

Content
Nave User Manual 2
Content
Foreword ................................................................................ 3
Hint ................................................................................ 3
Nave Development Team ................................................ 4
We would like to thank ................................................... 4
Introduction ............................................................................ 5
About this Manual ........................................................... 5
Symbols .......................................................................... 5
Highlighted Control Features and Parameters .................. 5
Basic Operation ..................................................................... 6
Audio Output .................................................................. 6
MIDI Input ...................................................................... 6
Preset Patch Selection ..................................................... 6
Control Elements ............................................................. 6
The Controls ........................................................................... 9
Overview of Functions .................................................... 9
The Top Section .............................................................. 9
The Wave Menu Page ................................................... 12
The Wavetable Display ................................................. 15
The Oscillator Module ................................................... 20
Filter and Envelope Menu Page (Filter & Env) ................. 24
Modulation and Keyboard Menu Page (Mod & Keys) ..... 30
Effect and Arpeggiator Menu Page (FX & Arp) ................ 38
Tape and System Menu Page (Tape & Sys) ..................... 47
Sound Synthesis Basics ..................................................... 54
Wavetable Synthesis in Nave ......................................... 54
Oscillators Introduction ................................................. 55
Filter Introduction .......................................................... 59
Appendix .............................................................................. 61
MIDI Controller Numbers .............................................. 61
Nave Modulation Sources .............................................. 61
Nave Modulation Destinations ...................................... 62
Nave Wavetable List ...................................................... 63
Knowledge about the iTunes Folder ............................... 65
Glossary ........................................................................ 66
Product Support ............................................................. 71

Foreword
3 Nave User Manual
Foreword
Thank you for purchasing the Waldorf Nave Advanced
Wavetable. You now own a synthesizer with one of the
most progressive sound synthesis. Nave raises the Wavetable synthesis to a higher sonic level which leads to
completely new and fresh sounds.
If you decide to read the following manual, we promise
you a lot of fun while reading about and working with
the Nave.
Your Waldorf Team
Hint
Waldorf Music GmbH is not liable for any erroneous
information contained in this manual. The contents of
this manual may be updated at any time without prior
notice. We made every effort to ensure the information
herein is accurate and that the manual contains no contradictory information. Waldorf Music GmbH extends no
liabilities in regard to this manual other than those required by local law.
This manual or any portion of it may not be reproduced
in any form without the manufacturer’s written consent.
Waldorf Music GmbH, Landskroner Straße 52, D-53474
Bad Neuenahr, Germany

Foreword
Nave User Manual 4
Nave Development Team
Software: Stefan Stenzel,
Rolf Wöhrmann
Design: Axel Hartmann
Manual: Holger Steinbrink
Version: 1.0, June 2013
w Please visit our website www.waldorfmusic.de
Here you will find information of all our products.
We would like to thank
Christian Bacaj, Karsten Dubsch, Willie Eckl, Joachim
Flor, Michael von Garnier, Frédéric Meslin, Frank
Schneider, Kurt "Lu" Wangard,
吴海彬.
Introduction
5 Nave User Manual
Introduction
About this Manual
This manual was written to help you to become familiar
with the Nave synthesizer. It will also aid experienced
users with routine tasks.
To avoid confusion, the terminology in this manual is
based on the Nave parameter names. You will find the
various terms explained in a glossary at the end of this
manual.
We also used a uniform set of symbols to show you topics of particular interest or significance. Important terms
are highlighted in bold letters.
Symbols
m Caution – The comments that follow this symbol
will help you avoid errors and malfunctions.
w Info – Additional information on a given topic.
✻ Example – Real-world examples to try out.
Highlighted Control Features and Parameters
All of the Nave’s buttons, controls and parameters are
highlighted in bold letters throughout the manual.
example:
• Tip on Mod Source
• Tip and hold the Cutoff dial
The Nave’s different parameter pages are illustrated in a
depiction of the display.

Basic Operation
Nave User Manual 6
Basic Operation
Audio Output
Use the volume buttons of your iPad to control the overall level. We recommend to use a suited Class Compliant
Audio interface, a headphone or a connected amplifier /
loudspeaker system to receive the best sound quality.
MIDI Input
Nave can be played via the internal keyboard. We
recommend to connect a suited MIDI keyboard via a
Core MIDI iPad interface. You can also send MIDI data
via WIFI MIDI as well as a virtual MIDI connection.
Please read more in the chapter "Tape & Sys Menu Page".
w By using the iPad Camera Connection Kit you can
also connect USB Class Compliant keyboards as
the Waldorf Blofeld Keyboard or the Zarenbourg.
Preset Patch Selection
Tap on the name of a preset in the center of the Nave
Top section to open the Preset list. Here you can choose
your favorite Bank as well as the included Patches. Additionally you can filter sounds by category.
w More about loading and saving of Patches can be
found on page 10 of the manual.
Control Elements
To edit a sound patch you have to change its parameters.
Therefore, Nave offers different types of control elements:
Dials
To set a value, tap on the dial, hold down and
drag your finger up or down.
Buttons
A simple tap on a button activates or deactivates
its function. Buttons light up in blue when they
have been used.

Basic Operation
7 Nave User Manual
Pop-up Menus
Tap on the corresponding parameter to open a pop-up menu where
you can choose the desired option
by tapping. Tap on Close to close
the pop-up menu.
Fader
Tap on the corresponding fader and hold it. Move
your finger to the left or the right to change the
value. Some faders need to move vertically to
change values.
Selection Symbols
Selection symbols can be easily tapped.
The corresponding symbol lits, when activated. Tapping on another symbol deactivates the first selected. The Filter and Drive
types can be deactivated by tapping again.
Switches
Switches can be simply tapped. The switch of
the corresponding function switches to the
respective position. Keep in mind that some
switches can have up to three positions.
Graphical Elements
Tap on the corresponding graphic and slide it vertical or horizontal to change values. This is
valid for the 3D representation
of the wavetables, the envelopes, the filter graph as well as
the equalizer.
Nave User Manual 8
Wheels
To change the value, tap on the
wheel and drag it up or down. The
Pitch bend wheel snaps
automatically back into its center
position as soon as you release your
finger.
The Virtual Keyboard
Nave provides a virtual keyboard with 77 keys. Tap on a
key to hear the corresponding note. The vertical position
of the initial touchdown of the key determines the velocity. You can also use different play modes. Please read
more about this on page 35 of this manual.
X-Y Pad
Tap on the illuminated button
within the X-Y pad and move your
finger. A double tap will center the
button exactly in the middle of the
pad. A single tap on any position
within the pad will set the button to
this position.
Additional Controls
Double tap a parameter to open an additional window.
The corresponding parameter can be routed to incoming
MIDI controller data. You can also set the parameter to
its default value (Default Value) or cancel the process
(Cancel).
w Routed MIDI controller can be checked and dele-
ted with the MAP parameter on the Tape & Sys
menu page.

The Controls
9 Nave User Manual
The Controls
Overview of Functions
Nave consists of numerous sound-shaping components.
w Is this your first synthesizer? Are you curious
about sound synthesis? If so, we recommend to
read the chapter "Sound Synthesis Basics" in this
manual.
You should know that Nave consists of two different
types of components for sound generation and sound
shaping:
• Sound synthesis: (Wavetable-)Oscillator, Filter,
Amplifier, Effects: These modules represent the audio
signal flow. Sound generation actually occurs within
the Oscillator. It produces wavetables and other
waveforms. The Filter then shapes the sound by
amplifying (boosting) or attenuating (dampening)
certain frequencies. The Amplifier is located at the
end of the signal chain. It setss the overall volume of
the signal and can add some saturation. Additionally,
effects can be added to the signal.
• Modulators: The Modulators are designed to manipu-
late or modulate the sound generating components to
add dynamics to the sound. The Low-frequency Oscillators (LFO) are designed for periodic or recurring
modulations while the Envelopes are normally used
for modulations that occur once.
The Top Section
The Top section provides the global overview and includes the following options:
Menu Page Selection
Tap on the desired menu page (Wave, Filter & Env,
Mod & Keys, FX & Arp or Tape & Sys) to open it. The
actual menu page will be shown with a blue selection.
Preset Selection
Tap on the Preset name to open the preset pop-up menu.
Here you find three columns for selection sound (Bank),
sound categories (Category) and Patches.
• Tap on the desired bank. The patch list will be up-
dated automatically with the included sounds.

The Controls
Nave User Manual 10
• Tap on the desired sound category. The patch list
automatically shows all sounds which belong to this
category. To set back the category list tap on --- all ---.
• Tap on the desired patch to load it.
The right section of this window offers additional functions:
w Some patch functions are only available for User
patches and User banks.
• Rename Patch (only for User patches) opens the input
keyboard to rename the actual patch.
• Delete Patch (only for User patches) deletes the actual patch after a security confirmation.
• Email Patch (only for User patches) opens the standard email editor. Here you can send the actual
patch to a desired email adress.
• Import Patch imports a patch from your iTunes Folder
to Nave. A separate selection window opens automatically to proceed.
w A deeper explanation of the iTunes Folder can be
found in the manual appendix.
• New Bank creates a new bank with the standard
name "User (number)".
• Rename Bank (only for User banks) opens the input
keyboard to rename the actual bank.
• Delete Bank (only for User banks) deletes the actual
bank with all included patches after a security confirmation.
• Email Bank (only for User patches) opens the standard
email editor. Here you can send the actual bank to a
desired email adress.
Tap on Close at the bottom of the window to close it.
Compare
Tap on Compare to compare the actual edited patch
with the original one (the Compare button will lit, when
activated). Tap the button to deactivate the compare
function.
The Save Function for Patches
Tap on Save to save the actual patch:
• Tap on the patch name to change it before finally
saving the patch.

The Controls
11 Nave User Manual
• Tap on a Bank name to allocate the patch to this
bank.
• Tap on Category to allocate the patch to a desired
sound category.
• Tap on Save to finally save the patch.
• Tap on Cancel to cancel the process.
w You can transfer User patches and banks from
your iPad to your computer and vice versa by
using the iTunes Folder. A deeper explanation of
the iTunes Folder can be found in the manual appendix.
Init
Tap on Init to initialize the actual patch. All parameters
will be set to default values. To avoid accidently initialization you have to confirm this process before.
The Controls
Nave User Manual 12
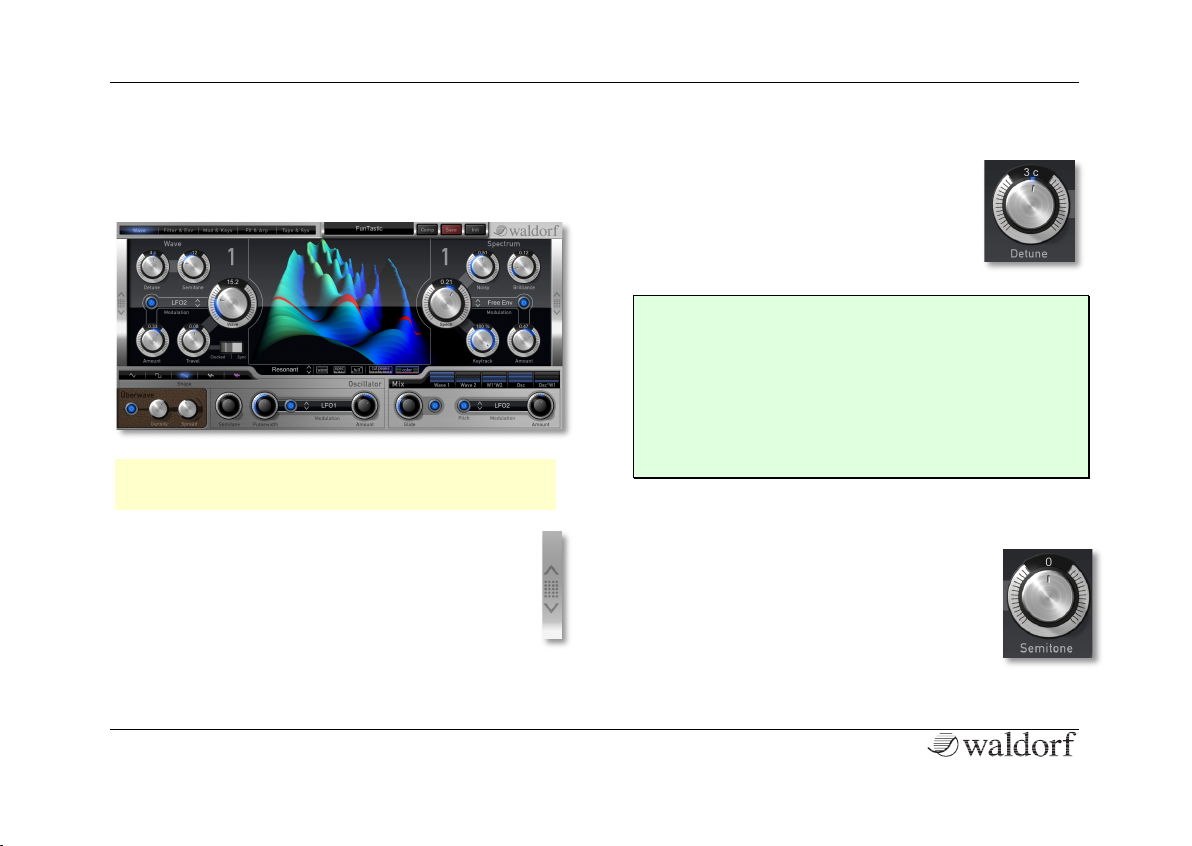
The Wave Menu Page
This is the heart of Nave. Nave offers two Wave modules
as well as an Oscillator module with up to eight oscillators.
w An explanation of wavetable synthesis can be
found in the chapter "Sound Synthesis Basics".
Use the slip field to the left and right side of the
Wave menu page to switche between Wave module
1 and 2. The number above the Wave and Spectrum
parameter shows the selected wave module.
Detune -50c...+50c
Fine-tunes the oscillator in steps of
1/100th of a semitone. The audible result
of detuned oscillators is a chorus or flanger effect. Use a positive setting for one
oscillator and an equivalent negative
setting for another
✻ A low value of ±1 results in a slow and soft flanger
effect.
✻ Mid-ranged settings of ±5 are perfect for pads and
other fat sounding programs.
✻ High values of ±12 or above will give a strong
detune that can be used for accordions or effect
sounds.
Semitone -24...+24
Sets the pitch of the wavetable oscillator in
semitone steps. The standard setting for this
parameter is 0, but there are cases where
different values are interesting as well.
The Controls
13 Nave User Manual
✻ Organ sounds often include a fifth, therefore one
oscillator’s semitone parameter must be set to +7.
✻ Lead and Solo sounds might sound interesting when
you set one Oscillator to a fourth (+5 semitones).
✻ When making ring modulated sounds, try to use
dissonant values, e.g. +6 or +8.
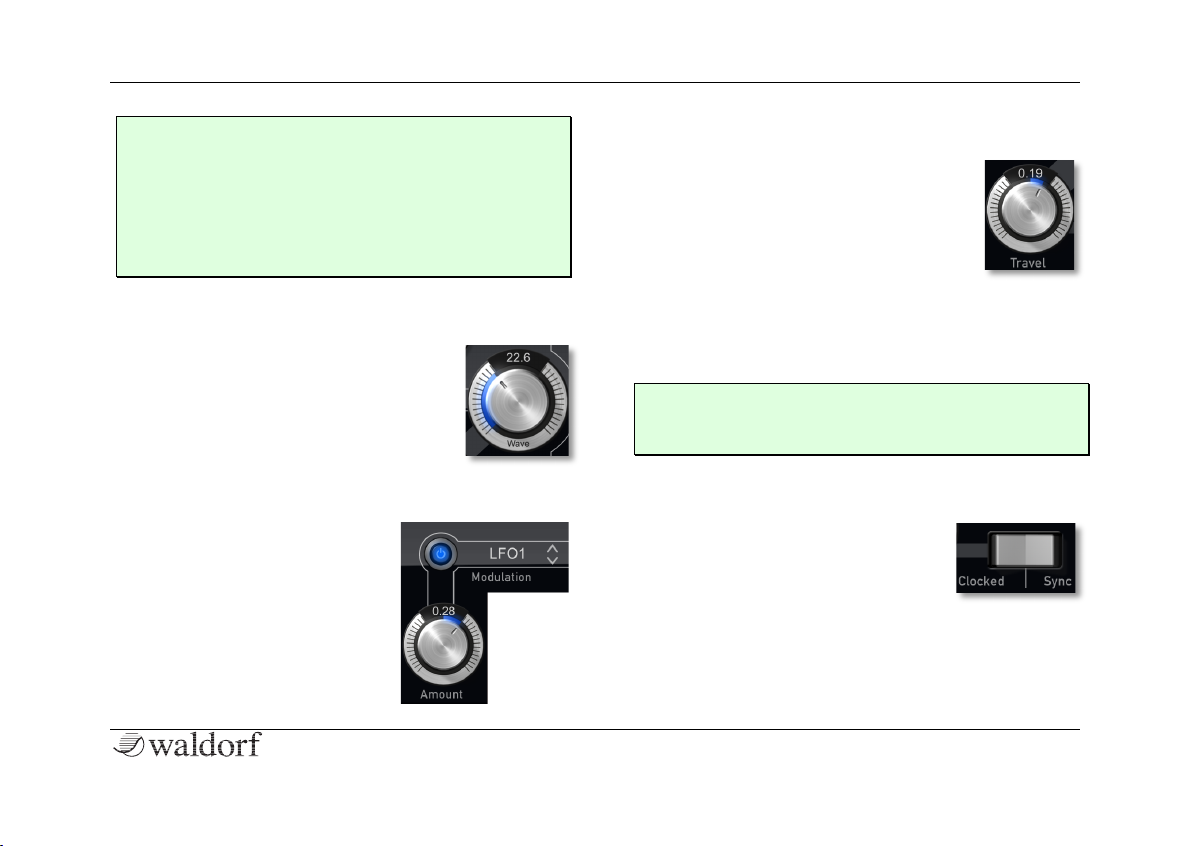
Wave 0.0...64.0
This parameter defines the startpoint of the
selected wavetable. A setting of 0 selects
the first wave, the maximum setting selects the last wave of the wavetable. The
actual wave position will be marked as a
thin red line within the display.
Wave Modulation diverse functions
Activate this parameter by tapping
on the button. Then select a Wave
modulation source by tapping on
the Modulation list. Amount
determines the amount of modulation that is applied. A common
source for Wave modulation is an
LFO or an envelope.
Travel -1.00...+1.00
Travel allows the cyclic moving through a
wavetable. Positive values allow a forward
movement, negative values a backward
movement. Lower values slow down the
movement speed, higher values speed it
up. Cyclic means, that a wavetable starts
automatically again from beginning when the end is
reached. If you don’t wish a cyclic modulation, use the
Wave parameter modulated with an envelope, a LFO or
any other modulation source.
✻ Use Travel with a value setting of 0.20 to become
an impression of the sound diversity of the wavetables.
Clocked / Sync
Here you can set up the synchronisation of the Travel parameter:
• There is no synchronisation in
the center setting (off).
• If Clocked is activated, Travel is controlled by the
internal tempo of Nave (adjustable with Arpeggiator
Speed on the FX & Arp menu page) or an inco-

The Controls
Nave User Manual 14
ming synchronisation signal by another App, MIDI
or WIST. If so, you can set up Travel in musical values. The highest amount is 1024, where one turn
needs 1024 beats. Keep in mind that Travel can
have positive or negative values. If Clocked is active, Travel reacts also as described below (Sync).
• If Sync is activated, all triggered notes of a patch
behave as a single triggered note. Travel is started
simultaneously for all triggered notes.
Wavetable Selection diverse Wavetables
Tap on the wavetable name to
open a pop-up menu with all
available factory wavetables
as well as your own custom wavetables. Here you can
select the desired wavetable by tapping. Subsequently
tap on Close to close the pop-up menu.
w A list of all Nave wavetables can be found in the
Appendix of this manual.
The Spectrum Section
Here you find novel functions regarding the wavetable
sound editing. The spectral envelope of a sound can be
controlled independant from the pitch. Further the Wave
oscillator can produce perfect a periodic sound up to
noisy components.
Spectrum -1.00...+1.00
This parameter transposes the spectrum
of a sound, specifically the spectral
envelope. Negative values move the
spectrum down, higher values moves it
up. The default setting is 0, where no
transposition happens. This is the
behaviour of the classic wavetable synthesis.
Spectrum Modulation diverse functions
Activate this parameter by tapping
on the button. Then select a Spectrum modulation source by tapping
on the Modulation list. Amount
determines the amount of modulation that is applied to the transposition of the spectrum.
The Controls
15 Nave User Manual
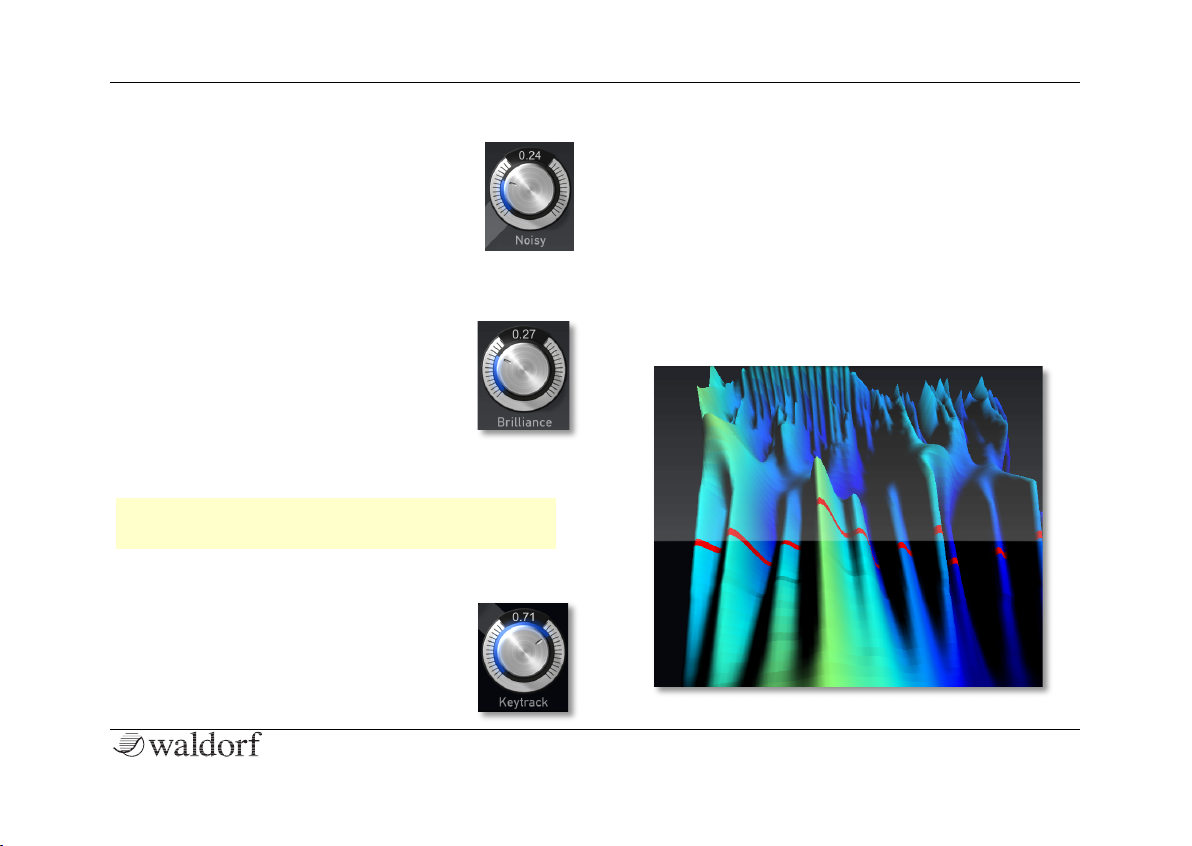
Noisy 0.00...1.00
This parameter adds a noisy sound character
to the Wave oscillator. The spectrum is
unaffected by the setting of this parameter.
Brilliance 0.00...1.00
A setting of this parameter is only audible,
when Spectrum is transposed relative to
the original pitch of a sound. Higher
settings result in narrow peaks. This can
lead to the effect, that the perceived pitch
comes from the sound spectrum instead of
the oscillators pitch. Sometimes value changes of this
parameter are partially subtle.
w You can modulate Noisy and Brilliance. Please
use the modulation matrix (see page 32).
Keytrack 0%...100%
The default setting is 100%, so that the
spectrum is in conjunction with the pitch of
a sound. The pitch doesn’t affect the
spectrum, when Keytrack is set to 0%. This
setting is recommend for speech or singing, so that the
formants are not influenced by the pitch. Based on this,
we have included a speech synthesizer for wavetables.
Keytrack can also be set to other values, so that the
spectrum is transposed to the pitch.
The Wavetable Display diverse functions
The Wavetable display shows a 3D representation of the
selected wavetable. The position of the Wave parameter
is shown by a thin red line.

The Controls
Nave User Manual 16
You can use the following gestures:
• Tap with one finger on the display and move it into
the corresponding direction to turn the wavetable
representation in all three dimensions.
• Move two fingers together or apart to decrease or
increase the 3D representation.
• Double tap leads to the initial dimension and position of the representation.
• Tap with a spread thumb and index finger on the
representation and twist it to rotate the display.
The Wavetable display offers some additional functions:
w Now you go down to the basic of the wavetable
synthesis where you can also create own wavetables.
• Tap on the Wave button to open a window with
additional presentation options for the wavetable
representation.
• Tap on the Spec button to open a window with
additional presentation options for the spectrum representation.
• Tap on the full button to open the wavetable re-
presentation in fullscreen mode. Read more about
this on the following pages.
• Tap on cut peaks to open a fader for smoothening
the peaks in the representation.
• Tap on color to open a fader for colouring the
peaks in the representation more intensively.
The wavetable display offers a fullscreen mode (full
button).
The Controls
17 Nave User Manual
Beside the additional representation options there are
more interesting functions:
m Pay attention! You have now entered the most
creative section of Nave!
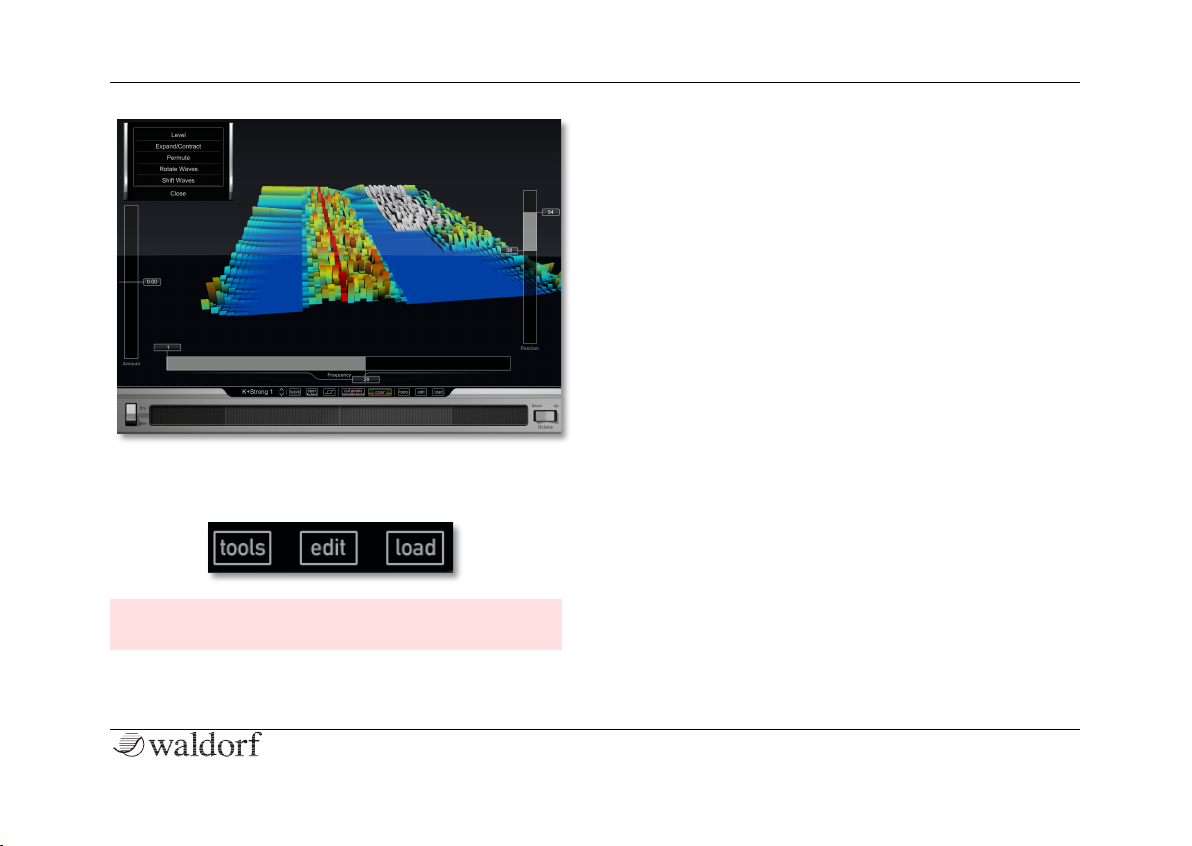
The Tools Buttons
Tap on tools to open a pop-up menu for creating and
exporting your own wavetables. The following options
are available:
• Talk allows you to enter one or more words with
the virtual input keyboard of your iPad. These
words will be automatically synthesized as a new
wavetable.
• Analyze Audio from: enables you to select and im-
port a WAV file with any sample rate and bit rate
from the Beatmaker pasteboard (BM Pasteboard),
the Sonoma pasteboard (Sonoma Pasteboard) or
your iTunes Folder. This audio file will be automatically synthesized as a new wavetable.
• Export Wavetable exports the current wavetable to
your iTunes Folder. This enables you to exchange
your own created wavetables with other Nave
users. By using Rename you can rename your
wavetable before the export process. A deeper explanation of the iTunes Folder can be found in the
manual appendix.
The Controls
Nave User Manual 18
The Edit Button
Tap on edit to open the Edit section of the wavetable
display. The following options and functions are available:
The Ribbon Band
The Ribbon Band easily enables you to play and hear the
current wavetable.
• Move your finger from left to right on the center
section of the Ribbon band to go forward through
the wavetable. Moving your finger from right to left
plays the wavetable backwards.
• Tap on any location of the center section of the
Ribbon band to play the corresponding single
wave.
w The last selected wavetable position on the Rib-
bon band will be automatically assigned to the
Wave parameter when the editor is closed.
• Tap on the right section of the Ribbon band to start
the Travel function. The more right you tap, the more faster the wavtable will be go through forward.
• Tap on the left section of the Ribbon band to start
the Travel function. The more left you tap, the more
faster the wavetable will be go through backwards.
• By using the Dry / Wet switch you can hear the
wavetable without any other oscillator, filter, drive
and effects (Dry).
• The Octave Down/ Up button sets the playback
signal of the Ribbon band one octave up or down
with any tap.
3D Editing with the Selection Sliders
In the Edit section you can use three sliders to edit the
spectrum of the current wavetable in a 3D space. This
gives you unlimited sound changing possibilities.
• Use the Frequency slider to select a frequency
area. Tap on front or the back section of the slider
to limit the frequency area. Tap on the middle section of the slider to move the selected frequency
area at once.

The Controls
19 Nave User Manual
• Use the Position slider to select a wavetable area
for editing. Tap on front or the back section of the
slider to limit the wavetable area. Tap on the middle section of the slider to move the selected frequency area at once.
• The Amount slider allows you a direct access to
the spectrum of the selected area of the wavetable.
You can perform positive or negative changes.
The pop-up menu in the topleft area offers some remarkable edit options for the wavetable spectrum:
• Level changes the level of the selected area.
• Expand/Contract works nearly similar as contrast
setting. A positive amount increases louder parts
and increases lower part. With a negative amount
all levels draw closer to the average level.
• Permute re-arranges the spectral components of the
selected area up to progressive chaos.
• Rotate Waves moves the spectrum of the selected
area in a cyclic way. The part that leaves the one
end will be pushed back at the other end.
• Shift Waves moves the spectrum of the selected
area to a new position. In opposite to Rotate, the
level of the pushed back spectrum is 0.
• Rotate Partials moves the spectrum of the selected
area to a new position of the frequency axis. The
parts that leave the one end will be pushed back at
the other end.
• Shift Partials moves the spectrum of the selected
area to a new spectral position. In opposite to Rota-
te, the level of the pushed back spectrum is 0.
• Gyrate rotates the selected area.
• Random mixes random values in the selected area.
w Sequentially changes of different areas and diffe-
rent edit options will be add up.
The Load Button
Tap on load to load a wavetable from your iTunes Folder
in the Editor. A deeper explanation of the iTunes Folder
can be found in the manual appendix.
To leave the fullscreen mode just tap on the
windows symbol or the Wave menu button.

The Controls
Nave User Manual 20
The Oscillator Module
Beside the Wave modules, Nave offers an additional
Oscillator module to create typical analog waveforms.
w You can use this additional oscillator as sub oscil-
lator in addition to the wavetable oscillators.
Shape Tri/ Pulse/ Saw/ Noise Types
Tap on the corresponding symbol to select the desired
waveform. The following waveforms are available:
• Triangle selects the triangle waveform. The triangle
mainly consists of the odd harmonics with very low
magnitudes.
• Pulse selects the pulse waveform. A pulse waveform with a pulse width of 50% has only the odd
harmonics of the fundamental frequency present.
This waveform produces a hollow / metallic sound.
If the Pulse waveform is selected, the parameter
Pulsewidth is used to change the pulsewidth of the
waveform.
• Saw selects the sawtooth waveform. A Sawtooth
wave has all the harmonics of the fundamental frequency in descending magnitude.
• White Noise is a fundamental source for any kind of
analog-type percussion. It offers the same level over
the complete frequency range. Also, wind and other
sound effects can be created by using noise.
• Pink Noise – This special kind of noise produces
higher levels in the deeper frequency range. It matches more with the human hearing as the unfiltered
white noise.
The Controls
21 Nave User Manual
Überwave Active On/ Off
Activates the Überwave function. This module can generate up to 8 oscillator signals simultaneously (only with
selected triangle, pulse or sawtooth shapes)
Überwave Density 0...8
Determines the number of played oscillators, when
Überwave is activated.
Überwave Spread 0.00...1.00
Detunes the oscillators, when Überwave is activated.
Semitone -24...+24
Sets the pitch of the oscillator in semitone
steps. The standard setting for this parameter is
0, but there are cases where different values
are interesting as well, e.g. with values of -12
or -24 you can use the oscillator as a sub
oscillator.
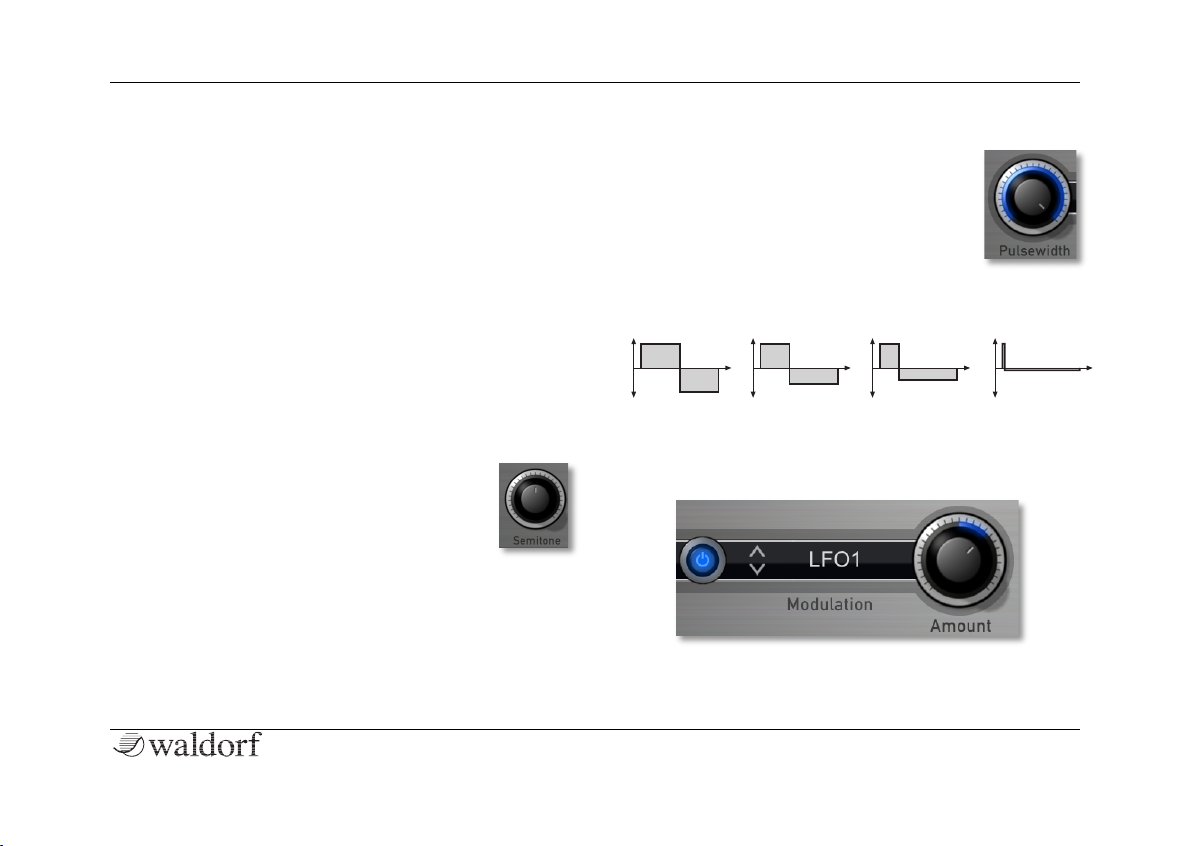
Pulsewidth 0.01%...50%
Sets the pulse width of the Pulse waveform
(when selected). The minimal value is
equivalent to a pulse ratio of <1%, the
maximum value is equivalent to 50%
(square wave). Other values creates asymetric square waves which contain equal
harmonics with different levels. The following picture
illustrates the effect of the pulsewidth parameter:
Pulsewidth Modulation diverse functions
Activate this parameter by tapping on the button. Then
select a modulation source by tapping on the Modulati-
!"#$%&'()*+&,-.
/01"23%4
!"#$%&'()*+&55. !"#$%&'()*+&6,. !"#$%&'()*+&78.
/9:;"#$%4
The Controls
Nave User Manual 22
on list. Amount determines the amount of modulation
that is applied. Common sources for pulsewidth modulations are a LFO or an envelope.
✻ To create a thick oscillator sound, use a triangular
LFO as Modulation Source with full Amount and
a Pulsewidth of around 40. This basic setting is
useful for very big string and lead sounds.
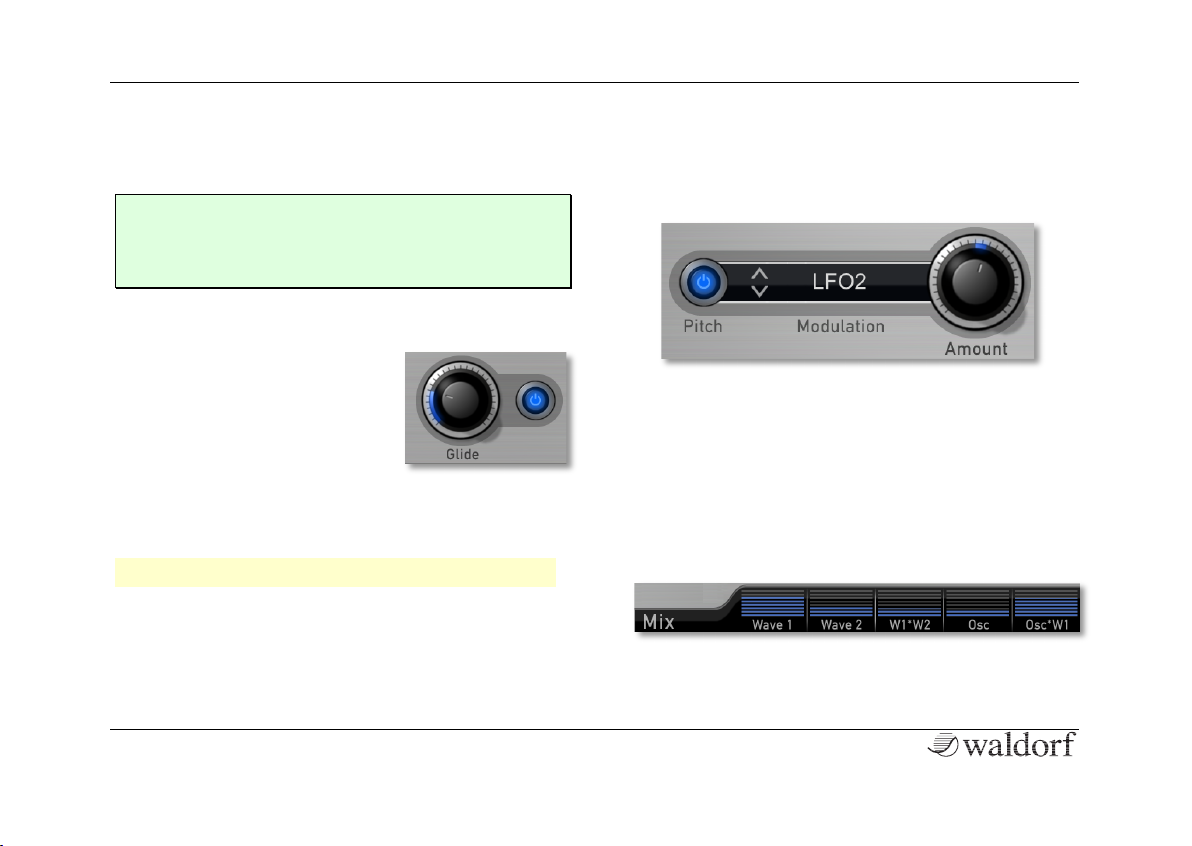
Glide diverse functions
Enables or disables the Glide
effect. "Glide" or "Portamento"
describes the continuous gliding
from one note to another. This
effect can be created on fretless
stringed instruments or some brass
instruments (e.g. trombone). It is very common on synthesizers and used throughout all music styles. Please
note that Glide affects the pitch of all oscillators.
w Glide works only with legato played notes.
Activate this parameter by tapping the corresponding
button. Use Glide to determine the glide time. Low values will give a short glide time in a range of milliseconds
that gives a special character to the sound. High values
will result in a long glide time of up to several seconds
which can be useful for solo and effect sounds.
Pitch Modulation diverse functions
Selects the source of the pitch modulation for all oscillators. Activate this parameter by tapping on the button.
Then select a modulation source by tapping on the Mo-
dulation list. Amount determines the amount of modulation that is applied. A common source for pulswidth
modulation is an LFO.
Mix diverse functions
The different Mix faders control the volume of each module as well as the ring modulation levels.
 Loading...
Loading...