Page 1

OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
For the
Model CT-7500
A Digital Circuit-Breaker Analyzer
Manufactured by
Vanguard Instruments Co., Inc.
1711 Grevillea Ct.
Ontario, California 91761
TEL: (909) 923-9390 Jan 2001
FAX: (909) 923-9391 Rev 2
Page 2

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1.0 INTRODUCTION…. …..
2.0 CT-7500 DESCRIPTION
2.1 On-Line Timing (Quick-Shot) Mode
2.2 Time-Versus-Travel Circuit Breaker Analyzer Mode
2.2.1 Contact Timing Channels
2.2.1 Analog Voltage Monitoring Channel
2.2.3 Digital Voltage Monitoring Channel
2.2.4 Trip/Close Current Monitoring
2.2.5 Travel Transducer Input Channels
2.2.6 Breaker Initiate Capability
2.2.7 Built-In Thermal Printer
2.2.8 Printer Port
2.2.9 Computer Interface Capabilities
2.2.10 Timing Shots Storage Capabilities
2.2.11 Breaker Test Plan Storage Abilities
2.2.12 Diagnostic Capabilities
2.2.13 CT-7500 Display Control Switches
3.0 TEST RESULTS TABULATION
3.1 Electrical Measurement Results
3.2 Mechanical Measurement Results
3.3 Analog Voltage Input Results
3.4 Digital Voltage Input Results
3.5 Initiate Current Results
3.6 Slow-Close Test
4.0 TEST-RESULT GRAPHICS
4.1 Thermal Printer Graphic Printout
4.2 Ink-Jet Printer Output
5.0 CONTROLS AND DISPLAY
6.0 CT-7500 ANALYZER SPECIFICATIONS
7.0 CT-7500 SPECIAL FEATURES
7.1 CT-7500 Operating Voltage
7.2 CT-7500 Main Power Fuse
7.3 CT-7500 Printer and Printer Paper
7.4 CT-7500 Printer Paper Control
7.5 Replacing CT-7500 Thermal Paper
7.6 CT-7500 LCD Contrast Control
8.0 TEST HOOKUP CONNECTIONS
8.1 Contact Cable Hookup
8.2 Initiate Cable Hookup
8.3 Analog Voltage Monitor Hookup
8.4 Digital Voltage Monitor Hookup
8.5 External Trigger Input
8.6 AC Current Sensor Hookup
9.0 OPERATING PROCEDURES
9.1 Timing a Circuit Breaker
9.1.1 Timing an Open Operation With No Resistor
9.1.2 Timing an Open Operation With Insertion Resistor
9.1.3 Timing Close-Open Operation Using Channel #1
9.2 Get Tabulated Results Using Thermal Printer
9.3 Get Graphic Timing Results Using Thermal Printer
9.4 Save Timing Shot in EEPROM
9.5 Print EEPROM Timing Shot Directory
9.6 Recall a Timing Shot
9.7 Deleting a Timing Shot
............ ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ .............
............ ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.......... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
......... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
..... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.... ............ ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
..... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
..... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.. ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
........... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
..... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
......... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
...... ............ ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
....... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
........... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
....... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
....... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.. ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
............ ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
........... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
..... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
......... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
........... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
........... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
. ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
...... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
..... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
........... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
........ ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
…… … 1
.......... ............. ............ ............. .............
............ ............. ............ ............. .............
.. ............. ............ ............. .............
.... ............. ............ ............. .............
..... ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
........... ............. ............ ............. .............
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
2
2
3
3
3
3
3
3
4
4
4
4
4
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
9
10
10
10
10
10
11
11
12
12
12
12
12
12
13
18
21
22
23
24
25
29
35
36
38
39
Page 3

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.8 Recall a Breaker Test Plan
9.9 Print a Breaker Test Plan
9.10 Print Breaker Test Plan Directory
9.11 Shot Description
9.12 CT-7500 Channel Configuration
9.13 Computer Interface
9.14 Breaker Travel Analysis
9.14.1 Breaker Stroke
9.14.2 Breaker Over-Travel Distance
9.14.3 Breaker Bounce-Back Distance
9.14.4 Contact Wipe
9.14.5 Breaker Contact Velocity
9.14.6 Analysis Point Selection
9.14.7 Analysis Point No 1
9.14.8 Analysis Point No 2
9.15 Set-Up Open Timer Analysis Points
9.16 English/Metric Selection
9.17 Set CT-7500 Internal Clock
9.18 Slow-Close Test
9.19 Transducer Self Test
9.20 Check Cable Hookup
9.21 Automatic Print Setting
10.0 Running the CT-7500s in Tandem
11.0 CT-7500 Trouble Shooting Guide
.... ............ ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.... ............ ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
. ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
............ ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
..... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
......... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
............ ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.. ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.. ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
..... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.......... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
......... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
....... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
........... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
...... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
....... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
.... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
40
41
43
44
46
47
48
48
48
48
48
48
48
49
49
50
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
APPENDIX
A. ITE Circuit Breaker Model 14.4K Timing Chart
B. CT-7500 Test Plan for ITE Circuit Breaker Model 14.4K.
C. CT-7500 Timing Chart for ITE Circuit Breaker Model 14.4K.
D. CT-7500 Tabulated Test Report for ITE Circuit Breaker Model 14.4K.
E. Timing Chart for Siemens TCP-149 Circuit Breaker
F. CT-7500 Test Plan for Siemens TCP-149 Circuit Breaker
. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
............ ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
...... ............. ............ ............. .............
...... ............. ............. ............ ............. .............
........... ............. ............ ............. .............
( i )
..... ............ ............. .............
I
II
III
IV
V
VI
Page 4

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 5-1. CT-7500 Control Panel
Figure 8-1. Typical Circuit-Breaker Test Cable Hookup
Figure 8-2. Typical Series Contacts Test Cable hookup
Figure 8-3. Typical Dc Trip and Close Control Test Cable Hookup
Figure 8-4. Typical DC Trip and AC Close Control Test Cable Hookup
Figure 8-5. Typical Voltage-Monitoring Test Cable Hookup
Figure 8-6. Typical External Trigger Hookup
Figure 8-7. Transducer Cable Hookup
Figure 8-8. AC Current Sensor Hookup
Figure 9-0. CT-7500 Operating Steps
Figure 9-1. Steering Map of Menus and User Options
Figure 9-2. Typical Tabulated Printout of Open Operation on Thermal Printer
Figure 9-3. Typical Tabular Printout of Open Operation on Ink-Jet Printer
Figure 9-4. Typical Graphic result on Thermal Printer
Figure 9-5. Typical Graphic report on Ink-Jet Printer
Figure 9-6. Typical Graphic-Expansion result Printout on Thermal Printer
Figure 9-7. Open and Close Timing Graph Interpretation
Figure 9-8. Open-Close and Close-Open Graph Interpretation
Figure 9-9. Typical Timing Shot Directory Printout on Thermal Printer
Figure 9-10 Typical Test-Plan Printout on Thermal Printer
Figure 9-11 Typical Test Plan Directory Printout
Figure 9-12 Typical Slow-Close Test Report
. ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
.... ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
... ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
............. ............ ............. ............. ............
....... ............ ............. ............. ............
............ ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
........ ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
.... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
.. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
..... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
...... ............. ............. ............ ............. ............ ............
... ............ ............. ............. ............
....... ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
......... ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
... ............ ............. ............. ............
. ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
......... ............ ............. ............. ............
............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
......... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
......... ............. ............. ............
6
14
14
15
15
16
16
17
17
18
19
26
28
30
31
32
33
34
37
42
43
55
LIST OF TABLES
Table 5-1 Model CT-7500 Controls and Display
Table 7-1 Voltage Selection Jumper Setting
Table 9-1. Open Operation with No Resistor
Table 9-2. Open Operation with Insertion Resistor
Table 9-3. Close-Open Operation with No Resistor
Table 9-4. Get Tabulated Results
Table 9-5. Plot Chart and Tabulated Report
Table 9-6. Save Timing Shot in EEPROM
Table 9-7. Print Timing Shot Directory
Table 9-8. Recall a Timing Shot
Table 9-9. Delete a Timing Shot
Table 9-10.Recall a Test Plan
Table 9-11.Print a Breaker Test Plan
Table 9-12.Print a Breaker Test Plan Directory
Table 9-13.Entering Shot Identification Header
Table 9-14.Select Channel Configuration
Table 9-15.Selecting or Aborting Computer Control
Table 9-16.Setting Up "OPEN" Analysis Points Using Distance
Table 9-17.Select Metric Units of Measure
Table 9-18.Setting the Clock and Calendar
Table 9-19.Programming a Slow-Close Test
Table 9-20.Performing a Transducer Self Test
Table 9-21.Checking the Cable Hookup
Table 9-22.Automatic Print Setting
..... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
.... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
....... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
....... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
........... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
.. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
.... ...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
.. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
........ ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
........ ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............ .............
.......... ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
......... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
............ ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
..... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
.... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
............. ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
........... ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
............ ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
........... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
......... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
...... ............ ............. ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
...... ............. ............ ............. ............. ............
7
10
22
23
24
25
29
35
36
38
39
40
41
43
44
46
47
50
52
53
54
55
56
57
Page 5

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Page 6

Page 7

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
1.0 Introduction
The Model CT-7500 is a microprocessor-based digital time-versus-travel Circuit Breaker
Analyzer with a special on line test mode. This on line test mode (Quick-Shot mode) allows the
user to capture breaker contact close time and contact open (clear) time while the breaker is still in
service. In the off line test, the Model CT-7500 fully analyzes utility circuit-breaker performance:
contact time, stroke, velocity, over-travel, bounce-back, and contact wipe.
Contact-motion analysis includes: Open, Close, Open-Close, Close-Open, and Open-CloseOpen. A timing window is selectable between 1-second or 10-second periods. The 10-second
window allows timing of long events (e.g., circuit switcher contacts).
The CT-7500 is available in three models:
CT-7500-3; three contact channels.
CT-7500-6; six contact channels.
CT-7500-12; twelve contact channels.
All the CT-7500 models have the following input:
Three Digital Travel Transducer Input channels.
One Analog Voltage Monitor Input channel.
One Digital Voltage Monitor Input channel.
One Trip/Close current monitor channel.
There are two modes of operation for the CT-7500: Stand Alone Mode and Computer Control
Mode. This manual will focus on the CT-7500 Stand Alone Mode. The Computer Control Mode is
covered under the CT-7500 PC software manual.
2.0 CT-7500 Description
2.1 On-line Timing (Quick-Shot) mode
A clamp-on AC current probe connected to the breaker bushing CT lets the CT-7500
measure breaker switching time (while the breaker’s still in service). The CT-7500 can time an
OPEN operation by sensing the time when the OPEN coil is energized until the bushing CT
current returns to zero. CLOSE time is detected when the close coil is energized until the bushing
CT current is detected.
This “Quick-Shot” mode provides a quick way to diagnose breaker performance and savings in
maintenance cost.
2.2 Time-Versus-Travel Circuit Breaker Analyzer Mode
The CT-7500 applies a 35Vdc voltage to each of the contact channels. This test voltage is
sensed by an analog to digital converter (A/D) to determine the state of the contact (close, or
open, or insertion resistor). The CT-7500 records the A/D reading at a 10 KHz rate, and stores
these readings in memory. The contact/resistor time is then derived from data stored in memory.
The CT-7500 uses three up-down counters to sense the breaker’s transducer reading. The
CT-7500 travel transducer employs an optical encoder to send quadrature signals to the CT7500’s counters. With the use of the digital transducer and counters, the user never has to set up
1
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 8

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
or calibrate the transducer.
The CT-7500 has a built-in initiate circuit to operate circuit breakers. Since this solid-state
circuit is controlled by the micro-processor, the CT-7500 can perform multiple operations (O-C, CO, O-C-O) with ease. Each Trip and Close initiate circuit is fuse protected. The user is also
required to hold the “ARM” switch during a test to complete the initiate circuit.
The CT-7500 can also store up to 200 breaker-timing test records and 45 breaker test-plans in
FLASH EEPROM. Stored timing test records can be recalled and printed or transferred to the PC.
Using the breaker test plan during a test, the users do not have to set the velocity calculating
points. The CT-7500 will also print “PASS” and “FAIL” results on test report.
2.2.1 Contact Timing Channels
A breaker's interruption of contacts is timed with the dry-contact input channels. Each channel
can detect the main contacts and insertion resistor contacts times (in millisecond and cycles).
Note
The CT-7500 can detect insertion resistors in a 10-7000 ohm range. Resistances over 7000
ohms are detected as an open contact.
2.2.2 Analog Voltage Monitoring Channel
An analog voltage input is dedicated to monitoring a breaker's dc power supply or coil voltages
(0-255 V dc or peak ac).
Note
Input voltage range is 0-300Vdc or peak AC. Reading range is 0-255Vdc.
2.2.3 Digital Voltage Monitoring Channel
One digital voltage input channel monitors voltage on/off status. Voltage threshold from 30-255
Vdc is considered as “ON” status. Voltage threshold less than 30 Vdc is considered as “OFF”
status.
2.2.4 Trip/Close Current Monitoring
A built-in Hall-effect sensor records Trip and Close coil current levels and duration. The
breaker's operate coil current waveform is graphically plotted on a printout. Current reading is also
printed in the tabulated report.
2.2.5 Travel Transducer Input Channels
Each CT-7500 has 3 digital transducer input channels. These transducer channels require
neither setup nor calibration.
2.2.6 Breaker Initiate Capability
A built-in solid-state initiate device lets users operate a breaker from the CT-7500. Operational
modes include: Open, Close, Open-Close, Close-Open, Open-Close-Open. Multiple operations
2
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 9

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
(e.g., Open-Close, Close-Open, Open-Close-Open) can be initiated with a programmable delay
time or by sensing the breaker's contact state.
Because solid-state switching is used in the initiate circuitry, the CT-7500 can switch a
breaker's ac or dc control circuit. Each trip and close circuit is protected by a 3-ampere fuse. The
initiate circuit is also protected by an interlock "ARM" switch.
2.2.7 Built-in Thermal Printer
A 4.5-inch wide thermal printer prints the breaker's contact analysis results in both tabular and
graphic formats.
2.2.8 Printer Port
A parallel printer port can drive a H-P color ink-jet printer, from which a color graphic of timing
charts and tabulated results can be printed on 8½-11-inch paper.
An Ink-Jet printer is supplied with each CT-7500.
2.2.9 Computer Interface Capabilities
A built-in RS-232C port lets timing shots stored in CT-7500 EEPROMs to be down-loaded to an
IBM-compatible PC. Windows-based (Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows Me, Windows 2000,
and Windows NT) Breaker Analysis Software is supplied with the CT-7500. This software allows
the user to:
Time Circuit breakers from a PC.
Retrieve timing shots stored in CT-7500.
Recall timing shots from a hard drive for re-analysis (at an office PC).
Create breaker test plans on a PC and load into the CT-7500.
2.2.10 Timing Shots Storage Capabilities
The CT-7500 uses Electrical Erasable PROMs (EEPROM) to store timing-shot data. Unlike
other media, EEPROMs are immune to temperature, shock, and humidity. Stored shots can be
recalled to reanalyze test data, to re-print test reports, or transfer data to an IBM compatible PC
for record keeping. Up to 200 timing shots can be stored in the EEPROMs. The number of shots
stored in EEPROMs can vary, depending on the size of the shot records.
2.2.11 Breaker Test Plan Storage Abilities
Up to 45 breaker’s test plans can be stored in the CT-7500. Test plans comprise breaker
specifications (i.e., stroke, velocity, contact time). By recalling and using a test plan, operators
can immediately test breakers and view a pass/fail report (made by comparing test performance
with specifications in the test plan). Breaker specifications need not be referenced to compare
test results to determine if a breaker passed.
A breaker test plan can be created by using the Breaker Analysis Software (supplied with each
CT-7500). The test plan is then loaded into the CT-7500 via an RS-232C serial port.
2.2.12 Diagnostic Capabilities
The CT-7500 can run diagnostics on its own electronics. Self-testing of contact cable hook-ups
and transducers lets users checkout CT-7500 accessories whenever verification is required.
3
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 10

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
2.2.13 CT-7500 Display and Control Switches
An alpha-numeric keypad lets the user enter breaker’s name plate data (Substation name,
Breaker Model, etc) and control function. A 4-line by 20-character LCD readout displays user
messages. The LCD is back lighted so messages can be viewed in low light levels.
3.0 Test Result Tabulation
3.1 Electrical Measurement Results
Each CT-7500 contact channel provides the following test results:
Contact Close time, (Quick-Shot) Mode.
Contact Open (Clear) time, (Quick-Shot) Mode.
The CT-7500 can detect insertion resistors in a 10-7000 ohm range. Resistances over 7000
ohms are detected as an open contact.
Main contact and insertion resistor contact times (Time-Travel Test).
Contact bounce time (Time-Travel Test).
Contact spread time (Time-Travel Test).
NOTE
3.2 Mechanical Measurement Results
Each digital transducer channel provides the following test results:
Breaker stroke (Time-Travel Test).
Over travel (Time-Travel Test).
Bounce back (Time-Travel Test).
Contact wipe (Time-Travel Test).
Velocity (Time-Travel Test).
Breaker contact speed calculation is based on a contact's travel distance over a period of time,
which is defined by the manufacturer's specifications.
A CT-7500 not only calculates simple distance-over-time speeds, but can also support other
formulas. An example is Siemen TCP breaker calculation formula:
V=12.2 x a/b
The formula and analysis points can be stored in a test plan for use later in the field.
NOTE
If operators use a breaker test plan (see paragraph 9.8) during testing, the test report will also
indicate a Pass/Fail condition for each test parameter (i.e. contact time, stroke, velocity, etc.).
3.3 Analog Voltage Input Results
The analog voltage input channel (V1) measures the breaker's dc control voltage during
operation. Printed voltage readings include nominal voltage (supply voltage at no load) and
minimum voltage (supply voltage under load or when a coil is energized).
This connection allows the user to monitor the DC power supply voltage fluctuation during
breaker’s operation. This feature is handy to detect breaker’s power supply problem; which
4
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 11

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
normally can not be seen using a volt meter.
NOTE
Voltage reading range is 1.0-255 V dc.
3.4 Digital Voltage Input Results
The Digital Voltage Input channel (V2) monitors voltage on/off conditions and graphs the result.
A voltage level above 30Vdc is considered as “ON” condition. This input channel is dedicated to
monitor breaker’s auxiliary switch action during breaker’s operation.
NOTE
Input voltage range is 1.0-300 V ac/dc.
3.5 Initiate Current Results
The CT-7500 not only plots Trip or Close current waveforms, but also prints steady-state
current readings of trip and close coils during operation.
NOTE
1. If the CT-7500 initiates the OPEN test or CLOSE test under the Quick-Shot test, the test report
will show OPEN or CLOSE coil current reading and current wave form.
2. If the user operates the breaker for the Quick-Shot test (external trigger), no coil current reading
or waveform will be recorded.
3.6 Slow-Close Test
A slow-close test finds the contact touch distance and penetration by using the travel
transducer and dry contact channels.
4.0 Test-Results Graphics
4.1 Thermal Printer Graphic Printout
A 4.5” wide built-in thermal printer prints graphic waveforms of contact channels, travel curves,
and actuator-coil currents. With a zoom graphics mode, the user can select an enlargement by
specifying the timing zone.
4.2 Ink-Jet Printer Output
A color graphic report can be printed on the HP Ink-jet printer (supplied with each CT-7500).
The CT-7500 will print color graphics of contact channels, travel channels, current waveforms on
8½- by 11-inch paper.
5.0 Controls and Display
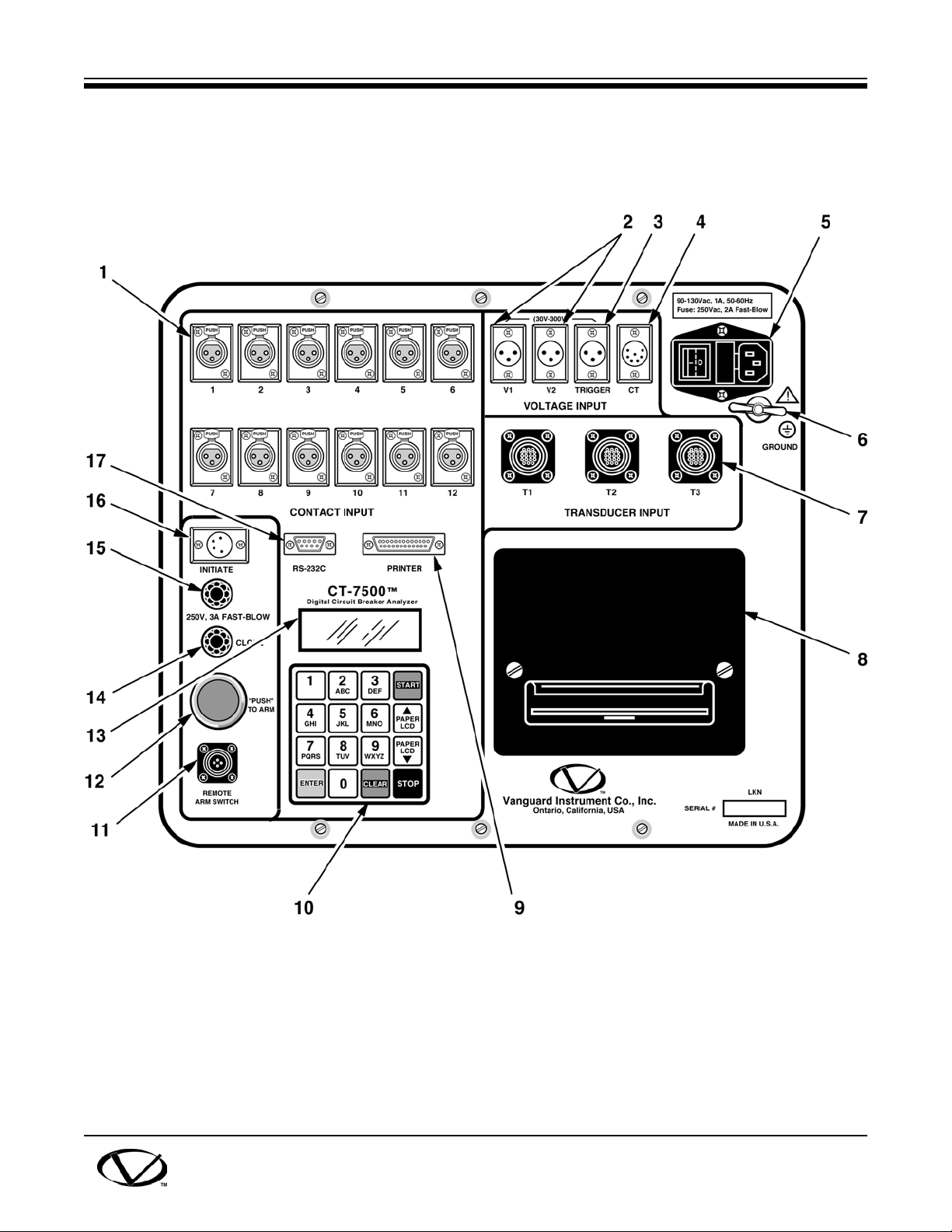
(See Figure 5-1 and Table 5-1.)
Before using the CT-7500 Analyzer, users should become familiar with all of its controls and
display indications. The keypad and display are used to operate the CT-7500 Analyzer. Figure 51 shows the control panel and numbered lines pointing to each control and indicator. The line
numbers refer to Table 5-1, which describes the function of each control and indication.
5
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 12
MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Figure 5-1. CT-7500 Control Panel
6
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 13
MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
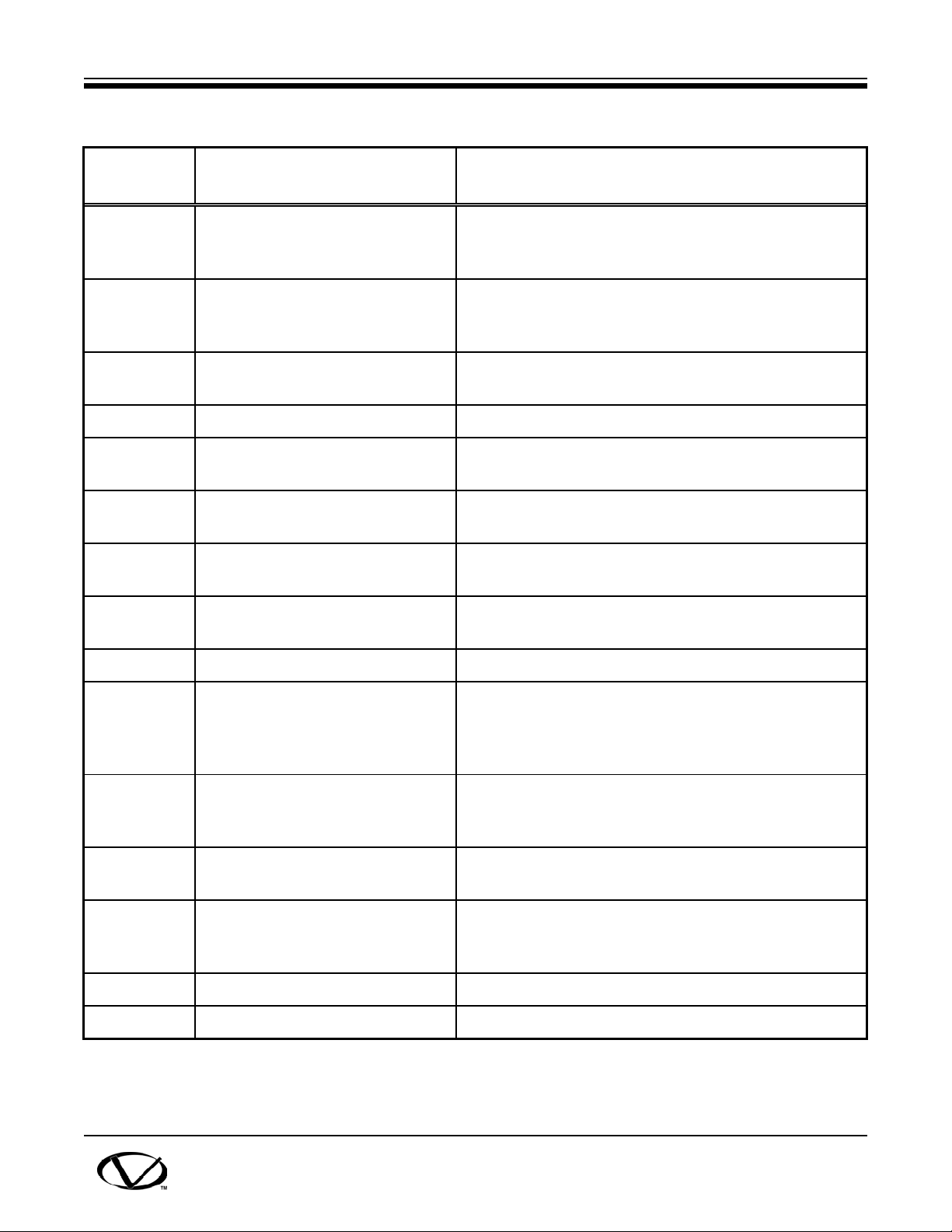
Table 5-1. Model CT-7500 Controls and Displays
Fig. 5-1
Index no. PANEL MARKING
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
CONTACT INPUT (1-12) Connector, 3-pin: each input is a continuity (dry)
sensor for detecting a contact closing or opening (a
timing input to the processor).
(30V-300V) VOLTAGE
V1 & V2/ VOLTAGE INPUT
TRIGGER/VOLTAGE INPUT Connector, 3-pin: input (30-300 Vac, dc, or peak)
CT AC current sensor input channel.
AC 100-240V; 5A MAX Power plug (3-wire), ac fuse, ON/OFF switch: Switch
GROUND Stud, 5/16-18 threads, with wing nut; safety ground
TRANSDUCER INPUT
(T1, T2, T3)
(Printer; No panel marking) Thermal printer; prints on specially treated 4½-inch
PRINTER Printer port connector, 25-pin.
Connector, 3-pin: each input is a voltage detector for
timing voltage (30-300 V dc/peak) of trip or close coil
switching (active period).
triggers timing functions.
is 2-pole rocker, input power on & off.
terminal.
Connector, 16-pin: each input (T1-T3) is a Travel
Encoder output (contact motion data).
wide paper; processor controlled.
10
11
12
13
14
15
1-9, 0, ENTER, START, STOP,
CLEAR, ↑ PAPER LCD,
PAPER LCD
↓
REMOTE ARM SWITCH Remote Arm Switch connector. The remote Arm
"PUSH" TO ARM Pushbutton switch, spring-loaded: press & hold to
(Display; no panel marking) Liquid-Crystal Display (LCD), back lighted: 4-line by
CLOSE/ 3 A Close circuit fuse (3 amperes).
OPEN/ 3 A Open circuit fuse (3 amperes).
Keypad, 16-key; keys are momentary-contact
pushbutton switches: makes menu selections, enters
alpha-numeric data, adjusts LCD contrast, and
moves paper.
switch with a 15ft cable is provided with each CT-
7500.
complete trip & close circuits for breaker tests.
20 characters per line: displays menus, options,
prompts, and test-result data.
7
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 14
MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
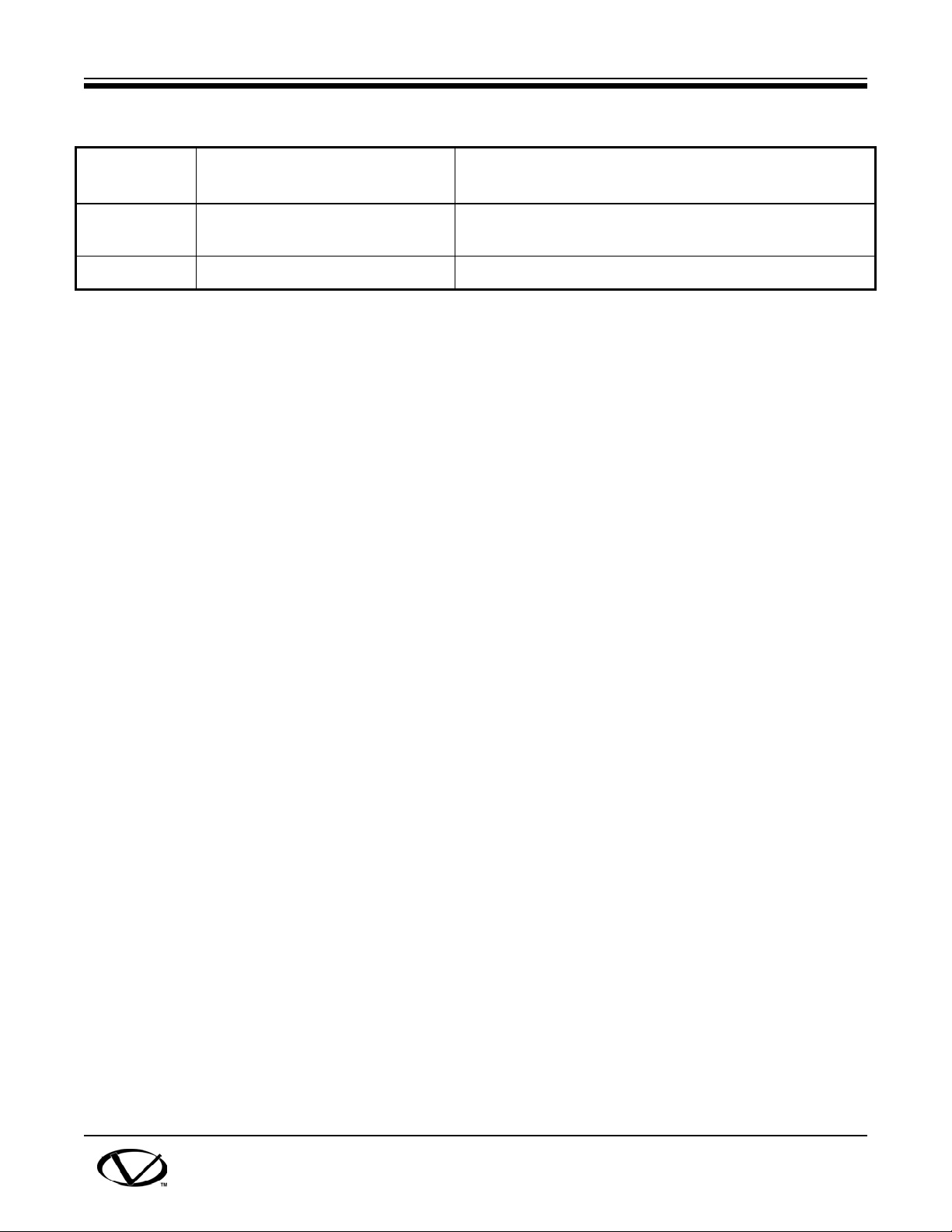
Table 5-1. Model CT-7500 Controls and Displays (cont’)
Fig. 5-1
Index no. PANEL MARKING
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
16
17
INITIATE Connector, 4-pin; switching circuit for operating the
circuit breaker being tested.
RS-232C Connector, 9-pin:RS-232C computer interface.
8
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 15

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
6.0 CT-7500 Analyzer Specifications
CONTACT TIMING
SIZE & WEIGHT
OPERATING POWER
AC CURRENT SENSOR
DRY-CONTACT INPUTS
TIMING WINDOW
RESOLUTION
DRY-CONTACT
CHANNEL PROTECTION
CONTACT RESISTANCE
INSERTION RESISTANCE
TRIGGER INPUT
Open, Close, Open-Close, Close-Open, and Open-Close-Open
16d by 14w by 11h (inches); Less than 32 pounds
3 amps, 90-120Vac/200-240Vac 50/60 Hz
0-25 Ampere, non-contact AC current sensor
3, 6, or 12 dry-input channels; Each detects Main & Insertion-Resistor contacts
Selectable: 1 second or 10 seconds
± 100 microseconds at 1-second duration; ±1.0 millisecond at 10-seconds duration
Fuses protect all isolated power supplies; All contact inputs are grounded until test;
Inputs are MOV protected
CLOSED: <20 ohms; OPEN: >10,000 ohms
Range: 10 to 7,000 ohms
Open/Close: 30 to 300 volts, dc or peak ac
(See table below.)
VOLTAGE INPUTS
CURRENT-SENSOR INPUT
BREAKER INITIATE
TRAVEL TRANSDUCERS
CONTACT TRAVEL
POINT DIFFERENCE
BREAKER ANALYSIS
display,
SOFTWARE (included)
COMPUTER INTERFACE
DISPLAY
HARD-COPY PRINTOUT
COLOR PRINTER
Two: 1.0-300 volts, dc/peak ac; analog voltage recording 1.0-255 V dc
One: Non-contact, Hall-Effect sensor, 0.2 to 25 amp ranges, dc to 5 kHz
Initiate Open, Close, Open-Close, Close-Open, Open-Close-Open
3 travel-transducer channels; Linear motion: 0.0-60.0 (±0.01) inches;
Rotary Range: 0-360o (± 0.36
Measures"Slow-Close" contact point distance (Hard Copy)
Analysis software runs on IBM-compatible. Software package for graphic
numerical reports, and database utility for shop or office
RS-232C Port
Back-lighted LCD screen: 4 lines by 20 characters, sunlight viewable
Contact travel waveforms & tabulated results print on 4.5-inch thermal paper
Built-in parallel printer port. CT-7500 produces both graphic and tabulated test
results in color on 8.5 by 11 (inches) paper via external ink-jet printer
o)
CARRYING CASE (optional)
Hard shipping case for both CT-7500 and Travel Transducer
9
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 16

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
WARRANTY
One year warranty on parts and labor; post-warranty service contracts available
10
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 17
MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
7.0 CT-7500 Special Features
7.1 CT-7500 Operating Voltages
The CT-7500 operating voltage is selectable between 110/120 V, 50/60 Hz or 220/240 V,
50/60 Hz. Voltage selection is set by one jumper/connector on the Initiate PCB (JP3) and one
jumper/connector on the Power Supply PCB (JP1). Jumper setting for both connectors is shown
in table 7-1.
Table 7-1. Voltage Selection Jumper Setting
VOLTAGE SELECTION CONNECTOR PIN
110/120 Vac Pin 1& 2, 3 & 4
220/240 Vac Pin 2 & 3
Note:
Operating voltage is set from the factory.
7.2 CT-7500 Main Power Fuse
The CT-7500 uses an AC input module containing the AC receptacle, Power switch, and
Protective fuse. Replacement fuse should be: 20mm, 2A-250Vac slow blow.
7.3 CT-7500 Printer and Printer Paper
The CT-7500 built-in thermal printer uses 4.5-inch wide thermal paper for printing test
results. To maintain the highest quality test-result printing and to avoid paper jamming, the use
of paper supplied by our factory is highly recommended. Additional paper can be ordered from
either of the two sources listed below:
Vanguard Instruments Co, Inc.
1710 Grevillea Court
Ontario, CA 91761
Tel: 909-923-9390
Fax: 909-923-9391
Part Number: TP-4 Paper
OR
BG Instrument Co.
13607 E. Trent Avenue
Spokane, WA 99216
Tel: 509-893-9881
Fax: 509-893-9803
Part Number: TP4 paper
7.4 CT-7500 Printer Paper Control
To advance paper from the printer, press and release the “↑ PAPER LCD” switch; to
retract the paper from the printer, press and release “↓ PAPER LCD” switch.
11
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 18

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
7.5 Replacing CT-7500 Thermal Paper
The thermal paper roll is residing in the pocket under the printer cover. To replace the
thermal paper roll, follow these steps:
Remove printer cover.
Remove leftover thermal paper roll from paper holder.
Unroll new thermal paper roll.
Feed thermal paper into the slot between the paper pocket and roller.
The printer will pull paper under the thermal head.
Roll thermal paper roll and place this paper roll in paper holder.
Lift thermal head and align thermal paper if necessary.
Reinstall printer cover.
Note
Thermal paper will show a red stripe to indicate “Close to End of Paper”.
7.6 CT-7500 LCD Contrast Control
To Darken the LCD display, press and hold the “↑ PAPER LCD” switch for two seconds; to
lighten the LCD display, press and hold the “↓ PAPER LCD” switch for two seconds.
12
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 19

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
8.0 TEST HOOKUP CONNECTIONS
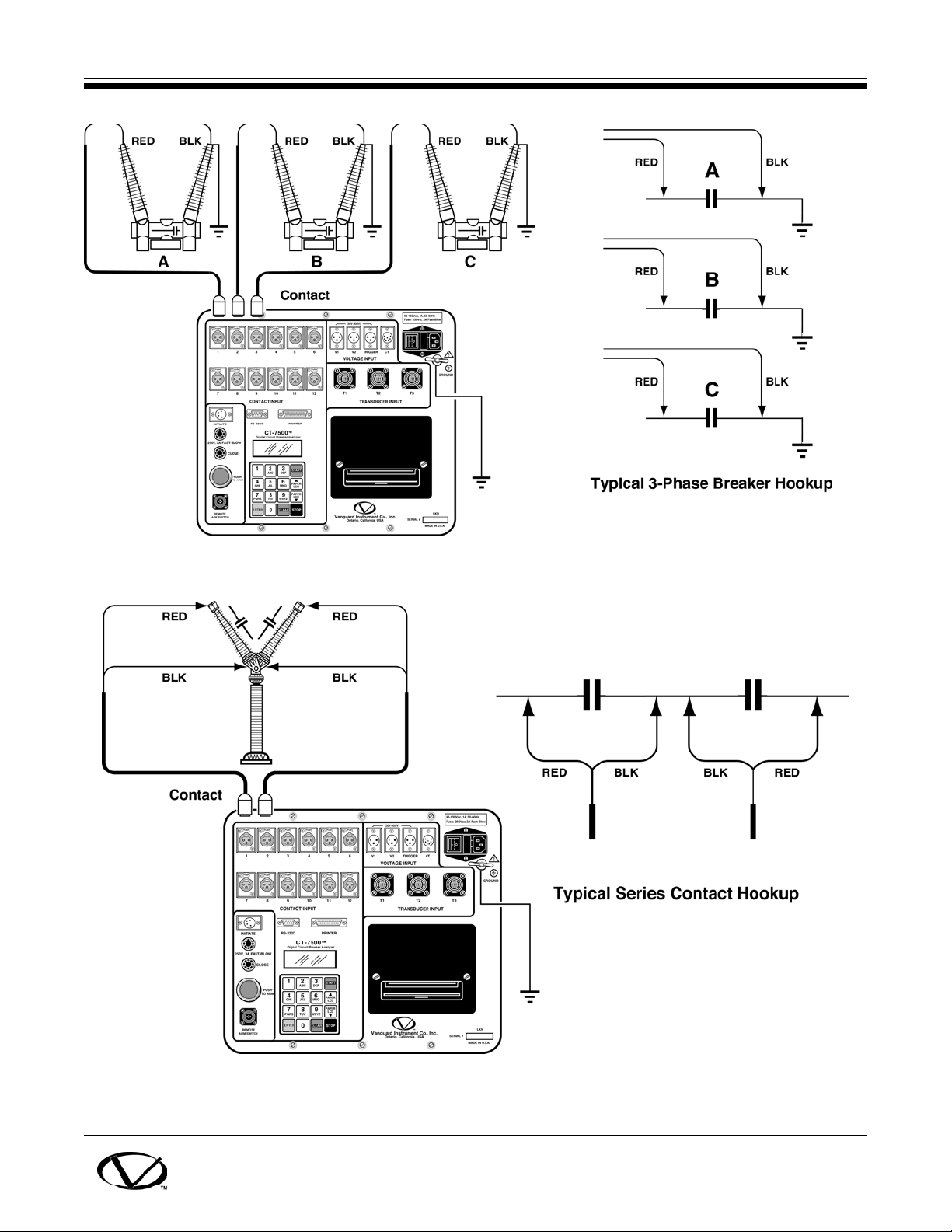
8.1 Contact Cable Hookup
A typical contact cable connection to a circuit breaker is shown in Figure 8-1.
NOTE
It is advisable to ground one side of the contacts for most testing. If a breaker is floating
(i.e., ungrounded), ensure contact-channel inputs are protected against static discharge.
A typical series contact connection is shown in Figure 8-2.
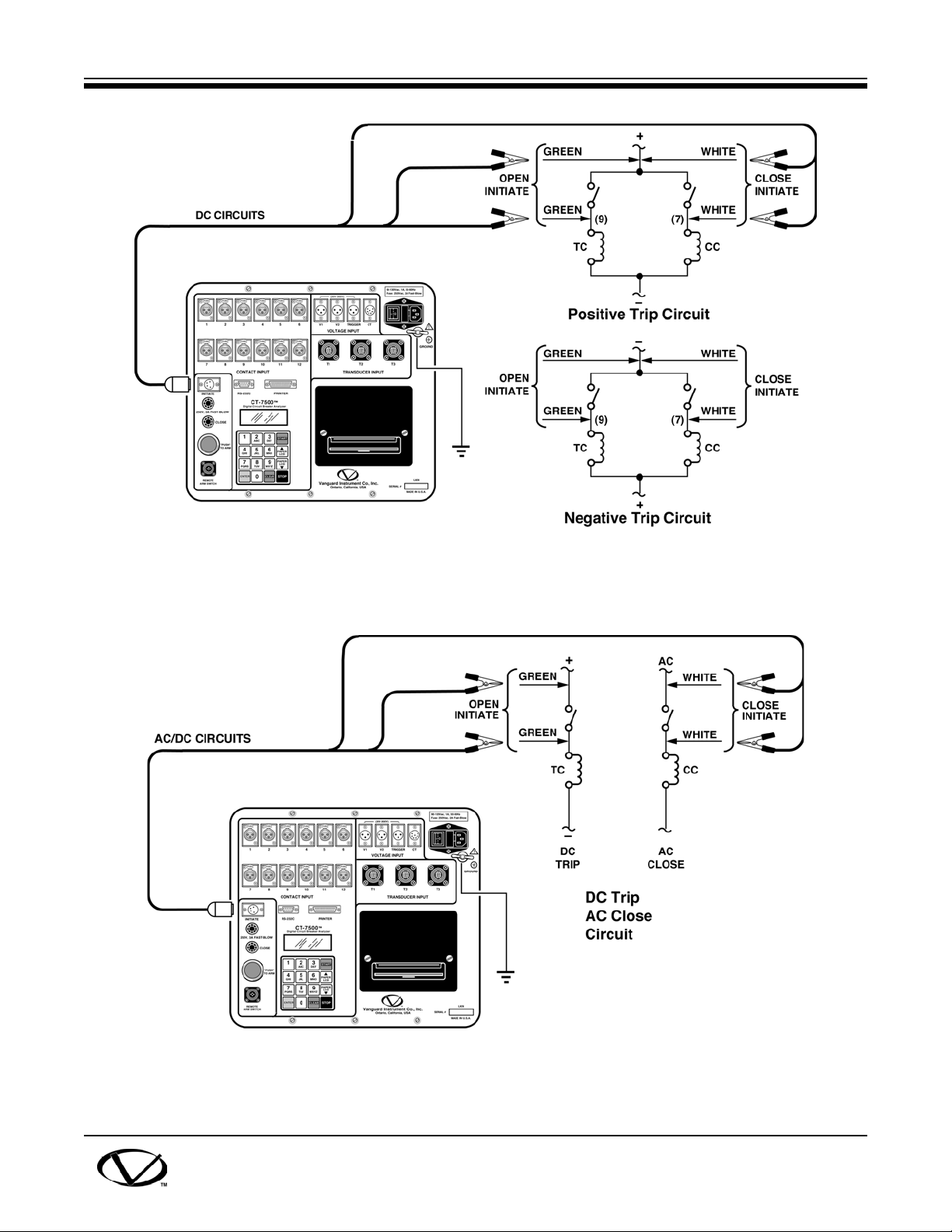
8.2 Initiate Cable Hookup
A CT-7500 will trip or close breakers with a solid-state device, which will operate on any ac or
dc control voltage from 10 to 300 volts. Both the trip and close circuits are protected by 3-ampere
fuses.
A typical dc trip and dc close control circuit test hookup is shown in Figure 8-3.
A typical dc trip and ac close control circuit is shown in Figure 8-4.
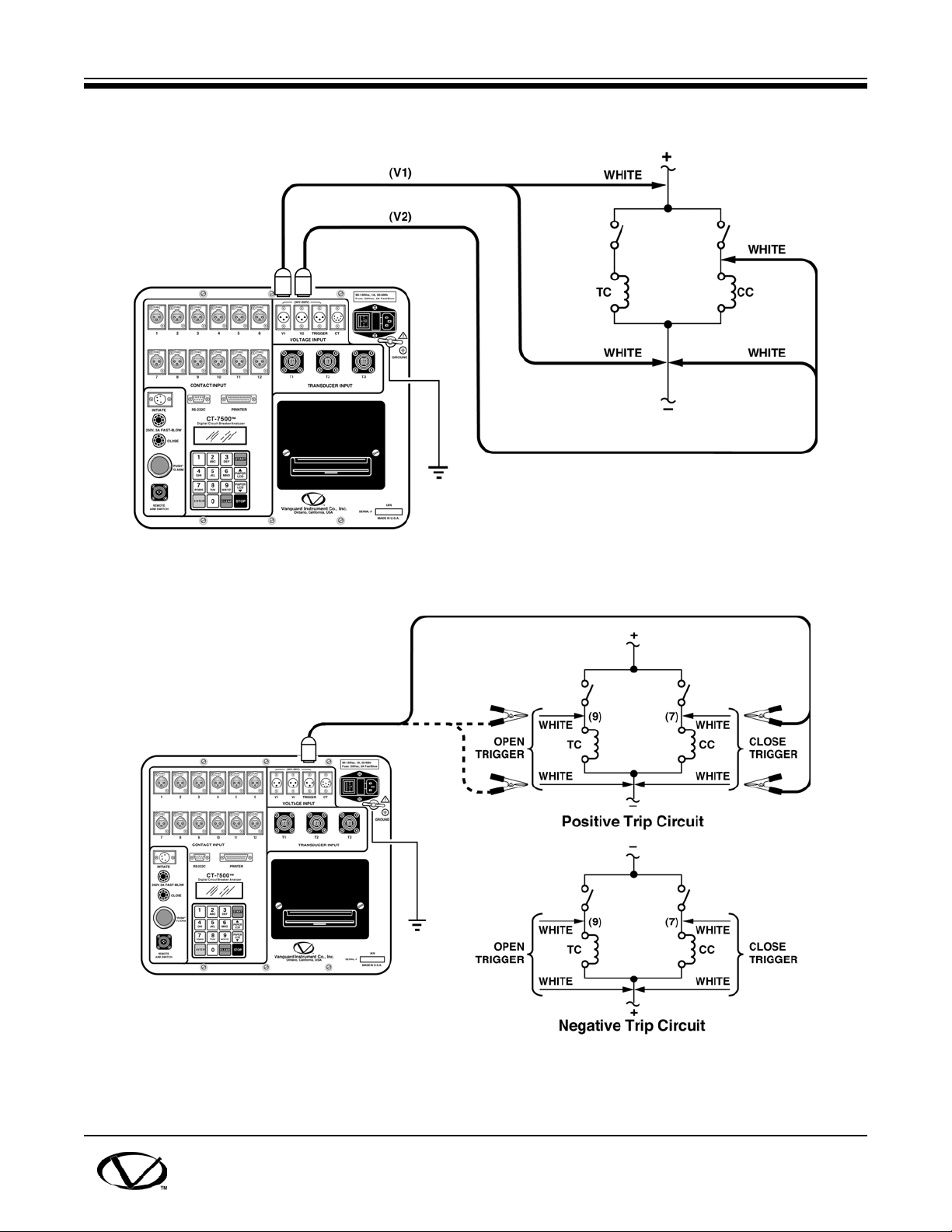
8.3 Analog Voltage Monitor Hookup
The analog voltage input (V1) lets users monitor a breaker's dc-control voltage during
operation. The analog voltage input (V1) will record the norminal dc voltage (at no load) and the
minimum dc voltage (while the Trip or Close coil is energized).
Nominal and minimum voltage readings will print on a tabulated report. Analog waveform will
also plot in a graphic report. This lets the user see the breaker's dc control voltage "dip" under
load. Problems, such as a poor connection or an excessive voltage drop, during operation can
thus be easily detected.
A typical voltage monitoring hook up is shown on Figure 8.5.
NOTE
Maximum voltage recorded is 255 Vdc.
8.4 Digital Voltage Monitor Hookup
The Digital V2 voltage input channel lets users monitor the voltage ON/OFF state. The voltage
ON/OFF state will be plotted on the graphic report. A typical hook up is shown on Figure 8.5.
8.5 External Trigger Input
External trigger mode lets a user start a recording when the CT-7500 senses a voltage. A
typical application for this external trigger mode is to time a circuit breaker in a close operation and
to start timing only when the close coil is energized (bypassing the 52X relay delay time).
Since the 52X relay carries the close coil current, the user wants to connect the CT-7500’s initiate
cable to the close terminal (figure 8-4). The CT-7500 will energize the 52X relay to start the close
operation. The CT-7500 then will start the timing when it senses the voltage across the closing
coil. See Figure 8.6 for a typical test hookup.
Another application (for external trigger) is to start timing the breaker when the user trips or closes
the breaker remotely.
13
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 20

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
NOTE
Minimum trigger voltage is set for 30 V ac/dc. Maximum continous voltage is 300Vac/dc.
Different trigger voltages can be set at the factory, based on specific requests from users.
The CT-7500 will start looking for the external trigger input voltage after the CT-7500 Initiate
Sequence is completed (CT-7500 stops beeping after the user presses “START” key) and
message “LOOKING FOR TRIGGER VOLTAGE” is shown on LCD.
This external trigger voltage needs to be sensed by the CT-7500 within 5 second after the
Initiate sequence. The CT-7500 will return to main menu if no voltage is sensed.
8.6 AC Current Sensor Hookup
A clamp-on AC current sensor connecting to the breaker bushing CT allows the CT-7500 to
sense breaker bushing current. The AC current sensor requires a 100mA current to operate.
Maximum current is 25 amperes. Typical hookup is shown on figure 8-8.
14
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 21
MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Figure 8-1. Typical Single Break Contact Cable Hookup
Figure 8-2. Typical Series Contacts Test Cable Hookup
15
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 22
MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Firgure 8-3. Typical DC Trip and Close Control Test Cable Hookup
Figure 8-4. Typical DC Trip and AC Close Control Test Cable Hookup
16
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 23
MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Figure 8-5. Typical Voltage-Monitoring Test Cable Hookup
Figure 8-6. Typical External Trigger Hookup
17
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 24

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Figure 8-7. Transducer Cable Hookup
Figure 8-8. AC Current Sensor Hookup
18
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 25

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.0 OPERATING PROCEDURES
The main steps to time a circuit breaker are listed below (Figure 9-0). Figure 9-1 is a user's
"map" of all menus for operating a CT-7500.
HOOKUP CT-7500
1. GROUND CT-7500 (See note)
2. CONNECT CT-7500 CABLES TO BREAKER
3. INSTALL TRANSDUCER
APPLY POWER
1. TURN CT-7500 POWER ON
2. PERFORM SELF TEST (HOOK-UP TEST,
CABLE TEST)
TIMER BREAKER
1. SELECT CT-7500 TEST
2. OPERATE BREAKER
GET RESULTS
1. GET TABULATED RESULTS
2. GET GRAPHIC RESULTS
Figure 9-0. CT-7500 Operating Steps
Note
To reduce the possibility of damaging the CT-7500 contact channels by static discharge in the
high voltage substation, we recommend the user to ground one side of the breaker’s bushings.
19
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 26

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Figure 9-1 CT-7500 Menu Map
20
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 27

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
21
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 28

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Figure 9-1 CT-7500 Menu Map
22
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 29

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.1 Timing A Circuit Breaker
Timing Breaker Under Quick-Shot Mode.
The CT-7500 will provide OPEN or CLOSE time only under the Quick-Shot mode. The user
can have the CT-7500 to initiate the OPEN or CLOSE test, in this case the test report will show
OPEN or CLOSE coil current reading and current wave form.
If the user operates the breaker for the Quick-Shot test (using External Trigger), no coil current
reading or wave form will be recorded.
Timing Breaker Under Time-Travel Mode
The CT-7500 will initiate the breaker operation and do a timing test on the following operations:
OPEN
CLOSE
OPEN-CLOSE
CLOSE-OPEN
OPEN-CLOSE-OPEN
Note
1. The CT-7500 can start OPEN-CLOSE operations, using a programmable delay (between
OPEN and CLOSE commands) or no delay.
2.The CLOSE-OPEN can be started by the CT-7500, using several options:
Contact #1 Close:
CT-7500 initiates a CLOSE command then OPEN command after detecting circuit
breaker’s contact closed. The CT-7500 detects breaker contact closed through contact
channel #1.
Set DELAY:
CT-7500 initiates a CLOSE command then OPEN command after a programmable
delay (from a CLOSE command).
No DELAY:
CT-7500 initiates a CLOSE command and OPEN command together. Since the circuit
breaker is in the open state, the circuit breaker 52B contact allows the close coil to be
energized to start the close command. When the circuit breaker is making the transition
from open state to close state, the 52A contact will close allowing the breaker to initiate
the open command.
3.The OPEN-CLOSE-OPEN operations can be initiated by the CT-7500, using a programmable
delay between each of the operations (e.g., delays between OPEN to CLOSE and between
CLOSE to OPEN).
23
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 30

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.1.1 Timing an OPEN Operation With No Insertion Resistor
Table 9-1. Open Operation With No Resistor
STEP
1 READY TIMER FOR BREAKER OPERATION. PRESS #1 KEY. INSERTION RESISTOR?
2 SELECT NO INSERTION RESISTOR. PRESS #1 KEY. TIMING WINDOWS:
3 SELECT 1-SECOND WINDOW. PRESS #1 KEY. 1.INTERNAL TRIGGER
4 SELECT INTERNAL TRIGGER. PRESS #1 KEY. TIMING MODE:
5 SELECT OPEN OPERATION. PRESS KEY #1. OPEN TIMING
6 INITIATE OPEN COMMAND. HOLD "ARM" KEY AND
OPERATION
ACTION DISPLAY
1.NO
2.YES
1.WINDOW = 1 SECOND
2.WINDOW = 10 SECONDS
2.EXTERNAL TRIGGER
1. OPEN 2. CLOSE
3. O-C 4. C-0
5. O-C-O
Hold "ARM" Switch,
Then "START".
"STOP" to ABORT
TEST IN PROGRESS
PRESS "START" KEY.
Hold "ARM" Until
Test complete.
(Up to 15 seconds)
7 ANALYZER IS READY TO OUTPUT RESULTS. NONE. 1.TIME BREAKER
2.GET RESULT
3.SET-UP
4.DIAGNOSTIC
Note
One-second timing windows are used for breaker timing; 10-second timing windows are used
for circuit-switcher timing.
24
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 31

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.1.2 Timing an OPEN Operation With Insertion Resistors
The CT-7500 can time breakers with insertion resistors. The insertion resistor range is 10 to
7000 ohms. Any insertion resistor more than 7,000 ohms is detected as open circuit. Timing
window results will show main contact timing and insertion resistor contact timing. Graphic reports
show main contact and resistor contact activities on each of the channels.
Table 9-2. Open Operation With Insertion Resistor
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 READY TIMER FOR BREAKER OPERATION. PRESS #1 KEY. INSERTION RESISTOR?
1.NO
2.YES
2 SELECT INSERTION RESISTOR. PRESS #2 KEY. TIMING WINDOWS:
1.WINDOW = 1 SECOND
2.WINDOW = 10 SECONDS
3 SELECT 1-SECOND WINDOW. PRESS #1 KEY. 1.INTERNAL TRIGGER
2.EXTERNAL TRIGGER
4 SELECT INTERNAL TRIGGER. PRESS #1 KEY. TIMING MODE:
1. OPEN 2. CLOSE
3. O-C 4. C-0
5. O-C-O
5 SELECT OPEN OPERATION. PRESS KEY #1. OPEN TIMING
Hold "ARM" Switch,
Then "START".
"STOP" to ABORT
6 INITIATE OPEN COMMAND. HOLD "ARM" KEY AND
PRESS "START" KEY.
7 ANALYZER IS READY TO OUTPUT RESULTS. NONE. 1.TIME BREAKER
TEST IN PROGRESS
Hold "ARM" Until
Test complete.
(Up to 15 seconds)
2.GET RESULT
3.SET-UP
4.DIAGNOSTIC
Note
The User can set the CT-7500 to print tabulated and graphic reports automatically after it
completes a test. See section 9-21 for automatic print setting.
25
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 32

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.1.3 Timing CLOSE-OPEN Operation Using Contact Channel #1
The CLOSE-OPEN operation of the breaker simulates a condition where a breaker is closed on
a fault. The CT-7500 first initiates a CLOSE command then sends an OPEN command only when
it detects that main contact #1 is closed. This mode truly simulates the breaker closing into a fault
condition in the field.
Table 9-3. Close-Open Operation with No Resistor
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 READY TIMER FOR BREAKER OPERATION. PRESS #1 KEY. INSERTION RESISTOR?
1.NO
2.YES
2 SELECT NO INSERTION RESISTOR. PRESS #1 KEY. TIMING WINDOWS:
1.WINDOW = 1 SECOND
2.WINDOW = 10 SECONDS
3 SELECT 1-SECOND WINDOW. PRESS #1 KEY. 1.INTERNAL TRIGGER
2.EXTERNAL TRIGGER
4 SELECT INTERNAL TRIGGER. PRESS #1 KEY. TIMING MODE:
1. OPEN 2. CLOSE
3. O-C 4. C-0
5. O-C-O
5 SELECT CLOSE-OPEN OPERATION. PRESS #4 KEY. C-O SECOND TRIGGER
1. CONTACT #1 CLOSE
2. SET DELAY
3. NO DELAY
6 SELECT CONTACT #1 CLOSE. PRES #1 KEY. CLOSE-OPEN TIMING
Hold "ARM" Switch,
Then "START".
"STOP" to ABORT
7 INITIATE OPEN COMMAND. HOLD "ARM" KEY AND
PRESS "START" KEY.
8 ANALYZER IS READY TO OUTPUT RESULTS. NONE. 1.TIME BREAKER
TEST IN PROGRESS
Hold "ARM" Until
Test complete.
(Up to 15 seconds)
2.GET RESULT
3.SET-UP
4.DIAGNOSTIC.
Note
1. Users can program a delay from 10 to 500 ms between the CLOSE and OPEN commands.
When a delay is used in this operation, it may not represent a true breaker condition.
2. Users can also program in no delay for this operation, in which case, the CLOSE and OPEN
26
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 33

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
commands are initiated at the same time. The breaker will start closing, the
OPEN circuit
is
then enabled (by the A/B switch) allowing the OPEN operation.
9.2 Get Tabulated Timing Results Using Thermal Printer
Table 9-4. Get Tabulated Results
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 GET TIMING RESULTS. PRESS #1 KEY. 1.PRINT TEST RESULTS
2.PLOT FULL CHART
3.PLOT EXPANSION
4.PLOT 0-200 MS
2 PRINT TABULATED RESULTS. PRESS #1 KEY. SELECT PRINTER
1. INTERNAL THERMAL
2. EXTERNAL INKJET
3 OUTPUT TABULATED RESULTS ON
THERMAL PRINTER.
PRESS #1 KEY. 1. PRINT TEST RESULTS
2. PLOT FULL CHART
3. PLOT EXPANSION
4. PLOT 0-200 MS
Note
To get a tabulated report on the ink-jet printer, press key #2 in step #2. Ensure the ink-jet printer
is connected to the CT-7500 for this report.
27
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 34

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Figure 9-2. Typical Tabulated Printout of Open Operation on Thermal Printer
28
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 35

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Note
1. Contact time is shown in both millisecond and cycles. From figure 9-2, contact channel #1 time
is 181.50 ms or 10.89 cycles.
2. Contact bounce duration is 1.70 ms
3. Contact wipe is measured as .77 inch.
4. The slowest contact and fastest contact differential time is shown as contact delta:0.10 ms.
5. AC current sensor time is shown as CT Channel Analysis time in millisecond cycles. The CT
time is shown as 184.70ms or 11.08 cycles.
Since this print out was generated to show both Quick-Shot mode and Time-Travel mode; both
CT time and contact-travel readings are shown on this report.
6. Breaker contact stroke is 7.08 inches.
7. Contact velocity calculation is 5.72 feet per second.
8. Contact over-travel distance is 0.29 inch.
9. Contact bounce-back distance is 0.16 inch.
10. Contact velocity calculation is from the 2 analysis points:
Analysis point # 1 is 1.00 inch from fully closed position.
Analysis point # 2 is 5.00 inches from fully closed position.
11. The DC power supply was monitored during test. The nominal voltage is 52V and the
minimum is 37 V.
12. Initiate current is 5.1 amperes.
13. Timing shot duration is 1 second.
14. There is no insertion resistor in this test (no insertion resistor time is measured).
15. Trigger mode is internal (timing window starts at the same time the CT-7500 energized the
circuit breaker).
29
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 36

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Pass/Fail on Contact
Parameters
Pass/Fail on Travel
Parameters
Figure 9-3. Typical tabulated Printout of an Open Operation on Ink-jet Printer.
30
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 37

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.3 Get Graphic Timing Results Using Thermal Printer
Table 9-5. Plot Chart and Tabulated Report
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 GET TIMING RESULTS. PRESS #2 KEY. 1 PRINT TEST RESULTS
2 PLOT FULL CHART
3 PLOT EXPANSION
4 PLOT 0-200 MS
2 PLOT FULL CHART. PRESS #2 KEY. SELECT PRINTER
1. INTERNAL THERMAL
2. EXTERNAL INKJET
3 PRINT CHART ON THERMAL PAPER. PRESS #1 KEY. PLEASE WAIT
PLOTTING GRAPH
4 RETURN TO MAIN MENU AFTER
PRINT CHART.
NO ACTION. 1. TIME BRKR
2. GET RSLT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTIC
Note
1. Figure 9-4 shows a timing chart of a circuit breaker with contact activity on channel 1 and 3. A
CT channel is also shown on this chart. Since this print out was generated to show both QuickShot mode and Time-Travel mode; both CT time and contact-travel readings are shown on this
chart.
2. To get a graphic report on the ink-jet color printer, press key #2 in step # 2.
31
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 38

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
g
yp
p
Contact Trace
Travel Trace
Initiate Current Trace
AC Current Sensor
Digital Voltage Channel V2
Analog Voltage Channel V1
hic Result on Thermal Printer
ical Gra
ure 9-4. T
Fi
32
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 39

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Figure 9-5. Typical Graphic Report on Ink-Jet Printer
33
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 40

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Analysis Point #1
Analysis Point #2
Figure 9-6. Expansion Graph from 0ms to 200ms on Thermal Printer
Note
Analysis point # 1 and point #2 is shown on chart.
34
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 41

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Figure 9-7. Open Timing Shot Graphics Interpretation
Figure 9-7A. Close Timing Shot Graphics Interpretation
35
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 42

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Figure 9-8. Open-Close and Close-Open Timing Shot Graphics Interpretation
36
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 43

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.4 Save Timing Shot in EEPROM
Table 9-6. Save Timing Shot In EEPROM
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT SAVE/RECALL MENU. PRESS #3 KEY. 1 ANALYSIS POINTS
2 MEASUREMENT UNITS
3 SAVE / RESTORE
4 NEXT PAGE
2 SELECT SAVE MENU. PRESS #3 KEY. 1. SAVE SHOT
2. RECALL SHOT
3. SHOT DIRECTORY
4. ERASE SHOT
3 SELECT SAVE SHOT. PRESS #1 KEY. SAVE SHOT # XXXX
TEST: CLOSE
DATE: MM/DD/YY HH:MM
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
4 CONFIRM SAVING SHOT. PRESS "ENTER"
KEY.
5 RETURN TO MAIN MENU. PRESS ANY KEY. 1. TIME BRKR
SAVE IN PROCESS
PLEASE WAIT
2. GET RSLT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTIC
Notes
Timing shot storage capability varies, depending upon the size of the shots.
The CT-7500 will assign an ID for each of the shots stored in EEPROM.
37
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 44

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.5 Print EEPROM Timing Shot Directory
Table 9-7. Print Timing Shot Directory
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
SELECT SAVE / RESTORE MENU.
1
2 SELECT SHOT DIRECTORY MENU. PRESS #3 KEY. 1. SAVE SHOT
3 SELECT SHORT DIRECTORY. PRESS # 1 KEY. 1. SHORT DIRECTORY
4 PRINT SHOT DIRECTORY NOW. NO ACTION. PRINTING ABBREVIATED
PRESS #3 KEY. 1. ANALYSIS POINT
2. MEASUREMENT UNITS
3. SAVE / RESTORE
4. NEXT PAGE
2. RESTORE SHOT
3. SHOT DIRECTORY
4. ERASE SHOT
2. FULL DIRECTORY
"STOP" TO QUIT
DIRECTORY
"STOP" TO QUIT
5 RETURN TO MAIN DIRECTORY. NO ACTION. 1. TIME BRKR
2. GET RSLT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTIC
Note
1. The CT-7500 will print out shot IDs of 10 last timing shots stored in EEPROM when "Short
Directory" is selected.
2. The CT-7500 will print out shot IDs of all timing shots stored in EEPROM if "Full Directory" is
selected.
A typical shot directory print out is shown on next page.
38
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 45

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Figure 9-9. Timing Shot Directory Printout On Thermal Printer
39
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 46

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.6 Recall a Timing Shot
The following steps are used to recall a timing shot stored in EEPROM to working memory.
Once a timing shot is recalled, the user can ask for test results from the thermal printer or the
color ink-jet printer.
Table 9-8. Recall a Timing Shot
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT SETUP MENU. PRESS #3 KEY. 1. ANALYSIS POINT
2. MEASUREMENT UNITS
3. SAVE / RESTORE
4. NEXT PAGE
2 SELECT SAVE/RESTORE SHOT. PRESS # 3 KEY. 1. SAVE SHOT
2. RESTORE SHOT
3. SHOT DIRECTORY
4. ERASE SHOT
3 SELECT RESTORE SHOT. PRESS #2 KEY. ENTER SHOT NUMBER TO BE RESTORED
xxxx
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
4 ENTER SHOT NUMBER TO BE
RESTORED.
5 CONFIRM SHOT TO BE RESTORED. PRESS "ENTER"
6 RETURN TO MAIN MENU. PRESS ANY KEY. 1. TIME BRKR
PRESS KEY 0 TO 9
FOR SHOT ID THE
"ENTER" KEY.
KEY.
ENTER SHOT NUMBER TO BE RESTORED
XXXX
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
RESTORING SHOT # XXXX
TEST: YYYY
DATE: MM\DD\YY HH:MM
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
2. GET RSLT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTICS
40
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 47

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.7 Deleting a Timing Shot
Users can delete a specific timing shot from the CT-7500 EEPROM memory by using the steps
described in the table below.
Table 9-9. Delete a Timing Shot
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT SET UP MENU. PRESS # 3 KEY. 1. ANALYSIS POINTS
2. MEASUREMENT UNITS
3. SAVE / RESTORE
4. NEXT PAGE
2 SELECT SAVE / RESTORE MENU. PRESS # 3 KEY. 1. SAVE SHOT
2. RESTORE SHOT
3. SHOT DIRECTORY
4. ERASE SHOT
3 SELECT ERASE SHOT. PRESS # 4 KEY. ENTER SHOT NUMBER
TO BE ERASED
XXXX
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
4 ENTER SHOT NUMBER. PRESS KEY 0-9 TO
SELECT SHOT
NUMBER, PRESS
"ENTER" TO
CONFIRM.
5 CONFIRM ERASE SHOT. PRESS "ENTER". ERASE IN PROCESS
6 WAIT FOR SHOT BEING ERASED. NO ACTION. ERASE COMPLETE
7 RETURN TO MAIN MENU. PRESS ANY KEY. 1. TIME BRKR
ERASE SHOT # XXXX
TEST: YYYY
DATE: MM\DD\YY HH:MM
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
PLEASE WAIT
2. GET RSLT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTIC
41
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 48

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.8 Recall a Breaker Test Plan
A breaker test plan contains breaker maximum/minimum operating parameters. A typical list of
operating parameters is shown as follows:
Max/Min Contact/Resistor Trip Time.
Max/Min Contact/Resistor Close Time.
Max Contact Spread Time.
Max Resistor Contact Spread Time.
Max/Min Stroke.
Max/Min Trip Velocity.
Max/Min Close Velocity.
Max/Min Over Travel.
Max/Min Bounce Back.
Trip Analysis Points.
Close Analysis Points.
By recalling a Test Plan before testing, a user doesn't have to set analysis points to calculate
the Trip or Close velocity of the circuit-breaker contacts. Since a Test Plan contains other breaker
test parameters, the test report also displays a Pass/Fail status for each parameter tested.
Table 9-10. Recalling a Test Plan
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT SET UP MENU. PRESS #3 KEY. 1. ANALYSIS POINTS
2. MEASUREMENT UNIT
3. SAVE / RESTORE
4. NEXT PAGE
2 SELECT ANALYSIS MENU. PRES # 1 KEY. 1. OPEN TIMING
2. CLOSE TIMING
3. PRINT SETTING
4. TEST PLANS
3 SELECT TEST PLANS. PRESS # 4 KEY. 1. LOAD TEST PLAN
2. PRINT TEST PLAN
3. PRINT DIRECTORY
4 SELECT LOAD TEST PLAN. PRESS # 1 KEY. LOAD TEST PLAN
"UP" TO SCROLL
"ENTER" TO SELECT
5 VIEW TEST PLAN HEADER. PRESS UP ARROW
KEY TO SCROLL.
6 CONFIRM TEST PLAN TO BE
LOADED.
PRESS "ENTER"
KEY.
DISPLAY TEST PLAN HEADER
1. TEST BRKR
2. GET RSLT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTIC
42
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 49

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.9 Print a Breaker Test Plan
The user can print a breaker test plan stored in the CT-7500 EEPROM
Table 9-11. Print a Breaker Test Plan
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT SET UP MENU. PRESS # 3 KEY. 1. ANALYSIS POINT
2. MEASUREMENT UNITS
3. SAVE / RESTORE
4. NEXT PAGE
2 SELECT ANALYSIS POINTS. PRESS # 1 KEY. 1. OPEN TIMING
2. CLOSE TIMING
3. PRINT SETTINGS
4. TEST PLAN
3 SELECT TEST PLAN. PRESS # 4 KEY. 1. LOAD TEST PLAN
2. PRINT TEST PLAN
3. PRINT DIRECTORY
4 SELECT PRINT TEST PLAN. PRESS # 2 KEY. ENTER PLAN NUMBER
"ENTER" TO CONTINUE
5 ENTER PLAN NUMBER. PRESS # 0-9 KEY. ENTER PLAN NUMBER:
02
"ENTER" TO CONTINUE
6 CONFIRM TEST PLAN. PRESS “ENTER" KEY. SELECT PRINTER
1. INTERNAL THERMAL
2. EXTERNAL INK JET
7 PRINT ON THERMAL PRINTER. PRESS # 1 KEY. 1. TIMER BRKR
2. GET RESLT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTIC
43
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 50

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Figure 9-10. Typical Test-Plan Printout on Thermal Printer
44
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 51

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.10 Print Breaker Test Plan Directory
The user can print a breaker test plan directory stored in the CT-7500 EEPROM using the
steps in table below:
Table 9-12. Print a Breaker Test Plan Directory
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT SET UP MENU. PRESS # 3 KEY. 1. ANALYSIS POINT
2. MEASUREMENT UNITS
3. SAVE / RESTORE
4. NEXT PAGE
2 SELECT ANALYSIS POINTS. PRESS # 1 KEY. 1. OPEN TIMING
2. CLOSE TIMING
3. PRINT SETTINGS
4. TEST PLAN
3 SELECT TEST PLAN. PRESS # 4 KEY. 1. LOAD TEST PLAN
2. PRINT TEST PLAN
3. PRINT DIRECTORY
4 SELECT PRINT TEST PLAN DIRECTORY. PRESS # 3 KEY. 1. TIMER BRKR
2. GET RESLT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTIC
Figure 9-11. Typical Test Plan Directory Printout.
45
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 52

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.11 Shot Description
The CT-7500 lets users enter breaker and test data identification (ID). This data includes the
names of the company, station, circuit, and manufacturer, as well as the breaker's model and
serial number, and the operator's name. These ID data will print out on the header section of the
shot tabulated report.
If the user saves the timing shot, this data will also be saved with the timing shot and the time
and date.
The user selects the alpha-numeric entry by pressing the appropriate key: To select a letter "A,"
the user must press key #2 twice. To select letter "C," the user must press key #2 four times etc.
To move the cursor forward, use the UP ARROW key. To move cursor backwards, use the
DOWN ARROW key. Use the CLEAR key to enter a space.
Table 9-13. Entering Shot Identification Header
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT SET UP MENU. PRESS #3 KEY. 1. ANALYSIS POINTS
2. MEASUREMENT UNIT
3. SAVE / RESTORE
4. NEXT PAGE
2 SELECT NEXT PAGE. PRESS # 4 KEY. 1. SHOT DESCRIPTION
2. NUMBER OF CHANNELS
3. COMPUTER IF
4. SET CLOCK
3 SELECT SHOT DESCRIPTION. PRESS # 1 KEY. ENTER COMPANY NAME
XXXXXX
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
4 ENTER COMPANY NAME. PRESS # 0-9 KEYS
PRESS "ENTER"
TO CONFIRM.
5 ENTER STATION NAME. PRESS # 0-9 KEYS
PRESS "ENTER"
TO CONFIRM.
6 ENTER CIRCUIT NAME. PRESS # 0-9 KEYS
PRESS "ENTER"
TO CONFIRM.
7 ENTER MANUFACTURER NAME. PRESS # 0-9 KEYS
PRESS "ENTER"
TO CONFIRM.
ENTER STATION NAME
XXXXXX
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
ENTER CIRCUIT NAME
XXXXXX
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
ENTER MANUFACTURER NAME
XXXXXX
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
ENTER BREAKER MODEL
XXXXXX
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
46
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 53

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Table 9-13. Entering Shot Identification Header (Con’t)
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
8 ENTER SERIAL NUMBER. PRESS # 0-9 KEYS
PRESS "ENTER"
TO CONFIRM.
9 ENTER OPERATOR NAME. PRESS # 0-9 KEYS
PRESS "ENTER"
TO CONFIRM.
10 RETURN TO MAIN MENU. NO ACTION. 1. TIME BRKR
ENTER SERIAL NUMBER
XXXX
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
ENTER OPERATOR NAME
XXXX
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
2. GET RSLT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTIC
47
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 54

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.12 CT-7500 Channel Configuration
The CT-7500 is available with 3-, 6-, or 12- contact inputs. Under most common timing
conditions, the user needs to use only 3 contact timing channels and 1 travel transducer. There is
no need to print more than 3 timing channels and 1 transducer channel on the graphic and
tabulated report. The CT-7500 will always default to 3 contact channels (channel 1, 2, and 3) and
1 transducer channel (transducer channel #1) after power is applied to the unit. The user can
always turn on the rest of the timing channels and transducer channels by following steps shown
in table below:
Table 9-14. Select Channel Configuration
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT SET UP MENU. PRESS #3 KEY. 1. ANALYSIS POINTS
2. MEASUREMENT UNIT
3. SAVE / RESTORE
4. NEXT PAGE
2 SELECT NEXT PAGE. PRESS #4 KEY. 1. SHOT DESCRIPTION
2. NUMBER OF CHANNELS
3. COMPUTER IF
4. SET CLOCK
3 SELECT NUMBER OF CHANNEL. PRESS #2 KEY. NUMBER OF CHANNELS
1. 3 CONTACTS
2. 6 CONTACTS
3. 12 CONTACTS
SELECT 3 CHANNELS ,OR 6
4
CHANNELS, OR 12 CHANNELS.
5 SELECT 1 TRANSDUCER, OR 2, OR 3. PRESS # 1, OR 2, OR
PRESS # 1, OR 2, OR
3 KEY.
3 KEY.
1. TRANSDUCER 1
2. TRANSDUCER 1,2
3. TRANSDUCER 1,2,3
1. TIME BRKR
2. GET RSLT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTIC
48
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 55

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.13 Computer Interface
Each CT-7500 has an RS-232C port. A Breaker Analysis Software package (provided with the
CT-7500) allows an IBM PC to communicate with a CT-7500. This software (operating under
Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows Me, Windows 2000, and Windows NT environment) allows
users to upload timing shots stored in EEPROM to the IBM PC. From the user's IBM PC, the user
can now re-analyze breaker timing shots and output timing report through an office printer. Since
timing shots are stored in an office PC, users can create a data base of a breaker's timing history.
A breaker's test plan can also be downloaded and stored in the CT-7500 EEPROM. Up to 20
test plans can be stored in a CT-7500. Consult the CT-7500 software manual for further details.
Follow the steps in the Table 9-15 below to put the CT-7500 under computer control:
Table 9-15. Selecting or Aborting Computer Control
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT SET UP MENU. PRESS # 3 KEY. 1. ANALYSIS POINT
2. MEASUREMENT UNITS
3. SAVE / RESTORE
4. NEXT PAGE
2 SELECT NEXT PAGE. PRESS # 4 KEY. 1. SHOT DESCRIPTION
2. NUMBER OF CHANNELS
3. COMPUTER IF
4. CLOCK 5.PRINT
3 SELECT COMPUTER INTERFACE. PRESS # 3 KEY. COMPUTER IF MODE
"STOP" TO ABORT
Notes
1. An interconnect cable must be run between Timer's RS-232C port and a compatible IBM PC.
2. Refer to the Breaker timing software manual for the software to run on the IBM-compatible
computer.
3. The CT-7500's RS-232 connector pinout is in the chart at
the right:
4. The operator is required to put the CT-7500 under
PIN No. SIGNAL NAME
2 Tx
computer control before executing the PC program.
3 Rx
49
5 GND
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 56

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.14. Breaker Travel Analysis
The CT-7500 travel analysis includes breaker stroke, over-travel, bounce-back, and contact-
wipe distances, and contact velocity calculation.
9.14.1 Breaker Stroke
The CT-7500 uses a digital transducer to measure a breaker's contact stroke, over-travel, and
bounce-back. The digital transducer output is 200 counts per linear inch of travel; the resolution is
accurate to 1/200 inch. The output resolution is ±0.01 inch on the test result report.
Unlike slide-wire transducers, the CT-7500 transducer needs no calibration or setup. A user
verifies transducer function by selecting a diagnostic test for the transducer (paragraph 9.19).
9.14.2 Breaker Over-travel Distance
Over-travel is a distance the contact moves beyond the resting position. Over-travel is typically
found in the Close Operation.
9.14.3 Breaker Bounce-Back Distance.
Bounce-back is the distance the breaker contact moves before the resting position after overtravel. Again, bounce-back is typically found in the Close Operation.
9.14.4 Contact Wipe
.
Contact wipe is the distance measured from the close position to the contacts touching (or
parting). In the Close Operation, contact wipe is measured from the contacts touching position to
the final close position.
In the Open Operation, contact wipe is measured from the close position to contact break (or
parting) position.
NOTE
Contact wipe is measured during operation. This measurement may not be as accurate as
measurement done using the slow close mode. It is recommended the user use the Slow
Close Test (paragraph 9.18) to verify wipe measurement if required.
9.14.5 Breaker Velocity
The CT-7500, when used with a travel transducer, calculates the breaker contact velocity
through the arc zone. Users must program the calculation points (analysis points) on the travel
curve for the unit to calculate contact velocity. Analysis points selection and setup are discussed
in the following paragraphs.
9.14.6 Analysis Point Selections.
Analysis points are used to calculate average contact speed through the contact's arc zone.
The analysis points are usually specified by the breaker manufacturers. The analysis points are
fully programmable in the Timer by the user. The Timer will store two setups for calculating
velocity (one each for open and close). These setups remain in the Timer's RAM memory until
changed by the operator.
50
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 57

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.14.7 Analysis Point No.1.
Three selections are available to the user for setting analysis point No. 1:
1. PERCENTAGE OF STRK
2. DISTANCE FROM CLOSE
3. CONTACT #1
a. Percentage of Stroke:
Percentage of stroke is distance based upon percentage of total breaker stroke distance.
This distance is always measured from the starting point at the fully closed position of the
breaker contacts.
b. Distance From Close:
Distance from Close range is selectable from 00.0 inch to 99.99 inches or from 0.0
centimeter to 99.90 centimeters.
closed position.
c. Contact Point #1:
Contact point is the distance from the contact's closed position to the point where it is in
transition from close-to-open (or open-to-close position).
this selection.
Again, this distance is referenced from the contact's
Contact channel #1 will be used for
9.14.8 Analysis Point No. 2.
Only two selections for analysis point 2 are available to the user:
1. PERCENTAGE OF STRK
2. DISTANCE FROM CLOSE
The selection of analysis point No. 2 is the same as for analysis point No. 1.
1. Average velocity through the arc zone is calculated by using the following formula:
2. The current breaker contact velocity will be recalculated based on data stored in memory
(RAM) after any new analysis point(s) is selected. The user does NOT need to operate the
breaker again to acquire new contact velocity data after changing the analysis points (a new
velocity is calculated from travel data stored in memory from the last operation).
3. For complex velocity calculations, the user can download a test plan to the CT-7500 from an
IBM PC. This test plan can be recalled and used to calculate a breaker's contact velocity.
NOTE
V
= Distance
ave
÷
Time
51
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 58

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.15 Set-Up Open Analysis Points
Table 9-16. Setting Up "OPEN" Analysis Points Using Distance
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT SET UP MENU. PRESS # 3 KEY. 1. ANALYSIS POINT
2. MEASUREMENT UNITS
3. SAVE / RESTORE
4. NEXT PAGE
2 SELECT ANALYSIS POINT. PRESS # 1 KEY. 1. OPEN TIMING
2. CLOSE TIMING
3. PRINT SETTING
4. TEST PLAN
3 SELECT OPEN ANALYSIS. PRESS # 1 KEY. OPEN ANALYSIS PT 1
1. PERCENT OF STROKE
2. DISTANCE FROM CLOSE
3. CONTACT #1
4 SELECT DISTANCE FROM CLOSE. PRESS # 2 KEY. OPEN ANALYSIS PT 1
DISTANCE FROM CLOSE
VALUE: XX.XX in
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
5 ENTER 1 INCH. PRESS # 0-9 KEY. OPEN ANALYSIS PT 1
DISTANCE FROM CLOSE
VALUE: 01.00 in
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
6 CONFIRM ENTRY. PRESS "ENTER" KEY. OPEN ANALYSIS PT 2
1. PERCENTAGE OF STROKE
2. DISTANCE FROM CLOSE
7 SELECT DISTANCE FROM CLOSE. PRESS # 2 KEY. OPEN ANALYSIS PT 2
DISTANCE FROM CLOSE
VALUE: XX.XX in
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
52
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 59

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Table 9-16. Setting Up "OPEN" Analysis Points Using Distance (Con’t)
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
8 ENTER 5 INCHES. PRESS # 0-9 KEYS. OPEN ANALYSIS PT 2
DISTANCE FROM CLOSE
VALUE: 02.00 in
"ENTER" TO CONFIRM
9 CONFIRM ENTRY. PRESS "ENTER"
KEY.
1.TIME BRKR
2.GET RSLT
3.SET UP
4.DIAGNOSTICS
NOTES
1. If an entry is not correct, re-enter digits until display shows desired numbers, then press
“ENTER” key.
2. Analysis Point #1 is 1.00 inch from the fully closed position.
3. Analysis Point #2 is 2.00 inches from the fully closed position.
53
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 60

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9-16. English/Metric Selection
The CT-7500 supports and displays both English and Metric calculations from the breaker's
travel parameters (stroke, velocity, (etc.). The user can switch from one to the other by following
the steps in Table 9-17, below:
Table 9-17. Select Metric Units of Measure
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT SET UP MENU. PRESS # 3 KEY. 1. ANALYSIS POINT
2. MEASUREMENT UNITS
3. SAVE / RESTORE
4. NEXT PAGE
2 SELECT MEASUREMENT UNITS. PRESS # 2 KEY. SELECT UNITS
1. ENGLISH
2. METRIC
3 SELECT METRIC. PRESS # 2 KEY. 1. TIME BRKR
2. GET RSLT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTIC
54
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 61

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.17 Set CT-7500 Internal Clock
The CT-7500 has an internal clock with a lithium battery. The clock's time and date is
displayed on the LCD screen. When a timing shot is stored in EEPROM, time and date are also
stored. To set the clock, perform the steps in the following table:
Table 9-18. Setting the Clock and Calendar
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT SET UP MENU. PRESS # 3 KEY. 1. ANALYSIS POINT
2. MEASUREMENT UNITS
3. SAVE / RESTORE
4. NEXT PAGE
2 SELECT NEXT PAGE. PRESS # 4 KEY. 1. SHOT DESCRIPTION
2. NUMBER OF CHANNELS
3. COMPUTER IF
4. CLOCK 5.PRINT
3 SELECT SET CLOCK. PRESS # 4 KEY. TIME: HH:MM:00
XX:YY:00
4 ENTER HOURS AND MINUTES. PRESS # 0-9 KEY. TIME: HH:MM:00
XX:YY:00 XX:YY:00
DATE: MM/DD/YY
XX/YY/ZZ
5 ENTER MONTH, DATE, YEAR. PRESS # 0-9 KEY. TIME: HH:MM:00
XX:YY:00 XX:YY:00
DATE: MM/DD/YY
XX/YY/ZZ XX/YY/ZZ
6 RETURN TO MAIN MENU. NO ACTION. 1. TIME BRKR
2. GET RSLT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTIC
Note
The real time clock battery is good for 3 years. Loosing the clock battery will not affect the CT7500 performance.
55
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 62

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.18 Slow-Close Test
The CT-7500 offers a unique feature called a "slow-close" test. This test lets users measure
the distance of a breaker's contact travel from fully opened position to contact "touch" position and
contact wipe (or penetration) distance. This test requires the operator manually jack the breaker's
contact from the fully open position to the fully closed position.
Contact channel 1, 2, 3, and transducer channel 1 will be used for this test. The CT-7500 will
measure the contact touch and contact wipe (penetration) of each contact channel.
Contact touch is the distance measured from contact fully open to the first position contact
channel electrically closed.
Contact wipe (or penetration) distance is measured from the contact position first electrically
closed to the final closed (latching) position.
Table 9-19. Performing a Slow-Close Test
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT DIAGNOSTIC MENU. PRESS # 4 KEY. 1. SLOW CLOSE TEST
2. PRINT DATA
3. TEST TRANSDUCER
4. CHECK HOOK UP
2 SELECT SLOW CLOSE TEST. PRESS # 1 KEY. BREAKER SLOW CLOSE TEST
RMV CB GND (1 SIDE)
"ENTER" TO BEGIN
3 START SLOW CLOSE TEST. PRESS "ENTER" KEY. CONTACT 1:OPEN
CONTACT 2:OPEN
CONTACT 3:OPEN
LIFT TO CLS BREAKER NOW
4 CONTINUE TO CLOSE BREAKER. NO ACTION. LIFT BRKR TO CLS POS
THEN PRESS "ENTER"
TO FIND CONTACT WIPE
5 RETURN TO MENU. NO ACTION. 1. TIME BRKR
2. GET RSLT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTIC
Notes
The user can also save a slow-close test report in EEPROM. A typical report of a slow-close test
is shown on next page.
56
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 63

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Figure 9-12. Typical Slow-Close test report
9.19 Transducer Self-Test
The users can check transducer electronics by connecting transducer to the CT-7500 and
running a “Transducer Self Test”.
Table 9-20. Performing a Transducer Self Test
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT DIAGNOSTIC. PRESS # 4 KEY. 1. SLOW-CLOSE TEST
2. PRINT DATA
3. TEST TRANSDUCER
4. CHECK HOOKUP
2 SELECT TRANSDUCER. PRESS # 3 KEY. TRANSDUCER TEST
1= XXX.XX INCHES
2= XXX.XX INCHES
3= XXX.XX INCHES
Note
1. After selecting transducer test mode, move transducer slider and observe display on the CT7500 LCD.
2. If slider is moved 1.00”, the CT-7500 LCD should display 1.00”.
3. Press STOP key to return to main menu.
57
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 64

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9.20 Check Cable Hookup
Table 9-21. Checking the Cable Hookup
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT DIAGNOSTIC. PRESS # 4 KEY. 1. SLOW-CLOSE TEST
2. PRINT DATA
3. TEST TRANSDUCER
4. CHECK HOOKUP
2 SELECT CHECK HOOK UP. PRESS # 3 KEY. MAKE SURE BREAKER
IS IN CLOSE POSITION,
THEN PRESS "START"
3 INITIATE TEST. PRESS "START" KEY. 1 2 3 4 5 6
C - - - - -
7 8 9 10 11 12
- - - - - -
4 RETURN TO MAIN MENU. PRESS "STOP" KEY. 1. TIME BREAKER
2. GET RESULT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTIC
Notes
1. The CT-7500 will also print the test report with the thermal printer.
2. A contact closure is shown as "C" on the LCD and printout.
3. An open contact is shown as "-" on the LCD and printout.
58
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 65

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
9-21 Automatic Print Setting
The CT-7500 can be set to print graph and tabulated results automatically after timing a
breaker. To turn on “Auto Print Results” mode, follows steps in table below
Table 9-22. Automatic Print Setting
STEP OPERATION ACTION DISPLAY
1 SELECT SET UP MENU. PRESS # 3 KEY. 1. ANALYSIS POINT
2. MEASUREMENT UNITS
3. SAVE / RESTORE
4. NEXT PAGE
2 SELECT NEXT PAGE. PRESS # 4 KEY. 1. SHOT DESCRIPTION
2. NUMBER OF CHANNELS
3. COMPUTER IF
4. CLOCK 5.PRINT
3 SELECT SET PRINT. PRESS # 5 KEY. SET PRINT MODE
1. AUTOMATIC PRINT
2. BY REQUEST ONLY
4 SELECT “AUTOMATIC PRINT”. PRESS # 1 KEY. 1. TIME BREAKER
2. GET RESULT
3. SET UP
4. DIAGNOSTIC
Note
Select print “BY REQUEST ONLY” will disable Automatic Print mode.
59
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 66

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
10.0 Running CT-7500s in Tandem
For timing application requiring more than 12 timing contact channels, the user can use two or
more CT-7500s to time a circuit breaker. A typical application is to use a CT-7500-12 and a CT7500-6 to time a 18 contact ATB. To time this circuit breaker, the user can use the following steps:
Connect the CT-7500-12 to phase A and B of the circuit breaker.
Connect the CT-7500-6 to phase C on the circuit breaker.
Connect the CT-7500-12 initiate cable to the breaker control circuit. The
operate
the circuit breaker.
CT-7500-12
Connect the external trigger cable of the CT-7500-6 to the OPEN coil for the OPEN test or
CLOSE coil for the CLOSE test. The
Set the CT-7500-6 to start a test using
Set the CT-7500-12 to start a test using
Press the “START” key on the CT-7500-6 to start the sequence then press the “START”
CT-7500-6
will
operate as the slave device
“External Trigger”.
“Internal Trigger”.
.
key and hold the “ARM” switch on the CT-7500-12.
The CT-7500-12 will operate the circuit breaker and start the timing sequence; The CT-7500-6 will
start its timing sequence as soon as it senses the voltage applied to the breaker coil.
The timing report of the CT-7500-12 will show the contact time for phase A and B. The timing
report of the CT-7500-6 shows contact time for phase C.
If the user down-loads the test results of both the CT-7500s to the PC, the user then can combine
the 2 test reports to generate a 18 channel test report.
will
60
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 67

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
11.0 CT-7500 Trouble Shooting Guide
Problems Suggestion
1. CT-7500 will not trip or close breaker.
2. No contact time (0 ms) in Trip or Close test.
3. No contact time (0 ms) in Close-Open.
Make sure you hold the “ARM” switch down during
test.
Check OPEN or CLOSE fuses.
Check initiate leads. For a “Positive Trip” circuit,
one Close lead and one Open lead should be
connected to the Positive of the power supply.
Check initiate leads. For a “Negative Trip” circuit,
one Close lead and one Open lead should be
connected to the Negative of the power supply.
Make sure one side of breaker in not grounded.
Make sure the breaker operates on OPEN or Close
test only. A dual operation OPEN-CLOSE or CLOSEOPEN will resulting in 0ms reading.
Bad CT-7500 contact channels or bad cables. Try
“CHECK HOOK-UP” test.
Make sure breaker contacts complete the transition
from Open (initial state) to Close then Open (final
state). You can see this transition by looking at the
timing chart.
4. Select Open-Close test. The breaker opens and will
not close.
5. No tabulated and timing chart for contact channels
above #3.
6. No tabulated or timing chart for travel 2 and 3.
7. No data or erratic reading on travel transducer.
8. No activity on V2 voltage input channel.
Make sure the contact close state is longer than
10ms. The CT-7500 has a 10ms de-bounce time, any
contact state less than or equal to 10ms is invalid.
If you have this problem, your delay time is probably
too slow.
Try Close-Open using contact channel #1 option.
Delay between Open to Close is probably too
small. Increase delay time.
The CT-7500 always defaults to contact channels
1,2 and 3. You need to turn on contact channels
above 3.
Turn on travel channel 2 and 3.
Bad transducer. Try “TRANSDUCER” test.
Transducer slider is not secured to timing rod.
Transducer is not secured properly.
The V2 voltage input channel requires a voltage
change (0v to above 30v) to see activities on the
timing chart.
61
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 68

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Problems Suggestion
9. No “PASS/FAIL” on tabulated report.
10. CT-7500 will not communicate with PC.
11. Turn on Automatic Print Results mode.
12. CT-7500 will not print results on external printer.
13. Where can I get some thermal paper?
14. How do I darken or lighten the LCD?
15. How do I move thermal paper forward or
backward?
Test plan is not loaded before taking test. You can
load test plan then re-print the tabulated report.
Make sure CT-7500 is under computer control.
Make sure your PC com port is selected correctly.
Make sure your serial cable is connected properly.
See section 9-21.
The CT-7500 will support HP ink-jet printer only.
Check your printer cable.
Call the factory at 909-923-9390 or BG Instruments
at 509-893-9881. The CT-7500 uses TP-4 thermal
paper.
In case of an emergency, you can get thermal
paper from Radio Shack. Radio Shack carries 4.25”
wide thermal paper. It is not the right size but it will
work.
Press and hold the “↑ PAPER LCD” key for 3
seconds will darken LCD.
Press and hold the “↓ PAPER LCD” key for 3
seconds will lighten LCD.
Press and release the “↑ PAPER LCD” key will
advance thermal paper.
Press and release the “↓ PAPER LCD” key will
move thermal paper backward.
62
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 69

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
APPENDIX A
ITE Circuit Breaker model 14.4K Timing Chart.
AP1= 1.5”
AP2= 3.5”
I
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 70

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
II
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 71

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
APPENDIX B
CT-7500 Test Plan for ITE Circuit Breaker Model 14.4K.
III
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 72

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
APPENDIX C
CT-7500 Timing Chart for ITE Circuit Breaker Model 14.4K.
IV
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 73

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
APPENDIX D
CT-7500 Tabulated Report for ITE Circuit Breaker Model 14.4K.
CT-7500 Timing Chart for ITE Circuit Breaker Model
V
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 74

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
APPENDIX E
Timing Chart for Siemens TCP-149 Circuit Breaker.
AP1= Contact Point
b= Breaker Stroke
a= Distance between AP1 & AP2
AP2= Contact - 10ms
Note
Velocity calculation for this breaker requires a formula:
V= 31.5 x (a/b) m/s
VI
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 75

MODEL CT-7500 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
APPENDIX F
CT-7500 Test Plan for Siemens TCP-149 Circuit Breaker.
Note
Formula to calculate velocity is programmed in breaker test plan.
VII
Rev 2 Jan 2001
Page 76

www.vanguard-instruments.com
 Loading...
Loading...