Page 1
Installation
Variable Refrigerant Flo w (VRF) System
Mini Outdoor Unit Series
Models:
Only qualified personnel should install and service the equipment. The installation, starting up, and
servicing of heating, ventilating, and air-conditioning equipment can be hazardous and requires specific
knowledge and tr aining. Impr op er ly in stalled, adjust ed or alt er e d equipment b y an unqualified person could
result in death or serious injury. When working on the equipment, observe all precautions in the literature
and on the tags, stickers, and labels that are attached to the equipment.
May 201 3 VRF-SVN33A-EN
4TVH0036B100NB
4TVH0048B100NB
4TVH0053B100NB
SAFETY WARNING
Page 2
Introduction
Read this manual thoroughly before operating or servicing
this unit.
Warnings, Cautions, and Notices
Safety advisories appear throughout this manual as
required. Y our personal safety and the proper operation of
this machine depend upon the strict observance of these
precautions.
The three types of advisories are defined as follows:
WARNING
CAUTIONs
NOTICE
Important Environmental Concerns
Scientific research has shown that certain man-made
chemicals can affect the earth’s naturally occurring
stratospheric ozone layer when released to the
atmosphere. In particular, several of the identified
chemicals that may affect the ozone layer are refrigerants
that contain Chlorine, Fluorine and Carbon (CFCs) and
those containing Hydrogen, Chlorine, Fluorine and Carbon
(HCFCs). Not all refrigerants containing these compounds
have the same potential impact to the environment. T rane
advocates the responsible handling of all refrigerantsincluding industry replacements for CFCs such as HCFCs
and HFCs.
Important Responsible Refr iger ant Pr actices
Trane believes that responsible refrigerant practices are
important to the environment, our customers, and the air
conditioning industry. All technicians who handle
refrigerants must be certified. The Federal Clean Air Act
(Section 608) sets forth the requirements for handling,
reclaiming, recovering and recycling of certain refrigerants
and the equipment that is used in these service procedures.
In addition, some states or municipalities may have
additional requirements that must also be adhered to for
responsible management of refrigerants. Know the
applicable laws and follow them.
Indicates a potentially hazardous
situation which, if not avoided, could
result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous
situation which, if not avoided, could
result in minor or moderate injury. It
could also be used to alert against
unsafe practices.
Indicates a situation that could result in
equipment or property-damage only.
WARNING
Proper Field Wiring and Grounding
Required!
Failure to follow code could result in death or serious
injury. All field wiring MUST be performed by qualified
personnel. Improperly installed and grounded field
wiring poses FIRE and ELECTROCUTION hazards. To
avoid these hazards, you MUS T follo w requir ements for
field wiring installation and grounding as described in
NEC and your local/state electrical codes.
WARNING
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Required!
Failure to w ear proper PPE for the job being undertaken
could result in death or serious injury. Technicians, in
order to protect themselves from potential electrical,
mechanical, and chemical hazards, MUST follow
precautions in this manual and on the tags, stickers,
and labels, as well as the instructions below:
• Before installing/servicing this unit, technicians
MUST put on all PPE recommended for the work
being undertaken. ALWAYS refer to appropriate
MSDS sheets and OSHA guidelines for proper PPE.
• When working with or around hazardous chemicals,
ALWAYS refer to the appropriate MSDS sheets and
OSHA guidelines for information on allowable
personal exposure levels, proper respiratory
protection, and handli ng recommendations.
• If there is a risk of arc or flash, tec hnicians MUST put
on all PPE in accordance with NFPA 70E or other
country-specific requirements for arc flash
protection, PRIOR t o servicin g the un it.
Copyright
This document and the information in it are the property of
Trane and may not be used or reproduced in whole or in
part, without the written permission of Trane. Trane
reserves the right to revise this publication at any time and
to make changes to its content without obligation to notify
any person of such revision or c hange.
Trademarks
All trademarks referenced in this document are the
trademarks of their respective owners.
2 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 3

Table of Contents
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Warnings, Cautions, and Notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Preparing for Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Unit Dimensions and Weights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Dimensional Drawing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Maximum Quantity of Indoor Units by Mini Outdoor Unit Capacity . . . . . . . 6
Service Clearances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Location Considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Moving the Mini Outdoor Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Unit Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Base Recommendations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Securing the Mini Outdoor Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Condenser Air Discharge Duct (optional) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Important Environmental Concerns . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Important Responsible Refrigerant Practi ce s . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
General guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Minimizing Vibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Refrigerant Piping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Selecting Refrigerant Piping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Pipe Diameter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Branch Joint Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Pipe Thickness and Temper Grade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Refrigerant Piping Maximum Length and Height Differences . . . . . . . . 15
Storing Refrigerant Piping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Evacuating Refrigerant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Installing Refrigerant Piping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Pipe Cutting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Nitrogen Flushing While Brazing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Flared Pipe Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Connecting Piping to the Mini Outdoor Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Refrigerant Piping Installation Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Electrical Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Power Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Grounding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Installing a Grounding Rod . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Installing the Grounding Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Communications Wiring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Leak Testing Pipe Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
VRF-SVN33A-EN 3
Page 4

Vacuum Drying Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Insulating Refrigerant Pipes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Refrigerant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Calculating the Refrigerant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Charging the Refrigerant . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Connecting the Drain Hose . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Control System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
System Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Configuring the System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Initiating System Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Monitoring System Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Pre-Start Checks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Test Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Refrigerant detection operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Service: Pump Down Process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Collecting Refrigerant into a Refrigerant Container . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Pump Down Process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Warranty For Trane Advantage™ VRF Systems and Related Accessories . . . 49
Basic Warranty . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Exclusions and Limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
4 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 5
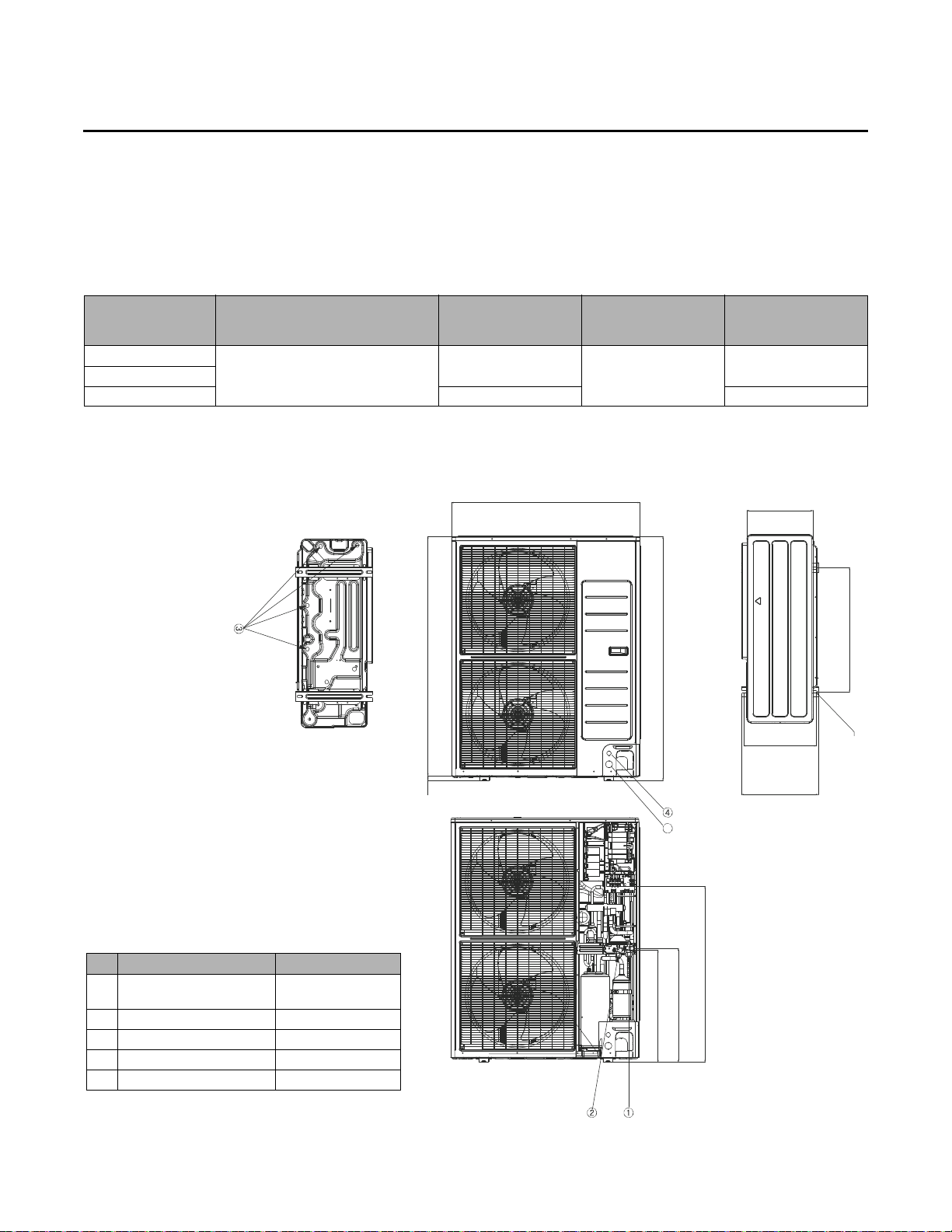
Preparing for Installation
No. Item Dimension/Size
1 Gas refrigerant pipe
3, 4 ton: 5/8 (15.88)
5 ton: 3/4 (19.05)
2 Liquid refrigerant pipe 3/8 (9.52)
3 Condensate drain holes 0.79 (20)
4 Communication cable holes 0.87 (22.2) x 3
5 Power cable holes 1.36 (34.5) x 3
Unit Dimensions and Weights
Table 1. Unit dimensions and weights
Preparing for Installation
Unit model number
4TVH0036B100NB
4TVH0048B100NB
4TVH0053B100NB 227.1 (103.0) 238.1 (108.0)
Dimensions (WxHxD)
in. (mm)
37 (940) x 47.6 (1210) x 13 (330)
Weight
lb (kg)
220.5 (100.0)
Shipping dimensions
(WxHxD)
in. (mm)
39.2 (995) x 53.9 1368)
x 16.8 (426)
Shipping weight
lb (kg)
231.5 (105.0)
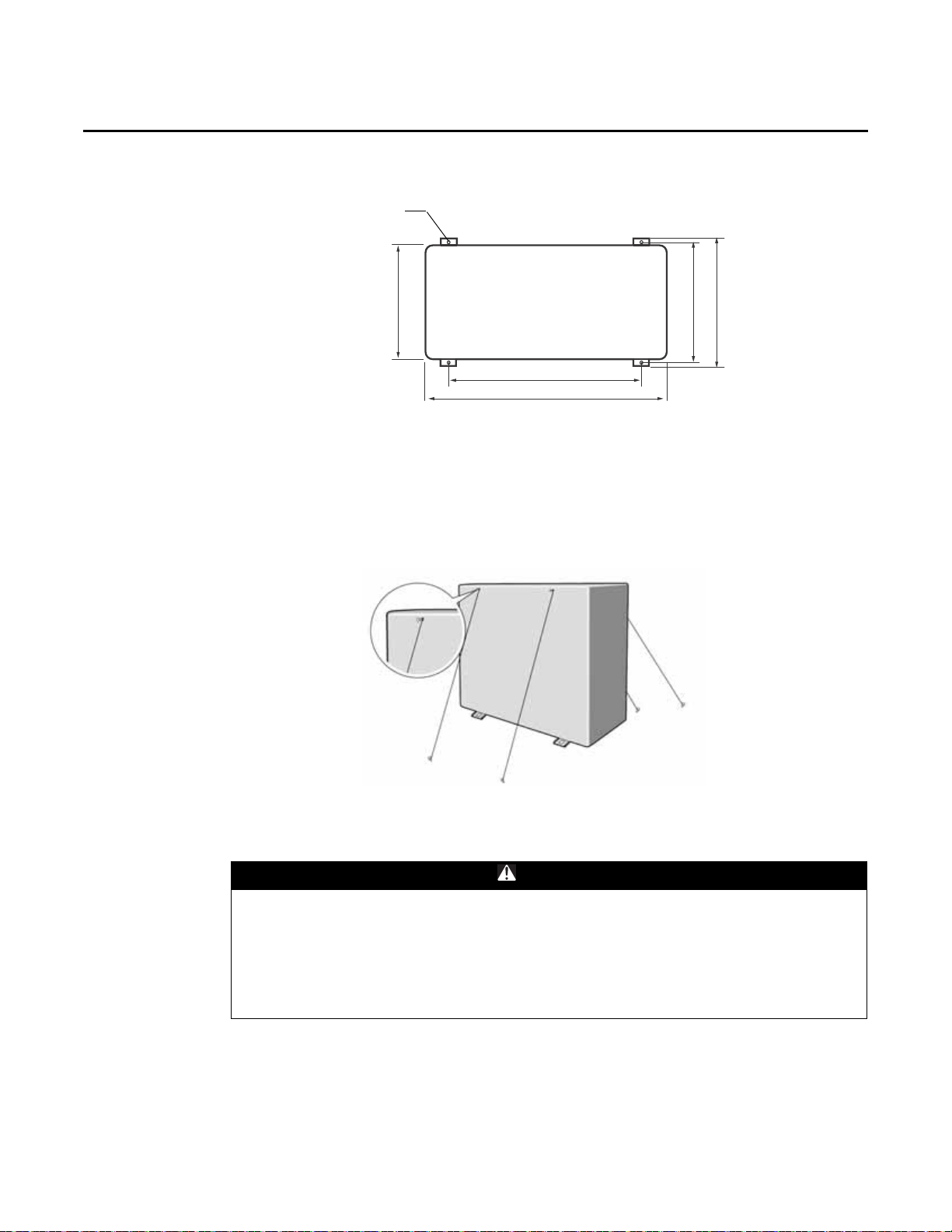
Dimensional Drawing
Unit : inch (mm)
46.65 (1185)
37.01 (940)
47.64 (1210)
12.99 (330)
14.17 (360)
24.42 (620)
VRF-SVN33A-EN 5
0.98 (25)
5
21.97 (558)
22.32 (567)
15.12 (384)
4: Ø 0.47 (12)
34.84 (885)
Page 6
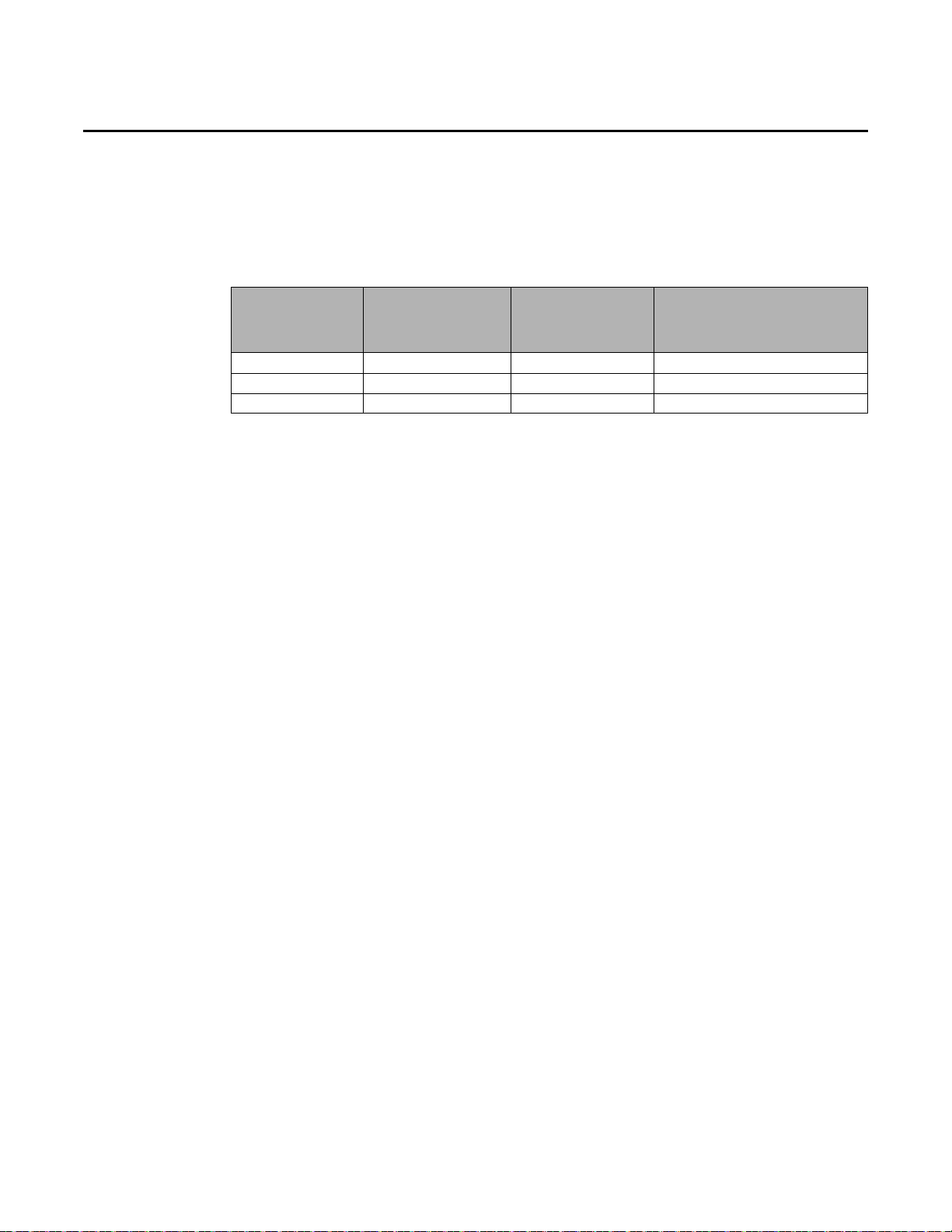
Preparing for Installation
Maximum Quantity of Indoor Units by Mini Outdoor Unit Capacity
To prevent reducing indoor unit capacity, the sum capacity of indoor units connected to a mini
outdoor unit should be no greater than the capacity of the mini outdoor unit. Refer to Table 2.
Table 2. Maximum number of indoor units determined by mini outdoor unit capacity
Mini outdoor unit
model number
4TVH0036B100NB 3 6 19000–49000
4TVH0048B100NB 4 8 24000–62000
4TVH0053B100NB 5 9 27000–69000
Mini outdoor unit
capacity
(tons)
Maximum quantity
of indoor units
connected to a mini
outdoor unit
Total capacity of connected
indoor units
(Btu/h)
6 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 7
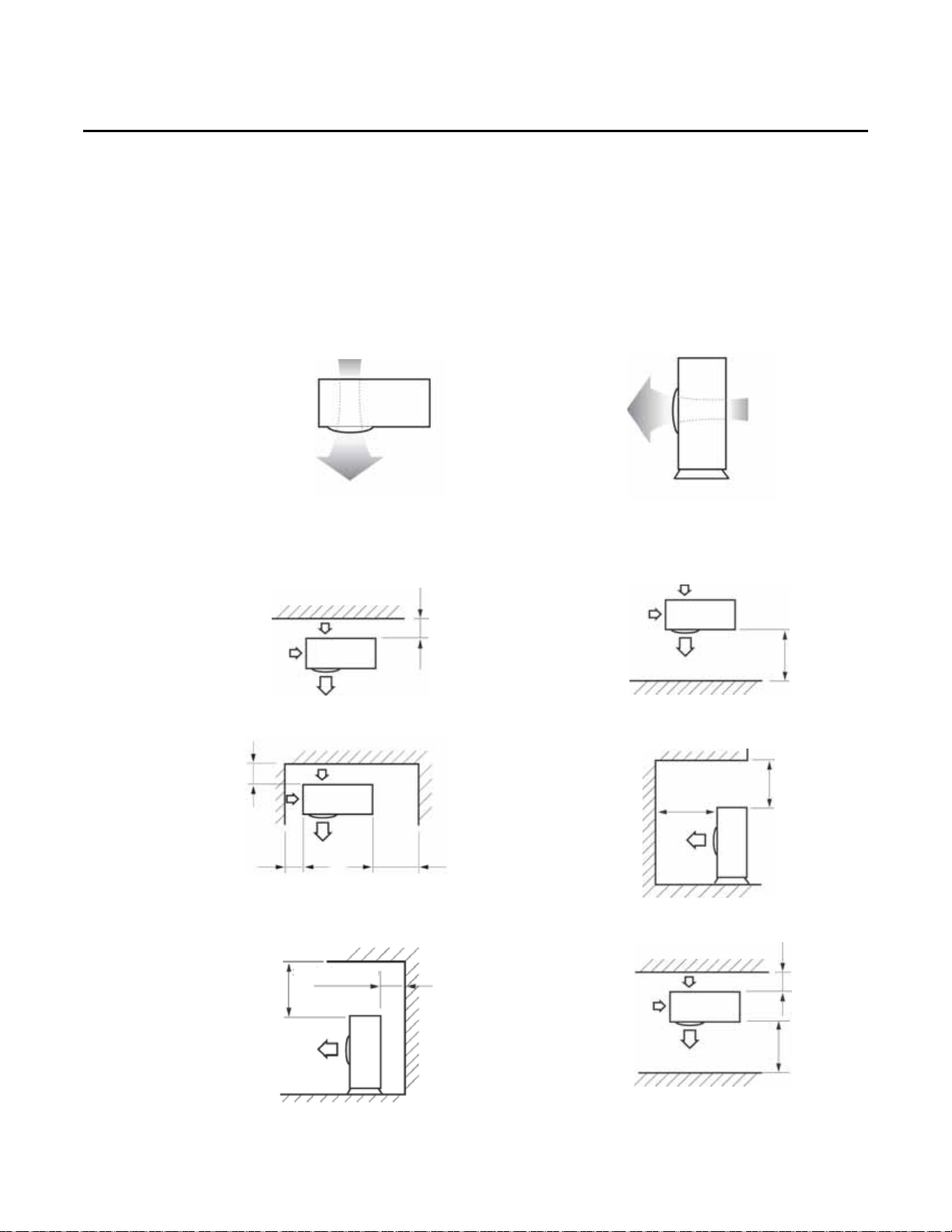
Service Clearances
Side view
Top view
Back
Front
Front
Back
12 (300)
12 (300)
60 (1500)
60 (1500)
80 (2000)
12 (300)
6 (150)
24 (600)
60 (1500)
12 (300)
When the air outlet is opposite a wall
When air outlet is toward a wall
When three sides are blocked by a wall
Top of unit is blocked and the air
outlet is toward a wall
When top of unit is blocked and the air outlet
is opposite the wall
When from and back of unit are blocked by walls
Install units as shown in the illustrations below (Figure 1, Figure 2, and Figure 3), observing
ventilation and service requirements. Space requirements are based on cooling mode operation
and an outdoor temperature of 95°F (35°C). More space is required if the outdoor temperature is
higher than 95°F (35°C) or if the area is easily heated by solar radiation.
Note: The front of the unit is curved and has the name brand logo on it.
Figure 1. Air flow dire ction
Figure 2. Minimum service clearances for a single mini outdoor unit installation
Preparing for Installation
VRF-SVN33A-EN 7
20 (500)
Page 8
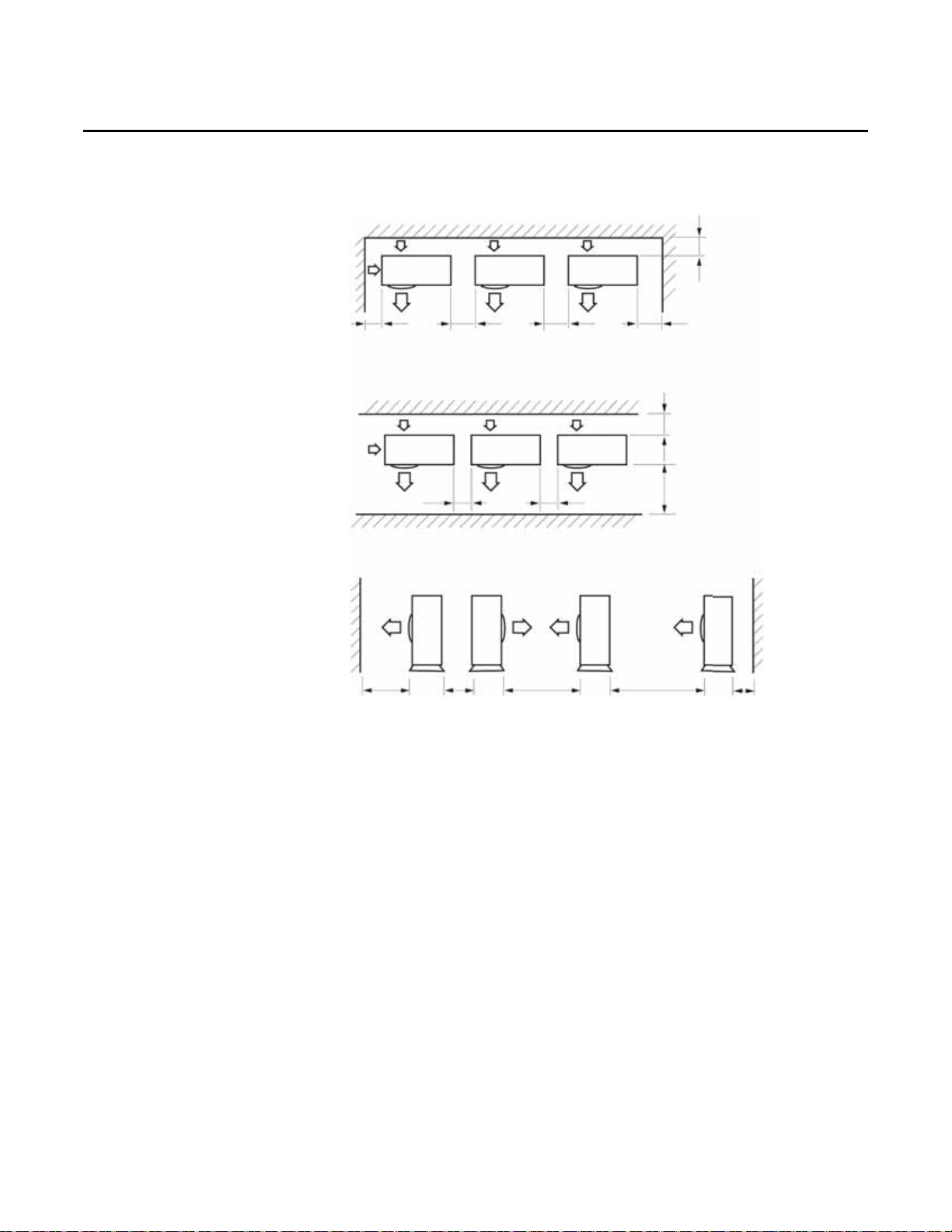
Preparing for Installation
12 (300)
24 (600)
24 (600)
24 (600)
24 (600)
24 (600)
12 (300)
12 (300)
60 (1500)
60 (1500) 24 (600)
120 (3000)
12 (300)
120 (3000)
Figure 3. Minimum service clearances for multiple mini outdoor unit installations
Location Considerations
Choose an installation location based on the following consider ations.
• Install the outdoor unit:
– On a suppo rting structure that can bear the weight of the outdoor unit.
– With sufficient clearances around the unit for service and repairs.
– Install the outdoor unit.
– On a flat surface that does not collect rain water.
– In a well ventilated location.
– Away from strong wind.
– Away from direct exposure to rain or snow.
– Where there is no risk of flamma ble gas leakage
– Where there is no exposure to salt, machine oil, sulfide gas, or corrosive environmental
conditions.
– Away from sea breeze.
Note: For seacoast applications, bloc k the unit from direct exposure to sea breez e by installing
the unit behind a structure (suc h as a building) or a protective wall that is 1 .5 t imes higher
than the unit, leaving 28 in. (700 mm) of space between the wall and unit for air
8 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 9

Preparing for Installation
ODU
Sea breeze
Sea breeze
Sea
Sea
Sea
Sea breeze
ODU
ODU
ODU
ODU
Protection walls
circulation. Consult an installation expert about taking anti-corrosion measures, suc h as
removing salinity on the heat exchanger and applying a rust i nhibitor more frequen tly
than once a year.
– At least 9.84 ft (3 m) away from equipment that generates electromagnetic waves.
– Away from interfering sources, such as radio, computer, and stereo equipment.
– Far enough away from people living and working nearby so that hot discharge air or noise
do not disturb them.
– Away from inflammable materials.
• Ensure that condensate water generated b y the outdoor unit can drain smoothly away from the
unit.
• Install the power and communication cables in a separately installed enclosure.
• If installing on a high place such as a roof, with a fence or guard rail around it.
• If there is a potential for accumulated snow to block the air inlet or heat exc hanger, install the
unit on a higher base.
• R-410A refrigerant is a safe, nontoxic and nonflammable refrigerant. However, if there is a
concern about a dangerous level of refrigerant concentration in the case of refrigerant leakage,
add extra ventilation.
• Avoid in stalling the o utdoor unit w here cor rosive g ases, suc h as sulfur o xides, ammonia, and
sulfurous gas, are produced. If unavoidabl e, consult with an installation specialist about using
a corrosion-proof or anti-rust additive to protect the unit coils.
Moving the Mini Outdoor Unit
Follow these guidelines when moving the mini outdoor unit:
• Before moving the unit, determine a path that can support its weight.
• Do not lay the unit on its side and do not slant the unit more than 30 degrees.
• Take care to avoid injury while moving the unit; the surface of the heat exchanger is sharp.
– If moving the unit with a crane, fasten the wire rope as shown in Figure 4. T o protect damage
or scratches to the unit, use a spreader bar.
– If the unit is being moved a short distance by hand, two people should lift and carry it
together using the transportation handles on the side of the unit, as shown in Figure 4.
VRF-SVN33A-EN 9
Page 10
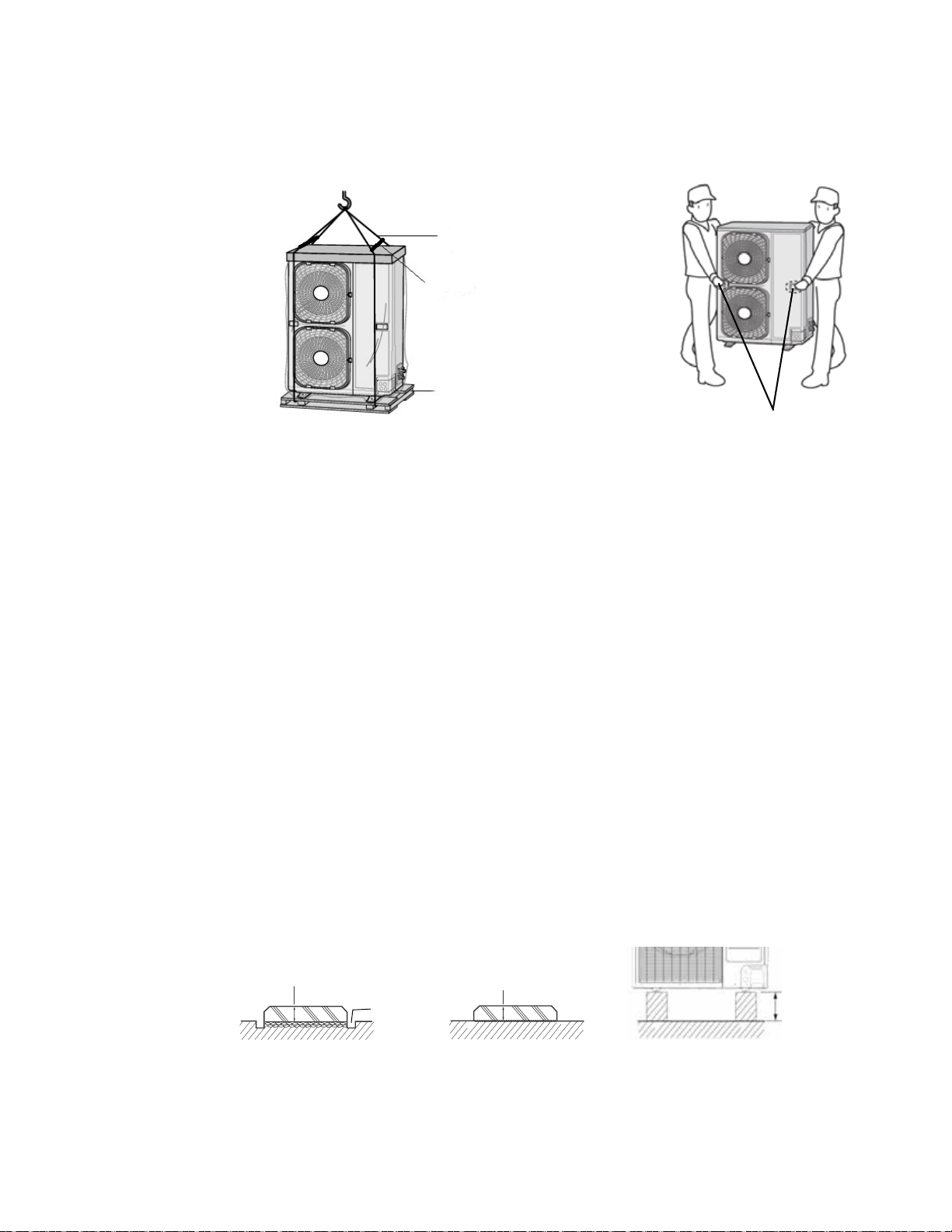
Figure 4. Moving the mini outdoor unit
Moving by hand
Wire rope/straps
Moving with a crane
Transportation handles
Spreader bar
Wood palette
Ground installation
Base installation: Surface of
base must be horizontally level
6 in. (150 mm) min.
Drain pit
6 in. (150 mm) min.
Raised base
6 in. (150 mm)
minimum
Unit Installation
Follow these guidelines for installing the mini outdoor unit.
Important: The manufacturer is not responsible for d amage incurred for installatio ns that have
The unit must be installed:
• On a horizontally level surface.
• On a surface that is strong enough to support the unit and to minimize noise.
not followed these guidelines.
Base Recommendations
General guidelines
A supporting base for the mini outdoor unit:
• Is typically made of concrete.
• Should typically be 1 .5 tim es larger than the bottom of the unit. However , for installatio ns that
are subject to snow accumulation, the base should be no larger than the bottom of the unit.
• Should be 6 in. (150 mm) or higher to protect the unit from rain water or other conditions that
may cause damage to the unit.
Note: The base height or , if the unit is installed on a frame (see “Minimizing V ibration ” p. 11),
the base height plus the frame height, should be greater than the highest expected
snowfall.
• If necessary, has wire mesh or steel bars added to the concrete to prevent damages or cracks.
10 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 11
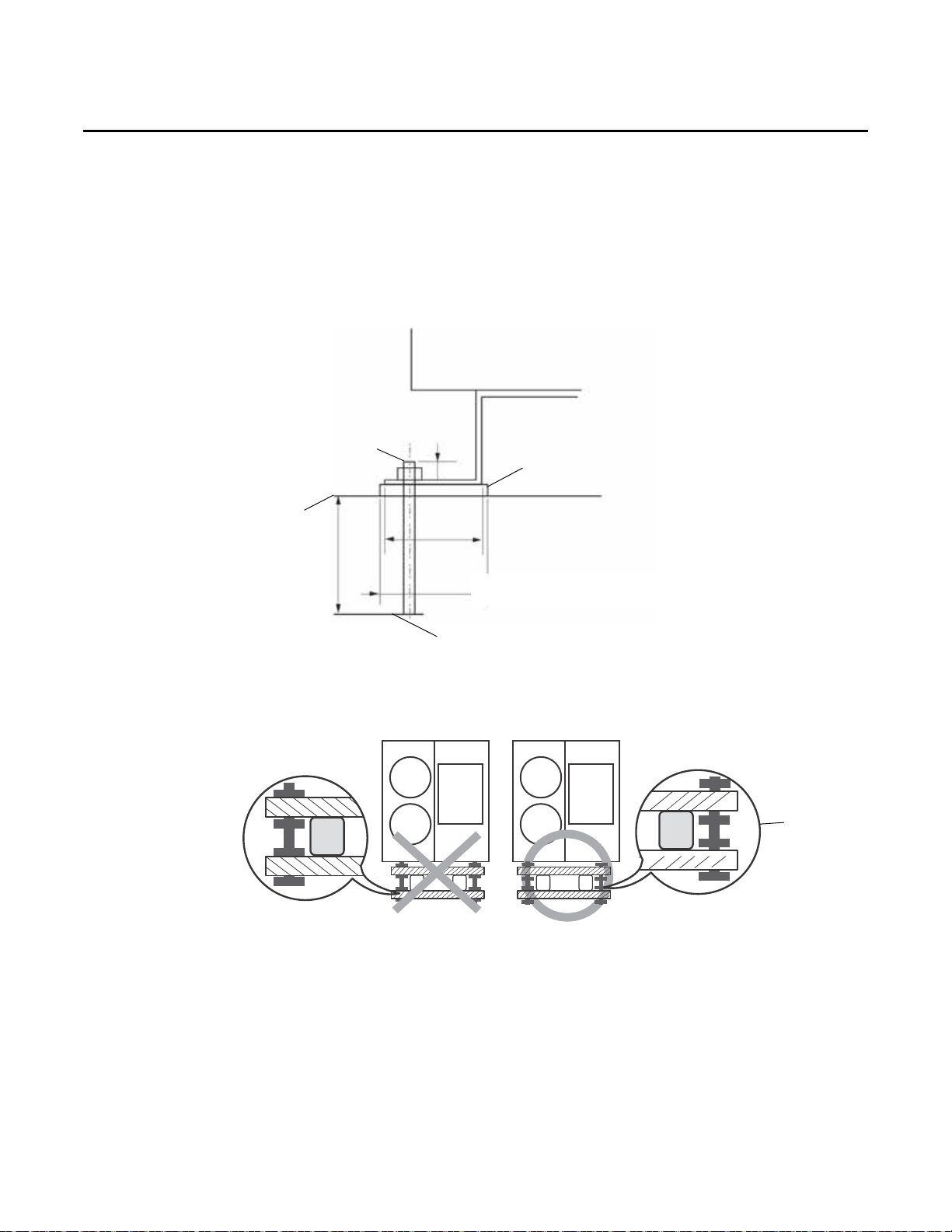
Minimizing Vibration
Outdoor unit
Anchor bolt with nut/spring/washer
Isolation pad minimum thickness: 1 in. (20 mm)
H-beam
3 in. (75 m m) min.
A: Width of unit mounting foot
1 in.
(20 mm)
Base
Isolation pad dimensions: A + 1/2 to 1 in. (10–20 mm) minimum
Ensure that
bolts are loose.
When installing multiple mini outdoor units side by side, or when there is a need to minimize unit
vibrations, use a vibration-minimizing structure such as an H-beam frame or a vibration-isolation
frame, and an isolation pad. Refer to the specifications in Figure 5.
After installation, apply corrosion-protection to the frame.
Figure 5. Vibration-minimizing structure specifications
Unit Installation
After installing a vibration-isolation frame, loosen the bolts so that the isolat ors are capable of
absorbing vibrations (Figure 6).
Figure 6. Bolts on vibration-isolation frame
Securing the Mini Outdoor Unit
The mini outdoor unit must be secured so th at it can withstand a wind speed of 67 mph (30 m/s).
Secure the unit firmly to the base with M10 anchor bolts (see Figure 7).
• Use zinc-plated or stainless steel nuts and bolts.
• Use a rubber washer between the bolt and the unit to prevent bimetallic corrosion.
VRF-SVN33A-EN 11
Page 12
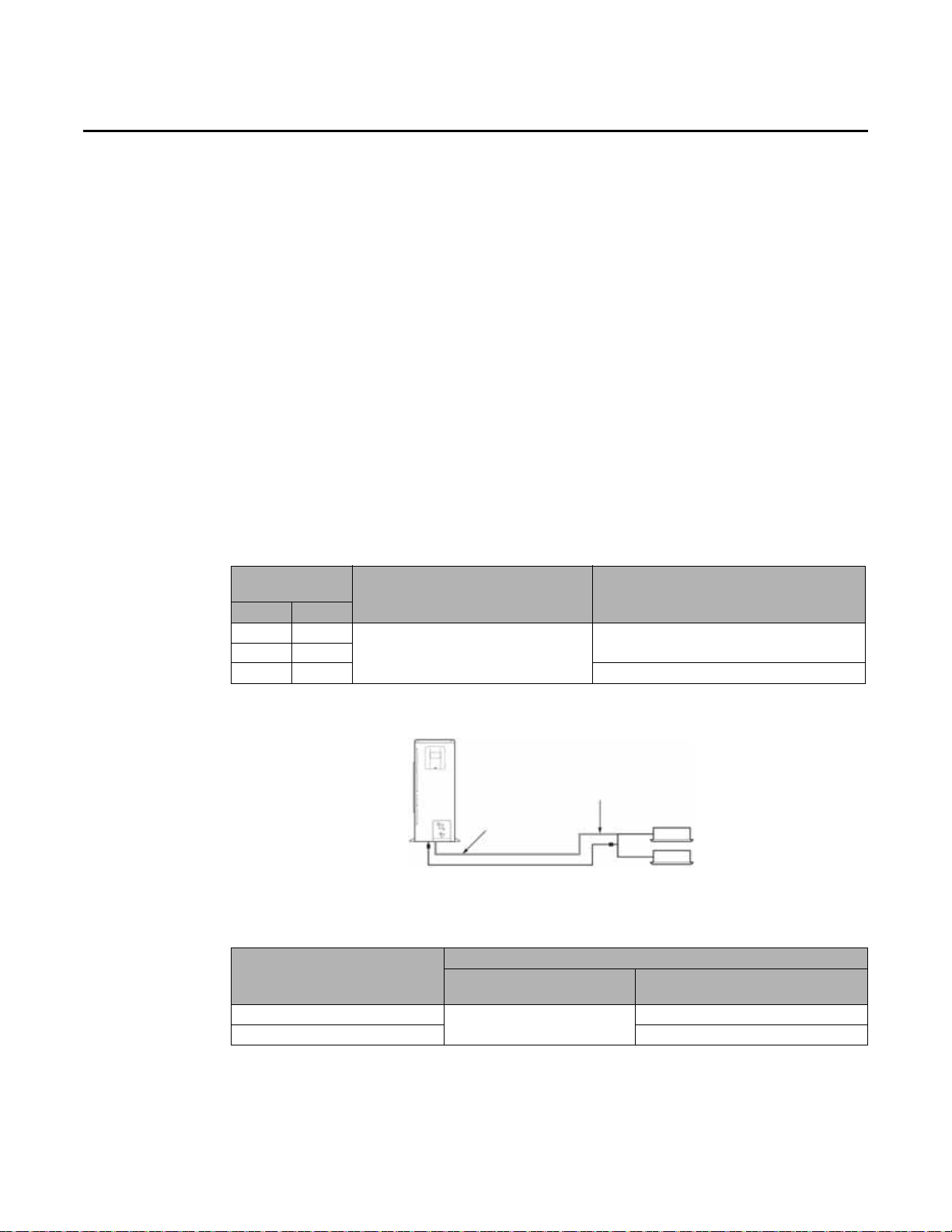
Unit Installation
14.2 (360)
15.1 (384)
24.4 (620)
37.0 (940)
13.0 (330)
Anchor bolt holes (4)
Figure 7. Anchor bolt positions
If you cannot attac h the unit to the base or if the unit needs additional suppor t, secure it with wires
as follows:
1. Loosen the four screws at the top of the unit and wrap wire around each of them.
2. Tighten the screws.
3. Stake the wires to the ground (see Figure 8).
Figure 8. Securing the unit with wire
Condenser Air Dischar ge Duct (optional)
12 VRF-SVN33A-EN
CAUTION
Sharp Edges!
Working with galvanized sheet metal involves working with sharp edges. To avoid being cut,
technicians MUST put on all necessary Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), including gloves
and arm guards.
If you remove the fan guard to install th e di scharge duct, make sure to install a safety net on
the duct outlet to prevent foreign substances from entering the unit and to prevent the risk of
personal injury from sharp fan blades.
Page 13
Refrigerant Piping
Main pipe
First branch joint
This section contains information on selecting, storing, and connecting refrigerant piping.
Selecting Refrigerant Piping
Refrigerant piping diameter, thic kness, and temper is selected according to length, as sp ecified in
this section.
Notes:
• Use insulated, unw elded, degreased, and deoxidized copper pipe (Cu-DHP type according
to ISO 1337 or UNI EN 12735-1) suitable for an operating pressure of at least 609.15 psi
(4200 kPa) and a burst pressure of at least 3002.28 psi (20,700 kPa). Copper pipe for hydrosanitary applications is unsuitable.
• If there is a risk of decreased performance caused by pipe length, use piping that is one
size larger than that specified in this section.
Pipe Diameter
Table 3 specifies the diameter of the main pipe based on unit capacity.
Table 3. Mini outdoor unit main pipe size based on unit capacity
Refrigerant Piping
Mini outdoor unit
capacity
Ton MBH
338
448
553 3/4 in. (19.05 mm)
(a) Increase the gas pipe from the outdoor unit to the first branch joint by one size if the pipe length between the outdoor
unit and the farthest indoor unit, including the elbow, exceeds 295 ft (90 m); or if the outdoor unit capacity declines due to
pipe length.
Liquid pipe
in. (mm)
3/8 in. (9.52 mm)
Gas pipe
in. (mm)
5/8 in. (15.88 mm)
(a)
Table 4 specifies the pipe size between branch joints.
Table 4. Pipe size between branch joints
Pipe size (OD)
Indoor unit total capacity
(MBH)
Less than 51
51-79.2 3/4 (19.05)
Liquid
in. (mm)
3/8 (9.52)
Gas
in. (mm)
5/8 (15.88)
VRF-SVN33A-EN 13
Page 14
Refrigerant Piping
Branch Joint Selection
Table 5 specifies the first branch joint according to mini outdoor unit capacity.
Table 5. First branch joint according to mini outdoor unit capacity
Mini outdoor unit total capacity
(ton) Branch joint model
3
4
5 4YDK2512B0138A
Table 6 specifies branch joints connected after the first branch, according to the total capacity of
all indoor units connected after the first branch.
Table 6. Branch joints connected after the first branch, according to total indoor unit capacity
Total indoor unit capacity
(MBH) Branch joint model
Less than 51 4YDK1509B0051A
51–138.5 4YDK2512B0138A
Pipe Thickness and Temper Grade
Table 7 specifies pipe minimum thickness and temper grade based on pipe diameter.
Risk of Pipes Breaking!
If pipes with a diameter larger than 3/4 in. (19.05 mm) are specified, use semi-hard (C1220T1/2H) or hard (C1220T-H) copper piping. If a soft er copper pipe (C1220T-O) is used, the pipe may
break due to its low pressure resistance and cause personal injury.
Table 7. Refrigerant pipe minimum thickness and temper grade
4YDK1509B0051A
CAUTION
Outer diameter
in. (mm)
1/4 (6.35) 0.028 (0.70)
3/8 (9.52) 0.028 (0.70)
1/2 (12.70) 0.031 (0.80)
5/8 (15.88) 0.039 (1.00)
3/4 (19.05) 0.035 (0.9)
7/8 (22.22) 0.035 (0.9)
14 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Minimum thickness
in. (mm)
Temper grade
Annealed
(C1220T-O)
Drawn
(C1220T-1/2H or C1220T-H)
Page 15
Refrigerant Piping
Outdoor unit
Indoor units
Y-j o int s
EEV kit
Outdoor unit
Indoor units
Y-j oin ts
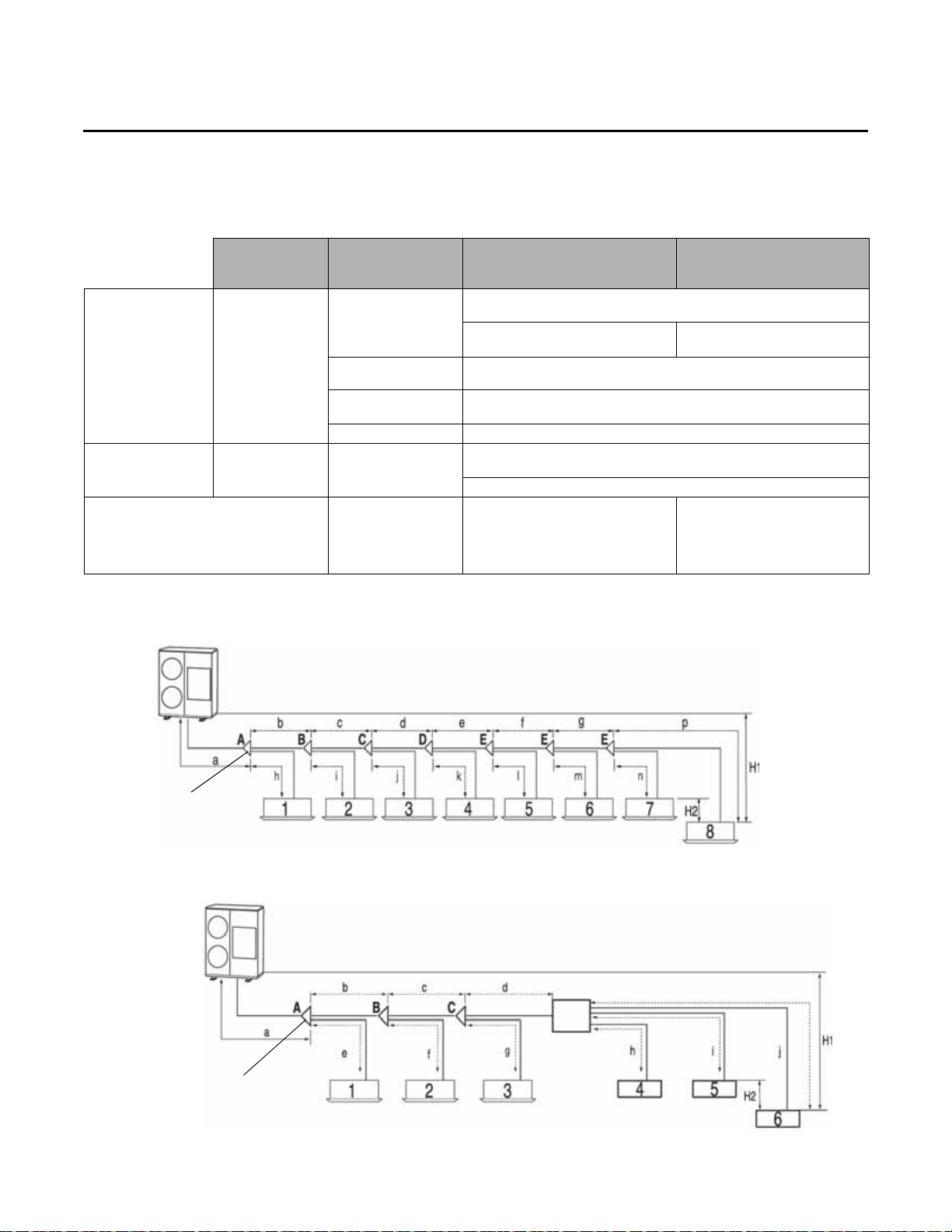
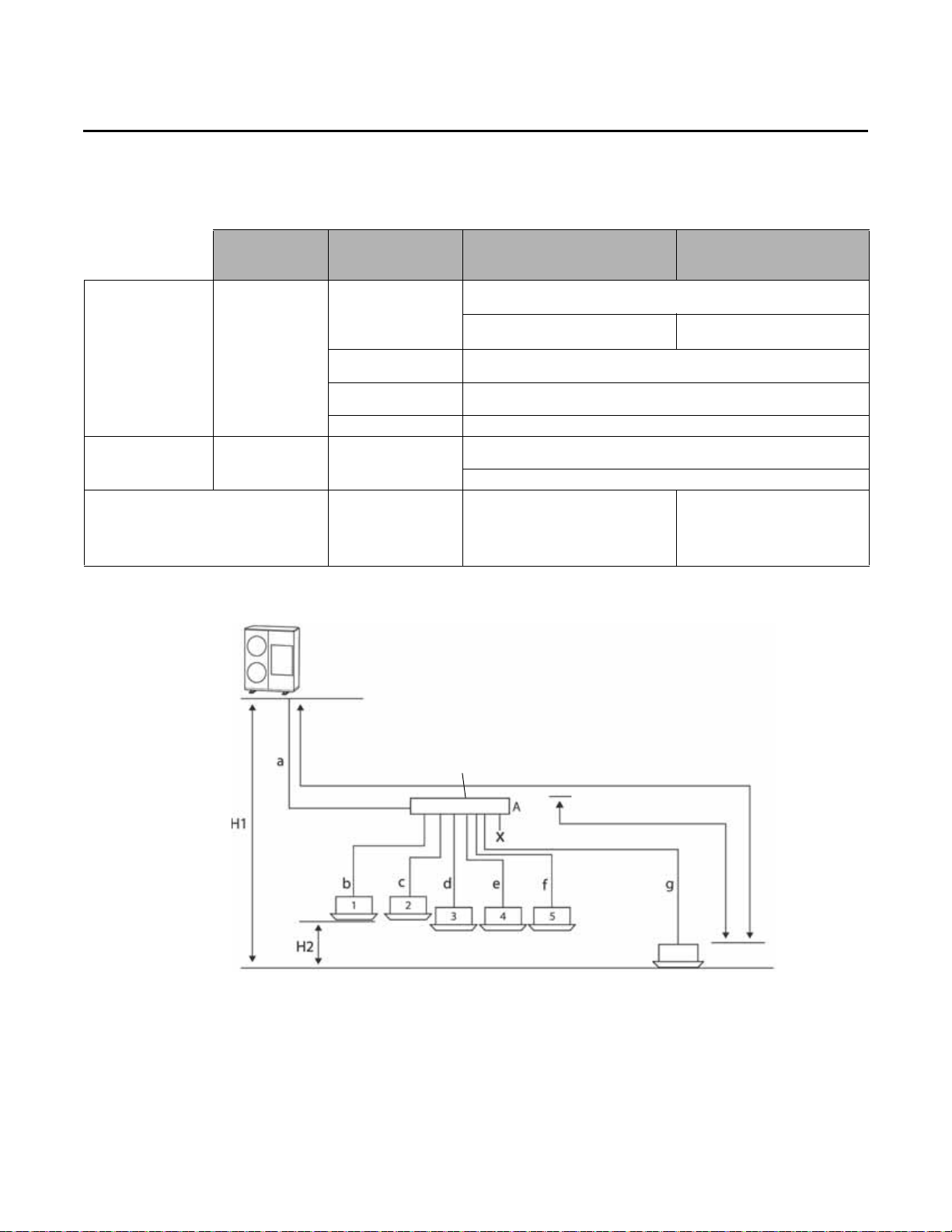
Refrigerant Piping Maximum Length and Height Differences
Table 8. Maximum refrigerant piping length and height differences for installations with Y-joints and EEV kits
Piping length and
Piping location
Maximum allowable
piping length
Maximum allowable
height difference
Maximum allowable length after
Y-joint
(a) If the equivalent length between an outdoor unit and the farthest indoor unit exceeds 295 ft (90 m), increase the gas pipe by one size.
Mini outdoor unit to
indoor units
Mini outdoor unit to
indoor units
(ft [m])
Actual length
Equivalent length
Main pipe length
Total length The sum of the total length of pipes should be less than 984 ft (300 m)
Height
Actual length
height difference
Y-joint connection
(refer to Figure 9)
The distance between the mini outdoor unit and the farthest indoor unit ≤
492 ft (150 m)
Example: 8 indoor units
a+b+c+d+e+f+g+p ≤ 492 ft (150 m)
The distance between a mini outdoor unit and the farthest indoor unit ≤
574 ft (175 m)
The main pipe (a) from the mini outdoor unit to the first Y-joint should be
less than 361 ft (110 m)
H1: Height difference between a mini outdoor unit and indoor unit < 164 ft
(50 m)
H2: Height difference between indoor units ≤ 49 ft (15 m)
The distance between the first Y-joint
and the farthest indoor unit ≤ 131 ft
(40 m)
Example: 8 indoor units
b+c+d+e+f+g+p ≤ 131 ft (40 m)
(a)
Y-joint and EEV kit
connection
(refer to Figure 10)
Example: 6 indoor units
a+b+c+d+j ≤ 492 ft (150 m)
Allowable length between EEV kit
and an indoor unit ≤ 65 ft (20 m)
Example: h, l, j ≤ 65 ft (20 m)
Figure 9. Y-joint connection
Figure 10. Y-joint and EEV kit connection
VRF-SVN33A-EN 15
Page 16
Refrigerant Piping
Distribution header
Mini outdoor unit
Indoor units
Table 9. Maximum refrigerant piping length and height differences for installations with Y-joints and EEV kits
Piping length and
Piping location
Maximum allowable
piping length
Maximum allowable
height difference
Maximum allowable length after
Y-joint
(a) If the equivalent length between a mini outdoor unit and the farthest indoor unit exceeds 295 ft (90 m), increase the main gas pipe by one size.
Mini outdoor unit to
indoor units
Mini outdoor unit to
indoor units
(ft [m])
Actual length
Equivalent length
Main pipe length
Total length The sum of the total length of pipes should be less than 984 ft (300 m)
Height
Actual length
height difference
Distribution header connection
(refer to Figure 11)
The distance between the mini outdoor unit and the farthest indoor unit ≤
492 ft (150 m)
Example: 8 indoor units
a+g ≤ 492 ft (150 m)
The distance between a mini outdoor unit and the farthest indoor unit ≤
574 ft (175 m)
The main pipe (a) from the mini outdoor unit to the first Y-joint should be
less than 361 ft (110 m)
H1: Height difference between a mini outdoor unit and indoor unit < 164 ft
(50 m)
H2: Height difference between indoor units ≤ 49 ft (15 m)
The distance between the first Y-joint
and the farthest indoor unit ≤ 131 ft
(40 m)
Example: b+c–f+g ≤ 131 ft (40 m)
(a)
Y-joint and distribution
header connection
(refer to Figure 12)
Example: 8 indoor units
a+b+c ≤ 492 ft (150 m)
The distance between the first Yjoint and the farthest indoor unit ≤
131 ft (40 m)
Example: 8 indoor units
b+c, d+g ≤ 131 ft (40 m)
Figure 11. Distribution header connection
16 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 17

Figure 12. Y-joint and distribution header connection
Indoor units
Distribution header
Mini outdoor unit
Refrigerant Piping
Storing Refrigerant Piping
T o prevent foreign materials or water from entering the pipe, storing method and sealing method
(especially during installation) is very important. Apply correct sealing method depending on the
environment (see Table 10).
Table 10. Refrigerant pipe storage factors
Storage location
Outdoor
Indoor — Taping
Evacuating Refrigerant
The mini outdoor unit ships with the following amount of refrigerant. Evacuate the un it of all shipwith refrigerant before installing refrigerant piping.
3 ton unit 4 ton unit 5 ton unit
7.1 lbs 7.1 lbs 7.3 lbs
Storage
Longer than one
Shorter than one
Ship-with refrigerant amount by unit type
time
month
month Taping
Sealing
Pipe
type
pinch
VRF-SVN33A-EN 17
Page 18

Refrigerant Piping
Correct: 90º
Oblique
Rough
Burr
Installing Refrigerant Piping
Hazard of Explosion and Deadly Gases!
Failure to follow all proper safe refrigerant handling practices could result in death or serious
injury. Never solder, braze or weld on refrigerant lines or any unit componen t s that are above
atmospheric pressure or where refrigerant may be present. Always remove refrigerant by
following the guidelines established by the EPA Federal Clean Air Act or other state or local
codes as appropriate. After refrigerant removal, use dry nitrogen to bring system back to
atmospheric pr essur e bef or e open ing syst em f or r epairs. Mixt ur es of r efrigerants and air under
pressure may become combustible in the presence of an ignition source leading to an
explosion. Excessive heat from soldering, brazing or welding with refrigerant vapors present
can form highly toxic gases and extremely corrosive acids.
System Component Damage!
Do not remove the seal caps from refrigerant connections, or open the service valves until
prepared to braze refrigerant lines to the connections. Excessive exposure to atmosphere (> 5
min.) may allow moist ur e or dirt t o contaminat e the syst em, damagin g v alve s eals and causing
ice formation in system components.
WARNING
NOTICE:
Overview
Pipe Cutting
1. Cut or extend field-supplied piping as needed. To extend pipes, braze or using flared pipe
connections (not supplied). Refer to “Pipe Cutting” p. 18, “Nitrogen Flushing While Brazing”
p. 19, and “Flared Pipe Connections” p. 19.)
2. Make sure that pipes are free of dirt, debris, and moisture, and do not leak. (Refer to “Leak
Testing Pipe Connections” p. 29).
3. Braze or use flared pipe connections to install piping. Refer to “Connecting Piping to the Mini
Outdoor Unit” p. 21).
Required tools:
•Pipe cutter
•Reamer
• Pipe holder
1. Using a pipe cutter, cut the pipe so that the cut edge is at 90° to the side of the pipe.
2. Use a reamer to remove all burrs at the cut edge.
Examples of correctly and incorrectly cut pipes.
18 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 19

Nitrogen Flushing While Brazing
Flow meter
Pressure regulator
Stop valve
Nitrogen
Nitrogen
Length of pipe extending above flare bar
Pipe
Flaring
bar
Avoid Unit Damage!
Never braze pipe connections without performing nitrogen flushing. Failure to perform this
procedure will damage the unit, resulting in capacity loss and reduced long-term reliability.
While brazing refrigerant pipes, flush them with nitrogen gas. Use a pressure regulator to maintain
a flow rate of 1.76 ft3/h (0.05 m3/h) or more.
Figure 13. Nitrogen flushing while brazing refrigerant pipes
Refrigerant Piping
NOTICE
Flared Pipe Connections
Clutch type and wing nut type flare tools are available for flared pipe connections.
1. Slide the flare nut over the pipe to be flared.
2. Slide the end of the pipe into the hole on the flaring bar that fits the pipe, leaving a length of
pipe, determined by tool type (see table), extending above the flaring bar. Clamp it down.
R-410A clutch type
Conventional flare tool
Clutch type Wing nut type
0–0.020 in. 0.04–0.06 in. 0.06–0.08 in.
VRF-SVN33A-EN 19
Page 20

Refrigerant Piping
Yok e
Flaring bar
Copper pipe
Flare nut
Inclined
Damaged
surface
Uneven
thickness
Correct
Cracked
R.016–.031
45°±2°
90°±2°
3. Attach the yoke to the flaring bar, centering the conical part over the end of the pipe that is
extending above the flaring bar.
4. Tighten the yoke securely to flare the end of the pipe.
5. R emove the pipe. The end of the pipe that you flared should look like the end of a trumpet. See
examples of correctly and incorrectly flared pipes.
6. Align the pipes and tighten the flare nuts manually and then with a spanner torque wrench,
applying the torque according to pipe dimensions:
Outer diameter
in. (mm)
1/4 (6.35) 10.3–13.3 ft·lb 0.34–0.36
3/8 (9.52) 25.1–31.0 ft·lb 0.50–0.52
1/2 (12.70) 36.1–45.0 ft·lb 0.64–0.65
5/8 (15.88) 50.2–60.5 ft·lb 0.76–0.78
Connection
torque (ft·lb)
Flare dimension
(in.) Flare shape (in.)
20 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 21

Connecting Piping to the Mini Outdoor Unit
Service valve: low pressure
(gas side)
Service valve:
high pressure (liquid side)
Radiant heat vents
Liquid pipe
Gas pipe
Important: Ensure that all pipe connections are accessible for servicing and maintenance.
Pipes can be connected to the mini outdoor unit at the front, back, bottom, left, or right of the unit:
1. Remove the pipe cover from the unit. See Figure 14.
Figure 14. Pipe connections on unit
Refrigerant Piping
VRF-SVN33A-EN 21
2. R emove the knock-out that you are going to use. Unused knock-outs should remain closed to
prevent damage to the unit.
• Take care to prevent damage to the exterior of the unit.
• Remove burrs from knock-out hole edges and apply rust inhibitor.
3. Connect the pipes to the unit using flared connections or by brazing. If brazing the pipe
connection, avoid damaging the service valves by wrapping them with a wet cloth.
• Avoid damaging the temperature sensor.
• Ensure that the connected pipes do not touch each other or make contact with the unit.
Page 22

Refrigerant Piping
Outdoor
unit
Indoor units
Branch
joint (4)
Indoor units
Y-j oin ts ( 5)
Outdoor
unit
Indoor units
EEV kit
Y-j o int s (5 )
Outdoor
unit
Distribution headers
Indoor units
Outdoor
unit
Distribution header
Indoor units
Example with Y-Joints
Outdoor
unit
Example with Y-Joints and EEV Kit
Example with Y-joints and distribution header
Example with distribution headers
Y-j oi n ts
4. Af ter making electrical connections (see “Electrical Wiring” p. 23) and insulating the pipes (see
“Insulating Refrigerant Pipes” p. 32), replace the pipe cover and close the remaining gap. Make
sure the radiant heat vents (Figure 14, p. 21) are not blocked.
Refrigerant Piping Installation Examples
22 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 23

Electrical Wiring
circuit
breaker or
disconnect
Communication between
outdoor and indoor units
Power cable
Indoor unit
Indoor unit
Indoor unit
Ground
Ground
Ground
Wired
remote
controller
Wired
remote
controller
Wired
remote
controller
Ground
Power cable
Communication between
outdoor and indoor units
circuit
breaker or
disconnect
Single-phase, 2-wire, 208-230 V
Mini outdoor unit
Notes:
• Remove burrs from the knock-out hole.
• Use cable conduit and bushing to prevent cables from being
damaged when passing through the knock-out holes.
• Apply rust-resistant paint around the knock-out hole.
See Figure 17, p. 26 for wiring details.
Observe the following precautions when making electrical connections. Refer to wiring diagrams
(Figure 15 and Figure 16).
Hazardous Voltage!
Disconnect all electric power, including remote disconnects before servicing. Follow proper
lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the power can not be inadvertently energized. Failure to
disconnect power before servicing could result in death or serious injury.
Use Copper Conductors Only!
Unit terminals are not designed to accept other types of conductors. Failure to use copper
conductors could result in equipment damage.
• Make all electrical connections in accordance with electrical codes and ordinances.
• All wiring must be protected from weather and damage.
• Do not disconnect or change the factory wiring inside the unit.
Electrical Wiring
WARNI NG
NOTICE
Figure 15. Typical system installation wiring with internal EEV
VRF-SVN33A-EN 23
Page 24

Electrical Wiring
Ground
Power cable
circuit
breaker or
disconnect
Communication between
outdoor and indoor units
Power cable
Indoor unit
Indoor unit
Indoor unit
Ground
Ground
Ground
circuit
breaker or
disconnect
Wired
remote
controller
Wired
remote
controller
Wired
remote
controller
EEV kit
Power cable
Power cable
Communication
Communication
Communication
Single-phase, 2-wire, 208-230 V
Mini outdoor unit
See Figure 17, p. 26 for wiring details.
Notes:
• Remove burrs from the knock-out holes.
• Use cable conduit and bushing to prevent cables from being
damaged when passing through the knock-out holes.
• Apply rust-resistant paint around the knock-out hole.
Figure 16. Typical system installation wiring with external EEV kit
24 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 25

Power Wiring
Electrical Wiring
• Multi-pole circuit breaker or disconnect is required to fully isolate the unit from all power.
• Install circuit breakers/disconnects in accordance with local and national codes.
• Select the power cable in accordance with relevant local and national regulations.
• Power cable specifications are based on an und ergro un d/am bien t tem per atur e of 8 6º F (30ºC )
and single multi-conductor cables. If conditions are different from these, consult an electrical
installation expert and re-select the power cable. If the length of power cable exceeds 164.04 ft
(50 m), re-select the power cable considering the voltage drop.
• Do not use power cable that has exposed wire.
• Unbalanced power must be maintained within 1 0% of su pply rating among all indoor units or
the unit will stop and an error code will be generated. (Significantly unbalanced power may
shorten the life of the system.)
• Use a power cable made out of incombustible material for the insulator (inner cover) and the
sheath (outer cover).
• Provide strain relief for power cables.
WARNING
Avoid Risk of Fire or Explosion!
Do not let the power cable come into contact with the pipes inside the outdoor unit. If the
power supply cable touches the pipes, the vibration of the compressor will be transferred to
the pipes and can damage the pow er su pply cables o r pipes. The damag e coul d r esult in fire or
explosion, causing death or serious injury.
Follow this procedure:
1. Refer to Table 11 for power cable and circuit break e r specifications, and Table 12 for conduit
specifications.
Table 11. Circuit breaker and power cable specifications
Power RLA FLA
MCA MOPModel Hz V Fan1 Fan2
4TVH0036B100NB
4TVH0048B100NB 22.1 0.6 0.6 29 50
4TVH0053B100NB 26.0 0.6 0.6 34 55
Notes:
• RLA is based on AHRI 210/240 cooling standard condition (indoor temperature: 80°F (26.7°C) DB/67°F (19.46°C)
WB; outdoor temperature: 95°F (35°C) DB.
• Voltage tolerance is ± 10%.
• Maximum allowable voltage between phases is 2%.
• Abbreviations: RLA: Rated load ampere; FLA: Full load ampere; MCA: Minimum circuit amperes ; MOP: Maximum
overcurrent protective device (amperes).
60 208/230
16.9 0.6 0.6 23 40
Table 12. Cable conduit specifications
Name Te mper grade Application conditions
Flexible PVC conduit PVC
Class 1 flexible conduit Galvanized steel sheet
Class 1 PVC-coated flexible
conduit
Galvanized steel sheet and
soft PVC compound
If conduit is installed indoors and not exposed to outside
elements (embedded in concrete)
If conduit is installed indoors but exposed to outside
elements
If conduit is installed outdoors and requires waterproofing
VRF-SVN33A-EN 25
Page 26

Electrical Wiring
Solderless
ring termina
l
Thin cable
Thick cable
Cable tie
Detail for connecting
two cables to one terminal
Detail for connecting
two cables to one terminal
L, N: AC power terminals
2. Cut the power cable to an approp riate length and connect it to terminals L and N in the power
supply box with a solderless ring terminal (see Figure 17).
Screw Tightening torque for terminal Terminals
M4 0.9–1.1 lbf/ft (1.2–1.5 N.m) Communication: F1, F2
.
M5 1.5–1.8 lbf/ft (2.0–2.5 N
3. If two cables are connected to one terminal, place the cables back to back with the thin cable
upward and the thick cable downward, as shown in the detail in Figure 17.
4. Secure the cable(s) with a cable tie and provide strain relief.
5. Replace the cover on the terminal board.
Note: Make sure that the section of the power supply cable that has the sheath removed is
inside the power supply box. If this is not possible, connect the power cable conduit to
the power supply box.
6. P ull the power cable through the designated knock-out at the bottom right of the mini outdoor
unit (refer to Figure 15, p. 23/Figure 16, p. 24).
Figure 17. Power wiring connections
m) Single-phase AC power: L1, L2
26 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 27

Grounding
Grounded to exclusive
grounding terminal that
is part of the structure
Grounding at the
electrical panel
Grounded to grounding rod
Important: Grounding must be done by a qualified electrician. T he unit cannot be ground by a
Ground the unit at an exclusive grounding terminal, at the electrical panel (see Figure 18), or—if
the power distribution circuit is not grounded or its grounding does not comply with electrical
codes and specifications—to a grounding rod.
Figure 18. Mini outdoo r unit grounding examples
Installing a Grounding Rod
If the installation requires a grounding rod is required, follow this proc ed ure:
1. Select a grounding rod that complies with national and local codes.
2. Select a location for the grounding rod that:
• Contains hard damp soil rather than loose sand or gravel.
• Is located away from underground structures such as gas and water pipes, telephone lines,
and underground cables.
• Is at least 6.6 ft (2 m) away from a lightning conductor.
3. Install the grounding rod in accordance with national and local codes.
4. P r oc eed with “Installing the Grounding Cable.”
Electrical Wiring
gas or water pipe, a lightning rod, or a telephone lin e grou nd in g w ire.
Installing the Grounding Cable
1. Select rated grounding cable by referring to the mini outdoor unit power cable specifications
(Table 11, p. 25).
2. Connect the grounding cable to the grounding hole inside the power supply box and pull it
through the designated grounding knock-out.
Note: If the grounding cable length needs to be extended, make the cable connection in
accordance with national and local codes.
3. If a grounding rod was installed to ground the unit, measure the resistance with a ground
resistance tester. Refer to Table 13 for resistance requirements.
• If the resistance is above the requirements, drive the grounding rod deeper into the ground
or increase the number of grounding rods until the resistance requirement is achieved.
VRF-SVN33A-EN 27
Page 28

Electrical Wiring
F1, F2: Communication between indoor and outdoor units
• If you have grounded the unit to a grounding terminal or electrical panel, ensure that the
resistance meets the requirements.
Table 13. Grounding resistance requirements
Power condition at
installation site
Voltage to ground is ≤ 150 V
Voltage to ground is > 150 V
• Ensure that the grounding resistance is <100 .
• If a circuit breaker is installed that disconnects the
High or average humidity Low humidity
circuit within 0.5 seconds, the allowable grounding
resistance is 30–500 .
Communications Wiring
• Refer to BAS-SVX51 for communicatio ns wirin g speci ficatio ns an d best practices.
•Refer to Table 12, p. 25 for cable conduit specifications.
Hazardous Voltage!
Disconnect all electric power, including remote disconnects before servicing. Follow proper
lockout/tagout procedures to ensure the power can not be inadvertently energized. Failure to
disconnect power before servicing could result in death or serious injury.
• Ideally, grounding resistance should be <100 and
should not exceed 250 .
• Ensure that the grounding resistance is <100 .
• If a circuit breaker is installed that disconnects the
circuit within 0.5 seconds, the allowable grounding
resistance is 30–500 .
WARNING
1. Connect the communications cable wires to the terminals, as shown in Figure 19.
Notes:
• Ensure that mor e than 1 in. (20 mm) of the outer sheath of the power and communication
cable conduit are inside the electrical component box.
• To reduce interference, ensure that power and communication cables run in parallel with
a minimum space of 2 in. (50 mm) between the cables or, if crossing is necessary, cross
at 90 degrees.
• The communication cable between mini outd oor units and between indoor and outdoor
units has no polarity.
Figure 19. Communications board and wiring terminals
2. Provide strain relief for the communications cable.
3. Pull the communications cable through the designated knock-out at the bottom right of the mini
outdoor unit (refer to Figure 15, p. 23/Figure 16, p. 24).
28 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 29

Leak Testing Pipe Connections
Before leak testing pipe connections, read all safety prec au tio ns and notes.
Confined Space Hazards!
Do not work in confined spaces where refrigerant or other hazardous, toxic or flammable gas
may be leaking. Refr igerant or other gases could displace av ailable oxygen to breathe, causing
possible asphyxiation or other serious health risks. Some gases may be flammable and or
explosive. If a leak in such spaces is detected, evacuate the area immediately and contact the
proper rescue o r response au thor ity. Failur e to tak e appr opr iate pr ecautions or t o react pr oper ly
to such potential hazards could result in death or serious injury.
Explosion Hazard!
Never use an open flame to detect gas leaks. It could result in an explosion. Use a leak test
solution for leak testing. Failure to follow recommended safe leak test procedures could result
in death or serious injury or equipment or property-only-damage.
Use only dry nitrogen with a pressure regulator for pressurizing unit. Do not use acetylene,
oxygen or compressed air or mixtures containing them for pressure testing. Do not use
mixtures of a hydrogen containing refrigerant and air above atmospheric pressure for pr essure
testing as they may become flammable and could result in an explosion. Refrigerant, when
used as a trace gas should only be mixed with dry nitrogen for pressurizing units. Failure to
follow these recommendations could result in death or serious injury or equipment or
property-only damage.
Do not exceed unit nameplate design pressures when performing a leak test. Failure to follow
these instructions could r e sult in an explosio n causi ng death or serious injury.
Leak Testing Pipe Connections
WARNING
WARNING
Notes:
• All required piping pressure tests must be completed in accordance with national and/or
local codes.
• When leak-testing refrigerant systems, observe all safety precautions.
• Leak test only one circuit at a time to minimize system exposure to potentially harmful
moisture in the air.
• Use R-41 0A refrigerant gas as a tracer for leak detection and use oil-pumped dry nitrogen
to develop required test pressures.
• Use tools rated for R-410A.
• Do not remove the valve core of the charging port.
• Perform the leak test with the outdoor unit service valves closed.
VRF-SVN33A-EN 29
Page 30

Leak Testing Pipe Connections
High-pressure side
Nitrogen gas
Low-pressure side
Service ports
Low-pressure (gas
side) service valve
High-pressure (liquid
side) service valve
Use the following procedure for leak testing pipe connections.
Refrigerant Pipe Damage!
When performing a leak test, use a pressur e r egulator t o pr event an ex cess amount of nitrogen
(over 594.6 psi [4.1 MPa]) from entering the pipes. If the pipe is filled with more than the
specified amount of nitrogen in a short period of time, pipe damage may occur.
1. Connect the refrigerant manifold gauge hoses to the liquid side and gas side service por ts on
the unit, and connect the center hose to a nitrogen gas tank fitted with a pressure regulator (see
Figure 20).
Figure 20. Leak testing pipe connections with a manifold gauge
NOTICE
2. Fill the lines with nitrogen to no more than 594.6 psi (4.1 MPa).
3. Monitor the pressure periodically for a minimum of 24 hours. If the pressure drops, use soapy
water to check for leaks. Bubbles will occur if joints are not tight.
4. Release pressure in pipelines gradually.
5. Repair leaks.
6. Repeat the previous steps until the pressure remains constant.
7. Maintain 145 psi (1.0 MPa) of pressure for 15 minutes and chec k for further leakage. If the
pressure drops, check for leaks and repair them. Repeat this step as necessary until 145 psi
(1.0 MPa) of pressure is maintained for 15 minutes.
8. Remove hoses from service ports.
30 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 31

Vacuum Drying Procedure
After performing a successful leak test, follow this vacuum drying procedure:
Notes:
• Use tools rated for R-410A.
• Use a vacuum pump that allows vacuuming under 29.7 inH2O.
• Use a vacuum pump with an installed check valve so that pump oil is prevented from
flowing into the pipes when the vacuum pump is stopped.
1. Completely close both the liquid and the gas side service valves.
2. Connect the refrigerant manifold gauge hoses to the liquid side and gas side pipe service ports
and connect the center hose to the vacuum pump.
3. Open bot h manifold ga uge valves and turn on the vacuum pump. With vacuum pr essure less
than 29.7 inH
Note: More time may be needed depending on pipe length or outdoor temperature.
4. Close both manifold gauge valves to isolate the system. Then quickly shut off the vacuum
pump.
5. Wait 1 hour. Then use the vacuum gauge to verify that the pressure remains at 29.7 inH
it has, proceed to Step 7.
6. If the pressure increases to o ver 29.7 inH
pipes. Repair as necessary using the following procedure:
a. Using a nitrogen gas tank fitted with a pressure regulator , attac h hoses from the tank to the
liquid side and gas side service ports on the unit (see location in Figure 20, p. 30).
b. Apply nitrogen at 7.25 psi (0.05 MPa) to help remove moisture in the lines.
c. Perform the vacuum drying procedure again (steps 1–3) for a minimum of 2 hours.
d. Repeat the leak test and the vacuum drying procedure as necessary until the pressure
remains at 29.7 inH
7. Proceed with insulating the pipes (p. 32) and charging the refrigerant (p. 34).
O, allow the vacuum drying to continue for at least 2.5 hours.
2
O for 1 hour.
2
O. If
2
O in an hour, eit her leaks or moisture rem ain i n the
2
VRF-SVN33A-EN 31
Page 32

Insulating Refrigerant Pipes
Insulation
Insulation
Gas pipe
Liquid pipe
3/8 in.
(10 mm)
3/8 in.
(10 mm)
3/8 in.
(10 mm)
Insulating Refrigerant Pipes
After determining that there are no leaks in the refrigerant pipes, insulate them as described:
1. Use Table 14 to select the insulation thickness according to pipe siz e and humi dity conditions.
Table 14. Pipe insulation selector
Insulation Type
Standard conditions
86°F (30°C), < 85%
Pipe
Liquid pipe
Gas pipe
(a) When installing insulation in any of the following environments, use insulation required for high humidity conditions: Buildings with close proximity to
bodies of water or hot springs or on the side of a hill in which the building is partly covered by earth; ceilings frequently exposed to moisture such as
in restaurants, saunas, swimming pools, and corridors of dormitories or studios near a frequently-used outdoor exit; buildings with no ventilation system.
(b) Internal temperature of gas pipe is higher than 248°F (120°C).
1/4 (6.35) – 3/8 (9.52) 3/8 (9) 3/8 (9)
1/2 (12.70) – 2 (50.80) 1/2 (13) 1/2 (13)
1/4 (6.35) 1/2 (13) 3/4 (19)
3/8 (9.52)
1/2 (12.70)
(b)
5/8 (15.88)
3/4 (19.05)
7/8 (22.23)
Pipe size
in. (mm)
3/4 (19) 1.0 (25)
EPDM or NBR
(in. (mm)
High humidity conditions
86°F (30°C), 85%
(a)
2. W rap insulation around the entire surface of each pipe, including the refrigerant pipes from the
indoor unit to the service valves inside the outdoor unit, the branc h joints, distribution header ,
and connection points on each pipe.
Note: For details on insulating branc h joints, refer to the branc h joint installation manual (VRF -
SVN41).
• Do not wrap the gas and liquid refrigerant pipes together.
• If gas and liquid pipes are in contact with one another , use thic ker insulation and make sure
the pipes are not pressing tightly against one another.
• Pipe connections between the indoor unit and EEV kit: Leave 3/8 in. (10 mm) of space
between gas and liquid side pipes.
32 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 33

Insulating Refrigerant Pipes
Clamp
Insulation
Gas side pipe
Liquid side pipe
• Overlap insulation to avoid gaps.
• Avoid compressing the insulation as much as possible.
• Be sure there are no cracks or deformities in the insulation at bends in pipes or where
hangers are attached to pipes.
• If necessary, double the insulation to prevent condensation from forming in warm or humid
areas.
3. Clamp insulation tightly to pipes.
4. Cut off excess insulation.
VRF-SVN33A-EN 33
Page 34

Refrigerant
Refrigerant
After successful leak testing and vacuum drying, calculate the amount of refrigerant needed and
then charge the system, as explained in this section.
Calculating the Refrigerant
The initial refrigerant quantity (given in Table 15) is charged into the unit at the factory.
Calculate the total amount of additional refrigerant to add to the system as follows:
T otal additional refrigerant = [total length of 3/8 in. (0.52 mm) liquid piping x 2.12 oz (60 g)] + [total
length of 1/4 in. (6.35 mm) liquid piping x 0.71 oz (20 g)] + [total refrigerant quantity for all
connected indoor units (refer to Table 16)].
Table 15. Initial refrigerant quantity for each mini outdoor unit model
Model
4TVH0036B100NB (3 ton) 4TVH0048B100NB (4 ton) 4TVH0053B100NB (5 ton)
Initial refrigerant
quantity: lb (kg)
Table 16. Refrigerant quantity for each indoor unit
7.5 9 9.5 12 18 20 24 30 36 48 76.8 96
Model
1-way cassette
(4TVE00**B100NB)
Mini 4-way cassette
(4TVB00**B100NB)
4-way cassette
(4TVC00**B100NB)
Slim duct
(4TVL00**B100NB)
MSP duct
(4TVD00**B100NB)
HSP duct
(4TVA00**B100NB)
High-wall
(4TVW00**B100NB)
Convertible
ceiling/floor
(4TVX00**B100NB)
0.55
(0.25)
0.53
(0.24)
0.53
(0.24)
0.55
(0.25)
0.82
(0.37)
0.99
(0.45)
0.53
(0.24)
0.53
(0.24)
0.55
(0.25)
0.82
(0.37)
0.53
(0.24)
0.53
(0.24)
7.1 (3.2) 7.1 (3.2) 7.3 (3.3)
Capacity (MBH)
Refrigerant quantity: lb (kg)
0.82
(0.37)
0.99
(0.45)
0.99
(0.45)
0.62
(0.28)
0.79
(0.36)
0.86
(0.39)
0.82
(0.37)
0.79
(0.36)
0.99
(0.45)
0.99
(0.45)
0.62
(0.28)
0.79
(0.36)
0.86
(0.39)
1.52
(0.69)
0.93
(0.42)
1.19
(0.54)
1.52
(0.69)
0.93
(0.42)
1.19
(0.54)
1.50
(0.68)
1.52
(0.69)
1.37
(0.62)
1.50
(0.68)
1.50
(0.68)
2.60
(1.18)
2.60
(1.18)
34 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 35

Charging the Refrigerant
After calculating the correct amount of refrigerant needed by the system (see “Calculating the
Refrigerant” p. 34), charge the system as described in the following procedure:
Hazard of Explosion and Deadly Gases!
Do not heat the refrigerant container to speed up the charging process. An explosion could
result, resulting in death or serious injury.
Risk of Unit Malfunction!
Do not leave the front panel open while charging refrigerant. If the front panel is open, the
amount charged into the unit will be incorrect.
Unit Component Damage!
Open the gas side and liquid side service valves completely after charging the refrigerant. If
you operate the unit with the service valves closed, the unit may be damaged.
Refrigerant
WARNING
NOTICE
NOTICE
1. Attach the liquid manifold hose to the liquid side service port and open the manifold gauge
valve.
2. Add the liquid refrig erant, making sure the refrigerant bottle is held in an upright position. Use
a scale to determine that the correct amount has been added.
3. Close the refrigerant container immediately after adding the refrigerant.
4. If you are unable to add all of the refrigerant needed into the liquid side, close the liquid side
service port and remove the liquid manifol d hos e.
5. At tach the gas manifold hose to the gas side service port and open the manifold gauge valve.
Figure 21. Charging additional refrigerant
6. Press K2 once to initiate refrigerant charging in cooling mode.
7. To determine if the amount of refrigerant added is correct, use the automatic refrigerant
function (see “Refrigerant detection operation” p. 46).
8. After charging the refrigerant, close the service valves and replace caps.
VRF-SVN33A-EN 35
Page 36

Connecting the Drain Hose
1.96 in. (50 mm)
0.51 in. (13 mm)
Base
Drain hose
Bottom of outdoor unit
Drain
plug
Connecting the Drain Hose
When using the air conditioner in the heating mode, ice may accumulate. When the unit is in defrost
mode, condensed water must be safely drained away from the unit through a drain hose.
To install the drain hose:
Note: A minimum space of 1.96 in. (50 mm) must be allowed between the bottom of the mini
outdoor unit and the supporting base to facilitate drain hose installation.
1. Insert the drain connector into the drain hole on the underside of the mini outdoor unit.
2. Connect the drain hose to the drain connector.
3. Plug the unused drain holes with drain plugs.
36 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 37

Control System
K1 K2 K3 K4
SW01 SW02
7-segment display
K5 K6 K7 K8 K9 K10 K11 K12 K13 K14 K15 K16
Tens Digit Ones Digit
The control board contains a 7 -segment display , th ree DIP switc hes, two rotary switc hes, and four
buttons, as shown in Figure 22. Their functions are explained in this section.
Hazardous Voltage!
Before making contact with the inverter circuit board, w ait for at least 15 minutes after
powering down the mini outdoor unit to allow the unit to fully discharge high DC voltage.
Failure to allow the high DC voltage to discharge completely could result in death or serious
injury.
Figure 22. Control board
Control System
WARNING
System Monitoring
The 7-segment display indicates system power and communication status.
Table 17. 7-segment display
Event Digit 1 Digit 2 Digit 3 Digit 4
Power up
Establishing
communication between
outdoor and indoor units
Transmit/receive
(normal operation)
(a) 7-segment display example showing power-up is shown in Figure 22.
VRF-SVN33A-EN 37
(a)
“8”“8”“8”“8”
“A” “d” Number of connected indoor units
Indoor unit: “A” Indoor unit: “0” Unit address (decimal number)
Page 38

Control System
Configuring the System
The control board contains two rotary switches and three DIP switches (shown in Figure 22). The
following tables explain their functions.
Table 18. Configuration using rotary switches SW01 and SW02
SW01/SW02 Total number of installed indoor units
Tens digit/Ones digit
Table 19. Configuration using DIP switches K5–K8
DIP switch Setting Function description
K5 Not used Not used. Default is 0.
K6
K7 On
K8 On
K7 On
K8 Off
K7 Off
K8 On
K7 Off
K8 Off
(a) If enabled, the mini outdoor unit fan will operate for 1 minute every 30 minutes to prevent snow build-up.
(b) Maintain optimal evaporating temperature in the cooling mode if long line lengths exist. Refer to cooling long pipe
performance data in the technical data book. If you upgrade the performance at your discretion, low discharge air
temperature of an indoor unit might cause discomfort.
Use to set total number of installed indoor units.
Notes:
1. For example, if 3 indoor units are installed: Set SW01 to “0”; set SW02 to “3”.
2. Set at mini outdoor unit only.
Snow prevention control
On Disables snow prevention control (default).
Off Enables snow prevention control.
Cooling capacity correction
44.6–48.2°F (7–9°C) (default)
41.0–44.6°F (5–7°C)
48.2–51.8°F (9–11°C)
50.0–53.6°F (10–12°C)
(b)
(a)
38 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 39

Control System
Table 20. Configuration using DIP switches K9–K12
DIP switch Setting Function description
Night-time silent mode
K9 On
K10 On
K9 On Mode 1
K10 Off
K9 Off Mode 2
K10 On
K9 Off Mode 3
K10 Off
Heating capacity correction
K11 On
K12 On
K11 On
K12 Off
K11 Off
K12 On
K11 Off
K12 Off
(a) Reduces fan speed for quiet operation.
(b) Maintaining factory default status is recommended. However, if the desire is to reduce energy consumption or improve
heating performance, control the operation according to the surrounding environment.
(c) As the target high pressure is decreased, energy consumption and noise may decrease but the indoor air discharge
temperature will also decrease.
(d) Heating operation increases frequency when the current high pressure is higher than the target high pressure; and vice
versa.
(e) If the target high pressure is high, the discharge air temperature of an indoor unit will increase, but energy consumption
will also increase.
Disable
3 ton: 600 rpm
4 ton: 600 rpm
5 ton: 620 rpm
3 ton: 540 rpm
4 ton: 540 rpm
5 ton: 560 rpm
3 ton: 480 rpm
4 ton: 480 rpm
5 ton: 500 rpm
Default: 426.7 psi
Default – 28.4 psi
Default – 14.2 psi
Default + 14.2 psi
(a)
(b),(c),(d),(e)
VRF-SVN33A-EN 39
Page 40

Control System
Table 21. System configuration using DIP switches K13–K16
Maximum current per unit model
4TVH0036B100NB
3 ton
DIP switch
K13 On
K14 On
K13 On
K14 Off
K13 Off
K14 On
K13 Off
K14 Off
K15 On
K16 On
K15 On
K16 Off
K15 Off
K16 On
K15 Off
K16 Off
(a) This option is used in locations where humidity is high and, as a result, defrost mode occurs frequently.
(b) Maintaining factory default status is recommended. If set to Low, the temperature at which it enters defrost mode will
decrease. If the temperature at which it enters defrost mode decreases, the duration of defrost operation will increase. As
a result, the overall heating capacity will be reduced.
(c) Defrost mode will start when the difference between the outdoor temperature and the outdoor coil temperature has
exceeded its t.
Maximum current default: 22 A Maximum current default: 24 A Maximum current default: 32 A
Default – 4 A Default – 2 A Default – 2 A
Default – 6 A Default – 4 A Default – 4 A
Default – 8 A Default – 6 A Default – 6 A
4TVH0048B100NB
4 ton
Current limit option
Defrost optimization
Default: Mid
Default: Mid
Low1
Low2
4TVH0053B100NB
5 ton
(a),(b),(c)
40 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 41

Initiating System Operations
Buttons K1, K2, and K3 are used to initiate system operations. The first two digits of the 7 -segment
display respond as shown in the last column of the following tables.
Table 22. Button K1
Control System
Number of times K1
is pressed Operation
1 (hold for 5 seconds) Test operation
1
2
3
4 Vacuum
5
Refrigerant
Te s t o p e r at i on
Pump down
Completion
charging in heating mode
in heating mode
in heating
mode
Table 23. Button K2
Number of times
button K2 is
pressed Operation
7-segment display:
Digits 1 and 2
Blank
7-segment display:
Digits 1 and 2
1 Refrigerant charging in cooling mode
2 Test operation in cooling mode
3 Pump down in cooling mode
4 Refrigerant detection operation
5Completion Blank
Table 24. Button K3
Number of times
button K3 is
pressed Operation 7-segment display
1
VRF-SVN33A-EN 41
Initialize (reset)
operation
Same
as
power up: “8888”
Page 42

Control System
Monitoring System Settings
Buttons K4 is used to monitor system settings and software versions.
Table 25. Button K4
Number of
times button
K4 is pressed Setting Description
1 Current frequency 15 Hz 1,0,1,5
2
3
4
5
6
7 Double pipe out tube temperature 113°F (45°C) 7,4,5,0
8 High pressure value 221.9 psi (15.6 kg/cm
9 Fan speed 700 rpm 9,7,0,0
10 ESC(EVI)EEV 180 step A,1,8,0
11 MAIN EEV 1500 step B,1,5,0
12 Present running current 15 A C,1,5,0
13 Number of connected indoor units 10 D,0,1,0
14 Number of operating mini outdoor units 8 E,0,0,8
15 Sum of indoor unit capacity 47,640 Btu/h (12,000 kcal/h) F,1,2,0
(a) Gauge pressure
Low pressure
Outdoor temperature
Discharge temperature
OLP temperature
COND Out
temperature 79.3°F (26.3°C) 6,2,6,3
37.0 psi (2.6 kg/cm2)
74.3°F (23.5°C) 3,2,3,5
177.3°F (80.7°C) 4,8,0,7
203°F (95°C) 5,9,5,0
(a)
2)(a)
Table 26. Button K4 (press and hold for 3 seconds)
7-segment display
Number of times button K4 is
pressed and held 3 seconds
0
1Inverter
2 EEPROM version 0,9,1,2
3
4
Software version/
Unit address
Main circuit board
Automatically assigned unit
addresses
Manually assigned unit
addresses
board
version
version
Version examples
Digits 1, 2, 3, 4
0,9,1,2
Digit 1 Digit 2 Digit 3, 4
Address examples
A00, 5
A00, 1
7-segment display
Digits 1, 2, 3, 4
2,0,2,6
8,1,5,6
0,9,1,2
42 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 43

Pre-Start Checks
After installation and before the test operation is conducted, perform the following pre-start checks:
Avoid Damage to the Communication Circuit!
Do not measure the communication terminal with an insulation tester. Doing so will damage
the communication circuit.
1. E nsu re that the power and communication cables of the indoor and mini outdoor uni t s are
properly connected.
2. Before supplying power, use a resistance tester to verify that resistance to ground is greater
than 30 M.
3. Ensure that the indoor units are connected.
4. Check for a short-circuit between the communication terminal and ground.
5. Ensure that the pre-start checklist (Table 27) has been completed.
Table 27. Pre-start checklist
Installation
Refrigerant pipe
Drain pipe
Electrical
Setting address
Option
Mini outdoor
unit
Indoor unit
Pre-Start Checks
NOTICE
• Have you checked the external surface and the inside of the unit for damage?
• Is there any possibility of short circuit due to the heat produced by the outdoor unit?
• Is the place well-ventilated and meets recommended requirements for clearances
and service?
• Is the outdoor unit installed securely to withstand external forces?
• Have you checked the external surface and the inside of the indoor unit?
• Is there enough space for service?
• Have you ensured that the center of the indoor unit is installed horizontally and is
level?
• Have you selected the correct pipes?
• Are the liquid and gas valve open?
• Is the total number of connected indoor units within the allowable range?
• Are the length and the height difference between the refrigerant pipes within the
allowable range?
• Are the branch joints properly installed?
• Has the connection of liquid and gas pipes been correctly performed?
• Have you selected correct insulator for pipes and insulated them correctly?
• Is the pipe or connection part properly insulated?
• Is the quantity of the additional refrigerant correctly weighed in? (You must record
the amount of additional refrigerant charging on the service record paper placed
outside the outdoor unit.)
• Have you checked whether the drain pipes of the indoor unit and outdoor unit are
connected together?
• Have you completed the drain test?
• Is the drain pipe properly insulated?
• Are the power cable and communication cable tightened firmly on the terminal
board within the rated torque recommendations?
• Have you checked for cross connection of the power and communication cables?
• Have the outdoor unit been properly grounded?
• Is the communication cable shielded?
• Is the wire length within the recommended limit?
• Is the wiring route correct?
• Are the address of the indoor and outdoor units properly set?
• Are the address of the indoor and outdoor units properly set, if multiple remote
controllers are to be used?
• Ensure that the vibration-isolation structure is correctly installed or if one needs to
be installed.
VRF-SVN33A-EN 43
Page 44

Test Operation
122 (50)
104 (40)
86 (30)
68 (20)
50 (10)
32 (0)
14 (-10)
-4 (-20)
41 (5) 50 (10) 59 (15) 68 (20) 77 (25) 86 (30) 95 (35) 104 (40) 113 (45)
Cooling
Heating
Outdoor temperature: °F (°C)
Indoor temperature: °F (°C)
Notes:
• During the test operation, cooling/heating modes are selected automatically.
• Within the temperature range marked with hashed lines, system protection control may trigger during the test
operation. If this occurs, test results may be inaccurate.
• When the temperature is outside of the guaranteed range, test accuracy may decrease to the borderline area shown
in the graph.
Test Operation
After all pre-start c hecks (refer to “Pre-Start Chec ks” p. 43) have been have been completed, run the
test operation under the following temperature conditions:
WARNING
Hazardous Voltage, Rotating Components!
Do not operate the product with the panel or duct outlet protection net off. There is risk of
personal injury from parts that rotate or contain high voltage.
CAUTION
Risk of Burn or Frostbit!
Refriger ant pipe ma y be hot or cold dur ing or r ight af ter the operation depending on the status
of the refrigerant which flows through the refrigerant pipe, compresso r, and other parts of th e
refrigerant cycle. Do not touch the refrigerant pipe during or right after the operation to avoid
getting burned our frostbit.
NOTICE
Avoid Unit Damage!
44 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Wait at least 5 minutes bef o re turning off the main po wer after the test operation is finished. If
you do not, wate r leakage or other problems may occur.
Wait at least 3 hours after power is supplied to the outdoor unit before operating it to allow
time for the crank case heater to pre-heat. If the crank case heater is not pre-heated before
operation, unit parts are at risk of being seriously damaged.
1. Before powering the unit, heed the precautions given above for the test operation.
Page 45

Test Operation
Note: When power is supplied to the outdoor unit, it will check for and verify communications
with the indoor units.
2. Ensure that the front of the outdoor unit is closed.
3. Press and hold button K1 for 5 seconds to run the test operatio n (see Table 22, p. 41.)
• During the test operation, the compressor is restricted from operating.
• UP (for “unprepared”) will appear on the digital display. When the test operation has
completed, the display will clear.
• The test operation may continue from 30–50 minutes, depending on the operating status.
• During the test operation, noise may occur due to valve inspection. (Examine the unit if
abnormal noises continue to occur.)
4. When the test operation ends, use VRF Enterprise Management Software or VRF AutoCommissioning T ool to issue a test results report. If an y items in the report are marked with an
“inspection required” sign, refer to the service manual for information on correcting the items
and run the test operation again.
5. Ensure the following:
• The system has the correct refrigerant amount (see “Refrigerant detection operation” p. 46)
after the unit has been operating in cooling mode for at least 30 minutes
• Cooling/heating operation runs normally.
• Air flow direction and fan speed of indoor units runs normally.
• There are no abnormal operating noises from indoor or outdoor units.
• During cooling operation, the indoor units drain properly.
6. Use VRF Enterprise Management Software to check operating status details.
7. Explain to the user how to use the indoor unit and leave them with the indoor unit manual for
their reference.
VRF-SVN33A-EN 45
Page 46

Refrigerant detection operation
Start
Press the K2 button 4 times
Detect amount of refrigerant
Judge the amount of
refrigerant
Satisfy the temperature
condition
Inpu t VRF Technicial Utilities signal
End
(Normal) (Excessive) (Insufficient) (Judgment not
available)
Refrigerant detection operation
Perform the refrigerant detection operation only under the fol lo wing conditions:
• After the unit has been operating in cooling mode for at least 30 minutes.
• Within the following operating envelope:
– Indoor: 68–86°F (20–30°C)
– Outdoor: 41–109.4°F (5–43°C)
Failure to comply may result in the operation ending before completion or in inaccurate results. If
the unit triggers protection control, the results may be inaccurate.
46 VRF-SVN33A-EN
After the refrigerant detection operation is complete, take the following actions:
• If the amount of refrigerant is excessive, discharge 5% of the detected amount and restart the
refrigerant amount detection operation.
• If the amount of refrigerant is insufficient, add 5% of the detected amount and restart the
refrigerant amount detection operation.
• If the degree of supercooling is insufficient, add 1 0% of the detected amount of refrigerant and
restart the refrigerant detection operation.
• If the result is unavailable, chec k that the refrigerant detection operation was conducted within
the operating envelope stated above. Perform a test operation to determine if there are any
other problems with the system.
Page 47

Service: Pump Down Process
Outdoor unit
Scale
Liquid side
service valve
Gas side
service valve
Manifold gauge
valve 1
Manifold gauge
valve 2
Refrigerant
container
valve
The pump down process pulls all of the refrigerant in the system into the outdoor unit condenser
so that repairs can be made to the system.
Collecting Refrigerant into a Refrigerant Container
WARNING
Refrigerant under High Pressure!
Failure to follow code concerning could result in an explosion which could result in death or
serious injury or equipment damage. The refrigerant container used to collect refrigerant from
the system must be one that is exclusiv ely designed for that purpose.
The maximum amount of refrigerant that can be put into a mini outdoor unit is 176.4 oz. Because
of this limitation, some of the refrigerant should be removed from the system to a refrigerant
container before performing the pump down pro c ess.
1. Have ready an empty refrigerant container, a weighing scale, and a manifold gauge.
2. Determine through calculation the current amount of refrigerant in the system.
3. Connect the refrigerant container to the mini outdoor unit and operate 50% o f all indoor units
in cooling mode.
Service: Pump Down Process
Figure 23. Removing refrigerant from the system to a refrigerant container
4. Af ter 1 0 minutes of operation, use the manifold gauge to check the liquid side pressure. When
the pressure is higher than 420.61 psig (2.9 MPa), decrease the number of operating indoor
units.
5. Check the pressure again. When it has decreased to less than 420.61 psig (2.9 MPa), open the
liquid side service valve and the manifold gauge valve that is connected to the liquid pipe to
let the refrigerant run into the refrigerant container.
Important: The amount of refrigerant that can be put into the refrigerant container should be
approximately 50% of the total refrigerant in the system. Do not fill the refrigerant
container more than 85% of its capacity (average temperature 77°F).
6. Use the scale to determine how much refrigerant that has been collected.
7. After the proper amount of refrigerant has been collected, turn off the manifold gauge valve and
the liquid side service valve.
VRF-SVN33A-EN 47
Page 48

Service: Pump Down Process
Pump Down Process
Equipment Damage!
Do not allow the amount of system refrigerant that is pulled into the outdoor unit during the
pump down process to exceed the capacity of the outdoor unit or equipment damage may
occur.
1. Follow the procedure for “Collecting Refrigerant into a Refrigerant Container” p. 47”.
2. Press the K2 button on the outdoor unit control board three times to initiate the pump down
process (Table 23, p. 41.)
3. Using a manifold gauge, observe the pressure drop when the compressor starts operating.
4. When the pressure reaches lower than 0 psig (0 MPa), turn off the gas side service valve.
5. Press the K3 button once.
6. R emove manifold gauge.
NOTICE
48 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 49

Warranty For Trane Advantage™ VRF Systems and Related Accessories
Warranty For Trane Advantage™ VRF Systems and
Related Accessories
Products Covered. This warranty is extended by T rane, and applies to all T rane Advantage™ VRF
systems and accessories for these products whic h are sold by T rane and applied in accordance with
Trane specifications.
Basic Warranty
The warrantor w ar rants for a period of 12 month s from the initial star t-up or 18 mo nths from date
of shipment, whichever is less, against failure due to defects in material and manufacture and that
it has the capacities and ratings set forth in Company’s catalogs and bulletins (“Warranty”).
If the following conditions are met, the warrantor extends this basic warranty period to five (5)
years from date of start-up:
• The system is designed using an approved application tool (VRF S e lect).
• The system is installed by a contractor who has successfully completed a T rane factory training
class.
• A verified commissioning report from the Trane VRF Commissioning Tool is submitted.
Exclusions and Limitations
Exclusions from this Warranty include damage or failure arising from: wear and tear; corrosion,
erosion, deterioration; modifications made by others to the Equipment; repairs or alterations by
a party other than Company that adversely affects the stability or reliability of the Equipment;
vandalism; neglect; accident; adverse weather or environmental conditions; abuse or improper
use; improper installation; commissioning by a party other than Company; unusual physical or
electrical or mechanical stress; operation with any accessory, equipment or part not specifically
approved by Company; refrigerant not supplied by Company; and/or lack of proper maintenance
as recommended by Company. Company shall not be obligated to pay for the cost of lost
refrigerant or lost product. Company's obligations and liabilities under this Warranty are limited to
furnishing replacement equipment or parts, at its option, FCA (Incoterms 2000) factory or
warehouse (f.o.b. factory or warehouse for US domestic purposes) at Company-designated
shipping point, freight-allowed to Company's warranty agent's stock location, for all nonconforming Company-manufactured Equipment (which have been returned by Customer to
Company. Returns must have prior written approval by Company and are subject to restocking
charge where applicable. Equipment, material and/or parts that are not manufactured by Company
are not warranted by Company and have such warranties as may be extended by the respective
manufacturer. COMPANY MAKES NO REPRESENTATION OR W ARRANT Y, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED ,
REGARDING PREVENTION OF MOLD/MOULD, FUNGUS, BACTERIA, MICROBIAL GROWTH, OR
ANY OTHER CONTAMINATES. No warranty liability whatsoever shall attach to Company until
Customer’s complete order has been paid for in full and Company's liability under this Warranty
shall be limited to the purchase price of the Equipment shown to be defective. EXCEPT FOR
COMPANY’S WARRANTY EXPRESSLY SET FORTH HEREIN, COMPANY DOES NOT MAKE, AND
HEREBY EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS, ANY WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED CONCERNING ITS
PRODUCTS, EQUIPMENT OR SERVICES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, ANY WARRANTY
OF DESIGN, MERCHANTABILITY OR OF FITNESS FOR A PA RTICULAR PURPOSE, OR OTHERS
THAT ARE ALLEGED TO ARISE FROM COURSE OF DEALING OR TRADE.
Additional warranty protection is available on an extra-cost basis and must be in writing and
agreed to by an authorized signatory of the Company . Additional terms and conditions of warranty
coverage are applicable for refrigeration equipment. If you wish further help or information
concerning this warranty, contact: Trane—Warrantor, 2701 Wilma Rudolph Blvd., Clarksville, TN
37040.
VRF-SVN33A-EN 49
Page 50

Warranty For Trane Advantage™ VRF Systems and Related Accessories
50 VRF-SVN33A-EN
Page 51

Page 52

Trane optimizes the performance of homes and buildings around the world. A business of Ingersoll Rand, the
leader in creating and sustaining safe, comfortable and energy efficient environments, Trane offers a broad
portfolio of advanced controls and HVAC systems, comprehensive building services, and parts. For more
information, visit www.Trane.com.
Trane has a policy of continuous product and product data improvement and reserves the right to change design and specifications without notice.
© 2013 Trane. All rights reserved.
VRF-SVN33A-EN 31 May 2013
NEW
We are committed to using environmentally
conscious print practices that reduce waste.
 Loading...
Loading...