Page 1

VMware vSphere
Replication
Administration
vSphere Replication 8.1
Page 2

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
You can find the most up-to-date technical documentation on the VMware website at:
https://docs.vmware.com/
If you have comments about this documentation, submit your feedback to
docfeedback@vmware.com
VMware, Inc.
3401 Hillview Ave.
Palo Alto, CA 94304
www.vmware.com
Copyright © 2012–2018 VMware, Inc. All rights reserved. Copyright and trademark information.
VMware, Inc. 2
Page 3

Contents
vSphere Replication Administration 6
Overview of VMware vSphere Replication 7
1
Contents of the vSphere Replication Appliance 8
Site Recovery Client Plug-In 8
Local and Remote Sites 9
How vSphere Replication Works 10
Replication Data Compression 13
vSphere Replication System Requirements 16
2
vSphere Replication Licensing 16
vSphere Replication Network Ports 17
Operational Limits of vSphere Replication 17
Compatibility of vSphere Replication with Other vSphere Features 18
vSphere Replication Compatibility with Other Software 19
Bandwidth Requirements for vSphere Replication 19
Installing and Uninstalling vSphere Replication 22
3
Install vSphere Replication 23
Uninstall vSphere Replication 31
Unregister vSphere Replication from vCenter Server If the Appliance Was Deleted 32
Configuring the Customer Experience Improvement Program 34
4
Categories of Information That VMware Receives 34
Join or Leave the Customer Experience Improvement Program in the vSphere Web Client 34
Isolating the Network Traffic of vSphere Replication 35
5
Set Up a VMkernel Adapter for vSphere Replication Traffic on a Source Host 36
Set Up a VMkernel Adapter for vSphere Replication Traffic on a Target Host 37
Create a VM Network Adapter to Use for Incoming Replication Traffic on the Combined
vSphere Replication Appliance 38
Create VM Network Adapters to Isolate the Network Traffic of a vSphere Replication Server 39
Deploying Additional vSphere Replication Servers 41
6
Deploy an Additional vSphere Replication Server 41
Register an Additional vSphere Replication Server 42
Replication Server Connection States 43
Reconfigure vSphere Replication Server Settings 43
VMware, Inc.
3
Page 4

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Unregister and Remove A vSphere Replication Server 45
Disable the Embedded vSphere Replication Server 45
Upgrading vSphere Replication 47
7
Order of Upgrading vSphere and vSphere Replication Components 48
Upgrade Additional vSphere Replication Servers 48
Upgrade the vSphere Replication Appliance 50
Upgrade vSphere Replication 8.0 to Version 8.1 52
Update the vCenter Server IP Address in the vSphere Replication Management Server 54
Reconfigure the vSphere Replication Appliance 55
8
Reconfigure General vSphere Replication Settings 56
Change the SSL Certificate of the vSphere Replication Appliance 57
Change the Password of the vSphere Replication Appliance 60
Change the Keystore Passwords of the vSphere Replication Appliance 61
Change the Truststore Passwords of the vSphere Replication Appliance 62
Configure vSphere Replication Network Settings 63
Configure vSphere Replication System Settings 64
Update the NTP Server Configuration 65
Reconfigure vSphere Replication to Use an External Database 66
Use the Embedded vSphere Replication Database 69
vSphere Replication Roles and Permissions 71
9
vSphere Replication Roles Reference 71
Assign vSphere Replication Roles to Users 74
Assign VRM Replication Viewer Role 74
Assign VRM Virtual Machine Replication User Role 75
Assign VRM Virtual Machine Recovery User Role and Perform a Recovery Operation 75
Clone Existing VRM Administrator Role and Modify Privileges 76
Replicating Virtual Machines 77
10
How the Recovery Point Objective Affects Replication Scheduling 78
How the 5 Minute Recovery Point Objective Works 78
How Retention Policy Works 79
Replicating a Virtual Machine and Enabling Multiple Point in Time Instances 80
Using vSphere Replication with vSAN Storage 81
Using vSphere Replication with vSphere Storage DRS 83
How vSphere Replication Synchronizes Data Between vCenter Server Sites During Initial
Configuration 83
Replicating Virtual Machines Using Replication Seeds 85
Replicating a Virtual Machine in a Single vCenter Server Instance 85
Best Practices for Using and Configuring vSphere Replication 85
VMware, Inc. 4
Page 5

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Configure Replication 87
Move a Replication to a New vSphere Replication Server 89
Stop Replicating a Virtual Machine 89
Reconfiguring Replications 91
Monitoring and Managing Replications in vSphere Replication 95
11
Monitor Replication for Virtual Machines 95
View Replication Reports for a Site 97
Identifying Replication Problems 99
Manage vSphere Replication Connections 99
Manage vSphere Replication Servers 100
Performing a Recovery with vSphere Replication 102
12
Recover Virtual Machines with vSphere Replication 102
Failback of Virtual Machines in vSphere Replication 104
Troubleshooting vSphere Replication 105
13
Generate vSphere Replication Support Bundle 105
vSphere Replication Events and Alarms 106
Solutions for Common vSphere Replication Problems 110
VMware, Inc. 5
Page 6

vSphere Replication Administration
vSphere Replication Administration provides information about installing, configuring, and using
VMware vSphere Replication.
Intended Audience
This information is intended for anyone who wants to protect the virtual machines in their virtual
infrastructure by using vSphere Replication. The information is written for experienced Windows or Linux
system administrators who are familiar with virtual machine technology and data center operations.
VMware, Inc. 6
Page 7
Overview of
VMware vSphere Replication 1
VMware vSphere Replication is an extension to VMware vCenter Server that provides a hypervisor-based
virtual machine replication and recovery.
vSphere Replication is an alternative to storage-based replication. It protects virtual machines from partial
or complete site failures by replicating the virtual machines between the following sites:
n
From a source site to a target site
n
Within a single site from one cluster to another
n
From multiple source sites to a shared remote target site
vSphere Replication provides several benefits as compared to storage-based replication.
n
Data protection at a lower cost per virtual machine.
n
A replication solution that allows flexibility in the storage vendor selection at the source and target
sites.
n
Lower overall cost per replication.
You can use vSphere Replication with the vCenter Server Appliance or with a standard vCenter Server
installation. You can have a vCenter Server Appliance on one site and a standard vCenter Server
installation on the other.
With vSphere Replication, you can replicate virtual machines from a source data center to a target site
quickly and efficiently.
You can deploy additional vSphere Replication servers to meet your load balancing needs.
After you set up the replication infrastructure, you can choose the virtual machines to be replicated at a
different recovery point objective (RPO). You can enable the multi-point-in-time retention policy to store
more than one instance of the replicated virtual machine. After recovery, the retained instances are
available as snapshots of the recovered virtual machine.
You can use VMware vSAN datastores as target datastores and choose destination storage profiles for
the replica virtual machine and its disks when configuring replications.
Note vSAN is a fully supported feature of vSphere 5.5 Update 1 and later.
You can configure all vSphere Replication features in the vSphere Web Client. You can manage sites
monitor the status of a replication through the replication management and monitoring dashboard.
VMware, Inc.
7
Page 8

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
n
Contents of the vSphere Replication Appliance
The vSphere Replication appliance provides all the components that vSphere Replication requires.
n
Site Recovery Client Plug-In
The vSphere Replication appliance adds a plug-in to the vSphere Web Client and vSphere Client.
The plug-in is also shared with Site Recovery Manager and is named Site Recovery.
n
Local and Remote Sites
In a typical vSphere Replication installation, the local site provides business-critical data center
services. The remote site is an alternative facility to which you can migrate these services.
n
How vSphere Replication Works
With vSphere Replication, you can configure the replication of a virtual machine from a source site to
a target site, monitor and manage the status of the replication, and recover the virtual machine at the
target site.
n
Replication Data Compression
You can configure vSphere Replication to compress the data that it transfers through the network.
Contents of the vSphere Replication Appliance
The vSphere Replication appliance provides all the components that vSphere Replication requires.
n
Site Recovery user interface that provides full functionality for working with vSphere Replication.
n
A plug-in to the vSphere Web Client and vSphere Client that provides a user interface for
troubleshooting vSphere Replication health status and links to the Site Recovery standalone user
interface.
n
An embedded database that stores replication configuration and management information.
n
A vSphere Replication management server:
n
Configures the vSphere Replication server.
n
Enables, manages, and monitors replications.
n
Authenticates users and checks their permissions to perform vSphere Replication operations.
n
A vSphere Replication server that provides the core of the vSphere Replication infrastructure.
The vSphere Replication appliance provides a virtual appliance management interface (VAMI). You can
use the VAMI to configure the appliance after deployment. For example, you can use the VAMI to change
the appliance security settings, change the network settings, or configure an external database. You can
deploy additional vSphere Replication Servers using a separate .ovf package.
Site Recovery Client Plug-In
The vSphere Replication appliance adds a plug-in to the vSphere Web Client and vSphere Client. The
plug-in is also shared with Site Recovery Manager and is named Site Recovery.
VMware, Inc. 8
Page 9
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
You use the Site Recovery client plug-in to perform all vSphere Replication actions.
n
View the vSphere Replication status for all vCenter Server instances that are registered with the
same vCenter Single Sign-On.
n
Open the Site Recovery user interface.
n
View a summary of the replication configuration parameters on the Summary tab of virtual machines
that are configured for replication.
n
Reconfigure the replications of one or more virtual machines by selecting the VMs and using the
context menu.
Note Site Recovery user interface opens in a new browser tab.
Local and Remote Sites
In a typical vSphere Replication installation, the local site provides business-critical data center services.
The remote site is an alternative facility to which you can migrate these services.
The local site can be any site where vCenter Server supports a critical business need. The remote site
can be in another location, or in the same facility to establish redundancy. The remote site is usually
located in a facility that is unlikely to be affected by environmental, infrastructure, or other disturbances
that might affect the local site.
vSphere Replication has the following requirements for the vSphere® environments at each site:
n
Each site must have at least one data center.
n
The remote site must have hardware, network, and storage resources that can support the same
virtual machines and workloads as the local site.
n
The sites must be connected by a reliable IP network.
n
The remote site must have access to networks (public and private) comparable to the ones on the
local site, although not necessarily the same range of network addresses.
Connecting Local and Remote Sites
Before you replicate virtual machines between two sites, you must connect the sites. When connecting
sites, users at both sites must have the VRM remote.Manage VRM privilege assigned.
When you connect sites that are part of the same vCenter Single Sign-On domain, you must select the
remote site only, without providing authentication details, because you are already logged in.
VMware, Inc. 9
Page 10

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
When you connect sites that belong to different vCenter Single Sign-On domains, the
vSphere Replication Management Server must register with the Platform Services Controller on the
remote site. You must provide authentication details for the remote site, including IP or FQDN of the
server where Platform Services Controller runs, and user credentials. See Configure vSphere Replication
Connections.
After connecting the sites, you can monitor the connectivity state between them in the Site Recovery user
interface.
How vSphere Replication Works
With vSphere Replication, you can configure the replication of a virtual machine from a source site to a
target site, monitor and manage the status of the replication, and recover the virtual machine at the target
site.
When you configure a virtual machine for replication, the vSphere Replication agent sends changed
blocks in the virtual machine disks from the source site to the target site. The changed blocks are applied
to the copy of the virtual machine. This process occurs independently of the storage layer.
vSphere Replication performs an initial full synchronization of the source virtual machine and its replica
copy. You can use replication seeds to reduce the network traffic that is generated by data transfer during
the initial full synchronization.
During replication configuration, you can set a recovery point objective (RPO) and enable retention of
instances from multiple points in time (MPIT).
As administrator, you can monitor and manage the status of the replication. You can view information for
forward and reverse replications, local and remote site status, replication issues, and for warnings and
errors.
When you manually recover a virtual machine, vSphere Replication creates a copy of the virtual machine
connected to the replica disk, but does not connect any of the virtual network cards to port groups. You
can review the recovery and status of the replica virtual machine and attach it to the networks. You can
recover virtual machines at different points in time, such as the last known consistent state.
vSphere Replication presents the retained instances as ordinary virtual machine snapshots to which you
can revert the virtual machine.
vSphere Replication stores replication configuration data in its embedded database. You can also
configure vSphere Replication to use an external database.
You can replicate a virtual machine between two sites. vSphere Replication is installed on both source
and target sites. Only one vSphere Replication appliance is deployed on each vCenter Server. You can
deploy additional vSphere Replication Servers.
VMware, Inc. 10
Page 11
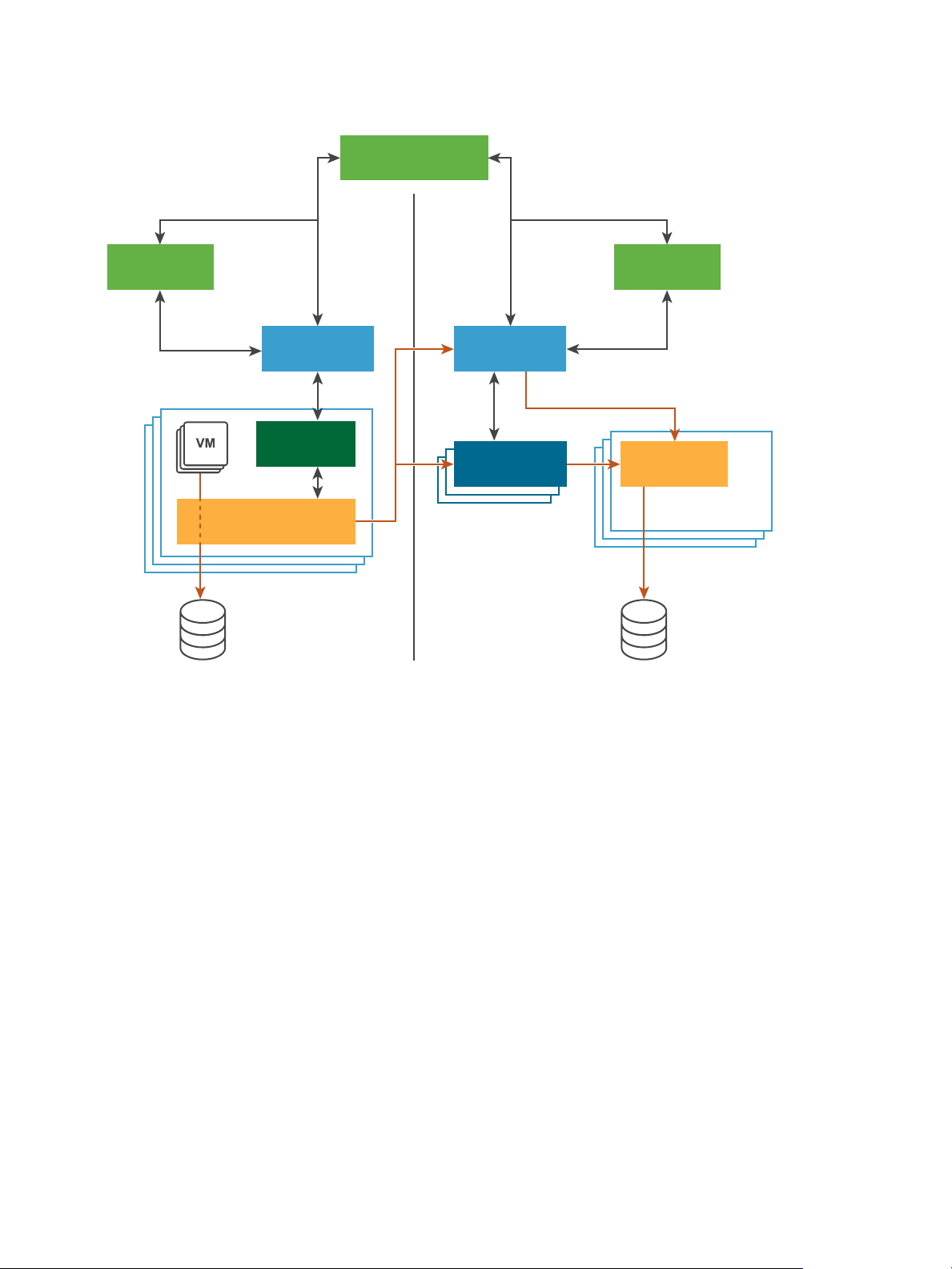
(Further VR
Servers)
vCenter vCenter
VR Agent
VR vSCSI Filter
VR Appliance VR Appliance
Site Recovery UI
Protected Site Recovery Site
NFC Service
ESX
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
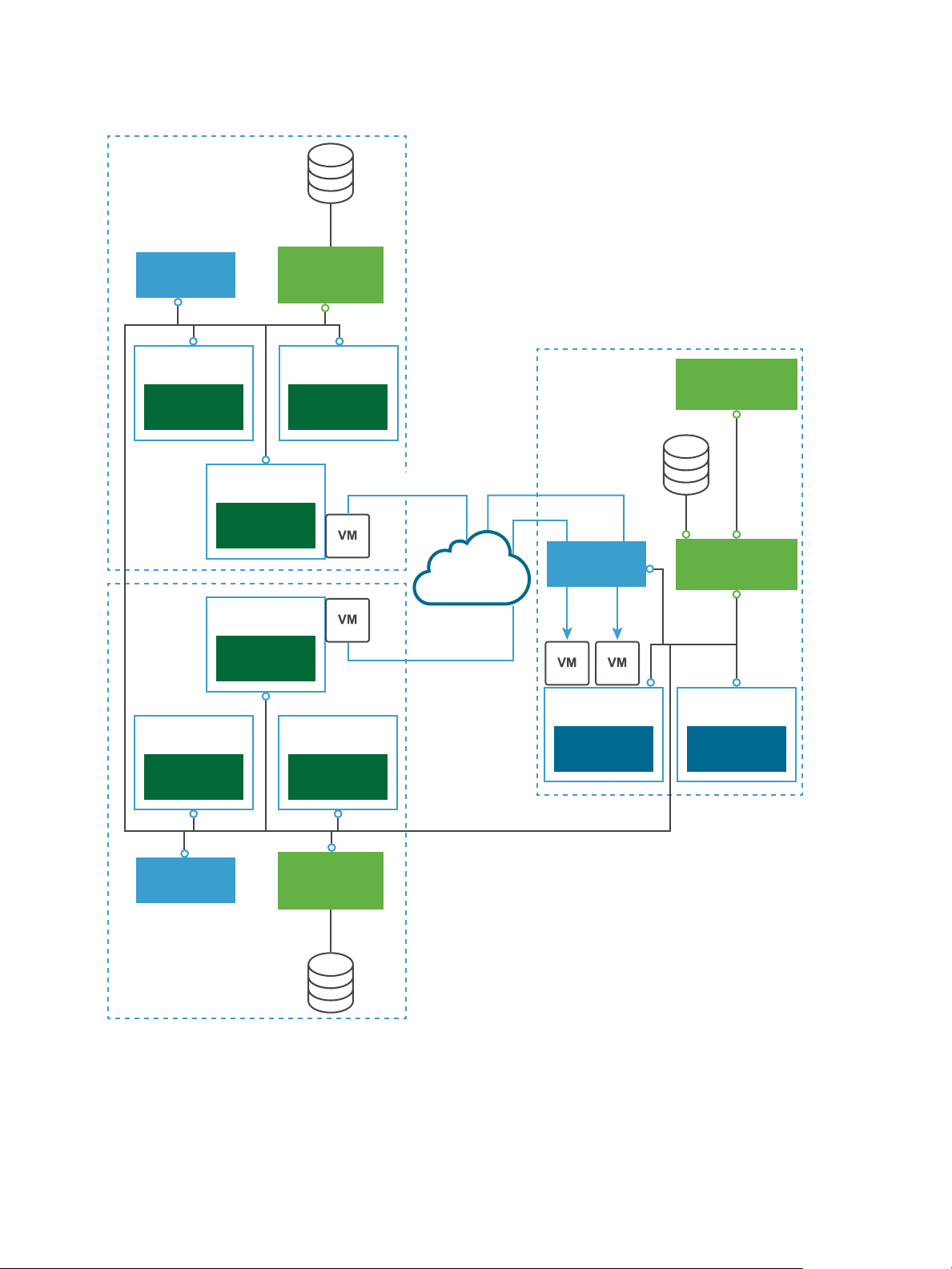
Figure 1‑1. Replication Between Two Sites
You can also replicate a virtual machine between datastores at the same vCenter Server. In that topology
one vCenter Server manages hosts at the source and at the target. Only one vSphere Replication
appliance is deployed on the single vCenter Server. You can add multiple Additional vSphere Replication
servers in a single vCenter Server to replicate virtual machines to other clusters.
To perform recovery, the vCenter Server managing the target datastore, the vSphere Replication
appliance, and any additional vSphere Replication Servers managing the replication must be up and
running.
VMware, Inc. 11
Page 12
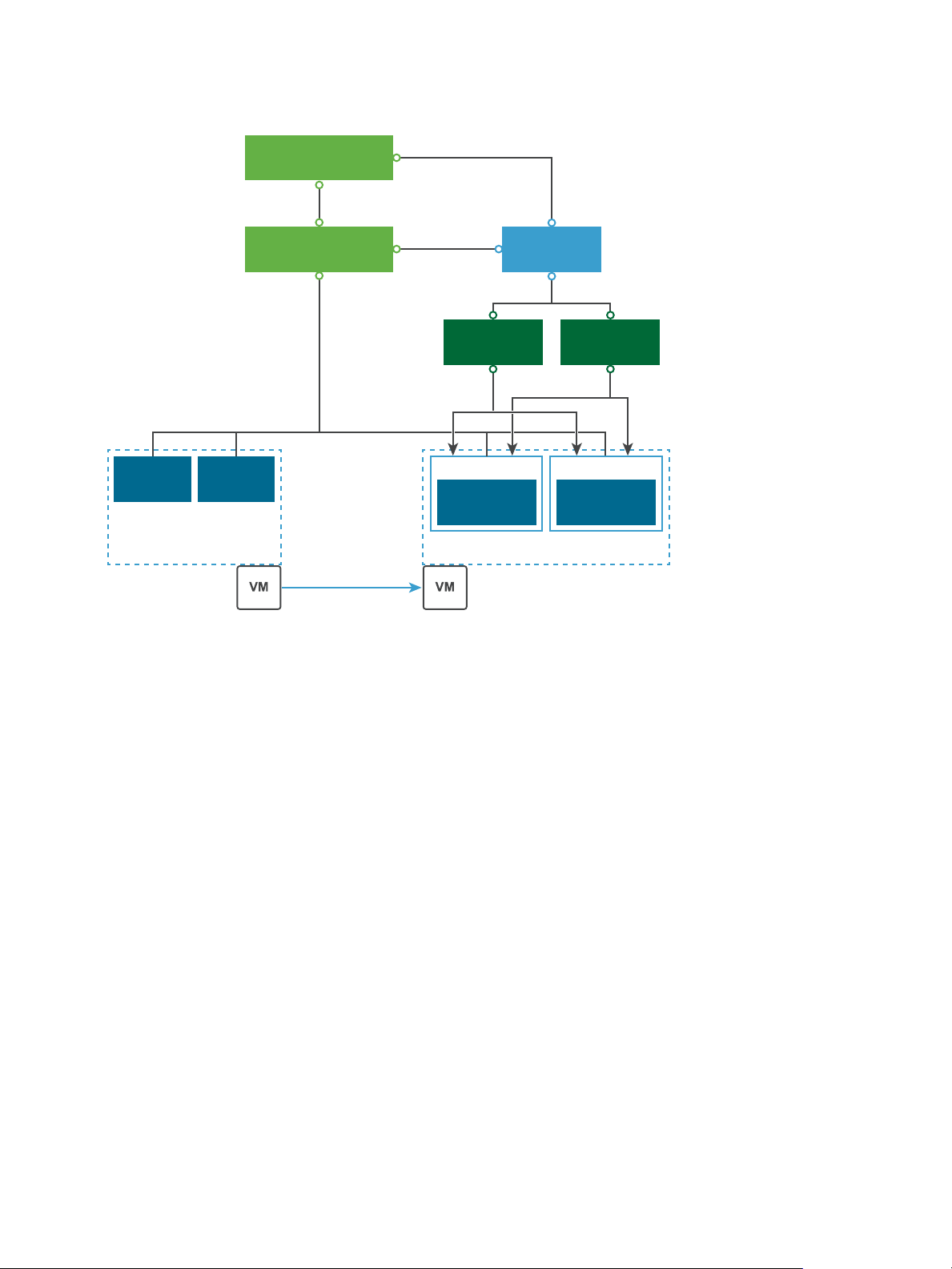
Network
FileCopy
ESXi
Network
FileCopy
ESXi
vCenter Server
ESXi ESXi
VR Server VR Server
VR Appliance
Site Recovery UI
Replication
Cluster 1 Cluster 2
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Figure 1‑2. Replication in a Single vCenter Server
You can replicate virtual machines to a shared target site.
VMware, Inc. 12
Page 13
Network
FileCopy
ESXi
Network
FileCopy
ESXi
vCenter
Server
ESXi
VR Agent
ESXi
VR Agent
ESXi
VR Agent
VR Appliance
VR Appliance
vCenter
Server
vSphere
Web Client
Source Site
vCenter
Server
ESXi
VR Agent
ESXi
VR Agent
ESXi
VR Agent
VR Appliance
Source Site
Target Site
Replicate
Replication
Replication
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Figure 1‑3. Replication to a Shared Target Site
Replication Data Compression
You can configure vSphere Replication to compress the data that it transfers through the network.
VMware, Inc. 13
Page 14
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Compressing the replication data that is transferred through the network saves network bandwidth and
might help reduce the amount of buffer memory used on the vSphere Replication server. However,
compressing and decompressing data requires more CPU resources on both the source site and the
server that manages the target datastore.
Data Compression Support
vSphere Replication 6.x supports end-to-end compression when the source and target ESXi hosts are
version 6.0. The support of data compression for all other use cases depends on the versions of source
and target ESXi hosts. The vSphere Replication servers on both the source and target sites must be 6.x.
Table 1‑1. Support for Data Compression Depending on Other Product Versions
ESXi Host that Manages the Target
Source ESXi host
Earlier than 6.0 Any supported version vSphere Replication does not support
Datastore Data Compression Support
data compression for the source ESXi
host, so the option Enable network
compression for VR data is disabled in
the Configure Replication wizard.
6.0 Earlier than 6.0 The ESXi host on the source site sends
compressed data packets to the
vSphere Replication server on the target
site. The vSphere Replication server
searches the target site for ESXi 6.0 hosts
that can decompress the data. If no 6.0
hosts are available for the target
datastore, the vSphere Replication server
uses the resources of the
vSphere Replication appliance to
decompress the data, and sends the
uncompressed data to the ESXi host.
6.0 6.0 This is an environment that supports full
end-to-end compression. The ESXi host
on the source site compresses the data,
and the vSphere Replication server on the
target site passes the data off to the ESXi
host where the host decompresses the
data and writes it to disk.
Data Compression and vSphere vMotion
If data compression is disabled, you can perform vMotion operations on replication source machines
between any pair of hosts that support vMotion and vSphere Replication.
VMware, Inc. 14
Page 15

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
When data compression is enabled, if both the source and the target ESXi hosts support data
compression, vMotion operations can be performed as usual. However, if the target ESXi host is earlier
than 6.0, vSphere Replication prevents vMotion from moving replication source VMs to that host because
it does not support data compression. This prevents DRS from performing automated vMotion operations
to hosts that do not support compression. Therefore, if you need to move a replication source VM to an
ESXi host earlier than 6.0, before you perform the vMotion operation, you must reconfigure the replication
to disable data compression.
VMware, Inc. 15
Page 16
vSphere Replication System
Requirements 2
The environment in which you run the vSphere Replication virtual appliance must meet certain hardware
requirements.
vSphere Replication is distributed as a 64-bit virtual appliance packaged in the .ovf format. It is
configured to use a dual-core or quad-core CPU, a 13 GB and a 9 GB hard disk, and 8 GB of RAM.
Additional vSphere Replication servers require 716 MB of RAM.
You must deploy the virtual appliance in a vCenter Server environment by using the OVF deployment
wizard on an ESXi host.
vSphere Replication consumes negligible CPU and memory on the source host ESXi and on the guest
OS of the replicated virtual machine.
Note vSphere Replication can be deployed with either IPv4 or IPv6 address. Mixing IP addresses, for
example having a single appliance with an IPv4 and an IPv6 address, is not supported. To register as an
extension, vSphere Replication relies on the VirtualCenter.FQDN property of the vCenter Server. When
an IPv6 address is used for vSphere Replication, the VirtualCenter.FQDN property must be set to a
fully qualified domain name that can be resolved to an IPv6 address or to a literal address. When
operating with an IPv6 address, vSphere Replication requires that all components in the environment,
such as vCenter Server and ESXi hosts are accessible using the IPv6 address.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
vSphere Replication Licensing
n
vSphere Replication Network Ports
n
Operational Limits of vSphere Replication
n
Compatibility of vSphere Replication with Other vSphere Features
n
vSphere Replication Compatibility with Other Software
n
Bandwidth Requirements for vSphere Replication
vSphere Replication Licensing
You can use vSphere Replication with certain editions of vSphere that include vSphere Replication in the
license.
VMware, Inc.
16
Page 17

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
vSphere Replication does not have a separate license as it is a feature of certain vSphere license
editions.
n
vSphere Essentials Plus
n
vSphere Standard
n
vSphere Enterprise
n
vSphere Enterprise Plus
If you have the correct vSphere license, there is no limit on the number of virtual machines that you can
replicate by using vSphere Replication.
You cannot use vSphere Replication to replicate virtual machines on ESXi hosts that do not have the
correct vSphere license. If you install vSphere Replication on an ESXi host that does not have the correct
license and try to configure replication for virtual machines on that host, the replication fails with a
licensing error.
If you configure a virtual machine for replication on a host with the correct vSphere license and move it to
a host with an unsupported license, vSphere Replication stops replication of that virtual machine. You can
disable vSphere Replication on a configured virtual machine on the unlicensed host.
vSphere Replication Network Ports
vSphere Replication uses default network ports for intrasite communication between hosts at a single site
and intersite communication between hosts at the protected and recovery sites.
For a list of all the ports that must be open for vSphere Replication, see
http://kb.vmware.com/kb/2087769.
For the list of default ports that all VMware products use, see http://kb.vmware.com/kb/1012382.
Operational Limits of vSphere Replication
vSphere Replication has certain operational limits.
To ensure successful virtual machine replication, you must verify that your virtual infrastructure respects
certain limits before you start the replication.
n
You can only deploy one vSphere Replication appliance on a vCenter Server instance. When you
deploy another vSphere Replication appliance, during the boot process vSphere Replication detects
another appliance already deployed and registered as an extension to vCenter Server. You have to
confirm if you want to proceed with the new appliance and recreate all replications or shut it down and
reboot the old appliance to restore the original vSphere Replication extension thumbprint in
vCenter Server.
n
Each newly deployed vSphere Replication appliance can manage a maximum of 2000 replications.
See http://kb.vmware.com/kb/2102453 for more information.
VMware, Inc. 17
Page 18
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
n
Upgraded vSphere Replication appliances that use the embedded vSphere Replication database
require additional configuration to enable the support of a maximum of 2000 replications. See
http://kb.vmware.com/kb/2102463. No additional configuration is required for vSphere Replication
appliances that are configured to use an external database.
Compatibility of vSphere Replication with Other vSphere Features
vSphere Replication is compatible with certain other vSphere management features.
You can safely use vSphere Replication with certain vSphere features, such as vSphere vMotion. Some
other vSphere features, for example vSphere Distributed Power Management, require special
configuration for use with vSphere Replication.
Note You cannot upgrade VMware Tools in the vSphere Replication appliance.
Table 2‑1. Compatibility of vSphere Replication with Other vSphere Features
Compatible with
vSphere Feature
vSphere Replication Description
vSphere vMotion Yes You can migrate replicated virtual machines by using vMotion. Replication
continues at the defined recovery point objective (RPO) after the migration is
finished.
vSphere Storage
vMotion
vSphere High
Availability
vSphere Fault
Tolerance
vSphere DRS Yes Replication continues at the defined RPO after resource redistribution is
vSphere Storage
DRS
vSAN datastore Yes You can use vSAN datastores as the source and target datastore when
Yes You can move the disk files of a replicated virtual machine on the source site
using Storage vMotion with no impact on the ongoing replication.
Yes You can protect a replicated virtual machine by using HA. Replication continues
at the defined RPO after HA restarts a virtual machine. vSphere Replication
does not perform any special HA handling. You can protect the
vSphere Replication appliance itself by using HA.
No vSphere Replication cannot replicate virtual machines that have fault tolerance
enabled. You cannot protect the vSphere Replication appliance itself with FT.
finished.
Yes On the source site, Storage DRS can move the disk files of replicated virtual
machines with no impact on the ongoing replication.
On the target site, you must register the vSphere Replication appliance with the
vCenter Single Sign-On service to enable the communication between Storage
DRS and the vSphere Replication Management server. See Register the
vSphere Replication Appliance with vCenter Single Sign-On.
configuring replications.
Note vSAN is a fully supported feature of vSphere 5.5 Update 1 and later.
vSphere
Distributed Power
Management
VMware, Inc. 18
Yes vSphere Replication coexists with DPM on the source site. vSphere Replication
does not perform any special DPM handling on the source site. You can disable
DPM on the target site to allow enough hosts as replication targets.
Page 19
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Table 2‑1. Compatibility of vSphere Replication with Other vSphere Features (Continued)
Compatible with
vSphere Feature
vSphere Replication Description
VMware vSphere
Flash Read Cache
vCloud APIs Not applicable No interaction with vSphere Replication.
vCenter
Chargeback
VMware Data
Recovery
Yes You can protect virtual machines that contain disks that use VMware vSphere
Flash Read Cache storage. Since the host to which a virtual machine recovers
might not be configured for Flash Read Cache, vSphere Replication disables
Flash Read Cache on disks when it starts the virtual machines on the recovery
site. vSphere Replication sets the reservation to zero. Before performing a
recovery on a virtual machine that is configured to use vSphere Flash Read
Cache, take note of the virtual machine's cache reservation from the
vSphere Web Client. After the recovery, you can migrate the virtual machine to
a host with Flash Read Cache storage and restore the original Flash Read
Cache setting on the virtual machine manually.
Not applicable No interaction with vSphere Replication
Not applicable No interaction with vSphere Replication.
vSphere Replication Compatibility with Other Software
vSphere Replication is compatible with certain versions of ESXi, vCenter Server, Site Recovery Manager,
databases, and Web browsers.
vSphere Replication is compatible with the same versions as vCenter Server, except for ESXi:
vSphere Replication requires ESXi 5.0 or later. See the following documents for more information.
n
Compatibility Matrices for vSphere Replication 8.1 at https://docs.vmware.com/en/vSphere-
Replication/8.1/rn/vsphere-replication-compat-matrix-8-1.html.
n
For vSphere Replication interoperability with backup software when using VSS, see
http://kb.vmware.com/kb/2040754.
n
VMware Compatibility Guide at http://partnerweb.vmware.com/comp_guide2/search.php
n
Browser compatibility at vSphere Client and vSphere Web Client Software Requirements in vSphere
Installation and Setup.
Bandwidth Requirements for vSphere Replication
Before configuring replications, best practice is to determine the storage and network bandwidth
requirements for vSphere Replication to replicate virtual machines efficiently.
Storage and network bandwidth requirements can increase when using vSphere Replication. The
following factors play a role in the amount of network bandwidth vSphere Replication requires for an
efficient replication.
VMware, Inc. 19
Page 20

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Network Based Storage
Network bandwidth requirements increase if all storage is network-based because data operations
between the host and the storage also use network. When you plan your deployment, be aware of the
following levels of traffic:
n
Between the host running the replicated virtual machine and the vSphere Replication server.
n
Between the vSphere Replication server and a host with access to the replication target datastore.
n
Between the host and storage.
n
Between storage and the host during redo log snapshots.
Network-based storage is a concern when you are replicating virtual machines within a single vCenter
Server instance that shares the network for the levels of traffic listed. When you have two sites with a
vCenter Server instance on each site, the link speed between the two sites is the most important as it can
slow down replication traffic between the two sites.
Dataset Size
vSphere Replication might not replicate every virtual machine nor every VMDK file in the replicated virtual
machines. To evaluate the dataset size that vSphere Replication replicates, calculate the percentage of
the total storage used for virtual machines, then calculate the number of VMDKs within that subset that
you have configured for replication.
For example, you might have 2 TB of virtual machines on the datastores and usevSphere Replication to
replicate half of these virtual machines. You might only replicate a subset of the VMDKs and assuming all
the VMDKs are replicated, the maximum amount of data for replication is 1 TB.
Data Change Rate and Recovery Point Objective
The data change rate is affected by the recovery point objective (RPO). To estimate the size of the data
transfer for each replication, you must evaluate how many blocks change in a given RPO for a virtual
machine. The data change rate within the RPO period provides the total number of blocks that
vSphere Replication transfers. This number might vary throughout the day, which alters the traffic that
vSphere Replication generates at different times.
vSphere Replication transfers blocks based on the RPO schedule. If you set an RPO of one hour,
vSphere Replication transfers any block that has changed in that hour to meet that RPO.
vSphere Replication only transfers the block once in its current state at the moment that
vSphere Replication creates the bundle of blocks for transfer. vSphere Replication only registers that the
block has changed within the RPO period, not how many times it changed. The average daily data
change rate provides an estimation of how much data vSphere Replication transfers or how often the
transfers occur.
VMware, Inc. 20
Page 21

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
If you use volume shadow copy service (VSS) to quiesce the virtual machine, replication traffic cannot be
spread out in small sets of bundles throughout the RPO period. Instead, vSphere Replication transfers all
the changed blocks as one set when the virtual machine is idle. Without VSS, vSphere Replication can
transfer smaller bundles of changed blocks on an ongoing basis as the blocks change, spreading the
traffic throughout the RPO period. The traffic changes if you use VSS and vSphere Replication handles
the replication schedule differently, leading to varying traffic patterns.
If you change the RPO, vSphere Replication transfers more or less data per replication to meet the new
RPO.
Link Speed
If you have to transfer an average replication bundle of 4 GB in a one hour period, you must examine the
link speed to determine if the RPO can be met. If you have a 10Mb link, under ideal conditions on a
completely dedicated link with little overhead, 4GB takes about an hour to transfer. Meeting the RPO
saturates a 10Mb WAN connection. The connection is saturated even under ideal conditions, with no
overhead or limiting factors such as retransmits, shared traffic, or excessive bursts of data change rates.
You can assume that only about 70% of a link is available for traffic replication. This means that on a
10Mb link you obtain a link speed of about 3GB per hour. On a 100Mb link, you obtain a speed of about
30GB per hour.
To calculate the bandwidth, see Calculate Bandwidth for vSphere Replication.
Calculate Bandwidth for vSphere Replication
To determine the bandwidth that vSphere Replication requires to replicate virtual machines efficiently, you
calculate the average data change rate within an RPO period divided by the link speed.
If you have groups of virtual machines that have different RPO periods, you can determine the replication
time for each group of virtual machines. For example, you might have four groups with RPO of 15
minutes, 1 hour, 4 hours, and 24 hours. Factor in all the different RPOs in the environment, the subset of
virtual machines in your environment that is replicated, the change rate of the data within that subset, the
amount of data changes within each configured RPO, and the link speeds in your network.
Prerequisites
Examine how data change rate, traffic rates, and the link speed meet the RPO. Then look at the
aggregate of each group.
Procedure
1 Identify the average data change rate within the RPO by calculating the average change rate over a
longer period, then dividing it by the RPO.
2 Calculate how much traffic this data change rate generates in each RPO period.
3 Measure the traffic against your link speed.
For example, a data change rate of 100GB requires approximately 200 hours to replicate on a T1
network, 30 hours to replicate on a 10Mbps network, 3 hours on a 100Mbps network.
VMware, Inc. 21
Page 22

Installing and Uninstalling
vSphere Replication 3
vSphere Replication uses the replication technologies included in ESXi with the assistance of virtual
appliances to replicate virtual machines between source and target sites.
Installing vSphere Replication
To use vSphere Replication, you must deploy the vSphere Replication appliance on an ESXi host by
using the vSphere Web Client.
The vSphere Replication appliance registers as an extension with the corresponding vCenter Server
instance. For example, on the source site, the vSphere Replication appliance registers with the
vCenter Server instance on the source site. Only one vSphere Replication appliance is allowed per
vCenter Server.
The vSphere Replication appliance contains an embedded vSphere Replication server that manages the
replication process. To meet the load balancing needs of your environment, you might need to deploy
additional vSphere Replication servers at each site. Additional vSphere Replication servers that you
deploy are themselves virtual appliances. You must register any additional vSphere Replication server
with the vSphere Replication appliance on the corresponding site.
The vSphere Replication appliance provides a virtual appliance management interface (VAMI). You can
use the VAMI to perform initial configuration and reconfigure the vSphere Replication database, network
settings, public-key certificates, and passwords for the appliances.
Uninstalling vSphere Replication
To uninstall vSphere Replication from your environment, you must unregister the appliance from the
vCenter Single Sign-On service and from the vCenter Server, and then delete the vSphere Replication
appliance.
If you delete the vSphere Replication appliance before unregistering it from the vCenter Single Sign-On
server and the vCenter Server, a special procedure must be performed to clean up your environment. For
more information, see Unregister vSphere Replication from vCenter Server If the Appliance Was Deleted.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
Install vSphere Replication
n
Uninstall vSphere Replication
VMware, Inc.
22
Page 23
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
n
Unregister vSphere Replication from vCenter Server If the Appliance Was Deleted
Install vSphere Replication
The installation procedure of vSphere Replication involves several steps.
Procedure
1 Prepare Your Environment to Install vSphere Replication
Before you deploy the vSphere Replication appliance, you must prepare the environment.
2 Deploy the vSphere Replication Virtual Appliance
vSphere Replication is distributed as an OVF virtual appliance.
3 Register the vSphere Replication Appliance with vCenter Single Sign-On
You must register the vSphere Replication Management Server with vCenter Single Sign-On on both
the source and the target sites.
4 Configure vSphere Replication Connections
To use vSphere Replication between two sites managed by different vCenter Server instances, you
must configure a connection between the two vSphere Replication appliances.
Prepare Your Environment to Install vSphere Replication
Before you deploy the vSphere Replication appliance, you must prepare the environment.
Procedure
1 Verify that you have vSphere and vSphere Web Client installations for the source and target sites.
2 In the vSphere Web Client, select the vCenter Server instance on which you are deploying
vSphere Replication, click Configure > Settings > Advanced Settings, and verify that the
VirtualCenter.FQDN value is set to a fully qualified domain name or a literal address.
Note vSphere Replication can be deployed with either IPv4 or IPv6 address. Mixing IP addresses,
for example having a single appliance with an IPv4 and an IPv6 address, is not supported. To register
as an extension, vSphere Replication relies on the VirtualCenter.FQDN property of the
vCenter Server. When an IPv6 address is used for vSphere Replication, the VirtualCenter.FQDN
property must be set to a fully qualified domain name that can be resolved to an IPv6 address or to a
literal address. When operating with an IPv6 address, vSphere Replication requires that all
components in the environment, such as vCenter Server and ESXi hosts are accessible using the
IPv6 address.
3 If you configure vSphere Replication in an IPv6 network, verify that the IPv6 address of the
vSphere Replication appliance, vCenter Server, the ESXi hosts, and an external database, if used,
are mapped to fully qualified domain names on the DNS server. Install the vSphere Replication
appliance by using FQDN and post installation, make sure that the VRM Host text box in the VAMI is
set to the FQDN of the vSphere Replication appliance. Do not use a static IPv6 address.
VMware, Inc. 23
Page 24
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
What to do next
You can deploy the vSphere Replication appliance.
Deploy the vSphere Replication Virtual Appliance
vSphere Replication is distributed as an OVF virtual appliance.
You deploy the vSphere Replication appliance by using the standard vSphere OVF deployment wizard.
Important If you use the HTML5-based vSphere Client to deploy the OVF virtual appliance, the
deployment succeeds, but the vSphere Replication fails to start.
Note vSphere Replication can be deployed with either IPv4 or IPv6 address. Mixing IP addresses, for
example having a single appliance with an IPv4 and an IPv6 address, is not supported. To register as an
extension, vSphere Replication relies on the VirtualCenter.FQDN property of the vCenter Server. When
an IPv6 address is used for vSphere Replication, the VirtualCenter.FQDN property must be set to a
fully qualified domain name that can be resolved to an IPv6 address or to a literal address. When
operating with an IPv6 address, vSphere Replication requires that all components in the environment,
such as vCenter Server and ESXi hosts are accessible using the IPv6 address.
Prerequisites
Download the vSphere Replication ISO image and mount it on a system in your environment.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Web Client on the source site.
2 On the home page, select Hosts and Clusters.
3 Right-click a host and select Deploy OVF template.
4 Provide the location of the OVF file from which to deploy the vSphere Replication appliance, and click
Next.
n
Select URL and provide the URL to deploy the appliance from an online URL.
n
If you downloaded and mounted the vSphere Replication ISO image on a system in your
environment, select Local file > Browse and navigate to the \bin directory in the ISO image,
and select the vSphere_Replication_OVF10.ovf, vSphere_Replication-system.vmdk, and
vSphere_Replication-support.vmdk files.
5 Accept the name, select or search for a destination folder or data center for the virtual appliance, and
click Next.
You can enter a new name for the virtual appliance. The name must be unique within each
vCenter Server virtual machine folder.
6 Select a cluster, host, or resource pool where you want to run the deployed template, and click Next.
7 Review the virtual appliance details and click Next.
VMware, Inc. 24
Page 25
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
8 Accept the end-user license agreements (EULA) and click Next.
9 Select the number of vCPUs for the virtual appliance and click Next.
Note Selecting higher number of vCPUs ensures better performance of the vSphere Replication
Management Server, but might slow down the replications that run on ESXi host systems that have 4
or less cores per NUMA node. If you are unsure what the hosts in your environment are, select 2
vCPUs.
10 Select a destination datastore and disk format for the virtual appliance and click Next.
11 Select a network from the list of available networks, set the IP protocol and IP allocation, and click
Next.
vSphere Replication supports both DHCP and static IP addresses. You can also change network
settings by using the virtual appliance management interface (VAMI) after installation.
12 On the Customize template page, enter one or more NTP server host names or IP addresses.
13 Set the password for the root account for the customized template, and click Next.
The password must be at least eight characters long.
14 Review the settings and click Finish.
The vSphere Replication appliance is deployed.
15 Power on the vSphere Replication appliance. Take a note of the IP address of the appliance and log
out of the vSphere Web Client.
16 To deploy vSphere Replication on the target site, repeat the procedure.
What to do next
Register the vSphere Replication appliance with the vCenter Single Sign-On service.
Register the vSphere Replication Appliance with vCenter Single Sign-On
You must register the vSphere Replication Management Server with vCenter Single Sign-On on both the
source and the target sites.
After you deploy the vSphere Replication appliance, you use the Virtual Appliance Management Interface
(VAMI) to register the endpoint and the certificate of the vSphere Replication Management Server with the
vCenter Lookup Service, and to register the vSphere Replication solution user with the vCenter Single
Sign-On administration server.
If you do not register vSphere Replication with vCenter Single Sign-On on the target site,
vSphere Replication cannot operate as expected. In addition, storage DRS does not detect the replicated
data that vSphere Replication stores on the target site and might destroy it.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication appliance is powered on.
VMware, Inc. 25
Page 26
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
n
Verify that you have administrator privileges to configure the vSphere Replication appliance.
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication management server is synchronized with the time of the Single
Sign-On server.
Procedure
1 Use a supported browser to log in to the vSphere Replication VAMI.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-appliance-address:5480.
2 Enter the root user name and password for the appliance.
You configured the root password during the OVF deployment of the vSphere Replication appliance.
3 On the VR tab, click Configuration.
4 In the LookupService Address text box, enter the IP address or domain name of the server where
the lookup service runs.
5 Enter the credentials of a user with administrator privileges to vCenter Single Sign-On.
Initially, only the user administrator@vsphere.local has these privileges.
6 Click Save and Restart Service.
7 To register vSphere Replication on the target site, repeat the procedure.
vSphere Replication appears on the Home tab in the vSphere Web Client.
What to do next
Note If you registered the vSphere Replication appliance with vCenter Single Sign-On as part of the
upgrade procedure, all existing connections will turn into Connection issue status. See Reconfigure the
Connection to a Remote Site.
If you competed this procedure as part of the installation process, you can configure connections between
the source and target sites.
Perform an optional reconfiguration of the vSphere Replication appliance by using the VAMI. You can
install a certificate, change the appliance root password, change the trust policy, or configure
vSphere Replication to use an external database.
States of vSphere Replication Displayed in the vSphere Web Client or vSphere Client
You can see the vSphere Replication status on each vCenter Server in your environment and if
vSphere Replication does not function properly, find the appropriate remediation.
Before you can begin using vSphere Replication, you must register the vSphere Replication appliance
with the vCenter Lookup Service and the Single Sign-On administration server in the environment.
VMware, Inc. 26
Page 27
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
After the registration, in the vSphere Web Client or vSphere Client, when you click Site Recovery, you
can see the list of vCenter Server instances in the Single-Sign On domain and the status of
vSphere Replication on each vCenter Server instance. If you have Site Recovery Manager deployed in
your environment, you can also see the status of Site Recovery Manager. You can change the
configuration of each vSphere Replication appliance by clicking the Configure icon next to the status
icon.
The following table lists the vSphere Replication states that you can observe, their meanings, and what
you can do to change a state back to normal.
Table 3‑1. vSphere Replication States on vCenter Server Instances
Status Description Remediation
Not installed The vSphere Replication extension is not
registered in the vCenter Server
Extension Manager.
The vSphere Replication appliance is
either not deployed or the
vSphere Replication extension has been
deleted from the vCenter Server
Extension Manager.
Not configured A configuration error occurred.
The vSphere Replication Management
Server is either not registered with the
vCenter Single Sign-On components, or
the configuration is incorrect and must
be updated.
You cannot manage existing replications,
or configure new replications to this
server .
If a vSphere Replication appliance is
deployed on this vCenter Server, restart
the appliance or the vSphere Replication
Management service on the appliance.
1 Use a supported browser to log in to
the vSphere Replication VAMI as the
root user.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-
appliance-address:5480.
2 On the Configuration tab, click Save
and Restart Service.
Configure the vSphere Replication
appliance.
1 Point to the Enabled
(Configuration issue) status.
The detailed error message appears
in a tooltip.
2 Click the Configure icon.
The vSphere Replication VAMI opens.
3 On the VR tab, click Configuration,
and enter the parameters indicated in
the error message.
4 Click Save and Restart Service .
Not compatible There is a vSphere Replication appliance
with earlier version than 8.0, registered
in the vCenter Server.
VMware, Inc. 27
Install vSphere Replication 8.0 or later.
Page 28
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Table 3‑1. vSphere Replication States on vCenter Server Instances (Continued)
Status Description Remediation
Not accessible The vSphere Replication Management
Server is not accessible.
The vSphere Replication extension is
registered in the vCenter Server
Extension Manager, but the
vSphere Replication appliance is missing
or powered off, or the
vSphere Replication Management
service is not running.
You cannot manage existing replications,
or configure new replications to this
server .
OK The vSphere Replication appliance is
installed, configured, and functioning
properly.
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication
appliance exists on the vCenter
Server.
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication
appliance is powered on.
n
Restart the VRM service.
a Click the Configure icon.
b On the VR tab, click
Configuration and restart the
VRM service.
Not needed.
Configure vSphere Replication Connections
To use vSphere Replication between two sites managed by different vCenter Server instances, you must
configure a connection between the two vSphere Replication appliances.
If the source and target vCenter Server instances use the same vCenter Single Sign-On domain, the
connection is considered local. vSphere Replication uses the vCenter Single Sign-On service on the local
site to authenticate with each vCenter Server in the vCenter Single Sign-On domain.
If the source and the target vCenter Server instances use different vCenter Single Sign-On domains, the
connection is considered remote. The vSphere Replication Management Server on the source site
registers with the Platform Services Controller of the remote vCenter Single Sign-On domain.
You can use vSphere Replication to replicate virtual machines between ESXi hosts that the same
vCenter Server manages. In this case, you deploy only one vSphere Replication appliance and do not
need to connect the local and remote sites.
You can configure a connection on either site on which you have installed a vSphere Replication
appliance. If you are using an untrusted certificate, certificate warnings might appear during the process.
You can also set up a connection between two sites while you configure a replication between them.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you have installed vSphere Replication at the local and remote sites.
n
If you plan to configure a remote connection, obtain the IP address or domain name of the server
where the PSC runs. The address appears in the LookupService Address text box on the
Configuration tab under VR in the vSphere Replication VAMI on the remote site.
Procedure
1 On the home page, click Site Recovery and click Open Site Recovery.
VMware, Inc. 28
Page 29
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
2 On the Site Recovery home page, click the New Site Pair button.
3 Select the first site from the list.
4 Enter the address of the Platform Services Controller for the vSphere Replication Management
Server on the second site, provide the user name and password, and click Next.
5 Select the vCenter Server and the services you want to pair, and click Next.
6 On the Ready to complete page, review the pairing settings, and click Finish.
The local and the remote sites are connected. The pair appears under on the home page of the
Site Recovery user interface.
vSphere Replication Site Connection States
You can view the states of the connections to target sites in the Site Recovery user interface.
The following table lists the states that you can observe, their meanings, and what you can do to change
a state back to normal. You can view the states by clicking View Details for a site pair in the
Site Recovery user interface.
Table 3‑2. Replication Server Connection States
Icon Status Description Remediation
Connected The connection between the
local and remote
vSphere Replication
management servers is
working properly.
Not Connected
n
The SSL certificate on the
local or remote
vSphere Replication
Management Server has
been changed.
n
The network connection
between the local and
remote
vSphere Replication
Management Servers is
not functioning properly or
one of the servers is
offline.
n
The user that is used for
authentication with the
Lookup Service or the
VRMS extension user in
the vCenter Single Sign-
On might be disabled or
deleted.
In this state, configured
replications might not be
running.
Not needed.
n
To reconfigure the site
connection, click
Reconfigure Site Pair.
n
In the vSphere Client or
vSphere Web Client,
navigate to the
vCenter Server, select the
Monitor tab, and select
Events under Tasks and
Events to search for
events related to
vSphere Replication.
n
Verify the status of the
remote
vSphere Replication
appliances in the
Site Recovery plug-in for
vSphere Client or
vSphere Web Client.
VMware, Inc. 29
Page 30
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Reconfigure the Connection to a Remote Site
If the state of the connection to a target site is Not connected, you must repair the connection to
manage existing replications, and to enable the creation of new replications.
The states of connections to target sites appear in the Site Recovery user interface.
For reconnecting to cloud sites, see topic Reconnect to a Cloud Provider Site in the vSphere Replication
for Disaster Recovery to Cloud documentation.
If the source and the target vCenter Server instances use different vCenter Single Sign-On domains, the
connection is considered remote. The vSphere Replication Management Server on the source site
registers with the Platform Services Controller of the remote vCenter Single Sign-On domain. To establish
a connection to a remote site, you provide the address of the vCenter Server and the
Platform Services Controller, and enter the credentials of a user that has the VRM remote.VRM
Server.Manage VRM privilege assigned. If the Platform Services Controller address changes or there is
a change in the certificate, the connection status changes to Not connected and you must reconnect the
two sites.
Note You cannot use the Reconfigure Site Pair action to add a missing pairing or a pairing that was
manually broken with Break Site Pair. If your site pair is missing a pairing, you must use New Site Pair
to configure it.
Prerequisites
Verify that the vCenter Server and the vSphere Replication Management Server on the local site are up
and running, and that the Not connected status is not caused by a network problem.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
2 On the home page, click Site Recovery and click Open Site Recovery.
3 On the Site Recovery home page, select a site pair and click View Details.
4 From the list of target sites, select the connection that indicates Not connected status.
5 Click the Reconfigure Site Pair button.
The Reconfigure Site Pair wizard starts.
6 Enter the PSC address and the credentials of a user that has the VRM remote.Manage VRM
privilege assigned, and click Next.
Note If you upgraded from an earlier vSphere Replication version, the text box for the
Platform Services Controller address may be automatically populated with the IP address of the
target vSphere Replication Management server. In this case, you must replace it with the address of
the Platform Services Controller on the target site before providing the credentials.
VMware, Inc. 30
Page 31
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
7 Select a vCenter Server on the second site, select vSphere Replication from the list of services, and
click Next.
8 Review the settings and click Finish.
The connection status changes to Connected.
Uninstall vSphere Replication
You uninstall vSphere Replication by unregistering the appliance from vCenter Server and removing it
from your environment.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication appliance is powered on.
n
Stop all existing forward or reverse replications to the site.
n
Disconnect any connections to other vSphere Replication sites.
Procedure
1 Use a supported browser to log in to the vSphere Replication VAMI.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-appliance-address:5480.
2 On the VR tab, click Configuration.
3 Click Unregister VRMS.
4 In the vSphere Web Client, power off and delete the vSphere Replication appliance.
The Site Recovery plug-in is uninstalled automatically.
You removed vSphere Replication from your environment.
What to do next
Note If a vSphere Replication appliance is deleted before all replications that it manages are stopped,
target datastores remain tagged with the com.vmware.vr.HasVrDisks tag. If a target datastore that is
tagged with com.vmware.vr.HasVrDisks is part of a datastore cluster where Storage DRS is enabled,
some operations, like Enter maintenance mode, might not succeed when the vSphere Replication
Management server is missing. To prevent errors, you must remove the tags from all target datastores
that were used for replications by the deleted vSphere Replication appliance. See Search and Remove
the vSphere Replication Tag from Target Datastores.
Search and Remove the vSphere Replication Tag from Target Datastores
If a vSphere Replication appliance is deleted before all replications that it manages are stopped, target
datastores remain tagged with the com.vmware.vr.HasVrDisks tag.
VMware, Inc. 31
Page 32

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
If a target datastore that is tagged with com.vmware.vr.HasVrDisks is part of a datastore cluster where
Storage DRS is enabled, some operations, like Enter maintenance mode, might not succeed when the
vSphere Replication Management server is missing.
Prerequisites
n
The vSphere Replication appliance is deleted.
n
Required privilege: Inventory Service.vSphere Tagging.Assign or Unassign vSphere Tag on the
root vCenter Server instance.
Procedure
1 Use the vSphere Web Client to log in to the target vCenter Server.
2 In the search text box on the upper right, enter com.vmware.vr.HasVrDisks and search for the tag.
The list of users and groups that have permissions to manage the com.vmware.vr.HasVrDisks tag
appears.
3 Click the Related Objects tab.
The list of datastores that have the com.vmware.vr.HasVrDisks tag assigned appears.
4 Right-click a datastore and select Tags > Remove Tag.
5 In the Remove Tag dialog box, select the row that contains com.vmware.vr.HasVrDisks and click
Remove.
6 Repeat steps 4 and 5 for all datastores that are assigned the com.vmware.vr.HasVrDisks tag.
Unregister vSphere Replication from vCenter Server If the Appliance Was Deleted
If the vSphere Replication appliance was deleted before you unregistered it from the environment , you
cannot use the virtual appliance management interface (VAMI) to unregister vSphere Replication from
vCenter Server.
Only a vSphere administrator can clean up the environment.
The procedures on removing the permissions for a solution user and on removing a solution user from the
vCenter Single Sign-On domain are documented in the vSphere 6.5 Security document. See topics
Remove Permissions and Delete vCenter Single Sign-On Solution Users.
Prerequisites
Verify that you know the credentials of a vSphere administrator.
Procedure
1 Log in to https://<vCenter_Server_address>/mob/?moid=ExtensionManager with
vCenter Server credentials.
VMware, Inc. 32
Page 33
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
2 In the extensionList property, click the link for the com.vmware.vcHms extension key to check the key
details.
3 Verify that the displayed data is for a vSphere Replication appliance that is already lost.
4 In ExtensionManager, click unregisterExtension.
5 Enter com.vmware.vcHms for the extension key value, and click Invoke Method.
6 Verify that the result displays void and not an error message.
An error message might appear if the specified extension is not registered, or if an unexpected
runtime error occurs.
7 Close the window.
8 Refresh the ExtensionManager page and verify that the extensionList entry does not include
com.vmware.vcHms.
9 Remove the permissions for the HMS solution user from all vCenter Server instances in the Single
Sign-On domain.
10 Remove the HMS solution user from the vCenter Single Sign-On domain.
What to do next
You can deploy a new vSphere Replication appliance.
Note If a vSphere Replication appliance is deleted before all replications that it manages are stopped,
target datastores remain tagged with the com.vmware.vr.HasVrDisks tag. If a target datastore that is
tagged with com.vmware.vr.HasVrDisks is part of a datastore cluster where Storage DRS is enabled,
some operations, like Enter maintenance mode, might not succeed when the vSphere Replication
Management server is missing. To prevent errors, you must remove the tags from all target datastores
that were used for replications by the deleted vSphere Replication appliance. See Search and Remove
the vSphere Replication Tag from Target Datastores.
VMware, Inc. 33
Page 34

Configuring the Customer
Experience Improvement
Program 4
When you choose to participate in the Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP), VMware
receives anonymous information to improve the quality, reliability, and functionality of VMware products
and services.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
Categories of Information That VMware Receives
n
Join or Leave the Customer Experience Improvement Program in the vSphere Web Client
Categories of Information That VMware Receives
This product participates in the VMware Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP).
Details regarding the data collected by CEIP and the purposes for which it is used by VMware are
available at the Trust & Assurance Center at http://www.vmware.com/trustvmware/ceip.html.
To join or leave the CEIP for this product, see Join or Leave the Customer Experience Improvement
Program in the vSphere Web Client.
Join or Leave the Customer Experience Improvement
Program in the vSphere Web Client
You can choose to join the Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP), or leave the CEIP at any
time.
Prerequisites
Verify that you are a member of the Administrators@vsphere.local group.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vCenter Server instance as a member of Administrators@vsphere.local by using the
vSphere Web Client.
2 On the vSphere Web Client Home page, under Administration, click Customer Experience
Improvement Program.
3 Click Join to enable the CEIP or Leave to disable the CEIP.
VMware, Inc.
34
Page 35
Isolating the Network Trac of
vSphere Replication 5
You can isolate the network traffic of vSphere Replication from all other traffic in a data center's network.
Isolating the replication traffic helps you ensure that sensitive information is not routed to the wrong
destination, and helps you enhance the network performance in the data center, because the traffic that
vSphere Replication generates does not impact other types of traffic. You isolate the network traffic to the
vSphere Replication Server by dedicating a VMKernel NIC on each ESXi host on the primary site that
sends data to the vSphere Replication Server. See Set Up a VMkernel Adapter for vSphere Replication
Traffic on a Source Host.
If you are using a distributed network switch, you can take advantage of the vSphere Network I/O Control
feature to set limits or shares for incoming and outgoing replication traffic on each ESXi host. The feature
allows you to manage the network resources that vSphere Replication uses.
By default, the vSphere Replication appliance has one VM network adapter that is used for various traffic
types.
n
Management traffic between vSphere Replication Management Server and vSphere Replication
Server.
n
Replication traffic from the source ESXi hosts to the vSphere Replication Server.
n
Traffic between vCenter Server and vSphere Replication Management Server.
You can add network adapters to the vSphere Replication appliance and use the VAMI to configure a
separate IP address to use for each traffic type.
In the combined vSphere Replication appliance, the IP address that is used for management traffic
between the vSphere Replication Management Server and vSphere Replication Server is localhost
127.0.0.1. Therefore, you do not need to add network adapters for this type of traffic.
When the vSphere Replication Management Server and the vSphere Replication Server run on separate
appliances, you can specify a non-localhost IP address to be used by the vSphere Replication
Management Server.
Note After the IP address of the vSphere Replication server on the target site changes, you must
manually reconfigure replications on the source site to point to the new IP address.
In addition you must configure static routes on each ESXi host at the source site with how to
communicate with the target site and the reverse. See http://kb.vmware.com/kb/2001426. For replications
to flow in the opposite direction, you must configure reverse routes on the target site ESXi hosts.
VMware, Inc.
35
Page 36

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
Set Up a VMkernel Adapter for vSphere Replication Traffic on a Source Host
n
Set Up a VMkernel Adapter for vSphere Replication Traffic on a Target Host
n
Create a VM Network Adapter to Use for Incoming Replication Traffic on the Combined vSphere
Replication Appliance
n
Create VM Network Adapters to Isolate the Network Traffic of a vSphere Replication Server
Set Up a VMkernel Adapter for vSphere Replication
Trac on a Source Host
You create VMkernel adapters to isolate the outgoing replication traffic on source ESXi hosts.
Note One VMkernel adapter must handle one traffic type.
Perform this procedure for every ESXi host that is used as a replication source, and for which you want to
isolate the replication traffic.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication virtual appliance is deployed and registered with the
vCenter Server.
n
Verify that the ESXi host is version 6.0 or later.
n
For distributed network switches, verify that you have a port group that you can dedicate to the new
VMkernel adapter.
Procedure
1 In the vSphere Web Client, navigate to the ESXi host.
2 Click the Configure tab and under Networking, select VMkernel adapters.
3
Click the Add host networking icon .
The Add Networking wizard opens.
4 On the Select connection type page, select VMkernel Network Adapter and click Next.
5 On the Select target device page, select a port group or a standard switch and click Next.
6 On the Port properties page, under VMkernel port settings, configure the IP settings and TCP/IP
stack to comply with your environment.
Note vSphere Replication requires that all components in your environment, such as
vCenter Server, ESXi hosts, and the vSphere Replication appliance use the same IP version, IPv4 or
IPv6.
7 Under Available services, select vSphere Replication and click Next.
VMware, Inc. 36
Page 37

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
8 Apply the IP settings, click Next, and Finish to complete the wizard.
The VMkernel adapter that you created for outgoing vSphere Replication traffic appears in the list of
adapters. The outgoing replication data from the ESXi host is sent to the vSphere Replication server
through this adapter.
What to do next
You can add a vNIC to the vSphere Replication appliance and use the VAMI to configure an IP address to
use for incoming replication data.
Set Up a VMkernel Adapter for vSphere Replication
Trac on a Target Host
You create VMkernel adapters to isolate the incoming replication traffic on target ESXi hosts.
Note One VMkernel adapter must handle one traffic type.
Perform this procedure for every ESXi host that is used as replication target, and for which you want to
isolate the replication traffic.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the ESXi host is version 6.0 or later.
n
For distributed network switches, verify that you have a port group that you can dedicate to the new
VMkernel adapter.
Procedure
1 In the vSphere Web Client, navigate to the ESXi host.
2 Click the Configure tab and under Networking, select VMkernel adapters.
3
Click the Add host networking icon .
The Add Networking wizard opens.
4 On the Select connection type page, select VMkernel Network Adapter and click Next.
5 On the Select target device page, select a port group or a standard switch and click Next.
6 On the Port properties page, under VMkernel port settings, configure the IP settings and TCP/IP
stack to comply with your environment.
Note vSphere Replication requires that all components in your environment, such as
vCenter Server, ESXi hosts, and the vSphere Replication appliance use the same IP version, IPv4 or
IPv6.
7 Under Available services, select vSphere Replication NFC traffic and click Next.
8 Apply the IP settings, click Next, and Finish to complete the wizard.
VMware, Inc. 37
Page 38

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
The VMkernel adapter that you tagged for NFC traffic appears in the list of adapters. The
vSphere Replication Server routes the replication data to the adapter, and the ESXi host saves the data
to a datastore.
Create a VM Network Adapter to Use for Incoming
Replication Trac on the Combined vSphere Replication
Appliance
By default, the combined vSphere Replication appliance has one VM network adapter that is used by the
vSphere Replication server for replication traffic, and by the vCenter Server for virtual machine
management.
The IP address that is used for vSphere Replication management traffic is localhost 127.0.0.1. Because
the default VM network adapter is used for different types of traffic, you can add a second adapter to the
appliance, and configure vSphere Replication to use the second adapter only for incoming replication
traffic.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication virtual appliance is deployed and registered with the
vCenter Server.
n
Make a note of the IP address of the VM network adapter.
Procedure
1 Power off the vSphere Replication appliance and edit the VM Hardware settings to add a new VM
NIC.
a Right-click the VM and select Edit Settings.
b From the New Device drop-down menu at the bottom of the Virtual Hardware tab, select
Network, and click Add.
The new network adapter appears in the list of devices at the right.
c Expand the properties of the new network adapter to verify that Connect At Power On is
selected.
You can assign a static MAC address or leave the text box empty to obtain an IP address
automatically.
d Click OK to close the Edit Setting dialog box.
2 Power on the vSphere Replication appliance.
3 From the Summary tab of the vSphere Replication appliance, take a note of the IP address of the
new network adapter.
You can click View all XX IP addresses to check the IP address of the new NIC.
4 Use a supported browser to log in to the vSphere Replication VAMI.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-appliance-address:5480.
VMware, Inc. 38
Page 39

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
5 On the VR tab, click Configuration.
6 In the IP Address for Incoming Storage Traffic text box, enter the IP address of the new network
adapter that you added.
7 Click Apply Network Settings.
The vSphere Replication appliance uses the IP address that you assigned only for incoming replication
traffic.
Create VM Network Adapters to Isolate the Network
Trac of a vSphere Replication Server
By default, the vSphere Replication Server appliance has one VM network adapter that is used by the
vSphere Replication Server for management and replication traffic.
Because the default VM network adapter is used for different types of traffic, you can add network
adapters to the appliance, and configure vSphere Replication to use a separate adapter for each traffic
type.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have deployed the vSphere Replication Server appliance in your environment and that it is
registered as a vSphere Replication Server in the vSphere Web Client.
Procedure
1 Power off the vSphere Replication appliance and edit the VM Hardware settings to add a new VM
NIC.
a Right-click the VM and select Edit Settings.
b From the New Device drop-down menu at the bottom of the Virtual Hardware tab, select
Network, and click Add.
The new network adapter appears in the list of devices at the right.
c Expand the properties of the new network adapter to verify that Connect At Power On is
selected.
You can assign a static MAC address or leave the text box empty to obtain an IP address
automatically.
d Click OK to close the Edit Setting dialog box.
2 Repeat Step 1 to add another VM NIC.
3 Power on the vSphere Replication appliance.
4 From the Summary tab of the vSphere Replication appliance, take note of the IP address of the new
network adapters.
You can click View all XX IP addresses to check the IP addresses of the new NICs.
VMware, Inc. 39
Page 40

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
5 Use a supported browser to log in to the vSphere Replication VAMI.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-appliance-address:5480.
6 On the VRS tab, click Configuration.
7 Enter the IP addresses of the new VM NICs that you want to use to isolate the network traffic of
vSphere Replication.
Option Description
IP Address for Incoming Storage
Traffic
IP Address for VRMS Management
Traffic
The IP address to be used by the vSphere Replication Server for incoming
replication data.
The IP address to be used by the vSphere Replication Management Server to
manage the vSphere Replication Server.
8 Click Apply Network Settings.
The different types of traffic that vSphere Replication generates are handled by separate NICs.
VMware, Inc. 40
Page 41
Deploying Additional
vSphere Replication Servers 6
Depending on replication traffic, you might need to deploy one or more additional vSphere Replication
servers.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
Deploy an Additional vSphere Replication Server
n
Register an Additional vSphere Replication Server
n
Replication Server Connection States
n
Reconfigure vSphere Replication Server Settings
n
Unregister and Remove A vSphere Replication Server
n
Disable the Embedded vSphere Replication Server
Deploy an Additional vSphere Replication Server
The vSphere Replication appliance includes a vSphere Replication server. However, you might need to
deploy multiple vSphere Replication servers to meet your load balancing needs.
You can deploy multiple vSphere Replication servers to route traffic from source hosts to target
datastores without traveling between different sites managed by the same vCenter Server.
Important If you use the HTML5-based vSphere Client to deploy the OVF virtual appliance, the
deployment succeeds, but the vSphere Replication fails to start.
For information about the loads that a vSphere Replication management server and a
vSphere Replication server can support, see http://kb.vmware.com/s/article/2102453.
Prerequisites
n
Deploy vSphere Replication appliances on the source and target sites.
n
Deploy vSphere Replication servers on a network that allows them to communicate with the
vSphere Replication appliances on the source and target sites.
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication servers can communicate with the ESXi Server instances on the
source site that hosts the replicated virtual machines.
VMware, Inc.
41
Page 42

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Web Client on the site where you want to deploy the additional
vSphere Replication server.
2 On the home page, select Hosts and Clusters.
3 Right-click on a data center, host or cluster, and select Deploy OVF Template.
4 Provide the location of the OVF file from which to deploy the additional vSphere Replication server,
and click Next.
n
Select URL and provide the URL to deploy the appliance from an online URL.
n
If you downloaded and mounted the vSphere Replication ISO image on a system in your
environment, select Local file > Browse and navigate to the \bin directory in the ISO image,
and select the vSphere_Replication_AddOn_OVF10.ovf, vSphere_Replication-
system.vmdk, and vSphere_Replication-support.vmdk files.
5 Accept the name, select or search for a destination folder or data center for the virtual appliance, and
click Next.
You can enter a new name for the virtual appliance. The name must be unique within each
vCenter Server virtual machine folder.
6 Select a cluster, host, or resource pool where you want to run the deployed template, and click Next.
7 Review the virtual appliance details and click Next.
8 Select a destination datastore and disk format for the virtual appliance and click Next.
9 Set the network properties. Select DHCP or set a static IP address.
You can change network settings after deployment in the VAMI.
10 Enter a password for the appliance that is at least eight characters long.
11 Review your settings and click Finish.
12 Power on the vSphere Replication appliance.
What to do next
When the OVF file has deployed, register the vSphere Replication server with the vSphere Replication
appliance.
Register an Additional vSphere Replication Server
If you deploy additional vSphere Replication servers, you must register these servers with the
vSphere Replication appliance to enable them as traffic handlers at the recovery site.
Note You can register additional vSphere Replication servers that run within the same vSphere
environment.
VMware, Inc. 42
Page 43
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication appliance is deployed and configured.
n
Verify that an additional vSphere Replication Server is deployed.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
2 On the home page, click Site Recovery and click Open Site Recovery.
3 On the Site Recovery home page, select a site pair and click View Details.
4 On the Site Pair tab, select Configure > Replication Servers.
5 Click the Register icon.
6 From the list, select a virtual machine that is a working vSphere Replication server and click Select.
The newly registered vSphere Replication server appears in the list of vSphere Replication servers.
Replication Server Connection States
You can view the states of the connections with the replication servers and determine if they need a
remediation.
The following table lists the states that you can observe, their meanings, and what you can do to change
a state back to normal.
Table 6‑1. Replication Server Connection States
Icon Status Description Remediation
Connected The connection between the
source replication server and
the target replication server is
working properly.
Disconnected The SSL certificate on the
remote replication server has
been changed.
Not needed.
n
Click the Reconnect icon.
n
Verify that the replication
server has network
connectivity.
Reconfigure vSphere Replication Server Settings
The vSphere Replication appliance contains a vSphere Replication server. If you deploy additional
vSphere Replication servers, the server settings are established during deployment. You can modify the
settings after you deploy the server.
A vSphere Replication server does not require additional configuration through the virtual appliance
management interface (VAMI) after deployment. To increase security, you can change the root password
of the vSphere Replication server and install a new certificate. Using a self-signed certificate provides the
benefit of public-key based encryption and authentication, although using such a certificate does not
provide the level of assurance offered when you use a certificate signed by a certificate authority.
VMware, Inc. 43
Page 44

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
You can also reconfigure the network settings for the vSphere Replication server virtual appliance.
Note vSphere Replication can be deployed with either IPv4 or IPv6 address. Mixing IP addresses, for
example having a single appliance with an IPv4 and an IPv6 address, is not supported. To register as an
extension, vSphere Replication relies on the VirtualCenter.FQDN property of the vCenter Server. When
an IPv6 address is used for vSphere Replication, the VirtualCenter.FQDN property must be set to a
fully qualified domain name that can be resolved to an IPv6 address or to a literal address. When
operating with an IPv6 address, vSphere Replication requires that all components in the environment,
such as vCenter Server and ESXi hosts are accessible using the IPv6 address.
Prerequisites
You deployed an optional vSphere Replication server in addition to the vSphere Replication appliance,
and the server is powered on.
Procedure
1 Use a supported browser to log in to the VAMI of the additional vSphere Replication Server that you
deployed.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-server-address:5480.
Use the root password that you set when you deployed the vSphere Replication server.
2 Click the VRS tab.
3 (Optional) Click Configuration to generate or upload a new certificate.
Option Action
Generate and install a self-signed
certificate
Upload an existing SSL certificate Click Choose File next to the Upload PKCS#12 (*.pfx) file text box to browse for
Click Generate and Install.
an existing certificate, and click Upload and Install.
4 (Optional) Click Security to change the Super User password for the vSphere Replication server.
root is the Super User.
5 (Optional) Click the Network tab to change the network settings.
Option Action
View current network settings Click Status.
Set static or DHCP IPv4 or IPv6
addresses
n
Click Address, and select DHCP, Static, or None for IPv4 addresses.
n
Select Auto, DHCP, or Static for IPv6 addresses. If you select Static, enter
the default gateway and DNS server addresses to use.
VMware, Inc. 44
Page 45

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Option Action
Configure proxy server Click Proxy, select the Use a proxy server check box, and enter the proxy
server address and port number.
Save Settings If you do not click Save Settings, changes are discarded.
Note After the IP address of the vSphere Replication server on the target site changes, you must
manually reconfigure replications on the source site to point to the new IP address.
6 (Optional) Select VRS > Configuration > Restart to restart the vSphere Replication service.
7 (Optional) Select the System tab and click Reboot to reboot the vSphere Replication server
appliance.
Unregister and Remove A vSphere Replication Server
If you deployed additional vSphere Replication server instances that you no longer require, you must
unregister them from the vSphere Replication appliance before you delete them.
Prerequisites
Verify that the vSphere Replication server that you want to unregister does not serve any replications,
otherwise the operations will fail.
Procedure
1 On the Site Recovery home page, select a site pair and click View Details.
2 On the Site Pair tab, select Replication Servers and find the vSphere Replication server in the list.
If you have both vSphere Replication and Site Recovery Manager installed, Replication Servers is
located on the Site Pair tab, under Configure.
3 Select the server and click the Unregister icon.
4 In the Hosts and Clusters view of the vSphere Client, power off and delete the vSphere Replication
server virtual machine.
Disable the Embedded vSphere Replication Server
The vSphere Replication appliance includes an embedded vSphere Replication Server by default. If you
want to disable the embedded vSphere Replication server, you can do so using ssh.
Prerequisites
Make sure that no replications are using the embedded server. Stop the replications or move them to a
different server.
VMware, Inc. 45
Page 46

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Procedure
1 Use SSH into the vSphere Replication appliance and enter:
# /opt/vmware/hms/bin/hms-configtool -cmd reconfig -property hms-embedded-hbr=false
2 Restart the HMS service.
# service hms restart
You can now unregister the embedded vSphere Replication server from the vSphere Replication user
interface.
What to do next
Rebooting vSphere Replication does not automatically register the embedded server. To restore the
default behavior to register automatically the embedded vSphere Replication server, enter:
# /opt/vmware/hms/bin/hms-configtool -cmd reconfig -property hms-embedded-hbr=true
# service hms restart
VMware, Inc. 46
Page 47

Upgrading vSphere Replication 7
You upgrade the vSphere Replication appliance and any additional vSphere Replication servers by using
a downloaded ISO image.
The downloadable ISO image is the only means of upgrading from vSphere Replication 6.1.2 or 6.5.1 to
vSphere Replication 8.1. You cannot upgrade vSphere Replication from version 6.1.2 or 6.5.1 to version
8.1 by using vSphere Update Manager or the virtual appliance management interface (VAMI) of the
vSphere Replication appliance. After you have installed vSphere Replication 8.1 or upgraded to version
8.1 by using the ISO image, you can use the VAMI or Update Manager to install later 8.1.x update
releases.
After you upgrade vSphere Replication to version 8.1, you can no longer use the old vSphere Replication
plug-in to manage the updated vSphere Replication sites. You must use the new standalone
vSphere Replication user interface and plug-in instead.
You cannot downgrade to an earlier version of vSphere Replication.
Example: vSphere Replication Upgrade Scenarios
You use the ISO file to upgrade to a major version of vSphere Replication, for example from 6.1.2 or 6.5.1
to 8.1.
You use Update Manager, the VAMI, or the ISO file to install an update release of vSphere Replication,
for example upgrade 5.5.0 to 5.5.1.
These examples of upgrade and update scenarios are not exhaustive. For the full list of supported
upgrade paths, see the Compatibility Matrices for vSphere Replication 8.1 at
https://docs.vmware.com/en/vSphere-Replication/8.1/rn/vsphere-replication-compat-matrix-8-1.html.
n
You can upgrade vSphere Replication 6.1.2 or 6.5.1 to 8.1 by using the ISO file for
vSphere Replication 8.1.
n
You cannot upgrade vSphere Replication 6.1.2 or 6.5.1 to 8.1 by using Update Manager or the VAMI.
n
You can upgrade vSphere Replication 5.5.0 to 5.5.1 by using Update Manager, the VAMI, or the ISO
file.
VMware, Inc.
47
Page 48
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
Order of Upgrading vSphere and vSphere Replication Components
n
Upgrade Additional vSphere Replication Servers
n
Upgrade the vSphere Replication Appliance
n
Upgrade vSphere Replication 8.0 to Version 8.1
n
Update the vCenter Server IP Address in the vSphere Replication Management Server
Order of Upgrading vSphere and vSphere Replication
Components
To upgrade vSphere Replication, you must upgrade certain components of your vSphere environment in
the correct order.
Upgrade the components on the protected site before you upgrade the components on the recovery site.
If you encounter problems that prevent you from using the protected site when you upgrade the protected
site, you can use the recovery site to perform a recovery. The ESXi hosts can be upgraded at any time.
1 Upgrade all components of vCenter Server on the protected site.
2 Upgrade any additional vSphere Replication server deployments on the protected site.
3 Upgrade the vSphere Replication appliance on the protected site.
4 Upgrade all components of vCenter Server on the recovery site.
5 Upgrade any additional vSphere Replication server deployments on the recovery site.
6 Upgrade the vSphere Replication appliance on the recovery site.
7 Upgrade the ESXi host on the recovery site.
8 Upgrade the ESXi host on the protected site.
9 Upgrade VMware Tools for the replicated VMs.
Upgrade Additional vSphere Replication Servers
You upgrade the additional vSphere Replication servers by using a downloadable ISO image.
You must deploy your additional vSphere Replication servers before the vSphere Replication
Management Server. If you deploy the vSphere Replication Management Server before the additional
servers, you must restart the management server after you complete the upgrade procedure of the
additional servers.
Important If you use the HTML5-based vSphere Client to deploy the OVF virtual appliance, the
deployment succeeds, but the vSphere Replication fails to start.
VMware, Inc. 48
Page 49

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Prerequisites
n
Download the VMware-vSphere_Replication-8.1.x.x-build_number.iso image from the
vSphere Downloads page. Copy the ISO image file to a datastore that is accessible from the
vCenter Server instance that you use with vSphere Replication.
n
If the vSphere Replication version that you run is not supported for direct upgrade to
vSphere Replication 8.1, upgrade your vSphere Replication instance to a supported version. For
example, to upgrade vSphere Replication 6.0 to 8.1, you must first upgrade 6.0 to 6.1.2, and then
upgrade 6.1.2 to 8.1. See the interoperability matrix at
http://www.vmware.com/resources/compatibility/sim/interop_matrix.php for solution upgrade paths for
vSphere Replication.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Web Client on the site where you want to upgrade vSphere Replication.
2 On the home page, select Hosts and Clusters.
3 Right-click on a data center, host or cluster, and select Deploy OVF Template.
4 Provide the location of the OVF file from which to deploy the vSphere Replication server, and click
Next.
n
Select URL and provide the URL to deploy the appliance from an online URL.
n
If you downloaded and mounted the vSphere Replication ISO image on a system in your
environment, select Local file > Browse and navigate to the \bin directory in the ISO image,
and select the vSphere_Replication_Migrate_AddOn_OVF10.ovf, vSphere_Replication-
system.vmdk, and vSphere_Replication-support.vmdk files.
5 Accept the name, select or search for a destination folder or data center for the virtual appliance, and
click Next.
You can enter a new name for the virtual appliance. The name must be unique within each
vCenter Server virtual machine folder.
6 Select a cluster, host, or resource pool where you want to run the deployed template, and click Next.
7 Review the virtual appliance details and click Next.
8 Select a destination datastore and disk format for the virtual appliance and click Next.
9 Select a network from the list of available networks, set the IP protocol and IP allocation, and click
Next.
vSphere Replication supports both DHCP and static IP addresses. You can also change network
settings by using the virtual appliance management interface (VAMI) after installation.
10 Set the password for the root account for the customized template, and click Next.
11 Review the binding to the vCenter Extension vService and click Next.
12 Review the settings and click Finish.
The vSphere Replication appliance is deployed.
VMware, Inc. 49
Page 50
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
13 Power on the vSphere Replication virtual machine.
14 Open the console of the newly deployed vSphere Replication server.
15 Enter the IP address of the additional vSphere Replication server that you want to upgrade.
16 Enter the root password of the additional vSphere Replication server that you want to upgrade.
What to do next
n
Upgrade the vSphere Replication appliance. See Upgrade the vSphere Replication Appliance.
n
Delete the virtual machine of the old vSphere Replication server.
Upgrade the vSphere Replication Appliance
You upgrade the vSphere Replication appliance and the vSphere Replication server by using a
downloadable ISO image.
Important If you use the HTML5-based vSphere Client to deploy the OVF virtual appliance, the
deployment succeeds, but the vSphere Replication fails to start.
Prerequisites
n
Download the VMware-vSphere_Replication-8.1.x.x-build_number.iso image from the
vSphere Downloads page. Copy the ISO image file to a datastore that is accessible from the
vCenter Server instance that you use with vSphere Replication.
n
If the vSphere Replication version that you run is not supported for direct upgrade to
vSphere Replication 8.1, upgrade your vSphere Replication instance to a supported version. For
example, to upgrade vSphere Replication 6.0 to 8.1, you must first upgrade 6.0 to 6.1.2, and then
upgrade 6.1.2 to 8.1. See the interoperability matrix at
http://www.vmware.com/resources/compatibility/sim/interop_matrix.php for solution upgrade paths for
vSphere Replication.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Web Client on the site where you want to upgrade vSphere Replication.
2 On the home page, select Hosts and Clusters.
3 Right-click on a data center, host or cluster, and select Deploy OVF Template.
Note You must deploy your additional vSphere Replication servers before the vSphere Replication
appliance.
VMware, Inc. 50
Page 51

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
4 Provide the location of the OVF file from which to deploy the vSphere Replication server, and click
Next.
n
Select URL and provide the URL to deploy the appliance from an online URL.
n
If you downloaded and mounted the vSphere Replication ISO image on a system in your
environment, select Local file > Browse and navigate to the \bin directory in the ISO image,
and select the vSphere_Replication_OVF10.ovf, vSphere_Replication-system.vmdk, and
vSphere_Replication-support.vmdk files.
5 Accept the name, select or search for a destination folder or data center for the virtual appliance, and
click Next.
You can enter a new name for the virtual appliance. The name must be unique within each
vCenter Server virtual machine folder.
6 Select a cluster, host, or resource pool where you want to run the deployed template, and click Next.
7 Review the virtual appliance details and click Next.
8 Accept the end-user license agreements (EULA) and click Next.
9 Select the number of vCPUs for the virtual appliance and click Next.
Note Selecting higher number of vCPUs ensures better performance of the vSphere Replication
appliance, but might slow down the replications that run on ESXi host systems that have 4 or less
cores per NUMA node. If you are unsure what the hosts in your environment are, select 2 vCPUs.
10 Select a destination datastore and disk format for the virtual appliance and click Next.
11 Select a network from the list of available networks, set the IP protocol and IP allocation, and click
Next.
vSphere Replication supports both DHCP and static IP addresses. You can also change network
settings by using the virtual appliance management interface (VAMI) after installation.
12 On the Customize template page, enter one or more NTP server host names or IP addresses.
13 Set the password for the root account for the customized template, and click Next.
14 Review the binding to the vCenter Extension vService and click Next.
15 Review the settings and click Finish.
The vSphere Replication appliance is deployed.
16 Power on the vSphere Replication virtual machine.
17 Open the console of the newly deployed vSphere Replication appliance.
VMware, Inc. 51
Page 52
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
18 Select Upgrade.
Option Description
Continue Continue with the deployment of a new vSphere Replication appliance. After
successful deployment, you must register the vSphere Replication appliance to
the vCenter Server from the VAMI. As a result, you can no longer use the existing
replications. You must create new ones.
Shutdown Shut down the machine if you do not want to proceed with the upgrade.
Upgrade Continue with the upgrade of the vSphere Replication appliance. During the
upgrade process, the existing configuration of the vSphere Replication appliance
is migrated to the new vSphere Replication appliance. After successful upgrade,
all replications continue working.
19 Enter the root password of the vSphere Replication appliance that you want to upgrade.
20 Confirm that you want to continue with the upgrade process.
21 Enter the credentials of a user with administrator privileges to vCenter Single Sign-On.
Initially, only the user administrator@vsphere.local has these privileges.
What to do next
n
If your infrastructure uses more than one vSphere Replication Server, you must upgrade all
vSphere Replication Server instances to version 8.1 on the protected and the recovery site.
n
Delete the virtual machine of the old vSphere Replication server.
Important If the vSphere Replication appliance that you upgraded uses the embedded database, you
must apply additional configuration to enable the support of up to 2000 replications. See
http://kb.vmware.com/kb/2102463. No additional configuration is required for vSphere Replication
appliances that are configured to use an external database.
Upgrade vSphere Replication 8.0 to Version 8.1
If you are using vSphere Replication 8.0 as part of the VMware Site Recovery service, you can upgrade
vSphere Replication 8.0 by using a downloadable ISO image.
Important If you use the HTML5-based vSphere Client to deploy the OVF virtual appliance, the
deployment succeeds, but the vSphere Replication fails to start.
Prerequisites
n
Download the VMware-vSphere_Replication-8.1.x.x-build_number.iso image from the
vSphere Downloads page. Copy the ISO image file to a datastore that is accessible from the
vCenter Server instance that you use with vSphere Replication.
Procedure
1 In the vSphere Web Client, right-click the vSphere Replication appliance virtual machine and select
Open Console.
VMware, Inc. 52
Page 53

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
2 Log in as the root user, and run the following command.
if [ -d '/var/run' ] && [ ! -L '/var/run' ] ; then mv -f /var/run/* /run/; rm -
rf /var/run; ln -sf /run /var/; fi
3 Right-click the vSphere Replication virtual machine and select Edit Settings.
4 Increase the vSphere Replication Management Server appliance memory to 8 GB.
5 On the Virtual Hardware tab, select CD/DVD Drive > Datastore ISO File.
6 Navigate to the ISO image in the datastore.
7 For File Type, select ISO Image and click OK.
8 Select the option to connect at power-on and follow the prompts to add the CD/DVD drive to the
vSphere Replication virtual machine.
9 Power on the vSphere Replication virtual machine.
10 In a Web browser, log in to the virtual appliance management interface (VAMI).
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr_appliance_address:5480.
11 Click the Update tab.
12 Click Settings, select Use CDROM Updates, and click Save Settings.
13 Click Status and click Check Updates.
The appliance version appears in the list of available updates.
14 Click Install Updates and click OK.
15 After the updates install, click the System tab and click Reboot.
16 After the vSphere Replication appliance reboots, log in to the VAMI and repeat the steps to register
the vSphere Replication appliance with vCenter Single Sign-On.
This registers the vSphere Replication appliance in the Lookup Service and vCenter Single Sign-On
or updates an existing vSphere Replication registration.
17 Log out of the vSphere Web Client, clear the browser cache, and log in again to see the upgraded
appliance.
18 Reboot the vSphere Replication appliance.
What to do next
n
If your infrastructure uses more than one vSphere Replication Server, you must upgrade all
vSphere Replication Server instances to version 8.1 on the on-premises site.
VMware, Inc. 53
Page 54

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
n
Delete the virtual machine of the old vSphere Replication server.
Important If the vSphere Replication appliance that you upgraded uses the embedded database, you
must apply additional configuration to enable the support of up to 2000 replications. See
http://kb.vmware.com/kb/2102463. No additional configuration is required for vSphere Replication
appliances that are configured to use an external database.
Update the vCenter Server IP Address in the vSphere Replication Management Server
After you upgrade vCenter Server and the vSphere Replication appliance, if the vCenter Server certificate
or the IP address changed during the upgrade, you must perform additional steps.
To update the vCenter Server certificate, see vSphere Replication is Inaccessible After Changing vCenter
Server Certificate.
If vCenter Server uses a static IP address, it preserves the IP address by default after upgrade. If the
vCenter Server uses a DHCP address that changed during the upgrade, and the vSphere Replication
Management Server is configured to use the vCenter Server IP address and not FQDN, update the IP
address in the vSphere Replication Management Server.
Prerequisites
Verify that the vCenter Server and vSphere Replication components are upgraded. For more information,
see Order of Upgrading vSphere and vSphere Replication Components.
Procedure
1 Power off the vSphere Replication appliance and power it on to retrieve the OVF environment.
2 Use a supported browser to log in to the vSphere Replication VAMI.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-appliance-address:5480.
3 On the Configuration tab, enter the new IP address of the vCenter Server.
4 Click Save and Restart.
VMware, Inc. 54
Page 55

Reconfigure the
vSphere Replication Appliance 8
If necessary, you can reconfigure the vSphere Replication appliance settings by using the virtual
appliance management interface (VAMI).
You provide the settings for the vSphere Replication appliance in the Deploy OVF wizard when you
deploy the appliance. If you selected automatic configuration of the appliance using an embedded
database, you can use the vSphere Replication appliance immediately after deployment. If necessary you
can modify the configuration settings of the vSphere Replication appliance after you deploy it.
n
Reconfigure General vSphere Replication Settings
You can use vSphere Replication immediately after you deploy the vSphere Replication appliance. If
necessary, you can reconfigure the general settings after deployment in the virtual appliance
management interface (VAMI).
n
Change the SSL Certificate of the vSphere Replication Appliance
You can change the initial vSphere Replication SSL certificate by generating a new self-signed
certificate or uploading an SSL certificate signed by a trusted Certificate Authority.
n
Change the Password of the vSphere Replication Appliance
You set the password of the vSphere Replication appliance when you deploy the appliance. You can
change the password after installation by using the virtual appliance management interface (VAMI).
n
Change the Keystore Passwords of the vSphere Replication Appliance
To increase security, you can change the passwords of the vSphere Replication appliance keystore.
If you copy the keystores from the appliance to another machine, you must change the passwords
before the copy operation.
n
Change the Truststore Passwords of the vSphere Replication Appliance
To increase security, you can change the passwords of the vSphere Replication appliance truststore.
n
Configure vSphere Replication Network Settings
You can review current network settings and change address and proxy settings for
vSphere Replication. You might make these changes to match network reconfigurations.
n
Configure vSphere Replication System Settings
You can view the vSphere Replication system settings to gather information about the
vSphere Replication appliance. You can also set the system time zone, and reboot or shut down the
appliance.
VMware, Inc.
55
Page 56

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
n
Update the NTP Server Configuration
Change the NTP server configuration of your vSphere Replication server if you change the NTP
servers that your vSphere Replication server uses.
n
Reconfigure vSphere Replication to Use an External Database
The vSphere Replication appliance contains an embedded vPostgreSQL database that you can use
immediately after you deploy the appliance, without any additional database configuration. If
necessary, you can reconfigure vSphere Replication to use an external database.
n
Use the Embedded vSphere Replication Database
If you configured vSphere Replication to use an external database, you can reconfigure
vSphere Replication to use the embedded database.
Reconfigure General vSphere Replication Settings
You can use vSphere Replication immediately after you deploy the vSphere Replication appliance. If
necessary, you can reconfigure the general settings after deployment in the virtual appliance
management interface (VAMI).
The general settings of the vSphere Replication appliance include the name and IP address of the
vSphere Replication appliance, the address, and port of the vCenter Server instance to which it connects,
and an administrator email address. You can change the general settings from the default values in the
virtual appliance management interface (VAMI).
For example, you can reconfigure the address of the vSphere Replication appliance if you did not specify
a fixed IP address when you deployed the appliance, and DHCP changes the address after deployment.
Similarly, you can update the address of the vCenter Server instance if the address changes after
deployment.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication appliance is powered on.
n
Verify that you have administrator privileges to configure the vSphere Replication appliance.
n
Verify that the vCenter Server version is upgraded to vCenter Server 6.5.
Procedure
1 Use a supported browser to log in to the vSphere Replication VAMI.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-appliance-address:5480.
2 (Optional) Review and confirm the browser security exception to proceed to the login page.
3 Enter the root user name and password for the appliance.
You configured the root password during the OVF deployment of the vSphere Replication appliance.
4 On the VR tab, click Configuration.
5 In the VRM Host text box, enter the address of the vSphere Replication appliance or click Browse to
select an IP address from a list.
VMware, Inc. 56
Page 57

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
6 In the LookupService Address text box, enter the Platform Services Controller address to use with
this installation.
You must use the same address format that you used when you installed vCenter Server. For
example, if you used a fully qualified domain name during installation, you must use that FQDN. If
you used an IP address, you must use that IP address.
7 In the SSO Administrator text box, enter a Platform Services Controller administrator email address.
8 Click Save and Restart Service to apply the changes.
You reconfigured the general settings of the vSphere Replication appliance.
Change the SSL Certificate of the vSphere Replication
Appliance
You can change the initial vSphere Replication SSL certificate by generating a new self-signed certificate
or uploading an SSL certificate signed by a trusted Certificate Authority.
vSphere Replication generates a standard SSL certificate when the appliance first boots and registers
with vCenter Server. The vSphere Replication self-signed certificate expires after five years from the first
boot of the appliance. The default certificate policy uses trust by thumbprint.
You can change the SSL certificate, for example if your company's security policy requires that you use
trust by validity and thumbprint or a certificate signed by a certification authority. You change the
certificate by using the virtual appliance management interface (VAMI) of the vSphere Replication
appliance. For information about the SSL certificates that vSphere Replication uses, see vSphere
Replication Certificate Verification and Requirements When Using a Public Key Certificate with vSphere
Replication.
See vSphere Replication Certificate Verification for details of how vSphere Replication handles
certificates.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication appliance is powered on.
n
Verify that you have administrator privileges to configure the vSphere Replication appliance.
Procedure
1 Use a supported browser to log in to the vSphere Replication VAMI.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-appliance-address:5480.
2 Enter the root user name and password for the appliance.
You configured the root password during the OVF deployment of the vSphere Replication appliance.
3 (Optional) Click the VR tab and click Security to review the current SSL certificate.
4 Click Configuration.
VMware, Inc. 57
Page 58
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
5 (Optional) To enforce verification of a certificate validity, select the Accept only SSL certificates
signed by a trusted Certificate Authority check box.
6 Generate or install a new SSL certificate.
Option Action
Generate a self-signed certificate Click Generate and Install. Using a self-signed certificate provides trust by
thumbprint only and might not be suitable for environments that require high
levels of security. You cannot use a self-signed certificate if you selected Accept
only SSL certificates signed by a trusted Certificate Authority.
Upload a certificate Click Choose File to select a PKCS#12 certificate and click Upload and Install.
Public key certificates must meet certain requirements. See Requirements When
Using a Public Key Certificate with vSphere Replication.
7 Click Save and Restart Service to apply the changes.
You changed the SSL certificate and optionally changed the security policy to use trust by validity and
certificates signed by a certificate authority.
Note If you change a certificate on one of the source or target sites, the connection status to this site
changes to Connection issue. In the vSphere Web Client, you can check the list of target sites under
vSphere Replication on the Manage tab, and reconnect the sites.
vSphere Replication Certificate Verification
vSphere Replication verifies the certificates of vCenter Server and remote vSphere Replication servers.
All communication between vCenter Server, the local vSphere Replication appliance, and the remote
vSphere Replication appliance goes through a vCenter Server proxy at port 80. All SSL traffic is
tunnelled.
VMware, Inc. 58
Page 59

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
vSphere Replication can trust remote server certificates either by verifying the validity of the certificate
and its thumbprint or by verifying the thumbprint only. The default is to verify by thumbprint only. You can
activate the verification of the certificate validity in the virtual appliance management interface (VAMI) of
the vSphere Replication appliance by selecting the option Accept only SSL certificates signed by a
trusted Certificate Authority when you upload a certificate.
Thumbprint Verification vSphere Replication checks for a thumbprint match. vSphere Replication
trusts remote server certificates if it can verify the the thumbprints through
secure vSphere platform channels or, in some rare cases, after the user
confirms them. vSphere Replication only takes certificate thumbprints into
account when verifying the certificates and does not check certificate
validity.
Verification of
Thumbprint and
Certificate Validity
vSphere Replication checks the thumbprint and checks that all server
certificates are valid. If you select the Accept only SSL certificates
signed by a trusted Certificate Authority option, vSphere Replication
refuses to communicate with a server with an invalid certificate. When
verifying certificate validity, vSphere Replication checks expiration dates,
subject names and the certificate issuing authorities.
In both modes, vSphere Replication retrieves thumbprints from vCenter Server. vSphere Replication
refuses to communicate with a server if the automatically determined thumbprint differs from the actual
thumbprint that it detects while communicating with the respective server.
You can mix trust modes between vSphere Replication appliances at different sites. A pair of
vSphere Replication appliances can work successfully even if you configure them to use different trust
modes.
Requirements When Using a Public Key Certificate with vSphere
Replication
If you enforce verification of certificate validity by selecting Accept only SSL certificates signed by a
trusted Certificate Authority in the virtual appliance management interface (VAMI) of the
vSphere Replication appliance, some fields of the certificate request must meet certain requirements.
vSphere Replication can only import and use certificates and private keys from a file in the PKCS#12
format. Sometimes these files have a .pfx extension.
n
The certificate must be issued for the same server name as the value in the VRM Host setting in the
VAMI. Setting the certificate subject name accordingly is sufficient, if you put a host name in the VRM
Host setting. If any of the certificate Subject Alternative Name fields of the certificate matches the
VRM Host setting, this will work as well.
n
vSphere Replication checks the issue and expiration dates of the certificate against the current date,
to ensure that the certificate has not expired.
VMware, Inc. 59
Page 60

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
n
If you use your own certificate authority, for example one that you create and manage with the
OpenSSL tools, you must add the fully qualified domain name or IP address to the OpenSSL
configuration file.
n
If the fully qualified domain name of the appliance is VR1.example.com, add subjectAltName =
DNS: VR1.example.com to the OpenSSL configuration file.
n
If you use the IP address of the appliance, add subjectAltName = IP: vr-appliance-ip-
address to the OpenSSL configuration file.
n
vSphere Replication requires a trust chain to a well-known root certificate authority.
vSphere Replication trusts all the certificate authorities that the Java Virtual Machine trusts. Also, you
can manually import additional trusted CA certificates in /opt/vmware/hms/security/hms-
truststore.jks on the vSphere Replication appliance.
n
vSphere Replication accepts MD5 and SHA1 signatures, but VMware recommends that you use
SHA256 signatures.
n
vSphere Replication does not accept RSA or DSA certificates with 512-bit keys. vSphere Replication
requires at least 1024-bit keys. VMware recommends using 2048-bit public keys. vSphere Replication
shows a warning if you use a 1024-bit key.
Change the Password of the vSphere Replication Appliance
You set the password of the vSphere Replication appliance when you deploy the appliance. You can
change the password after installation by using the virtual appliance management interface (VAMI).
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication appliance is powered on.
n
Verify that you have administrator privileges to configure the vSphere Replication appliance.
n
Verify that the vCenter Server version is upgraded to vCenter Server 6.5.
Procedure
1 Use a supported browser to log in to the vSphere Replication VAMI.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-appliance-address:5480.
2 Enter the root user name and password for the appliance.
You configured the root password during the OVF deployment of the vSphere Replication appliance.
3 Click the VR tab and click Security.
4 Enter the current password in the Current Password text box.
5 Enter the new password in the New Password and the Confirm New Password text boxes.
The password must be a minimum of eight characters. vSphere Replication does not support blank
passwords.
VMware, Inc. 60
Page 61

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
6 Click Apply to change the password.
Change the Keystore Passwords of the vSphere Replication Appliance
To increase security, you can change the passwords of the vSphere Replication appliance keystore. If you
copy the keystores from the appliance to another machine, you must change the passwords before the
copy operation.
The keystore passwords might be stored in an access restricted configuration file. vSphere Replication
has the following keystores:
n
/opt/vmware/hms/security/hms-keystore.jks, which contains the vSphere Replication
appliance private key and certificate.
n
/opt/vmware/hms/security/hms-truststore.jks, which contains additional CA certificates
besides the ones that Java already trusts.
Procedure
1 To change the password for the hms-keystore.jks keystore, open the remote console of your
vSphere Replication virtual machine and log in as root.
2 Obtain the current keystore password.
# /opt/vmware/hms/bin/hms-configtool -cmd list | grep keystore
Example of the output hms-keystore-password = old_password
3 Change the keystore password.
# /usr/java/default/bin/keytool -storepasswd -storepass old_password -new new_password -
keystore /opt/vmware/hms/security/hms-keystore.jks
4 Change the vSphere Replication appliance private key password.
The following command is a long, single command and must be run at once. There are breaks in the
command for better visibility. Verify that the command returns a success message.
# /usr/java/default/bin/keytool -keypasswd -alias jetty -keypass
old_password -new new_password -storepass new_password -keystore
/opt/vmware/hms/security/hms-keystore.jks
5 Update the configuration with the new password.
/opt/vmware/hms/bin/hms-configtool -cmd reconfig -property 'hms-keystore-password=new_password'
6 Update the tomcat server.xml file with the new password.
sed -i -- 's/old_password/new_password/g' /var/opt/apache-tomcat/conf/server.xml
VMware, Inc. 61
Page 62
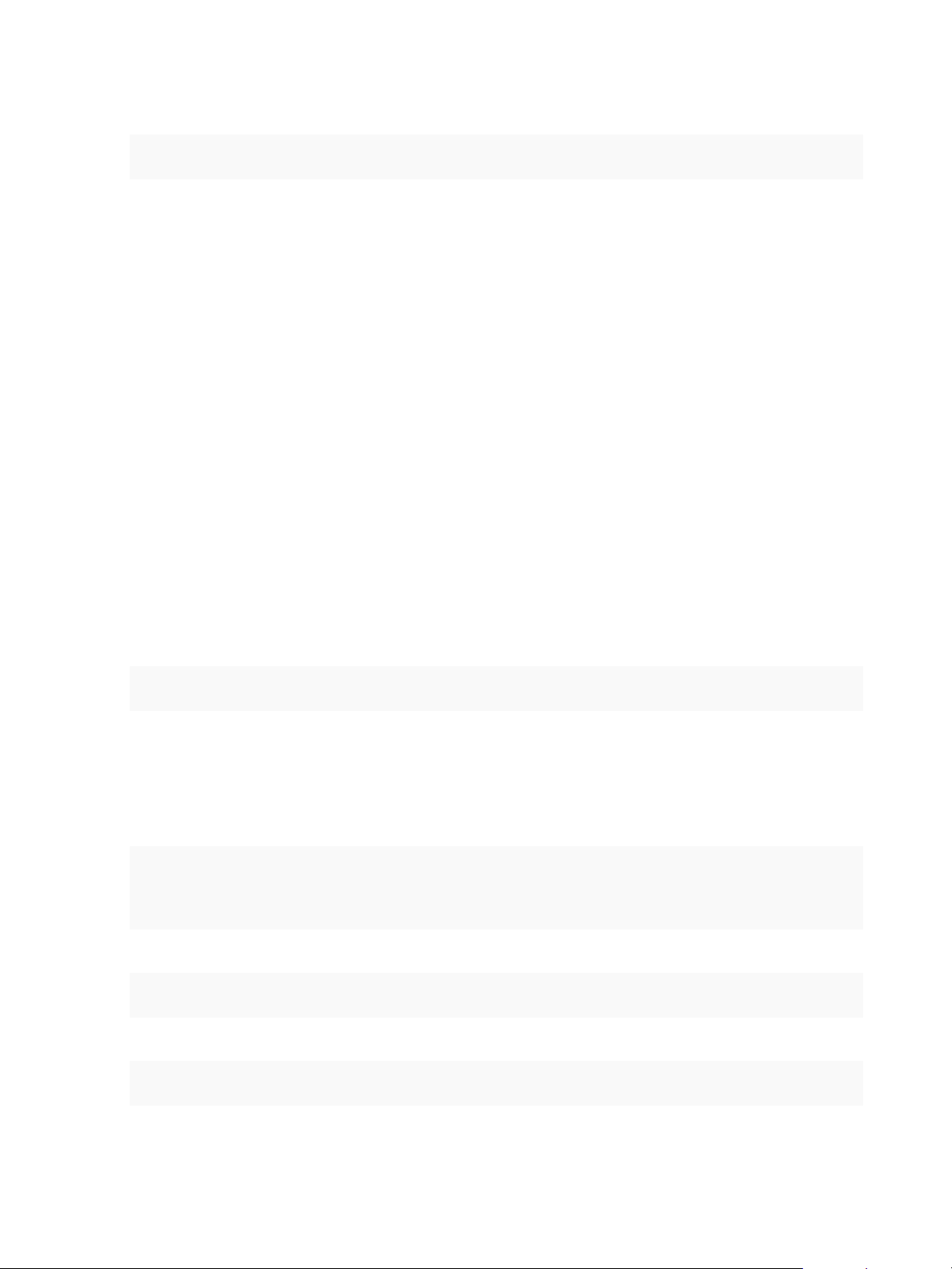
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
7 Reboot the appliance for the changes to take effect.
# reboot
8 Use a supported browser to log in to the vSphere Replication VAMI.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-appliance-address:5480.
9 On the VR tab, click Configuration, and click Save and Restart Service.
What to do next
If you want to change the truststore passwords of the vSphere Replication appliance, see Change the
Truststore Passwords of the vSphere Replication Appliance.
Change the Truststore Passwords of the vSphere Replication Appliance
To increase security, you can change the passwords of the vSphere Replication appliance truststore.
The truststore passwords might be stored in an access restricted configuration file.
Procedure
1 To change the password for the hms-truststore.jks keystore, open the remote console of your
vSphere Replication virtual machine and log in as root.
2 Obtain the current truststore password.
# /opt/vmware/hms/bin/hms-configtool -cmd list | grep truststore
Example of the output: hms-truststore-password = old_password
3 Change the truststore password.
The following command is a long, single command and must be run at once. There are breaks in the
command for better visibility. Verify that the command returns a success message.
# /usr/java/default/bin/keytool -storepasswd -storepass
old_password -new new_password -keystore
/opt/vmware/hms/security/hms-truststore.jks
4 Update the configuration with the new password.
/opt/vmware/hms/bin/hms-configtool -cmd reconfig -property 'hms-truststore-password=new_password'
5 Restart the vSphere Replication service.
# service hms restart
VMware, Inc. 62
Page 63

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
What to do next
If you want to change the keystore passwords of the vSphere Replication appliance, see Change the
Keystore Passwords of the vSphere Replication Appliance.
Configure vSphere Replication Network Settings
You can review current network settings and change address and proxy settings for vSphere Replication.
You might make these changes to match network reconfigurations.
Note vSphere Replication can be deployed with either IPv4 or IPv6 address. Mixing IP addresses, for
example having a single appliance with an IPv4 and an IPv6 address, is not supported. To register as an
extension, vSphere Replication relies on the VirtualCenter.FQDN property of the vCenter Server. When
an IPv6 address is used for vSphere Replication, the VirtualCenter.FQDN property must be set to a
fully qualified domain name that can be resolved to an IPv6 address or to a literal address. When
operating with an IPv6 address, vSphere Replication requires that all components in the environment,
such as vCenter Server and ESXi hosts are accessible using the IPv6 address.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication appliance is powered on.
n
Verify that you have administrator privileges to configure the vSphere Replication appliance.
n
Verify that the vCenter Server version is upgraded to vCenter Server 6.5.
Procedure
1 Use a supported browser to log in to the vSphere Replication VAMI.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-appliance-address:5480.
2 Enter the root user name and password for the appliance.
You configured the root password during the OVF deployment of the vSphere Replication appliance.
3 Click the Network tab.
4 Click Status to review current network settings.
5 Click Address to review or modify IPv4 and IPv6 address settings.
IP Address Type Option Description
IPv4 DHCP DHCP is not recommended if the IP address of the appliance might change if it reboots.
IPv4 Static With a static IPv4 address, you can modify the IP settings, DNS settings, net mask, and host
name information.
IPv4 None Disabling IPv4 addresses forces the use of IPv6 addresses only.
IPv6 Auto Automatic assignment of IPv6 addresses is not recommended if the IP address of the appliance
might change if it reboots.
IPv6 DHCP DHCP is not recommended if the IP address of the appliance might change if it reboots.
IPv6 Static With a static IPv6 address, you can modify the IP address and the address prefix.
VMware, Inc. 63
Page 64
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
6 Click Save Settings.
If you do not click Save Settings, changes are discarded.
Note After the IP address of the vSphere Replication server on the target site changes, you must
manually reconfigure replications on the source site to point to the new IP address.
7 Click Proxy to review or modify proxy settings.
a Select the Use a proxy server check box to use a proxy server.
b Enter a proxy server name in the HTTP Proxy Server text box.
c Enter a proxy port in the Proxy Port text box.
d (Optional) Enter a proxy server user name and password.
8 Click Save Settings.
If you do not click Save Settings, changes are discarded.
What to do next
A network address change might require you to reconnect the source and target sites and might also
require a change of certificate if you have activated verification of certificate validity.
Configure vSphere Replication System Settings
You can view the vSphere Replication system settings to gather information about the
vSphere Replication appliance. You can also set the system time zone, and reboot or shut down the
appliance.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication appliance is powered on.
n
Verify that you have administrator privileges to configure the vSphere Replication appliance.
n
Verify that the vCenter Server version is upgraded to vCenter Server 6.5.
Procedure
1 Use a supported browser to log in to the vSphere Replication VAMI.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-appliance-address:5480.
2 Enter the root user name and password for the server.
3 Click the System tab.
VMware, Inc. 64
Page 65

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
4 Click Information.
You can review information about vSphere Replication, and reboot or shutdown the appliance.
Option Description
Vendor Vendor name
Appliance Name vSphere Replication appliance name
Appliance Version vSphere Replication version
Hostname Hostname of the appliance
OS Name Operating system name and version
OVF Environment: View Displays information about the OVF environment
Reboot Reboots the virtual appliance
Shutdown Shuts down the virtual appliance
Shutting down the vSphere Replication appliance stops configured replications and prevents you from
configuring a replication of new virtual machines and modifying existing replication settings.
5 Click Time Zone.
Option Description
System Time Zone Time zones are available from the drop-down menu
Save Settings Saves settings
Cancel Changes Discards changes
Update the NTP Server Configuration
Change the NTP server configuration of your vSphere Replication server if you change the NTP servers
that your vSphere Replication server uses.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the remote console of your vSphere Replication virtual machine is open and that you use
root credentials.
n
Verify that the status of the NTP service of your vSphere Replication server is running.
Procedure
1 Open the /etc/ntp.conf file.
2 Update the IP address or name of the NTP server or servers.
3 (Optional) To add an additional NTP server add the following line.
server your_NTP_server_IP_address_or_name
4 Save the change and close ntp.conf file.
5 Run the service ntp reload command to reload the NTP configuration.
VMware, Inc. 65
Page 66
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Your vSphere Replication server is synchronized with the new NTP server.
Reconfigure vSphere Replication to Use an External
Database
The vSphere Replication appliance contains an embedded vPostgreSQL database that you can use
immediately after you deploy the appliance, without any additional database configuration. If necessary,
you can reconfigure vSphere Replication to use an external database.
Each vSphere Replication appliance requires its own database. If the database at either site is corrupted,
vSphere Replication does not function. vSphere Replication cannot use the vCenter Server database
because it has different database schema requirements. However, if you do not use the embedded
vSphere Replication database, you can use the vCenter Server database to create and support an
external vSphere Replication database.
You might need to use an external database to improve performance or load balancing, for easier backup,
or to meet your company's database standards.
Note vSphere Replication server inside the vSphere Replication appliance uses its own embedded
database and config files. Configuring VRMS to use external database does not provide protection of
losing the vSphere Replication appliance or any additional vSphere Replication Server appliance.
If you reinitialize the database after you deploy vSphere Replication, you must go to the
vSphere Replication virtual appliance management interface (VAMI) to reconfigure vSphere Replication to
use the new database connection.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication appliance is powered on.
n
Verify that you have administrator privileges to configure the vSphere Replication appliance.
n
You must create and configure the external database before you connect it to vSphere Replication.
See vSphere Replication Supported Databases for the configuration requirements for each supported
type of database.
Procedure
1 Use a supported browser to log in to the vSphere Replication VAMI.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-appliance-address:5480.
2 (Optional) Review and confirm the browser security exception to proceed to the login page.
3 Enter the root user name and password for the appliance.
You configured the root password during the OVF deployment of the vSphere Replication appliance.
4 On the VR tab, click Configuration.
5 Select Manual configuration to specify a configuration or select Configure from an existing VRM
database to use a previously established configuration.
VMware, Inc. 66
Page 67
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
6 In the DB text boxes, provide information about the database for vSphere Replication to use.
Option Setting
DB Type Select SQL Server or Oracle.
DB Host IP address or fully qualified domain name of the host on which the database server is running.
DB Port Port on which to connect to the database.
DB user name User name for the vSphere Replication database user account that you create on the database server.
DB Password Password for the vSphere Replication database user account that you create on the database server.
DB Name Name of the vSphere Replication database instance.
7 (Optional) Select the Show DB URL check box.
Advanced users can fine-tune other database properties by modifying the URL, for example if you
use a named instance of SQL Server.
8 Click Save and Restart Service to apply the changes.
You configured vSphere Replication to use an external database instead of the database that is
embedded in the vSphere Replication appliance.
vSphere Replication Supported Databases
The vSphere Replication virtual appliance includes the VMware standard embedded vPostgreSQL
database. You can also configure vSphere Replication to use an external database.
Automated migration between the embedded database and any external databases is not supported in
any direction. If you must configure an external database, you must manually migrate the data or
manually recreate all replications.
You can configure vSphere Replication to use one of the supported external databases.
n
Microsoft SQL
n
Oracle
External vPostgreSQL databases are not supported. vSphere Replication supports the same database
versions as vCenter Server. For supported database versions, see the VMware Product Interoperability
Matrixes at http://partnerweb.vmware.com/comp_guide2/sim/interop_matrix.php?.
Configure Microsoft SQL Server for vSphere Replication
When you create a Microsoft SQL Server database, you must configure it correctly to support
vSphere Replication.
You use SQL Server Management Studio to create and configure an SQL Server database for
vSphere Replication.
This information provides the general steps that you must perform to configure an SQL Server database
for vSphere Replication. For instructions about how to perform the relevant steps, see the SQL Server
documentation.
VMware, Inc. 67
Page 68

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Prerequisites
Verify that the SQL Server Browser service is running.
Procedure
1 Select Mixed Mode Authentication when you create the database instance.
The vSphere Replication appliance and the database server run on different hosts, so you must use
mixed mode authentication and not Windows Authentication.
2 Use either a named instance or the default instance of SQL Server.
If you intend to use dynamic TCP ports, you must use a named instance of SQL Server.
3 Enable TCP on the database instance.
4 Set a TCP port.
Option Action
Static TCP port Set the TCP port to the default of 1433.
Dynamic TCP port a Use a named instance of SQL Server. You can only use dynamic ports with a
named instance of SQL Server.
b Select the Show DB URL check box in the virtual appliance management
interface (VAMI) of the vSphere Replication appliance.
c Modify the DB URL value. Replace port=port_number with
instanceName=instance_name in the URL.
d Use the PortQuery command from a remote machine to check that the port
on which the SQL Server Browser service runs is not blocked by a firewall.
The SQL Server Browser runs on port 1434. Enter the PortQuery command
in a terminal window.
PortQry.exe -n Machine_Name -p UDP -e 1434
5 Verify that the firewall on the database server permits inbound connections on the TCP port.
6 Create the vSphere Replication security login.
7 Create the vSphere Replication database and set the vSphere Replication security login as the
database owner.
8 Keep the dbo user and dbo schema settings.
Because the vSphere Replication security login is the database owner, it maps to the database user
dbo and uses the dbo schema.
Configure Oracle Server for vSphere Replication
You must configure an Oracle Server database correctly to support vSphere Replication.
You create and configure an Oracle Server database for vSphere Replication by using the tools that
Oracle Server provides.
VMware, Inc. 68
Page 69

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
This information provides the general steps that you must perform to configure an Oracle Server
database for vSphere Replication. For instructions about how to perform the relevant steps, see the
Oracle documentation.
Procedure
1 When creating the database instance, select UTF-8 encoding.
2 Create the vSphere Replication database user account.
3 If they are not selected already, select the CONNECT and RESOURCE roles.
These roles provide the privileges that vSphere Replication requires.
Use the Embedded vSphere Replication Database
If you configured vSphere Replication to use an external database, you can reconfigure
vSphere Replication to use the embedded database.
The vSphere Replication appliance includes an embedded vPostgreSQL database. The embedded
database is preconfigured for use with vSphere Replication and is enabled if you accept the default
Performs initial configuration of the appliance using an embedded database option when you
deploy the vSphere Replication appliance. If you reconfigured vSphere Replication to use an external
database after deployment, you can switch to the embedded database. After switching databases, you
must manually configure replications again as the replication management data is not migrated to the
database. You can use the reset feature in the embedded database to drop replications, site connections
and external vSphere Replication registrations.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication appliance is powered on.
n
Verify that you have administrator privileges to configure the vSphere Replication appliance.
n
You must have reconfigured vSphere Replication to use an external database.
Procedure
1 Use a supported browser to log in to the vSphere Replication VAMI.
The URL for the VAMI is https://vr-appliance-address:5480.
2 (Optional) Review and confirm the browser security exception to proceed to the login page.
3 Enter the root user name and password for the appliance.
You configured the root password during the OVF deployment of the vSphere Replication appliance.
4 On the VR tab, click Configuration.
5 Select Configure using the embedded database.
6 (Optional) Click Reset Embedded Database to reset the database.
7 Click Save and Restart Service to apply the changes.
VMware, Inc. 69
Page 70

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
You configured vSphere Replication to use the embedded vSphere Replication database.
VMware, Inc. 70
Page 71
vSphere Replication Roles and
Permissions 9
You can use any predefined roles or clone an existing role, and add or remove privileges from it based on
your needs.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
vSphere Replication Roles Reference
n
Assign vSphere Replication Roles to Users
n
Assign VRM Replication Viewer Role
n
Assign VRM Virtual Machine Replication User Role
n
Assign VRM Virtual Machine Recovery User Role and Perform a Recovery Operation
n
Clone Existing VRM Administrator Role and Modify Privileges
vSphere Replication Roles Reference
vSphere Replication includes a set of roles. Each role includes a set of privileges, which enable users
with those roles to complete different actions.
For information about how to assign roles, see Assigning Roles in the vSphere Web Client in vSphere
Security.
Note When assigning permissions with no propagation, make sure that you have at least Read-only
permission on all parent objects.
VMware, Inc.
71
Page 72
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Table 9‑1. vSphere Replication Roles
Role Actions that this Role Permits Privileges that this Role Includes
Objects in vCenter Server
Inventory that this Role Can
Access
VRM
replication
viewer
VRM virtual
machine
replication user
n
View replications.
n
Cannot change replication
parameters.
n
View replications.
n
Manage datastores.
n
Configure and unconfigure
replications.
n
Manage and monitor
replications.
n
View defined storage
capabilities and storage
profiles.
Requires a corresponding user
with the same role on the target
site and additionally
vSphere Replication target
datastore user role on the target
datacenter, or datastore folder or
each target datastore.
VRM remote.View VR
VRM remote.View VRM
VRM datastore mapper.View
Host.vSphere Replication.Manage
replication
Virtual machine.vSphere
Replication.Monitor replication
Datastore.Browse Datastore
VRM remote.View VR
VRM remote.View VRM
VRM datastore mapper.Manage
VRM datastore mapper.View
Host.vSphere Replication.Manage
replication
Virtual machine.vSphere
Replication.Configure replication
Virtual machine.vSphere
Replication.Manage replication
Virtual machine.vSphere
Replication.Monitor replication
Profile-driven storage .Profile-
driven storage view
vCenter Server root folder with
propagation, at source site
(forward replications) and target
site (reverse replications).
Alternatively, vCenter Server root
folder without propagation on
both sites and virtual machine
without propagation on the
source site.
vCenter Server root folder with
propagation on both sites.
Alternatively, vCenter Server root
folder without propagation on
both sites, virtual machine
without propagation on the
source site, source datastores
without propagation on the
source site.
VMware, Inc. 72
Page 73

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Table 9‑1. vSphere Replication Roles (Continued)
Role Actions that this Role Permits Privileges that this Role Includes
Objects in vCenter Server
Inventory that this Role Can
Access
VRM
administrator
Incorporates all
vSphere Replication privileges.
VRM remote.Manage VR
VRM remote.View VR
VRM remote.Manage VRM
VRM remote.View VRM
VRM datastore mapper.Manage
VRM datastore mapper.View
VRM diagnostics .Manage
VRM session .Terminate
Datastore.Browse datastore
Datastore.Low level file operations
Host.vSphere Replication.Manage
replication
Resource.Assign virtual machine to
resource pool
Virtual machine.Configuration.Add
existing disk
Virtual machine.Configuration.Add
or remove device
Virtual machine.Interaction.Power
On
Virtual machine.Interaction.Device
connection
Virtual machine.Inventory.Register
Virtual machine.vSphere
Replication.Configure replication
Virtual machine.vSphere
Replication.Manage replication
Virtual machine.vSphere
Replication.Monitor replication
Profile-driven storage .Profile-
driven storage view
vCenter Server root folder with
propagation on both sites.
Alternatively, vCenter Server root
folder without propagation on
both sites, virtual machine
without propagation on the
source site, target datastore,
target virtual machine folder with
propagation on the target site,
target host or cluster with
propagation on the target site.
VRM
diagnostics
VMware, Inc. 73
Generate, retrieve, and delete log
bundles.
VRM remote.View VR
VRM remote.View VRM
VRM diagnostics .Manage
vCenter Server root folder on
both sites.
Page 74
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Table 9‑1. vSphere Replication Roles (Continued)
Role Actions that this Role Permits Privileges that this Role Includes
Objects in vCenter Server
Inventory that this Role Can
Access
VRM target
datastore user
VRM virtual
machine
recovery user
Configure and reconfigure
replications.
Used on target site in combination
with the VRM virtual machine
replication user role on both sites.
Recover virtual machines. Datastore.Browse datastore
Datastore.Browse datastore
Datastore.Low level file operations
Datastore.Low level file operations
Host.vSphere Replication.Manage
replication
Virtual machine.Configuration.Add
existing disk
Virtual machine.Configuration.Add
or remove device
Virtual machine.Interaction.Power
On
Virtual machine.Interaction.Device
connection
Virtual machine.Inventory.Register
Resource.Assign virtual machine to
resource pool
Datastore objects on target site,
or datastore folder with
propagation at target site, or
target datacenter with
propagation.
Secondary vCenter Server root
folder with propagation.
Alternatively, secondary
vCenter Server root folder
without propagation, target
datastore without propagation,
target virtual machine folder with
propagation, target host or
cluster with propagation.
Assign vSphere Replication Roles to Users
You create roles and assign permissions for vSphere Replication in the same way as you do in vCenter.
See vSphere Users and Permissions in vSphere Security.
Assign VRM Replication Viewer Role
In this example, you create a vSphere Replication user that can view replication sites and replications
configured between them, but cannot perform modifications.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you have two sites connected and replication configured between them.
n
Verify that you have another user account for each site.
Procedure
1 Log in as Administrator on the source site.
2 Select vCenter > Permissions and assign the VRM replication viewer role with the propagate
option to this user.
3 Assign the same privilege on the target replication site.
VMware, Inc. 74
Page 75

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
4 Log in as the user with the assigned VRM replication viewer role.
The user with the VRM replication viewer role cannot perform modifications on the configured replication,
nor on the replication sites. The following error message appears when this user tries to run an operation:
Permission to perform this operation was denied.
Assign VRM Virtual Machine Replication User Role
In this example, you create a vSphere Replication user who can only configure replication between sites
and use a specific datastore on the target site.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that two sites are connected.
n
Verify that you have another user account for each site.
Procedure
1 Log in as the Administrator user on the source site.
2 Select vCenter > Permissions and assign to this user the VRM virtual machine replication user
role with the propagate option.
3 Assign the same privilege on the target replication site.
4 On the target site, select the datastore to store your replica files, and select Manage > Permissions.
5 Edit the assigned permission and assign the VRM target datastore user role.
6 Log in as that user on the source site, select the virtual machine, and click Configure Replication to
start the configuration wizard.
7 Select the target site and enter the same user credentials.
8 Accept the default selections until Target Location.
9 For the target location, select the datastore to which you granted permission.
Selecting a datastore for which the user lacks the Target datastore user role results in the error
message Permission to perform this operation was denied.
Assign VRM Virtual Machine Recovery User Role and Perform a Recovery Operation
You can assign specific permissions to a vSphere Replication user, so that they can perform only
recovery operations.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you have two sites connected and replication configured between them.
n
Verify that you have another user account for the target site apart from the Administrator user.
VMware, Inc. 75
Page 76

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Procedure
1 Log in as the Administrator user on the target site.
2 Select vCenter > Permissions and assign to a different user account the VRM virtual machine
recovery user role with the propagate option.
3 Log in as that user on the target site.
4 On the home page, click Site Recovery and click Open Site Recovery.
5 On the Site Recovery home page, select a site pair and click View Details.
6 Click the Replications tab and select Reverse replications.
7 Select a replication from the list.
8 Click the Recover icon and follow the prompts to finish the recovery.
Clone Existing VRM Administrator Role and Modify Privileges
In this example, you create a vSphere Replication user who cannot modify the replication infrastructure.
The user cannot register additional vSphere Replication servers.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that you have a replication site.
n
Verify that you have another user account to which you can assign the modified privileges.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
2 On the home page, click Administration and click Roles.
3 Select the VRM Administrator role and click the Clone role action icon.
4 In the cloned role, deselect the VRM Remote > VR Server > Manage VR Server privilege.
5 Navigate to the vCenter Server instance.
6 On the Permissions tab click the Add permission icon.
7 Select the user that must have the privileges defined by the selected role.
8 Select the cloned VRM Administrator role from the Assigned Role drop-down menu.
9 Select the Propagate to children check box.
Trying to register a vSphere Replication server results in the error message Permission to perform
this operation was denied.
VMware, Inc. 76
Page 77

Replicating Virtual Machines 10
You can replicate virtual machines from a source site to a target site with vSphere Replication.
You can set a recovery point objective (RPO) to a certain time interval depending on your data protection
needs. vSphere Replication applies all changes made to virtual machines configured for a replication at
the source site to their replicas at the target site. This process reoccurs periodically to ensure that the
replicas at the target site are not older than the RPO interval that you set. See How the Recovery Point
Objective Affects Replication Scheduling.
To replicate a virtual machine using vSphere Replication, you must deploy the vSphere Replication
appliance at the source and target sites. A vSphere Replication infrastructure requires one
vSphere Replication appliance at each site.
The source and target sites must be connected if you want to configure replications. You cannot perform
replications if one of the sites is in the Not Connected state. See vSphere Replication Site Connection
States.
vSphere Replication does not support the recovery of multiple virtual machines from the same workflow.
Each recovery workflow is for an individual virtual machine.
You can configure replications for powered-off virtual machines, but the data synchronization begins when
the virtual machine is powered on. While the source virtual machine is powered off, the replication
appears in Not active status.
You cannot use vSphere Replication to replicate virtual machine templates.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
How the Recovery Point Objective Affects Replication Scheduling
n
How the 5 Minute Recovery Point Objective Works
n
How Retention Policy Works
n
Replicating a Virtual Machine and Enabling Multiple Point in Time Instances
n
Using vSphere Replication with vSAN Storage
n
Using vSphere Replication with vSphere Storage DRS
n
How vSphere Replication Synchronizes Data Between vCenter Server Sites During Initial
Configuration
VMware, Inc.
77
Page 78

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
n
Replicating Virtual Machines Using Replication Seeds
n
Replicating a Virtual Machine in a Single vCenter Server Instance
n
Best Practices for Using and Configuring vSphere Replication
n
Configure Replication
n
Move a Replication to a New vSphere Replication Server
n
Stop Replicating a Virtual Machine
n
Reconfiguring Replications
How the Recovery Point Objective Aects Replication
Scheduling
When you set a Recovery Point Objective (RPO) value during replication configuration, you determine the
maximum data loss that you can tolerate.
The RPO value affects replication scheduling, but vSphere Replication does not adhere to a strict
replication schedule. For example, when you set the RPO to 15 minutes, you instruct vSphere Replication
that you can tolerate losing the data for up to 15 minutes. This does not mean that data is replicated
every 15 minutes.
If you set an RPO of x minutes, and the RPO is not violated, the latest available replication instance can
never reflect a state that is older than x minutes. A replication instance reflects the state of a virtual
machine at the time the synchronization starts.
Assume that during replication configuration you set the RPO to 15 minutes. If the synchronization starts
at 12:00 and it takes five minutes to transfer to the target site, the instance becomes available on the
target site at 12:05, but it reflects the state of the virtual machine at 12:00. The next synchronization can
start no later than 12:10. This replication instance is then available at 12:15 when the first replication
instance that started at 12:00 expires.
If you set the RPO to 15 minutes and the replication takes 7.5 minutes to transfer an instance,
vSphere Replication transfers an instance all the time. If the replication takes more than 7.5 minutes, the
replication encounters periodic RPO violations. For example, if the replication starts at 12:00 and takes 10
minutes to transfer an instance, the replication finishes at 12:10. You can start another replication
immediately, but it finishes at 12:20. During the time interval 12:15-12:20, an RPO violation occurs
because the latest available instance started at 12:00 and is too old.
The replication scheduler tries to satisfy these constraints by overlapping replications to optimize
bandwidth use and might start replications for some virtual machines earlier than expected.
To determine the replication transfer time, the replication scheduler uses the duration of the last few
instances to estimate the next one.
How the 5 Minute Recovery Point Objective Works
If the target and the source sites use VMFS 6.0, VMFS 5.x, NFS 4.1, NFS 3, VVOL, or vSAN 6.0 storage
and later, you can use the 5 minute Recovery Point Objective (RPO).
VMware, Inc. 78
Page 79

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
vSphere Replication 6.5 displays the 5 minute RPO setting when the target and the source site use
VMFS 6.0, VMFS 5.x, NFS 4.1, NFS 3, VVOL, or vSAN 6.0 storage and later.
If you are using different datastore types between the source and the target site, you can use the 5
minute RPO setting .
The 5 minute RPO can be applied to a maximum of 100 VMs on VMFS 6.0, VMFS 5.x, NFS 4.1, NFS 3,
and vSAN 6.0 storage and later. The maximum for VVOL datastore is 50 VMs.
Note RPO lower than 15 minutes is not supported when you select the OS quiescing option.
How Retention Policy Works
When you configure a replication, you can enable the retention of up to 24 VM replica instances from
Multiple Points in Time (MPIT).
For example, you can configure the retention of 3 instances per day for the last 5 days.
After you recover a replicated virtual machine, the retained replicas appear as snapshots of the virtual
machine in the vSphere Web Client. The list of snapshots includes the retained instances according to the
retention policy that you set, and the latest instance. By the example above, the list will contain 15
snapshots and the latest saved instance of the virtual machine, or a total of 16 snapshots. You can use
the snapshots to revert to an earlier state of the recovered virtual machine.
Administrators cannot configure the precise time when replica instances are created, because the
retention policy is not directly related to replication schedule and RPO. As a consequence, replications
with the same retention policy might not result in replicas retained at the same time instants.
RPO Without Retention Policy
By default, vSphere Replication is configured to a 4-hour RPO. This means that the latest available
replica instance can never reflect a state of the virtual machine that is older than 4 hours. You can adjust
the RPO interval when you configure or reconfigure a replication.
When the age of the latest replication instance approaches the RPO interval, vSphere Replication starts a
sync operation to create a new instance on the target site. The replication instance reflects the state of
the virtual machine at the time the synchronization starts. If no retention policy is configured, when the
new instance is created, the previous instance expires and the vSphere Replication Server deletes it.
How RPO and the Retention Policy Combine
To save some of the replica instances that are created during RPO synchronizations, you can configure
vSphere Replication to keep up to 24 instances per replication. The exact instances that
vSphere Replication keeps are determined by applying a specific algorithm. Using this algorithm, the
vSphere Replication Server tries to match each instance to a slot of the retention policy. Instances that do
not match any slot expire and are deleted. If a slot contains more than one instance, the instances that do
not match the retention criteria are also deleted. vSphere Replication always keeps the latest created
instance and it is not taken into account when determining the number of instances to keep.
VMware, Inc. 79
Page 80

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
When the age of the latest instance approaches the RPO interval, vSphere Replication starts creating a
new replica instance. The start time of the sync operation is the time of the new instance. When the sync
operation completes, vSphere Replication assesses the existing replica instances to determine which
ones to keep:
1 The granularity of the retention policy is determined based on the replication settings. For example, if
you configured vSphere Replication to keep 3 instances for the last 1 day, it means that you want to
keep 3 replica instances that are relatively evenly distributed over 24 hours. This equals
approximately 1 instance in an 8-hour interval, or the granularity of this retention policy is 8 hours.
2 The time of the last saved instance is rounded down to the nearest slot time. If the granularity is 8
hours, the slot times are 0:00, 8:00, and 16:00.
3 The instances that are between the nearest slot time and the last saved instance are traversed. Let
us assume that the time of the last saved instance is 10:55. Following our example, the nearest slot
time is 8:00 o'clock. Let us also assume that the RPO is 1 hour, and each sync operation takes 5
minutes to complete. Between 8:00 o'clock and 10:55, the slot contains an 8:55 instance, and a 9:55
instance.
4 The earliest instance that is newer than the nearest slot time is saved, and the rest of the instances in
this slot are deleted, except for the latest created instance that vSphere Replication always keeps.
Following our example, the 8:55 instance is saved, and the 9:55 instance is deleted. The 10:55
instance is the latest created instance, so it is also saved.
5 The slot time is decremented by the granularity of the retention policy and a check is performed for
the earliest instance between the beginning of the current slot and the beginning of the previous slot.
If the slot contains expiring instances, they are deleted.
6 The number of slots that contain saved instances is analyzed. If the number of slots with saved
instances is higher than the number of slots determined by the retention policy, the oldest saved
instance expires and is deleted. The last saved instance is not included in this count. In our example,
if we had an instance saved for the interval 8:00 - 16:00 o'clock of the previous day, that instance
would be deleted.
The number of replication instances that vSphere Replication keeps depends on the configured retention
policy, but also requires that the RPO period is short enough for these instances to be created. Because
vSphere Replication does not verify whether the RPO settings will create enough instances to keep, and
does not display a warning message if the instances are not enough, you must ensure that you set
vSphere Replication to create the instances that you want to keep. For example, if you set
vSphere Replication to keep 6 replication instances per day, the RPO period must not exceed 4 hours, so
that vSphere Replication can create 6 instances in 24 hours.
Replicating a Virtual Machine and Enabling Multiple Point in Time Instances
You can recover virtual machines at specific points in time (PIT) such as the last known consistent state.
VMware, Inc. 80
Page 81
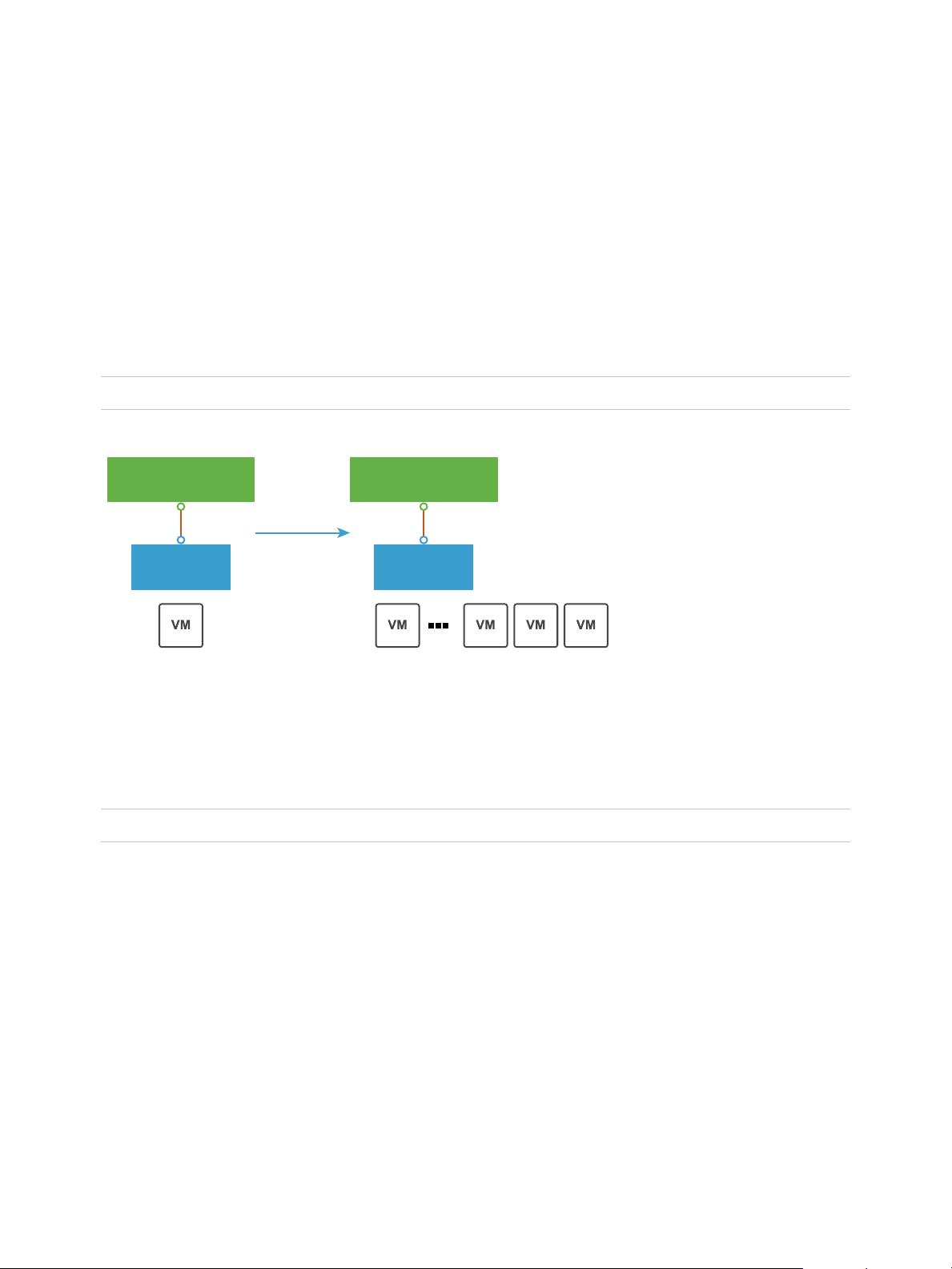
VR Appliance
Source Site
Target Site
Replication
t0 t1 t2 t3
VR Appliance
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
When you configure replication of a virtual machine, you can enable multiple point in time (MPIT)
instances in the recovery settings in the Configure Replication wizard. vSphere Replication retains a
number of snapshot instances of the virtual machine on the target site based on the retention policy that
you specify. vSphere Replication supports a maximum of 24 snapshot instances. After you recover a
virtual machine, you can revert it to a specific snapshot.
During replication, vSphere Replication replicates all aspects of the virtual machine to the target site,
including any potential viruses and corrupted applications. If a virtual machine suffers from a virus or
corruption and you have configured vSphere Replication to keep PIT snapshots, you can recover the
virtual machine and then revert it to a snapshot of the virtual machine in its uncorrupted state.
You can also use the PIT instances to recover the last known good state of a database.
Note vSphere Replication does not replicate virtual machine snapshots.
Figure 10‑1. Recovering a Virtual Machine at Points in Time (PIT)
Using vSphere Replication with vSAN Storage
You can use VMware vSAN datastores as target datastores when configuring replications. Follow the
guidelines when using vSphere Replication with vSAN storage.
Note vSAN is a fully supported feature of vSphere 5.5 Update 1 and later.
Because user-friendly names of directories on vSAN datastores might change and cause errors during
replication or recovery operations, vSphere Replication automatically replaces the user-friendly name of a
directory with its UUID, which is constant. Therefore, you may see the UUID displayed in the
Site Recovery user interface instead of a human-readable name.
Limits of Using vSphere Replication with vSAN Storage
For reasons of load and I/O latency, vSAN storage is subject to limits in terms of the numbers of hosts
that you can include in a vSAN cluster and the number of virtual machines that you can run on each host.
See the Limits section in the VMware vSAN Design and Sizing Guide at
https://storagehub.vmware.com/#!/vmware-vsan/vmware-r-vsan-tm-design-and-sizing-guide.
VMware, Inc. 81
Page 82

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Using vSphere Replication adds to the load on the storage. Every virtual machine generates regular read
and write operations. Configuring replications on those virtual machines adds another read operation to
the regular read and write operations, which increases the I/O latency on the storage. The precise
number of virtual machines that you can replicate to vSAN storage by using vSphere Replication depends
on your infrastructure. If you notice slower response times when you configure replications for virtual
machines in vSAN storage, monitor the I/O latency of the vSAN infrastructure. Potentially, reduce the
number of virtual machines that you replicate in the vSAN datastore.
Note When you stop a replication, vSphere Replication does not delete the replica directory at the target
datastore. As a result, stale directories remain on VMFS and NFS target datastores, and unused
namespaces remain on vSAN and Virtual Volume target datastores. Because the maximum number of
directories and namespaces on a datastore is limited, you must manually clean them up to free resources
on the datastore. See Clean up the Target Datastore After You Stop a Replication.
Retaining Point-in-Time Snapshots When Using vSAN Storage
vSAN storage stores virtual machine disk files as a set of objects and components. Each disk object in
vSAN storage has mirror and witness objects. In the default vSAN storage policy, a disk object has two
mirrors and one witness. The number of mirror components is determined by the size of the virtual
machine disk and the number of failures to tolerate that you set in your vSAN storage policy. A mirror
object is divided into components of a maximum size of 256 GB each.
n
If a virtual machine has one 256 GB disk and you use the default vSAN storage policy, the disk object
will have 2 mirror components of 256 GB each and 1 witness, to make a total of 3 components.
n
If a virtual machine has one 512 GB disk and you use the default vSAN storage policy, the disk object
will have 4 mirror components of 256 GB each and 1 witness, to make a total of 5 components.
See the VMware vSAN Design and Sizing Guide at https://storagehub.vmware.com/#!/vmware-
vsan/vmware-r-vsan-tm-design-and-sizing-guide for explanations of objects, components, mirrors,
witnesses, and vSAN storage policies.
If you enable multiple point-in-time (MPIT) snapshots, you must make allowances for the additional
components that each snapshot creates in the vSAN storage, based on the number of disks per virtual
machine, the size of the disks, the number of PIT snapshots to retain, and the number of failures to
tolerate. When retaining PIT snapshots and using vSAN storage, you must calculate the number of extra
components that you require for each virtual machine:
Number of disks x number of PIT snapshots x number of mirror and witness components
Examples of using this formula demonstrate that retaining PIT snapshots rapidly increases the number of
components in the vSAN storage for every virtual machine that you configure for vSphere Replication:
n
You have a virtual machine with two 256 GB disks for which you retain 10 MPIT snapshots, and you
set the default vSAN storage policy:
n
2 (number of disks) x 10 (number of PIT snapshots) x 3 (2 mirror components + 1 witness) = 60
components for this one virtual machine.
VMware, Inc. 82
Page 83
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
n
You have a virtual machine with two 512 GB disks for which you retain 10 PIT snapshots, and you set
the default vSAN storage policy:
n
2 (number of disks) x 10 (number of PIT snapshots) x 5 (4 mirror components of 256 GB each + 1
witness) = 100 components for this one virtual machine.
The number of PIT snapshots that you retain can increase I/O latency on the vSAN storage.
Using vSphere Replication with vSphere Storage DRS
vSphere Replication can operate with target sites that have VMware vSphere® Storage DRS™ enabled.
Storage DRS can detect the data that vSphere Replication copies on the target site and can move
replications without affecting the replication process.
How vSphere Replication Synchronizes Data Between
vCenter Server Sites During Initial Configuration
When you configure a virtual machine for replication, vSphere Replication starts an initial configuration
task during which a replica virtual machine is created on the target site, and data synchronization occurs
between the source and the target vCenter Server site.
The speed of data synchronization depends on the availability of information about block allocation of the
VMDK files. vSphere Replication uses this information to find empty regions of the disks and accelerate
the sync operations by skipping these regions. The speed of data synchronization also depends on the
site for which block allocation information is available.
n
If the allocation information is available at both sites, data synchronization occurs at the highest
possible speed.
n
If the allocation information is available only at the source or the target site, vSphere Replication skips
the empty regions on the VMDK disks at that site, but processes the entire disk at the site where
allocation information is not available. Therefore, data synchronization is slower.
n
If the allocation information is not available at either site, data synchronization is done by comparing
all blocks between the source site and the target site, even if many of the blocks have not been
allocated on the disk by the guest OS. This is the slowest method for data synchronization.
Note The availability of block allocation information has little effect on the speed of data synchronization
for VMDK disks that are almost full.
VMware, Inc. 83
Page 84

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Factors That Aect the Availability of Block Allocation
Information
The availability of allocation information and the degree to which vSphere Replication can use it to
accelerate data synchronization depend on the ESXi versions, the vSphere Replication Management
server versions, the type of VMDK disks, and the type of volumes on which the disks reside.
Product Versions at the
Source and the Target
Site
The Type of the
Datastore
The acceleration of initial synchronization is supported only on ESXi hosts
6.0.x or later.
If the ESXi and the vSphere Replication Server on the source site are 6.x or
later, but the vSphere Replication Server or the hosts at the target site are
not 6.x or later, the allocation information will be available only on the
source site.
If the vSphere Replication Management servers at the source and at the
target site are both 6.x, but one or more ESXi hosts at the target site are
not 6.0 or later, if the vSphere Replication Management server selects a
target host that is not 6.0 or later, there will be no allocation information
available on the target site.
Note Because vSphere Replication Management server 6.x cannot select
only ESXi 6.0 hosts for the initial synchronization, the acceleration of the
operations might vary depending on the selected host. To achieve
maximum acceleration, all ESXi hosts at the target site that act as storage
servers for vSphere Replication should be ESXi 6.0 or later.
Disks on VMFS or VSAN datastores provide full allocation information.
NFS datastores cannot provide allocation information for the disks that are
located on them.
Note Replication disks on the source and the target site can be on
different datastore types. The acceleration of the initial synchronization
depends on whether both sites can provide allocation information, or only
one site. If none of the sites can provide allocation information, no
acceleration occurs.
The Type of Virtual Disk Lazy zeroed thick disks, thin disks, and vSAN sparse disks, Space-Efficient
sparse disks, and VMDK sparse snapshots provide allocation information.
Eager zeroed thick disks do not provide allocation information.
Virtual disks that are based on VVOLs are native to the volume.
vSphere Replication 6.x can get allocation information from them only when
they are on the target site. For this reason, the acceleration of the initial
synchronization will be partial.
VMware, Inc. 84
Page 85

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Replicating Virtual Machines Using Replication Seeds
You can reduce the network traffic that data transfer generates during the initial full synchronization.
vSphere Replication allows you to copy virtual disk files or use existing files in the target datastore, and
point the files as replication seeds when you configure a replication.
vSphere Replication compares the differences on the source and target site, and replicates only the
changed blocks.
When, during replication configuration, you select a target datastore for the virtual machine or a specific
disk, vSphere Replication looks for disks with the same filename in the target datastore. If a file with the
same name exists, a warning appears in the wizard. You can review and configure the replication seeds
or choose not to use any replication seeds. If you choose not to use the discovered seeds, then replica
files are placed in a new directory with a unique name. If you choose to configure seeds by selecting the
Select seeds check box, then a new page appears in the wizard where you can configure seeds for each
disk on each virtual machine.
Note If you plan to copy files from the source to the target datastore, the source virtual machine must be
powered off before downloading the VMDK files that will be used as seeds for the replication.
Replicating a Virtual Machine in a Single vCenter Server Instance
You can use vSphere Replication to replicate a virtual machine in a single vCenter Server even if the
vCenter Server instance has only one host in its inventory.
When you configure replication in a single vCenter Server instance, you can select the source site as the
target site for replication. You then configure replication in the same way as for an infrastructure with a
source and a target site. For example, you can replicate a virtual machine to a different datastore
attached to the same host or another host. vSphere Replication prevents you from using the source or
replicated virtual machine's vmdk files as the target of the replication.
The virtual machine name must be unique in the same folder in the vCenter Server inventory. In the
recovery wizard, vSphere Replication does not allow you to select a folder if there is already a virtual
machine with the same name registered to it. During recovery if there is a virtual machine with the same
name, you might see an error message. See Error Recovering Virtual Machine in a Single vCenter Server
Instance for more information.
Best Practices for Using and Configuring
vSphere Replication
Best practices for using and configuring vSphere Replication can prevent your environment from possible
issues during replication.
VMware, Inc. 85
Page 86

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Setting the Optimal Recovering Point Objective (RPO) Time
The replication of several thousand virtual machines (VMs) is a bandwidth consuming process.
vSphere Replication lets you set the RPO to 15 minutes, but you must estimate the optimal RPO time to
save bandwidth for the replication and to cover your business requirements for protection of your VMs.
For example, if your business requires replication of 2,000 VMs with an 8-hour RPO, set the RPO time to
8 hours to meet the business needs and save bandwidth. See Calculate Bandwidth for vSphere
Replication for details.
Using Multiple Point in Time (MPIT) Recovery
Each point in time snapshot consumes storage. The amount consumed depends on the data change rate
in the VM. When you set multiple point in time instances for replication of a VM between two
vCenter Server sites, vSphere Replication presents the retained instances as standard snapshots after
recovery. The time required to consolidate snapshots after recovery, increases with the number of
snapshots.
Although vSphere Replication supports up to 24 recovery points, you must set the MPIT to the lowest
number of recovery points that meets your business requirements. For example, if the business
requirement is for 10 recovery points, you must set up vSphere Replication to save only 10 snapshots.
You can set up two recovery points per day for the last five days. As a result, the consumed storage and
the time needed to consolidate the snapshots after recovery are less than if you use the maximum
number of recovery points.
Configuring Quiescing
For VMs with high levels of storage I/O, quiescing of the file system and applications can take several
minutes and impact the performance of the VM . When quiescing a file system and applications for
Windows VMs, vSphere Replication requires a regular VM snapshot before replication. When you
estimate the RPO time, consider the time and resource consumption for the quiescing and for the
consolidation of the snapshots. For example, if you configure a replication of a Windows VM with an RPO
of 15 minutes and quiescing is enabled, vSphere Replication generates a VM snapshot and consolidates
it every 15 minutes.
Configuring Replication Seeds
You can copy virtual disk files of source VMs to the target location and use these files as replication
seeds. By using replication seeds, vSphere Replication reduces the amount of time and network
bandwidth required for the initial full sync process. The UUID of the source and target VMDK files must
match for the replication to be successful and to prevent unintentional overwrites of disk files that belong
to other VMs at the target location.
VMware, Inc. 86
Page 87

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Monitoring a Datastore on the Target Site
vSphere Replication requires enough disk space at the target site to replicate a VM. If the available space
is not enough to save the replication files, the replication might fail. You can create an alarm that alerts
you about insufficient storage capacity at the target site.
Configure Replication
vSphere Replication can protect one or more virtual machines and their virtual disks by replicating them
from one vCenter Server instance to another.
This procedure is for configuring replications to a target vCenter Server. To configure a replication to a
cloud provider, see vSphere Replication for Disaster Recovery to the Cloud.
When you configure a replication, you set a recovery point objective (RPO) to determine the maximum
data loss that you can tolerate. For example, an RPO of 1 hour seeks to ensure that a virtual machine
loses the data for no more than 1 hour during the recovery. For smaller RPO values, less data is lost in a
recovery, but more network bandwidth is consumed keeping the replica up to date. The RPO value affects
replication scheduling, but vSphere Replication does not adhere to a strict replication schedule. See How
the Recovery Point Objective Affects Replication Scheduling and How the 5 Minute Recovery Point
Objective Works.
Every time that a virtual machine reaches its RPO target, vSphere Replication records approximately
3800 bytes of data in the vCenter Server events database. If you set a low RPO period, this can quickly
create a large volume of data in the database. To reduce the volume of data that is kept in the
vCenter Server events database, limit the number of days that vCenter Server retains event data. See
Configure Database Retention Policy in the vCenter Server and Host Management Guide. Alternatively,
set a higher RPO value.
vSphere Replication guarantees crash consistency among all the disks that belong to a virtual machine. If
you use quiescing, you might obtain a higher level of consistency. The available quiescing types are
determined by the operating system of the virtual machine. See Compatibility Matrices for vSphere
Replication 8.1 for quiescing support for Windows and Linux virtual machines.
You can configure virtual machines to replicate from and to vSAN datastores. See Using vSphere
Replication with vSAN Storage for the limitations when using vSphere Replication with vSAN.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that the vSphere Replication appliance is deployed at the source and the target sites.
n
To enable the quiescing of virtual machines that run Linux guest OS, install the latest version of
VMware Tools on each Linux machine that you plan to replicate.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
2 On the home page, click Site Recovery and click Open Site Recovery.
VMware, Inc. 87
Page 88

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
3 On the Site Recovery home page, select a site pair and click View Details.
4 Click the Replications tab, select Forward replications or Reverse replications, and click the
Create new replication icon.
5 On the Virtual machines page of the Configure Replication wizard, select the virtual machines you
want to replicate and click Next.
6 Accept the automatic assignment of a vSphere Replication server or select a particular server on the
target site and click Next.
7 On the Target datastore page, select a datastore on which to replicate files.
When replicating multiple virtual machines, you can configure a different target datastore for each
virtual machine.
8 (Optional) Select the Select seeds check box.
Replication seeds can reduce the network traffic during the initial full synchronization, but unintended
use of replication seeds might lead to data loss.
9 Click Next.
10 (Optional) On the Select seed page, review the suggested replication seeds and change them if
necessary.
You can select seed files for each virtual machine disk and search for seeds by using the dropdown
menu and clicking Browse.
The replica files for the disk are written in the seeds file directory.
11 Select the The selected seeds are correct check box and click Next.
12 On the Replication settings page, use the RPO slider to set the acceptable period for which data
can be lost if a site failure occurs.
The available RPO range is from 5 minutes to 24 hours.
13 (Optional) To save multiple replication instances that can be converted to snapshots of the source
virtual machine during recovery, select Enable point in time instances and adjust the number of
instances to keep.
Note You can keep up to 24 instances for a virtual machine. For example, if you configure
vSphere Replication to keep 6 replication instances per day, the maximum number of days you can
set is 4 days.
The number of replication instances that vSphere Replication keeps depends on the configured
retention policy, but also requires that the RPO period is short enough for these instances to be
created. Because vSphere Replication does not verify whether the RPO settings will create enough
instances to keep, and does not display a warning message if the instances are not enough, you
must ensure that you set vSphere Replication to create the instances that you want to keep. For
example, if you set vSphere Replication to keep 6 replication instances per day, the RPO period must
not exceed 4 hours, so that vSphere Replication can create 6 instances in 24 hours.
VMware, Inc. 88
Page 89
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
14 (Optional) Enable quiescing for the guest operating system of the source virtual machine.
Note Quiescing options are available only for virtual machines that support quiescing.
vSphere Replication does not support VSS quiescing on Virtual Volumes.
15 (Optional) Select Enable network compression for VR data.
Compressing the replication data that is transferred through the network saves network bandwidth
and might help reduce the amount of buffer memory used on the vSphere Replication server.
However, compressing and decompressing data requires more CPU resources on both the source
site and the server that manages the target datastore.
16 On the Ready to complete page, review the replication settings, and click Finish.
vSphere Replication starts an initial full synchronization of the virtual machine files to the designated
datastore on the target site.
Move a Replication to a New vSphere Replication Server
After configuring vSphere Replication, you can move replications to other vSphere Replication Server
instances. You might do this to complete maintenance tasks on existing servers or to balance the load on
the servers if one server becomes overloaded with replications.
Prerequisites
You must have an additional vSphere Replication Server deployed and registered, apart from the
embedded vSphere Replication Server.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client on the source site.
2 On the home page, click Site Recovery and click Open Site Recovery.
3 On the Site Recovery home page, select a site pair and click View Details.
4 Click the Replications tab and select a replication from Forward replications or Reverse
replications.
5 Click the Reconfigure icon.
6 On the Target site page of the Reconfigure Replication wizard, select Manually select vSphere
Replication Server.
7 Select a different vSphere Replication Server instance from the list and click Next until you finish the
wizard.
The newly assigned server is updated in the Replication Server column.
Stop Replicating a Virtual Machine
If you do not need to replicate a virtual machine, you can stop the replication of that virtual machine.
VMware, Inc. 89
Page 90
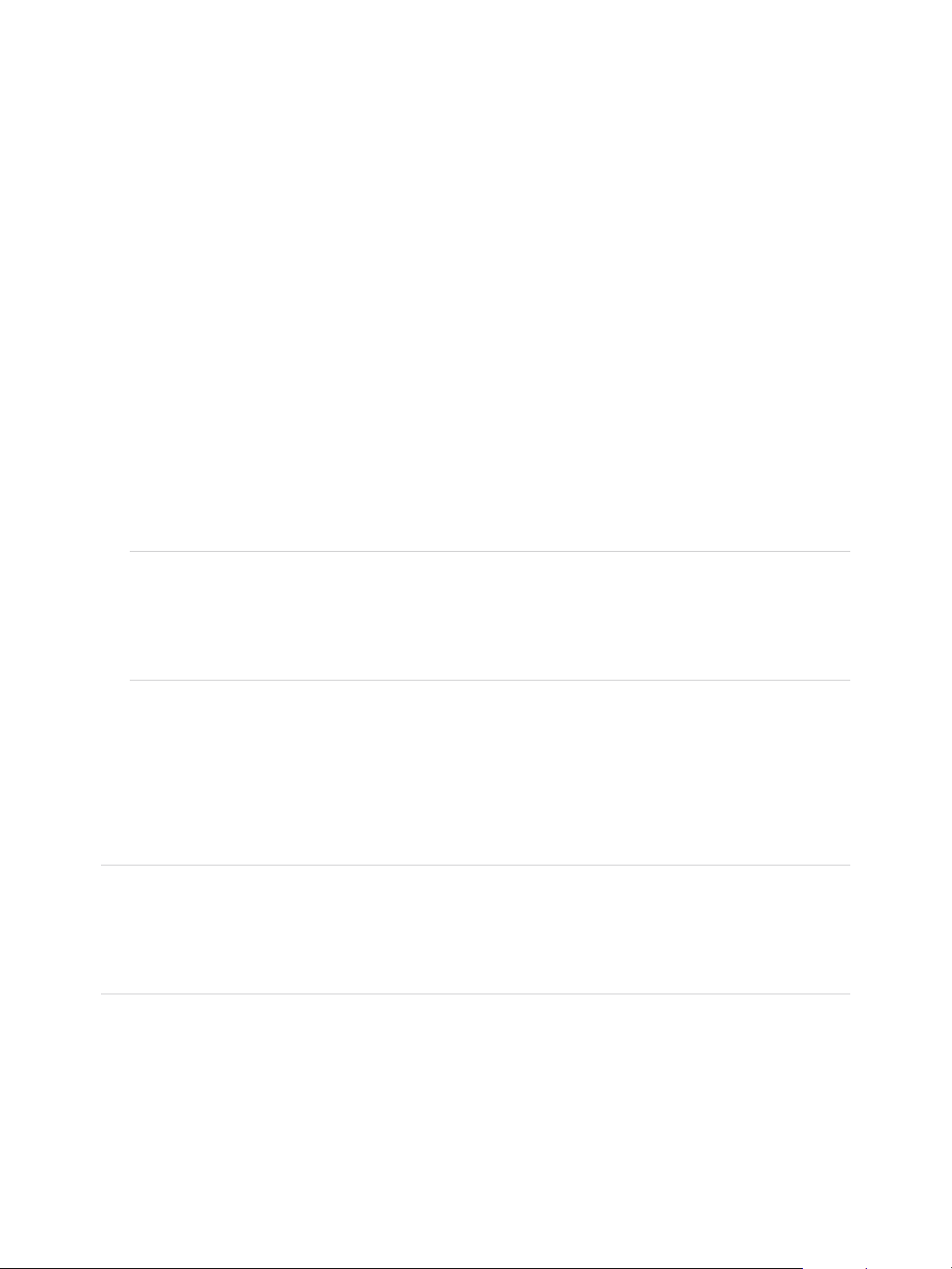
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Take a note of the target datastore and the name of the replication that you are about to stop. You need
this information to clean up your environment after you stop the replication.
Prerequisites
Verify that you are logged in the vSphere Web Client or vSphere Client as a VRM virtual machine
replication user or a VRM administrator user. See vSphere Replication Roles Reference.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
2 On the home page, click Site Recovery and click Open Site Recovery.
3 On the Site Recovery home page, select a site pair and click View Details.
4 Click the Replications tab and select a replication from Forward replications or Reverse
replications.
5 Click the Remove icon.
vSphere Replication asks you if you want to stop permanently the replication for the selected virtual
machine.
Note The connection between the vSphere Replication sites must be working to stop a replication
on both sites. Alternatively, you can force stop the replication on the local site by selecting Force
stop replication. If the remote site is available, you must also use the Site Recovery user interface to
force stop the corresponding replication on the remote site. If you force stop a forward replication, the
replication can still be recovered by using the Site Recovery user interface on the remote site.
6 Click Remove to confirm that you want to stop replicating this virtual machine.
The virtual machine does not replicate to the target site.
When you stop a replication, the following operations are performed at the replication target site.
n
If the VMDK files were created when the replication was first configured, the VMDK files are deleted
from the target site datastore.
Note When you stop a replication, vSphere Replication does not delete the replica directory at the target
datastore. As a result, stale directories remain on VMFS and NFS target datastores, and unused
namespaces remain on vSAN and Virtual Volume target datastores. Because the maximum number of
directories and namespaces on a datastore is limited, you must manually clean them up to free resources
on the datastore. See Clean up the Target Datastore After You Stop a Replication.
n
If you configured the replication to use existing disks at the target site as seeds, the VMDK files are
not deleted and remain on the target datastore.
Clean up the Target Datastore After You Stop a Replication
When you stop a replication, vSphere Replication does not delete the replica directory at the target
datastore.
VMware, Inc. 90
Page 91

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
As a result, stale directories remain on VMFS and NFS target datastores, and unused namespaces
remain on vSAN and Virtual Volume target datastores. Because the maximum number of directories and
namespaces on a datastore is limited, you must manually clean them up to free resources on the
datastore.
Prerequisites
Verify that you know the name of the replication that was stopped and its target datastore.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Web Client or vSphere Client as an administrator user and navigate to the
datastore that was the target for the stopped replication.
2 Select the files tab, enter the name of the stopped replication in the search text box, and locate the
folder that corresponds to this name.
3 Verify that the folder is empty and delete it.
Reconfiguring Replications
You can reconfigure a replication to modify its settings.
For example, you can reconfigure the replication to enable or disable a virtual machine disk file for
replication, modify replication options, such as RPO, MPIT retention policy, or quiescing method. You can
also specify a different target datastore for replica configuration and disk files.
Reconfigure Recovery Point Objectives in Replications
You can modify the settings for already configured replications to specify different recovery point
objectives (RPOs).
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
2 On the home page, click Site Recovery and click Open Site Recovery.
3 On the Site Recovery home page, select a site pair and click View Details.
4 Click the Replications tab and select a replication from Forward replications or Reverse
replications.
5 Click the Reconfigure icon.
6 Click Next until you reach the Replication settings page of the Reconfigure Replication wizard.
7 Modify the RPO settings for this replication and click Next.
8 Click Finish to save your changes.
VMware, Inc. 91
Page 92

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Resize the Virtual Machine Disk Files of a Replication that Uses Replication Seeds
vSphere Replication prevents you from resizing the virtual machine disk files during replication. If you
used replication seeds for the target disk, you can resize the disk manually.
Procedure
1 Stop the replication on the source site.
2 Resize the disk of the source virtual machine.
3 On the target site, resize the disk that is left over after you stopped the replication.
4 Configure the replication on the source virtual machine and use the resized disk on the target site as
seed.
Resize Virtual Machine Disk Files of a Replication That Does Not Use Replication Seeds
vSphere Replication prevents you from resizing the virtual machine disk files during replication. If you did
not use replication seeds during configuration of the target disk, vSphere Replication deletes the target
disk when you stop the replication.
To resize a virtual machine disk if you did not initially use replication seeds, you must perform a recovery,
resize the disk on source and target site manually, and use the target disk as a replication seed to
configure a new replication.
Procedure
1 Recover a virtual machine.
2 Stop the replication.
3 Resize the disk on the source site.
4 Resize the disk of the recovered virtual machine on the target site.
5 Unregister the recovered virtual machine on the target site, but do not delete the disks.
6 Configure a replication by using the disks of the recovered virtual machine as seeds.
Change the Point in Time Settings of a Replication
You can reconfigure a replication to enable or disable the saving of point in time instances, or to change
the number of instances that vSphere Replication keeps.
vSphere Replication can save replication instances that can be used as snapshots after recovery or
planned migration operations. You can save up to 24 point in time instances per VM.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
VMware, Inc. 92
Page 93

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
2 On the home page, click Site Recovery and click Open Site Recovery.
3 On the Site Recovery home page, select a site pair and click View Details.
4 Click the Replications tab and select a replication from Forward replications or Reverse
replications.
5 Click the Reconfigure icon.
6 Click Next until you reach the Replication settings page of the Reconfigure Replication wizard.
7 In the Point in time instances pane, make the changes that you want to apply and click Next.
Action Procedure
Enable the saving of point in time
instances
Disable the saving of point in time
instances
Adjust the number of instances to keep
and for how long to keep them
Select the Enable point in time instances check box.
Deselect the Enable point in time instances check box.
Use the spin-boxes to adjust the number of instances to keep per day and the
number of past days for which you want to keep replication instances.
Note You cannot keep more than 24 replication instances per virtual machine.
8 Click Finish to save your changes.
If you selected to disable the saving of point in time instances, the instances that exist on the target site
are deleted when the next replication instance appears on the target site. The moment when a new
replication instance is saved on the target site depends on the RPO setting.
Change the Target Datastore Location of a Replication
You can reconfigure a replication to change the datastore where replicated data is saved.
Note The old target datastore from which you want to move the replication data must be online. If the
old datastore is inaccessible, the reconfiguration task fails. To change the target datastore when the old
datastore is inaccessible, you must stop the replication to the old datastore and configure another
replication to the new datastore.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
2 On the home page, click Site Recovery and click Open Site Recovery.
3 On the Site Recovery home page, select a site pair and click View Details.
4 Click the Replications tab and select a replication from Forward replications or Reverse
replications.
5 Click the Reconfigure icon.
6 Click Next to reach the Target datastore page of the Reconfigure Replication wizard.
VMware, Inc. 93
Page 94

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
7 Select the new target datastore.
8 Click Next until you reach the Ready to complete page and click Finish to save your settings.
vSphere Replication moves all replicated instances and configuration files to the new target datastore
according to your settings.
VMware, Inc. 94
Page 95

Monitoring and Managing
Replications in
vSphere Replication 11
vSphere Replication provides a management interface where you can monitor and manage virtual
machine replication and connectivity states for local and remote sites.
On the home page of the Site Recovery user interface, you can see all vSphere Replication site
connections and the number of forward and reverse replications between the sites.
To see details about the status of a connection, replication problems, and to manage and monitor
replications between a site pair, click the View Details button.
This chapter includes the following topics:
n
Monitor Replication for Virtual Machines
n
View Replication Reports for a Site
n
Identifying Replication Problems
n
Manage vSphere Replication Connections
n
Manage vSphere Replication Servers
Monitor Replication for Virtual Machines
You can monitor the replication status and view information for virtual machines configured for replication.
For more information about how to identify replication errors, see Identifying Replication Problems.
Prerequisites
n
Verify that vSphere Replication is running.
n
Verify that the virtual machines are configured for replication.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
2 On the home page, click Site Recovery and click Open Site Recovery.
3 On the Site Recovery home page, select a site pair and click View Details.
VMware, Inc.
95
Page 96

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
4 To see details of the virtual machines replicated from this site, select the Replications tab and click
Forward Replications or Reverse replications.
Table 11‑1. Replication Statuses
Status Description Remediation
OK The replication is running. Not needed.
Not Active The replication is not running at the
moment.
n
The source virtual machine is
powered off.
n
A communication problem might
have occurred between the source
ESXi host and the target site.
Paused The replication is not running at the
moment. A vSphere Replication user
has paused the replication.
Error The replication is not running at the
moment.
n
A configuration error occurred.
n
A replication error occurred. For
example, the target site
infrastructure is not accessible.
Status (RPO violation) For replication status OK, Sync, or Full
Sync, the replication is running, but the
RPO that is set for the replication is not
met and is violated.
For replication status Not Active or
Error, the replication is not running,
and the RPO that is set for the
replication is violated.
n
The network connection between
the source and the target site is
dropping intermittently.
n
The bandwidth of the connection
between the source and the target
site is too low.
n
The replication is not running, so
data cannot be replicated on the
target site.
n
Power on the source virtual
machine.
n
If all replications for an ESXi host
are in Not Active state, verify that
the security rule Replication-to-
Cloud Traffic is enabled on the host.
This rule opens TCP ports from
10000 to 10010 for outgoing
communication.
From the list of replications, select the
paused replication and click the Resume
icon.
n
Reconfigure the replication.
n
Verify whether some problem
occurred on the virtual machine by
clicking the Site Pair tab and
clicking Issues.
n
Improve the network connection
between the source and target site.
n
Increase the RPO period.
n
For replication status Not Active
or Error, address the cause for the
status and wait for the next sync.
Note If a replication is in the Not Active replication state, you might have connected the source
and target sites using network address translation (NAT). vSphere Replication does not support NAT.
Use credential-based authentication and network routing without NAT when connecting the sites.
Another cause for a Not Active replication state might be that the source virtual machine is powered
off. Automatic replication works only on virtual machines that are powered on.
VMware, Inc. 96
Page 97

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
View Replication Reports for a Site
If you observe frequent RPO violations, want to learn more about the network usage of
vSphere Replication, or check the status of your forward and reverse replications, you can view
replication statistics for source and target vCenter Server sites.
Prerequisites
Verify that vSphere Replication is running.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
2 On the home page, click Site Recovery and click Open Site Recovery.
3 On the Site Recovery home page, select a site pair and click View Details.
4 Click the Site Pair tab and click vSphere Replication reports.
The Reports page displays historic data for vSphere Replication for a certain time period.
n
Transferred Bytes - total bytes transferred for all forward replications
n
Replications Count - number of forward replications
n
RPO Violation Count - number of RPO violations
n
Target Sites Count - number of vSphere Replication site connections
n
VR Sites Count - number of registered replication servers
Note Data is collected in 5 minute intervals and the graphs represent aggregated data for each interval.
Therefore, you cannot see the exact moment when a peak value occurred. The displayed data combines
all site pairs.
What to do next
n
You can use the drop-down menu above the reports to change the time range of the reports.
n
You can zoom in the data.
Interpreting Replication Statistics for a Site
You can use the reports that vSphere Replication compiles to optimize your environment for replication,
identify problems in your environment, and reveal their most probable cause.
Server and site connectivity, number of RPO violations, and other metrics give you, as an administrator,
the information you need to diagnose replication issues.
The following sections contain examples of interpreting the data displayed under vSphere Replication
reports on the Site Pair tab of vSphere Replication.
VMware, Inc. 97
Page 98
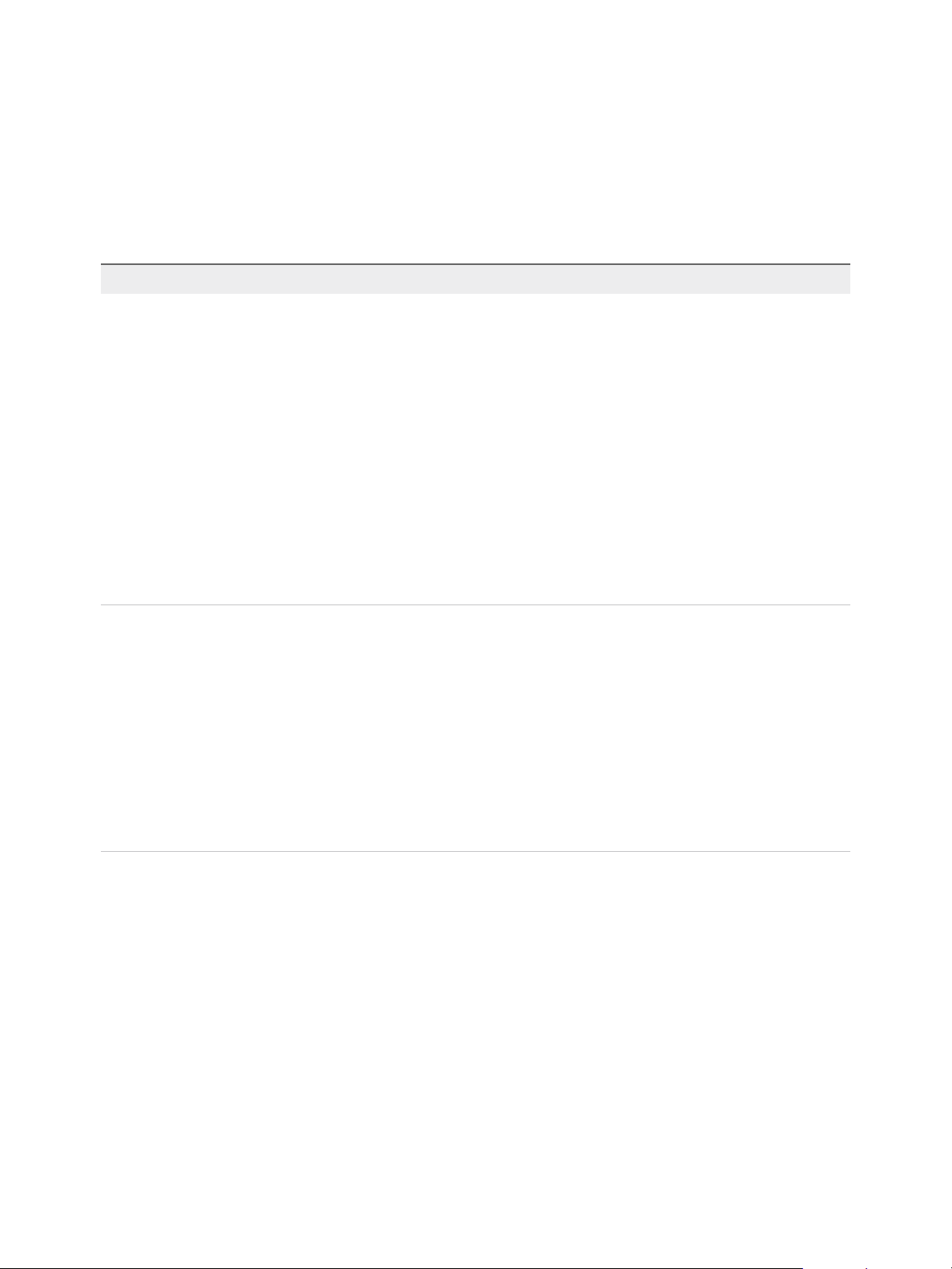
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
RPO Violations
The large number of RPO violations can be caused by various problems in the environment, on both the
protected and the recovery site. With more details on historical replication jobs, you can make educated
decisions on how to manage the replication environment.
Table 11‑2. Analyzing RPO Violations
Probable Cause Solution
n
The network bandwidth cannot accommodate all
replications.
n
The replication traffic might have increased.
n
The initial full sync for a large virtual machine is taking
longer than the configured RPO for the virtual machine.
n
A connectivity problem exists between the protected and the
recovery site.
n
An infrastructure change might have occurred on the
recovery site.
n
To allow lower change rate virtual machines to meet their
RPO objectives, disable the replication on some virtual
machines with high change rate.
n
Increase the network bandwidth for the selected host.
n
Check if the replication traffic has increased. If the traffic has
increased, investigate possible causes, for example the
usage of an application might have changed without you
being informed.
n
Check the historical data for average of transferred bytes for
a notable and sustained increase. If an increase exists,
contact application owners to identify recent events that
might be related to this increase.
n
Adjust to a less aggressive RPO or look at other ways to
increase bandwidth to accommodate the current RPO
requirements.
n
To verify the connection between the protected and recovery
site, check the site connectivity data.
n
Check if the infrastructure on the recovery site has changed
or is experiencing problems that prevent
vSphere Replication from writing on the recovery datastores.
For example, storage bandwidth management changes
made to recovery hosts might result in storage delays during
the replication process.
n
Check on the vSphere Replication Management Server
appliance and the vSphere Replication Server appliance.
Someone might have shut down the appliance or it might
have lost connection.
Transferred Bytes
Corelating the total number of transferred bytes and the number of RPO violations can help you decide
on how much bandwidth might be required to meet RPO objectives.
VMware, Inc. 98
Page 99

VMware vSphere Replication Administration
Table 11‑3. Analyzing the Rate of Transferred Bytes and RPO Violations
Graph Values Probable Cause Solution
n
High rate of transferred bytes and high number of RPO
violations
n
Low rate of transferred bytes and high number of RPO
violations
n
High rate of transferred bytes and a few or no RPO
violations
n
Low rate of transferred bytes and a few or no RPO violations
The network bandwidth might
be insufficient to
accommodate all replications.
The environment operates as
expected.
n
Maximize the transferred
bytes graph and use the
drop-down menu to filter
the data by virtual
machine. To allow lower
change rate virtual
machines to meet their
RPO objectives, disable
the replication on some
virtual machines with high
change rate.
n
Increase the network
bandwidth for the selected
host.
N/A
Identifying Replication Problems
You can view and troubleshoot possible vSphere Replication problems that might occur during replication.
Under Issues on the Site Pair tab of vSphere Replication, you can view and identify possible replication
problems.
Table 11‑4. Possible Replication Problems
Problem Cause Solution
Not
Active
Paused If you paused the replication, a warning icon appears. Resume the paused replication from the Issues
Error If you added a disk on a virtual machine which is already
Error While configuring replication, the replication fails with the incorrect
RPO
Violation
The replication is not active because the virtual machine is
powered off and a warning icon appears. Replication is not running
for that virtual machine.
configured for replication, the replication pauses and goes to an
error state.
UUID. For example, the replication seed found and intended for
use has a different UUID from the original hard disk.
A replication contains an RPO violation. See Reconfigure Recovery Point Objectives in
Power on the virtual machine to resume the
replication.
tab.
Reconfigure the replication and enable or disable
the newly added disk.
Reconfigure the replication.
Replications.
Manage vSphere Replication Connections
You can reconfigure or break the connections between vSphere Replication sites.
VMware, Inc. 99
Page 100
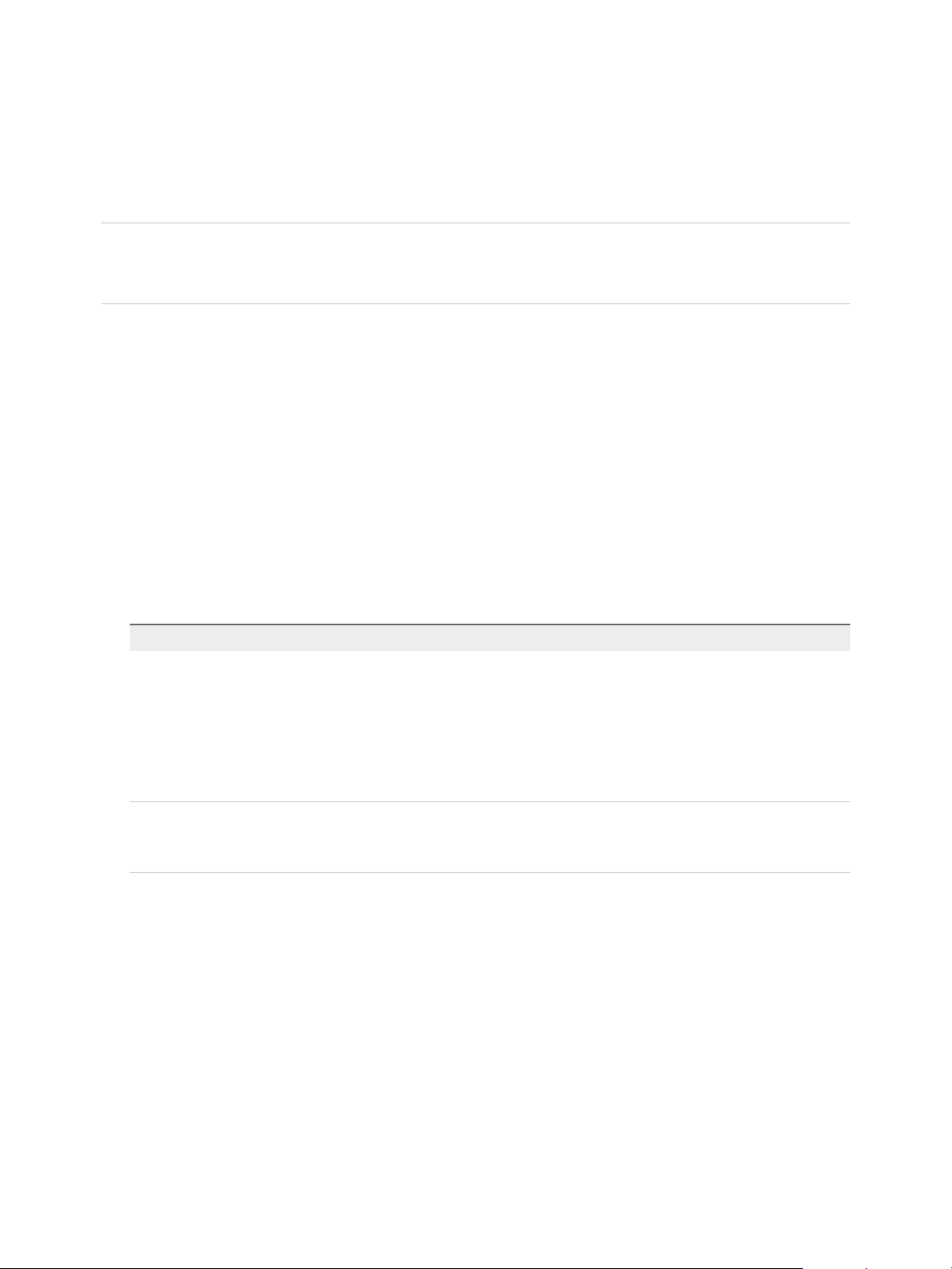
VMware vSphere Replication Administration
If you have problems with an existing site pair, you can attempt to reconfigure the site pair with the
Reconfigure Site Pair action. When you provide the required credentials, the reconfiguration operation
attempts to repair the existing site pair.
With the Break Site Pair action, you can disconnect vSphere Replication sites.
Note You cannot use the Reconfigure Site Pair action to add a missing pairing or a pairing that was
manually broken with Break Site Pair. If your site pair is missing a pairing, you must use New Site Pair
to configure it.
Prerequisites
Verify that you have paired your protected site with at least one recovery site. To create a connection to a
new recovery site, see Configure vSphere Replication Connections.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
2 On the home page, click Site Recovery and click Open Site Recovery.
3 On the Site Recovery home page, select a site pair and click View Details.
4 Click the Site Pair tab and click Summary.
5 Manage the site pair.
Option Description
Reconfigure a site pair a Click Reconfigure Site Pair.
b Enter the address of the Platform Services Controller for the
vSphere Replication Management Server on the second site, provide the user
name and password, and click Next.
c Select the vCenter Server and the services you want to pair, and click Next.
d On the Ready to complete page, review the pairing settings, and click
Finish.
Break a site pair a Click Break Site Pair.
b Select the services you want to disconnect.
c Click Disconnect.
Manage vSphere Replication Servers
You can view, configure, reconnect, and unregister vSphere Replication Server instances that are
registered in your environment.
Prerequisites
Verify that vSphere Replication is running.
Procedure
1 Log in to the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
VMware, Inc. 100
 Loading...
Loading...