Page 1

95
115
1
Art # A-09089
FP-95
MINI MIG
PORTABLE MIG WELDER
Operating Manual
Revision: AA Issue Date: March 19, 2009 Manual No.: 0-5122
Operating Features:
Page 2
WE APPRECIATE YOUR BUSINESS!
Congratulations on your new Thermal Arc product. We are proud
to have you as our customer and will strive to provide you with
the best service and reliability in the industry. This product
is backed by our extensive warranty and world-wide service
network. To locate your nearest distributor or service agency call
1-800-752-7621, or visit us on the web at www.Thermalarc.com.
This Operating Manual has been designed to instruct you on the
correct use and operation of your Thermal Arc product. Your
satisfaction with this product and its safe operation is our ultimate
concern. Therefore please take the time to read the entire manual,
especially the Safety Precautions. They will help you to avoid potential
hazards that may exist when working with this product.
YOU ARE IN GOOD COMPANY!
The Brand of Choice for Contractors and Fabricators Worldwide.
Thermal Arc is a Global Brand of Arc Welding Products for Thermadyne
Industries Inc. We manufacture and supply to major welding industry
sectors worldwide including; Manufacturing, Construction, Mining,
Automotive, Aerospace, Engineering, Rural and DIY/Hobbyist.
We distinguish ourselves from our competition through marketleading, dependable products that have stood the test of time. We
pride ourselves on technical innovation, competitive prices, excellent
delivery, superior customer service and technical support, together
with excellence in sales and marketing expertise.
Above all, we are committed to develop technologically advanced
products to achieve a safer working environment within the welding
industry.
Page 3
!
WARNINGS
Read and understand this entire Manual and your employer’s safety practices before installing,
operating, or servicing the equipment.
While the information contained in this Manual represents the Manufacturer’s best judgement, the
Manufacturer assumes no liability for its use.
Operating Manual Number 0-5122 for:
FirePower 95 Mini MIG System MIG Welder Part No. 1444-0322
Published by:
Thermadyne Industries Inc.
82 Benning Street
West Lebanon, New Hampshire, USA 03784
(603) 298-5711
www.thermalarc.com
Copyright
Thermadyne Industries Inc.
®
All rights reserved.
Reproduction of this work, in whole or in part, without written permission of the publisher is prohibited.
The publisher does not assume and hereby disclaims any liability to any party for any loss or damage
caused by any error or omission in this Manual, whether such error results from negligence, accident, or
any other cause.
Publication Date: March 19, 2009
Record the following information for Warranty purposes:
Where Purchased: ____________________________________
Purchase Date: ____________________________________
Equipment Serial #: ____________________________________
©
2009 by
i
Page 4

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1:SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS ................................................ 1-1
1.01 Arc Welding Hazards ....................................................................................... 1-1
1.02 Principal Safety Standards .............................................................................. 1-4
1.03 Symbol Chart .................................................................................................. 1-5
1.04 Precautions De Securite En Soudage A L’arc .................................................. 1-6
1.05 Dangers relatifs au soudage à l’arc ................................................................. 1-6
1.06 Principales Normes De Securite ..................................................................... 1-9
1.07 Graphique de Symbole .................................................................................. 1-10
SECTION 2:INTRODUCTION ............................................................................... 2-1
2.01 How to Use This Manual ................................................................................. 2-1
2.02 Equipment Identification ................................................................................. 2-1
2.03 Receipt of Equipment ...................................................................................... 2-1
2.04 General ........................................................................................................... 2-1
2.05 Handle and Foot Assembly ............................................................................. 2-2
2.06 Specifications ................................................................................................. 2-2
2.07 Volt - Amp Curves .......................................................................................... 2-3
2.08 Duty Cycle ...................................................................................................... 2-4
2.09 MIG Gun Maintenance ................................................................................... 2-4
SECTION 3:INSTALLATION ................................................................................ 3-1
3.01 Location ......................................................................................................... 3-1
3.02 Safety ............................................................................................................. 3-1
3.03 Grounding ...................................................................................................... 3-1
3.04 Electrical Input Requirements ......................................................................... 3-1
3.05 Requirements for Maximum Output .............................................................. 3-2
3.06 Installing Wire Spool ..................................................................................... 3-2
3.07 Feedrolls ......................................................................................................... 3-3
3.08 Install Wire into the Feedhead ........................................................................ 3-3
3.09 Install Wire into the Welding Gun .................................................................. 3-5
SECTION 4:OPERATION .................................................................................... 4-1
4.01 General Safety Precautions ............................................................................. 4-1
4.02 FirePower Controls ........................................................................................ 4-2
4.03 Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) .................................................................... 4-4
4.04 Shutdown Procedures .................................................................................... 4-4
4.05 Basic Welding Technique ................................................................................ 4-4
4.06 Welding Gun Positions .................................................................................. 4-5
4.07 Establishing the Arc and Making Weld Beads ................................................ 4-6
4.08 Pre-Weld Procedure ....................................................................................... 4-6
4.09 Welding Procedure ........................................................................................ 4-6
4.10 Reference Table .............................................................................................. 4-7
4.11 FirePower FP-95 Welding Setting Selection Guide .......................................... 4-8
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 5:SERVICE ....................................................................................... 5-1
5.01 Cleaning of the Unit ....................................................................................... 5-1
5.02 Cleaning of the Feed Rolls ............................................................................. 5-1
5.03 Basic Troubleshooting ................................................................................... 5-1
5.04 Welding Problems ......................................................................................... 5-2
5.05 Power Source Problems ................................................................................. 5-3
APPENDIX 1: OPTIONS AND ACCESSORIES ............................................................ A-1
APPENDIX 2: power supply replacement parts ........................................................ A-2
APPENDIX 3: FIREPOWER 95 SYSTEM SCHEMATIC .................................................. A-4
GLOBAL CUSTOMER SERVICE CONTACT INFORMATION ........................... Inside Rear Cover
Page 6

This Page Intentionally Blank
Page 7
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS FIREPOWER FP-95
!
SECTION 1:
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING
PROTECT YOURSELF AND OTHERS FROM POSSIBLE SERIOUS INJURY OR DEATH. KEEP CHILDREN AWAY. PACEMAKER WEARERS KEEP
AWAY UNTIL CONSULTING YOUR DOCTOR. DO NOT LOSE THESE INSTRUCTIONS. READ OPERATING/INSTRUCTION MANUAL BEFORE
INSTALLING, OPERATING OR SERVICING THIS EQUIPMENT.
Welding products and welding processes can cause serious injury or death, or damage to other equipment or property, if the operator does not
strictly observe all safety rules and take precautionary actions.
Safe practices have developed from past experience in the use of welding and cutting. These practices must be learned through study and
training before using this equipment. Some of these practices apply to equipment connected to power lines; other practices apply to engine
driven equipment. Anyone not having extensive training in welding and cutting practices should not attempt to weld.
Safe practices are outlined in the American National Standard Z49.1 entitled: SAFETY IN WELDING AND CUTTING. This publication and other
guides to what you should learn before operating this equipment are listed at the end of these safety precautions. HAVE ALL INSTALLATION,
OPERATION, MAINTENANCE, AND REPAIR WORK PERFORMED ONLY BY QUALIFIED PEOPLE.
1.01 Arc Welding Hazards
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK can kill.
Touching live electrical parts can cause fatal shocks or
severe burns. The electrode and work circuit is electrically live whenever the output is on. The input power
circuit and machine internal circuits are also live when
power is on. In semi-automatic or automatic wire welding, the wire, wire reel, drive roll housing, and all metal
parts touching the welding wire are electrically live.
Incorrectly installed or improperly grounded equipment
is a hazard.
1. Do not touch live electrical parts.
2. Wear dry, hole-free insulating gloves and body protection.
3. Insulate yourself from work and ground using dry insulating mats
or covers.
4. Disconnect input power or stop engine before installing or
servicing this equipment. Lock input power disconnect switch
open, or remove line fuses so power cannot be turned on
accidentally.
5. Properly install and ground this equipment according to its Owner’s
Manual and national, state, and local codes.
6. Turn off all equipment when not in use. Disconnect power to
equipment if it will be left unattended or out of service.
7. Use fully insulated electrode holders. Never dip holder in water to
cool it or lay it down on the ground or the work surface. Do not
touch holders connected to two welding machines at the same
time or touch other people with the holder or electrode.
8. Do not use worn, damaged, undersized, or poorly spliced
cables.
9. Do not wrap cables around your body.
10. Ground the workpiece to a good electrical (earth) ground.
11. Do not touch electrode while in contact with the work (ground)
circuit.
12. Use only well-maintained equipment. Repair or replace damaged
parts at once.
13. In confined spaces or damp locations, do not use a welder with AC
output unless it is equipped with a voltage reducer. Use equipment
with DC output.
14. Wear a safety harness to prevent falling if working above floor
level.
15. Keep all panels and covers securely in place.
WARNING
ARC RAYS can burn eyes and skin; NOISE can damage
hearing. Arc rays from the welding process produce
intense heat and strong ultraviolet rays that can burn
eyes and skin. Noise from some processes can damage
hearing.
1. Wear a welding helmet fitted with a proper shade of filter (see
ANSI Z49.1 listed in Safety Standards) to protect your face and
eyes when welding or watching.
2. Wear approved safety glasses. Side shields recommended.
3. Use protective screens or barriers to protect others from flash and
glare; warn others not to watch the arc.
4. Wear protective clothing made from durable, flame-resistant
material (wool and leather) and foot protection.
5. Use approved ear plugs or ear muffs if noise level is high.
Safety Instructions 1-1 Manual 0-5122
Page 8
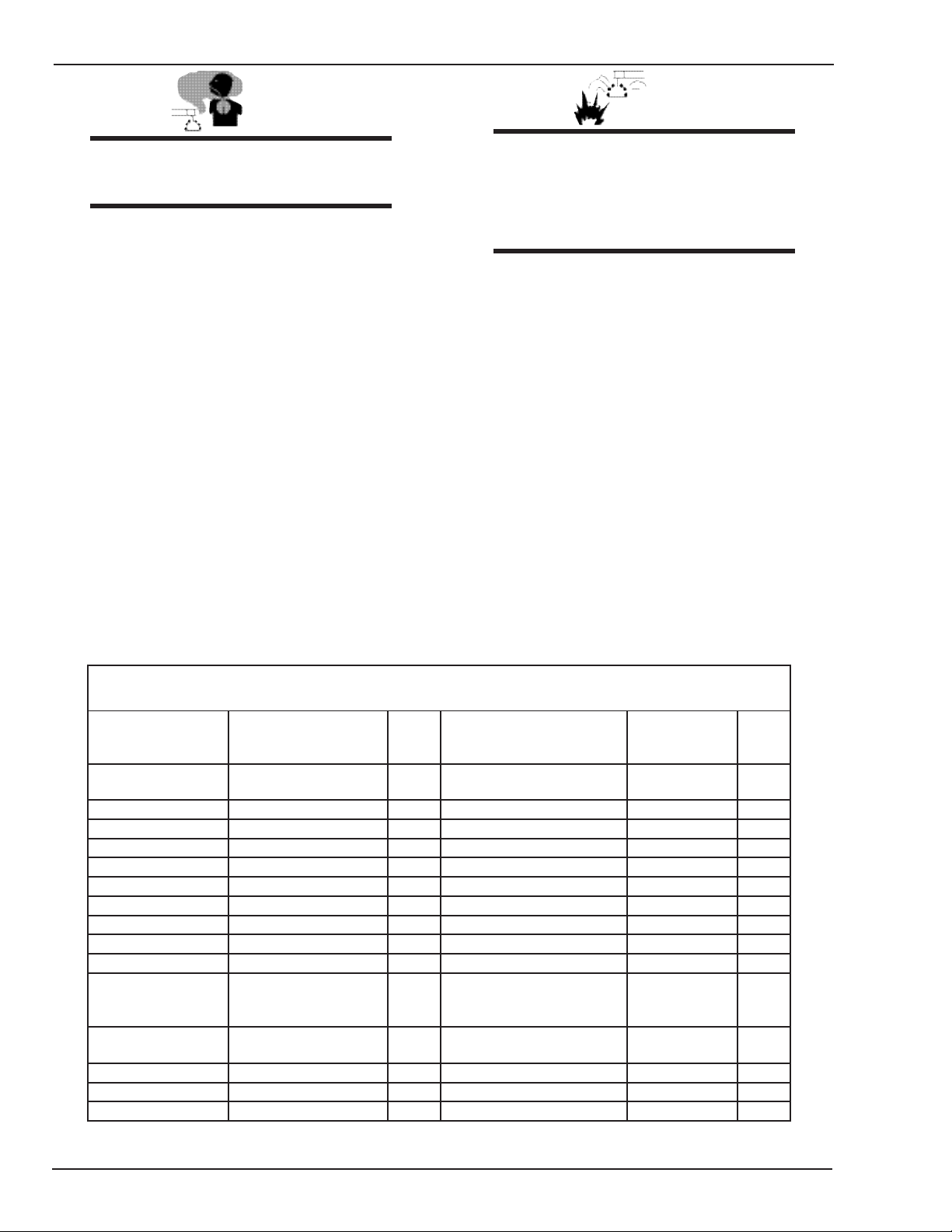
FIREPOWER FP-95 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Welding or Cutting
Operation
Electrode Siz
e
Metal Thickness
or Weldin
g
Current
Filter
Shade
No.
Welding or Cutting
Operation
Electrode Siz
e
Metal Thickness
or Weldin
g
Filter
Shade
No.
Torch soldering 2
Gas metal-arc
welding (MIG)
Torch brazing 3 or 4 Non-ferrous base metal All 11
Oxygen Cutting
Non-ferrous base metal All 12
Light Under 1 in., 25 mm 3 or 4 Gas tungsten arc welding All 12
Medium 1 to 6 in., 25-150 mm 4 or 5 (TIG) All 12
Heavy Over 6 in., 150 mm 5 or 6 Atomic hydrogen welding All 12
Gas welding
Carbon arc welding All 12
Light Under 1/8 in., 3 mm 4 or 5 Plasma arc welding
Medium 1/8 to 1/2 in., 3-12 mm 5 or 6
Carbon arc air gouging
Heavy Over 1/2 in., 12 mm 6 or 8 Light 12
Shielded metal-arc
welding
(stick) electrodes
Under 5/32 in., 4 mm 10 Heavy 14
5/32 to 1/4 in.,
4 to 6.4 mm
12
Plasma arc cutting
Over 1/4 in., 6.4 mm 14 Light Under 300 Amp 9
Medium 300 to 400 Amp 12
Heavy Over 400 Amp 14
Eye protection filter shade selector for welding or cutting
(goggles or helmet), from AWS A6.2-73.
WARNING
FUMES AND GASES can be hazardous to your health.
Welding produces fumes and gases. Breathing these
fumes and gases can be hazardous to your health.
1. Keep your head out of the fumes. Do not breathe the fumes.
2. If inside, ventilate the area and/or use exhaust at the arc to remove
welding fumes and gases.
3. If ventilation is poor, use an approved air-supplied respirator.
4. Read the Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDSs) and the
manufacturer’s instruction for metals, consumables, coatings,
and cleaners.
5. Work in a confined space only if it is well ventilated, or while
wearing an air-supplied respirator. Shielding gases used for
welding can displace air causing injury or death. Be sure the
breathing air is safe.
6. Do not weld in locations near degreasing, cleaning, or spraying
operations. The heat and rays of the arc can react with vapors to
form highly toxic and irritating gases.
7. Do not weld on coated metals, such as galvanized, lead, or
cadmium plated steel, unless the coating is removed from the weld
area, the area is well ventilated, and if necessary, while wearing
an air-supplied respirator. The coatings and any metals containing
these elements can give off toxic fumes if welded.
WARNING
WELDING can cause fire or explosion.
Sparks and spatter fly off from the welding arc. The flying
sparks and hot metal, weld spatter, hot workpiece, and
hot equipment can cause fires and burns. Accidental
contact of electrode or welding wire to metal objects
can cause sparks, overheating, or fire.
1. Protect yourself and others from flying sparks and hot metal.
2. Do not weld where flying sparks can strike flammable material.
3. Remove all flammables within 35 ft (10.7 m) of the welding arc.
If this is not possible, tightly cover them with approved covers.
4. Be alert that welding sparks and hot materials from welding can
easily go through small cracks and openings to adjacent areas.
5. Watch for fire, and keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
6. Be aware that welding on a ceiling, floor, bulkhead, or partition
can cause fire on the hidden side.
7. Do not weld on closed containers such as tanks or drums.
8. Connect work cable to the work as close to the welding area as
practical to prevent welding current from traveling long, possibly
unknown paths and causing electric shock and fire hazards.
9. Do not use welder to thaw frozen pipes.
10. Remove stick electrode from holder or cut off welding wire at
contact tip when not in use.
Manual 0-5122 1-2 Safety Instructinos
Page 9
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS FIREPOWER FP-95
!
WARNING
FLYING SPARKS AND HOT METAL can cause injury.
Chipping and grinding cause flying metal. As welds cool,
they can throw off slag.
1. Wear approved face shield or safety goggles. Side shields
recommended.
2. Wear proper body protection to protect skin.
WARNING
CYLINDERS can explode if damaged.
Shielding gas cylinders contain gas under high pressure.
If damaged, a cylinder can explode. Since gas cylinders
are normally part of the welding process, be sure to treat
them carefully.
1. Protect compressed gas cylinders from excessive heat, mechanical
shocks, and arcs.
2. Install and secure cylinders in an upright position by chaining
them to a stationary support or equipment cylinder rack to prevent
falling or tipping.
3. Keep cylinders away from any welding or other electrical
circuits.
4. Never allow a welding electrode to touch any cylinder.
5. Use only correct shielding gas cylinders, regulators, hoses, and
fittings designed for the specific application; maintain them and
associated parts in good condition.
6. Turn face away from valve outlet when opening cylinder valve.
7. Keep protective cap in place over valve except when cylinder is in
use or connected for use.
8. Read and follow instructions on compressed gas cylinders,
associated equipment, and CGA publication P-1 listed in Safety
Standards.
WARNING
ENGINE FUEL can cause fire or explosion.
Engine fuel is highly flammable.
1. Stop engine before checking or adding fuel.
2. Do not add fuel while smoking or if unit is near any sparks or open
flames.
3. Allow engine to cool before fueling. If possible, check and add fuel
to cold engine before beginning job.
4. Do not overfill tank — allow room for fuel to expand.
5. Do not spill fuel. If fuel is spilled, clean up before starting
engine.
WARNING
MOVING PARTS can cause injury.
Moving parts, such as fans, rotors, and belts can cut fingers and hands
and catch loose clothing.
1. Keep all doors, panels, covers, and guards closed and
securely in place.
2. Stop engine before installing or connecting unit.
3. Have only qualified people remove guards or covers for
maintenance and troubleshooting as necessary.
4. To prevent accidental starting during servicing, disconnect
negative (-) battery cable from battery.
5. Keep hands, hair, loose clothing, and tools away from moving
parts.
6. Reinstall panels or guards and close doors when servicing
is finished and before starting engine.
WARNING
WARNING
Engines can be dangerous.
WARNING
ENGINE EXHAUST GASES can kill.
Engines produce harmful exhaust gases.
1. Use equipment outside in open, well-ventilated areas.
2. If used in a closed area, vent engine exhaust outside and away
from any building air intakes.
Safety Instructions 1-3 Manual 0-5122
SPARKS can cause BATTERY GASES TO EXPLODE;
BATTERY ACID can burn eyes and skin.
Batteries contain acid and generate explosive gases.
1. Always wear a face shield when working on a battery.
2. Stop engine before disconnecting or connecting battery cables.
3. Do not allow tools to cause sparks when working on a battery.
4. Do not use welder to charge batteries or jump start vehicles.
5. Observe correct polarity (+ and –) on batteries.
Page 10

FIREPOWER FP-95 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
!
WARNING
STEAM AND PRESSURIZED HOT COOLANT can burn
face, eyes, and skin.
The coolant in the radiator can be very hot and under
pressure.
1. Do not remove radiator cap when engine is hot. Allow engine to
cool.
2. Wear gloves and put a rag over cap area when removing cap.
3. Allow pressure to escape before completely removing cap.
LEAD WARNING
This product contains chemicals, including lead, or
otherwise produces chemicals known to the State of
California to cause cancer, birth defects and other reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling. (California
Health & Safety Code § 25249.5 et seq.)
NOTE
Considerations About Welding And The Effects of Low
Frequency Electric and Magnetic Fields
ABOUT PACEMAKERS:
The above procedures are among those also normally
recommended for pacemaker wearers. Consult your
doctor for complete information.
1.02 Principal Safety Standards
Safety in Welding and Cutting, ANSI Standard Z49.1, from American
Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJeune Rd., Miami, FL 33126.
Safety and Health Standards, OSHA 29 CFR 1910, from Superintendent
of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C.
20402.
Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for Welding and
Cutting of Containers That Have Held Hazardous Substances, American
Welding Society Standard AWS F4.1, from American Welding Society,
550 N.W. LeJeune Rd., Miami, FL 33126.
National Electrical Code, NFPA Standard 70, from National Fire
Protection Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders, CGA Pamphlet P-1,
from Compressed Gas Association, 1235 Jefferson Davis Highway,
Suite 501, Arlington, VA 22202.
Code for Safety in Welding and Cutting, CSA Standard W117.2, from
Canadian Standards Association, Standards Sales, 178 Rexdale
Boulevard, Rexdale, Ontario, Canada M9W 1R3.
The following is a quotation from the General Conclusions Section of
the U.S. Congress, Office of Technology Assessment, Biological Effects
of Power Frequency Electric & Magnetic Fields - Background Paper,
OTA-BP-E-63 (Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office, May
1989): “...there is now a very large volume of scientific findings based
on experiments at the cellular level and from studies with animals
and people which clearly establish that low frequency magnetic fields
interact with, and produce changes in, biological systems. While most
of this work is of very high quality, the results are complex. Current
scientific understanding does not yet allow us to interpret the evidence
in a single coherent framework. Even more frustrating, it does not
yet allow us to draw definite conclusions about questions of possible
risk or to offer clear science-based advice on strategies to minimize
or avoid potential risks.”
To reduce magnetic fields in the workplace, use the following
procedures.
1. Keep cables close together by twisting or taping them.
2. Arrange cables to one side and away from the operator.
3. Do not coil or drape cable around the body.
4. Keep welding power source and cables as far away from body
as practical.
Safe Practices for Occupation and Educational Eye and Face Protection,
ANSI Standard Z87.1, from American National Standards Institute,
1430 Broadway, New York, NY 10018.
Cutting and Welding Processes, NFPA Standard 51B, from National Fire
Protection Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
Manual 0-5122 1-4 Safety Instructinos
Page 11
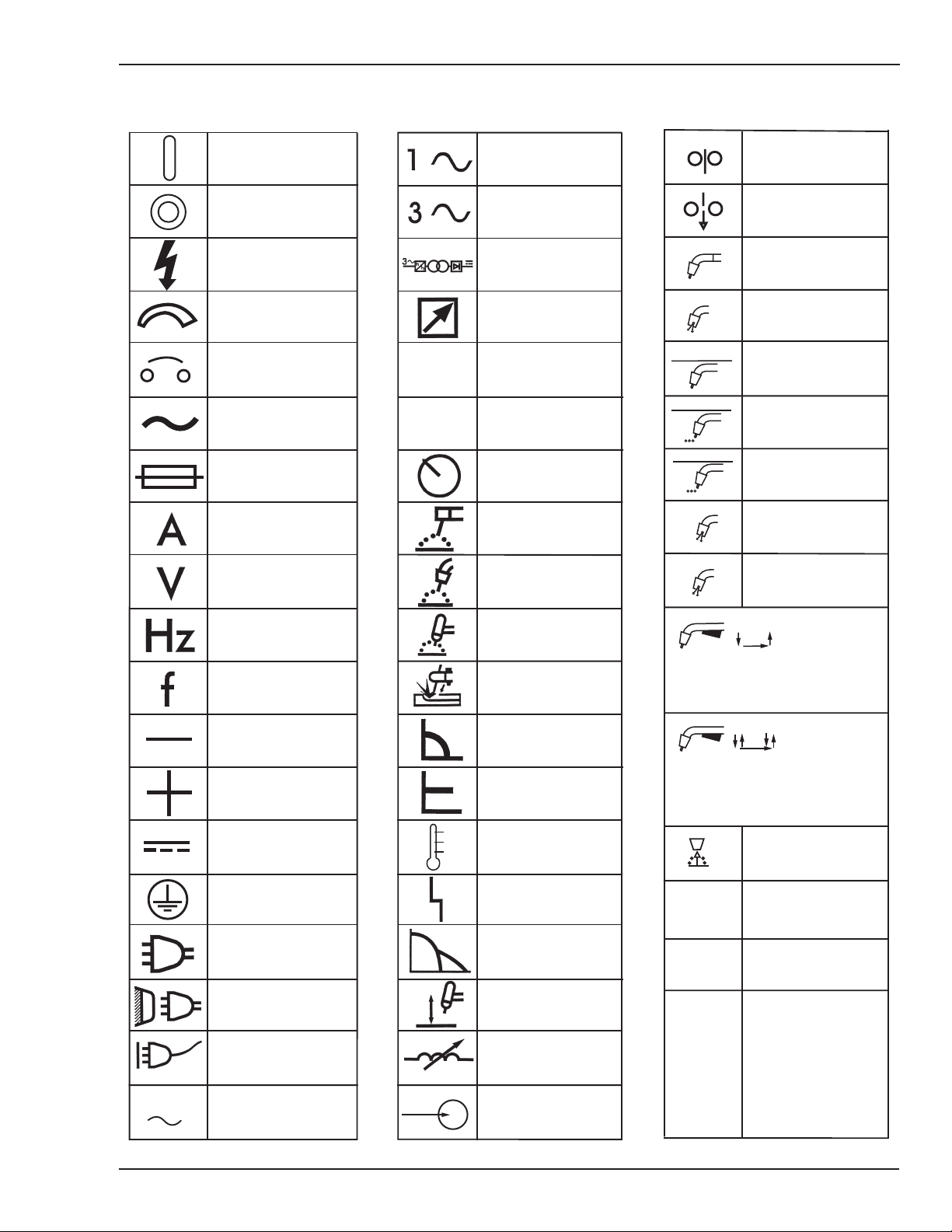
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS FIREPOWER FP-95
Gas Tungsten Arc
Welding (GTAW)
Air Carbon Arc
Cutting (CAC-A)
Constant Current
Constant Voltage
Or Constant Potential
High Temperature
Fault Indication
Arc Force
Touch Start (GTAW)
Variable Inductance
Voltage Input
Single Phase
Three Phase
Three Phase Static
Frequency ConverterTransformer-Rectifier
Dangerous Voltage
Off
On
Panel/Local
Shielded Metal
Arc Welding (SMAW)
Gas Metal Arc
Welding (GMAW)
Increase/Decrease
Circuit Breaker
AC Auxiliary Power
Remote
Duty Cycle
Percentage
Amperage
Voltage
Hertz (cycles/sec)
Frequency
Negative
Positive
Direct Current (DC)
Protective Earth
(Ground)
Line
Line Connection
Auxiliary Power
Receptacle RatingAuxiliary Power
Art # A-04130
115V 15A
t
t1
t2
%
X
IPM
MPM
t
V
Fuse
Wire Feed Function
Wire Feed Towards
Workpiece With
Output Voltage Off.
Preflow Time
Postflow Time
Spot Time
Spot Weld Mode
Continuous Weld
Mode
Press to initiate wirefeed and
welding, release to stop.
Purging Of Gas
Inches Per Minute
Meters Per Minute
Welding Gun
Burnback Time
Press and hold for preflow, release
to start arc. Press to stop arc, and
hold for preflow.
4 Step Trigger
Operation
2 Step Trigger
Operation
1.03 Symbol Chart
Note that only some of these symbols will appear on your model.
Safety Instructions 1-5 Manual 0-5122
Page 12
FIREPOWER FP-95 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
!
1.04 Precautions De Securite En Soudage A L’arc
MISE EN GARDE
LE SOUDAGE A L’ARC EST DANGEREUX
PROTEGEZ-VOUS, AINSI QUE LES AUTRES, CONTRE LES BLESSURES GRAVES POSSIBLES OU LA MORT. NE LAISSEZ PAS LES ENFANTS
S’APPROCHER, NI LES PORTEURS DE STIMULATEUR CARDIAQUE (A MOINS QU’ILS N’AIENT CONSULTE UN MEDECIN). CONSERVEZ CES
INSTRUCTIONS. LISEZ LE MANUEL D’OPERATION OU LES INSTRUCTIONS AVANT D’INSTALLER, UTILISER OU ENTRETENIR CET EQUIPEMENT.
Les produits et procédés de soudage peuvent sauser des blessures graves ou la mort, de même que des dommages au reste du matériel et à la
propriété, si l’utilisateur n’adhère pas strictement à toutes les règles de sécurité et ne prend pas les précautions nécessaires.
En soudage et coupage, des pratiques sécuritaires se sont développées suite à l’expérience passée. Ces pratiques doivent être apprises par
étude ou entraînement avant d’utiliser l’equipement. Toute personne n’ayant pas suivi un entraînement intensif en soudage et coupage ne devrait
pas tenter de souder. Certaines pratiques concernent les équipements raccordés aux lignes d’alimentation alors que d’autres s’adressent aux
groupes électrogènes.
La norme Z49.1 de l’American National Standard, intitulée “SAFETY IN WELDING AND CUTTING” présente les pratiques sécuritaires à suivre.
Ce document ainsi que d’autres guides que vous devriez connaître avant d’utiliser cet équipement sont présentés à la fin de ces instructions
de sécurité.
SEULES DES PERSONNES QUALIFIEES DOIVENT FAIRE DES TRAVAUX D’INSTALLATION, DE REPARATION, D’ENTRETIEN ET D’ESSAI.
1.05 Dangers relatifs au soudage à l’arc
AVERTISSEMENT
L’ELECTROCUTION PEUT ETRE MORTELLE.
Une décharge électrique peut tuer ou brûler gravement.
L’électrode et le circuit de soudage sont sous tension dès
la mise en circuit. Le circuit d’alimentation et les circuits
internes de l’équipement sont aussi sous tension dès
la mise en marche. En soudage automatique ou semiautomatique avec fil, ce dernier, le rouleau ou la bobine
de fil, le logement des galets d’entrainement et toutes les
pièces métalliques en contact avec le fil de soudage sont
sous tension. Un équipement inadéquatement installé ou
inadéquatement mis à la terre est dangereux.
1. Ne touchez pas à des pièces sous tension.
2. Portez des gants et des vêtements isolants, secs et non troués.
3 Isolez-vous de la pièce à souder et de la mise à la terre au moyen
de tapis isolants ou autres.
4. Déconnectez la prise d’alimentation de l’équipement ou arrêtez le
moteur avant de l’installer ou d’en faire l’entretien. Bloquez le commutateur en circuit ouvert ou enlevez les fusibles de l’alimentation
afin d’éviter une mise en marche accidentelle.
7. N’utilisez que des porte-électrodes bien isolés. Ne jamais plonger
les porte-électrodes dans l’eau pour les refroidir. Ne jamais les
laisser traîner par terre ou sur les pièces à souder. Ne touchez
pas aux porte-électrodes raccordés à deux sources de courant en
même temps. Ne jamais toucher quelqu’un d’autre avec l’électrode
ou le porte-électrode.
8. N’utilisez pas de câbles électriques usés, endommagés, mal épissés ou de section trop petite.
9. N’enroulez pas de câbles électriques autour de votre corps.
10. N’utilisez qu’une bonne prise de masse pour la mise à la terre de
la pièce à souder.
11. Ne touchez pas à l’électrode lorsqu’en contact avec le circuit de
soudage (terre).
12. N’utilisez que des équipements en bon état. Réparez ou remplacez
aussitôt les pièces endommagées.
13. Dans des espaces confinés ou mouillés, n’utilisez pas de source
de courant alternatif, à moins qu’il soit muni d’un réducteur de
tension. Utilisez plutôt une source de courant continu.
14. Portez un harnais de sécurité si vous travaillez en hauteur.
15. Fermez solidement tous les panneaux et les capots.
AVERTISSEMENT
5. Veuillez à installer cet équipement et à le mettre à la terre selon le
manuel d’utilisation et les codes nationaux, provinciaux et locaux
applicables.
6. Arrêtez tout équipement après usage. Coupez l’alimentation de
l’équipement s’il est hors d’usage ou inutilisé.
Manual 0-5122 1-6 Safety Instructinos
LE RAYONNEMENT DE L’ARC PEUT BRÛLER LES YEUX
ET LA PEAU; LE BRUIT PEUT ENDOMMAGER L’OUIE.
L’arc de soudage produit une chaleur et des rayons
ultraviolets intenses, susceptibles de brûler les yeux
et la peau. Le bruit causé par certains procédés peut
endommager l’ouïe.
Page 13
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS FIREPOWER FP-95
1. Portez une casque de soudeur avec filtre oculaire de nuance appropriée (consultez la norme ANSI Z49 indiquée ci-après) pour
vous protéger le visage et les yeux lorsque vous soudez ou que
vous observez l’exécution d’une soudure.
2. Portez des lunettes de sécurité approuvées. Des écrans latéraux
sont recommandés.
3. Entourez l’aire de soudage de rideaux ou de cloisons pour protéger
les autres des coups d’arc ou de l’éblouissement; avertissez les
observateurs de ne pas regarder l’arc.
4. Portez des vêtements en matériaux ignifuges et durables (laine et
cuir) et des chaussures de sécurité.
5. Portez un casque antibruit ou des bouchons d’oreille approuvés
lorsque le niveau de bruit est élevé.
AVERTISSEMENT
LES VAPEURS ET LES FUMEES SONT DANGEREUSES
POUR LA SANTE.
Le soudage dégage des vapeurs et des fumées dangereuses à respirer.
1. Eloignez la tête des fumées pour éviter de les respirer.
2. A l’intérieur, assurez-vous que l’aire de soudage est bien ventilée
ou que les fumées et les vapeurs sont aspirées à l’arc.
3. Si la ventilation est inadequate, portez un respirateur à adduction
d’air approuvé.
4. Lisez les fiches signalétiques et les consignes du fabricant relatives
aux métaux, aux produits consummables, aux revêtements et aux
produits nettoyants.
5. Ne travaillez dans un espace confiné que s’il est bien ventilé;
sinon, portez un respirateur à adduction d’air. Les gaz protecteurs
de soudage peuvent déplacer l’oxygène de l’air et ainsi causer
des malaises ou la mort. Assurez-vous que l’air est propre à la
respiration.
6. Ne soudez pas à proximité d’opérations de dégraissage, de nettoyage ou de pulvérisation. La chaleur et les rayons de l’arc peuvent
réagir avec des vapeurs et former des gaz hautement toxiques et
irritants.
7. Ne soudez des tôles galvanisées ou plaquées au plomb ou au
cadmium que si les zones à souder ont été grattées à fond, que
si l’espace est bien ventilé; si nécessaire portez un respirateur à
adduction d’air. Car ces revêtements et tout métal qui contient
ces éléments peuvent dégager des fumées toxiques au moment
du soudage.
SELECTION DES NUANCES DE FILTRES OCULAIRS POUR LA PROTECTION
DES YEUX EN COUPAGE ET SOUDAGE (selon AWS á 8.2-73)
Opération de coupage
ou soudage
Brassage tendre
au chalumeau
Brassage fort
au chalumeau
Oxycoupage métaux ferreux toutes conditions 12
mince moins de 1 po. (25 mm) 2 ou 3
moyen de 1 á 6 po. (25 á 150 mm) 4 ou 5
épais plus de 6 po. (150 mm) 5 ou 6
Soudage aux gaz Soudage á l'arc Plasma (PAW) toutes dimensions 12
mince moins de 1/8 po. (3 mm) 4 ou 5
moyen de 1/8 á 1/2 po. (3 á 12 mm) 5 ou 6 mince 12
épais plus de 1/2 po. (12 mm) 6 ou 8 épais 14
Soudage á l'arc avec
électrode enrobees
(SMAW)
Dimension d'électrode ou
Epiasseur de métal ou
Intensité de courant
toutes conditions 2
toutes conditions 3 ou 4 métaux non-ferreux toutes conditions 11
moins de 5/32 po. (4 mm) 10 Coupage á l'arc Plasma (PAC)
5/32 á 1/4 po. (4 á 6.4 mm) 12 mince moins de 300 amperès 9
plus de 1/4 po. (6.4 mm) 14 moyen de 300 á 400 amperès 12
Nuance de
filtre oculaire
Opération de coupage
ou soudage
Soudage á l'arc sous gaz
avec fil plein (GMAW)
Soudage á l'arc sous gaz avec
électrode de tungstène
(GTAW)
Soudage á l'hydrogène
atomique (AHW)
Soudage á l'arc avec
électrode de carbone (CAW)
Gougeage Air-Arc avec
électrode de carbone
Dimension d'électrode ou
Epiasseur de métal ou
Intensité de courant
toutes conditions 12
toutes conditions 12
toutes conditions 12
épais plus de 400 amperès 14
Nuance de
filtre
oculaire
Safety Instructions 1-7 Manual 0-5122
Page 14
FIREPOWER FP-95 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
AVERTISSEMENT
LE SOUDAGE PEUT CAUSER UN INCENDIE OU UNE
EXPLOSION
L’arc produit des étincellies et des projections. Les particules volantes, le métal chaud, les projections de soudure
et l’équipement surchauffé peuvent causer un incendie
et des brûlures. Le contact accidentel de l’électrode ou
du fil-électrode avec un objet métallique peut provoquer
des étincelles, un échauffement ou un incendie.
1. Protégez-vous, ainsi que les autres, contre les étincelles et du
métal chaud.
2. Ne soudez pas dans un endroit où des particules volantes ou des
projections peuvent atteindre des matériaux inflammables.
3. Enlevez toutes matières inflammables dans un rayon de 10, 7
mètres autour de l’arc, ou couvrez-les soigneusement avec des
bâches approuvées.
4. Méfiez-vous des projections brulantes de soudage susceptibles
de pénétrer dans des aires adjacentes par de petites ouvertures
ou fissures.
5. Méfiez-vous des incendies et gardez un extincteur à portée de la
main.
6. N’oubliez pas qu’une soudure réalisée sur un plafond, un plancher,
une cloison ou une paroi peut enflammer l’autre côté.
7. Ne soudez pas un récipient fermé, tel un réservoir ou un baril.
8. Connectez le câble de soudage le plus près possible de la zone
de soudage pour empêcher le courant de suivre un long parcours inconnu, et prévenir ainsi les risques d’électrocution et
d’incendie.
AVERTISSEMENT
LES BOUTEILLES ENDOMMAGEES PEUVENT EXPLOSER
Les bouteilles contiennent des gaz protecteurs sous
haute pression. Des bouteilles endommagées peuvent
exploser. Comme les bouteilles font normalement partie
du procédé de soudage, traitez-les avec soin.
1. Protégez les bouteilles de gaz comprimé contre les sources de
chaleur intense, les chocs et les arcs de soudage.
2. Enchainez verticalement les bouteilles à un support ou à un cadre
fixe pour les empêcher de tomber ou d’être renversées.
3. Eloignez les bouteilles de tout circuit électrique ou de tout soudage.
4. Empêchez tout contact entre une bouteille et une électrode de
soudage.
5. N’utilisez que des bouteilles de gaz protecteur, des détendeurs,
des boyauxs et des raccords conçus pour chaque application
spécifique; ces équipements et les pièces connexes doivent être
maintenus en bon état.
6. Ne placez pas le visage face à l’ouverture du robinet de la bouteille
lors de son ouverture.
7. Laissez en place le chapeau de bouteille sauf si en utilisation ou
lorsque raccordé pour utilisation.
8. Lisez et respectez les consignes relatives aux bouteilles de gaz
comprimé et aux équipements connexes, ainsi que la publication
P-1 de la CGA, identifiée dans la liste de documents ci-dessous.
9. Ne dégelez pas les tuyaux avec un source de courant.
10. Otez l’électrode du porte-électrode ou coupez le fil au tube-contact
lorsqu’inutilisé après le soudage.
11. Portez des vêtements protecteurs non huileux, tels des gants en
cuir, une chemise épaisse, un pantalon revers, des bottines de
sécurité et un casque.
AVERTISSEMENT
LES ETINCELLES ET LES PROJECTIONS BRULANTES
PEUVENT CAUSER DES BLESSURES.
Le piquage et le meulage produisent des particules
métalliques volantes. En refroidissant, la soudure peut
projeter du éclats de laitier.
1. Portez un écran facial ou des lunettes protectrices approuvées. Des écrans latéraux sont recommandés.
2. Portez des vêtements appropriés pour protéger la peau.
AVERTISSEMENT
LES MOTEURS PEUVENT ETRE DANGEREUX
LES GAZ D’ECHAPPEMENT DES MOTEURS PEUVENT
ETRE MORTELS.
Les moteurs produisent des gaz d’échappement nocifs.
1. Utilisez l’équipement à l’extérieur dans des aires ouvertes et bien
ventilées.
2. Si vous utilisez ces équipements dans un endroit confiné, les
fumées d’échappement doivent être envoyées à l’extérieur, loin
des prises d’air du bâtiment.
AVERTISSEMENT
LE CARBURANT PEUR CAUSER UN INCENDIE OU UNE
EXPLOSION.
Le carburant est hautement inflammable.
1. Arrêtez le moteur avant de vérifier le niveau e carburant ou de
faire le plein.
Manual 0-5122 1-8 Safety Instructinos
Page 15

SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS FIREPOWER FP-95
2. Ne faites pas le plein en fumant ou proche d’une source d’étincelles
ou d’une flamme nue.
3. Si c’est possible, laissez le moteur refroidir avant de faire le plein
de carburant ou d’en vérifier le niveau au début du soudage.
4. Ne faites pas le plein de carburant à ras bord: prévoyez de l’espace
pour son expansion.
5. Faites attention de ne pas renverser de carburant. Nettoyez tout
carburant renversé avant de faire démarrer le moteur.
AVERTISSEMENT
DES PIECES EN MOUVEMENT PEUVENT CAUSER DES
BLESSURES.
Des pièces en mouvement, tels des ventilateurs, des
rotors et des courroies peuvent couper doigts et mains,
ou accrocher des vêtements amples.
1. Assurez-vous que les portes, les panneaux, les capots et les
protecteurs soient bien fermés.
2. Avant d’installer ou de connecter un système, arrêtez le moteur.
3. Seules des personnes qualifiées doivent démonter des protecteurs
ou des capots pour faire l’entretien ou le dépannage nécessaire.
4. Pour empêcher un démarrage accidentel pendant l’entretien,
débranchez le câble d’accumulateur à la borne négative.
5. N’approchez pas les mains ou les cheveux de pièces en mouvement; elles peuvent aussi accrocher des vêtements amples et des
outils.
6. Réinstallez les capots ou les protecteurs et fermez les portes après
des travaux d’entretien et avant de faire démarrer le moteur.
AVERTISSEMENT
LA VAPEUR ET LE LIQUIDE DE REFROIDISSEMENT
BRULANT SOUS PRESSION PEUVENT BRULER LA
PEAU ET LES YEUX.
Le liquide de refroidissement d’un radiateur peut être
brûlant et sous pression.
1. N’ôtez pas le bouchon de radiateur tant que le moteur n’est pas
refroidi.
2. Mettez des gants et posez un torchon sur le bouchon pour
l’ôter.
3. Laissez la pression s’échapper avant d’ôter complètement le
bouchon.
PLOMB AVERTISSEMENT
Ce produit contient des produits chimiques, comme
le plomb, ou engendre des produits chimiques,
reconnus par l’état de Californie comme pouvant être à l’origine de cancer, de malformations
fœtales ou d’autres problèmes de reproduction.
Il faut se laver les mains après toute manipulation.
(Code de Californie de la sécurité et santé, paragraphe
25249.5 et suivants)
1.06 Principales Normes De Securite
Safety in Welding and Cutting, norme ANSI Z49.1, American Welding
Society, 550 N.W. LeJeune Rd., Miami, FL 33128.
AVERTISSEMENT
DES ETINCELLES PEUVENT FAIRE EXPLOSER UN ACCUMULATEUR; L’ELECTROLYTE D’UN ACCUMU-LATEUR
PEUT BRULER LA PEAU ET LES YEUX.
Les accumulateurs contiennent de l’électrolyte acide et
dégagent des vapeurs explosives.
1. Portez toujours un écran facial en travaillant sur un accumu-lateur.
2. Arrêtez le moteur avant de connecter ou de déconnecter des câbles
d’accumulateur.
3. N’utilisez que des outils anti-étincelles pour travailler sur un accumulateur.
4. N’utilisez pas une source de courant de soudage pour charger un
accumulateur ou survolter momentanément un véhicule.
5. Utilisez la polarité correcte (+ et –) de l’accumulateur.
Safety and Health Standards, OSHA 29 CFR 1910, Superintendent
of Documents, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C.
20402.
Recommended Safe Practices for the Preparation for Welding and
Cutting of Containers That Have Held Hazardous Substances, norme
AWS F4.1, American Welding Society, 550 N.W. LeJeune Rd., Miami,
FL 33128.
National Electrical Code, norme 70 NFPA, National Fire Protection
Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
Safe Handling of Compressed Gases in Cylinders, document P-1,
Compressed Gas Association, 1235 Jefferson Davis Highway, Suite
501, Arlington, VA 22202.
Code for Safety in Welding and Cutting, norme CSA W117.2 Association
canadienne de normalisation, Standards Sales, 276 Rexdale Boulevard,
Rexdale, Ontario, Canada M9W 1R3.
Safe Practices for Occupation and Educational Eye and Face Protection, norme ANSI Z87.1, American National Standards Institute, 1430
Broadway, New York, NY 10018.
Cutting and Welding Processes, norme 51B NFPA, National Fire Protection Association, Batterymarch Park, Quincy, MA 02269.
Safety Instructions 1-9 Manual 0-5122
Page 16

FIREPOWER FP-95 SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Soudage á L’arc Avec
Electrode Non Fusible
(GTAW)
Decoupe Arc Carbone
(CAC-A)
Courant Constant
Tension Constante
Ou Potentiel Constant
Haute Température
Force d'Arc
Amorçage de L’arc au
Contact (GTAW)
Inductance Variable
Tension
Mono Phasé
Trois Phasé
Tri-Phase Statique
Fréquence Convertisseur
Transformateur-Redresseur
Tension dangereuse
Hors Tension
Sous Tension
Panneau/Local
Soudage Arc Electrique
Avec Electrode Enrobé
(SMAW)
Soudage á L’arc Avec
Fil Electrodes Fusible
(GMAW)
Augmentez/Diminuer
Disjoncteur
Source AC Auxiliaire
Distant
Facteur de Marche
Pourcentage
Intensité de Courant
Tension
Hertz (cycles/sec)
Fréquence
Négatif
Positif
Courant Continue (DC)
Terre de Protection
Ligne
Connexion de la Ligne
Source Auxiliaire
Classement de PriseSource Auxiliaire
Art # A-07639
115V 15A
t
t1
t2
%
X
IPM
MPM
t
Fusible
Déroulement du Fil
Alimentation du Fil Vers
la Pièce de Fabrication
Hors Tension
Durée de Pré-Dèbit
Durée de Post-Dèbit
Duréc du Pulse
Soudure Par Point
Appuyez pour dèruarer
l’alimentation du fils et la soudure,
le relâcher pour arrêter.
Purge Du Gaz
Mode Continu de
Soudure
Pouces Par Minute
Mètres Par Minute
Torch de
Soudage
Probléme de Terre
Maintenez appuyez pour pré-dèbit,
relailez pour initier l'arc. Appuyez
pour arrêter l'arc, et mainteuir pour
pré-dèbit.
Détente à 4-Temps
Détente à 2-Temps
V
1.07 Graphique de Symbole
Seulement certains de ces symboles apparaîtront sur votre modèle.
Manual 0-5122 1-10 Safety Instructinos
Page 17

INTRODUCTION FIREPOWER FP-95
!
SECTION 2:
INTRODUCTION
2.01 How to Use This Manual
This Operating Manual usually applies to the part numbers
listed on page i. If none are underlined, they are all covered
by this manual. To ensure safe operation, read the entire
manual, including the chapter on safety instructions and
warnings. Throughout this manual, the word WARNING,
CAUTION and NOTE may appear. Pay particular attention
to the information provided under these headings. These
special annotations are easily recognized as follows:
WARNING
Gives information regarding possible personal
injury. Warnings will be enclosed in a box
such as this.
CAUTION
Refers to possible equipment damage.
Cautions will be shown in bold type.
NOTE
Offers helpful information concerning certain
operating procedures. Notes will be shown
in italics
Additional copies of this manual may be purchased by
contacting Thermal Arc at the address and phone number
in your area listed in the inside back cover of this manual.
Include the Owner’s Manual number and equipment identification numbers.
Electronic copies of this manual can also be downloaded at
no charge in Acrobat PDF format by going to the Thermal
Arc web site listed below and clicking on the Literature
Library link:
http://www.thermalarc.com
2.02 Equipment Identification
The unit’s identification number (specification or part
number), model, and serial number usually appear on
a nameplate attached to the machine. Equipment which
does not have a nameplate attached to the machine is
identified only by the specification or part number printed
on the shipping container. Record these numbers for
future reference.
2.03 Receipt of Equipment
When you receive the equipment, check it against the
invoice to make sure it is complete and inspect the
equipment for possible damage due to shipping. If there is
any damage, notify the carrier immediately to file a claim.
Furnish complete information concerning damage claims
or shipping errors to the location in your area listed in the
inside back cover of this manual. Include all equipment
identification numbers as described above along with a
full description of the parts in error.
2.04 General
The FirePower FP-95 Machine is a single-phase input
welding machine and comes equipped with the following:
1. Built-in Wire Feeder and Wire Spool Hub
2. Welding Gun and Cable (6.5' / 2m)
3. Work Cable and Clamp (5' / 1.6m)
4. Input Cord (7' / 2.25m)
5. Operational Manual
6. Spare parts kit (2 contact tips)
7. 0.5 lb Wire spool
The welding system is designed for use with the following processes:
1. FCAW – Flux-cored arc welding – Does not require
the use of a shielding gas.
Introduction 2-1 Manual 0-5122
Page 18

FIREPOWER FP-95 INTRODUCTION
1
2
3
4
Art # A-09101
2.05 Handle and Foot Assembly
2.06 Specifications
Description Firepower FP-95
Package System Part Number 1444-0322
Power Source Weight 37.15 lb ( 16.8 kg)
Power Source Dimensions HxWxD
Number of Phases 1 Ø
Frequency 60Hz
Flexible Supply Cable Size 7 ft (2.25 m) 14AWG
Supply Lead Plug Type 5-15P
Nominal Input Voltage
Rated Input Current 15A
Rated kVA @ 100% Duty Cycle 1.2kVA
Rated Input Current 15A (60A@20%)
Minimum Mains Circuit to suit factory fitted Plug &
Maximum Input Current 28A (85A@17%)
Generator Requirements 98145.4519
98145.4519 # 3.4kVA
Open Circuit Voltage Range 15 – 27V
Output Current Range 23 – 90A
Duty Cycle Period 10 Minutes
Number of Output Voltage Values 2
Lead (Weld Current @ Duty Cycle)
14"x7"x15"
(355.6 x 177.8 x 381mm)
120V AC
(+) 15A (60A@20%)
Maximum Mains Circuit to suit factory fitted Plug &
Lead (Weld Current @ Duty Cycle)
Wire Size Range (Flux Core)
(+) 28A (85A@17%)
.023” - .030”
(0.6 - 0.8mm)
Table 2-1: System Specifications
Manual 0-5122 2-2 Introduction
Page 19

INTRODUCTION FIREPOWER FP-95
FP-95 FIREPOWER Vin=115V 60Hz
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100
OUTPUT CURRENT
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
Art # A-09068
∆ The recommended time delay fuse or circuit breaker size is 20 amp. An individual branch circuit capable of carrying 30 amperes
and protected by fuses or circuit breaker is recommended for this application. Fuse size is based on not more than 200 percent
of the rated input amperage of the welding power source (Based on Article 630, National Electrical Code)
Thermal Arc continuously strives to produce the best product possible and therefore reserves the right to change, improve or
revise the specifications or design of this or any product without prior notice. Such updates or changes do not entitle the buyer
of equipment previously sold or shipped to the corresponding changes, updates, improvements or replacement of such items.
The values specified in the table above are optimal values, your values may differ. Individual equipment may differ from the above
specifications due to in part, but not exclusively, to any one or more of the following; variations or changes in manufactured
components, installation location and conditions and local power grid supply conditions.
2.07 Volt - Amp Curves
Introduction 2-3 Manual 0-5122
Figure 2-1: Volt/Amp curves of the FirePower 95
Page 20

FIREPOWER FP-95 INTRODUCTION
FirePower FP-95 at Rated Duty Cycle
0
1
2 3
4 5 6 7 8
Min ute s
9 10
Art # A-09034
2.08 Duty Cycle
Duty Cycle is the amount of arc-on time (actual welding time) during any 10 minute period that a machine can operate
at it’s rated output without damaging internal components. For example, the FirePower FP-95 is designed for 17%
duty cycle at 85 amps. This means that it has been designed and built to provide the rated amperage, 85 amps, for1.7
minutes out of every 10 minute period. During the other 8.3 minutes of the 10 minute period, the FirePower FP-95
must idle and be allowed to cool. The thermal cutout will operate if the duty cycle is exceeded.
If the unit overheats and the thermostat opens, wait 15 minutes for unit to cool.
Figure 2-2: Duty Cycle of FirePower95
2.09 MIG Gun Maintenance
Remove dust and metallic particles from the gun conduit by forcing clean, dry compressed air into the conduit once
a week. This will minimize wire feeding problems.
Manual 0-5122 2-4 Introduction
Page 21

INSTALLATION FIREPOWER FP-95
SECTION 3:
INSTALLATION
3.01 Location
For best operating characteristics and longest unit life,
take care in selecting the installation site. Avoid locations
exposed to high humidity, dust, high ambient temperature,
or corrosive fumes. Moisture can condense on electrical
components, causing corrosion or shorting of circuits.
Dirt on components will retain this moisture and also
increases wear on moving parts.
Adequate air circulation is needed at all times in order
to assure proper operation. Provide a minimum of 12”
(300mm) of free air space at both the front and rear of
the unit. Make sure that the ventilation openings are not
obstructed.
CAUTION
The FP-95 is not suitable for use in rain.
3.02 Safety
Refer to additional installation instructions under the
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS AND WARNINGS (Section 1)
in this manual.
3.03 Grounding
The internal frame of this welding machine should be
grounded for personal safety. Where grounding is mandatory under state or local codes, it is the responsibility of the
user to comply with all applicable rules and regulations.
Where no state or local codes exist, it is recommended
that the National Electrical Code be followed.
The Firepower FP-95's power cord is equipped with a
NEMA 5-15P plug and will only connect to a NEMA 5-15P
receptacle.
CAUTION
Consult the nameplate for proper input voltage
and input amperage. The method of installation, conductor size, and over-current protection shall conform to the requirements of the
local electrical code. All installation wiring
and machine connection shall be done by a
competent electrician.
The National Electrical Code (Article 630B) provides
standards for amperage handling capability of supply
conductors based on the duty cycle of the welding power
source. The FirePower 95 has a 17% duty cycle (1 minute
and 40 secondss of every 10 minutes can be used for
welding).The power cord supplied with this unit complies
with these standards. Ensure that the building supply and
receptacle comply with NEC standards and any additional
state and local codes.
NOTE
The supply wiring for the welding power source
must be capable of handling a minimum of 20
amperes. The welding power source must be
the only load connected to the supply circuit.
Poor unit performance or frequently opening
line fuses or circuit breakers can result from
an inadequate or improper supply.
CAUTION
3.04 Electrical Input Requirements
Plug the input cord into a properly grounded and protected
(by fuse or circuit breaker) mains receptacle capable of
handling a minimum of 20 Amperes. The Firepower FP-95
requires a 120VAC supply voltage.
Installation 3-1 Manual 0-5122
Do not connect the FirePower 95 to an input
power supply with a rated voltage that is
greater than 120 +10% VAC. Do not remove
the power cord ground prong.
Page 22

FIREPOWER FP-95 INSTALLATION
Spring
Hub
D-Ring
Wire Spool
Spool Locking
Knob
Art # A-09088
3.05 Requirements for Maximum Output
In order to obtain the maximum output capability of the
FirePower 95, a branch circuit capable of 20 amperes at
115 to 125 Volts 60 Hz is required. This generally applies
when welding steel that is equal to or greater than 12
gauge (0.105” 2.5mm) in thickness.
The rated output with this installation is 85 amperes, 18.25
Volt, 17% duty cycle (1 minute 40 seconds out of every
10 minutes used for welding).
3.06 Installing Wire Spool
As delivered from the factory, the unit is set with a 4”
(102mm) spool.
Installation of Wire Spool
Assemble parts in sequence (shown in Figure 3-1 from
right to left).
1. Retaining Spring
2. "D" Washer
3. Spool
4. Locking knob (press the two tabs to remove it).
Figure 3-1: 4" Spool Installation
Manual 0-5122 3-2 Installation
Page 23

INSTALLATION FIREPOWER FP-95
.030
0.8
Art # A-07963
Pressure Adjust Device
Pressure Arm
Gun Cable
Wire Spool
Inlet Wire Guide
Feed Roll
Art # A-09069
3.07 Feedrolls
A feedroll consists of two different sized grooves. As
delivered from the factory, the drive roll is installed for
.030" (0.8mm) Firepower FP-95.
The branding inside at the end of the feedroll refers to the
size nearest to the mark
This also applies to optional feedrolls which are available
for this machine.
3.08 Install Wire into the Feedhead
If Not Installed Load the Wire Spool per directions in section 3.06 onto the hub so that the wire will feed off the
spool as the spool rotates counter- clockwise.
Figure 3-2 : Feedroll Example
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL! Make certain
the machine is unplugged from the power
receptacle. Do not plug machine in until told
to do so in these instructions.
CAUTION
Use care in handling the spooled wire as it
will tend to “unravel” when loosened from the
spool. Grasp the end of the wire firmly and do
not let go of it. Make sure that the end of the
wire is free of any burrs and is straight.
Figure 3-3: Wire Feeder Components
Route the Wire Through the Feedhead
1. Loosen Pressure Adjust Device (Fig. 3-3).
2. Open Pressure Adjust Device (Fig. 3-3).
Installation 3-3 Manual 0-5122
Page 24

FIREPOWER FP-95 INSTALLATION
Pressure Adjust Device
Pressure Arm
Art # A-09070
Pressure Adjust Device
Pressure Arm
Wire Spool
Wire
Feed Roll
Art # A-09071
Art # A-09072
3. Open Pressure Arm (Fig. 3-4).
4. Place the end of the wire into the Inlet Wire Guide,
feeding it over the Feedroll. Make certain that the proper
groove is being used (Fig. 3-5).
5. Pass the wire into the Gun Liner of the Gun Cable End
(Fig. 3-5).
6. Close the Pressure Arm (Fig. 3-5).
7. Close the Pressure Adjust Device. Tighten it to a “snug”
condition (Fig. 3-6).
8. Figure 3-6 shows the result with the wire installed.
NOTE
If there is too much pressure on the drive roll
the wire gets locked and the motor could get
damaged, If it is too loose the wire will not
feed properly.
Figure 3-5: Inserting Wire
Figure 3-4: Opening Pressure Arm
Manual 0-5122 3-4 Installation
Figure 3-6: Wire Installed
Page 25

INSTALLATION FIREPOWER FP-95
MIN
MAX
Art # A-09073
MIN
MAX
Art # A-09073
Contact Tip
Nozzle
Gun Switch
Wire
Art # A-09074
!
3.09 Install Wire into the Welding Gun
1. Plug the Welding Power Source into the 120VAC
receptacle.
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL! With the gun
switch (located on the gun) activated, welding power is applied to the output terminals,
feedroll, ground clamp, gun cable connection
and welding wire. Do not touch these parts
with the gun switch activated.
2. Turn the welding machine ON with the front panel
Voltage Power Switch set to "Min"
5. Activate the gun switch until the wire feeds
out past the gun nozzle and deactivate the gun
switch.
Figure 3-9: Feed Wire Through Gun
Figure 3--7: Power ON
3. Set the wire feed speed to half-way or "5".
Figure 3-8: Wire Speed Half-way
4. Straighten the gun cable. Remove the nozzle and
contact tip from the MIG welding gun (see Section
2.08).
6. Set the Voltage Power Switch to "OFF" and unplug
the supply cord.
7. Replace the contact tip and nozzle. Cut the wire
within ¼” (6mm) from the nozzle.
WARNING:
The drive rollers, when moving, may crush the
fingers. Periodically, check the drive rollers.
Replace them when they are worn and compromise the regular feeding of the wire.
CAUTION:
The FP-95’s welding torch is a “live” contact
torch and is ALWAYS in the power on position.
Wear eye protection at all times when handling
this torch.
WARNING
WARNING
If ground connection clamp is in place on the
workpiece the electrode wire is electrically
“hot” when the gun switch is activated.
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL! With the gun
switch (located on the gun) activated, welding power is applied to the output terminals,
feedroll, ground clamp, gun cable connection
and welding wire. Do not touch these parts
while the gun switch is activated.
Installation 3-5 Manual 0-5122
Page 26

FIREPOWER FP-95 INSTALLATION
This Page Intentionally Blank
Manual 0-5122 3-6 Installation
Page 27

OPERATION FIREPOWER FP-95
!
!
SECTION 4:
OPERATION
4.01 General Safety Precautions
Read and understand the safety instructions at the beginning of this manual prior to operating this machine.
WARNING
Be sure to put on proper protective clothing and eye safeguards (welding coat, apron, gloves, and welding helmet, with proper
lenses installed). See Safety Instructions and Warnings chapter included in this manual. Neglect of these precautions may result
in personal injury.
WARNING
Make all connections to the power source including electrode and work cables, as well as remote control cables, with the power
source turned off. These connections could be electrically live with the power switch ON.
WARNING
ELECTRIC SHOCK CAN KILL! Do not operate the machine with the door open.
CAUTION
Do not pull the machine with the gun. Damage can occur to the gun, gun liner and machine. Avoid bending the gun cable with a
sharp radius. Damage can occur to the gun liner.
Operation 4-1 Manual 0-5122
Page 28

FIREPOWER FP-95 OPERATION
4.02 FirePower Controls
Genuine TWECO contact tips should be used.
Refer to Figure 4-1
NOTE
1. Power ON / OFF switch turns the power on and
off. It also lights when the power supply has gone
into overtemp.
2. The Wire Speed Control knob controls the welding
current via the electrode wire feed rate (i.e. the
speed of the wire feed motor).
3. The Voltage Power Switch selects between MIN
and MAX voltage levels to the welding terminals.
CAUTION
The Voltage Power Switch MUST NOT BE SWITCHED
during the welding process.
4. Welding Torch and Cable
5. The Work Cable & Clamp connects to the item
being welded.
6. Main Power Cable.
7. The moveable tension knob applies pressure to
the grooved roller via screw-adjustable spring
pressure. The adjustable spring screw should be
adjusted to a minimum pressure that will provide
satisfactory wire feed without slippage. If slipping occurs, and inspection of the wire contact
tip reveals no wear, distortion or burn-back jam,
the conduit liner should be checked for kinks and
clogging by metal flakes and slag. If this is not
the cause of slipping, the feedroll pressure can
be increased by rotating the adjustable spring
screw clockwise. The use of excessive pressure
may cause rapid wear of the feed roller, motor
shaft and motor bearings.
CAUTION
Loose welding terminal connections can cause overheating and result in the cables being fused to the welding
terminals.
(8) The wire reel hub incorporates a friction brake
which is adjusted during manufacture for optimum braking.
Manual 0-5122 4-2 Operation
Page 29

OPERATION FIREPOWER FP-95
FP-95
MIN
MAX
v
RATED OUTPUT
VOLTS 17.3
AMPS 90
DUTY CYCLE 16%
MAX OCV 27
AMP RANGE 23-90
CSA
21
60
20%
27
23-90
120V Wire Feed Welder
Welds 22 gauge to 1/8"(3.2mm) Mild Steel
1
Art # A-09064
3
2
4
5
6
7
8
Figure 4-1: FirePower Controls
Operation 4-3 Manual 0-5122
Page 30

FIREPOWER FP-95 OPERATION
!
!
4.03 Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
4.04 Shutdown Procedures
See Welding Guidelines included in this manual.
1. Make all necessary connections as instructed in
the INSTALLATION chapter.
2. Place the WELDING OUTPUT VOLTAGE SELECTOR
at the desired setting.
3. Rotate the WIRE SPEED FEED control to the desired setting.
4. Plug the supply cord into a 120 VAC 20 Ampere
receptacle.
5. Connect the WORK CLAMP to the workpiece
(material to be welded).
6. Extend wire from the gun, and cut to proper stickout for that type of wire (when welding always
maintain this distance).
7. Position gun to where it is at approximately right
angles to the workpiece with proper wire stickout. Lower your welding helmet and pull the gun
trigger switch.
WARNING
Be sure to put on proper protective clothing and eye safeguards (welding coat, apron, gloves, and welding helmet
with proper lenses installed). See Safety Instructions and
Warnings chapter included in this manual. Neglect of
these precautions may result in personal injury.
Travel at a speed necessary to maintain a bead width from
1/8" to ¼" (3mm to 6mm) depending on the thickness of
the material. For material that may require larger weldments, either change to a larger diameter filler wire or use
multi pass beads. On some applications, it may be necessary to adjust the voltage range to stabilize the arc.
Upon completion of the weld, release the gun trigger
switch, raise the welding helmet, and visually examine
the weld.
NOTE
To help you overcome any problems that might arise,
you will find useful information in section 4.05 Basic
Welding Techniques.
Place the POWER ON/OFF SWITCH in the OFF position.
WARNING
After releasing the gun switch, the electrode wire will
remain electrically “hot” for several seconds.
4.05 Basic Welding Technique
General
Two different welding processes are covered in this
section, with the intention of providing the very basic
concepts in using the semi-automatic mode of welding.
In this mode, the welding gun is hand-held. The electrode
(welding wire) is then fed into a weld puddle and the arc
is shielded by a gas or gas mixture.
Setting of the Power Supply
The settings of the FP 95 requires some practice by the
operator in that the welding Power Supply has two control
settings that need to balance. These are the Wire Speed
control and the Voltage Control switches. The welding
current is determined by the Wire Speed control (i.e., the
current will increase with increased wire speed, resulting
in a shorter arc). Slower wire speed will reduce the current and lengthen the arc. Increasing the welding voltage
hardly alters the welding current level, but lengthens the
arc. By decreasing the voltage, a shorter arc is obtained
with little change in welding current.
When changing to a different electrode wire diameter,
different control settings are required. A thinner electrode
wire needs more wire speed to achieve the same current
level.
A satisfactory weld cannot be obtained if the wire speed
and voltage switch settings are not adjusted to suit the
electrode wire diameter and dimensions of the work
piece.
If the wire speed is too high for the welding voltage,
“stubbing” will occur as the wire dips into the molten pool
and does not melt. Welding in these conditions normally
produces a poor weld due to lack of fusion. If however,
the welding voltage is too high, large drops will form on
the end of the electrode wire, causing spatter. The correct setting of voltage and wire speed can be seen in the
shape of the weld deposit and heard by a smooth regular
arc sound.
Manual 0-5122 4-4 Operation
Page 31

OPERATION FIREPOWER FP-95
Arc
Flux Cored
Electrode
Nozzle (optional)
Gas (optional)
Molten Metal
Molten
Slag
Solid Weld
Metal
Slag
Art: A-05104
!
Direction of
Travel
90º
Transverse
Angle
5º to 15º
Longitudinal
Angle
Art: A-05105
Direction of Travel
30º
to 60º
Transverse
Angle
10 to 20º Longitudinal
Angle
30 to 60º
Transverse
Angle
10º Longitudinal Angle
Art: A-05106
5 to 15º
Longitudinal Angle
30 to 60º
Transverse Angle
Direction of
Travel
Art: A-05107
Direction of Travel
30 to 60º
Transverse Angle
5 to 15º
Longitudinal
Angle
Art: A-05108
Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
This process also known as Open Arc, Innershield, FAB
Shield, etc., is an electric arc welding process which fuses
together the parts to be welded by heating them with an
arc between a continuous flux filled electrode wire and
the work. Shielding is obtained through decomposition of
the flux within the tubular wire. The process is normally
applied semi-automatically; however the process may be
applied automatically or by machine. It is commonly used
to weld large diameter electrodes in the flat and horizontal
position and small electrode diameters in all positions. The
process is used to a lesser degree for welding stainless
steel and for overlay work.
The electrode wire is not energized until the gun trigger
switch is depressed. The wire may therefore be placed on
the seam or joint prior to lowering the helmet.
Figure 4-4: Butt and Horizontal Welds
Figure 4-3: FCAW Process
WARNING
Follow these instructions only after referring to the Safety
Instructions and Warnings chapter of this manual, and
the instructions in the Installation chapter
Check List Before Starting
Wire Feed Speed – 1 to 10
Voltage Range Switch Setting – MIN or MAX
Electrode Wire Stick-out – approx 3/8” (10mm)
4.06 Welding Gun Positions
The welding gun should be held at an angle to the weld
joint. Hold the gun so that the welding seam is viewed
at all times. Always wear the welding helmet with proper
filter lenses.
Figure 4-5: Vertical Weld
Figure 4-6: Horizontal Fillet Weld
Figure 4-7: Overhead
CAUTION
Do not pull the welding gun back when the arc is
established. This will create excessive wire extension
(stickout) and make a very poor weld.
Operation 4-5 Manual 0-5122
Page 32

FIREPOWER FP-95 OPERATION
4.07 Establishing the Arc and Making
4.09 Welding Procedure
Weld Beads
Before attempting to weld on a finished piece of work, it
is recommended that practice welds be made on a sample
metal of the same material as that of the finished piece.
The easiest MIG welding procedure for the beginner to
experiment with, is the flat position. This equipment is
capable of flat, vertical and overhead positions.
For practicing MIG welding, secure some pieces of 16 or
18 gauge (0.06” 1.5mm or 0.08” 2.0mm) mild steel plate
6” x 6” (150 x 150mm). Use 0.024” (0.6mm) wire.
4.08 Pre-Weld Procedure
1. Check the OPERATION chapter of this manual for
details on this equipment.
2. Set the welding voltage range switch at position
MIN or MAX.
3. Set the wire feed speed control to about the 2.5
setting. Readjust as necessary.
4. Review standard safe practice procedures in ventilation, eye and face protection, fire, compressed
gas and preventative maintenance. See Safety
Instructions and Warnings chapter included in
this manual.
1. Maintain the tip to work distance (stickout) at 5/16”
to 3/8” (8 to 9mm) at all times.
2. For transverse and longitudinal nozzle angles, see
section 4.06 Welding Gun Positions.
3. Hold the gun about 3/8” (9mm) from the work,
lower the helmet by shaking your head and
squeeze the trigger to start the wire feeding, and
establish the arc.
NOTE
Get in the habit of shaking the helmet down, rather than
using the hands. One hand must hold the gun, and the
other is often needed to hold pieces to be tacked or
positioned.
4. Make a single down-hand (pulling) stringer weld
bead.
5. Practice welding beads. Start at one edge and weld
across the plate to the opposite edge.
NOTE
When the equipment is properly adjusted, a rapidly
cracking or hissing sound of the arc is a good indicator
of correct arc length.
6. Practice stopping in the middle of the plate, restarting into the existing weld crater and continuing
the weld bead across the plate.
NOTE
When the gun trigger is released after welding, the
electrode forms a ball on the end. To the new operator,
this may present a problem in obtaining the penetration
needed at the start of the next weld. This can be corrected
by cutting the ball off with wire cutters.
Manual 0-5122 4-6 Operation
Page 33

OPERATION FIREPOWER FP-95
4.10 Reference Table
The following table is provided as a user aid when performing FLUX CORED welding.
Result Desired Welding Variable
Arc
Voltage
Welding Current
(wire speed)
Travel
Speed Nozzle Angle Stick out
Wire
size
Deeper
Penetration 1Increase
Shallower
Penetration 1Decrease 3Leading 2Increase 4Larger
Larger Bead 1Increase 2Decrease 3Increase (*)
Smaller Bead 2Decrease 2Increase
Higher Narrower
Bead 1Decrease 2Trailing 3Increase
Flatter Wider
Bead 1Increase 290° or Leading 3Decrease
Faster
Deposition Rate 1Increase 2Increase (*) 3Larger
Slower
Deposition Rate 1Decrease
Key: 1 - First Choice, 2 - Second Choice, 3 - Third Choice, 4 - Fourth Choice
3Trailing Max
25° 2Decrease
4Smaller
(*)
3Decrease
(*)
2Decrease
(*) 3Smaller
Table 4-1: Welding Reference Table
Operation 4-7 Manual 0-5122
Page 34

FIREPOWER FP-95 OPERATION
Art # A-09033
Steel
Flux Core
E71T-GS
None
Required
.030" (0.8mm)
.035" (0.9mm)
Material
Type
Wire
Type
Shielding Gas
and Flow Rate
Wire Size
(Diameter)
24 ga.
(0.6mm)
22 ga.
(0.7mm)
20 ga.
(0.9mm)
18 ga.
(1.2mm)
16 ga.
(3mm)
1/8"
(3.2mm)
THICKNESS
Wire
Speed
Voltage
Step
L (MIN)
H (MAX)
L
6
L
4
L
4
L
3
L
3
7
L
8
H
2
L
H
H
7
10
4.11 FirePower FP-95 Welding Setting Selection Guide
Figure 4-8 Welding Settings Guide
Manual 0-5122 4-8 Operation
Page 35

SERVICE FIREPOWER FP-95
SECTION 5:
SERVICE
5.01 Cleaning of the Unit
Periodically remove the right side panel (after disconnecting the supply cord from the receptacle) and blow out the
interior with clean, dry, compressed air of not more than
25 PSI air pressure. Do not strike any components with
the air hose nozzle.
5.02 Cleaning of the Feed Rolls
Clean the wire groove on the feed roll at frequent intervals.
This cleaning operation can be done by using a small
wire brush. To clean the wire groove, loosen the pressure
device and lift the feedroll pressure arm. Remove all wire
from the feedhead. Wipe off the bearing roll (the “top” roll
in the feedhead).
5.03 Basic Troubleshooting
The basic level of troubleshooting is that which can be
performed without special equipment or knowledge, and
without removing the covers from the Power Source.
If major components are faulty, then the Power Source
should be returned to an Accredited THERMAL ARC Service Agent for repair.
1. Porosity
When there is a gas problem the result is usually porosity
within the weld metal. Porosity always stems from some
contaminant within the molten weld pool which is in the
process of escaping during solidification of the molten
metal.
Contaminants range from no gas around the welding arc
to dirt on the work piece surface. Porosity can be reduced
by checking the following points:
1. Welding dirty, oily, painted, oxidized or greasy
plate.
a. Clean contaminates off the plate.
2. Distance between the MIG torch nozzle and the
work piece.
a. Keep the distance between the MIG torch nozzle
and the work piece to a minimum.
2. Inconsistent wire feed
Wire feeding problems can be reduced by checking the
following points:
1. Wire spool brake is too tight.
a. Feed roller driven by motor in the cabinet will
slip.
2. Wire spool brake is too loose.
a. Wire spool can unwind and tangle.
3. Worn or incorrect feed roller size.
a. Use ‘V’ groove drive feed roller matched to the
steel wire size you are welding.
4. Misalignment of inlet/outlet guides.
a. Wire will rub against the misaligned guides and
reduces wire feedability.
5. Liner blocked with slag.
a. Slag is produced by the wire passing through
the feed roller, if excessive pressure is applied
to the pressure roller adjuster. Slag can also
be produced by the wire passing through an
incorrect feed roller groove shape or size. Slag
is fed into the liner where it accumulates, thus
reducing wire feedability.
6. Incorrect or worn contact tip.
a. The contact tip transfers the weld current to
the electrode wire. If the hole in the contact
tip is too large, then arcing may occur inside
the contact tip resulting in the electrode wire
jamming in there. When using soft electrode
wire such as aluminum, the wire may become
jammed in the contact tip due to expansion of
the wire when heated. A contact tip designed
for soft electrode wires should be used.
7. Poor work lead contact to work piece.
a. If the work lead has a poor electrical contact to
the work piece, then the connection point will
heat up and result in a reduction of power at
the arc.
8. Bent liner.
a. This will cause friction between the wire and
the liner thus reducing wire feedability
Service 5-1 Manual 0-5122
Page 36

FIREPOWER FP-95 SERVICE
5.04 Welding Problems
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
1 Undercut. A Welding arc voltage too
high.
B Incorrect torch angle B Adjust angle
C Excessive heat input C Increase the torch travel speed and/or reduce weld-
2 Lack of penetration. A Welding current too low A Increase welding current by increasing wire feed
B Joint preparation too nar-
row or gap too tight
3 Lack of fusion. Voltage too low Increase voltage by increasing voltage selection
4 Excessive spatter. A Voltage too high A Lower voltage by reducing the voltage selection
B Voltage too low B Raise voltage by increasing the voltage selection
5 Irregular weld shape. A Incorrect voltage and
current settings. Convex =
voltage too low. Concave
= voltage too high.
A Reduce voltage by reducing the voltage selection
switch position or increase the wire feed speed.
ing current by reducing the voltage selection switch
position or reducing the wire feed speed.
speed and increasing voltage selection switch
position.
B Increase joint angle or gap
switch position.
switch or increase wirespeed control.
switch or reduce wirespeed control.
A Adjust voltage and current by adjusting the voltage
selection switch and the wirespeed control.
B Wire is wandering B Replace contact tip
C Insufficient or excessive
heat input
6 Weld cracking A Weld beads too small A Decrease travel speed
B Weld penetration narrow
and deep
C Excessive weld stresses C Increase weld metal strength or revise design.
D Excessive voltage D Decrease voltage by reducing the voltage selec-
E Cooling rate too fast E Slow the cooling rate by preheating part to be
7 Cold weld puddle A Faulty rectifier unit A Have an Accredited THERMAL ARC Service Agent
B Loose welding cable con-
nection.
C Low Primary Voltage C Contact supply authority.
D Adjust the wirespeed control or the voltage selec-
tion switch
B Reduce current and voltage and increase MIG
torch travel speed or select a lower penetration
shielding gas.
tion switch.
welded or cool slowly.
to test then replace the faulty component.
B Check all welding cable connections.
Table 5-1: Welding Problems
Manual 0-5122 5-2 Service
Page 37

SERVICE FIREPOWER FP-95
5.05 Power Source Problems
FAULT CAUSE REMEDY
1
Primary line voltage is
ON. Welding arc can not
be established.
2
Primary line voltage is
ON but when the MIG
Gun trigger switch is
depressed nothing happens.
3
Primary line voltage is
ON, no wire feed but gas
flows from the MIG Gun
when the torch trigger
switch is depressed.
A Primary fuse is blown. A Replace primary fuse.
B Broken connection in pri-
mary circuit.
MIG Gun trigger switch leads
are disconnected.
A Electrode wire stuck in wire
liner or contact tip (burnback jam).
B Have an Accredited THERMAL ARC Service Agent check
primary circuit.
Reconnect.
A Check for clogged / kinked MIG Gun wire liner or worn
contact tip. Replace faulty component(s).
B Faulty control PCB B Have an Accredited THERMAL ARC Service Agent in-
vestigate the fault.
4
Wire feeds when the
MIG Gun trigger switch
is depressed but arc can
not be established.
5
Jerky wire feed A Worn or dirty contact tip A Replace
Thermal Overtemp Light
6
is ON and Fan motor is
running
Thermal Overtemp Light
turns on in less than 30
7
seconds during welding.
Poor or no work lead connection.
B Worn feed roller. B Replace
C Excessive back tension from
wire reel hub.
D Worn, kinked or dirty conduit
liner
The machine duty cycle has
been exceeded.
Fan has stopped running or
fuse on PCB has blown
Clean work clamp area and ensure good electrical
contact.
C Reduce brake tension on spool hub
D Clean or replace conduit liner
Allow the fan to run so machine can cool down. When
light goes out, welding may resume.
Have an Accredited THERMAL ARC Service Agent replace the fuse.
Table 5-2: Power Source Problems
Service 5-3 Manual 0-5122
Page 38

FIREPOWER FP-95 SERVICE
This Page Intentionally Blank
Manual 0-5122 5-4 Service
Page 39

APPENDIX FIREPOWER FP-95
Art # A-09029
FEED ROLL INSTALLATION & CONSUMABLE GUIDE
Wire Feed Rolls & MIG Gun Consumables
Part No.
Description
1444-0427
Wire Feed Roll, Knurle, .023" - .030" /.035"
(0.6- 0.8mm/0.9mm), Hard/Cored
1444-0050
Nozzle
1444-0026
Contact Tip, .030" (0.8mm)
1444-0027 Contact Tip, .035" (0.9mm)
1444-0740
MIG Gun, Complete Assembly
Weld Wires
Part No.
Description
E71T-GS Flux Cored Wire, .030" (0.8mm), 2 lbs (0.9kg) Spool
E71T-GS Flux Cored Wire, .030" (0.8mm), 10 lbs (4.5kg) Spool
E71T-GS Flux Cored Wire, .035" (0.9mm), 2 lbs (0.9kg) Spool
E71T-GS Flux Cored Wire, .035" (0.9mm), 10 lbs (4.5kg) Spool
1444-0230
1444-0231
1444-0235
1444-0236
.030"
0.8mm
*
Refer to Warranty Schedule.
The branding size at the
end of the feedroll refers
to the size nearest to the mark.
APPENDIX 1: OPTIONS AND ACCESSORIES
• Contact your Thermal Arc distributor to order options and accessories. For assistance in locating a Thermal Arc
distributor, contact the Thermadyne office listed in the inside rear cover that is nearest to you.
• Note the model and specification number shown on the equipment nameplate.
Call 1-800-318-6819 Consumable Parts Management Group
Figure A-1: Feed Roll Replacements
Appendix A-1 Manual 0-5122
Page 40

FIREPOWER FP-95 APPENDIX
APPENDIX 2: POWER SUPPLY REPLACEMENT PARTS
ITEM DESCRIPTION PART NO.
1 CABLE CLAMP FOR CABLE DIAM.6+ SCREW 1444-0806
2 CABLE CLAMP, FP-95/125/135 1444-0807
3 DOOR LATCH 1444-0426
4 INPUT POWER CABLE, FP-95/125/135 1444-0433
5 PLASTIC HINGE FOR SIDE PANEL 1444-0435
6 YELLOW PILOT-LIGHT SWITCH 1444-0440
7 CHOKE, FP-95/125 1444-0846
8 CURRENT SWITCH 1444-0438
9 DIVIDING PANEL FP-95 + LABEL 1444-0814
10 EARTH CABLE, FP-95 1444-0724
11 EARTH CLAMP, FP-95 1443-0025
12 FRONT FRAME, FP-95 1444-0829
13 HANDLE, FP-95 1444-0827
14 KIT SPOOL HOLDER FOR D.16 SPOOLS
- COMP.
15 LEFT SIDE PANEL FP-95 W/SILKS. 1444-0813
16 LOWER PANEL FP-95 +SILKSCR. 1444-0810
17 MIG GUN, FP-95 1444-0740
18 P.C. BOARD, FP-95 1444-0441
19 POTENTIOMETER KNOB, FP-95 1445-0952
20 RECTIFIER, FP-95 1444-0851
21 RIGHT UPPER PANEL FP-95
+SILKSC.+LAB.+HINGES
22 SIDE PANEL.FP-95 +SILKS.+LABEL+HINGES 1444-0812
23 SLOW MOTOR D.28 +PINION 1444-0805
24 THERMOSTAT 1444-0443
25 TORCH GROMMET, FP-95 1444-0832
26 TRANSFORMER, FP-95 1444-0845
27 WIRE FEEDER, FP-95 1444-0849
Table A-1: Replacement Parts
1444-0801
1444-0811
Manual 0-5122 A-2 Appendix
Page 41

APPENDIX FIREPOWER FP-95
FP-95
MIN
MAX
v
RATED OUTPUT
VOLTS 17.3
AMPS 90
DUTY CYCLE 16%
MAX OCV 27
AMP RANGE 23-90
CSA
21
60
20%
27
23-90
120V Wire Feed Welder
Welds 22 gauge to 1/8"(3.2mm) Mild Steel
22 5
3
15
13
25
8
19
6
21
17
16 10
11
18
23
9
20
24
14 27
1
7
26
2
4
Art # A-09067
12
Figure A-2: FP-95 Parts List Callouts
Appendix A-3 Manual 0-5122
Page 42

FIREPOWER FP-95 APPENDIX
Art # A-09025
APPENDIX 3: FIREPOWER 95 SYSTEM SCHEMATIC
Figure A-3: FP-95 Simple System Schematic
Manual 0-5122 A-4 Appendix
Page 43

STATEMENT OF WARRANTY (as of March 15, 2009)
LIMITED WARRANTY: THERMADYNE warrants that its products will be free of defects in workmanship or material.
Should any failure to conform to this warranty appear within the time period applicable to the THERMADYNE products
as stated below, THERMADYNE shall, upon written notification thereof and substantiation that the product has
been stored, installed, operated, and maintained in accordance with THERMADYNE’s specifications, instructions,
recommendations and recognized standard industry practice, and not been subject to misuse, repair, neglect,
alteration, or accident, correct such defects by suitable repair or replacement, at THERMADYNE’s sole option, of any
components or parts of the product determined by THERMADYNE to be defective.
THIS WARRANTY IS EXCLUSIVE AND IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING
ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: THERMADYNE shall not under any circumstances be liable for special, indirect or consequential
damages, such as, but not limited to, damage or loss of purchased or replacement goods, business interruption
or loss of profit, or claims of customers of distributor (hereinafter the “Purchaser”) for service interruption. The
remedies of the Purchaser set forth herein are exclusive and the liability of THERMADYNE with respect to any contract,
or anything done in connection therewith such as the performance or breach thereof, or from the manufacture, sale,
delivery, resale, or use of any goods covered by or furnished by THERMADYNE whether arising out of contract,
negligence, strict tort, or under any warranty, or otherwise, shall not, except as expressly provided herein, exceed the
price of the goods upon which such liability is based.
THIS WARRANTY BECOMES INVALID IF REPLACEMENT PARTS OR ACCESSORIES ARE USED WHICH MAY IMPAIR
THE SAFETY OR PERFORMANCE OF ANY THERMADYNE PRODUCT.
THIS WARRANTY IS INVALID IF THE PRODUCT IS SOLD BY NON-AUTHORIZED PERSONS.
This warranty is effective for the time stated in the Warranty Schedule beginning on the date that the authorized
distributor delivers the products to the Purchaser.
Warranty repairs or replacement claims under this limited warranty must be submitted by an authorized THERMADYNE
repair facility within thirty (30) days of the repair. No transportation costs of any kind will be paid under this warranty.
Transportation charges to send products to an authorized warranty repair facility shall be the responsibility of the
Purchaser. All returned goods shall be at the Purchaser’s risk and expense. This warranty supersedes all previous
THERMADYNE warranties.
Page 44

WARRANTY SCHEDULE (as of March 15, 2009)
The warranty is effective below for the time stated in the Warranty Schedule beginning on the date that the authorized
distributor delivers the products to the purchaser. THERMADYNE reserves the right to request documented evidence
of date of purchase.
ENGINE DRIVEN WELDERS Parts / Labor
Scout®, Raider®, Explorer™
Original Main Power Stators and Inductors 5 years / 3 years
Original Main Power Rectifiers, Control P.C. Boards 3 years / 3 years
All Other Original Circuits and Components Including, but not Limited to, Relays, 1 year / 1 year
Switches, Contactors, Solenoids, Fans, Power Switch Semi-Conductors
Engines and Associated Components are NOT Warranted by Thermal Arc®, See the Engine
Although Most are Warranted by the Engine Manufacturer. SEE THE ENGINE Manufacturers’ Warranty
MANUFACTURERS’ WARRANTY FOR DETAILS. for Details
GMAW/FCAW (MIG) WELDING EQUIPMENT Parts / Labor
Fabricator® 140, 180, 190, 210, 251, 281; Fabstar® 4030;
PowerMaster® 350, 350P, 500, 500P, 320SP, 400SP, 500SP; Excel-Arc® 6045;
Wire Feeders: Ultrafeed®, Porta-feed®
Original Main Power Transformer and Inductor 5 years / 3 years
Original Main Power Rectifiers, Control P.C. Boards, Power Switch Semi-Conductors 3 years / 3 years
All Other Original Circuits and Components Including, but not Limited to, Relays, 1 year / 1 year
Switches, Contactors, Solenoids, Fans, Electric Motors
GTAW (TIG) & MULTI-PROCESS INVERTER WELDING EQUIPMENT Parts / Labor
160TS, 300TS, 400TS, 185AC/DC, 200AC/DC, 300AC/DC, 400GTSW, 400MST,
300MST, 400MSTP
Original Main Power Magnetics 5 years / 3 years
Original Main Power Rectifiers, Control P.C. Boards, Power Switch Semi-Conductors 3 years / 3 years
All Other Original Circuits and Components Including, but not Limited to, Relays, 1 year / 1 year
Switches, Contactors, Solenoids, Fans, Electric Motors
PLASMA WELDING EQUIPMENT Parts / Labor
Ultima® 150
Original Main Power Magnetics 5 years / 3 years
Original Main Power Rectifiers, Control P.C. Boards, Power Switch Semi-Conductors 3 years / 3 years
Welding Console, Weld Controller, Weld Timer 3 years / 3 years
All Other Original Circuits and Components Including, but not Limited to, Relays, 1 year / 1 year
Switches, Contactors, Solenoids, Fans, Electric Motors, Coolant Recirculators
SMAW (Stick) WELDING EQUIPMENT Parts / Labor
Dragster™ 85; 95S
Original Main Power Magnetics 1 year / 1 year
Original Main Power Rectifiers, Control P.C. Boards 1 year / 1 year
All Other Original Circuits and Components Including, but not Limited to, Relays, 1 year / 1 year
Switches, Contactors, Solenoids, Fans, Power Switch Semi-Conductors
160S, 300S, 400S
Original Main Power Magnetics 5 years / 3 years
Original Main Power Rectifiers, Control P.C. Boards 3 years / 3 years
All Other Original Circuits and Components Including, but not Limited to, Relays, 1 year / 1 year
Switches, Contactors, Solenoids, Fans, Power Switch Semi-Conductors
GENERAL ARC EQUIPMENT Parts / Labor
FirePower® MIG Welders 5-2-1 years / NA
Water Recirculators 1 year / 1 year
Plasma Welding Torches 180 days / 180 days
Gas Regulators (Supplied with Power Sources) 180 days / NA
MIG and TIG Torches (Supplied with Power Sources) 90 days / NA
Replacement Repair Parts 90 days / NA
MIG, TIG and Plasma Welding Torch Consumable Items NA / NA
Page 45

GLOBAL CUSTOMER SERVICE CONTACT INFORMATION
Thermadyne USA
2800 Airport Road
Denton, Tx 76207 USA
Telephone: (940) 566-2000
800-426-1888
Fax: 800-535-0557
Email: sales@thermalarc.com
Thermadyne Canada
2070 Wyecroft Road
Oakville, Ontario
Canada, L6L5V6
Telephone: (905)-827-1111
Fax: 905-827-3648
Thermadyne Europe
Europe Building
Chorley North Industrial Park
Chorley, Lancashire
England, PR6 7Bx
Telephone: 44-1257-261755
Fax: 44-1257-224800
Thermadyne Asia Sdn Bhd
Lot 151, Jalan Industri 3/5A
Rawang Integrated Industrial Park - Jln Batu Arang
48000 Rawang Selangor Darul Ehsan
West Malaysia
Telephone: 603+ 6092 2988
Fax : 603+ 6092 1085
Cigweld, Australia
71 Gower Street
Preston, Victoria
Australia, 3072
Telephone: 61-3-9474-7400
Fax: 61-3-9474-7510
Thermadyne Italy
OCIM, S.r.L.
Via Benaco, 3
20098 S. Giuliano
Milan, Italy
Tel: (39) 02-36546801
Fax: (39) 02-36546840
Thermadyne, China
RM 102A
685 Ding Xi Rd
Chang Ning District
Shanghai, PR, 200052
Telephone: 86-21-69171135
Fax: 86-21-69171139
Thermadyne International
2070 Wyecroft Road
Oakville, Ontario
Canada, L6L5V6
Telephone: (905)-827-9777
Fax: 905-827-9797
Page 46

World Headquarters
Thermadyne Holdings Corporation
Suite 300, 16052 Swingley Ridge Road
St. Louis, MO 63017
Telephone: (636) 728-3000
FAX:
(636) 728-3010
Email: sales@thermalarc.com
www.thermalarc.com
 Loading...
Loading...