Page 1
SB-INTERPRETER
-- SELF TRAINING GUIDE ––
By:
Tony M. Ramirez
April 2010
Page 2

g
e
Triton Imaging Inc.
Engineerin
2121 41st Avenue, Suite 211
Capitola, CA 95010
831-722-7373
831-475-8446
sales@tritonimaginginc.com
support@tritonimaginginc.com
USA
Offic
© 2010 TRITON
This training guide is provided as a means to become familiar with TRITON’s software through a series of steps typical for
processing data from most sub-bottom surveys, and is not intended as a complete user manual. The user interface presented
in this guide is subject to change to accommodate software upgrades and revisions. While every precaution has been taken
to eliminate errors in this guide, TRITON assumes no responsibility for errors in this document.
Users of this document are required to have a valid license and dongle for SB-Interpreter in order to activate the software.
TRITON hereby grants licensees of TRITON’s software the right to reproduce this document for internal use only.
Page i
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter 1 – Training Overview 1
Chapter 2 – Map Window 2
MAP WINDOW REVIEW .......................................... 3
IMPORTING SUB-BOTTOM DATA ................... 4-5
IMPORTING BACKGROUND IMAGES .............. 6-8
BACKGROUND IMAGE ADJUSTMENTS ....... 9-11
PROCESS NAVIGATION .................................. 12-14
MAP VIEW PAN/ZOOM OPTIONS ............... 15-16
VIEW/OPEN PROFILES .......................................... 17
Chapter 3 – Profile Window 18
PROFILE WINDOW REVIEW .......................... 18-19
PROFILE TOOLBAR REVIEW ............................... 20
REVERSE PROFILE IMAGE .................................... 21
PROFILE SETTINGS/CHANNEL OPTIONS .... 22
TIME/DEPTH RANGE ....................................... 23-24
ANNOTATION ......................................................... 25
LUT COLOR/GAIN OPTIONS ........................ 26-28
SIGNAL OPTIONS .................................................. 29
FILTER OPTIONS ................................................... 30
BOTTOM TRACK OPTIONS ............................ 31-33
SWELL FILTERING ................................................. 34
DIGITIZE REFLECTORS ................................. 35-41
PROFILE MEASUREMENT TOOL ........................ 42
PROFILE FOLDING TOOL ............................... 43-44
Chapter 4 – Exporting and Printing 45
TUTORIAL
STEP 1: Open Program ...................... 2
STEP 2: Import Data Files ................. 5
STEP 3A: Import Images: .................. 7,8
STEP 3B: Image Adjustments ........... 10,11
STEP 4: Navigation Processing ......... 12,14
STEP 5: Map View Measurements ..... 15,16
STEP 6: Open Sub-bottom Profiles ....... 17
STEP 7: Reverse Direction of
Select Profiles .................... 21
STEP 8: Channel Settings .................. 22
STEP 9: Time/Depth Range Adjustments . 23
STEP 10: Annotation Settings .............. 25
STEP 11: LUT Adjustments ......... 26,27,28
STEP 12: Signal Settings .................... 29
STEP 13: Filters ............................. 30
STEP 14: Bottom Tracking .............. 32,33
STEP 15: Swell Corrections ................. 34
STEP 16A: Digitize Water Bottom ... 36,37,38
STEP 16B: Digitize Basement ............. 39,40
STEP 16C: Digitize Horizon1 ................. 41
STEP 17: Profile Measurements ............ 42
STEP 18: Profile Folding ................. 43,44
STEP 19A: Export All Reflectors ......... 46,47
STEP 19B: Export Thickness between
‘Water Bottom’ and
‘Basement’ ......................... 48
OUTPUT OPTIONS ................................................. 45
STEP 19C: Export Processed
Navigation for all Survey
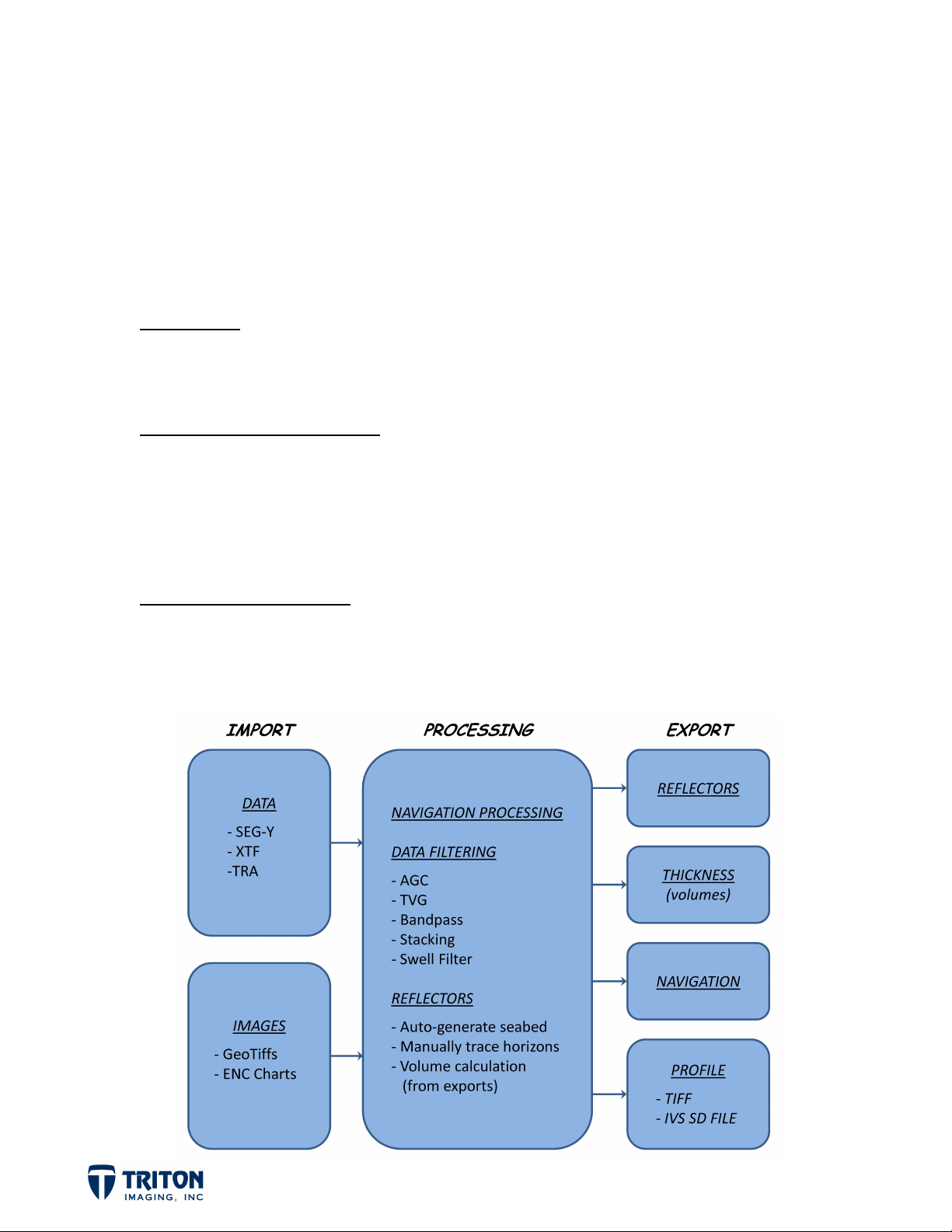
EXPORT REFLECTORS ...................................... 46-47
EXPORT THICKNESS ............................................. 48
EXPORT PROCESSED NAVIGATION ................ 49
EXPORT IMAGE CURTAIN ............................. 50-53
EXPORT IVS SD FILE ............................................ 54
STEP 19D: Export Image Curtain .... 51,52,53
STEP 19E: Export Folded Profile to IVS .... 54
STEP 20A: Print Map Window ................ 55
Lines ............................... 49
STEP 20b: Print Profiles ...................... 56
PRINTING MAPS AND PROFILES ................ 55-57
Page ii
Page 4
Chapter 1 – Training Overview
This document serves as a self-training guide for SB-Interpreter. Sample data for this
tutorial is available on the included DVD located at the back of this booklet.
Following along the instructions in this booklet will introduce you to most of the options
available within SB-Interpreter. A brief overview of the training program is presented
below:
Data Import
• Sub-bottom data (SEG-Y, XTF, TRA files)
• GeoTiffs (Chart, Aerial/Sat. Imagery, Bathy/Sidescan)
Processing and Interpretation
• Navigation Smoothing and Line Intersection Check
• Data Filtering (AGC, TVG, Bandpass, etc.)
• Auto-generate Seabed, Draw Reflectors/Horizons
• Volume Calculations
Export to Other Programs
• Saving Profile and Processed Navigation to SEG-Y
• Export Individual or Folded Profile to IVS 3D object
Page 1
Page 5
Chapter 2 – Map Window
MAP WINDOW REVIEW
SB-Interpreter has two primary interfaces. These are a GIS-based map window of the
project data and a profile window to display vertical sections. In this chapter we will
review the map window and most of the options available. The remaining options, profile
folding, exporting and printing, will be reviewed later in the training guide.
STEP 1: Open Program
Launch from Desktop Icon
OR
Launch from Start Menu
Page 2
Page 6
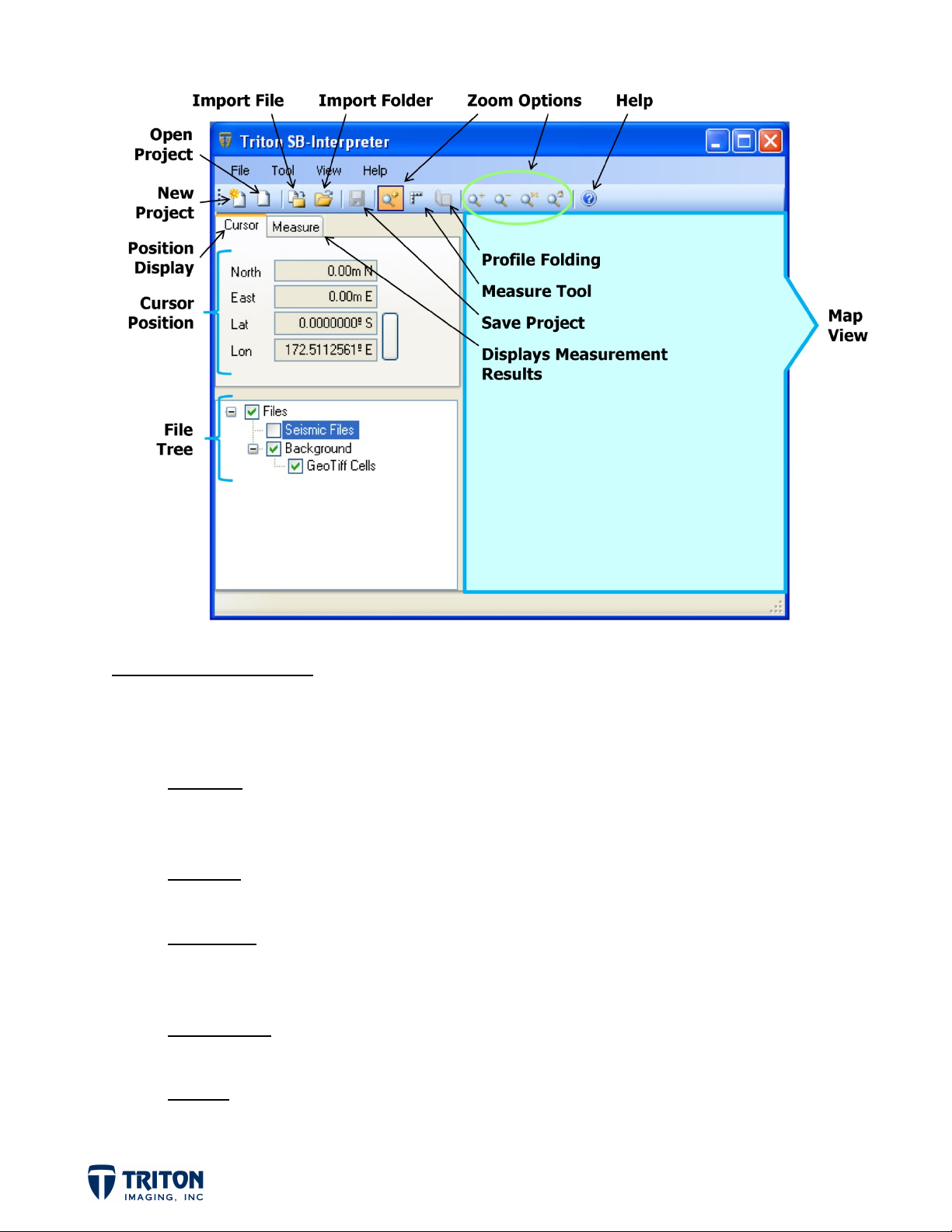
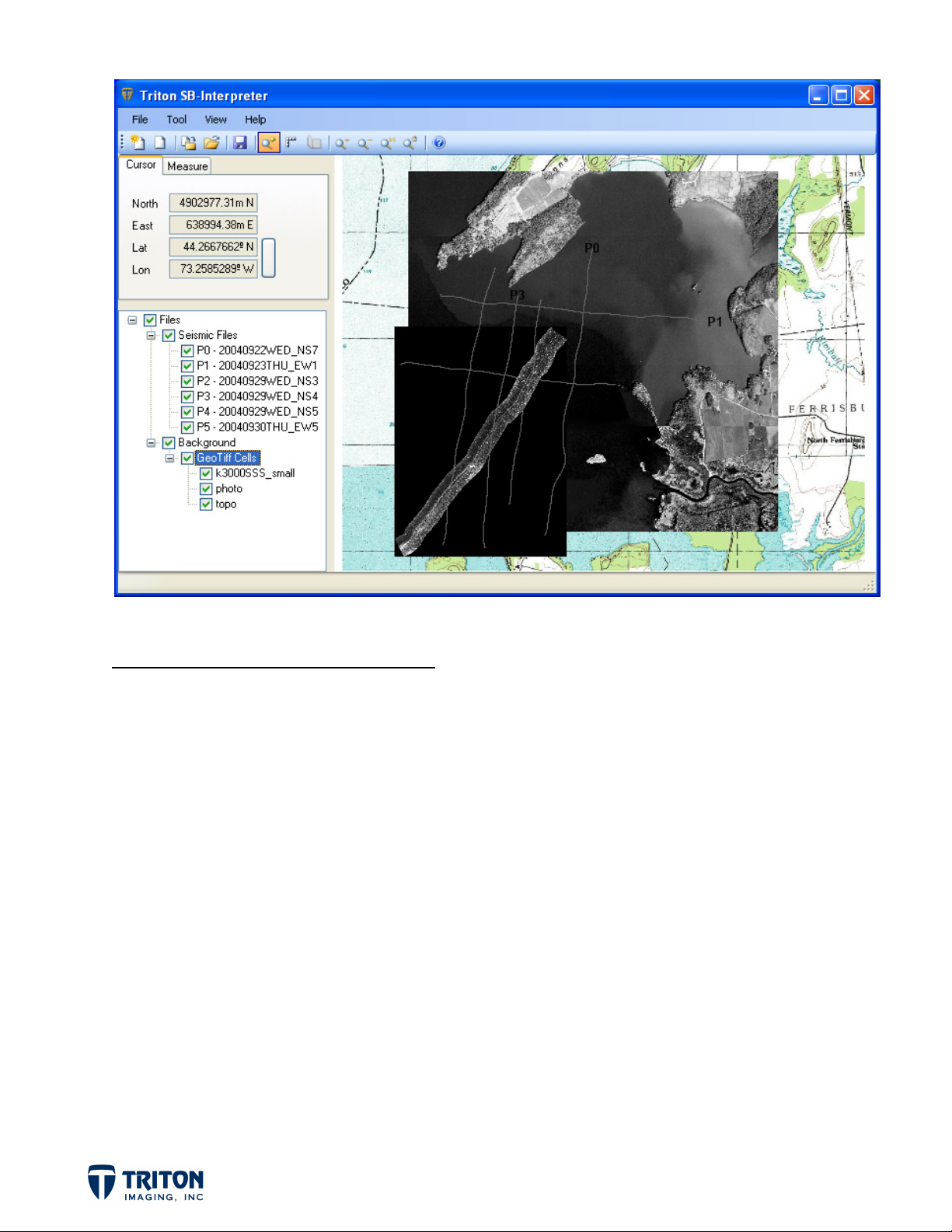
MAP WINDOW REVIEW
Upon launching SB-Interpreter, the map window will open as shown above. Important things to
note are:
• Map View
displayed using the embedded navigation in the seismic files. Geo-referenced imagery
can be used as a backdrop for spatial referencing.
• File Tree
higher in the tree list will display in the map view over images lower in the tree list.
• Cursor Tab
projected, the Northing and Easting will be displayed in addition to the Latitude and
Longitude.
• Measure Tab
to the distance, the component distances in the X and Y directions are also displayed.
– This is a GIS based view of the project data. Survey tracklines are
– This is where the imported files will be listed. For background images, files
– Shows the position of the cursor in the map view. If the data is
– Shows the results of measurements made in the map view. In addition
• Toolbar
available in the toolbar. Many of these tools are located in the menu options as well.
– Common tools used for importing data and navigating the map view are
Page 3
Page 7
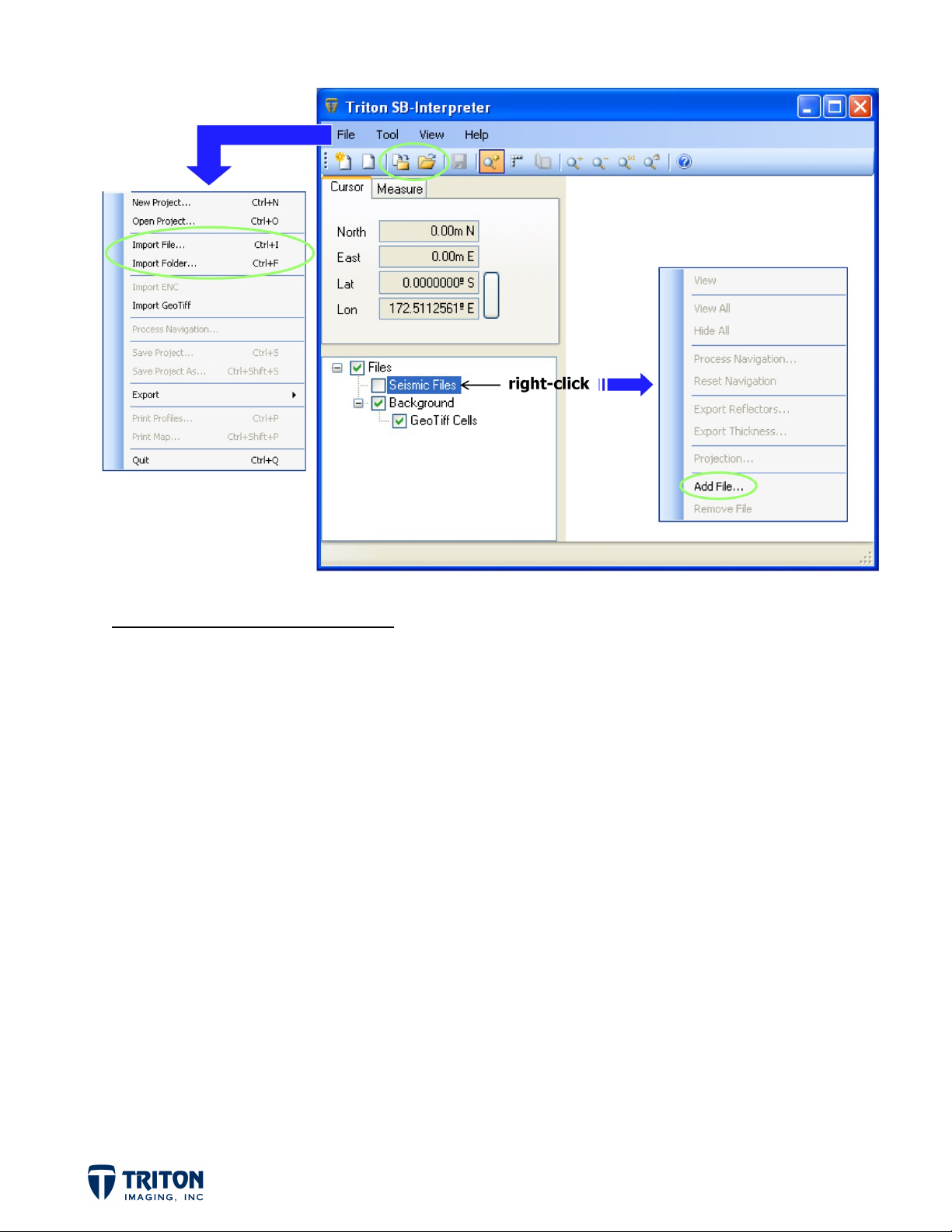
IMPORTING SUB-BOTTOM DATA
There are currently 3 file types compatible with SB-Interpreter:
a. SEG-Y (*.seg, *.sgy, *.segy)
b. Triton XTF (*.xtf)
c. Delph SEG-Y (*.tra)
Sub-bottom files can be imported into the project from the ‘File’ menu, toolbar buttons, and
by right-clicking in the ‘Seismic Files’ section of the file tree via two methods. These options
are:
a. Import File – can select a single file or multiple files in a folder
b. Import Folder – brings in all files in a selected folder
By default SB-Interpreter assumes that the navigation data are in Lat/Lon related to the
WGS84 datum. If so, SB-Interpreter will read the navigation, automatically selecting the
correct UTM Grid Zone. If the navigation is projected, a projection dialog box will pop up.
It is possible to set the projection prior to importing data in the ‘Projections’ tab in
‘Application Settings’ in the ‘View’ menu. This is important if the navigation coordinates in the
data file are in Lat/Lon coordinates, but they are related to another datum than WGS84.
Page 4
Page 8
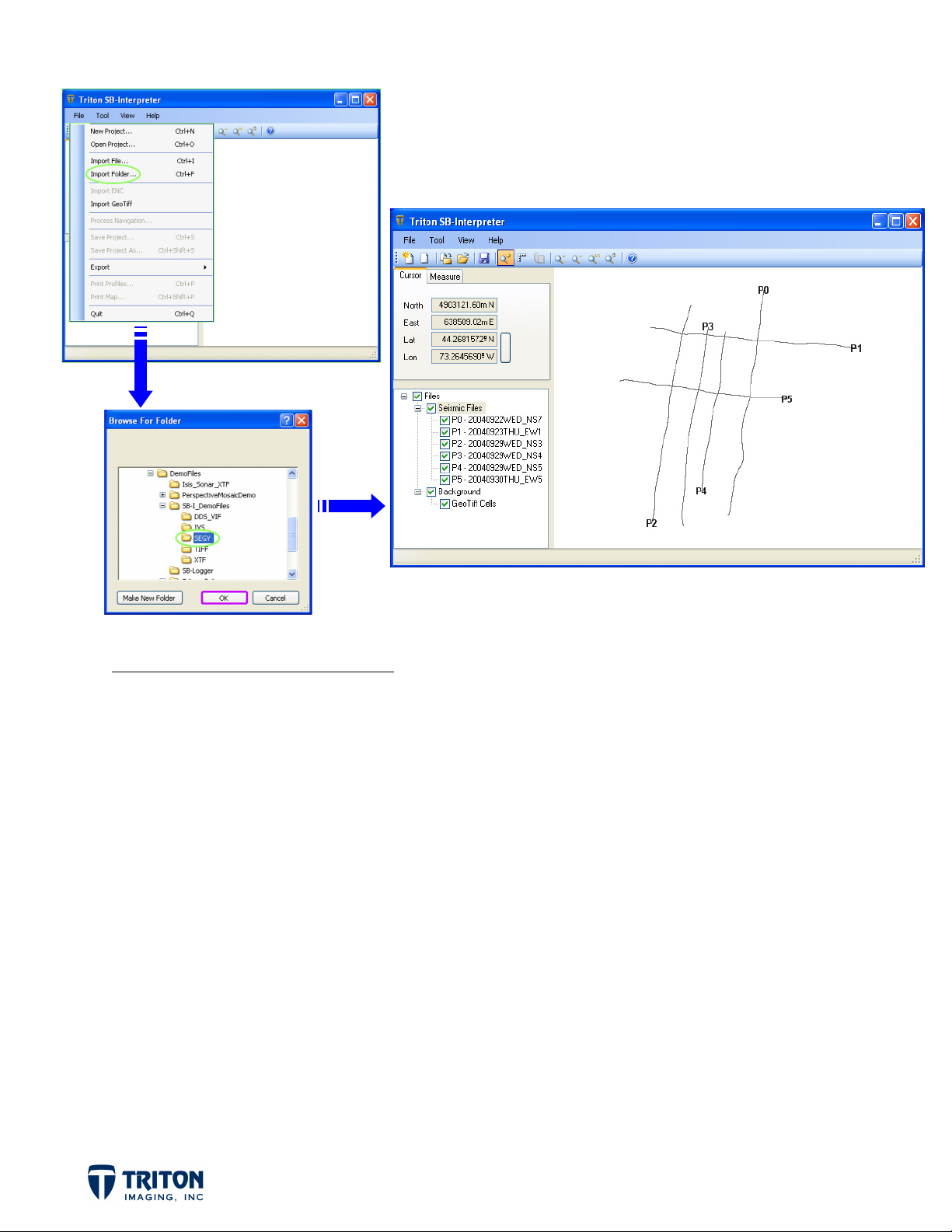
IMPORTING SUB-BOTTOM DATA
For this training guide our demo data is in Lat/Lon so SB-Interpreter will automatically set
the display projection.
STEP 2: Import Data Files
Select ‘Import Folder’ from the ‘File’ menu
a.
Select the folder where the demo data was copied to on your hard drive
b.
…/DemoFiles/SB-I_DemoFiles/SEGY
Once complete, the map view now shows the location of the imported profile lines and the file
tree contains line names and reference numbers for each line (P0 to P5).
Another thing that occurs upon import is the creation of cache files in the SEGY folder. The
creation of these cache files is an integral part of the processing and only occurs once, the
next time you access these files they will load more quickly.
Page 5
Page 9
IMPORTING BACKGROUND IMAGES
• There are 3 background file types compatible with SB-Interpreter:
a. GeoTiff (*.tif, *.tiff)
with embedded spatial data or *.tfw file
b. Geo-referenced JPEG (*.jpg, *.jpeg)
must have *.jgw file
c. ENC Chart (*.enc)
must have ENC license to activate this option
• SB-Interpreter currently only supports geo-referenced background images with
coordinates in meters.
• In the current release of SB-Interpreter there is a limit to the size of any single image,
the maximum number of pixels is around 12,000 x 12,000. If this size is exceeded an ‘Out
of Memory’ error will result.
Page 6
Page 10
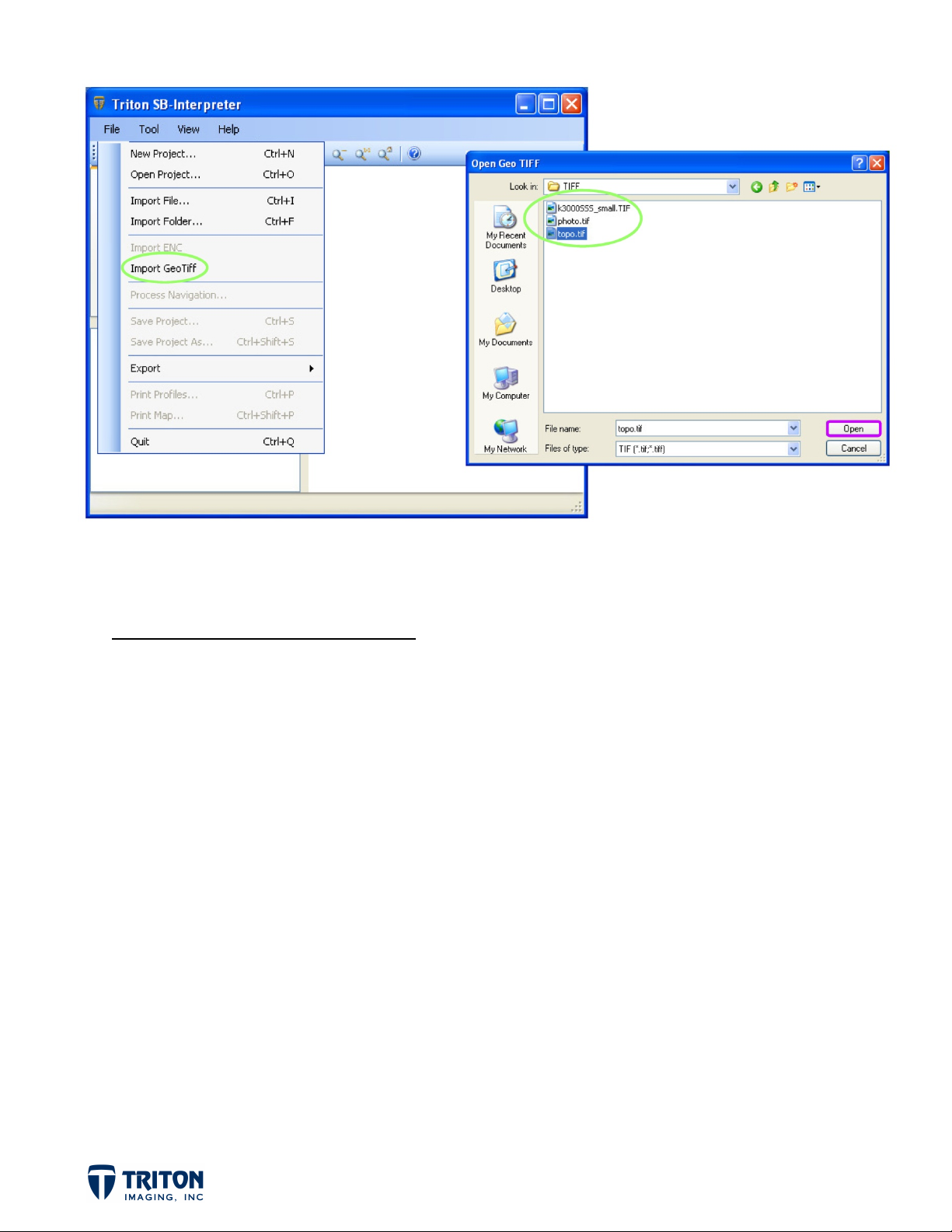
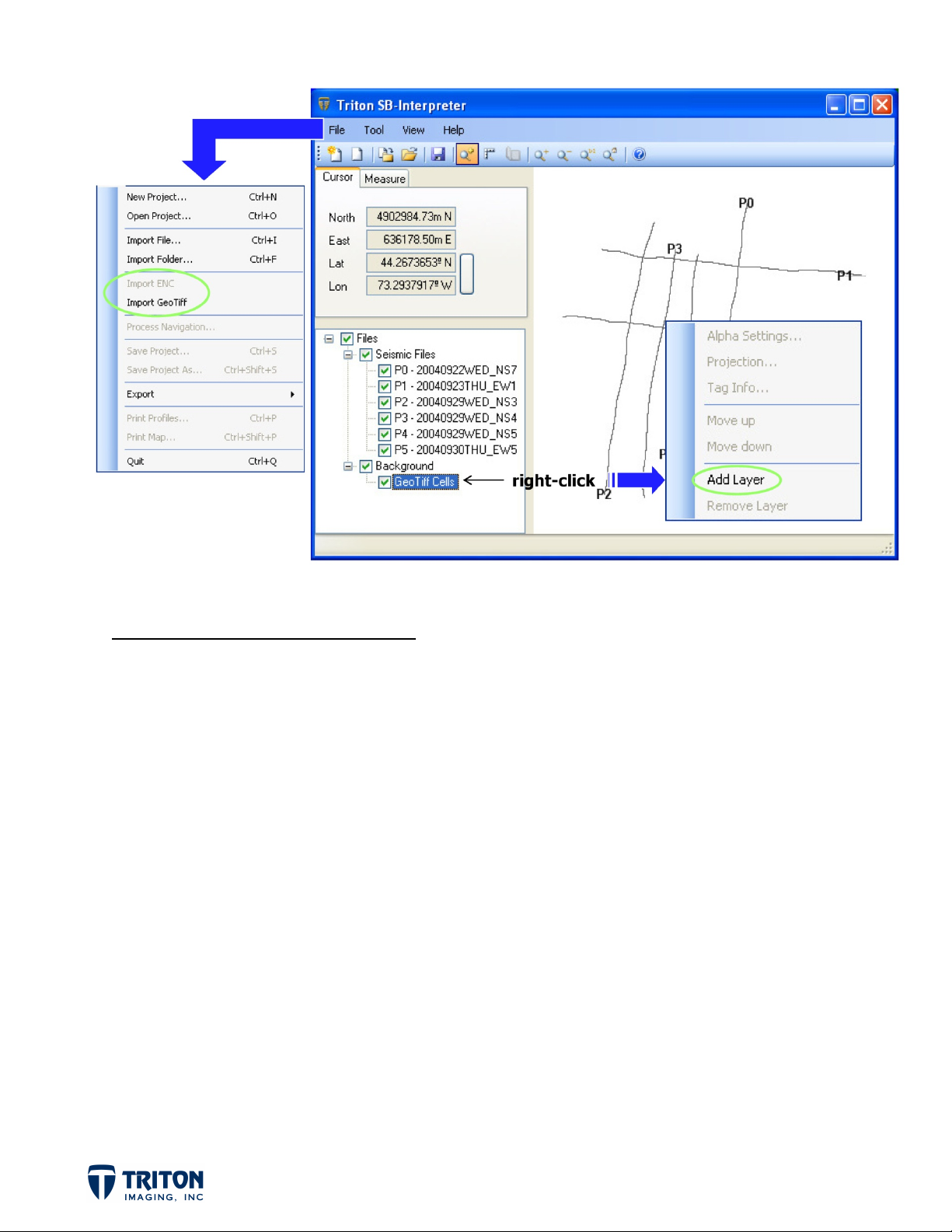
IMPORTING BACKGROUND IMAGES
Background imagery can be imported into the project by selecting the ‘Import GeoTiff’ option
from the ‘File’ menu, or by right-clicking in the ‘GeoTiff Cells’ section of the file tree and
selecting ‘Add Layer’.
STEP 3A: Import Images:
Select ‘Import GeoTiff’ from the ‘File’ menu
a.
Select the folder where the demo data was copied to on your hard drive
b.
…/DemoFiles/SB-I_DemoFiles/TIFF
Select the file ‘Topo.tif’
c.
For background imagery, the import projection must be manually set. This can be
accomplished prior to importing via the ‘Projections’ tab in ‘Application Settings’
(as mentioned previously) or at the time of import.
Page 7
Page 11
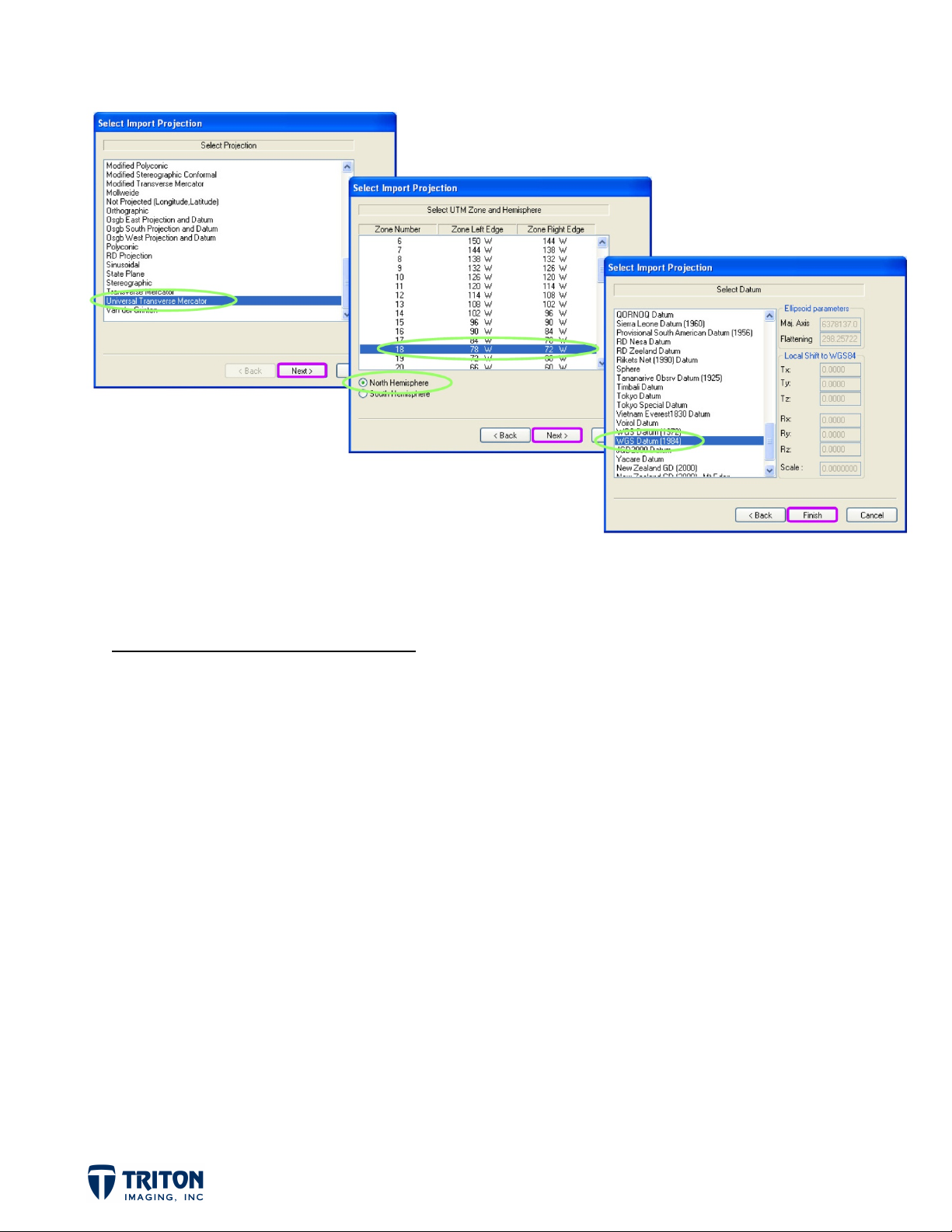
IMPORTING BACKGROUND IMAGES
The projection only needs to be set once. The same projection will then be used for all
subsequent background imports.
STEP 3A: Import Images (cont.)
Select ‘Universal Transverse Mercator’
d.
Select ‘Zone 18 North’
e.
Select ‘WGS Datum (1984)’
f.
Repeat import process for remaining image files (photo.tif &
g.
k3000SSS_small.tif)
This will bring in the three background images layered on top of one another as shown on the
following page.
Page 8
Page 12
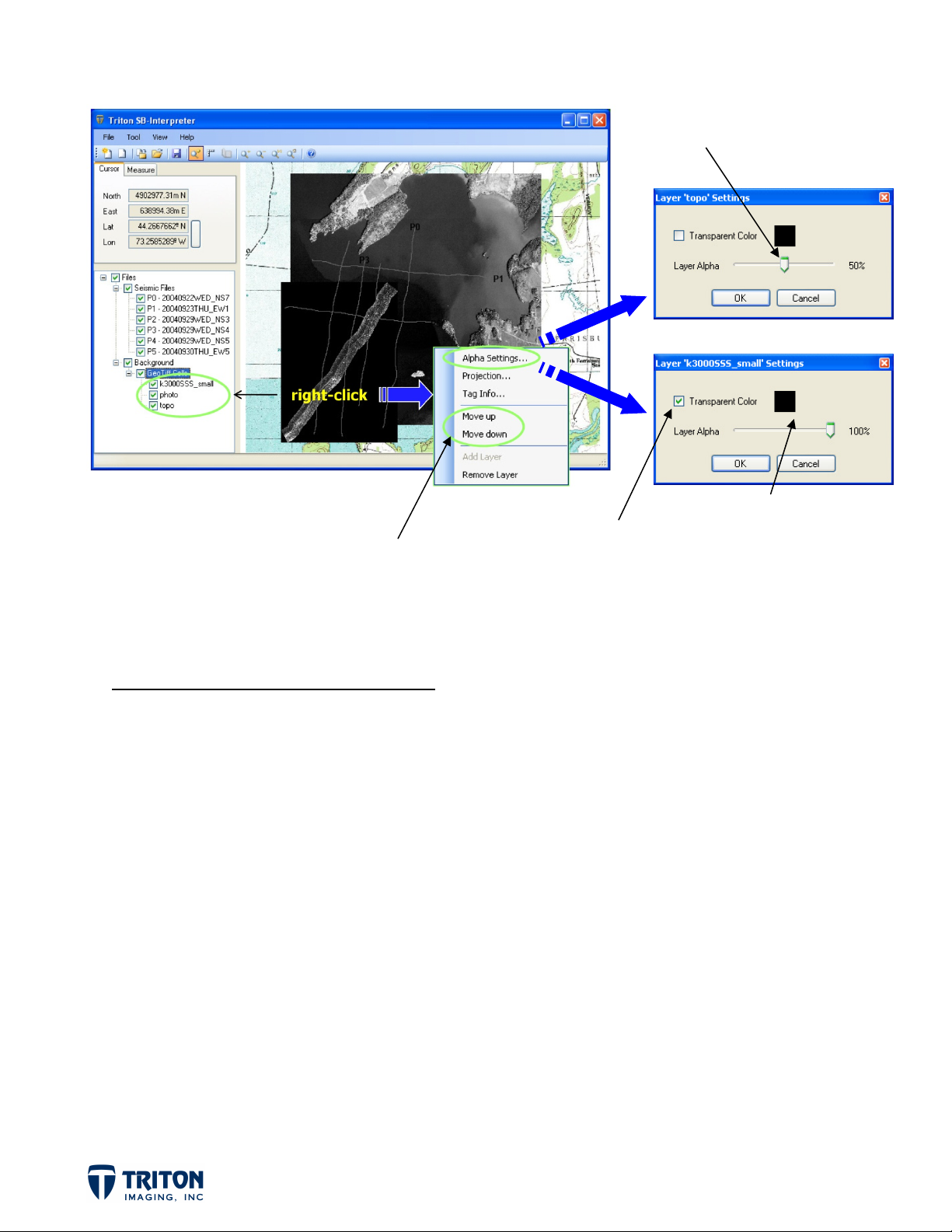
BACKGROUND IMAGE ADJUSTMENTS
As mentioned previously, the file tree order controls the order of files displayed in the map
view. The tiffs located higher in the file tree structure are shown on top of those lower in
the file tree. In this example the sidescan tiff is on top of the aerial photo, which is
displayed over the background topo.
There are a few options in SB-Interpreter that can make these images more useful for spatial
referencing. By right-clicking on the individual tiffs, the file tree order and transparency
settings can be changed.
One of the more obvious changes needed is to remove the ‘no data’ region of the sidescan tiff.
If we decide we want the chart (topo) to overlay the aerial photo, we can either move the
photo down in the list or move the chart up the list and also change its transparency so we can
still view the aerial photo now located beneath it.
Page 9
Page 13
Usetheslidingbarto
controltheamountof
transparency
Checkboxformaking
Tochangetheorder,
right‐clickontheGeoTiff
andselect‘Moveup’or
‘Movedown’
selectedcolor
transparent
Imagecolorchosentobe
transparent,tochange
clickoncolorandselect
alternate color
BACKGROUND IMAGE ADJUSTMENTS
Image adjustments are made by right-clicking on the individual tiffs. Options for adjusting
the background images include changing the view order and adjusting transparency in ‘Alpha
Settings’.
STEP 3B: Image Adjustments
Right-click on ‘photo’ in the file tree and select ‘Move down’
a.
b.
Right-click on ‘topo’ in the file tree and select ‘Alpha Settings’
Change the ‘Layer Alpha’ value to 50% using the slider bar
c.
Right-click on ‘k3000SSS_small’ in the file tree and select ‘Alpha Settings’
Check ‘Transparent Color’ box for making selected color transparent
Select ‘Black’ as image color to be transparent
These quick adjustments allow the user to see the topo chart draped over the aerial photo
with the sidescan image shown crossing the sub-bottom survey lines.
Page 10
Page 14
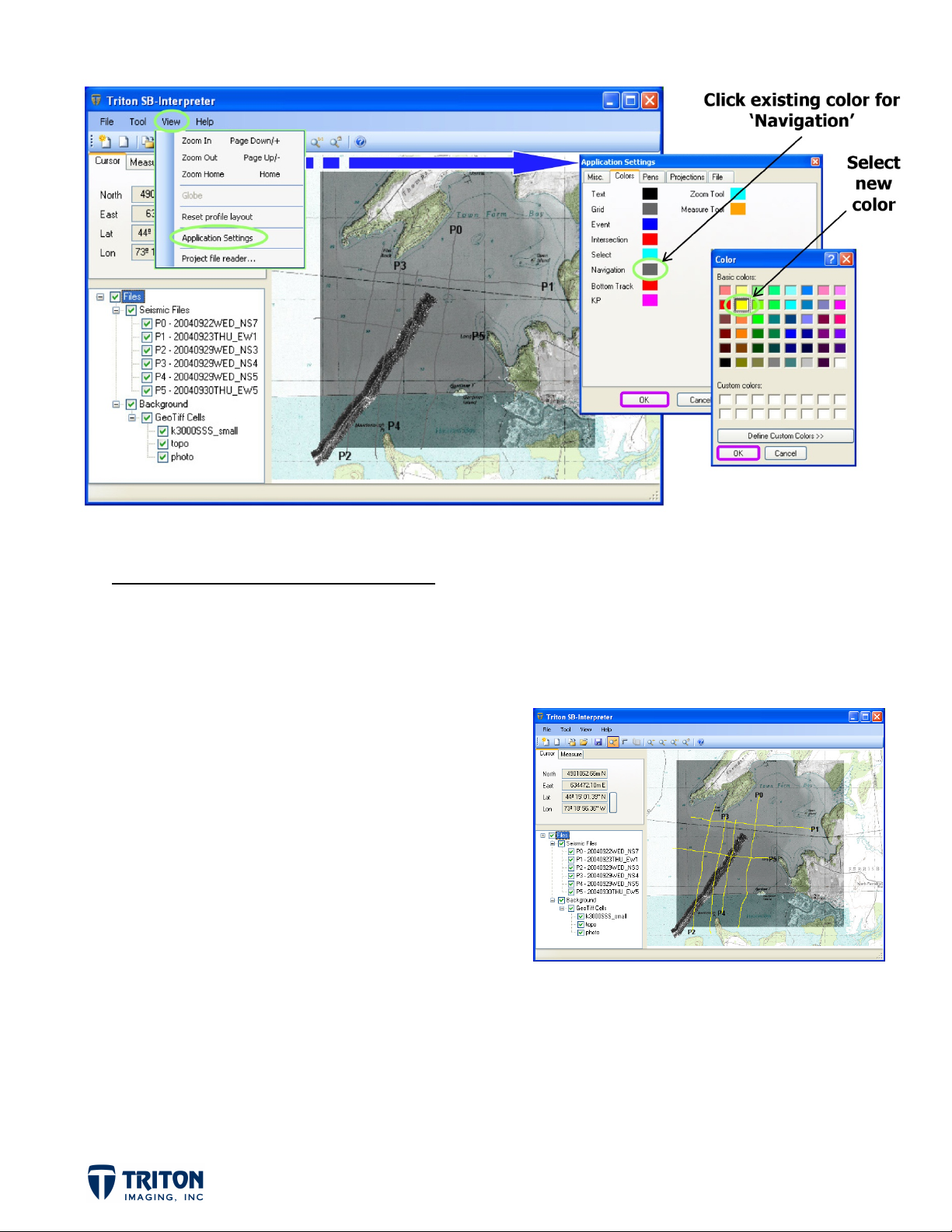
BACKGROUND IMAGE ADJUSTMENTS
With the aerial photo showing through the chart, the default color for the sub-bottom profile
navigation lines is too dark. Color options for survey navigation are located in the ‘Application
Settings’.
STEP 3B: Image Adjustments (cont.)
d.
Select the ‘Colors’ tab in ‘Application
Settings’ in the ‘View’ menu
Click on the current color for
e.
‘Navigation’
Select ‘Yellow’ as the new color
f.
Adjusting the background imagery and default color settings in the map view assists with
interpretation by allowing cross-referencing between data types (multibeam, sidescan, and
sub-bottom) and regional features shown in topo maps, navigation charts and aerial
photographs.
Page 11
Page 15
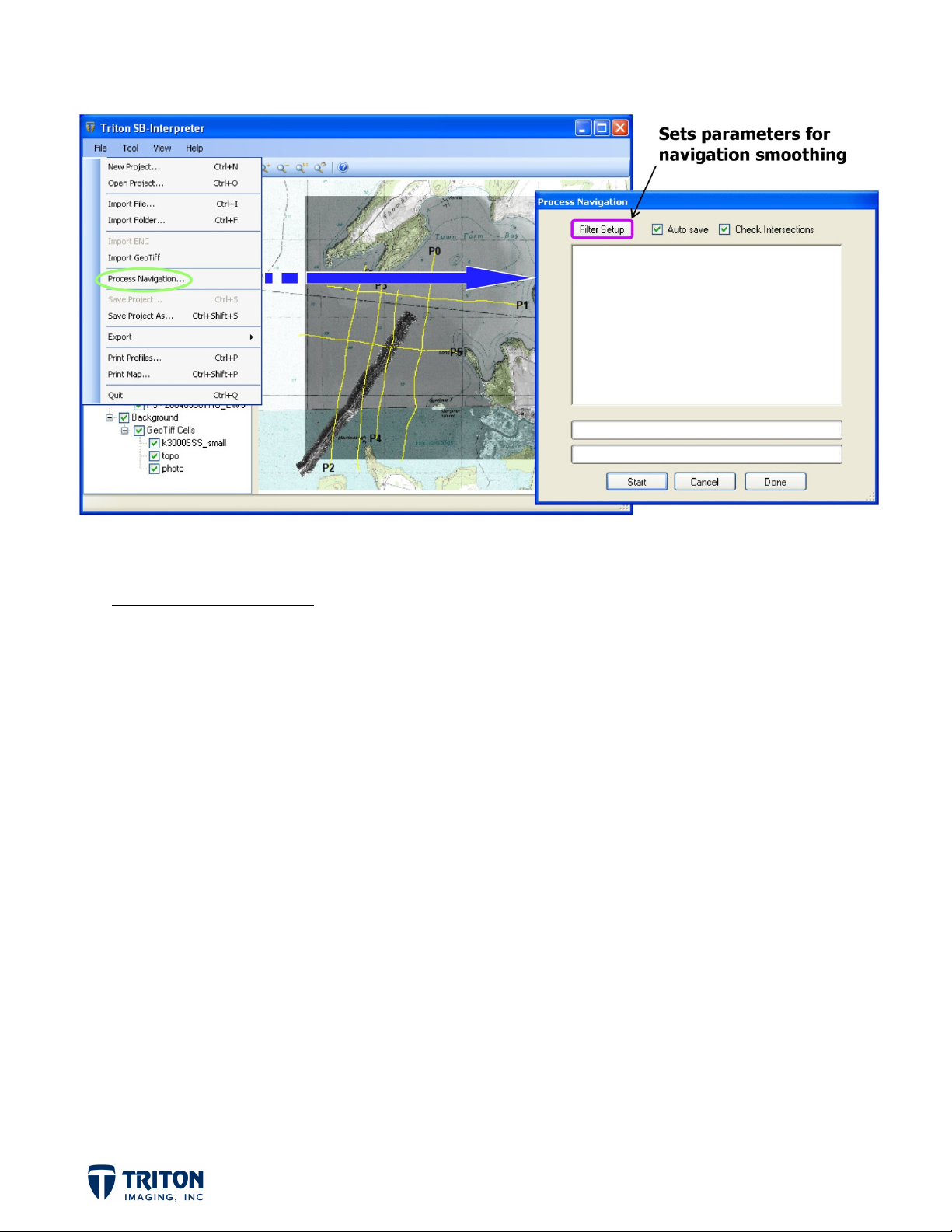
PROCESS NAVIGATION
An important step to take once the sub-bottom data is imported is to process the navigation
in the data files. This process will smooth navigation and place markers in each sub-bottom
line at locations where lines intersect.
Navigation processing can be launched from the ‘File’ menu or by right-clicking on individual
data files to process just that lines navigation or on the root ‘Seismic Files’ folder to process
the navigation for all files.
STEP 4: Navigation Processing
Select ‘Process Navigation’ in the ‘File’ menu
a.
Select ‘Filter Setup’
b.
This will open a new window called ‘Boxcar Settings’ with options for filtering the raw
navigation data. It is important to note that navigation smoothing does not affect the original
data. The results are stored in cache files which are placed in the same folder as the data
files but have a *.sgc file extension for SEG-Y files and *.xtc for XTF files.
Page 12
Page 16
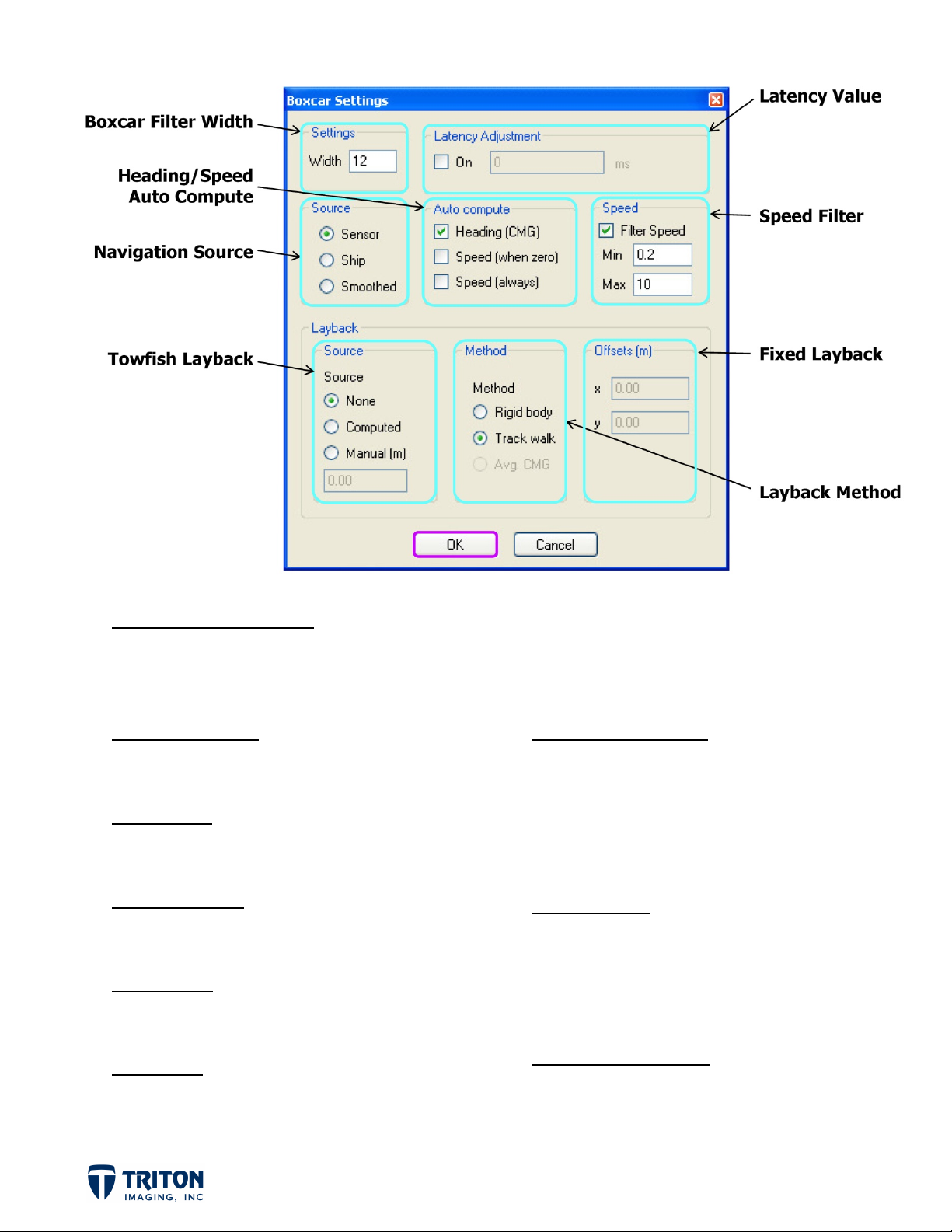
PROCESS NAVIGATION
Boxcar Settings is a collection of common navigation processing steps for removing errors in navigation
data. A brief description of the processing parameters and their options is presented below.
Boxcar Filter Width
• A larger number smoothes over a longer time
period
Latency Value
• If known, latency values for the acquisition
system can be entered here
Navigation Source
• ‘Smoothed’ is for the previously smoothed
navigation stored in cache file
Auto Compute
• Use this if heading or speed is not available
in original file
Speed Filter
• Removes large jumps in navigation by
removing values outside known speed range
Towfish Layback Source
• Use ‘None’ if hull mounted or if navigation is
from the sensor
• ‘Computed’ calculates layback from x-y values
entered in ‘Offsets’ field or from values stored
in XTF file
• ‘Manual’ is for a fixed cable out value
Layback Method
• ‘Rigid body’ will use the heading computed or
stored in the cache file
• Track walk - project the entered layback value
back along the vessel track to compute the
position
Offsets (Fixed Layback)
• Location to manually enter static layback value
or fixed offsets
Page 13
Page 17
:
S(c
In
b
W
Pnacl
n
e
a
o
io
o
xc
c
c
h
v
pr
t
v
d
r
o
in
ow
g
a
d
d
in
is
h
o
c
c
)
in
u
ow
k
e
er
,
o
i
s
e
c
o
t
gs
N
a
a
’
)
Ch
‘
s
5
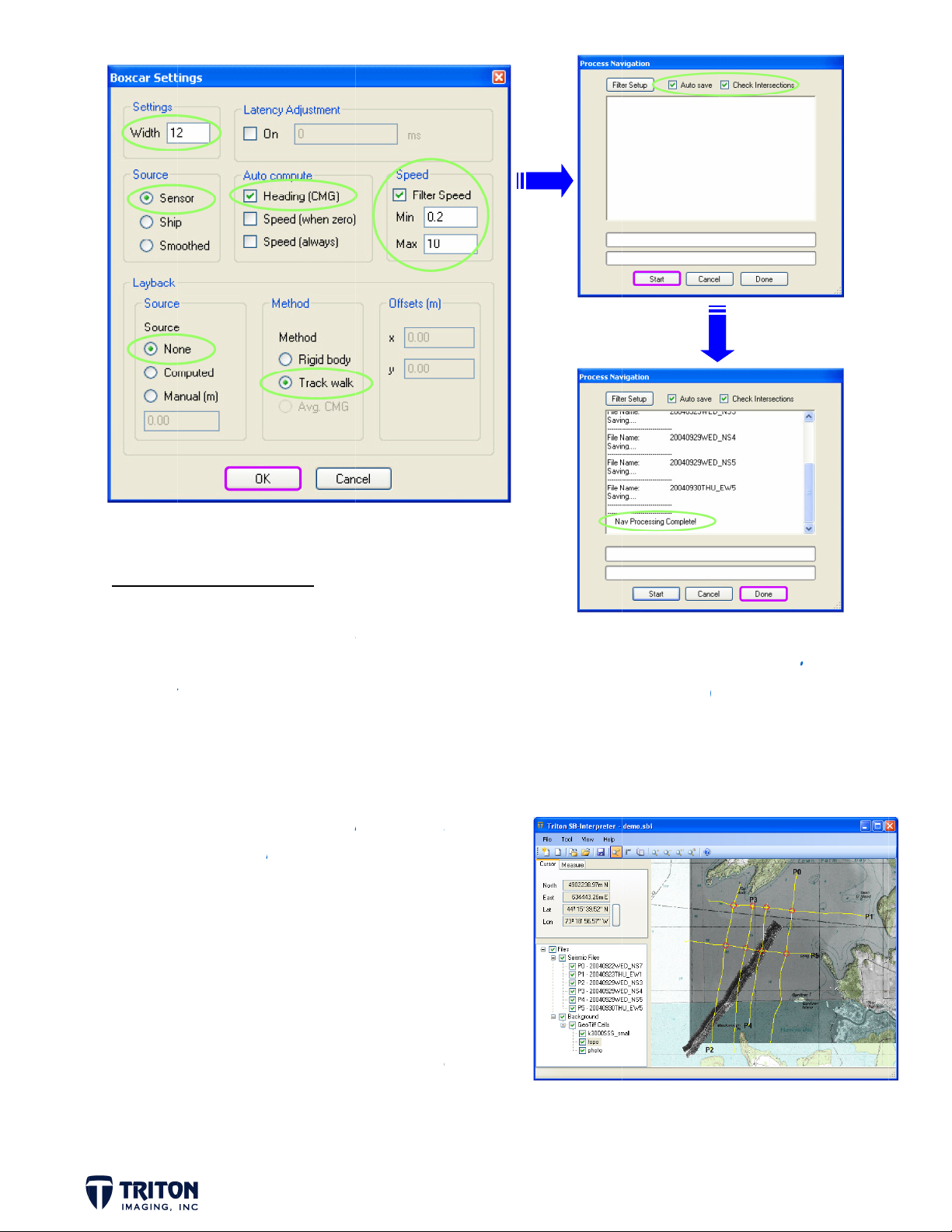
PROCES
STEP 4
c.
d.
e.
Navigati
S NAVIGA
Navigat
elect the
loses ‘Bo
the ‘Pro
oxes are
hen finis
‘
rocess Na
vigation
ick ‘Done’
on lines ha
TION
n Process
ptions sh
ar Settin
ess Navig
ecked an
ed, scroll
igation’ w
ocessing
o close t
e been sm
g (cont.
n above
s’ and ret
tion’ wind
then clic
own in th
dow to v
complete
e window
othed per
the ‘Box
rns you t
, verify
‘Start’
ify
then
ptions
ar Settin
‘Process
he ‘Auto s
’ window
avigation
ve’ and ‘
nd select
eck Inter
OK’
ections’
chosen i
cross ar
in the m
are imp
correlat
for prof
the filter
identifie
p view as
rtant when
ing reflect
ile folding.
setup. Pla
as interse
ed circles.
viewing sei
rs/horizon
es where l
tions and
The inters
smic sectio
s across lin
nes
hown
ections
ns and
s and
Page 1
Page 18
E
a
m
u
1
o
t
:
S
O
a
m
m
m
m
m
m
n
w
‘
O
e
o
m
e
v
e
x
,
m
’
e
o
a
ut
m
5
a
u
o
e
t
e
u
c
a
e
t
y
n
n
o
c
r
e
6
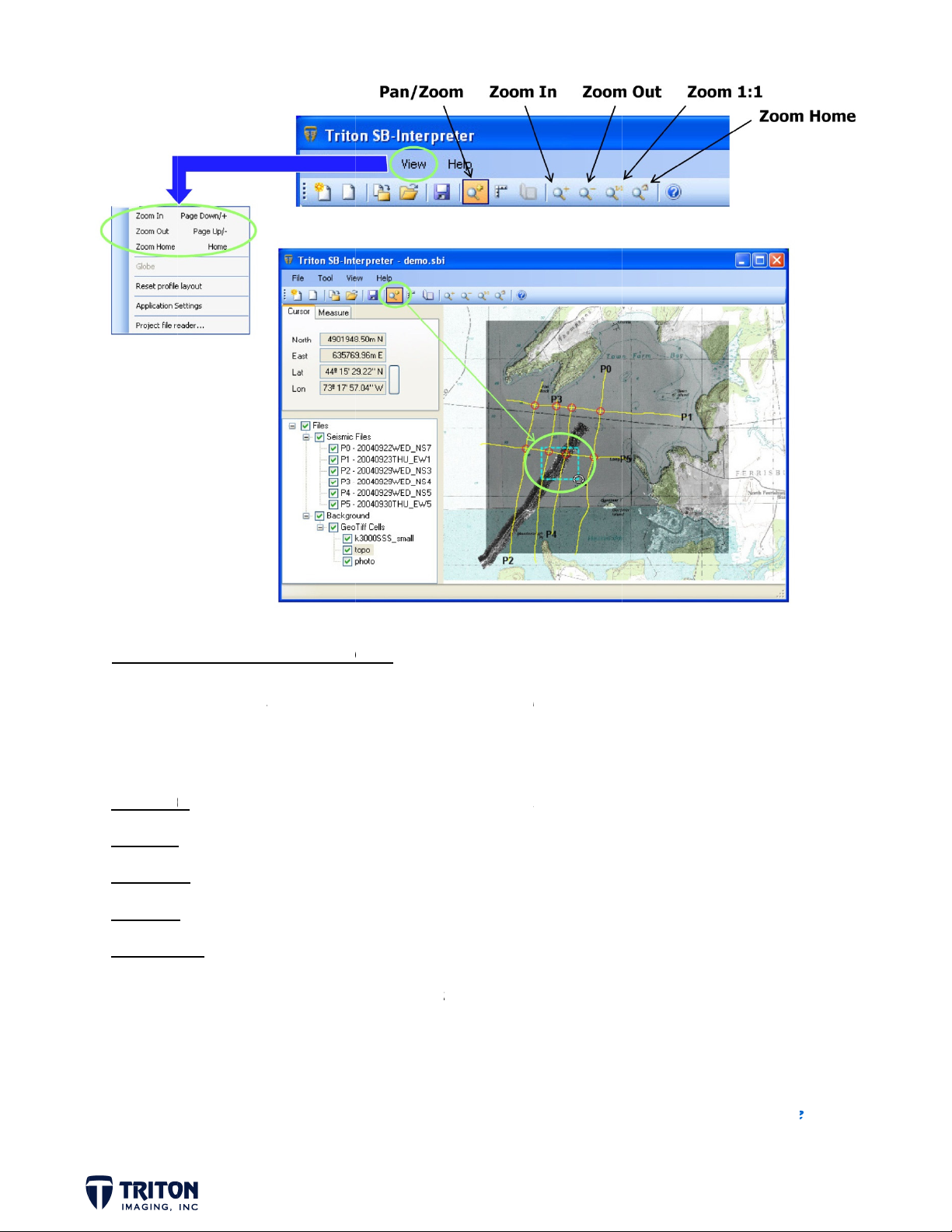
MAP VI
Now tha
moving
also avai
Pan/Zoo
Zoom In
Zoom O
Zoom 1:
Zoom H
In addit
an inser
W PAN/Z
t we have
round the
lable under
pan
zoo
t zoo
zoo
me zoo
ion to zoo
ed sidesca
OM OPTI
ll of our fil
ap. As sh
the ‘View’
across scr
in one le
out one l
to 1 pixel
to full e
ing options
tiff.
NS
s of inter
wn earlier,
enu.
en (left cli
el
vel
by 1 pixel
tent of pr
we may w
st in the
there are
ck) and dr
ect data a
nt to meas
ap view, th
zoom but
g a specifi
nd backgro
re line spa
re are a s
on options
d zoom ex
nd imager
ing or the
veral optio
with some
ent (right-
swath cove
s for
f these
lick)
age of
STEP 5
a.
Map Vie
elect the
Measure
Pan/Zoom
ents
toolbar b
ton and z
om to are
shown o
map abov
Page 1
Page 19

E
c
o
t
e
e
n
h
:bc
d
O
a
s
t
m
n
w
th
c
Z
O
i
u
c
A
m
re
a
e
d
o
a
e
c
t
b
ar
bu
e
o
g
e
X
a
n
e
o
k
M
h
t
ho
d
o
m
b
e
g
o
v
t
e
w
7
MAP VI
Zooming
more ac
spacing
‘Cursor’
measur
To mak
shown i
shows t
STEP 5
W PAN/Z
into the m
urate mea
r the swat
ab which s
ment resul
a measure
the examp
e direct li
Map Vie
. Select
OM OPTI
p view will
urements.
h width of
hows the c
s.
ent, left-
le above.
e spanning
Measure
e ‘Measu
NS
enlarge an
Using the ‘
nserted si
rsor positi
lick and dr
n orange r
the distan
ents (con
’ toolbar
area of int
Measure’ t
escan ima
n is chang
g the curs
ctangle wil
e plus the
.)
utton
rest in th
olbar butt
es. By clic
d to the ‘
or across t
l appear in
-Y compon
view wind
n we can
ing on the
easure’ ta
e space to
he map vie
ents of th
w which all
easure sur
toolbar bu
to display
be measur
w window
direct line
ws for
ey line
ton, the
d as
hich
.
. Left-cli
. Select ‘
k on map
oom Hom
nd draw
’ toolbar
ea to me
tton whe
sure as s
finishe
wn in ima
e above
Page 1
Page 20
O
r1.
:ab
I
e
c
c
e
ub
i
V
o
n
u
P
s
d
toj
’
b
m
t
e
r
o
i
t
o
o
8
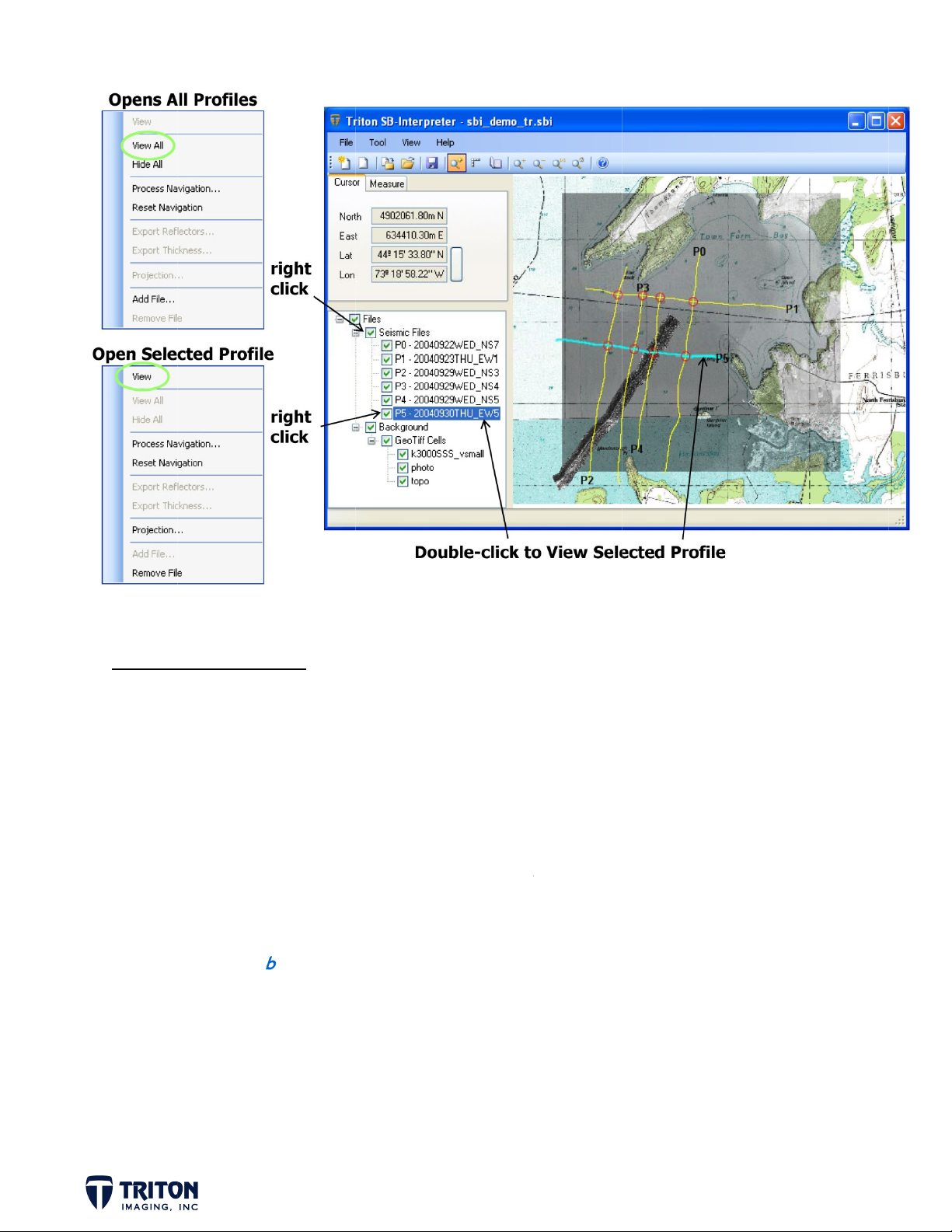
VIEW/
There a
STEP 6
PEN PROF
e a few m
Double-c
. Right-cli
2
individua
3
. Right-cli
all profil
Open S
. Right-cl
LES
thods for
lick on the
k on the s
profile.
k on the fi
s in the pr
-bottom
ck on ‘Sei
pening and
avigation l
b-bottom
le tree roo
ect.
rofiles
mic Files
viewing su
ine in the
ata file in
folder ‘S
-bottom p
ap view to
he file tre
ismic Files’
ofiles.
pen an ind
e and selec
and select
vidual prof
‘View’ to
‘View All’ t
ile.
pen an
open
. Select ‘
iew All’
Page 1
Page 21

r
E
f
a
c
t
.
4
h
t
W
G
f
g
e
w
s
p
t
r
m
h
o
p
w
m
t
d
p
e
t
n
a
d
e
e
p
,
o
j
e
c
d
d
o
m
S
p
o
n
n
t
h
o
e
a
o
v
e
t
d
t
e
g
h
i
q
9
Chapte
PROFIL
In addit
window
was to o
viewing
them so
In this
options
3–Profil
WINDO
ion to the
or viewing
pen all pro
nd workin
they can b
hapter we
o be discu
1
Image o
2
. Bottom
3
. Filtering
. Reflecto
eWindo
REVIEW
IS-based
the sub-bo
iles embed
with multi
easily acc
ill review
sed in this
tions
racking
s
ap window
tom profil
ed in the
le profiles
ssed, refe
he profile
chapter all
of the pro
s. At the
roject. Ea
it is a goo
rred to an
window and
fall within
ect data,
nd of the
h profile
idea to sp
compared.
most of th
the followi
B-Interpr
revious ch
pens in its
end a little
e options a
g categori
ter has a s
pter the f
wn window
time arran
ailable. T
s:
parate
inal step
. When
ing
e
First, t
applied.
the bot
applying
e profile i
Some of t
om track t
filters hel
ages are e
e filters h
be define
s delineat
hanced to
ve options
prior to a
horizons f
improve int
to apply fr
pplying the
r reflecto
erpretatio
m the bot
. After t
r digitizati
. Next, bo
om track
e bottom
n.
tom track
own and re
rack is def
ng is
uire
ined,
Page 1
Page 22

E
o
V
T
W
e
W
a
e
s
i
i
t
a
t
n
h
p
t
c
e
t
e
h
e
p
d
d
t
s
e
b
a
t
e
n
o
:
p
e
i
d
h
h
t
f
v
h
d
a
e
r
w
b
a
e
0
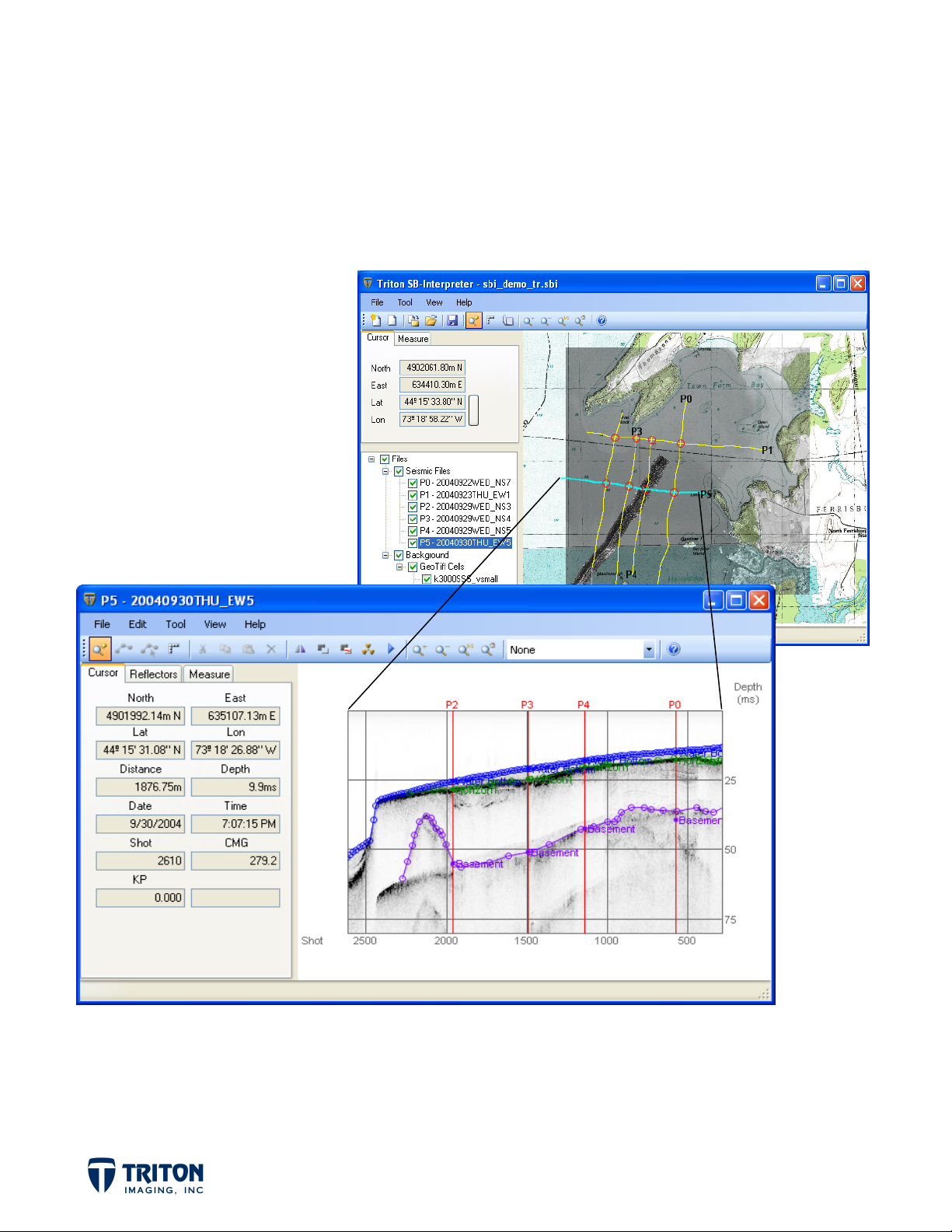
PROFIL
Each pr
‘200409
Profile
Display
WINDO
file will op
23THU_E
iew
•
Displays
•
When th
spatial po
features
features
•
Intersec
abs
•
Cursor T
REVIEW
n into a se
1’. Impor
vertical se
cursor mov
ition along
n the map vi
n the profil
ions with ot
b shows the
arate win
ant things
tion of the
s across th
he navigatio
ew such as
.
er profiles
position of
ow. Shown
o note are
ub-bottom
profile, th
n trackline.
right spots
re displaye
he cursor in
above is t
rofile.
cursor posi
This is very
n the sidesc
on the pro
the profile
e profile w
ion in the m
useful when
an imagery
ile section f
iew.
indow for f
ap view sho
correlating
nd sub-surf
or cross ref
ile
s the
etween
ce
rencing.
Reflector
•
•
Measure
the dista
slope of t
tab lists th
ab shows th
ce, the com
e measure
digitized r
e results of
onent dista
line are als
flectors.
measuremen
ces in the
displayed.
ts made in t
orizontal an
e profile vi
vertical di
w. In addit
ections and
ion to
the
Page 2
Page 23

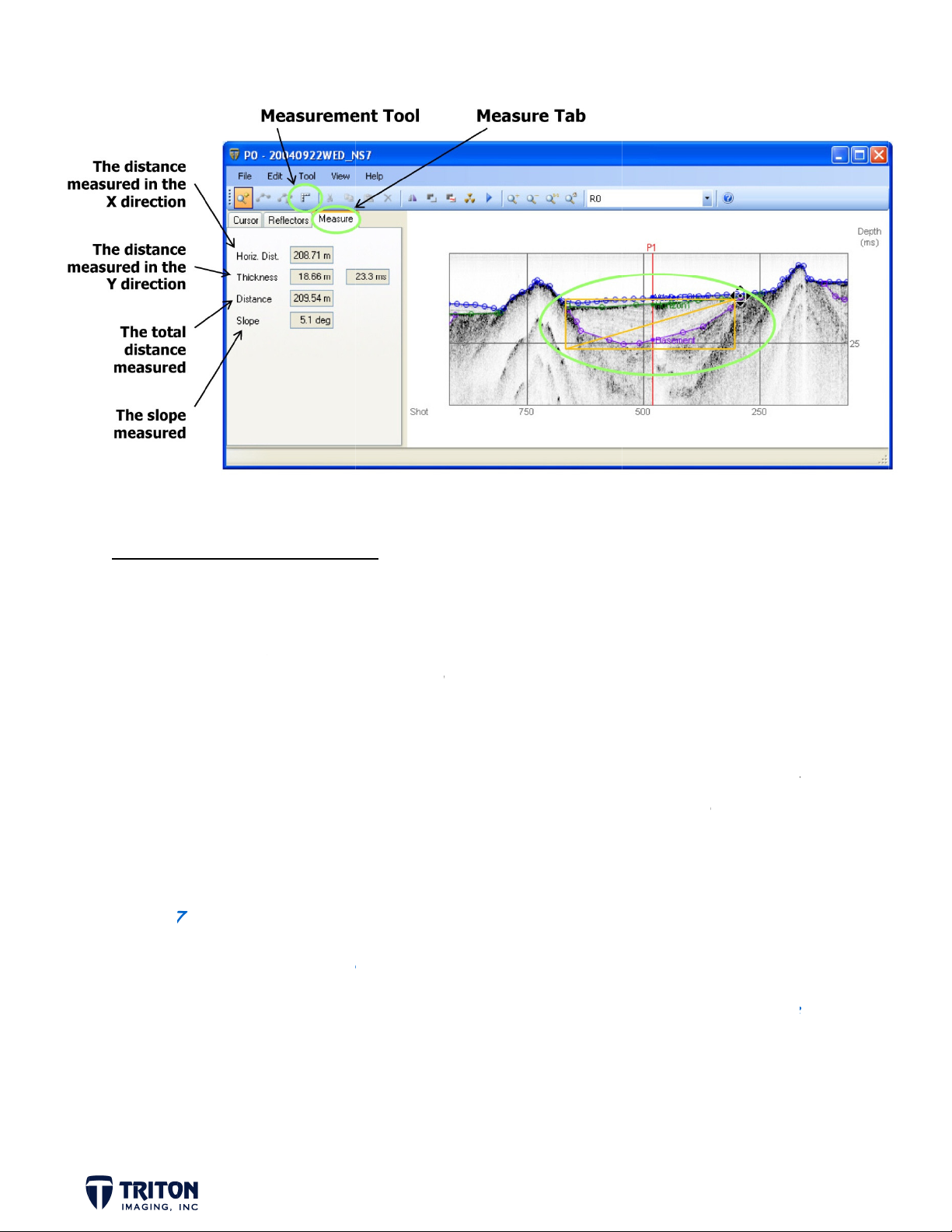
E
t
c
a
d
m
i
o
-
-
I
t
t
R
b
m
k
’
m
e
v
d
t
a
h
m
t
s
n
i
n
e
s
o
o
S
•
S•N
•R•
o
C
I
t
B
t
e
e
b
s
n
n
s
b
n
k
n
s
y
a
u
t
a
0
PROFIL
Some of
tool, fun
are avail
presente
Settings
• opens
• for i
Digitize
• use t
• left-c
• right
Select
• left-c
• right
track
TOOLBA
he toolbar
tion the sa
ble for wor
below.
the ‘Settings
age enhance
ng
digitize refl
lick to add po
click to remo
lick to move
click to selec
REVIEW
uttons in t
e as in the
ing with ref
dialog box
ents and bot
ctors
ints
e points
igitized point
multiple poi
e profile wi
ap window.
lectors. Bri
om
ts
dow, such a
Editing opti
f descripti
the pan/zo
ns include
ns of the re
how/Hide
toggle bu
the sub-b
how/Hide
toggle bu
the botto
ext Chann
toggles b
of the su
eflector Li
m options a
ut, Copy, Pa
maining tool
mage
ton to turn o
ottom profile
ottom Trac
ton to turn o
m tracking re
l
tween displa
-bottom dat
t
d the meas
te and Dele
ar buttons
or off the d
or off the d
ults
ing channels
rement
e, and
re
isplay of
isplay of
, 1, & 2
Reverse
• flips
direc
mage
he profile im
ion
ge in the hor
drop-dow
zontal
menu of the
available refl
ectors
Page 2
1
Page 24

n
n
F
e
:
a
b
u
f
e
o
r
h
o
t
e
h
r
h
o
h
o
o
m
r
h
r
Pr
e
a
d
h
t
s
o
d
w
f
w
i
n
m
i
o
n
s
e
n
n
e
REVERS
The link
Profiles
were ra
To get c
may be
above.
and hav
STEP 7
E PROFILE
between c
are drawn
east to w
ursor move
ecessary t
or survey l
the curso
Reverse
. For eac
and the
IMAGE
rsor positi
rom the s
st or west
ment in th
reverse t
ines ran no
tracking t
Direction
profile c
map view
n in the pr
art of line
to east.
profile to
e image di
th to sout
e same fo
f Select
eck the r
ofile view
n the left
atch the
ection. T
or south
all north-
ofiles
lative curs
nd map vie
to end of li
irection o
is is done
o north, it
outh lines.
r moveme
is someti
ne on the r
movement
ith the to
s best to c
t betwee
es out of
ght wheth
in the map
lbar butto
hoose a co
the profil
ync.
r they
view it
circled
vention
view
. Reverse
profiles f
r lines P0,
P1, P3 an
P5
Page 2
1
Page 25

PIw
w
C
•
•
A
•
•
S•A
•
S
ROFILE S
E
n
t
t
a
1
e
e
o
p
C
C
o
s
e
s
e
a
r
g
tt
O
h
o
f
le
a
u
i
e
e
r
e
O
•
•C•
•R•
•
A
e
n
e
e
o
o
e
o
l
g
w
n
s
s
e
‘A
t
t
o
p
s
2
TTINGS/
HANNEL
PTIONS
mage enha
indow set
indow and
hannel Sett
Indicates
Can selec
vailable Ch
Channels
Channel 1
elect Profil
Allows us
profiles t
pply Button
cements t
ings acces
the ‘Chann
ings
what channel
which chann
nnels
, 2 & 3 are av
is selected fo
r to select an
apply settin
assist wit
ed using th
l’ tab as sh
are available
l to display
ilable
viewing
individual pr
s to
interpret
e toolbar b
own in the
file or all
tion can b
tton. A b
mage abov
made usin
ief descrip
is describ
kay Button
Click whe
Applies s
‘Profile S
ancel Butt
Closes ‘Pr
applying s
Cancels si
eset
Resets all
applies d
g options f
tion of the
d below.
done with al
lected settin
ttings’ windo
n
file Settings
elected setti
nce the last t
settings tab
fault setting
und in the
‘Profile Se
settings
s and closes
’ window with
gs
ime clicked ‘A
to default o
to all profile
profile
tings’
he
ut
pply’
tions and
Click to a
TEP 8:
ply setting to
hannel Se
selected pro
ings – Se
iles
ct ‘Chann
l 1’ and ‘
Restores
ll’ profiles
profiles to pr
and click
-processed s
pply’
tate
Page 2
Page 26

S
D
t
s
g
a
S
t
r
m
R
a
T
A
S
s
t
e
e
s
s
g
h
w
p
o
u
p
d
t
t
j
ic
nd
e
o
f
p
v
0
e
f
’
g
d
r
a
s
g
r
e
t
c
p
s
f
f
m
a
a
e
e
3
TIME/
Within
indicate
we can i
options
Velocity
• Selec
• Sedi
Vertical
• Adjus
sound
conve
water
for e
bottom is di
EPTH RAN
his tab it i
that mos
nore the r
re describ
ettings
the average
velocity to u
sions
ent velocity i
ange
ts the viewab
ch profile
GE
possible t
of the ret
st of the
d below.
water and se
e for time to
only used af
itized
le range (dep
adjust th
rns are fr
rofile and
iment
depth
er the
h) shown
viewable
m above 1
ocus on th
ertical ran
0ms. By a
times (de
Select P
• Allow
or all
Time Us
• Adju
durin
Reco
e. Reviewi
usting th
pths) of in
ofile
s user to sele
profiles to a
ge
ts depths ba
acquisition
ding Delay
ng the pro
display ti
erest. Av
t an individu
ply settings t
ed on values
or Towfish D
iles
e range
ilable
l profile
o
ntered
pth or
TEP 9:
a.
b.
ime/Dept
djust ‘Vie
elect ‘All’
Range Ad
able Vert
rofiles a
ustments
al Range’
click ‘Ap
rom 0 to
ly
100ms
Page 2
Page 27

D
h
o
Tth
T
o
Fth
F
o
i
e
c
s
o
d
b
f
e
a
a
r
g
h
b
s
e
d
s
-
g
e
r
j
t
o
s
a
t
o
u
t
f
d
a
o
o
a
u
d
o
n
e
o
e
v
v
e
r
0
u
r
w
n
a
s
U
o
o
i
4
TIME/
Shown a
one of t
things t
bove is the
1.
e
xtending t
2.
c
3.
or this pro
EPTH RAN
e six profi
note in th
he depth s
is profile
he adjuste
ntains usa
e viewabl
GE
time/dept
les in the p
images a
ale on the
hows from
100ms ba
profile b
le data an
ile we can
range to 0
scale adju
ect tha
ro
ove.
right side
0 to 150m
ed on the s
tter deline
enlarges
ee that m
50ms.
stment res
was adjus
f each pro
, and the a
ettings cho
tes the po
he display
st reflect
lts for pr
ed simulta
ile indicat
usted pr
sen.
rtion of th
f the feat
rs are abo
file P1 (20
eously. Th
s the defa
file time/d
original p
ures in the
e 50ms so
40923TH
ere are a c
lt settings
epth range
ofile that
profile.
e could re
_EW1),
uple
for
only
duce
4.
or real dat
b
y profile b
mputer sc
c
v
ewable ran
processin
sis to maxi
een. How
e that wo
efforts it
mize the di
ver, for th
ks for all p
is best to
splay resol
is tutorial (
rofiles is a
djust the
tion of th
and for fas
equate fo
iewable ra
profile im
ter proces
our needs.
ge on a pr
ge on your
ing) select
file
ng a
Page 2
Page 28
w
w
w
w
w
0
h
hva
S- V- H- Nlabau
i
fpr
t
o
x
g
t
y
n
r
g
T
e
h
v
D
g
c
t
i
r
t
o
o
t
a
e
c
r
t
h
d
e
t
o
t
l
b
ag
e
r
t
w
w
d
y
an
t
e
l
w
p
5
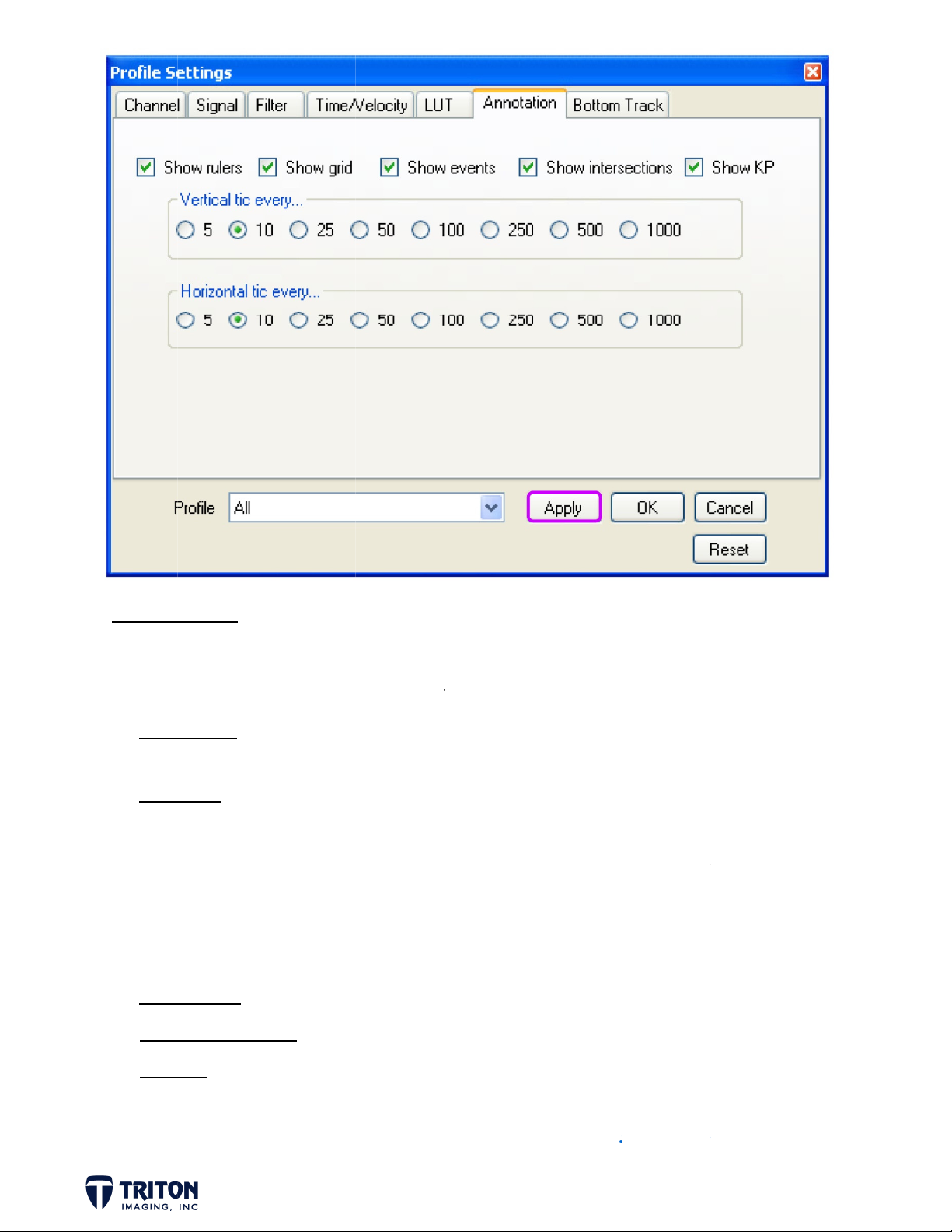
ANNOT
Shown a
window.
Sho
Sho
Sho
ATION
bove are t
A descript
Rulers T
Grid -
Events D
e annotati
ion of each
is is the a
lues.
hows the
ertical tic
orizontal
ote: Grid
el overlap.
tomaticall
splays eve
n options.
item is pr
is labels w
rid lines o
every: Def
ic every:
line spacin
If reduce
show the
t marks in
his contr
sented bel
ich indica
erlaying th
ines the sp
efines the
cannot be
d to a valu
losest spa
he data fil
ls what is
w.
e the horiz
e profile.
cing of th
spacing of
reduced t
too small
ing interva
e.
isplayed in
ontal and v
vertical g
he horizon
the point
o display, t
the windo
the profile
rtical grid
id lines.
al grid lin
here grid
he window
size will a
line
s.
ines and
ill
llow.
Sho
Intersect
Sho
KP I
STEP 1
: Annota
ions Inte
KP’s were
ofile windo
ion Settin
sections w
marked du
w.
s – Selec
th other p
ing acquisi
options s
ofiles can
ion they ca
own in im
e displaye
n be displa
e above
or turned
ed in the
d click ‘A
off.
ply’
Page 2
Page 29
L
g
r
l
n
n
1
abc
t
v
j
o
jmax
t
d
B
A
a
m
p
b
s
y
s
1
t
s
i
t
e
v
e
u
n
e
t
k
n
t
o
s
p
y
t
a
a
d
r
l
6
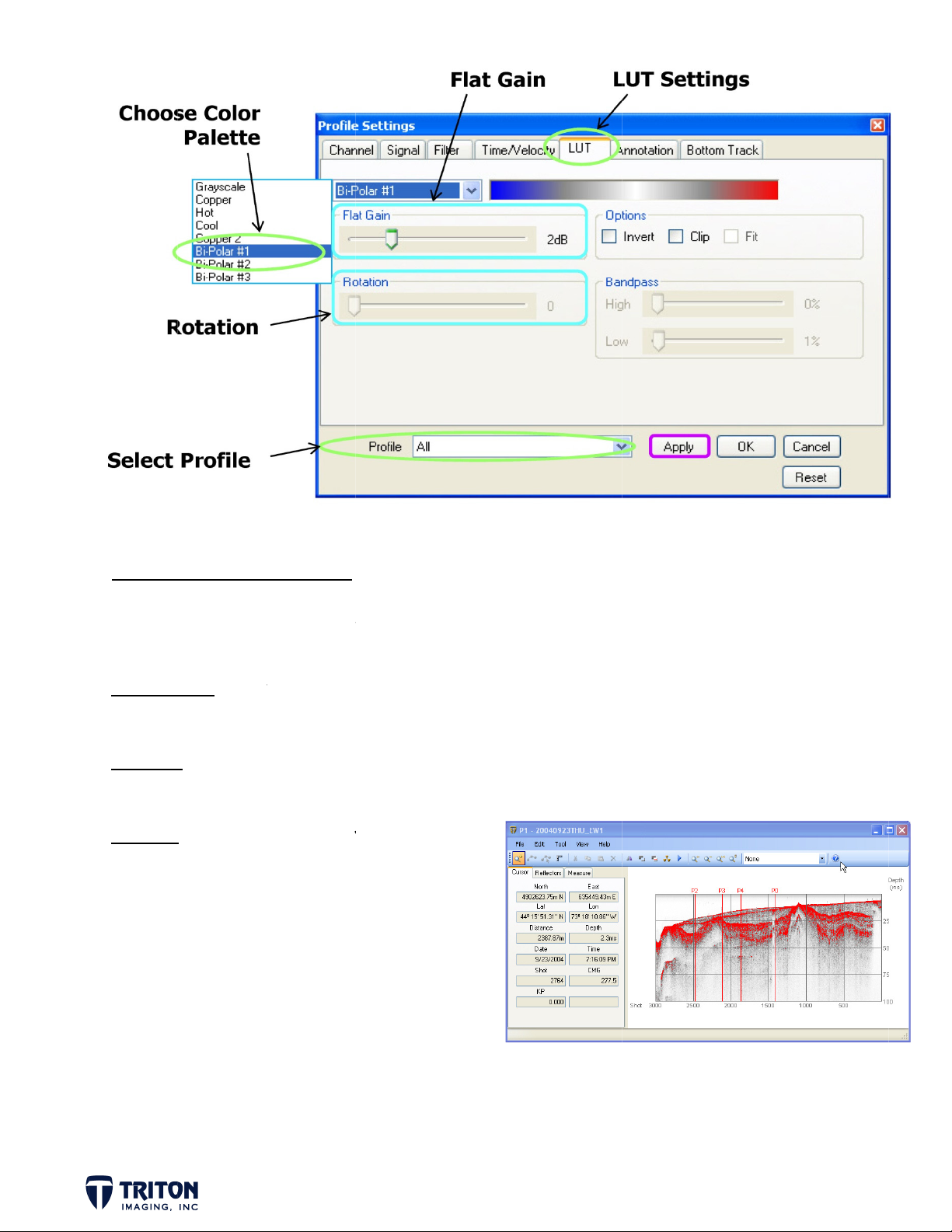
LUT CO
Changin
structu
Color Pa
Flat Gai
Rotatio
OR/GAIN
color pale
es. Here a
ette Se
for
Ad
wh
Ad
of
OPTIONS
tes is gre
e some co
eral color
displaying
usts signal
le profile i
usts LUT b
/min from
he scale.
t for bring
ments on
alettes ar
oth positi
gain for th
washed o
shifting t
the endpoi
ng out wea
he options
available i
e and nega
entire pr
t.
he
ts
reflector
available.
cluding bi-
ive signals
file with a
and poorl
olar palet
in analog d
constant v
delineate
es which a
ta.
lue. Usefu
e best
when
STEP 1
: LUT A
. Select ‘
. Set the
. Select ‘
ustment
-Polar #
‘Flat gain’
ll’ profile
’ color pal
o +2dB
and click
tte
‘Apply’
Page 2
Page 30

L
d
h
r
B
1
def
a
e
p
r
s
c
d
o
t
A
o
s
s
g
t
j
s
ip
as
p
s
p
a
t
g
g
’
f
r
a
f
to
’
w
w
s
f
e
d
j
n
.
n
7
LUT CO
In the p
returne
range t
• Inve
• Clip
• Fit
• High
• Low
STEP 1
OR/GAIN
revious ex
signal int
e color is s
t Reve
Adju
affe
Used
Bandpass
andpass
: LUT A
OPTIONS
mple the c
nsities. U
read acro
ses the col
ts the ran
t the color
with ‘Clip’
Adjusts t
usts t
Ad
ustment
lor palette
ing the ‘Cli
s. Here is
or palette.
e the sign
range.
o squeeze
he outer si
he inner si
(cont.)
was stretc
’ and ‘Fit’ o
a quick ove
ls are displ
he range o
nal range.
nal range.
hed across
ptions allo
view on ho
yed. If u
colors to
the entire
users to a
to use th
ed without
it in the a
range of po
ust the i
d
se options
‘Fit’, it doe
usted sig
tential
tensity
s not
al range.
. Check b
. Adjust
. Select ‘
th the ‘Cl
he ‘Bandp
ll’
rofile
’ and ‘Fit
s’ range
and click
options
rom 15%
‘Apply
90%
Page 2
Page 31

L
a
e
-
t
a
1
g
hi.
j.
e
a
u
.
t
e
e
d
ck
h
t
A
s
t
c
s
n
l
e
n
a
s
o
a
n
w
k
n
n
n
t
f
s
c
b
e
o
m
s
s
h
t
8
LUT CO
This pro
of the d
with int
It is alw
the sub
options
Note th
settings
STEP 1
OR/GAIN
cess reduc
ta. Fine t
rpretation
ays best to
bottom da
o the defa
t if the ‘R
will be res
: LUT A
. Un-che
OPTIONS
d the over
ning these
play with
a. Before
lt setting
set’ butto
t to defau
ustments
both th
aturation
settings c
hese setti
ontinuing
.
in any tab
t values.
(cont.)
‘Clip’ and
f the stro
n significa
gs during i
ith the tu
in the ‘Pro
‘Fit’ option
g returns
tly enhanc
terpretati
orial, let’s
ile Setting
ut also wa
image qua
n to pull t
anually re
’ window is
hed out pa
lity and ass
e most out
urn our col
clicked, all
rts
ist
of
or
. Reset t
Change
Select ‘
e ‘Flat gai
he color p
ll’ profile
’ to 0dB
lette bac
and click
to ‘Grays
‘Apply’
ale’
Page 2
Page 32

L
w
a
W
W
h
m
D
M
2
abc
S
a
t
o
S
N
M
A
a
o
v
a
e
e
ot
s
e
c
o
t
r
c
e
o
w
ns
’
s
s
’
n
g
h
c
s
9
SIGNA
Options
profile
Rectific
Downsa
STEP 1
•
•
t
•
•
OPTION
in the sign
indow.
tion
ith unipolar
ith bi-polar
e entire sig
pling
iscards por
ax seems t
: Signal
l settings
data ‘None’
data it is p
nal to positi
ions of sign
work best,
ettings
llow the us
is the best
ssible to sh
e and ‘None’
l for display
specially fo
r the sele
hoice.
w either th
will display
on PC monit
r long lines
t how the
positive or
both the po
rs.
ith high sho
ignal is dis
negative sig
itive and ne
t density.
played in t
als. ‘Rect’
ative signal
e
onverts
.
. Check ‘
. Check ‘
. Select ‘
one’ in th
ax’ for b
ll’ profile
‘Rectifica
h the ‘Ve
and click
ion’ optio
tical’ and
‘Apply
‘Horizontal
options
Page 2
Page 33

p
l
s
e
n• O
i
e
t
a
a
t
3
r
e
-
p
y
b
m
e
a
e
s
o
A
n
s
i
s
te
t
a
r
0
u
c
d
ts
s
g
u
e
e
s
g
u
t
f
g
d
a
a
r
e
r
i
y
o
t
e
f
0
FILTER
Four ty
To enab
Bandpas
• P
• A
• S
Stack F
• P
TVG Fil
• C
• C
OPTIONS
es of filte
e each filt
Filter
rforms Fast
podization ap
etting the del
ding at Dela
e
nly use with
lter
rforms horiz
er
n set custom
n select ‘Fro
s are avail
r check th
Fourier Tran
lies a taperin
ay and durati
+ Duration.
i-polar data (
ontal stack u
TVG value or
Seabed’ to
ble to enh
‘On’ box.
form process
g function bri
n values will
duration of
ot valid for
ing window of
use default.
gnore water
nce the di
ing on input si
nging the inp
esult in proc
ms uses the
nipolar signal
specified len
olumn, but m
play of the
nal. Enter a
t signal value
ssing a clippe
ntire signal
).
th for decre
st have wate
profiles as
high pass and
to zero at eit
signal start
fter the dela
sing signal n
bottom digit
described
low pass valu
her end.
ng at Delay ti
.
ise.
ized first.
below.
.
me and
AGC Fil
STEP 1
• G
er
ood for old s
: Filters
ismic system
– Turn fil
done tes
.
rs on an
ing effec
adjust se
of each
tings to s
ilte
e affect,
urn all of
when
Page 3
Page 34
M
e
t
i
g
w
i
a
s
o
s
t
u
O
c
s
p
t
s
g
h
o
o
m
m
i
y
t
e
e
g
L•H•m
•
D
•
D
•
i
g
a
v
n
k
s
u
i
l
a
n
l
D
t
e
p
s
a
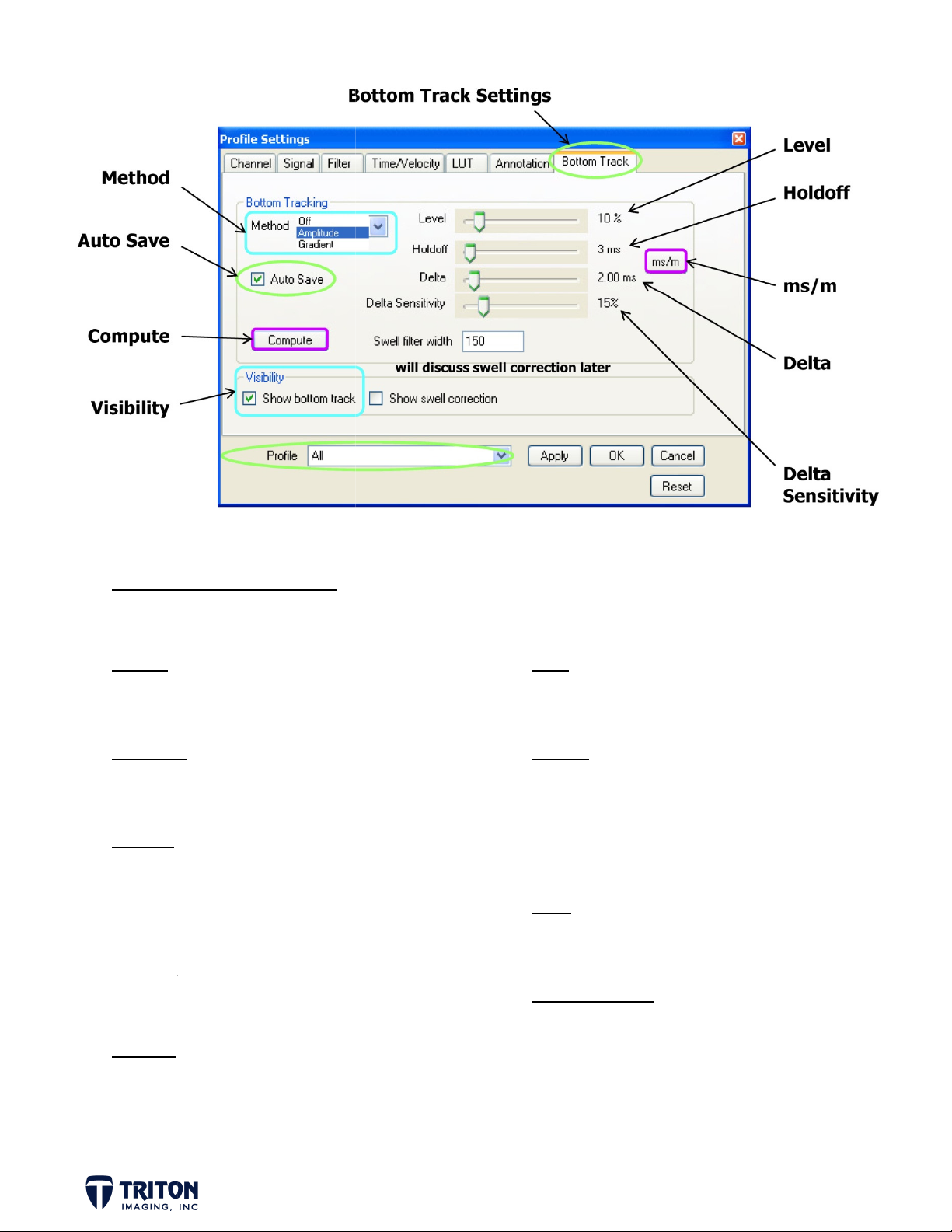
BOTTO
The wat
Method
• Selec
track
Auto Sav
• Will a
havin
Compute
• Click
track
• Very
gener
apply
may n
discu
Visibility
• Selec
the s
TRACK
r bottom
a method to
ng
e
utomatically
to save the
hen ready to
mportant not
ting the bot
well filterin
t want (swell
sed later in t
to display b
b-bottom pr
PTIONS
an be auto
enable botto
ave results w
roject
generate bot
to click ‘Appl
om track as i
to your data
filtering will
is tutorial)
ttom track r
files
atically d
thout
tom
’ when
will
which you
be
sults on
fined usin
the follow
evel
Percent c
(10% is a
oldoff
Set just
s/m
Toggles b
on sound
elta
Use to co
start, ma
elta Sensit
Changes
finer adj
ng ‘Bottom
hange in ampl
ood starting
bove the sha
etween time
elocity setti
strain the fi
e sure not at
ivity
ensitivity of
stments
Track’ set
tude or gradi
value)
lowest data
nd depth (de
gs)
ter gate (2m
0ms)
elta slider b
ings.
nt level
th based
good
r for
Page 3
1
Page 35

M
n
4
a
6
f
b
6
e
O
t
g
m
th
n
o
t
e
n
c
f
g
d
adj
S
d
e
p
o
t
h
’
t
w
r
h
s
s
T
s
d
e
o
a
o
e
e
h
a
a
t
e
h
p
u
m
e
a
a
n
e
c
k
o
e
u
2
BOTTO
To get t
iteratio
previous
STEP 1
Of the
results
settings
constrai
TRACK
he bottom
s adjustin
page (Page
: Botto
. Select
profiles i
rom the b
need to be
n the filter
. Change
‘Comput
PTIONS
racking to
the settin
31) are a g
Tracking
e options
the demo
ttom track
usted.
gate.
he ‘Delta
closely alig
s and com
ood place t
shown on
ata set, t
ing options
To remove
ensitivity
n with the
uting the
start wit
he previou
e top two
selected.
large spike
to 5% an
ater bott
esults. Th
most data
page and
hown abov
o refine t
, the ‘Delt
the ‘Delt
m, it gener
options s
sets.
click ‘Com
represent
e tracking
’ value sho
’ to 0.25
ally takes
own on the
ute’
the best a
results, th
ld be redu
s and clic
few
d worst
ed to
Of the
and the
right sti
refinem
profiles i
bottom tra
ll shows of
nt.
the demo
king, as sh
sets betw
ata set, 5
own on the
en the bot
showed a v
left image
om track
ry good fi
f the lowe
nd the wat
between t
r set abov
r bottom
he water b
. The imag
nd needs f
ttom
on the
rther
Page 3
Page 36

M
4
c
d
e
e
t
O
f
m
-
a
a
do
c
om
a
n
(
ty
m
m
e
h
h
e
wn
h
e
l
l
t
e
o
0
e
,
a
k
H
a
e
t
e
t
3
BOTTO
Since all
profile.
STEP 1
The low
TRACK
other pro
: Botto
. Change
‘Delt
‘Delt
‘Hol
Sele
. Click ‘C
r right im
PTIONS
iles have a
Tracking
Sensitivi
’ to 0.28
ff’ to 10
t from th
pute’
ge above s
good fit, w
cont.)
’ to 5%
s (deeper
drop-do
ow a fairly
will just r
profile)
‘Profile’
good fit, a
fine the b
ist ‘P5 – 2
though th
ttom trac
040930T
bottom tr
ing for th
U_EW5’
cking does
last
depart
from th
The bot
less wor
tracking
water bot
om tracki
k is needed
results.
tom at the
g does not
later to co
crest of t
ave to fit
rrect the s
e slope.
exactly to
eabed refl
he seabed
ctor gener
but the b
ted from
tter the fi
he bottom
the
Page 3
Page 37

F
u
a
e
l
r
y
S
S
5
a
b
f
i
G
b
e
o
e
e
m
c
C
M
A
p
h
n
c
n
l
w
s
ot
s
o
W
o
y
e
r
o
t
s
n
t
’
l
b
l
d
t
’
w
e
p
i
e
g
t
n
4
SWELL
Once yo
image c
using th
Swell Fi
• d
•
Visibilit
• ‘
• ‘
STEP 1
ILTERIN
have the
used by sw
following
ter Width
efault valu
educe valu
how botto
how swell
: Swell
. Check ‘
ottom tra
ll motion.
ptions.
is 150
if removi
track’ wil
orrection’
rrection
ax’ for b
k defined
This is don
g real data
overlay bo
ill display
h the ‘Ve
ou may wa
in the ‘Bo
ttom track
the results
tical’ and
t to try an
tom Track
results on
of the swe
‘Horizontal
remove d
’ tab of th
he profile
ll filtering
options
stortions i
‘Profile Se
the
ttings’
. Select ‘
The pro
after fil
distingu
ile close-u
tering on t
sh betwee
ll’ profile
s above sh
e right.
swell moti
and click
w the rec
hen using
n artifact
‘Apply
his filter,
rded signa
and actua
prior to s
e very car
seabed to
ell filterin
ful, SB-In
ography!
on the lef
erpreter d
t and
oes not
Page 3
Page 38

Z
o
e
R
C
o
T
o
U
h
m
T
t
n
h
o
g
y
r
u
e
e
o
t
t
o
c
t
p
b
a
e
u
e
a
h
e
s
a
l
y
r
a
c
n
t
f
R
b
e
y
a
o
t
S
g
t
b
a
b
t
h
e
e
e
t
y
a
b
r
i
u
T
y
e
y
a
t
5
DIGITI
Reflect
Here ar
•
•
•
• I
• I
E REFLEC
rs seen in
a few thi
eflectors c
licking on t
t
olbar butt
he ‘Select’
o
r relocatin
nitially onl
ftware to
s
f bottom t
igitized val
d
ORS
he sub-bo
gs to know
an be digiti
e ‘Reflect
n will be a
toolbar bu
digitized
the ‘R0’ re
be the sea
acking was
es for ‘R0’
tom profil
about digit
zed using a
r’ tab will
tivated w
ton allows
oints.
flector exi
ed.
used to tr
.
s can be tr
izing refle
manual poi
utomatical
en a reflec
xisting re
ts in the ‘
ck the sea
ced using
tors with
t and click
ly enter di
or is selec
lectors to
eflector’ t
ed, it can
he ‘Digitiz
B-Interpr
method.
itize mode.
ed.
e edited b
b which is
e used to
’ toolbar b
ter.
he ‘Digit
adding, r
assumed b
uto-gener
tton.
ize’
moving
the
te
•
Shown a
with so
sing the ‘S
t
e actual s
bove is an
e commen
lect’ toolb
abed to b
verview of
s on their
r button a
removed b
the toolba
se.
lows discr
manually
buttons c
pancies be
djusting t
mmonly us
ween the
e reflecto
d for digit
ottom trac
node posi
zing reflec
ker and
ion.
tors
Page 3
Page 39

Z
z
a
6
S
th
S
R‘A
R
a
s
T
l
w
h
a
z
‘Z
f
‘
o
ra
a
p
a
t
w
e
t
B
e
t
’
d
e
d
c
t
s
o
b
a
e
p
r
t
t
w
re
e
t
y
c
n
d
g
o
c
r
e
s
6
DIGITI
Clicking
default,
tutorial,
the hori
horizon
STEP 1
a.
b.
c.
d.
E REFLEC
on the ‘Ref
there is al
we will use
on using t
nd for an
A: Digiti
elect the
e full pro
elect the
ight-click
uto Gene
epeat for
ORS
ector’ tab
ays an ‘R0’
‘R0’ for th
e bottom
dditional p
e Water
oom Hom
ile exten
Reflectors
n the ‘R0
te Seabe
ll lines
ill display
reflector
water bo
racking re
rominent h
ottom
’ toolbar
’ tab from
reflector
the list of
reated, bu
tom and au
ults. We
rizon.
utton to
the profil
nd select
eflectors
without a
omatically
ill then ad
turn to
window
reated for
y points di
generate p
reflectors
this proje
itized. Fo
sition nod
for the ba
t. By
this
s along
ement
This will
results
Setting
generate
t an interv
shown to
osition nod
l specifie
he right wi
s along th
in the ‘Ap
ll generate
bottom tr
lication Se
nodes ever
ack
tings’.
20 shots.
Page 3
Page 40
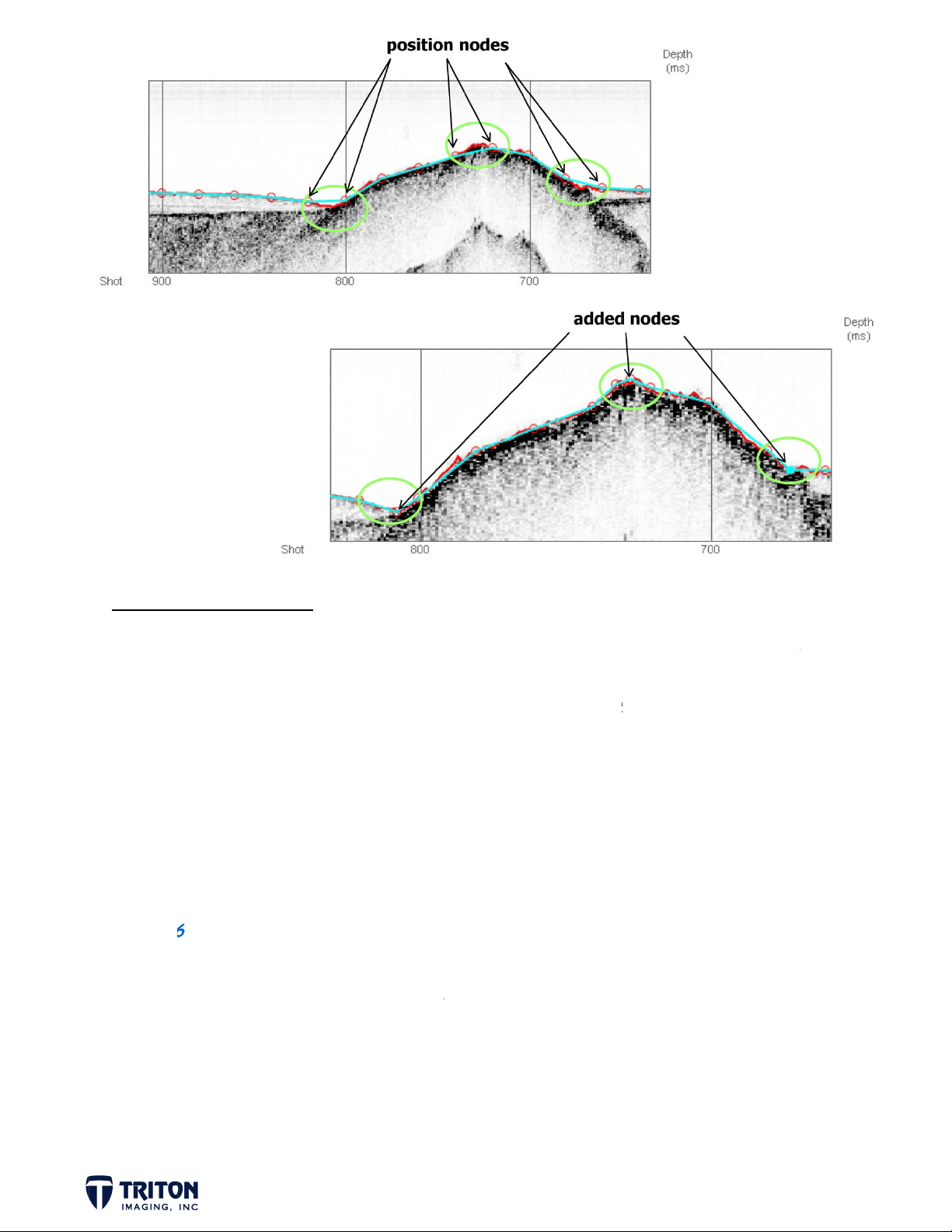
DIGITI
Z
t
s
o
a
6
d
e
f
T
n
b
c
z
p
z
a
t
p
y
r
c
m
e
b
P
B
t
a
m
r
c
A
l
e
o
r
n
t
he
es
s
r
o
d
n
e
w
o
o
t
n
g
e
l
e
u
l
b
b
n
l
o
o
r
g
m
v
b
t
e
t
o
n
m
f
7
E REFLEC
ORS
As seen
the bot
deviate
position
found in
By using
reflecto
are exp
next ch
STEP 1
in the top i
om track a
from the
nodes and
the ‘Tools’
the ‘Digiti
r to the to
rted so clo
pter.
A: Digiti
. Use the
along se
. Where
points
. Repeat
mage, with
d the ‘R0’
ottom tra
an be mini
menu of th
e’ toolbar
ography.
ser spacing
e Water
Pan/Zoom
ed to m
here is a
ocess fo
a node spa
eflector.
k. This wil
ized by d
map wind
utton, ext
lease note
is better.
ottom (co
oolbar bu
ke sure t
isfit, use
all profil
ing of 20 s
few spot
occur whe
creasing n
w (see win
a nodes ca
that when
Exporting
t.)
ton to zo
fit is go
the ‘Selec
(auto-ge
hots there
still stand
e the topo
de spacing
ow on pag
be manua
xporting r
ill be disc
m to smal
’ toolbar
erate sea
is an overal
out where
raphy cha
in the ‘App
36).
ly added t
flectors,
ssed in mo
area alon
utton to
ed and re
l good fit
the reflec
ges betwe
ication Set
better ma
nly node p
e detail in
seabed a
ove or re
iew/edit
etween
or
n
tings’
ch the
sitions
the
d pan
ove bad
or
accurac
Page 3
Page 41

Z
a
p
6
g
h
c
y
T
p
z
r
t
ng
r
t
g
c
e
a
f
r
B
a
th
m
o
th
o
c
e
f
f
n
o
0
o
d
p
e
g
o
er
B
,
t
e
e
n
’
d
(
t
p
a
n
c
i
h
8
DIGITI
When m
very hel
STEP 1
E REFLEC
king multi
ful when c
A: Digiti
. Change
Righ
‘Cha
. Change
Righ
Chan
ORS
le reflecto
rrelating
e Water
eflector n
-click on
e the na
eflector c
-click on
e the col
rs it is use
eflectors
ottom (co
me -
e reflect
e from ‘R
lor -
e reflect
from ‘Re
ul to chan
rom one pr
t.)
r ‘R0’ and
’ to ‘Wat
r ‘Water
’ to ‘Blue’
e the refl
file to th
select ‘Re
Bottom
ottom’ an
as shown
ctor name
next.
ame’
select ‘Li
above)
nd colors.
e Color’
This is
Sele
t ‘OK’
To help
Therefo
will appl
orrelate r
re when m
to the re
flectors a
king chang
lectors wit
ross multi
s to reflec
h that nam
le profiles
tor proper
in all prof
the reflec
ies such as
iles in the
ors are lin
name and
roject.
ked via the
olor, the c
r name.
anges
Page 3
Page 42

Z
e
T
r
6
R‘A
C
Rchco
a
S
d
Sonb
T
t
e
z
o
t
o
r
t
in
‘
u
‘
fi
o
n
n
to
m
en
c
(
e
o
t
n/
u
e
e
a
t
se
ig
f
to
o
n
d
r
t
e
dr
t
e
)
o
p
38 op
t
t
r
9
DIGITI
To delin
added.
on the p
STEP 1
a.
b.
c.
E REFLEC
ate other
he reflec
evious pag
B: Digiti
ight-click
dd Reflec
hange the
ight-click
ange the
lor ‘Blue’
nd shown
ORS
horizons se
or name ca
(page 38)
e Baseme
n ‘Reflec
or’
name fro
n ‘Basem
eflector
o ‘Purple’
the imag
en in the s
be enter
.
rs’ and s
‘R1’ to ‘B
t’, select
olor from
as discus
to the r
b-bottom
d during th
lect
sement’
‘Line Colo
he defaul
d on pag
ht)
ata, additi
e creation
’ and
nal reflec
hase or la
ors can be
er as desc
ibed
d.
elect the
Basement’
reflector
rom the
own men
e.
elect the
the pro
asement h
Digitize’ t
le window
rizon (Pa
olbar but
o place p
Zoom as
n and lef
ints on th
eeded
-click
Page 3
Page 43

DIGITI
Z
r
o
e
6
fgh
.
j.
s
n
k
.
T
t
l
z
Z
t
th
c
f
B
f
o
he
e
e
h
n
cr
d
te
m
co
m
he
e
b
n
w
ut
i
o
’
op
e
p
u
e
Paton
n
t
h
u
e
d
e
e
to
t
t
u
e
r
it
v
c
t
l
)
to
ed
h
wa
a
0
E REFLEC
ORS
There a
water b
must br
STEP 1
We can
baseme
e two loca
ttom refle
ak the ref
B: Digiti
.
oom in
. Select
. Left-cli
breaks
i
Select ‘
Repeat
ee in the l
t horizon.
. Using t
the refl
ions where
ctor. To r
ector at t
e Baseme
o the out
e ‘Select’
k on the
rom selec
reak’ fro
or the se
wer image
‘Pan/Zoo
ctor to t
the basem
move the
ese locatio
t (cont.)
op areas
toolbar b
igitized po
d point t
the ‘Edit
nd outcr
that there
’, ‘Digitiz
horizon
nt crops o
asement r
s.
ith the ‘
show
nt just af
point of
menu (or
is some dis
’ and ‘Sel
t at the s
flector wh
n/Zoom’
above
er the ou
igher sho
se shortc
crepancy b
ct’ toolba
abed and o
re the out
olbar but
crop to se
number)
t ‘CTRL B’
tween the
buttons
erlaps wit
rops occur
on
ect it (al
reflector
carefully
our
, we
ys
nd the
match
l
Digitize
‘Basement’
on other
rofiles an
break/ed
as need
Page 4
Page 44

Z
t
a
6
Uthth
U
on
p
Rth
S
a
J
e
T
r
z
a
en
n
P
t
d
o
-
-
p
m
1
u
nt
o
b
r
i
n
E
B
d
t
d
e
o
om
s
c
i
g
r
l
B
r
o
h
e
e
n
L
e
e
r
ct
t
r
e
p
r
d
b
a
r
f
f
)
k
s
o
d
f
n
L
t
DIGITI
The nex
addition
STEP 1
a.
b.
Other o
•
•
E REFLEC
step afte
l horizons.
C: Digiti
sing the s
e promin
e ‘Horizo
sing the ‘
intersec
tions for
eflector n
e node, or
tandard ed
P
ste (CTRL
ORS
the water
In the de
e Horizon
me steps
t sedime
1’ reflect
an/Zoom’
ing lines a
igitizing re
des can be
right-click
iting optio
V), Delete
bottom an
o data se
sed for a
layer se
r on all pr
utton, zo
e at the
flectors in
selected w
ng and dra
s apply to
(DEL), and
basement
, there is a
ding the ‘
n in the p
files
to horiz
ame dept
lude:
th the ‘Sel
ging to sel
eflectors i
Undo (CTR
are digitiz
distinct se
asement’
ofiles and
n interse
and if no
ct’ toolba
ct multipl
cluding Co
-Z).
d is to ad
dimentary
eflector,
call it ‘Ho
ions, veri
adjust re
button, by
nodes.
y (CTRL-C
reflector
oundary.
dd one m
izon1’ an
y that re
lectors as
left-clicki
, Cut (CTR
for any
re for
digitize
lectors
needed
g on
-X),
• ‘
oin’ (CTRL
r
flector (o
J) in the ‘
posite of ‘
dit’ menu a
reak’) by s
lows users
electing th
to connect
points ac
two points
oss a brea
in a discon
.
inuous
Page 4
1
Page 45
E
c
t
b
i
c
f
w
7
abc
E
r
s
e
u
th
c
a
n
b
b
s
n
e
e
re
p
l
i
w
p
l
b
w
a
e
o
l
s
r
A
m
t
i
o
y
a
e
l
m
n
e
m
o
w
a
t
e
2
t
PROFIL
Zooming
more ac
and wid
toolbar
tab to d
Left-cli
depth o
profile
STEP 1
MEASUR
into the p
urate mea
h of the s
utton, the
splay meas
k and drag
the basin,
indow whic
: Profile
. Select
MENT TO
ofile will e
urements.
dimentary
‘Cursor’ ta
rement re
the cursor
as shown i
h shows th
Measurem
e ‘Measu
OL
large an ar
Using the ‘
asin seen i
which sho
ults.
across the
the exam
horizonta
nts
’ toolbar
ea of inter
Measure’ t
n the profi
s the cur
sedimenta
le above.
and vertic
utton
st in the v
olbar butt
e above. B
or position
y basin sp
n orange r
al extent p
ew window
n we can
clicking o
is changed
nning the e
ctangle wil
us the slop
which allo
easure the
the ‘Meas
to the ‘Me
ntire width
l appear in
line.
s for
depth
ure’
sure’
and
he
. Left-cli
. Results
k on
rofi
re shown
and dra
n the ‘Me
area to
sure’ tab
easure as
o the left
shown in i
of the pr
age abov
file
Page 4
Page 46

E
f
d
T
o• W• TOw• Y
8
a
G
m
s
r
e
t
g
t
at
p
i
l
f
d
i
o
f
g
n
i
e
c
p
s
n
s
n
n
t
"
h
g
m
tt
f
d
r
e
h
t
ec
k
e
d
nu
3
PROFIL
Profile
intersec
the ‘Fol
to know:
•
FOLDIN
olding atte
tions acros
ing’ toolba
his featur
c
mputed.
hen selec
o add data
nly the se
indow, not
ields 2D re
TOOL
pts to re
lines and
button or
is not avai
ed, opens a
to the ‘Pro
ment boun
he whole l
presentati
roduce the
s a special
by selectin
able until
new empty
ile Folding’
ed by line
ne.
n of inters
"folded pa
mode acce
‘Folding’ i
avigation i
profile wi
window, se
ntersectio
cting prof
er record
sed from t
the ‘Tools
processed
dow.
lect line se
s will be i
ile sections
method o
e map win
’ menu. He
and inters
ments in t
ported to
.
checking r
ow by clic
e are som
ctions are
e map win
he ‘Profile
eflector
ing on
things
ow.
Folding’
STEP 1
: Profile
. To initi
Folding
e profile
olding, cli
k on the
oolbar bu
on or sel
t the me
option
Page 4
Page 47

E
i
o
n
r
8
b
c
G
t
s
d
o
e
t
d
c
o
e
pr
r
s
n
w
w
d
p
o
e
h
f
m
r
w
c
d
o
o
m
o
or
n
b
h
t
e
r
n
d
t
-
h
e
r
t
d
v
e
n
vi
h
o
o
s
o
t
s
le
t
o
ec
m
l
e
s
h
s
t
r
li
d
4
)
PROFIL
To add l
the map
added t
As with
moveme
In orde
reflecto
STEP 1
FOLDIN
ne segmen
window. A
the folde
the normal
t in the pr
to compar
r colors in
: Profile
. To add
TOOL
s to the p
each line
profile wi
profile vie
file windo
the folde
he folded
Folding (c
ata to th
ofile windo
egment is
dow, boun
, the curs
.
profiles t
rofile to
nt.)
folded pr
, click on
licked, th
ed by the
r position i
the indivi
atch.
file, lef
he connect
profile da
ed lines in
the map
ual profil
click on li
ed navigati
a for that
icating pr
iew will foll
s, it helps
e segment
n line seg
egment wi
file inters
ow the cur
o change t
of intere
ents in
l be
ctions.
or
e
. Change
clicking
d
.
Using th
across
olors of t
n the pro
‘Pan/Zoo
ofile inte
e reflect
ile name i
’ toolbar
section (s
s to matc
the ‘Refl
utton, ve
ould be no
the indi
ctors’ tab
ify that t
umps acr
dual profi
and selec
e reflect
ss inters
s by righ
‘Line Colo
rs are in-
tion boun
-
ne
aries
Page 4
Page 48

e
T
g
-
n
Rin
T
a
e
e
a
x
S
e
w
:
m
r
a
d
d
e
:
a
X
a
B
f
r
s
j
s
e
t
p
e
n
t
i
s
t
h
j
n
(
t
a
a
t
f
a
Y
s
o
h
t
l
t
e
t
t
s
a
n
n
IVS
B
t
f
t
t
e
o
s
5
Chapt
OUTPU
Followin
in third
exporti
1.
2.
3. P
4. I
r 4 – E
OPTION
data proc
party soft
g and print
eflectors:
formation.
hicknesses
d
epth infor
rocessed N
n
vigation f
mage Curt
h
eight to wi
porting
ssing and i
are or for
ing from S
Exports re
Exports
ation.
av
: Export
om the pro
in: Export
th is corr
nd Prin
nterpretat
publication
-Interpre
lectors to
eflector t
profile to
ect.
to a TIFF
ct accordi
ing
on, it is of
. Below is
er.
an ASCII
ickness to
new SEG-
image who
g to the al
en desirab
a list of ou
ile containi
n ASCII f
or XTF fil
e ratio of
ng track
e to expor
put option
ng coordin
ile containi
s containi
the resul
available
te and dep
g coordina
g the proc
s to use
or
h
e and
ssed
istance an
d
v
5. I
VS SD File
f
ile for view
Bas
ment surf
locity ent
the compu
red in the
Exports
ing with th
ce
ed depth
profile set
rofiles to
ir free 3D
based on t
ings).
Fledermau
viewer sof
e sedimen
s SD image
ware.
SD files
prof
iles proces
in S
-Interpre
f
ed
ter
gener
ted from
refl
ector expo
Image
YZ
rt
produced i
Flederm
us 7
Page 4
Page 49
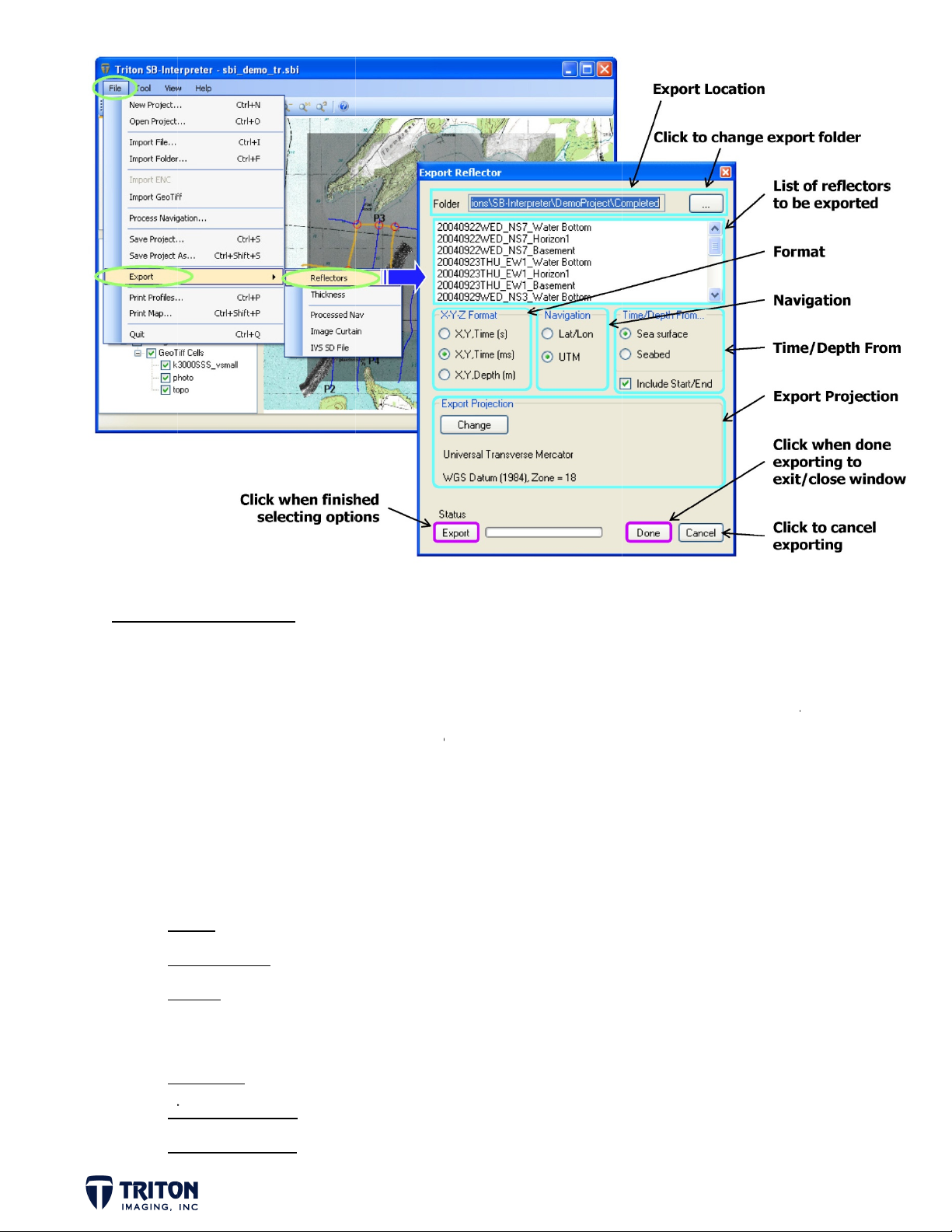
T
o
a
9
a
d
afo
N
T
O
e
r
m
i
rt
E
a
t
s
o
O
F
c
d
ec
fl
o
e
e
t
s
f
s
r
o
r
k
p
i
d
u
h
c
i
p
o
A
p
s
r
n
m
w
v
M
Z
d
t
c
’
d
f
o
m
e
e
n
r
p
s
t
c
g
f
t
l
l
v
6
EXPOR
Reflect
position
profiles
node sp
survey li
STEP 1
A brief
• F
• R
• F
REFLECT
rs can be
node eithe
from the
cing, the h
ne spacing.
: Expo
. Select ‘
escription
older: Displ
eflector Lis
ormat: Can
v
lues in prof
r entire pr
RS
xported to
for indivi
ap window.
gher the al
All Refl
xport/Re
of the refl
ys export l
: Lists all r
elect the v
ile settings
file).
an ASCII
ual profile
Since only
ong track
tors
ectors’ fr
ector expo
cation. Clic
flectors in
rtical units
o calculate
ile contain
using the
the node p
esolution.
m the ma
t options i
button to
roject whe
n seconds,
epth, if no
ng the XY
rofile win
sitions ge
cross tra
view ‘File
presente
ight to chan
exporting
illiseconds
ater botto
values of
ow export
exported,
k resolutio
menu
below.
ge the expo
rom the ma
r meters (u
defined wil
ach digitiz
options or
the closer
is control
t folder.
view.
es sound ve
l use water
ed
or all
he
ed by
ocity
elocity
•
•
• E
avigation:
ime/Depth
xport Proje
ption to out
rom: Outpu
tion: Must
put to Latit
ts the dept
elect proje
de-Longitud
value relati
tion if ‘UT
e or project
e to the sel
’ is selected
d coordina
ected surfa
in the ‘Navi
es.
e.
ation’ field.
Page 4
Page 50
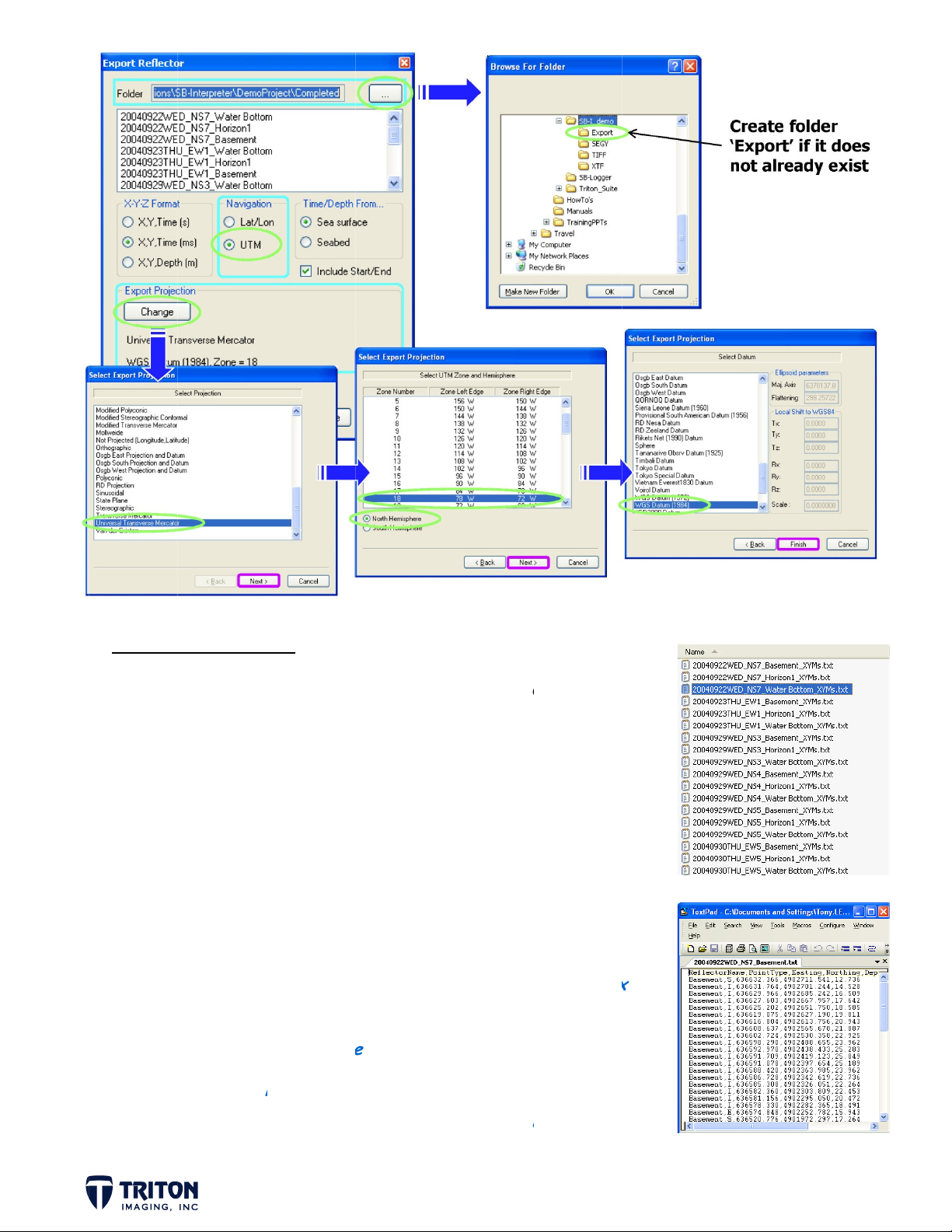
T
9
b
c
def
g
O
o
u
o
rt
r
e
(
n
e
r
C
s
xp
o
,
e
ec
e
n
em
s
‘E
ve
fi
d
r
t
o
a
p
i
oj
s
p
e
a
n
d
vi
d
e
le
o
s
x
h
s
e
7
EXPOR
To keep
‘Export’
helps to
STEP 1
REFLECT
track of y
folder to p
make subf
: Expo
. Click on
an expo
. Navigat
create
already
. Make su
. Select ‘
options
RS
ur exports
t all expor
lders for
All Refl
the chang
t locatio
to the d
ew folder
xist)
e ‘UTM’ i
hange’ in
hown abo
it is a goo
ts into. Fo
ach export
tors (con
export f
o folder
called ‘Ex
selected
xport Pr
idea to cr
large dat
type.
.)
lder butto
nd select
ort’ if it
n the ‘Na
ection’ an
ate an
sets, it als
and choo
‘Export’
oesn’t
gation’ bo
choose t
listofexport
dfiles
e
example
file
e
. Click ‘E
. Click ‘D
ort’ when
ne’ when
done adju
nished ex
ting the s
orting ref
ttings
ctor
Page 4
Page 51

T
n
w
r
n
s
9abcd
s
S
k
e
f
t
E
th
W
E
e
i
e
e
e
f
s
c
x
t
d
e
x
r
s
m
er
a
e
e
o
a
e
u
t
o
d
Z
y
l
f
x
i
e
B
m
e
b
o
y
e
b
t
menu
n
f
t
k
p
f
8
EXPOR
Exporti
export
values f
betwee
thickne
STEP 1
THICKNE
g the thic
indow. As
om that pr
the select
ses and re
: Expor
. Select ‘
. Select
. Select ‘
S
ness betw
with the r
ofile while
d reflecto
lectors is
Thicknes
xport/Thi
e same e
ater Bot
en two refl
flectors, e
xporting f
rs for all p
or thickne
between
kness’ fro
port fold
om’ and ‘B
ectors has
porting fr
rom the m
ofiles. Th
ses the bo
‘Water Bo
the map
used for
sement’ t
a very simi
m the pro
p window e
primary d
nding refl
tom’ and ‘
view ‘File’
reflector
measure
ar interfac
ile window
ports valu
fference
ctors mus
asement’
xports
etween
e to the re
only expor
s for thic
etween ex
be selecte
lector
s the
ness
orting
d.
. Select ‘
As with
creates
thickne
the reflect
an XYZ fil
s or of hor
xport’ an
or exports,
which can
zon surfac
‘Done’ wh
combining
be gridded
s for refl
n finishe
all the XY
in 3rd part
ctors.
data into
software
ne file per
for creati
unit (or re
g surfaces
lector)
of unit
Page 4
Page 52

T
e
t
g
t
9ab
c
d
m
d
E
o
v
p
x
o
t
E
th
f
al
E
e
t
A
n
h
m
d
c
x
o
f
d
s
o
T
p
o
v
er
a
in
e
e
e
h
n
o
Su
x
d
s
h
h
e
e
s
‘F
x
o
w
e
o
d
a
s
u
s
o
b
o
i
i
h
in
e
9
EXPOR
Process
replace
option w
raw navi
that pro
export
STEP 1
PROCESS
d navigati
he raw na
hich will wr
ation. Ex
file while e
he navigati
: Expor
. Select ‘
. Select
change
folder)
D NAVIG
n resides i
igation in t
ite a new S
orting fro
porting fr
n for.
Processe
xport/Pro
e same e
older butt
TION
the cache
e SEG-Y (
EG-Y (or X
the profil
om the ma
Navigati
essed Na
port fold
n to activ
files creat
r XTF) fil
F) file wit
e window o
window all
n for all
’ from the
used for
te the ‘E
d during t
, we use th
the proc
ly exports
ws the us
rvey Line
map view
previous e
port’ butt
e file imp
e ‘Processe
ssed navig
the proces
r to select
ile’ men
ports (mu
n, even if
rt process.
Nav’ exp
tion in plac
ed navigat
which prof
t select t
not chang
To
rt
e of the
on for
les to
e
g the
. Select
. Select ‘
When i
through
importe
porting th
the naviga
lines.
l profiles
xport’ an
processed
ion proces
or export
‘Done’ wh
navigation
ing step in
n finishe
SEG-Y file
order to c
into a ne
eck for int
project, y
rsections
u must stil
etween th
l go
Page 4
Page 53

T
e
d
d
d
,
a
a
e
M
T
U
e
o
a
x
e
e
w
e
s
e
d
e
s
x
n
c
d
a
p
r
n
d
o
t
f
e
b
b
o
o
g
r
o
c
e
t
t
h
m
n
0
EXPOR
A geo-r
exporte
exporte
map win
tiff file
export.
options
Image
• C
• V
Muting
• A
•
Navigati
IMAGE C
ference v
from the
simultane
ow. For e
a small te
An exampl
re discuss
n set image
rtical exagg
llows portion
ust have wat
on
RTAIN
rtical tiff i
profile win
usly using
ch profile
t file is al
of the te
d below.
idth by setti
ration will in
of profile to
r bottom digi
mage of a
ow or all p
the export
xported, i
o generate
t file is sh
g each shot
rease the ver
be muted or
tized to work
rofile can
ofiles can
options fr
addition t
containin
wn to the
o be 1 pixel w
tical resoluti
illed
e
e
m the
the
some basi
ight. Som
ide (best) or
n of the expo
metadata
importan
he total widt
rted profile i
for the
export
can be set i
age data
pixels
• S
elect UTM or
•
his is strictly
Lat/Lon coor
for the ancill
inates
ry text file
xported with
the tiff
Page 5
Page 54

T
i
t
9ab
c
c
h
y
U
t
rt
F
/I
ex
op
h
y
i
t
u
f
t
e
sh
b
m
h
e
P
P
r
e
m
n
e
P5 (
00
a
c
i
HU
e
r
t
E
q
s
r
f
a
EXPOR
Image s
the ver
STEP 1
As you
poor. T
IMAGE C
ze and ver
ical exagge
: Expo
. In the ‘
‘Export
. Select
. Select
an see in t
is results i
RTAIN
ical resolu
ration will i
Image C
ile’ menu
mage Cur
port fold
tions as
e images a
n a fairly s
ion are set
ncrease th
rtain for
or profile
ain’
r used fo
own abov
ove, at 5x
all file of
by adjusti
vertical r
file 2
thickness
and click
vertical ex
3.2MB whi
g the vert
solution an
40930T
export
‘Export’
ggeration,
h shows th
cal exagge
d the resul
_EW5.S
the image
basic sub
ation. Inc
ing image
G), select
uality is f
urface str
easing
ile size.
irly
ucture
with ver
little def
nition of t
e thin sedi
entary be
ds.
Page 5
1
Page 55

T
d
9de
r
n
U
t
rt
‘V
E
a
x
s
e
t
u
x
e
5
e
s
r
n
a
a
h
P
n
e
e
c
n
n
w
)
s
u
h
u
p
m
o
a
t
o
v
e
.
a
r
a
n
c
u
e
2
EXPOR
Increasi
profile
STEP 1
There a
those o
IMAGE C
ng the ver
ata.
: Expo
. Change
. Select ‘
e a few m
page 51 e
•
The resu
lower re
RTAIN
ical exagge
Image C
ertical E
xport’
or differ
ported at
lts above b
olution ver
ration of t
rtain for
aggeratio
nces betw
x.
tter repr
ion.
e export
5 (cont.
’ to 30x a
en the res
sent the t
ill increase
shown ab
lts shown
in sedimen
the vertic
ve
bove expor
layers ba
l resolutio
ted at 30x
ely seen in
of the
to
the
Since th
•
a pre-se
therefor
be set in
data is sp
line thick
e show up
the ‘Applic
ead over a
ess do not
s thinner li
tion Setti
greater ve
over as m
es on the
gs’ in the
rtical secti
ch of the
rofile. Th
ap window
n, the refl
ertical dat
reflector
ectors whi
as previo
line thickn
h have
sly and
ss can
Page 5
Page 56

T
h
o
r
g
9
f
g
m
e
t
r
U
t
W
e
o
c
rt
o
E
e
n
n
c
r
g
e
e
e
u
C
d
e
m
f
c
P
e
n
t
t
f
o
e
t
e
u
)
c
d
a
t
n
r
e
S
b
s
o
e
p
t
o
a
T
o
a
a
u
c
e
f
3
EXPOR
Along tr
interpre
best to
using al
‘Along T
If ‘Alon
STEP 1
In the i
IMAGE C
ack correc
tability.
ave this f
ng track c
ack Corre
Track Cor
: Expo
. Turn ‘Al
. Select ‘
ages abov
RTAIN
ion is impo
hen pickin
ature turn
rrections.
tion’ will yi
rection’ is
Image C
ng Track
xport’ an
we can se
tant when
reflectors
d off. Thi
However, i
ld more a
nabled the
rtain for
orrection’
‘Done’ wh
the stripi
a user is m
or interpr
s is due to
locating f
curate res
n the box f
5 (cont.
on by che
n finishe
g effect c
re concer
ting featu
he gaps or
atures se
lts.
or ‘1 Pixel/
king the
used by u
ed about s
es seen in
striping se
n in the pr
hot’ must
ox
ing ‘Along
atial accur
he profile,
en in the d
file data,
lso be che
rack Corr
cy than
it is
ta when
sing
ked.
ction’
for the
seen at
‘Along T
xport. Si
his scale i
ack Corre
ce the navi
the place
tion’ is not
gation for
ent of fea
necessary
his datase
ures along
or accurat
is fairly g
the profile
e spatial r
od, there i
line and th
presentati
s little dif
erefore usi
n.
erence
ng
Page 5
Page 57

T
e
d
3
w
9abcd
u
I
o
A
i
D
t
F
ex
op
E
e
D
e
p
r
r
p
e
sh
d
e
s
o
d
r
e
i
V
p
r
e
e
o
d
t
r
e
S
rt
d
m
m
i
f
x
t
d
e
a
d
e
f
i
u
p
8
I
4
EXPOR
Profiles
their fr
or indivi
can be e
pages 4
Options
box sho
STEP 1
IVS SD F
can be exp
e viewer.
ually from
xported to
-44), we w
for IVS S
n above.
: Expor
. In the ‘
. Select
. Select
LE
rted to 3
ll profiles
the profil
an IVS SD
ll use this
exports a
Folded P
ile’ menu,
ort fold
tions as
image file
can be exp
view. In a
file. Retu
rofile to g
e very sim
ofile to I
select ‘Ex
r used fo
own abov
formatte
rted simul
dition to
ning to the
nerate ou
lar to imag
ort/IVS
image cu
as Fleder
taneously f
he survey l
folded pro
3D export
curtain e
D File’
ain expor
aus SD fil
rom the m
ne profiles
ile create
.
ports as s
s for view
p view men
, a ‘folded
in Step 1
en in the d
ng in
option
rofile’
(see
ialog
. Select ‘
The res
lting imag
xport’ an
s above ar
‘Done’ wh
captures
n finishe
f the 3D i
age viewe
in free so
tware by
VS.
Page 5
Page 58
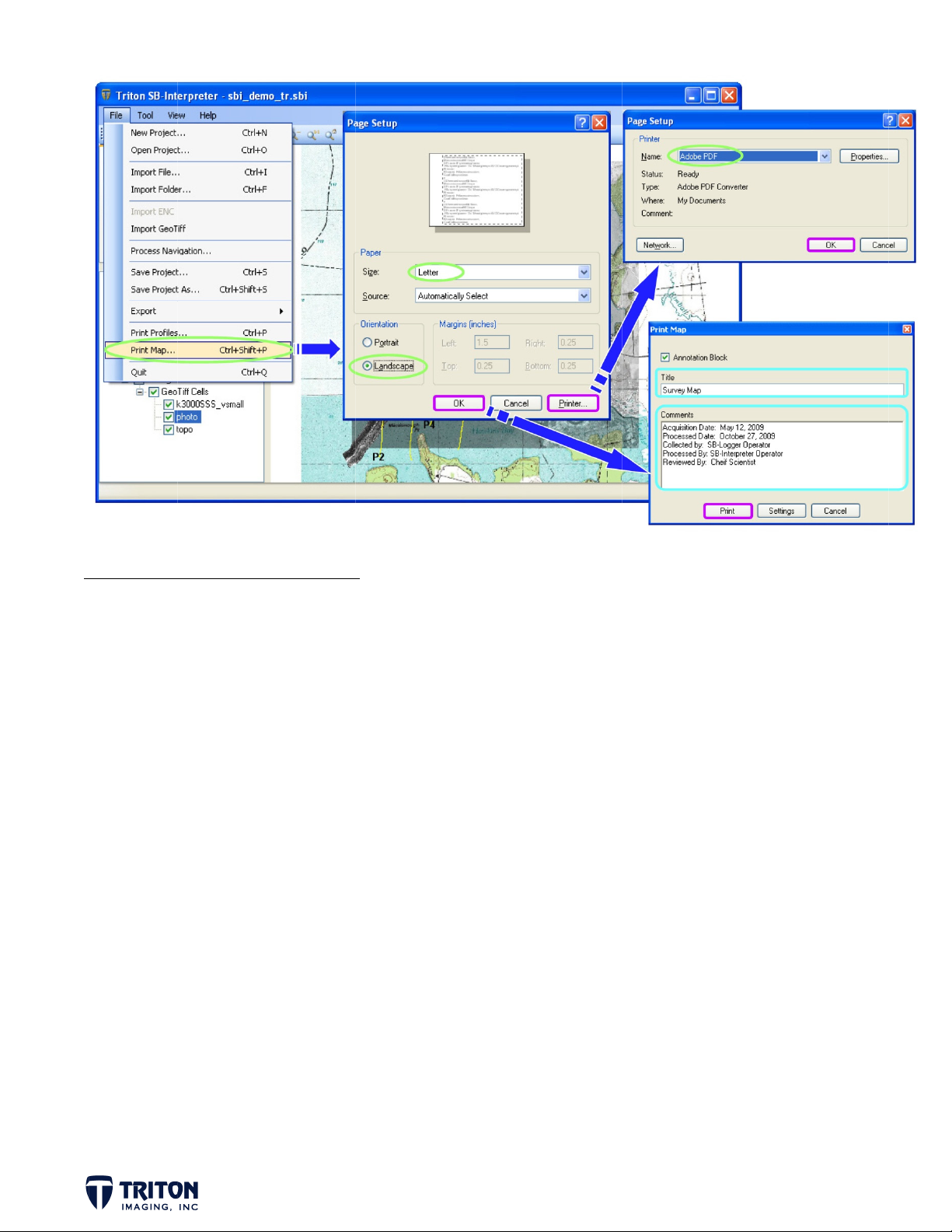
PThSP
o
In
In
S
C
In
E
C
F
fi
u
D
m
o
p
e
b
n
t
e
a
t
o
S
,
t
le
pt
o
d
m
F
t
o
e
k
op
p
k
nd
P
w
me
d
t
n
t
w
o
o
o
n
c
i
r
e
t
t
h
n
l
’
f
t
I
ri
n
s
5
RINTING
o save a c
ave Adobe
TEP 20A:
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
MAPS AN
py of the
Acrobat, y
Print Ma
the map
the ‘Pag
elect ‘Ado
lick ‘OK’ i
the ‘Prin
nter a titl
PROFILE
ap window
u can prin
Window
window ‘Fi
Setup’ o
e PDF’ fr
the main
Map’ win
and com
SB-Interp
directly t
’ menu, s
ions, clic
m the dr
‘Page Setu
ow, chec
ents as i
reter inclu
a pdf.
lect ‘Prin
‘Printer’ i
down lis
’ window
the box f
icated ab
es the opt
Map’
the lowe
and click
hen finish
r ‘Annota
ve (5 line
on to print
right cor
‘OK’ (or se
ion Block
maximum
the map.
er
ect any p
or comme
f you
nter)
ts)
g.
lick ‘Print’
h.
or PDF’s,
le destina
rinting res
lts are sh
when done
‘Save PD
ion, enter
wn on the
with the ‘
File As’
a file na
op of page
rint map’
indow ope
and sele
57.
ptions
s, select
t ‘Save’ w
he ‘Expor
en done
’ folder a
the
Page 5
Page 59
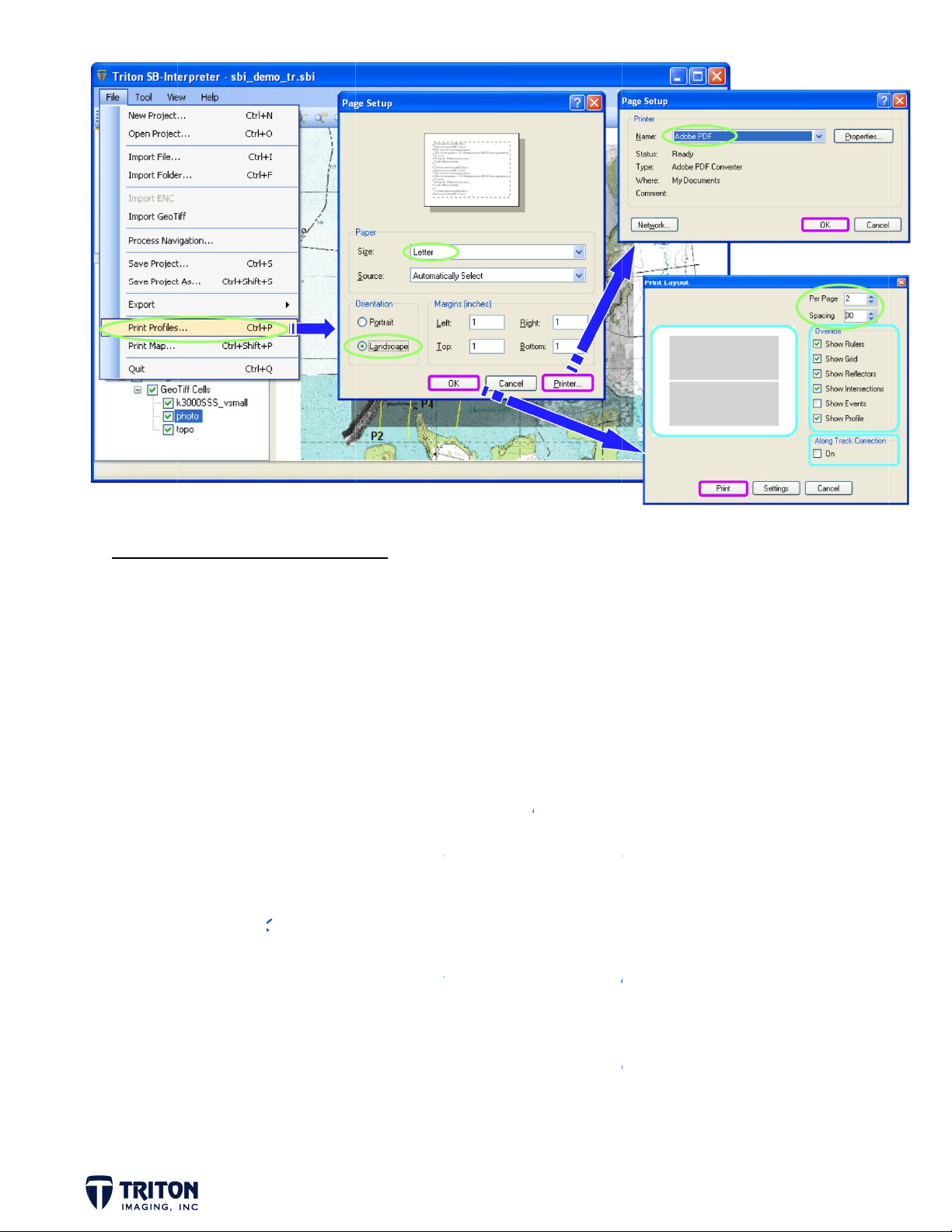
N
d
o
t
0
a
bcd
efg
A
n
m
P
m
P
A
K
P
i
F’
f
t
u
o
p
’
a
t
do
nt
s
a
u
c
d
Se
s
h
A
n
o
w
r
r
er
ow
r
a
o
se
l
t
w
es
ow
ic
n
p
s
ec
e
m
n
e
c
r
p
a
p
ne
b
y
o
r
6
PRINTI
Profiles
map win
option f
applied
STEP 2
G MAPS
can be prin
ow. Optio
r printing
o the profi
: Print
. In the
. In the ‘
. Select ‘
printer)
. Click ‘O
ND PROFI
ted individ
s for print
ultiple pr
les during
rofiles
ap window
age Setup
dobe PDF
’ in the m
LES
ally from t
ing profile
files per p
rinting in t
‘File’ men
’ options,
from the
in ‘Page
he profile
are simila
ge. If des
he ‘Print La
, select ‘P
lick ‘Print
rop down
tup’ wind
indow or a
to map pri
ired, along
yout’ windo
int Profil
’ in the l
list and cl
when fi
l at the sa
nting optio
rack corr
.
er right
k ‘OK’ (o
ished
e time fro
s with an e
ctions can
orner
select an
m the
xtra
e
. In the ‘
. Click ‘Pr
. For PD
ile des
Printing
results are
rint Layou
nt’ when
s, a ‘Save
ination, e
shown on t
’ window,
ne with t
PDF File
er a file
he bottom
elect 2 p
e ‘Print m
s’ window
ame and
f page 57.
ofiles per
p’ option
pens, sel
lect ‘Sav
age with
t the ‘Ex
’ when do
spacing
ort’ folde
f 30
as the
Page 5
Page 60

7
Page 5
 Loading...
Loading...