Page 1

Wireless-G
USB
U S E R’S G U I D E
Page 2

Contents
Overview .................................................................. 3
Installation Instructions .......................................... 4
Installing the Wireless-G USB Adapter................... 5
The Adapter LED.................................................. 10
Setting Security ..................................................... 11
WPA2-PSK (Pre-Shared Key) .............................. 14
WPA-PSK (Pre-Shared Key) ................................ 15
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) .......................... 16
WPA2-Enterprise.................................................. 18
WPA ..................................................................... 20
Certificate (WPA2-Enterprise and WPA) .............. 23
Changing your Security Setting ............................ 24
Advanced Options................................................. 25
Creating Profiles................................................... 25
Monitoring Link Status.......................................... 28
Using Site Survey and Rescan............................. 29
Advanced Configuration ....................................... 31
Appendix A. TCP/IP Settings................................ 32
Appendix B. Troubleshooting .............................. 41
Appendix C. Zoom Technical Support Services. 43
Appendix D. Regulatory Information ................... 47
2
Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 3
Overview
The chapters in this User Guide describe how to:
®
• Install the Zoom Wireless-G USB adapter on a Windows
PC
• Connect to a wireless network
• Enable security on the Wireless-G USB adapter
• Use the advanced features of the Wireless-G USB
configuration software
Chapters 1 and 2 cover the basics – what you need to get
connected and to enable security.
If you are interested in the more advanced features of the
Wireless-G USB adapter, please see Chapter 3. This chapter
explains how to create profiles so you can switch your
connection from one network to another, monitor the strength of
your network connection, and scan a list of available networks.
Overview
3
Page 4

1
Installation Instructions
This chapter provides simple instructions for installing the
Wireless-G USB adapter on a Windows PC. If you have already
installed the adapter on a computer (using the separate Quick
Start guide), you can skip this chapter and begin with Chapter 2:
Setting Security.
What’s in the Package
The adapter package includes the following:
• Wireless-G USB adapter
• CD containing the
Installation Wizard and
documentation
• USB extension cable
• Quick Start manual
Before You Begin
Before you install the Wireless-G USB adapter, check that your
computer has the following:
• Available USB port
• Windows Vista, XP, 2000,
Me, or 98SE
If you are using Windows 98SE: Your computer must have at
least 64MB RAM and a 300 MHz or faster CPU. Also, you may
need the Windows 98SE Installation CD during the setup
process.
4
Wireless-G USB Adapter
• CD drive
• 6 MB of free hard drive
space
Page 5

Installing the Wireless-G USB Adapter
Important! Install the software BEFORE you plug the WirelessG USB adapter into your computer.
If you are running Windows XP, 2000, Me or 98SE, please go
to page
Windows Vista
1 Insert the Wireless-G USB CD into the CD or DVD drive. The
2 On the Language Selection screen, select your language.
3 On the next screen, select Installation Wizard, and then on
8 for instructions.
Installing and connecting on
CD should start automatically.
If the AutoPlay dialog box appears, click Run Setup.exe.
If the User Account Control dialog box appears, click
Continue.
the following screen select USB.
Chapter 1: Installation Instructions
5
Page 6

4 On the Zoom Wireless-G USB Installation Wizard Welcome
screen, click OK to install the adapter.
If a message tells you that Windows can't verify the publisher
of the driver software, select Install this driver software
anyway.
5 At the prompt, plug in the USB Adapter and click OK.
A pop-up notification message tells you that your hardware
has been installed successfully.
6 On the Zoom installation menu, select Exit.
If a message appears saying that the program might not have
installed correctly, click This program installed correctly.
To connect to a network:
1 From the Start menu select Connect to.
2 In the Connect to a network dialog box, highlight the desired
network and click Connect.
• If your desired network is secured, in the next dialog box
enter the security key or password and click Connect.
6
Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 7
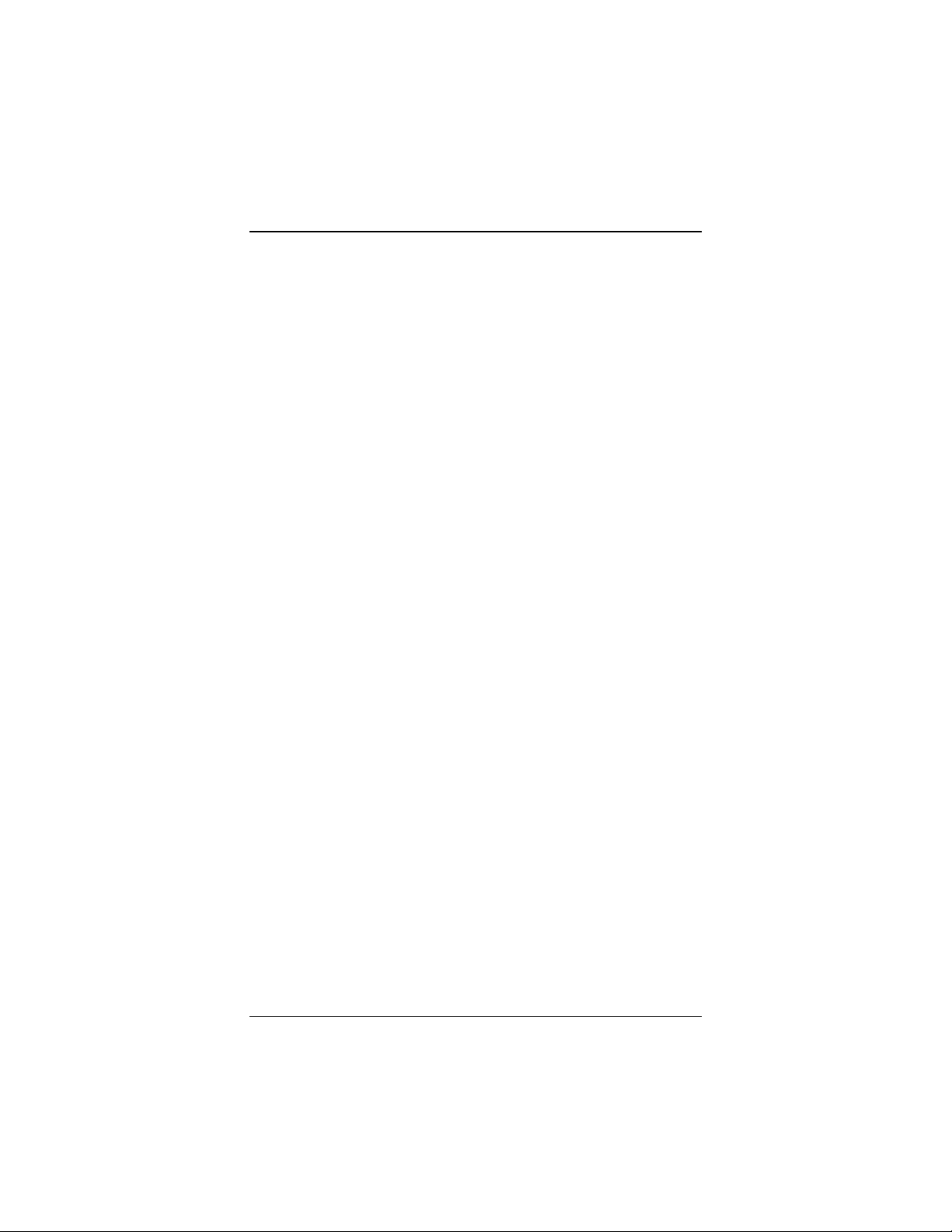
• If your desired network is unsecured, in the message box
select Connect Anyway.
Note: We strongly recommend that you choose a secured
network. For information on wireless security, see Setting
Security on page 11.
If you have difficulty connecting, make sure you have
entered the correct password. Then perform a power cycle
on your computer and router/gateway/access point as
described in the Troubleshooting Tips on page
41.
3 In the Successfully connected to [desired network] dialog
box, you have three options. You can:
• Select Save the network and Start this connection
automatically if you always want to connect to the same
network. Then click Close. The next time you start your
computer you will automatically connect to the selected
network.
• Select Save the network and clear the Start this
connection automatically check box if you don't want to
automatically connect to this network every time you start
your computer but you will want to connect in the future.
Click Close to display the Select a location . . . dialog box
where you choose a location. Windows Vista automatically
applies the correct network security settings.
If the User Account Control dialog box appears, click
Continue.
• Click Close to complete the connection procedure. Select
this option if you are connecting to this network only one
time.
Chapter 1: Installation Instructions
7
Page 8

To disconnect from the current network:
1
From the Start menu, select Connect to.
2 In the Disconnect or Connect to another network dialog
box, select the current network and click Disconnect.
In the Are You Sure? message box, click Disconnect again.
3 In the next dialog box, you can connect to another network or
click Close to complete the disconnect procedure.
Installing and connecting on Windows XP, 2000, Me and 98SE
1 Insert the USB Adapter CD into your CD drive. The CD
should start automatically. (If it does not, on the Windows
desktop click the Start button, click Run, and then type
e:\setup.exe where e is the letter of your CD drive.)
2 On the Language Selection screen, select your language.
3 On the next screen select Installation Wizard, and then on
the following screen select USB.
4 Windows Me users: if prompted, restart your computer.
5 Follow the prompts to complete the installation.
Windows 2000 users: If the Digital Signature Not Found
message appears, click Yes to continue.
6 On the final screen, click Finish.
7 On the Zoom installation screen, click Exit, remove the
installation CD, then turn off your computer.
(If the Zoom screen is minimized to a button on the taskbar,
maximize the screen so you can exit the installation.)
8 While the computer is off, plug the USB adapter into a USB
port on your computer.
9 Turn the computer back on. Windows will find your new
hardware. If you see an Unsigned driver message, click
Continue anyway.
8
Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 9
Windows 2000: If the Digital Signature Not Found
message appears, click Yes to continue.
Windows Me and 98: If prompted, restart your computer.
Congratulations! Your installation is complete. Follow the
instructions below to get connected.
To connect to a network:
1 Double-click the Zoom Wireless-G USB icon on your
desktop to open the configuration software.
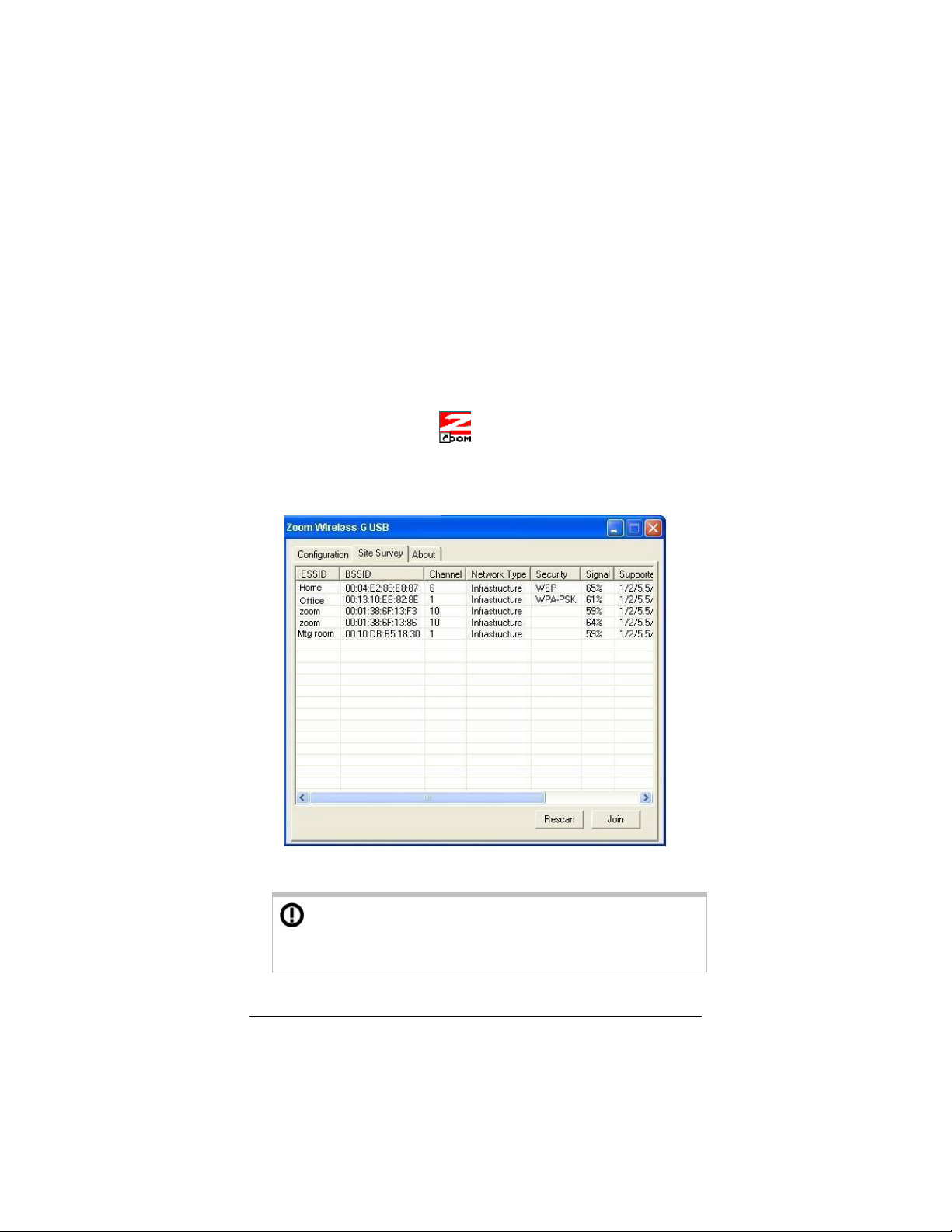
2 In the Zoom Wireless-G USB window, click the Site Survey
tab to see a list of available wireless networks.
3 Highlight the network you want and click Join.
If the network you select has security configured, you
must enable and configure security on your computer before
you can connect. See Chapter 2, Setting Security.
Chapter 1: Installation Instructions
9
Page 10
4 If you join a wireless network that does not have security, you
should now be connected. To check your connection, open
your Web browser and go to your favorite site.
We highly recommend security. Chapter 2, Setting Security on
11 has descriptions of the five security options and setup
page
instructions.
If you have difficulty accessing the Internet, follow the
suggestions in your browser’s “Page cannot be displayed”
message. You may need to adjust your LAN settings.
As you work online, you can monitor your connection easily
using the Link Status icon that appears in the right corner of the
taskbar when you open the Wireless-G USB utility:
The icon’s color indicates the link status:
Blue indicates an excellent or good link.
Yellow indicates a usable but weak link.
Red indicates no link or a very poor link.
The Adapter LED
The states of the LED on the Wireless-G USB adapter are
explained below.
LED Status Meaning
Flashing The Wireless-G USB adapter is attempting to
connect to a wireless network.
Steady The Wireless-G USB adapter is connected to a
wireless network and is transmitting or
receiving data.
10
Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 11
2
Setting Security
This chapter is for users who have Windows XP, 2000, Me or
98SE. If you are using Windows Vista, the operating system
automatically handles security configuration.
We strongly recommend security, although you do not need to
use it to get your wireless connection working.
Important! You must first enable security on the the wireless
access point. You then enable security on the adapter using the
same configuration that you used for the access point. For
example, if the wireless access point is configured for WPA2PSK, you must select WPA2-PSK security in the Wireless-G
USB configuration software and enter the same encryption key.
Select one of five ways to configure and implement security for
your wireless network:
• WPA2-PSK (WiFi ® Protected Access 2 Pre-Shared Key) is
the recommended option if it is supported by the access
point and the devices in your network. WPA2-PSK protects
your communications with AES (Advanced Encryption
Standard). Some access points permit a “mixed mode”
network composed of both WPA and WPA2 wireless clients.
WPA2-PSK requires you to enter an encryption key shared
by the access point.
• WPA PSK (WiFi ® Protected Access Pre-Shared Key)
If the devices in your network do not all support WPA2-PSK,
Chapter 2: Setting Security
11
Page 12
select WPA-PSK. WPA-PSK protects your communications
with TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol).
This option requires you to enter an encryption key shared
by the access point.
• WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
If the devices in your network do not support WPA2-PSK or
WPA-PSK, select WEP data encryption.
This method requires you to enter an encryption key. The
keys can be 64 or 128 bits in length.
• WPA2-Enterprise
If you are linking to a network that accesses a RADIUS
(Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) authentication
server, and if the devices in the network support WPA2,
select WPA2-Enterprise. This option provides security with
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). AES has a key size
of 128, 192, or 256-bits. In order for eavesdroppers to
decipher a message, they would have to try every possible
key.
• WPA is an option for users who access a RADIUS (Remote
Authentication Dial-In User Service) authentication server
that does not support WPA2. WPA provides security with
TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol), which dynamically
changes keys as the system is used.
Accessing the Security Screen
1 On your desktop, double-click the Zoom Wireless-G USB
icon:
12
Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 13
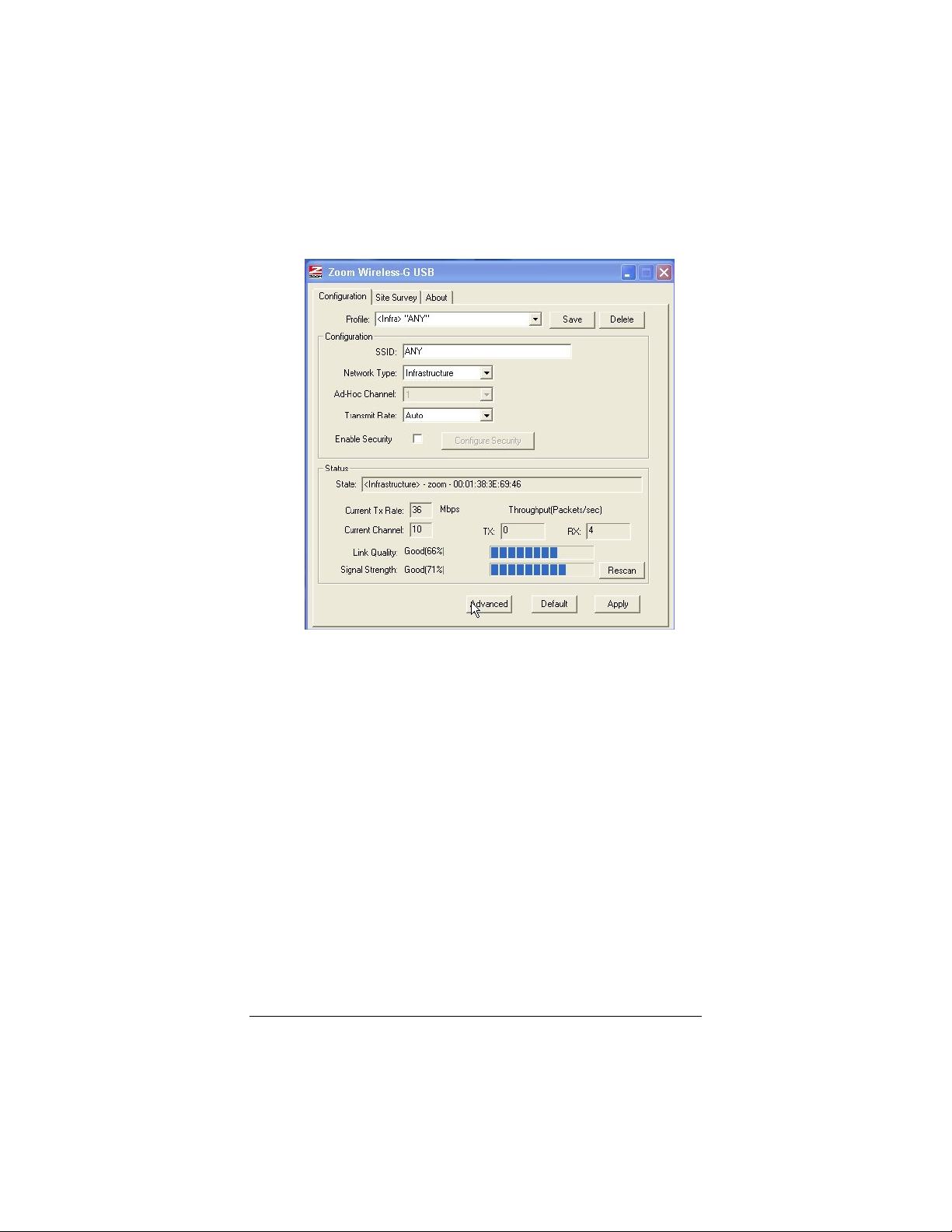
2 The Zoom Wireless-G USB configuration software opens to
display the configuration parameters:
3 Make sure that the desired wireless network is displayed in
the Profile and SSID text boxes (the term <Infra>
designates an Infrastructure network) and that the Network
Type is correct.
There are two types of wireless networks: Infrastructure and
Ad Hoc.
• In an Infrastructure network, wireless devices
communicate with each other via a wireless access point,
router, or ADSL modem with built-in wireless technology.
• In an Ad Hoc network, a group of wireless devices
communicate directly with other “client” devices that are
using wireless adapters. The network does not include a
wireless access point or wireless router.
In the unlikely event that you use an Ad Hoc network, you
must set up Static IP addressing. See Appendix A:
TCP/IP Settings.
Chapter 2: Setting Security
13
Page 14
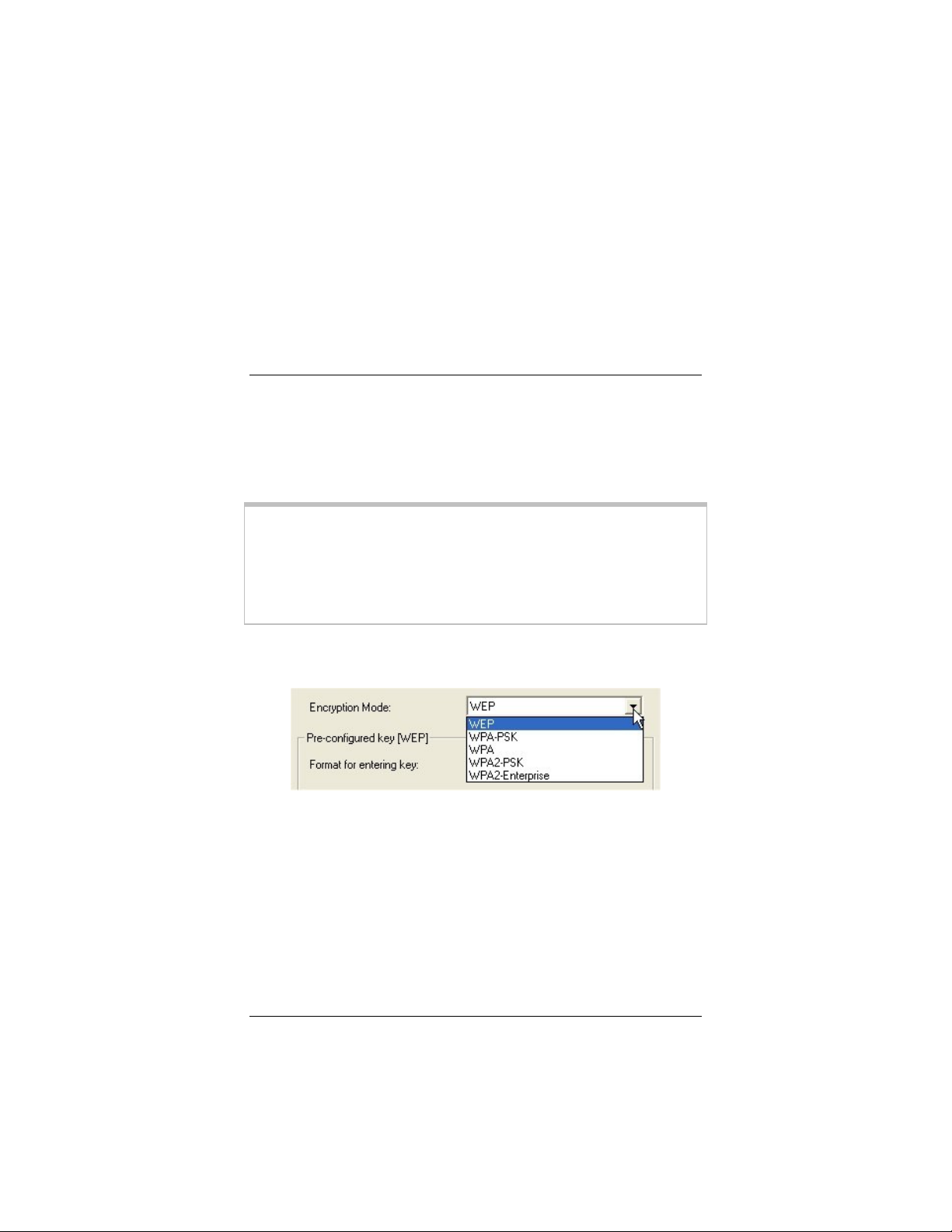
4 Select the Enable Security check box to open the Security
Configuration window. For Step 5, consult the table below:
To configure Go to page
WPA2-PSK 14
WPA-PSK 15
WEP 16
WPA2-Enterprise 18
WPA 20
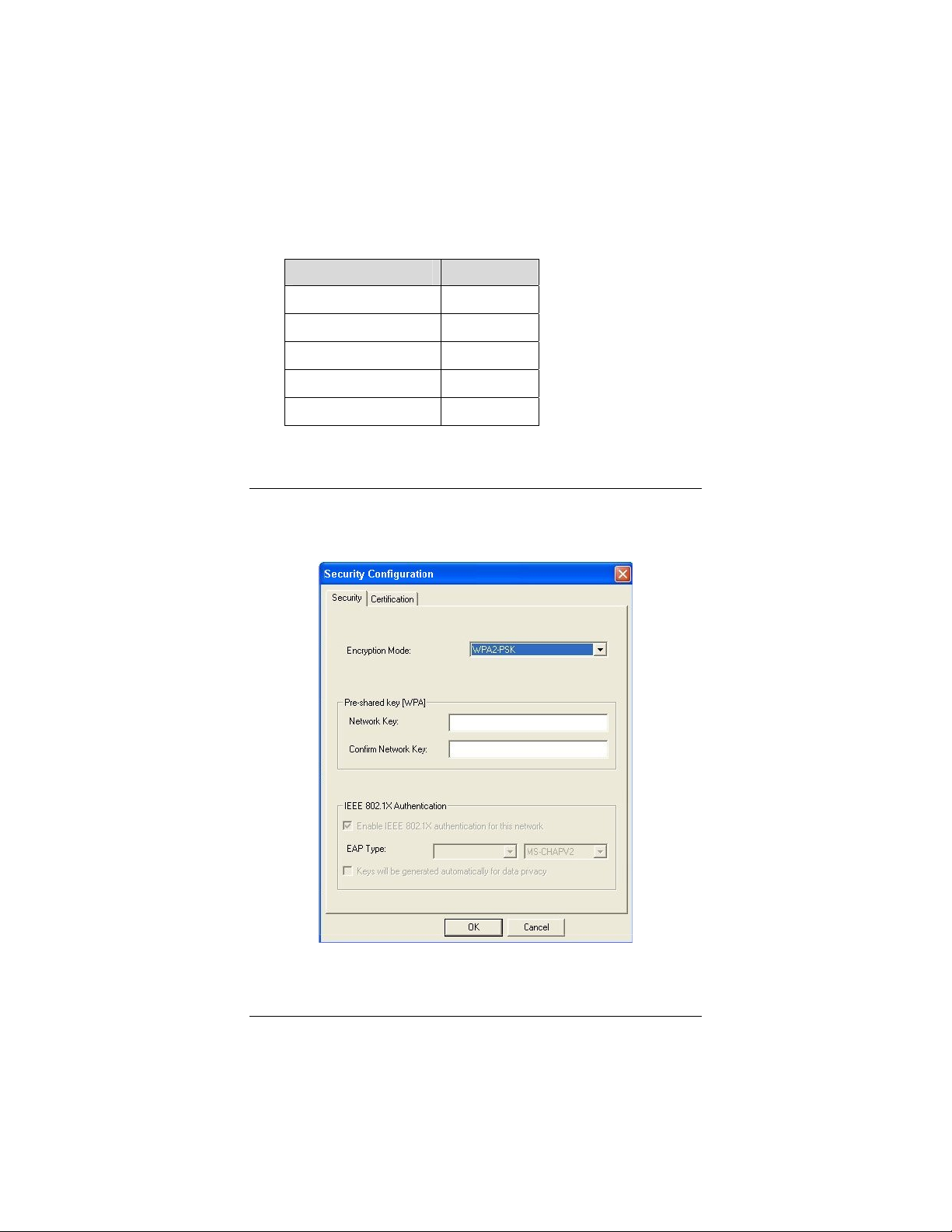
WPA2-PSK (Pre-Shared Key)
1 In the Security Configuration window, click the Encryption
Mode drop-down arrow and select WPA2-PSK.
14
Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 15
2 In the Pre-shared key [WPA] area, enter the same network
key that is used on the wireless access point. We advise you
to enter a key with a minimum of 20 random characters.
3 Click OK to save your settings and return to the
Configuration tab.
4 On the Configuration tab, click Apply.
5 Click the Close box to exit the configuration software.
That’s it! You have configured WPA2-PSK security for your
wireless connection, and you’re ready to use the Internet.
WPA-PSK (Pre-Shared Key)
If not all of the wireless devices in your network support the
recommended WPA2-PSK, select WPA-PSK.
1 In the Security Configuration window, click the Encryption
Mode drop-down arrow and select WPA-PSK.
Chapter 2: Setting Security
15
Page 16

2 In the Pre-shared key [WPA] area, enter the same network
key that is used on the wireless access point. We advise a
key with a minimum of 20 random characters.
3 Click OK to save your settings and return to the
Configuration tab.
4 On the Configuration tab, click Apply.
5 Click the Close box to exit the configuration software.
That’s it! You have configured WPA-PSK security for your
wireless connection, and you’re ready to use the Internet.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
1 In the Security Configuration window, click the Encryption
Mode drop-down arrow and select WEP:
16
Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 17

2 In the Preconfigured key [WEP] area, do the following:
a
In the Format for entering key drop-down list, select
• ASCII characters if your network uses all Zoom
wireless products
• Hexadecimal digits if an access point, router, or
some adapters are not Zoom products
b
In the Key Length drop-down list, select 128 bits or 64
bits.
Note: 128-bit WEP provides more security than 64-bit,
but 128-bit could diminish network performance.
c
In the Key Index drop-down list, if you are using a 64-bit
key, select which of four keys – 1, 2, 3, or 4 – will be
used to encrypt the data. The key you select must be the
same one that is selected on the access point. We
recommend that you use Key 1.
128-bit WEP uses just a single key.
d
In the Network Key text box, enter a key using the table
below as a guide.
The key must be the same for all the devices on your
network.
If you selected key
type…
Hexadecimal digits
– 128 bits
Hexadecimal digits
– 64 bits
ASCII – 128-bits 13 characters. The characters can
ASCII – 64 bits 5 characters. The characters can be
Enter exactly…
26 characters A–F, a–f and 0–9. For
example,
00112233445566778899AABBCC.
10 characters. The characters can
be A-F, a-f, and 0-9. For example,
11AA22BB33.
be any upper- or lower-case letters
and numbers. For example:
MyKey12345678.
any upper- or lower-case letters and
numbers. For example, MyKey.
3 Re-enter the key in the Confirm Network Key text box.
Chapter 2: Setting Security
17
Page 18

4 Click OK to save your settings and return to the
Configuration tab.
5 On the Configuration tab, click Apply.
6 Click the Close box to exit the configuration software.
That’s it! You have configured WEP security for your wireless
connection, and you’re ready to use the Internet.
WPA2-Enterprise
Select WPA2-Enterprise if
• you are linking to a corporate network that uses a RADIUS
(Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) authentication
server
• all of the devices in the network support WPA2, or your
access point offers both WPA2 and WPA.
18
Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 19

1 In the Security Configuration window, click the Encryption
Mode drop-down arrow and select WPA2-Enterprise.
2 In the IEEE 802.1X Authentication area, note that the check
box marked Enable IEEE 802.1X authentication for this
network is selected. With IEEE 802.1X authentication, each
wireless device (client) sends a signal to the wireless access
point, which in turn sends the signal to the RADIUS server.
The server determines whether or not the client is allowed to
join the network.
3 Click the EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) Type
drop-down list and select an authentication protocol:
• PEAP (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol –
the (default). With PEAP, you can select from three
authentication extensions:
MS-CHAPV2. Microsoft’s version of CHAP
(Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol
(default)
GTC
TLS/SmartCard
• TLS (Transport Layer Security). There are no
authentication extension options with TLS.
• TTLS (Tunneled Transport Layer Security). With TTLS,
you can select from four authentication extensions:
Chapter 2: Setting Security
19
Page 20

PAP (Password Authentication Protocol)
CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication
Protocol)
MS-CHAP (Microsoft’s version of CHAP).
MS-CHAPV2 (the default).
4 Click the Certification tab and enter the required information
(see page
23).
5 Click OK to save your settings and return to the
Configuration tab.
6 On the Configuration tab, click Apply.
7 Click the Close box to exit the configuration software.
That’s it! You have configured WPA2-Enterprise security for your
wireless connection, and you’re ready to use the Internet.
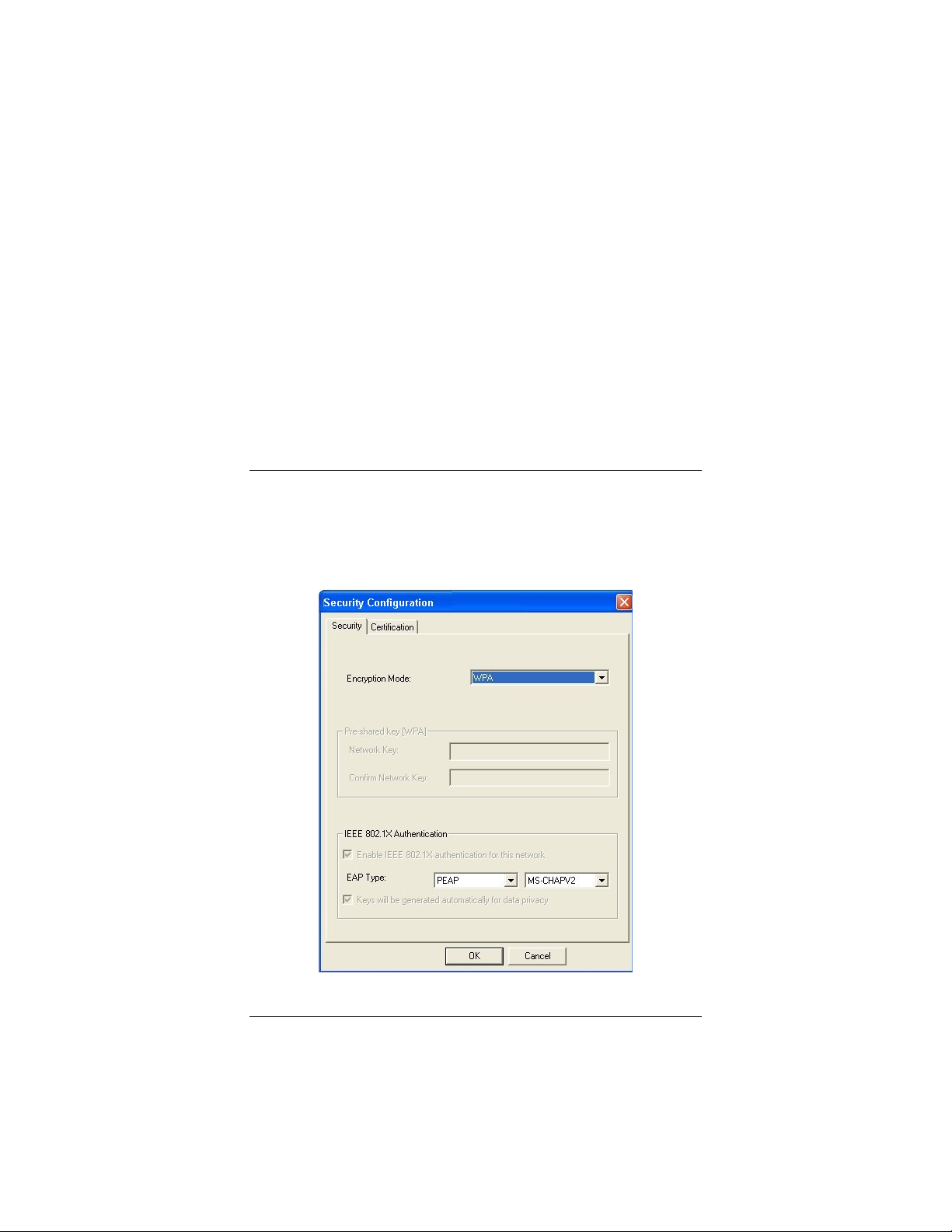
WPA
Select WPA if you are linking to a corporate network that uses a
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) server
that does not support WPA2.
1 In the Security Configuration window, click the Encryption
Mode drop-down arrow and select WPA.
20
Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 21

2 In the IEEE 802.1X Authentication area, note that the
check box marked Enable IEEE 802.1X authentication for
this network is selected. With IEEE 802.1X authentication,
each wireless device (client) sends a signal to the wireless
access point, which in turn sends the signal to the RADIUS
server. The server determines whether or not the client is
allowed to join the network.
3 Click the EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol) Type
drop-down list and select an authentication protocol:
• PEAP (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol –
the default). With PEAP, you can select from three
authentication extensions:
Chapter 2: Setting Security
21
Page 22

MS-CHAPV2 (the default). This is Microsoft’s
version of CHAP (Challenge-Handshake
Authentication Protocol.
GTC
TLS/SmartCard
• TLS (Transport Layer Security). There are no
authentication extension options with TLS.
• TTLS (Tunneled Transport Layer Security). With TTLS,
you can select from four authentication extensions:
PAP (Password Authentication Protocol), the most
basic form of authentication.
CHAP (Challenge Handshake Authentication
Protocol)
MS-CHAP (Microsoft’s version of CHAP).
MS-CHAPV2
4 Click the Certification tab and enter the required information
(see page
23).
5 Click OK to save your settings and return to the
Configuration tab.
6 On the Configuration tab, click Apply.
7 Click the Close box to exit the configuration software.
That’s it! You have configured WPA security for your wireless
connection, and you’re ready to use the Internet.
22
Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 23

Certificate (WPA2-Enterprise and WPA)
A certificate is issued to a wireless network user by a Certificate
Authority – often the corporate network administrator – to confirm
the user’s identity and thereby maintain the security of the
network.
If you are linking to a corporate network that uses an
authentication server and you have configured WPA2 Enterprise
or WPA security, your MIS staff will assist you in completing the
the Certification information.
Chapter 2: Setting Security
23
Page 24

Changing your Security Setting
If the type of security on your wireless network changes, you
need to modify your security settings.
On the Configuration tab, click the Configure Security button
to select a different security option and enter the required
information.
24
Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 25

3
Advanced Options
Note: This chapter is for users who have Windows XP, 2000, Me
or 98SE.
The Zoom Wireless-G USB utility provides options so you can
create profiles, monitor the signal strength of your network
connection, scan available networks, and specify advanced
settings. This chapter tells you when and how to use each of
these options.
Creating Profiles
A profile is a collection of settings needed for a particular
wireless connection. If you plan to use more than one network,
you can create a profile for each one and then switch to its
profile when you want to connect to that particular network.
For example, you may want to set up profiles for a work network
and a home network, each of which has different configuration
settings. By creating two profiles, you can store the settings for
each network and then switch quickly and easily from one
network to the other by selecting the appropriate profile.
1 On your desktop, double-click the Zoom Wireless-G USB
icon.
2 On the Configuration tab, in the Profile text box, enter a
name for the profile you want to create.
Appendix A: TCP/IP Settings 25
Page 26

For example, let’s say you have a small home network to
which you want to be able to switch quickly when you arrive
home. Give the profile the name “Home”:
3 In the Configuration area, enter the following settings:
• SSID – Enter the network name. In the example above,
the SSID is Home.
• Network Type – From the drop-down list, select Ad
Hoc.
• Ad Hoc channel – From the drop-down list, select the
channel used by the other device(s) in the network. If
you are setting up the first computer in the network,
select a channel.
Also, to avoid interference, it is desirable to have a 5channel difference between your channel and the
channel being used by another network within range.
Click Site Survey, then Rescan to check the channel
settings of other networks within range.
If you are unsure of which channel to use, select the
default, Channel 6.
Transmit Rate – Select Auto to allow your device to
adjust automatically in the case of interference or a weak
connection. If you want to specify a fixed speed, choose
one from the drop-down list. Most people should select
Auto.
26 Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 27

• Enable Security – Select this check box to open the
Security Configuration window. Note: If you are setting
up an ad hoc network, as in this example, only WEP
security is available to you.
After you enter your security settings, click OK to return
to the Configuration tab.
4 In the Configuration area, click the Apply button to save
the settings.
5 Click the Save button to save the Profile.
Appendix A: TCP/IP Settings 27
Page 28

Monitoring Link Status
The Status area on the Configuration tab displays information
about your wireless connection:
• State: In an Infrastructure
network, the name and the
MAC address of the wireless
access point to which your
computer is connected.
In an ad hoc network, the
virtual MAC address used by
computers in the network.
• Current Tx (Transmission)
Rate: Highest transmission
speed in Megabytes per
second of the last received
packet.
• Current Channel: The Wi-Fi
frequency channel.
• Throughput (Packets/sec):
TX = number of packets
transmitted per second without
errors.
RX = number of packets
received per second without
errors.
• Link Quality (Infrastructure
only): The transmission quality
of the last received packet.
80 – 100% = Excellent
60 – 80% = Good
40 – 60% = Fair
Under 40% = Poor or no
connection
• Signal Strength (Infrastructure
only): The transmission signal
strength of the last received
packet, expressed as a percent
of maximum allowable power.
Note: you may be able to
improve the signal strength by
using the supplied extension
cable to place the adapter in a
more favorable location.
80 – 100% = Excellent
60 – 80% = Good
40 – 60% = Fair
Under 40% = Poor or no signal
strength
28 Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 29

Using Site Survey and Rescan
Use the Site Survey window and the Rescan button when you
need to do any of the following:
• Find a list of network names (ESSIDs) so you can connect to a
network
• Identify the MAC address (BSSID) of your wireless access
point or wireless router
• Check the channel difference between your network and other
networks within range
• Check the network type (infrastructure or ad hoc) of your
network
• Verify whether security is enabled for your network
To use this window, click the Site Survey tab, then click the
Rescan button to refresh the list.
Appendix A: TCP/IP Settings 29
Page 30

The information displayed on the Site Survey tab is as follows:
ESSID (Extended Service Set
•
Identifier): An Extended Service Set
consists of two or more Basic
Service Sets (see below). An
ESSID, also known as an SSID or
Network Name, is chosen by the
person who sets up the network.
The ESSID is a code attached to all
packets sent over an infrastructure
wireless network. The code can
contain up to 32 alphanumeric
characters. All devices in the
network must share the same
ESSID.
• BSSID (Basic Service Set
Identifier): A Basic Service Set
consists of a wireless access point
connected to wired network and a
set of wireless devices. In an
infrastructure network, the BSSID is
the MAC address of the wireless
router or wireless access point. In
an ad hoc network, the BSSID is the
MAC address of the first computer in
the network to be powered up.
• Channel: The Wi-Fi frequency
channel.
• Network Type: Infrastructure or Ad
Hoc (see page 13).
• Security: The type of security
configured for the network.
• Signal: The strength and quality of
your transmissions.
• Supported rates (data transfer
speeds): In wireless networks the
data rates are typically 11Mb/s or
54Mb/s. The rates depend on
signal strength and quality.
30 Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 31

Advanced Configuration
To access this window, click the Advanced button on the
Configuration tab.
RTS (Request To Send)
•
Power Save Enabled: When
you select this option, the
Wireless-G USB adapter
immediately signals the access
point that it is in Power Save
mode. The access point buffers
all packets until it is polled by
the adapter.
Note: The access point you use
must also support Power Save.
• Nitro XM: Selected by default.
This technology lets devices
communicate directly with each
other while they remain linked
to a Nitro XM-enabled access
point. Nitro XM enables data
compression and can
significantly enhance data
transfer speed.
•
Nitro Mode: Selected by
default. Provides special
protocol enhancements to
improve the throughput of your
wireless connection.
•
Threshold: This is a
mechanism designed to ensure
that all devices in a network
can send data to the access
point. If some laptops are
having trouble communicating,
enter the maximum packet size
of data to be sent – 0 to 1500
is recommended. If the packet
size exceeds the value you set,
RTS will be activated. The
default is Disabled (2347).
• Frag (Data fragmentation)
Threshold: If your adapter
often transmits large files, you
can set a limit on packet size. If
the limit is exceeded, the
adapter will split the packet.
The default is Disabled (2346).
Appendix A: TCP/IP Settings 31
Page 32

Appendix A
TCP/IP Settings
By default, Windows is set for dynamic addressing (DHCP).
Generally, this is the correct setting for an Infrastructure network,
but needs to be changed if you are using an Ad Hoc network.
(Note: Use our instructions as a basic guide. Advanced users will
know other ways to set up their networks.)
Please go to the section that corresponds to your Windows
operating system.
Windows Vista
1 Follow these steps to open the TCP/IPv4 or TCP/IPv6
Properties dialog box.
a From the desktop, click the Start button, select Control
Panel, and then double-click Network and Sharing
Center.
b In the Network and Sharing Center window, under
Tasks, select Manage Network Connections:
32 Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 33

c In the Network Connections window, double-click the
Wireless Network Connection option:
d In the Wireless Network Connection Status dialog
box, click the Properties button:
Appendix A: TCP/IP Settings 33
Page 34

e In the Wireless Network Connection Properties dialog
box, highlight the version of TCP/IP (Transmission
Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) that you are using
and click the Properties button:
f If you have an ad hoc network, continue with Step 2
below. If you have an infrastructure network, continue
with Step 3 below. If you're not sure what kind of
network you have, refer to page
13.
2 For Ad Hoc Networks: In the TCP/IPv4 or TCP/IPv6
Properties dialog box, on the General tab, complete the
following to set static IP addressing:
a Ensure that Obtain an IP address automatically is not
selected. Then select the buttons labeled: Use the
following IP address and Use the following DNS
server addresses.
b If this is the first computer to be set up in the ad hoc
network, enter 10.0.0.5 for an IP address. If you are
adding it to an existing ad hoc network, increment the
last digit by one, for example, 10.0.0.6, 10.0.0.7
34 Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 35

c Enter 255.255.255.0 for Subnet mask. The Subnet
mask should be the same for each computer in your ad
hoc network.
d Enter 10.0.0.5 for Default gateway and Preferred DNS
server. (This is the IP address of the first computer that
was set up in your ad hoc network.) The Default
Gateway and Preferred DNS server should be the
same for each computer in your ad hoc network.
e Click OK twice.
That’s it! You have set static IP addressing for a Windows Vista
computer in an ad hoc network.
3 For Infrastructure Networks: To verify your DHCP settings,
complete the following:
a Ensure that Obtain an IP address automatically is
selected.
b Select either Obtain a DNS server address
automatically or Use the following DNS server
addresses. All text boxes for static IP addressing should
be blank.
If you select Use the following DNS server addresses,
enter your preferred and alternate server addresses.
Appendix A: TCP/IP Settings 35
Page 36

c Click OK twice to exit.
That’s it! You have verified your DHCP settings for a Windows
Vista computer in an infrastructure network.
Windows XP
1 Follow these steps to open the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Properties dialog box.
a From the desktop, click the Start button, select Control
Panel, and then click Network Connections.
b Right-click the Wireless Network Connection icon, and
select Properties.
c In the Wireless Network Connection Properties dialog
box, select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) from the list, and
click the Properties button.
d If you have an ad hoc network, continue with step 2a. If
you have an infrastructure network, continue with step
3a. If you’re not sure what kind of network you have,
refer to page
13.
2 For Ad Hoc Networks: Complete the following to set static IP
addressing:
a Ensure that Obtain an IP address automatically is not
selected. Then select the buttons labeled: Use the
following IP address and Use the following DNS
server addresses.
b If this is the first computer to be set up in the ad hoc
network, enter 10.0.0.5 for an IP address. If you are
adding it to an existing ad hoc network, increment the
last digit by one, for example, 10.0.0.6, 10.0.0.7
c Enter 255.255.255.0 for Subnet mask. The Subnet
mask should be the same for each computer in your ad
hoc network.
d Enter 10.0.0.5 for Default gateway and Preferred DNS
server. (This is the IP address of the first computer that
was set up in your ad hoc network.) The Default
36 Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 37

Gateway and Preferred DNS server should be the
same for each computer in your ad hoc network.
e Click OK twice.
That’s it! You have set static IP addressing for a Windows XP
computer in an ad hoc network.
3 For Infrastructure Networks: To verify your DHCP settings,
complete the following:
a Ensure that Obtain an IP address automatically is
selected.
b Ensure that either Obtain a DNS server address
automatically or Enable DNS is selected. All text boxes
for static IP addressing should be blank.
c Click OK twice to exit.
That’s it! You have verified your DHCP settings for a Windows
XP computer in an infrastructure network.
Windows 2000
1 Follow these steps to open the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Properties dialog box.
a From the desktop, click the Start button, point to
Settings, then click Network and Dial-up
Connections.
b Right-click the Local Area Connection icon, and select
Properties.
c In the Properties dialog box, in the Connect Using box,
make sure the Zoom Wireless-G USB adapter is
displayed.
From the Components list, select Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) and click the Properties button.
d If you have an ad hoc network, continue with step 2. If
you have an infrastructure network, continue with step 3.
Appendix A: TCP/IP Settings 37
Page 38

2 Complete the following steps to set static IP addressing:
a In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties dialog
box, ensure that Obtain an IP address automatically is
selected. Then make sure the buttons labeled Use
not
the following IP address and Use the following DNS
server addresses are selected.
b If this is the first computer to be set up in the ad hoc
network, enter 10.0.0.5 for IP address. If you are adding
it to an existing ad hoc network, increment the last digit
by one, for example, 10.0.0.6, 10.0.0.7
c Enter 255.255.255.0 for Subnet mask. The Subnet
mask remains the same for each computer in your ad
hoc network.
d Enter 10.0.0.5 for Default gateway and Preferred DNS
server. (This is the IP address of the first computer that
was set up in your ad hoc network.) The Default
Gateway and Preferred DNS server should be the
same for each computer in your ad hoc network.
e Click OK twice.
That’s it! You have set static IP addressing for a Windows 2000
computer in an ad hoc network.
3 For Infrastructure Networks: To verify your DHCP settings,
complete the following:
a Ensure that Obtain an IP address automatically is
selected.
b Ensure that either Obtain a DNS server address
automatically or Enable DNS is selected. All text boxes
for static IP addressing should be blank.
c Click OK twice to exit.
That’s it! You have verified the DHCP settings for your Windows
2000 computer in an infrastructure network.
38 Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 39

Windows 98SE/Me
1 Follow these steps to open the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
Properties dialog box:
a From the desktop, click the Start button, point to
Settings, then click Control Panel.
b In the Control Panel window, double-click the Network
icon.
c In the Network dialog box, select the Zoom Wireless-G
USB TCP/IP from the list, click the Properties button
and then click OK.
d If you have an ad hoc network, continue with step 2a. If
you have an infrastructure network, continue with step
3a.
2 Complete the following to set static IP addressing:
a Ensure that Obtain an IP address automatically is not
selected. Then click the Specify an IP Address button.
b If this is the first computer to be set up in the ad hoc
network, enter 10.0.0.5 for IP address. If you are adding
a computer to an existing ad hoc network, increment the
last digit by one, for example, 10.0.0.6, 10.0.0.7
c Enter 255.255.255.0 for Subnet mask. The Subnet
mask should be the same for each computer in your ad
hoc network.
d Click the Gateway tab and enter 10.0.0.5 for Default
Gateway. (This is the IP address of the first computer
that was set up in your ad hoc network.) The Default
Gateway should be the same for each computer in your
ad hoc network.
e Enter 10.0.0.5 for Preferred DNS server. (This is the IP
address of the first computer that was set up in your ad
hoc network.) Click the DNS Configuration tab then
click Enable DNS. Enter 10.0.0.5 for Preferred DNS
server. The Preferred DNS server should be the same
for each computer in your ad hoc network.
Appendix A: TCP/IP Settings 39
Page 40

f Click OK twice.
That’s it! You have set static IP addressing for a Windows
98SE/Me computer in an ad hoc network.
3 For Infrastructure Networks: To verify your DHCP settings,
complete the following:
a Ensure that Obtain an IP address automatically is
selected.
b Ensure that either Obtain a DNS server address
automatically or Enable DNS is selected. All text boxes
for static IP addressing should be blank.
c Click OK twice to exit.
That’s it! You have verified the DHCP settings for your Windows
98SE/Me computer in an infrastructure network.
40 Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 41

Appendix B
Troubleshooting
If your Zoom Wireless-G USB adapter is not working properly, try
these suggestions.
• Make sure the adapter is securely connected to the
computer, either directly or through its USB extender cable.
• Perform a power cycle – take the following steps in the order
given:
1. Turn off the computer.
2. Turn off your wireless router, gateway or access point
and wait a few seconds.
3. Turn the router, gateway or access point back on.
4. Turn on the computer.
Windows Vista users: Try again to connect your wireless
adapter to a network using Windows Networking.
• If you are using the short USB cable, try changing the
orientation of the USB adapter.
• Turn the computer off, then on, and then check to see if the
adapter is working.
• Make sure that the adapter is not physically damaged.
• Try the adapter in another USB port.
• Unplug other USB devices from your computer one at a time
and see if that causes the adapter to work.
• If possible, try installing the adapter on another computer.
Windows XP, 2000, Me and 98 troubleshooting options
If the problem does not seem to be hardware-related, click the
Zoom icon on your desktop to run the Wireless-G USB software.
1 Check the Configuration tab to make sure that the SSID and
Network Type settings for the adapter are the same as these
settings for the other devices in your wireless network.
Appendix B: Troubleshooting 41
Page 42

2 Then click the Security tab and check the settings to make
sure that the adapter is configured for the same security
system as the other devices in your wireless network. Make
sure that your security key is the same – remember that the
keys are case-sensitive.
3 Check your TCP/IP settings as discussed in Appendix A of
the User Guide.
4 If the adapter still does not work, uninstall the software and
then re-install it. Unplug the adapter from the USB port, then
select Start – All Programs – Zoom Wireless-G USB –
Uninstall Zoom Wireless-G USB. Then re-install the
Wireless-G USB software.
If the above solutions do not work, consult Technical Support.
Please see Appendix C: Zoom Technical Support Services
on page
43.
42 Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 43

Appendix C
Zoom Technical Support
Services
Zoom has a variety of technical support services available to our
customers. We strive to provide convenient, professional support
responsive to our customers’ needs and capabilities. If you find
yourself unable to get your Zoom product to operate, and you
have thoroughly reviewed your owner’s manual and all relevant
documentation, please feel free to contact us for help.
For your records, and to facilitate Technical Support from either
your equipment supplier or Zoom, please record the following
information when you receive your Zoom product.
Product Information
Product Name
__________________________________
Product Model Number
__________________________________
Product Serial Number
__________________________________
Date Installed
_______________________
The serial number (S/N) is located on the adapter next to the S/N
barcode. Please be sure to write the number down. This will
greatly speed up your service and insure that the service
representative is addressing the proper Zoom product.
Calls to Zoom’s voice technical support staff are the most time
consuming, and at times you may find it difficult to get through.
We do not want you left on hold for long periods of time, so we
limit the queue length. We recommend that you take the time to
familiarize yourself with the other services described in this
section before calling. Many questions can be answered more
quickly using e-mail or our World Wide Web Home page.
Appendix C: Zoom Technical Support Services 43
Page 44

World Wide Web
Zoom’s Web page lets you send email for assistance, register
on-line, access product reviews and descriptions, and do a
whole lot more. Visit the Zoom Technical Support area for the
latest Flash Files and Drivers for your Zoom Product. To access
Zoom’s Web page, please log onto your local Internet Service
Provider, then go to the Web browser and select:
www.zoom.com
From Zoom’s Homepage you can easily go to Technical Support
or many other useful areas.
Smart Facts™ Q&A Search Engine (English Only)
Smart Facts™ is an automated intelligent database of Frequently
Asked Questions (FAQ’s) about Zoom products. It allows you to
search for solutions to your Technical Support questions, by
product or via a powerful Keyword Search Engine. If you still
cannot find a solution to your question, SmartFacts lets you
access our Technicians via email for a personalized response.
SmartFacts provides you with a way to track the history of your
problem and to add or change the description without having to
enter any information that was previously sent. SmartFacts can
even contact you automatically if there is an update to your
hardware or software that helps to address the question you had.
You can access SmartFacts from
www.zoom.com/techsupport
44 Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 45

Contact Zoom by Email
You can email Zoom with any tech support questions you might
have and one of our Technical Support Engineers will respond
by email within 2 business days. You may request personal
assistance via email at
Zoom, be sure to include the following:
• Serial number of your adapter
• Your full name and address
• A detailed description of your problem
www.zoom.com/techmail. When emailing
Contact Zoom by Phone
You can reach Technical Support by calling these numbers:
In the United States, call (561) 241-4371.
In the UK, call 0870 720 0090.
From continental Europe, call 44 (0)1252 580624.
Appendix C: Zoom Technical Support Services 45
Page 46

Return of Defective Units
Please contact your local distributor or reseller for Factory
Authorized Repair or Replacement of your In-Warranty
Defective Product. If you are unable to reach your distributor,
you can contact the Zoom Factory Customer Service by calling:
US: (561) 241-7712
UK: 0870 720 0090
From continental Europe: 44 (0)1252 580624
Please note that the customer is responsible for any charges
(including brokerage or customs and duties) associated with
shipping the defective unit to Zoom for repair. During the first
year Zoom will pay return shipping to the customer by common
carrier. After the first year the customer may be required to pay a
shipping and handling fee. Any applicable customs, duties and
brokerage charges to import the product are the responsibility of
the customer. Zoom encourages all customers to return
defective units to their respective reseller whenever possible.
46 Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 47

Appendix D
Regulatory Information
U.S. FCC Part 15 Emissions Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee
that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does
cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to
correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user's authority to operate this
equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
IEEE 802.11b or 802.11g operation of this product in the U.S.A. is firmwarelimited to channels 1 through 11.
Industry Canada Emissions Statement
This Class B digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian
Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B respecte toutes les exigences du
Règlement sur le matériel brouilleur du Canada.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1) this device may not cause interference and
2) this device must accept any interference, including interference that may
cause undesired operation of the device.
Appendix D: Regulatory Information 47
Page 48

Countries of Operation & Conditions of Use in the European Community
This device is intended to be operated in all countries of the European
Community.
Requirements for indoor vs. outdoor operation, license requirements and allowed
channels of operation apply in some countries as described below:
Note: The user must ensure that the channels of operation are in conformance
with the spectrum usage rules for European Community countries as described
below.
• This device will automatically limit the allowable channels, as determined by
the setup program during installation, by examining the operating system's
current country of operation. If the country of operation is not determined, the
device will default to US settings. Use of the incorrect country of operation
may result in operation not in accordance with local regulations, and may
cause harmful interference to other systems. The user is obligated to ensure
that the device is operating according to the channel limitations,
indoor/outdoor restrictions and license requirements for each European
Community country as described in this document. If configured incorrectly,
you can contact technical support for instructions on changing the device's
spectrum usage.
• This device may be operated indoors or outdoors in all countries of the
European Community using the 2.4 GHz band: Channels 1 - 13, except where
noted below.
− In Italy the end-user must apply for a license from the national spectrum
authority to operate this device outdoors.
− In Belgium outdoor operation is only permitted using the 2.46 - 2.4835 GHz
band: Channel 13.
− In France outdoor operation is only permitted using the 2.4 - 2.454 GHz
band: Channels 1 - 7.
Electrostatic Discharge Statement
The unit may require resetting after a severe electrostatic discharge event.
48 Wireless-G USB Adapter
Page 49

Declaration of Conformity
Declaration of Conformity Overensstemmelseserklæring
Déclaration de conformité Conformiteitsverklaring van de EU
Konformitätserklärung Δήλωση Συμμόρφωσης
Dichiarazione di conformità Deklaracja zgodności
Declaração de Conformidade Declaración de conformidad
Konformitetsdeklaration Cam kết về sự tuân thủ ở Châu Âu
Manufacturer/Producent/Fabrikant/
Constructeur/Hersteller/Κατασκευαστής/
Fabbricante/ Fabricante/Tillverkare/
Nhà sản xuất
Brand/Varemærke/Merk/Marque/Marke/
Μάρκα/Marchio/Marka/Marca/Thương hiệu
Type/Typ/Μάρκα/Tipo/Kiểu mẫu Model 4410A
The manufacturer declares under sole responsibility that this equipment is compliant to
Directive 1999/5/EC via the following. This product is CE marked.
Producenten erklærer under eneansvar, at dette udstyr er i overensstemmelse med
direktivet 1999/5/EC via følgende. Dette produkt er CE-mærket.
De fabrikant verklaart geheel onder eigen verantwoordelijkheid dat deze apparatuur voldoet
aan Richtlijn 1999/5/ EC op grond van het onderstaande. Dit product is voorzien van de CEmarkering.
Le constructeur déclare sous son entière responsabilité que ce matériel est conforme à la
Directive 1999/5/EC via les documents ci-dessous. Ce produit a reçu le marquage CE.
Hiermit erklärt Zoom die Übereinstimmung des Gerätes modem mit den grundlegenden
Anforderungen und den anderen relevanten Festlegungen der Richtlinie 1999/5/EC. Dieses
Produkt ist das gekennzeichnete CE.
Ο κατασκευαστής δηλώνει με αποκλειστική του ευθύνη ότι αυτό το προϊόν συμμορφώνεται
με την Οδηγία 1999/5/ΕC μέσω των παρακάτω. Αυτό το προϊόν φέρει τη Σήμανση CE.
Il fornitore dichiara sotto la sola responsabilità che questa apparecchiatura è compliant a
1999/5/EC direttivo via quanto segue. Questo prodotto è CE contrassegnato.
Producent stwierdza że to urządzenie zostało wyprodukowane zgodnie z Dyrektywą
1999/5/EC. Jest to potwierdzone poprzez umieszczenie znaku CE na urządzeniu.
O fabricante declara sob sua exclusiva responsabilidade que este equipamento está em
conformidade com a Directiva 1999/5/EC através do seguinte. Este produto possui
Marcação CE.
El fabricante declara bajo su exclusiva responsabilidad que este equipo satisface la Directiva
1999/5/EC por medio de lo siguiente. Este producto tiene marca CE.
Nhà sản xuất cam kết với trách nhiệm của mình là thiết bị này tuân theo Hướng dẫn
1999/5/EC thông qua các mục sau. Sản phẩm này được đánh dấu là CE.
73/23/EEC – LVD EN 60950-1:2001
89/336/EEC – EMC
1999/5/EC EN 300 328, v1.4.1: 2003-04
EN 301 489-1, v1.4.1: 2002-08
EN 301 489-17, v1.2.1: 2002-08
Andy Pollock
7 June, 2007
4410A/TF, Boston, MA, USA
Zoom Technologies, Inc.
207 South Street
Boston, MA 02111 USA / 617-423-1072
www.zoom.com
Zoom Wireless-G USB Adapter
Director, Hardware Engineering/Direktør, Hardware
Engineering/Director, Sustaining Engineering
/Directeur, Ingénierie de soutien/Direktør, Sustaining
Engineering /Διευθυντής, Μηχανικής Διατήρησης
/Direttore, Hardware Engineering /Dyrektor,
Inżynieria ciągła/Director, Engenharia de
Manutençã/Director, Ingeniería de apoyo/Giám Đốc
Kỹ thuật Phần cứng
Appendix D: Regulatory Information 49
Page 50

NOTICE
This document contains proprietary information protected by
copyright, and this User Guide and all the accompanying hardware,
software, and documentation are copyrighted. No part of this
document may be photocopied or reproduced by mechanical,
electronic, or other means in any form.
The manufacturer does not warrant that the hardware will work
properly in all environments and applications, and makes no
warranty or representation, either expressed or implied, with respect
to the quality, performance, merchantability, or fitness for a
particular purpose of the software or documentation. The
manufacturer reserves the right to make changes to the hardware,
software, and documentation without obligation to notify any person
or organization of the revision or change.
All brand and product names are the trademarks of their respective
owners.
Wi-Fi® is a registered trademark of the Wi-Fi Alliance.
Microsoft® and Windows® are registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation.
© Copyright 2007
All rights reserved.
1587-B 27433 ©2007
 Loading...
Loading...