Page 1

Operating System for Ubiquiti M Series Products
Release Version: 5.5.4
Page 2

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Overview ................................................1
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Supported Products ..............................................................1
airOS v5.5.4 Network Modes ......................................................1
airOS v5.5.4 Wireless Modes ......................................................2
System Requirements ............................................................2
Getting Started ...................................................................2
M Series Product Verification .....................................................2
Navigation .......................................................................3
Chapter 2: Ubiquiti Logo Tab .......................................4
airMAX Settings ..................................................................4
airSelect ..........................................................................5
airView ...........................................................................6
airSync (GPS Series Only) .........................................................8
Table of ContentsairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Chapter 3: Main Tab ...............................................10
Status ...........................................................................10
Monitor .........................................................................12
Chapter 4: Wireless Tab ............................................18
Basic Wireless Settings ...........................................................19
Wireless Security ................................................................22
Chapter 5: Network Tab ...........................................26
Network Role ....................................................................26
Bridge ...........................................................................27
Configuration Mode .............................................................27
Management Network Settings ..................................................28
Router ..........................................................................31
Configuration Mode .............................................................32
WAN Network Settings ..........................................................32
LAN Network Settings ...........................................................35
SOHO Router ....................................................................40
Configuration Mode .............................................................40
WAN Network Settings ..........................................................40
LAN Network Settings ...........................................................44
Chapter 6: Advanced Tab ..........................................49
Advanced Wireless Settings ......................................................49
Advanced Ethernet Settings .....................................................51
Signal LED Thresholds ...........................................................51
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
i
Page 3

Chapter 7: Services Tab ...........................................52
Ping Watchdog ..................................................................52
SNMP Agent. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Telnet Server ....................................................................54
NTP Client .......................................................................54
Dynamic DNS ...................................................................54
System Log ......................................................................55
Device Discovery ................................................................55
Chapter 8: System Tab ............................................56
Firmware Update ................................................................56
Device ..........................................................................57
Date Settings ....................................................................57
System Accounts ................................................................57
Miscellaneous ...................................................................57
Location ........................................................................58
Device Maintenance .............................................................58
Configuration Management .....................................................58
Table of ContentsairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Chapter 9: Tools ...................................................59
Align Antenna ...................................................................59
Site Survey ......................................................................60
Discovery .......................................................................60
Ping .............................................................................60
Traceroute ......................................................................60
Speed Test ......................................................................61
airView ..........................................................................61
Appendix A: Contact Information ..................................64
Ubiquiti Networks Support ......................................................64
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
ii
Page 4

Chapter 1: OverviewairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Chapter 1: Overview
Introduction
Welcome to airOS™ v5.5.4 – the latest evolution of the
airOS Configuration Interface by Ubiquiti Networks™.
airOSv5.5.4 provides new features, including:
• Maps commonly used VoIP TOS values (0x68, 0xb8) to
Voice queue
• Alternative data rate algorithm option
• Audio option for Antenna Alignment tool
• Signal strength from remote radio shown in Station
information window (airMAX™ mode only)
• TX/RX bit rate statistics shown in AP or Station
information
• Feed only option for antenna type (airGrid™ and
NanoBridge™ models only)
airOS is an advanced operating system capable of
powerful wireless and routing features, built upon a
simple and intuitive user interface foundation.
This User Guide describes the airOS operating system
version 5.5.4, which is integrated into all M Series products
provided by Ubiquiti Networks.
Note: For compatibility, legacy or 802.11 a/b/g
devices should use legacy firmware with airMAX
support (such as airOS firmware v4.0). Legacy
clients can only work as airMAX clients with the M
Series device acting as an airMAX AP.
Supported Products
airOS v5.5.4 supports the M Series product versions,
including the following:
• Rocket™M
• Rocket™M GPS
• Rocket™M Titanium
• NanoBridge™M
• NanoStation™M/NanoStation loco™M
• Bullet™M
• Bullet™M Titanium
• PicoStation™M
• PowerBridge™M
• airGrid™M
• WispStation™M
For more information, visit www.ubnt.com.
airOS v5.5.4 Network Modes
airOS supports the following network modes:
• Transparent Layer 2 Bridge
• Router
• SOHO Router
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
1
Page 5
Chapter 1: OverviewairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
airOS v5.5.4 Wireless Modes
airOS supports the following wireless modes:
• Access Point
• Station / Client
• AP-Repeater
System Requirements
• Microsoft Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7,
Windows 8, Linux, or Mac OS X
• Java Runtime Environment 1.6 (or above)
• Web Browser: Mozilla Firefox, Apple Safari, Google
Chrome, or Microsoft Internet Explorer 8 (or above)
Getting Started
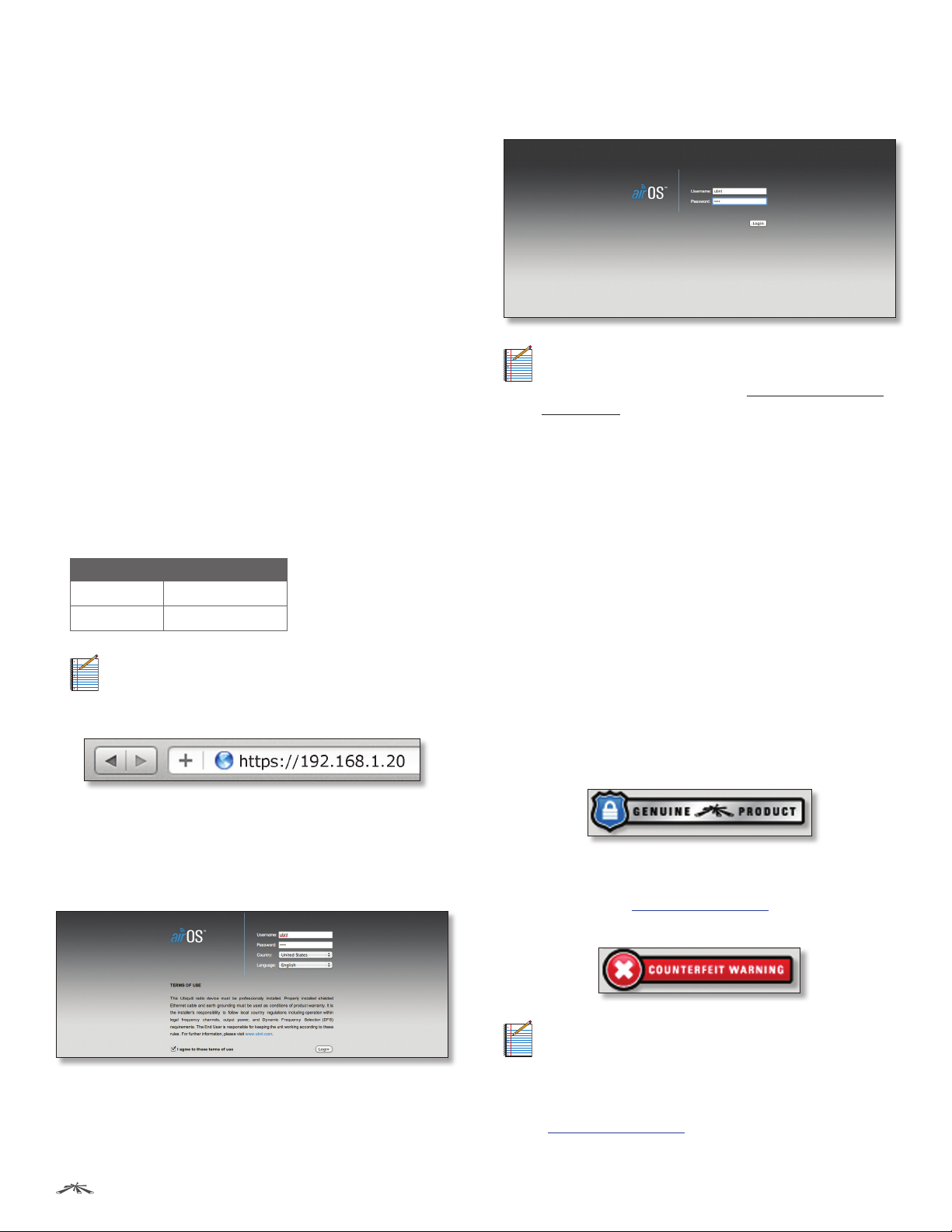
To access the airOS Configuration Interface, perform the
following steps:
1. Configure the Ethernet adapter on your computer
with a static IP address on the 192.168.1.x subnet (for
example, IP address: 192.168.1.100 and subnet mask:
255.255.255.0).
2. Launch your web browser. Enter https:// and the
default IP address of your device in the address field.
Press Enter (PC) or Return (Mac).
Device Default IP Address
airRouter 192.168.1.1
Other Devices 192.168.1.20
Note: HTTPS is the default protocol starting with
airOS v5.5.4.
For example, enter 192.168.1.20 to access the Rocket.
4. Upon subsequent login, the standard login screen
appears. Enter ubnt in the Username and Password
fields, and click Login.
Note: To enhance security, we recommend that you
change the default login on the System > System
Accounts tab. For details, go to “System Accounts”
on page 57.
M Series Product Verification
Starting with M series product models manufactured in
2012, the airOS Configuration Interface (v5.5.2 or later) will
verify whether a product is genuine or counterfeit.
Prior to 2012
For M series product models manufactured prior to 2012,
airOS will NOT display any logo in the lower left corner of
the screen.
Starting in 2012
For new M series product models introduced in 2012 or
later, airOS will display a Genuine Product logo in the
lower left corner of the screen.
New production versions of existing M series product
models began using the Genuine Product logo in 2012.
(Notall Mseries product models manufactured in 2012
will display a Genuine Product logo.)
3. Upon initial login, the Terms of Use appear on the login
screen. Enter ubnt in the Username and Password fields,
and select the appropriate choices from the Country
and Language drop-down lists. Check the box next to
Iagree to these terms of use, and click Login.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
For any M series product that is not an official Ubiquiti
product, airOS will display a counterfeit warning. Please
contact Ubiquiti at support@ubnt.com regarding
thisproduct.
Note: If neither the Genuine Product logo nor
counterfeit warning appears, the device was
manufactured prior to the genuine product
verification process and is probably genuine.
If you have any questions, please email
support@ubnt.com.
2
Page 6

Navigation
The airOS Configuration Interface contains seven main
tabs, each of which provides a web-based management
page to configure a specific aspect of the Ubiquiti device:
• Ubiquiti Logo The “Ubiquiti Logo Tab” on page
4 controls Ubiquiti’s proprietary technologies, such
as airMAX, airView, airSelect, and airSync (GPS Series
devices only).
Note: By default, indoor products, such as the
airRouter, do not display the Ubiquiti logo tab.
However, you can enable the Ubiquiti logo tab
through the System tab > Miscellaneous > airMAX
Technology Features. For more information, see
“Miscellaneous” on page 57.
• Main The “Main Tab” on page 10 displays device
status, statistics, and network monitoring links.
• Wireless The “Wireless Tab” on page 18 configures
basic wireless settings, including the wireless mode,
Service Set Identifier (SSID), 802.11 mode, channel and
frequency, output power, data rate module, and wireless
security.
• Network The “Network Tab” on page 26 configures
the network operating mode; Internet Protocol (IP)
settings; IP aliases; VLANs; packet filtering, bridging, and
routing routines; and traffic shaping.
• Advanced The “Advanced Tab” on page 49
provides more precise wireless interface controls,
including advanced wireless settings, advanced
Ethernet settings, and signal LED thresholds.
• Services The “Services Tab” on page 52 configures
system management services: Ping Watchdog, Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP), servers (web,
SSH, Telnet), Network Time Protocol (NTP) client,
Dynamic Domain Name System (DDNS) client, system
log, and device discovery.
• System The “System Tab” on page 56 controls
system maintenance routines, administrator account
management, location management, device
customization, firmware update, and configuration
backup. You can also change the language of the web
management interface.
Each page also contains network administration and
monitoring tools:
• “Align Antenna” on page 59
• “Site Survey” on page 60
• “Discovery” on page 60
• “Ping” on page 60
• “Traceroute” on page 60
• “Speed Test” on page 61
• “airView” on page 61
Chapter 1: OverviewairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
3
Page 7
Chapter 2: Ubiquiti Logo TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Chapter 2: Ubiquiti Logo Tab
The Ubiquiti logo tab displays settings to enable, launch,
and change settings for Ubiquiti’s proprietary features,
including:
• airMAX™ Provides superior wireless performance, more
clients per Access Point (AP), and lower latency under
load.
• airSelect™ Dynamically changes the wireless channel to
avoid interference.
• airView™ Ubiquiti’s spectrum analyzer.
• airSync™ Synchronizes transmissions by GPS Series
devices to eliminate co-location transmit interference.
Note: By default, indoor products, such as the
airRouter, do not display the Ubiquiti logo tab.
However, you can enable the Ubiquiti logo tab
through the System tab > Miscellaneous > airMAX
Technology Features. For more information, see
“Miscellaneous” on page 57.
Change To save or test your changes, click Change.
A new message appears. You have three options:
• Apply To immediately save your changes, click Apply.
• Test To try the changes without saving them, click
Test. To keep the changes, click Apply. If you do not
click Apply within 180 seconds (the countdown is
displayed), the device times out and resumes its earlier
configuration.
• Discard To cancel your changes, click Discard.
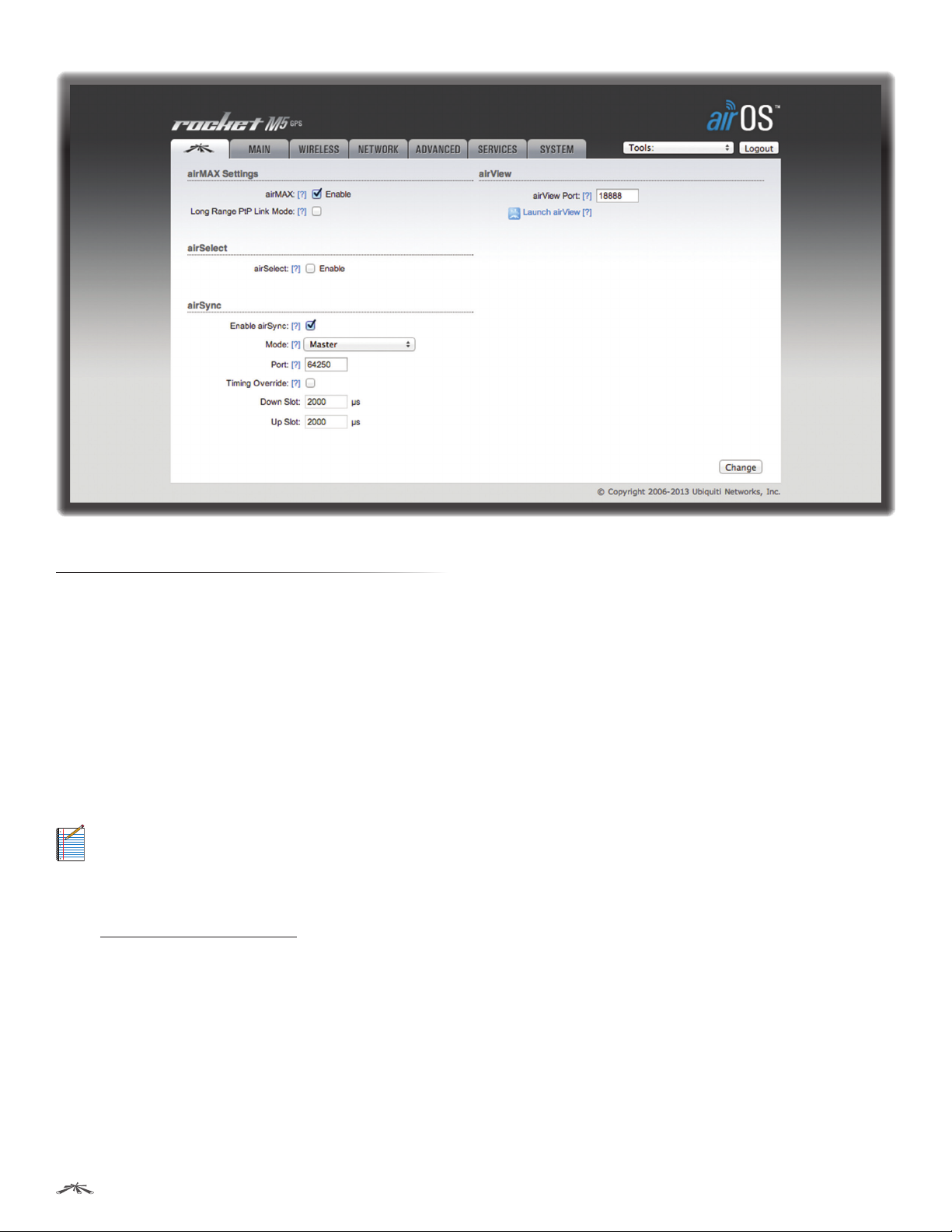
airMAX Settings
airMAX is Ubiquiti’s proprietary Time Division Multiple
Access (TDMA) polling technology. airMAX improves
overall performance in Point-to-Point (PtP) and
Point-to-MultiPoint (PtMP) installations and noisy
environments because it reduces latency, increases
throughput, and offers better tolerance against
interference. Because of its advantages, airMAX also
increases the maximum possible number of users that can
associate with an AP that uses airMAX.
airMAX assigns time slots for each device communication
to avoid the “hidden node” problem, which occurs when
a node is visible from a wireless AP, but not from other
nodes communicating with the originating AP.
airMAX also features advanced Quality of Service (QoS)
autodetection settings. For airMAX to classify and
differentiate types of traffic when applying QoS rules,
the traffic must have a special value within the TOS
(Type of Service) range and set in the IP Header DSCP
(Differentiated Services Code Point) field. The original
software or hardware device is responsible for setting this
value; airMAX will prioritize traffic only if this value is set.
There are four WME (Wireless Multimedia Enhancements)
categories, which range from lowest to highest priority in
this order:
• Best Effort
• Background
• Video
• Voice
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
4
Page 8
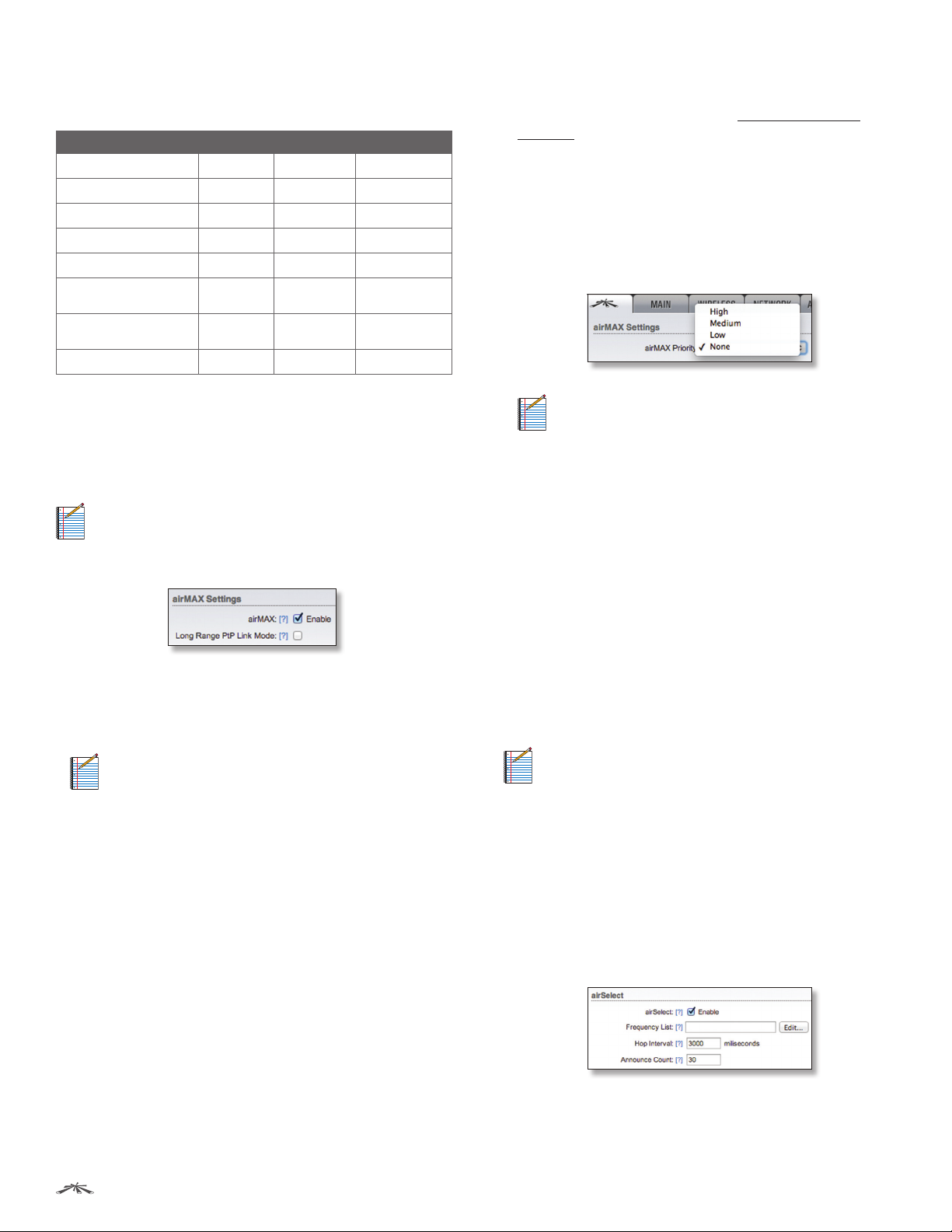
Chapter 2: Ubiquiti Logo TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
By default, all traffic is classified as Best Effort, so no
prioritization is applied. The categories can be defined
using the following values:
802.1p Class of Service TOS Range DSCP Range WME Category
0 – Best Effort 0x00-0x1f 0-7 Best Effort
1 – Background 0x20-0x3f 8-15 Background
2 – Spare 0x40-0x5f 16-23 Background
3 – Excellent Effort 0x60-0x7f 24-31
4 – Controlled Load 0x80-0x9f 32-39 Video
5 – Video
(<100 ms latency)
6 – Voice
(<10 ms latency)
7 – Network Control 0xe0-0xff 56-63 Voice
¹ AF31 - Low Drop Probability (26-27) maps to Voice.
² 46 (2E) - Expedited Forwarding (46-47) maps to Voice.
0xa0-0xbf 40-47
0xc0-0xdf 48-55 Voice
1
2
Best Effort
Video
For compatibility, legacy or 802.11 a/b/g devices should use
legacy firmware with airMAX support (such as airOS firmware
v4.0). Legacy clients can only work as airMAX clients with
the M Series device acting as an airMAX AP.
Note: To support legacy clients using airMAX, the
M Series device must run airOS v5.5 or above.
airMAX Settings include:
• airMAX (Available in Access Point or AP‑Repeater
mode only.) If airMAX is enabled, the device operates
in airMAX mode and only accepts connections from
airMAX devices.
If you have multiple stations or clients, then use
automatically adjusted values. Enable the Auto Adjust
setting on the Advanced tab (see “Auto Adjust” on
page 50 for additional details). If you use Auto Adjust,
then Long Range PtP Link Mode is not available.
• airMAX Priority (Available in Station mode only.) It
defines the number of time slots (or amount of airtime)
assigned to each client. By default the AP gives all active
clients the same amount of time. However, if the clients
are configured with different priorities, the AP will give
clients more or less time, depending on the priority.
Note: airMAX Priority only functions when
multiple clients have it enabled.
airMAX Priority options include:
- High 4 time slots (4:1 ratio)
- Medium 3 time slots (3:1 ratio)
- Low 2 time slots (2:1 ratio)
- None 1 time slot (Default setting for clients; 1:1 ratio)
Clients with a higher priority have access to more of the
AP’s airtime, providing higher possible throughput and
lower latency when sharing with other active clients.
For example, if there are 3 clients, 1 set to None, 1 set to
Medium, and 1 set to High, the None client will get 1 time
slot, the Medium client will get 3 time slots, and the High
client will get 4 time slots.
airSelect
Note: If airMAX is enabled, you cannot connect
standard Wi-Fi devices, such as laptops, tablets,
or smartphones, to the AP.
If the device is in Station mode under the Wireless tab
> Wireless Mode, the device will automatically enable
airMAX when it is connecting to an airMAX AP.
• Long Range PtP Link Mode (Available in Access
Point or AP‑Repeater mode only.) Acknowledgment
(ACK) timeout settings are limited by device hardware
specifications. Use this option if you have a single
station or client (a PtP situation), and the actual link
distance exceeds hardware ACK timeout limits:
• 27 km or 17 miles (40 MHz mode)
• 51 km or 32 miles (20 MHz mode)
If you use Long Range PtP Link Mode, then the Auto
Adjust setting on the Advanced tab is not available.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
Note: If you enable airSelect, then airSync is not
available.
(Available in Access Point mode only.) airSelect is a
technology that avoids interference and increases
throughput. It dynamically changes the wireless channel
by periodically hopping to the least used channel in the
Frequency List (user-defined) within a designated time
interval (user-defined in milliseconds). airSelect tracks
interference levels on each channel used, hopping more
frequently to those with the least amount of interference.
airSelect options include:
• airSelect Check the box to enable airSelect. When
airSelect is enabled, the AP and all associated clients
quickly hop between frequencies to avoid interference.
5
Page 9

Chapter 2: Ubiquiti Logo TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
• Frequency List Available when airSelect is enabled.
Click Edit to select the frequencies that the AP will
use for airSelect. Available frequencies are devicedependent.
• Hop Interval Available when airSelect is enabled. The
duration (in milliseconds) that the AP will stay on one
frequency before moving to the next. The default value
is 3000 milliseconds (ms).
• Announce Count Available when airSelect is
enabled. The number of times between hops the
AP will announce the next hop information (such as
frequency) to clients. For example, if the Hop Interval
is set to 3000ms (default), and the AnnounceCount is
set to 30 (default), then every 100 ms the AP will send
an announcement with upcoming hop information
tothe clients. The larger the time period between the
Announce Count and Hop Interval, the higher the risk
of timing drift (hops not being synchronized), so we
recommend that you keep the defaults or configure
the AP to send an announcement every 100ms (set
theAnnounce Count to 1/100th of the Hop Interval).
airView
Use the airView Spectrum Analyzer to analyze the noise
environment of the radio spectrum and intelligently select
the optimal frequency to install a PtP airMAX link.
airView options include:
• Launch airView Click Launch airView to download the
Java Network Launch Protocol (jnlp) file and complete
the launch of airView.
• airView Port Defines the TCP port used by airView on
the device. The default port is 18888.
• Launch airView There are two system requirements for
the airView Spectrum Analyzer:
• Your system is connected to the device via Ethernet.
Launching airView will terminate all wireless
connections on the device.
• Java Runtime Environment 1.6 (or above) is required
on your client machine to use airView.
Click Launch airView to use the airView Spectrum
Analyzer. On first use, the following window appears.
Main View
Device Displays the device name, MAC (Media Access
Control) address, and IP address of the device running
airView.
Total RF Frames Displays the total number of Radio
Frequency (RF) frames gathered since the start of the
airView session or since the Reset All Data button was last
clicked.
FPS Displays the total number of frames per second (FPS)
gathered since the start of the airView session or since
the Reset All Data button was last clicked. The wider the
interval amplitude, the fewer the FPS will be gathered.
Reset All Data Click to reset all gathered data. Use this
option to analyze the spectrum for another location or
address.
• Do NOT warn me about this in the future Check the
box to bypass this window in future launches of the
airView Spectrum Analyzer.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
6
Page 10
Chapter 2: Ubiquiti Logo TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
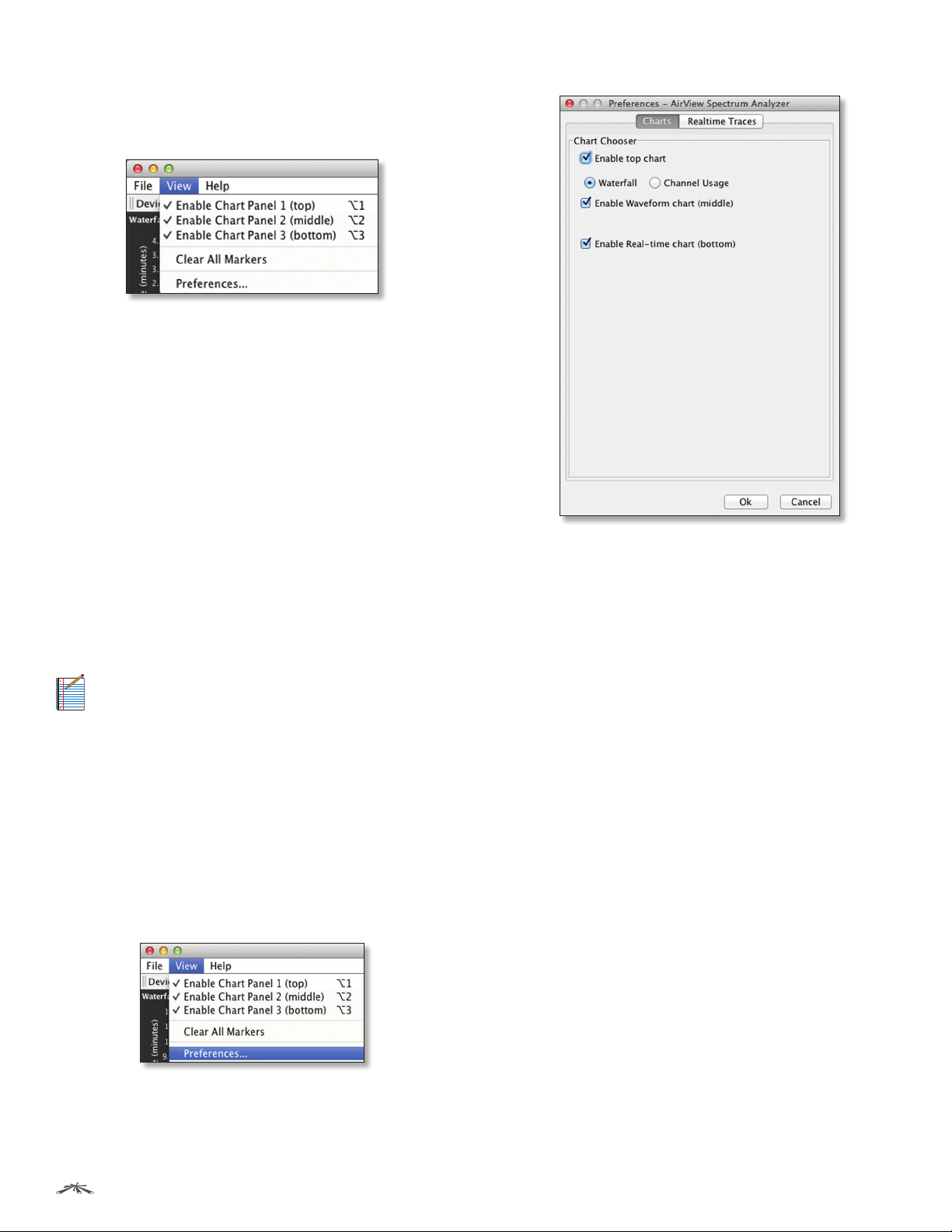
File Menu
Click Exit to end the airView session.
View Menu
Enable Chart Panel 1 (top) Displays the Waterfall or
Channel Usage chart in Chart Panel 1, depending on
which option you have selected in Preferences. This
time-based graph shows the aggregate energy collected
or channel usage for each frequency since the start of the
airView session.
Enable Chart Panel 2 (middle) Displays the Waveform
chart in Chart Panel 2. This time-based graph shows the RF
signature of the noise environment since the start of the
airView session. The energy color designates its amplitude.
Cooler colors represent lower energy levels (with blue
representing the lowest levels) in that frequency bin, and
warmer colors (yellow, orange, or red) represent higher
energy levels in that frequency bin.
Enable Chart Panel 3 (bottom) Displays the Real-time
chart (traditional spectrum analyzer) in Chart Panel 3.
Energy (in dBm) is shown in real time as a function of
frequency.
Note: Energy is the power ratio in decibels (dB) of
the measured power referenced to one milliwatt
(mW).
Clear All Markers Resets all previously assigned
markers. Markers are assigned by clicking a point, which
corresponds with a frequency on the Real-time chart.
Preferences Changes airView settings, such as enabling
or disabling charts and traces, or specifying the frequency
interval.
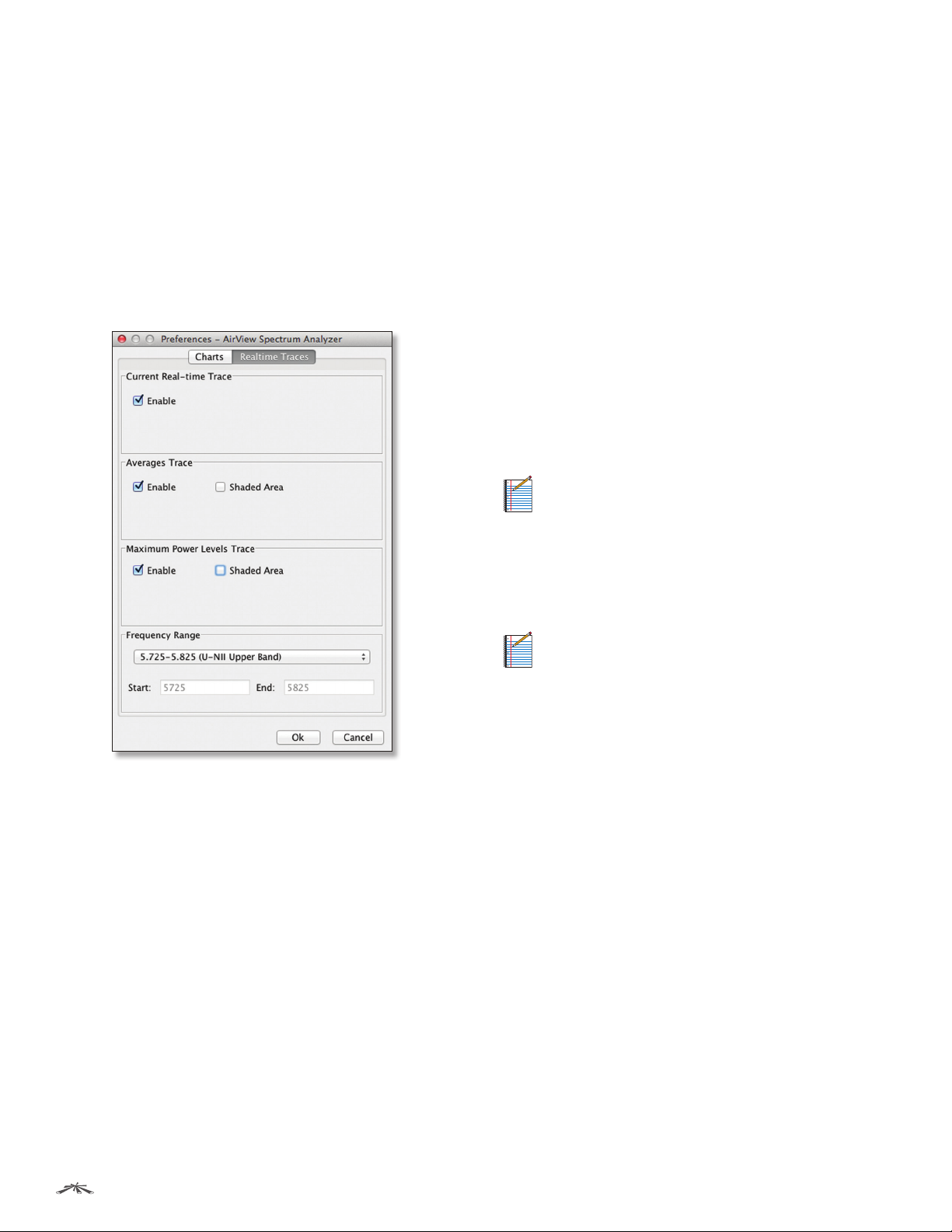
Preferences
Select View > Preferences to display the Preferences ‑
airView Spectrum Analyzer window.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
Charts
Enable top chart Check the box to enable the top chart.
Select the desired chart to display in the top chart panel
on the main view. There are two options:
• Waterfall This time-based graph shows the aggregate
energy collected for each frequency since the start
of the airView session. The energy color designates
its amplitude. Cooler colors represent lower energy
levels (with blue representing the lowest levels) in that
frequency bin, and warmer colors (yellow, orange, or
red) represent higher energy levels in that frequency
bin.
The Waterfall View’s legend (top-right corner) provides
a numerical guide associating the various colors to
power levels (in dBm). The low end of that legend (left)
is always adjusted to the calculated noise floor, and the
high end (right) is set to the highest detected power
level since the start of the airView session.
• Channel Usage For each Wi-Fi channel, a bar displays
a percentage showing the relative “crowdedness” of
that specific channel. To calculate this percentage, the
airView Spectrum Analyzer analyzes both the popularity
and strength of RF energy in that channel since the start
of an airView session.
Enable Waveform chart (middle) Check the box to
enable the middle chart. This time-based graph shows
the RF signature of the noise environment since the
start of the airView session. The energy color designates
its amplitude. Cooler colors represent lower energy
levels (with blue representing the lowest levels) in that
frequency bin, and warmer colors (yellow, orange, or red)
represent higher energy levels in that frequency bin.
The spectral view over time will display the steady-state RF
energy signature of a given environment.
7
Page 11
Chapter 2: Ubiquiti Logo TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Enable Real-time chart (bottom) Check the box to
enable the bottom chart. This graph displays a traditional
spectrum analyzer in which energy (in dBm) is shown in
real time as a function of frequency. There are three traces
in this view:
• Current (Yellow) Shows the real-time energy seen by
the device as a function of frequency.
• Average (Green) Shows the running average energy
across frequency.
• Maximum (Blue) Shows updates and maximum power
levels across frequency.
Realtime Traces
Maximum Power Levels Trace Check the Enable box to
enable the maximum power trace. When enabled, the
maximum power trace is represented by the blue area on
the Real‑time chart, which displays the maximum received
power level data since the start of the airView session. To
enable a shaded blue area, check the Shaded Area box.
To display only a blue outline without the shaded area,
uncheck the Shaded Area box.
Frequency Range Select the amplitude of the
frequency interval to be scanned from the Frequency
Range drop-down list. Available frequencies are device-
dependent. There are pre-defined ranges for the most
popular bands. You can enter a custom range; select
Custom Range from the Frequency Range drop-down list
and enter the desired values in the Start and End fields.
Help
Click About to view the version and build number of the
airView Spectrum Analyzer.
airSync (GPS Series Only)
Note: If you enable airSync, then airSelect is not
available.
The following settings apply only to the Real‑time chart:
Current Real-time Trace Check the Enable box to enable
the real-time trace. When enabled, the yellow outline on
the Real‑time chart represents the real-time power level of
each frequency. The refresh speed depends on the FPS.
Averages Trace Check the Enable box to enable the
averages trace. When enabled, the averages trace is
represented by the green area on the Real‑time chart,
which displays the average received power level data
since the start of the airView session. To enable a shaded
green area, check the Shaded Area box. To display only
a green outline without the shaded area, uncheck the
Shaded Area box.
(Available in Access Point mode only.) airSync (available on
GPS Series devices only) synchronizes airMAX APs with a
satellite reference timing signal. When enabled, airSync
eliminates receive (RX) errors due to co-location transmit
interference.
Note: To use airSync, all Stations must run airOS
v5.5 or higher; otherwise, they cannot connect to
any of the APs.
We recommend the following guidelines:
• Adjacent sectors should use different frequencies.
• Back-to-back sectors can use the same frequency.
• Do not use the same frequency on ALL of your
co-located APs. Some of your co-located APs may be
able to use the same frequency, depending on the
scenario. See the following examples: Four APs and
TwoAPs.
• The number of frequencies you should use depends on
the number of APs you have on a single tower because a
client can get confused if it receives signals on the same
frequency from two different APs.
• If you are using more than one frequency, ensure that
you have 20 MHz separation between the frequency
band edges. For example: if frequency range A ends at
5815 MHz, then frequency range B should start at 5835
MHz or higher.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
8
Page 12
Chapter 2: Ubiquiti Logo TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
We have the following examples:
• Four APs Use two different frequencies. Set the same
frequency on each back-to-back pair of APs (this is the
ABAB channel design). For example, a client is located
equidistant from two APs (one set to frequency A and
one set to frequency B). The client will only receive
signals from the AP that shares its frequency.
Three APs Set a different frequency on each AP (this is
the ABC channel design). For example, a client is located
equidistant from two APs (one set to frequency A and
one set to frequency B). The client will only receive signals
from the AP that shares its frequency. A different client is
located equidistant from a different pair of APs (one set
to frequency B and one set to frequency C). This client will
only receive signals from the AP that shares its frequency.
After you configure these durations, or slots, on the
master AP, they are passed along to all slave APs. The same
transmit and receive durations allow each AP to determine
when to start transmitting, and when to start receiving.
Slots are configured in µs (microseconds) and specify the
period of time the AP will transmit (Down Slot), and receive
(Up Slot). The Down Slot sets the amount of time for client
users to download, while the Up Slot sets the amount of
time for client users to upload.
You can think of the Down Slot period and Up Slot period
as a ratio. If the Down Slot is set to 4000 µs, and the Up Slot
is set to 2000 µs, the AP allocates 66% [4000/(4000+2000)]
of its time providing clients’ download slots, while the AP
allocates the remaining 33% to clients’ upload slots.
Some usage scenarios may require use of the Timing
Override feature, depending on users’ upload and
download traffic. If an AP group’s users will primarily be
downloading, increase the ratio of Down Slots to Up Slots.
Similarly, if an AP group has more business users and
needs higher upload speeds, use a more even Down Slot/
Up Slot ratio. Depending on traffic patterns, you may need
to adjust the Down Slot/Up Slot ratio as needed.
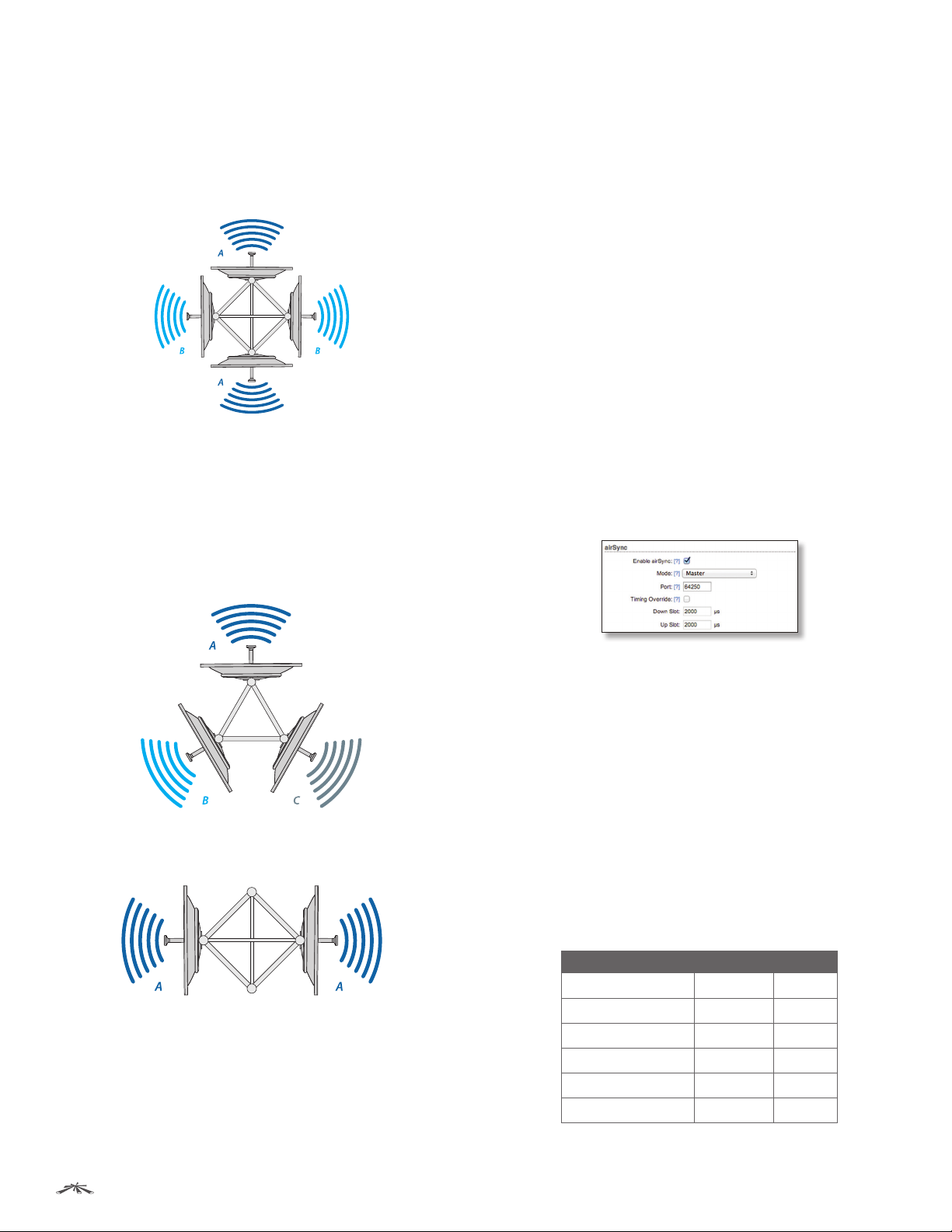
airSync options include:
• Two APs Set the same frequency on both APs located
back to back (this is the AA channel design).
To sync multiple APs, these are the requirements:
• The master AP has IP connectivity (specifically UDP) to
the slave APs.
• All APs have an active GPS signal.
• You have configured the transmit and receive durations
on the master AP.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
• Enable airSync Check the box to enable airSync.
• Mode Available when airSync is enabled. Select Master
or Slave depending on which device is configured in
Master mode and which devices are configured in Slave
mode. The device in Master mode synchronizes with all
connected peers in Slave mode.
• Port Available when airSync is enabled. By default, the
port is set to 64250 but you can change the value in the
field.
• Timing Override (Master) Available when airSync
is enabled on the Master AP. Check the box to enable
Timing Override. Uncheck the box to disable Timing
Override and restore default settings, which vary
depending on the channel bandwidth:
Channel Bandwidth Down Slot Up Slot
40 MHz 2000 µs 2000 µs
30 MHz 4000 µs 4000 µs
20 MHz 4000 µs 4000 µs
10 MHz 4000 µs 4000 µs
8 MHz 4000 µs 4000 µs
5 MHz 8000 µs 8000 µs
• Master IP (Slave) Available when airSync is enabled on
the slave AP. Enter the IP address of the master AP.
9
Page 13

Chapter 3: Main TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Chapter 3: Main Tab
The Main tab displays a summary of the link status
information, current values of the basic configuration
settings (depending on the operating mode), network
settings and information, and traffic statistics.
Status
Device Name Displays the customizable name or
identifier of the device. The Device Name (also known
as host name) is displayed in registration screens and
discovery tools.
Network Mode Displays the network operating mode.
airOS supports three modes: Bridge, Router, and SOHO
Router. The default setting is device-specific. Configure the
Network Mode on the Network tab.
Wireless Mode Displays the operating mode of the
radio interface. airOS supports three operating modes:
Station, Access Point, and AP‑Repeater. The default setting
is device-specific. Configure the Wireless Mode on the
Wireless tab. If Station or Access Point mode is enabled,
then you can also select WDS (Wireless Distribution
System) as needed.
airOS also supports airView (spectrum analyzer) mode, a
temporary mode that terminates all wireless connections.
To select airView mode, click Tools > airView or click
Launch airView on the Ubiquiti Logo tab. When the device
is running in airView mode, all wireless connections will be
terminated during the airView session. Close the airView
window to return to the previous wireless mode. Any M
Series device may operate in only one of these modes at a
time. For example, if the device is running in Access Point
mode, it cannot simultaneously run in Station mode.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
10
Page 14

Chapter 3: Main TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
SSID Displays the wireless network name (SSID). The
wireless network name depends upon the wireless mode
selected:
• In Station mode, this displays the SSID of the AP the
device is associated with.
• In Access Point mode, this displays the SSID configured
on the device using the Wireless tab.
Security Displays the wireless security method being
used on the device. If None is displayed, then wireless
security has been disabled, although you can still use
RADIUS MAC authentication.
Version Displays the airOS software version.
Uptime This is the total time the device has been running
since the latest reboot (when the device was powered up)
or software upgrade. The time is displayed in days, hours,
minutes, and seconds.
Date Displays the current system date and time. The
date and time are displayed in YEAR-MONTH-DAY
HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS format. The system date and
time is retrieved from the Internet using NTP (Network
Time Protocol). The NTP Client is disabled by default on
the Services tab. The device doesn’t have an internal clock,
and the date and time may be inaccurate if the NTP Client
is disabled or the device isn’t connected to the Internet.
Channel/Frequency Displays the channel number and
corresponding operating frequency. The device uses
the channel and radio frequency specified to transmit
and receive data. Valid channel and frequency ranges
will vary depending on local country regulations. If the
Channel/Frequency is labeled as “DFS”, then the device is
using a DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection) channel. (DFS
channels/frequencies are not available on all devices.)
Channel Width This is the spectral width of the radio
channel used by the device. airOS v5.5 supports 3, 5, 7,
8, 10, 14, 20, 25, 28, 30, and 40 MHz; however, available
channel widths are device-specific. In Station mode, Auto
20/40 MHz is the value by default.
Distance Displays the current distance between devices
in kilometers and miles for Acknowledgement (ACK)
frames. Changing the distance value will change the
ACK (Acknowledgement) timeout accordingly. The ACK
timeout specifies how long the device should wait for
an acknowledgement from a partner device confirming
packet reception before it concludes that there has been
an error and resends the packet. You can adjust the
Distance value; for more information, see “Distance” on
page 50).
TX/RX Chains Displays the number of independent
spatial data streams the device is transmitting (TX)
and receiving (RX) simultaneously within one spectral
channel of bandwidth. This ability is specific to 802.11n
devices that rely on Multiple-Input Multiple-Output
(MIMO) technology. Multiple chains increase data transfer
performance significantly. The number of chains Ubiquiti
devices use is hardware-specific because every TX/RX
chain requires a separate antenna.
Antenna (Only applicable to the NanoStationM900 loco.)
The antenna type (Internal, External, or External + Internal)
is displayed. For more information, see “Antenna” on
page 21.
WLAN0 MAC Displays the MAC address of the device as
seen on the wireless network.
LAN0 MAC Displays the MAC address of the device as
seen on the LAN.
LAN1 MAC Displays the MAC address of the device
as seen on the WAN interface. This is the device’s MAC
address as seen over the Internet.
LAN0/LAN1 Indicates the current status of the WAN and
LAN Ethernet port connections. This can indicate that a
cable is not plugged into a device or there is no active
Ethernet connection.
AP MAC In Access Point or AP‑Repeater mode, this
displays the MAC address of the device. In Station mode,
this displays the MAC address of the AP the device is
associated with.
Signal Strength (Available in Station mode only.)
Displays the received wireless signal level (client-side).
The represented value coincides with the graphical bar.
Use the antenna alignment tool to adjust the device
antenna to get a better link with the wireless device. The
antenna of the wireless client has to be adjusted to get
the maximum signal strength. Signal Strength is measured
in dBm (the decibels referenced to 1 milliwatt). The
conversion is defined as dBm=10log10(P/1mW). So, 0dBm
would be 1 mW and -72 dBm would be 0.0000006 mW.
A signal strength of -80 dBm or better (-50 to -70 dBm) is
recommended for stable links.
Chain or Horizontal/Vertical or External/Internal
(Vertical) (Available in Station mode only.) Displays
the wireless signal level (in dBm) of each signal. Devices
with fixed antennas display Horizontal/Vertical instead of
Chain. When chains are displayed, the number of chains is
device-specific.
The NanoStationM900 loco displays External/Internal
(Vertical) if the Antenna option on the Wireless tab is set
to External + Internal (2x2). For more information, see
“Antenna” on page 21.
Connections (Available in Access Point or AP‑Repeater
mode only.) Displays the number of wireless devices
connected to the device.
Noise Floor Displays the current value (in dBm) of the
environmental noise (from interference) the receiver hears
on the operating frequency. airOS considers the Noise
Floor while evaluating the signal quality (Signal-to-Noise
Ratio SNR, RSSI). The value mean depends on the signal
strength above the Noise Floor.
Transmit CCQ This index evaluates the wireless Client
Connection Quality (CCQ). The level is based on a
percentage value for which 100% corresponds to a perfect
link state.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
11
Page 15

Chapter 3: Main TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
TX Rate/RX Rate (Available in Station mode only.)
Displays the current 802.11 data transmission (TX) and
data reception (RX) rates.
airMAX Indicates the airMAX status. If airMAX is enabled,
the device will only accept airMAX clients. airMAX also
features advanced QoS autodetection settings. For more
information, refer to “airMAX Settings” on page 4.
Note: For compatibility, legacy or 802.11 a/b/g
devices should use legacy firmware with airMAX
support (such as airOS firmware v4.0). Legacy
clients can only work as airMAX clients with the M
Series device acting as an airMAX AP.
airMAX Priority Available if airMAX is enabled in Station
mode only. Indicates the airMAX Priority set on the Ubiquiti
logo tab. By default the AP gives all active clients the same
amount of time. However, if the clients are configured with
different priorities, the AP will give clients more or less
time, depending on the priority.
airMAX Quality Available if airMAX is enabled. airMAX
Quality (AMQ) is based on the number of retries and the
quality of the physical link. If this value is low, you may
have interference and need to change frequencies. If AMQ
is above 80% and you do not notice any other issues, then
you do not need to make any changes.
airMAX Capacity Available if airMAX is enabled. airMAX
Capacity (AMC) is based on airtime efficiency. For example,
if you have one client with a low data rate or you are using
a 1x1 device (such as Bullet or airGrid) alongside other
clients that are 2x2, then it will use up more airtime (slots)
for the same amount of data, reducing time (or capacity)
for other clients. The lower the AMC, the less efficient the
AP is. If you only have one client, this may not matter, but
when you have many clients (for example, more than 30),
then AMC becomes very important, and you want it to be
as high as possible.
If you are looking at the client, AMC shows the theoretical
capacity of that client, based on current TX/RX rates and
quality. AMC is a percentage based on what the maximum
performance would be if the link were perfect. Clients
with poor airtime efficiency can negatively affect other
clients by taking up more airtime while transmitting at
lower speeds. For example, client A is at MCS 12 (78Mbps)
because of low signal. The client could theoretically
do MCS 15 (130 Mbps), so AMC is based on the ratio
of current rate/maximum rate (78 Mbps divided by
130Mbps), which is 60%. In a similar fashion, a 1x1 device
will always have a maximum AMC of 50%, because it
provides half the performance of a 2x2 device.
If you are looking at the AP, then AMQ and AMC are
averages of all clients’ values. If you want to discover
what is lowering your values on heavily populated APs,
single out the weak clients. You can either use airControl™
(recommended), or you can go to each client individually.
Try to upgrade to a higher-gain antenna (to allow a better
data rate), or upgrade to a 2x2 device if you are using a
1x1 device.
airSelect Indicates the airSelect status. If airSelect is
enabled, airSync is not available. Access airSelect setup
through the Ubiquiti Logo tab > airSelect.
Hop Interval Available if airSelect is enabled. The duration
(in milliseconds) that the AP will stay on one frequency
before moving to the next.
airSync (GPS Series Only) Indicates the airSync status. If
airSync is enabled, airSelect is not available, and the device
in Master mode reports the number of airSync-enabled
devices in Slave mode. Access airSync setup through the
Ubiquiti Logo tab > airSync.
GPS Signal Quality (GPS Series Only) Displays GPS
signal quality as a percentage value on a scale of 0-100%.
Latitude/Longitude (GPS Series Only) Based on
GPS tracking, reports the device’s current latitude and
longitude. Clicking the link opens the reported latitude
and longitude in a browser using Google Maps
(http://maps.google.com).
Altitude (GPS Series Only) Based on GPS tracking,
reports the device’s current altitude above sea level.
Custom Scripts Displayed if custom scripts are present
on the device. If custom scripts are running, then the Main
tab displays the status of this option as “Enabled”.
™
Monitor
There are various monitoring tools accessible via the
links on the Main tab. The default is Throughput, which is
displayed when you first open the Main tab.
Throughput
Throughput displays the current data traffic on the LAN
and WLAN in both graphical and numerical form. The
chart scale and throughput dimension (Bps, Kbps, Mbps)
change dynamically depending on the mean throughput
value. The statistics are updated automatically.
Refresh If there is a delay in the automatic update, click
Refresh to manually update the statistics.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
12
Page 16

Chapter 3: Main TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Stations
(Available in Access Point or AP‑Repeater mode only.)
This selection lists the stations that are connected to the
device.
The following statistics for each station are displayed in
the station statistics window:
Station MAC Displays the MAC address of the station.
This is a clickable link that will display additional station
information.
Device Name Displays the station’s host name. The
device name can be changed on the System tab.
Signal/Noise, dBm The Signal value represents the
last received wireless signal level, and the Noise value
represents the noise level.
Distance (Available if the Auto Adjust setting is enabled
through the Advanced Wireless tab > Advanced Wireless
Settings.) Displays the current distance between
devices in kilometers and miles for Acknowledgement
(ACK) frames. With Auto Adjust enabled, the device’s
auto-acknowledgement timeout algorithm dynamically
optimizes the frame acknowledgement timeout value
without user intervention.
TX/RX, Mbps The TX value represents the data rates, in
Mbps, of the last transmitted packets, and the RX value
represents the data rates, in Mbps, of the last received
packets.
CCQ, % This index evaluates the wireless Client
Connection Quality (CCQ). The level is a percentage value
for which 100% corresponds to a perfect link state.
Connection Time Displays the connection time of each
station connected to the device. The time is expressed in
days, hours, minutes, and seconds.
Last IP Displays the station’s last IP address.
Action Displays available options for this station. For
example, click kick to drop the connection to this station.
Refresh To update the information, click Refresh.
Station Information
Detailed information is displayed when you click a specific
MAC address:
• Station Displays the MAC address of the station.
• Device Name Displays the host name of the station.
• Product Displays the product name of the device.
• Firmware Displays the firmware version of airOS.
• Connection Time Displays the amount of time the
station has been connected to the device. The time is
expressed in days, hours, minutes, and seconds.
• Signal Strength (TX/RX) The values represent, in dBm,
the last transmitted wireless signal level and the last
received wireless signal level.
• Noise Floor Displays the current value (in dBm) of the
environmental noise (from interference) the receiver
hears on the operating frequency. airOS considers
the Noise Floor while evaluating the signal quality
(Signal-to-Noise Ratio SNR, RSSI). The value mean
depends on the signal strength above the Noise Floor.
• Distance (Available if the Auto Adjust setting is enabled
through the Advanced Wireless tab > Advanced Wireless
Settings.) Displays the current distance between
devices in kilometers and miles for Acknowledgement
(ACK) frames. With Auto Adjust enabled, the device’s
auto-acknowledgement timeout algorithm dynamically
optimizes the frame acknowledgement timeout value
without user intervention.
• CCQ The value represents the quality of the connection
to the AP. This index evaluates the wireless Client
Connection Quality (CCQ). The level is a percentage
value for which 100% corresponds to a perfect link state.
• airMAX Priority The airMAX Priority of this station’s
traffic in comparison to the other stations.
• airMAX Quality The airMAX Quality level is based on
a percentage value for which 100% corresponds to a
perfect link state.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
13
Page 17
Chapter 3: Main TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
• airMAX Capacity This is an index of the maximum data
rate the link is operating at. A lower capacity number
indicates a unit that is slowing down the system.
• Last IP Displays the station’s last IP address.
• TX/RX Rate Displays the data rates, in Mbps, of the last
transmitted and received packets.
• TX/RX Bit Rate Displays the data rates, in bps, of the
last transmitted and received packets.
• TX/RX Packets Displays the total number of packets
transmitted and received from the station during the
connection uptime.
• TX/RX Packet Rate, pps Displays the mean value of the
transmitted and received packet rates.
• Bytes Transmitted Displays the total amount of data
(in bytes) transmitted during the connection.
• Bytes Received Displays the total amount of data (in
bytes) received during the connection.
• Negotiated Rate/Last Signal, dBm Values represent
the received wireless signal level along with the data
rates of recently received packets. N/A is displayed as the
Last Signal if no packets were received on that specific
data rate.
• Kick To drop the connection to the station, click Kick.
• Refresh To update the information, click Refresh.
• Close To close the Station Info window, click Close.
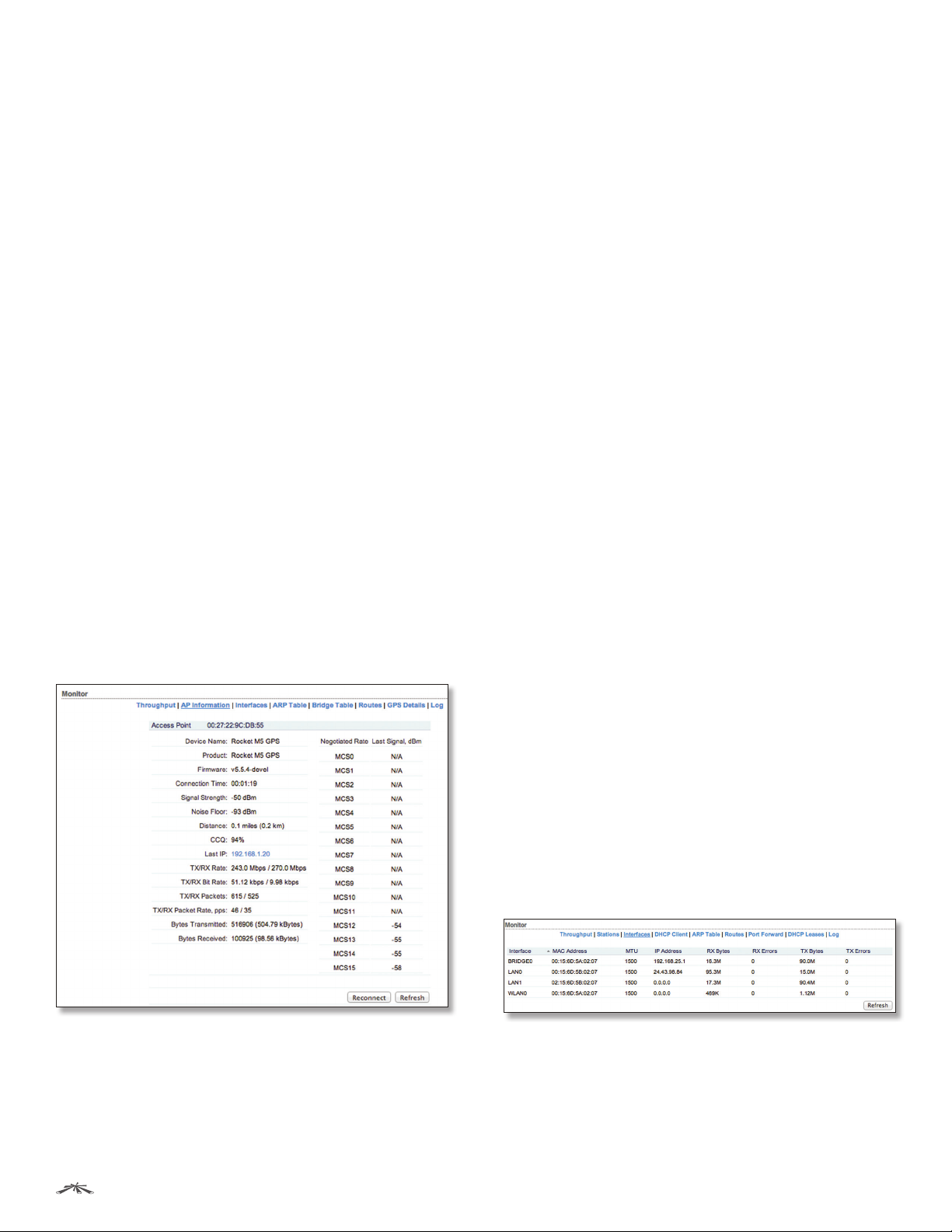
AP Information
(Available in Station mode only.) This selection lists the
connection statistics of the AP associated with the device.
Connection Time Displays the amount of time the device
has been connected to the AP. The time is expressed in
days, hours, minutes, and seconds.
Signal Strength The value represents, in dBm, the last
received wireless signal level.
Noise Floor Displays the current value (in dBm) of the
environmental noise (from interference) the receiver hears
on the operating frequency. airOS considers the Noise
Floor while evaluating the signal quality (Signal-to-Noise
Ratio SNR, RSSI). The value mean depends on the signal
strength above the Noise Floor.
CCQ The value represents the quality of the connection to
the AP. This index evaluates the wireless Client Connection
Quality (CCQ). The level is a percentage value for which
100% corresponds to a perfect link state.
Last IP Displays the device’s last IP address.
TX/RX Rate Displays the data rates, in Mbps, of the last
transmitted and received packets.
TX/RX Bit Rate Displays the data rates, in bps, of the last
transmitted and received packets.
TX/RX Packets Displays the total number of packets
transmitted and received from the station during the
connection uptime.
TX/RX Packet Rate, pps Displays the mean value of the
transmitted and received packet rates.
Bytes Transmitted Displays the total amount of data (in
bytes) transmitted during the connection.
Bytes Received Displays the total amount of data (in
bytes) received during the connection.
Negotiated Rate/Last Signal, dBm Values represent the
received wireless signal level along with the data rates
of recently received packets. N/A is displayed as the Last
Signal if no packets were received on that specific data
rate.
Reconnect To establish the wireless link to the AP again,
click Reconnect.
Refresh To update the information, click Refresh.
Access Point Displays the MAC address of the AP.
Device Name Displays the host name of the AP.
Product Displays the product name of the device.
Firmware Displays the firmware version of airOS.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
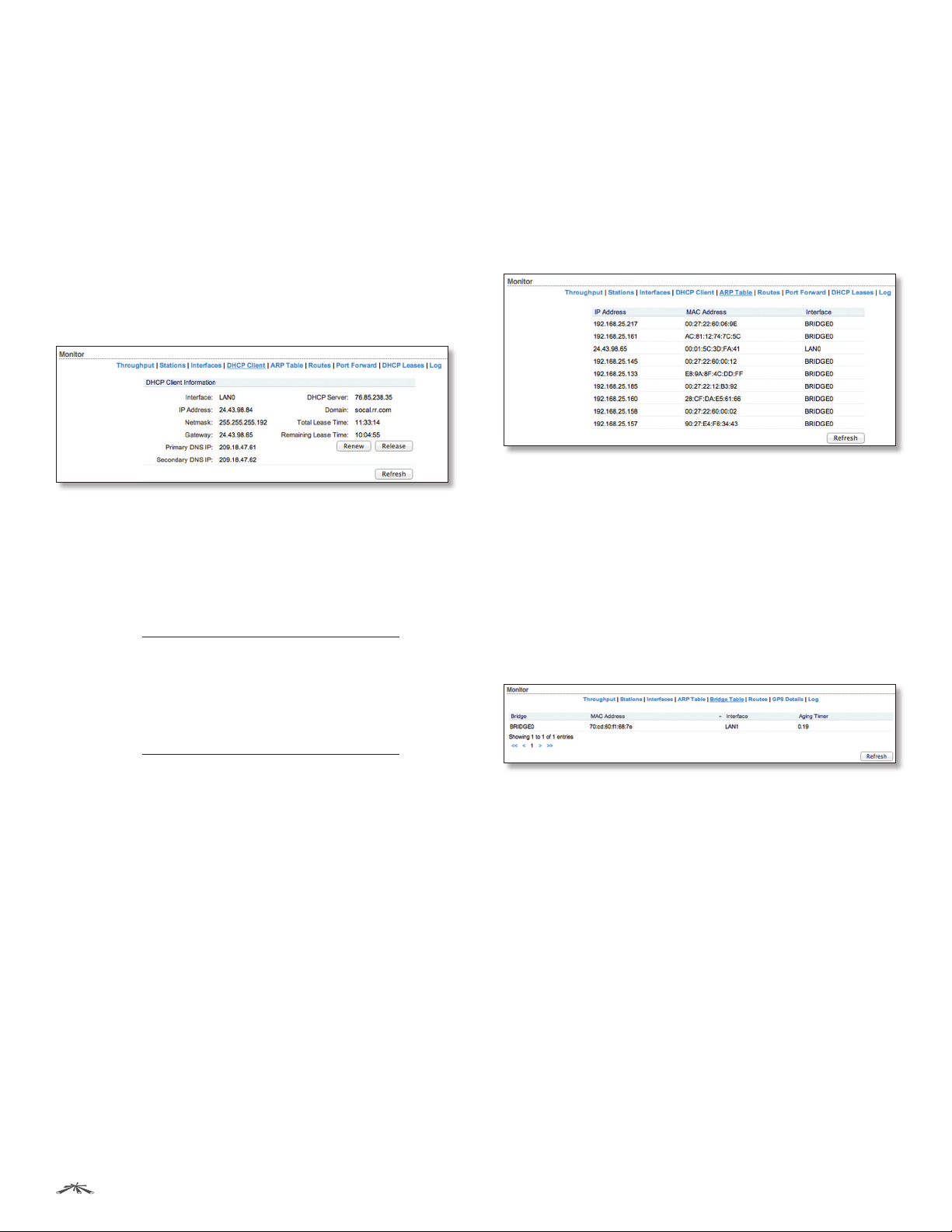
Interfaces
Displays the name, MAC address, MTU, IP address, and
traffic information for the device’s interfaces.
Interface Displays the name of the interface.
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the interface.
MTU Displays the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU),
which is the maximum packet size (in bytes) that a
network interface can transmit. The default is 1500.
IP Address Displays the IP address of the interface.
14
Page 18
Chapter 3: Main TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
RX Bytes Displays the total amount of data (in bytes)
received by the interface.
RX Errors Displays the number of receive errors.
TX Bytes Displays the total amount of data (in bytes)
transmitted by the interface.
TX Errors Displays the number of transmit errors.
Refresh To update the information, click Refresh.
DHCP Client
(Available in Router or SOHO Router mode only.) Displays
the device’s WAN IP address, netmask, DNS servers, and
gateway while the device is operating as a DHCP client of
an external DHCP server.
Interface Displays the interface that connects to the
WAN.
IP Address Displays the IP address assigned by an
external DHCP server connected to the WAN interface.
If an external DHCP server is not found, the IP address
will use the DHCP Fallback IP defined in the WAN Network
Settings. See “WAN Network Settings” on page 32 for
additional details.
Netmask Displays the Netmask assigned by an external
DHCP server connected to the WAN interface. If an
external DHCP server is not found, the IP address will use
the DHCP Fallback Netmask defined in the WAN Network
Settings. See “WAN Network Settings” on page 32 for
additional details.
Gateway Displays the gateway address assigned by an
external DHCP server connected to the WAN interface.
Primary/Secondary DNS IP The Domain Name System
(DNS) is an Internet “phone book” that translates domain
names to IP addresses. These fields identify the server IP
addresses that the device uses for translation.
DHCP Server Displays the IP address of the external
DHCP server that assigns the WAN IP address to the
device.
Domain Displays the domain name.
Total Lease Time Shows the total time (validity) of the
leased IP address assigned by the external DHCP server.
Remaining Lease Time Displays the remaining time
of the leased IP address assigned by the external DHCP
server.
Renew To request new IP settings from the external
DHCP server, click Renew.
Release To release the current IP settings, click Release.
Refresh To update the information, click Refresh.
ARP Table
Lists all the entries of the Address Resolution Protocol
(ARP) table currently recorded on the device.
ARP is used to associate each IP address to the unique
hardware MAC address of each device on the network. It
is important to have unique IP addresses for each MAC
address or else there will be ambiguous routes on the
network.
IP Address Displays the IP address assigned to a network
device.
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the device.
Interface Displays the interface that connects to the
device.
Refresh To update the information, click Refresh.
Bridge Table
(Available in Bridge mode only.) The table displays the
entries in the system Bridge Table.
Bridge The name of the bridge.
MAC Address The network device identified by its MAC
address.
Interface The Bridge Table shows which bridge port
or interface, LAN (Ethernet) or WLAN (Wireless), the
specific network device is associated with. airOS can
forward packets only to the specified port of the device,
eliminating redundant copies and transmits.
Aging Timer Displays aging time for each address entry
(in seconds). After a specific timeout, if the device has not
seen a packet coming from a listed address, it will delete
that address from the Bridge Table.
Refresh To update the information, click Refresh.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
15
Page 19
Chapter 3: Main TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
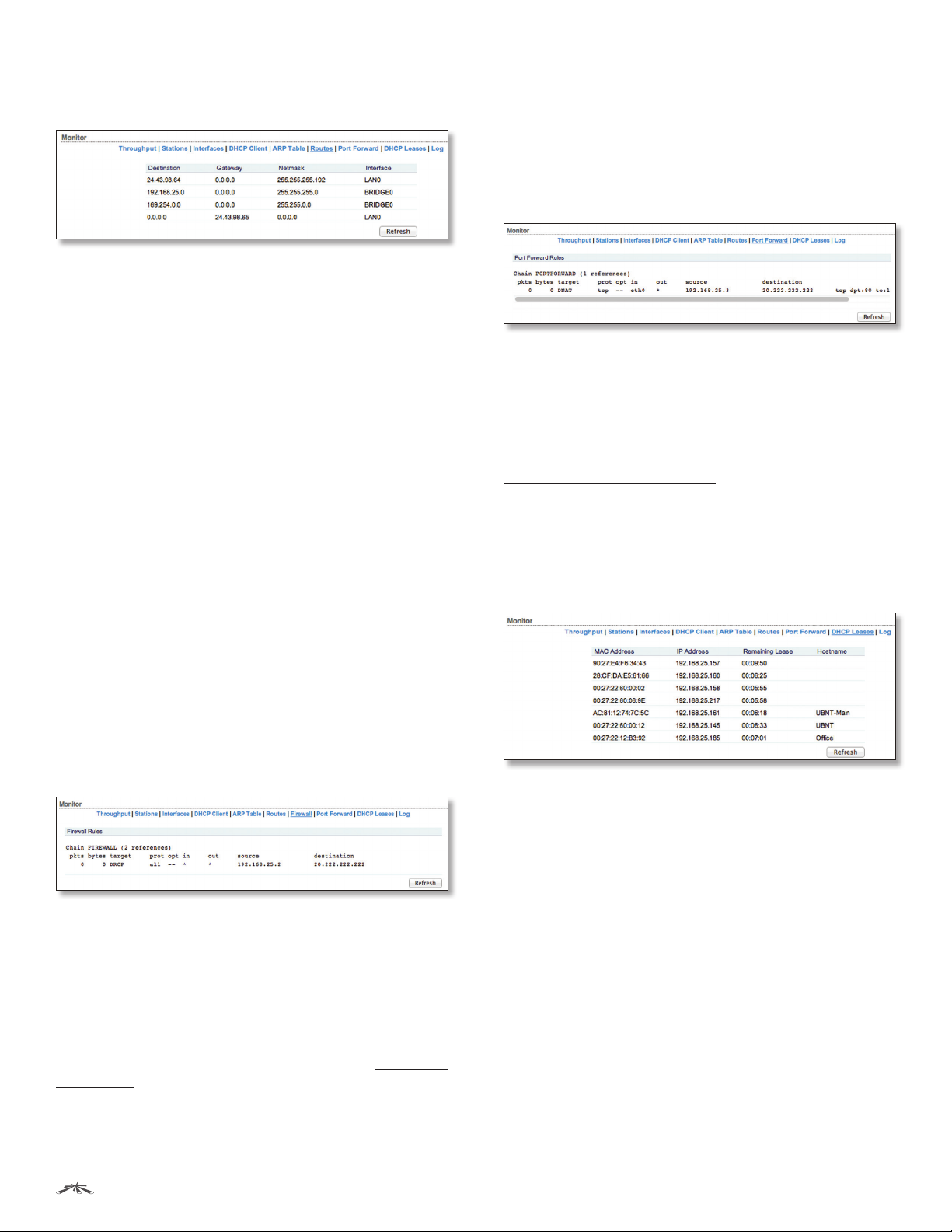
Routes
Lists all the entries in the system routing table.
airOS examines the destination IP address of each data
packet traveling through the system and chooses the
appropriate interface to forward the packet to. The system
choice depends on static routing rules, the entries that
are registered in the system routing table. Static routes to
specific hosts, networks, or the default gateway are set up
automatically according to the IP configuration of all the
airOS Configuration Interfaces.
Destination Displays the IP address of the destination
device.
Gateway Displays the IP address of the appropriate
gateway.
Netmask Displays the netmask of the destination device.
Interface Displays the interface that the destination
device is on.
Refresh To update the information, click Refresh.
Firewall
When the firewall is enabled on the Network tab, this
option is available. By default, there are no firewall rules.
If the device is operating in Bridge mode, the table lists
active firewall entries in the FIREWALL chain of the
standard ebtables filter table.
If the device is operating in Router or SOHO Router mode,
the table lists active firewall entries in the FIREWALL chain
of the standard iptables filter table.
Firewall Rules IP and MAC level access control and
packet filtering in airOS are implemented using an
ebtables (bridging) or iptables (routing) firewall that
protects the resources of a private network from outside
threats by preventing unauthorized access and filtering
specified types of network communication.
Refresh To update the information, click Refresh.
Configure firewall rules on the Network tab. See “Firewall”
on page 30 for additional details.
Port Forward
(Available in Router or SOHO Router mode only.) Port
forwarding allows you to connect to a specific service such
as an FTP server or web server. Port forwarding creates a
transparent tunnel through a firewall/NAT, granting access
from the WAN side to the specific network service running
on the LAN side.
Port Forward Rules Lists active port forward entries in
the PREROUTING chain of the standard iptables nat table,
while the device is operating in Router or SOHO Router
mode.
Refresh To update the information, click Refresh.
Configure port forwarding rules on the Network tab. See
“Port Forwarding” on page 38 for additional details.
DHCP Leases
(Available in Router or SOHO Router mode only with the
DHCP server feature enabled.) Displays the current status
of the IP addresses assigned by the device’s DHCP server
to its local DHCP clients.
MAC Address Displays the client’s MAC address.
IP Address Displays the client’s IP address.
Remaining Lease Displays the remaining time of the
leased IP address assigned by the DHCP server.
Hostname Displays the device name of the client.
Refresh To update the information, click Refresh.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
16
Page 20

GPS Details (GPS Series Only)
GPS Details (available on GPS Series devices only) displays
GPS Satellite details and Signal quality.
Refresh To update the information, click Refresh.
Log
When logging is enabled (see “System Log” on page
55 to enable logging), this option lists all registered
system events. By default, logging is not enabled.
Chapter 3: Main TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Clear To delete all entries in the system log, click Clear.
Refresh To update the log content, click Refresh.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
17
Page 21
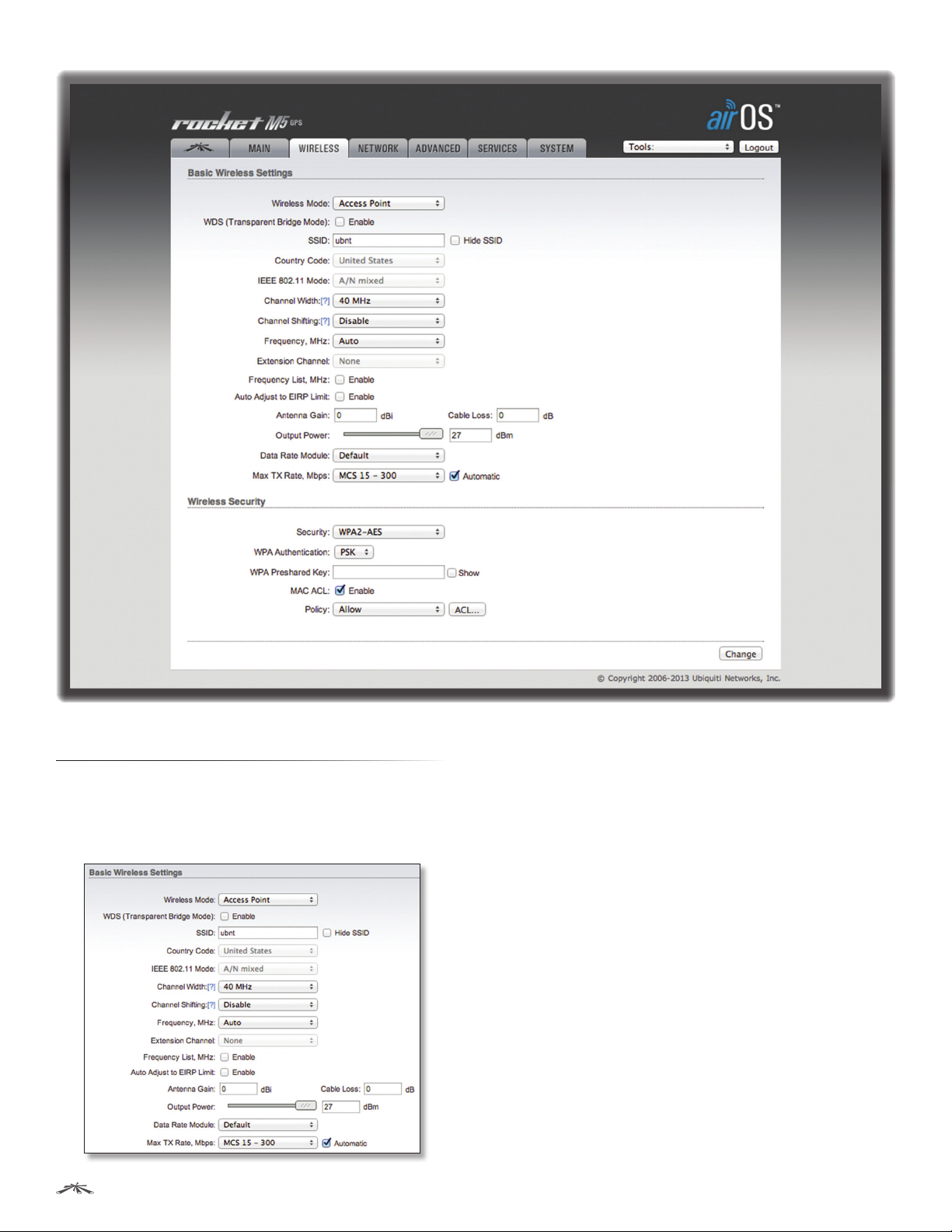
Chapter 4: Wireless TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Chapter 4: Wireless Tab
The Wireless tab contains everything needed to set up the
wireless part of the link. This includes SSID, channel and
frequency settings, device mode, data rates, and wireless
security.
Change To save or test your changes, click Change.
A new message appears. You have three options:
• Apply To immediately save your changes, click Apply.
• Test To try the changes without saving them, click
Test. To keep the changes, click Apply. If you do not
click Apply within 180 seconds (the countdown is
displayed), the device times out and resumes its earlier
configuration.
• Discard To cancel your changes, click Discard.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
18
Page 22

Chapter 4: Wireless TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Basic Wireless Settings
In this section, configure the basic wireless settings, such
as wireless mode, wireless network name (SSID), country
code, 802.11 mode, output power, and data rates.
Wireless Mode Specify the Wireless Mode of the
device. The mode depends on the network topology
requirements. airOS supports the following modes:
• Station If you have a client device to connect to an
AP, configure the client device as Station mode. The
client device acts as the subscriber station while it is
connecting to the AP. The SSID of the AP is used, and all
the traffic to and from the network devices connected to
the Ethernet interface is forwarded.
Note: If WDS (Transparent Bridge Mode) is
disabled, the radio uses arpnat, which results
in non-transparent bridging. To have a fully
transparent bridge, select Station and then
enable WDS (Transparent Bridge Mode).
• Access Point If you have a single device to act as
an AP, configure it as Access Point mode. The device
functions as an AP that connects multiple client devices.
If you have multiple APs repeating signals where
Ethernet connections are not readily available, then use
AP‑Repeater mode.
Note: For Access Point (WDS) mode, select Access
Point and then enable WDS (Transparent Bridge
Mode).
• AP‑Repeater If you have multiple APs, configure them
as AP‑Repeater mode to create a wireless network
infrastructure, WDS. If the Auto option is enabled, all APs
using the same wireless mode (AP‑Repeater) and SSID
automatically establish the WDS connections. (Client
devices can still connect to APs in AP‑Repeater mode.)
Note: For AP‑Repeater mode, the WPA™/WPA2
security methods will not work; instead, use
none or the WEP security method (this may
compromise the security of your network).
You still have the option of using RADIUS MAC
authentication and MAC ACL.
WDS (Transparent Bridge Mode) (Available in Access
Point or Station mode only.) In most cases, we recommend
that you use WDS because it enables transparent Layer2
traffic. To use WDS with Station or Access Point mode,
check the Enable box.
The WDS protocol is not defined as a standard, so there
may be compatibility issues between equipment from
different vendors.
• Station (WDS) Station (WDS) mode should be used if
the device is connecting to an AP in Access Point (WDS)
mode.
• Access Point (WDS) Access Point (WDS) mode allows
Layer2 bridging with devices in Station (WDS) mode.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
™
Note: If you connect devices running in Station
(WDS) mode to a device running in Access
Point (WDS) mode, then all security methods
(including WPA/WPA2 encryption) are available
and work properly.
Auto (Available in AP‑Repeater mode only.) Check the
Auto box to automatically establish WDS connections
between APs in AP‑Repeater mode. If the Auto option
is enabled, the device will choose WDS Peers (APs in
AP‑Repeater mode) according to the SSID setting. While
the device is in AP‑Repeater mode, you cannot enable the
Auto option if you use any type of WPA or WPA2 security
because WPA or WPA2 requires different roles on AP
configuration (authenticator or supplicant).
Note: All APs in AP‑Repeater mode (WDS Peers)
must operate on the same frequency channel, use
the same channel spectrum width, and share the
same security settings.
WDS Peers (Available in AP‑Repeater mode only.) If you
do not enable the Auto option, then specify the APs in
AP‑Repeater mode. Enter the MAC address of each AP
in each WDS Peers field. One MAC address should be
specified for a Point-to-Point (PtP) connection use case.
You can specify up to six WDS Peers for a Point-to-MultiPoint (PtMP) connection use case.
SSID If the device is operating in Access Point or
AP‑Repeater mode, specify the wireless network name or
SSID (Service Set Identifier) used to identify your WLAN.
All the client devices within range will receive broadcast
messages from the AP advertising this SSID.
If the device is operating in Station mode, specify the
SSID of the AP the device is associated with. There can be
several APs with an identical SSID.
Select (Available in Station mode only.) To display the list
of available APs, click Select.
The Site Survey tool will search for available wireless
networks in range on all supported channels and allow
you to select one for association. In case the selected
network uses encryption, you’ll need to configure security
on the Wireless tab and save those changes before you use
the Site Survey tool.
• Lock to AP Select the AP from the list. Click Lock to AP
to allow the station to always maintain a connection to
an AP with a specific MAC address.
• Select Select the AP from the list and click Select for
association.
• Scan Click Scan to refresh the list of available wireless
networks.
You can change the list of Scanned Frequencies for the
Site Survey using the Frequency Scan List option.
19
Page 23

Chapter 4: Wireless TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Lock to AP MAC (Available in Station mode only.) This
allows the station to always maintain a connection
to an AP with a specific MAC address. This is useful as
sometimes there can be multiple APs using the same SSID.
Enter a MAC address in the Lock to AP MAC field, and the
station will lock to the AP with this specific MAC address
and not roam between several APs with the same SSID.
Hide SSID (Available in Access Point or AP‑Repeater
mode only.) When Hide SSID is enabled, the SSID (wireless
network name) will not be broadcast to wireless stations.
Country Code Each country has their own power level
and frequency regulations. To ensure the device operates
under the necessary regulatory compliance rules, you must
select the country where your device will be used. The IEEE
802.11 mode, channel and frequency settings, and output
power limits will be tuned according to the regulations of
the selected country.
IEEE 802.11 Mode This is the radio standard used for
operation of your device. 802.11b, 802.11a, and 802.11g
are older standards, while 802.11n is a newer standard
that provides higher capacity and better performance.
Options include:
• A/N mixed Connects to an 802.11a or 802.11n network.
This mode offers better compatibility. A/N mixed mode is
selected by default on the following devices:
- M900 Series devices
- M3 Series devices
- M365 Series devices
- M5 Series devices
• B/G/N mixed Connects to an 802.11b, 802.11g, or
802.11n network. This mode offers better compatibility.
B/G/N mixed mode is selected by default on the
following devices:
- M2 Series devices
DFS (Only applicable to specific 5GHz devices configured
with specific Country Codes.) Radar systems use specific
frequencies in the 5GHz range. DFS (Dynamic Frequency
Selection) technology avoids interference with radar
signals. Depending on the regulations of the country
selected in the Country Code option:
• Specific 5GHz devices may be allowed use of DFS
frequencies in the UNII‑2 band (5.25 ‑ 5.725 GHz) if they
use DFS technology.
• The DFS option may be available in airOS. If available,
then you can use this option to enable or disable DFS
functionality.
Before your device starts using a DFS frequency, it
may lose connection for 1 or 10minutes during the
Channel Availability Check (CAC) time, depending on
the frequency. (In particular, weather radar frequencies,
5600‑5650MHz, may have long wait times.)
If your device detects a radar on that frequency, it adds
this frequency to a blacklist for 30 minutes. If only one
frequency is on the Frequency List, then the device will
lose connection for 30-40 minutes after it detects the
radar. Also, any radio operating with Equivalent Isotropic
Radiated Power (EIRP) > 200 mW will lose connection for
30 minutes if it detects a radar.
Channel Width Displays the spectral width of the radio
channel. You can use this option to control the bandwidth
consumed by your link.
Using higher bandwidth increases throughput. Using
lower bandwidth:
• Reduces throughput proportional to the reduction in
channel size. For example, as 40 MHz increases possible
speeds by 2x, half spectrum channel (10 MHz) decreases
possible speeds by 2x.
• Increases the number of available, non-overlapping
channels, so networks can scale better.
• Increases the Power Spectral Density (PSD) of the
channel, so you can increase the link distance – more
robust links over long distances.
Available channel widths are device-specific. Supported
wireless channel spectrum widths include:
• 3 MHz The channel spectrum with the width of 3 MHz.
• 5 MHz The channel spectrum with the width of 5 MHz
(known as Quarter-Rate mode).
• 7 MHz The channel spectrum with the width of 7MHz.
• 8 MHz The channel spectrum with the width of 8MHz.
• 10 MHz The channel spectrum with the width of
10MHz (known as Half‑Rate mode).
• 14 MHz The channel spectrum with the width of
14MHz.
• 20 MHz The standard channel spectrum width of
20MHz (selected by default).
Note: To connect standard Wi-Fi devices that use
the 2.4 GHz band, ensure that 20 MHz is selected.
• 25 MHz The channel spectrum with the width of
25MHz.
• 28 MHz The channel spectrum with the width of
28MHz.
• 30 MHz The channel spectrum with the width of
30MHz.
• 40 MHz The channel spectrum with the width of
40MHz.
• Auto 20/40 MHz (Available in Station mode only.)
Offers better compatibility.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
20
Page 24

Chapter 4: Wireless TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Channel Shifting Enables special channels with a
frequency offset regarding standard 802.11b/g/n and
802.11a channels. This is a proprietary feature developed
by Ubiquiti Networks. While 802.11 networks have
standard channels (for example, Channel 36 (5180 MHz),
Channel 40 (5200 MHz), and so forth, spaced every 5MHz
apart), channel shifting uses non-standard (non-802.11)
channels offset from the standard channels. All the
channels can be shifted by 5MHz (in 802.11a/n) or
2MHz (in 802.11b/g/n) from the default central channel
frequency.
Note: Channel Shifting is not compatible with
legacy products.
The benefits of Channel Shifting include private
networking and inherent security, so your network is less
likely to be detected by other Wi-Fi devices.
Frequency, MHz The default, Auto, allows the device
to automatically select the frequency. You can specify a
frequency from the drop-down list.
If DFS frequencies in the UNII‑2 band (5.25 ‑ 5.725 GHz)
should be available for your device but are not displayed
in the drop-down list, then the DFS frequencies are locked.
For information on how to unlock the DFS frequencies,
refer to this option, “UNII‑2 Band” on page 58.
Extension Channel (Available in Access Point or
AP‑Repeater mode only with 40 MHz channel width
enabled.) A 40 MHz channel is two 20 MHz channels
bonded together. The Extension Channel tells the radio
to append an additional channel either above or below
the existing standard channel. For example, if you select
5805MHz (40 MHz channel) and Below, the radio will use
(5775 to 5795 MHz) + (5795 to 5815 MHz), but if you select
5805MHz (40 MHz channel) and Above, the radio will use
(5795 to 5815 MHz) + (5815 to 5835 MHz).
Frequency List, MHz (Available in Access Point or
AP‑Repeater mode only.) Multiple frequencies are available
to avoid interference between nearby APs. The frequency
list varies depending on the selected Country Code, IEEE
802.11 Mode, Channel Width, and Channel Shifting options.
Once enabled, click Edit to open the Frequency List
window.
Select the frequencies and click OK, or click Close to close
the window without any selections.
Frequency Scan List, MHz (Available in Station mode
only.) This restricts scanning to only the selected
frequencies. The benefits are faster scanning as well as
filtering out unwanted APs in the results. The Site Survey
tool will look for APs in selected frequencies only. Once
enabled, click Edit to open the Frequency List window.
Select the frequencies that you want to scan and click OK,
or click Close to close the window without any selections.
Auto Adjust to EIRP Limit (Not applicable to the
NanoStationM900 loco.) This option should remain
enabled so it forces the transmit output power to comply
with the regulations of the selected country. If enabled,
you cannot set EIRP above the amount allowed per
regulatory domain (different maximum output power
levels and antenna gains are allowed for each IEEE
802.11b/g/n regulatory domain or country).
To disable Auto Adjust to EIRP Limit, you must enable the
Installer EIRP Control setting on the Advanced tab.
Antenna (Only applicable to the NanoStationM900loco,
NanoBridge, and airGrid models.) Follow the instructions
for yourdevice:
• NanoStationM900 loco Select the appropriate option:
Internal (2x2), External (1x1), or External + Internal (2x2).
The external RP-SMA maps to chain 0, which is the
horizontal polarity internally.
• NanoBridgeM2 Select the size of the dish reflector, 400
‑ 18 dBi. If you are not using a dish reflector, then select
Feed only ‑ 3 dBi. The default is Not specified, which
means no gain.
• NanoBridgeM5 Select the size of the dish reflector,
300 ‑ 22 dBi or 400 ‑ 25 dBi. If you are not using a dish
reflector, then select Feed only ‑ 3 dBi. The default is
Not specified, which means no gain.
• airGridM2/M2 HP Select the size of the grid reflector,
11x14 – 16dBi or 17x24 – 20 dBi. If you are not using a
grid reflector, then select Feed only ‑ 3 dBi. The default
is Not specified, which means no gain.
• airGridM5/M5 HP Select the size of the grid reflector,
11x14 – 23dBi or 17x24 – 28 dBi. If you are not using a
grid reflector, then select Feed only ‑ 3 dBi. The default
is Not specified, which means no gain.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
21
Page 25

Chapter 4: Wireless TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Antenna Gain (Only applicable to devices with external
antenna connectors.) Enter the antenna gain in dBi. With
Auto Adjust to EIRP Limit enabled, Antenna Gain calculates
the TX power backoff needed to remain in compliance
with local regulations. The Antenna Gain setting
complements the Cable Loss setting; they both affect the
TX power of the device.
Cable Loss (Only applicable to devices with external
antenna connectors.) Enter the cable loss in dB. With
Auto Adjust to EIRP Limit enabled, Cable Loss affects the TX
power of the device. In case you have high amounts of
cable loss, you may increase the TX power while remaining
in compliance with local regulations. The Cable Loss
setting complements the Antenna Gain setting; they both
affect the TX power of the device.
Output Power Defines the maximum average transmit
output power (in dBm) of the device. To specify the output
power, use the slider or manually enter the output power
value. The transmit power level maximum is limited
according to country regulations. (If the device has an
internal antenna, then Output Power is the output power
delivered to the internal antenna.)
Data Rate Module (Not applicable to the airGateway.)
You have a choice of data rate algorithms to use for your
link, Default or Alternative. If the Default is not working
well for your link, you can try the Alternative to determine
which is the best data rate algorithm for your individual
situation. The Alternative tries to move the link to a higher
data rate but continuously monitors the packet failure
counters. You should get more stable data rates when
using the Alternative; however, results will vary depending
on the link’s specific environment and configuration. For
example, if a problematic link has traffic stability issues
and uses the Default, you may want to try the Alternative
to see if it improves the situation.
Note: You can select Default or Alternative on
a single device; this option does not depend
on which algorithm is selected on the AP or its
stations.
Max TX Rate, Mbps Defines the data rate (in Mbps) at
which the device should transmit wireless packets. You
can fix a specific data rate between MCS 0 and MCS7 (or
MCS 15 for 2x2 chain devices). We recommend that you
use the automatic option, especially if you are having
trouble getting connected or losing data at a higher rate.
In this case, the lower data rates will be used automatically.
If you select 20 MHz Channel Width, the maximum data
rate is MCS7 (65Mbps) or MCS 15 (130 Mbps). If you select
40MHz Channel Width, the maximum data rate is MCS 7
(150 Mbps) or MCS 15 (300 Mbps).
• Automatic If enabled, the rate algorithm selects the
best data rate, depending on link quality conditions. We
recommend that you use this option, especially if you
are having trouble getting connected or losing data at a
higher rate. For more information about data rates, refer
to ”Advanced Wireless Settings” on page 49.
Wireless Security
In Access Point or AP‑Repeater mode, configure the wireless
security settings that will be used by the devices on your
wireless network.
In Station mode, enter the security settings of the AP that
the device is associated with.
The following table lists the wireless security methods
available for each wireless mode:
Security Method Access Point AP‑Repeater Station
none ✓
WEP ✓
WPA
WPA-TKIP
WPA-AES
WPA2
WPA2-TKIP
WPA2-AES
¹ If you select none as your security method, then this may compromise the
security of your network; however, you have the options of using RADIUS MAC
Authentication and MAC ACL.
² If you select WEP as your security method, then this may compromise the
security of your network; however, you have the option of using MAC ACL.
1
2
✓ ✓
✓ ✓
✓ ✓
✓ ✓
✓ ✓
✓ ✓
Security airOS supports the following wireless security
methods:
• none If you want an open network without wireless
security, select none. You still have the option of using
RADIUS MAC authentication and MAC ACL.
• WEP WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is the oldest
and least secure security algorithm. Use WPA or WPA2
security methods when possible.
• WPA WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) was developed as a
stronger encryption method than WEP.
• WPA‑TKIP WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) security mode
with TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) support
only. TKIP uses the RC4 encryption algorithm. There is a
performance limitation to using TKIP, so we recommend
using AES.
• WPA‑AES WPA security mode with AES (Advanced
Encryption Standard) support only. AES is also known
as CCMP (Counter Mode with Cipher Block Chaining
Message Authentication Code Protocol), which uses the
AES algorithm.
• WPA2 WPA2 was developed to strengthen wireless
encryption security and is stronger than WEP and WPA.
• WPA2‑TKIP WPA2 security mode with TKIP support
only. TKIP uses RC4 encryption algorithm. There is a
performance limitation to using TKIP, so we recommend
using AES.
• WPA2‑AES WPA2 security mode with AES support only.
This is the strongest security option available. If all of the
wireless devices on your network support this option,
we recommend that you select it.
1
✓
2
✓
✓
✓
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
22
Page 26

Chapter 4: Wireless TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
None
RADIUS MAC Authentication You can authenticate
devices using their MAC addresses.
MAC Format Select the appropriate format of the MAC
address.
Use Empty Password To submit the MAC address
without a password, check the Enable box.
Auth Server IP/Port In the first field, enter the IP
address of the RADIUS authentication server. RADIUS is a
networking protocol providing centralized Authentication,
Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) management for
computers to connect to and use a network service.
In the second field, enter the UDP port of the RADIUS
authentication server. The most commonly used port is
the default, 1812, but this may vary depending on the
RADIUS server you are using.
Auth Server Secret Enter the password. A shared
secret is a case-sensitive text string used to validate
communication between two RADIUS devices.
Show Check the box if you want to view the characters of
the Auth Server Secret.
Accounting Server If you are using a separate accounting
server, check the Enable box.
Acct Server IP/Port If the Accounting Server is enabled,
enter the IP address of the accounting server.
In the second field, enter the UDP port of the RADIUS
accounting server. The most commonly used port is the
default, 1813, but this may vary depending on the RADIUS
server you are using.
Acct Server Secret If the Accounting Server is enabled,
enter the password. A shared secret is a case-sensitive
text string used to validate communication between two
RADIUS devices.
Show Check the box if you want to view the characters of
the Acct Server Secret.
Mac ACL This option enables the MAC address Access
Control List. For details, refer to “MAC ACL” on page 25.
WEP
Authentication Type Select one of the following
authentication methods:
• Open This option is selected by default. The station is
authenticated automatically by the AP.
• Shared Key The station is authenticated after the
challenge, which is generated by the AP.
WEP Key Length Specifies the length of the WEP security
key. Select one of the two options:
• 64‑bit This option is selected by default. A 64-bit key is
10 HEX or 5 ASCII characters in length.
• 128‑bit The 128-bit option provides more security and
is 26 HEX or 13 ASCII characters in length.
Key Type Specifies the character format of the WEP key:
• HEX By default, this option uses hexadecimal
characters. 0-9, A-F, or a-f are valid characters.
• ASCII ASCII uses the standard English alphabet and
numeric characters.
WEP Key Enter the appropriate WEP encryption key:
Type HEX ASCII
64-bit
128-bit
10 hexadecimal characters
(0-9, A-F or a-f)
Example: 00112233AA
26 hexadecimal characters
(0-9, A-F or a-f)
Example:
00112233445566778899AABBCC
Key Index Specifies the index of the WEP key used. Four
different WEP keys can be configured at the same time,
but only one is used. To set the effective key, select 1, 2, 3,
or 4.
Mac ACL This option enables the MAC address Access
Control List. For details, refer to “MAC ACL” on page 25.
5 ASCII characters
Example:
ubnt1
13 ASCII characters
Example:
ubntproducts1
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
23
Page 27

Chapter 4: Wireless TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
WPA or WPA2
The configuration options are the same for all of the WPA
and WPA2 options. WPA2-AES is the strongest security
method. If all of the wireless devices on your network
support this option, we recommend that you select it.
WPA Authentication Specify one of the following WPA
key selection methods:
• PSK Pre-shared Key method (selected by default).
• EAP EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol)
IEEE 802.1x authentication method. This method is
commonly used in enterprise networks.
PSK
WPA Preshared Key Specify a passphrase. The preshared
key is an alpha-numeric password between 8 and 63
characters long.
Show Check the box if you want to view the characters of
the WEP Preshared Key.
Mac ACL This option enables the MAC address Access
Control List. For details, refer to “MAC ACL” on page 25.
EAP
EAP ‑ Station Mode
The options below apply in Station mode only.
EAP‑TTLS / EAP‑PEAP Select the authentication protocol
used by your AP.
MSCHAPV2 Inner authentication protocol.
WPA Anonymous Identity Enter the identification
credential used by the supplicant for EAP authentication
in unencrypted form.
WPA User Name Enter the identification credential used
by the supplicant for EAP authentication.
WPA User Password Enter the password credential used
by the supplicant for EAP authentication.
Show Check the box if you want to view the characters of
the WPA User Password.
EAP‑ Access Point Mode
The options below apply in Access Point or AP‑Repeater
mode only.
Auth Server IP/Port In the first field, enter the IP
address of the RADIUS authentication server. RADIUS is a
networking protocol providing centralized Authentication,
Authorization, and Accounting (AAA) management for
computers to connect to and use a network service.
In the second field, enter the UDP port of the RADIUS
authentication server. The most commonly used port is
1812, but this may vary depending on the RADIUS server
you are using.
Auth Server Secret Enter the password. A shared
secret is a case-sensitive text string used to validate
communication between two RADIUS devices.
Show Check the box if you want to view the characters of
the Auth Server Secret.
Accounting Server If you are using a separate accounting
server, check the Enable box.
Acct Server IP/Port If the Accounting Server is enabled,
enter the IP address of the accounting server.
In the second field, enter the UDP port of the RADIUS
accounting server. The most commonly used port is 1813,
but this may vary depending on the RADIUS server you
are using.
Acct Server Secret If the Accounting Server is enabled,
enter the password. A shared secret is a case-sensitive
text string used to validate communication between two
RADIUS devices.
Show Check the box if you want to view the characters of
the Acct Server Secret.
Mac ACL This option enables the MAC address Access
Control List. For details, refer to “MAC ACL” on page 25.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
24
Page 28

MAC ACL
The options below apply in Access Point or AP‑Repeater
mode only.
MAC ACL The MAC address Access Control List (ACL) lets
you allow or deny clients connectivity to the device. When
enabled, you have the following options:
Policy Select one of the policy types:
• Allow Wireless clients on the list can access the device.
Any wireless client that is not on the list is denied access
to the device.
• Deny Wireless clients on the list are denied access to
the device. Any wireless client that is not on the list can
access the device.
• ACL To add MAC addresses of wireless clients, click ACL.
Chapter 4: Wireless TabairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
- Enabled The policy is applied to this wireless client.
- MAC Enter the MAC address in this format:
XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX (each X represents a valid
hexadecimal character: 0-9, A-F, or a-f).
- Comment Enter a description of the wireless client.
- Action Click Add to add the MAC address of a
wireless client. Click Del to remove the MAC address
of a wireless client. Click Edit to make changes to an
entry.
Note: MAC ACL should be used in combination
with a security method such as WPA or WPA2.
It should not be used as the only method of
security on your network.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
25
Page 29

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Chapter 5: Network Tab
The Network tab allows you to configure bridge or routing
functionality and IP settings.
Change To save or test your changes, click Change.
A new message appears. You have three options:
• Apply To immediately save your changes, click Apply.
• Test To try the changes without saving them, click
Test. To keep the changes, click Apply. If you do not
click Apply within 180 seconds (the countdown is
displayed), the device times out and resumes its earlier
configuration.
• Discard To cancel your changes, click Discard.
Network Role
airOS supports the following modes: Bridge, Router, and
SOHO Router. Only the routers can support the router
modes.
Network Mode Specify the Network Mode of the device.
The default setting is device-specific. The mode depends
on the network topology requirements.
Bridge mode is adequate if you have a very small network.
However, a larger network has significantly more traffic
that requires management by a device using Router or
SOHO Router mode. Router or SOHO Router mode keeps
broadcast traffic within its respective broadcast domain,
so that broadcast traffic will not overload the overall traffic
in the network.
• Bridge The device acts as a transparent bridge and
operates in Layer 2, like an unmanaged switch.
There is only one IP address for the device in Bridge
mode.
• Router The device is separated into two networks or
subnets (one WAN and one LAN). In Router mode, the
WLAN functions as the Wide Area Network (WAN). The
Ethernet ports function as the LAN. Each wireless or
wired interface on the WAN or LAN has an IP address.
For example, Router mode is used in a typical Customer
Premises Equipment (CPE) installation. The device acts
as the demarcation (demarc) point between the CPE
and Wireless Internet Service Provider (WISP), with the
wireless interface of the device connecting to the WISP.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
26
Page 30

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
The following diagram shows the NanoStation at a
residence wirelessly connecting to a WISP tower.
WISP Tower
NanoStation
• SOHO Router SOHO (Small Office/Home Office) Router
mode is derived from Router mode. In SOHO Router
mode, the main Ethernet port labeled <···> functions
as the WAN port. The WLAN and other Ethernet ports
function as the LAN. Each wireless or wired interface on
the WAN or LAN has an IP address.
For example, SOHO Router mode is used in an
installation where the main Ethernet port connects to
the Internet Service Provider (ISP) via a modem. The
following diagram shows the airRouter HP wired to a
modem, which is wired to the ISP.
ISP
Disable Network Disables the WLAN, LAN, or WAN
interface(s). Use this setting with caution as you cannot
establish any Layer 2 or Layer 3 connection through the
disabled interface. You cannot access the device from
the wireless or wired network that is connected to the
disabled interface.
For more information about the Network Mode you have
specified, go to:
• “Bridge” on page 27
• “Router” on page 31
• “SOHO Router” on page 40
Bridge
In Bridge mode, the device forwards all network
management and data packets from one network
interface to the other without any intelligent routing. For
simple applications, this provides an efficient and fully
transparent network solution.
There is no network segmentation, and the broadcast
domain is the same. Bridge mode does not block any
broadcast or multicast traffic. You can configure additional
firewall settings for Layer 2 packet filtering and access
control.
WLAN and LAN interfaces belong to the same network
segment and share the same IP address space. They form
the virtual bridge interface while acting as bridge ports.
The device features IP settings for management purposes.
Configuration Mode
The Network tab has two views, Simple and Advanced.
Simple Basic configuration settings are available.
Advanced configuration settings are hidden.
Advanced Displays the advanced configuration settings:
• Management Interface (in “Management Network
Settings” on page 28)
• “Interfaces” on page 29
• “IP Aliases” on page 29
• “VLAN Network” on page 29
• “Bridge Network” on page 29
• “Firewall” on page 30
• “Static Routes” on page 30
• “Traffic Shaping” on page 31
Modem and airRouter HP
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
27
Page 31

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Management Network Settings
Management Interface (Available in Advanced view.)
Select the interface used for management.
Management IP Address The device can use a static IP
address or obtain an IP address from its DHCP server.
• DHCP The local DHCP server assigns a dynamic IP
address, gateway IP address, and DNS address to the
device.
- DHCP Fallback IP Specify the IP address for the
device to use if a DHCP server is not found.
- DHCP Fallback Netmask Specify the netmask for the
device to use if a DHCP server is not found.
• Static Assign static IP settings to the device.
Note: IP settings should be consistent with the
address space of the device’s network segment.
- IP Address Specify the IP address of the device. This
IP will be used for device management purposes.
- Netmask When the netmask is expanded into its
binary form, it provides a mapping to define which
portions of the IP address range are used for the
network devices and which portions are used for host
devices. The netmask defines the address space of
the device’s network segment. The 255.255.255.0 (or
“/24”) netmask is commonly used on many Class C IP
networks.
- Gateway IP Typically, this is the IP address of the host
router, which provides the point of connection to the
Internet. This can be a DSL modem, cable modem, or
WISP gateway router. The device directs data packets
to the gateway if the destination host is not within the
local network.
Note: In Bridge mode, the gateway IP address
should be from the same address space (on the
same network segment) as the device.
- Primary DNS IP Specify the IP address of the primary
DNS (Domain Name System) server.
- Secondary DNS Specify the IP address of the
secondary DNS server. This entry is optional and used
only if the primary DNS server is not responding.
MTU (Available in Simple view.) The Maximum
Transmission Unit (MTU) is the maximum packet size (in
bytes) that a network can transmit. The default is 1500.
Management VLAN (Available in Simple view.) If enabled,
automatically creates a management Virtual Local Area
Network (VLAN).
• VLAN ID Enter a unique VLAN ID from 2 to 4094.
Auto IP Aliasing If enabled, automatically generates an
IP address for the corresponding WLAN/LAN interface.
The generated IP address is a unique Class B IP address
from the 169.254.X.Y range (netmask 255.255.0.0), which
is intended for use within the same network segment only.
The Auto IP always starts with 169.254.X.Y, with X and Y
as the last two octets from the MAC address of the device.
For example, if the MAC is 00:15:6D:A3:04:FB, then the
generated unique Auto IP will be 169.254.4.251.
The Auto IP Aliasing setting can be useful because you
can still access and manage devices even if you lose,
misconfigure, or forget their IP addresses. Because an
Auto IP address is based on the last two octets of the MAC
address, you can determine the IP address of a device if
you know its MAC address.
STP Multiple interconnected bridges create larger
networks using IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol
(STP), which is used for finding the shortest path within a
network and eliminating loops from the topology.
If enabled, the device bridge communicates with other
network devices by sending and receiving Bridge Protocol
Data Units (BPDU). STP should be disabled (default setting)
when the device is the only bridge on the LAN or when
there are no loops in the topology, as there is no need for
the bridge to use STP in this case.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
28
Page 32

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Interfaces
(Available in Advanced view.) The Maximum Transmission
Unit (MTU) is the maximum packet size (in bytes) that a
network can transmit. You can configure a different MTU
for each of the interfaces.
Click the + button to display the Interfaces section.
Interface Displays the name of the interface.
MTU The default is 1500.
Action Click Edit to change the MTU. Then click Save to
apply your change.
IP Aliases
(Available in Advanced view.) You can configure IP
aliases for the local and external network interfaces for
management purposes. For example, you may need
multiple IP addresses (one private IP address and one
public IP address) for a single device. If a CPE uses PPPoE,
the CPE obtains a public PPPoE address, but the network
administrator assigns an internal IP alias to the device. This
way the network administrator can manage the device
internally without going through the PPPoE server.
Click the + button to display the IP Aliases section.
Enabled Enables the specific IP alias. All the added IP
aliases are saved in the system configuration file; however,
only the enabled IP aliases are active on the device.
Interface Select the appropriate interface.
IP Address The alternative IP address for the interface.
This can be used for routing or device management
purposes.
Netmask The network address space identifier for the IP
alias.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the IP alias.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Adds a IP alias.
• Edit Make changes to an IP alias. Click Save to save your
changes.
• Del Delete an IP alias.
VLAN Network
(Available in Advanced view.) You can create multiple
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs). Click the + button to
display the VLAN Network section.
Enabled Enables the specific VLAN. All the added VLANs
are saved in the system configuration file; however, only
the enabled VLANs are active on the device.
Interface Select the appropriate interface.
VLAN ID The VLAN ID is a unique value assigned to
each VLAN at a single device; every VLAN ID represents a
different VLAN. The VLAN ID range is 2 to 4094.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the VLAN.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a VLAN.
• Edit Make changes to a VLAN. Click Save to save your
changes.
• Del Delete a VLAN.
Bridge Network
(Available in Advanced view.) You can create one or
more bridge networks if you need complete Layer 2
transparency. This is similar to using a switch – all traffic
flows through a bridge, in one port and out another
port, regardless of VLANs or IP addresses. For example,
if you want to use the same IP subnet on both sides of a
device, then you create a bridge network. There are many
different scenarios that could require bridged interfaces,
so the Bridge Network section is designed to allow
flexibility.
Click the + button to display the Bridge Network section.
Enabled Enables the specific bridge network. All
the added bridge networks are saved in the system
configuration file; however, only the enabled bridge
networks are active on the device.
Interface The interface is automatically displayed.
STP Multiple interconnected bridges create larger
networks using IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol
(STP), which is used for finding the shortest path within a
network and eliminating loops from the topology.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
29
Page 33

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
If enabled, the device bridge communicates with other
network devices by sending and receiving Bridge Protocol
Data Units (BPDU). STP should be disabled (default setting)
when the device is the only bridge on the LAN or when
there are no loops in the topology, as there is no need for
the bridge to use STP in this case.
Ports Select the appropriate ports for your bridge
network. (Virtual ports are available if you have created
VLANs.)
• Add Select a port.
• Del Delete a port.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the bridge network.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a bridge network.
• Del Delete a bridge network.
Firewall
(Available in Advanced view.) You can configure firewall
rules for the local and external network interfaces. Click
the + button to display the Firewall section.
Source Port Check the box and specify the source port of
the packet (specified within the packet header). Usually it
is the port of the host system application that sends the
packets.
Destination IP/Mask Check the box and specify the
destination IP of the packet (specified within the packet
header). Usually it is the IP of the system which the packet
is addressed to. The mask is in slash notation. For example,
if you enter 192.168.1.0/24, you are entering the range of
192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.255.
Destination Port Check the box and specify the
destination port of the packet (specified within the
packet header). Usually it is the port of the host system
application which the packet is addressed to.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the firewall rule.
All active firewall entries are stored in the FIREWALL chain
of the ebtables filter table.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a firewall rule.
• Edit Make changes to a firewall rule. Click Save to save
your changes.
• Del Delete a firewall rule.
Enable Enables firewall functionality.
Enabled Enables the specific firewall rule. All the added
firewall rules are saved in the system configuration file;
however, only the enabled firewall rules are active on the
device.
Target To allow packets to pass through the firewall
unmodified, select ACCEPT. To block packets and send no
response, select DROP.
Interface Select the appropriate interface where the
firewall rule is applied. To apply the firewall rule to all
interfaces, select ANY.
IP Type Sets which specific Layer 3 protocol type (IP, ICMP,
TCP, UDP) should be filtered.
! Can be used to invert the Source IP/Mask, Source Port,
Destination IP/Mask, and/or Destination Port filtering
criteria. For example, if you enable ! (Not) for the specified
Destination Port value 443, then the filtering criteria will
be applied to all the packets sent to any Destination Port
except port 443, which is commonly used by HTTPS.
Source IP/Mask Check the box and specify the source IP
of the packet (specified within the packet header). Usually
it is the IP of the host system that sends the packets.
The mask is in slash notation. For example, if you enter
192.168.1.0/24, you are entering the range of 192.168.1.0
to 192.168.1.255.
Static Routes
(Available in Advanced view.) You can manually add
static routing rules to the system routing table; you can
set a rule that a specific target IP address (or range of IP
addresses) passes through a specific gateway. Click the +
button to display the Static Routes section.
Enabled Enables the specific static route. All the added
static routes are saved in the system configuration file;
however, only the enabled static routes are active on the
device.
Target Network IP Specify the IP address of the
destination.
Netmask Specify the netmask of the destination.
Gateway IP Specify the IP address of the gateway.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the static route.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a static route.
• Edit Make changes to a static route. Click Save to save
your changes.
• Del Delete a static route.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
30
Page 34

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Traffic Shaping
(Available in Advanced view.) Traffic Shaping controls
bandwidth from the perspective of the client (who is
connected on the Ethernet interface). Bursting allows
fast downloads when a user downloads small files (for
example, viewing different pages of a website), but
prevents a user from using excessive bandwidth when
downloading large files (for example, streaming a movie).
As Layer 3 QoS, you can limit the traffic at the device at the
port level, based on a rate limit you define. Each port has
two types of traffic:
• Ingress traffic entering the port
• Egress traffic exiting the port
We recommend using Traffic Shaping to control egress
traffic, because it is more efficient in the egress direction.
When a port accepts ingress traffic, it cannot control how
quickly the traffic arrives – the sending device controls
that traffic. However, when a port sends out egress traffic,
it can control how quickly the traffic exits.
Bursting allows the bandwidth to spike higher than the
maximum bandwidth you configure in the Ingress and
Egress Rate settings – for a short period of time. Once the
Ingress or Egress Burst (volume of data) is used up, the
throughput drops back down to the corresponding Ingress
or Egress Rate setting (maximum bandwidth) you have set.
For example, you have the following conditions:
• Ingress Burst is set to 2048 kBytes.
• Ingress Rate is set to 512 kbit/s.
• Actual maximum bandwidth is 1024 kbit/s.
Bursting allows 2048 kBytes to pass at 1024 kbit/s before
throttling down to 512 kbit/s.
Egress
• Enable Enables the egress values.
• Rate, kbit/s Specify the maximum bandwidth value (in
kilobits per second) for traffic passing from the Ethernet
interface to the wireless interface.
• Burst, kBytes Specify the data volume (in kilobytes)
that is allowed before the egress maximum bandwidth
applies.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a rule.
• Edit Make changes to a traffic shaping rule. Click Save
to save your changes.
• Del Deletes a traffic shaping rule.
Router
In Router mode, the device operates in Layer 3 to perform
routing and enable network segmentation – wireless
clients are on a different IP subnet. Router mode blocks
broadcasts and can pass through multicast packet traffic.
You can configure additional firewall settings for Layer 3
packet filtering and access control.
The device can act as a DHCP server and use Network
Address Translation (Masquerading), which is widely used
by APs. NAT acts as the firewall between the LAN and
WAN.
In Router mode, the WLAN functions as the Wide Area
Network (WAN). The Ethernet ports function as the LAN.
Each wireless or wired interface on the WAN or LAN has
an IP address. For example, the following diagram shows
the NanoStation at a residence wirelessly connecting to a
WISP tower.
Enable Enables bandwidth control on the device.
Enabled Enables the specific rule. All the added rules are
saved in the system configuration file; however, only the
enabled rules are active on the device.
Interface Select the appropriate interface.
Ingress
• Enable Enables the ingress values.
• Rate, kbit/s Specify the maximum bandwidth value (in
kilobits per second) for traffic passing from the wireless
interface to the Ethernet interface.
• Burst, kBytes Specify the data volume (in kilobytes)
that is allowed before the ingress maximum bandwidth
applies.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
WISP Tower
NanoStation
31
Page 35

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Configuration Mode
The Network tab has two views, Simple and Advanced.
Simple Displays the basic configuration settings:
• “WAN Network Settings” on page 32
• “LAN Network Settings” on page 35
• “Port Forwarding” on page 38
• “Multicast Routing Settings” on page 39
Advanced configuration settings are hidden.
Advanced Displays the advanced configuration settings:
• “Management Network Settings” on page 36
• “Interfaces” on page 36
• “IP Aliases” on page 37
• “VLAN Network” on page 37
• “Bridge Network” on page 37
• “Firewall” on page 38
• “Static Routes” on page 38
• “Traffic Shaping” on page 39
WAN Network Settings
WAN Interface Select the interface used for
management.
WAN IP Address The IP address of the WAN interface
connected to the external network. You can use this IP
address for routing and device management purposes.
The device can use one of the following:
• “DHCP” on page 32
• “Static” on page 33
• “PPPoE” on page 34
DHCP
The external DHCP server assigns a dynamic IP address,
gateway IP address, and DNS address to the device.
DHCP Fallback IP Specify the IP address for the device to
use if an external DHCP server is not found.
DHCP Fallback Netmask Specify the netmask for the
device to use if an external DHCP server is not found.
MTU (Available in Simple view.) The Maximum
Transmission Unit (MTU) is the maximum packet size (in
bytes) that a network can transmit. The default is 1500.
NAT Network Address Translation (NAT ) enables packets
to be sent from the external network (WAN) to the local
interface IP address and then sub-routed to other client
devices on its local network while the airOS device is
operating in Access Point or AP‑Repeater mode. Packets are
routed in the reverse direction in Station mode.
NAT is implemented using the masquerade type firewall
rules. NAT firewall entries are stored in the iptables
nat table. Specify static routes to allow packets to pass
through the airOS device if NAT is disabled.
• NAT Protocol If NAT is enabled, you can modify data
packets to allow them to pass through the device. To
avoid modification of some specific types of packets,
such as SIP, PPTP, FTP, or RTSP, then uncheck the
respective box(es).
Block management access To block device management
from the WAN interface, check this box. This feature makes
Router mode more secure if the device has a public IP
address.
DMZ DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) specifically allows one
computer/device behind NAT to become “demilitarized”,
so all ports from the public network are forwarded to the
ports of this private network, similar to a 1:1 NAT.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
32
Page 36

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
• DMZ Management Ports The web management port
(TCP/IP port 80 by default) of the airOS device will be
used for the host device. The airOS device responds to
requests from the external network as if it were the host
device that is specified with the DMZ IP address. DMZ
Management Ports is disabled by default; the device is
accessible from the WAN port. If DMZ Management Ports
is enabled, all management ports will be forwarded to
the device, so you’ll only be able to access the device
from the LAN side.
• DMZ IP Specify the IP address of the local host network
device. The DMZ host device will be completely exposed
to the external network.
Auto IP Aliasing If enabled, automatically generates an
IP address for the corresponding WLAN/LAN interface.
The generated IP address is a unique Class B IP address
from the 169.254.X.Y range (netmask 255.255.0.0), which
is intended for use within the same network segment only.
The Auto IP always starts with 169.254.X.Y, with X and Y
as the last two octets from the MAC address of the device.
For example, if the MAC is 00:15:6D:A3:04:FB, then the
generated unique Auto IP will be 169.254.4.251.
The Auto IP Aliasing setting can be useful because you
can still access and manage devices even if you lose,
misconfigure, or forget their IP addresses. Because an
Auto IP address is based on the last two octets of the MAC
address, you can determine the IP address of a device if
you know its MAC address.
MAC Address Cloning When enabled, you can change
the MAC address of the respective interface. This is
especially useful if your ISP only assigns one valid IP
address and it is associated to a specific MAC address. This
is usually used by cable operators or some WISPs.
• MAC Address Enter the MAC address you want to clone
to the respective interface. This becomes the new MAC
address of the interface.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
Static
Assign static IP settings to the device.
Note: IP settings should be consistent with the
address space of the device’s network segment.
IP Address Specify the IP address of the device. This IP
will be used for device management purposes.
Netmask When the netmask is expanded into its
binary form, it provides a mapping to define which
portions of the IP address range are used for the network
devices and which portions are used for host devices.
The netmask defines the address space of the device’s
network segment. The 255.255.255.0 (or “/24”) netmask is
commonly used on many Class C IP networks.
Gateway IP Typically, this is the IP address of the host
router, which provides the point of connection to the
Internet. This can be a DSL modem, cable modem, or
WISP gateway router. The device directs data packets to
the gateway if the destination host is not within the local
network.
Primary DNS IP Specify the IP address of the primary DNS
(Domain Name System) server.
Secondary DNS IP Specify the IP address of the
secondary DNS server. This entry is optional and used only
if the primary DNS server is not responding.
MTU (Available in Simple view.) The Maximum
Transmission Unit (MTU) is the maximum packet size (in
bytes) that a network can transmit. The default is 1500.
NAT Network Address Translation (NAT ) enables packets
to be sent from the external network (WAN) to the local
interface IP address and then sub-routed to other client
devices on its local network while the airOS device is
operating in Access Point or AP‑Repeater mode. Packets are
routed in the reverse direction in Station mode.
NAT is implemented using the masquerade type firewall
rules. NAT firewall entries are stored in the iptables
nat table. Specify static routes to allow packets to pass
through the airOS device if NAT is disabled.
33
Page 37

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
• NAT Protocol If NAT is enabled, you can modify data
packets to allow them to pass through the device. To
avoid modification of some specific types of packets,
such as SIP, PPTP, FTP, or RTSP, then uncheck the
respective box(es).
Block management access To block device management
from the WAN interface, check this box. This feature makes
Router mode more secure if the device has a public IP
address.
DMZ DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) specifically allows one
computer/device behind NAT to become “demilitarized”,
so all ports from the public network are forwarded to the
ports of this private network, similar to a 1:1 NAT.
• DMZ Management Ports The web management port
(TCP/IP port 80 by default) of the airOS device will be
used for the host device. The airOS device responds to
requests from the external network as if it were the host
device that is specified with the DMZ IP address. DMZ
Management Ports is disabled by default; the device is
accessible from the WAN port. If DMZ Management Ports
is enabled, all management ports will be forwarded to
the device, so you’ll only be able to access the device
from the LAN side.
• DMZ IP Specify the IP address of the local host network
device. The DMZ host device will be completely exposed
to the external network.
Auto IP Aliasing If enabled, automatically generates an
IP address for the corresponding WLAN/LAN interface.
The generated IP address is a unique Class B IP address
from the 169.254.X.Y range (netmask 255.255.0.0), which
is intended for use within the same network segment only.
The Auto IP always starts with 169.254.X.Y, with X and Y
as the last two octets from the MAC address of the device.
For example, if the MAC is 00:15:6D:A3:04:FB, then the
generated unique Auto IP will be 169.254.4.251.
The Auto IP Aliasing setting can be useful because you
can still access and manage devices even if you lose,
misconfigure, or forget their IP addresses. Because an
Auto IP address is based on the last two octets of the MAC
address, you can determine the IP address of a device if
you know its MAC address.
MAC Address Cloning When enabled, you can change
the MAC address of the respective interface. This is
especially useful if your ISP only assigns one valid IP
address and it is associated to a specific MAC address. This
is usually used by cable operators or some WISPs.
• MAC Address Enter the MAC address you want to clone
to the respective interface. This becomes the new MAC
address of the interface.
PPPoE
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) is a virtual
private and secure connection between two systems
that enables encapsulated data transport. Subscribers
sometimes use PPPoE to connect to Internet Service
Providers (ISPs), typically DSL providers.
Select PPPoE to configure a PPPoE tunnel. You can
configure only the external network interface as a PPPoE
client because all the traffic will be sent via this tunnel.
After the PPPoE connection is established, the device will
obtain the IP address, default gateway IP, and DNS server
IP address from the PPPoE server. The broadcast address
is used to discover the PPPoE server and establish the
tunnel.
If there is a PPPoE connection established, then the IP
address of the PPP interface will be displayed on the
Main tab next to the PPP interface statistics; otherwise
a Not Connected message and Reconnect button will be
displayed. To re-connect a PPPoE tunnel, click Reconnect.
Username Specify the username to connect to the PPPoE
server; this must match the username configured on the
PPPoE server.
Password Specify the password to connect to the PPPoE
server; this must match the password configured on the
PPPoE server.
Show Check the box if you want to view the characters of
the password.
Service Name Specify the name of the PPPoE service.
Fallback IP Specify the IP address for the device to use if
the PPPoE server does not assign an IP address.
Fallback Netmask Specify the netmask for the device to
use if the PPPoE server does not assign a netmask.
MTU/MRU The size (in bytes) of the Maximum
Transmission Unit (MTU) and Maximum Receive Unit
(MRU) used for data encapsulation during transfer through
the PPP tunnel. The default value is 1492.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
34
Page 38

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Encryption Enables the use of Microsoft Point-to-Point
Encryption (MPPE).
NAT Network Address Translation (NAT ) enables packets
to be sent from the external network (WAN) to the local
interface IP address and then sub-routed to other client
devices on its local network while the airOS device is
operating in Access Point or AP‑Repeater mode. Packets are
routed in the reverse direction in Station mode.
NAT is implemented using the masquerade type firewall
rules. NAT firewall entries are stored in the iptables
nat table. Specify static routes to allow packets to pass
through the airOS device if NAT is disabled.
• NAT Protocol If NAT is enabled, you can modify data
packets to allow them to pass through the device. To
avoid modification of some specific types of packets,
such as SIP, PPTP, FTP, or RTSP, then uncheck the
respective box(es).
Block management access To block device management
from the WAN interface, check this box. This feature makes
Router mode more secure if the device has a public IP
address.
DMZ DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) specifically allows one
computer/device behind NAT to become “demilitarized”,
so all ports from the public network are forwarded to the
ports of this private network, similar to a 1:1 NAT.
• DMZ Management Ports The web management port
(TCP/IP port 80 by default) of the airOS device will be
used for the host device. The airOS device responds to
requests from the external network as if it were the host
device that is specified with the DMZ IP address. DMZ
Management Ports is disabled by default; the device is
accessible from the WAN port. If DMZ Management Ports
is enabled, all management ports will be forwarded to
the device, so you’ll only be able to access the device
from the LAN side.
• DMZ IP Specify the IP address of the local host network
device. The DMZ host device will be completely exposed
to the external network.
Auto IP Aliasing If enabled, automatically generates an
IP address for the corresponding WLAN/LAN interface.
The generated IP address is a unique Class B IP address
from the 169.254.X.Y range (netmask 255.255.0.0), which
is intended for use within the same network segment only.
The Auto IP always starts with 169.254.X.Y, with X and Y
as the last two octets from the MAC address of the device.
For example, if the MAC is 00:15:6D:A3:04:FB, then the
generated unique Auto IP will be 169.254.4.251.
The Auto IP Aliasing setting can be useful because you
can still access and manage devices even if you lose,
misconfigure, or forget their IP addresses. Because an
Auto IP address is based on the last two octets of the MAC
address, you can determine the IP address of a device if
you know its MAC address.
MAC Address Cloning When enabled, you can change
the MAC address of the respective interface. This is
especially useful if your ISP only assigns one valid IP
address and it is associated to a specific MAC address. This
is usually used by cable operators or some WISPs.
• MAC Address Enter the MAC address you want to clone
to the respective interface. This becomes the new MAC
address of the interface.
LAN Network Settings
LAN Interface The interface is displayed. Click Del to
delete the interface. If there is no interface selected, select
an interface from the Add LAN drop-down list, and click
Add.
IP Address The IP address of the LAN (including WLAN)
interface connected to the local network. This IP will
be used for routing of the local network; it will be the
gateway IP for all the devices on the local network. This IP
address is used for management of the device.
Netmask Defines the device IP classification for the
chosen IP address range. 255.255.255.0 is a typical
netmask value for Class C networks, which support the
IP address range of 192.0.0.x to 223.255.255.x. A Class
C network netmask uses 24 bits to identify the network
(alternative notation “/24”) and 8 bits to identity the host.
MTU (Available in Simple view.) The Maximum
Transmission Unit (MTU) is the maximum packet size (in
bytes) that a network can transmit. The default is 1500.
DHCP Server The built-in DHCP server assigns IP
addresses to clients connected to the wireless interface
and LAN interface while the device is operating in Access
Point or AP‑Repeater wireless mode. The built-in DHCP
server assigns IP addresses to clients connected to the
LAN interface while the device is operating in Station
mode.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
35
Page 39

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
• Disabled The device does not assign local IP addresses.
• Enabled The device assigns IP addresses to client
devices on the local network.
• Relay Relays DHCP messages between DHCP clients
and DHCP servers on different IP networks.
- DHCP Server IP Specify the IP address of the DHCP
server that should get the DHCP messages.
- Agent-ID Specify the identifier of the DHCP relay
agent.
UPnP Allows the use of Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
for gaming, videos, chat, conferencing, and other
applications.
Add LAN (Available in Advanced view.) Select an interface,
and then click Add.
- Range Start and End Determines the range of IP
addresses assigned by the DHCP server.
- Netmask Defines the device IP classification for the
chosen IP address range. 255.255.255.0 is a typical
netmask value for Class C networks, which support
an IP address range of 192.0.0.x to 223.255.255.x. A
Class C network netmask uses 24 bits to identify the
network (alternative notation “/24”) and 8 bits to
identity the host.
- Lease Time The IP addresses assigned by the DHCP
server are valid only for the duration specified by
the lease time. Increasing the time ensures client
operation without interruption, but could introduce
potential conflicts. Decreasing the lease time avoids
potential address conflicts, but might cause more
slight interruptions to the client while it acquires a
new IP address from the DHCP server. The time is
expressed in seconds.
- DNS Proxy The Domain Name System (DNS) proxy
server forwards the DNS requests from the hosts on
the local network to the DNS server.
Management Network Settings
Management Interface (Available in Advanced view.)
Select the interface used for management.
Interfaces
(Available in Advanced view.) The Maximum Transmission
Unit (MTU) is the maximum packet size (in bytes) that a
network can transmit. You can configure a different MTU
for each of the interfaces.
Click the + button to display the Interfaces section.
Interface Displays the name of the interface.
MTU The default is 1500.
Action Click Edit to change the MTU. Then click Save to
apply your change.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
36
Page 40

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
IP Aliases
(Available in Advanced view.) You can configure IP
aliases for the local and external network interfaces for
management purposes. For example, you may need
multiple IP addresses (one private IP address and one
public IP address) for a single device. If a CPE uses PPPoE,
the CPE obtains a public PPPoE address, but the network
administrator assigns an internal IP alias to the device. This
way the network administrator can manage the device
internally without going through the PPPoE server.
Click the + button to display the IP Aliases section.
Enabled Enables the specific IP alias. All the added IP
aliases are saved in the system configuration file; however,
only the enabled IP aliases are active on the device.
Interface Select the appropriate interface.
IP Address The alternative IP address for the interface.
This can be used for routing or device management
purposes.
Netmask The network address space identifier for the IP
alias.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the IP alias.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add an IP alias.
• Edit Make changes to an IP alias. Click Save to save your
changes.
• Del Delete an IP alias.
VLAN Network
(Available in Advanced view.) You can create multiple
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs). Click the + button to
display the VLAN Network section.
Enabled Enables the specific VLAN. All the added VLANs
are saved in the system configuration file; however, only
the enabled VLANs are active on the device.
Interface Select the appropriate interface.
VLAN ID The VLAN ID is a unique value assigned to
each VLAN at a single device; every VLAN ID represents a
different VLAN. The VLAN ID range is 2 to 4094.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the VLAN.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a VLAN.
• Edit Make changes to a VLAN. Click Save to save your
changes.
• Del Delete a VLAN.
Bridge Network
(Available in Advanced view.) You can create one or
more bridge networks if you need complete Layer 2
transparency. This is similar to using a switch – all traffic
flows through a bridge, in one port and out another
port, regardless of VLANs or IP addresses. For example,
if you want to use the same IP subnet on both sides of a
device, then you create a bridge network. There are many
different scenarios that could require bridged interfaces,
so the Bridge Network section is designed to allow
flexibility.
Click the + button to display the Bridge Network section.
Enabled Enables the specific bridge network. All
the added bridge networks are saved in the system
configuration file; however, only the enabled bridge
networks are active on the device.
Interface The interface is automatically displayed.
STP Multiple interconnected bridges create larger
networks using IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol
(STP), which is used for finding the shortest path within a
network and eliminating loops from the topology.
If enabled, the device bridge communicates with other
network devices by sending and receiving Bridge Protocol
Data Units (BPDU). STP should be disabled (default setting)
when the device is the only bridge on the LAN or when
there are no loops in the topology, as there is no need for
the bridge to use STP in this case.
Ports Select the appropriate ports for your bridge
network. (Virtual ports are available if you have created
VLANs.)
• Add Select a port.
• Del Delete a port.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the bridge network.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a bridge network.
• Del Delete a bridge network.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
37
Page 41

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Firewall
(Available in Advanced view.) You can configure firewall
rules for the local and external network interfaces. Click
the + button to display the Firewall section.
Enable Enables firewall functionality.
Enabled Enables the specific firewall rule. All the added
firewall rules are saved in the system configuration file;
however, only the enabled firewall rules are active on the
device.
Target To allow packets to pass through the firewall
unmodified, select ACCEPT. To block packets and send no
response, select DROP.
Interface Select the appropriate interface where the
firewall rule is applied. To apply the firewall rule to all
interfaces, select ANY.
IP Type Sets which specific Layer 3 protocol type (IP, ICMP,
TCP, UDP) should be filtered.
! Can be used to invert the Source IP/Mask, Source Port,
Destination IP/Mask, and Destination Port filtering criteria.
For example, if you enable ! (Not) for the specified
Destination Port value 443, then the filtering criteria will
be applied to all the packets sent to any Destination Port
except port 443, which is commonly used by HTTPS.
Source IP/Mask Check the box and specify the source IP
of the packet (specified within the packet header). Usually
it is the IP of the host system that sends the packets. For
example, if you enter 192.168.1.0/24, you are entering the
range of 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.255.
Source Port Check the box and specify the source port of
the packet (specified within the packet header). Usually it
is the port of the host system application that sends the
packets.
Destination IP/Mask Check the box and specify the
destination IP of the packet (specified within the packet
header). Usually it is the IP of the system which the packet
is addressed to. For example, if you enter 192.168.1.0/24,
you are entering the range of 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.255.
Destination Port Check the box and specify the
destination port of the packet (specified within the
packet header). Usually it is the port of the host system
application which the packet is addressed to.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the firewall rule.
All active firewall entries are stored in the FIREWALL chain
of the iptables filter table.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a firewall rule.
• Edit Make changes to a firewall rule. Click Save to save
your changes.
• Del Delete a firewall rule.
Static Routes
(Available in Advanced view.) You can manually add
static routing rules to the system routing table; you can
set a rule that a specific target IP address (or range of IP
addresses) passes through a specific gateway. Click the +
button to display the Static Routes section.
Enabled Enables the specific static route. All the added
static routes are saved in the system configuration file;
however, only the enabled static routes are active on the
device.
Target Network IP Specify the IP address of the
destination.
Netmask Specify the netmask of the destination.
Gateway IP Specify the IP address of the gateway.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the static route.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a static route.
• Edit Make changes to a static route. Click Save to save
your changes.
• Del Delete a static route.
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding allows specific ports of the hosts on the
local network to be forwarded to the external network
(WAN). This is useful for a number of applications (such
as FTP servers, VoIP, gaming) that require different host
systems to be seen using a single common IP address/
port. Click the + button to display the Port Forwarding
section.
Enabled Enables the specific port forwarding rule. All
the added port forwarding rules are saved in the system
configuration file; however, only the enabled port
forwarding rules are active on the device.
Private IP The IP address of the local host that needs to
be accessible from the external network.
Private Port The TCP or UDP port of the application
running on the local host. The specified port will be
accessible from the external network.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
38
Page 42

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Type The Layer 3 protocol (IP) type that needs to be
forwarded from the local network.
Source IP/mask The IP address and netmask of the
source device.
Public IP/mask The public IP address and netmask of the
device that will accept and forward the connections from
the external network to the local host.
Public Port The TCP or UDP port of the device that will
accept and forward the connections from the external
network to the local host.
Comment Enter a brief description of the port
forwarding functionality, such as FTP server, web server, or
game server.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a port forwarding rule.
• Edit Make changes to a port forwarding rule. Click Save
to save your changes.
• Del Delete a port forwarding rule.
Multicast Routing Settings
With a multicast design, applications can send one copy
of each packet and address it to a group of computers
that want to receive it. This technique addresses packets
to a group of receivers rather than to a single receiver. It
relies on the network to forward the packets to the hosts
that need to receive them. Common routers isolate all the
broadcast (thus multicast) traffic between the local and
external networks; however, the device provides multicast
traffic pass-through functionality.
As Layer 3 QoS, you can limit the traffic at the device at the
port level, based on a rate limit you define. Each port has
two types of traffic:
• Ingress traffic entering the port
• Egress traffic exiting the port
We recommend using Traffic Shaping to control egress
traffic, because it is more efficient in the egress direction.
When a port accepts ingress traffic, it cannot control how
quickly the traffic arrives – the sending device controls
that traffic. However, when a port sends out egress traffic,
it can control how quickly the traffic exits.
Bursting allows the bandwidth to spike higher than the
maximum bandwidth you configure in the Ingress and
Egress Rate settings – for a short period of time. Once the
Ingress or Egress Burst (volume of data) is used up, the
throughput drops back down to the corresponding Ingress
or Egress Rate setting (maximum bandwidth) you have set.
For example, you have the following conditions:
• Ingress Burst is set to 2048 kBytes.
• Ingress Rate is set to 512 kbit/s.
• Maximum bandwidth is 1024 kbit/s.
Bursting allows 2048 kBytes to pass at 1024 kbit/s before
throttling down to 512 kbit/s.
Enable Enables bandwidth control on the device.
Enabled Enables the specific rule. All the added rules are
saved in the system configuration file; however, only the
enabled rules are active on the device.
Interface Select the appropriate interface.
Multicast Routing Enables multicast packet pass-through
between local and external networks while the device is
operating in Router mode. Multicast intercommunication
is based on Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP).
Multicast Upstream Specify the source of multicast
traffic.
Multicast Downstream Specify the destination(s) of
multicast traffic.
Add Add a destination.
Del Delete a destination.
Traffic Shaping
(Available in Advanced view.) Traffic Shaping controls
bandwidth from the perspective of the client (who is
connected on the Ethernet interface). Bursting allows
fast downloads when a user downloads small files (for
example, viewing different pages of a website), but
prevents a user from using excessive bandwidth when
downloading large files (for example, streaming a movie).
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
Ingress
• Enable Enables the ingress values.
• Rate, kbit/s Specify the maximum bandwidth value (in
kilobits per second) for traffic passing from the wireless
interface to the Ethernet interface.
• Burst, kBytes Specify the data volume (in kilobytes)
that is allowed before the ingress maximum bandwidth
applies.
Egress
• Enable Enables the egress values.
• Rate, kbit/s Specify the maximum bandwidth value (in
kilobits per second) for traffic passing from the Ethernet
interface to the wireless interface.
• Burst, kBytes Specify the data volume (in kilobytes)
that is allowed before the egress maximum bandwidth
applies.
39
Page 43

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a rule.
• Edit Make changes to a traffic shaping rule. Click Save
to save your changes.
• Del Delete a rule.
SOHO Router
In SOHO Router mode, the device operates in Layer 3 to
perform routing and enable network segmentation –
wireless clients are on a different IP subnet. SOHO Router
mode blocks broadcasts and can pass through multicast
packet traffic. You can configure additional firewall
settings for Layer 3 packet filtering and access control.
The device can act as a DHCP server and use Network
Address Translation (Masquerading), which is widely used
by APs. NAT acts as the firewall between the LAN and
WAN.
In SOHO Router mode, the main Ethernet port labeled <···>
functions as the WAN port. The WLAN and other Ethernet
ports function as the LAN. Each wireless or wired interface
on the WAN or LAN has an IP address. For example, the
following diagram shows the airRouter HP wired to a
modem, which is wired to the ISP.
ISP
In devices with one Ethernet port (while operating in
Access Point or AP‑Repeater mode), SOHO Router mode
works like Router mode, except that the LAN port works
as a WAN port, and the WLAN works as the local network.
In devices with two or more Ethernet ports, the main
Ethernet port becomes the WAN port, and the WLAN and
other LAN ports become the local network.
Note: Do not use the SOHO Router mode in
combination with Station wireless mode; this may
cause the device to become inaccessible. If this
did happen, reset the device to defaults; press and
hold the Reset button for eight seconds and then
release it.
Configuration Mode
The Network tab has two views, Simple and Advanced.
Simple Displays the basic configuration settings:
• “WAN Network Settings” on page 40
• “LAN Network Settings” on page 44
• “Port Forwarding” on page 47
• “Multicast Routing Settings” on page 47
Advanced configuration settings are hidden.
Advanced Displays the advanced configuration settings:
• “Management Network Settings” on page 45
• “Interfaces” on page 45
• “IP Aliases” on page 45
• “VLAN Network” on page 45
• “Bridge Network” on page 46
• “Firewall” on page 46
• “Static Routes” on page 47
• “Traffic Shaping” on page 48
Modem and airRouter HP
SOHO Router mode only works properly in Access Point or
AP‑Repeater mode, since it has not been designed to act as
a wireless client.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
WAN Network Settings
WAN Interface (Available in Advanced view.) Select the
interface used for management.
WAN IP Address The IP address of the WAN interface
connected to the external network. You can use this IP
address for routing and device management purposes.
40
Page 44

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
The device can use one of the following:
• “DHCP” on page 41
• “Static” on page 42
• “PPPoE” on page 43
DHCP
The external Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
server assigns a dynamic IP address, gateway IP address,
and DNS address to the device.
DHCP Fallback IP Specify the IP address for the device to
use if an external DHCP server is not found.
DHCP Fallback Netmask Specify the netmask for the
device to use if an external DHCP server is not found.
MTU (Available in Simple view.) The Maximum
Transmission Unit (MTU) is the maximum packet size (in
bytes) that a network can transmit. The default is 1500.
NAT Network Address Translation (NAT ) enables packets
to be sent from the external network (WAN) to the local
interface IP address and then sub-routed to other client
devices residing on its local network while the airOS
device is operating in Access Point or AP‑Repeater mode.
NAT is implemented using the masquerade type firewall
rules. NAT firewall entries are stored in the iptables
nat table. Specify static routes to allow packets to pass
through the airOS device if NAT is disabled.
• NAT Protocol If NAT is enabled, you can modify data
packets to allow them to pass through the device. To
avoid modification of some specific types of packets,
such as SIP, PPTP, FTP, or RTSP, then uncheck the
respective box(es).
Block management access By default, device
management from the WAN interface is blocked. This
feature makes SOHO Router mode more secure if the
device has a public IP address.
DMZ DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) specifically allows one
computer/device behind NAT to become “demilitarized”,
so all ports from the public network are forwarded to the
ports of this private network, similar to a 1:1 NAT.
• DMZ Management Ports The web management port
(TCP/IP port 80 by default) of the airOS device will be
used for the host device. The airOS device responds to
requests from the external network as if it were the host
device that is specified with the DMZ IP address. DMZ
Management Ports is disabled by default; the device is
accessible from the WAN port. If DMZ Management Ports
is enabled, all management ports will be forwarded to
the device, so you’ll only be able to access the device
from the LAN side.
• DMZ IP Specify the IP address of the local host network
device. The DMZ host device will be completely exposed
to the external network.
Auto IP Aliasing If enabled, automatically generates an
IP address for the corresponding WLAN/LAN interface.
The generated IP address is a unique Class B IP address
from the 169.254.X.Y range (netmask 255.255.0.0), which
is intended for use within the same network segment only.
The Auto IP always starts with 169.254.X.Y, with X and Y
as the last two octets from the MAC address of the device.
For example, if the MAC is 00:15:6D:A3:04:FB, then the
generated unique Auto IP will be 169.254.4.251.
The Auto IP Aliasing setting can be useful because you
can still access and manage devices even if you lose,
misconfigure, or forget their IP addresses. Because an
Auto IP address is based on the last two octets of the MAC
address, you can determine the IP address of a device if
you know its MAC address.
MAC Address Cloning When enabled, you can change
the MAC address of the respective interface. This is
especially useful if your ISP only assigns one valid IP
address and it is associated to a specific MAC address. This
is usually used by cable operators or some WISPs.
• MAC Address Enter the MAC address you want to clone
to the respective interface. This becomes the new MAC
address of the interface.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
41
Page 45

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Static
Assign static IP settings to the device.
Note: IP settings should be consistent with the
address space of the device’s network segment.
IP Address Specify the IP address of the device. This IP
will be used for device management purposes.
Netmask When the netmask is expanded into its
binary form, it provides a mapping to define which
portions of the IP address range are used for the network
devices and which portions are used for host devices.
The netmask defines the address space of the device’s
network segment. The 255.255.255.0 (or “/24”) netmask is
commonly used on many Class C IP networks.
Gateway IP Typically, this is the IP address of the host
router, which provides the point of connection to the
Internet. This can be a DSL modem, cable modem, or
WISP gateway router. The device directs data packets to
the gateway if the destination host is not within the local
network.
Primary DNS IP Specify the IP address of the primary DNS
(Domain Name System) server.
Secondary DNS IP Specify the IP address of the
secondary DNS server. This entry is optional and used only
if the primary DNS server is not responding.
MTU (Available in Simple view.) The Maximum
Transmission Unit (MTU) is the maximum packet size (in
bytes) that a network can transmit. The default is 1500.
NAT Network Address Translation (NAT ) enables packets
to be sent from the external network (WAN) to the local
interface IP address and then sub-routed to other client
devices residing on its local network while the airOS
device is operating in Access Point or AP‑Repeater mode.
NAT is implemented using the masquerade type firewall
rules. NAT firewall entries are stored in the iptables
nat table. Specify static routes to allow packets to pass
through the airOS device if NAT is disabled.
• NAT Protocol If NAT is enabled, you can modify data
packets to allow them to pass through the device. To
avoid modification of some specific types of packets,
such as SIP, PPTP, FTP, or RTSP, then uncheck the
respective box(es).
Block management access By default, device
management from the WAN interface is blocked. This
feature makes SOHO Router mode more secure if the
device has a public IP address.
DMZ DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) specifically allows one
computer/device behind NAT to become “demilitarized”,
so all ports from the public network are forwarded to the
ports of this private network, similar to a 1:1 NAT.
• DMZ Management Ports The web management port
(TCP/IP port 80 by default) of the airOS device will be
used for the host device. The airOS device responds to
requests from the external network as if it were the host
device that is specified with the DMZ IP address. DMZ
Management Ports is disabled by default; the device is
accessible from the WAN port. If DMZ Management Ports
is enabled, all management ports will be forwarded to
the device, so you’ll only be able to access the device
from the LAN side.
• DMZ IP Specify the IP address of the local host network
device. The DMZ host device will be completely exposed
to the external network.
Auto IP Aliasing If enabled, automatically generates an
IP address for the corresponding WLAN/LAN interface.
The generated IP address is a unique Class B IP address
from the 169.254.X.Y range (netmask 255.255.0.0), which
is intended for use within the same network segment only.
The Auto IP always starts with 169.254.X.Y, with X and Y
as the last two octets from the MAC address of the device.
For example, if the MAC is 00:15:6D:A3:04:FB, then the
generated unique Auto IP will be 169.254.4.251.
The Auto IP Aliasing setting can be useful because you
can still access and manage devices even if you lose,
misconfigure, or forget their IP addresses. Because an
Auto IP address is based on the last two octets of the MAC
address, you can determine the IP address of a device if
you know its MAC address.
MAC Address Cloning When enabled, you can change
the MAC address of the respective interface. This is
especially useful if your ISP only assigns one valid IP
address and it is associated to a specific MAC address. This
is usually used by cable operators or some WISPs.
• MAC Address Enter the MAC address you want to clone
to the respective interface. This becomes the new MAC
address of the interface.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
42
Page 46

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
PPPoE
Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE) is a virtual
private and secure connection between two systems
that enables encapsulated data transport. Subscribers
sometimes use PPPoE to connect to Internet Service
Providers (ISPs), typically DSL providers.
Select PPPoE to configure a PPPoE tunnel. You can
configure only the external network interface as a PPPoE
client because all the traffic will be sent via this tunnel.
After the PPPoE connection is established, the device will
obtain the IP address, default gateway IP, and DNS server
IP address from the PPPoE server. The broadcast address
is used to discover the PPPoE server and establish the
tunnel.
If there is a PPPoE connection established, then the IP
address of the PPP interface will be displayed on the
Main tab next to the PPP interface statistics; otherwise
a Not Connected message and Reconnect button will be
displayed. To re-connect a PPPoE tunnel, click Reconnect.
Username Specify the username to connect to the PPPoE
server; this must match the username configured on the
PPPoE server.
Password Specify the password to connect to the PPPoE
server; this must match the password configured on the
PPPoE server.
Show Check the box if you want to view the characters of
the password.
Service Name Specify the name of the PPPoE service.
Fallback IP Specify the IP address for the device to use if
the PPPoE server does not assign an IP address.
Fallback Netmask Specify the netmask for the device to
use if the PPPoE server does not assign a netmask.
MTU/MRU The size (in bytes) of the Maximum
Transmission Unit (MTU) and Maximum Receive Unit
(MRU) used for data encapsulation during transfer through
the PPP tunnel. The default value is 1492.
Encryption Enables the use of Microsoft Point-to-Point
Encryption (MPPE).
NAT Network Address Translation (NAT ) enables packets
to be sent from the external network (WAN) to the local
interface IP address and then sub-routed to other client
devices residing on its local network while the airOS
device is operating in Access Point or AP‑Repeater mode.
NAT is implemented using the masquerade type firewall
rules. NAT firewall entries are stored in the iptables
nat table. Specify static routes to allow packets to pass
through the airOS device if NAT is disabled.
• NAT Protocol If NAT is enabled, you can modify data
packets to allow them to pass through the device. To
avoid modification of some specific types of packets,
such as SIP, PPTP, FTP, or RTSP, then uncheck the
respective box(es).
Block management access By default, device
management from the WAN interface is blocked. This
feature makes SOHO Router mode more secure if the
device has a public IP address.
DMZ DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) specifically allows one
computer/device behind NAT to become “demilitarized”,
so all ports from the public network are forwarded to the
ports of this private network, similar to a 1:1 NAT.
• DMZ Management Ports The web management port
(TCP/IP port 80 by default) of the airOS device will be
used for the host device. The airOS device responds to
requests from the external network as if it were the host
device that is specified with the DMZ IP address. DMZ
Management Ports is disabled by default; the device is
accessible from the WAN port. If DMZ Management Ports
is enabled, all management ports will be forwarded to
the device, so you’ll only be able to access the device
from the LAN side.
• DMZ IP Specify the IP address of the local host network
device. The DMZ host device will be completely exposed
to the external network.
Auto IP Aliasing If enabled, automatically generates an
IP address for the corresponding WLAN/LAN interface.
The generated IP address is a unique Class B IP address
from the 169.254.X.Y range (netmask 255.255.0.0), which
is intended for use within the same network segment only.
The Auto IP always starts with 169.254.X.Y, with X and Y
as the last two octets from the MAC address of the device.
For example, if the MAC is 00:15:6D:A3:04:FB, then the
generated unique Auto IP will be 169.254.4.251.
The Auto IP Aliasing setting can be useful because you
can still access and manage devices even if you lose,
misconfigure, or forget their IP addresses. Because an
Auto IP address is based on the last two octets of the MAC
address, you can determine the IP address of a device if
you know its MAC address.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
43
Page 47

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
MAC Address Cloning When enabled, you can change
the MAC address of the respective interface. This is
especially useful if your ISP only assigns one valid IP
address and it is associated to a specific MAC address. This
is usually used by cable operators or some WISPs.
• MAC Address Enter the MAC address you want to clone
to the respective interface. This becomes the new MAC
address of the interface.
LAN Network Settings
• Disabled The device does not assign local IP addresses.
• Enabled The device assigns IP addresses to client
devices on the local network.
LAN Interface The interface is displayed. Click Del to
delete the interface. If there is no interface selected, select
an interface from the Add LAN drop-down list, and click
Add.
IP Address The IP address of the LAN (including WLAN)
interface connected to the local network. This IP will
be used for routing of the local network; it will be the
gateway IP for all the devices on the local network. This IP
address is used for management of the device.
Netmask Defines the device IP classification for the
chosen IP address range. 255.255.255.0 is a typical
netmask value for Class C networks, which support the
IP address range of 192.0.0.x to 223.255.255.x. A Class
C network netmask uses 24 bits to identify the network
(alternative notation “/24”) and 8 bits to identity the host.
MTU (Available in Simple view.) The Maximum
Transmission Unit (MTU) is the maximum packet size (in
bytes) that a network can transmit. The default is 1500.
DHCP Server The built-in DHCP server assigns IP
addresses to clients connected to the wireless interface
and LAN interface while the device is operating in Access
Point or AP‑Repeater wireless mode. The built-in DHCP
server assigns IP addresses to clients connected to the
LAN interface while the device is operating in Station
mode.
- Range Start and End Determines the range of IP
addresses assigned by the DHCP server.
- Netmask Defines the device IP classification for the
chosen IP address range. 255.255.255.0 is a typical
netmask value for Class C networks, which support
an IP address range of 192.0.0.x to 223.255.255.x. A
Class C network netmask uses 24 bits to identify the
network (alternative notation “/24”) and 8 bits to
identity the host.
- Lease Time The IP addresses assigned by the DHCP
server are valid only for the duration specified by
the lease time. Increasing the time ensures client
operation without interruption, but could introduce
potential conflicts. Decreasing the lease time avoids
potential address conflicts, but might cause more
slight interruptions to the client while it acquires a
new IP address from the DHCP server. The time is
expressed in seconds.
- DNS Proxy The Domain Name System (DNS) proxy
server forwards the DNS requests from the hosts on
the local network to the DNS server.
- Primary DNS If the DNS proxy is disabled, specify the
local IP address of the primary DNS server.
- Secondary DNS If the DNS proxy is disabled, specify
the IP address of the secondary DNS server. This entry
is optional and used only if the primary DNS server is
not responding.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
44
Page 48

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
• Relay Relays DHCP messages between DHCP clients
and DHCP servers on different IP networks.
- DHCP Server IP Specify the IP address of the DHCP
server that should get the DHCP messages.
- Agent-ID Specify the identifier of the DHCP relay
agent.
UPnP Allows the use of Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP)
for gaming, videos, chat, conferencing, and other
applications.
Add LAN Select an interface, and then click Add.
Management Network Settings
Management Interface (Available in Advanced view.)
Select the interface used for management.
Interfaces
(Available in Advanced view.) The Maximum Transmission
Unit (MTU) is the maximum packet size (in bytes) that a
network can transmit. You can configure a different MTU
for each of the interfaces.
Click the + button to display the Interfaces section.
IP Aliases
(Available in Advanced view.) You can configure IP
aliases for the local and external network interfaces for
management purposes. For example, you may need
multiple IP addresses (one private IP address and one
public IP address) for a single device. If a CPE uses PPPoE,
the CPE obtains a public PPPoE address, but the network
administrator assigns an internal IP alias to the device. This
way the network administrator can manage the device
internally without going through the PPPoE server.
Click the + button to display the IP Aliases section.
Enabled Enables the specific IP alias. All the added IP
aliases are saved in the system configuration file; however,
only the enabled IP aliases are active on the device.
Interface Select the appropriate interface.
IP Address The alternative IP address for the interface.
This can be used for routing or device management
purposes.
Netmask The network address space identifier for the IP
alias.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the IP alias.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add an IP alias.
• Edit Make changes to an IP alias. Click Save to save your
changes.
• Del Delete an IP alias.
VLAN Network
(Available in Advanced view.) You can create multiple
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs). Click the + button to
display the VLAN Network section.
Interface Displays the name of the interface.
MTU The default is 1500.
Action Click Edit to change the MTU. Then click Save to
apply your change.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
Enabled Enables the specific VLAN. All the added VLANs
are saved in the system configuration file; however, only
the enabled VLANs are active on the device.
Interface Select the appropriate interface.
VLAN ID The VLAN ID is a unique value assigned to
each VLAN at a single device; every VLAN ID represents a
different VLAN. The VLAN ID range is 2 to 4094.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the VLAN.
45
Page 49

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a VLAN.
• Edit Make changes to a VLAN. Click Save to save your
changes.
• Del Delete a VLAN.
Bridge Network
(Available in Advanced view.) You can create one or
more bridge networks if you need complete Layer 2
transparency. This is similar to using a switch – all traffic
flows through a bridge, in one port and out another
port, regardless of VLANs or IP addresses. For example,
if you want to use the same IP subnet on both sides of a
device, then you create a bridge network. There are many
different scenarios that could require bridged interfaces,
so the Bridge Network section is designed to allow
flexibility.
Click the + button to display the Bridge Network section.
Enabled Enables the specific bridge network. All
the added bridge networks are saved in the system
configuration file; however, only the enabled bridge
networks are active on the device.
Interface The interface is automatically displayed.
STP Multiple interconnected bridges create larger
networks using IEEE 802.1d Spanning Tree Protocol
(STP), which is used for finding the shortest path within a
network and eliminating loops from the topology.
If enabled, the device bridge communicates with other
network devices by sending and receiving Bridge Protocol
Data Units (BPDU). STP should be disabled (default setting)
when the device is the only bridge on the LAN or when
there are no loops in the topology, as there is no need for
the bridge to use STP in this case.
Ports Select the appropriate ports for your bridge
network. (Virtual ports are available if you have created
VLANs.)
• Add Select a port.
• Del Delete a port.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the bridge network.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a bridge network.
• Del Delete a bridge network.
Firewall
(Available in Advanced view.) You can configure firewall
rules for the local and external network interfaces. Click
the + button to display the Firewall section.
Enable Enables firewall functionality.
Enabled Enables the specific firewall rule. All the added
firewall rules are saved in the system configuration file;
however, only the enabled firewall rules are active on the
device.
Target To allow packets to pass through the firewall
unmodified, select ACCEPT. To block packets and send no
response, select DROP.
Interface Select the appropriate interface where the
firewall rule is applied. To apply the firewall rule to all
interfaces, select ANY.
IP Type Sets which specific Layer 3 protocol type (IP, ICMP,
TCP, UDP) should be filtered.
! Can be used to invert the Source IP/Mask, Source Port,
Destination IP/Mask, and Destination Port filtering criteria.
For example, if you enable ! (Not) for the specified
Destination Port value 443, then the filtering criteria will
be applied to all the packets sent to any Destination Port
except port 443, which is commonly used by HTTPS.
Source IP/Mask Check the box and specify the source IP
of the packet (specified within the packet header). Usually
it is the IP of the host system that sends the packets. For
example, if you enter 192.168.1.0/24, you are entering the
range of 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.255.
Source Port Check the box and specify the source port of
the packet (specified within the packet header). Usually it
is the port of the host system application that sends the
packets.
Destination IP/Mask Check the box and specify the
destination IP of the packet (specified within the packet
header). Usually it is the IP of the system which the packet
is addressed to. For example, if you enter 192.168.1.0/24,
you are entering the range of 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.255.
Destination Port Check the box and specify the
destination port of the packet (specified within the
packet header). Usually it is the port of the host system
application which the packet is addressed to.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the firewall rule.
All active firewall entries are stored in the FIREWALL chain
of the iptables filter table.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
46
Page 50

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a firewall rule.
• Edit Make changes to a firewall rule. Click Save to save
your changes.
• Del Delete a firewall rule.
Static Routes
(Available in Advanced view.) You can manually add
static routing rules to the system routing table; you can
set a rule that a specific target IP address (or range of IP
addresses) passes through a specific gateway. Click the +
button to display the Static Routes section.
Enabled Enables the specific static route. All the added
static routes are saved in the system configuration file;
however, only the enabled static routes are active on the
device.
Target Network IP Specify the IP address of the
destination.
Netmask Specify the netmask of the destination.
Gateway IP Specify the IP address of the gateway.
Comment You can enter a brief description of the
purpose for the static route.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a static route.
• Edit Make changes to a static route. Click Save to save
your changes.
• Del Delete a static route.
Type The Layer 3 protocol (IP) type that needs to be
forwarded from the local network.
Source IP/mask The IP address and netmask of the
source device.
Public IP/mask The public IP address and netmask of the
device that will accept and forward the connections from
the external network to the local host.
Public Port The TCP or UDP port of the device that will
accept and forward the connections from the external
network to the local host.
Comment Enter a brief description of the port
forwarding functionality, such as FTP server, web server, or
game server.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a port forwarding rule.
• Edit Make changes to a port forwarding rule. Click Save
to save your changes.
• Del Delete a port forwarding rule.
Multicast Routing Settings
With a multicast design, applications can send one copy
of each packet and address it to a group of computers
that want to receive it. This technique addresses packets
to a group of receivers rather than to a single receiver. It
relies on the network to forward the packets to the hosts
that need to receive them. Common routers isolate all
the broadcast (thus multicast) traffic between the local
and external networks; however, the device can provide
multicast traffic pass-through functionality.
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding allows specific ports of the hosts on the
local network to be forwarded to the external network
(WAN). This is useful for a number of applications (such
as FTP servers, VoIP, gaming) that require different host
systems to be seen using a single common IP address/
port. Click the + button to display the Port Forwarding
section.
Enabled Enables the specific port forwarding rule. All
the added port forwarding rules are saved in the system
configuration file; however, only the enabled port
forwarding rules are active on the device.
Private IP The IP address of the local host that needs to
be accessible from the external network.
Private Port The TCP or UDP port of the application
running on the local host. The specified port will be
accessible from the external network.
Multicast Routing Enables multicast packet pass-through
between local and external networks while the device is
operating in Router mode. Multicast intercommunication
is based on Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP).
Multicast Upstream Specify the source of multicast
traffic.
Multicast Downstream Specify the destination(s) of
multicast traffic.
Add Add a destination.
Del Delete a destination.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
47
Page 51

Chapter 5: Network Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Traffic Shaping
(Available in Advanced view.) Traffic Shaping controls
bandwidth from the perspective of the client (who is
connected on the Ethernet interface). Bursting allows
fast downloads when a user downloads small files (for
example, viewing different pages of a website), but
prevents a user from using excessive bandwidth when
downloading large files (for example, streaming a movie).
As Layer 3 QoS, you can limit the traffic at the device at the
port level, based on a rate limit you define. Each port has
two types of traffic:
• Ingress traffic entering the port
• Egress traffic exiting the port
We recommend using Traffic Shaping to control egress
traffic, because it is more efficient in the egress direction.
When a port accepts ingress traffic, it cannot control how
quickly the traffic arrives – the sending device controls
that traffic. However, when a port sends out egress traffic,
it can control how quickly the traffic exits.
Bursting allows the bandwidth to spike higher than the
maximum bandwidth you configure in the Ingress and
Egress Rate settings – for a short period of time. Once the
Ingress or Egress Burst (volume of data) is used up, the
throughput drops back down to the corresponding Ingress
or Egress Rate setting (maximum bandwidth) you have set.
For example, you have the following conditions:
• Ingress Burst is set to 2048 kBytes
• Ingress Rate is set to 512 kbit/s
• Actual maximum bandwidth is 1024 kbit/s
Bursting allows 2048 kBytes to pass at 1024 kbit/s before
throttling down to 512 kbit/s.
Egress
• Enable Enables the egress values.
• Rate, kbit/s Specify the maximum bandwidth value (in
kilobits per second) for traffic passing from the Ethernet
interface to the wireless interface.
• Burst, kBytes Specify the data volume (in kilobytes)
that is allowed before the egress maximum bandwidth
applies.
Action You have the following options:
• Add Add a rule.
• Edit Make changes to a traffic shaping rule. Click Save
to save your changes.
• Del Delete a rule.
Enable Enables bandwidth control on the device.
Enabled Enables the specific rule. All the added rules are
saved in the system configuration file; however, only the
enabled rules are active on the device.
Interface Select the appropriate interface.
Ingress
• Enable Enables the ingress values.
• Rate, kbit/s Specify the maximum bandwidth value (in
kilobits per second) for traffic passing from the wireless
interface to the Ethernet interface.
• Burst, kBytes Specify the data volume (in kilobytes)
that is allowed before the ingress maximum bandwidth
applies.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
48
Page 52

Chapter 6: Advanced Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Chapter 6: Advanced Tab
The Advanced tab handles advanced routing and wireless
settings. Only technically advanced users who have
sufficient knowledge about WLAN technology should use
the advanced wireless settings. These settings should not
be changed unless you know the effects the changes will
have on the device.
Change To save or test your changes, click Change.
A new message appears. You have three options:
• Apply To immediately save your changes, click Apply.
• Test To try the changes without saving them, click
Test. To keep the changes, click Apply. If you do not
click Apply within 180 seconds (the countdown is
displayed), the device times out and resumes its earlier
configuration.
• Discard To cancel your changes, click Discard.
Advanced Wireless Settings
The following table displays the available 802.11n data
rates:
Devices with Chains Data Rates
1x1
2x2
MCS 0, MCS 1, MCS 3, MCS4,
MCS 5, MCS 6, MCS 7
MCS 8, MCS 9, MCS 10, MCS11,
MCS 12, MCS 13, MCS 14, MCS 15
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
49
Page 53

RTS Threshold (If airMAX is enabled, RTS Threshold is not
required.) Determines the packet size of a transmission
and, through the use of an AP, helps control traffic flow.
The range is 0-2346 bytes. The default setting is the value
2346; this means that RTS is disabled.
Note: As an alternative, you can select Off to
disable this option.
The 802.11 wireless networking protocol uses the 802.11
wireless networking Request to Send (RTS)/Clear to Send
(CTS) mechanisms to reduce frame collisions introduced
by the hidden terminal problem. The RTS/CTS packet size
threshold is 0-2346 bytes. If the packet size that the device
wants to transmit is larger than the threshold, then the
RTS/CTS handshake is triggered. If the packet size is equal
to or less than the threshold, then the data frame is sent
immediately.
The system uses RTS/CTS frames for the handshake;
this reduces collisions for APs with hidden stations. The
station sends an RTS frame first; the AP responds with a
CTS frame. After the handshake with the AP is completed,
the station sends data. CTS collision control management
has a time interval defined; during this interval, all other
stations do not transmit and wait until the requesting
station finishes transmission.
Distance To specify the distance value in miles (or
kilometers), use the slider or manually enter the value.
The signal strength and throughput fall off with range.
Changing the distance value will change the ACK
(Acknowledgement) timeout value accordingly.
Auto Adjust We recommend enabling the Auto Adjust
option. Every time the station receives a data frame, it
sends an ACK frame to the AP (if transmission errors are
absent). If the station does not receive an ACK frame
from the AP within the set timeout, then it re-sends the
frame. If too many data frames are re-sent (whether the
ACK timeout is too short or too long), then there is a poor
connection, and throughput performance drops.
The device has a new auto-acknowledgement
timeout algorithm, which dynamically optimizes the
frame acknowledgement timeout value without user
intervention. This critical feature is required for stabilizing
long-distance 802.11n outdoor links.
Chapter 6: Advanced Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
If two or more stations are located at considerably
different distances from the AP they are associated with,
the distance to the farthest station should be set on the
AP side.
Aggregation A part of the 802.11n standard that allows
sending multiple frames per single access to the medium
by combining frames together into one larger frame. It
creates the larger frame by combining smaller frames with
the same physical source, destination end points, and
traffic class (QoS) into one large frame with a common
MAC header.
• Frames Determines the number of frames combined in
the new larger frame.
• Bytes Determines the size (in bytes) of the larger frame.
• Enable Check the box to use the Aggregation option.
Multicast Data Allows multicast packets to pass through.
By default this option is enabled.
Multicast Enhancement (Available in Access Point or
AP‑Repeater mode only.) If clients do not send IGMP
(Internet Group Management Protocol) messages, then
they are not registered as receivers of your multicast
traffic. Using IGMP snooping, the Multicast Enhancement
option isolates multicast traffic from unregistered
clients and allows the device to send multicast traffic to
registered clients using higher data rates. This lessens the
risk of traffic overload on PtMP links and increases the
reliability of multicast traffic since packets are transmitted
again if the first tranmission fails. If clients do not send
IGMP messages but should receive multicast traffic, then
you may need to disable the Multicast Enhancement
option. By default this option is enabled.
Installer EIRP Control Allows you to control the Auto
Adjust to EIRP Limit setting on the Wireless tab.
Extra Reporting Reports additional information, such
as device name, in the 802.11 management frames. This
information is commonly used for system identification
and status reporting in discovery utilities and router
operating systems.
Client Isolation (Available in Access Point or AP‑Repeater
mode only.) Allows packets to be sent only from the
external network to the CPE and vice versa. If Client
Isolation is enabled, wireless stations connected to the
same AP will not be able to interconnect on both the Layer
2 (MAC) and Layer 3 (IP) levels. This also affects associated
stations and WDS peers as well.
Sensitivity Threshold, dBm Defines the minimum client
signal level accepted by the AP for the client to connect.
If the client signal level subsequently drops, the client
remains connected to the AP.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
50
Page 54

Chapter 6: Advanced Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Advanced Ethernet Settings
LAN0/1 Speed By default, the option is Auto. The device
automatically negotiates transmission parameters, such as
speed and duplex, with its counterpart. In this process, the
networked devices first share their capabilities and then
choose the fastest transmission mode they both support.
To manually specify the maximum transmission link
speed and duplex mode, select one of the following
options: 100 Mbps‑Full, 100Mbps-Half, 10 Mbps‑Full,
or 10Mbps-Half. If you are running extra long Ethernet
cables, a link speed of 10Mbps could help to achieve
better stability.
Full-duplex mode allows communication in both
directions simultaneously. Half-duplex mode allows
communication in both directions, but not simultaneously
and only in one direction at a time.
POE Passthrough (Availability is device-specific.) When
enabled, the device allows Power over Ethernet (PoE)
power to pass from the main port to the secondary
port, thereby powering an additional device, such as a
compatible IP camera.
Signal LED Thresholds
(This feature is not available on all devices.) You can
configure the LEDs on the device to light up when
received signal levels reach the values defined in the
following fields. This allows a technician to easily deploy
an airOS CPE without logging into the device (for example,
for antenna alignment operation).
The following tables list the default threshold values for
devices with two, three, four, or six LEDs.
Two LEDs
LED Default Threshold Value
1 -94 dBm
2 -65 dBm
Three LEDs
LED Default Threshold Value
1 - 94 dBm
2 -77 dBm
3 -65 dBm
Four LEDs
LED Default Threshold Value
1 -94 dBm
2 -80 dBm
3 -73 dBm
4 -65 dBm
Six LEDs
Signal The type of signal, such as wireless or GPS.
Thresholds, dBm The number of LEDs is device-specific,
and the default values vary depending on the number of
LEDs. The specified LED will light up if the signal strength
reaches the value set in the field.
For example, if the device has four LEDs and the signal
strength (on the Main tab) fluctuates around -63 dBm,
then the LED threshold values can be set to the following:
-70, -65, -62, and -60.
Note: The “-” character is outside of the field and
should not be used for the signal strength value
specification.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
LED Default Threshold Value
1 -94 dBm
2 -88 dBm
3 -82 dBm
4 -77 dBm
5 -71 dBm
6 -65 dBm
51
Page 55

Chapter 7: Services Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Chapter 7: Services Tab
The Services tab configures system management services:
Ping Watchdog, SNMP, servers (web, SSH, Telnet), NTP,
DDNS, system log, and device discovery.
Change To save or test your changes, click Change.
A new message appears. You have three options:
• Apply To immediately save your changes, click Apply.
• Test To try the changes without saving them, click
Test. To keep the changes, click Apply. If you do not
click Apply within 180 seconds (the countdown is
displayed), the device times out and resumes its earlier
configuration.
• Discard To cancel your changes, click Discard.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
Ping Watchdog
Ping Watchdog sets the device to continuously ping a
user-defined IP address (it can be the Internet gateway,
for example). If it is unable to ping under the user-defined
constraints, then the device will automatically reboot. This
option creates a kind of “fail-proof” mechanism.
Ping Watchdog is dedicated to continuous monitoring of
the specific connection to the remote host using the Ping
tool. The Ping tool works by sending ICMP echo request
packets to the target host and listening for ICMP echo
response replies. If the defined number of replies is not
received, the tool reboots the device.
52
Page 56

Ping Watchdog Enables use of Ping Watchdog.
• IP Address To Ping Specify the IP address of the target
host to be monitored by Ping Watchdog.
• Ping Interval Specify the time interval (in seconds)
between the ICMP echo requests that are sent by Ping
Watchdog. The default value is 300 seconds.
• Startup Delay Specify the initial time delay (in seconds)
until the first ICMP echo requests are sent by Ping
Watchdog. The default value is 300 seconds.
The Startup Delay value should be at least 60 seconds
as the network interface and wireless connection
initialization takes a considerable amount of time if the
device is rebooted.
• Failure Count to Reboot Specify the number of ICMP
echo response replies. If the specified number of ICMP
echo response packets is not received continuously,
Ping Watchdog will reboot the device. The default value
is 3.
• Save Support Info This generates a support
information file.
SNMP Agent
Simple Network Monitor Protocol (SNMP) is an
application layer protocol that facilitates the exchange
of management information between network
devices. Network administrators use SNMP to monitor
network-attached devices for issues that warrant
attention.
The device contains an SNMP agent, which does the
following:
• Provides an interface for device monitoring using SNMP
• Communicates with SNMP management applications
for network provisioning
• Allows network administrators to monitor network
performance and troubleshoot network problems
Chapter 7: Services Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
For the purpose of equipment identification, configure the
SNMP agent with contact and location information:
SNMP Agent Enables the SNMP agent.
• SNMP Community Specify the SNMP community
string. It is required to authenticate access to
Management Information Base (MIB) objects and
functions as an embedded password. The device
supports a read-only community string; authorized
management stations have read access to all the objects
in the MIB except the community strings, but do not
have write access. The device supports SNMP v1. The
default SNMP Community is public.
• Contact Specify the contact who should be notified in
case of emergency.
• Location Specify the physical location of the device.
Web Server
The following Web Server parameters can be set:
Web Server By default, HTTP service is enabled.
Secure Connection (HTTPS) By default, the web server
uses secure HTTPS mode.
• Secure Server Port If secure HTTPS mode is used,
specify the TCP/IP port of the web server. The default is
443.
Server Port If HTTP mode is used, specify the TCP/IP port
of the web server. The default is 80.
Session Timeout Specifies the maximum timeout before
the session expires. Once a session expires, you must log
in again using the username and password. The default is
15 minutes.
SSH Server
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
The following SSH Server parameters can be set:
SSH Server This option enables SSH access to the device.
• Server Port Specify the TCP/IP port of the SSH server.
• Password Authentication If enabled, you must
authenticate using administrator credentials to grant
SSH access to the device; otherwise, an authorized key is
required.
53
Page 57

Chapter 7: Services Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
• Authorized Keys Click Edit to import a public key file
for SSH access to the device instead of using an admin
password.
- Choose File Click Choose File to locate the new key
file. Select the file and click Open.
- Import Imports the file for SSH access.
- Enabled Enables the specific key. All the added keys
are saved in the system configuration file; however,
only the enabled keys are active on the device.
- Type Displays the type of key.
- Key Displays the key.
- Comment You can enter a brief description of the
key.
- Action You have the following options:
• Add Adds a public key file.
• Edit Make changes to a public key file. Click Save to
save your changes.
• Del Deletes a public key file.
- Save Saves your changes.
- Close Discards your changes.
NTP Client
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a protocol for
synchronizing the clocks of computer systems over
packet-switched, variable-latency data networks. You
can use it to set the system time on the device. If the Log
option is enabled, then the system time is reported next to
every log entry that registers a system event.
NTP Client Enables the device to obtain the system time
from a time server on the Internet.
• NTP Server Specify the IP address or domain name of
the NTP server.
Dynamic DNS
Domain Name System (DNS) translates domain names
to IP addresses; each DNS server on the Internet holds
these mappings in its respective DNS database. Dynamic
Domain Name System (DDNS) is a network service that
notifies the DNS server in real time of any changes in the
device’s IP settings. Even if the device’s IP address changes,
you can still access the device through its domain name.
Telnet Server
The following Telnet Server parameters can be set:
Telnet Server This option activates Telnet access to the
device.
• Server Port Specify the TCP/IP port of the Telnet server.
Dynamic DNS If enabled, the device allows
communications with the DDNS server.
• Host Name Enter the host name of the DDNS server.
• Username Enter the user name of the DDNS account.
• Password Enter the password of the DDNS account.
• Show Check the box to display the password
characters.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
54
Page 58

System Log
System Log This option enables the registration routine
of system log (syslog) messages. By default it is disabled.
• Remote Log Enables the syslog remote sending
function. System log messages are sent to a remote
server, which is specified in the Remote Log IP Address
and Remote Log Port fields.
- Remote Log IP Address The host IP address that
receives syslog messages. Properly configure the
remote host to receive syslog protocol messages.
- Remote Log Port The TCP/IP port that receives syslog
messages. 514 is the default port for the commonly
used system message logging utilities.
Every logged message contains at least a system time and
host name. Usually a specific service name that generates
the system event is also specified within the message.
Messages from different services have different contexts
and different levels of detail. Usually error, warning, or
informational system service messages are reported;
however, more detailed debug level messages can also
be reported. The more detailed the system messages
reported, the greater the volume of log messages
generated.
Chapter 7: Services Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Device Discovery
Discovery Enables device discovery, so the device can
be discovered by other Ubiquiti devices through the
Discovery tool.
CDP Enables Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)
communications, so the device can send out CDP packets
to share its information.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
55
Page 59

Chapter 8: System Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Chapter 8: System Tab
The System tab contains administrative options. This page
enables the administrator to reboot the device, reset
it to factory defaults, upload new firmware, back up or
update the configuration, and configure the administrator
account.
Change To save or test your changes, click Change.
A new message appears. You have three options:
• Apply To immediately save your changes, click Apply.
• Test To try the changes without saving them, click
Test. To keep the changes, click Apply. If you do not
click Apply within 180 seconds (the countdown is
displayed), the device times out and resumes its earlier
configuration.
• Discard To cancel your changes, click Discard.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
Firmware Update
This section manages the firmware maintenance.
Firmware Version Displays the current firmware version.
Build Number Displays the build number of the firmware
version.
Check for Updates By default, the firmware automatically
checks for updates. To manually check for an update, click
Check Now.
Upload Firmware Click this button to update the device
with new firmware.
The device firmware update is compatible with all
configuration settings. The system configuration is
preserved while the device is updated with a new
firmware version. However, we recommend that you back
up your current system configuration before updating the
firmware.
56
Page 60

Chapter 8: System Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
This is a three-step procedure:
1. Click Choose File to locate the new firmware file. Select
the file and click Open.
2. Click Upload to upload the new firmware to the device.
3. The Uploaded Firmware Version is displayed. Click
Update to confirm.
If the firmware update is in process, you can close the
firmware update window, but this does not cancel the
firmware update. Please be patient, as the firmware
update routine can take three to seven minutes. You
cannot access the device until the firmware update
routine is completed.
Note: Do not power off, do not reboot, and do
not disconnect the device from the power supply
during the firmware update process as these
actions will damage the device!
Device
The Device Name (host name) is the system-wide device
identifier. The SNMP agent reports it to authorized
management stations. The Device Name will be used in
popular router operating systems, registration screens,
and discovery tools.
System Accounts
You can change the administrator password to protect
your device from unauthorized changes. We recommend
that you change the default administrator password on
the very first system setup:
Administrator Username Specifies the name of the
administrator.
Key button Click this button to change the administrator
password.
• Current Password Enter the current password for
the administrator account. It is required to change the
Password or Administrator Username.
• New Password Enter the new password for the
administrator account.
• Verify New Password Re-enter the new password for
the administrator account.
Device Name Specifies the host name.
Interface Language Allows you to select the language
displayed in the web management interface. English is the
default language.
You may upload additional language profiles. Refer to our
wiki page at the following URL:
www.ubnt.com/wiki/How_to_import_Language_Profile
Date Settings
Time Zone Specifies the time zone according to
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT).
Startup Date When enabled, you are able to change the
device’s startup date.
• Startup Date Specifies the device’s startup date. Click
the Calendar icon or manually enter the date in the
following format: 2 digit month/2 digit day/4 digit year.
For example, for December 20, 2011, enter 12/20/2011
in the field.
Note: The password length is 8 characters
maximum; passwords exceeding 8 characters will
be truncated.
Read-Only Account Check the box to enable the read-
only account, which can only view the Main tab. Configure
the username and password to protect your device from
unauthorized changes.
• Read-Only Account Name Specifies the name of the
system user.
• Key button Click this button to change the read-only
password.
- New Password Enter the new password for the
read-only account.
- Show Check the box to display the read-only
password characters.
Miscellaneous
Reset Button To allow use of the device’s physical reset
button, check the box. To prevent an accidental reset to
default settings, uncheck the box (this also disables the
remote POE reset functionality).
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
Note: You can reset the device to default settings
through the System tab > Reset to Defaults.
57
Page 61

Chapter 8: System Tab airOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
UNII-2 Band This option is available if DFS (Dynamic
Frequency Selection) frequencies in the UNII-2 band
(5.25 - 5.725 GHz) should be available for your device but
are locked. To unlock the DFS frequencies, follow these
instructions:
1. Visit www.ubnt.com/fcclabelrequest and follow the
online instructions to request the activation key and
FCC labels.
2. After you have received your activation key and FCC
labels, check the box next to UNII-2 Band.
3. In the Company Name field, enter the company name
you provided when you requested the activation key.
4. In the Key field, enter the activation key.
5. Apply the FCC labels to the appropriate device(s).
airMAX Technology Features (Available on the System
tab if the Ubiquiti logo tab is not displayed.) airMAX is
Ubiquiti’s proprietary Time Division Multiple Access
(TDMA) polling technology. airMAX offers better tolerance
against interference and increases the maximum number
of users that can associate with an AP that is airMAXcapable.
After you have enabled this setting on the System tab,
the Ubiquiti logo tab appears. For more information, see
“airMAX Settings” on page 4.
Location
Latitude and longitude define the device’s coordinates;
they are used to automatically update the device’s
location in airControl.
Latitude The latitude of the device’s location is displayed.
Valid values for latitude are -90 to +90.
Longitude The longitude of the device’s location is
displayed. Valid values for longitude are -180 to +180.
Device Maintenance
The controls in this section manage the device
maintenance routines: reboot and support information
reports.
Support Info This generates a support information
file that the Ubiquiti support engineers can use when
providing customer support. This file only needs to be
generated at their request.
Configuration Management
The controls in this section manage the device
configuration routines and the option to reset the device
to factory default settings.
The device configuration is stored in plain text file (cfg
file). You can back up, restore, or update the system
configuration file:
Back Up Configuration Click Download to download the
current system configuration file.
Note: We strongly recommend that you save
the configuration file in a secure location. The
configuration file includes confidential information,
such as WPA keys in plain text.
Upload Configuration Click Choose File to locate the
new configuration file. Select the file and click Open.
We recommend that you back up your current system
configuration before uploading the new configuration.
Note: Use only configuration files for the same
type of the device. Behavior may be unpredictable
if you mix configuration files from different types
of devices. (For example, upload a RocketM5
configuration file to a RocketM5; do NOT upload a
BulletM5 configuration file to a RocketM5.)
Upload Click this button to upload the new configuration
file to the device. Click Apply to confirm.
After the device reboots, the settings of the new
configuration are displayed in the Wireless, Network,
Advanced, Services, and System tabs of the web
management interface.
Reset to Factory Defaults Resets the device to the
factory default settings. This option will reboot the
device, and all factory default settings will be restored.
We recommend that you back up your current system
configuration before resetting the device to its defaults.
Reboot Device Initiates a full reboot cycle of the device.
Reboot is the same as the hardware reboot, which is
similar to the power-off and power-on cycle. The system
configuration stays the same after the reboot cycle
completes. Any changes that have not been applied are
lost.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
58
Page 62

Chapter 9: ToolsairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Chapter 9: Tools
Each tab of the airOS interface contains network
administration and monitoring tools. Click the Tools
drop‑down list at the top right corner of the page.
Align Antenna
Use the Align Antenna tool to point and optimize the
antenna in the direction of maximum link signal. The
Antenna Alignment window reloads every second.
Signal Level Displays the signal strength of the last
received packet.
Chain Displays the wireless signal level (in dBm) of each
chain, if there is more than one chain. (The number of
chains is device‑specific.)
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
Noise Level Displays the noise level (in dBm) of the
received wireless signal.
Max Signal Displays the maximum signal strength (in
dBm). To adjust the range of the Max Signal meter, use
the slider or manually enter the new value. If you reduce
the range, the color change will be more sensitive to
signal fluctuations, indicating the offset of the maximum
indicator value and the scale itself.
Alignment Beep You can enable the audio option so
a technician can easily align the antenna of an airMAX
device without looking at the airOS Configuration
Interface. The higher the pitch, the stronger the signal
strength. Each rise in pitch correlates to an increase in the
received signal level, which is represented by a color in the
airOS Configuration Inteface:
• Red (weakest received signal level)
• Yellow
• Green
• Blue (strongest received signal level)
59
Page 63

Chapter 9: ToolsairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Site Survey
The Site Survey tool searches for wireless networks in
range on all supported channels. In Station mode, you
can change the frequency list; for details, see “Frequency
Scan List, MHz” on page 21.
The Site Survey tool reports the MAC Address, SSID, Device
Name, Encryption type (if any), Signal/Noise in dBm,
Frequency in GHz, and the wireless Channel of each AP in
the surrounding environment.
To refresh the window, click Scan.
Discovery
The Device Discovery tool searches for all Ubiquiti devices
on your network. The Search field automatically filters
devices containing specified names or numbers as you
enter them.
Network Ping
Select Destination IP You have two options:
• Select a remote system IP from the drop‑down list,
which is generated automatically.
• Select specify manually and enter the IP address in the
field displayed below.
Packet Count Enter the number of packets to send for
the ping test.
Packet Size Specify the size of the packet.
Start Click this button to start the test.
Packet loss statistics and latency time evaluation are
displayed after the test is completed.
Traceroute
The Traceroute tool traces the hops from the device to a
specified outgoing IP address. Use this tool to find the
route taken by ICMP packets across the network to the
destination host.
It reports the MAC Address, Device Name, Mode, SSID,
Product type, Firmware version, and IP Address for each
Ubiquiti device. To access a device configuration through
its web management interface, click the device’s IP
address.
To refresh the window, click Scan.
Ping
You can ping other devices on the network directly from
the device. The Ping tool uses ICMP packets to check the
preliminary link quality and packet latency estimation
between two network devices.
Destination Host Enter the IP address of the destination
host.
Resolve IP Addresses Select this option to resolve the IP
addresses symbolically rather than numerically.
Start Click this button to start the test.
Responses are displayed after the test is completed.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
60
Page 64

Chapter 9: ToolsairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Speed Test
This utility allows you to test the connection speed
between two airOS devices that are using firmware
version 5.2 or above. You can use Speed Test to estimate a
preliminary throughput between two network devices.
Note: If traffic shaping is enabled on either
device, then the Speed Test results will be limited
accordingly.
Select Destination IP You have two options:
• Select a remote system IP from the drop‑down list,
which is generated automatically.
• Select specify manually and enter the IP address in the
field displayed below.
User Enter the administrator username.
Note: Enter the remote system access credentials
required for communication between two airOS
devices. Administrator username and password are
required to establish the TCP/IP‑based throughput
test.
Password Enter the administrator password.
Remote WEB port Enter the remote web port of the
airOS device to establish a TCP/IP‑based throughput test
(for example, specify port 443 if HTTPS is enabled in the
remote device). If the web port of the remote device is not
correct, then the ICMP throughput measurement routine
will be initiated.
Show Advanced Options Enables additional Speed Test
utility options.
Direction Select one of three directions:
• duplex Estimates the incoming (RX) and outgoing (TX)
throughput at the same time.
• receive Estimates the incoming (RX) throughput.
• transmit Estimates the outgoing (TX) throughput.
Run Test Click this button to start the test.
Test Results Displays three result categories:
• RX Displays the estimated incoming throughput.
• TX Displays the estimated outgoing throughput.
• Total Displays the aggregate throughput.
airView
Use the airView Spectrum Analyzer to analyze the noise
environment of the radio spectrum and intelligently select
the optimal frequency to install a PtP airMAX link.
There are two system requirements for the airView
Spectrum Analyzer:
• Your system is connected to the device via Ethernet.
Launching airView will terminate all wireless
connections on the device.
• Java Runtime Environment 1.6 (or above) is required on
your client machine to use airView.
On first use, the following window appears.
• Do NOT warn me about this in the future Check the
box to bypass this window in future launches of the
airView Spectrum Analyzer.
• Launch airView Click Launch airView to download the
Java Network Launch Protocol (jnlp) file and complete
the launch of airView.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
61
Page 65

Chapter 9: ToolsairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
Main View
Device Displays the device name, MAC (Media Access
Control) address, and IP address of the device running
airView.
Total RF Frames Displays the total number of Radio
Frequency (RF) frames gathered since the start of the
airView session or since the Reset All Data button was last
clicked.
FPS Displays the total number of frames per second (FPS)
gathered since the start of the airView session or since
the Reset All Data button was last clicked. The wider the
interval amplitude, the fewer the FPS will be gathered.
Reset All Data Click to reset all gathered data. Use this
option to analyze the spectrum for another location or
address.
File Menu
Click Exit to end the airView session.
View Menu
Preferences Changes airView settings, such as enabling
or disabling charts and traces, or specifying the frequency
interval.
Preferences
Select View > Preferences to display the Preferences airView Spectrum Analyzer window.
Charts
Enable Chart Panel 1 (top) Displays the Waterfall or
Channel Usage chart in Chart Panel 1, depending on
which option you have selected in Preferences. This
time‑based graph shows the aggregate energy collected
or channel usage for each frequency since the start of the
airView session.
Enable Chart Panel 2 (middle) Displays the Waveform
chart in Chart Panel 2. This time‑based graph shows the RF
signature of the noise environment since the start of the
airView session. The energy color designates its amplitude.
Cooler colors represent lower energy levels (with blue
representing the lowest levels) in that frequency bin, and
warmer colors (yellow, orange, or red) represent higher
energy levels in that frequency bin.
Enable Chart Panel 3 (bottom) Displays the Real‑time
chart (traditional spectrum analyzer) in Chart Panel 3.
Energy (in dBm) is shown in real time as a function of
frequency.
Note: Energy is the power ratio in decibels (dB) of
the measured power referenced to one milliwatt
(mW).
Clear All Markers Resets all previously assigned
markers. Markers are assigned by clicking a point, which
corresponds with a frequency on the Real‑time chart.
Enable top chart Check the box to enable the top chart.
Select the desired chart to display in the top chart panel
on the main view. There are two options:
• Waterfall This time‑based graph shows the aggregate
energy collected for each frequency since the start
of the airView session. The energy color designates
its amplitude. Cooler colors represent lower energy
levels (with blue representing the lowest levels) in that
frequency bin, and warmer colors (yellow, orange, or
red) represent higher energy levels in that frequency
bin.
The Waterfall View’s legend (top‑right corner) provides
a numerical guide associating the various colors to
power levels (in dBm). The low end of that legend (left)
is always adjusted to the calculated noise floor, and the
high end (right) is set to the highest detected power
level since the start of the airView session.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
62
Page 66

Chapter 9: ToolsairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
• Channel Usage For each Wi‑Fi channel, a bar displays
a percentage showing the relative “crowdedness” of
that specific channel. To calculate this percentage, the
airView Spectrum Analyzer analyzes both the popularity
and strength of RF energy in that channel since the start
of an airView session.
Enable Waveform chart (middle) Check the box to
enable the middle chart. This time‑based graph shows
the RF signature of the noise environment since the
start of the airView session. The energy color designates
its amplitude. Cooler colors represent lower energy
levels (with blue representing the lowest levels) in that
frequency bin, and warmer colors (yellow, orange, or red)
represent higher energy levels in that frequency bin.
The spectral view over time will display the steady‑state RF
energy signature of a given environment.
Enable Real-time chart (bottom) Check the box to
enable the bottom chart. This graph displays a traditional
spectrum analyzer in which energy (in dBm) is shown in
real time as a function of frequency. There are three traces
in this view:
• Current (Yellow) Shows the real‑time energy seen by
the device as a function of frequency.
• Average (Green) Shows the running average energy
across frequency.
• Maximum (Blue) Shows updates and maximum power
levels across frequency.
Realtime Traces
the Real-time chart represents the real‑time power level of
each frequency. The refresh speed depends on the FPS.
Averages Trace Check the Enable box to enable the
averages trace. When enabled, the averages trace is
represented by the green area on the Real-time chart,
which displays the average received power level data
since the start of the airView session. To enable a shaded
green area, check the Shaded Area box. To display only
a green outline without the shaded area, uncheck the
Shaded Area box.
Maximum Power Levels Trace Check the Enable box to
enable the maximum power trace. When enabled, the
maximum power trace is represented by the blue area on
the Real-time chart, which displays the maximum received
power level data since the start of the airView session. To
enable a shaded blue area, check the Shaded Area box.
To display only a blue outline without the shaded area,
uncheck the Shaded Area box.
Frequency Range Select the amplitude of the
frequency interval to be scanned from the Frequency
Range drop‑down list. Available frequencies are device‑
dependent. There are pre‑defined ranges for the most
popular bands. You can enter a custom range; select
Custom Range from the Frequency Range drop‑down list
and enter the desired values in the Start and End fields.
Help
Click About to view the version and build number of the
airView Spectrum Analyzer.
The following settings apply only to the Real-time chart:
Current Real-time Trace Check the Enable box to enable
the real‑time trace. When enabled, the yellow outline on
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
63
Page 67

Appendix A: Contact Information
Ubiquiti Networks Support
Ubiquiti Support Engineers are located around the world
and are dedicated to helping customers resolve software,
hardware compatibility, or field issues as quickly as
possible. We strive to respond to support inquiries within
a 24-hour period.
Online Resources
Support: support.ubnt.com
Wiki Page: wiki.ubnt.com
Support Forum: forum.ubnt.com
Downloads: downloads.ubnt.com
Appendix A: Contact InformationairOS™ v5.5.4 User Guide
2580 Orchard Parkway
San Jose, CA 95131
www.ubnt.com
© 2012-2013 Ubiquiti Networks, Inc. All rights reserved. airControl™,
airGrid™, airMAX™, airOS™, airSelect™, airSync™, airView™, Bullet™,
NanoBridge™, NanoStation™, PicoStation™, PowerBridge™, Rocket™, and
Ubiquiti Networks™ are trademarks of Ubiquiti Networks, Inc. Google
Maps™ is a trademark of Google, Inc. WPA™ and WPA2™ are trademarks of
the Wi-Fi Alliance.
Ubiquiti Networks, Inc.
JL031513
64
 Loading...
Loading...