Page 1

Instruction
Manual
IM 77J01P08-01E
Model VJP8
Pulse Rate Converter (Multi-function)
1. CAUTIONARY NOTES FOR SAFE
USE OF THE PRODUCT
For the correct use of this product, read through this manual before
use. The following safety symbol is indicated on the product to ensure safe use.
CAUTION
If this symbol is indicated on the product, the operator
should refer to the explanation given in the instruction
manual in order to avoid personnel injury or death to either
themselves or other personnel, and/or damage to the instrument. The manual describes the special care the operator
should exercise to avoid shock or other dangers that may result in injury or loss of life.
The following symbol marks are used only in this manual.
IMPORTANT
Indicates that operating the hardware or software in a particular manner may damage it or result in a system failure.
NOTE
Draws attention to information that is essential for understanding the operations and/or features of the product.
4. MOUNTING METHODS
4.1 Wall Mounting
Loosen the main unit-fixing screw of the converter to disconnect
the main unit from the socket. Next, anchor the socket onto the
wall with screws. Then, plug the main unit into the socket and secure the main unit with the main unit-fixing screw.
Socket
Threaded hole for
fixing the main unit
Main unit
Main
unit-fixing
screw
Fig. 4.1
4.1.1 Mounting Dimensions
29.5 or more
22±0.2
Unit: mm
2-M4 or 2-ø4.5 or more
Mounting
screws
2. CHECKING PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS AND THE CONTENTS
OF PACKING
(1) Model Number and Specification Check
Check that the model number and specifications shown on the
nameplate attached on the side of the product are as ordered.
(2) Contents of the Packing
Check that the packing contains the following items:
● VJP8 main unit, 1
● Instruction Manual (IM 77J01P08-01E), 1
Accessories:
● Tag number label, 1
● Range label, 1
● Shunt registor (when optional code/R is specified), 1
3. GENERAL
The VJP8 is a plug-in pulse rate converter that receives contact, voltage or current pulse from a field, and converts it into isolated transistor-contact pulse or contactless AC switch pulse at a preset pulse rate.
The VJP8 can also be used as a pulse signal repeater by setting the
pulse rate and pulse width type.
The VJP8 pulse rate scaler features:
• Either pulse output or communication function (RS-485) is se-
lectable as Output-2.
Keep this manual in a safe place.
59±0.3
Fig. 4.2
4.2 DIN Rail Mounting
Locate the converter so that the DIN rail fits into the upper part of
the DIN-rail groove at the rear of the socket, and fasten the socket
using the slide lock at the lower part of the socket.
DIN rail
VIEW A
Fig. 4.3
VIEW A (Rear of socket)
DIN rail
Slide lock
Network Solutions Business Divisiion
2-9-32, Naka-cho Musashino-shi, Tokyo 180-8750 Japan
Phone: +81-422-52-7179 Facsimile: +81-422-52-6793
IM 77J01P08-01E
1st Edition Feb. 2000
2nd Edition June 2004
Page 2
2
NOTE
4.3 Mounting Using a Multi-mounting Base
For mounting using a multi-mounting base, see the Instruction
Manual for VJCE (VJ Mounting Base).
4.4 Using Ducts
Wiring ducts should be installed at least 30 mm away from the top
or bottom of the main unit.
4.5 I
n case of top-and-bottom close mounting
Transmitter should be mounted horizontally with its top and bottom slits being vertical. The top and bottom slits should not be
covered.
The area for wiring is required above and below the transmitter
(the area with slant lines).
40 or more40 or more
ALM1
ALM1
ALM2
ALM1
ALM2
ALM2
(72)
(29.5)
29.5 or more
78 or more
150 or more
ALM1
ALM1
ALM2
ALM1
ALM2
ALM2
(72)
Fig. 4.4
5. INSTALLATION LOCATION
• For installation, avoid any location where the product may be
subject to vibrations, corrosive gases, or large amounts of
dust, or where the product is exposed to water, oil, solvents,
direct sunlight, radioactive rays, or strong electric or magnetic
fields.
• If there is a possibility that lightning could induce a high surge
voltage on the power and signal lines, provide lightning arresters on the line between the field instrument and indoor instrument in order to protect the product. Install a dedicated arrester on the field side and another on the indoor side.
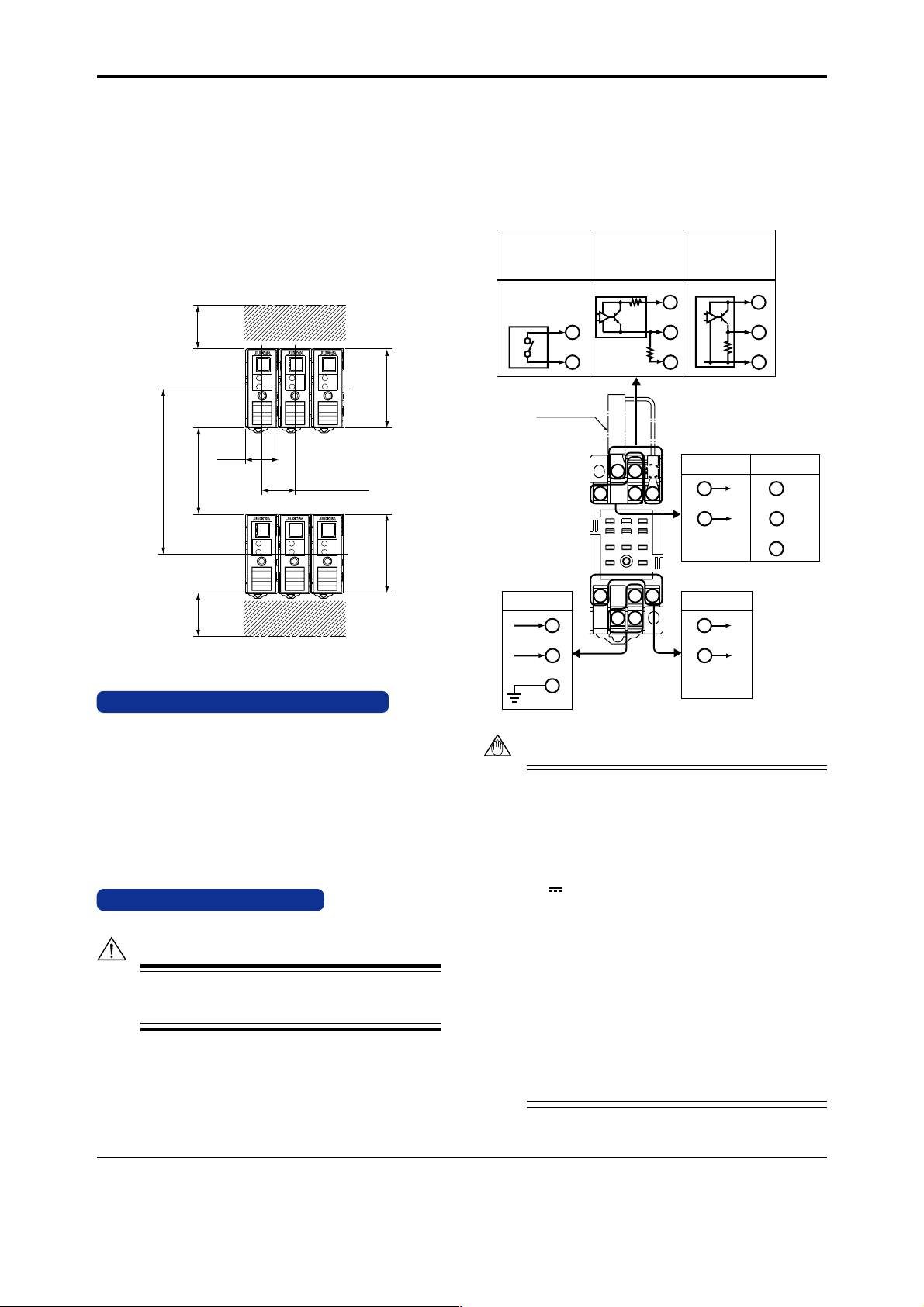
6. EXTERNAL WIRING
WARNING
Turn OFF the power supply and make sure that none of the
cables are not in the hot-line state before carrying out the
wiring to avoid the possibility of electric shock.
Wires are connected to the terminals of the isolator’s socket. M3
screw terminals are provided for the connection of external signals.
Attach a crimp-on lug to each wire for connection to the terminals.
• Recommended cables: A nominal cross-sectional area of 0.5
mm2 or thicker for signal cables, and that of 1.25 mm2 or
thicker for power cables, and shielded twisted-pair cables
(AWG24) for communication wiring cables.
• For mounting, use M3 screws and crimp-on terminals with insulating sleeves appropriate for the wires used.
Tool of the crimp-on terminals to be used should be appropriate for the crimp-on terminals.
• Mount a breaker on the external place.
Mount a switch or 5A circuit breaker on the place near by the
instrument, within operator’s reach. And attach the indication
that it is for disconnecting the instrument.
Input signal
When receiving nonvoltage contact signal
or voltage pulse
Transmitter
(Externally connected
for current pulse input)
Power supply
+
-
Shunt resistor
L+
10
N-
11
GND
8
3
4
When receiving
current pulse by
running a transmiter
on an internal power
supply
Transmitter
R
R:200Ω
23
654
8
9
11 10
PS+
1
7
1
+
3
-
4
When receiving
voltage pulse by
running a transmiter
on an internal power
supply
Transmitter
Output-2 signal
Pulse output
Output-1 signal
Pulse output
PS+
+
2
-
5
+
7
-
9
1
+
3
-
4
RS485
communication
2
5
6
B+
A-
COM
Fig. 6.1
● Keep all sources of noise away from the power and sig-
nal cables. Otherwise, accuracy cannot be assured.
● Provide grounding to a grounding resistance of 100 ⍀.
The length of the grounding cable should be 20 m or
less. Directly connect the lead from the ground terminal
(terminal no. 8) of the isolator to the ground. Do not
carry out daisy-chained inter-ground terminal wiring.
● Direct Current
●
“Overvoltage category (Installation category)” describes
a number which defines a transient overvoltage condition. It implies the regulation for impulse withstand voltage. “II” applies to electrical equipment which is supplied from the fixed installation like distribution board.
●
“Pollution degree” describes the degree to which a solid,
liquid, or gas which deteriorates dielectric strength or
surface resistivity is adhering. “2” applies to normal indoor atmosphere. Normally, only non-conductive pollution occurs. Occasionally, however, temporary conductivity caused by condensation must be expected.
● Rated fuse of 125VDC, 1A is stored. However, opera-
tors can not replace the fuse.
All Rights Reserved. Copyright © 1999, Yokogawa M&C Corporation IM 77J01P08-01E 3rd Edition Mar.31,1997-00
Page 3

3
IMPORTANT
● If this instrument is used in a manner not sepecified in
this manual, the protection provided by this instrument
may be impaired.
● If the product is operated by a power supply exceeding
the specifications, the product may become extremely
hot and, as a result, damaged. To prevent this, ensure
the following before turning on the power.
(a) The voltage of the supplied power and the input
signal level meet the specifications of the product.
(b) External wires are connected to the correct termi-
nals (refer to Chapter 5).
● Do not operate the product in the presence of flammable
or explosive gases or vapors. To do so is highly dangerous.
● The product is sensitive to static electricity; exercise
care in operating it. Before you operate the product,
touch a nearby metal part to discharge static electricity.
7. DESCRIPTION OF FRONT PANEL
AND CONNECTION OF SETTING
TOOLS
7.1 Front Panel
The communications connector in the front panel is used for setting up parameters through a PC (VJ77 PC-based Parameters Setting Tool) or the Handy Terminal.
Communications connector
* The LEDs are provided only when output-2
is specified for contact output.
Fig. 7.1 Front Panel
7.2 Connecting the Setting Tools
Connect the modular jack-to-connector adapter (E9786WH) to the
JUXTA communication cable with 5-pin connector (F9182EE)
and then connect this adapter to the communication connector of
JUXTA.
JUXTA communication cable with
5-pin connectors (F9182EE)
JHT200
Handy T erminal
Fig. 7.2 Connecting the Setting Tools
[Provided with VJ77, JHT200]
Modular jack conversion
adapter (E9786WH)
[Provided with VJ77]
Dedicated adapter (E9789HA)
[Provided with VJ77]
Dedicated cable (E9786WK)
[Provided with VJ77]PC
8. SETTING PARAMETERS
Set the parameters using a PC (VJ77 PC-based Parameters Setting
Tool) or the Handy Terminal. Refer to the list of parameters in this
manual and the Instruction Manual for Handy Terminal (IM JF8102E) and VJ77 PC-based Parameters Setting Tool (IM 77J01J7701E).
8.1 Settings Related to inputs and outputs
8.1.1 Input Display Unit
The input display unit is used for referring the input signal. Select
and set "Hz" or "kHz" in D10: UNIT.
8.1.2 Pulse Rate
Set the pulse rate within the numerically specified range in D41:
PULSE RATE.
Setting range: 0.0001 to 2.0000(settable up to 4 decimal
When the pulse width type is set to
"THROUGH" (no change), effective range
is 0.0001 to 1.0000.
8.1.3 Pulse Width Type
Select and set "THROUGH" or "ON PULSE" in D42: PULSE
TYPE..
THROUGH: Outputs ON-state pulse time of frequency
ON PULSE: Outputs ON-state pulse time after chang
When the instrument is used as a pulse signal repeater, set the
pulse width type to "THROUGH", and the pulse rate to "1."
8.1.4 Pulse Width Time
The pulse width time is set when the pulse width type is set to "ON
PULSE."
Select and set "12.5s", "50s", "100s", "12.5ms", "30ms",
"50ms", or "100ms" in D43: PULSE WIDTH.
8.1.5 Input Filter
When the chattering noise is generated in input, the input filter is
used to restrain the influence.
Select and set "ON" in D50: INPUT FILTER, then the input filter
for time constant of about 10ms will be connected.
8.2
Settings Related to Communication Function
Set the following parameters when output-2 is specified for communication function. For more information on the communication
function, see the Instruction Manual for VJ Series Communication
Function (IM 77J1J11-01E).
8.2.1 Communication Protocol
Set the communication protocol by selecting from among PCLINK, PC-LINK WITH SUM, MODBUS ASCII, MODBUS
RTU, and LADDER in F01: PROTOCOL.
8.2.2 Communication Address
Set the address number of the isolator numerically in a range of 1
to 99 in F02: ADDRESS.
8.2.3 Baud Rate
Set the baud rate by selecting from among 1200, 2400, 4800, and
9600 bps in F03: BAUD RATE.
8.2.4 Parity
Select and set NONE, EVEN, or ODD in F04: PARITY.
8.2.5 Data Length
Select and set 7 bits or 8 bits in F05: DATA LEN.
8.2.6 Stop Bit
Select and set 1 bit or 2 bits in F06: STOP BIT.
8.2.7 Input Decimal Point Position
Namber of digits of decimal places can be set.
Select and set among 0 to 5 digits in F07: INPUT DEC PT.
places)
as it is.
ing it to the set value.
All Rights Reserved. Copyright © 1999, Yokogawa M&C Corporation IM 77J01P08-01E 3rd Edition Mar.31,1997-00
Page 4

9.LIST OF PARAMETERS
No. Item Display Remarks No. Item Display Remarks
01 Model MODEL
02 Tag No. TAG NO
03 Self-check result SELF CHK
A Display1 DISPLAY1 B Display2 DISPLAY2
A01 Input value INPUT1 B01 Input value INPUT1
A33 Temporary memory 1 T1 B31 Integrating counter 1 COUNTER1
A34 Temporary memory 2 T2 B32 Integrating counter 2 COUNTER2
A54 Temporary memory 3 T3 B33 Integrating counter 3 COUNTER3
A55 Temporary memory 4 T4 B34 Integrating counter 4 COUNTER4
A54 Status STATUS *1 B60 Self-check result SELF CHK
A56 Rev. no REV NO
A58 MENU REV MENU REV
A60 Self-check SELF CHK
D Setting (I/O) SET(I/O) F Setting (communication) SET (COM)
D01 Tag no. 1 TAG NO.1 F01 Communication protocol PROTOCOL
D02 Tag no. 2 TAG NO.2 F02 Address ADDRESS
D03 Comment 1 COMMENT1 F03 Baud rate BAUD RATE
D04 Comment 2 COMMENT2 F04 Parity PARITY
D10 Range unit UNIT F05 Data length DATA LEN
D41 Pulse rate range PULSE RATE F06 Stop bit STOP BIT
D42 Pulse width type PULSE TYPE F07 Decimal point position of input
D43 Pulse width time PULSE TIME F60 Self-check result SELF CHK
D50 Input filter INPUT FILTER
D60 Self-check result SELF CHK
Adjusting items There are items not displayed depending on what output-2 is specified.
P Adjustment ADJUST1
P60 Self-check result SELF CHECK
4
Display items
*1 The Status is displayed for service personnel to see history records.
Setting items
INPUT DEC PT
10.MAINTENANCE
The product starts running immediately when the power is turned on;
however, it needs 10 to 15 minutes of warm-up before it meets the
specified performance.
For cleaning the instrument, use a soft and dry cloth.
10.1 Calibration Apparatus
Pulse generator (Yokogawa FG100 or the equivalent): 1
A counter(Yokogawa TC100 or the equivalent) or oscilloscope
(Yokogawa DL1540 or the equivalent): 1
A precision resistor (1k⍀, 1.6 k⍀): 1 each
6V battery: 1
10.2 Calibration Procedure
Connect the instruments as shown in Fig.10.1. First adjust the output-1 signal and then the output-2 signal.
Produce a rectangular pulse of any frequency from the pulse generator to measure the value using a counter or oscilloscope. (Connect the
counter or oscilloscope as the broken line shown in figure 10.1.)
Next, connect the counter to the terminals 7 and 9, or terminals 2 and
5, then check that the frequency (input frequency x set rate) is output.
When using a oscilloscope, the wave shaping of output pulse can be
confirmed.
3 2
56
1011
Power supply
L+
N-
GND
1110 8
Calibration for output-1
3
1
4
4
+
-
+
Pulse
Generator
Counter or
-
Osilloscope
7
9
789
Calibration for output-2
3
4
2
5
1kΩ
1.6kΩ
+
-
+
-
1kΩ
1.6kΩ
6V
Battery
Pulse
Generator
Counter or
Osilloscope
6V
Battery
Fig. 10.1
All Rights Reserved. Copyright © 1999, Yokogawa M&C Corporation IM 77J01P08-01E
 Loading...
Loading...