Page 1

ADSL X6
U S E R G U I D E
Page 2

NOTICE
This document contains proprietary information protected by
copyright, and this Manual and all the accompanying hardware,
software, and documentation are copyrighted. No part of this
document may be photocopied or reproduced by mechanical,
electronic, or other means in any form.
The manufacturer does not warrant that the hardware will work
properly in all environments and applications, and makes no
warranty or representation, either expressed or implied, with respect
to the quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for a
particular purpose of the software or documentation. The
manufacturer reserves the right to make changes to the hardware,
software, and documentation without obligation to notify any person
or organization of the revision or change.
All brand and product names are the trademarks of their respective
owners.
© Copyright 2007
All rights reserved.
Page 3

Contents
Overview............................................................................6
1. Installation Instructions ...............................................7
Package Contents........................................................7
Before You Begin.........................................................8
Installing the X6...............................................................9
Step 1: Installing the Software .....................................9
Step 2: Installing the Hardware..................................10
Step 3: Establishing Communication .........................12
Step 4: Setting Up a Wired or Wireless Network .......17
Universal Plug and Play ................................................19
If You Need Help...........................................................19
2. Setting Up Your Wireless Network ...........................20
Connecting a Wireless-enabled Computer to the X6.21
Connecting a Windows XP Computer with Built-in
Wireless Capabilities..................................................23
Checking Your Settings .............................................25
3. Setting Wireless Security ..........................................26
Overview ....................................................................26
Setting Up Security Using WPA2 or WPA .................27
Setting Up Security Using WEP.................................29
4. The X6 and Online Gaming........................................31
Do I Need to Do Anything? ........................................31
Setting Up the X6 for Online Gaming............................32
Step 1: Choosing an IP Address for Gaming .............32
Step 2: Setting Up a Virtual Server or DMZ ...............38
Table of Contents 3
Page 4

5. Using Advanced Setup ..............................................45
Viewing the Advanced Setup Options...........................46
Using the WAN Configuration Settings .........................50
Using the Ethernet Configuration Settings ....................56
Setting Up a Static Routing Table .................................57
Adding Extra Security with Advanced Firewall Filtering 59
Setting Security Logging ...............................................64
Configuring Intrusion Detection.....................................65
Adding a DNS Server Name .........................................67
Creating a Virtual Server or a DMZ...............................68
Using the ADSL Settings...............................................70
Changing Your LAN Settings ........................................72
Creating a Fixed IP Address .........................................74
Assigning a Half Bridge Device.....................................75
Enabling or Disabling UPnP..........................................76
Assigning Ports to a PVC..............................................77
Changing HTTP and Telnet Ports .................................79
Filtering Out MAC Addresses........................................80
Managing Access to Services .......................................82
Configuring Quality of Service.......................................83
Monitoring ADSL, Wireless, and Ethernet Status..........86
Changing Your Password..............................................89
Restoring Factory Settings............................................90
Backing Up and Restoring Your Configurations............91
Updating Your Firmware ...............................................92
Appendix A. ADSL Internet Settings ............................93
Appendix B. Front and Back Panels.............................97
Appendix C. TCP/IP Network Settings..........................99
Macintosh TCP/IP Settings ......................................100
Linux TCP/IP Settings..............................................102
Windows TCP/IP Settings........................................103
Appendix D. Troubleshooting .....................................106
4
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 5

Appendix E. Configuring Your Web Browser ............112
Appendix F. Wireless Channels by Country ..............116
Appendix G. Regulatory Information..........................117
Safety Notices..........................................................118
Declaration of Conformity ........................................119
Table of Contents 5
Page 6
Overview
This User Guide provides instructions for setting up your X6,
connecting the
and securing your network. There are also instructions for setting
X6 for gaming.
up the
For most customers, Chapter 1 covers what you need to get
connected to the Internet. Chapter 2 applies if you want to set up a
network. Chapter 3 provides security information, and Chapter 4
provides what you need for gaming.
Chapter 5 Advanced Setup is primarily for System Administrators.
This chapter explains how to use advanced features of the
as adding extra security with firewall filtering, backing up and
restoring the
creating a fixed IP address.
X6 to wired and wireless computers on a network,
X6 such
X6 configuration, updating the X6 firmware, and
You can find new and updated information about the
Zoom Web site:
www.zoom.com/techsupport/adsl/adsl_x6.shtml
X6 at the
6
ADSL X6 User’s Guide
Page 7

1
Installation Instructions
This chapter covers the basic instructions needed to install your
X6 and connect to the Internet. These instructions can be used
by those with a Macintosh®, Linux, or Windows® operating
system. Note: Windows users - . If you did not successfully set
up the X6 using the Install Assistant, follow these instructions to
install the X6 manually. If you already installed and connected
your X6 (using the separate Quick Start booklet provided for
Windows users), you can skip this chapter and begin with
Chapter 2.
Package Contents
Your package contains the following items:
•
Zoom ADSL
Ethernet cable
•
Phone cord
•
Power cube
•
CD
•
The CD contains the installation software, documentation,
warranty, and Customer Support information.
If anything is missing or damaged, please contact Zoom Customer
Support or whoever sold you the modem.
Chapter 1: Installation Instructions
X6 modem
7
Page 8

In addition, the package may include:
•
A splitter to enable you to use a single ADSL wall jack for both
an Internet connection and for telephone service (certain
countries only)
•
Phone-jack adapter to adapt the phone cord to a particular
phone jack (certain countries only)
•
ADSL line filter(s) (certain models only)
Before You Begin
Before you begin installing the X6 modem using this guide, you
must have the following available to you:
•
ADSL service enabled on your telephone line. To do this, you
need to sign up with an ADSL service provider. Once this
service is enabled, you should have an ADSL-enabled
telephone wall jack to plug the
provider may refer to ADSL service as DSL service).
X6 modem into. (Your service
•
One or more computers or laptops that you want to connect
to the Internet. The
X6 supports Macintosh, Linux, and
Windows 98/Me/2000/XP operating systems.
•
Any computer or laptop that you want to connect without
wires to your network. These must be equipped with a wireless
adapter or have built-in wireless capabilities. The
X6 supports
802.11b and 802.11g compatible adapters.
•
Any computer that you want to physically connect to your
X6
LAN port. The X6 has four LAN ports to which you can
connect devices. A computer must have an Ethernet port to
make these connections.
•
Additional Ethernet cables. If you plan to connect more than
one computer
directly to the modem, you will need additional
Ethernet cables to make the connection. The modem supports
up to four direct connections with its four LAN ports.
8
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 9
Installing the X6
Installing the X6 involves four steps: Installing the Software,
Installing the Hardware, Establishing Communication, and
Setting Up a Wired Network.
Step 1: Installing the Software
Note:
This section is for Windows computer users who did not already
run the Install Assistant on the CD. If you already ran the Install
Assistant or are using a Macintosh or Linux computer, skip this
section and begin with the next one, Installing the Hardware.
Regardless of how many computers you plan to use with the X6,
you only have to install the software on one of them.
You will install the software on a Windows computer that you
directly connect to the
the modem. This computer must have an Ethernet port. If it does
not, you can purchase an Ethernet card (sometimes called a
Network Interface Card or NIC) to add an Ethernet port.
Important!
If possible, use a computer that is centrally located in your home or
office and that has easy access to an ADSL line. A central location
helps assure good wireless performance. If you do not have a
desktop computer located centrally in your home (for example, it is
in the basement), or you only have notebook computers, you
should still directly connect this desktop computer or one of your
notebooks to the X6 to configure it. Once the X6 is set up and your
Internet connection is working, you can unplug the computer from
the unit and move the X6 to a more central location.
X6, and then use that computer to configure
Chapter 1: Installation Instructions
9
Page 10
Turn your computer on.
For Windows Vista only, follow these steps to turn on Telnet
Client:
a Click Start, select Control Panel, then double-click
Programs and Features.
b In Programs and Features, in the Tasks pane, click Turn
Windows features on or off.
c At the User Account Control message, click Continue.
d In the Windows Features dialog box, select Telnet Client,
click OK, and wait while the feature is configured.
e In the Uninstall or Change a Program window, click the
Close box to exit.
1 Insert the supplied CD into the CD drive of your computer.
The CD should start automatically. (If the CD does not start
automatically, on the desktop, click the Start button, click
Run, and then type E:\setup.exe, where E is the letter of
your CD drive.)
2 Follow the prompts to install the software. Click Next to
bypass the screens for setting up the hardware.
Congratulations! You have installed the software. Now continue
with the next section,
Step 2: Installing the Hardware.
Step 2: Installing the Hardware
Windows users only: Be sure that you have already installed
the software BEFORE beginning this section. Software
installation is not required for Macintosh and Linux
computers.
1 Shut down and power off your computer.
¾ For Windows users, this is the computer on which you just
installed the software.
10
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 11

¾ For Macintosh or Linux users, this can be any one of the
computers that you plan to use with the
situation, this would be the computer that is closest to
your ADSL wall jack.
X6. In a typical
2 Rotate the antenna on the back of the modem to a vertical
position.
3 Connect the modem to the computer’s Ethernet port.
Plug one end of the Ethernet cable
X6 modem’s LAN ports (LAN 1, LAN 2, LAN 3, or LAN 4)
and plug the other end into your computer’s Ethernet port.
into any one of the
4 Plug the power cube into a power strip or wall outlet and then
plug the power cube’s other end into the modem’s power
(PWR) jack.
Important!
Only use the power cube shipped with the X6. Other power
cubes may damage your hardware.
5 After you plug in the power cube, the PWR and WLAN lights
on the front panel of the modem should become steady on,
and the LINK light should blink. If the PWR light does not
turn on, make sure there is power at the wall outlet or power
strip where you plugged in the power cube.
6 Turn the computer on.
7 Plug one end of the supplied phone cord into the modem’s
ADSL port and the other into the ADSL wall jack. The
blinking LINK light should become steady on. If it does not,
refer to
Troubleshooting on page 106.
Chapter 1: Installation Instructions
11
Page 12
Note:
In some countries, including the UK, the modem comes with a
splitter. Plug the splitter into the wall jack with ADSL service.
Then plug the supplied phone cord between the modem's
ADSL jack and the splitter's MODEM jack.
We recommend that you put an ADSL filter on every
phone connected to the ADSL phone line. DO NOT put a
filter between the X6 and the wall jack that it is connected to.
If you are using a splitter, you can plug a phone into the
splitter's PHONE jack, which has a built-in filter.
Congratulations! You have installed the hardware. Now
continue with the next section
Communication
.
Step 3: Establishing
Step 3: Establishing Communication
Important!
Macintosh and Linux users must make sure that the computer’s
TCP/IP settings are configured properly BEFORE starting this
section. See Macintosh TCP/IP Settings on page 100 or Linux
TCP/IP Settings on page 102 for instructions.
You must set up the X6 so that it can communicate with your
Internet service provider. To do this, you must use the Zoom
Configuration Manager.
1 Close all programs including antivirus software and pop-up
blockers.
2 Log into the Zoom Configuration Manager from the
computer on which you installed the
a Open your Web browser and, in its address bar, type
http://10.0.0.2 and then press the Enter key on your
keyboard.
X6 software:
12
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 13
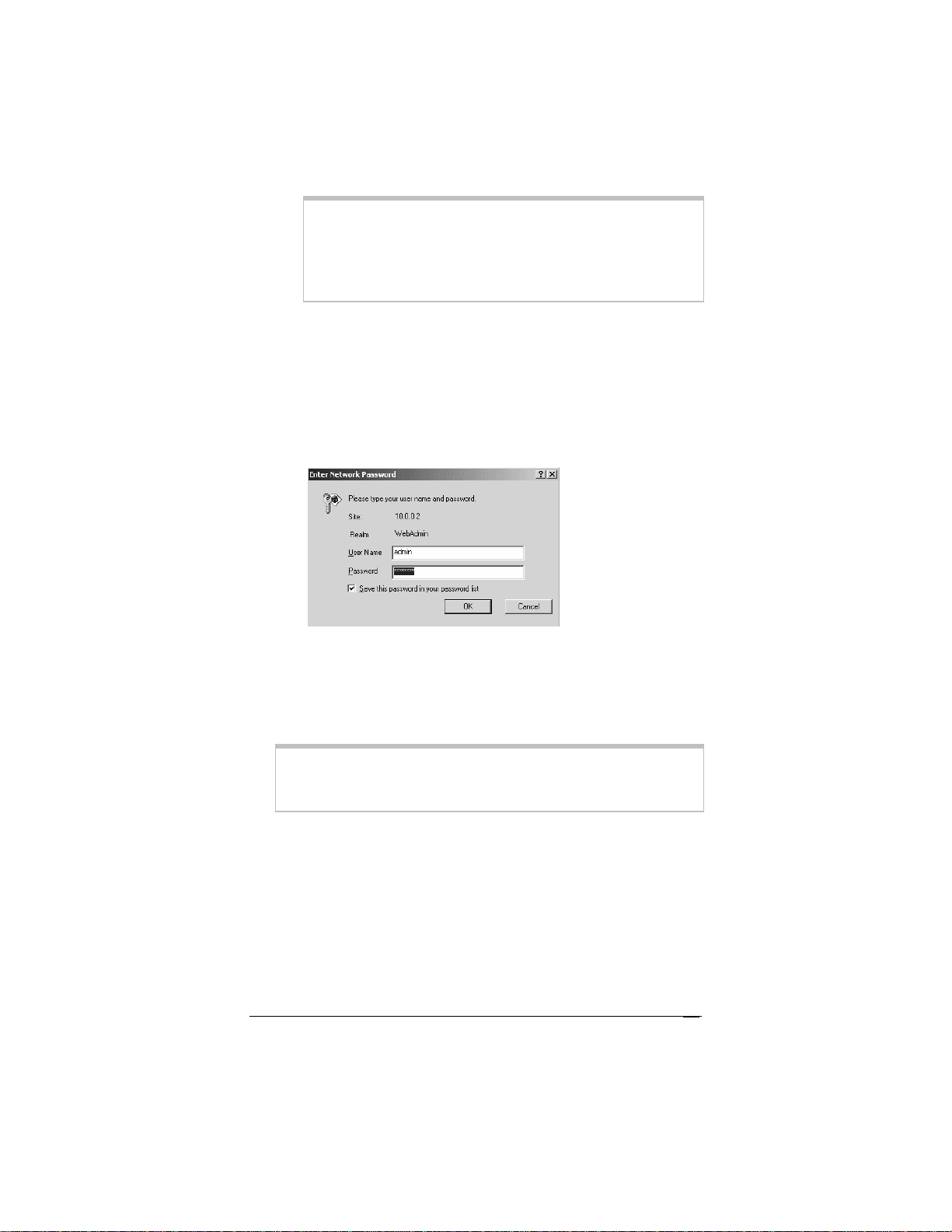
Tip!
If you are using a Windows computer, a Zoom icon
should have been placed on your desktop automatically.
Instead of typing the address above in your Web browser,
you can double-click the Zoom icon.
b On the Enter Network Password dialog box, type the
following user name and password in lowercase then click
OK. (The User Name and Password you enter here are
not the same as the User Name and Password that your
Internet service provider may have given you.)
User Name: admin
Password: zoomadsl
If you are not prompted for a User Name and Password,
do the following in this order: Recheck all connections;
restart the modem and computer; and reset the modem by
inserting a paper clip into the Reset pinhole in the
modem’s back panel and press it three times.
Important:
For security, choose your own password after the setup is
complete. See Changing Your Password on page 89.
Chapter 1: Installation Instructions
13
Page 14
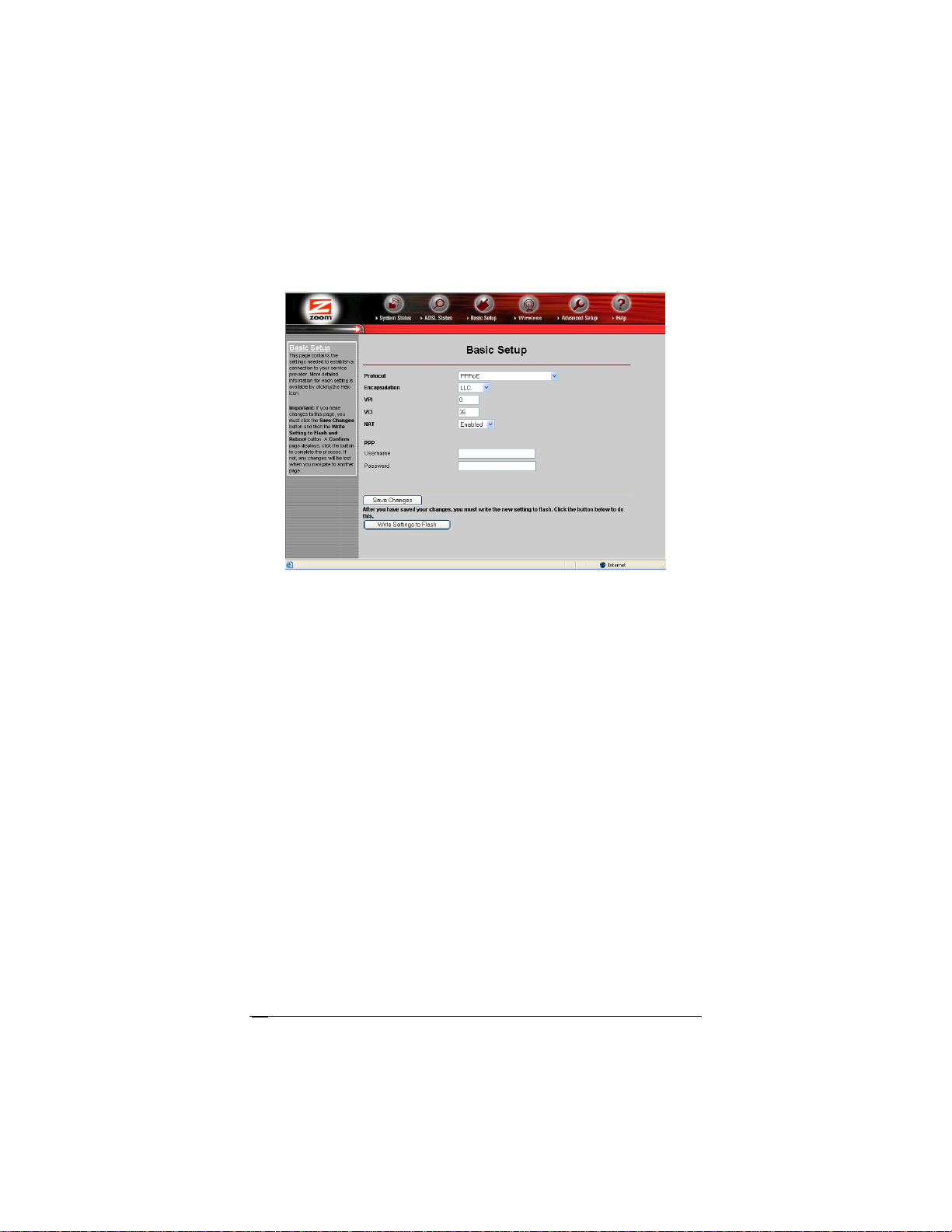
2 After you log in, use the Basic Setup page to configure the
modem so it can connect with your Internet service provider.
Do the following:
a
Enter your Protocol, Encapsulation, VPI, and VCI
settings in the appropriate boxes. Your service provider
should supply these values. If you do not know these
settings, refer to the tables starting on page
b
NAT (Network Address Translation) is Enabled by
default. This feature lets multiple users access the Internet
sharing a single IP address. Enabled is typically the right
setting. Select Disable in the unlikely event that you want
to assign different public IP addresses to each network
user.
93.
14
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 15

c Depending on the Protocol setting you selected the
bottom half of the page will change so that you can enter
additional information.
If you selected PPPoA or PPPoE, enter your ADSL
Username and Password in the appropriate boxes.
Your Internet service provider should have given this
information to you. (Your Username is typically your
email address or the characters preceding the @ sign
in your email address. This is NOT the same
Username and Password that you used earlier to open
the Zoom Configuration Manager.)
If you selected 1483 Bridged or 1483 Routed, you
have the option of using either dynamic or static IP
addressing. Depending on your situation, select the
appropriate option button:
− [MOST USERS] Ensure that Obtain an IP
address Automatically is selected if you are
using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (also
known as DHCP or dynamic IP addressing). This
option is selected by default because most Internet
service providers use DHCP.
− Select Use the following IP Address only if you
are using a static IP address. (You should know if
you are using static IP addressing. There is
typically an extra charge for a static IP address and
you usually have to make special arrangements
with your Internet service provider to get one.)
Then enter the IP Address, Subnet Mask,
Default Gateway, and DNS that you plan to use.
Click the Save Changes button, then click the
Write Settings to Flash button.
Chapter 1: Installation Instructions
15
Page 16
3 Verify that you Internet connection is working. Open your
Web browser (for instance, Internet Explorer or Netscape
Navigator) and try to connect to a familiar Web address. If you
connect successfully, you are ready to set up the rest of your
network.
(If you do not connect, see Appendix D on page 106).
Tip!
If you configured the X6 using a notebook computer, you can keep
it plugged in or you can disconnect it from the unit’s LAN port. As
long as the X6 remains plugged into an ADSL wall jack and a
power source, the X6 can function as a stand-alone device. You can
then make the notebook part of your wireless network.
Congratulations! You have established communication and your
computer is now connected to the Internet. Now continue with
Step 4: Setting Up a Wired or Wireless Network.
16
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 17

Step 4: Setting Up a Wired or Wireless Network
Once a computer that is directly connected to the X6 modem is
able to browse the Web, you know for certain that your Web
connection is working. Now you can set up the rest of your
network.
It is up to you whether you want to have some computers
connected directly to the
X6 supports both wired and wireless connections. You can have up
to 253 connections, four of which can be wired directly through
X6’s four LAN ports. You can also plug a network device
the
(such as a hub, switch, or router) into one of the LAN ports.
To set up your network, you can do any or all of the following, in
any order that you choose:
X6 and others connected wirelessly. The
•
If you want to connect additional computers directly to the
To Connect Additional Wired Computers below.
see
•
If you want to connect a hub, switch, or router directly to the
X6, see To Connect a Network Device on page 18.
•
If you want to connect additional computers using a wireless
network, see
Setting Up Your Wireless Network on page 20.
X6,
To Connect Additional Wired Computers
You can connect up to four computers that have Ethernet ports
directly to the
X6.
1 Shut down and power off the computer you want to connect
X6. (This is important because the computer must locate
to the
the correct IP address for the modem. This is done when the
computer is turned back on in step 3 below.)
2 Plug one end of an Ethernet cable into one of the modem’s
LAN ports and plug the other end into the computer’s
Ethernet port.
Chapter 1: Installation Instructions
17
Page 18

3 Turn on the computer.
4 Verify that your Internet connection is working. Open your
Web browser (for instance, Internet Explorer or Netscape
Navigator) and try to connect to a familiar Web address.
5 Repeat steps 1–4 for each computer you want to add.
To Connect a Network Device
You can use one of the LAN ports on the X6 to plug in a network
device (for example, a hub, switch, or router).
1 Plug one end of an Ethernet cable into one of the modem’s
LAN ports and the other end into the network device’s
Ethernet port. (For a hub or a switch, this is typically called an
Uplink or Expansion port. For a router, this is typically called
a WAN port.)
2 Set up your network. Refer to the documentation provided
with your particular network device for instructions on how to
do this.
3 Once your network is set up, reboot any computer that is part
of the network.
4 Verify that your Internet connection is working. Open the
Web browser (for instance, Internet Explorer or Netscape
Navigator) on each computer and try to connect to a familiar
Web address.
Congratulations! You have set up your wired devices. If you
have wireless devices that you want to add to your network, go to
Setting Up Your Wireless Network on page 20.
18
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 19
Universal Plug and Play
The X6 supports Universal Plug and Play (UPnP™). This means
that other devices plugged into your computer or network (for
example, a gaming application, router, or stand-alone firewall) that
use UPnP should automatically detect the
configurations for them to work together. There is no setup for
you to do.
X6 and make the needed
If You Need Help
Zoom has many Technical Support services available to its
customers. You can access these services in a variety of ways:
• Visit our Web site at www.zoom.com and select Technical
Support. From there, you can register your X6 and/or
contact our technical support experts and/or use our
intelligent database SmartFacts
information.
tm
and/or get warranty
Tip:
From time to time, Zoom may release improved firmware.
This is also available at www.zoom.com, along with upgrade
instructions. We recommend that you check our Web site
periodically for updates.
• Call our support office. The appropriate number depends on your
country:
US: (561) 241-7170
UK: 0870 720 0090
Other (US number) (561) 997-9683
• Some retailers of Zoom products provide support or can
recommend a convenient support center.
Chapter 1: Installation Instructions
19
Page 20
2
Setting Up Your Wireless
Network
This chapter discusses how to set up a wireless network using
wireless adapters and/or computers that have built-in wireless
capabilities. Chapter 3 provides information about
implementing network security.
Note that for each computer added to your wireless network, you
will need to take appropriate steps for setting up that computer. To
do that, select one of the three possibilities for that computer
below:
1. Some newer Windows XP notebooks and desktops have built-
in wireless networking capabilities and do not require the
installation of a wireless component. If this is the case, you
should set up that computer’s wireless connection using
Windows XP. See
with Built-in Wireless Capabilities
Tip!
To see if your notebook has built-in wireless capabilities: On
the Windows desktop, click Start, click Connect to, and then
locate the Wireless Network Connection option. If Connect
to does not appear, or if there is no Wireless Network
Connection option, then your notebook does not have
wireless capabilities.
2. Some desktop and notebook computers may have built-in wireless
networking capabilities, but do not use Windows XP. If this is so,
set up your computer’s wireless connection using
Wireless-enabled Computer to the X6
Connecting a Windows XP Computer
.
Connecting a
on page 21.
20
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 21

3. Some desktop and notebook computers may need a wireless
network adapter installed. This can be a USB adapter, PC Card
adapter, or PCI adapter. When you install the adapter, make
sure that it is set to infrastructure or access point mode
(NOT ad-hoc or peer-to-peer mode). If you need help
installing your wireless adapter or setting its mode, refer to the
documentation that came with it. After you install the adapter,
Connecting a Wireless-enabled Computer to the X6.
see
Connecting a Wireless-enabled Computer to the X6
1 Go to the wireless-enabled computer that you want to add to
the network. The computer should have software that will let it
perform a site search to scan for available wireless networks
in your area. When the SSID (Service Set Identifier) of your
wireless network appears in the list—the SSID is zoom—
select it as the network you want to use to connect to the
Internet.
X6
Tip!
For most wireless adapters, you will use its wireless
configuration manager software and click a Scan button or
select a Site Scan, Scan Networks, or other similarly named
tab to do a site search. If you need help, refer to the
documentation that came with your wireless adapter.
Chapter 2: Setting Up Your Wireless Network
21
Page 22

There are several site scan issues you should be aware of:
¾ If you installed a wireless adapter on a Windows XP
computer, Windows XP may try to automatically configure
the adapter (rather than let you use the software provided
with the wireless adapter). You will know this is happening
because you will be prompted with a message about one or
more wireless networks being available. You will also be
able to click a link to open the Wireless Network
Connection Properties dialog box. If this happens, click
the link, and clear the Use Windows to configure my
wireless network settings check box then click OK. You
can then use the software provided with your wireless
adapter without interruption from Windows XP.
¾ More than one wireless network may appear in the list.
These are other wireless networks that are within range of
your network. Your neighbors for instance may be within
range of your network. Each wireless network has a
channel associated with it. We recommend there be at least
a five-channel difference between your network and those
of your neighbors. Having less than a five-channel
difference may result in interference with your connection.
By default, the
this channel, you must do so using the Wireless Setup
page of the Zoom Configuration Manager.
X6 uses channel 10. If you need to change
¾ If you want to secure your wireless network so it won’t be
accessible by others, you should specify security settings.
To learn how, see
(By default, the wireless connections provided by the
do not have any security applied.)
Setting Wireless Security on page 26.
X6
2 Test your wireless connections. From each desktop or
notebook computer that you set up, open your Web browser
(for instance, Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator) and try
to connect to a familiar Web address.
If you connect successfully, you are ready to browse the Web!
Important!
If you want to add security to your network, see Setting Wireless
Security on page 26.
22
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 23

Connecting a Windows XP Computer with Built-in Wireless Capabilities
This section applies to Windows XP notebooks and computers
that have built-in wireless capabilities.
1 On your Windows desktop, click the Start button then click
Control Panel.
2 Double-click the Network Connections icon.
3 Right-click the Wireless Network Connection icon, then
select Properties.
4 On the Wireless Network Connection Properties dialog
box, select the Wireless Networks tab. Windows XP will
automatically scan for available wireless networks in your area.
Any compatible networks within range will appear in the
Available networks list. It should find the wireless network of
X6—named zoom. (The scan is done automatically
the
because the Use Windows to configure my wireless
network settings check box is selected by default).
5 Select zoom from the Available networks list, then click the
Configure button to add it to the Preferred networks list.
The notebook will try to connect to the Internet using the
wireless networks listed here, in the order in which they
appear. (If you already have networks listed here, we
recommend you either remove them or use the Move up
button to move zoom to the top of the list.)
6 Click OK.
Chapter 2: Setting Up Your Wireless Network
23
Page 24
7 Test your wireless connection. From the computer or
notebook that you set up, open your Web browser (for
instance, Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator) and try to
connect to a familiar Web address.
If you connect successfully, your notebook’s wireless
capability is configured and you are ready to browse the Web!
Important!
If you want to add security to your network, please see Setting
Wireless Security on page 26.
24
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 25

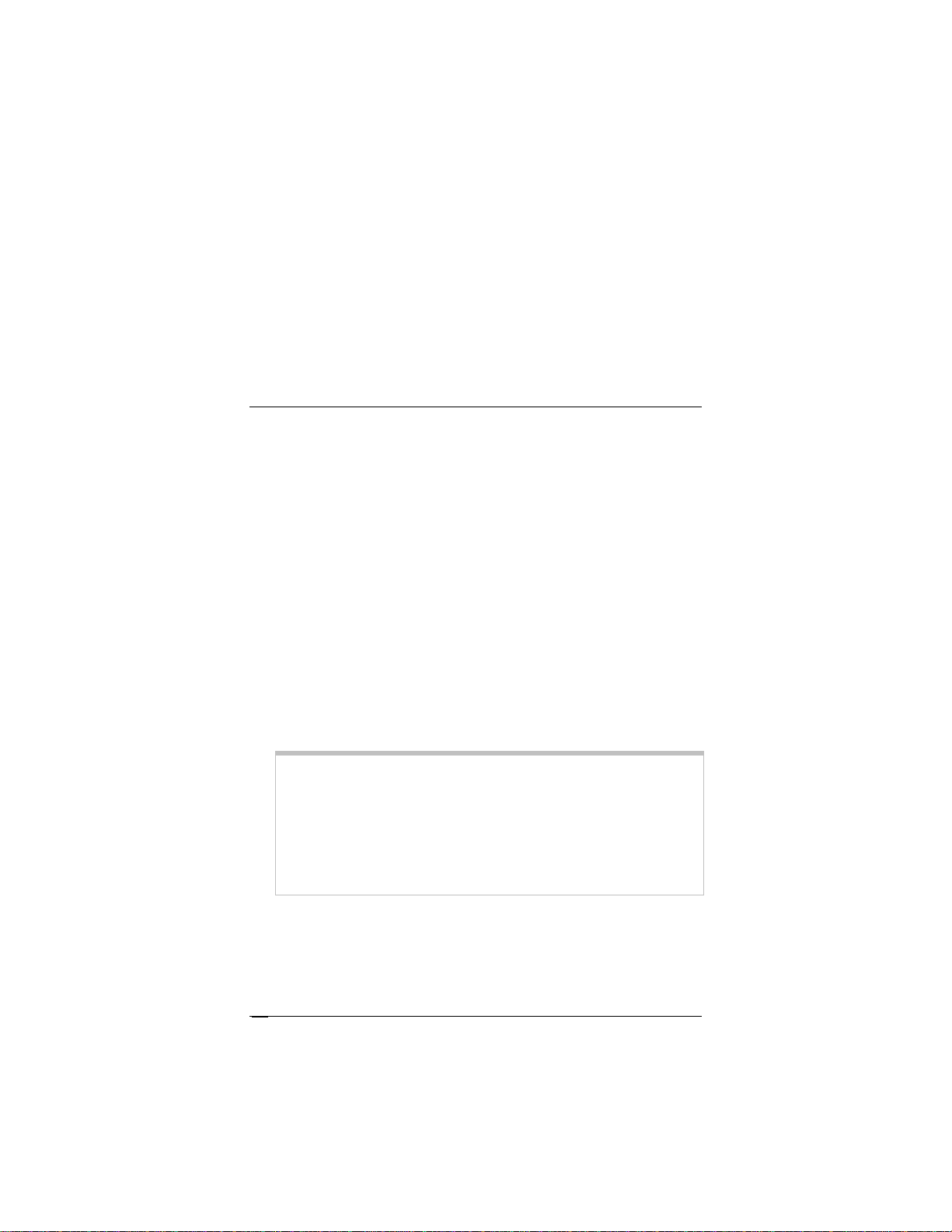
Checking Your Settings
If you ever need to check your wireless settings, you can do so
from the Wireless Setup page. This page is available in the Zoom
Configuration Manager by clicking the Wireless icon.
The table below explains the settings:
This setting… Lets you specify…
Wireless Status Enable shows that your wireless network is up.
Disable indicates that your wireless network is
down.
SSID
Default Channel
Profile
Encryption
Country If your country is not listed, select Other.
The Service Set Identifier for your wireless network.
By default, the SSID for the
change the SSID to any name that you want.
The channel your wireless connection uses by
default for your wireless connection. The
set for channel 10.
The standard used by your wireless adapters. This
drop-down list contains 802.11b Only, 802.11g
Only, or Mixed Mode.
The default is Mixed Mode, which allows you to
mix both b and g wireless adapters.
The type of encryption used for your wireless
Internet signal. This drop-down list contains None,
WEP-64 bit, WEP 128 bit, WPA and WPA2.
The default is None, meaning that no security is
enabled.
X6 is zoom. You can
X6 comes
Chapter 2: Setting Up Your Wireless Network
25
Page 26

3
Setting Wireless Security
When you first set up your X6 wireless network, security is turned off
by default. This means that your wireless signal is not encrypted and
that anyone with compatible wireless technology can access your
computer network and the Internet using your wireless connection.
This chapter explains how to set up wireless security to protect your
network and Internet connection.
Overview
To set up wireless security, you will create and enter a unique
passphrase or an alphanumeric key. Once entered, only devices
with the proper key or passphrase will be allowed to establish a
connection to the network.
There are two basic ways to configure and implement a passphrase
or key. They are WPA (WiFi Protected Access) or WPA2 and
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) 64 and 128 bit). WPA2 is best,
but you can use it only if all your wireless devices support the
802.11g profile.
You can check to see if all other clients that you plan to put on the
network support WPA2 or WPA. You can do this by checking the
manual that came with each device or by checking the
configuration software for the installed device. Look under
Security or Encryption or Setup or Advanced Features. If all
the clients support WPA2 or WPA, proceed with Setting Up
Security Using WPA2 or WPA. If they do not, skip to
Up Security Using WEP
.
Setting
26
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 27
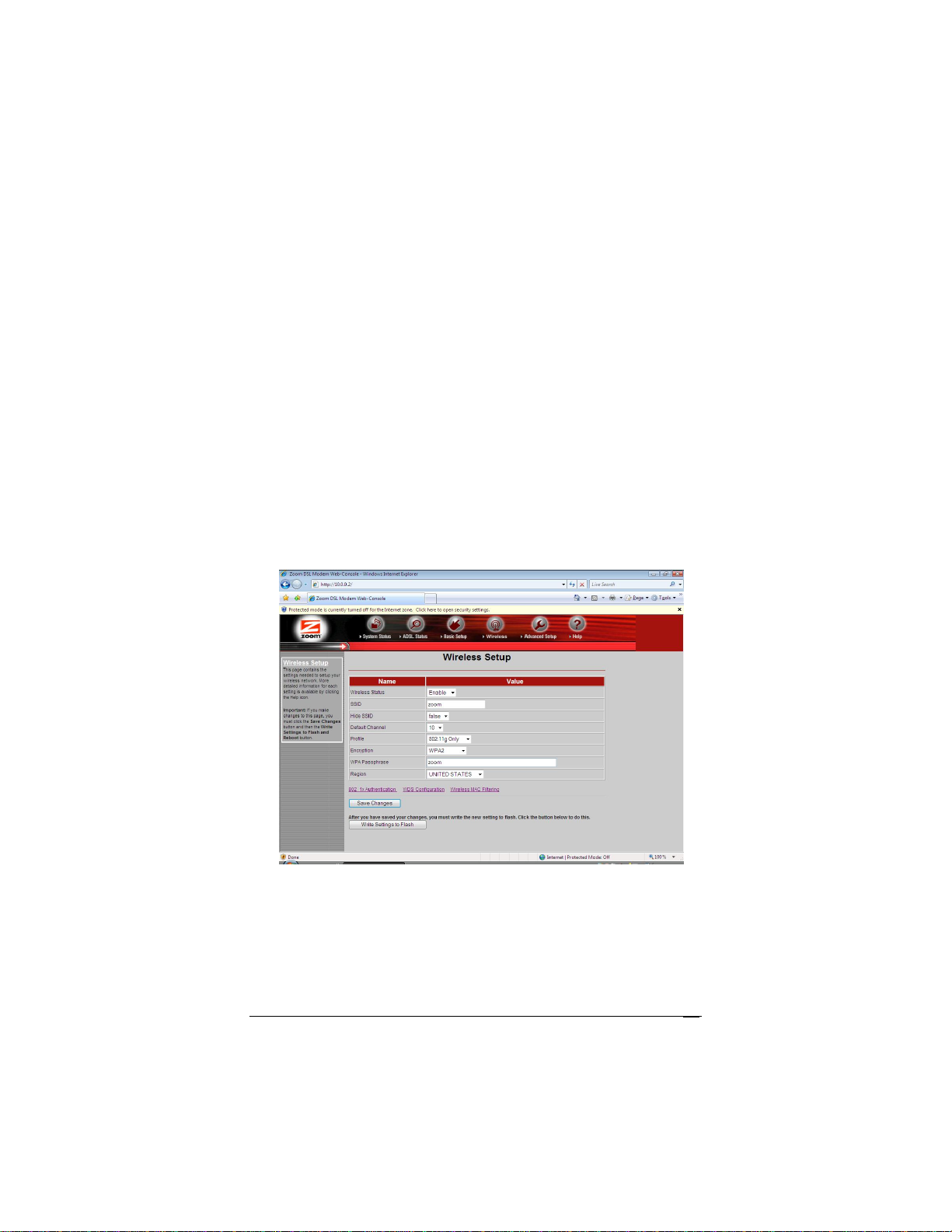
Setting Up Security Using WPA2 or WPA
WPA2 and WPA use a passphrase that you choose and enter on
the X6 and other wireless devices on the network (clients) to set up
security. To use WPA2 or WPA, all of the wireless devices on your
network must support that encryption method.
1 Check to see that all other clients that you plan to put on the
network support WPA2 or WPA. If they do not, skip to
Setting Up Security Using WEP.
2 Click the Wireless icon in the Zoom Configuration Manager.
This will open the Wireless Setup page. Go to Encryption
(which should say None) and select WPA2 or WPA from the
drop-down menu. A new fill-in box labeled WPA Passphrase
will open directly below the Encryption box.
3 Choose and enter a Passphrase. You can enter a word or
phrase, or for greater security you can enter a combination of
numbers and letters. The Passphrase is case-sensitive and can
be up to 8 characters.
Chapter 3: Setting Wireless Security
27
Page 28

4 Every wireless network client needs to be set individually by
entering the Passphrase on all wireless devices on the
network. Open the software that came with the device, which
should be running on the computer where the device is
installed. Find the configuration menu for security, choose
WPA2 or WPA, and enter the Passphrase, exactly as you
entered it on the
Your security setup configuration is now complete!
X6 Wireless Setup page.
28
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 29
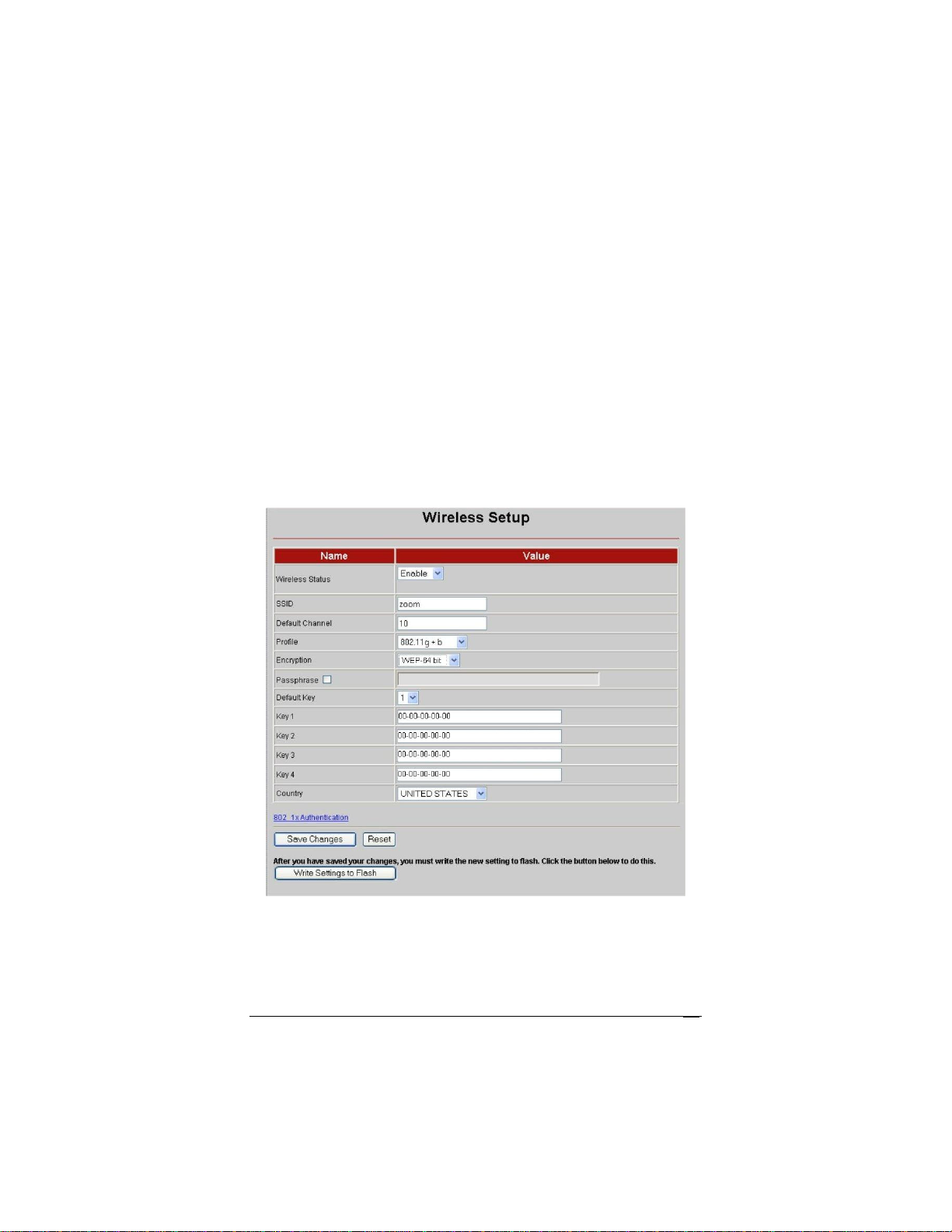
Setting Up Security Using WEP
If all of your network devices DO NOT support WPA2 or WPA,
you can use WEP to configure network security. WEP can be
configured two ways: 64-bit and 128-bit. 128-bit WEP provides a
bit more security than 64-bit, but 128-bit WEP also tends to
diminish network performance. We recommend that most people
configure their WEP for 64-bit security.
1 Click the Wireless icon in the Zoom Configuration
Manager. This will open the Wireless Setup page. Go to
Encryption (which should say None) and select WEP-64 bit
(or WEP-128 bit for more security, but diminished network
performance) from the drop-down menu. Six new boxes open
directly below the Encryption box.
2 Check the box marked Passphrase and then choose and enter
a Passphrase. You can enter a word or a phrase, or for greater
security you can enter a combination of numbers and letters.
The Passphrase is case-sensitive and can be up to 8 characters.
Chapter 3: Setting Wireless Security
29
Page 30

If ALLof the wireless devices (clients) on the network are Zoom
devices, go to step 3. If some or all or the devices are not Zoom
devices, go to step 4.
3 If ALL of the wireless devices (clients) on the network are
Zoom devices, you need to enter the Passphrase that you
just entered for each device.
Every wireless network client needs to be set individually.
Open the software that came with the device, which should be
running on the computer where the device is installed. Find the
configuration menu for security, choose WEP, and enter the
Passphrase, exactly as you entered it on the
Setup page.
Your security setup configuration is now complete!
X6 Wireless
4 If any or all of the other wireless devices on the network
(clients) are not Zoom devices, you will enter one of the
keys shown below the Passphrase on each client. You must
enter the same key for each device. The key that you must use
is the key corresponding to the Default Key number shown. If
the number in the default key box is 1, use Key 1, and so on.
You can choose the default key you prefer using the pull-down
Default Key menu box.
Now that you have a key, enter it for each client. Every
wireless network client needs to be set individually. Open the
software that came with the device, which should be running
on the computer where the device is installed. Find the
configuration menu for security, choose WEP (64-bit or 128-
bit depending on what you selected), and enter the Default
Key, exactly as it appears on the
Your security setup configuration is now complete!
X6 Wireless Setup page.
30
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 31

4
The X6 and Online Gaming
This chapter covers the set up of the X6 for online gaming with
a desktop, notebook, Xbox® Live, or Playstation® 2.
Do I Need to Do Anything?
There are three cases where you need to set up your modem in
order to play online games:
•
If you are using your computer to play a peer-to-peer or headto-head game over the Internet, you always have to set up the
modem unless you linked up to your partner by going to a
Web site. A peer-to-peer game is a game where two players are
competing directly against one another. Popular peer-to-peer
games include Age of Empires, Command and Conquer,
Dark Reign 2, and Unreal Tournament. If you are unsure
whether your game is a peer-to-peer game, check the game
instructions.
If you are using your computer to play a multi-player game
•
and you want to host the game. Popular multi-player games
include Half Life, Diablo II, Delta Force, Hexen II, Myth,
Quake II, and Warcraft II, III.
If you are playing an online game using Xbox® Live or
•
PlayStation® 2.
In all three cases you will need to do the steps described in the
next section,
Setting Up the X6 for Online Gaming.
Chapter 4: The X6 and Online Gaming
31
Page 32

Setting Up the X6 for Online Gaming
Setting up the X6 for online gaming involves two basic steps:
Choosing an IP Address for Gaming and Setting Up a Virtual
Server or DMZ. This section provides instructions for doing these
tasks on your computer, Xbox®, or Playstation® 2.
Step 1: Choosing an IP Address for Gaming
You need to make sure that the computer or gaming system you
use for playing games always has the same IP address. By default,
the X6 assigns addresses dynamically (using Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol or DHCP) to the devices on the local area
network whenever they reboot. Therefore, the addresses won’t
necessarily always be the same. The modem, however, can be set
up to assign the same address to your computer or gaming system
every time.
To ensure that your computer or gaming system always uses the
same address, follow the steps below.
1 If you are using Xbox or PlayStation 2, connect the device to
your modem with an Ethernet cable. On your TV screen,
locate Network Settings and select Connect.
2 Click the Advanced Setup icon in the Zoom Configuration
Manager.
32
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 33

3 On the Advanced Setup page, click the LAN Configuration
button. Next click the Add DHCP Fixed Host button. The
Create New DHCP Server Fixed Host page appears:
4 Before you can enter an IP address, you need to enter the
MAC (Media Access Control) address of your computer or
gaming system. Follow the next set of instructions for your
gaming system to find the gaming system’s MAC address.
Chapter 4: The X6 and Online Gaming
33
Page 34

If you are using a computer to play an online game:
¾ If you know the name of your computer or if you have
only one computer connected, you can find the MAC
address under DHCP Clients at the bottom of the Create
New DHCP Server Fixed Host page. You can also find
the MAC address on the System Status page. Click the
System Status icon and scroll down until you see DHCP
Client Status.
¾ If you do not know the name of your computer or you
have more than one computer connected, follow these
steps to find the MAC address:
a
Go to the computer you want to use for gaming.
b
Click the Start button and select Run.
c
In the Run dialog box, type command and click OK
to open the Command or MS-DOS window.
d
In the Command Prompt or MS-DOS window
(after C:\> or C:\WINDOWS>), type ipconfig, leave
a space, then type /all
It should look like this: ipconfig /all
e
Press Enter. The MAC address is displayed as the 12digit Physical Address or Internet Adapter address.
Go to Step 5.
34
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 35

If you are using Xbox® Live to play an online game:
a
You can find the MAC address on the Xbox
Dashboard in the lower right corner of the Network
Settings menu. You will see something like
MAC=0050F24ADC29. Your address will be
different. You will also need to assign an IP address
now. To do this, on the Xbox Network Settings
menu select IP Addresses.
b
On the IP Addresses screen, enter the following:
Configuration Manual
IP Address 10.0.0.50
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Gateway 10.0.0.2
c
Press B to go back to the Network Settings menu.
d
On the Network Settings menu, select DNS
Servers.
e
On the DNS Servers screen, enter the following:
Configuration Manual
Primary DNS 10.0.0.2
Alternate DNS 10.0.0.2
f Press B twice to return to the main menu. Then go to
Step 5.
Chapter 4: The X6 and Online Gaming
35
Page 36

If you are using PlayStation® 2 to play an online game:
a
Insert your Network Access Disc into the PlayStation.
b
On the main menu, select ISP Setup, then I have an ISP,
then Automatic Configuration.
c
On the Select an Internet service provider menu, select
Other.
d
On the Connection Test menu, select Advanced. The
MAC address is displayed on the Advanced Broadband
Settings screen.
e
Now, to configure the Playstation 2’s network settings, on
the main menu select ISP Setup again. If a message
displays, press X to disconnect from the Internet.
f
On the Edit Network Setting menu, select New
Network Setting.
g
On the Connect to the Internet menu, select Local Area
Network.
h
On the Local Area Network Setup menu, select
Automatic Configuration.
i
On the Connection Test menu, select Test Settings.
j
At the Test for connecting to your ISP was successful
message, select Continue. Then follow the instructions to
save your settings and return to the main menu. Now go
to Step 5.
36
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 37

5 Now that you have determined the MAC address, you can
assign your computer or gaming system an IP address. On the
Create New DHCP Server Fixed Host page, make these
entries:
Setting Values
IP Address Enter 10.0.0.50. If you are setting up more
than one computer or gaming system, you
should use different IP addresses. For
example, if you are setting up a Xbox and
a computer, enter 10.0.0.50 for the Xbox,
and 10.0.0.51 for the computer.
MAC
Address
Maximum
Lease Time
Type the MAC address from Step 4.
Leave the default setting.
6 Click Save Changes and then Write Setting to Flash to save
the IP address to permanent memory. Now your computer or
gaming system will always be assigned this address.
Chapter 4: The X6 and Online Gaming
37
Page 38

Step 2: Setting Up a Virtual Server or DMZ
You set up either a virtual server or a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone)
so that the modem’s firewall won’t block the other players from
your system during your gaming. The main difference between the
virtual server and the DMZ is the amount of access someone has
to your system.
A virtual server will allow access to your computer on certain ports.
A port is like a channel that is used by applications (such as games)
to communicate on. For example, the directions for the game you
want to play over the Internet might tell you to open up port 6000.
A DMZ differs from a virtual server in that it allows access on all
ports to the computer. Because of this, DMZ's are less secure than
virtual servers and should be used with caution on your computer.
For Xbox® Live and Playstation®2, a DMZ is OK since security is
not as much of an issue as it is for your computer.
•
If you are playing a peer-to-peer or multi-player game on
your computer, go to
on Your Computer
•
If you are using Xbox Live, go to
Xbox® Live
•
If you are using Playstation 2, go to
Playstation® 2
38
ADSL X6 User Guide
page 41.
Setting Up a Virtual Server or DMZ
on page 39.
Setting Up a DMZ on a
Setting Up a DMZ on a
on page 43.
Page 39

Setting Up a Virtual Server or DMZ on Your Computer
Note:
If you have third-party firewall software, such as the Windows XP
firewall, installed on your computer, you may need to deactivate it
before setting up the virtual server or DMZ. Otherwise your
computer may block the ports you want to open.
1 Click the Advanced Setup icon. Then, click the Virtual
Server/DMZ button:
2 On the Virtual Server/DMZ page, click the Add Virtual
Server/DMZ link to display the Add Virtual Server/DMZ
page:
Chapter 4: The X6 and Online Gaming
39
Page 40

3 Make the following entries:
Setting Values
IP Address Enter the IP address that you specified on
the Create New DHCP Fixed Host
Server page.
Transport
Type
(Protocol)
Ports
If you know your protocol (udp or tcp)
and port number(s) from your game
instructions, select the protocol from the
list.
If you do not know your protocol or port
number(s), you need to set up your
computer as a DMZ by selecting DMZ
from the Protocol list. This will open up all
ports on the computer to all
communication over the Internet.
Warning: Setting up a DMZ removes the
protection provided by the ADSL
Ethernet’s firewall. We therefore
recommend that a DMZ be used only when
necessary.
If you designated your computer as a
DMZ, you do not have to enter anything
here.
If you are playing another peer-to-peer
or multi-player game, your game
instructions should tell you what ports to
enter here. To enter a number, you must
enter tcp or udp in the Protocol box.
If you need to enter multiple ports, add a
new virtual server for each port. If you have
several ports to enter, you may wish to set
up your PC as a DMZ.
The highest supported port number is
65535.
4 Click Save Changes and then Write Settings to Flash.
Your set up is complete!
40
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 41

Setting Up a DMZ on a Xbox® Live
1 Click the Advanced Setup icon. Then, click the Virtual
Server/DMZ button:
2 On the Virtual Server/DMZ page, click the Add Virtual
Server/DMZ link to display the Add Virtual Server/DMZ
page:
3 Make the following entries:
Setting Values
IP Address Enter the IP address that you specified on
the Create New DHCP Fixed Host
Server page.
Transport
Type
(Protocol)
Ports The field remains unavailable because you
Chapter 4: The X6 and Online Gaming
Select DMZ to enable your Xbox as a
DMZ.
selected DMZ. No entry is required.
41
Page 42

4 Click Save Changes and then Write Settings to Flash.
5 Update the Xbox Dashboard:
Make sure you have your Xbox Live Starter Kit at hand. Insert
the Xbox Live CD into your Xbox. Once the update is
complete, the main menu will include a Xbox Live entry.
6 Insert the Xbox Communicator module into the Xbox
Controller expansion slot (top slot). Then insert the headset
plug into the Communicator module.
7 Activate your Xbox Live account:
The Xbox Live CD should still be in your Xbox. We
recommend that you watch a video that explains the
installation process: Select Xbox Live from the menu. Then
from the Dashboard, select Xbox Live and follow the
prompts. Note: You will need your subscription code to
activate your account—this number is located on the CD’s
sleeve. (If you require more detailed instructions, please refer
to your Xbox Live documentation.)
Your setup is complete!
42
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 43

Setting Up a DMZ on a Playstation® 2
1 Click the Advanced Setup icon. Then, click the Virtual
Server/DMZ button:
2 On the Virtual Server/DMZ page, click the Add Virtual
Server/DMZ link to display the Add Virtual Server/DMZ
page:
Chapter 4: The X6 and Online Gaming
43
Page 44

3 Make the following entries:
Setting Values
Internal IP
Address
Enter the IP address that you specified on
the Create New DHCP Fixed Host
Server page.
Transport
Type
(Protocol)
Ports The field remains unavailable because you
Select DMZ to enable your Playstation as a
DMZ.
selected DMZ.
4 Click Save Changes and then Write Settings to Flash.
Your setup is complete!
44
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 45

5
Using Advanced Setup
Advanced Setup is primarily for technically advanced users. For
most people, the options that are set by default when the
installed are sufficient.
X6 is
However, those who want or need to change the
can do so using the Advanced Setup page in the Zoom
Configuration Manager. This chapter explains the advanced
options and features of the
to your network.
The information in this chapter applies to you if:
•
Your Internet service provider instructs you to enable,
disable, or change the default settings for your
You need to change your Wide Area Network settings
•
•
You want to change the default firewall settings to block
particular IP addresses and intrusive hosts
•
You want to change your ADSL password
•
You have customized your configuration and want to back
it up for future use or apply it to additional modems
You want to set up fixed IP addresses for your computer(s)
•
Note: Users who want to set up Quality of Service (described
in this section) can do so more easily using the Zoom Install
Assistant.
X6 modem and how to apply them
X6 settings
X6
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
45
Page 46

Viewing the Advanced Setup Options
You open the Advanced Setup page by clicking the Advanced
Setup icon at the top of the Zoom Configuration Manager. The
page opens and displays buttons organized into three groups:
Configuration, Status, and Administration:
Configuration Options
When you click a Configuration button, a page opens to the
option you selected. The following table describes each option and
the tasks you can perform.
This button… Opens a page that lets you…
WAN
Configuration
46
ADSL X6 User Guide
Specify how the Wide Area Network (WAN) ADSL
setup is configured. Some of the values need to
be supplied by your ISP/DSL provider.
Page 47

This button… Opens a page that lets you…
Firewall
Define an additional layer of security for the
computers in your network. For example, if you
create a DMZ interface using the Virtual
Server/DMZ page (see below), you can enable
the firewall filtering and add a security policy that
blocks certain protocols from reaching the DMZ
machine.
ADSL
Configuration
Adjust the ADSL settings on your modem.
Typically, you do not need to change these ADSL
settings unless instructed by your service
provider.
Ethernet
Configuration
View and change the settings on the Ethernet
ports on your
X6. Typically you should not need to
change these settings.
DNS
Allows you to specify multiple DNS servers.
Typically, most users do not need to enter a DNS
server unless instructed by their ISP.
LAN
Configuration
Specify the settings that control the connection
between the
X6 modem and your Ethernet jack.
Set a fixed IP address for your computer.
Routing Table
Set up the routes on which you want the X6 to
send data that it receives on a particular interface,
such as a LAN or Ethernet interface. Routes
specify the IP address of the next device,
interface, or Internet destination to forward data
to, based on the ultimate destination of the data.
Virtual
Server/DMZ
Open access to your computer by creating a
virtual server or a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone). By
default, your modem uses NAT (Network Address
Translation) to hide your networked computers
from users on the Internet. However, there are
times when you may want to give outside access
to the computers in your network. If so, you can
set up a virtual server or DMZ to allow outside
users access to a computer on your network. You
may want to allow access, for example, if a LAN
computer is hosting Internet games or running a
Web server.
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
47
Page 48

This button… Opens a page that lets you…
PPP Half
Bridge
UPnP
(Universal Plug
and Play)
Per Port PVC Assign a LAN port to a Permanent Virtual Circuit
Port Settings
MAC Filtering
Management
Control
QoS (Quality
of Service)
Share the public IP address assigned by your ISP
with a single PC on the LAN. This avoids
problems caused by certain applications having to
work through NAT (such as online games or FTP
servers) and avoids the need to run a PPP
software stack on the PC.
Connect automatically with other UPnP-enabled
software and hardware. The Internet Gateway
Device (IGD) protocol makes it possible for
applications running on the network to
automatically configure NAT routing.
(PVC). This feature is commonly used for
delivering video.
Conveniently change the default port settings.
You will need to use this feature if the X6 is
hosting a web server or a Telnet server.
Prevent network devices with the specified MAC
addresses from accessing the Internet.
Enable or deny access to X6 services – HTTP,
Telnet, UPnP, SNMP, TFTP – to local network
devices and/or remote users.
Assign each port (LAN ports 1-4 and the wireless
port) a priority of High or Medium. This lets you
assure better performance for gaming and VoIP,
for example.
Status Options
The Status buttons open reports that provide real-time
information about your connections and networks. The reports
refresh themselves to give you the most current information.
Typically, these reports are used for maintenance purposes and
troubleshooting.
The following table describes each report in the Status group:
48
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 49

This button… Opens a page that lets you…
ADSL Status
Wireless
Status
Ethernet
Status
View information, such as the ADSL Line State,
and Upstream and Downstream speeds.
View information, such as your Link Speed, SSID,
Default Channel, and Mac Address of your
wireless computer.
View information about Rx (Receive) and Tx
(Transmit) Packets.
To see sample reports, go to page
86.
Administration Options
The buttons in the Administration group are typically used for
administrative tasks, such as updating the modem’s firmware,
changing your Zoom Configuration Manager password, putting
back your modem’s configuration file.
The following table lists each button in the Administration group
and gives a brief description of the things that you can do with that
feature.
This button… Opens a page that lets you…
Admin Password
Firmware Update
System Log
Restore Factory
Change the password to the Zoom
Configuration Manager. The original user
name and password are:
User name: admin
Password: zoomadsl
Specify the path to the upgrade file you
need to update your firmware. Use the
Browse button on this page to navigate to
the file, then click the Upload button to
perform the firmware update.
View data generated or acquired by routine
system communication with other devices.
This information does not necessarily
represent unexpected or improper
functioning and is not captured by the
system traps that create alarms. You can
save the system log to a file.
Reboot the
X6 and reset its configuration to
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
49
Page 50

Settings
Backup/Restore
Config
the factory defaults.
Save your current configuration settings so
that they may be restored at a later time.
Using the WAN Configuration
Settings
When do I need the WAN Configuration page?
The WAN Configuration page contains critical information about
your Wide Area Network (WAN), ADSL setup, and Internet
access. Some of these values are provided by your ISP/DSL
provider and need to be entered on this page. To determine if you
need to add other values, read the table descriptions that follow the
picture. Note that Protocol, Encapsulation, VPI, VCI, PPP, and
NAT also appear on the Basic Setup page. Most likely you have
already entered values for these settings and only need the WAN
Configuration page for setting up an advanced feature such as
enabling a disconnect timeout on your PPP connection.
50
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 51

WAN Configuration page
The table on the next page describes the settings on the WAN
Configuration page and the values that you can enter. After you
enter your values, click Save Changes and then Write Settings to
Flash.
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
51
Page 52

Note: The table shows settings in addition to the ones shown in
the picture. Depending upon your protocol setting, your WAN
configuration may have all or only some of the settings shown in
the table.
Setting Description
Protocol (Internet
Connection type)
Encapsulation
VPI Virtual Path Identifier ranges from 0 – 256.
VCI Virtual Circuit Identifier ranges from 0 –
Username
Password
Service Name
Your Internet Service Provider supplies this
value.
If your service provider instructs you to use
1483 Bridged mode, select 1483 Bridged
+ NAT to take advantage of your modem’s
advanced routing and firewall features.
The encapsulation value should match your
DSL provider’s encapsulation. The value
refers to the way that data is passed over
the Internet. An example value is LLC
(Logical Link Control). Your DSL provider
supplies this value when you sign up for
ADSL service.
Your DSL provider supplies the VPI when
you sign up for ADSL service.
65536. Your DSL provider supplies the VCI
when you sign up for ADSL service.
Your DSL provider supplies this username
when you sign up for ADSL service. (It is
not the same as the username and
password for the Zoom Configuration
Manager.)
Your DSL provider supplies this password
when you sign up for ADSL service.
This is an optional value that your service
provider may ask you to enter.
52
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 53

Setting Description
Disconnect timeout
The amount of time before the PPP
connection drops if there is no activity. A
value of 0 means stay connected even if
your network stays idle.
Authentication
The type of authentication protocol used
during the negotiation of the PPP
connection. This protocol may be specified
by your ISP. One option, CHAP (Challenge
Handshake Authentication Protocol),
encrypts your user name and password
during the negotiation. Password
Authentication Protocol does not.
NAT
Network Address Translation. By default,
this setting is Enabled. NAT keeps a table
of individual private IP addresses in your
network and refers to the table when
incoming requests are made. If no matches
are found, the incoming data cannot come
into your network. An Enabled setting
keeps your IP addresses hidden from
outside users. Disabled is some times
used if you want to use Public IP
addresses.
MTU
Maximum Transmission Unit. Largest
physical packet size, measured in bytes,
that the modem can send. Any messages
larger than the MTU have to be fragmented
before being sent.
Obtain IP Address
Enable this button if your service provider
is using DHCP and you are using the 1483
protocol. If you are unsure of what your
service provider is using select this button.
Specify an IP
Address
Enable this button if you are using a static
IP address and you are using 1483
protocol. Typically you have to request and
pay extra for a static IP address.
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
53
Page 54

Setting Description
IP Address, Subnet
Mask, Default
Gateway, and DNS
Ethernet Filter Type
ATM
Traffic Class
Peak Cell Rate
Burst Tolerance
Max Cell Rate
Max Burst Rate
Sustainable Cell
Rate
If you are using a Static IP address, enter
the values for IP Address, Subnet Mask,
Default Gateway, and DNS server that
your service provider gave you. You must
also be using the 1483 protocol.
Specifies the type of Ethernet filtering that
is performed by the bridge interface. All-
Allows all types of Ethernet packets
through the port. Ip-Allows only IP/ARP
types of Ethernet packets through the port.
PPPoE-Allows only PPPoE types of
Ethernet packets through the port.
These settings allow you to give priority to
data that is sent over the network.
Important! You must make arrangements
with your DSL provider to use anything
except UBR (Unspecified Bit Rate) in the
Traffic Class setting. Your service provider
will also supply you with the Cell, Burst,
and Tolerance Rates.
54
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 55

Setting Description
RIP
RIP is an Internet protocol that you can set
up to share routing table information with:
•
LAN devices that support RIP
•
Remote networks connected via the
ADSL line
•
Your ISP’s location
Most small home or office networks do not
need to use RIP since they have only one
router and one path to an ISP. In these
cases there is no need to share routes
because all Internet data from the network
is sent to the same ISP gateway.
You may want to configure RIP if any of the
following circumstances apply to your
network:
•
Your home network setup includes an
additional router or RIP-enabled PC or
device. These routers will need to
communicate via RIP to share their
routing table information.
Your network connects via the ADSL
•
line to a remote network, such as a
corporate network. In order for your
modem to learn the routes used within
your corporate network, they should
both be configured with RIP.
•
Your ISP requests that you run RIP for
communication with devices on their
network
Accept V1
Accept V2
Sent V1
Accept Version 1 of the RIP protocol.
Accept Version 2 of the RIP protocol.
Send Version 1: Send RIP information to
other RIP-enabled devices.
Sent V2
Send Version 2: Send RIP Information to
other RIP-enabled devices.
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
55
Page 56

Using the Ethernet Configuration Settings
Do I need to change my Ethernet settings?
The Ethernet Configuration page contains information about the
Ethernet ports on your ADSL modem. Typically you should not
need to change these settings. However, if you are having problems
establishing your Ethernet connection, you may need to change the
Speed/Duplex value to match that of the Ethernet NIC in your
computer. Here is a picture of the Ethernet Configuration page:
The following table describes the Ethernet Configuration settings.
If you change any of the settings, click Save Changes, and then
Write Settings to Flash.
Setting Description
Port
Configuration
56
ADSL X6 User Guide
The Ethernet Ports 1-4 on the back of your
modem.
Shows how your Ethernet ports are set up.
Page 57

Setting Description
Linked
Speed/Duplex
A check mark indicates that the Ethernet
port is connected.
If you are having problems establishing
your Ethernet connection, try setting the
Speed/Duplex value to match that of the
Ethernet NIC in your computer.
Setting Up a Static Routing Table
Do I need static routing?
Most users do not need to set up static routes. The default route
used in your modem will forward all packets correctly. However, if
you set up your network with different subnets, you can use static
routing to ensure your packets are handled correctly.
You can manually create a static route to tell the modem how to
reach a specific IP network. The route entry specifies a destination
network (or single host), together with a mask to indicate what
range of addresses the network covers, and a next-hop gateway
address or interface. If there is a choice of routes for a destination,
the route with the most specific mask is chosen.
To route to a destination that is not on any local network, a route
may be added via a gateway, for instance another router. The
gateway IP address must be on the same subnet as one of the
router's interfaces. Here is a picture of the Static Routes page:
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
57
Page 58

The following table describes Routing Table settings. If you change
any of the settings, click Add, and then Write Settings to Flash.
Setting Description
Existing Routes
Destination Enter the subnet IP address of the
Gateway Enter the Gateway IP address of your
Mask Enter the subnet mask (range of IP
Metric
Advertise
This table shows the existing Static routes
set up on your ADSL Modem.
destination.
destination’s subnet. The HOP gateway
must be on the same subnet as the
modem.
addresses) of the destination IP addresses
based on the above subnet IP address of
the destination.
The number of hops. This should usually
be left at 1.
Enable this if you want to advertise this
route.
58
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 59

Adding Extra Security with Advanced Firewall Filtering
Do I need extra security?
Setting up advanced firewall security provides an additional layer of
security. For example, if you create a DMZ interface for gaming
using the Virtual Server/DMZ page, you can enable the firewall
filtering and add a security policy that blocks IP addresses, ports,
aliases, and certain protocols from reaching the DMZ machine.
When you use the Advanced Firewall Filtering feature, you will
move through multiple screens. Follow the steps below to set up
this feature.
1 Open the Firewall Configuration page by clicking Firewall
on the Advanced Setup page:
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
59
Page 60

2 Important! Do not Enable Advanced Firewall Filtering on
the Firewall Configuration page until you create your security
policy. Otherwise, if you Enable Firewall Filtering before
you create your policy, you will block all outgoing and
incoming traffic. To set up your policy, click the link to
Security Policy Configuration and open the page.
3 Choose the Policy Type that you want then click the Policy
Rules link. You can set one of three Policy Types. Choose
the External – Internal policy to allow or block what is sent
from the WAN to the LAN. Choose the External –DMZ
policy to allow or block what is sent from the WAN to the
DMZ machine or the Virtual Server. Choose the DMZ-
Internal policy to allow or block what is sent from a DMZ
machine to your LAN.
60
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 61

4 Click the Policy Rules link of the Policy Type that you want.
The Firewall Add Filter Rules page opens. Click the Add
Policy Rule link.
5 After you click the link, the Firewall Add Policy Rule page
opens:
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
61
Page 62

You use the settings on the Firewall Add Policy Rule page to
configure your firewall security. In setting your criteria or rules, it is
important to know whether you want to block traffic or allow
traffic into your network. This is controlled by the Traffic
Inbound and Traffic Outbound settings where you choose Allow
or Block. After you determine what you want to do, you then fill
in the other settings to specify what it is that you want to block or
allow.
Suppose you enter Allow in the Traffic Inbound and Outbound
settings and Any in the Src Address setting. This sets the firewall
to allow any traffic into your network. Conversely, suppose you
choose Block for Traffic Inbound, choose Assign for Src
Address and specify a range of IP addresses. This sets the
firewall to block all traffic that has the IP addresses you specified.
The table that follows shows you the criteria that you can enter:
Setting Description
Src Address Source Address lets you specify Any for all
IP addresses or a specific range of IP
addresses from a particular source to be
blocked or allowed.
Des Address Destination Address lets you specify Any
for all IP addresses or a specific range of
IP addresses of a destination to be blocked
or allowed.
Protocol
Source Port
Destination Port
Traffic Inbound
Traffic Outbound
Protocol lets you specify a protocol to be
blocked or allowed. eq is equals and neq is
not equal. For example, eq TCP will allow
only TCP. neq TCP will allow everything
including TCP.
Lets you block or allow traffic from a
particular port.
Lets you block or allow traffic going to a
destination port.
Lets you block or allow inbound traffic
based on the rules you set up in the policy.
Lets you block or allow outbound traffic
based on the rules you set up in the policy.
6 Click Save Changes then Write Settings to Flash.
62
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 63

7 Go back to the Firewall Configuration page and select
Enable. Then click Write Settings to Flash.
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
63
Page 64

Setting Security Logging
What is security logging?
Security logging is a list of events (computer activity and user
activity) that alerts you to potential security issues. Based on the
Level selected, you can record all or some of these events. It also
lets you examine the effectiveness of your blocking and intrusion
detection. You can set the level of importance of the logged event
and receive alerts if particular IP addresses are trying to gain access
to your network.
To set security logging on, follow these steps:
1 Click Firewall on the Advanced Setup page. Then, click the
link to Configure Security Logging. The Security Logging
page opens:
2 Enable the Logging Types that you want and set the Level.
You can also print (Output to) the information to your
console or to a file (Event Log).
64
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 65

Configuring Intrusion Detection
What is intrusion detection?
Intrusion detection protects your network from hackers who use
the Internet to damage your network. Your modem’s default
Intrusion Detection setting should work fine for most hacker
attacks, but there is additional functionality that you can set up.
Your modem offers protection from various Denial of Service
(DOS) attacks; prevents users from scanning your ports to try to
access your computer; and can blacklist any host trying to damage
your network.
Follow these steps to enable additional intrusion detection:
From the Advanced Setup page, click Firewall. Then click the
link to Configure Intrusion Detection. The Configuration page
opens:
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
65
Page 66

The following table shows you the values you can enter:
Setting Description
Use Blacklist
Victim Protection
Block Duration
Use Victim
Protection
DOS Attack Block
Duration
Scan Attack Block
Duration
Maximum TCP Open
Handshaking Count
Maximum Ping
Count
Maximum ICMP
Count
Blacklisting denies an external host access
to your computer/network if an intrusion
from a host has been detected. Access to
the network is denied for ten minutes.
The length of time that packets destined for
the victim of a spoofing attack are blocked.
Protection for your system against
broadcast pings. An attacker sends out a
ping with a broadcast destination address
and a spoofed source address.
Packets destined for the victim of a
spoofing attack are blocked for a specified
duration.
The duration that hosts are blocked once a
Denial of Service (DOS) attack is detected.
The length of time that traffic from IP
addresses doing the port scan are blocked
once a port scan is detected. Port scans
are used to determine if you have any open
ports that can be accessed.
Sets the maximum number of TCP open
session requests allowed per second
before a SYN flood attack is detected. SYN
Flood is a specific type of DOS attack.
Sets the maximum number of pings per
second before an Echo Storm is detected.
Echo Storm is a DOS attack where the
attacker sends oversized ICMP datagrams
to the network using the ping command.
Sets the maximum number of ICMP
packets per second before an ICMP Flood
is detected. ICMP Flood is a DOS attack
where the attacker tries to flood the
network with ICMP packets in order to
prevent legitimate network traffic.
66
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 67

Adding a DNS Server Name
Do I need to add a DNS server name?
Typically you should not need to enter a DNS server name as it is
assigned automatically when your connection is established.
However, your ISP may instruct you to enter an IP address for a
DNS server name. Here is a picture of the DNS page where you
add the IP address:
The following table shows you the values to enter. After you enter
the value, click Add, then Write Settings to Flash.
Setting Description
DNS Server List
New DNS Server IP
Address
Shows the list of currently configured DNS
servers.
Enter the IP address of the DNS server
that your ISP instructed you to enter.
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
67
Page 68

Creating a Virtual Server or a DMZ
Do I need to create a virtual server or DMZ?
By default, your modem uses NAT to hide your computers from
users on the Internet; however, there may be times when you want
to allow access by outside users to a computer on your network.
For instance, you would want to allow access if a computer in your
network is hosting Internet games or running a web server. For
more information about the Virtual Server/DMZ feature and the
differences between a virtual server and a DMZ, see page
information about setting up a Virtual Server or DMZ for gaming,
Setting Up the X6 for Online Gaming on page 32.
see
Here is a picture of the Virtual Server/DMZ page:
38. For
68
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 69

Clicking the Add Virtual Server/DMZ link opens the Add
Virtual Server/DMZ page:
The following table shows you the values you can enter. After you
enter the value, click Save Changes, then Write Settings to
Flash.
Setting Description
Internal IP Address
Transport Type
(Protocol)
The IP address of the computer where you
will set up the virtual server or DMZ.
Note: You should use fixed IP mapping to
ensure that the computer you are setting
up as the virtual server or DMZ is always
assigned the same IP address by your
modem's DHCP server. To assign a fixed
IP map, see
Address for Gaming
Select the protocol that you want to allow
through to the computer. Select DMZ if you
want to allow all protocols and all ports to
be open on the computer.
Step 1: Choosing an IP
on page 32.
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
69
Page 70

Setting Description
Port If you selected TCP or UDP, you must
specify the port where you want to allow
access. If you want multiple ports to be
open, add a virtual server for each port that
you want open. If you selected DMZ, you
cannot specify a port.
Using the ADSL Settings
Do I need to change my ADSL settings?
Typically you should not need to change your ADSL settings;
however, you may be instructed to do so by your service provider.
Or, if you are having problems establishing a physical layer
connection, you may want to change a couple of the settings on the
ADSL Configuration page. Here is a picture of the ADSL page
where you change your settings:
The following table shows you the values to enter. After you enter
the values, click Save Changes, then Write Settings to Flash.
70
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 71

Setting Description
Standard
EC/FDM Mode
Activate Line Select None if there are no changes to the
If you are having problems establishing the
physical layer connection, you can try
selecting the different settings to see if it
helps you connect. (If the link light on the
modem is blinking than the physical layer
connection is down, if the link light is solid
than the problem is elsewhere.)
If you are having problems establishing the
physical layer connection than you can try
changing this value to EC.
current mode.
Select Abort if you want to stop the
modem from connecting. The status will
show up as idle on the ADSL Status page.
Select Start to restart the connection.
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
71
Page 72

Changing Your LAN Settings
When would I need to change my LAN settings?
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a protocol that
enables your modem to manage the assignment of IP addresses to
computers and devices on your LAN network. Enabling DHCP on
your modem allows it to assign temporary IP addresses to your
computers whenever they connect to your network. You can
control the amount of time that lapses before a new address is
issued or renewed. You can extend the range of IP addresses that
are assigned to your network devices should you add new devices
to your network. You can also change the default LAN IP address
for your modem.
Here is a picture of the LAN Configuration page:
72
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 73

The following table shows you the values to enter. After you enter
the values, click Save Changes, then Write Settings to Flash.
Setting Description
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Status You should leave this setting on Enable.
Maximum Lease
Time
Default Lease Time
Start IP Address
End IP Address
The IP address of your modem.
The modem's subnet mask address.
Disable would require you to set up fixed IP
addresses for all of the devices in your
network.
The maximum amount of time, in seconds,
that a device in your network will have the
temporary IP address before a new one is
issued by the modem’s DHCP server.
(86,400 seconds equals 24 hours)
The Default amount of time that your
modem's DHCP server will assign an IP
address.
The first IP address of a range that you
specify using the Start and End IP Address
settings. Your modem's DHCP server will
assign the IP addresses in this range at
random to the computers and devices in
your network
The last IP address of a range that you
specify using the Start and End IP Address
settings. Your modem’s DHCP server will
assign numbers from this range at random
to the computers and devices in your
network. By default the DHCP server has
12 addresses available to assign. If you
plan on attaching more than 12 devices to
your network, change the ending IP
address to allow for more devices.
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
73
Page 74

Creating a Fixed IP Address
How do I create a fixed IP address?
You create a fixed IP Address for a computer on your network
using the DHCP Server Fixed Host page. The button to this
page is found on the LAN Configuration page.
You will want to create a fixed IP Address if you are setting up a
computer, Xbox, or Playstation for gaming. To create a fixed IP
address, see steps 2-6 in
Gaming
on page 32.
Step 1: Choosing an IP Address for
74
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 75

Assigning a Half Bridge Device
When would I assign a half bridge device?
Assigning a PPP Half Bridge assigns a public IP address to a
computer that you choose so you can bypass the modem’s NAT
feature and open up all ports on your computer. You may want to
do this if you are using an application that requires multiple ports
on a computer in your network. Some examples are video
conferencing applications, gaming applications, and instant
messaging.
Here is a picture of the Half Bridge Configuration page:
To set up a half bridge configuration, you set the Half Bridge status
to Enable. From the drop-down list, choose the computer that
you want to share the public IP address. This default setup for the
PPP Half Bridge works for most applications. You should not need
to make additional changes using the Advanced PPP Half
Bridge.
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
75
Page 76

Enabling or Disabling UPnP
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) with Internet Gateway Device
(IGD) protocol is installed in X6 units when they are shipped by
Zoom. Change this setting only if you have a good reason to do so.
To change the status of Universal Plug and Play, on the Advanced
Setup page click UPnP:
Setting Description
Enable UPnP IGD
Function
Select this check box to enable or disable
Universal Plug and Play with Internet
Gateway Device (IGD) protocol. By default
UPnP is enabled.
Click Save Changes and then Write Settings to Flash to save
your UPnP setting to permanent memory.
76
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 77

Assigning Ports to a PVC
Normally you should not change Per Port PVC (Permanent Virtual
Circuit) settings unless your ISP tells you to do so.
If you have more than one PVC set up, you can use this feature to
assign Ethernet ports to the additional PVC(s). Per Port PVC is
typically used to assign different video streams to particular
Ethernet ports.
To assign ports to a PVC, on the Advanced Setup page click Per
Port PVC:
Click Edit to
assign a port
or ports to
Vlan Group 2.
To assign a port to PVC 1, in the Add column for Vlan2 (see
above) click
Edit to display the Assign Ports screen:
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
77
Page 78

Setting Description
WLAN
Ethernet Port
PVC
Return to Per Port
PVC screen
If you are assigning a wireless device – for
example, a wireless set-top box for your
television set – to an additional PVC, select
this check box to assign PVC 1 to the X6’s
wireless port. This port will no longer be
assigned to PVC 0.
If you are assigning a wired device to PVC 1,
select the LAN port or ports. These ports will
no longer be assigned to PVC 0.
Select the PVC number.
Note: While you can create up to eight
separate PVCs (0 to 7) by assigning different
VPI and VCI settings (see page
can be used for Per Port PVC..
Click this link to return to the main Per Port
PVC screen.
14) only four
If you assigned Ethernet (LAN) ports 3 and 4 to PVC 1, note that
those ports are no longer available to PVC 0:
Click Write Settings to Flash to save your PVC port settings to
permanent memory.
78
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 79

Changing HTTP and Telnet Ports
This feature lets you change the default X6 ports for Internet and
Telnet traffic. If, for example, you are running another Internet
server on the network and that server is using Port 80, you need to
assign a different port to the X6 to avoid a conflict.
To assign Internet (HTTP) or Telnet ports, on the Advanced
Setup page click Port Settings:
Setting Description
HTTP Port
Telnet Port
Enter a port number between 61000 and
62000. (The default is 80.)
Enter a port number between 61000 and
62000. (The default is 23.)
Click Save Changes and then Write Settings to Flash to save the
new port settings to permanent memory. Reboot your PC to make
the settings active.
When the new port settings are saved, network users who want to
access the X6 via the Internet must add a colon [ : ] plus the new
port number after the X6’s IP address. For example, in their
browser’s address bar, users would enter 10.0.0.2:61101, where
61101 is the new Internet port.
To access the X6 via Telnet, users would type
telnet[space]10.0.0.2[space]61102, where 61102 is the new port.
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
79
Page 80

Filtering Out MAC Addresses
Most users will not need this feature.
However, if there is a PC or other device on the X6 network that
you don’t want using the Internet, you can use MAC address
filtering to deny the device Internet access. (That computer or
device will still be able to communicate with other devices on the
LAN, such as printers.)
To block Internet access, on the Advanced Setup page click MAC
Filtering:
Setting Description
Status Select Enabled to deny Internet access to the
specified MAC address. The default is
Disabled.
Name
MAC Address
Save Changes
Reset Before you click Save Changes, you can click
80
ADSL X6 User Guide
Enter the name associated with the MAC
address.
Enter the 12-digit address without separators.
Click this button to display the MAC address
information in the MAC Filters List (see next
page).
this button to clear all entries.
Page 81

MAC Filters List
Edit/Delete
Click this link to display
the associated MAC
address information in the
top half of the screen,
where you can edit it or
delete it from the MAC
Filters List.
Click this link to edit or delete the associated
MAC address information. To delete, click the
Reset button in the top half of the screen.
Click Save Changes and then Write Settings to Flash to save the
MAC Filters List to permanent memory.
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
81
Page 82

X6
services
Managing Access to Services
To change access settings, on the Advanced Setup page click
Management Control:
Setting Description
LAN Access
WAN Access
If a check box is selected, the associated
service is enabled for local network users. The
default for all services is Enabled.
Select a check box to enable the associated
service for remote network users. By default, all
the services are Disabled for remote users.
Click Save Changes and then Write Settings to Flash to save the
service availability configuration to permanent memory.
82
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 83

Configuring Quality of Service
Quality of Service (QoS) helps guarantee upstream bandwidth for
applications that require fast and dependable throughput. For
example, QoS can slow down a photo upload so a phone call can
proceed without garbling, and/or a gamer can enjoy faster
response time.
With QoS you can assign each of the four LAN ports and the
wireless port a priority of High, Medium or Standard. High priority
ports together share a guaranteed percentage of upstream
bandwidth, typically 70%. Medium priority ports share a lower
guaranteed percentage, typically 20%. Standard priority ports share
the remaining upstream bandwidth that is guaranteed to them. If
ports aren’t using their guaranteed bandwidth, the excess
bandwidth becomes available to other ports in order of priority.
For VoIP, you normally assign a High Priority QoS port. For a
gaming device, you may want to assign a High or Medium priority.
For ports used for web browsing, normally you use Standard
priority .
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
83
Page 84

QoS is normally set up by using the Install Assistant CD that
comes with the X6. To configure Quality of Service on the
Advanced Setup page instead, click QoS. For a help message,
select the
Click here link in the first paragraph.
Note that on the QoS screen, Port 1 is the Ethernet port labeled
LAN 1 on the X6 back panel. Port 2 is LAN 2, and so forth.
Setting Description
Do you want to turn
on QoS . . . .?
Which ports should
be High Priority?
Which ports should
be Medium Priority?
84
ADSL X6 User Guide
If you click YES to assign priorities to the
X6’s LAN and wireless ports, by default
LAN port 1 is set to High Priority, LAN port
2 is set to Medium Priority, and LAN ports 3
and 4 as well as the wireless port are set to
Standard priority. These default settings
can be changed.
The default is NO.
Select one to three ports. By default, these
ports will together share 70% of the
upstream bandwidth. You can configure a
different percentage on the Advanced
QoS page (see page
Select one to three ports. By default, these
ports will together share 20% of the
upstream bandwidth. You can configure a
different percentage on the Advanced
85).
Page 85

Advanced QoS page
QoS page (see below).
Click this link to specify a different
upstream bandwidth percentage for High,
Medium and Standard priorities.
Setting Description
What guaranteed
bandwidth should
High Priority Ports
share?
What guaranteed
bandwidth should
Medium Priority Ports
share?
Return Main QoS page
The default is 70%. You can enter a
different whole number percent. The
High Priority and Medium Priority
percentages together must be less than
100.
Note: Standard Priority ports must have
at least 1% of the upstream bandwidth.
The default is 20%. You can enter a
different whole number percent. The
Medium Priority and High Priority
percentages together must be < 100.
Note: Standard Priority ports must have
at least 1% of the upstream bandwidth.
Click to return to the main QoS page.
After you make your selections, click Save Changes, then Write
Settings to Flash.
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
85
Page 86

Monitoring ADSL, Wireless, and Ethernet Status
How should I use the ADSL, Wireless, and Ethernet Status Reports?
These reports are useful tools for evaluating your system and for
troubleshooting. Should a problem arise, a Technical Support
Representative may ask you for the information that is contained in
the reports.
Wireless Status Report
Here is a picture of a typical Wireless Status Report:
The Wireless Status Report shows you the modem speed (Link
Speed), the SSID, your default channel, the Mac Address of the
modem, and the number of packets that are being received and
transmitted (Rx and Tx Packets). You can also tell if your modem
has wireless encryption enabled. (To encrypt your information,
click the Wireless icon in the Zoom Configuration Manager).
ADSL Status Report
Here is a picture of the ADSL Status Report:
86
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 87

The ADSL Line State tells you where your modem is in the
connection process. The three states are Training, Handshake,
and ShowTime. A line state of ShowTime shows that your
modem has established a physical connection to the DSLAM (DSL
Access Multiplexer – a device used in the process of connecting
your computers, and/or network to the Internet). Training is at the
beginning of the connection and Handshake is right after Training.
The Downstream and Upstream values tell you the speed at
which information is being downloaded from the Internet
(Downstream) and uploaded to the Internet (Upstream).
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
87
Page 88

Ethernet Status Report
Here is a picture of the Ethernet Status Report:
The Ethernet Status Report gives you information about the
receive (Rx) and transmission (Tx) rates of packets.
88
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 89

Changing Your Password
When should I change my password?
For added protection of your X6 settings, you should change the
Zoom login password after you have logged into the Zoom
Configuration Manager. Here is a picture of the page where you
enter your Old Password and New Password:
Be sure to write your new settings to Flash, and to remember your
new password. If you forget your password, see
Factory Settings
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
on page 90.
Restoring
89
Page 90

Restoring Factory Settings
When would I need to restore my factory settings?
Should you forget your password, you can restore your modem to
the factory settings. This will restore the admin/zoomadsl login
to the Zoom Configuration Manager on your computer. You
can login using the Zoom login and then change your password.
Here is a picture of the Restore Factory Settings page:
Follow the instructions on the page to reset your ADSL modem to
its original firmware. Please see
Configurations
stored X6 configuration.
90
ADSL X6 User Guide
on page 91 for information about restoring a
Backing Up and Restoring Your
Page 91

Backing Up and Restoring Your Configurations
When would I need to back up and restore my configuration settings?
It is a good idea to back up your configuration settings after you set
up the X6, and also before you upload new firmware. Then if the
update overwrites your configurations, you can put them back
using the Restore option. You may also want to back up your
configurations so you can use them to set up the same
configurations in other modems.
Here is a picture of the Backup/Restore Configuration page:
Follow the instructions on the page to back up or restore your
configuration settings.
Chapter 5: Using Advanced Setup
91
Page 92

Updating Your Firmware
How do I update my firmware?
Periodically you may want to update the firmware on your X6
modem. To do this, you download the Image file from the Zoom
Web Site to your computer. You then use the Firmware Update
option to upload the file to your modem.
Important! It is recommended that you backup your modem’s
configurations before you upload the firmware. (See Backing Up
and Restoring Your Configurations on page 91). Also, do not
turn off the modem or unplug it while the upload is in progress.
Here is a picture of the Firmware Update page:
Click Browse to go to the firmware update file. Then click Image
Upload.
92
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 93

Appendix A
ADSL Internet Settings
Tables
Below are two tables, one for the USA and one for other countries.
These tables are for customers whose service providers do not
supply them with ADSL settings. Many ADSL providers use
different settings depending on the region where they are
operating. This is why there may be more than one setting for your
service provider. If you refer to the tables and there is more than
one listing for your service provider, the most common is labeled
(1), the next (2), and so on. We recommend that you try them in
order starting with 1.
We post updated tables on our Web site. If your service provider
or country is not listed in the tables below, please consult
www.zoom.com
Note to USA customers
If your ADSL service provider is not shown below, use the settings
for Service Provider Not Shown at the bottom of the table. If
those settings do not work, use the settings for the company that
provides local telephone service in your area.
Appendix A: ADSL Internet Settings Tables
93
Page 94

Table A: USA
Service Provider VPI VCI Encapsulation
AllTel (1) 0 35 PPPoE LLC
AllTel (2) 0 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
AT&T (1) 0 35 PPPoE LLC
AT&T (2) 0 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
AT&T (3) 8 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
August.net (1) 0 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
August.net (2) 8 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
BellSouth 8 35 PPPoE LLC
CenturyTel (1) 8 35 PPPoE LLC
CenturyTel (2) 8 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
Covad 0 35 PPPoE LLC
Earthlink (1) 0 35 PPPoE LLC
Earthlink (2) 8 35 PPPoE LLC
Embarq (Sprint) (1) 0 35 PPPoA LLC
Embarq (Sprint) (2) 8 35 PPPoE LLC
GWI 0 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
Hotwire 0 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
Internet Junction 0 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
Qwest (1) 0 32 PPPoA LLC
Qwest (2) 0 32 PPPoA VC-MUX
SBC (1) 0 35 PPPoE LLC
SBC (2) 0 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
SBC (3) 8 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
Socket (1) 8 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
Socket (2) 0 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
Socket (3) 0 35 PPPoE LLC
Sonic 0 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
Sprint (Embarq) (1) 0 35 PPPoA LLC
Sprint (Embarq) (2) 8 35 PPPoE LLC
Uniserve 0 33 1483 Bridged IP LLC
Verizon (1) 0 35 PPPoE LLC
Verizon (2) 0 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
Service Provider Not Shown 0 35 PPPoE LLC
94
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 95

Table B: Countries Other Than the USA
Service Provider VPI VCI Encapsulation
Australia-Telstra 8 35 PPPoA LLC
Argentina-Telecom 0 33 PPPoE LLC
Argentina-Telefonica 8 35 PPPoE LLC
Belgium-ADSL Office 8 35 1483 Routed IP LLC
Belgium-Turboline 8 35 PPPoA LLC
Bolivia 0 34 1483 Routed IP LLC
Brazil-Brasil Telcom 0 35 PPPoE LLC
Brazil-Telefonica 8 35 PPPoE LLC
Brazil-Telmar 0 33 PPPoE LLC
Brazil-South Region 1 32 PPPoE LLC
Colombia-EMCALI 0 33 PPPoA VC-MUX
Denmark-Cybercity, Tiscali 0 35 PPPoA VC-MUX
France (1) 8 35 PPPoE LLC
France (2) 8 67 PPPoA LLC
France (3) 8 35 PPPoA VC-MUX
Germany 1 32 PPPoE LLC
Hungary-Sci-Network 0 35 PPPoE LLC
Iceland-Islandssimi 0 35 PPPoA VC-MUX
Iceland-Siminn 8 48 PPPoA VC-MUX
Israel 8 48 PPPoA VC-MUX
Italy 8 35 PPPoA VC-MUX
Jamaica (1) 8 35 PPPoA VC-MUX
Jamaica (2) 0 35 PPPoA VC-MUX
Jamaica (3) 8 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC SNAP
Jamaica (4) 0 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC SNAP
Kazakhstan 0 33 PPPoA VC-MUX
Mexico 8 35 PPPoE LLC
Netherlands-BBNED 0 35 PPPoA VC-MUX
Netherlands-MX Stream 8 48 PPPoA VC-MUX
Portugal 0 35 PPPoE LLC
Saudi Arabia (1) 0 33 PPPoE LLC
Saudi Arabia (2) 0 35 PPPoE LLC
Saudi Arabia (3) 0 33 1483 Bridged IP LLC
Saudi Arabia (4) 0 33 1483 Routed IP LLC
Saudi Arabia (5) 0 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
Saudi Arabia (6) 0 35 1483 Routed IP LLC
Appendix A: ADSL Internet Settings Tables
95
Page 96

Table B (Continued): Countries Other Than the USA
Service Provider VPI VCI Encapsulation
Spain-Albura, Tiscali 1 32 PPPoA VC-MUX
Spain-Colt Telecom, Ola Internet 0 35 PPPoA VC-MUX
Spain-EresMas, Retevision 8 35 PPPoA VC-MUX
Spain-Telefonica (1) 8 32 PPPoE LLC
Spain-Telefonica (2), Terra 8 32 1483 Routed IP LLC
Spain-Wanadoo (1) 8 35 PPPoA VC-MUX
Spain-Wanadoo (2) 8 32 PPPoE LLC
Spain-Wanadoo (3) 8 32 1483 Routed IP LLC
Sweden-Telenordia 8 35 PPPoE
Sweden-Telia 8 35 1483 Bridged IP LLC
Switzerland 8 35 PPPoE LLC
Turkey(1) 8 35 PPPoE LLC
Turkey(2) 8 35 PPPoA VC-MUX
UK (1) 0 38 PPPoA VC-MUX
UK (2) 0 38 PPPoE LLC
Venezuela-CANTV 0 33 1483 Routed IP LLC
Vietnam 0 35 PPPoE LLC
96
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 97

Appendix B
Front and Back Panels
The front panel of the X6 looks like this:
The following table describes each light on the front panel.
Light Description
LAN
WLAN
LINK
STATUS
PWR
Lights if any LAN port of the
Ethernet port of a powered-up device. Blinks when data is
sent. Additional lights for each LAN port are on the back
of the
X6.
Lights when the wireless access point is running and
enabled. Blinks when data is sent.
Blinks when the
Stays on solid when the unit has synched up with its
ADSL connection.
Note: If the light fails to switch from blinking to steady
after a minute or two, check with your ADSL provider that
the ADSL connection is activated, or refer to Appendix D,
Troubleshooting on page
Blinks red once while the
only light when there is a problem with the unit. See If
You Need Help
information.
Lights when the
X6 is performing its startup sequence.
on page 19 for Customer Support contact
X6 is plugged into a power source.
X6 is plugged into the
106.
X6 is powering up. Then it will
Appendix B: Front and Back Panels
97
Page 98

The following table describes the back panel.
Port Description
PWR
RESET
LAN 1
LAN 2
LAN 3
LAN 4
ADSL
Port to connect the unit to the
Recessed button to reset the modem to its factory settings.
To reset, insert a paper clip and press the button three times.
LAN ports that can connect the unit to an access point, a
network hub, or the Ethernet port of a computer. The
four LAN ports.
Each port has a yellow and a green light above it. The yellow
light turns on when the port is connected to a 100 megabit
per second Ethernet port. The green light blinks when there
is activity on that particular LAN line.
Jack to connect the modem to the ADSL telephone wall jack.
X6’s power cube.
X6 has
98
ADSL X6 User Guide
Page 99

Appendix C
TCP/IP Network Settings
If you are using a Macintosh or Linux computer, you must ensure
that your computer’s TCP/IP network settings are configured
properly. Otherwise you will not be able to connect to the Internet.
Note:
If you are using a Windows computer, you do not have to
configure the TCP/IP settings. This is because your Windows
computer will automatically configure them for you. Only
Windows users who are troubleshooting the X6 will need to verify
the TCP/IP settings.
Depending on your operating system, follow the steps in the
appropriate section to ensure your TCP/IP settings are correct.
•
If you are using Macintosh, see
on page
•
If you are using Linux, see
page
•
If you are using Windows, see
page
100.
102.
103.
Macintosh TCP/IP Settings
Linux TCP/IP Settings on
Windows TCP/IP Settings on
Appendix C: TCP/IP Network Settings
99
Page 100

Macintosh TCP/IP Settings
How you configure your Macintosh computer’s network settings
differs, depending on your Mac OS. For OS X, follow the
instructions
below. Otherwise go to page 101.
Mac OS X
1 From the Dock, choose System Preferences and then
Network to display the Network pane. (For OS X 3, you also
have to click the Configure button.)
2 Ensure that Automatic is selected from the Location list box.
3 Under the Show drop-down tab, choose Built-in Ethernet.
4 Under the TCP/IP tab, make sure that Using DHCP is
highlighted in the Configure: list box. Do not enter anything
into the DHCP Client ID field.
5 Click Apply Now (or Save if prompted) and close the
Network pane.
6 Continue with Step 3: Establishing Communication on
12.
page
100
ADSL X6 User Guide
 Loading...
Loading...