Page 1

User’s
Manual
Model STED (Style R)
mV,Temperature and Potentiometer
/Voltage Converters
IM 01B04J01-02E
IM 01B04J01-02E
9th Edition
Page 2

Blank Page
Page 3

Model STED (Style R)
mV ,Temperature and Potentiometer/V oltage Converters
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition
CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION ........................................................................................... 1-1
1.1 Inspection ............................................................................................................... 1-2
1.2 Documentation Conventions ................................................................................. 1-3
1.3 Notice ...................................................................................................................... 1-3
2. GEN ERA L ..................................................................................................... 2-1
2.1 Standard Specifications......................................................................................... 2-2
2.2 Model and Suffix Codes ......................................................................................... 2-3
2.3 Accessories ............................................................................................................ 2-3
Toc-1
3. INS TALLA T ION............................................................................................. 3-1
3.1 External Wiring ....................................................................................................... 3-1
3.2 Applicable Cables................................................................................................... 3-2
4. PRINCIPLES OF OPERA TION...................................................................... 4-1
4.1 mV DC Input T ype (STED-1 and STED-7 Types) .................................................... 4-1
4.2 Thermocouple Input T ype (STED-2 and STED-7 Types) ....................................... 4-2
4.3 RTD Input T ype (STED-3 and STED-7 Types) ........................................................ 4-3
4.4 Potentiometer Input T ype (STED-4 Type) .............................................................. 4-4
5. SETTING ....................................................................................................... 5-1
5.1 Names of Components........................................................................................... 5-1
5.2 Setting Jumper ....................................................................................................... 5-2
5.2.1 Check of Setting Jumper ......................................................................... 5-2
5.2.2 Position of Setting Jumper....................................................................... 5-3
5.3 Setting of Parameters............................................................................................. 5-4
5.3.1 Configuration of Parameters.................................................................... 5-4
5.3.2 Description of Parameters ....................................................................... 5-5
5.4 Parameter List......................................................................................................... 5-6
6. MAINTENANCE ............................................................................................ 6-1
6.1 T est Equipment....................................................................................................... 6-1
6.2 Reference T able of Thermocouple and RTD ......................................................... 6-1
6.3 Adjustment.............................................................................................................. 6-1
6.3.1 Adjustment for STED-1 to -4 T ypes (One Input-only T ype)....................... 6-1
6.3.2 Adjustment for STED-7 T ype (Universal T ype)......................................... 6-3
6.4 Check of Reference Junction T emperature Compensation Action ..................... 6-4
6.5 Replacement of Fuse.............................................................................................. 6-5
6.6 Replacement of Capacitor...................................................................................... 6-5
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 4

Toc-2
7. TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................................................. 7-1
7.1 Troubleshooting Flowchart.................................................................................... 7-1
7.2 Action in Fault Condition. ...................................................................................... 7-2
7.3 Replacement of Parts ............................................................................................. 7-2
7.3.1 Replacement Procedure.......................................................................... 7-2
7.3.2 Replacement of Power Supply Unit ......................................................... 7-3
7.3.3 Replacement of Main Board .................................................................... 7-3
Appendix / TB Power Supply Terminal Connections for Rack-mounted Instru-
ments (Option) ...................................................................................App.-1
Appendix-1 GENERAL ........................................................................................... App.-1
Appendix-2 APPLICABLE INSTRUMENTS............................................................ App.-1
Appendix-3 EXTERNAL VIEW AND NAMES OF COMPONENTS ......................... App.-1
Appendix-4 POWER SUPPL Y AND GROUND WIRING ......................................... App.-2
Customer Maintenance Parts List....................................... CMPL 01B04J01-02E
CMPL 01B04F02-1 1E
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Electric Electric Corporation
Page 5

<T oc> < 1. INTRODUCTION >
1. INTRODUCTION
This manual describes the functions and operations of the STED mV,T emperature,
and Potentiometer/V oltage Converters.
■ Intended Readers
This manual is intended for personnel in charge:
● Installation and wiring
● Instrumentation and setup of the function
● Operation and monitoring of the controller
● Maintenance of equipment
■ Related Documents
The following documents all relate to the STED mV ,Temperature, and Potentiometer/
Voltage Converters. Read them as necessary. The codes enclosed in parentheses are the
document numbers.
● Rack-Mounted Instruments (IM 1B4F2-01E)
Describes mounting and wiring for the YS80 rack-mounted instruments.
1-1
● Model JHT200 Handy Terminal (IM JF81-02E)
Describes operation of JHT200.
● YEWSERIES 80 Installation Manual (TI 1B4A9-01E)
Describes the installation conditions of YS80 instruments.
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 6
<T oc> < 1. INTRODUCTION >
1.1 Inspection
The STED converter is shipped only after stringent inspection at the factory . V isually
inspect the product upon delivery to make sure it is not damaged in any way .
Store the box and inner packing material of the package in a safe place - they may be
needed if there is a problem with the product and it needs to be sent back for repair .
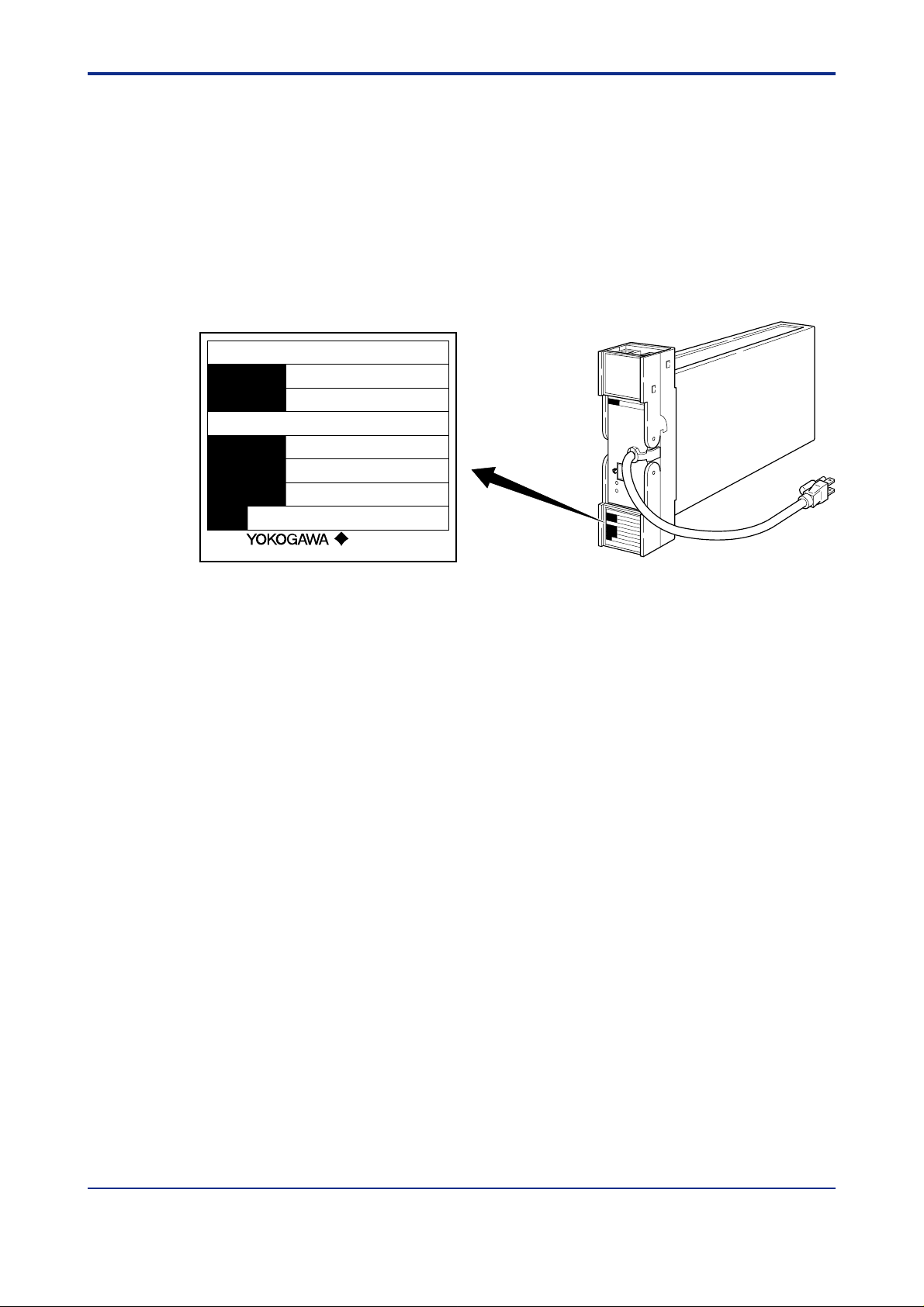
■ Check of Model and Suffix Codes
The model and suffix codes are indicated on the Name plate attached to the front cover of
the instrument. Crosscheck this information with the model and suffix codes of Section 2.2
to ensure that the product is as specified in the order .
TC CONVERTER
MODEL
SUFFIX
STED
-210-TK*R
1-2
SUPPLY
INPUT
80–138V AC 47–63Hz
/20–130V DC
0 - 300 °C
Type K
NO.
Made in Korea
Yokogawa Electric Corporation
Figure 1-1 Name plate for Thermocouple Input
■ Confirmation of the Package Contents
Check the package contents against the list below . If anything is missing or damaged,
immediately contact the sales office from which you purchased the product or your nearest
Y okogawa representative.
● STED mV, T emperature, and Potentiometer/V oltage Converters......................1
● Fuse (Parts No. : S9510VK)...............................................................................1
● Instruction Manual (This manual).......................................................................1
F0101.EPS
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 7

<T oc> < 1. INTRODUCTION >
1.2 Documentation Conventions
This manual uses the following notational conventions.
■ Symbols
The following symbols are used in this manual.
WARNING
Indicates that operating the hardware or software in a particular manner may damage it or
result in a system failure.
NOTE
Draws attention to information that is essential for understanding the operation and/or
features of the product.
TIP
Gives additional information to complement the present topic and/or describe terms specific to this document.
1-3
See Also
Gives reference locations for further information on the topic.
■ Description of Displays
Some of the representations of product displays shown in this manual may be exaggerated
, simplified, or partially omitted for reasons of convenience when explaining them.
1.3 Notice
■ This Instruction Manual
● This manual should be passed on to the end user . Keep at least one extra copy of the
manual in a safe place.
● Read this manual carefully to gain a thorough understanding of how to operate this
product before you start using it.
● This manual is intended to describe the functions of this product. Yokogawa Electric
Corporation (hereinafter simply referred to as Yokogawa) does not guarantee that these
functions are suited to the particular purpose of the user .
● Under absolutely no circumstances may the contents of this manual, in part or in whole,
be transcribed or copied without permission.
● The contents of this manual are subject to change without prior notice.
● Every effort has been made to ensure accuracy in the preparation of this manual.
Should any errors or omissions come to your attention however , please contact your
nearest Yokogawa representative or sales office.
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 8

<T oc> < 1. INTRODUCTION >
■ Protection, Safety , and Prohibition against Unauthorized Modification
● In order to protect the product and the system controlled by it against damage and
ensure its safe use, make certain that all of the instructions and precautions relating to
safety contained in this document are strictly adhered to. Yokogawa does not guarantee
safety if products are not handled according to these instructions.
● The following safety symbols are used on the product and in this manual.
CAUTION
If this symbol is indicated on the product, the operator should refer to the explanation given
in the instruction manual in order to avoid personal injury or death to either themselves or
other personnel, and/or damage to the instrument. The manual describes that the operator
should exercise special care to avoid shock or other dangers that may result in injury or
loss of life.
Protective ground terminal:
This symbol indicates that the terminal must be connected to ground prior to operating the
equipment.
1-4
Function ground terminal:
This symbol indicates that the terminal must be connected to ground prior to operating the
equipment.
AC voltage:
This symbol indicates that AC voltage is present.
DC voltage:
This symbol indicates that DC voltage is present.
● Do not turn off the power of the product during adjustment.
● Be sure to confirm the parameters referring to ‘‘5.4 Parameter List’ ’ before installing the
product in a system or plant. After confirming them, install the product in a system or
plant and turn on the power.
● If protection/safety circuits are to be used for the product or the system controlled by it,
they should be externally installed on the product.
● When you replace the parts or consumables of the product, only use those specified by
Yokogawa.
● Do not modify the product.
■ Force Majeure
● Yokogawa does not make any warranties regarding the product except those
mentioned in the WARRANTY that is provided separately.
● Yokogawa assumes no liability to any party for any loss or damage, direct or
indirect, caused by the use or any unpredictable defect of the product.
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 9
<T oc> < 2. GENERAL >
2. GENERAL
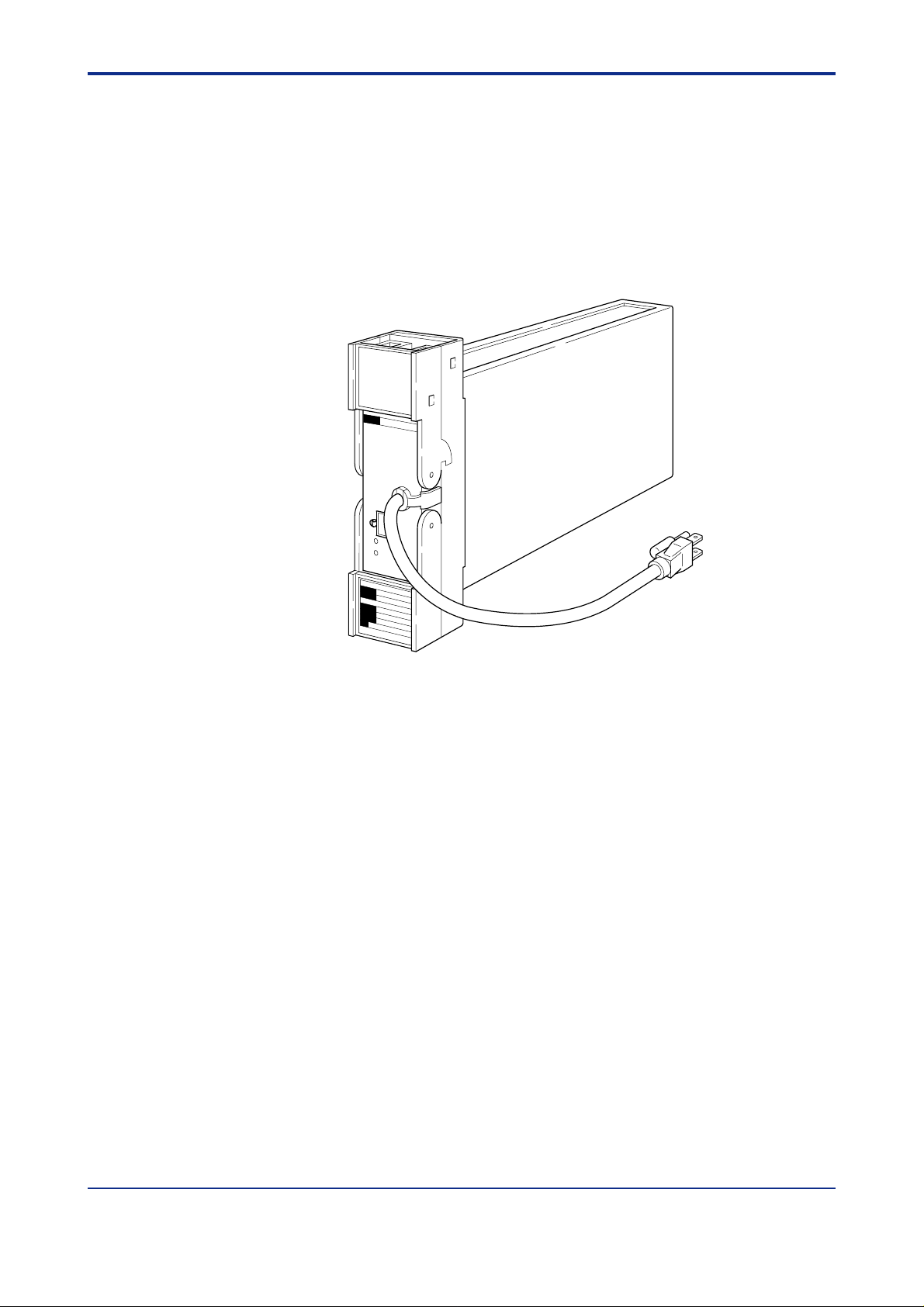
The STED mV ,Temperature and Potentiometer/Voltage Converters are used to convert mV
DC, thermocouple, RTD (resistance temperature detector) or potentiometer input signals to
isolated two 1 to 5 V DC signals and 4 to 20 mA DC signal.
Both thermocouple input type STED-210 and RTD input type STED-310 have built-in input
linearizers as standard equipment.
Also, an upscale or downscale burnout function is provided in all types as a standard
specification.
2-1
Figure 2-1 External View
F0201.EPS
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 10
<T oc> < 2. GENERAL >
2.1 Standard Specifications
Item Description
Type of Input Signal (1) mV DC input mV DC
and Standard (For STED-1 and -7)
(2) Thermocouple input Type K, T, J, E, B, R, S, and N, W3, W5 (for STED-7 only)
(For STED-2 and -7) Standards: JIS, IEC, ANSI, BS, and ASTM E988
(3) RTD input 3-wire system, JPt100 (JIS '89), Pt100 (JIS '89, JIS '95, DIN)
(For STED-3 and -7) Rated current: 0.5 mA DC
(4) DC potentiometer input 3-wire system, Rated voltage: Up to 0.5 V DC
(For STED-4)
Input Resistance 1M Ω (power on), 4k Ω (power off) (for mV DC input and thermocouple input)
Input External Resis- (1) mV DC and thermocouple input: Up to 500 Ω
tance (2) RTD input: No greater than input span (°C) x 0.4 Ω or 10 Ω per wire, whichever is smaller
Input Lead Wire Res- (Each lead wire resistance should be equal.)
istance for Resistan- (3) DC potentiometer input: Maximum 10 Ω per wire
ce Input (Each lead wire resistance should be equal.)
Input Overload Up to ±4 V DC ( for mV DC input and thermocouple input)
Output Signal and • 1 to 5 V DC, Load resistance: At least 2k Ω, Number of output: 2
Number of Output • 4 to 20 mA DC, Load resistance: Up to 750 Ω, Number of output: 1
Accuracy (1) ± 0.5 % of span (However, for thermocouple input type, the reference junction temperature
compensation accuracy is not included.)
(2) Thermocouple reference junction temperature compensation accuracy
• For temperatures at least 0 °C: Up to ± 0.5 % (except for types R and S - their accuracy is ± 1°C)
• For temperatures less than 0 °C: Multiply accuracy for temperatures up to 0 °C by K, where
K =
(Thermocouple output change/°C at measurement temperaure)
Burnout Time Less than 60 seconds
Power Supply AC or DC (No change to instrument) 100 V version DC: 20 to130 V(polarity reversible)
Power Consumption DC: 24 V DC, 110 mA
AC: 100 V AC, 7.7 VA
220 V AC, 10.5 VA
Ambient Temperature 0 to 50°C
Ambient Humidity 5 to 90% R.H. (non-condensing)
Mounting Indoor, rack mounting
Weight 1.7 kg
(Thermocouple output change/°C near 0 °C)
AC: 80 to138 V, 47 to 63 Hz
220 V version DC: 120 to 340 V(polarity reversible)
AC: 138 to 264 V, 47 to 63 Hz
2-2
T0201.EPS
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 11

<T oc> < 2. GENERAL >
2.2 Model and Suffix Codes
Model Suffix Codes Description
STED mV•Temperature•Potentiometer
/Voltage Converters
Input signal -1 mV DC input
-2 Thermocouple input
-3 RTD input
-4 Potentiometer input
-7 Universal input
Number of inputs 1 One input
0 Always 0
Suffix Codes -MV mV DC input
-TK Type K(IEC 584-1-1995)
“-MV” for STED-110 -TT Type T(IEC 584-1-1995)
“-TK” to “-TS” for -TJ Type J(IEC 584-1-1995)
STED-210 -TE Type E(IEC 584-1-1995)
“-PA” and “-PD” for -TB Type B(IEC 584-1-1995)
STED-310 -TR Type R(IEC 584-1-1995)
“-RS” for STED-410 -TS Type S(IEC 584-1-1995)
“-UN” for STED-710 -PA JPt100(JIS '89)
-PD Pt100(ITS-90, IPTS-68)
-RS Potentiometer
-UN Universal
Style Code *R Style R
Option /A2ER 220 V power supply
/NHR Without case
/TB Power supply terminal
/FBP Power supply fuse bypass
/WSW With spring washers
/LOCK With special lock
T0202.EPS
2-3
2.3 Accessories
Fuse 1A: 1
NOTE
The fuse (S9510VK) is the dedicated fuse. Do not use it for other products.
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 12

Blank Page
Page 13
<T oc> < 3. INST ALLA TION >
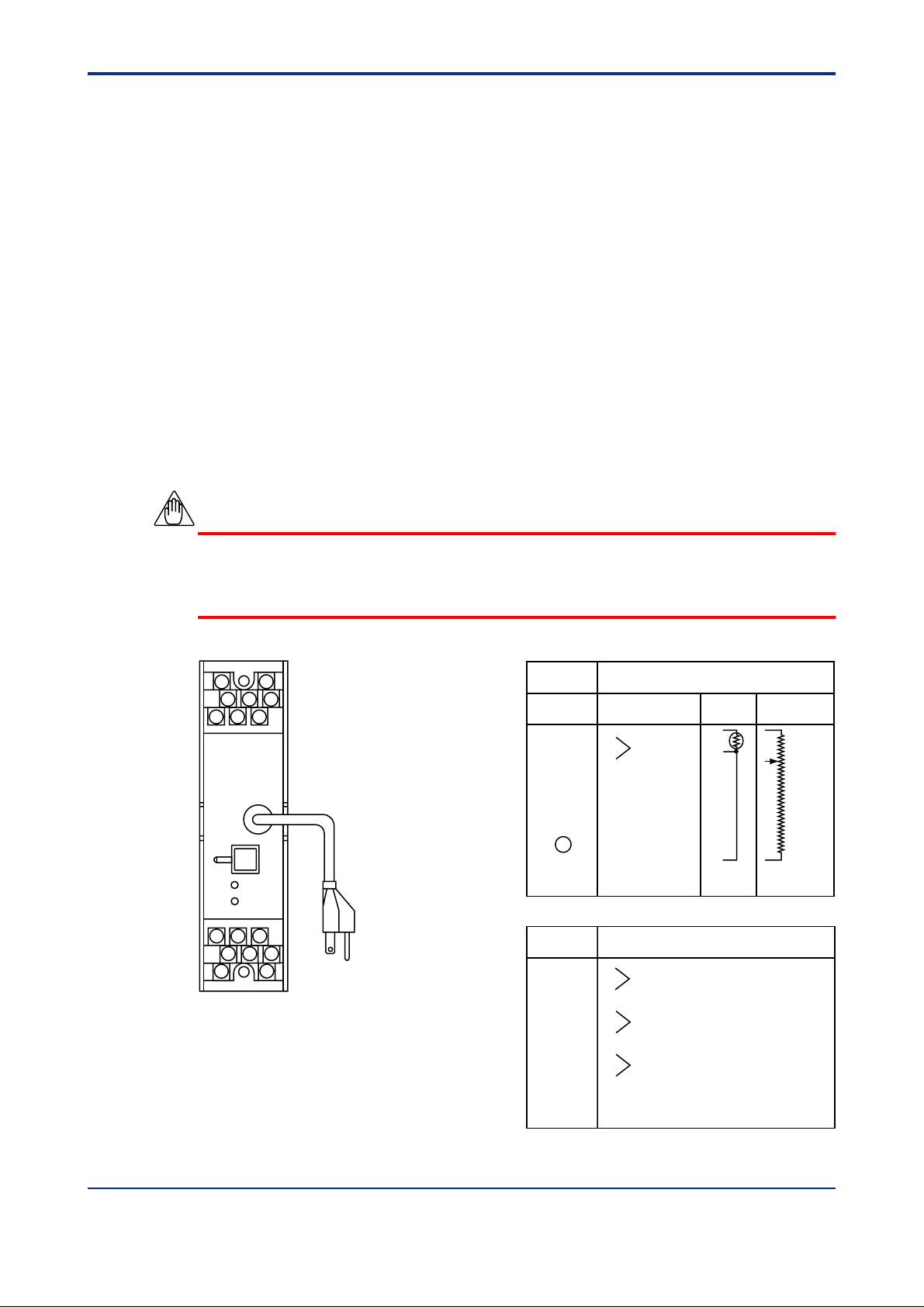
3. INST ALLA TION
For details of the installation procedure and wiring precautions, refer to the technical
information “YEWSERIES 80 Installation Manual ” (TI 1B4A9-01E) or the instruction
manual “Installation of Rack-Mounted Instruments” (IM 1B4F2-01E).
3.1 External Wiring
(a) T o prepare cables for connection to each terminal, install crimp-on solderless lugs for
4 mm screw on the end of each cable.
(b) Draw the internal unit out from the rack case.
(c) Connect the cables to the correct terminals by referring to Table 3-1.
(d) Replace the internal unit into the rack case after completing the wiring.
(e) The reference junction block (RJC) for STED-2 or STED-7 type should be securely
installed to the screw on terminal 6.
(f) Always replace the terminal cover after completing the wiring.
3-1
NOTE
The terminal cover cannot be replaced if the internal unit is not installed in the rack case.
The terminal cover should be securely replaced because it has the function of locking the
internal unit.
T able 3-1 Terminal Connections
JK
HDB
ACF
SPAN
ZERO
531
642
78
F0301.EPS
Figure 3-1 T erminal Layout
Terminal
Designation
Model
When using STED-7 type, the input is selected from mV
DC, thermocouple or RTD.
Terminal
Designation
When not using outputs 1 to 3, the terminals remain opened.
STED-1 and STED-3 STED-4
1+ A 0%
2 – B
3
4
5
6
7 B 100%
8
A+
B –
C+
D –
F+
H –
J
K
mV DC input
or thermocouple input
(Reference junction
block installation
terminal)
Output 1 (1 to 5 V DC)
Output 3 (4 to 20 mA DC)
Output 2 (1 to 5 V DC)
Description
STED-2
Description
RTD
input
Potentiometer
input
T0301.EPS
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 14

<T oc> < 3. INST ALLA TION >
3.2 Applicable Cables
(1) Signal circuit wiring
● Cross-sectional area of the cable conductor: 0.5 to 0.75 mm
● Examples of applicable cables: Signal core PVC insulated flexible cable (VSF)
stranded wires (JIS C 3306); heat-resistant vinylinsulated cable (UL style 1007)
● Solderless lugs: All cable ends must be furnished with crimp-on
solderless lugs for 4 mm screw.
(2) Power supply wiring
● Cross-sectional area of the cable conductor: 1.25 to 2.00 mm
● Examples of applicable cables: 600 V PVC insulated cable (1 V) stranded wires
(JIS C 3307); PVC insulated cable for electrical
apparatus (KIV) stranded wires (JIS C 3316)
● Solderless lugs: All cable ends must be furnished with crimp-on
solderless lugs for 4 mm screw. The cable used
should fulfill the amperage requirement of each
instrument, and should also be small in voltage
drop.
2
2
3-2
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 15

<T oc> < 4. PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION >
4. PRINCIPLES OF OPERA TION
4.1 mV DC Input T ype (STED-1 and STED-7 Types)
The mV DC input signals are converted into digital data in A/D conversion circuit. The
digital data has signal processing (range conversion) in micro-processor to be Pulse Width
Modulation (PWM). The Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is converted into 1 to 5 V DC or 4
to 20 mA DC signals in output circuit after passing through optical insulation circuit.
4-1
Insulation Circuit
Insulation Circuit
Power
Supply
Circuit
mV DC Input
Handy
Terminal
No switch for
STED-7 type
+
1
2
Push Switch
for Adjustment
SPAN
ZERO
Input
Processing
Circuit
A/D
Conversion
Circuit
Micro-
Processor
Figure 4-1 Functional Block Diagram for mV Input T ype
Output
Circuit
Output
Circuit
V/I
+
A
Output 1 (1 to 5 V DC)
––
B
L+
Supply
N–
GND
+
F
Output 2 (1 to 5 V DC)
–
H
+
C
Output 3 (4 to 20 mA DC)
–
D
F0401.EPS
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 16

<T oc> < 4. PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION >
4.2 Thermocouple Input T ype (STED-2 and STED-7 Types)
The Thermocouple input signals are converted into digital data in A/D conversion circuit.
The digital data has signal processing (linearizing computation, RJC computation, and
range conversion) in micro-processor to be Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). The Pulse
Width Modulation (PWM) is converted into 1 to 5 V DC or 4 to 20 mA DC signals in output
circuit after passing through optical insulation circuit.
Insulation Circuit
+
A
Output 1 (1 to 5 V DC)
–
B
L+
Supply
N–
GND
Thermocouple Input
Handy
Terminal
1
2
RJC
6
Input
Processing
Circuit
A/D
Conversion
Circuit
Micro-
Processor
Power
Supply
Circuit
Output
Circuit
4-2
Output
Circuit
V/I
No switch for
STED-7 type
Push Switch
for Adjustment
SPAN
ZERO
Insulation Circuit
Figure 4-2 Functional Block Diagram for Thermocouple Input T ype
+
F
Output 2 (1 to 5 V DC)
–
H
+
C
Output 3 (4 to 20 mA DC)
–
D
F0402.EPS
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 17

<T oc> < 4. PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION >
4.3 RTD Input T ype (STED-3 and STED-7 Types)
The RTD input signals are converted into digital data in A/D conversion circuit. The digital
data has signal processing (linearizing computation and range conversion) in microprocessor to be Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). The Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is
converted into 1 to 5 V DC or 4 to 20 mA DC signals in output circuit after passing through
optical insulation circuit.
4-3
Insulation Circuit
Insulation Circuit
Power
Supply
Circuit
RTD Input
Handy
Terminal
No switch for
STED-7 type
A
1
B
2
B
7
Push Switch
for Adjustment
SPAN
ZERO
Input
Processing
Circuit
A/D
Conversion
Circuit
Micro-
Processor
Figure 4-3 Functional Block Diagram for RTD Input Type
Output
Circuit
Output
Circuit
V/I
+
A
Output 1 (1 to 5 V DC)
–
B
L+
Supply
N–
GND
+
F
Output 2 (1 to 5 V DC)
–
H
+
C
Output 3 (4 to 20 mA DC)
–
D
F0403.EPS
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 18

<T oc> < 4. PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION >
4.4 Potentiometer Input T ype (STED-4 Type)
The Potentiometer input signals are converted into digital data in A/D conversion circuit.
The digital data has signal processing (linearizing computation and range conversion) in
micro-processor to be Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). The Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
is converted into 1 to 5 V DC or 4 to 20 mA DC signals in output circuit after passing
through optical insulation circuit.
4-4
0%
100%
Potentiometer Input
Handy
Terminal
1
2
7
Push Switch
for Adjustment
SPAN
ZERO
Input
Processing
Circuit
A/D
Conversion
Circuit
Micro-
Processor
Insulation Circuit
Insulation Circuit
Power
Supply
Circuit
Output
Circuit
Output
Circuit
V/I
Figure 4-4 Functional Block Diagram for Potentiometer Input T ype
+
A
Output 1 (1 to 5 V DC)
–
B
L+
Supply
N–
GND
+
F
Output 2 (1 to 5 V DC)
–
H
+
C
Output 3 (4 to 20 mA DC)
–
D
F0404.EPS
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 19

<T oc> < 5. SETTING >
5. SETTING
The STED converters are made ready for operation by simply turning on the power once
the installation and wiring are completed. The instrument does not require parameter
settings and the like if there is no change in the specifications at order.
5.1 Names of Components
Tag plate
BRAIN connector
Span adjustment
push switch
Zero adjustment
push switch
(No switch for STED-7 type)
Name plate
5-1
Rack case
Input terminal block
Multi-pin connector
Two-pole plug with earthing contact
Output terminal block
Reference junction block (RJC)
(provided for STED-2 or STED-7 type)
Main board
Terminal cover and handle for
drawing out the internal unit
F0501.EPS
Figure 5-1 Names of Components
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 20

<T oc> < 5. SETTING >
ypes and functions of setting jumper
5.2 Setting Jumper
This instrument has the following setting jumpers:
• Reference junction compensation(JP1): ON/OFF (only for STED-2 type)
• Parameter Write Protect (JP2): ON/OFF
• Burnout (JP3, JP4): UP/DOWN/OFF (except for STED-7 type)
5.2.1 Check of Setting Jumper
NOTE
For STED-2 and STED-7 types, first remove the reference junction block ((RJC) from the
terminal block, then draw the internal unit.
(a) Pull forward the terminal cover, and draw the internal unit out from the rack case.
(b) Check that the jumper on the main board of the internal unit is set to obtain the desired
action.
5-2
(c) Use the tweezers to change the position of jumper .
(d) Put the internal unit back into the rack case.
(e) Replace the terminal cover.
NOTE
For STED-2 and STED-7 types, attach the reference junction block (RJC) to the terminal
block, then replace the terminal cover.
Types and functions of setting jumper
Setting jumper (factory-set default)
JP1 2 3 4
Burnout action
Reference
junction
compensation
(RJC) (W.P.)
OFF ON
Parameter
write protect
(BURN OUT)
JP3 JP4
UP DOWN
Burnout up
setting
UP OFF
Burnout down
setting
OFF DOWN
OFF OFF
SpecifyUPSpecify
ON
OFF:
Reference junction
compensation is
unavailable.
OFF
ON:
Parameter change
by Handy Terminal
is prohibited.
Figure 5-2 Types of Setting Jumper
DOWN
JP 3 4 JP 3 4
No burnout
setting
OFF OFF
JP 3 4
Note: The setting above is out of
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
UP DOWN
JP 3 4
burnout function. The action
is not guaranteed.
Page 21

<T oc> < 5. SETTING >
5.2.2 Position of Setting Jumper
The setting jumper is on the main board of the internal unit.
Setting jumper (factory-set default)
5-3
For STED-1,-3, & -4 types
JP1 2 3 4
Note: The configuration of setting jumper is
different according to the type.
JP1 is not provided for STED-1,-3, and -4 types.
Only JP2 is provided for STED-7 type.
For STED-2 type
JP1 2 3 4
For STED-7 type
JP1 2 3 4
Internal unit of STED
Figure 5-3 Configuration of Setting Jumper
F0502.EPS
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 22

<T oc> < 5. SETTING >
5.3 Setting of Parameters
This instrument has BRAIN communication parameters for specifying functions and
adjusting input/output. Connect JHT200 Handy T erminal (Note1) to the instrument to
display or set parameters.
Note 1: BT200 BRAIN Terminal of YOKOGAW A ELECTRIC Corporation can also be used.
NOTE
• BRAIN communication parameters are not used for STED-1 to STED-4 types.
• For details of operation and adjusting procedures of JHT200 Handy Terminal, refer to the
instruction manual “JHT200 Handy Terminal” (IM JF81-02E).
<Connection>
Cable of 5-pin
connector type
JHT200
Handy Terminal
(F9182EE)
BRAIN connector
5-4
Figure 5-4 Connection
5.3.1 Configuration of Parameters
BRAIN communication parameters consist of the following parameters.
• Display (A & B parameters)
• Setting (D parameters)
• Adjustment (P parameters)
• Test (Q parameters)
Adapter for modular jack
(E9786WH)
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 23

<T oc> < 5. SETTING >
5.3.2 Description of Parameters
The description of main parameters is as follows.
● Setting-related parameters
(1) D07: SENSOR TYPE1
Sets the input type for STED-7 type.
(2) D08: TC TYPE1
Sets the thermocouple input type for STED-7 type.
(3) D09: RTD TYPE1
Sets the RTD input type for STED-7 type.
(4) D13: RESIST1
Sets the total resistance for DC potentiometer input.
(5) D25: UNIT
Sets the unit for thermocouple input or RTD input.
(6) D27: INPUT1L_RNG
Sets 0% side of input range.
(7) D28: INPUT1H_RNG
Sets 100% side of input range.
(8) D31: BURN OUT1
Sets the burnout scale for STED-7 type.
5-5
(9) D33: OUT1 DR and D34: OUT2 DR
Sets the action direction for output 1 and output 2.
(10) D37: RJC
Sets available/unavailable of the reference junction temperature compensation-action
for STED-7 type.
(1 1) D38: RJC CONST (The setting value is available when D37: RJC = OFF)
Can fix the reference junction temperature in the reference junction temperature
compensation-action for STED-7 type.
● Adjustment-related parameters
(1) P01: WIRING R 1
Corrects the wiring resistance of input.
(2) P03: ZERO ADJ1
Performs zero adjustment of input.
(3) P04: SP AN ADJ1
Performs span adjustment of input.
(4) P13: OUT1 0% (Note1)
Adjusts 0% of output 1.
(5) P14: OUT1 100% (Note1)
Adjusts 100% of output 1.
(6) P15: OUT2 0% (Note1)
Adjusts 0% of output 2.
(7) P16: OUT2 100% (Note1)
Adjusts 100% of output 2.
● Test-related parameters
(1) Q02: OUT1 TEST (Note1)
Outputs the set value forcibly regardless of input condition.
Q03 has the same function.
Note1: After completing adjustment and test, press the [F4] (OK) key of the Handy T ermi-
nal to return to normal condition (release of forced output).
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 24

<T oc> < 5. SETTING >
5.4 Parameter List
BRAIN communication parameters for STED are as follows.
No. Symbol Parameter Name Setting Range Unit Default Setting Type
01 MODEL Model Name Display –––– unfixed Display
02 TAG NO Tag Number Display –––– unfixed Display
03 SELF CHK Self Check GOOD/ERROR –––– unfixed Display
<Display Parameters>
A DISPLAY1 Menu Name
A01 INPUT1 Input Display Display unfixed Display
A09 OUTPUT1 Output1 Display Display % unfixed Display
A10 OUTPUT2 Output2 Display Display % unfixed Display
A54 STATUS Status Display (Note1) 0000 to FFFF –––– unfixed Display
A55 WRT PROTECT Parameter Write Protect ON/OFF –––– OFF Display
A56 REV NO Revision number Display –––– unfixed Display
A58 MENU REV Menu Revision number Display –––– unfixed Display
A60 SELF CHK Self Check GOOD/ERROR –––– unfixed Display
B DISPLAY2 Menu Name
B01 INPUT1 Input Display Display unfixed Display
B09 OUTPUT1 Output1 Display Display % unfixed Display
B10 OUTPUT2 Output2 Display Display % unfixed Display
B60 SELF CHK Self Check GOOD/ERROR –––– unfixed Display
<Setting Parameters>
D SET(I/O) Menu Name
D01 TAG NO.1 Tag Number1 Up to 8-single-byte –––– unfixed Alphanumeric
D02 TAG NO.2 Tag Number2 Up to 8-single-byte –––– unfixed Alphanumeric
D03 COMMENT1 Comment1 Up to 8-single-byte –––– unfixed Alphanumeric
D04 COMMENT2 Comment2 Up to 8-single-byte –––– unfixed Alphanumeric
D07 SENSOR TYPE1 Sensor Type (Note2) TC/mV/RTD –––– TC Selection
D08 TC TYPE1 TC Type (Note10) (Note6) –––– TYPE K Selection
D09 RTD TYPE1 RTD Type (Note11) (Note7) –––– Pt100-90 Selection
D13 RESIST1 Resistance (Note3) 1 to 32000 OHM ordered Real number
D25 UNIT1 Unit (Note4) degC/K/degF –––– degF Selection
D27 INPUT1 L_RNG Input Low Range -32000 to 32000 Note8 ordered Real Number
D28 INPUT1 H_RNG Input High Range -32000 to 32000 Note8 ordered Real Number
D31 BURN OUT1 Burn Out OFF/UP/DOWN –––– OFF
D33 OUT1 DR Output1 Direction DIRECT/REVERSE –––– DIRECT Selection
D34 OUT2 DR Output2 Direction DIRECT/REVERSE –––– DIRECT Selection
D37 RJC RJC On/Off (Note12) ON/OFF –––– ON
D38 RJC CONST RJC Constant (Note10) -20.0 to 80.0 Note15 000.0 Real Number
D60 SELF CHK Self Check GOOD/ERROR –––– unfixed Display
<Adjustment Parameters>
P ADJUST Menu Name
P01 WIRING R1 Wiring Resistance (Note5) RESET/EXECUTE –––– RESET Selecton
P03 ZERO ADJ1 Zero Adjustment (Note5) Display Note9 00.00 Selection
P04 SPAN ADJ1 Span Adjustment (Note5) Display Note9 00.00 Selection
P13 OUT1 0% Output1 0% -20.0 to 20.0 % 00.00 Real Number
P14 OUT1 100% Output1 100% -20.0 to 20.0 % 00.00 Real Number
P15 OUT2 0% Output2 0% -20.0 to 20.0 % 00.00 Real Number
P16 OUT2 100% Output2 100% -20.0 to 20.0 % 00.00 Real Number
P60 SELF CHK Self Check GOOD/ERROR –––– unfixed Display
<Test Parameters>
Q TEST Menu Name
Q02 OUT1 TEST Output1 Test -25.0 to 125.0 % 000.0 Real Number
Q03 OUT2 TEST Output2 Test -25.0 to 125.0 % 000.0 Real Number
Q60 SELF CHK Self Check GOOD/ERROR –––– unfixed Display
Note 1: The condition of the instrument is displayed. Note 10: Displayed only for TC input of STED-7 type.
Note 2: Displayed only for STED-7 type. Note 11: Displayed only for RTD input of STED-7 type.
Note 3: Displayed only for STED-4 type. Note 12: Displayed only for TC input of STED-2 and -7 type.
Note 4: Not displayed for STED-1, -4, and -7 types. Note 13: STED-7 displays “Selection“.
Note 5: Not displayed only for STED-4 type. Note 14: STED-2 displays “Display“.
Note 6: TYPE K/E/J/T/R/S/B/N/W3/W5 (N/W3/W5 are only for STED-7 type.)
Note 7: Pt100-90/Pt100-68/JPt100 Note 15: Specified in D25.
Note 8: “mV” is for mV input, “deg C, deg F or K” is for TC/RTD input, and “OHM” is for potentiometer input.
Note 9: ** RST/** INC/** HINC/** HDEC/** DEC
(**;“mV” is for mV & TC inputs, and “OHM” is for RTD and potentiometer inputs.)
5-6
Display(Note13)
Selection(Note14)
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 25

<T oc> < 6.
6. MAINTENANCE
This chapter describes the calibration procedures and part replacements that can be
done in the instrument room or service shop.
6.1 T est Equipment
For efficient maintenance of this converter , it is recommended that the user have the
following test equipment manufactured by Yokogawa or their equivalent.
● DC V oltage/Current Standard, T ype 7651 and T ype 2553…….........1 set
(Required for mV DC and thermocouple input type equipment)
● Decade Resistance Boxes, Type 2793-01……….............................1 set
(Required for RTD input type equipment)
● Digital V oltmeter, T ype 7562…………………….................................1 set
● Cold Junction Bottle, T ype T-MJ………………..................................1 set
(To be made available only as required)
MAINTENANCE
>
6-1
6.2 Reference T able of Thermocouple and RTD
This instrument has been adjusted in accordance with the JIS thermoelectromotive force
table and the resistance ratio table amended in 1995.
For the input signals used to adjust the instruments, refer to JIS C1602-1995* for the
thermocouple input type and to JIS C1604-1997* for the platinum resistance temperature
detector (RTD) input type.
* Identical to IEC, ANSI and BS standards.
6.3 Adjustment
6.3.1 Adjustment for STED-1 to -4 Types (One Input-only T ype)
The inputs of STED-1 to -4 types are different, but the way for adjustment is the
same.
(a) Connect the test equipment corresponding to each input referring to Figure 6-1 through
Figure 6-4.
(b) T urn on the power while the equipment is connected to the instrument, and allow a
warm-up period of about 5 minutes.
(c) Press the Zero adjustment push-switch on the front panel for 3 seconds or more to enter
the adjustment mode.
(d) Apply an input equivalent to 0 % of the input range and read the output on the digital
voltmeter. It should be within the range 1 V ± 0.02 V . If the error is too large, apply an
input equivalent to 0 % of the input range, then press the Zero adjustment push-switch
for adjustment. When pressing the push-switch for 1 second or more, the output in creases in the fixed ratio. When pressing the push-switch again for 1 second or more
after releasing the push-switch, the output decreases in the fixed ratio. Perform the
adjustment while checking the output.
(e) Apply an input equivalent to 100 % of the input range and read the output on the digital
voltmeter. It should be within the range 5 V ± 0.02 V . If the error is too large, apply an in put equivalent to 100 % of the input range, then press the Span adjustment push-switch
for adjustment. When pressing the push-switch for 1 second or more, the output in creases in the fixed ratio. When pressing the push-switch again for 1 second or more
afterreleasing the push-switch, the output decreases in the fixed ratio. Perform the
adjustment while checking the output.
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 26

<T oc> < 6.
(f) Adjustable range is ± 5 % of span for mV DC/RTD/Thermocouple input and ± 10 % of
span for potentiometer input.
(g) Check that the output error for 25 %, 50 %, and 75 % of input range is within the accu racy . If necessary, apply inputs equivalent to 25 %, 50 %, and 75 % of input range, then
press the Zero adjustment push-switch for adjustment.
(h) This instrument is provided with 3 outputs, but the adjustment for only one of the 3 out puts is enough.
NOTE
• Do not open the terminal cover while adjusting the thermocouple input in order to maintain
all terminals at the same temperature.
• When the lead wire resistance is large (when using the safety barrier such as BARD in
combination with the instrument, it is equivalent to the increase of the lead wire resistance
), the error of zero point may occur . Perform zero adjustment in the condition close to
mounting condition.
• When performing the adjustment by current output, connect the parallel resistance (250 Ω
± 0.05 %) and check voltage.
• When performing span adjustment immediately after the zero adjustment (shorter than 1
minute), pressing the Zero adjustment push-switch for 3 seconds or more is not required.
• The adjustment mode ends if the push-switch is not pressed for 1 minute or more, then
the instrument enters the normal mode.
MAINTENANCE
>
6-2
YOKOGAWA Type 7562 or equivalent
Digital Voltmeter
Digital Voltmeter
250Ω±0.05%
Note: The broken line shows
4 to 20 mA DC output
test circuit.
YOKOGAWA Type 7651 or equivalent
DC Voltage/Current
Standard
Figure 6-1 mV DC Input Converter Adjustment
YOKOGAWA Type 7562 or equivalent
Digital Voltmeter
Digital Voltmeter
250Ω±0.05%
Note: The broken line shows
4 to 20 mA DC output
test circuit.
YOKOGAWA Type 2553 or equivalent
DC Voltage/Current
Standard
r: Resistance equivalent to that of
the actual lead wire.
Reference Junction Block
–
+
–
+
+
–
–
+
–
+
r
+
–
JK
DBH
FCA
SPAN
ZERO
531
246
87
JK
HDB
ACF
SPAN
ZERO
135
642
7
Power Supply
F0601.EPS
Power Supply
F0603.EPS
Figure 6-3 Thermocouple Input Converter Adjustment
YOKOGAWA Type 7562 or equivalent
Digtal Voltmeter
Digital Voltmeter
250Ω±0.05%
Note: The broken line shows
4 to 20 mA DC output
test circuit.
YOKOGAWA Type 2793-01or equivalent
Decade Resistance
Boxes
–
+
–
+
JK
BDH
ACF
A
135
B
78
B
SPAN
ZERO
642
Power Supply
Figure 6-2 RTD Input Converter Adjustment
YOKOGAWA Type 7562 or equivalent
Digtal Voltmeter
Digital Voltmeter
Note: The broken line shows
4 to 20 mA DC output
test circuit.
YOKOGAWA Type 2793-01 or equivalent
Decade Resistance
Boxes
Decade Resistance
Boxes
–
+
–
+
250Ω±0.05%
100%
0%
KJ
HDB
FCA
SPAN
ZERO
135
642
78
Power Supply
Figure 6-4 DC Potentiometer Input Converter
Adjustment
F0602.EPS
F0604.EPS
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 27

<T oc> < 6.
MAINTENANCE
6.3.2 Adjustment for STED-7 Type (Universal T ype)
The adjustment for STED-7 type without Zero/Span adjustment push-switches on
the front panel is to be performed using JHT200 Handy T erminal.
(a) Connect the test equipment corresponding to each input referring to Figure 6-1 through
Figure 6-3.
(b) Set the parameter write protect (W .P.) of setting jumper to OFF . (refer to “5.2 Setting
Jumper”.)
(c) Turn on the power while the equipment is connected to the instrument, and allow a
warm-up period of about 5 minutes.
(d) Connect JHT200 Handy Terminal.
<Connection>
Cable of 5-pin connector
JHT200
Handy Terminal
type for communication
(F9182EE)
BRAIN
connector
>
6-3
Adapter for Modular
jack(E9786WH)
Figure 6-5 Connection
NOTE
• For details of operation and adjusting procedures of JHT200 Handy Terminal, refer to the
instruction manual ‘‘JHT200 Handy T erminal’’ (IM JF81-02E).
• Do not turn off the power of the instrument during adjustment.
(e) Call the adjustment item (P:ADJUST).
(f) P03:ZERO ADJ1 is displayed.
(g) Apply an input equivalent to 0 % of the input range. Check the input value and the input
display of P03:ZERO ADJ1. If the input value does not correspond to the display value,
select P03:ZERO ADJ1 to enter the adjustment mode.
Mainly select INC (addition) or DEC (subtraction) for adjustment. (Selecting RST resets
the adjusted value and retrieves the factory-set default.) Selecting HINC or HDEC
performs adjustment using a value ten times as large as INC or DEC.
(h) Apply an input equivalent to 100 % of the input range. Check the input value and the
input display of P04:SP AN ADJ1. If the input value does not correspond to the display
value, select P04:SP AN ADJ1 to enter the adjustment mode.
Mainly select INC (addition) or DEC (subtraction) for adjustment. (Selecting RST resets
the adjusted value and retrieves the factory-set default.) Selecting HINC or HDEC
performs adjustment using a value ten times as large as INC or DEC.
(i) After completing the adjustment, set the parameter write protect (W.P .) of setting jumper
to ON. (refer to “5.2 Setting Jumper”.)
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 28

<T oc> < 6.
MAINTENANCE
>
6.4 Check of Reference Junction T emperature Compensation Action
For thermocouple input, check the action of reference junction temperature
compesation using the cold junction bottle. The figure of connection is shown in
Figure 6-6.
NOTE
When using the cold junction bottle, install the reference junction block (RJC), then replace
the terminal cover and warm up the instrument for about 15 minutes.
6-4
YOKOGAWA Type 7562 or equivalent
Digital Voltmeter
Note: The broken line shows
4 to 20 mA DC output
test circuit.
r: Resistance equivalent to that of
the actual lead wire.
Copper Wire
YOKOGAWA Type 2553 or equivalent
DC Voltage/Current
Standard
+
–
Digital Voltmeter
250Ω±0.05%
Thermocouple element or
compensating lead wire
r
+
+
–
METER COUPLE
Cold Junction Bottle
Figure 6-6 Thermocouple Input Converter
(Using reference junction compensator)
–
+
–
+
–
JK
CF
A
+
135
–
7
HDB
SPAN
ZERO
642
Power Supply
Reference Junction Block
F0605.EPS
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 29

<T oc> < 6.
6.5 Replacement of Fuse
When the fuse blows or requires replacement, replace it according to the following procedure. Recommended replacement interval: About 3 years.
NOTE
• When the fuse below , first check for the case because the fuse itself may not be
responsible for the problem. Then change the fuse.
• Use the dedicatd fuse (S9510VK). Do not use a fuse for other products.
(1) Remove the fuse holder cap, then pull the fuse out in the direction shown in Figure 6-
7.
(2) When installing a new fuse, use a fuse with the correct rating. Fasten the cap se-
curely.
Fuse
Rating: 1A
[ ]
Parts No.: S9510VK
MAINTENANCE
>
6-5
Figure 6-7 Replacement of Fuse
6.6 Replacement of Capacitor
Degradation of the aluminum electrolytic capacitor in the power supply unit depends on
operating temperature condition or operating environment.
Recommended replacement interval: 5 to 10 years.
NOTE
Ask your nearest Yokogawa sales staff for replacing the capacitor .
Do not replace the capacitor by yourself, because the parts number of power supply unit
(refer to CMPL 01B04J01-02E) and capacitor to be used are dif ferent according to the
power supply specifications.
F0606.EPS
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 30

Blank Page
Page 31

<Toc> < 7. TROUBLESHOOTING >
7. TROUBLESHOOTING
If any fault occurs in the instrument, note the symptoms and follow Section 7-1
T roubleshooting Flowchart. T o find the fault, first wire the instruments according to
Figures 6-1 through 6-4, apply an input signal, and note the symptoms.
If the fault is difficult to find, contact your nearest Yokogawa sales staff.
7.1 T roubleshooting Flowchart
Instrument operates
abnormally.
7-1
Is output lower
than 0% ?
Is output higher
than 100% ?
Is
input/output accuracy
abnormal ?
Does
burnout detection
operate ?
Recheck instrument
abnormality.
Normal ?
No
No
No
No
YES
End
YES
YES
YES
YES
Is fuse blown ?
No
For STED-1 to -4 types, set setting
jumper in internal unit correctly, and
recheck (see section 5.2).
Perform zero and span
adjustment.
(See section 6.3)
Are zero and
span normal ?
YES
Replace fuse
and recheck.
Is burnout Jumper
set correctly ?
No
For STED-7 type, confirm D31
parameter and recheck.
YES
(See section 6.5)
YES
End
Replace power supply
unit and recheck.
(See subsection 7.3.2)
Is power supply
unit normal ?
No
Recheck abnormality.
YES
End
Figure 7-1 Troubleshooting Flowchart
No
Replace main board
and recheck.
(See subsection 7.3.3)
F0701.EPS
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 32

<Toc> < 7. TROUBLESHOOTING >
7.2 Action in Fault Condition.
The output condition and error codes (BRAIN communication parameters) in fault
condition are shown in the table below.
NOTE
• ST ATUS is displayed in A54 of A:DISPLAY (display), and SELF CHK is displayed in 60 of
each item.
• ST ATUS error code is to be the addition display (hexadecimal number) when two errors or
more occur.
(Note1)
STATUS SELF CHK Error Information(Note2) Output Condition Description of Error Remedy
0001
0002
0008
0010
0040
0080
Main board error, Power supply board error, and RAM error other than the errors mentioned above may occur.
Each output state of these errors is 0 % or less, and the error information can not be called using JHT200 Handy Terminal.
Note1: Displays for the BRAIN communication parameters, ■60: SELF CHK and A54: STATUS.
Note2: Displayed when calling ■60: SELF CHK.
Note3: After checking the action, write ‘‘0’’ in STATUS to clear.
Note4: Compensation action in the limited reference junction temperature (-20 °C or -80 °C).
ERROR
ERROR
ERROR
ERROR
GOOD None Normal action Check power failure during Write ‘‘0’’ to clear.
ERROR
EEPROM ERROR
EEPROM SUM ERROR
INPUT OVER RANGE
RANGE SET ERROR
RJC ERROR
0 % or less EEPROM error Replace a main board.
0 % or less EEPROM sum check error Reset the parameter showing
an error. (Note3)
Normal action Excessive input, out of -25 to Set the input within the range.
125 %
Normal action Input range setting is L range Check the input range setting
≥ H range and change it.
operation
Normal action(Note4) RJC sensor error or temp- Replace RJC or check terminal
erature is out of range (ambient) temperature.
-20 to 80 °C
7-2
T0701.EPS
7.3 Replacement of Parts
WARNING
Nobody except members of Yokogawa service staff is allowed to replace the parts.
Never replace the parts by yourself because there is a possibility of damage to the instrument or of danger.
7.3.1 Replacement Procedure
(1) Replacement of Power Supply Unit
(2) Replacement of Main Board
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 33

<Toc> < 7. TROUBLESHOOTING >
NOTE
• Disassemble only those parts that disassembly is required at parts replacement.
• Disassemble the instrument carefully .
• For the input type fixed to thermocouple and universal iput type, first remove the reference
junction block(RJC) form the terminal block and pull out the internal unit form the case.
7.3.2 Replacement of Power Supply Unit
(a) Pull the terminal cover (13) outward to draw the internal unit out from the rack case.
(b) Unplug the connector (1) from the power supply unit (2).
(c) Remove two screws (3) to separate the power supply unit (2) from the bracket (10).
NOTE
• Use the power supply unit for style R for replacement (refer to CMPL).
• The power supply unit of former style without compatibility can not be used.
7-3
7.3.3 Replacement of Main Board
(a) Remove the power supply unit (2).
(Refer to Subsection 7.3.2 for operating procedure.)
(b) Remove two screws (8) to separate the bracket (9).
(c) Remove four screws (4) to separate the bracket (10) and the front bracket (5) from
the main board (6).
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 34

<Toc> < 7. TROUBLESHOOTING >
Internal Unit
7-4
2
1
3
6
7
4
6
11
5
13
4
9
12
4
7
2
1
10
8
Figure 7-2 Disassembled View
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 35

<T oc>
< Appendix /TB POWER SUPPLY TERMINALS for RACK-MOUNTED INSTRUMENTS (Option) >
Appendix / TB Power Supply T erminal
Connections for Rack-mounted
Instruments (Option)
Appendix-1 GENERAL
If you specify the terminal block to which the power source is directly connected (suffix
code /TB), the external wiring to the terminal block is necessary; therefore, drawing out the
internal unit requires previous turning off of the power source and disconnection of the
wiring from the terminal block.
Appendix-2 APPLICABLE INSTRUMENTS
Model Description
STED mV, Temperature and Potentiometer/Voltage Converters
SKYD Alarm Unit
SALD Emf- and RTS- input Alarm Unit
SPLR Programmable Computing Unit
SIND Integrator
SISD Isolator
SDBT Distributor (for 1 point)
SDBS Distributor (for 4 points)
SDBU-21 Distributor (for single loop)
App.-1
Appendix-3 EXTERNAL VIEW AND NAMES OF
COMPONENTS
Output Terminal Block
Output Terminal Cover
Power Fuse
Power Terminal Cover
Input Terminal Block
Power Terminal
Input Terminal Cover
Terminal
Designation
L AC or DC Power Supply
N (DC: polarity reversible)
Ground
Description
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 36

<T oc>
< Appendix /TB POWER SUPPLY TERMINALS for RACK-MOUNTED INSTRUMENTS (Option) >
App.-2
Appendix-4 POWER SUPPLY AND GROUND WIRING
(1) All cable ends must be furnished with crimp-on type solderless lugs (for 4 mm screw).
(2) Examples of applicable cables:
2
Cross-sectional area of the cable conductor: 2.0 mm
Applicable cable: 600 V vinyle insulated cable (IV) stranded wires, conforming to JIS
C3307.
Vinyle sheathed cables for electric appliances (KIV) stranded
wires, conforming to JIS C3316.
Note *: Power supply cables should be determined from the instrument power consumption-they must have
conductors with cross-sectional area of at least 1.25mm2.
(3) Wirings to power supply and ground terminals should be made after completion of
signal terminal wirings. (To facilitate connecting input signal, pull the internal unit
approximately half way out of the housing. Do not remove the power terminal block.)
(4) After completing the power supply and ground wiring, mount the power terminal cover.
. *
IM 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00All Rights Reserved, Copyright© 2001, Y okogawa Electric Corporation
Page 37

Customer
Maintenance
Parts List
Model STED (Style R)
mV, Temperature and Potentiometer
/Voltage Converters
4
20
20
1
18
7
3
11
2
20
20
20
5
12
10
15
19
6
All Right Reserved, Copyright © 1983, Yokogawa Electric Corporation.
Subject to change without notice. Printed in Japan.
CMPL 01B04J01-02E
9th Edition: May. 2004
Page 38

Qty
Model
STED-110
STED-210- *1
STED-310
STED-410
Item Part No. Description
1 L3040BA 1 Main Board Assembly
L3040BB 1 Main Board Assembly
L3040BC 1 Main Board Assembly
L3040BD 1 Main Board Assembly
L3040BE 1 Main Board Assembly
2 A1211JS 1 1 1 1 1 Socket & Holder
3 L4040EA 1 1 1 1 1 Cap
STED-710
2
4 L3040YA 1 1 1 1 1 Power Supply Unit (for 100V Version)
L3040YR 1 1 1 1 1 Power Supply Unit (for 220V Version)
5 S9510VK 1 1 1 1 1 Fuse(1A)
6 E9713CA 1 1 1 1 1 Cover
7 E9713CK 1 1 1 1 1 Cover
10 E9713EG 1 1 1 1 1 Cable Assembly(for 100V Version)
E9713FS 1 1 1 1 1 Cable Assembly(for 220V Version)
11 E9713CE 1 1 1 1 1 Cover
12 S9079PB 1 1 1 1 1 Bushing
15 Y9422NP 1 1 1 1 1 Tag No. Label (blank)
18 Y9306JB 1 1 Pan H.Screw, M3x6 *2
19 G9320EY 1 1 Bushing *2
20 Y9306JB 8 8 8 8 8 Pan H. Screw, M3x6
Note *1: TK, TT, TJ, TE, TR or TS in
*2: Only for thermocouple input type.
CMPL 01B04J01-02E 9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00
Page 39

Customer
4
8
76
3
1
2
5
Maintenance
Parts List
/TB
Power Supply Terminals
For Rack-Mounted Instruments
(Option)
All Right Reserved, Copyright © 1984, Yokogawa Electric Corporation.
Subject to change without notice. Printed in Japan.
CMPL 01B04F02-11E
8th Edition: May 2004
Page 40

Part No. Qty Descripion
Item
1
−−−
2
E9713CJ
3
−−−
4
E9713ET
5
S9510VK
6
E9713CV
7
Y9306JB
8
E9714DM
Table 1. Power Supply Unit Part Number.
Model
SPLR
STED, SISD, SDBT
SALD, SKYD, SIND, SDAU
SDBS, SDBU-21
SPCM
1
Power Supply Unit (see Table 1)
1
Cover
1
Bracket (see Table 2)
1
Terminal Assembly
1
Fuse (1A)
1
Cover
2
Pan H. Screw, M3 × 6
1
Label (1A/250V)
Power Supply Unit Part No.Applicable Instruments
100 V Version 200 V V ersion
E9715YH
L3040YH
L3040YJ
E9715YK
E9715YL
Table 2. Bracket Part Number.
Applicable Instruments
Model
STED-110/310/410
STED-210
STED-710
SISD,SIND-100/200, SDBT-21
SKYD-200/201/302
SKYD-100/101,SALD-110/310
SKYD-204/304
SKYD-104
SALD-210/710
SALD-724
SALD-214/714
SIND-104/204
SDBS
SDBT-11
SDAU-xxx/TB
SDAU-100/RLY4/TB
SDAU-270/RLY4/TB
SDAU-xxx/TB/COM
SDAU-100/RLY4/TB/COM
SDAU-270/RLY4/TB/COM
Bracket Part No.
L4040CA
L4040CB
L4040CC
L4040CE
L4040CG
L4040CH
L4040CL
L4040CM
L4040CQ
L4040CS
L4040CT
L4040CX
E9713DR
E9713DL
L4040DA
L4040DB
L4040DE
L4040DF
Page 41

<Int> <Toc> <Ind>
Revision Information
● Manual Title: Model STED (Style R) mV, Temperature and Potentiometer/Voltage Converters
● Manual No. : IM 01B04J01-02E
9th Edition/May 2004
Change of the company name.
i
Written by Yokogawa Electric Corporation
Published by Yokogawa Electric Corporation
2-9-32 Nakacho, Musashino-shi, Tokyo 180-8750, JAPAN
IM 01B04J01-02E
9th Edition : 2004.05.01-00
Page 42

Blank Page
Page 43

Page 44

YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORPORATION
Network Solutions Business Division
2-9-32, Nakacho, Musashino-shi, Tokyo, 180-8750 JAPAN
Phone: +81-422-52-7179 Facsimile: +81-422-52-6793
Sales Branch Offices
Tokyo, Nagoya, Osaka, Hiroshima, Fukuoka
YOKOGAWA CORPORATION OF AMERICA
Headquaters
2 Dart Road, Newnan, GA. 30265-1094 U.S.A.
Phone: +1-770-253-7000 Facsimile: +1-770-251-0928
Sales Branch Offices / Texas, Chicago, Detroit, San Jose
YOKOGAWA EUROPE B. V.
Headquaters
Databankweg 20, 3821 AL Amersfoort THE NETHERLANDS
Phone: +31-334-64-1611 Facsimile: +31-334-64-1610
Sales Branch Offices / Houten (The Netherlands), Wien (Austria), Zaventem
(Belgium), Ratingen (Germany), Madrid (Spain), Bratislava (Slovakia), Runcorn (United
Kingdom), Milano (Italy), Velizy villacoublay(France), Johannesburg(Republic of South
Africa)
YOKOGAWA AMERICA DO SUL S.A.
Headquarters & Plant
Praca Acapulco, 31-Santo Amaro, Sao Paulo/SP, BRAZIL CEP-04675-190
Phone: +55-11-5681-2400 Facsimile: +55-11-5681-4434
YOKOGAWA ENGINEERING ASIA PTE. LTD.
Head office
5 Bedok South Road, Singapore 469270 SINGAPORE
Phone: +65-6241-9933 Facsimile: +65-6241-2606
YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC KOREA CO., LTD.
Seoul Sales office
395-70, Shindaebang-dong, Dongjak-gu, Seoul,156-010, KOREA
Phone: +82-2-3284-3000 Facsimile: +82-2-3284-3019
YOKOGAWA TAIWAN CORPORATION
Head office
17F, No.39, Sec. 1, Chung Hwa Road Taipei, 100 TAIWAN
Phone: +886-2-2314-9166 Facsimile: +886-2-2314-9918
YOKOGAWA AUSTRALIA PTY. LTD.
Head office
Centrecourt D1, 25-27 Paul Street North, North Ryde, N. S. W. 2113, AUSTRALIA
Phone: +61-2-9805-0699 Facsimile: +61-2-9888-1844
YOKOGAWA INDIA LTD.
Head office
40/4 Lavelle Road, Bangalore, 560 001, INDIA
Phone: +91-80-227-1513 Facsimile: +91-80-227-4270
LTD. YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC
Grokholskiy per. 13, Build. 2, 4th Floor, 129010, Moscow, RUSSIA FEDERATION
Phone: +7-095-737-7868 Facsimile: +7-095-737-7869
 Loading...
Loading...