Toyota Prius, Plug-in Hybrid 2010, 2010 PRIUS, 2012 PRIUS User Manual

Plug-in Hybrid
2010 Model
Revised (includes 2012 Model)
© 2012 Toyota Motor Corporation
All rights reserved. This document may not be
altered without the written permission of Toyota Motor Corporation.
Prius Plug-in hybrid ERG REV A – (02/22/12)

F
-i-
oreword
This Prius Plug-in hybrid Emergency Response Guide has been revised
to include the changes of the 2012 model year Prius Plug-in hybrid.
These changes include minor updates to the vehicle exterior, interior
and hybrid system. The important changes affecting the emergency
responder are the reshaped high voltage battery assembly, HV battery
voltage, and location of charge inlet door. While many features of the
Prius Plug-in hybrid are shared with the 2010 3rd generation Prius
hybrid, emergency responders should recognize and understand the
new features of the Prius Plug-in hybrid covered in this guide.
High voltage electricity powers the electric motor, generator, air
conditioning compressor and inverter/converter. All other automotive
electrical devices such as the headlights, radio, and gauges are powered
from a separate 12 Volt system. Numerous safeguards have been
designed into the Prius Plug-in hybrid to help ensure the high voltage,
approximately 346 *1/207.2 *2 Volt, Li-ion Hybrid Vehicle (HV)
battery assembly is kept safe and secure in an accident.
*1: 2010 Model
*2: 2012 Model
The 2010 Model Prius Plug-in hybrid utilizes the following electrical
systems:
• Maximum 650 Volts AC
• Nominal 346 Volts DC
• Nominal 120/240 Volts AC
• Maximum 27 Volts DC
• Nominal 12 Volts DC
The 2012 Model Prius Plug-in hybrid utilizes the following electrical
systems:
• Maximum 650 Volts AC
• Nominal 207.2 Volts DC
• Nominal 120/240 Volts AC
• Maximum 27 Volts DC
• Nominal 12 Volts DC
2010 Model Prius Plug-in hybrid features:
• An electric vehicle charge cable rated at 120 Volts.
• An onboard battery charger with a 120 Volt /240 Volt AC input and
346 Volt DC output.
• A boost converter in the inverter/converter that boosts the available
voltage to the electric motor to 650 Volts.
• A high voltage Hybrid Vehicle (HV) Li-ion battery assembly rated
at 346 Volts.
• A high voltage motor driven Air Conditioning (A/C) compressor
rated at 346 Volts and a heat pump type remote air conditioning
system.
• A body electrical system rated at 12 Volts, negative chassis ground.
• Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) – dual stage frontal airbags,
front seat mounted side airbags, side curtain airbags, front seatbelt
pretensioners, and driver knee airbag.
2012 Model Prius Plug-in hybrid features:
• An electric vehicle charge cable rated at 120 Volts.
• An onboard battery charger with a 120 Volt /240 Volt AC input and
207.2 Volt DC output.
• A boost converter in the inverter/converter that boosts the available
voltage to the electric motor to 650 Volts.
• A high voltage Hybrid Vehicle (HV) Li-ion battery assembly rated
at 207.2 Volts.
• A high voltage motor driven Air Conditioning (A/C) compressor
rated at 207.2 Volts and remote air conditioning system.
• A body electrical system rated at 12 Volts, negative chassis ground.
• Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) – dual stage frontal airbags,
front seat mounted side airbags, side curtain airbags, front seatbelt
pretensioners, and driver knee airbag.
High voltage electrical safety remains an important factor in the
emergency handling of the Prius Plug-in Hybrid Synergy Drive. It is
important to recognize and understand the disabling procedures and
warnings throughout the guide.

F
-ii-
oreword (Continued)
Additional topics in the guide include:
The following indicates the key identification points for each model.
Make sure to identify the target vehicle using this and refer to the
corresponding rescue methods.
• Prius Plug-in hybrid identification.
•
Major Hybrid Synergy Drive component locations and descriptions.
•
Extrication, fire, recovery, and additional emergency response
information.
Key Identification Points:
•
Roadside assistance information.
The main difference is that the charge inlet door has been relocated
from the driver side front fender to the passenger side rear quarter
panel.
2012 Model Year Prius Plug-in Hybrid 2010 Model Year Prius Plug-in Hybrid
Charge Inlet Door
2010 Model
This guide is intended to assist emergency responders in the safe
handling of a Prius Plug-in hybrid vehicle during an incident.
NOTE:
Emergency Response Guides for Toyota hybrid and alternative fuel
vehicles may be viewed at http://techinfo.toyota.com.
2012 Model
Charge Inlet Door
Charge Inlet Door

-iii-
Table of Contents (2010 Model) Page
About the Prius Plug-in Hybrid 1
Prius Plug-in Hybrid Identification 2
Hybrid Synergy Drive Component Locations & Descriptions 5
Plug-in Charging System Component Locations & Descriptions 8
Smart Key System 9
Electronic Gearshift Selector 11
Hybrid Synergy Drive Operation 12
Hybrid Vehicle (HV) Battery Assembly 13
Plug-in Charging System 14
Remote Air Conditioning System 16
Low Voltage Battery 18
High Voltage Safety 19
Plug-in Charging Safety 20
SRS Airbags & Seat Belt Pretensioners 22
Emergency Response 24
Extrication 24
Fire 31
Overhaul 32
Recovery of Li-ion HV Battery Assembly 32
Spills 33
First Aid 33
Submersion 34
Table of Contents (2010 Model) Page
Roadside Assistance 35

-i-
Table of Contents (2012 Model) Page
About the Prius Plug-in Hybrid 39
Prius Plug-in Hybrid Identification 40
Hybrid Synergy Drive Component Locations & Descriptions 43
Plug-in Charging System Component Locations & Descriptions 46
Smart Key System 47
Electronic Gearshift Selector 49
Hybrid Synergy Drive Operation 50
Hybrid Vehicle (HV) Battery Assembly 51
Plug-in Charging System 52
Remote Air Conditioning System 54
Low Voltage Battery 55
High Voltage Safety 56
Plug-in Charging Safety 57
SRS Airbags & Seat Belt Pretensioners 59
Emergency Response 61
Extrication 61
Fire 68
Overhaul 69
Recovery of Li-ion HV Battery Assembly 69
Spills 70
First Aid 70
Submersion 71
Table of Contents (2012 Model) Page
Roadside Assistance 72
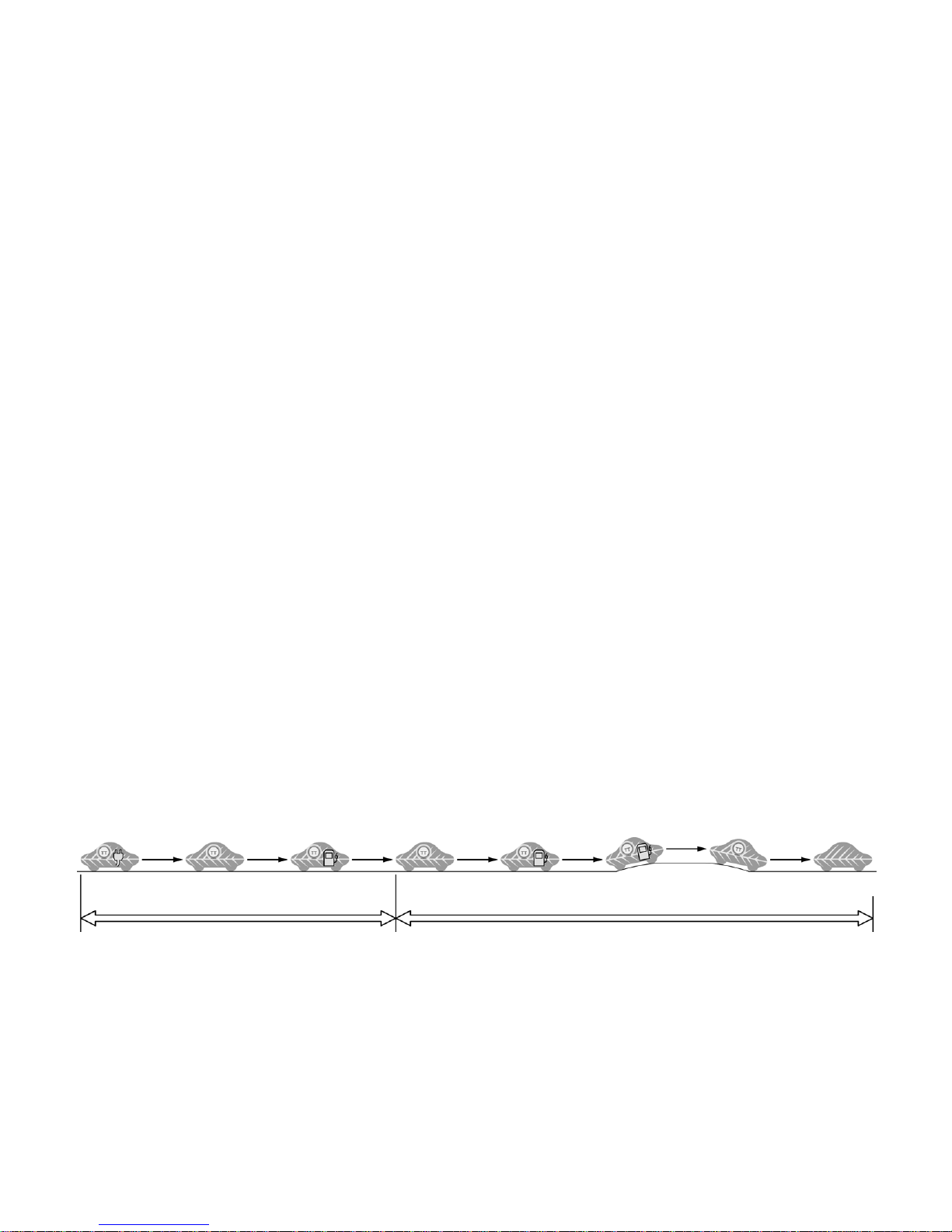
About the Prius Plug-in Hybrid (2010 Model)
The Prius Plug-in hybrid contains a gasoline engine, an electric motor,
and a newly developed large capacity Li-ion battery. It is the first
Toyota hybrid that allows the HV battery to be plugged-in and charged
by an external power source. Two power sources are stored on board
the vehicle:
When the HV battery is discharged the vehicle operates in Hybrid Vehicle
mode
1. Gasoline stored in the fuel tank for the gasoline engine.
2. Electricity stored in a large capacity externally chargeable high
voltage Hybrid Vehicle (HV) battery assembly for the electric
motor.
HV (Hybrid Vehicle) Mode:
During light acceleration at low speeds, the vehicle is powered by
the electric motor. The gasoline engine is shut off.
Depending on the driving conditions, one or both sources are used to
power the vehicle. The following illustration demonstrates how the
Prius Plug-in hybrid operates in various driving modes.
During normal driving, the vehicle is powered mainly by the
gasoline engine. The gasoline engine also powers the generator to
recharge the HV battery assembly and to drive the electric motor.
Plug-in EV (Electric Vehicle) Mode:
During full acceleration, such as climbing a hill, both the gasoline
engine and the electric motor power the vehicle.
Utilizing the charge cable assembly connected to a 120 Volt outlet,
the vehicle’s HV battery can be charged within 3 hours.
During deceleration, such as when braking, the vehicle regenerates
the kinetic energy from the front wheels to produce electricity that
recharges the HV battery assembly.
When the HV battery is sufficiently charged, the vehicle will
basically run on the power of the electric motor for approximately
13 miles.
While the vehicle is stopped, the gasoline engine and electric motor
are off, however the vehicle remains on and operational.
If the vehicle exceeds approximately 60 mph (100 km/h) or
accelerates suddenly when traveling in plug-in EV mode, the
gasoline engine and electric motor work together to power the
vehicle.
Normal Driving
-
1-
Plug-in charging
Electricity Electricity and gasoline Electricity and gasoline Electricity
Electricity and gasoline
(Additional electricity
extracted from batteries)
Charging batteries
Engine automatically stopped
Hard Acceleration
Starting Normal Driving Acceleration Deceleration Stopping Plug-in Charging
Exceeds
Approximately 60 mph (100 km/h)
Plug-in EV Mode HV (Hybrid Vehicle) Mode
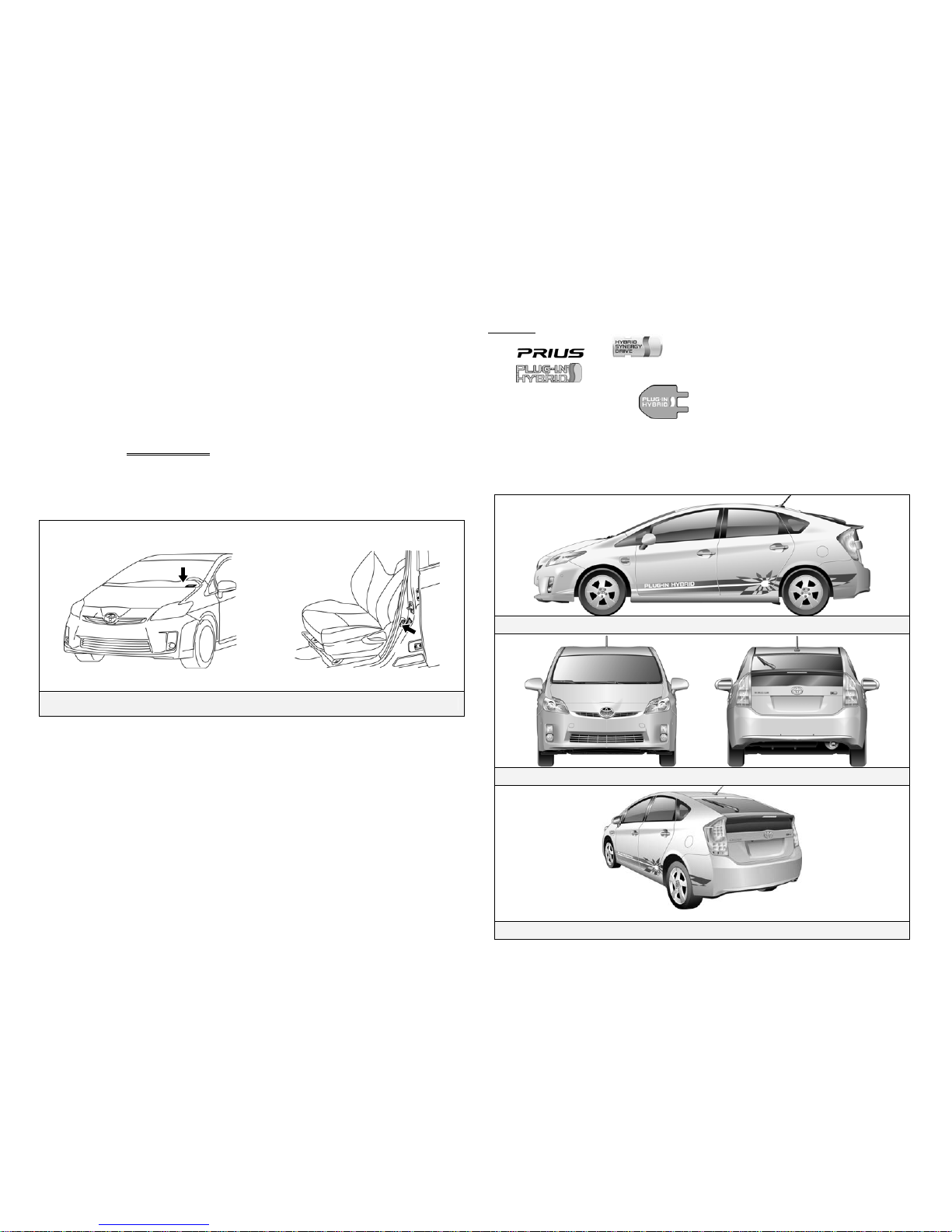
Prius Plug-in Hybrid Identification (2010 Model) Prius Plug-in Hybrid Identification (2010 Model)
-2-
In appearance, the 2010 model year Prius Plug-in hybrid is a 5-door
hatchback. Exterior, interior, and engine compartment illustrations are
provided to assist in identification.
In appearance, the 2010 model year Prius Plug-in hybrid is a 5-door
hatchback. Exterior, interior, and engine compartment illustrations are
provided to assist in identification.
The alphanumeric 17 character Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is
provided in the front windshield cowl and on the driver door pillar.
The alphanumeric 17 character Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) is
provided in the front windshield cowl and on the driver door pillar.
Example VIN: JTDKN3DPExample VIN: JTDKN3DPA82020211
A Prius Plug-in hybrid is identified by the first 8 alphanumeric characters
JTDKN3DP.
Driver Side Windshield and Driver Side B Pillar
Exterior
and logos on the hatch.
logo on the passenger side front fender.
Charge inlet door with logo, located on the driver side front
fender.
Plug-in Hybrid decals located on the sides of the vehicle.
Exterior Driver Side View
Exterior Front and Rear View
Exterior Rear and Driver Side View
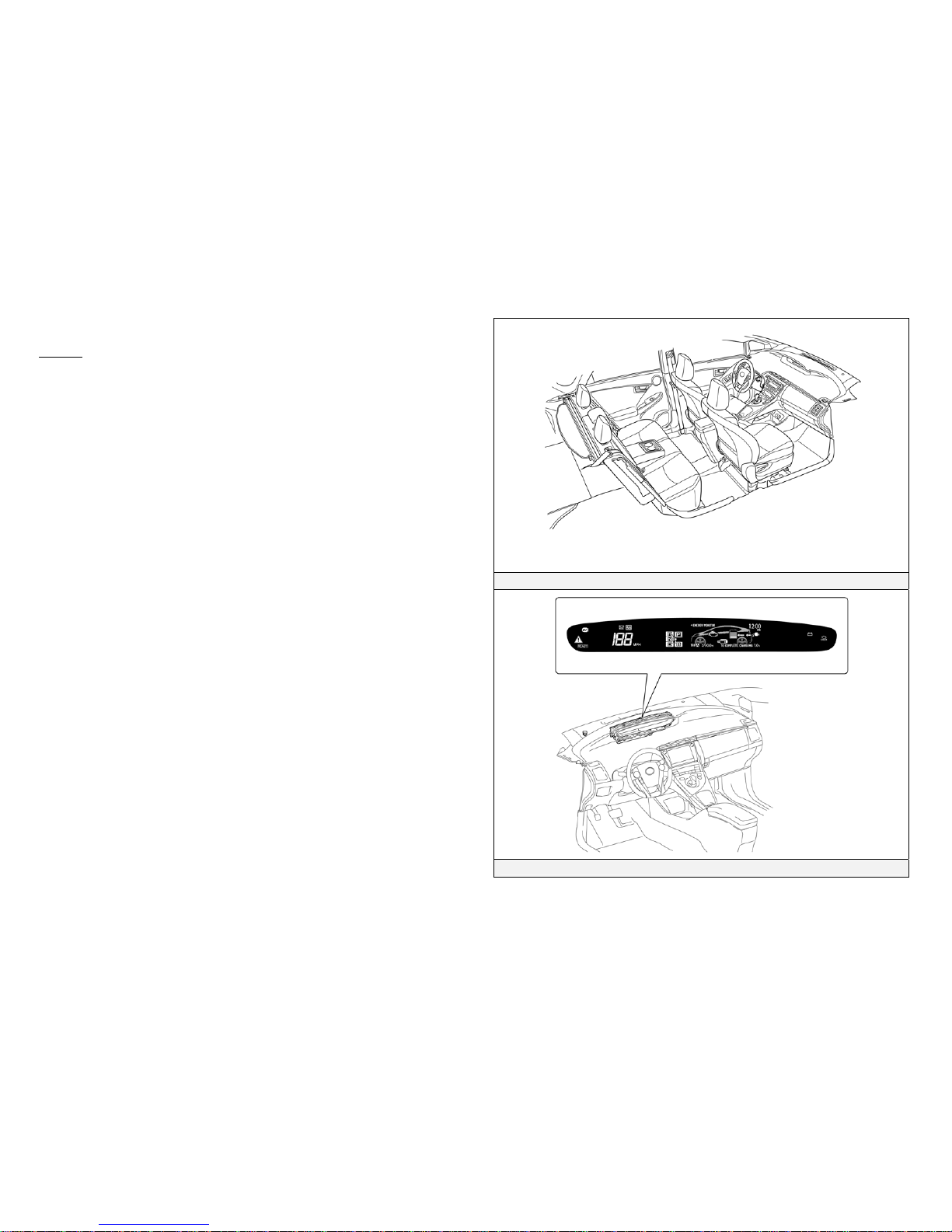
Prius Plug-in Hybrid Identification (2010 Model Continued)
-3-
Interior
Interior View
Instrument Cluster View
An instrument cluster (speedometer, READY light, shift position indicators,
warning lights) located in center of the dash and near the base of the
windshield.
A plug-in charge indicator light located on the upper dash near the driver
side windshield.
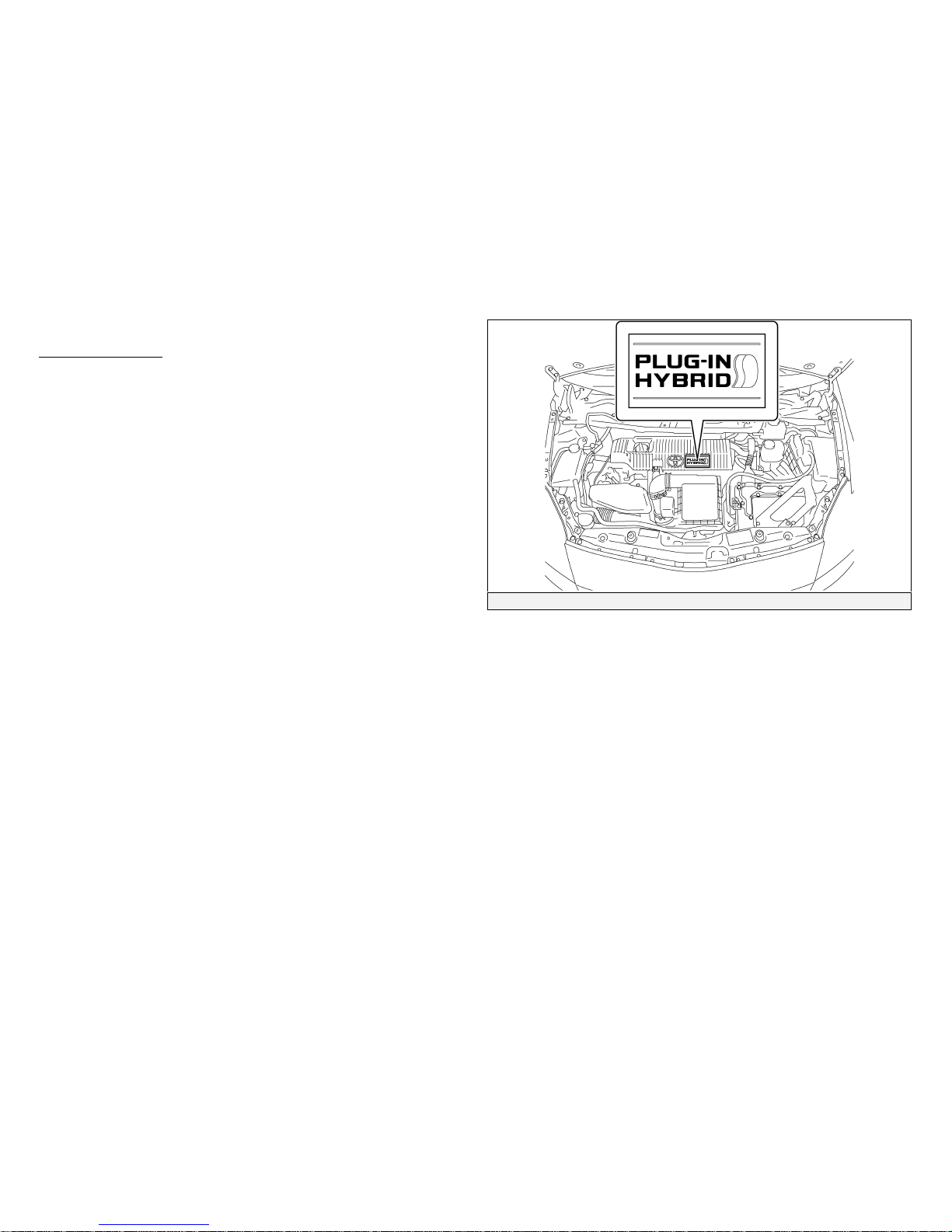
Prius Plug-in Hybrid Identification (2010 Model Continued)
Prius Plug-in Hybrid Identification (2010 Model Continued)
-4-
Engine CompartmentEngine Compartment
Engine Compartment View
1.8-liter aluminum alloy gasoline engine.
Logo on the plastic engine cover.
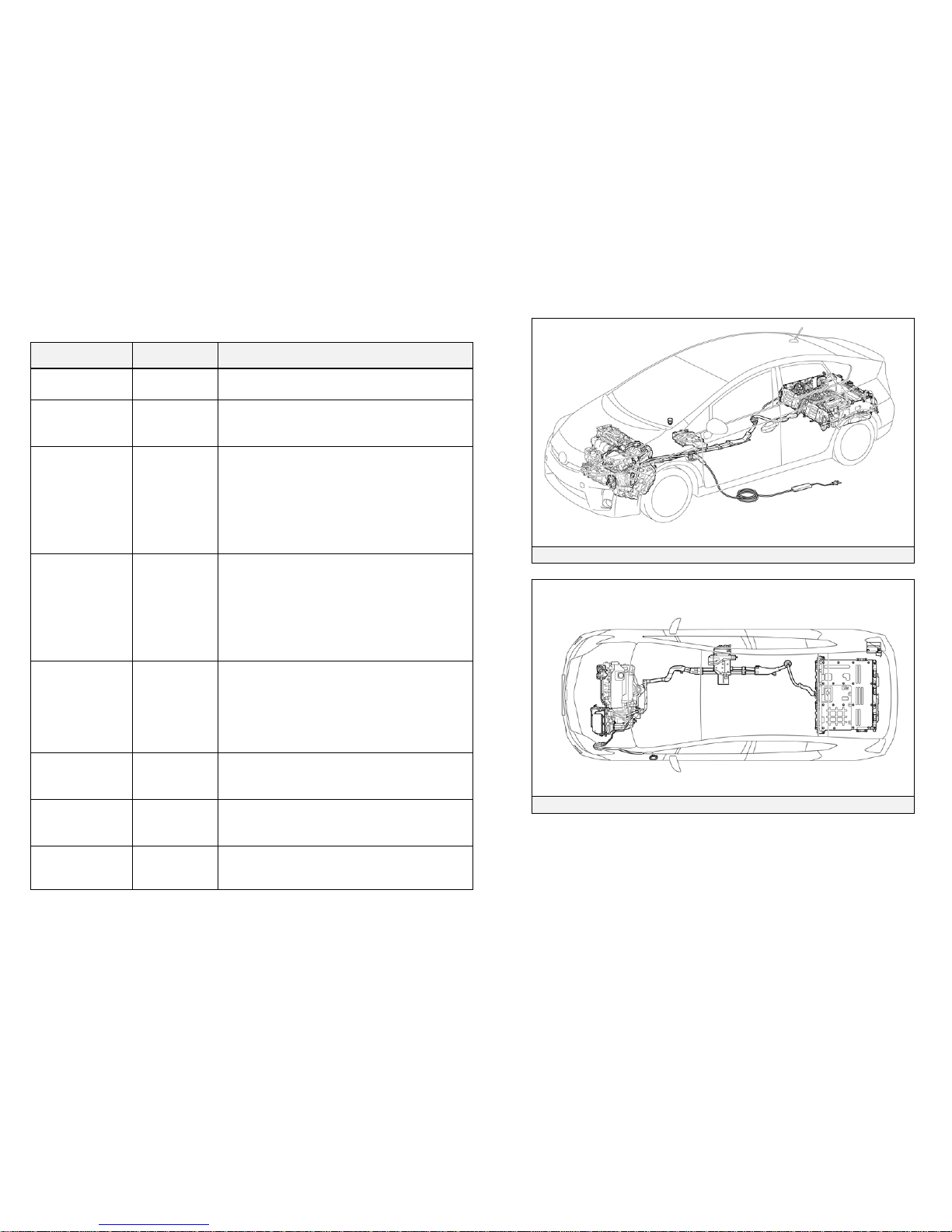
Hybrid Synergy Drive Component Locations &
Descriptions (2010 Model)
Hybrid Synergy Drive Component Locations &
Descriptions (2010 Model)
-5-
Component Location Description
12 Volt
Auxiliary Battery
Passenger Side
of Cargo Area
A lead-acid battery that supplies power to the
low voltage devices.
Hybrid Vehicle
(HV) Battery
Assembly
Cargo Area 346 Volt Lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery pack
consisting of 3.6 Volt cells connected in a
series-parallel circuit.
Power Cables Undercarriage
and Engine
Compartment
Orange colored power cables carry high
voltage Direct Current (DC) between the HV
battery assembly, inverter/converter, and A/C
compressor. These cables also carry 3-phase
Alternating Current (AC) between the
inverter/converter, electric motor, and
generator.
Inverter/
Converter
Engine
Compartment
Boosts and inverts the high voltage electricity
from the HV battery assembly to 3-phase AC
electricity that drives the electric motor. The
inverter/converter also converts AC
electricity from the electric generator and
electric motor (regenerative braking) to DC
that charges the HV battery assembly.
Gasoline
Engine
Engine
Compartment
Provides two functions:
1) Powers vehicle.
2) Powers generator to charge the HV battery
assembly.
The engine is started and stopped under
control of the vehicle computer.
Electric
Motor
Engine
Compartment
3-phase high voltage AC motor contained in
the front transaxle. It is used to power the
front wheels.
Electric
Generator
Engine
Compartment
3-phase high voltage AC generator that is
contained in the transaxle and charges the
HV battery assembly.
A/C Compressor
(with Inverter)
Engine
Compartment
3-phase high voltage AC electrically driven
motor compressor.
Hybrid Synergy Drive Components
Components (Top View) and High Voltage Power Cables
Hybrid Synergy Drive Component Locations &
Descriptions (2010 Model - Continued)
Hybrid Synergy Drive Component Locations &
Descriptions (2010 Model - Continued)
-6-
Component Location Description
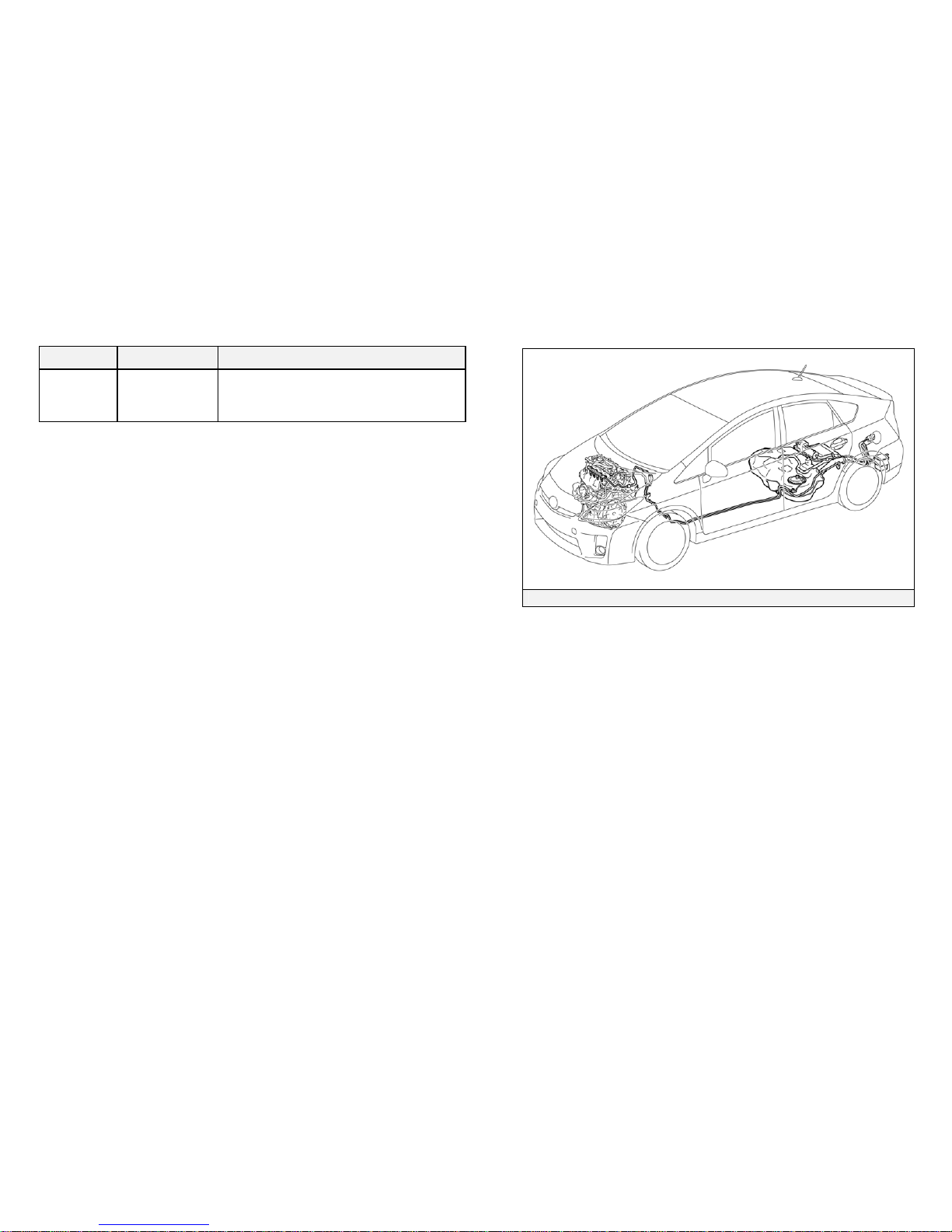
Fuel Tank
and Fuel Line
Undercarriage
and Center
The fuel tank provides gasoline via a fuel
line to the engine. The fuel line is routed
under the center of vehicle.
Fuel Tank and Fuel Line
Hybrid Synergy Drive Component Locations &
Descriptions (2010 Model - Continued)
Hybrid Synergy Drive Component Locations &
Descriptions (2010 Model - Continued)
Key Specifications:Key Specifications:
-7-
Gasoline Engine: 98 hp (73 kW), 1.8-liter Aluminum Alloy Engine
Electric Motor: 80 hp (60 kW), AC Motor
Transmission: Automatic Only (electrically controlled
continuously variable transaxle)
HV Battery Assembly: 346 Volt Sealed Li-ion
Battery
Curb Weight: 3,362 lbs/1,525 kg
Fuel Tank: 10.6 gals/40.0 liters
Frame Material: Steel Unibody
Body Material: Steel Panels except for Aluminum Hood and
Hatch
Seating Capacity: 5 passenger
Steel Unibody
Aluminum Hood
Aluminum Hatch
P
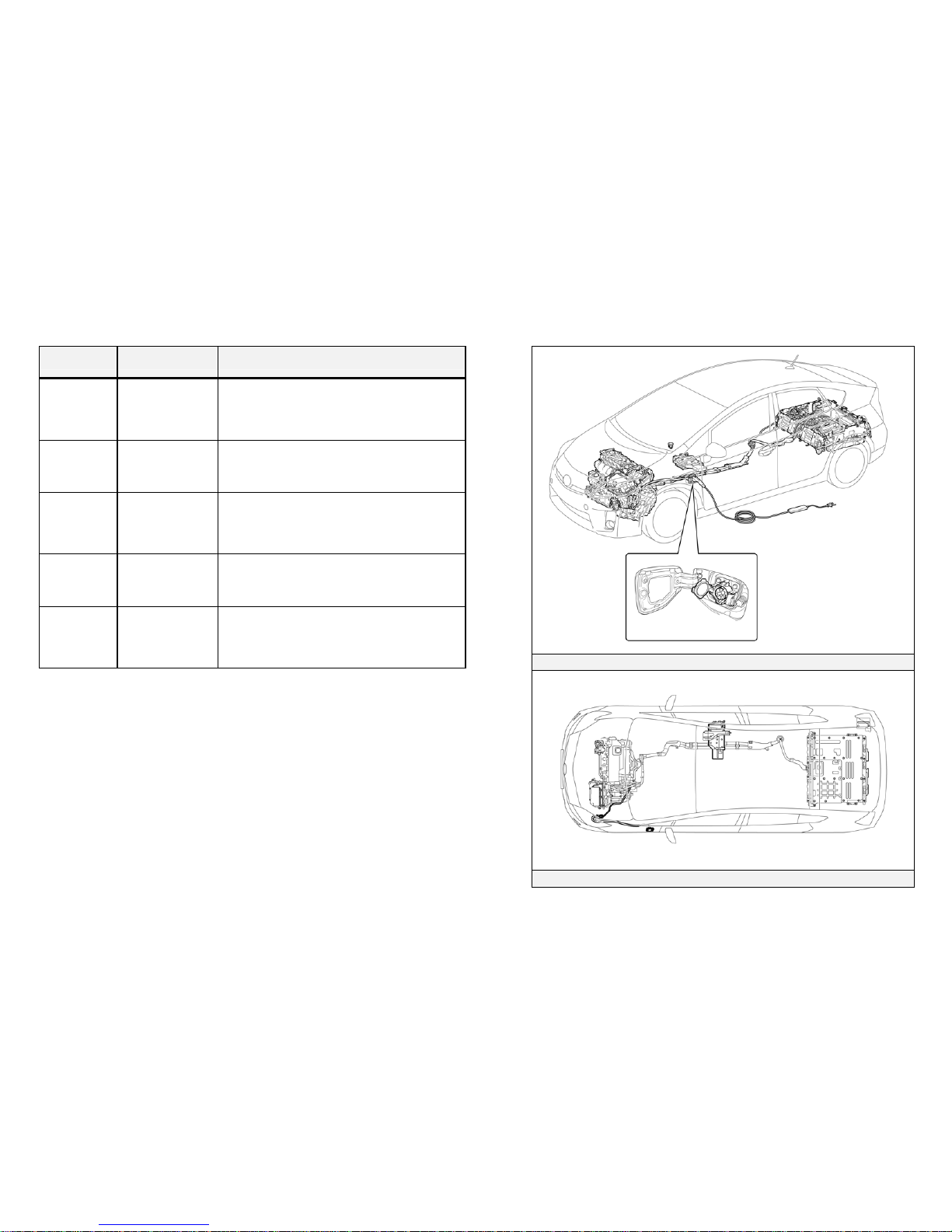
-8-
lug-in Charging System Component Locations &
Descriptions (2010 Model)
Component Location Description
Charge Inlet Driver Side Front
Fender
Connects to the charge cable assembly
charge connector. Supplies the electrical
power from an external power source to the
vehicle.
Power Cable
for Charging
Driver Side
behind front
fender
Power cable connecting the charge inlet and
charger assembly.
Charger
Assembly
Under Front
Passenger Seat
Boosts the AC power supplied from an
external power source and converts it to DC
to charge the HV battery assembly and
operate the A/C compressor.
Charge Cable
Assembly
Driver Side Front
Fender
Connects to the charge inlet and supplies
power from an external power source to the
vehicle.
Charge
Indicator
Upper Dash near
Driver Side
Windshield
Illuminates, flashes, or goes off to indicate
the plug-in charging status. Also
illuminates to indicate the operation of the
remote air conditioning system.
Plug-in Charging System Components
Components (Top View) and Charge Inlet Power Cables
S
-9-
mart Key System (2010 Model)
The Prius Plug-in hybrid smart key system consists of a smart key
transceiver that communicates bi-directionally, enabling the vehicle to
recognize the smart key in proximity to the vehicle. Once recognized,
the smart key will allow the user to lock and unlock the doors without
pushing smart key buttons, and start the vehicle without inserting it into
an ignition switch.
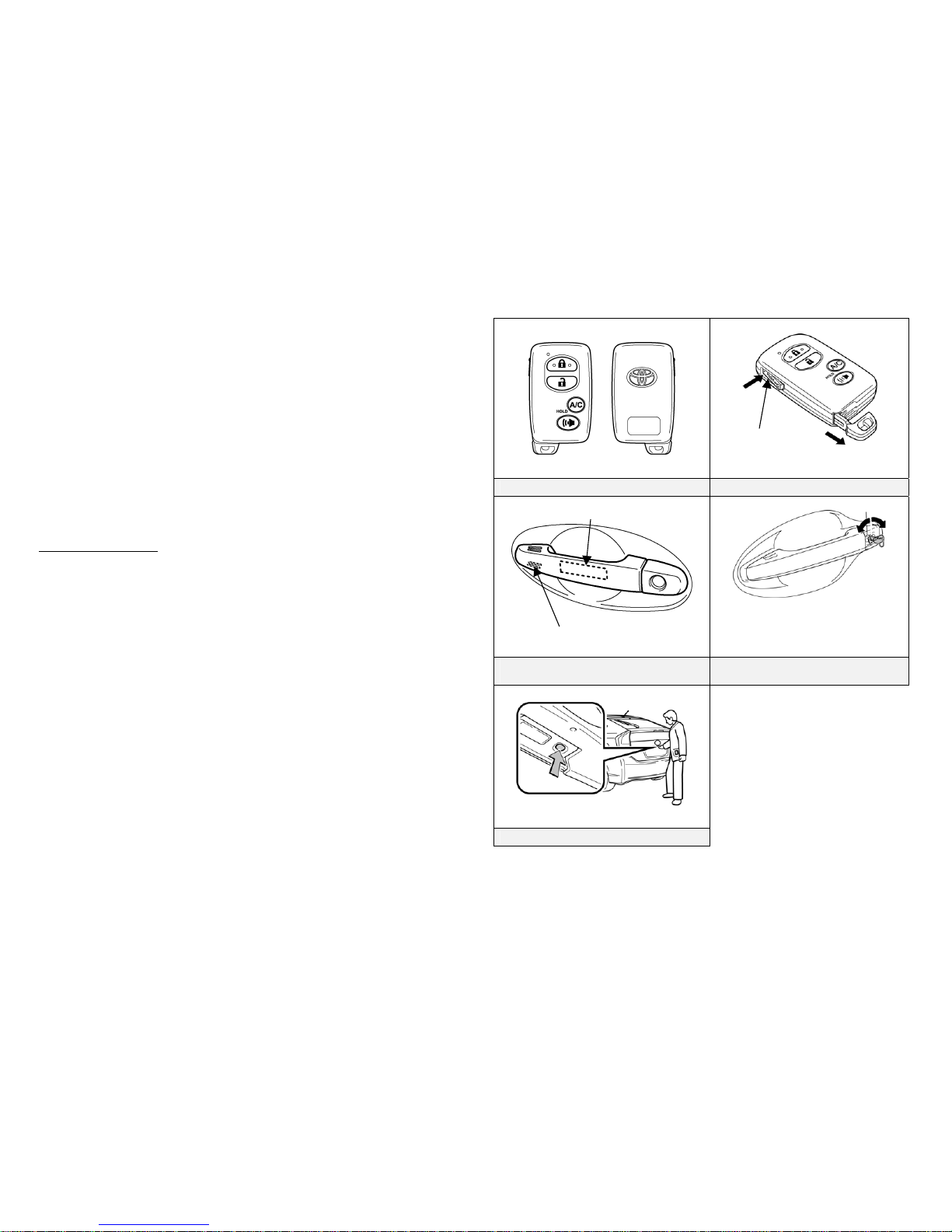
Smart key features:
•
Passive (remote) function to lock/unlock the doors and start the
vehicle.
•
Wireless transmitter buttons to lock/unlock all 5 doors.
•
Hidden metal cut key to lock/unlock the doors.
Door (Lock/Unlock)
There are several methods available to lock/unlock the doors.
• Pushing the smart key lock button will lock all doors including the hatch.
Pushing the smart key unlock button once unlocks the driver door, twice
unlocks all doors.
• Touching the sensor on the backside of the driver door exterior handle, with
the smart key in proximity to the vehicle, unlocks the driver door.
Touching the sensor on the backside of the front passenger door exterior
handle, with the smart key in proximity to the vehicle, unlocks all doors.
Touching the lock sensor on either front door, or the lock button for the
hatch will lock all doors.
• Inserting the hidden metal cut key in the driver door lock and turning
clockwise once unlocks the driver door, twice unlocks all doors. To lock
all doors turn the key counter clockwise once. Only the driver door
contains an exterior door lock for the metal cut key.
Smart Key (Fob) Hidden Metal Cut Key for Door Lock
Driver Door Unlock Touch Sensor and
Lock Touch Sensor
Front Driver Door Lock
Hatch Lock Button
Release Button
Unlock Touch Sensor
Use the Hidden Metal Cut Key
Lock Touch Sensor
S
-10-
mart Key System (2010 Model - Continued)
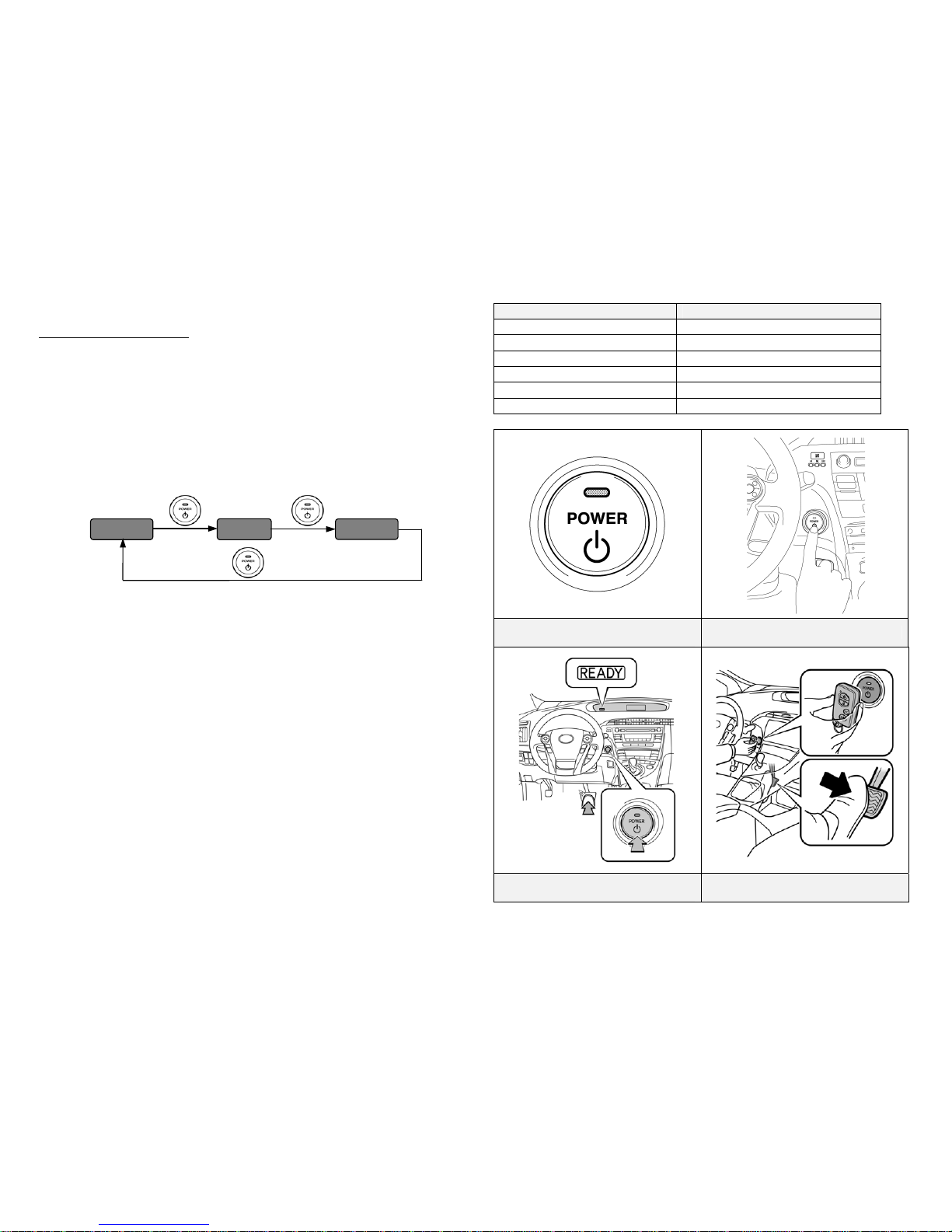
Vehicle Starting/Stopping
The smart key has replaced the conventional metal cut key, and the power
button with an integral status indicator light has replaced the ignition switch.
The smart key only needs to be in proximity to the vehicle to allow the system
to function.
• With the brake pedal released, the first push of the power button operates
the accessory mode, the second push operates the ignition-on mode, and the
third push turns the ignition off again.
Ignition Mode Sequence (brake pedal released):
• Starting the vehicle takes priority over all other ignition modes and is
accomplished by depressing the brake pedal and pushing the power button
once. To verify the vehicle has started, check that the power button status
indicator light is off and the READY light is illuminated in the instrument
cluster.
• If the internal smart key battery is dead, use the following method to start
the vehicle.
1. Touch the Toyota emblem side of the smart key to the power button.
2. Within the 5 seconds after the buzzer sounds, push the power button
with the brake pedal depressed (the READY light will illuminate).
• Once the vehicle has started and is on and operational (READY-ON), the
vehicle is shut off by bringing the vehicle to a complete stop and then
depressing the power button once.
• To shut off the vehicle before coming to a stop in an emergency, push and
hold down the power button for more than 3 seconds. This procedure may
be useful such as at an accident scene in which the READY indicator is on
and the drive wheels remain in motion.
Ignition Mode
Power Button Indicator Light
Off Off
Accessory Amber
Ignition-On Amber
Brake Pedal Depressed Green
Vehicle Started (READY-ON) Off
Malfunction Blinking Amber
Power Button with Integral Status
Indicator Light
Ignition Modes (Brake Pedal Released)
Starting Sequence
(Brake Pedal Depressed)
Smart Key Recognition
(When Smart Key Battery is Dead)
Accessory
Ignition-On
Vehicle Of
f
Button Push
Button Push
Button Push
-11-
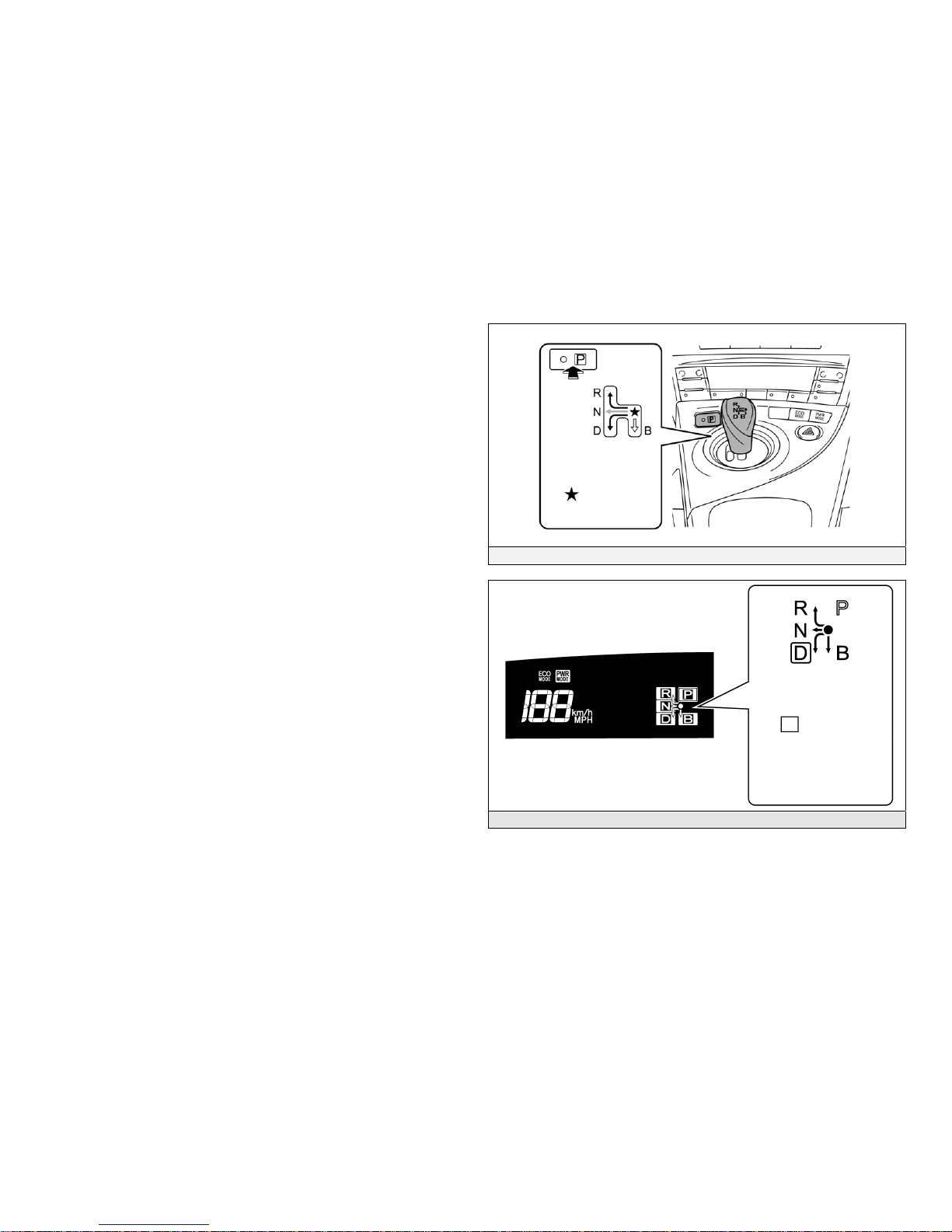
Electronic Shift Selector (2010 Model)
The Prius Plug-in hybrid electronic shift selector is a momentary select
shift-by-wire system that can be used to select reverse (R), neutral (N),
drive (D), or engine brake (B) states.
• These states may only be selected while the vehicle is on and operational
(READY-on), except for neutral (N) which may also be selected while in
the ignition-on mode. After R, N, D, or B is selected, the transaxle remains
in that state, identified on the instrument cluster, but the shift selector
returns to the home position. To select neutral (N), it is necessary to hold
the shift selector in the N position for approximately 0.5 seconds.
• Unlike a conventional vehicle, the electronic shift selector does not contain
a park (P) position. Instead, a separate P position switch located above the
shift selector selects park (P).
• When the vehicle is stopped, regardless of shift state, the electromechanical parking lock pawl is engaged to lock the transaxle into park (P)
by either pressing the P position switch or pressing the power button to shut
off the vehicle.
• Being electronic, the shift selector and park (P) systems depend on the low
voltage 12 Volt auxiliary battery for power. If the 12 Volt auxiliary battery
is discharged or disconnected, the vehicle cannot be started and cannot be
shifted into or out of park (P). There is no manual override except to
reconnect the auxiliary battery or jump start the vehicle, refer to Jump
Starting on page 38.
Electronic Shift Selector and P Position Switch
Home
Position
Instrument Cluster Shift State Indicator
Indicates
Gear Positio
n
H
-12-
ybrid Synergy Drive Operation (2010 Model)
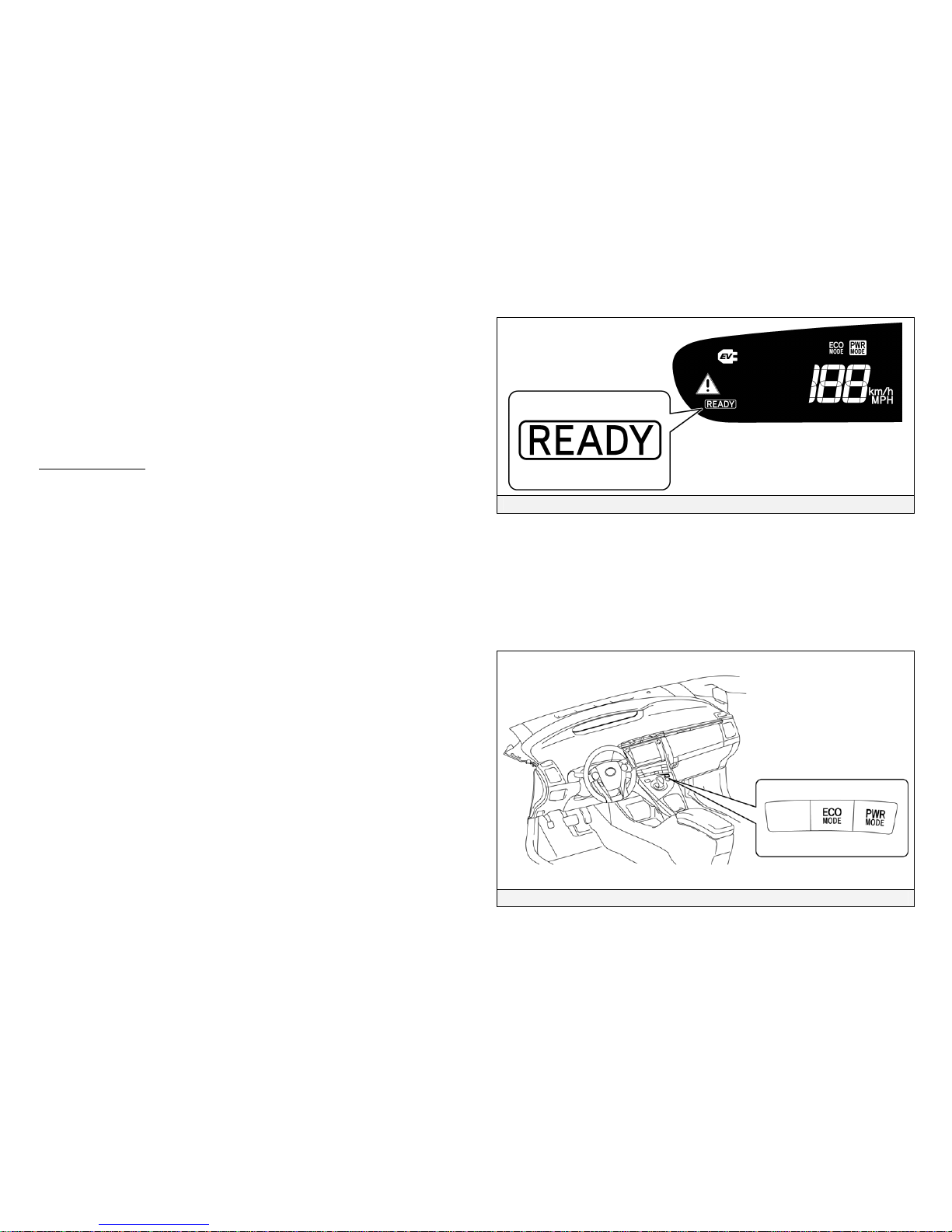
Once the READY indicator is illuminated in the instrument cluster, the
vehicle may be driven. However, the gasoline engine does not idle like a
typical automobile and will start and stop automatically. It is important
to recognize and understand the READY indicator provided in the
instrument cluster. When lit, it informs the driver that the vehicle is on
and operational even though the gasoline engine may be off and the
engine compartment is silent.
Vehicle Operation
• With the Prius Plug-in hybrid, the gasoline engine may stop and start at any
time while the READY indicator is on.
• Never assume that the vehicle is shut off just because the engine is off.
Always look for the READY indicator status. The vehicle is shut off when
the READY indicator and instrument cluster lights are off.
• The vehicle may be powered by:
1. The electric motor only.
2. A combination of both the electric motor and the gasoline engine.
• The vehicle computer determines the mode in which the vehicle operates in
order to improve fuel economy and reduce emissions. The Prius Plug-in
hybrid features plug-in EV (Electric Vehicle) mode, a mode that is
automatically selected when the HV battery is charged using an external
power source. Power and ECO (Economy) modes are driver selectable.
1. ECO Mode: When activated, this mode helps enhance fuel
economy on trips that involve frequent braking and acceleration.
2. Power Mode: Optimizes acceleration feel by increasing the power
output more quickly at the beginning of accelerator pedal
operation.
Instrument Cluster READY Indicator
Economy Drive Mode Switch/Power Mode Switch
H
-13-
ybrid Vehicle (HV) Battery Assembly (2010 Model)
The Prius Plug-in hybrid features a large capacity high voltage Hybrid
Vehicle (HV) battery assembly that contains newly developed sealed
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery cells.
HV Battery Assembly
• The HV battery assembly is enclosed in a metal case and is rigidly mounted
in the lower part of the cargo area behind the rear seat. The metal case is
isolated from high voltage and concealed by a carpeted panel in the cabin
area.
• The HV battery assembly consists of 3.6 Volt Li-ion battery cells connected
in series-parallel circuit to produce approximately 346 Volts. Each Li-ion
battery cell is non-spillable and contained in a sealed metal case.
• The electrolyte used in the Li-ion battery cells is a flammable organic
electrolyte. The electrolyte is absorbed into the battery cell separator and
will not normally leak, even in a collision.
Components Powered by the HV Battery Assembly
HV Battery Assembly Recovery
• If recovery of the HV battery assembly is necessary, please contact:
United States: (800) 331-4331
Canada: (888) TOYOTA 8 [(888) 869-6828]
HV Battery Assembly
HV Battery Assembly
Battery assembly voltage
346 V
Number of Li-ion battery cells in the battery
96 cells
Li-ion battery cell voltage
3.6 V
Li-ion battery cell dimensions
4.42 x 4.35 x 0.56 in.
(112.2 x 110.6 x 14.1 mm)
Li-ion cell weight
0.54 lbs (245 g)
Li-ion battery assembly dimensions
32.4 x 38.1 x 14.9 in.
(822.4 x 967.8 x 378.4 mm)
Li-ion battery assembly weight
333 lbs (151.1 kg)
•
Electric Motor
•
Inverter/Converter
• Power Cables • A/C Compressor
• Electric Generator
Pl
-14-
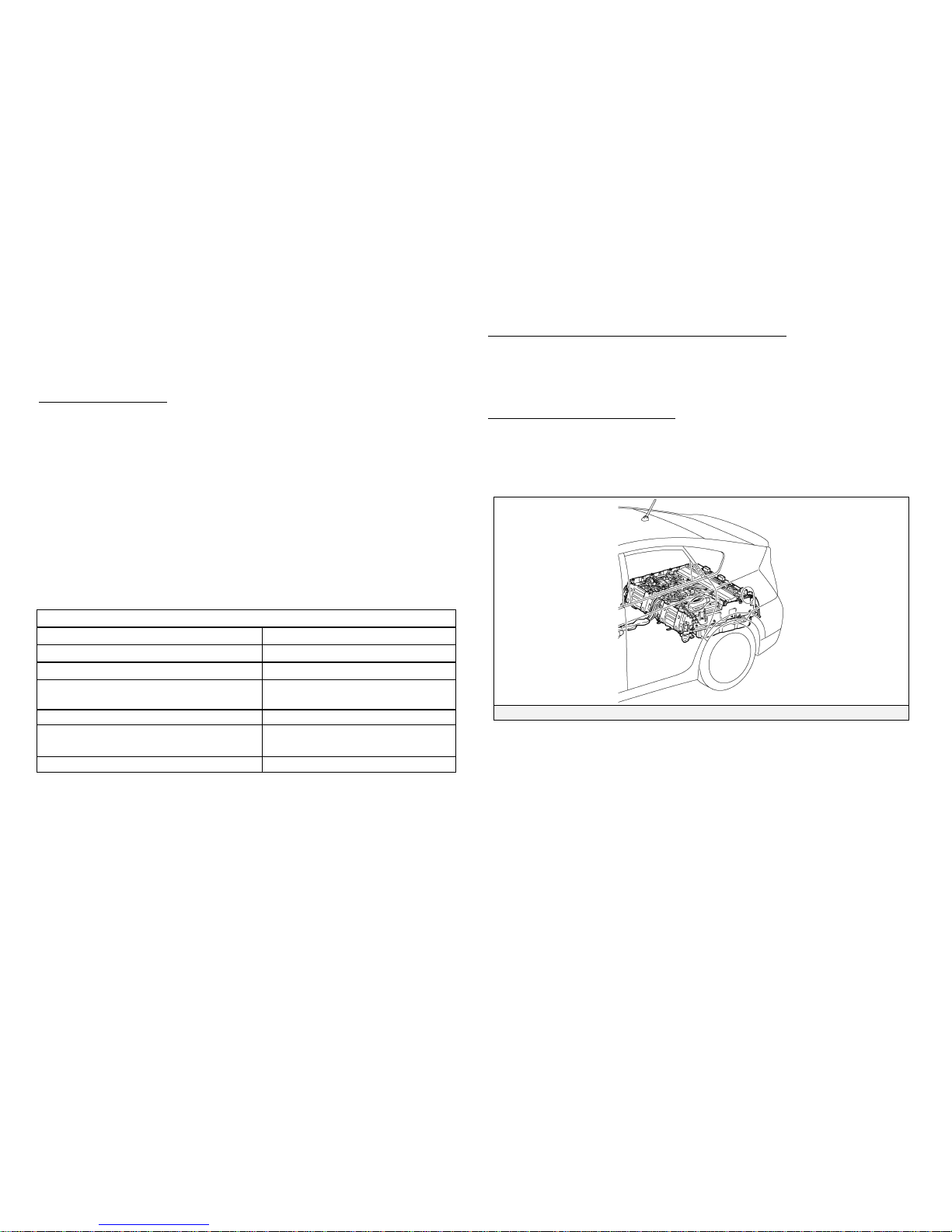
ug-in Charging System (2010 Model)
The plug-in charging system uses an on-board charger to convert AC power
supplied via the charge cable assembly to DC power that can be used to charge
the HV battery assembly. The charging system uses refined charging control to
ensure battery durability and prevent fires due to overcharging.
The utility power supplied by the charge cable assembly is converted by the
onboard charger assembly to the approximately 346 Volts DC used to charge
the HV battery assembly.
Prius Plug-in hybrid vehicles for North America are supplied with a charge
cable assembly designed to allow charging from a 120 Volt AC NEMA 5-15R
receptacle. The maximum current flow during charging is 12 A.
NOTE:
The Prius Plug-in hybrid is compatible with aftermarket chargers or Electric
Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) available from different manufacturers
other than Toyota. Some EVSE’s are available with 240 Volt input for quicker
charging.
Safety Concerns
Since the operation of the plug-in charging system allows high voltage
electrical flow when the vehicle is shut off, it is important to recognize how the
system is activated, deactivated, and disabled.
System Activation:
The following steps provide a simplified explanation on how to charge the
vehicle.
1. Confirm that the vehicle is off and in park (P).
2. Connect the charge cable assembly to a suitable 120 Volt wall
receptacle.
3. Confirm the presence of power, and test the CCID (Charging Circuit
Interrupter Device).
4. Connect the charge cable assembly to the vehicle charge inlet
connector.
5. Confirm that the vehicle’s charge indicator illuminates.
When charging, the high voltage cables are energized. Utility electricity flows
from the charge inlet, its voltage is then boosted and it is provided to the HV
battery assembly and air conditioning compressor. Charging normally
completes within 3 hours and will stop automatically.
Charge Cable Assembly and Charge
Indicator
CHARGE Indicator, TEST Button
and RESET Button
Plug-in Charging System Operation (READY Indicator Off)
Charge Indicator
DC Flow
(Charger to
Battery)
AC Flow
(Inlet to Charger)
HV Battery Assembly
Charge Inlet
-15-
Plug-in Charging System (2010 Model - Continued)
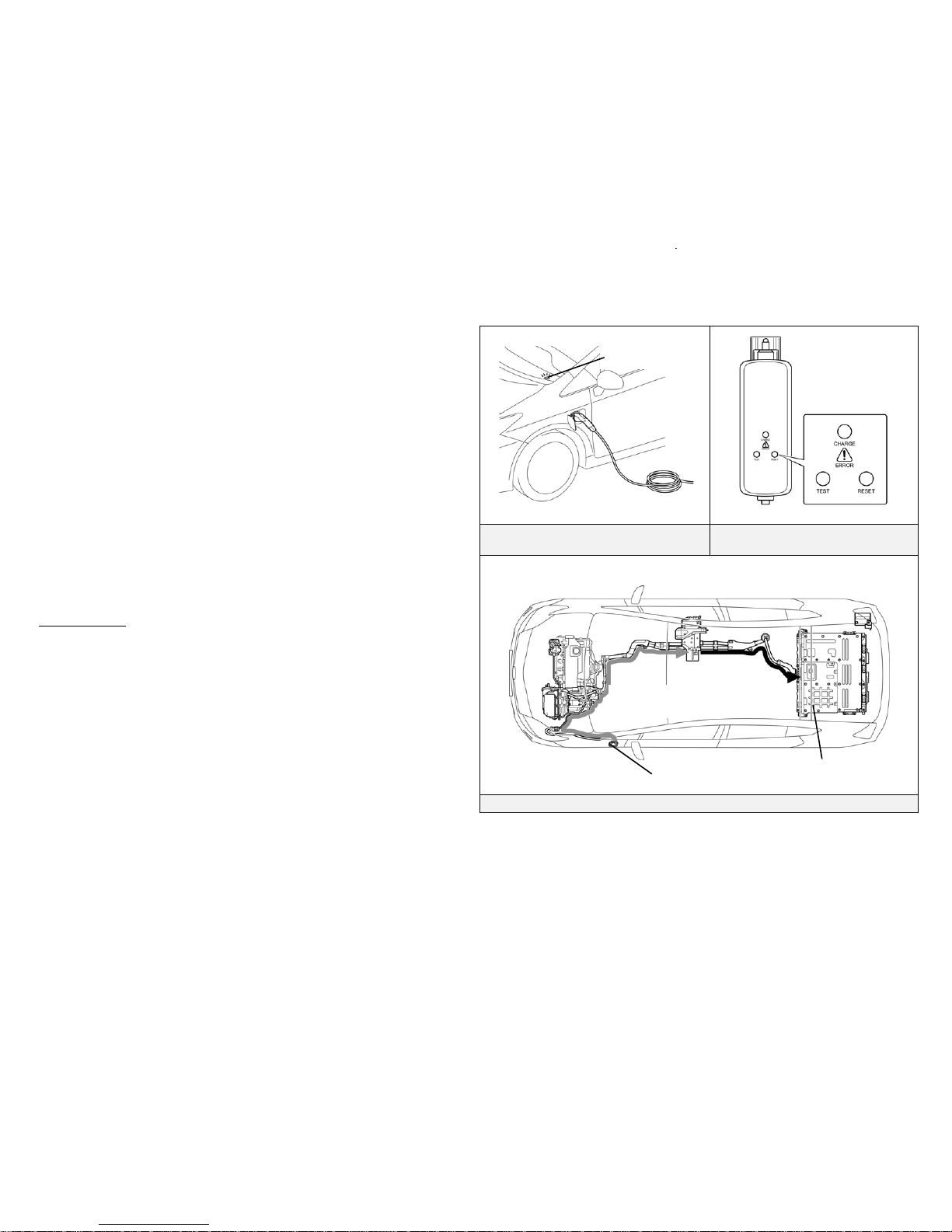
System Deactivation:
The following steps explain how to stop charging.
1. Disconnect the charge cable assembly connector from the vehicle.
To disconnect it, push the orange lock release button on the top of
the connector and pull it away from the vehicle.
2. Close the charge inlet cap and charge inlet door.
3. Disconnect the plug of the charge cable assembly from the
electrical outlet.
Disconnect Charge Cable Connector
Close Charge Inlet Cap and Charge
Inlet Door
Disconnect Plug Remove Battery Cover
Remove Tire Repair Kit and Foam Insert
When the charging system is deactivated, high voltage cables are deenergized and the high voltage electrical flow stops in the charge cable
assembly and vehicle.
WARNING:
The high voltage system, including the charging system, may remain
powered for up to 10 minutes after the vehicle is shut off, disabled, or
charging stops. To prevent serious injury or death from severe burns or
electric shock, avoid touching, cutting, or breaching any orange high
voltage power cable or high voltage component.
System Disabling:
To disable the charging system, disconnect the 12 Volt auxiliary battery
after performing the above deactivation procedure.
12 Volt Auxiliary Battery
-16-
Remote Air Conditioning System (2010 Model)
The following points can be used to confirm that the remote air
conditioning system is operating:
The remote air conditioning system is provided to enhance occupant comfort by
heating or cooling the vehicle interior while the vehicle is shut off and the
charge cable assembly is plugged in.
The remote air conditioning system is similar to a remote engine start system
used in a conventional gasoline vehicle to precondition the vehicle interior
while the vehicle is parked. Unlike a conventional gasoline vehicle, the Prius
Plug-in hybrid does not start the gasoline engine. Instead, to heat or cool the
vehicle interior, it utilizes power from the charge cable assembly to operate the
high voltage air conditioning compressor. The compressor operates in a
conventional manner for cooling, and it operates as a heat pump for heating.
The system can only be activated remotely by pushing the smart key A/C
button and will operate for up to 30 minutes when certain conditions are met.
Safety Concerns
Since the operation of the remote air conditioning system allows high voltage
electrical flow, it is important to recognize how the system is activated,
deactivated, and disabled.
System Activation:
When the remote air conditioning system is activated, the high voltage cables
are energized. Household electricity flows from the charge inlet, its voltage is
then boosted and it is provided to the HV battery assembly and air conditioning
compressor. The system can operate when all of the following operating
conditions are met:
• The charge cable assembly is connected.
• The doors and hood are closed.
• The vehicle Power switch is off.
• The brake pedal is not being depressed.
• The shift position is park (P).
• The charge level of the HV battery assembly is above a specified level.
• There is a difference between the set temperature and actual cabin
temperature.
• Air is flowing from the interior vehicle vents, and blower fan noise or
compressor noise is heard.
• The charge cable assembly is connected and the charge indicator is
illuminated.
• The instrument cluster lights are on, the READY indicator is off, and
all of the conditions in the preceding list are met.
Charge Indicator
Charge Cable Assembly and Charge
Indicator
Remote Air Conditioning System A/C
Button
Remote Air Conditioning System Operation (READY Indicator Off)
A/C Button
Charge Cable
Assembly
12 Volt Auxiliary
Battery
Air Conditioning
Compressor
Charger Assembly
DC Flow
DC Flow
AC Flow
HV Battery Assembly
Charge Inlet
-17-
Remote Air Conditioning System (2010 Model -Continued)
System Deactivation:
When the system is deactivated, the A/C system stops. The system is
deactivated when any one of the following conditions occurs:
• When the system has operated for more than about 30 minutes.
• When the vehicle interior nears the set temperature.
• When a door is opened, the hood is opened, or the brake pedal is
depressed.
• When the smart key A/C button is pushed twice within 3 seconds.
• When the operating conditions are not met.
NOTE:
• It is not possible to operate the remote A/C system and perform plug in
charging of the HV battery assembly at the same time. If plug in
charging is being performed and the remote A/C system is turned on,
plug in charging will stop.
• Plug in charging will not resume after the remote A/C system
deactivates.
WARNING:
The high voltage system, including the charging system, may remain powered
for up to 10 minutes after the vehicle is shut off, disabled, charging stops, or the
remote A/C system stops. To prevent serious injury or death from severe burns
or electric shock, avoid touching, cutting, or breaching any orange high
voltage power cable or high voltage component.
System Disabling:
Operation of the remote air conditioning system can be disabled by
disconnecting the charge cable assembly (see page 15 for illustration). Perform
the following steps to remove the charge cable assembly.
1. Disconnect the charge cable assembly connector from the vehicle.
To disconnect it, push the orange lock release button on the top of
the connector and pull it away from the vehicle.
2. Close the charge inlet cap and charge inlet door.
3. Disconnect the plug of the charge cable assembly from the
electrical outlet.
-18-
Low Voltage Battery (2010 Model)
Auxiliary Battery
• The Prius Plug-in hybrid contains a sealed lead-acid 12 Volt battery. The
12 Volt auxiliary battery powers the vehicle’s electrical system similar to a
conventional vehicle. As with conventional vehicles, the negative terminal
of the auxiliary battery is grounded to the metal chassis of the vehicle.
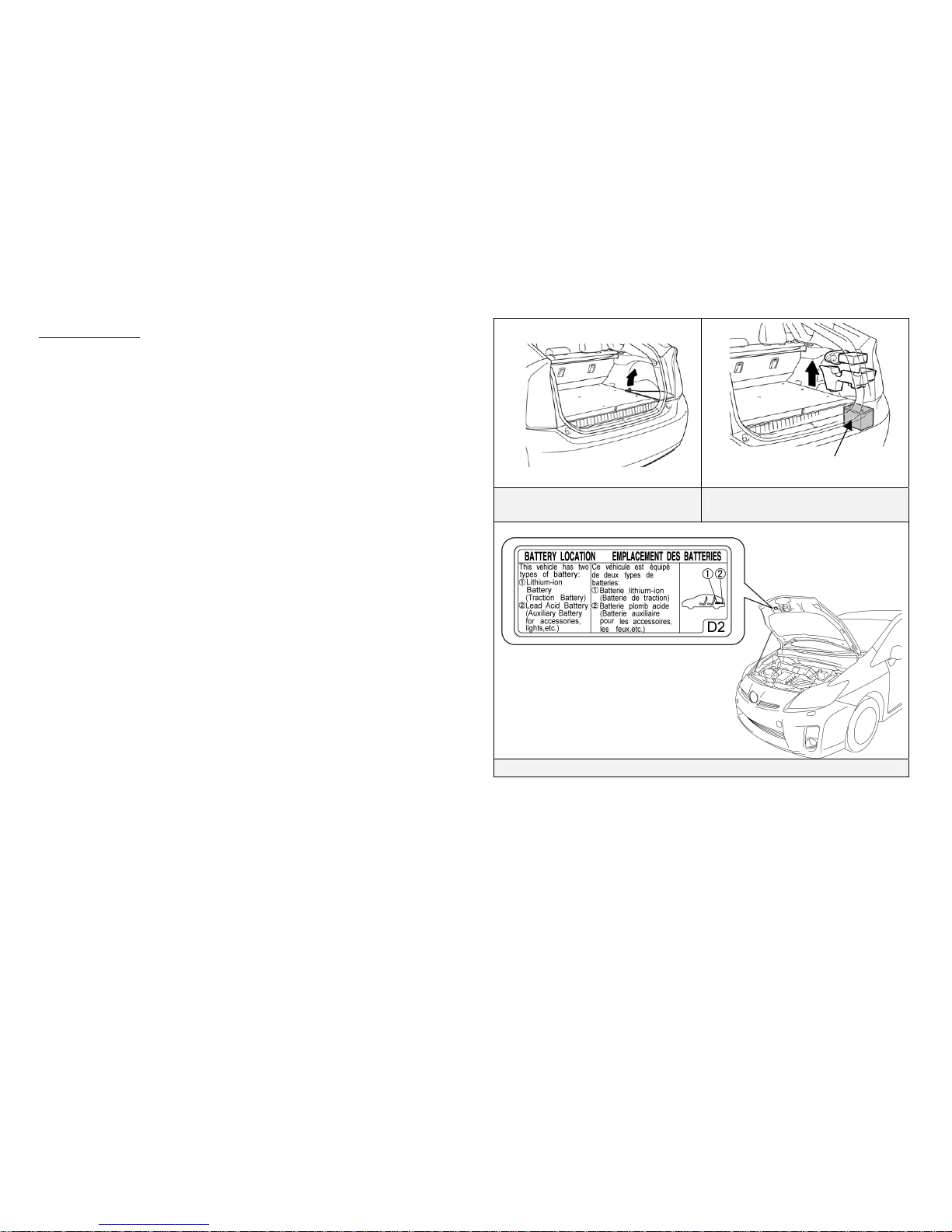
• The auxiliary battery is located in the cargo area. It is concealed by a fabric
cover, tire repair kit, and foam insert on the passenger side in the rear
quarter panel well.
NOTE:
An under hood label shows the location of the HV battery assembly
(traction battery) and 12 Volt auxiliary battery.
Remove Auxiliary Battery Cover
Remove Tire Repair Kit and Foam
Insert
Battery Location Label
12 Volt Auxiliary Battery

H
-19-
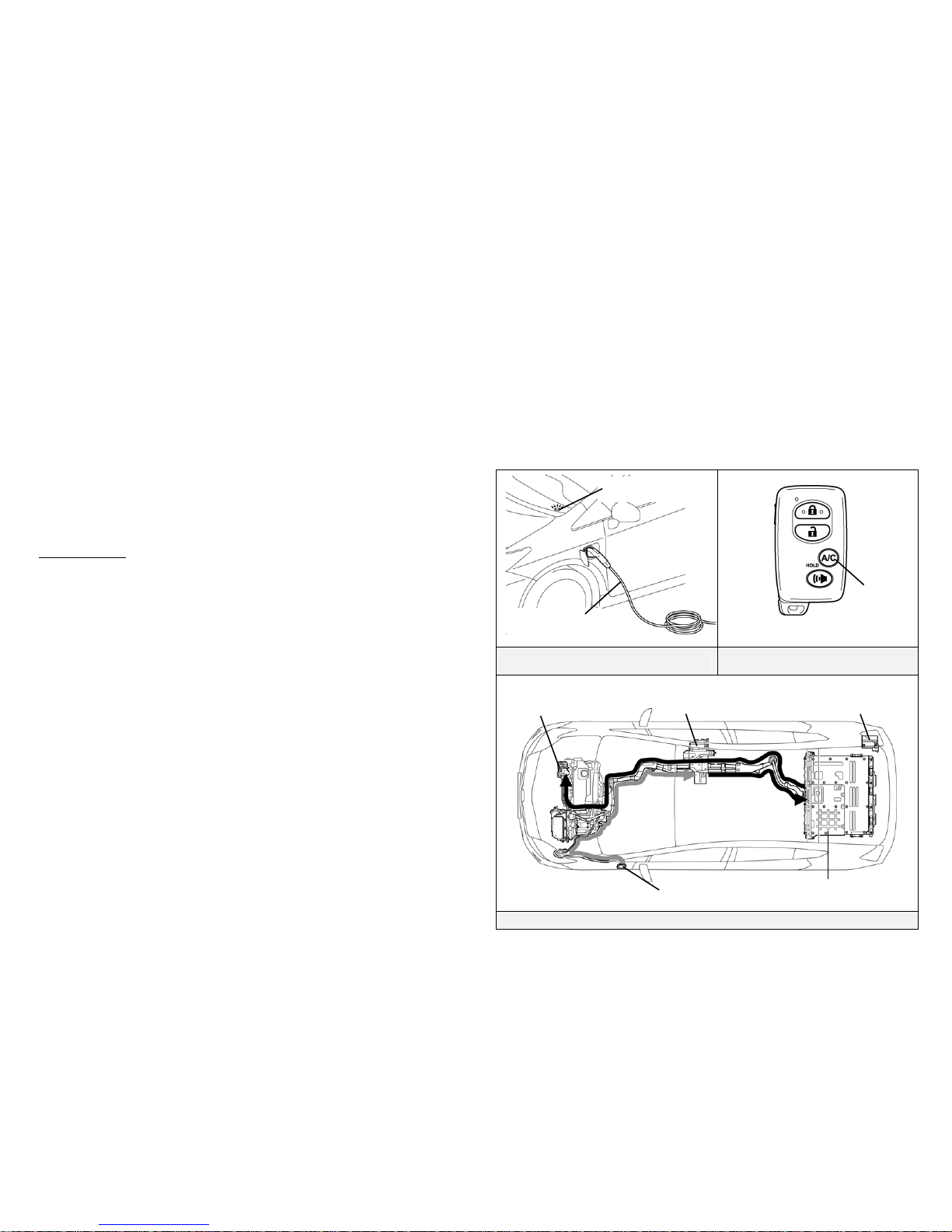
igh Voltage Safety (2010 Model)
The HV battery assembly powers the high voltage electrical system with DC
electricity. Positive and negative orange colored high voltage power cables are
routed from the HV battery assembly, under the vehicle floor pan, to the
inverter/converter. The inverter/converter contains a circuit that boosts the HV
battery voltage from 346 to 650 Volts DC. The inverter/converter creates 3phase AC to power the motor. Power cables are routed from the
inverter/converter to each high voltage motor (electric motor, electric generator,
and A/C compressor). The following systems are intended to help keep
occupants in the vehicle and emergency responders safe from high voltage
electricity:
High Voltage Safety System
• High voltage fuses provide short circuit protection in the HV battery
assembly.
• Positive and negative high voltage power cables connected to the HV
battery assembly are controlled by 12 Volt normally open relays . When
the vehicle is shut off and not charging, the relays stop electrical flow from
leaving the HV battery assembly.
WARNING:
The high voltage system, including the charging system, may remain
powered for up to 10 minutes after the vehicle is shut off, disabled, or
charging stops. To prevent serious injury or death from severe burns
or electric shock, avoid touching, cutting, or breaching any orange
high voltage power cable or high voltage component.
• Both positive and negative power cables are insulated from the metal
body. High voltage electricity flows through these cables and not through
the metal vehicle body. The metal vehicle body is safe to touch because it
is insulated from the high voltage components.
• A ground fault monitor continuously monitors for high voltage leakage
to the metal chassis while the vehicle is running. If a malfunction is
detected, the hybrid vehicle computer will illuminate the master warning
light
in the instrument cluster and indicate “Check Hybrid System” on
the multi-information display.
High Voltage Safety System – Vehicle Shut Off (READY-OFF)
High Voltage Safety System – Vehicle On and Operational (READY-ON)
Hybrid Vehicle Computer
00
Volt DC
12 Volt
Auxiliary
Battery
A/C
Compressor
Electric
Generator
Inverter/
Converter
00
Electric
Motor
Volt DC
00
Volt AC Volt DC
AC
00
3-Phase
Battery Charger
Assembly
HV Battery Assembly
Hybrid Vehicle Computer
346
Volt DC
12 Volt
Auxiliary
Battery
A/C
Compressor
Electric
Generator
Inverter/
Converter
HV Battery Assembly
AC
3-Phase
Electric
Moto
r
Volt DC
346
Volt AC
Volt AC
Volt DC
AC
00
Battery Charger
Assembly
00
3-Phase
 Loading...
Loading...