Page 1

Grid Tie Solar Inverter
Xantrex Grid Tie
Solar Inverter
GT2.5-NA
GT3.0-NA
GT3.3-NA
Owner’s Manual
Page 2

Page 3

Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter
Owner’s Manual
Page 4

About Xantrex
Xantrex Technology Inc. is a world-leading supplier of advanced power electronics and controls with products from
50 watt mobile units to one MW utility-scale systems for wind, solar, batteries, fuel cells, microturbines, and backup
power applications in both grid-connected and stand-alone systems. Xantrex products inclu de inverters, batt ery
chargers, programmable power supplies, and variable speed drives that convert, supply, control, clean, and distribute
electrical power.
Trademarks
Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter is a trademark of Xantrex International. Xantrex and Xanbus are registered
trademarks of Xantrex International.
Other trademarks, registered trademarks, and product names are the property of their respective owners and are used
herein for identification purposes only.
Notice of Copyright
Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter Owner’s Manual © October 2005 Xantrex International. All rights reserved.
Disclaimer
UNLESS SPECIFICALLY AGREED TO IN WRITING, XANTREX TECHNOLOGY INC. (“XANTREX”)
(a) MAKES NO WARRANTY AS TO THE ACCURACY, SUFFICIENCY OR SUITABILITY OF ANY
TECHNICAL OR OTHER INFORMATION PROVIDED IN ITS MANUALS OR OTHER DOCUMENTATION.
(b) ASSUMES NO RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY FOR LOSS OR DAMAGE, WHETHER DIRECT,
INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL, WHICH MIGHT ARISE OUT OF THE USE OF SUCH
INFORMATION. THE USE OF ANY SUCH INFORMATION WILL BE ENTIRELY AT THE USER’S RISK.
Date and Revision
October 2005 Revision C
Part Number
975-0245-01-01
Contact Information
Telephone: 1 800 670 0707 (toll free North America)
1 360 925 5097 (direct)
Fax: 1 360 925 5143 (direct)
Email: customerservice@xantrex.com
Web: www.xantrex.com
Page 5

About This Manual
The purpose of this Owner’s Manual is to provide expl anations and procedures for
installing, operating, maintaining, and troubleshooting the Xantrex Grid T ie Solar
Inverter™.
Scope
The manual provides safety guidelin es, detailed planning and setup informatio n. It
provides procedures for installing the inverter and information about operating
and troubleshooting the unit. It does not provide details about particular brands of
photovoltaic (PV) panels. You need to consult individual PV manufacturers for
this information.
Audience
The manual is intended for anyone who needs to install and operate the GT
Inverter. Installers should be fully educated on the hazards of installing electrical
equipment. Certified electricians or technicians are recommended.
Organization
This manual is organized into 6 chapters and an appendix.
Chapter 1, “Introduction”, contains information about the features and functions
of the Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter.
Chapter 2, “Installation”, provides information about planning for and installing
the GT Inverter. It contains information to help you plan wire routes, AC and DC
connections, and find a suitable location for installation. It also discusses
requirements for grounding the GT Inverter and your PVarray.
Chapter 3, “Wiring the Inverter”, provides procedures for making DC and AC
wiring connections, and grounding the GT Inverter and the PV array. Instructions
for wiring multiple inverters are also provided.
Chapter 4, “Starting the Inverter”, contains information on starting up the Xantrex
Grid Tie Solar Inverter and performing a Functional Test.
Chapter 5, “Monitoring the Inverter”, contains information for understanding the
LCD screens and the LED indicators.
Chapter 6, “Maintenance and Troubleshooting”, contains information about how to
provide general maintenance for the Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter. It also
provides information about troubleshooting the unit.
Appendix A, “Specifications”, contains information about the electrical and
environmental specifications of the Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter.
975-0245-01-01 iii
Page 6

About This Manual
Conventions Used
The following conventions are used in this guide.
WARNING
Warnings identify conditions that could result in personal injury or loss of life.
CAUTION
Cautions identify conditions or practices that could result in damage to the unit or other
equipment.
Important:
serious as a caution or warning.
These notes describe things which are important for you to know, but not as
Abbreviations and Acronyms
AC Alternating Current
CEC California Energy Commission
CSA Canadian Standards Association
DC Direct Current
GT Grid Tie
GUI Graphical User Interface
LCD Liquid Crystal Display
LED Light Emitting Diode
MPPT Maximum Power Point Tracking
NEC US National Electrical Code NFPA-70
PC Personal Computer
PV Photovoltaic
PVGFP PV Ground Fault Protection
PWM Pulse Width Modu lation
STC Standard Test Condition
UL Underwriters Laboratories
Vac Volts AC
Vdc Volts DC
V
MP
V
OC
iv 975-0245-01-01
Voltage at Maximum Power
Open Circuit Voltage
Page 7

Related Information
You can find more information about Xantrex Technology Inc. as well as its
products and services at www.xantrex.com.
About This Manual
975-0245-01-01 v
Page 8

vi
Page 9

Important Safety Instructions
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS—This manual contains important instructions that shall be followed
during the installation and maintenance of the Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter.
1. Before installing and using the GT Inverter, read all instructions and cautionary markings on the
inverter, wiring box, and all appropriate sections of this guide.
2. To reduce risk of fire hazard, do not cover or obstruct the heat sink.
3. Observe the clearance recommendations as described on page 2–18. Do not install the G T In verter in a
zero-clearance or non-ventilated compartment. Overheating may result.
4. Use only accessories recommended or sold by the manufacturer. Doing otherwise may result in a risk
of fire, electric shock, or injury to persons.
5. To avoid a risk of fire and electric shock, make sure that existing wiring is in good condition and that
wire is not undersized. Do not operate the GT Inverter with damaged or substandard wiring.
6. Do not operate the G T Inverter if it has received a sharp blow, been dropped, or otherwise damaged in
any way. If the GT Inverter is damaged, see the Warranty section.
7. Do not disassemble the G T Inverter. It contains no user -serviceable parts. See Warranty for instructions
on obtaining service. Attempting to service the GT Inverter yourself may result in a risk of electrical
shock or fire and will void the factory warranty.
8. To reduce the risk of electrical shock, disconnect both AC and DC power from the GT Inverter before
attempting any maintenance or cleaning or working on any circuits connected to the inverter. Turning
off controls will not reduce this risk. Internal capacitors remain charged for 5 minutes after
disconnecting all sources of power.
9. The GT Inverter must be connected to an equipment-groun din g conductor directly or via the AC
ground.
975-0245-01-01 vii
Page 10
Safety
Regulatory Compliance
The GT Inverter has complete on-board over-current, over-temperature and anti-islanding protection, and
meets U.S., Canadian and international safety operating standards and code requirements:
• UL 1741 1st Edition – Standard for Inverters, Converters, and Controllers for Use in Independent
Power Systems
• CSA C22.2 No. 107.1-01 General Use Power Supplies
• IEEE C62.41 Recommended Practice on Surge Voltages in Low-Voltage AC Power Circuits (Location
Category B3).
To locate the firmware version number
The firmware version number for the protection processor is visible on a screen that appears when the unit
starts up or is powered up after switching the DC/AC Disconnect switch to “on.” The screen reads:
Flash = 01.01
ROM = 01.01
The number appearing after “ROM” is the firmware version number for the protection processor.
FCC Information to the User
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant
to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can
be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference
by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
viii 975-0245-01-01
Page 11

Safety
Verification and Commissioning Test
Purpose
This procedure is designed to verify correct operation of the Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter both on initial
operation and periodically through its life as required by the utilities.
Commissioning Test
Follow the startup and monitoring procedures as documented in Chapters 4 and 5.
When operation of the inverter has been verified and the unit is producing power, run the disconnect test as
described in this section.
Verification Test
Periodically run the disconnect test. The inverter must respond within the 2-second limit for compliance
and then hold off on producing power for the required delay (default value of 5 minutes).
Disconnect Test
This test requires that the AC circuit for the inverter be switched off. This can be accomplished by
switching the breaker on the main panel that feeds the inverter(s). As an alternate, the disconnect for the
home or business may be used as well. Have someone watch the front panel of the inverter. Within 2
seconds of switching the breaker, the green light on the front of the inverter must go out. The display will
respond with an AC Fault display, indicating that the AC is out of the operating range.
Re-energize the breaker to the inverter. The unit will respond by beginning its countdown. The green light
will be off during this time. Five minutes after applying AC (default value), the green light will turn on and
the inverter will begin to push power to the grid. The display will then return to its on-line display showing
the power being produced along with the total kWh p r oduced to date.
Note: The default voltage, frequency and reconnect delay values as defined by UL1741 and CSA 107.1 -01
are programmed into the unit at time of shipment from the factory. No changes to these settings can be
made in the field by the user. Only authorized personnel with the utility’s permission may change these
settings. Contact Xantrex Technology to gain permission and the procedure/equipment to make these
changes.
975-0245-01-01 ix
Page 12

x
Page 13

Contents
Important Safety Instructions
Regulatory Compliance - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - viii
FCC Information to the User - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - viii
Verification and Commissioning Test - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ix
1
Introduction
About the Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–2
Standard Features - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–3
Front Panel Features - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–4
Wiring/Disconnect Box - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–4
Safety and Standards - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–6
2
Installation
Installation Options - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–2
Single Inverter Installation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–2
Multiple Inverter Installations - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–2
Planning the Installation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–2
Inverter Location - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–4
PV Array Requirements - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–5
Grounding Requirements - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–8
Routing the Wires - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–11
Preparing for the Installation - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–12
Wiring - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–13
Circuit Breakers and Disconnect Switch - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–13
Other Materials Needed - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–14
Equipment Needed - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–14
Mounting the Inverter - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–15
Overview - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–15
Preparing to Mount the Unit - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–16
Installing the Mounting Bracket - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–17
Mounting the Inverter on the Bracket - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–22
3
Wiring the Inverter
Accessing the Wiring Terminals - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–2
Connecting the DC Wiring - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–4
Connecting the AC Wiring - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–7
975-0245-01-01 xi
Page 14

Contents
Connecting Multiple Inverters - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–9
DC and AC Wiring for Multiple Inverters - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3–10
Communications Wiring for Multiple Inverters- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–12
Xanbus Network Technology - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3–12
Guidelines for Routing the Network Cables - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3–15
Connecting Network Cable Between Multiple Inverters - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3–16
Communications Wiring for Monitoring a Single Inverter - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -3–18
4
Starting the Inverter
Startup Procedure- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–2
Checking the PV Array DC Voltage - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–2
Checking the AC Utility Voltage - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–2
Replacing the Wiring/Disconnect Box Cover - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–3
Starting up the GT Inverter - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–4
Commissioning Multiple Inverters - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–4
Disconnect Test - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–6
5
Monitoring the Inverter
Monitoring the Front Panel Display- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–2
Front Panel Display Screens and What They Mean - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–3
Startup Mode - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–3
Normal Operation Mode - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–3
Offline Mode - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–5
Fault Mode - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–7
Special Screens - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–9
Custom Screens - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–9
Status Indicator Lights- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–10
6
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Factors Affecting GT Inverter Performance - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6–2
PV Array Factors - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6–2
Other Factors - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6–3
Performing General Maintenance - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6–3
Replacing Parts - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6–3
Replacing the Ground Fault Protection Fuse - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6–4
Replacing the Inverter - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6–6
Identifying Error/Fault Conditions and Solutions- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6–9
xii 975-0245-01-01
Page 15

Contents
A
Specifications
Electrical Specifications - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - A–2
Input - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -A–2
Output - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -A–2
Adjustable Disconnect Settings - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -A–3
Efficiency - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -A–5
Environmental Specifications - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - A–6
User Display - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -A–6
Mechanical Specifications - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - A–6
Warranty and Return Information - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -WA–1
Index- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -IX–1
975-0245-01-01 xiii
Page 16

xiv
Page 17

Figures
Figure 1-1 Basic System Overview - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–2
Figure 1-2 Main Features of the GT Inverter- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–4
Figure 1-3 Wiring Box and Removable Inverter - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–5
Figure 1-4 Safety and Data Label Locations - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 1–6
Figure 2-1 Installation Options Overview- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–3
Figure 2-2 Basic Grounding Overview- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–9
Figure 2-3 Long Distance Grounding Overview - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–10
Figure 2-4 Grounding With Extra Lightning Protection Overview - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–11
Figure 2-5 Conduit Hole and Knockout Locations- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–12
Figure 2-6 Installation Overview- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–15
Figure 2-7 Dimensions of GT Inverter and Knockout Locations- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–17
Figure 2-8 Mounting Bracket and GT Inverter - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–18
Figure 2-9 Examples of Mounting on a Pole or Rails - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–20
Figure 2-10 Installing the Mounting Bracket using Plywood Support - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–21
Figure 2-11 Proper Placement of the Inverter on the Mounting Bracket - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–22
Figure 3-1 Removing the Wiring Box Cover- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–2
Figure 3-2 AC and DC Terminal Block Location in the Wiring Box- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–3
Figure 3-3 DC/AC Disconnect Switch Positions - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–4
Figure 3-4 DC Connections for Multiple PV Strings - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–6
Figure 3-5 AC Connections from GT Inverter to Utility Service Panel - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–8
Figure 3-6 Improper Multiple Inverter Connections - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–9
Figure 3-7 DC and AC Wiring With Multiple GT Inverters- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–11
Figure 3-8 Daisy Chain Layout- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–12
Figure 3-9 Male Network Terminator - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–13
Figure 3-10 Xanbus RJ45 Ports in the GT Inverter Wiring Box - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–13
Figure 3-11 RJ45 Connector - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–14
Figure 3-12 Communications Wiring for Multiple GT Inverters - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–17
Figure 3-13 GT-View Display - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–19
Figure 3-14 GT-View Options - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–19
Figure 4-1 DC/AC Disconnect Switch Positions - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–4
Figure 4-2 Commissioning Sequence for Multiple Inverters - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 4–5
Figure 5-1 Front Panel LCD Location - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–2
Figure 5-2 Location of Status Indicator Lights - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–10
Figure 6-1 Location of Fuse, Front Panel Cover Removed - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6–5
Figure 6-2 Display Front Panel Assembly - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6–5
Figure 6-3 Wiring/Disconnect Box and Removable Inverter - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6–7
Figure 6-4 Inverter and Wiring/Disconnect Box Sections - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6–8
Figure A-1 Output Power vs. Ambient Temperature at Various DC Voltages - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -A–4
Figure A-2 Typical Efficiency- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -A–5
975-0245-01-01 xv
Page 18

xvi
Page 19

Tables
Table 2-1 MPPT Operational Window - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–6
Table 2-2 Inverter Clearance Requirements- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 2–18
Table 3-1 Torque Values for Wires* - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–5
Table 3-2 T568A Standard Wiring- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–14
Table 3-3 Network Components and Part Numbers- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 3–15
Table 5-1 Startup Screens on GT Inverter Front Panel Display - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–3
Table 5-2 Normal Operation Default Screen - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–4
Table 5-3 Normal Operation Screens for All GT Inverter Units - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–4
Table 5-4 Additional Normal Operation Screens for Each GT Inverter Unit in a Multiple Unit System
5–5
Table 5-5 Offline Mode Default Display- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–5
Table 5-6 Offline Mode Screens for All GT Inverter Units- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–6
Table 5-7 Additional Offline Mode Screens for Each GT Inverter Unit in a Multiple Unit System - 5–6
Table 5-8 Fault Message Screens- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–7
Table 5-9 Additional Fault Mode Screens - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–8
Table 5-10 Special Message Screens - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–9
Table 5-11 Status Indicator LEDs - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 5–10
Table 6-1 Troubleshooting the GT Inverter - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - 6–9
975-0245-01-01 xvii
Page 20

xviii
Page 21

1
Introduction
Chapter 1, “Introduction”, contains information about the features
and functions of the Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter.
The topics in this chapter are organized as follows:
• “Standard Features” on page 1–3
• “Safety and Standards” on page 1–6
Page 22
Introduction
About the Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter
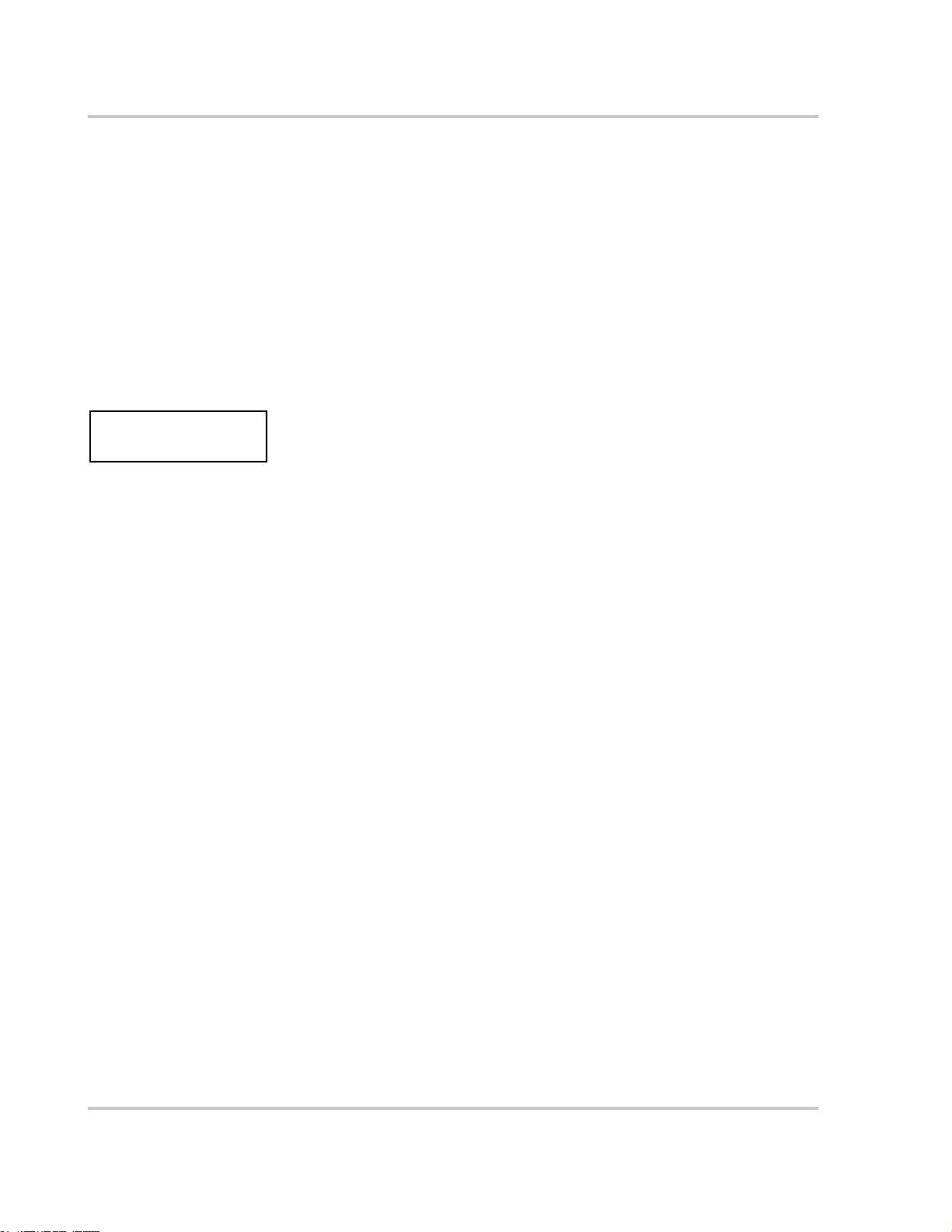
The Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter (GT Inverter) is designed to convert solar
electric (photovoltaic or PV) power into utility-grade electricity that can be used
by the home or sold to the local power company.
Installing the GT Inverter consists of mounting it to the wall and connecting the
DC input to a PV array and the AC output to the utility. See Figure 1-1 for a
simple diagram of a typical installation.
In order to operate, the GT Inverter must have grid power available and connected.
It will not provide backup power if the AC grid fails.
Photovoltaic (PV)
Panels - PV Array
Harvested
solar energy
Grid Tie Inverter
Figure 1-1 Basic System Overview
DC converted
to AC
Xantrex
GT Inverter
Utility
Meter
Utility Grid
Surplus power
route d to Utility Grid
Powe r ro ute d
to loads
Main Utility
Service Panel
Loads
1–2 975-0245-01-01
Page 23

About the Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter
PV compatibility The G T Invert er is designed to take advantage of solar modules configured as high
voltage PV string arrays—single crystalline, poly crystalline, or thin film—with a
195 to 550 Vdc input voltage Maximum Power Point range.
Maximum Power
Point Tracking
(MPPT)
The GT Inverter uses Xantrex proprietary Maximum Power Point Tracking
(MPPT) technology to harvest the maximum amount of energy from the solar
array. Xantrex MPPT learns your array’s specific characteristics, maximizing its
output at all times.
High efficiency The high-frequency, solid-state design of the GT Inverter is extremely efficient—
up to 95%.
Expandable Multiple GT Inverters may be networked together for increased net metering
capacity or future system growth.
Communications
protocol
The GT Inverter uses the Xanbus
communicate with multiple units connected within the system. For more
®
Communications protocol, enabling it to
information, see “Xanbus Network Technology” on page 3–12.
Standard Features
The GT Inverter has the following standard features:
• Sealed inverter section protecting power electronic components;
• Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) providing easy-to-read system status and daily
cumulative energy production information;
• Two LED indicator lights providing status and ground fault indication;
• Wiring/disconnect box providing protection for all AC and DC connections
and eliminating exposed “live” wiring if the inverter is removed.
WARNING: Shock hazard
The 600 volt DC/AC disconnect in the wiring/disconnect box meets NEC Article 690. It is
a non-serviceable component and shall remain in place. Removal can expose energized
conductors.
975-0245-01-01 1–3
Page 24
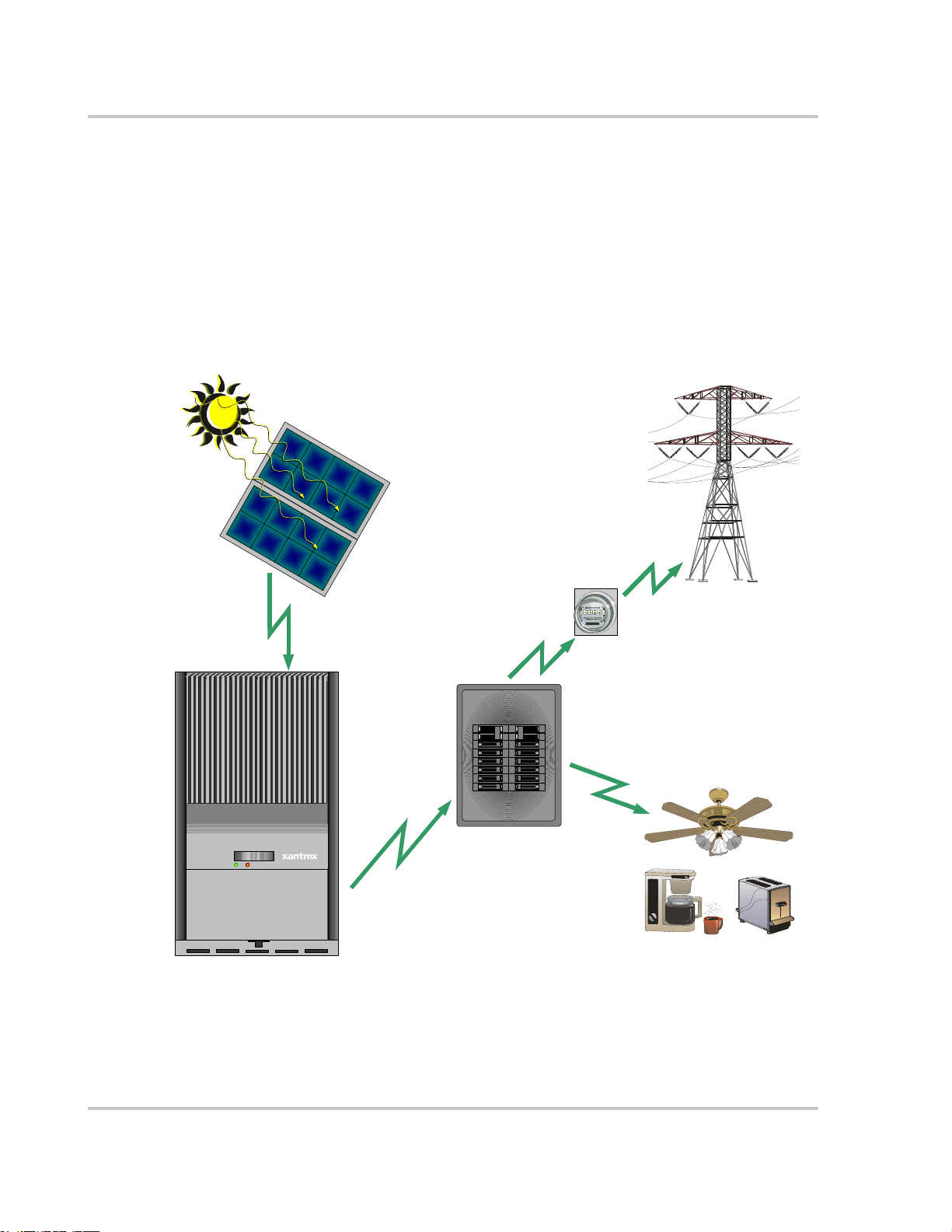
Introduction
Front Panel Features
Heat Sink
LCD
LED Indicator Lights
Grid Tie Solar Inverter
Wiring/Disconnect Box
Figure 1-2
Wiring/Disconnect Box
The wiring/disconnect box is standard for all North American models of the GT
Inverter.
The wiring/disconnect box provides a location for making AC, DC and ground
connections. It also contains the DC/AC (PV array/Utility) disconnect switch.
Although the GT Inverter is shipped as a complete system, it is essentially two
separable products: a PV inverter and a wiring/disconnect box. The manual
disconnect switch in the wiring box allows easy access and a quick one-turn
disconnect for both AC and DC inputs. It has been designed to be physically
mated to the electronics section of the GT Inverter at the factory, but remains in
place as a non-serviceable item in the event that the inverter electronics section is
ever required to be removed. When used with the GT Inverter, the DC/AC
disconnect switch is 600V AC and DC rated and also is identified on the outside
by an illustration showing the open and closed switch positions. The DC/AC
DC/AC Disconnect Switch
Mounting Slots
Main Features of the GT Inverter
1–4 975-0245-01-01
Page 25
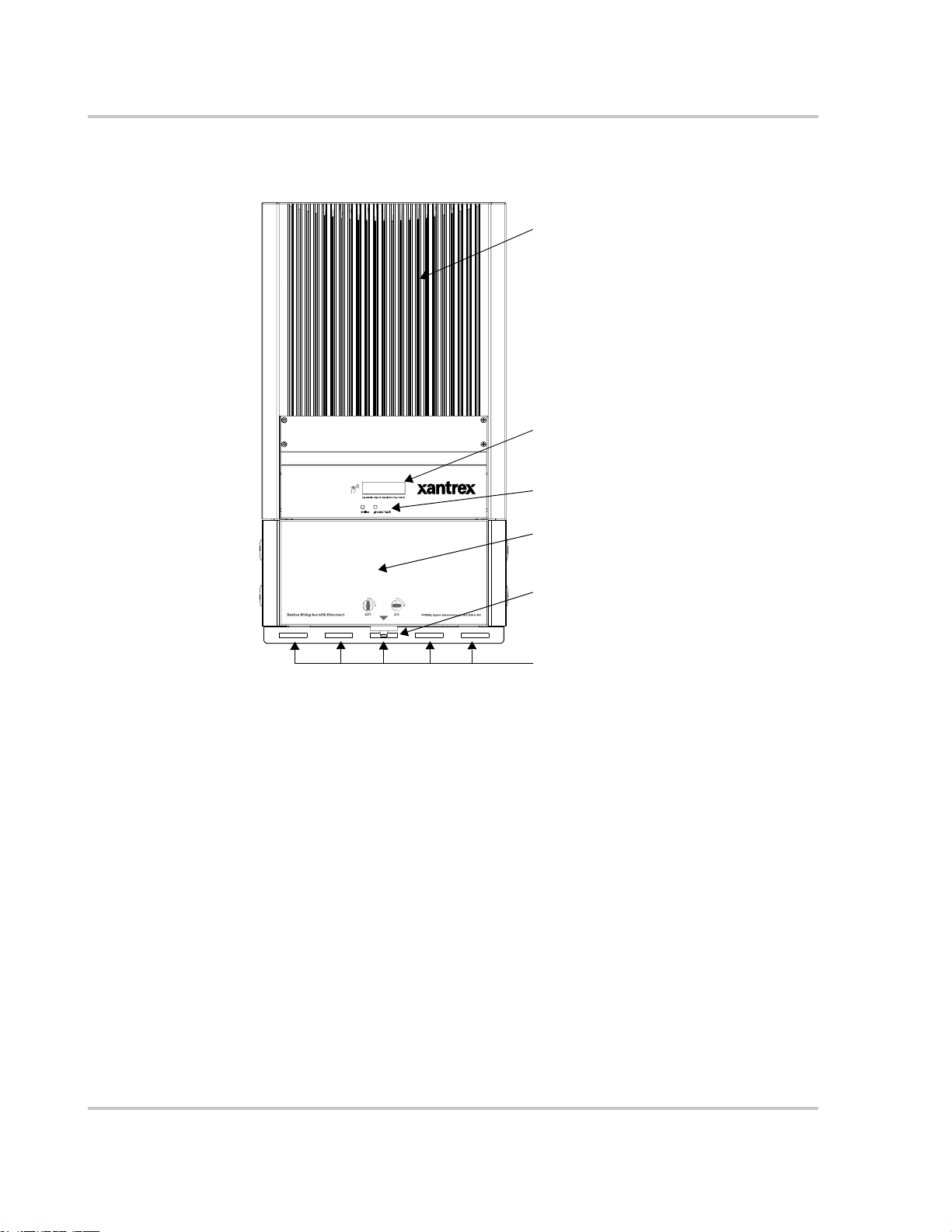
AC Disconnect
About the Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter
wiring/disconnect box is an NEMA 3R enclosure to allow outdoor installation and
is clearly marked as a PV system disconnect. The lockable switch meets NEC
section 690 requirements as a means of disconnect.
In some jurisdictions, where the local utility requires that the AC disconnect be
capable of being locked in the open position by its service personnel, this
disconnect switch can also serve as a lockable and visible break isolating device.
Important:
electrical code requirement. It must be attached during operation. Check with your local
authorities before removing the GT Inverter wiring/disconnect box.
DC Connect
holes
In North America and other locations the wiring/disconnect box is an
Removable inverter (for
servicing, if required)
Control Board Connect hole
AC Connect hole
Wiring/Disconnect Box
Front Cover
DC/AC Disconnect
Switch
Figure 1-3
975-0245-01-01 1–5
Wiring Box and Removable Inverter
27 mm (1”) threaded
conduit holes
Page 26
Introduction
Safety and Standards
The GT Inverter has complete on-board over-current, over-temperature and antiislanding protection, and meets U.S. and Canadian safety operating standards and
code requirements:
• UL 1741 – Standard for Inverters, Converters, and Controllers for Use in
• CSA C22.2 No. 107.1-01 General Use Power Supplies.
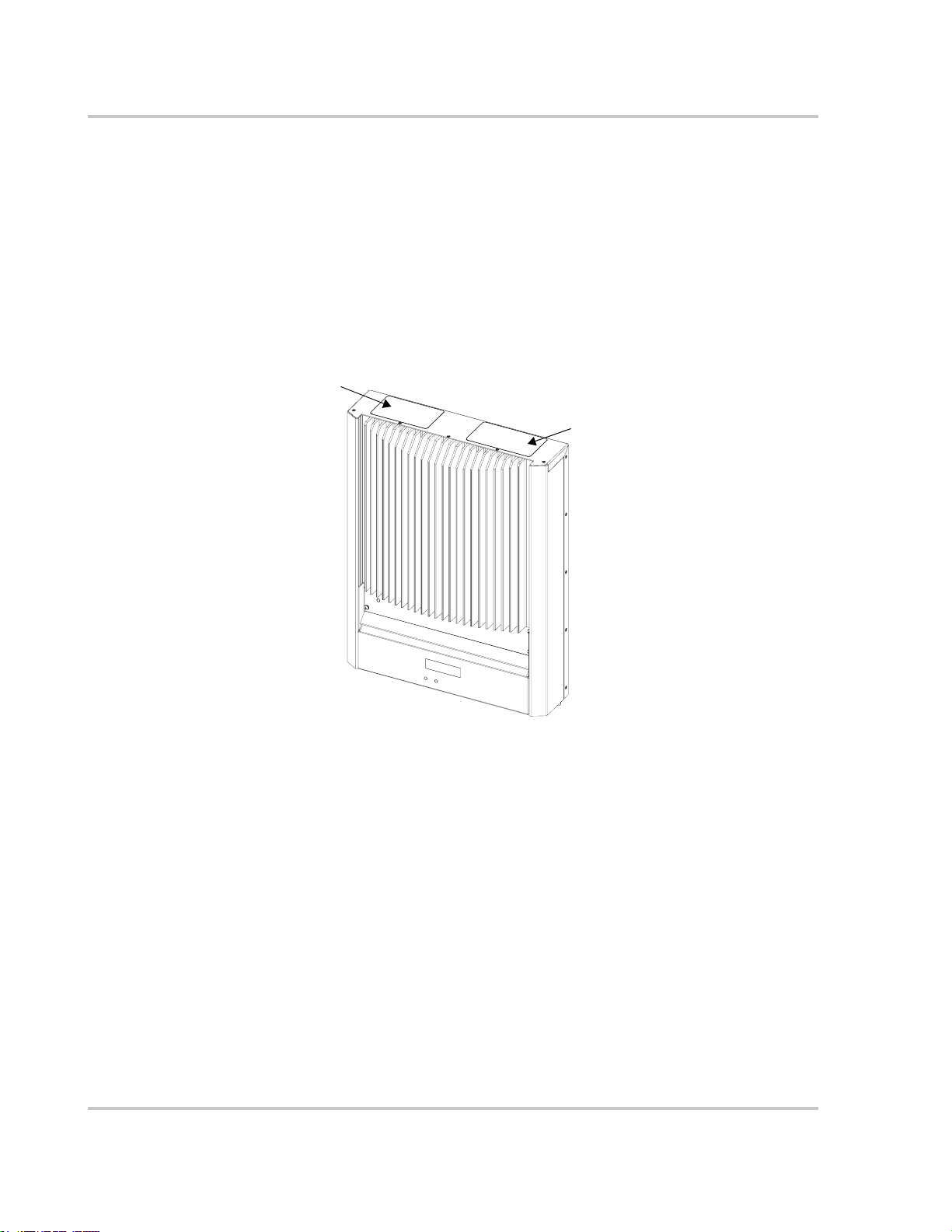
Figure 1-4 shows the location of the safety label and the data label with model,
serial and part number information.
Safety Label
Location
Independent Power Systems
Data Label
Location
Figure 1-4
1–6 975-0245-01-01
Safety and Data Label Locations
Page 27

2
Installation
Chapter 2, “Installation”, provides information about planning for and
installing the GT Inverter. It contains information to help you plan
wire routes, AC and DC connections, and find a suitable location for
installation. It also discusses requirements for grounding the GT
Inverter and your PVarray.
Procedures are provided for installing the Xantrex Grid Tie Solar
Inverter.
The topics in this chapter are organized as follows:
• “Installation Options” on page 2–2
• “Planning the Installation” on page 2–2
• “Preparing for the Installation” on page 2–12
• “Mounting the Inverter” on page 2–15
Page 28

Installation
Installation Options
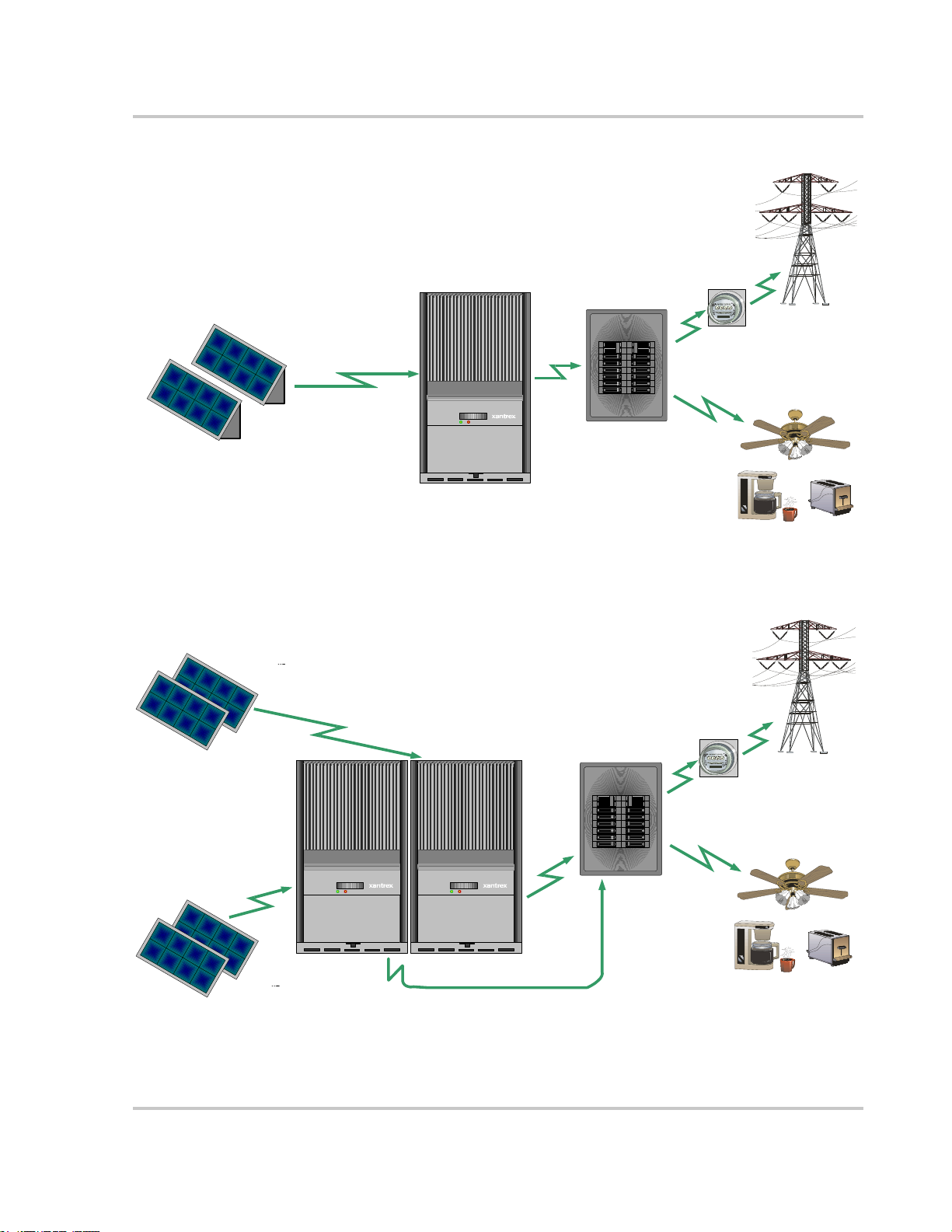
The GT Inverter may be installed as a single inverter for a single PV array of one
or two PV strings, or in a multiple inverter configuration for multiple PV arrays
(see Figure 2-1 for diagrams of both options).
Single Inverter Installation
In this configuration, a single inverter collects the harvested solar energy and
routes the power to the main utility service panel to be used by the loads. Any
surplus power not used by the loads will be directed to the utility grid.
Multiple Inverter Installations
If multiple inverters are used, each inverter must be wired to an independent PV
array . In this configuration, each inverter collects the harvested solar energy from
a separate PV array and routes the power to the main utility service panel to be
used by the loads. Any surplus power not used by the loads will be directed to the
utility grid.
Communications between inverters can be enabled by installing network cabling
to the inverter RJ45 ports. See “Connecting Network Cable Between Multiple
Inverters” on page 3–16.
Planning the Installation
The following issues need to be considered when planning for an installation
using the GT Inverter. See the specified sections for more information.
• “Inverter Location” on page 2–4
• “PV Array Requirements” on page 2–5
• “Grounding Requirements” on page 2–8
• “Routing the Wires” on page 2–11.
Ensure that you have obtained all permits required by local authorities or utilities
before commencing installation.
2–2 975-0245-01-01
Page 29
Single Inverter Installation
Planning the Installation
Utility Grid
Photovoltaic Panels - PV Array
PV String #1
PV String #2
PV Array #1
#2
Harvested solar energy
Multiple Inverter Installation
Xantrex
GT Inverter
Grid Tie Inverter
DC
converted
to AC
Main Utility
Service Panel
Power route d
to loads
Utility
Meter
Surplus power
routed to Utility Grid
Loads
Utility Grid
Utility
Meter
Surplus power
routed to Utility Grid
Loads
Powe r route d
to loads
Photovoltaic Panels:
Multiple PV Array s
Figure 2-1
solar energy
Harvested
solar energy
PV Array #2
Harvested
#1
Xantrex GT I nv ert ers
GT Inverter #1
Installation Options Overview
Main Utility
Service Panel
DC
converted
to AC
Grid Tie InverterGrid Tie Inverter
GT Inverter #2
DC converted to AC
975-0245-01-01 2–3
Page 30

Installation
Inverter Location
WARNING: Burn hazard
Do not install in a location where people can accidentally come into contact with the front
of the inverter. High temperatures can be present on the face of the inverter, causing a
potential burn hazard.
In extreme conditions, the GT Inverter chassis can reach temperatures over 70° C
(158° F), which can cause skin burns if accidentally touched. Ensure that the GT Inverter
is located away from normal traffic areas.
Inverter failure due to improper installation will void the inverter warranty.
Consider the following when determining where to install the inverter.
Fire Safety
Indoor/Outdoor
Orientation
Temperature
Ground
Clearance
• Do not install anywhere near combustible or flammable materials.
• The GT Inverter uses a Type 3R-rated enclosure (vertical mount
only) that can be mounted indoors or outdoors. (Type 3R
enclosures are intended for outdoor use primarily to provide a
degree of protection against falling rain; and to be undamaged by
the formation of ice on the enclosure.)
• While the 3R-rated enclosure protects the GT Inverter from
moisture, outdoor installations should be located away from lawn
sprinklers and other sources of spray.
• The GT Inverter must be mounted vertically on a wall or pole.
• Do not mount the GT Inverter horizontally.
• Ensure that the GT Inverter is mounted in a location where the
ambient temperature range is
• At extreme hot or cold temperatures, the front panel LCD may not
function normally.
• At higher temperatures, the GT Inverter may derate power.
See“Output Power vs. Ambient Temperature at Various DC
Voltages” on page A–4 and “Environmental Specifications” on
page A–6.
• Outdoors, the GT Inverter requires at least 100 cm (39 inches) of
clearance between the bottom of the unit and the ground.
• Indoors, it is recommended that the same clearance between the
bottom of the unit and the floor be used.
-25° to +65° C (-13° to +149° F).
Distance
2–4 975-0245-01-01
• To minimize copper losses, ensure that wire lengths between the
PV array and the GT Inverter and between the inverter and the
Main Utility Service Panel are kept to a minimum.
• Maximum distances will depend on wire gauges used and PV
array output voltages.
Page 31

Planning the Installation
Debris free
• Excessive debris (such as dust, leaves, and cobwebs) can
accumulate on the unit, interfering with wiring connections and
ventilation. Do not install in a location where debris can
accumulate (under a tree, for example).
PV Array Requirements
WARNING: Shock hazard
Whenever a PV array is exposed to sunlight, a shock hazard exists at the output wires or
exposed terminals. To reduce the risk of shock during installation, cover the array with an
opaque (dark) material before making any connections.
General Recommendations
It is important that the PV array is installed correctly to the manufacturer’s
specifications and to local code requirements.
Equipment and Installation Recommendations
Important:
small obstructions such as vent pipes, chimneys and power lines. A small amount of shade
can have a disproportionately high impact on system performance.
The PV array should be free of shade. This requirement includes even
Equipment
recommendations
Installation
recommendations
• All electrical equipment should be listed for the voltage and current ratings
necessary for the application.
• All wiring should be sized correctly to minimize voltage drop.
• All exposed wires or conduits should be sunlight resistant.
• All required overcurrent protections should be included in the system and
accessible for maintenance.
• Depending on the installation, an external disconnect may be required if the
inverter is installed in a location not easily accessible to utility or fire
personnel. Consult local authorities for additional information.
• Integral roofing products should be properly rated.
• All electrical terminations should be fully tightened, secured, and strain
relieved as appropriate.
• All mounting equipment should be installed according to the manufacturer’s
specifications.
• All roof penetrations should be sealed with an acceptable sealing method that
does not adversely impact the roof warranty.
• All wires, conduit, exposed conductors and electrical boxes should be secured
and supported according to code requirements.
975-0245-01-01 2–5
Page 32

Installation
Voltage and MPPT Requirements
MPPT operational
window
Voltage
requirements
Maximum PV
Power
The MPPT software maximizes the output energy of solar arrays as long as the
operating voltage is within the MPPT operational window. Ensure that the PV
array used in the system operates within the MPPT operational window.
Effects of array voltages outside of the MPPT operational window are shown in
Table 2-1.
Table 2-1
Voltage Effect of Array Voltage Inverter Mode
< 195 Vdc Operating voltage will be shifted to 195 Vdc;
195 to 550 Vdc Maximum harvest of solar energy MPPT window
550 to 600 Vdc Will not allow maximum harvest of solar
> 600 Will shut down and may cause damage to the
MPPT Operational Window
Low power
the array will not be at its maximum power
point
Power derating
energy
Shutdown
inverter; stops selling surplus energy
The maximum power point voltage of a string connected to the GT Inverter should
be a minimum of 195 Vdc. If it is less than 195 Vdc, the inverter will continue to
operate, but it will regulate the PV voltage to 195 V. Because the array will not be
operating at its maximum power point, this may result in lower than expected
energy harvest.
The solar array should be sized such that its maximum power output does not
exceed the limits of the MPPT operational window (195 to 550 Vdc). See
“Guidelines for Matching PV Array Size to Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter
Input”.
The array voltage should never exceed 600 V
(open circuit voltage) under any
OC
thermal condition.
Likewise, ensure that the Isc (short circuit current) rating of the array at any
temperature does not exceed the short circuit current rating of the inverter.
2–6 975-0245-01-01
Page 33

Planning the Installation
Guidelines for Matching PV Array Size to Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter Input
For determining the number of panels required in the PV string (panels connected
in series), you must ensure that the following requirements are met:
1. To avoid damage to the inverter, ensure that the PV array output will never
exceed 600 Vdc under any conditions.
2. Do not exceed the maximum array short circuit-current rating marked on the
inverter.
3. To achieve maximum energy harvest from your array, ensure that the V
(voltage at maximum power) does not drop below 195 Vdc or increase above
550 Vdc under most conditions.
Guidelines to help you meet these requirements:
• Consider the expected V
panel manufacturer provides a V
°C (77°F). Ensure that the V
25
does not exceed 600 Vdc. Panel voltage increases in cold temperatures—the
panel manufacturer should be able to provide a coefficient of voltage increase
per degree.
• The NEC also has required temperature/voltage deratings that must be used;
these can be found in Table 690.7 of the 2002 NEC handbook. You need to
determine the coldest temperatures expected on the site, and size the array
strings accordingly. The array’s maximum DC voltage in coldest expected
temperature, with both manufacturer coefficient and NEC derating, must not
exceed 600 Vdc to prevent inverter damage.
• Panel voltage decreases in high temperatures. This will affect the panels’
V
. Again, the manufacturer’s coefficient must be used with the highest
MP
expected temperature to determine the minimum V
Once you know the specifications of your panels, all these factors will help
determine the maximum and minimum number of panels that can be used.
of the string under all possible conditions. The
OC
rating per panel, but it is usually rated at
OC
rating at the coldest ambient temperature
OC
.
MP
MP
Note:
975-0245-01-01 2–7
The GT PV array sizing tool is available at www.xantrex.com.
Page 34

Installation
Grounding Requirements
WARNING: Shock hazard
The GT Inverter must be grounded by connection to a grounded permanent wiring system.
AC Grounding
North America The GT Inverter must be connected to a grounded, permanent wiring system via
the GT Inverter ground bar. See Figure 2-2 for the location of the GT Inverter
ground bar.
The ground bar must also be connected to the main utility breaker panel ground
bar and to the house grounding rod according to NEC requirements.
Elsewhere In other locations, AC grounding is governed by local codes. Consult with the
local utility for specific grounding requirements.
PV Grounding
The GT Inverter is designed to have all PV positive, negative, and ground
conductors connected inside its wiring box. The PV equipment ground should be
connected to the GT Inverter ground bar.
The size for the conductor is usually based on the size of the largest conductor in
the DC system.
A DC grounding electrode conductor may be required by the Authority Having
Jurisdiction (AHJ). Use the GT Inverter ground bar for this connection.
Important:
ground system within the inverter’s ground fault detection circuit. Inverter models marked
with the “-POS” suffix are positive grounded and have the positive PV conductor
internally bonded to the ground system through the inverter’s ground fault protection
circuit. It is important that the negative (or positive) PV conductor is not bonded to the
ground at any other point in the system.
Long Distance Grounding
If the PV array is more than 30 meters (100 feet) from the inverter, then there
must also be a direct connection from the array frame to an earth ground next to
the array. A connection between this ground and the primary earth ground
connection via a buried wire between the two points is also necessary (see
Figure 2-3).
In most models, the negative PV conductor is internally bonded to the
2–8 975-0245-01-01
Page 35
Lightning Protection
Planning the Installation
Reduce the risk of lightning damage by using a single-point grounding system. In
this system, all ground lines terminate at the same point—the primary earth
ground. This point normally is the main utility ground installed by the utility
company to provide a ground for the house wiring (see Figure 2-4). This ground
usually consists of a copper rod driven 1.5 to 2.5 meters (6 to 8 feet) into the earth.
G
PV String #1
PV String #2
G
PV Array
G
GND bar
Xantrex GT Inve rter
Wirin g Box
DC/AC Disconnect Switch
Main Utility
Service Pan el
L1
NEUTRAL
GROUND
G
L2
Neutral
-to-
Ground
Bond
AC Ground
Primary Eart h
Ground
DC Ground if required by AHJ
Figure 2-2
Basic Grounding Overview
975-0245-01-01 2–9
Page 36

Installation
Array
Earth
Ground
PV Array
G
PV String #2
G
Distance >30 m (100 ft)
PV String #1
When the distance between the PV Array and the GT
Inverter is greater than 30 m (100 ft), the array should have
its own earth ground, which should be connected to the
Primary Earth Ground by a buried wire.
Check your local codes for grounding requirements.
Main Utility
Service Pan el
L1
GROUND
L2
NEUTRAL
G
Neutral
-to-
Ground
Bond
G
Xantrex GT Invert er
Wiri ng Bo x
AC Gr ound
GND bar
Figure 2-3
Buried wire
DC G round
Long Distance Grounding Overview
G
DC/AC Disconnect Switch
Primary
Earth
Ground
2–10 975-0245-01-01
Page 37

Planning the Installation
PV Array
PV String #1
G
PV String #2
G
Main Utilit y
Service Pan el
L1
GROUND
G
L2
NEUTRAL
G
Neutral
-to-
Ground
Bond
Xantrex GT Inverter
Wiri ng Bo x
AC Gro u n d
GND bar
G
DC/AC Disconnect Switch
DC Ground
Primary
Earth
Ground
Figure 2-4
Grounding With Extra Lightning Protection Overview
Routing the Wires
Typical
configurations
975-0245-01-01 2–11
Determine all wire routes to and from the GT Inverter. Typical routing
configurations include:
• AC wiring from the GT Inverter to the main utility service panel
• DC input wiring from the PV array to the GT Inverter
• DC ground from the PV array to the Primary Earth Ground.
All wiring and installation methods should conform to applicable electrical and
building codes.
For installations in the United States, the National Electrical Code (NEC) and
local codes apply. For installations in Canada, the Canadian Electrical Code
(CEC) and local codes apply.
For all installations, local utilities may have additional requirements.
Page 38
Installation
WARNING: Shock hazard
Check for existing electrical or plumbing prior to drilling holes in the walls.
Conduit
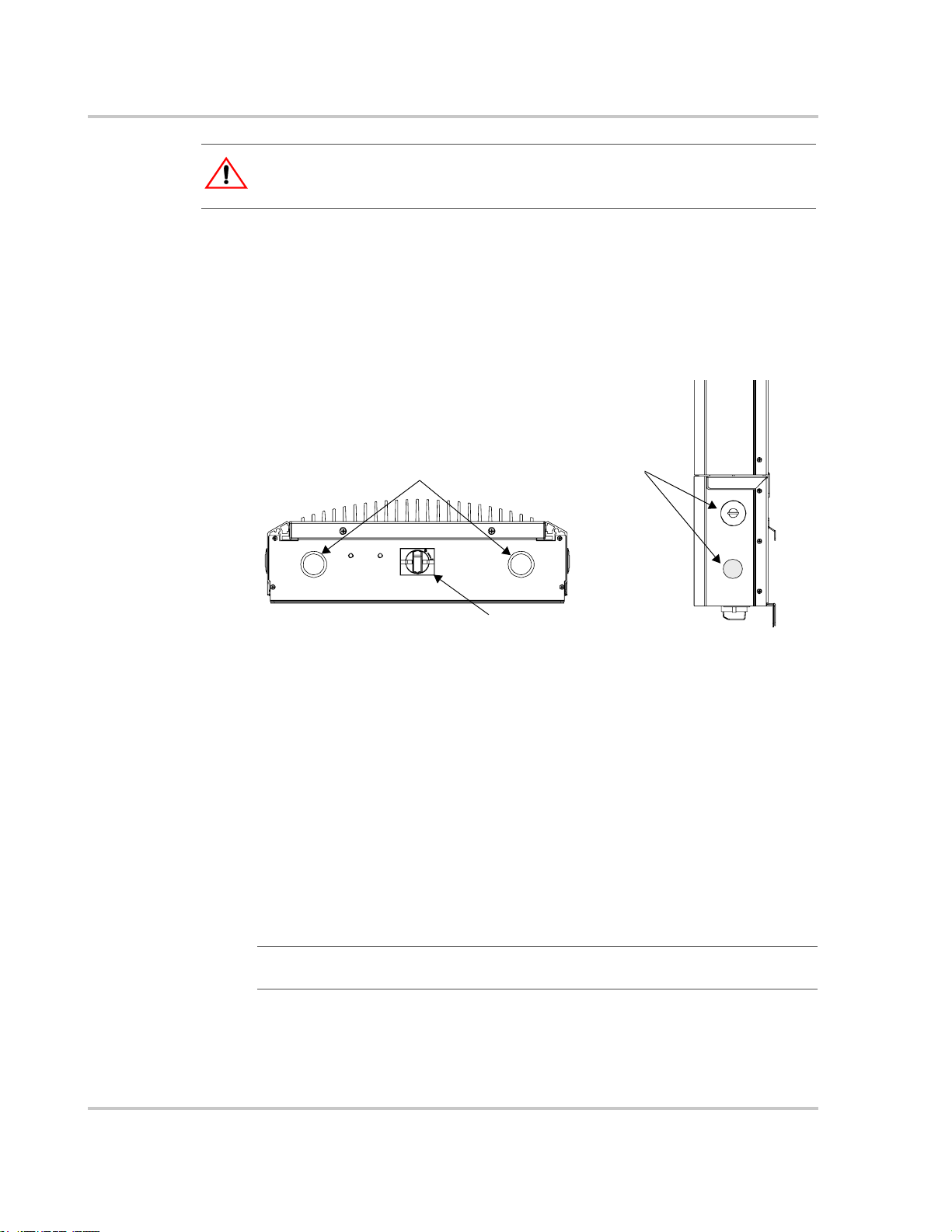
holes/knockouts
Pre-plan the wire and conduit runs. Dual knockouts for 35 mm (1 3/8 inch) or
27 mm (1 inch) conduit holes are located on the bottom and back of the wiring
box—four dual knockouts in total. T wo threaded 2 7 mm (1 inch) conduit holes are
located on each side of the wiring box (Figure 2-5).
For maximum safety , run AC, DC, and communication wires in separate conduits.
35 mm (1 3/8”) and 27 mm (1”)
dual knockouts
Figure 2-5
Bottom
Conduit Hole and Knockout Locations
27 mm (1”) threaded
conduit holes
DC/AC
Disconnect Switch
Side
Preparing for the Installation
Ensure your local utility is consulted for any requirements for connecting to or
returning power to the grid. Obtain all permits necessary to complete the
installation. Consult your local and national electrical codes for more information.
This section includes the following topics:
• “Wiring” on page 2–13
• “Circuit Breakers and Disconnect Switch” on page 2–13
• “Other Materials Needed” on page 2–14
• “Equipment Needed” on page 2–14.
Important:
DC wiring/cabling and wires/cables.
2–12 975-0245-01-01
In this manual “wiring” and “wires” are used in reference to both AC and
Page 39

Wiring
Preparing for the Installation
Wire size and length will be determined by the location of each component and
their relative distance to each other. W ire sizes may also be affected by whether or
not conduit is used.
Recommended wire
stripping length
Acceptable wire
sizes
Strip all wires 9 mm (3/8 inch).
The AC and DC terminal blocks in the GT Inverter accept wire sizes from
#14 AWG to #6 AWG.
Important:
significant power losses and reduction in system efficiency.
Wiring should not be undersized. Undersized wiring can result in
Circuit Breakers and Disconnect Switch
The following circuit breakers, disconnect switch and fuse are required for
installing this equipment.
AC Circuit Breaker Requirements
In North America, the main utility service panel must dedicate a double pole
breaker to operate each G T Inverter installed. This breaker must be sized to handle
the rated maximum output voltage and current of the GT Inverter (see “Electrical
Specifications”, “Output” on page A–2).
DC/AC Disconnect Switch
The wiring box includes a PV/Utility disconnect switch that switches both AC and
DC at the same time.
WARNING: Shock hazard
Do not remove the wiring/disconnect box. The 600 volt DC/AC disconnect in the wiring
box meets NEC Article 690. It is a non-serviceable component and shall remain in place.
Removal can expose energized conductors.
Use caution when working around sources of DC power. Although the DC/AC disconnect
switch disconnects the inverter from DC power, hazardous voltages from paralleled PV
strings may still be present upstream of the switch.
Ground Fault Fuse
The GT Inverter is equipped with a 600 volt 1-Amp ground fault protection fuse
(replace with Littelfuse KLKD 1 or equivalent).
975-0245-01-01 2–13
Page 40
Installation
WARNING: Shock hazard
Do not attempt to service the ground fault protection fuse yourself. This should only be
done by qualified service personnel, such as certified electricians or technicians.
Other Materials Needed
• Mounting support material, such as plywood or poles
• Conduit for wire runs and appropriate fittings/bushings
• Wood screws and anchors for screws, depending on mounting surface.
Equipment Needed
• Wire cutters/wire crimpers/wire strippers
• Assorted screwdrivers, drill, etc.
• Level
• Digital Voltmeter
• Frequency counter (optional, for troubleshooting).
2–14 975-0245-01-01
Page 41

Mounting the Inverter
Overview
WARNING: Fire, Shock and Energy Hazards
Before installing the GT Inverter, read all instructions and cautionary markings located in
this manual, on the PV array, and on the main service panel.
Mounting the Inverter
General installation
steps
There are four main steps in the installation of the GT Inverter:
1. Mounting the GT Inverter (this chapter)
2. Grounding the PV array (see your PV equipment documentation).
3. Making the DC connections from the PV array to the GT Inverter
(“Connecting the DC Wiring” on page 3–4)
4. Making the AC connections from the GT Inverter to the main utility service
panel (“Connecting the AC Wiring” on page 3–7)
Figure 2-6 summarizes these four steps.
PV Panels
Primary Earth/
Ground
2
Utility
Meter
600 Vdc
3
Open
Circuit
Maximum
Utility Grid
4
Grid Tie Inverter
Main Utility
1
Xantrex GT Inverter
Figure 2-6
Installation Overview
Service Panel
975-0245-01-01 2–15
Page 42

Installation
In this chapter only the first step, mounting the inverter and installing accessories,
is described.
Mounting steps Instructions for mounting the GT Inverter are described in the following sections:
• “Preparing to Mount the Unit” on page 2–16
• “Installing the Mounting Bracket” on page 2–17
• “Mounting the Inverter on the Bracket” on page 2–22.
Multiple inverter
instructions
Mounting instructions for multiple inverters are described in “Mounting Multiple
Inverters” on page 2–23.
Special wiring instructions for multiple inverter installations are described in
“Connecting Multiple Inverters” on page 3–9.
Preparing to Mount the Unit
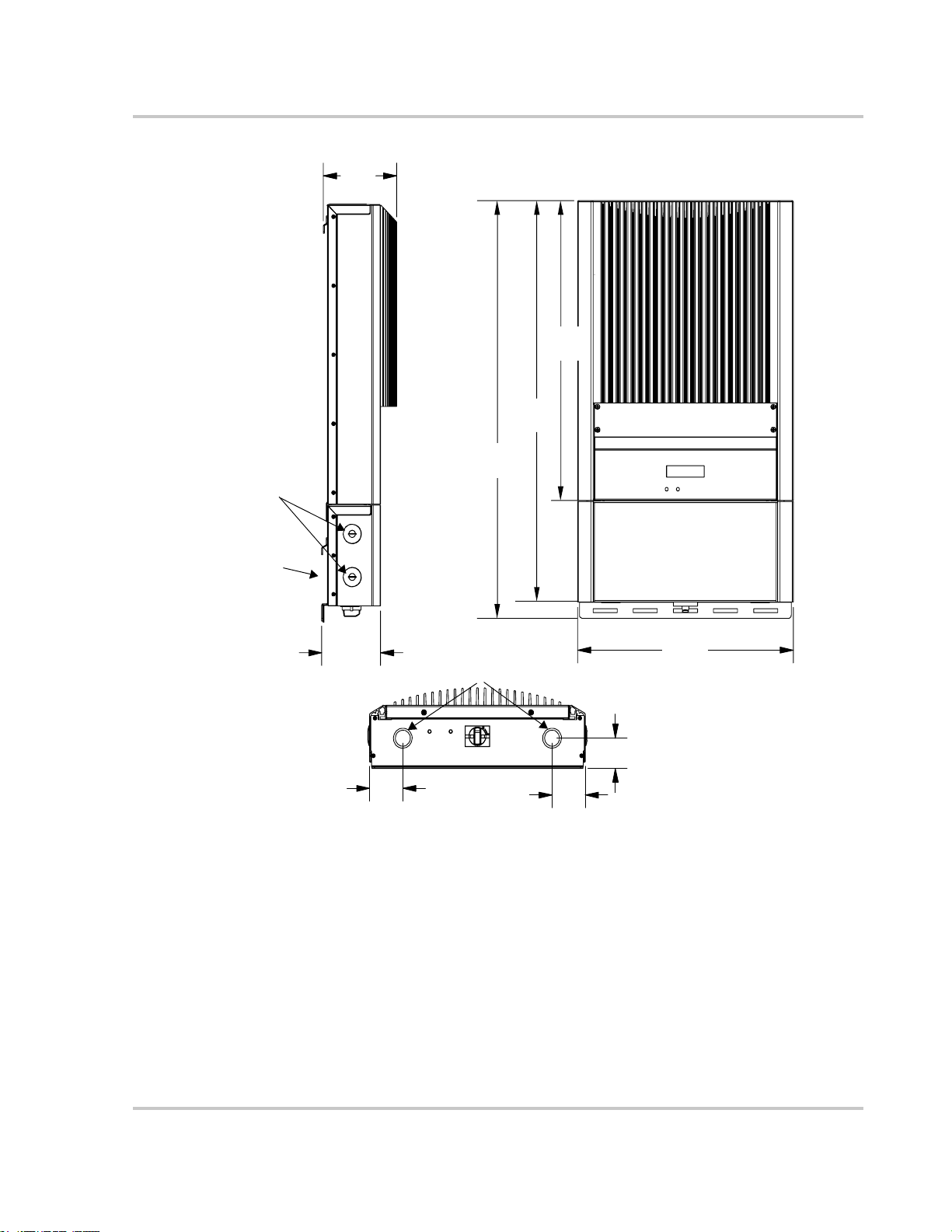
Dimensions and Knockout Locations
The dimensions of the inverter and the mounting bracket and some of the
knockout locations on the wiring/disconnect box are shown in Figure 2-7.
Four 27 or 35 mm (1 or 1 3/8 inch) dual knockouts are provided on the back and
bottom of the unit to accommodate wiring:
• two on the bottom, on either side of the DC/AC Disconnect Switch
• two on the back of the wiring/disconnect box.
Four 27 mm (1 inch) conduit holes on the sides of the wiring/disconnect box (two
on each side) are filled with plastic plugs, which can be removed to insert conduit
nipples as required for multiple inverter installations. One or two of these side
conduit holes may be used to accommodate Xanbus network cables connected
between multiple inverters.
CAUTION: Equipment damage
If your installation location requires that you drill additional conduit holes into the
wiring/disconnect box, ensure that there are no metal shavings left inside the unit. These
could cause a short circuit when the unit is operating.
Knockout Preparation
Remove your choice of knockouts from the wiring box to facilitate conduit
installation for wire runs. This is much easier to do prior to mounting the inverter.
Important:
knockouts. These could cause a short circuit when the unit is operating. Be sure to install
bushings or conduits in the knockout holes to protect the wires from damage.
Important:
2–16 975-0245-01-01
Ensure there are no metal shavings left inside the unit after removing the
If installed outdoors, conduit must be sealed where it enters the wiring box.
Page 43
Side view
13.7
(5 3/8)
Mounting the Inverter
Front view
55
(21 5/8)
69.9
(27 1/2)
2.7 cm (1") conduit
holes with threaded
caps, on both sides
Dual 3.5 cm or 2.7 cm
(1 3/8" or 1") knockouts
(on back panel).
Figure 2-7
11
(4 5/16)
7/16)
6.2 (2
Dimensions of GT Inverter and Knockout Locations
Dual 3.5 cm or 2.7 cm
(1 3/8" or 1") knockouts
Installing the Mounting Bracket
72.6
(21 5/8)
27.9 (11)
40.3
(15
All measurements
in cm (inches).
5.2 (2)
7/8)
The mounting bracket for the G T Inverter allows t he unit to be easily mounted and
dismounted for servicing. It has two hooks that match corresponding hooks on the
back side of the inverter and wiring box. The inverter can be separated from the
wiring/disconnect box and removed from the bracket, leaving the
wiring/disconnect box in place.
975-0245-01-01 2–17
Page 44

Installation
Rectangular slots × 25:
0.8 × 3 (5/16 × 1
Mounting bracket Back side of the inverter
25.3 (10)
3/16)
Mounting flanges
Figure 2-8
Mounting Bracket and GT Inverter
Clearance Requirements
For optimal and safe operation, ensure there is adequate clearance around the
inverter. The minimum clearance recommendations in Table 2-2 assume a vertical
mounting. If clearances are reduced below these minimums, rated power may not
be achieved.
Table 2-2
Location Minimum Clearance
Above 30 cm (12 inches)
Below:
•Inverter
• Bracket
In front Sufficient room to allow for easy access to read the display and to prevent
On sides
58.7 (23 1/8)
Mounting slots for securing the inverter
Inverter Clearance Requirements
Outdoors:
• 100 cm (39 inches)
• 110 cm (43 inches)
Indoors: the same clearances are
recommended but not required.
accidental contact with hot surface.
Units can be mounted side by side with no clearance between them, but 15
cm (6 inches) of clearance around the outermost two units is recommended.
In hot climates, some clearance between units may be needed to prevent
thermal derating.
Mounting flanges
All measurements
in cm (inches).
The inverter extends below the
bracket by approximately 10 cm
(4 inches)
2–18 975-0245-01-01
Page 45

Surfaces for Mounting
Mounting on poles
or rails
Mounting to
wallboard with
support
Mounting to siding
using wall studs
Mounting to
concrete surface
Mounting the Inverter
WARNING: Shock hazard
Before drilling holes to mount the GT Inverter, ensure there are no electrical wires or
plumbing in this area.
WARNING: Personal injury
The GT Inverter weighs approximately 20 kg (45 lbs.). Always use proper lifting
techniques during installation to prevent personal injury.
WARNING: Explosion hazard
Do not store combustible or flammable materials anywhere near the inverter.
The GT Inverter weighs approximately 20 kg (45 lbs.). The supporting surface
must be strong enough to handle 75 kg (160 lb.). If the supporting surface is not
strong enough to handle that weight, then supporting material such as a sheet of
plywood can be used to enhance the strength of the mounting surface.
The GT Inverter can be mounted to a vertical surface such as wallboard, wood
siding, concrete wall or pole assembly.
• See “Mounting on Poles or Rails” on page 2–20. Ensure the botto m of the unit
is a minimum of 100 cm (39 inches) from the ground if mounted outdoors.
• Installation onto wallboard requires either the use of a supporting material
such as plywood or securing the mounting screws to supporting wall studs.
Use at least two screws and anchors to secure the unit to the supporting
material.
• If mounting to exterior siding using a wall stud for support, the plywood
backing will not be needed. Use at least two lag screws to secure the unit to
the supporting material. Ensure the screws enter the stud at least 4 cm
(1.5 inches) to adequately support the weight of the unit. See “Mounting on
Wallboard, Siding or Concrete” on page 2–21 .
• If mounting the unit on a concrete surface using anchors with no supporting
material, use four screws and anchors, instead of two, to adequately secure the
unit and distribute the weight.
Important:
or other high-risk areas.
Important:
the GT Inverter. It is recommended to use 6 mm (¼ inch) diameter fasteners. However,
because mounting surfaces can vary, installers must select appropriate hardware for each
installation.
975-0245-01-01 2–19
Local codes may impose additional mounting requirements in earthquake
Other than the mounting bracket, no mounting hardware is supplied with
Page 46

Installation
Mounting on Poles or Rails
To mount the unit using poles:
1. Ensure that poles or rails are securely assembled in place. If using horizontal
rails, three rails are required: two for the mounting bracket and a third for
securing the bottom edge of the inverter wiring box (see Figure 2-9).
2. Connect the mounting bracket vertically to the poles or rails (Figure 2-9):
• Be sure to use at least two bolts to secure the mounting bracket to the
• Position the lower edge of the bracket a minimum of 110 cm (43 inches)
3. If using a single vertical pole, ensure that the inverter is secure and unable to
rotate around the pole.
support.
above the floor or ground.
110 (43)
Ground /
Floor
Mounting Bracket
At least 2 bolts to
secure bracket to
poles/rails.
For securing
the bottom of
the wiring box
All measurements
in cm (inches).
34
(13.5)
48
(18.9)
15
(5.9)
100 (39)
Ground /
Floor
Figure 2-9
2–20 975-0245-01-01
Examples of Mounting on a Pole or Rails
Page 47

Mounting on Wallboard, Siding or Concrete
To mount the GT Inverter to wallboard, siding, or concrete:
1. Locate the area where the GT Inverter is to be installed.
2. Install backing support material if required. See Figure 2-10.
Mounting the Inverter
34 (13.5)
At least 2 screws
with washers to
secure bracket
to plywood
110 (43)
Ground / Floor Ground / Floor
Single GT Inverter Multiple GT Inverters
40.6 (16)
O.C.
15
(6)
110 (43)
All measurements
in cm (inches).
Figure 2-10
Installing the Mounting Bracket using Plywood Support
3. Using a level, place the mounting bracket against the wall surface at least
110 cm (43 inches) from the ground. See Table 2-2 on page 2–18 to ensure
minimum clearance requirements are met.
4. Mark the location for mounting screws if using a wall stud for support. At
least four mounting screws and anchors are needed for concrete installations
or wallboard installations where no wall studs are available for support.
For multiple inverter installations, the brackets should be mounted at least
15 cm (6 inches) apart, or at least 40.6 cm (16 inches) on-center.
5. Remove the bracket and drill the holes using an appropriately sized drill bit.
Drill appropriately sized holes for screws or anchors.
6. Secure the bracket to the supporting surface using at least two screws and
washers.
975-0245-01-01 2–21
Page 48

Installation
Mounting the Inverter on the Bracket
Mounting a Single Inverter
To mount the inverter on the mounting bracket:
1. Place the GT Inverter’s mounting hooks, located on the back of the enclosure,
over the bracket and ensure the inverter is seated properly, as shown in
Figure 2-11.
2. After the unit is correctly seated on the bracket hooks, locate the mounting
slots in the flange below the wiring box and mark the location on the wall for
securing screws.
3. Remove the inverter and drill pilot holes in the wallboard or siding for the
securing screws.
4. Reinstall the G T Inverter on the bracket and secure the bottom of the unit with
appropriate screws or anchors, and tighten.
Slide the mounting hooks on the inverter
over the hooks on the mounting bracket.
Bracket hooks
flange with
mounting slots
Figure 2-11
2–22 975-0245-01-01
Proper Placement of the Inverter on the Mounting Bracket
110 cm (43") 100 cm (39")
Ground/floor
Ensure the inverter is seated
properly on the mounting bracket.
Page 49

Mounting Multiple Inverters
As shown in Figure 2-10, inverters can be mounted side by side on wallboard or a
plywood support.
Conduit nipples should be installed on one side of the first inverter before
mounting on the bracket. Ensure that the sealing ring is located on the conduit
nipple between inverters, i.e., on the outside of the wiring box. The lock nut is
attached after the nipple is inserted into the conduit hole of the second inverter.
Mounting the Inverter
975-0245-01-01 2–23
Page 50

2–24
Page 51

3
Wiring the Inverter
Chapter 3, “Wiring the Inverter”, provides procedures for making DC
and AC wiring connections, and grounding the GT Inverter and the
PV array. Instructions for wiring multiple inverters are also provided.
The topics in this chapter are organized as follows:
• “Accessing the Wiring Terminals” on page 3–2
• “Connecting the DC Wiring” on page 3–4
• “Connecting the AC Wiring” on page 3–7
• “Connecting Multiple Inverters” on page 3–9.
Page 52

Wiring the Inverter
Accessing the Wiring Terminals
You must remove the GT Inverter wiring box cover to access the terminal blocks,
ground bar and communications ports (for connecting multiple inverters).
To remove the wiring box cover:
1. Using a Phillips screwdriver, remove the two screws on the bottom side of the
wiring box and set in a safe place (see Figure 3-1 for location of screws).
2. Lift the cover off the wiring box.
When replacing the wiring box cover, be careful not to pinch any wires in the
wiring box.
Wiring box
cover screws
Figure 3-1
AC and DC connections are made at the wiring terminals shown in Figure 3-2.
Insulating barrier The clear plastic insulating barrier inside the wiring box is a permanent
component. It is intended to separate the high-voltage AC and DC wiring from
any communications cabling and to prevent wiring from coming into contact with
the wiring box cover.
When wiring the unit, it is necessary to pull the cover back to access the wiring
terminals. After completing the wiring, replace the insulating barrier to its original
position.
Removing the Wiring Box Cover
3–2 975-0245-01-01
Page 53

Accessing the Wiring Terminals
Figure 3-2
DC Terminals
for connecting
PV strings
DC/AC
Disconnect
Switch
AC and DC Terminal Block Location in the Wiring Box
AC Terminals for
connecting to main
utility service panel
975-0245-01-01 3–3
Page 54

Wiring the Inverter
Connecting the DC Wiring
WARNING: Shock hazard
Whenever a PV array is exposed to sunlight, a shock hazard exists at the output wires or
exposed terminals. To reduce the risk of shock during installation, cover the array with an
opaque (dark) material and ensure that the DC/AC Disconnect Switch is set to OFF before
commencing any wiring. See Figure 3-3.
WARNING: Shock hazard
The 600 volt DC/AC disconnect in the wiring box meets NEC Article 690. It is a
non-serviceable component and shall remain in place. Removal can expose energized
conductors.
WARNING: Shock hazard
Use caution when working around sources of DC power. Although the DC/AC disconnect
switch disconnects the inverter from DC power, hazardous voltages from paralleled PV
strings may still be present upstream of the switch. Before servicing a PV string, isolate
each string by completely removing PV wiring from the inverter terminal block.
Figure 3-3
3–4 975-0245-01-01
DC/AC Disconnect Switch Positions
Page 55

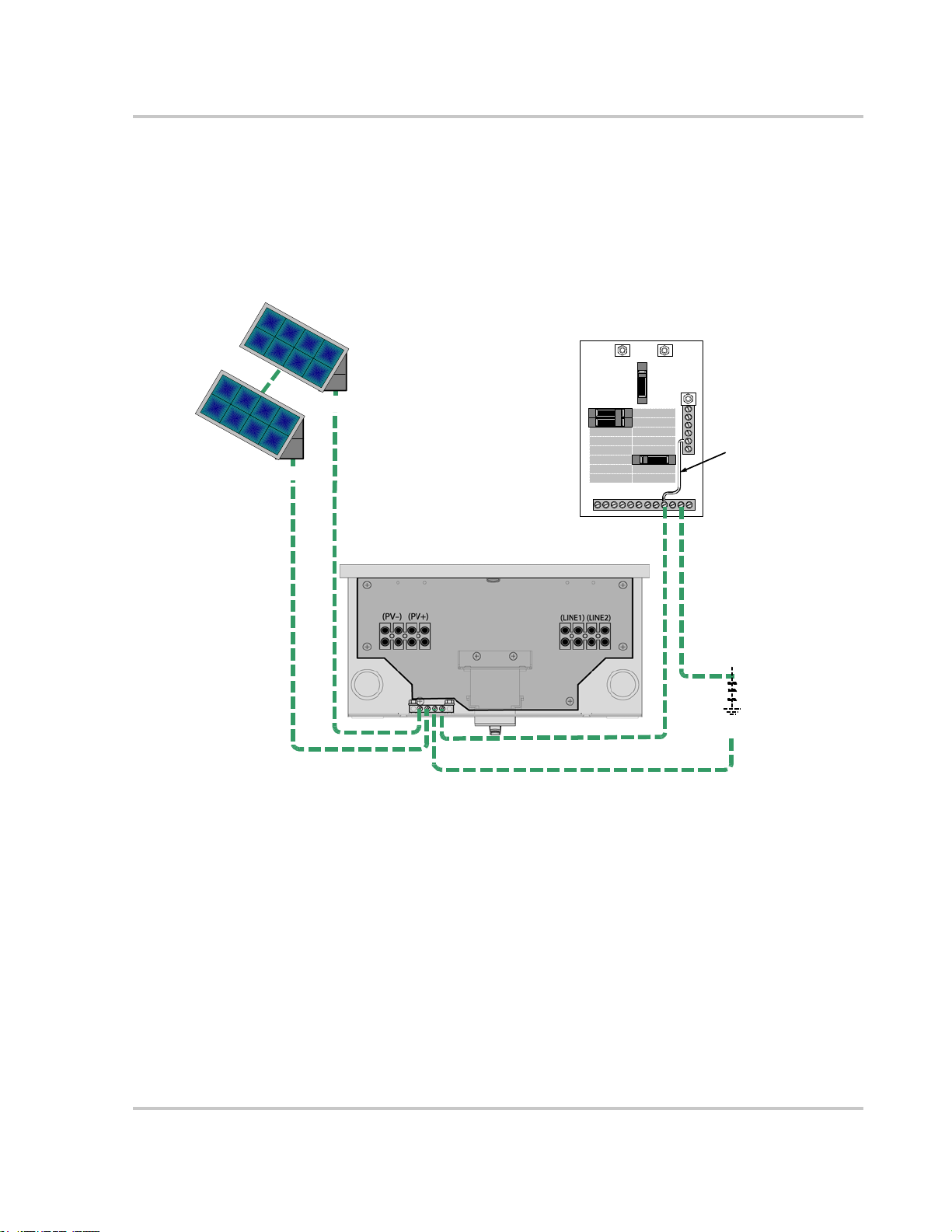
Connecting the DC Wiring
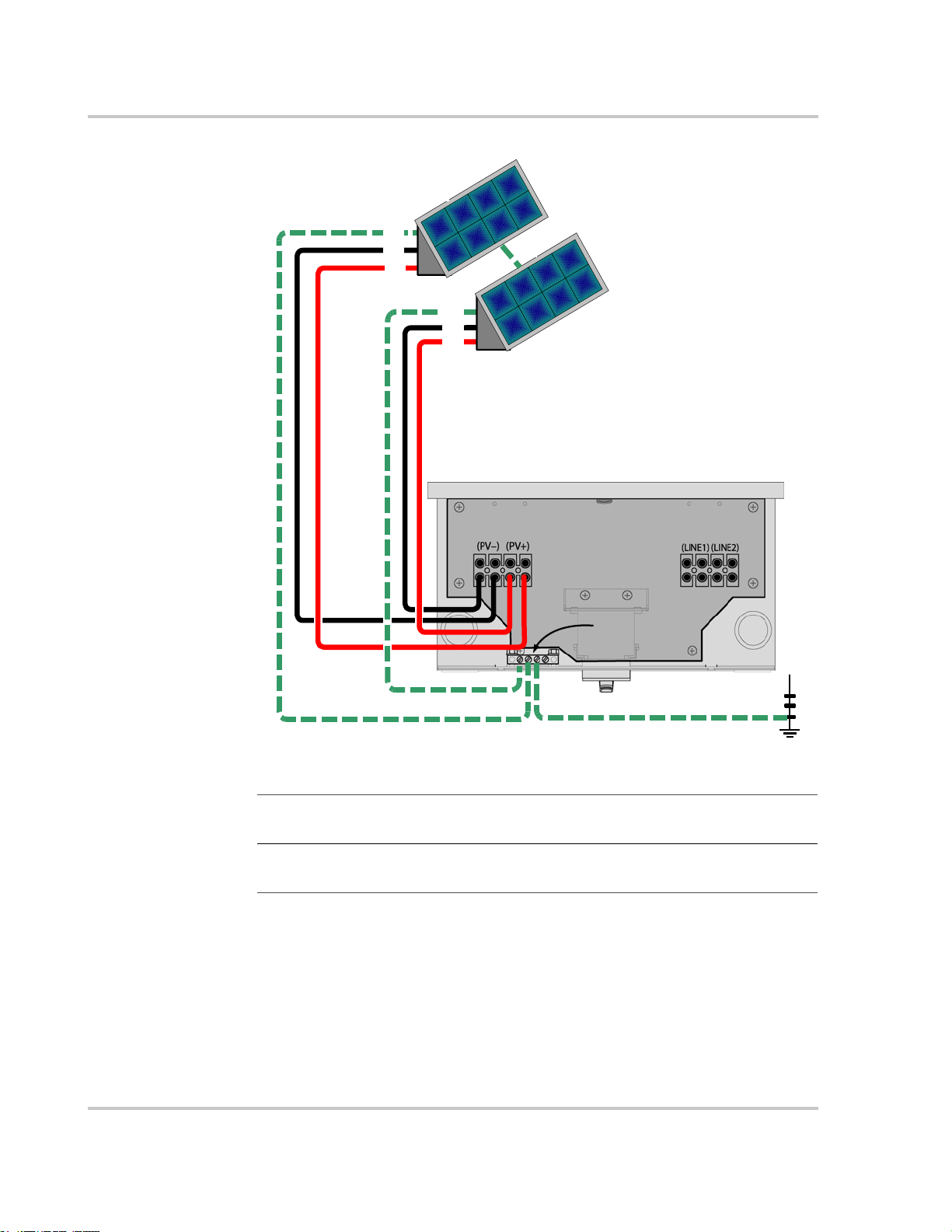
The following procedure is illustrated in Figure 3-4. If there is more than one PV
string, label the positive and negative wire pairs appropriately (for example:
PV1-String #1 POS, PV1-String #1 NEG, PV1-String #1 GND,
PV1-String #2 POS, etc.).
To wire the PV array to GT Inverter:
1. Remove the wiring/disconnect box cover (see page 3–2).
2. Install DC conduit from the PV string(s) to the GT Inverter wiring box,
through one of the knockout holes.
3. Route the wires from the PV string(s) through the conduit an d into the wiring
box.
4. Connect the DC Ground from each PV string to the GROUND bar in the
wiring box.
5. Connect the POSITIVE (+) wire from the PV1 string #1 to one of the PV+
terminals in the wiring box. Double check that the wire is in the proper
location and tighten the screw.
6. Connect the NEGATIVE (–) wire from the PV1 string #1 to one of the
PV– terminals. Double check that the wire is in the proper location and
tighten the screw.
7. Repeat for the PV1 string #2, if there is one.
a) Connect the POSITIVE (+) wire from the PV1 string #2 to the unused
PV+ terminal.
b) Connect the NEGATIVE (–) wire from the PV1 string #2 to the unused
PV– terminal.
Double check that the wires are in the proper locations and tighten the screws.
8. If required, connect the DC ground electrode conductor tot he DC or AC
ground electrode as per NEC 690.47.
9. Ensure all connections are correctly wired and properly torqued according to
values shown in Table 3-1.
Table 3-1
14 to 10 2.5 to 6.0 35 4.0
Torque Values for Wires*
Wire Size Torque
AWG mm
8 10.0 40 4.5
6 16.0 45 5.1
2
in-lb. Nm
*Use copper conductors only.
975-0245-01-01 3–5
Page 56
Wiring the Inverter
PV1 String #2
PV String #2
G
–
+
G
–
+
PV Array 1
G
PV1 String #1
PV String #1
Xantrex GT Inve rter
Wiring Box
GND bar
DC/AC Disconnect Switch
DC Gro und if r equir ed by AHJ
Figure 3-4
Important:
box may be required. This fusing and combiner box are to be provided by the installer.
Important:
local codes before installation.
DC Connections for Multiple PV Strings
Depending upon installation and local codes, fusing and/or a combiner
A DC grounding electrode conductor may be required by the AHJ. Check
3–6 975-0245-01-01
Page 57

Connecting the AC Wiring
WARNING: Shock hazard
AC utility wiring to the GT Inverter unit is performed directly at the main breaker panel.
This should be done only by a qualified installer or electrician.
WARNING: Shock hazard
Before wiring the G T Inverter , ensure the main br eaker in the primary utility breaker box
is switched OFF . Switch this breaker ON only after all wiring is completed as instructed in
the procedures.
Connecting the AC Wiring
Important:
inverter to be connected to a dedicated circuit and no other outlets or devices may be
connected to this circuit. The NEC also imposes limitations on the size of the inverter and
the manner in which it is connected to the utility grid. The circuit breakers that are used in
the main panel that feed the inverter circuit must be for back-fed operation and labeled as
such.
In the United States, the National Electrical Code (NEC) requires the
The GT Inverter can be connected to a single bi-directional meter, or to dual
meters, where one meter indicates power used and the second meter indicates
power sold (power supplied back to the utility). Consult with the local utility to
determine the proper components to install, and obtain any permits required prior
to installation.
The following procedure is illustrated in Figure 3-5.
Important:
Neutral conductor wiring is not required in this installation.
975-0245-01-01 3–7
Page 58

Wiring the Inverter
To wire the main utility service panel to the GT Inverter:
1. Install conduit from the main utility service panel to the wiring/disconnect
box of the GT Inverter. Run the two HOT wires (L1 and L2) and ground wire
from the service panel through the conduit and into the inverter wiring box.
2. Install or use an existing double-pole 20-Amp circuit breaker (or two
single-pole breakers, ganged) in the main utility service panel, and ensure that
the breakers are set to OFF.
3. Connect the ground wire (green or bare copper) from the ground bar in the
main utility service panel to the GND bar in the wiring box.
4. Connect the L1 HOT wire (black) from the double-pole breaker installed in
the main utility service panel, to the L1 GRID terminal in the wiring box.
5. Connect the L2 HOT wire (red) from the double-pole breaker installed in the
main utility service panel, to the L2 GRID terminal in the wiring box.
6. Ensure all connections are correctly wired and properly torqued according to
values shown in Table 3-1 on page 3–5.
Utility Grid
GND bar
Xantrex GT Inverter
Wiri ng Bo x
AC/DC Disconnect Switch
L1
L2
L1 L2 Neutral
Utility
Meter
L1 L2 Neutral
Main Utilit y
Service Panel
L1
NEUTRAL
GROUND
Primary Earth
Ground
L2
Neutral
-to-
Ground
Bond
G
Figure 3-5
AC Connections from GT Inverter to Utility Service Panel
3–8 975-0245-01-01
Page 59

Connecting Multiple Inverters
For installations with multiple GT Inverters, separate solar arrays are required for
each unit. The output of each GT Inverter feeds a separate dual-pole 20-Amp
circuit breaker (L1 and L2) in the main utility service panel.
For such installations, complete the wiring and perform the commissioning
procedure for each inverter one at a time. For wiring instructions, see “Connecting
the DC Wiring” on page 3–4 and “Connecting the AC Wiring” on page 3–7. For
the commissioning procedure, see “Commissioning Multiple Inverters” on
page 4–4.
WARNING: Shock hazard and equipment failure
If inverters “share” more than one PV array, an input current difference of over 1 A
between arrays can cause each inverter to fail—the ground fault protection fuse will blow ,
followed by short circuit failure. This failure will also generate hazardous voltages at the
DC/AC disconnect switch on each unit.
It is very important to ensure each inverter is correctly connected to its own PV array(s)
and that no wires are crossed. For example, connect PV1 positive (+) and PV1 negative
(–) to inverter 1 and PV2 positive (+) and PV2 negative (–) to inverter 2.
Do not connect PV1 positive (+) and PV2 negative (–) to inverter 1 and PV2 positive (+)
and PV1 negative (–) to inverter 2. See Figure 3-6.
Connecting Multiple Inverters
–
+
Figure 3-6
975-0245-01-01 3–9
Improper Multiple Inverter Connections
PV Array #1 (PV1)
GT Inverter #1
–
+
PV Array #2 (PV2)
Grid Tie Solar InverterGrid Tie Solar Inverter
GT Inverter #2
Page 60

Wiring the Inverter
DC and AC Wiring for Multiple Inverters
The following procedures are illustrated in Figure 3-7. The illustration and
instructions assume only two inverters, but in fact up to ten inverters can be
installed and networked together.
If there will be more than one PV array, label the positive and negative wire pairs
appropriately (for example: PV1 POS, PV1 NEG, PV1 GND, PV2 POS, etc.).
Connecting DC
wiring
Connecting AC
wiring
To wire the PV array to multiple GT Inverters:
1. Remove the wiring box cover from each unit (see page 3–2).
2. Install the DC conduit from the PV arrays to the GT Inverter wiring boxes,
through appropriate knockout holes. Metal conduit is highly recommended.
3. Route the wires from each PV array through the conduit and into the wiring
box of the unit intended for that PV array.
4. Connect the DC Ground from each PV array to the GND bar in the wiring box
of the unit intended for that PV array. Do not combine array ground wires.
5. Follow the instructions on page 3–4 for connecting POSITIVE (+) and
NEGATIVE (–) wires from each PV array to each GT Inverter.
6. If required by the AHJ, a DC grounding conductor may be connected to each
inverter’s ground bar. One inverter will connect to a common grounding
conductor. The other inverters will use tap connectors. Connection is then
made to the DC or AC grounding electrode as per NEC 690.47.
7. Ensure all connections are correctly wired and properly torqued according to
values shown in Table 3-1 on page 3–5.
To wire the main utility service panel with multiple GT Inverters:
1. Run conduit from the main utility service panel to the wiring boxes of the GT
Inverters.
2. Follow the instructions on page 3–7 for connecting L1 and L2 HOT wires and
ground wire from the main utility service panel to each GT Inverter.
3. Ensure all connections are correctly wired and properly torqued according to
values shown in Table 3-1 on page 3–5.
3–10 975-0245-01-01
Page 61

Connecting Multiple Inverters
PV Array #2 (PV2)
PV Array #2
Utility
G
–
+
PV Array #1
PV Array #1 (PV1)
G
–
+
Xantrex GT Inverter #1
Utility
Meter
Main Utility
Service Panel
Wiring Box
L1
L1
GND bar
G
DC/AC Disconnect Switch
L2
L1
L2
GROUND
Grid
L1 L2 Neutral
L1 L2 Neutral
L2
NEUTRAL
Neutral-
to-
Ground
Bond
Figure 3-7
Xantrex GT Inver ter #2
Wirin g Box
GND bar
G
Listed tap connector
or exothermic welding
DC/AC Disconnect Switch
DC and AC Wiring With Multiple GT Inverters
GG
Primary Earth
Ground
975-0245-01-01 3–11
Page 62
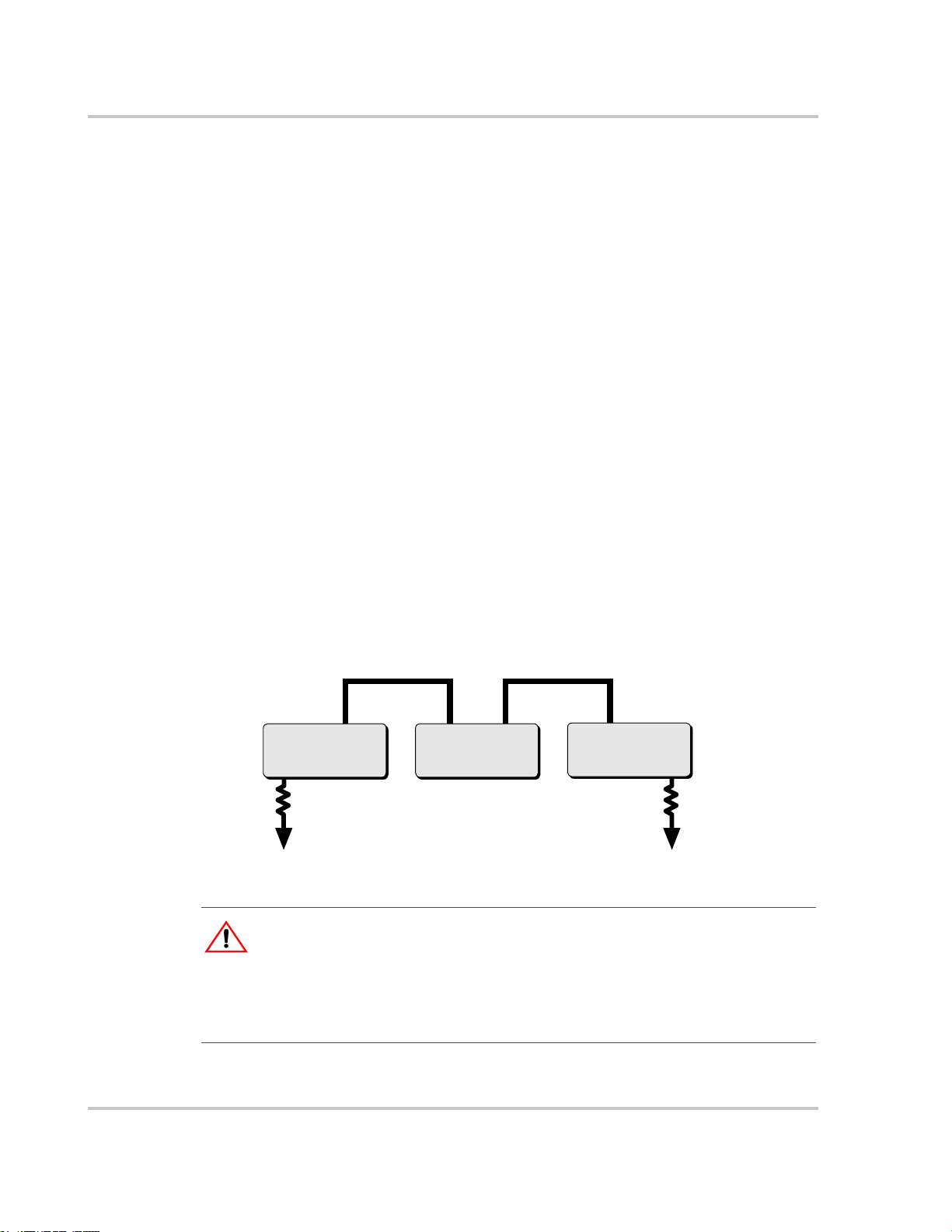
Wiring the Inverter
Communications Wiring for Multiple Inverters
Communications wiring between multiple GT Inverters allows information about
each inverter and its associated PV array to be communicated between all of the
inverters in the system. Information about the entire system can be displayed on
any inverter LCD in the system.
For example, in a two-inverter system, if inverter #1 is producing 1500 W and
inverter #2 is producing 2000 W, both inverters display a total system power of
3500 W. The cumulative energy produced by both inverters that day is also
displayed.
You can still view information for an individual inverter in a system. See “T o view
unit-specific screens in a multiple unit system:” on page 5–5.
Without communications wiring (network cables) each inverter in a system will
only display information pertinent to the unit and its associated PV array.
Xanbus Network Technology
GT Inverters use Xanbus technology to communicate with other GT Inverters.
Network connections for multiple inverters are laid out in a “daisy chain” pattern,
each device on the network linked together with separate lengths of cable, as
shown in Figure 3-8.
For more information on installing a Xanbus network, see the Xanbus System
Installation Guide, available at www.xantrex.com.
Xanbus-enabled
Device 1
Terminator
Figure 3-8
Daisy Chain Layout
Xanbus-enabled
Device 2
Xanbus-enabled
Device 3
Terminator
CAUTION: Equipment damage
Connect only Xanbus-enabled devices.
Although the cabling and connectors used in this network system are the same as ethernet
connectors, this network is not an ethernet system. Equipment damage may result from
attempting to connect Xanbus to different systems.
3–12 975-0245-01-01
Page 63

Communications Wiring for Multiple Inverters
T ermin ators Male network terminators (Figure 3-9) are required at both ends of the network to
ensure the communication signal quality on the network.
GT Inverter Xanbus
Ports
Figure 3-9
Male Network Terminator
Two RJ45 ports are provided in the GT Inverter, accessible from the wiring box.
See Figure 3-10 for the location of these ports.
RJ11 ports
(not used)
Figure 3-10
RJ45
Xanbus ports
RS-232 port (used to connect a PC to use GT-View.
See page 3–18 and page 5–9)
Male network terminator
Xanbus RJ45 Ports in the GT Inverter Wiring Box
975-0245-01-01 3–13
Page 64
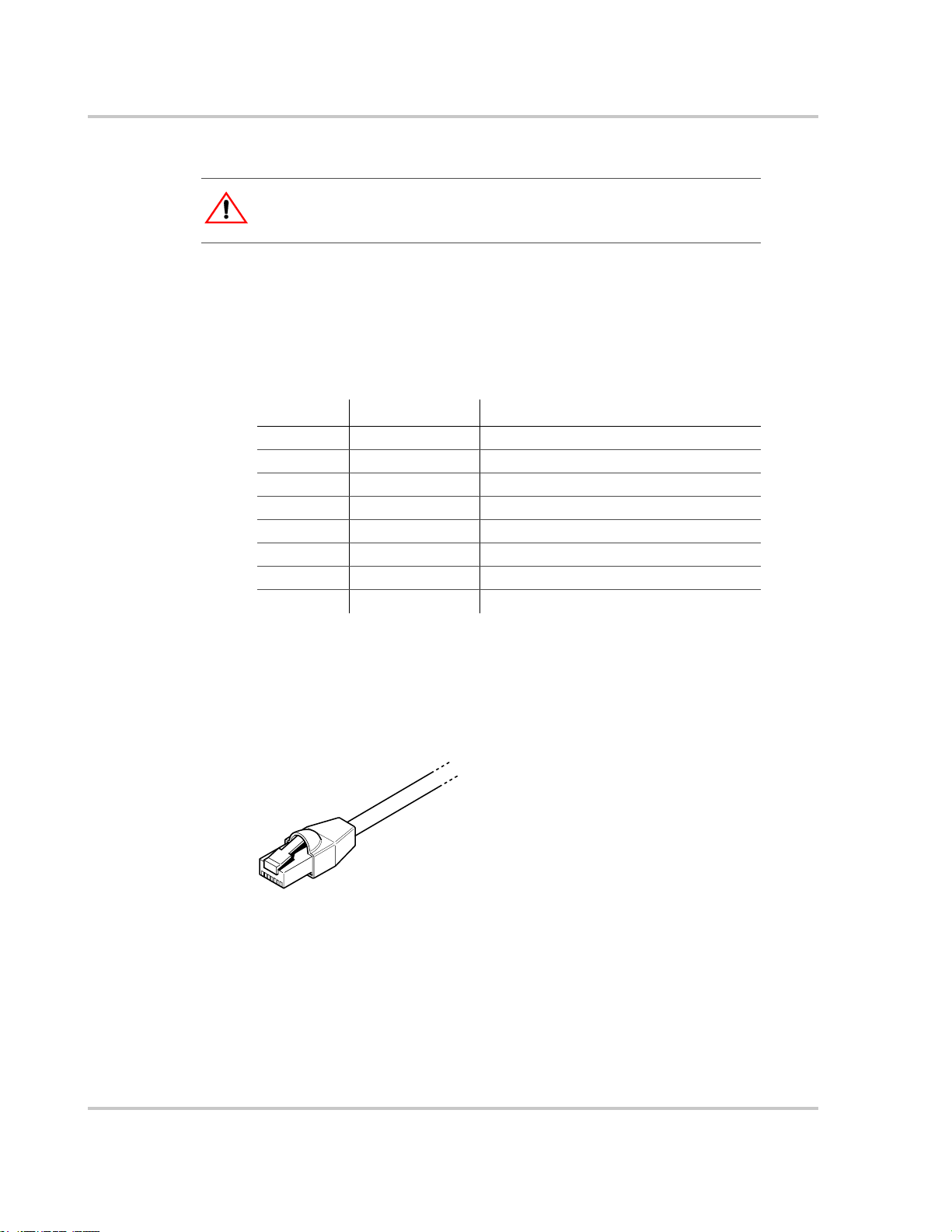
Wiring the Inverter
Cabling Requirements
CAUTION: Equipment damage
Do not use crossover cable in a Xanbus system.
The network uses Category 5 (CAT 5) cable, a standard cable available from any
computer supply store. The cable consists of eight conductors in four twisted pairs
with an RJ45 modular connector wired to the T568A standard. T a ble 3-2 contains
the arrangements of wire colors to pin numbers for the T568A standard.
Table 3-2
Pin Number Conductor Name CAT 5 Cable Insulation Color
1 NET_S White/Green
2 NET_S Green
3 NET_C White/Orange
4 CAN_L Blue
5 CAN_H White/Blue
6 NET_C Orange
7 NET_S White/Brown
8 NET_C Brown
RJ45 Connector Requirements
The network cable uses modular RJ45 connectors, as shown in Figure 3-11. The
connector is suitable for cost-sensitive applications and is easily installed. The
RJ45 connector should be a modular plug, 8-position, 8-contact for round,
stranded, unshielded cable.
T568A Standard Wiring
Figure 3-11
3–14 975-0245-01-01
RJ45 Connector
Page 65

Purchasing Network Components
Consult with your system designer to determine what network components will be
needed for your specific installation. Table 3-3 provides a partial list of network
components and part numbers. Pre-made cables are available in standard lengths
from 3 feet to 75 feet.
Call your dealer or visit www.xantrex.com to purchase network components.
Communications Wiring for Multiple Inverters
Table 3-3
Network Component Part Number
Network termination — Male (2 per pack) 809-0901
Network cable 3 ft. (0.9 m) 809-0935
Network cable 5 feet (1.5 m) 809-0936
Network cable 7 feet (2.0 m) 809-0937
Network cable 10 feet (3.0 m) 809-0938
Network cable 14 feet (4.3 m) 809-0939
Network cable 25 feet (7.6 m) 809-0940
Network cable 50 feet (15.2 m) 809-0941
Network cable 75 feet (22.9 m) 809-0942
Network Components and Part Numbers
Guidelines for Routing the Network Cables
WARNING: Shock hazard
:
Do not route the network cables in the same conduit or panel as the AC and DC power
cabling.
To ensure maximum performance of yo ur network, follow these guidelines when
routing the network cables. Route the cables before installing Xanbus-enabled
devices.
• Route the cables away from sharp edges that might damage the insulation.
Avoid sharp bends in the cable—no less than a 10 cm (4 inch) radius.
• Allow for some slack in the cable tension.
• Keep the alignment of wire pairs inside the sheath as straight as possible.
• Allow separation between data and power cables (data cables should only
cross a power cable at right angles).
• Do not staple the cable with metal cable staples. Use the appropriate hardware
fasteners to avoid damage to the cable.
CAUTION: Unpredictable device behavior
Do not connect one end of the network to the other to make a ring or loop.
975-0245-01-01 3–15
Page 66

Wiring the Inverter
Connecting Network Cable Between Multiple Inverters
WARNING: Shock hazard
If the inverter is already installed and operational, turn OFF the breaker switches in the
main utility service panel and the DC/AC Disconnect switch on the inverter wiring box
before performing this procedure.
WARNING: Shock hazard
Hazardous voltages may be present when cover is removed. After disconnecting all
sources of energy, wait 5 minutes before removing cover.
The following procedure is illustrated in Figure 3-12 on page 3–17. The
illustration and procedure assume only two inverters are connected. However,
there can be up to ten inverters wired in this configuration.
To provide communication between multiple inverters:
1. Remove the wiring/disconnect box cover from each unit.
2. On each unit, remove the plug from a side conduit hole and install appropriate
conduit between the two units.
3. Connect the network cable to any RJ45 port in Inverter #1.
4. Pass the cable through the conduit between Inverter #1 and Inverter #2.
Inside each unit’s wiring box, ensure the network cable runs horizontally
along the flat-bottomed channel formed when the insulation barrier is in
place. The cable should run on top of the insulation barrier and out the side
conduit hole, avoiding any contact with the AC and DC wiring.
5. Connect the network cable to any RJ45 port in Inverter #2.
6. For more than two inverters, continue connecting cable as described above.
7. Insert male network terminators into the empty RJ45 ports in the inverters at
the beginning and end of the network. There should be no empty RJ45 ports in
any of the inverters.
3–16 975-0245-01-01
Page 67

Communications Wiring for Multiple Inverters
PV Array #2 (PV2)
PV Array #2
G
–
+
PV Array #1 (PV1)
PV Array #1
G
–
+
Network cable in separate conduit
from AC and DC wiring.
Figure 3-12
Xantrex GT Inverter #1
Wiring Box
Male Terminator
GND bar
DC/AC Disconnect
Switch
Communications Wiring for Multiple GT Inverters
Xantrex GT Inverter #2
Wiring Box
GND bar
DC/AC Disconnect
Switch
G
L2
To Utility Service Panel. See
L1
Figure 3-7 on page 3–11 for
details of wiring connections.
Male Terminator
L2
G
L1
975-0245-01-01 3–17
Page 68

Wiring the Inverter
Communications Wiring for Monitoring a Single Inverter
You can view GT Inverter operational data on a personal computer using the
Xantrex GT Solar Inverter Viewer (“GT-View”), which you can download free of
charge at www.xantrex.com.
To use GT-View, you must connect your computer’s serial port to the GT Inverter
RS-232 port (see Figure 3-10).
RS-232 cable
requirements
T o connect your computer to the GT Inverter, you must use a serial DB9 “straight
through” cable.
The RS-232 connector on the GT is configured as follows:
• Pin 2: transmit
• Pin 3: received
• Pin 5: ground.
All other pins are unused.
To connect a single GT Inverter to a personal computer:
WARNING: Shock hazard
Before removing the wiring/disconnect box cover:
• Turn OFF the breaker switches in the main utility service panel.
• Turn the DC/AC Disconnect switch on the GT Inverter to the OFF position.
1. With DC and AC power disconnected from the inverter, remove the
wiring/disconnect box cover.
2. Feed the male end of the serial cable through a side conduit hole on the GT
Inverter.
If the end of the serial cable is too large to fit through the conduit hole, you
may need to use two DB9 to CAT 5 adaptors. Plug the DB9 end of the adapter
into the GT Inverter, and feed the CA T 5 end of the cable out the conduit hole.
Use another adapter to convert the CAT 5 end of the cable back to DB9.
3. Plug the male end of the serial cable into the GT Inverter RS-232 port.
4. Plug the female end of the serial cable into your computer’s serial port.
5. Replace the wiring/disconnect box cover.
6. Turn the DC/AC disconnect switch to the ON position and turn the main
utility panel breaker switches ON.
When power is restored to the GT Inverter, you can run GT-View on your
computer to monitor the inverter’s operation.
Note: In multiple installations, GT-View monitors only the inverter to which the
computer is connected. However, if the inverters are connected with a Xanbus cable,
GT-View will display total system wattage and the accumulated daily energy produced
by all inverters. To monitor multiple inverters, you require multiple DB9 cable
connections (one per inverter) to your computer.
3–18 975-0245-01-01
Page 69
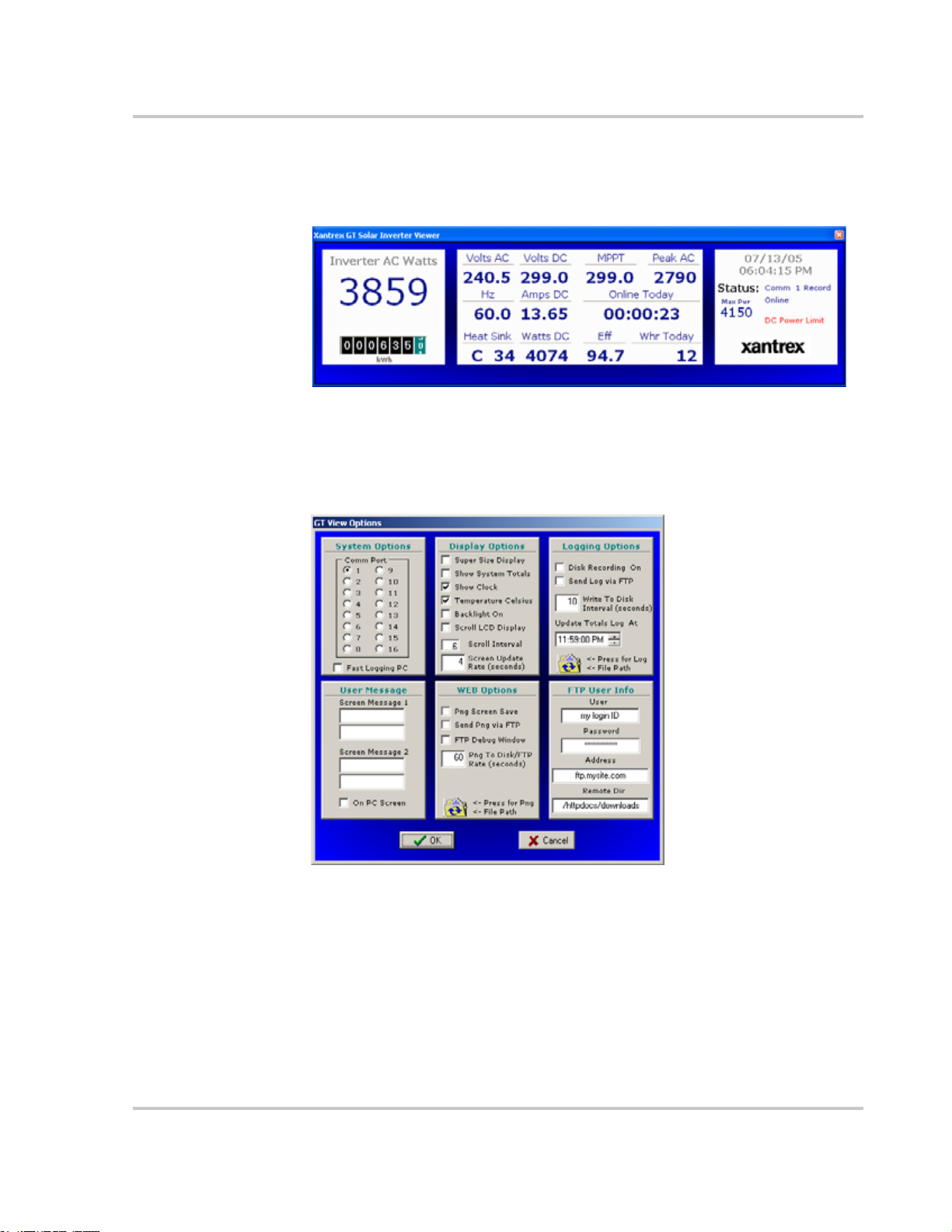
Communications Wiring for Multiple Inverters
GT-View displays operational data such as power output in AC watts, lifetime
energy produced, and inverter temperature. Data is updated every two seconds
(default setting).
Figure 3-13
GT -View Display
To configure GT-View, right click anywhere in the GT-View display and select
Settings from the pop-up menu. The GT-View Options window will appear.
Figure 3-14
GT -View Options
For more information about GT-View, see the GT-View User Manual, included
with the GT-View software.
975-0245-01-01 3–19
Page 70

3–20
Page 71

4
Starting the Inverter
Chapter 4, “Starting the Inverter”, contains information on starting up
the Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter and performing a Functional Test.
The topics in this chapter are organized as follows:
• “Startup Procedure” on page 4–2
• “Replacing the Wiring/Disconnect Box Cover” on page 4–3.
• “Disconnect Test” on page 4–6.
Page 72

Starting the Inverter
Startup Procedure
Starting up the GT Inverter requires several steps. You will need to:
1. Ensure the DC/AC Disconnect switch is in the OFF position (see Figure 4-1).
2. Check the PV array DC voltage (see procedure below).
3. Check the AC utility voltage (see procedure below).
4. Replace the cover on the wiring box (see “Replacing the Wiring/Disconnect
Box Cover” on page 4–3).
5. Start up the GT Inverter by switching the DC/AC Disconnect switch ON.
WARNING: Shock hazard
Hazardous voltages are present from two sources. Use extreme caution during startup
procedure. Before applying power to the GT Inverter, ensure all AC and DC wiring is
correct.
Checking the PV Array DC Voltage
To check the PV array DC voltage:
1. Uncover the PV arrays and expose them to full sunlight. The sunlight must be
intense enough to produce the required output voltage.
2. Measure the PV array open circuit DC voltage across the DC positive (+) and
negative (–) terminals. This voltage must be greater than 150 volts DC (to
energize the electronics) and less than 600 volts DC (to prevent damage to the
inverter).
Checking the AC Utility Voltage
To check the AC utility voltage:
1. Switch on the main and inverter breakers in the main electrical service panel.
2. Using an AC voltmeter, measure the AC open circuit utility voltage between
L1 and L2. Ensure this voltage is at approximately the nominal value. The
inverter operates with a line-to-line voltage (L1 to L2) range around the
nominal value.
See “Electrical Specifications”, “Output” on page A–2 for the utility voltage
operating range for your G T Inverter model.
4–2 975-0245-01-01
Page 73
Replacing the Wiring/Disconnect Box Cover
Replacing the Wiring/Disconnect Box Cover
After performing the voltage checks, replace all covers that were removed during
installation and startup.
WARNING: Shock hazard
Before reattaching covers, turn OFF the breaker switches in the main utility service panel
and the DC/AC Disconnect switch on the GT Inverter.
To replace the wiring/disconnect box cover :
1. Place the cover in position on the wiring box, being careful not to pinch any
wires inside.
2. Ensure that the two screw holes in the bottom of the wiring box cover are
aligned with the corresponding holes in the bottom of the wiring box.
3. Replace the two screws removed when the cover was removed (see
“Accessing the Wiring Terminals” on page 3–2), and tighten securely.
975-0245-01-01 4–3
Page 74
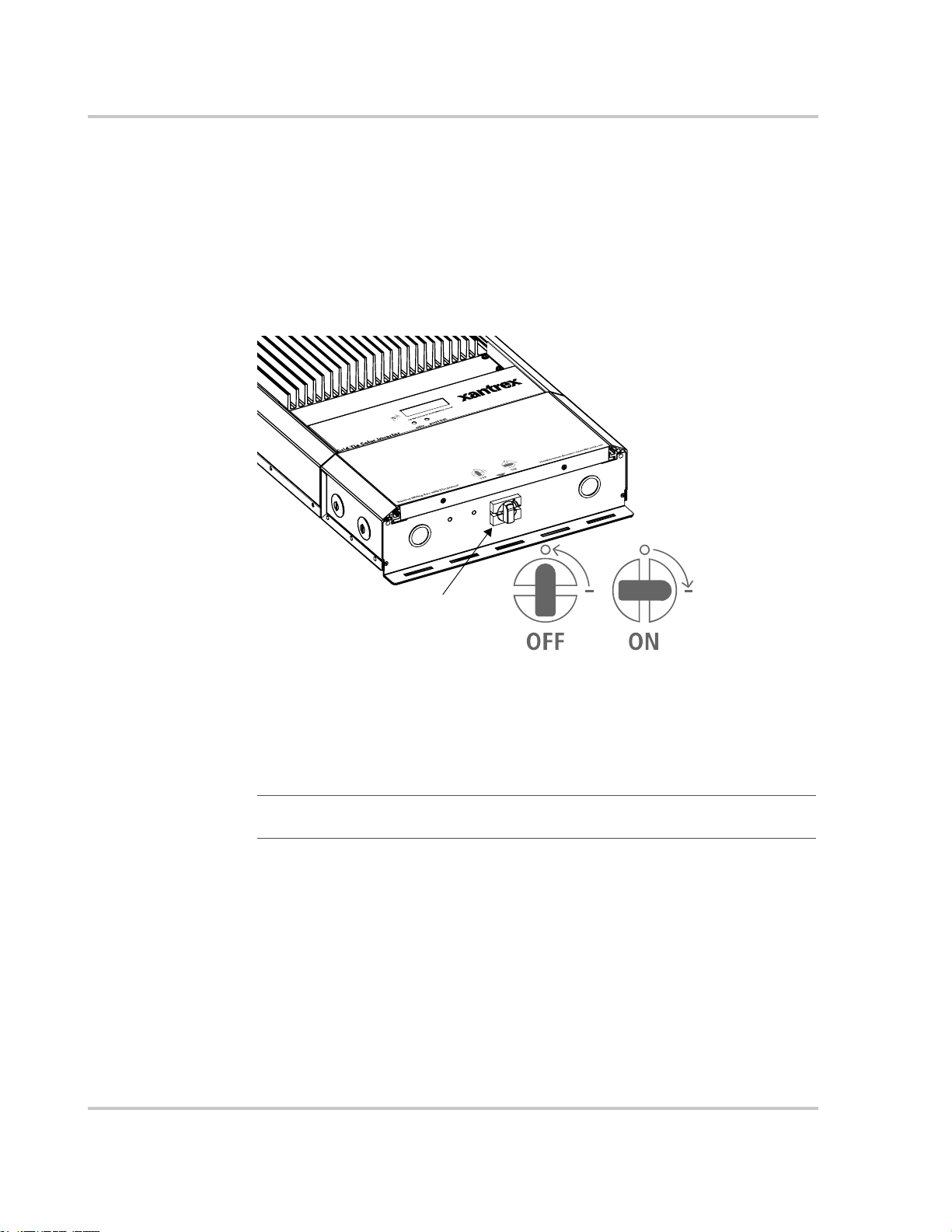
Starting the Inverter
Starting up the GT Inverter
To start up the inverter:
1. Switch the DC/AC Disconnect switch to the ON position (see Figure 4-1).
2. Check the GT Inverter LCD. The startup screens (see Table 5-1 on page 5–3)
should appear for five seconds each, and then the “Reconnecting in sss
seconds” special screen (see T able 5-10 on page 5–9) will appear until the 305
second (default value) protection timer countdown is completed.
DC/AC Disconnect Switch
Figure 4-1
DC/AC Disconnect Switch Positions
Commissioning Multiple Inverters
In an installation with multiple GT Inverters, special commissioning procedures
must be followed in order to safely determine if any DC wiring problems exist.
Important:
DC/AC disconnect switch in the OFF position.
To commission multiple inverters:
1. Uncover the PV arrays and/or close the main DC disconnect switch, if one is
installed.
2. Start the first inverter by turning the DC/AC disconnect switch to the ON
position.
3. Wait for the input current to rise above 1 A.
This information is displayed on the Array Readings screen. To display the
Array Readings screen, tap the unit four times.
Before performing this procedure, all inverters should be off, with the
4–4 975-0245-01-01
Page 75
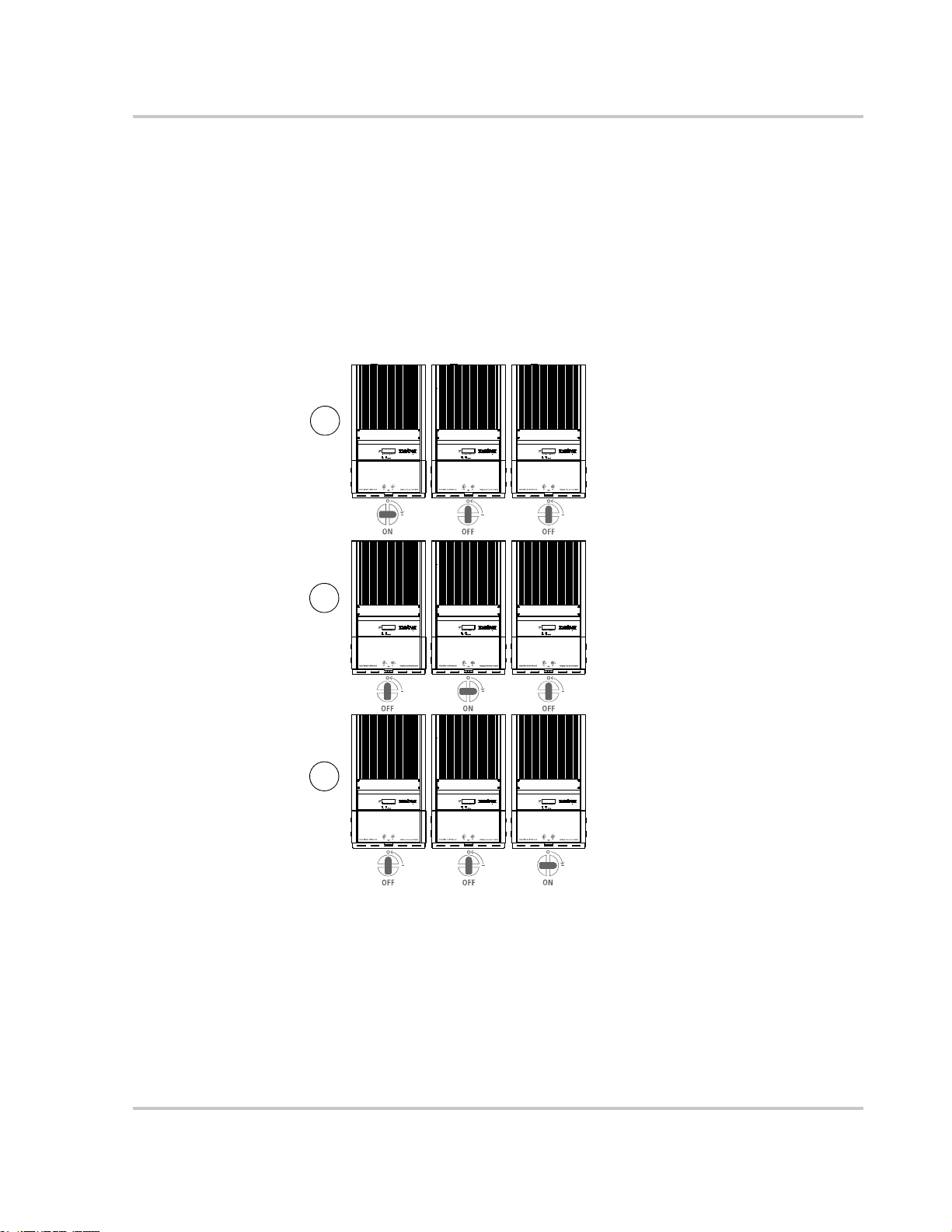
Replacing the Wiring/Disconnect Box Cover
4. After the input current has risen above 1 A, if the inverter is still operating
normally, switch off the inverter by turning the DC/AC disconnect switch to
the OFF position. Proceed to step 5.
If the inverter stops operating, turn the unit off, remove DC power, and have a
certified electrician or technician inspect the ground fault protection fuse. If
the fuse has blown, a DC wiring problem may exist. Check all DC wiring to
ensure that the unit is connected to a single PV array.
5. Proceed to the next inverter and perform the same test. See Figure 4-2 for an
example of the recommended commissioning sequence.
1
Grid Tie Solar Inverter Grid Tie Solar InverterGrid Tie Solar Inverter
2
3
Figure 4-2
Grid Tie Solar Inverter Grid Tie Solar InverterGrid Tie Solar Inverter
Grid Tie Solar Inverter Grid Tie Solar InverterGrid Tie Solar Inverter
Commissioning Sequence for Multiple Inverters
975-0245-01-01 4–5
Page 76

Starting the Inverter
Disconnect Test
The disconnect test is designed to verify correct operation of the GT Inverter both
on initial operation and periodically through its life as required by the utilities.
This test ensures that the Xantrex Grid Tie Solar Inverter does not send electricity
to the utility grid when the local utility has shut off the grid for repairs, or when
the utility wiring is damaged.
When operation of the inverter has been verified and the unit is producing power,
run the disconnect test as described in this procedure.
To run the disconnect test:
1. Switch off the AC circuit for the inverter.
2. Have someone watch the front panel of the inverter to ensure the green light
3. Switch on the AC circuit for the inverter.
This can be accomplished by switching the breaker on the main panel that
feeds the inverter(s). The disconnect for the home or business may be used as
well.
on the front of the inverter goes out within two seconds.
The green light goes out when the AC circuit is switched off, disconnecting
the inverter from the AC grid. The front panel display will show an AC Fault
display, indicating that the AC is out of the operating range.
The inverter responds by starting its 305 second protection timer. Ensure that
the inverter does not produce power before the countdown is over. After
completing the countdown, the green light turns on and the inverter begins to
send power to the grid. The display returns to showing the power being
produced and the total kWh produced to date.
Important:
into the unit at time of shipment from the factory. No changes to these settings can be
made in the field by the user. Only authorized personnel with the utility’s permission may
change these settings.
4. If you have another GT Inverter to commission, switch off the AC circuit for
the inverter you have just commissioned and tested by switching off the
breaker on the main panel. You can then run the commissioning procedure
and disconnect test on the next inverter.
4–6 975-0245-01-01
The default voltage, frequency and reconnect delay values are programmed
Page 77

5
Monitoring the Inverter
Chapter 5, “Monitoring the Inverter”, contains information for
understanding the LCD screens and the LED indicators.
The topics in this chapter are organized as follows:
• “Monitoring the Front Panel Display” on page 5–2
• “Front Panel Display Screens and What They Mean” on page 5–3
• “Status Indicator Lights” on page 5–10.
Page 78

Monitoring the Inverter
Monitoring the Front Panel Display
During startup During startup, the inverter’s front panel LCD (see Figure 5-1) shows the first
three screens described in Table 5-1, “Startup Screens on GT Inverter Front Panel
Display” on page 5–3.
During waiting
period
During operation When the protection timer stops, the GT Inverter begins selling power, indicated
When the inverter is
offline or there is
fault condition
When the 305 second protection timer begins, the inverter displays “Reconnecting
in sss seconds” (see Table 5-10, “Special Message Screens” on page 5–9).
by the power output reading in the display (see Table 5-2, “Normal Operation
Default Screen” on page 5–4).
When the GT Inverter is offline (e.g., at night) or a fault condition has been
detected, the LCD shows a message screen to indicate that state. The specific fault
condition will be identified. See Table 5-5, “Offline Mode Default Display” on
page 5–5 and Table 5-8, “Fault Message Screens” on page 5–7.
Important:
Grid Tie Solar Inverter
Front panel LCD
Figure 5-1
The values in the front panel LCD are not user adjustable.
Tap Xantrex logo for backlight
and status screens
Front Panel LCD Location
Vi ewing more
information
Additional screens of information about the performance of the G T Inverter can be
displayed by tapping the Xantrex logo on the inverter front panel. This causes the
LCD to cycle through a series of information screens in Normal Operation,
Offline or Fault modes. These are described in detail in the following section,
“Front Panel Display Screens and What They Mean”.
5–2 975-0245-01-01
Page 79

Front Panel Display Screens and What They Mean
Front Panel Display Screens and What They Mean
The front panel display shows different message screens during different modes of
operation (Startup, Normal, Offline, and Fault). All single units display a basic set
of message screens; multiple unit systems display additional screens in Normal
Operation and Offline modes.
In addition there are Special message screens that may appear in any operational
mode. All of these message screens are described in more detail in the following
tables.
Startup Mode
During startup, the GT Inverter displays three message screens on its front panel
LCD. These screens appear in the following order (Table 5-1).
Table 5-1
GT3.3-NA-240
Flash = 01.01
..ROM = 01.01
Vh=262 Vl=212
Fh=60.5 Fl=59.3
* all numbers in this and following tables are examples only.
The protection timer begins its countdown during startup and the “Reconnecting
in sss seconds” screen appears until the timer countdown is complete.
Normal Operation Mode
Startup Screens on GT Inverter Front Panel Display
Display*
Xantrex
Duration Description
5 sec. Startup message 1: Inverter name and model
number
5 sec Startup message 2: Model and revision
numbers for Flash and ROM memory on t he GT
Inverter. The ROM revision number applies to
the protection processor.
5 sec Startup message 3: Anti-islanding Utility Grid
trip points.
Vh: high voltage threshold
Vl: low voltage threshold
Fh: high frequency threshold
Fl: low frequency threshold
The LCD on the GT Inverter is refreshed every two seconds, so all readings are
current to within two seconds. There is a default display available at all times, and
a series of additional screens that can be displayed by tapping the Xantrex logo
near the LCD to change the display.
Normal Operation
default display
After the protection timer has completed its countdown and during normal
operation, the GT Inverter displays the normal operation message screen shown in
Table 5-2.
975-0245-01-01 5–3
Page 80

Monitoring the Inverter
More screens for all
systems
Table 5-2
System 2000W
Today 9.875kWh
Normal Operation Default Screen
Display Description
Power being produced by the system now.
Cumulative energy produced by the system today.
If there is sufficient energy from the PV array, this screen is displayed
continuously while the system is operating normally. In a multiple unit system
with communications cables properly connected, the power and cumulative
energy values displayed are for the entire system.
During low light conditions when the GT Inverter cannot produce any power, the
Normal Operation default screen flashes alternately (every two seconds) with the
Insufficient Solar Energy screen (see Table 5-10, “Special Message Screens” on
page 5–9).
Besides the default normal operation display, more system information messages
can be viewed.
To view more Normal Operation information:
• Tap the Xantrex logo near the LCD to advance the display to the next screen.
Normal operation screens shown in Table 5-3 are displayed in the order given,
as you tap successively on the unit. They are common to all GT Inverter
systems, no matter how many units are installed.
If you continue to tap the unit, then the LCD continues to cycle through all of the
available normal operation screens. Each screen is displayed for a maximum of
30 seconds. If you do not tap again during that time period, then the LCD
backlight turns off and the display reverts to the default system message screen.
Table 5-3
Tap Display* Description
1st time System 2000W
2nd time System Lifetime
3rd time Time Online
4th time Array Readings
5th time Grid Readings
5–4 975-0245-01-01
Normal Operation Screens for All GT Inverter Units
LCD backlight turns on for better readability
Today 2.500kWh
305kWh
Today hh:mm:ss
350.5V 8.4A
242.6V 60.0Hz
and default Normal Operation screen is
displayed.
Lifetime energy produced by the GT Inverter
system.
Length of time inverter has been online today, in
hours (hh), minutes (mm) and seconds (ss).
Immediate DC voltage and current readings
from the PV array.
Immediate AC voltage and frequency readings
from the Grid
Page 81

Front Panel Display Screens and What They Mean
* In a multiple unit system with network cables properly installed, the system
values displayed are for the entire system. For example, in a two-inverter
system, if inverter #1 is producing 1500 W and inverter #2 is producing
2000 W, both inverters display a total system power of 3500 W. Time online
and array readings are for the local inverter and PV array associated with that
inverter.
Additional screens
for multiple units
In addition, to the normal system message screens, additional screens specific to
each GT Inverter unit can be displayed when the unit is networked to other GT
Inverters. These screens are only available on multiple unit systems.
To view unit-specific screens in a multiple unit system:
1. Tap the Xantrex logo near the LCD to advance the display to the next screen.
Continue tapping until the final system message screen (“Grid Readings”, in
Table 5-3 above) is displayed.
2. Tap again. Normal operation screens shown in Table 5-4 are displayed in the
order given, as you tap successively on the unit.
If you continue to tap the unit, then the LCD will cycle through all of the available
normal operation screens. Each message is displayed for up to 30 seconds. If you
do not tap again within that time period, then the LCD backlight turns off and the
display reverts to the default normal operation screen (Table 5-2).
Table 5-4
Additional Normal Operation Screens for Each GT Inverter Unit in a
Multiple Unit System
Tap Display Description
6th time Unit 1500W
Today 1.250kWh
7th time Unit Lifetime
150kWh
Power being produced by this unit now.
Cumulative energy produced by this unit today.
Lifetime energy produced by this GT Inverter unit
Offline Mode
Offline default
display
Offline messages
for all systems
975-0245-01-01 5–5
At night and when no power is being produced by the PV array (offline mode), the
GT Inverter displays the screen shown in Table 5-5.
Table 5-5
Offline Mode Default Display
Display Description
Inverter
Offline
Displayed at all times while the system is offline.
Additional message screens can be viewed when the system is offline by tapping
the Xantrex logo near the LCD. Each additional tap displays the next screen, in
the order shown in Table 5-6.
Page 82
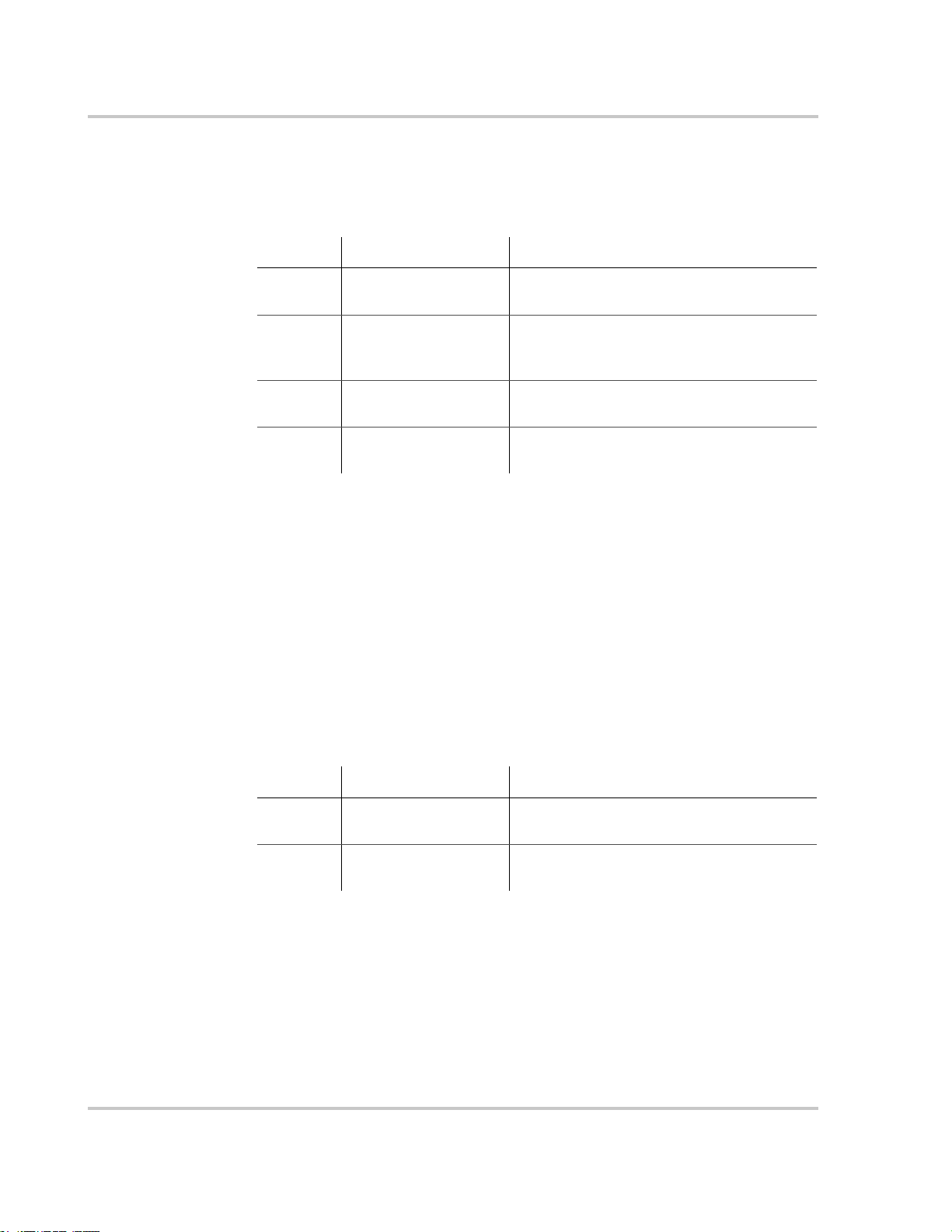
Monitoring the Inverter
These message screens are common to all GT Inverter systems, no matter how
many units are installed. If you continue to tap the unit, then the LCD will
continue to cycle through all of the available offline mode screens.
Additional Offline
messages for
multiple unit
systems
Table 5-6
Tap Display*
1st time Inverter
2nd time System 0W
3rd time System Lifetime
4th time Time Online
* In a multiple unit system with communications cables properly installed, the
Offline Mode Screens for All GT Inverter Units
Description
LCD back light turns on for better readability
Offline
Today 2.50kWh
305kWh
hh:mm:ss
system values displayed are for the entire system. Time online is for the local
inverter.
and default Offline Mode screen is displayed.
Power being produced by the system now.
Cumulative energy produced by the system
today.
Lifetime energy produced by the system.
Total time that the syst em was online today, in
hours (hh), minutes (mm) and seconds (ss).
Multiple unit systems in offline mode display all of the message screens shown in
Table 5-6, plus the additional screens shown in Table 5-7. These additional
screens are displayed following the “Time Online” screen.
These screens are only displayed on multiple unit GT Inverter systems with
communications cabling properly installed. If you continue to tap the unit, then
the LCD continues to cycle through all of the available offline mode screens.
Table 5-7
Additional Offline Mode Screens for Each GT Inverter Unit in a
Multiple Unit System
Tap Display Description
5th time Unit 0W
Today 1.25kWh
6th time Unit Lifetime
150kWh
5–6 975-0245-01-01
Power being produced by this unit now.
Cumulative energy produced by this unit today.
Lifetime energy produced by this unit.
Page 83

Front Panel Display Screens and What They Mean
Fault Mode
When a fault state is detected, the appropriate fault message appears on the front
panel display at the next screen refresh (i.e., within 2 seconds). The GT Inverter
fault message screens are shown in Table 5-8.
Fault Mode causes These message screens only appear when there is a fault, and then flash
alternately with the Inverter Offline default screen (Table 5-5) until the fault is
corrected.
Table 5-8
DC Voltage Fault
AC Voltage Fault
Frequency Fault
Over Temp Fault
81.4C 178.5F
Ground Fault
Reset System
Fault Message Screens
Display Description
145.5V
280V
0.0Hz
When the actual DC voltage is over or under the allowable
range, 165 to 600 Vdc. Self-clearing, no action required.
The PV array should be configured such that DC voltage
does not fall below 195 Vdc or rise above 600 Vdc.*
When the actual AC voltage is over or under the allowable
range, as specified in “Output” on page A–2.
This is a utility fault; it will clear itself when the AC voltage
comes within the specified range.†
When the actual Frequency is over or under the allowable
range, as specified in “Output” on page A–2. This is a utility
fault; it will clear itself when the frequency comes within the
specified range.†
When the unit’s internal temperature is greater than 80° C
(176° F), the unit will shut down automatically and only
restart when the temperature has dropped to less than 70° C
(158° F).
When a grounding fault is detected. The ground fault fuse
will be blown. The system must be shut down completely,
the fault corrected, the fuse replaced (see “Replacing the
Ground Fault Protection Fuse” on page 6–4) and then the
system restarted. Troubleshooting a grounding fault should
be performed by qualified personnel, such as a certified
electrician or technician.
Unit Shutdown
via Remote
Protection uP
Not Responding
* It is normal to receive this fault during low light conditions at dawn or dusk. At
such times, the array does not have sufficient energy to power the inverter, so
the PV voltage drops below 165 volts occasionally.
† Grid fault. When this fault is cleared the protection timer will begin its
countdown and you will see the “Reconnecting in sss seconds” and “Inverter
Offline” special screens (see Table 5-10) flashing alternately until the
countdown is complete.
975-0245-01-01 5–7
Appears if the GT Inverter unit has been shut down via a
computer connected to the RS-232 port.
The protection microprocessor is not responding.
Page 84
Monitoring the Inverter
Additional Fault
messages for all
systems
Additional message screens can be viewed in fault mode by tapping the Xantrex
logo near the LCD. Each additional tap displays the next screen in the order
shown in Table 5-9.
Table 5-9
Tap Display*
1st time Current fault message
2nd time System 0W
3rd time System Lifetime
4th time Time Online
5th time Array Readings
6th time Grid Readings
* In a multiple unit system with network cables properly installed, the system
Additional Fault Mode Screens
Description
LCD backlight turns on for better readability.
screen (see T able5-8)
Energy being produced by the system now.
Today 2.500kWh
305kWh
Today hh:mm:ss
350.5V 8.4A
242.6V 60.0Hz
values displayed are for the entire system. Time online and array readings are
for the local inverter and PV array associated with that inverter.
Cumulative energy produced by the system
today.
Lifetime energy produced by the GT Inverter
system.
Length of time inverter was online today, in
hours (hh), minutes (mm) and seconds (ss).
Immediate DC voltage and current readings of
power from the PV array.
Immediate AC voltage and frequency readings
of power from the Grid.
5–8 975-0245-01-01
Page 85

Special Screens
Front Panel Display Screens and What They Mean
Special message screens are displayed in specific situations that are not
considered fault situations. They can appear in any mode of operation. These
screens are described in Table 5-10.
Table 5-10
Reconnecting in
sss seconds
System *3500W
Today 15.56kWh
Unit *1800W
Today 7.82kWh
Insufficient
Solar Energy
Special Message Screens
Display Description
Inverter
Offline
Time remaining in seconds (sss) before the GT Inverter
reconnects to the Grid. This is a protection timer; it runs for
approximately five minutes at startup and after any Grid fault.
GT Inverter switching (or has switched) from Normal
Operation to Offline mode. This screen may flash alternately
with a Fault message screen.
The “*” in these two screens (see Table 5-2 and Table 5-4)
indicates that the unit is derating its output power because the
inverter heat sink temperature is above 75° C (167° F).
The asterisk only appears when the power is actually being
limited by the inverter.
Indicates the GT Inverter is not producing power due to
insufficient solar energy during low light conditions in early
morning or late afternoon or when the PV array is in shade.
This screen flashes alternately with the Normal Operation
default screen.
Custom Screens
Two custom screens are available. The inverter does not display them unless they
are configured using GT-View (see page 3–18). If programmed, the custom
screens display as the fourth and fifth screens during the startup sequence. They
can also be viewed by tapping the unit during normal operation and fault mode.
The first custom screen is intended for the home owner to display information
such as the name or location of the PV array associated with the inverter.
The second custom screen is intended for installers, who can configure the screen
to display, for example, contact information for service.
975-0245-01-01 5–9
Page 86

Monitoring the Inverter
Status Indicator Lights
The GT Inverter is equipped with two status indicator lights (LEDs) located below
the front panel LCD (Figure 5-2). These LEDs indicate the inverter’s current
status (Table 5-11) and assist in troubleshooting the performance of the unit.
Only one indicator light will be lit at any time.
Table 5-11
LED on Means
GREEN GT Inverter is on (DC voltage and AC voltage are qualified and the
RED Ground fault condition detected.
Status Indicator LEDs
protection timer has finished) and delivering energy to the grid. No
action required. Turns off when a fault state is detected.
Check for any fault messages on the display (see Table 5-8), and refer
also to Table 6-1, “Troubleshooting the GT Inverter” on page 6–9 to
resolve the fault condition.
Green LED
Red LED
Grid Tie Solar Inverter
Figure 5-2
5–10 975-0245-01-01
Location of Status Indicator Lights
Page 87

Maintenance and
6
Troubleshooting
Chapter 6, “Maintenance and Troubleshooting”, contains information
about how to provide general maintenance for the Xantrex Grid Tie
Solar Inverter. It also provides information about troubleshooting the
unit.
The topics in this chapter are organized as follows:
• “Factors Affecting GT Inverter Performance” on page 6–2
• “Performing General Maintenance” on page 6–3
• “Replacing Parts” on page 6–3
• “Identifying Error/Fault Conditions and Solutions” on page 6–9.
Page 88

Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Factors Affecting GT Inverter Performance
This section describes several factors that will affect the amount of power that a
properly installed and operating GT Inverter can produce.
PV Array Factors
PV array ratings PV arrays are rated at ideal factory conditions, such as specified illumination
(1000 W/m
which seldom reflect real-world installations. This is called the STC (Standard
Test Condition) rating and is the figure that appears on the PV module nameplate
label.
Expected
performance
Temperature and
reduced output
Because of several unavoidable environmental factors, you can expect your
PVarray to produce around 60% to 70% of its peak STC-rated output for a
properly designed and installed PV system on a typical day.
PV array temperature affects the output of the entire system. As the temperature
on the array surface heats up, its energy output goes down. Roof-mounted arrays
also collect the heat generated by the roof surface (or trapped under the array) and
will produce less output than pole-mounted arrays, which allow greater air
circulation behind the panels.
Important:
circuits from overheating and possible damage in high heat conditions. For maximum
output in hot climates, mount the GT Inverter in a shaded location with good air flow.
Angle of the sun The angle of the sun in relation to the PV array surface—the array
orientation—can dramatically affect the PV array output. The array ener gy out put
will vary depending on the time of day and time of year as the sun’s angle in
relation to the array changes. Sunlight output decreases as the sun approaches the
horizons (such as in winter in North America) due to the greater atmospheric air
mass it must penetrate, reducing both the light intensity that strikes the array’s
surface and spectrum of the light. In general, you can expect only four to six hours
of direct sunlight per day.
Partial shade Shading of only a single module of the array will reduce the output of the entire
system. Such shading can be caused by something as simple as the shadow of a
utility wire or tree branch on part of the array’s surface. This condition, in effect,
acts like a weak battery in a flashlight, reducing the total output, even though the
other batteries are good. However, the output loss is not proportionate to shading.
The GT Inverter is designed to maximize its energy production in all of the above
situations using its MPPT algorithm.
2
), spectrum of the light and specified temperature (25°C / 77°F),
The GT Inverter will reduce its energy output to protect its electronic
6–2 975-0245-01-01
Page 89

Other Factors
Other factors that contribute to system losses are:
• Dust or dirt on the array
• Fog or smog
• Mismatched PV array modules, with slight inconsistencies in performance
from one module to another.
• Inverter efficiency
• Wire losses
• Utility grid voltage.
For additional information and technical notes concerning PV array performance,
please visit our Web site at www.xantrex.com.
Performing General Maintenance
Follow these simple routines to ensure many years of service and optimal
performance of your solar energy system.
1. Keep the heat sink clear of dust and debris.
Performing General Maintenance
WARNING: Shock and fire hazard
Do not use a pressure washer to clean the GT Inverter, or use other cleaning methods that
could allow water to enter the unit.
2. Clean the PV array, during the cool part of the day, whenever it is visibly
3. Periodically inspect the system to make sure that all wiring and supports are
4. On a sunny day near noon on March 21 and September 21 of each year,
Replacing Parts
WARNING: Shock hazard
There are no user-replaceable parts on the GT Inverter. Do not attempt to service the unit
yourself.
See the “Warranty and Return Information” on page WA–1 for information on
how to get service for your GT Inverter.
dirty.
securely in place.
review the output of the system and compare with previous year’s reading.
Maintain a log of system performance readings so that you can recognize
when system performance becomes inconsistent.
975-0245-01-01 6–3
Page 90

Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Replacing the Ground Fault Protection Fuse
WARNING: Shock and fire hazard
Fuses should only be replaced by qualified service personnel, such as a certified
electrician or technician. For continued protection against risk of fire, replace only with
same type and ratings of fuse.
WARNING: Shock hazard
After disconnecting both AC and DC power from the GT Inverter, wait five minutes
before attempting any maintenance or cleaning or working on any circuits connected to
the inverter. Internal capacitors remain charged for five minutes after disconnecting all
sources of power.
WARNING: Shock hazard
• Dangerous voltages can exist inside the inverter. If there is leakage current from the
ungrounded conductor to ground at the array, touching the grounded lead could cause a
life-threatening shock even with the disconnect switch turned off. Ungrounded DC
current within the inverter presents an extreme shock hazard.
• Cover PV arrays with an opaque material during this procedure.
• When the fuse has blown due to a fault, incorrect handling can be life-threatening. Use
an insulated fuse puller.
The ground fault protection fuse will blow when severe leakage occurs between
the PV array and earth ground, or when the system has been installed with faulty
wiring. Before replacing the fuse, it is important to have qualified service
personnel, such as a certified electrician or technician, determine the cause of the
ground fault.
To replace a ground fault protection fuse:
1. Remove the wiring/disconnect box cover, as described on page 3–2.
2. Remove the display front panel cover (see Figure 6-3), located below the heat
sink. Use a Phillips screwdriver to remove the four external panhead screws
and washers (two screws on each side) and the two screws along the bottom
edge of the cover.
The ground fault protection fuse is located to the left side of the LCD panel
(see Figure 6-1), and to the left of the DC interconnect board for positive
grounded units (marked with the “-POS” suffix).
3. Using an insulated fuse puller, remove the blown fuse and replace it with a
new AC/DC midget cartridge, rated 600 Vdc, 1A (Littelfuse KLKD 1 or
equivalent).
4. Replace the display front panel cover.
• Slide the top flange of the panel beneath the heat sink.
• Ensure that all screw holes in the display front panel cover are aligned
with the corresponding holes in the inverter.
• Tighten all six screws securely.
6–4 975-0245-01-01
Page 91

5. Replace the wiring/disconnect box cover.
Replacing Parts
Ground Fault Protection
Fuse (“-POS” models)
Figure 6-1
Location of Fuse, Front Panel Cover Removed
Ground Fault
Protection Fuse
LCD
Figure 6-2
975-0245-01-01 6–5
Display Front Panel Assembly
Page 92

Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Replacing the Inverter
If your GT Inverter requires servicing, you can replace it with ano t her inverter,
leaving the existing wiring box in place. This means that you do not have to
disturb wiring connections in the wiring/disconnect bo x. However , y ou do have to
disconnect wiring between the inverter and the wiring/disconnect box.
WARNING: Shock hazard
• Separating the inverter from the wiring box breaks the ground path between the
grounded conductor and earth ground. See “PV Grounding” on page 2–8. When the
wires between the inverter and wiring box are disconnected and exposed, both PV
leads are floating at the array open circuit voltage. If there is leakage current from the
POSITIVE PV lead to ground at the array, touching the NEGATIVE PV lead could
cause a life-threatening shock even with the disconnect switch turned off. Ungrounded
DC current within the inverter presents an extreme shock hazard.
• Cover PV arrays with an opaque material during this procedure.
• Use insulated tools only when disconnecting wires between the inverter and wiring
box. Cap all disconnected wires with wire nuts.
Recommended tools:
• Insulated screwdriver
• Wire nuts
• 7 mm socket and small ratchet, or 7 mm open wrench.
WARNING: Shock hazard
i
The inverter should only be removed from the wiring box when a replacement inverter is
immediately available. When replacing an inverter, ensure the DC/AC Disconnect switch
is locked (or otherwise secured) in the OFF position. Do not leave the top of the wiring
box exposed for extended periods of time.
WARNING: Shock hazard
Before replacing the inverter, turn OFF the breaker switches in the main utility service
panel and the DC/AC Disconnect switch on the GT Inverter. Cover the PV arrays with an
opaque material.
To remove the inverter from the wi rin g box:
1. Turn OFF the breaker switches in the main utility service panel and the
DC/AC Disconnect switch on the GT Inverter. Disable the output of the PV
arrays by covering them with an opaque material.
2. Remove the wiring/disconnect box cover and the display front panel cover
(described on page 3–2 and page 6–4.).
3. Using an insulated screwdriver, disconnect the PV NEGATIVE (–) wire from
the terminal block inside the inverter. Cap the wire immediately with a wire nut.
6–6 975-0245-01-01
Page 93

Replacing Parts
4. Disconnect the remaining AC, DC and network cables be tween the inverter
and the wiring box, inside the inverter. Cap all disconnected AC and DC wires
with wire nuts.
5. Inside the inverter, remove the four nuts attaching the wiring bo x to the
inverter. See Figure 6-3.
6. Lift the inverter off the mounting bracket, leaving the wiring box in place.
Inverter terminal
blocks
Four nuts to
secure inverter
Figure 6-3
975-0245-01-01 6–7
Wiring/Disconnect Box and Removable Inverter
Page 94

Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Inverter
Back view
Top mounting hook goes over
wall-mounted bracket
Lower flange goes behind
wiring/disconnect box
Wiring/ disconnect box
permanently mounted
to bracket
Figure 6-4
Inverter and Wiring/Disconnect Box Sections
To replace the inverter on the wiring box:
1. If it has not already been removed, remove the display front panel cover on
the inverter.
2. Mount the inverter on the upper mounting bracket above the
wiring/disconnect box, ensuring that the inverter’s lower flange goes behind
the wiring/disconnect box. See Figure 6-4.
3. Replace the nuts that connect the inverter and the wiring/disconnect box.
Secure all nuts tightly.
4. Remove the wire nut from the PV NEGATIVE (–) wire and reconnect it to the
terminal block inside the inverter.
5. Uncap the remaining DC and AC wires and reconnect them to the terminal
blocks inside the inverter.
6. Ensure all connections are wired correctly and properly torqued according to
the values shown in Table 3-1 on page 3–5.
7. Follow the start-up procedure as described on page 4–2.
6–8 975-0245-01-01
Page 95
Identifying Error/Fault Conditions and Solutions
Identifying Error/Fault Conditions and Solutions
Most error or fault conditions will be identified by fault message screens on the
GT Inverter front panel LCD. These are described in the “Fault Mode” section on
page 5–7 of this manual. Most of these fault conditions are self-correcting and
require no user action to remedy.
See “Front Panel Display Screens and What They Mean” on page 5–3 for more
information.
Table 6-1 is intended to assist in determining fault conditions that may require
user action to remedy.
Table 6-1
Problem Possible Cause Solution
The inverter’s LEDs and display are
blank and the inverter does not
operate in sufficient sunlight.
The display reads “Inverter Offline”
and “AC Voltage Fault.”
The display reads “Inverter Offline”
with sufficient sunlight.
The display reads “Inverter Offline”
and “DC Voltage Fault” w ith
sufficient sunlight.
Troubleshooting the GT Inverter
DC/AC Disconnect Switch is off. Turn on DC/AC Disconnect Switch
Utility service panel breakers are
switched off.
AC grid voltage is not present or
incorrect.
DC breakers are switched off (if
installed), or external DC fuses are
blown (if installed).
DC array voltage is not present.
DC voltage is present but incorrect. Check DC connections at the
and breakers in the sequence
described in “Startup Procedure” on
page 4–2.
Turn on utility panel breakers.
Check AC connections at the
inverter’s terminals. Ensure AC
voltage within the range specified in
“Output” on page A–2 is present.
Turn on any DC breakers and check
any DC fuses.
Check DC connections at the
inverter’s positive and negative DC
terminals. Check for incorrectly
wired PV arrays.
inverter’s positive and negative DC
terminals. Check for incorrectly
wired PV arrays. Ensure a voltage of
195–550 VDC is present at the
inverter’s terminals.
Only the inverter RED LED is
illuminated and the display reads
“Ground Fault.”
975-0245-01-01 6–9
Ground fault condition detected on
the PV array.
The PV system should be checked
by a qualified electrician and
repaired. See Table 5-8 on page 5–7.
Page 96

6–10
Page 97

A
Specifications
Appendix A, “Specifications”, contains information about the
electrical and environmental specifications of the Xantrex Grid Tie
Solar Inverter.
The topics in this appendix are organized as follows:
• “Electrical Specifications” on page A–2
• “Environmental Specifications” on page A–6
• “Mechanical Specifications” on page A–6
Page 98

Specifications
Electrical Specifications
Input
GT2.5 GT3.0 GT3.3
Input voltage, Maximum Power Point range 195 to 550 Vdc
Absolute maximum array open circuit voltage 600 Vdc
Maximum input current 14.1 A DC 16.9 A DC 18.5 A DC
Maximum array short circuit current 24 A DC
Recommended PV array power Up to 2750 W Up to 3300 W Up to 3600 W
Reverse polarity protection Short circuit diode
Ground fault protection GF detection, I
DIF
> 1 A
Output
Model numbers
Maximum output power 2500 W AC 3000 W AC 3300 W AC 3300 W AC
Nominal output voltage 240 V 240 V 240 V 208 V
Operating range, utility
voltage (default)*
Nominal output frequency 60 Hz
Operating range, utility
frequency (default)*
Maximum continuous
output current
Output overcurrent
protection
Maximum utility backfeed
current
GT2.5-NA-DS-240
GT2.5-NA-DS-240-POS GT3.0-NA-DS-240
211 to 264 Vac 211 to 264 Vac 211 to 264 Vac 183 to 228 Vac
11.8 A 14.2 A 15.6 A 18 A
15 A RMS 20 A RMS
GT3.3-NA-DS-240
GT3.3-NA-DS-240-POS
59.3 to 60.5 Hz
0 A
GT3.3-NA-DS-208
GT3.3-NA-DS-208-POS
Total Harmonic Distortion <3% <3% <3% <3%
Power factor >0.9
Utility monitoring—
islanding protection
Output characteristics Current source
Output current waveform Sine wave
* Requires Uti lity permission and qualified service personnel to change settings.
A–2 975-0245-01-01
Vac, fac as per UL1741
Page 99

Adjustable Disconnect Settings
Islanding protection is an essential safety feature that ensures no person working
on the grid is harmed by a distributed energy source. Default software settings are
programmed into each GT Inverter at the factory to ensure it does not island
according to relevant safety regulations (UL1741, etc.).
In some instances it may be desirable from both a utility and customer point of
view to adjust these default settings. For example, the GT Inverter may experience
“nuisance trips” (taking the inverter “offline”) if the grid is weak and the voltage
falls outside the allowable range specified in the regulations. It may be difficult
for a utility to upgrade the grid to eliminate this problem. With permission from
the utility, the factory settings may be changed to allow the GT inverter to operate
over a wider grid voltage range.
These settings are password protected and should only be changed by qualified
service personnel, using a special software application provided by Xantrex.
Changing any values may compromise compliance with safety regulations. Do
not do so without first consulting with the utility and agreeing on acceptable
settings.
The default values of these settings differ from the utility specifications on
page A–2. These differences take into account the accuracy ranges listed in the
table below, and are intended to ensure that utility specifications are always met.
Electrical Specifications
Default Values
Setting
AC Low Vo ltage 186 Vac 214 Vac
AC High Vol tage 225 Vac 261 Vac
AC High Reconnection
Voltage
AC Low Frequency 59.4 Hz
AC High Frequency 60.4 Hz
Reconnect Delay 305 sec. 65 to 305 sec. ± 5 sec.
220.06 Vac 253.92 Vac
Adjustment Range Accuracy208 Vac/60 Hz 240 Vac/60 Hz
± 5 Vac ± 3 Vac
± 5 Vac ± 3 Vac
± 1 Hz ± 0.1 Hz
975-0245-01-01 A–3
Page 100

Specifications
Output Power Versus Ambient Temperature
Once the heat sink on the inverter reaches a maximum temperature limit, the GT
Inverter reduces its energy output to ensure maximum component ratings are not
exceeded.
3500.00
3000.00
GT3.3
GT3.0
GT Power Derating Curve
2500.00
2000.00
1500.00
Output Power (W)
1000.00
500.00
0.00
25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70
Figure A-1
GT2.5
195VDC
315VDC
550VDC
Ambient Temperature (ºC)
Output Power vs . Ambient Temperature at Various DC Voltages
A–4 975-0245-01-01
 Loading...
Loading...