3: Fuse for Working light power supply
-32FU4: Fuse for auxiliary winch speed inductorpower supply
-32FU5: Fuse for main winch speed inductorpower supply
-31FU2: Fuse for radio power supply
-31FU7: Fuse forcigarette lighterpower supply
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-7
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 81

B. Relay
Electrical movement mechanisms are equipped with individual relay which all been
placed in relay terminal for convenient searching and maintenance. The relay terminal
comprises of two parts: relay terminal of chassis control ; relay terminal of superstructure
control . Layout of relay terminal demonstrates as follows:
Relay terminal of chassis control
-1KA1 -11KA1 -11KA21 -3KA1
-1KA1: Relay for engine portfire
-11KA1: Relay for hydraulic fan
-11KA2: Relay for vehicle flexible valves
-3KA1: Relay for chassis power control
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-8
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 82

-3KA2 -8KA1 -8KA2 -8KA3 -8KA4
-3KA2: Relay for transmission controller power control
-8KA1: Relay for engine diagnose
-8KA2: Relay for engine diagnose page up
-8KA3: Relay for engine diagnose page down
-8KA4: Relay for low engine coolant level warning
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-9
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 83

Relay terminal of superstructurecontrol
-14KA1 -29KA1 -31KA1 -31KA2 -32KA1 -32KA2 -32KA3 -15KA1
-14KA1: Relay for emergency stop
-29KA1:Relay for air-condition
-31KA1:Relay for windshield wiper low speed
-31KA2: Relay for windshield wiper high speed
-32KA1: Relay for warning lamp
-32KA2: Relay for working lights
-32KA3: Relay for horn
-15KA1: Relay for superstructure power control
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-10
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 84

-17KA1 -24KA1
-17KA1: Relay for engine start
-24KA1:Relay for dead man valve
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-11
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 85

2.2 HYDRAULIC SYSTEM
Table 2-2
Part
System pressure does not
increase
Hydraulic pump makes
unusual noises
Electrical System
Hydraulic pump unusually
hot
Problem Cause Remedy
a) The fluid level in the
hydraulic tank is too low
b) Blockage in the relief valve
c) Central revolving joint
leaks
d) The pressure gauge is not
accurate
e) Hydraulic oil is too old
(decomposed) or dirty
a) The fluid level in the
hydraulic tank is too low
b) Air is in the suction union
c) Mounting bolts loose
d) Hydraulic oil is too old
(decomposed) or dirty
e) Drive shaft shaken
f) Universal joint worn
g) Hydraulic pump defective
a) The fluid level in the
hydraulic tank is too low
b) Hydraulic oil is too old
(decomposed) or dirty
c) Hydraulic pump defective
d) Radiator defective
e) Temperature of the
hydraulic system is too
high
Add hydraulic oil
Clean the valve
element
Inspect the joint and
seal ring
Repair or replace
Replace oil and filter
Add hydraulic oil
Repair the seal ring
Tighten bolts
Replace oil and filter
element.
Repair
Replace
Replace
Add hydraulic oil
Replace oil and filter
Repair or replace
Examine
Decrease the
temperature manually
or stop the engine
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-12
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 86

2.3 EXTEND / RETRACT SYSTEM
Table 2-3
Part
Boom cannot retract
Boom cannot extend
Electrical System
Boom retracts
automatically during
operation (will not hold its
position)
Problem Cause Remedy
a) Balance valve defective
b) Electrical system defective
c) Main valve leaks internally
d) Pilot control valve defective
e) Retraction rope and fittings
defective
a) Relief valve pressure is set
too low
b) Main boom length detector
is not adjusted correctly
c) Electrical system defective
d) Foot valve defective
e) Pilot control valve defective
f) Extension rope and fittings
defective
a) Cylinder internally leaks
b) Balance valve defective
c) O-ring for the balance
valve worn
d) Oil cylinder, valves or
fittings leak
Repair
Repair
Repair
Repair solenoid coil
Examine
Adjust or replace
Adjust or repair
Repair
Repair
Repair solenoid coil
Examine
Repair the seal ring
Repair
Replace the O-ring
Repair
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-13
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 87

2.4 DERRICKING MECHANISM
Cylinder retracts
Table 2-4
Part
Derricking Mechanism
Problem Cause Remedy
Cylinder cannot extend
Cylinder cannot retract
automatically during
operation (will not hold its
position)
Cylinder vibrates when
the boom is lowered
a) Main relief valve pressure
is set too low
b) Main valve leaks internally
c) Cylinder leaks internally
a) Derricking-control balance
valve defective
b) Electrical system defective
a) Cylinder leaks internally
b) Derricking-control balance
valve defective
a) The right joystick moves to
the neutral position too
quickly
b) Opening pressure of the
derricking-control balance
valve is not constant.
c) Blockage in the
derricking-control balance
valve core
d) Blockage in the
derricking-control main
valve core
Adjust
Repair
Repair the seal ring
Repair or replace
Repair
Repair
Repair
Move the joystick to
the neutral position
slowly
Examine the
accumulator of pilot
control valve block
for functional work
Clean or replace the
valve core
Clean or replace the
valve core
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-14
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 88

2.5 SWING MECHANISM
Table 2-5
Part Problem Cause Remedy
Brake defective.
Superstructure cannot
move left or right
Superstructure moves too
slow
Electrical System
Free swing function
defective
Brake pad is worn. Adjust or replace
a) Relief pressure of outrigger
control valve is too low
b) Relief valve pressure for
swing valve is set too low
c) Swing valve defective
d) Hydraulic motor damaged
e) Swing reducer defective
a) Relief valve pressure for
the chassis multiple unit
valve is set too low
b) Relief valve pressure for
the swing valve is set too
low
c) Swing valve defective
d) Swing cushion valve
defective
e) Hydraulic motor defective
a) Switch defective
b) Conducting wire broke
c) Solenoid controlled swing
valve defective
d) Swing cushion valve
defective
e) Swing brake does not
engage
f) Swing lock disengaged
Adjust
Adjust
Repair or replace
Replace
Repair
Adjust
Adjust
Repair
Repair
Repair
Repair or replace
Repair
Repair or replace
Repair or replace
Repair the oil pipeline
Engage
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-15
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 89

2.6 HOIST MECHANISM
Table 2-6
Part Problem Cause Remedy
Hook cannot go up
Hook cannot go down
Electrical System
Brake defective
a) Relief valve pressure for
the main valve is set too
low.
b) Hydraulic motor defective
c) Main valve defective
d) Electrical system defective
e) Winch reducer does not
turn
a) Relief valve pressure for
the main valve is set too
low
b) Hydraulic motor defective
c) Main valve defective
d) Electrical system defective
e) Balance valve defective
f) Winch reducer does not
turn
a) Brake cannot engage or
disengage (Pilot oil source
pressure for the main valve
is set too low).
b) Brake pad is seriously
worn.
c) Air in the brake system
d) Hydraulic motor defective
(pump volume is too low,
not enough oil flow to do
multiple tasks).
Set the pressure to 27
MPa.
Replace
Repair
Repair
Examine the pilot
valve and the brake
valve
Adjust or repair
Repair
Repair
Repair
Replace
Repair
Set the pressure to 3
MPa
Replace
Bleed the system
Repair or replace
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-16
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 90

2.7 OUTRIGGERS
Vertical cylinder retracts
Table 2-7
Part
Outriggers
Problem Cause Remedy
Do not move
Move too slow
automatically during
operation (will not hold its
position)
Vertical cylinder extends
automaticallyduring travel
(will not hold its position)
a) Relief pressure of outrigger
control valve is not
adjusted correctly.
b) Solenoid coil of outrigger
control valve defective
a) Chassis multiple unit valve
leaks internally
b) Relief valve pressure for
the chassis multiple unit
valve is set too low.
a) Bidirectional hydraulic lock
defective
b) Cylinder leaks internally
a) Bidirectional hydraulic lock
defective.
b) Cylinder leaks internally
c) Cylinder leaks externally
Adjust the pressure
Replace the solenoid
coil
Repair
Adjust
Remove sewage or
replace valve.
Replace the seal ring
Remove sewage or
replace valve
Replace the seal ring
Repair
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-17
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 91

2.8 TRANSMISSION
Table 2-8
Part
Transmission
Problem Cause Remedy
a) Pressure gauge defective Replace the pressure
gauge
Control
pressures in
the full gear
range are low
Transmission
overheating
b) Control oil pipeline leaks Examine oil pipeline and
replace control valve
c) Oil pump pressure is not sufficient Repair or replace oil pump
d) The control valve mount bolts are
loose.
a) Oil pump pressure is not sufficient
due to oil level to high or too low,
or incorrect oil type
b) Traveling on a slope over 12° for
a long period of time or exposed
to high ambient temperature
c) Traveling slow for a long period of
time
d) Engine RPM is too high. Examine and control the
Tighten bolts
Examine and adjust oil
quality & level to the
requirements.
Stop the engine and lower
the oil temperature.
Stop at an interval to let
the engine and
transmission temperatures
adjust.
engine control to make the
highest engine RPM agree
with the requirements.
Unusual
transmission
noise
a) Caused by bumping
between gear and tooth face
in the gear box which could
be verified by sparkle
generated by tooth face
compressing test. When the
gear is bearing load, the
noise could be more
extreme. It shows that the
Knocking Sound
gear is defected if you can
hear noise when the gear is
engaged.
Use whetstone and manual
grinding wheel to smooth
out rough spots.
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-18
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 92

Stages I and II
Part
Problem Cause Remedy
b) If the balls or rollers in the
bearingsare damaged, there
can be spots and scale on
the roller bed, which causes
noise when each gear is at
low rotational speed.
c) A knocking sound (at low
turning speed) and
screaming sound (at high
turning speed) can be heard
if the gear cracks at an
impulsive load or when the
component was assembly.
a) Caused by normal abrasion
of the gears, including spots
generated after long-period
application and screaming
sound before being
damaged.
b) Caused by incorrect
engagement of gears which
Screaming sound
could be verified by
unevenly tooth face
abrasion.
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
a) No electricity Examine power supply and
Backup light
illuminates all
the time or
does not
illuminate.
The ignition
switch cannot
turn.
of ignition
switch do not
function.
b) No supply of electricity to the
reverse gear of the gear selector
c) The control pin for reverse gear of
the gear selector is stuck or the
reverse gear is on or off all the
time
a) No electricity Examine power supply and
b) Air is in the oil pipeline Bleed the air from the
The switch to stop the current of
solenoid valve does not operate
repair
Examine corresponding
lines and Repair.
Replace related
component
repair
system
Replace the defected
solenoid valve
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-19
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 93

Pressure
Part
Part Problem
Problem Cause Remedy
Loss of
traction force
or increase in
oil
temperature
boosting time
in the full gear
range is short
All the gear
positions do
not operate
Cause Remedy
a) Head pressure of torque
converter is low
b) Pressure of the fuel supply
system for the engine is low
Blockage of the pressure control
valve
a) Fuel level low Fill the fuel tank to correct
b) Components that connect the
engine and torque converter
defective
c) The control valve has no
electricity
Adjust the opening
pressure of the safety
valve for torque converter.
Clean or replace the fuel
filter
Clean the pressure control
valve
level
Examine or repair the
components
Examine the fuse in the
gear selector cable and
test the output voltage of
the connector.
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-20
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 94

2.9 BRAKE SYSTEM
Table 2-9
Part Problem Cause Remedy
a) Brake force is not even Examine and adjust the
brakes (clearance between
brake disc and brake
caliper around 0.020 -
0.028 in (0.5 - 0.7 mm)).
Brake
deviation
Brake locked
Brake System
up
Brake system
does not stop
the crane at a
usual distance
(stopping
distance too
long)
b) Different tire inflation pressures
for different tires
c) The power to stop is not equal at
each wheel (unsynchronized
brake disc abrasion).
Brake pads wear is unusual
(some pads wear much more
that others).
a) Small clearance between brake
disc and brake caliper
b) Brake system pressure is not
sufficient.
c) Park brake will not disengage. Examine and disengage
a) Brake system pressure is not
sufficient.
b) Accumulator on the master
brake valve defective
c) Incorrect clearance between
brake disc and brake caliper
Inflate the tires to the
correct pressure
Examine or replace brake
pads
Examine and adjust the
brakes (clearance between
brake disc and brake
caliper around 0.020 -
0.028 in (0.5 - 0.7 mm)).
Adjust the relief valve
pressure or repairthe
master brake valve and
pre-fill valve.
Adjust the relief valve
pressure or repairthe
master brake valve and
pre-fill valve.
Replace or supply
hydraulic oil
Adjust clearance
d) Defective brake disc Replace
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-21
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 95

2.10 STEERING SYSTEM
Table 2-10
Part Problem Cause Remedy
Hard steering
Steering System
a) Oil level in the hydraulic system
is too low or the oil has a low
viscosity (causes low pressure or
air in the system (cavitations)).
b) Park brake is engaged Examine and
c) Steering system pressure is not
sufficient.
d) Relief valve core blocked Clean valve core
e) Priority valve defective Clean valve core
f) Oil pipe fittings leak, pipeline
blocked or twisted
g) Filter blockage, causing
unsatisfactory cleanliness and
decreased flow
h) Dangerous leaks and damage in
the steering gear
Examine oil level in
hydraulic tank, add oil
as necessary. Use the
correct type. Examine
sealing performance of
pipe fittings
disengage the park
brake
Make sure that the
relief valve pressure is
not too low
Examine, clean or
replace pipelines and
fittings
Clean filter and filter
element,replace oil
Repair or replace seal
ring
i) Steering cylinder leaks internally Replace seal ring
Hard rapid
steering
a) Oil supply from the oil pump is
not sufficient (low flow)
b) Oil pump suction pipeline weak
and collapsed (flat)
c) Heavy oil leaks at the two sides
of piston in the steering gear
caused by oil damage or too
much abrasion
d) Air is inhaled
Repair oil pump
Replace pipelines
Replace oil seal
Examine all pipe
fittings
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-22
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 96

Part Problem
Steering
sometimes
hard or
sometimes
uncontrolled
Left steering is
uncontrolled
while right
steering is hard
and vice versa
Cause Remedy
a) Floating brass bush of steering
pump is blocked and does not
touch the wheel end-face all the
time.
b) Hydraulic oil is seriously polluted
or air is inhaled into the system
c) Priority valve core blocked Clean valve core
d) Steering gear defective Repair or replace
a) Not even oil leaks occurred at the
two sides of the piston in the
steering gear.
b) Air is inhaled into one side of the
cylinder
c) Too much clearance between ball
pins of drive rod
a) Tire inflation pressure in tires on
left / right steer axles does not
agree with the requirements
(extremely inconsistent).
Repair oil pump
Replace oil or remove
air from the system
Replace seal ring
Remove air from the
system
Repair or replace
Examine and inflate the
tires to the correct
pressure
Traveling
deviation
Steering gear
oil leaks
b) One of the steer axles always in
brake status
c) Inconsistent clearance of the
bearings in left / right steer axle
(one is too loose, while the other
is too tight or blocked).
d) Steer axles are blocked. Examine where it is
e) Bubbles are in the oil and travel
direction is not stable
f) Uneven steer axle abrasion Tire rotation
g) Front axles are not aligned with
the rear axles or incorrectly
seated.
a) Oil seal Examine and replace
b) O-rings Examine and replace
c) Oil pipes damaged Examine or replace oil
Adjust or repair the
brake
Adjust bearing
clearance or replace
bearing
blocked and examine
the input shaft bears
radial resistance.
Examine and eliminate
Examine and adjust
oil seal
O-ring
pipelines
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-23
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 97

d) Oil pipe fittings Look for connection
that leaks, tighten fitting
e) Low oil viscosity Replace oil
Unusual noise
while you steer
f) Joint face of hydraulic elements
loosen
a) Oil pipe of hydraulic pipeline
twisted
b) Unstable oil pump displacement Replace oil pump
Examine and tighten
Examine and replace
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-24
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 98

2.11 FRONT / REAR AXLES
Table 2-11
Part Problem Cause Remedy
Unusual noise
Front / Rear Axles
a) Noise sounds like (si) during speed
increase or decrease. Gears do not
interconnect correctly(clearance of
gears too small or poorly aligned).
b) New gear poorly meshed Monitor after
c) Noise sounds like clash on
descending gradients or while
speed changes quickly. The Noise
fades away or decreases during
usual movement: clearance
between gears too large.
d) Continuous noise when the crane is
in motion. The noise increases with
the speed. But when noise fades
away or decreases during sliding:
the bearings (hub, main reducer or
differential) are worn or too loose.
e) Gear oil level too low or oil viscosity
does not agree with requirements.
f) No noise during straight traveling,
but the noise sounds during turning
caused by excessively large
clearance of bearings on both sides
of reducer or worn differential gear
or thrust bearing shim.
Adjust the clearance
or alignment
breaking-in
Adjust or replace gear
Adjust or replace
bearings
Add oil to the correct
level or replace the oil
with the correct type
Adjust or replace
Heat
generation
Oil leaks
a) Bearing installed too tightly.
Meshing clearance too small.
b) Oil level too low Add oil to the correct
c) Lubricant viscosity too low Replace with the
a) Oil seal defective Replace
b) Axle journal worn Replace the damaged
Adjust
level
correct type
one
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-25
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 99

Part Problem Cause Remedy
c) Oil level too high Drain oil to the correct
level
d) Seal gasket damaged Replace
e) Bolts loose Tighten
f) Vent cap soiled Clean
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-26
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
Page 100

2.12 DRIVE SHAFT
Table 2-12
Part Problem Cause Remedy
Unusual noise when
the crane begins to
move, increase speed
and decrease speed.
Periodical noise
during traveling. The
noise increases with
speed. In the worst
case condition, the
vehicle shakes and
Drive Shaft
steering wheel does
not move.
Unusual noise during
movement. The noise
level increases as the
speed increases.
a) Universal joint cross
trunnion, needle roller worn
and loosen or needle roller
broken.
b) Drive shaft spline and
expansion joint splineway
are at the wear limit.
a) Drive shaft bent or drive
shaft flange is not welded
correctly to the axle tube.
b) Retaining bolts at central
bearing stand loosen and
deflected.
c) Loose or missing bolts
between the two drive
shafts (adjacent drive
connecting shafts).
d) Drive shaft balance block
falls off
a) Central bearing is defective
and is at its wear limit.
b) Roller comes off from
central bearing
c) Inadequate lubricant for
central bearing
Replace the universal
joint
Replace
Replace drive shaft
Screw down or
replace
Tighten or replace
Replace (balance the
shaft)
Adjust or replace
Replace bearing
Add #2 lithium grease
Edition 2 Chapter 2 Page 2-27
Dec /2013 Troubleshooting
 Loading...
Loading...