ZILOG Z8932320FEC, Z8932320FSC, Z8932320VEC, Z893232YFSC, Z8932320VSC Datasheet
...
1
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
FEATURES
P
RELIMINARY
C
USTOMER PROCUREMENT SPECIFICATION
DSP ROM OTP DSP RAM Max Core
Device (K Words) (K Words) (Words) MIPS
Z89323 8 512 20
Z89373 8 512 16
Z89393 64* 512 20
* External
Package 44-Pin 68-Pin 44-Pin 80-Pin 100-Pin
Device PLCC PLCC QFP QFP QFP
Z89323 ✔✔✔✔
Z89373 ✔✔✔✔
Z89393 ✔
■ Operating Temperature Ranges:
0°C to +70°C (Standard)
–40°C to +85°C (Extended)
■ 4.5- to 5.5-Volt Operating Range
DSP Core
■ 20 MIPS @ 20 MHz, 16-Bit Fixed Point DSP
■ 50 ns Instruction Cycle Time
■ Single-Cycle Multiply and ALU Operations
■ Two Internal Data Buses and Address Generators
■ Six Register Address Pointers
■ Optimized Instruction Set (30 Instructions)
On-Board Peripherals
■ 4-Channel, 8-Bit Analog to Digital Converter (A/D)
■ On-Board Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
■ Up to 40 Bits of Programmable I/O
■ Two Channels of Programmable
Pulse Width Modulators (PWM)
■ Three General-Purpose Timer/Counters
■ Two Watch-Dog Timers (WDT)
■ Programmable PLL
■ Three Vectored Interrupts Servicing Eight
Interrupt Sources
■ Power-Down and Power-On Reset
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Z89323/373/393 DSP family of products builds on
Zilog's first generation Z893XX DSP core, integrating several
peripherals especially well suited for cost-effective voice,
telephony, and control applications.
These DSP devices feature a modified Harvard architecture
supported by one program bus and two on-chip data
buses. This bus structure is supported by two address
generators and six register pointers to ensure that the
20 MIPS DSP CPU is continually active.
The Z893X3 DSP family is designed to provide a complete
DSP and control system on a single chip. By integrating
various peripherals, such as a high-speed 4-channel, 8-bit
A/D, an SPI, three timers with PWM and WDT support, the
Z893X3 family provides a compact system solution and
reduces overall system cost.
To support a wide variety of development needs, the
Z893X3 DSP product family features the cost-effective
Z89323 with 8 Kwords of on-chip ROM, and the Z89373, a
16-MIPS OTP version of the Z89323, ideal for prototypes
and early production builds. For systems requiring more
than 8 Kwords of program memory, the Z89393 device can
address up to 64 Kwords of external program memory.
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGIT AL
SIGNAL PROCESSORS
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
2
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
GENERAL DESCRIPTION (Continued)
The Z893X3 DSP family is 100 percent source and objectcode compatible with the existing Z89321/371/391 devices,
providing users, who can benefit from increased integration
and reduced system cost, an easy migration path from one
DSP product to the next.
Throughout this specification, references to the Z89323
device applies equally to the Z89373 and Z89393, unless
otherwise specified.
Notes:
All Signals with a preceding front slash, "/", are active Low, e.g.,
B//W (WORD is active Low); /B/W (BYTE is active Low, only).
Power connections follow conventional descriptions below:
Connection Circuit Device
Power V
CC
V
DD
Ground GND V
SS
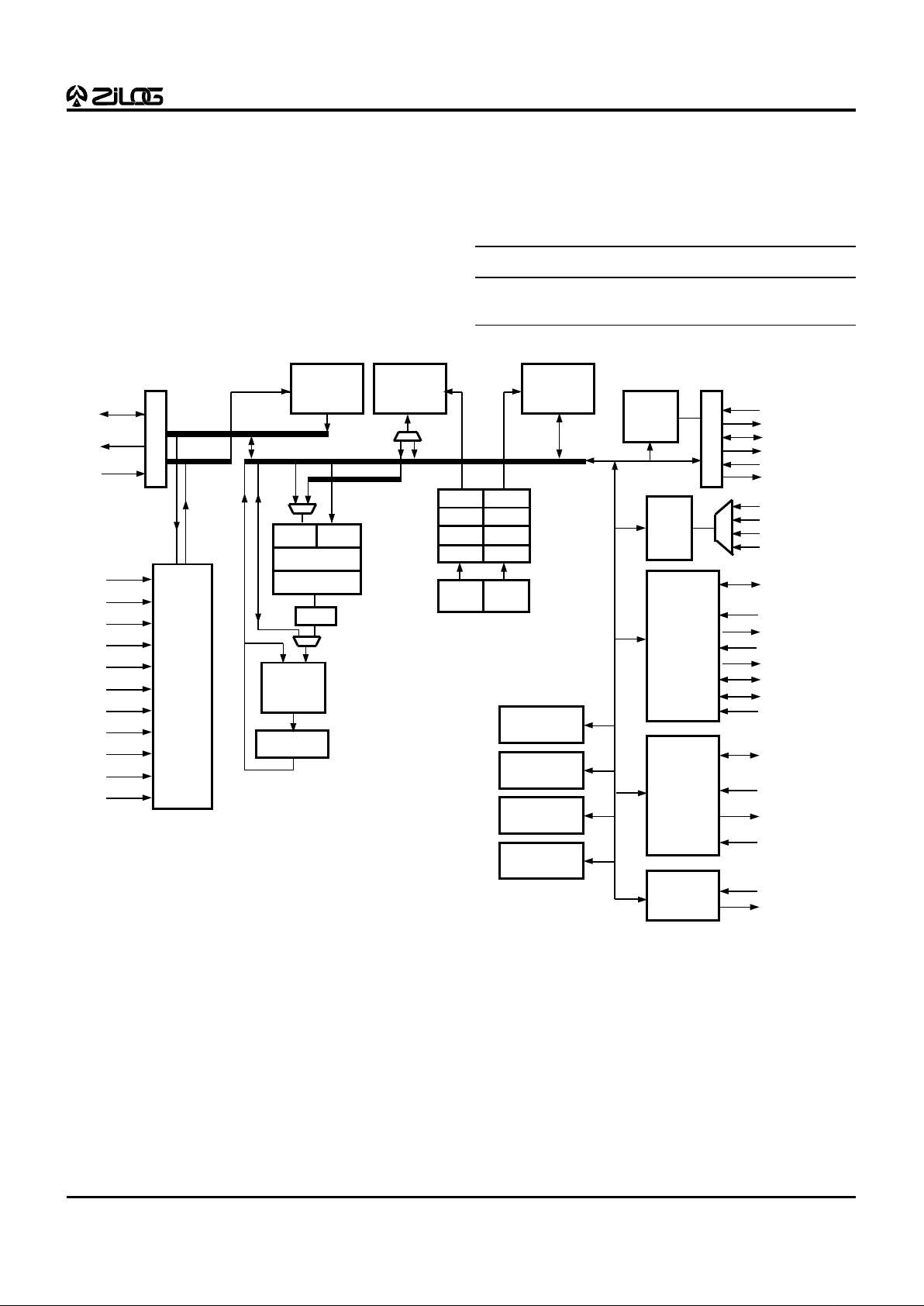
Figure 1. Z893X3 Functional Block Diagram
Program
ROM/OTP
8192x16
Data RAM0
256x16
EA0-2
EXT0-15/P00-15
/DS
WAIT
RD//WR
Data RAM1
256x16
DDATA
XDATA
PDATA
PADDR
PD0-15
PA0-15
Shifter
Arithmetic
Logic Unit
(ALU)
Program
Control
Unit
CLKO
HALT
/ROMEN
/RES
Accumulator
Port 1
P10-17
or
INT2
CLKOUT
SIN
SOUT
SK
SS
UI0-1
XY
Multiplier
P
DP0-3 DP4-6
P2 P2
P1 P1
P0 P0
ADDR
GEN0
ADDR
GEN1
8-Bit
A/D
AN0
AN1
AN2
AN3
16-Bit
Program
I/O
Port 0
8-Bit I/O
CLKI
/PAZ
VALI
AGND
ANVCC
VALO
VSS
VDD
/EXTEN
8-Bit I/O
Port 2
P20-27
UI2
UO0-2
INT0-1
or
16-Bit Timer ,
Counter
16-Bit Timer ,
Counter, PWM
16-Bit Timer ,
Counter, PWM
SPI
Port 3
P30-33
P34-37
4 Inputs
4 Outputs
3
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
PIN DESCRIPTION
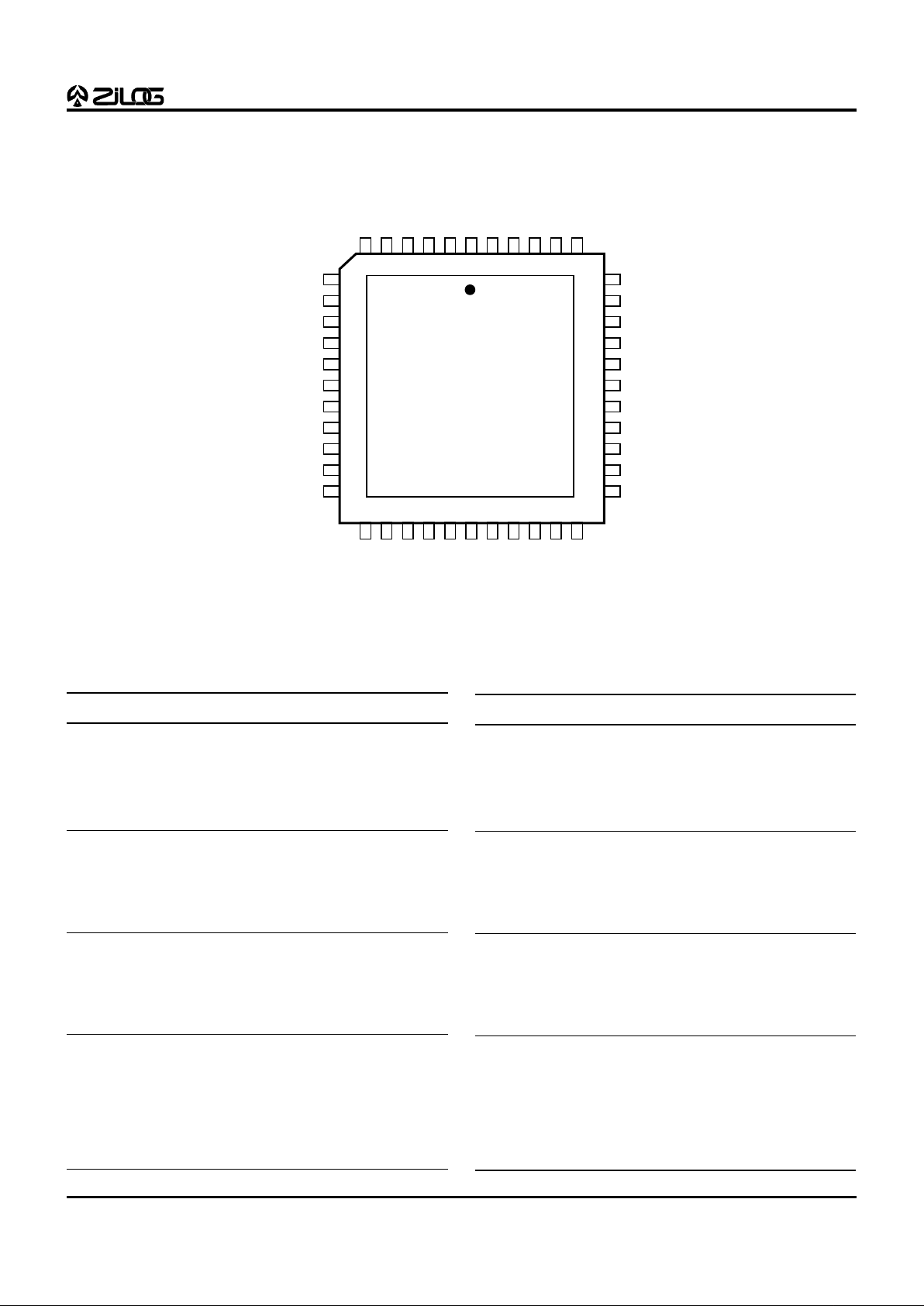
No. Symbol Function Direction
1 P20/INT0 Port 2 0/Interrupt 0 In/Output
2 EXT12/P012 Ext Data 12/Port 0 12 In/Output
3 EXT13/P013 Ext Data 13/Port 0 13 In/Output
4 EXT14/P014 Ext Data 14/Port 0 14 In/Output
5V
SS
Ground
6 EXT15/P015 Ext Data 15/Port 0 15 In/Output
7 EXT3/P03 Ext Data 3/Port 0 3 In/Output
8 EXT4/P04 Ext Data 4/Port 0 4 In/Output
9V
SS
Ground
10 EXT5/P05 Ext Data 5/Port 0 5 In/Output
11 EXT6/P06 Ext Data 6/Port 0 6 In/Output
12 EXT7/P07 Ext Data 7/Port 0 7 In/Output
13 P21/INT1 Port 2 1/Interrupt 1 In/Output
14 EXT8/P08 Ext Data 8/Port 0 8 In/Output
15 EXT9/P09 Ext Data 9/Port 0 9 In/Output
16 V
SS
Ground
17 EXT10/P010 Ext Data 10/Port 0 10 In/Output
18 EXT11/P011 Ext Data 11/Port 0 11 In/Output
19 VAHI Analog High Ref. Input
20 VALO Analog Low Ref. Input
21 ANGND Analog Ground Input
2 2 AN 0 A/D Input 0 Input
No. Symbol Function Direction
2 3 AN 1 A/D Input 1 Input
2 4 AN 2 A/D Input 2 Input
2 5 AN 3 A/D Input 3 Input
26 ANVCC Analog Power Input
27 V
DD
Power
28 RD//WR R/W External Bus Output
29 EA0 Ext Address 0 Output
30 EA1 Ext Address 1 Output
31 EA2 Ext Address 2 Output
32 P23/UO1 Port 2 3/User Output 1 In/Output
33 /DS Ext Data Strobe Output
34 CLKI Clock/Crystal In Input
35 CLKO Clock/Crystal Out Input
36 P22/UO0 Port 2 2/User Output 0 In/Output
37 P24/UO2 Port 2 4/User Output 2 In/Output
38 WAIT Wait for Ext Input
39 /RES Reset Input
40 V
SS
Ground
41 EXT0/P00 Ext Data 0/Port 0 0 In/Output
42 EXT1/P01 Ext Data 1/Port 0 1 In/Output
43 EXT2/P02 Ext Data 2/Port 0 2 In/Output
44 V
SS
Ground
Figure 2. 44-Pin PLCC Z89323/373 Pin Configuration
Table 1. 44-Pin PLCC Z89323/373 Pin Description
6
Z89323/373
44-Pin PLCC
EXT3/P03
543214443424140
18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
EXT4/P04
VSS
EXT5/P05
EXT6/P06
EXT7/P07
INT1/P21
EXT8/P08
EXT9/P09
VSS
EXT10/P010
/RES
WAIT
P24/UO2
P22/UO0
CLKO
CLKI
/DS
P23/UO1
EA2
EA1
EA0
EXT1
1/P01
1
V
AHI
V
ALO
ANGND
AN0
AN1
AN2
AN3
ANVCC
VDD
RD//WR
EXT15/P015
VSS
EXT14/P014
EXT13/P013
EXT12/P012
P20/INT0
VSS
EXT2/P02
EXT1/P01
EXT0/P00
VSS
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
4
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
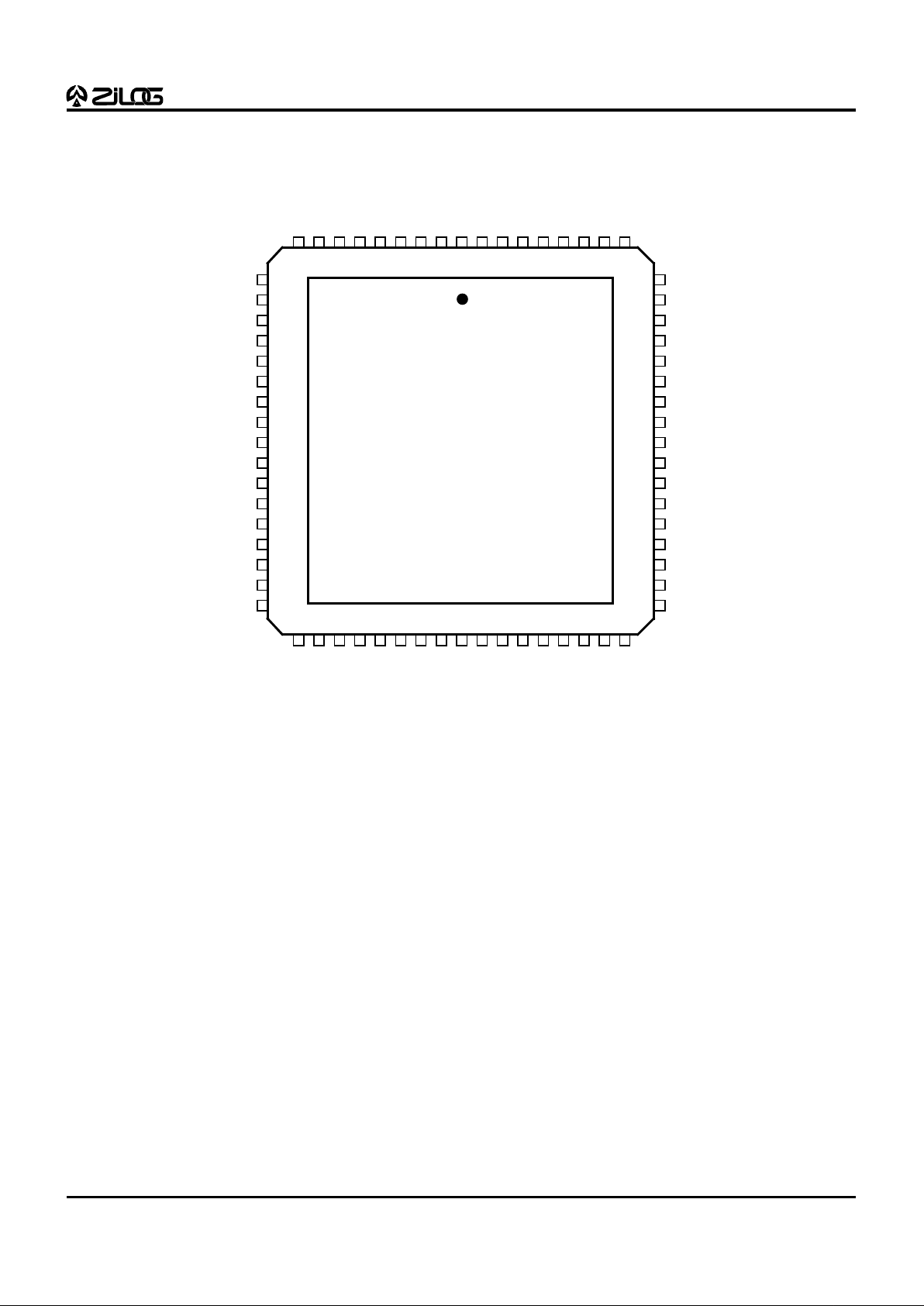
Figure 3. 68-Pin PLCC Z89323/373 Pin Configuration
Z89323/373
68-Pin PLCC
789 654321
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61
27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
EXT11/P011
VDD
VAHI
VSS
UI0/P16
VALO
UI1/P17
AGND
AN0
AN1
AN2
AN3
VSS
P21/INT1
ANVCC
VDD
RD//WR
VSS
/RES
WAIT
P25/UI2
P22/UO0
P26
CLKO
CLKI
P24/UO2
/DS
P23/UO1
VDD
NC
EA2
EA1
EA0
HALT
NC
EXT3/P03
EXT4/P04
VSS
VDD
EXT5/P05
SOUT/P13
EXT6/P06
SS/P14
EXT7/P07
SK/P15
P27
EXT8/P08
EXT9/P09
VSS
EXT10/P010
VSS
NC
EXT15/P015
VSS
EXT14/P014
VDD
EXT13/P013
EXT12/P012
P20/INT0
P12/SIN
P11/CLKOUT
VSS
P10
EXT2/P02
EXT1/P01
EXT0/P00
VSS
VDD

5
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
Table 2. 68-Pin PLCC Z89323/373 Pin Description
No. Symbol Function Direction
1 P12/SIN Port 1 2/Serial Input In/Output
2 P20/INT0 Port 2 0/Interrupt 0 In/Output
3 EXT12/P012 Ext Data 12/Port 0 12 In/Output
4 EXT13/P013 Ext Data 13/Port 0 13 In/Output
5VDD Power
6 EXT14/P014 Ext Data 14/Port 0 14 In/Output
7V
SS
Ground
8 EXT15/P015 Ext Data 15/Port 0 15 In/Output
9NC No Connection
10 NC No Connection
11 EXT3/P03 Ext Data 3/Port 0 3 In/Output
12 EXT4/P04 Ext Data 4/Port 0 4 In/Output
13 V
SS
Ground
14 V
DD
Power
15 EXT5/P05 Ext Data 5/Port 0 5 In/Output
16 P13/SOUT Port 1 3/Serial Output In/Output
17 EXT6/P06 Ext Data 6/Port 0 6 In/Output
18 P14/SS Port 1 4/Serial Select In/Output
19 EXT7/P07 Ext Data 7/Port 0 7 In/Output
20 P15/SK Port 1 5/Serial Clock In/Output
2 1 P2 7 Port 2 7 In/Output
22 EXT8/P08 Ext Data 8/Port 0 8 In/Output
23 EXT9/P09 Ext Data 9/Port 0 9 In/Output
24 V
SS
Ground
25 EXT10/P010 Ext Data 10/Port 0 10 In/Output
26 V
SS
Ground
27 EXT11/P011 Ext Data 11/Port 0 11 In/Output
28 V
DD
Power
29 VAHI Analog High Ref. Input
30 V
SS
Ground
31 P16/UI0 Port 1 6/User Input 0 In/Output
32 VALO Analog Low Ref. Input
33 P17/UI1 Port 1 7/User Input 1 In/Output
34 ANGND Analog Ground Input
No. Symbol Function Direction
3 5 A N0 A/D Input 0 Input
3 6 A N1 A/D Input 1 Input
3 7 A N2 A/D Input 2 Input
3 8 A N3 A/D Input 3 Input
39 V
SS
Ground
40 P21/INT1 Port 2 1/Interrupt 1 In/Output
41 ANVCC Analog Power Input
42 V
DD
Power Input
43 RD//WR R/W External Bus Output
44 HALT Halt Execution Input
45 EA0 Ext Address 0 Output
46 EA1 Ext Address 1 Output
47 EA2 Ext Address 2 Output
48 NC No Connection
49 V
DD
Power
50 P23/UO1 Port 2 3/User Output 1 In/Output
51 /DS Ext Data Strobe Output
52 P24/UO2 Port 2 4/User Output 2 In/Output
53 CLKI Clock/Crystal In Input
54 CLKO Clock/Crystal Out Input
5 5 P2 6 Port 2 6 In/Output
56 P22/UO0 Port 2 2/User Output 0 In/Output
57 P25/UI2 Port 2 5/User Input 2 In/Output
58 WAIT Wait for Ext Input
59 /RES Reset Input
60 V
SS
Ground
61 V
DD
Power
62 V
SS
Ground
63 EXT0/P00 Ext Data 0/Port 0 0 In/Output
64 EXT1/P01 Ext Data 1/Port 0 1 In/Output
65 EXT2/P02 Ext Data 2/Port 0 2 In/Output
66 P10/INT2 Port 1 0/Interrupt 2 In/Output
67 V
SS
Ground
68 P11/CLKOUT Port 1 1/Clock Output In/Output
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
6
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
EXT15/P015
VSS
EXT14/P014
EXT13/P013
P20/INT0
VSS
EXT2/P02
EXT1/P01
EXT0/P00
VSS
EXT11/P011
VAHI
VALO
ANGND
AN0
AN1
AN2
AN3
ANVCC
VDD
RD//WR
/RES
WAIT
P24/UO2
P22/UO0
CLK0
CLK1
/DS
P23/UO1
EA2
EA1
EA0
EXT3/P03
EXT4/P04
VSS
EXT5/P05
EXT6/P06
EXT7/P07
INT1/P21
EXT8/P08
EXT9/P09
VSS
EXT10/P010
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
33
Z89323/373
44-Pin QFP
44 43 42 41 40 39 38 37 36 35 34
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22
EXT12/P012
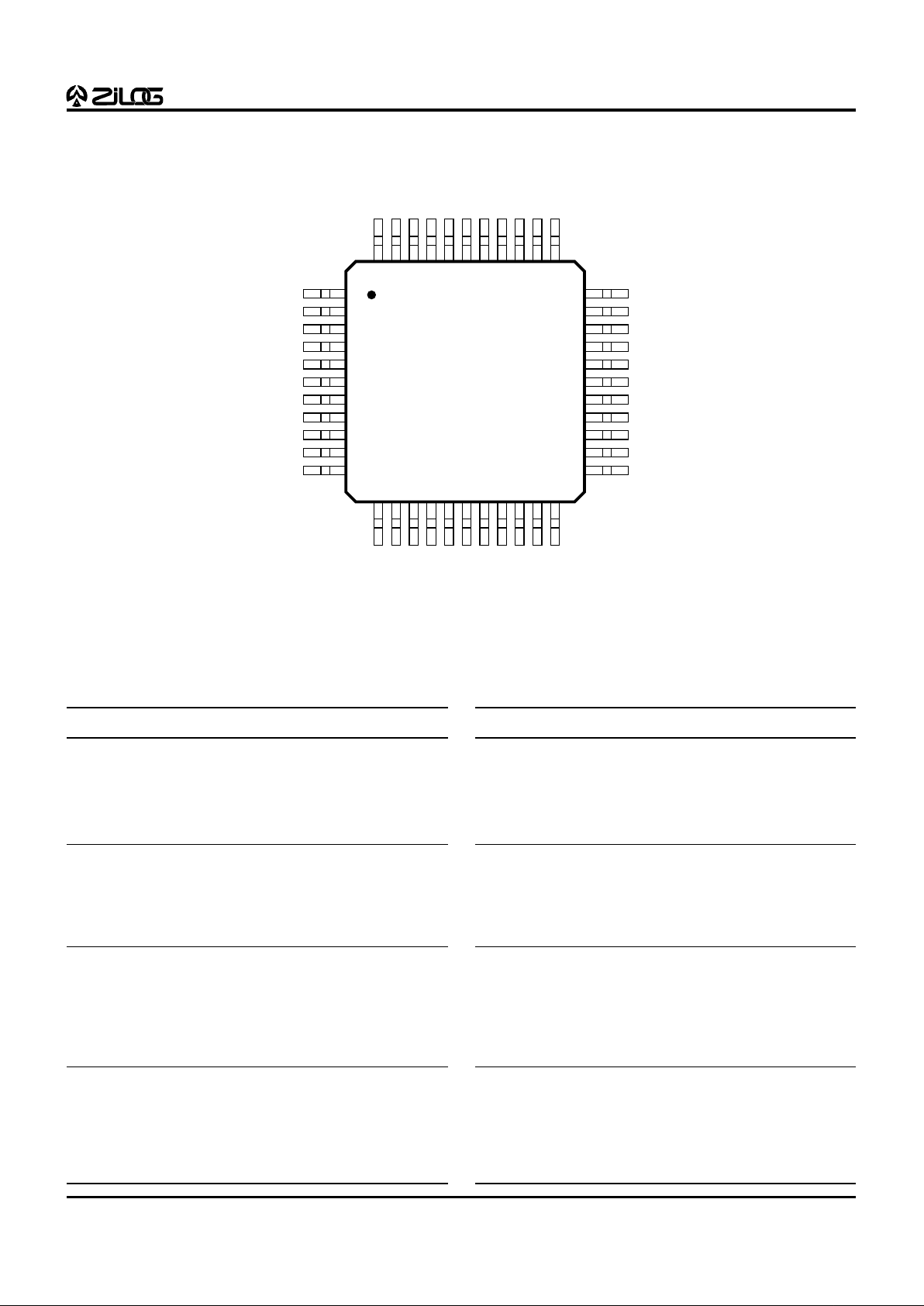
No. Symbol Function Direction
1 EXT3/P03 Ext Data 3/Port 0 3 In/Output
2 EXT4/P04 Ext Data 4/Port 0 4 In/Output
3V
SS
Ground
4 EXT5/P05 Ext Data 5/Port 0 5 In/Output
5 EXT6/P06 Ext Data 6/Port 0 6 In/Output
6 EXT7/P07 Ext Data 7/Port 0 7 In/Output
7 P21/INT1 Port 2 1/Interrupt 1 In/Output
8 EXT8/P08 Ext Data 8/Port 0 8 In/Output
9 EXT9/P09 Ext Data 9/Port 0 9 In/Output
10 V
SS
Ground
11 EXT10/P010 Ext Data 10/Port 0 10 In/Output
12 EXT11/P011 Ext Data 11/Port 0 11 In/Output
13 VAHI Analog High Ref. Input
14 VALO Analog Low Ref. Input
15 ANGND Analog Ground Input
1 6 A N0 A/D Input 0 Input
1 7 A N1 A/D Input 1 Input
1 8 A N2 A/D Input 2 Input
1 9 A N3 A/D Input 3 Input
20 ANVCC Analog Power Input
21 V
DD
Power
22 RD//WR R/W External Bus Output
No. Symbol Function Direction
23 EA0 Ext Address 0 Output
24 EA1 Ext Address 1 Output
25 EA2 Ext Address 2 Output
26 P23/UO1 Port 2 3/User Output 1 In/Output
27 /DS Ext Data Strobe Output
28 CLKI Clock/Crystal In Input
29 CLKO Clock/Crystal Out Input
30 P22/UO0 Port 2 2/User Output 0 In/Output
31 P24/UO2 Port 2 4/User Output 2 In/Output
32 WAIT Wait for Ext Input
33 /RES Reset Input
34 V
SS
Ground
35 EXT0/P00 Ext Data 0/Port 0 0 In/Output
36 EXT1/P01 Ext Data 1/Port 0 1 In/Output
37 EXT2/P02 Ext Data 2/Port 0 2 In/Output
38 V
SS
Ground
39 P20/INT0 Port 2 0/Interrupt 0 In/Output
40 EXT12/P012 Ext Data 12/Port 0 12 In/Output
41 EXT13/P013 Ext Data 13/Port 0 13 In/Output
42 EXT14/P014 Ext Data 14/Port 0 14 In/Output
43 V
SS
Ground
44 EXT15/P015 Ext Data 15/Port 0 15 In/Output
Table 3. 44-Pin QFP Z89323/373 Pin Description
Figure 4. 44-Pin QFP Z89323/373 Pin Configuration
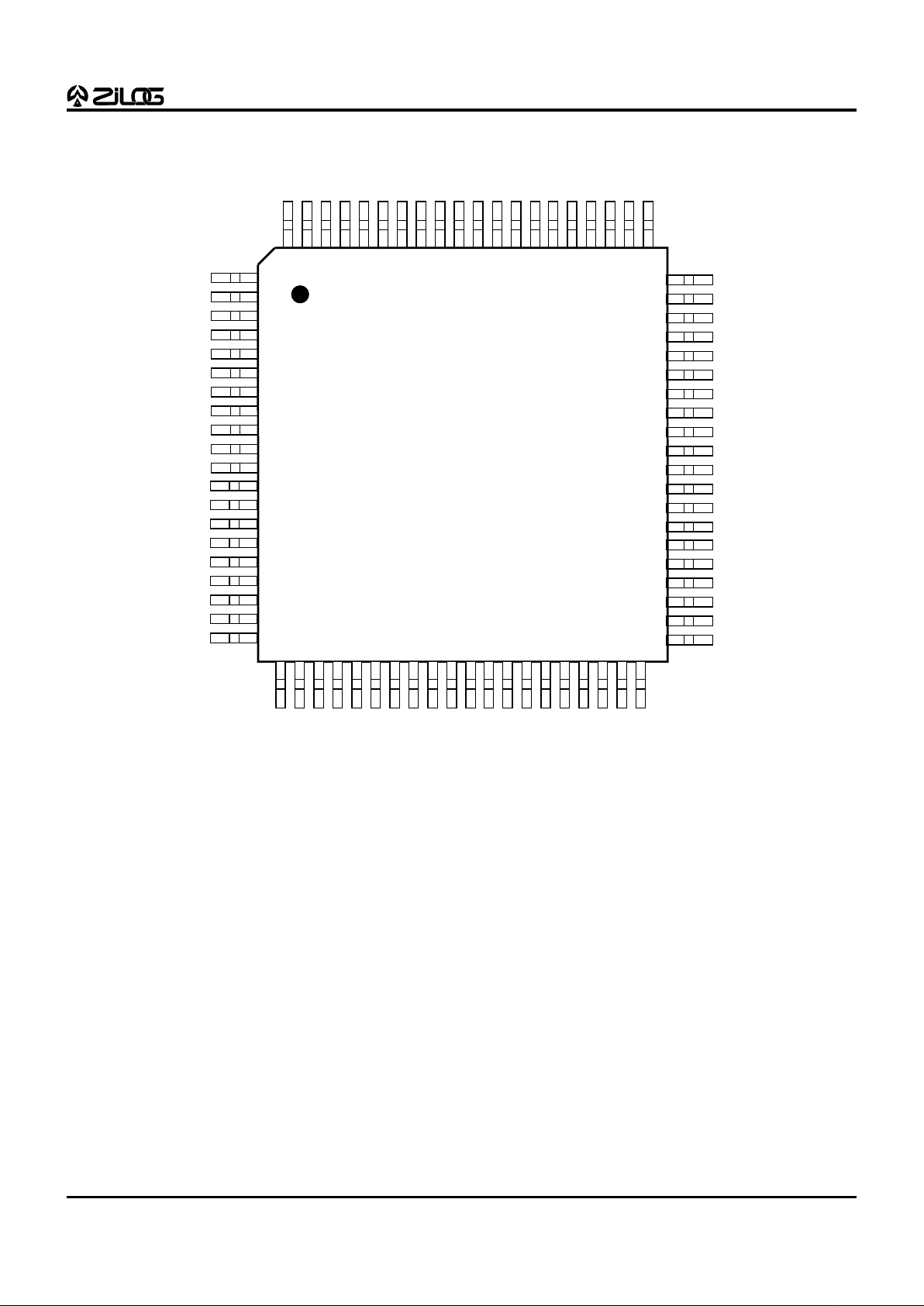
7
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
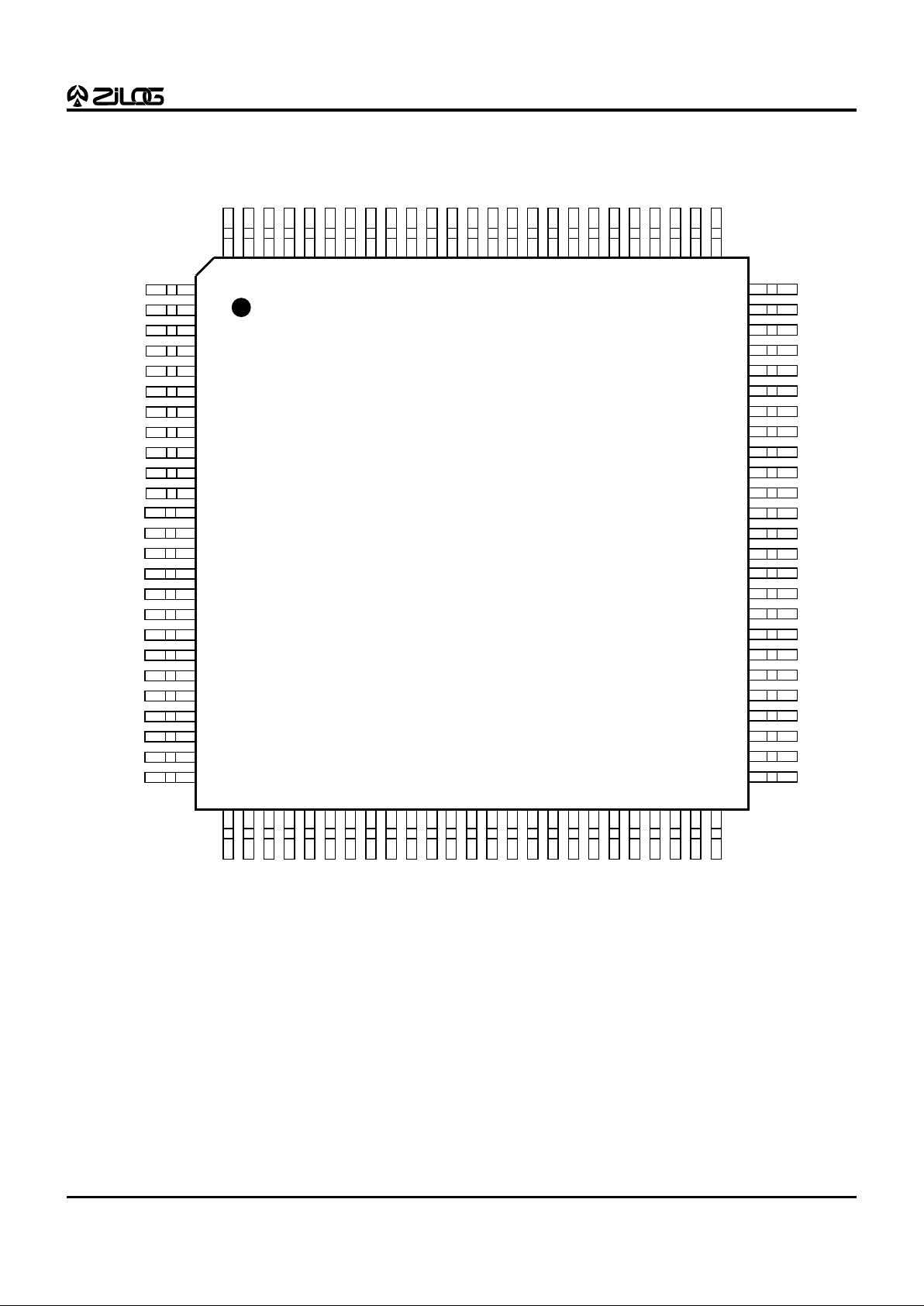
Figure 4a. 80-Pin QFP Z89323/373 Pin Configuration
41
RD//WR
42
P35
43
NC
44
HALT
45
EA0
46
P36
47
EA1
48
EA2
49
NC
50
VCC
51
P23/U01
53
P24/U02
54
CLKI
55
CLKO
56
P26
57
P22/UO0
59
WAIT
52
/DS
60
P37
58
P25/UI2
NC
EXT15/P015
/EXTEN
NC
EXT3/P03
P32
EXT4/P04
VSS
VCC
EXT5/P05
P13/SOUT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Z89323
80-Pin QFP
EXT6/P06
P14/SS
EXT7/P07
P15/SK
P27
EXT8/P08
EXT9/P09
VSS
P33
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
61
/RES
62
VSS
63
VCC
64
NC
65
VSS
66
P30
67
EXT0/P00
68
EXT1/P01
69
EXT2/P02
70
P10/INT2
71
VSS
73
P12/SIN
74
P20/INT0
75
EXT12/P012
76
EXT13/P013
77
VCC
79
VSS
72
P11/CLKOUT
80
P31
78
EXT14/P014
EXT10/P010
VSS
NC
P34
EXT11/P011
VCC
VAHI
VSS
P16/UI0
VAL0
P17/UI1
21
22
232425
26
27
28
29
30
31
ANGND
AN0
AN1
AN2
AN3
VSS
INT1/P21
ANVCC
VCC
323334353637383940

Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
8
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Table 4a. 80-Pin QFP Z89323/373 Pin Description
No. Symbol Function Direction
1NC No Connection
2 EXT15/P015 Ext Data 15/Port 0 15 In/Output
3 /EXTEN Ext Enable Input
4NC No Connection
5 EXT3/P03 Ext Data 3/Port 0 3 In/Output
6 P32 Port3 2 Input
7 EXT4/P04 Ext Data 4/Port 0 4 In/Output
8V
SS
Ground
9V
DD
Power
10 EXT5/P05 Ext Data 5/Port 0 5 In/Output
11 P13/SOUT Port 1 3/Serial Output In/Output
12 EXT6/P06 Ext Data 6/Port 0 6 In/Output
13 P14/SS Port 1 4/Serial Select In/Output
14 EXT7/P07 Ext Data 7/Port 0 7 In/Output
15 P15/SK Port 1 5/Serial Clock In/Output
1 6 P2 7 Port 2 7 In/Output
17 EXT8/P08 Ext Data 8/Port 0 8 In/Output
18 EXT9/P09 Ext Data 9/Port 0 9 In/Output
19 V
SS
Ground
2 0 P3 3 Port 3 3 Input
21 EXT10/P010 Ext Data 10/Port 0 10 In/Output
22 V
SS
Ground
23 NC No Connection
2 4 P3 4 Port 3 4 Output
25 EXT11/P011 Ext Data 11/Port 0 11 In/Output
26 V
DD
Power
27 VAHI Analog High Ref. Input
28 V
SS
Ground
29 P16/UI0 Port 1 6/User Input 0 In/Output
30 VAL0 Analog Low Ref. Input
31 P17/UI1 Port 1 7/User Input 1 In/Output
32 ANGND Analog Ground Input
3 3 A N0 A/D Input 0 Input
3 4 A N1 A/D Input 1 Input
3 5 A N2 A/D Input 2 Input
3 6 A N3 A/D Input 3 Input
37 V
SS
Ground
38 P21/INT1 Port 2 1/Interrupt 1 In/Output
39 ANVCC Analog Power Input
40 V
DD
Power Input
No. Symbol Function Direction
41 RD//WR R/W External Bus Output
4 2 P3 5 Port 3 5 Output
43 NC No Connection
44 HALT Halt Execution Input
45 EA0 Ext Address 0 Output
4 6 P3 6 Port 3 6 Output
47 EA1 Ext Address 1 Output
48 EA2 Ext Address 2 Output
49 NC No Connection
50 V
DD
Power
51 P23/UO1 Port 2 3/User Output 1 In/Output
52 /DS Ext Data Strobe Output
53 P24/UO2 Port 2 4/User Output 2 In/Output
54 CLKI Clock/Crystal In Input
55 CLKO Clock/Crystal Out Input
5 6 P2 6 Port 2 6 In/Output
57 P22/UO0 Port 2 2/User Output 0 In/Output
58 P25/UI2 Port 2 5/User Input 2 In/Output
59 WAIT Wait for Ext Input
6 0 P3 7 Port 3 7 Output
61 /RES Reset Input
62 V
SS
Ground
63 V
DD
Power
64 NC No Connection
65 V
SS
Ground
6 6 P3 0 Port 3 0 Input
67 EXT0/P00 Ext Data 0/Port 0 0 In/Output
68 EXT1/P01 Ext Data 1/Port 0 1 In/Output
69 EXT2/P02 Ext Data 2/Port 0 2 In/Output
70 P10/INT2 Port 1 0/Interrupt 2 In/Output
71 V
SS
Ground
72 P11/CLKOUT Port 1 1/Clock Output In/Output
73 P12/SIN Port 1 2/Serial Input In/Output
74 P20/INT0 Port 2 0/Interrupt 0 In/Output
75 EXT12/P012 Ext Data 12/Port 0 12 In/Output
76 EXT13/P013 Ext Data 13/Port 0 13 In/Output
77 V
DD
Power
78 EXT14/P014 Ext Data 14/Port 0 14 In/Output
79 V
SS
Ground
8 0 P3 1 Port 3 1 Input
9
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
/EXTEN
EXT3/P03
PA8
EXT4/P04
PA9
VSS
VDD
EXT5/P05
PA10
SOUT/P13
EXT6/P06
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Z89393
100-Pin QFP
PA11
SS/P14
EXT7/P07
SK/P15
P27
PA12
EXT8/P08
PA13
EXT9/P09
PA14
VSS
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
PA15
EXT10/P010
VSS
23
24
25
PD0
EXT11/P011
PD1
VDD
VAHI
VSS
UI0/P16
VALO
UI1/P17
PD2
ANGND
26
27
282930
31
32
33
34
35
36
AN0
AN1
AN2
AN3
VSS
INT1/P21
ANVCC
PD3
VDD
PD4
PD5
3738394041424344454647
RD//WR
PD6
PD7
484950
51
HALT
52
EA0
53
PD8
54
EA1
55
PD9
56
EA2
57
/ROMEN
58
VDD
59
PD10
60
P23/UO1
61
/DS
62
PD11
63
P24/UO2
64
CLKI
65
CLKO
66
P26
68
P22/UO0
69
PD13
70
P25/UI2
71
PD14
72
WAIT
74
/RES
67
PD12
75
VSS
73
PD15
76
VDD
77
VSS
78
PA0
79
EXT0/P00
80
PA1
81
EXT1/P01
82
PA283EXT2/P02
84
P10/INT2
85
PA3
86
VSS
87
P11/CLKOUT
88
P12/SIN
89
P20/INT0
90
PA4
91
EXT12/P012
93
EXT13/P013
94
VDD
95
EXT14/P14
96
PA6
97
VSS
99
EXT15/P015
92
PA5
100
/PAZ
98
PA7
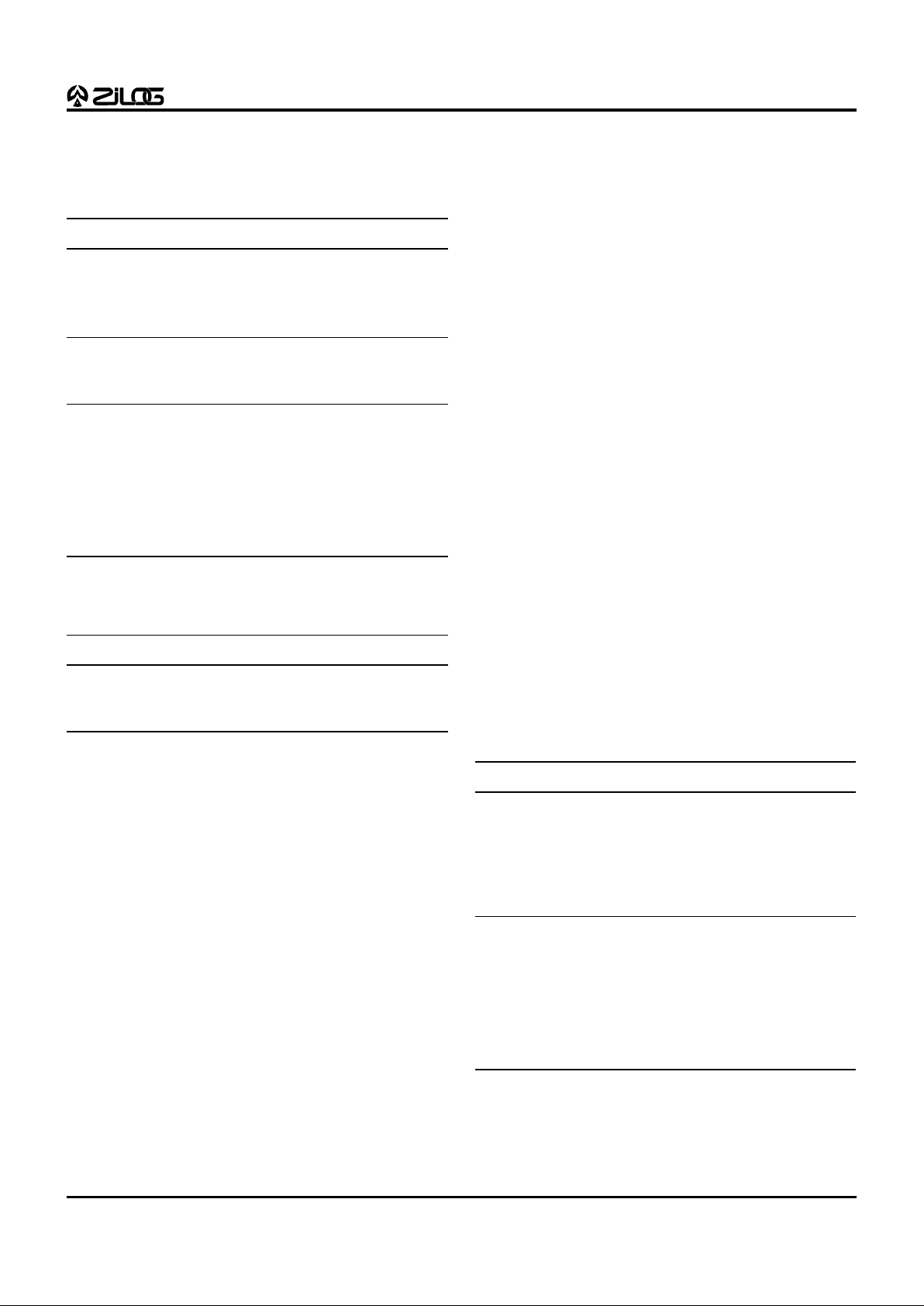
Figure 5. 100-Pin QFP Z89393 Pin Configuration

Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
10
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
PIN DESCRIPTION (Continued)
Table 4. 100-Pin QFP Z89393 Pin Description
No. Symbol Function Direction
1 /EXTEN EXT Enable Input
2 EXT3/P03 Ext Data 3/Port 0 3 In/Output
3 PA8 Program Address 8 Output
4 EXT4/P04 Ext Data 4/Port 0 4 In/Output
5 PA9 Program Address 9 Output
6V
SS
Ground
7V
DD
Power
8 EXT5/P05 Ext Data 5/Port 0 5 In/Output
9 PA10 Program Address 10 Output
10 P13/SOUT Port 1 3/Serial Output In/Output
11 EXT6/P06 Ext Data 6/Port 0 6 In/Output
12 PA11 Program Address 11 Output
13 P14/SS Port 1 4/Serial Select In/Output
14 EXT7/P07 Ext Data 7/Port 0 7 In/Output
15 P15/SK Port 1 5/Serial Clock In/Output
1 6 P2 7 Port 2 7 In/Output
17 PA12 Program Address 12 Output
18 EXT8/P08 Ext Data 8/Port 0 8 In/Output
19 PA13 Program Address 13 Output
20 EXT9/P09 Ext Data 9/Port 0 9 In/Output
21 PA14 Program Address 14 Output
22 V
SS
Ground
23 PA15 Program Address 15 Output
24 EXT10/P010 Ext Data 10/Port 0 10 In/Output
25 V
SS
Ground
26 PD0 Program Data 0 Input
27 EXT11/P011 Ext Data 11/Port 0 11 In/Output
28 PD1 Program Data 1 Input
29 V
DD
Power
30 VAHI Analog High Ref. Input
31 V
SS
Ground
32 P16/UI0 Port 1 6/User Input 0 In/Output
33 VALO Analog Low Ref. Input
34 P17/UI1 Port 1 7/User Input 1 In/Output
35 PD2 Program Data 2 Input
36 ANGND Analog Ground Input
3 7 A N0 A/D Input 0 Input
3 8 A N1 A/D Input 1 Input
3 9 A N2 A/D Input 2 Input
4 0 A N3 A/D Input 3 Input
41 V
SS
Ground
42 P21/INT1 Port 2 1/Interrupt 1 In/Output
43 ANVCC Analog Power Input
44 PD3 Program Data 3 Input
45 V
DD
Power
46 PD4 Program Data 4 Input
47 PD5 Program Data 5 Input
48 RD//WR R/W External Bus Output
49 PD6 Program Data 6 Input
50 PD7 Program Data 7 Input
No. Symbol Function Direction
51 HALT Halt Execution Input
52 EA0 Ext Address 0 Output
53 PD8 Program Data 8 Input
54 EA1 Ext Address 1 Output
55 PD9 Program Data 9 Input
56 EA2 Ext Address 2 Output
57 /ROMEN ROM Enable Input
58 V
DD
Power
59 PD10 Program Data 10 Input
60 P23/UO1 Port 2 3/User Output 1 In/Output
61 /DS Ext Data Strobe Output
62 PD11 Program Data 11 Input
63 P24/UO2 Port 2 4/User Output 2 In/Output
64 CLKI Clock/Crystal In Input
65 CLKO Clock/Crystal Out Input
6 6 P2 6 Port 2 6 In/Output
67 PD12 Program Data 12 Input
68 P22/UO0 Port 2 2/User Output 0 In/Output
69 PD13 Program Data 13 Input
70 P25/UI2 Port 2 5/User Input 2 In/Output
71 PD14 Program Data 14 Input
72 WAIT Wait for Ext Input
73 PD15 Program Data 15 Input
74 /RES Reset Input
75 V
SS
Ground
76 V
DD
Power
77 V
SS
Ground
78 PA0 Program Address 0 Output
79 EXT0/P00 Ext Data 0/Port 0 0 In/Output
80 PA1 Program Address 1 Output
81 EXT1/P01 Ext Data 1/Port 0 1 In/Output
82 PA2 Program Address 2 Output
83 EXT2/P02 Ext Data 2/Port 0 2 In/Output
84 P10/INT2 Port 1 0/Interrupt 2 In/Output
85 PA3 Program Address 3 Output
86 V
SS
Ground
87 P11/CLKOUT Port 1 1/Clock Output In/Output
88 P12/SIN Port 1 2/Serial Input In/Output
89 P20/INT0 Port 2 0/Interrupt 0 In/Output
90 PA4 Program Address 4 Output
91 EXT12/P012 Ext Data 12/Port 0 12 In/Output
92 PA5 Program Address 5 Output
93 EXT13/P013 Ext Data 13/Port 0 13 In/Output
94 V
DD
Power
95 EXT14/P014 Ext Data 14/Port 0 14 In/Output
96 PA6 Program Address 6 Output
97 V
SS
Ground
98 PA7 Program Address 7 Output
99 EXT15/P015 Ext Data 15/Port 0 15 In/Output
100 /PAZ Tri-state Program Bus Input

11
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
PIN FUNCTIONS
CLKO-CLKI Clock (output/input). These pins act as the
clock circuit input and output.
EXT15-EXT0 External Data Bus (input/output). These pins
act as the data bus for user-defined outside registers, such
as an ADC or DAC. The pins are normally tri-stated, except
when the outside registers are specified as destination
registers in the instructions. All the control signals exist to
allow a read or a write through this bus. If user I/O Port 0
is enabled, these signals function as user Programmable
I/O.
RD//WR Read/Write Strobe (output). This pin controls the
data direction signal for the EXT-Bus. Data is available
from the CPU on EXT15-EXT0 when this signal is Low. EXTBus is in input mode (high-impedance) when this signal is
High.
EA2-EA0 External Address (output). These pins control
the user-defined register address output (latched). One of
eight user-defined external registers is selected by the
processor with these address pins for read or write
operations. Since the addresses are part of the processor
memory map, the processor is simply executing internal
reads and writes. External Addresses are used internally
by the processor if the ADC, bit I/O (Port 0- 2), or SPI are
enabled. (See the banks allocation of the EXT registers in
Tables 6 and 7.)
/DS Data Strobe (output). This pin control the data strobe
signal for EXT-Bus. Data is read by the external peripheral
on the rising edge of /DS. Data is also read by the
processor on the rising edge of CK.
HALT Halt State (input). This pin controls Stop Execution.
The CPU continuously executes NOPs and the program
counter remains at the same value when this pin is held
High. An interrupt request must be executed (enabled) to
exit HALT mode. After the interrupt service routine, the
program continues from the instruction after the HALT
(active high).
/INT0-/INT2 Three Interrupts (input, active on rising edge).
These pins control interrupt requests 0-2. Interrupts are
generated on the rising edge of the input signal. Interrupt
vectors for the interrupt service starting address are stored
in the following program memory locations:
Device /INT0 /INT1 /INT2
Z89323/373 1FFFH 1FFEH 1FFDH
Z89393 FFFFH FFFEH FFFDH
Priority is: INT2 = lowest, INT0 = highest. (Note: INT2 pin
is not bonded out on the 44-pin QFP or PLCC packages.)
/RES Reset (input, active Low). This pin controls the
asynchronous reset signal. The /RES signal must be kept
Low for at least one clock cycle (clock output of the PLL
block). The CPU pushes the contents of the Program
Counter (PC) onto the stack and then fetches a new PC
value from program memory address 0FFCH (or FFFCH for
the Z89393) after the reset signal is released.
WAIT WAIT State (input). The wait signal is sampled at the
rising edge of the clock with appropriate setup and hold
times. The normal write cycle will continue when wait is
inactive on a rising clock. A single wait-state can be
generated internally by setting the appropriate bits in the
wait state register (Bank 15/Ext 3) (active high).
P00-P015 Port 0 (input/output). These pins control Port 0
input and output when EXT I/F is not in use.
P10-P17 Port 1 (input/output). These pins are used for
Port 1 programmable bit I/O when INT2, CLKOUT, SPI, or
UI0-1 are not being used.
P20-P27 Port 2 (input/output). These pins control Port 2
input or output when UI2, UO0-2 or INT0-INT1 are not
being used.
P30-P37 Port 3 Port3 (3:0) are four inputs and P3 (7:0) are
four outputs.
UI1-UI0 Two Input Pins (input). These general-purpose
input pins are directly tested by the conditional branch
instructions. These are asynchronous input signals that
have no special clock synchronization requirements.
UO1-UO0 Two Output Pins (output). These general-
purpose output pins reflect the value of two bits in the
status register S5 and S6. These bits have no special
significance and may be used to output data by writing to
the status register. Note: The user output value is the
opposite of the status register content.
SIN/SOUT. When enabled, these pins control SPI input
and output.
AN0-AN3. These pins are used for Analog-to-Digital
converter input.
ANGND and ANVCC. Analog to Digital ground and power
supply.

Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
12
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
PIN FUNCTIONS (Continued)
VAHI and VALO. Analog to Digital reference voltages.
/PAZ Tri-state Program Bus. This pin enables the Program
Address bus for emulation purposes.
/EXTEN Ext Enable. This pin enables Ext output
continuously for emulation purposes.
/ROMEN ROM Enable. This pin selects internal or external
Program Memory.
Program Memory. Programs of up to 8 Kwords can be
masked into internal ROM (OTP for Z89373). Four locations
are dedicated to the vector address for the three interrupts
(IFFDH-IFFFH) and the starting address following a Reset
(IFFCH). Internal ROM is mapped from 0000H to IFFFH,
and the highest location for program is IFFBH.
Internal Data RAM. The Z89323 has an internal 512 x 16bit word data RAM organized as two banks of 256 x 16-bit
words each: RAM0 and RAM1. Each data RAM bank is
addressed by three pointers: Pn:0 (n = 0-2) for RAM0 and
Pn:1 (n = 0-2) for RAM1. The RAM addresses for RAM0 and
RAM1 are arranged from 0-255 and 256-511, respectively.
The address pointers, which may be written to, or read
from, are 8-bit registers connected to the lower byte of the
internal 16-bit D-Bus and are used to perform modulo
addressing. Three addressing modes are available to
access the Data RAM: register indirect, direct addressing,
and short form direct. The contents of the RAM can be read
to, or written from, in one machine cycle per word, without
disturbing any internal registers or status other than the
RAM address pointer used for each RAM. The contents of
each RAM can be loaded simultaneously into the X and Y
inputs of the multiplier.
Registers. The Z89323 has 19 internal registers and eight
external registers and a secondary set of 15 peripheral
control registers. Both external and internal registers are
accessed in one machine cycle. The external registers are
used to access the on-chip peripherals when they are
enabled.
ADDRESS SPACE
Figure 6. Memory Map
Data Memory
Not Used
DRAM1
DRAM0
01FF
0100
00FF
0000
FFFF
Program Memory
Not Used
INT0-INT2 Vect.
RESET Vector
0FFF
0FFC
0000
FFFF
FFFC
4 Kwords
Or
INT0-INT2 Vect.
RESET Vector
64 Kwords
512 words
On-Chip Memory Off-Chip Memory
(Z89323/371) (Z89393)
13
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
Pn:b are the pointer registers for accessing data RAM, (n
= 0,1,2 refer to the pointer number) (b = 0,1 refers to RAM
Bank 0 or 1). They can be directly read from or written to,
and can point to locations in data RAM or Program Memory.
EXTn are external registers (n = 0 to 7). There are eight 16bit registers provided here for mapping external devices
into the address space of the processor. Note that the
actual register RAM does not exist on the chip, but would
exist as part of the internal or external device, such as an
ADC.
BUS is a read-only register which, when accessed, returns
the contents of the D-Bus. Bus is used for emulation only.
Dn:b refers to locations in RAM that can be used as a
pointer to locations in program memory which is efficient
for coefficient addressing. The programmer decides which
location to choose from two bits in the status register and
two bits in the operand. Thus, only the lower 16 possible
locations in RAM can be specified. At any one time, there
are eight usable pointers, four per bank, and the four
pointers are in consecutive locations in RAM. For example,
if S3/S4 = 01 in the status register, then D0:0/D1:0/D2:0/
D3:0 refer to register locations 4/5/6/7 in RAM Bank 0. Note
that when the data pointers are being written to, a number
is actually being loaded to Data RAM, so they can be used
as a limited method for writing to RAM.
SR is the status register (Figure 8) which contains the ALU
status and certain control bits (Table 5).
Table 5. Status Register Bit Functions
Status Register Bit Function
S15 (N) ALU Negative
S14 (OV) ALU Overflow
S13 (Z) ALU Zero
S12 (L) Carry
S11 (UI1) User Input 1
S10 (UI0) User Input 0
S9 (SH3) MPY Output Arithmetically
Shifted Right by three bits
S8 (OP) Overflow Protection
S7 (IE) Interrupt Enable
S6 (UO1) User Output 1
S5 (UO0) User Output 0
S4-S3 “Short Form Direct” bits
S2-S0 (RPL) RAM Pointer Loop Size
REGISTERS
The internal registers of the Z89323/373/393 are defined
below:
Register Register Definition
P Output of Multiplier, 24-bit
X X Multiplier Input, 16-bit
Y Y Multiplier Input, 16-bit
A Accumulator, 24-bit
SR Status Register, 16-bit
Pn:b Six Ram Address Pointers, 8-bit each
PC Program Counter, 16-bit
EXT 0
EXT 1
EXT 2
EXT 3
EXT 4
EXT 5
EXT 6
EXT 7
See Table 6 and Table 7 for the different assignments of
EXT7-EXT0 in the different banks.
Register Register Definition
EXTn External Registers, 16-bit
BUS D-Bus
Dn:b Eight Data Pointers*
Note:
* These data pointers occupy the first four locations in RAM bank.
P holds the result of multiplications and is read-only.
X and Y are two 16-bit input registers for the multiplier.
These registers can be utilized as temporary registers
when the multiplier is not being used.
A is a 24-bit Accumulator. The output of the ALU is sent to
this register. When 16-bit data is transferred into this
register, it is placed into the 16 MSBs and the least
significant eight bits are set to zero. Only the upper 16 bits
are transferred to the destination register when the
Accumulator is selected as a source register in transfer
instructions.
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
14
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
REGISTERS (Continued)
The Status Register
The status register can always be read in its entirety. S15S10 are set/reset by hardware and can only be read by
software. S9-S0 control hardware looping and can be
written by software (Table 8).
Table 8. RPL Description
S2 S1 S0 Loop Size
0 0 0 256
001 2
010 4
011 8
100 16
101 32
110 64
1 1 1 128
S15-S12 are set/reset by the ALU after an operation. S11S10 are set/reset by the user inputs. S6-S0 are control bits
described in Table 5. S7 enables interrupts. If S8 is set, the
hardware clamps at maximum positive or negative values
instead of overflowing. If S9 is set and a multiple/shift
option is used, then the shifter shifts the result three bits
right. This feature allows the data to be scaled and prevents
overflows.
PC is the Program Counter. When this register is assigned
as a destination register, one NOP machine cycle is added
automatically to adjust the pipeline timing.
Figure 7. Status Register
0 0 0
0 0 1
0 1 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 0 1
1 1 0
1 1 1
256
2
4
8
16
32
64
128
"Short Form Direct" bits
User Output 0-1*
Global Interrupt Enable
Overflow protection
MPY output arithmetically
shifted right by three bits
User Input 0-1
(Read Only)
Carry
Zero
Overflow
Negative
Ram
Pointer
Loop
Size
* The output value is the opposite of the status register content.
S7 S6 S5 S4 S3 S2 S1 S0
S15 S14 S13 S12 S11 S10 S9 S8
NOVZ C
UI1 UI0 SH3 OP IE UO1 UO0 RPL

15
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
EXT Register Assignments
The EXT registers support is extended in the Z893X3
family: In addition to up to seven external registers, there
are 28 internal registers on the EXT bus. There are 16
different pages of EXT registers. The same EXT7 register
exist in all the pages and control of the bank switching is
done via EXT7 register.
Banks 0 to 5 support different combinations of external
registers and internal data registers. The user should use
the bank that has the internal data registers and the
number of external registers to support his application and
to use this bank as a working bank to minimize the number
of bank switching. Bank 5 has all the A/D registers. Banks
13 to 15 are control registers bank. These control registers
are usually used only in the initialization routines.
Table 6. EXT Register Assignments Banks 0–4
EXT\Bank 01234
EXT0 Ext0-user Ext0-user Ext0-user Ext0-user Ext0-user
EXT1 Ext1-user Ext1-user Ext1-user Ext1-user Ext1-user
EXT2 Ext2-user Ext2-user Ext2-user Ext2-user Ext2-user
EXT3 SPI data Ext3-user Ext3-user SPI data Ext3-user
EXT4 Port0 Port0 Ext4-user Ext4-user Ext4-user
EXT5 Port1/Port2 Port1/Port2 Port3 Ext5-user Ext5-user
EXT6 A/D_ch0 A/D_ch1 A/D_ch2 A/D_ch3 Ext6-user
EXT7 Bank/Int_status Bank/Int_status Bank/Int_status Bank/Int_status Bank/Int_status
Table 7. EXT Register Assignments Banks 6–15
EXT\Bank 5 6-12 13 14 15
EXT0 A/D_ch1 A/D control Timer2 load P0 control
EXT1 A/D_ch2 Timer0 control Timer1 control P1 control
EXT2 A/D_ch3 Timer0 load Timer1 load P2 control
EXT3 SPI data Timer0 Timer1 Wait State
EXT4 Port0 Timer0 pr. load Timer1 pr. load SPI control
EXT5 Port1/Port2 Timer0 prescaler Timer1 prescaler PLL control
EXT6 A/D_ch0 A/D_ch0 A/D_ch0 A/D_ch0 Int. Allocation
EXT7 Bank/Int_status Bank/Int_status Bank/Int_status Bank/Int_status Bank/Int_status
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
16
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
EXT Register Assignments (Continued)
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8
Ext 7 Reg
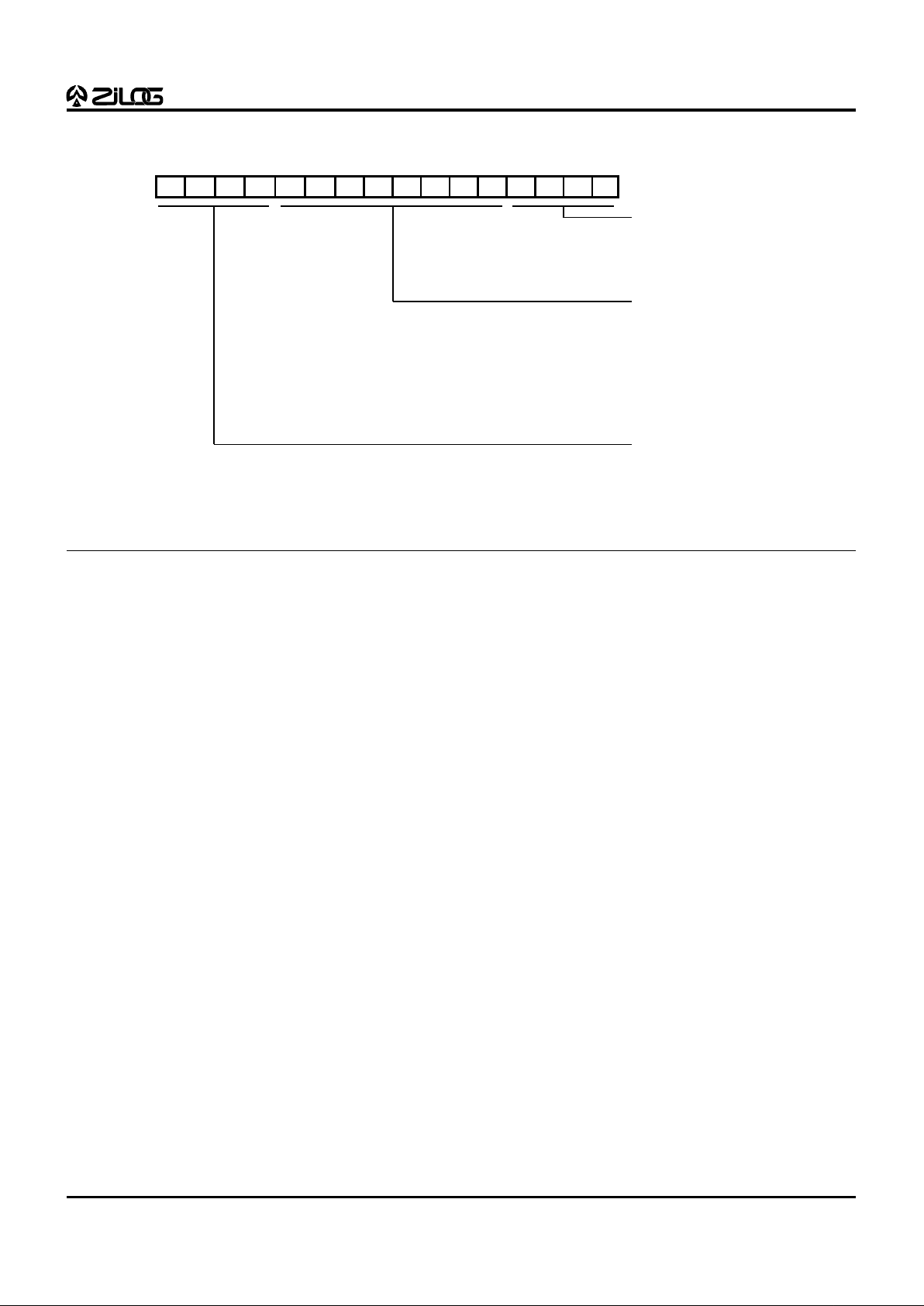
Interrupt Status Bits
Bit 4 = A/D Finish Interrupt
Bit 5 = SPI Interrupt
Bit 6 = Timer0 Interrupt
Bit 7 = Timer1 Interrupt
Bit 8 = Timer2 Interrupt
Bit 9 = INT0 (H/W) Interrupt
Bit 10 = INT1 (H/W) Interrupt
Bit 11 = INT2 (H/W) Interrupt
Bank Select
0000 : Bank0
0001 : Bank1
:
:
1111 : Bank15
Reserved
Figure 8. EXT7 Register Bit Assignment
Interrupt Status Bits
When read, these bits provide interrupt information to
identify the source for INT2, or when the DSP works in
Pending Interrupt mode, to warn the DSP of pending
interrupts. These bits also clear the interrupt status bits.
Writing 1 will clear these bits.
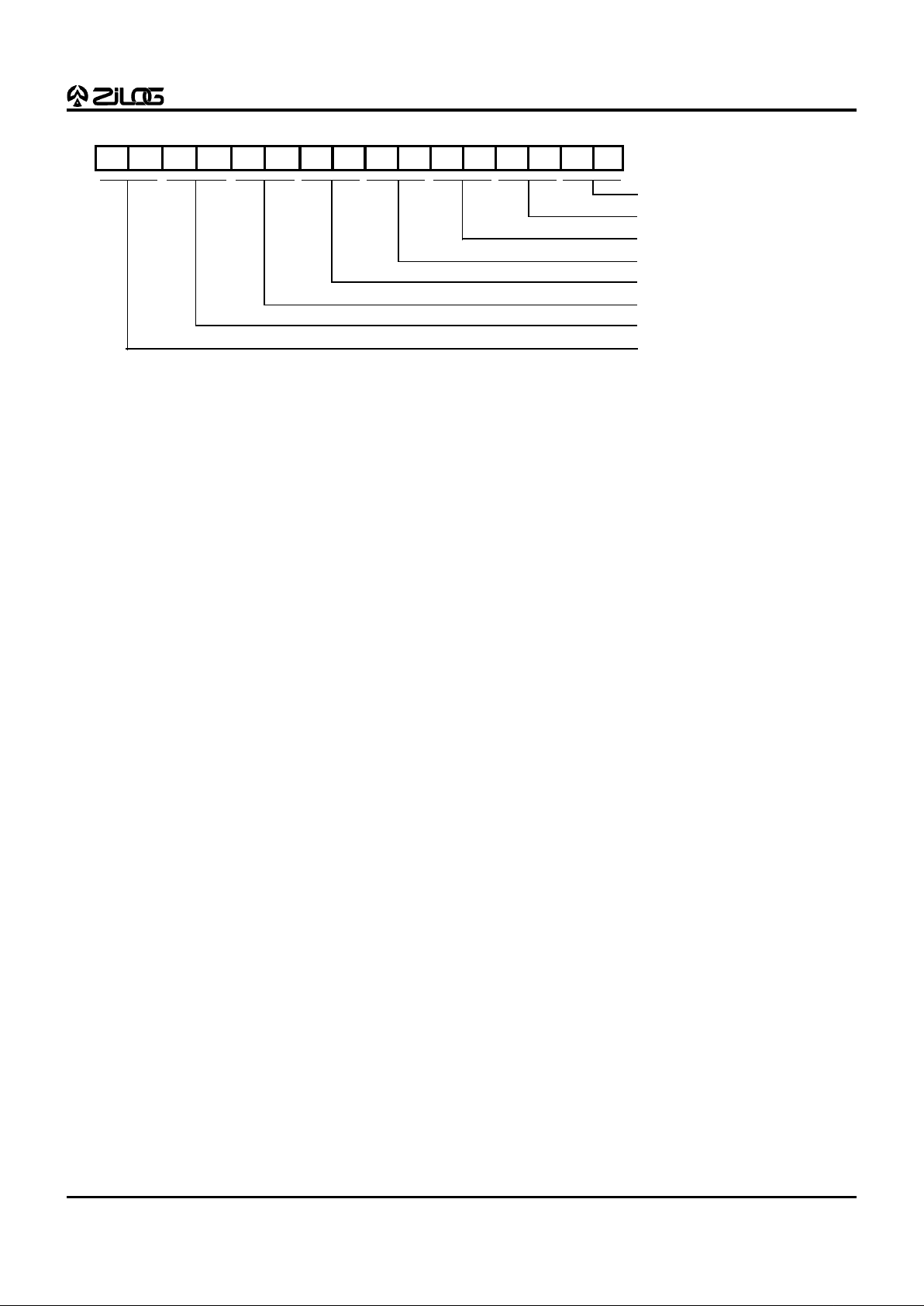
Wait-State Register
The Wait-State Control Register enables insertion of Wait
States when the DSP needs to access slow, inexpensive
peripherals. This software-controlled register enables
insertion of one Wait State when accessing EXT bus. (One
Wait State gives 100 nsec access time instead of 50 nsec
access time with a 20 MHz oscillator.) When more than one
Wait State is needed, an input pin (WAIT) coupled with
external logic can support more than one Wait State. The
Wait-State Control Register enables mapping specific EXT
register (from EXT0 to EXT6) and specific operation (read
or write) to include insertion of one Wait State. EXT7 is
always internal register, therefore no Wait State is needed
for EXT7.
Note:
When the programmer switches banks it is important to change the Wait
State mapping of the EXT registers to match the desired Wait State
mapping of the new bank.
17
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0D15 D14 D13 D12 D11 D10 D9 D8
Bank15/EXT3 Reg
Bits 13 -12 = Wait-State EXT6
Bits 1 - 0 = Wait-State EXT0
Bit14 = Reserved
Bit 15 = Test Mode
0 Normal Operation (default)
1 Test Mode: Bits 6-5 of the
Status Register drives,
P23 and P22, respectively
(VO0 and VO1).
Bits 11 -10 = Wait-State EXT5
Bits 9 - 8 = Wait-State EXT4
Bits 7 - 6 = Wait-State EXT3
Bits 5 - 4 = Wait-State EXT2
Bits 3 - 2 = Wait-State EXT1
Figure 8a. Bank 15/EXT3 Register

Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
18
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
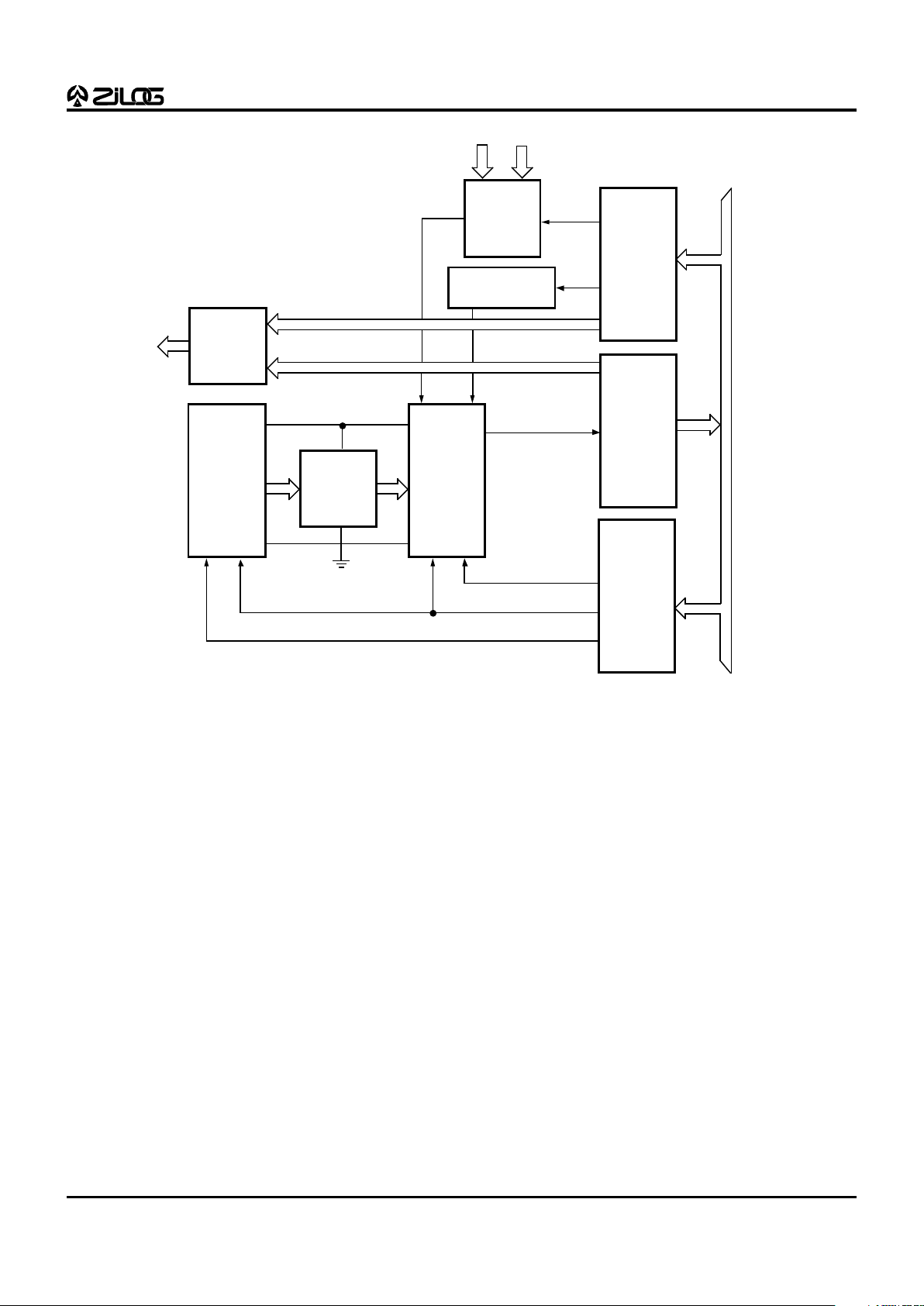
Analog to Digital Converter (ADC)
The ADC is an 8-bit half flash converter that uses two
reference resistor ladders for its upper 4 bits (Most
Significant Bits) and lower 4 bits (Least Significant Bits)
conversion. Two reference voltage pins, VA (High) and VA
(Low), are provided for external reference voltage supplies.
During the sampling period from one of the four channel
inputs, the converter is also being auto-zeroed before
starting the conversion. The conversion time is dependent
on the external clock frequency and the selection of the
prescaler value for the internal ADC clock source. The
minimum conversion time is 2.0 µs. (See Figure 9, ADC
Architecture.)
The ADC control register is Bank 13/Ext 0. A conversion
can be initiated in one of four ways: by writing to the
A/D control register, INT1 input pin, Timer 2 or Timer 0
equal 0. These four are programmable selectable. There
are four modes of operation that can be selected: one
channel converted four times with the results written to
each Result register, one channel continuously converted
and one Result channel updated for each conversion, four
channels converted once each and the four results written
to the Result registers, and four channels repeatedly
converted and the Result registers kept updated. The
channel to be converted is programmable and if one of the
four-channel modes is selected then the programmed
channel will be the first channel converted and the other
three will be in sequence following with wraparound from
Channel 3 to Channel 0.
The start commands are implemented in such a way as to
begin a conversion at any time, if a conversion is in
progress and a new start command is received, then the
conversion in progress will be aborted and a new conversion
will be initiated. This allows the programmed values to be
changed without affecting a conversion-in-progress. The
new values will take effect only after a new start command
is received.
The clock prescaler can be programmed to derive a
minimum 2 µs conversion time for clock inputs from 4 MHz
to 20 MHz. For example, with a 20 MHz crystal clock the
prescaler should be programmed for divide by 40, which
then gives a 2 µs conversion rate.
The ADC can generate an Interrupt after either the first or
fourth conversion is complete depending on the
programmable selection.
The ADC can be disabled (for low power) or enabled by a
Control Register bit.
Though the ADC will function for a smaller input voltage
and voltage reference, the noise and offsets remain constant
during the specified electrical range. The errors of the
converter will increase and the conversion time may also
take slightly longer due to smaller input signals.
19
Z89323/373/393
16-BIT DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSORS
PRELIMINARY
DS95DSP0101 Q4/95
Flash
A/D
Converter
Sample
and
Hold
Integrated
Logic
4-Channel
Multiplexer
A/D
Channel
Register
A/D
Controller
Register
4x8
Result
Register
A/D
Prescaler
Start
Converter
INT0
Timer
Internal
Bus
AGND
VREF
Dual
Scan
Channel Select
Figure 9. ADC Architecture
 Loading...
Loading...