Page 1

SERVICE MANUAL
DOCUMENT CREATED IN JAPAN, Nov., 2004
LCD TELEVISION AND DVD
FILE NO. 810-200450
COMBINATION
VIDEO PLAYER
SD-P7000
RMT CODE
POWER
1 2
SET UP SLEEP DIMMER E.A.M
MEMORY REPEAT REPEAT A-B CLEAR
MONO/
DISPLAY CAP/TEXT
STEREO/SAP
RANDOM
AUDIO
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
+10
100 0 T
TOP MENU MENU
ENTER
SKIP
VOLUME CHANNEL
MUTE
+
PLAY
-
REW PAUSE FWD
SLOW REW
STOP SLOW FWD
ZOOM ANGLE SUB TITLE RETURN
INPUT
SELECT
PICTURE
SKIP
Page 2

- 2 -
CONTENTS
CONTENTS .............................................................................................. 2
PRODUCT SAFETY ..................................................................................3
SPECIFICATION........................................................................................6
TIMING CHART........................................................................................11
REMOTE CONTROL ...............................................................................12
DISASSEMBLY........................................................................................13
TROUBLE SHOOTING............................................................................15
BLOCK DIAGRAM...................................................................................21
WIRING DIAGRAM..................................................................................23
EXPLODED VIEW .................................................................................. 24
EXPLODED VIEW PARTS LIST..............................................................25
REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST ............................................................... 26
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS .......................................................................40
Page 3
- 3 -
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
Many electrical and mechanical parts in this chassis have special safety-related characteristics. These parts are identified by in the
Schematic Diagram and Replacement Parts List.
It is essential that these special safety parts should be replaced with the same components as recommended in this manual to prevent
X-RADIATION, Shock, Fire, or other Hazards.
Do not modify the original design without permission of manufacturer.
General Guidance
An isolation Transformer should always be used during the
servicing of a receiver whose chassis is not isolated from the AC
power line. Use a transformer of adequate power rating as this
protects the technician from accidents resulting in personal injury
from electrical shocks.
It will also protect the receiver and it's components from being
damaged by accidental shorts of the circuitry that may be
inadvertently introduced during the service operation.
If any fuse (or Fusible Resistor) in this TV receiver is blown,
replace it with the specified.
When replacing a high wattage resistor (Oxide Metal Film Resistor,
over 1W), keep the resistor 10mm away from PCB.
Keep wires away from high voltage or high temperature parts.
X-RAY Radiation
Warning:
To determine the presence of high voltage, use an accurate high
impedance HV meter.
Adjust brightness, color, contrast controls to minimum.
Measure the high voltage.
The meter reading should indicate
23.5 ¡ 1.5KV: 14-19 inch, 26 ¡ 1.5KV: 19-21 inch,
29.0 ¡ 1.5KV: 25-29 inch, 30.0 ¡ 1.5KV: 32 inch
If the meter indication is out of tolerance, immediate service and
correction is required to prevent the possibility of premature
component failure.
Before returning the receiver to the customer,
always perform an AC leakage current check on the exposed
metallic parts of the cabinet, such as antennas, terminals, etc., to
be sure the set is safe to operate without damage of electrical
shock.
Leakage Current Cold Check(Antenna Cold Check)
With the instrument AC plug removed from AC source, connect an
electrical jumper across the two AC plug prongs. Place the AC
switch in the on position, connect one lead of ohm-meter to the AC
plug prongs tied together and touch other ohm-meter lead in turn to
each exposed metallic parts such as antenna terminals, phone
jacks, etc.
If the exposed metallic part has a return path to the chassis, the
measured resistance should be between 1MΩ and 5.2MΩ.
When the exposed metal has no return path to the chassis the
reading must be infinite.
An other abnormality exists that must be corrected before the
receiver is returned to the customer.
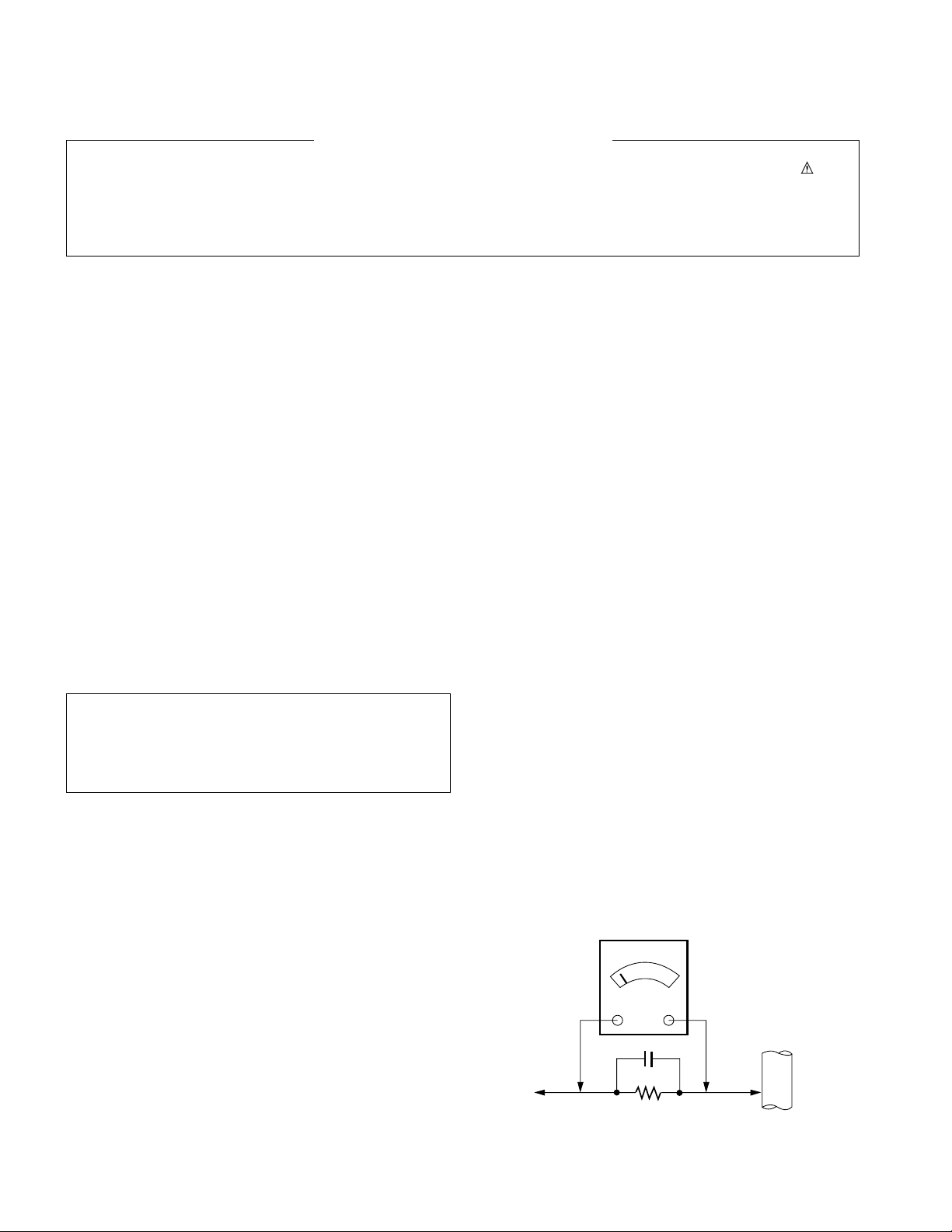
Leakage Current Hot Check (See below Figure)
Plug the AC cord directly into the AC outlet.
Do not use a line Isolation Transformer during this check.
Connect 1.5K/10watt resistor in parallel with a 0.15uF capacitor
between a known good earth ground (Water Pipe, Conduit, etc.)
and the exposed metallic parts.
Measure the AC voltage across the resistor using AC voltmeter
with 1000 ohms/volt or more sensitivity.
Reverse plug the AC cord into the AC outlet and repeat AC voltage
measurements for each exposed metallic part. Any voltage
measured must not exceed 0.75 volt RMS which is corresponds to
0.5mA.
In case any measurement is out of the limits specified, there is
possibility of shock hazard and the set must be checked and
repaired before it is returned to the customer.
Leakage Current Hot Check circuit
The source of X-RAY RADIATION in this TV receiver is the High
Voltage Section and the LCD PANEL.
For continued X-RAY RADIATION protection, the replacement
panel must be the same type panel as specified in the
Replacement Parts List.
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
0.15uF
To Instrument's
exposed
METALLIC PARTS
AC Volt-meter
1.5 Kohm/10W
Good Earth Ground
such as WATER PIPE,
CONDUIT etc.
Page 4

- 4 -
CAUTION: Before servicing receivers covered by this service
manual and its supplements and addenda, read and follow the
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS on page 3 of this publication.
NOTE: If unforeseen circumstances create conflict between the
following servicing precautions and any of the safety precautions on
page 3 of this publication, always follow the safety precautions.
Remember: Safety First.
General Servicing Precautions
1. Always unplug the receiver AC power cord from the AC power
source before;
a. Removing or reinstalling any component, circuit board
module or any other receiver assembly.
b. Disconnecting or reconnecting any receiver electrical plug or
other electrical connection.
c. Connecting a test substitute in parallel with an electrolytic
capacitor in the receiver.
CAUTION: A wrong part substitution or incorrect polarity
installation of electrolytic capacitors may result in an
explosion hazard.
2. Test high voltage only by measuring it with an appropriate high
voltage meter or other voltage measuring device (DVM,
FETVOM, etc) equipped with a suitable high voltage probe.
Do not test high voltage by "drawing an arc".
3. Do not spray chemicals on or near this receiver or any of its
assemblies.
4. Unless specified otherwise in this service manual, clean
electrical contacts only by applying the following mixture to the
contacts with a pipe cleaner, cotton-tipped stick or comparable
non-abrasive applicator; 10% (by volume) Acetone and 90% (by
volume) isopropyl alcohol (90%-99% strength)
CAUTION: This is a flammable mixture.
Unless specified otherwise in this service manual, lubrication of
contacts in not required.
5. Do not defeat any plug/socket B+ voltage interlocks with which
receivers covered by this service manual might be equipped.
6. Do not apply AC power to this instrument and/or any of its
electrical assemblies unless all solid-state device heat sinks are
correctly installed.
7. Always connect the test receiver ground lead to the receiver
chassis ground before connecting the test receiver positive
lead.
Always remove the test receiver ground lead last.
8. Use with this receiver only the test fixtures specified in this
service manual.
CAUTION: Do not connect the test fixture ground strap to any
heat sink in this receiver.
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices
Some semiconductor (solid-state) devices can be damaged easily
by static electricity. Such components commonly are called
Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices. Examples of typical ES
devices are integrated circuits and some field-effect transistors and
semiconductor "chip" components. The following techniques
should be used to help reduce the incidence of component
damage caused by static by static electricity.
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or
semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain off any electrostatic
charge on your body by touching a known earth ground.
Alternatively, obtain and wear a commercially available
discharging wrist strap device, which should be removed to
prevent potential shock reasons prior to applying power to the
unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ES
devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface such as
aluminum foil, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or
exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ES
devices.
4. Use only an anti-static type solder removal device. Some solder
removal devices not classified as "anti-static" can generate
electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate
electrical charges sufficient to damage ES devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ES device from its protective
package until immediately before you are ready to install it.
(Most replacement ES devices are packaged with leads
electrically shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum foil
or comparable conductive material).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the
leads of a replacement ES device, touch the protective material
to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be
installed.
CAUTION: Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit,
and observe all other safety precautions.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged
replacement ES devices. (Otherwise harmless motion such as
the brushing together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your
foot from a carpeted floor can generate static electricity
sufficient to damage an ES device.)
General Soldering Guidelines
1. Use a grounded-tip, low-wattage soldering iron and appropriate
tip size and shape that will maintain tip temperature within the
range or 500¡£F to 600¡£F.
2. Use an appropriate gauge of RMA resin-core solder composed
of 60 parts tin/40 parts lead.
3. Keep the soldering iron tip clean and well tinned.
4. Thoroughly clean the surfaces to be soldered. Use a mall wirebristle (0.5 inch, or 1.25cm) brush with a metal handle.
Do not use freon-propelled spray-on cleaners.
5. Use the following unsoldering technique
a. Allow the soldering iron tip to reach normal temperature.
(500¡£F to 600¡£F)
b. Heat the component lead until the solder melts.
c. Quickly draw the melted solder with an anti-static, suction-
type solder removal device or with solder braid.
CAUTION: Work quickly to avoid overheating the
circuitboard printed foil.
6. Use the following soldering technique.
a. Allow the soldering iron tip to reach a normal temperature
(500¡£F to 600¡£F)
b. First, hold the soldering iron tip and solder the strand against
the component lead until the solder melts.
c. Quickly move the soldering iron tip to the junction of the
component lead and the printed circuit foil, and hold it there
only until the solder flows onto and around both the
component lead and the foil.
CAUTION: Work quickly to avoid overheating the circuit
board printed foil.
d. Closely inspect the solder area and remove any excess or
splashed solder with a small wire-bristle brush.
SERVICING PRECAUTIONS
Page 5

- 5 -
IC Remove/Replacement
Some chassis circuit boards have slotted holes (oblong) through
which the IC leads are inserted and then bent flat against the
circuit foil. When holes are the slotted type, the following technique
should be used to remove and replace the IC. When working with
boards using the familiar round hole, use the standard technique
as outlined in paragraphs 5 and 6 above.
Removal
1. Desolder and straighten each IC lead in one operation by gently
prying up on the lead with the soldering iron tip as the solder
melts.
2. Draw away the melted solder with an anti-static suction-type
solder removal device (or with solder braid) before removing the
IC.
Replacement
1. Carefully insert the replacement IC in the circuit board.
2. Carefully bend each IC lead against the circuit foil pad and
solder it.
3. Clean the soldered areas with a small wire-bristle brush.
(It is not necessary to reapply acrylic coating to the areas).
"Small-Signal" Discrete Transistor
Removal/Replacement
1. Remove the defective transistor by clipping its leads as close as
possible to the component body.
2. Bend into a "U" shape the end of each of three leads remaining
on the circuit board.
3. Bend into a "U" shape the replacement transistor leads.
4. Connect the replacement transistor leads to the corresponding
leads extending from the circuit board and crimp the "U" with
long nose pliers to insure metal to metal contact then solder
each connection.
Power Output, Transistor Device
Removal/Replacement
1. Heat and remove all solder from around the transistor leads.
2. Remove the heat sink mounting screw (if so equipped).
3. Carefully remove the transistor from the heat sink of the circuit
board.
4. Insert new transistor in the circuit board.
5. Solder each transistor lead, and clip off excess lead.
6. Replace heat sink.
Diode Removal/Replacement
1. Remove defective diode by clipping its leads as close as
possible to diode body.
2. Bend the two remaining leads perpendicular y to the circuit
board.
3. Observing diode polarity, wrap each lead of the new diode
around the corresponding lead on the circuit board.
4. Securely crimp each connection and solder it.
5. Inspect (on the circuit board copper side) the solder joints of
the two "original" leads. If they are not shiny, reheat them and if
necessary, apply additional solder.
Fuse and Conventional Resistor
Removal/Replacement
1. Clip each fuse or resistor lead at top of the circuit board hollow
stake.
2. Securely crimp the leads of replacement component around
notch at stake top.
3. Solder the connections.
CAUTION: Maintain original spacing between the replaced
component and adjacent components and the circuit board to
prevent excessive component temperatures.
Circuit Board Foil Repair
Excessive heat applied to the copper foil of any printed circuit
board will weaken the adhesive that bonds the foil to the circuit
board causing the foil to separate from or "lift-off" the board. The
following guidelines and procedures should be followed whenever
this condition is encountered.
At IC Connections
To repair a defective copper pattern at IC connections use the
following procedure to install a jumper wire on the copper pattern
side of the circuit board. (Use this technique only on IC
connections).
1. Carefully remove the damaged copper pattern with a sharp
knife. (Remove only as much copper as absolutely necessary).
2. carefully scratch away the solder resist and acrylic coating (if
used) from the end of the remaining copper pattern.
3. Bend a small "U" in one end of a small gauge jumper wire and
carefully crimp it around the IC pin. Solder the IC connection.
4. Route the jumper wire along the path of the out-away copper
pattern and let it overlap the previously scraped end of the good
copper pattern. Solder the overlapped area and clip off any
excess jumper wire.
At Other Connections
Use the following technique to repair the defective copper pattern
at connections other than IC Pins. This technique involves the
installation of a jumper wire on the component side of the circuit
board.
1. Remove the defective copper pattern with a sharp knife.
Remove at least 1/4 inch of copper, to ensure that a hazardous
condition will not exist if the jumper wire opens.
2. Trace along the copper pattern from both sides of the pattern
break and locate the nearest component that is directly
connected to the affected copper pattern.
3. Connect insulated 20-gauge jumper wire from the lead of the
nearest component on one side of the pattern break to the lead
of the nearest component on the other side.
Carefully crimp and solder the connections.
CAUTION: Be sure the insulated jumper wire is dressed so the
it does not touch components or sharp edges.
Page 6
- 6 -
1. Application range
This specification is applied to ML-041C chassis.
2. Requirement for Test
Testing for standard of each part must be followed in below
condition.
(1) Temperature: 25°C ± 2°C
(2) Power: Standard input voltage (AC 90~132V, 50/60Hz)
(3) Measurement must be performed after heat-run more than
30min.
(4) Adjusting standard for this chassis is followed a special
standard.
SPECIFICATION
NOTE : Specifications and others are subject to change without notice for improvement
.
3.General Specification
1
Maker
Type
ActiveDisplay Area
Pixel Pitch [mm]
Electrical Interface
Color Depth
Size [mm]
Surface Treatment
Operating Mode
Back light Unit
R/T Typ.
LPL
TFT Color LCD Module
17.0 inches(434.38mm) diagonal(Aspect 15:9)
0.291mm(H)x0.291mm(V)xRGB
LVDS
8BIT, 16,777,216 colors
400(H)x258(V)x22(D)
Anti Glare Hard Coating(3H)
Normally Black
6 lamps
R.T.:12ms + F.T.:13ms
Item Specification Remark
No.
LPL
Page 7
- 7 -
4. Function
5.Optical Character
No Item Specification Remark
1 REMOCON TOSHIBA Code NTSC
2 AV Input 1 Side
3 S-Vedio Input 1 Side
4 Component input 1 Rear (NTSC)
5 RGB(VGA)Input 1 D-sub 15 pin
6 Ear-phone output 1 Side
7 PC Sound input 1
8 Film Mode x
9 Progressive Scan 0
10 ARC 0
No Item
Specification Remark
Module kind LPL
1 Viewing Angle R/L 85/88
<CR≥10> U/D 85/88
2 Luminance Luminance (cd/m
2
) 450 Typical
Variation 1.3 MAX
3 Contrast Ratio 400 All white / All black
4 CIE Color Coordinates White W
X Typ. 0.283 Min = Typ. - 0.03
W
Y Typ. 0.294 Max = Typ. + 0.03
RED X
r Typ. 0.631
Y
r Typ. 0.341
Green X
g Typ. 0.287
Y
g Typ. 0.609
Blue X
b Typ. 0.146
Y
b Typ. 0.064
Page 8
- 8 -
6-1.General Specification(TV)
6-2. Power
6. Engineering Specification
Item Specification Remark
Power Supply H/V Sync Video Power Consumption LED Color
Normal On/On Active ≤65W GREEN
Stand By, Off/On ≤2W AMBER
Suspend Mode On/Off Off ≤5W
GREEN
DPM Off Mode Off/Off ≤5W
Cut-off Switch off - - 0W OFF
PBP SWAP ON/OFF
1 ITEM Specification remark
2 D-SUB 1 : RED 2 : Green
Pin configuration 3 : Blue 4 : ID2 (GND)
5 : S.T (GND) 6 : RED GND
7 : Green GND 8 : Blue GND 10: Digital GND
9 : N.C 10: D-GND
11: ID0(GND) 12:SDA
13: H-Sync 14: V-Sync
15: SCL Shell: GND
3 Control Function 1) Contrast/Brightness
2) H-Position / V-Position
3) Tracking : Clock / Phase
4) Auto ConfigureRESET
4 Comoponent Jack 1 : Y
3 : Pb
5 : Pr
No Item Min Typ Max Unit Remark
1 AC Power Shut Down Voltage 90 264 V
2 DC Voltage, Inverter 22.8 24 25.2 V
3 DC Voltage, LCD Panel 11.4 12 12.6 V
4 DC Voltage, Audio 14.0 15 16.0 V
5 DC Voltage, Tuner(5) 4.5 5 5.5 V
6 DC Voltage, Tuning(31) 31 33 35 V
7 DC Voltage, VCTi(5) 4.5 5 5.5 V
DC Voltage, VCTi(8) 7.5 8 8.5 V
8. DC Voltage, VCTi(3.3) 3.1 3.3 3.5 V
DC Voltage, VCTi(1.8) 1.6 1.8 2.0 V
9 DC Voltage, GM2221 (3.3) 3.1 3.3 3.5 V
DC Voltage, GM2221 (1.8) 1.6 1.8 2.0 V
10 DC Voltage, Digital (3.3) 2.8 3.3 3.8 V
11 DC Voltage, Digital (5) 4.5 5 5.5 V
Page 9
- 9 -
6-3. External Interface
No Item Min Typ Max Unit Remark
1. Audio Input Level 0.3 0.4 0.5 V
2. Audio Input Frequency Response 0.1 7 KHz
3. Audio Input S/N 40 DB
4. Audio Input Distortion 2 %
5. Audio Input Dynamic Range 2 V
6. Video Output Level 0.85 1 1.15 Vpp
7. Video Output Frequency Response 3.8 MHz
8. Video Output S/N 40 DB
9. Audio Output Level 0.4 0.5 0.6 V
10. Audio Output Frequency Response 0.1 7 KHz
11. Audio Output S/N 40 DB
12. Audio Output Distortion 2 %
13. Video Input Level, R/G/B 0.6 0.7 0.8 Vpp 75 ohm
14. Video Input Level, Component(Y, PB, PR) 0.6 0.7 0.8 Vpp 75 ohm
15. RGB Input Resolution, Vertical 768 Pixel
16. RGB Input Resolution, Horizontal 1280 Pixel
17. RGB Input Horizontal Frequency KHz See table 5-5
18. RGB Input Frame Rate Hz See table 5-5
6-4. The Others
No Item Min Typ Max Unit Remark
1. Search Sensitivity -85 dBm
2. Soft Ware Functionality Test LGE Specification
3. REMOCON Working Sensitivity, Straight 0.1 10 m
4. REMOCON Working Sensitivity, T/B/L/R 0.1 9 m 30 degree
5. Closed Caption Sensitivity -70 dBm
6. Teletext Sensitivity -70 dBm
Page 10
- 10 -
7. Signal Timing(Resolution)
7-1. PC Mode
[Table 7] Timming chart of Receivable Mode * H [dot] / V [line]
Mode VGA-60 VGA-67 VGA-75 SVGA-56 SVGA-60 SVGA-72 SVGA-75 MAC-75 XGA-60 XGA-70 XGA-75
H_display 640 640 640 800 800 800 800 832 1024 1024 1024
V_display 480 480 480 600 600 600 600 624 768 768 768
V frequency 60 67 75 56 60 72 75 75 60 70 75
H_total 800 864 840 1024 1056 1040 1056 1152 1344 1328 1312
H_blanking 160 224 200 224 256 240 256 320 320 304 288
H_sync 96 64 64 72 128 120 80 64 136 136 96
H Polarity NEG. NEG. NEG POS POS POS POS NEG NEG NEG POS
H_bp 48 96 120 128 88 64 160 224 136 144 176
H_fp 16 64 16 24 40 56 16 32 160 24 16
H-freq[kHz] 31.469 35.0 37.5 35.156 37.879 48.077 46.875 49.725 48.363 56.476 60.023
/Clk[MHz] 25.175 30.24 31.5 36.0 40.0 50.0 49.5 57.283 65.0 75.0 78.75
V_total 525 525 500 625 628 666 625 667 806 806 800
V_blanking 45 45 20 25 28 66 25 43 38 38 32
V_sync 2 3 3 2 4 633663
V Polarity NEG NEG NEG POS POS POS POS NEG NEG NEG POS
V_bp 33 39 16 22 23 23 21 39 29 29 28
V_fp 10 3 1 1 1 37 11331
Page 11
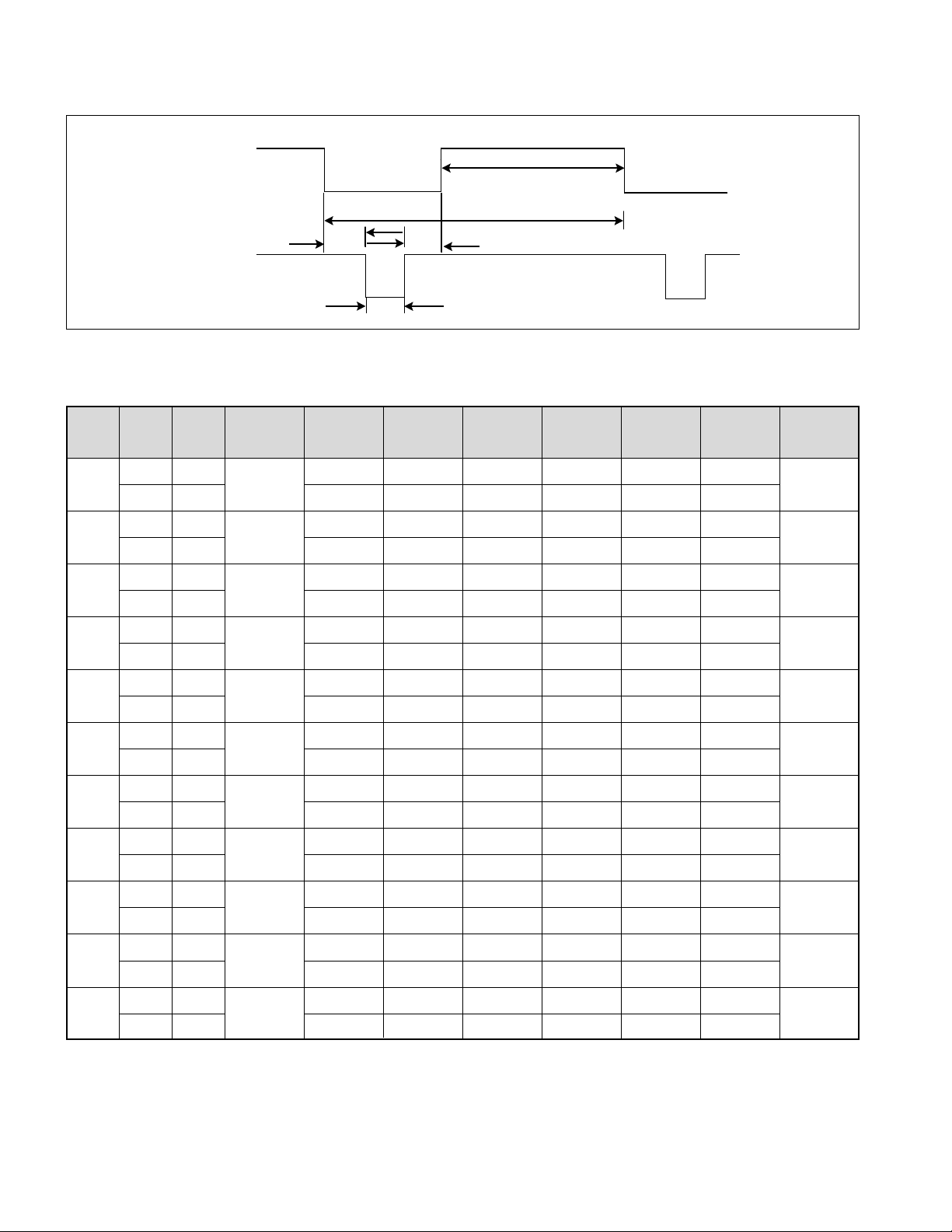
TIMING CHART
- 11 -
VIDEO
SYNC
D
B
C
E
A
<< Dot Clock (MHz), Horizontal Frequency (kHz), Vertical Frequency (Hz), Horizontal etc... (µs), Vertical etc... (ms) >>
Mode
H/V
Sort
Sync
Porarity
DOT
Clock
Frequency
Total
Period
(E)
Video
Active Time
(A)
Front
Porch
(C)
Sync
Duration
(D)
Back
Porch
(F)
Resolution
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
H(Pixels)
+
25.175
31.468 800 640 16 96 48
640 x 350
V(Lines)
- 70.090 449 350 37 2 60
H(Pixels)
-
28.324
31.469 900 720 18 108 54
720 X 400
V(Lines)
+ 70.082 449 400 13 2 34
H(Pixels)
-
25.175
31.469 800 640 16 96 48
640 x 480
V(Lines)
- 59.94 525 480 10 2 33
H(Pixels)
-
31.5
37.5 840 640 16 64 120
640 x 480
V(Lines)
- 75 500 480 1 3 16
H(Pixels)
+
40.0
37.879 1056 800 40 128 88
800 x 600
V(Lines)
+ 60.317 628 600 1 4 23
H(Pixels)
+
49.5
46.875 1056 800 16 80 160
800 x 600
V(Lines)
+ 75.0 625 600 1 3 21
H(Pixels)
+/-
57.283
49.725 1152 832 32 64 224
832 x 624
V(Lines)
+/- 74.55 667 624 1 3 39
H(Pixels)
-
65.0
48.363 1344 1024 24 136 160
1024 x 768
V(Lines)
- 60.004 806 768 3 6 29
H(Pixels)
+
78.75
60.023 1312 1024 16 96 176
1024 x 768
V(Lines)
+ 75.029 800 768 1 3 28
H(Pixels)
-
65.125
39.518 1648 1280 56 128 184
1280 x 768
V(Lines)
+ 49.959 791 768 1 7 15
H(Pixels)
-
80.125
47.693 1680 1280 64 136 200
1280 x768
V(Lines)
+ 59.992 795 768 1 7 19
Page 12
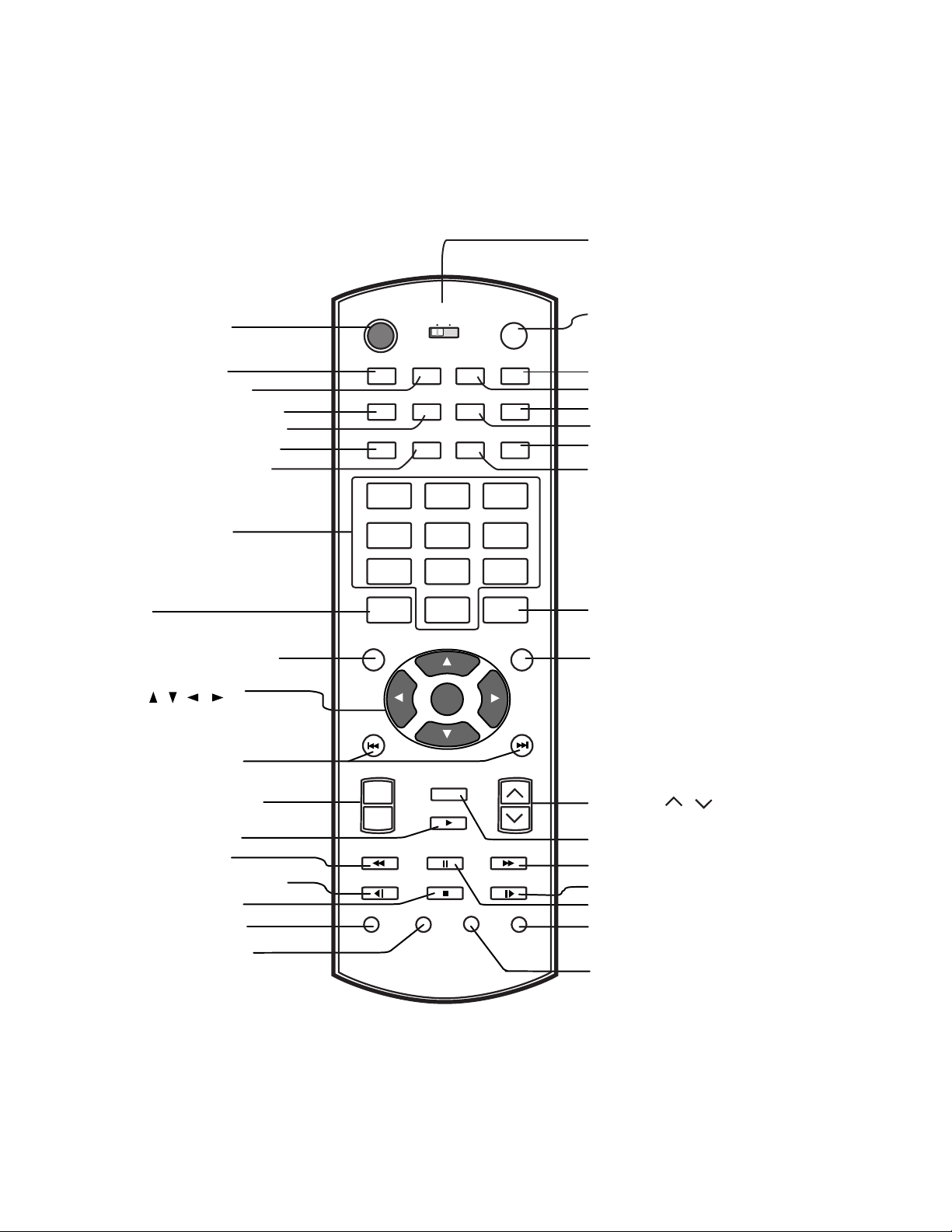
REMOTE CONTROL
- 12 -
SKIP buttons
ZOOM button
PAUSE button
SUB TITLE button
PLAY button
REV button
FWD button
MUTE button
SLOW FWD button
STOP button
SLOW REV buttons
Direction buttons
( / / / )
CHANNEL / button
ANGLE button
VOLUME +/- button
RETURN button
Numbered buttons (0
-
9)
POWER button
RMT CODE(1/2)
SET UP button
SLEEP button
REPEAT button
CAP/TEXT button
RANDOM button
+10 button
MEMORY button
DISPLAY button
TOP MENU button
100
INPUT SELECT button
Selects: TV, Video, S-Video, DVD,
Component, or PC mode.
[1]: For controlling SD-P7000 model
and other Toshiba brand TV.
[2]: For controlling SD-P7000 model only.
Switches the TV between ON
and STANDBY.
T button
MENU button
DIMMER button
REPEAT A-B button
MONO/STEREO/SAP button
AUDIO button
E.A.M. button
CLEAR button
PICTURE button
Direct channel selection
buttons (0
-
9)
INPUT
SELECT
SET UP SLEEP DIMMER E.A.M.
MEMORY REPEAT REPEAT A-B CLEAR
DISPLAY CAP/TEXT
MONO/
STEREO/SAP
PICTURE
RANDOM
+10
TOP MENU MENU
SKIP
MUTE
SKIP
AUDIO
RMT CODE
1 2
POWER
VOLUME CHANNEL
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
100 0 T
PLAY
REV PAUSE FWD
SLOW REV
ZOOM ANGLE SUB TITLE RETURN
STOP SLOW FWD
ENTER
+
-
Use to turn the sound on or off temporarily.
Allows you to go back to the last scene
you were watching.
Page 13
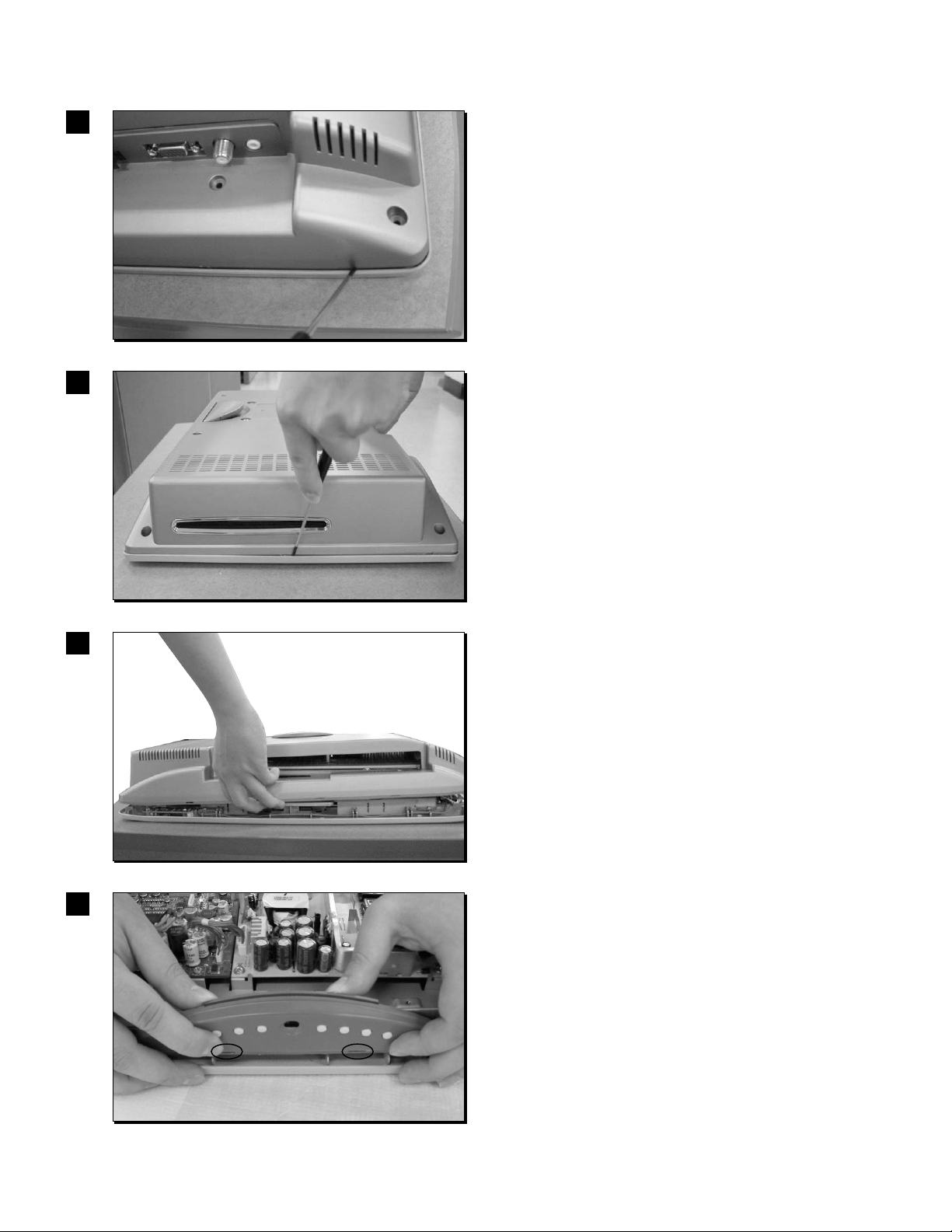
- 13 -
DISASSEMBLY
1
2
3
4
1-1. Remove 8 screws of the Back cover.
1-2. Using the Jig, disassemble points which was
latched under left and right sides .
2-1. Using the jig, disassemble points which was
latched at center of left and right sides.
3-1. Disclose the lower side of the Back cover.
4-1. At first, remove two screws from the small power
control PCB Ass'y.
4-2. Using the jig, disassemble point which was
latched and then remove the small Power jack
control PCB Ass'y from the cabinet.
Page 14

- 14 -
1. Application Object
This instruction is for the application to the LCD TV.
2. Adjustment
2.1 Adjustment overview
The unit is set to automatically adjust using the
factory automation equipment. However when errors
occur, it should be adjusted manually.
2.2 Auto Gain/Offset adjustment
2.2.1 RF Mode adjustment
2.2.1.1 Adjustment preparation
¡ÆConduct Heat Run at the RF fog signals for more than
30 minutes.
2.2.1.2 Auto Gain/Offset adjustment
¡ÆPress IN-START Key to convert to the adjustment
mode using the adjustment (SVC) remote controller,
and press VOL+ Key at the Auto Gain menu.
¡ÆOnce the adjustment is completed, press the Enter
Key to save and finish the adjustment.
2.2.2 Component Mode adjustment
2.2.2.1 Adjustment preparation
¡ÆConduct Heat Run at the RF fog signals for more than
30 minutes.
¡ÆConnect the Pattern Generator to the Component
Jack (Y, Pb, Pr) of LCD TV.
2.2.2.2 Auto Gain/Offset adjustment
¡ÆConvert the input mode to the component input.
¡ÆSelect Model: 228(480p Mode, Y 100%, Pb/Pr: 75%)
in Pattern Generator
Select PATTERN: 33(Color Bar Pattern signal)in
Pattern Generator
¡ÆPress the IN-START Key by using the Remote
Conroller(SVC), after converting to Adjustment-Mode,
press VOL+Key consecutively in AutoGain Menu.
¡Æ After adjustment complete, pressing enter key, stores
and completes process
2.2.3 PC Mode adjustment
2.2.3.1 Adjustment preparation
¡ÆConduct Heat Run at the RF fog signals for more than
30 minutes.
¡ÆConnect the Pattern Generator to 15 Pin D-Sub Jack
of LCD TV.
2.2.3.2 Auto Gain/Offset adjustment
¡ÆConvert the input mode to PC input.
¡ÆUsing the Pattern Generator (801GF, VG819) adjust
XGA (1024 X 768@60Hz) for resolution and 16 Step
Gray signals for the pattern. Or adjust the 16 Step (11
Step) Gray signals in accordance with VG819.
¡ÆConvert the input mode to PC input and convert to
the adjustment mode using the adjustment (SVC)
remote controller and pressing the IN-START Key,
and then press VOL+ Key at the AutoGain menu.
¡ÆOnce the adjustment is completed, press the Enter
Key to save and finish the adjustment.
2.3
EDID (The Extended Display Identification Data) setting
¡ÆConnect the 15 Pin D-Sub Cable to D-Sub Jack.
¡ÆSet the input mode of Set to PC.
¡ÆConnect the DDC automation equipment to write
DDC data.
2.3.1 EDID DATA
ADJUSTMENT INSTRUCTION
00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0A 0B 0C 0D 0E 0F
00 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF 00 1E 6D 85 43 67 2B 00 00
10 0B 0E 01 03 20 39 21 78 EE 1D 32 A2 57 47 9A 25
20 11 4A 4D A5 CE 00 61 4F 45 4A 31 4F 01 01 01 01
30 01 01 01 01 01 01 0E 1F 00 80 51 00 1E 30 40 80
40 37 00 74 DF 10 00 00 1E 00 00 00 FD 00 38 4B 1F
50 41 09 00 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 00 00 FC 00 54
60 31 37 4C 43 31 30 44 20 20 20 20 20 00 00 00 FC
70 00 0A 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 00 69
Page 15

- 15 -
TROUBLESHOOTING
No power
(LED indicator off)
Check short of main B/D
or Change Lips
Change IC1107, IC1104
Change LED Assy
Check 15V or 5V
of Lips
Check Output of
IC1107, IC1104
Check LED Assy
Check P1100, P206, P207
Connector
Fail
Fail
Change Q1100
Check Output of
Q1100
Fail
Pass
Fail
Pass
Pass
Pass
:[A]Process
Page 16

- 16 -
No Raster
Check LED Status
on display unit
Check the input/
Output of IC901
Check L900,L901
L902,L903
Check inverter
Connector or inverter
Check input source cable and jack
Repeat A PROCESS
Fail
Change L900,L901,
L902,L903
Fail
Change IC901
Fail
Change inverter
connector or inverter
Fail
Change panel link
cable or module
Fail
Change module
Fail
Check panel link
Cable or module
Pass
Pass
Pass
Pass
:[B]Process
Page 17

- 17 -
No Raster on Component signal
Check JA1200 or
RCA CABLE
Check the signal of
C1217, L1202, L1203
Repeat
[A] Process
Check the input/
output of IC1
Check the input/
output of IC901
Check input source cable and jack
Fail
Re-soldering or
Change the defect part,
Check X11
Fail
Re-soldering or
Change the defect part,
Check X900
Fail
Pass
Pass
Pass
Check the input/output
of IC800, IC851
Re-soldering or
Change the defect part
Fail
Pass
Page 18

- 18 -
No Raster on AV Signal
(Video, S-Video)
No Raster on TV(RF) signal
Change L2305, L2307,
L2306
Check the signal of
L2305, L2307, L2306
Repeat
[A] Process
Check the output of
TU1000
Check the input/output
of IC1
Check the input/output
of IC800, IC851
Check input source cable and jack
Fail
Fail
Fail
Fail
Re-soldering or
Change the defect part
Chek X11
Fail
Re-soldering or
Change the defect part
Check 5V, 33V of TU1000
Re-soldering or
Change the defect part
Pass
Pass
Pass
Check the input/output
of IC901
Fail
Re-soldering or
Change the defect part
Check X900
Pass
Pass
Page 19

- 19 -
No Raster on DVD Signal
Check input source
cable and jack
Check P1200, P1201
or FFC Cable
Repeat A PROCESS
Fail
Pass
Re-soldering or
Change the defect part
Check X11
Check the Signal of
L1201, L1202, L1203
Fail
Pass
Re-soldering or
Change the defect part
Check the input/output
of IC101
Fail
Pass
Re-soldering or
Change the defect part
Check X900
Check the input/output
of IC800, IC851
Fail
Pass
Check the input/output
of IC901
Pass
Page 20

- 20 -
No Sound
Check the speaker wire
Change source input
Check the
input source
Fail
Pass
Re-soldering or
Change the defect part
Check X11
Check the input/output
of IC1
Fail
Pass
Re-soldering or
Change the defect part
Check the input/output
of IC100,IC101
Fail
Pass
Change speaker
Check the speaker
Fail
Pass
Page 21

BLOCK DIAGRAM
- 21 -
Page 22

BLOCK DIAGRAM DESCRIPTION
- 22 -
1. Video Controller Unit & Display Data Conversion Unit
The video controller unit receives the video signals inputted through the tuner, DVD, AV port (Video, SVideo,component), and converts them into an analog RGB signal through the microcomputer (VCTI) combined
with the video decoder that integrates various functions in one chip.
Either the analog RGB, component YPbPr or PC RGB signal is selected by the switching IC and inputted to
ascaler (GM2221), which is sent to the LCD module after being modified to an LVDS signal through the
integrated LVDS IC.
Or, it is sent to the LCD module as a TTL output.
VCTi is the main microprocessor that handles video signal processing and sound signal processing.
It alsomanages the RF signals received from the tuner.
The scaler can control timing to fit into the LCD panel, and can also control the size and position of the input
signal.
2. Power Supply Unit
The power supply unit provides 15V and 5V DC power to the mainboard.
The PWM Step-Up DC/DC Converter circuit is used to generate the 33V used for the tuner.
15V power is directly used by the sound amplifier IC and is also used to generate 5V power through the
regulator.
12V power is used for the LCD panel power, and 5V power is converted to 3.3V and 1.8V power through the
regulator, which in turn supplies electrical power for ICs such as VCTI and scaler.
Page 23

- 23 -
WIRING DIAGRAM
Wiring Part List
No. Part No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
101112
6631T11012R - 20P
6631T11017T - 28P
6631T12006D - 8P
6631T25024C - 5P
6631T39001L - 4P
6631T39001L - 3P
6631T20028N - 4P
6631T25023C - 4P
6631T20036B - 9P, 10P
6631T11017R - 18P
6631T20028P - 11P, 12P
6631T20033X - 5P
Page 24

- 24 -
EXPLODED VIEW
030
Introduction
2
Connections
15
TV Operation
DVD&VCD Operation
MP3/WMA files Operation
Others
COMBINATION
LCD TELEVISION AND DVD
VIDEO PLAYER
SD-P7000
OWNER’S MANUAL
'2004 Toshiba Corporation
Before operating the unit, please read this manual thoroughly.
203543
Audio CD Operation
44
JEPG file Operation
46
46
120
040
200
070
140
160
100
060
090
080
130
150
190
110
INPUT
SELECT
PICTURE
MONO/
AUDIO
STEREO/SAP
1 2
RMT CODE
RANDOM
1 2 3
SET UP SLEEP DIMMER E.A.M
DISPLAY CAP/TEXT
MEMORY REPEATREPEAT A-B CLEAR
POWER
SKIP
PLAY
MUTE
STOP SLOW FWD
ENTER
4 5 6
7 8 9
+10
-
+
100 0 T
TOP MENU MENU
REW PAUSE FWD
SKIP
ZOOM ANGLE SUB TITLE RETURN
SLOW REW
VOLUME CHANNEL
050
020
170
180
010
Page 25

- 25 -
EXPLODED VIEW PARTS LIST
No.
LG PART NO.
TOSHIBA PART NO.
DESCRIPTION
3091TKC126A AF500146 CABINET ASSEMBLY, T17LC10D TOSHIBA 3090TKC094A
6306V17001C AF500169 LCD(LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY), LC171W03-A4K4 LG PHILPS TFT COLOR
3809TKC062A AF500155 BACK COVER ASSEMBLY, T17LC10D 3808TKC052A TOSHIBA
3043TKK198A AF500145 TILT SWIVEL ASSEMBLY, T17LC10D TOSHIBA
6401TZZ058A AF500171 SPEAKER ASSEMBLY, T17LC10D SPEAKER ASSY
4951TKS172A AF500162 METAL ASSEMBLY, FRAME MAIN(T17LC10D)
4950TKS314A AF500194 METAL, FRAME REAR(TOSHIBA 17 INCH)
6871TST722A AF500189
PWB(PCB) ASSEMBLY,SUB, T17LC10D CONTROL KEY CONTROL TOTAL TOSHIBA ASSY
6871TST725A AF500192
PWB(PCB) ASSEMBLY,SUB, T17LC10D POWER JACK CONTROL TOTAL TOSHIBA ASSY
6871TST724A AF500191 PWB(PCB) ASSEMBLY,SUB, T17LC10D SIDE LED & P/SW TOTAL TOSHIBA ASSY
3551TKK541A AF500152 COVER ASSEMBLY, T17LC10D REAR AV (TOSHIBA)
5040TKK037A AF500163 RUBBER, COVER MOLDING T17LC10D
6871TST721A AF500188
PWB(PCB) ASSEMBLY,SUB, T17LC10D REAL JACK INTERFACE TOTAL TOSHIBA ASSY
3911TKK808A AF500195 PACKAGE ASSEMBLY, T17LC10D DVD ASSY
6871TPT280E AF500187
PWB(PCB) ASSEMBLY,POWER, T17LC100 (TOSHIBA WIDE DVD) POWER TOTAL LIEN CHANG LIPS FOR 17" LPL
3313TN1022A AF500147 MAIN TOTAL ASSEMBLY, T17LC10D TOSHIBA ML041C
6871TST723A AF500190 PWB(PCB) ASSEMBLY,SUB, T17LC10D IR LED & P/SW TOTAL TOSHIBA ASSY
3871TZL317A AF500156
OWNER'S MANUAL(PRINTING PART ASSEMBLY), KIT, T17LC10D AAPTTA SD-P7000 TOSHIBA EN/FR(2)
6710T00014A AF500186
REMOTE CONTROLLER T17LC10D, SMK, SE-R0130, SSR51-ML, SD-P7000, TSB OEM
6410TUW009A AF500172
POWER CORD, LP-11W+LS-7 CWA LONGWELL UL/CSA 1870MM 2POLE WALL CD/PB FREE BLACK
010
020
030
040
050
060
070
080
090
100
110
120
130
140
150
160
170
180
190
200
Page 26

- 26 -
*S *AL LOC. NO.
TOSHIBAPART NO.
LG PART NO. DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
REMARKS
C1008 AF500008 0CE227BF638 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 220U KME 16V M FM5 TP5
C1101 AF500009 0CE227BH638 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 220U KME 25V M FM5 TP5
C1104 AF500009 0CE227BH638 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 220U KME 25V M FM5 TP5
C1107 AF500018 0CE477BH618 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 470UF KME TYPE 25V M FL TP 5
C1136 AF500018 0CE477BH618 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 470UF KME TYPE 25V M FL TP 5
C1140 AF500009 0CE227BH638 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 220U KME 25V M FM5 TP5
C1152 AF500006 0CE107BK638 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 100UF KME 50V M FM5 TP5
C1229 AF500008 0CE227BF638 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 220U KME 16V M FM5 TP5
C123 AF500018 0CE477BH618 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 470UF KME TYPE 25V M FL TP 5
C124 AF500018 0CE477BH618 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 470UF KME TYPE 25V M FL TP 5
C131 AF500018 0CE477BH618 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 470UF KME TYPE 25V M FL TP 5
C132 AF500018 0CE477BH618 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 470UF KME TYPE 25V M FL TP 5
C133 AF500018 0CE477BH618 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 470UF KME TYPE 25V M FL TP 5
C134 AF500018 0CE477BH618 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 470UF KME TYPE 25V M FL TP 5
C11 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C1150 AF500023 0CH3105F946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 1UF 16V Z F 2012 R/TP
C1151 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C1208 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C1209 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C1210 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C1211 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C1213 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C1220 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C1228 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C127 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C128 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C135 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C136 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C15 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C16 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C19 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C203 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C4 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C41 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C44 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C49 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C6 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C804 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C816 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C851 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C854 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C855 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C858 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C861 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C863 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST
For Capacitor & Resistors, the
charactors at 2nd and 3rd digit in the
P/No. means as follows;
CC, CX, CK, CN, CH : Ceramic
CQ : Polyestor
CE : Electrolytic
CF : Fixed Film
RD : Carbon Film
RS : Metal Oxide Film
RN : Metal Film
RH : CHIP, Metal Glazed(Chip)
RR : Drawing
TOSHIBA MODEL : SD-P7000
RUN DATE : 17-Nov-04
MAIN BOARD
CAPACITOR
Page 27

*S *AL LOC. NO.
TOSHIBAPART NO.
LG PART NO. DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
REMARKS
C865 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C866 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C867 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C869 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C871 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C874 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C875 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C877 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C909 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C910 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C917 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C920 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C925 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C926 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C927 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C928 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C929 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C930 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C934 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C935 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C936 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C937 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C938 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C939 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C940 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C943 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C944 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C945 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C946 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C947 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C948 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C949 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C950 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C956 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C964 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C965 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C967 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C968 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C970 AF500022 0CH3104K946 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100000PF 50V Z F 2012 R/TP
C1200 AF500030 0CH6221K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 220PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C1201 AF500030 0CH6221K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 220PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C1202 AF500030 0CH6221K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 220PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C1203 AF500030 0CH6221K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 220PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C1204 AF500030 0CH6221K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 220PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C1205 AF500030 0CH6221K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 220PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C1206 AF500028 0CH6150K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 15PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C1207 AF500028 0CH6150K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 15PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C1227 AF500026 0CH6101K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 100PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C1238 AF500031 0CH6331K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 330PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C1239 AF500029 0CH6151K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 150PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C1240 AF500029 0CH6151K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 150PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C1241 AF500031 0CH6331K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 330PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C13 AF500027 0CH6102K406 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 1000PF 50V J SL 2012 R/TP
C14 AF500027 0CH6102K406 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 1000PF 50V J SL 2012 R/TP
C2 AF500027 0CH6102K406 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 1000PF 50V J SL 2012 R/TP
C20 AF500027 0CH6102K406 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 1000PF 50V J SL 2012 R/TP
C21 AF500027 0CH6102K406 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 1000PF 50V J SL 2012 R/TP
- 27 -
Page 28

*S *AL LOC. NO.
TOSHIBAPART NO.
LG PART NO. DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
REMARKS
C46 AF500027 0CH6102K406 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 1000PF 50V J SL 2012 R/TP
C50 AF500027 0CH6102K406 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 1000PF 50V J SL 2012 R/TP
C53 AF500027 0CH6102K406 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 1000PF 50V J SL 2012 R/TP
C59 AF500027 0CH6102K406 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 1000PF 50V J SL 2012 R/TP
C7 AF500030 0CH6221K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 220PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C8 AF500030 0CH6221K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 220PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C9 AF500030 0CH6221K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 220PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C923 AF500025 0CH6080K116 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 8PF 50V D NP0 2012 R/TP
C924 AF500025 0CH6080K116 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 8PF 50V D NP0 2012 R/TP
C129 AF500139 181-007F "CAPACITOR,DRAWING" "MPE ECQ-V1H224JL3(TR), 50V 0"
C130 AF500139 181-007F "CAPACITOR,DRAWING" "MPE ECQ-V1H224JL3(TR), 50V 0"
C1007 AF500020 0CH3103K516 "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 10000PF 50V 10% B(Y5P) 2012
C1010 AF500040 0CK273DK51A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 27000PF 2012 50V 10% B(Y5P)
C1015 AF500024 0CH5390K416 "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 39PF 50V 5% NP0 2012 R/TP
C1016 AF500024 0CH5390K416 "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 39PF 50V 5% NP0 2012 R/TP
C107 AF500039 0CK225DFK4A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "2.2UF 2012 16V 20%,-20% F(Y5"
C109 AF500020 0CH3103K516 "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 10000PF 50V 10% B(Y5P) 2012
C110 AF500020 0CH3103K516 "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 10000PF 50V 10% B(Y5P) 2012
C113 AF500039 0CK225DFK4A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "2.2UF 2012 16V 20%,-20% F(Y5"
C1212 AF500020 0CH3103K516 "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 10000PF 50V 10% B(Y5P) 2012
C1222 AF500020 0CH3103K516 "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 10000PF 50V 10% B(Y5P) 2012
C1226 AF500020 0CH3103K516 "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 10000PF 50V 10% B(Y5P) 2012
C70 AF500039 0CK225DFK4A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "2.2UF 2012 16V 20%,-20% F(Y5"
C71 AF500039 0CK225DFK4A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "2.2UF 2012 16V 20%,-20% F(Y5"
C72 AF500039 0CK225DFK4A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "2.2UF 2012 16V 20%,-20% F(Y5"
C900 AF500020 0CH3103K516 "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 10000PF 50V 10% B(Y5P) 2012
C902 AF500020 0CH3103K516 "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 10000PF 50V 10% B(Y5P) 2012
C1001 AF500035 0CK103CK51A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.01UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP B(Y
C1002 AF500035 0CK103CK51A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.01UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP B(Y
C1003 AF500035 0CK103CK51A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.01UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP B(Y
C1004 AF500035 0CK103CK51A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.01UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP B(Y
C1005 AF500035 0CK103CK51A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.01UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP B(Y
C114 AF500039 0CK225DFK4A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "2.2UF 2012 16V 20%,-20% F(Y5"
C115 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C116 AF500042 0CK562CK51A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 5600PF 1608 50V 10% R/TP B(Y
C117 AF500042 0CK562CK51A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 5600PF 1608 50V 10% R/TP B(Y
C118 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C12 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C125 AF500038 0CK105EK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 1UF 3216 50V 10% X7R R/TP
C126 AF500038 0CK105EK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 1UF 3216 50V 10% X7R R/TP
C200 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C22 AF500043 0CK822CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 8200PF 1608 50V 10% X7R R/TP
C23 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C24 AF500043 0CK822CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 8200PF 1608 50V 10% X7R R/TP
C26 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C27 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C28 AF500041 0CK334CF94A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "0.33UF 1608 16V 80%,-20% F(Y"
C29 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C3 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C30 AF500041 0CK334CF94A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "0.33UF 1608 16V 80%,-20% F(Y"
C31 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C32 AF500041 0CK334CF94A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "0.33UF 1608 16V 80%,-20% F(Y"
C33 AF500041 0CK334CF94A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "0.33UF 1608 16V 80%,-20% F(Y"
C35 AF500041 0CK334CF94A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "0.33UF 1608 16V 80%,-20% F(Y"
C36 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C37 AF500041 0CK334CF94A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "0.33UF 1608 16V 80%,-20% F(Y"
C38 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
- 28 -
Page 29

*S *AL LOC. NO.
TOSHIBAPART NO.
LG PART NO. DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
REMARKS
C39 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C40 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C42 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C45 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C52 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C67 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C75 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C800 AF500037 0CK105CF94A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "1UF 1608 16V 80%,-20% R/TP F"
C801 AF500037 0CK105CF94A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "1UF 1608 16V 80%,-20% R/TP F"
C802 AF500037 0CK105CF94A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "1UF 1608 16V 80%,-20% R/TP F"
C803 AF500037 0CK105CF94A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "1UF 1608 16V 80%,-20% R/TP F"
C807 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C808 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C810 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C811 AF500037 0CK105CF94A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "1UF 1608 16V 80%,-20% R/TP F"
C812 AF500037 0CK105CF94A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "1UF 1608 16V 80%,-20% R/TP F"
C82 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C901 AF500035 0CK103CK51A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.01UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP B(Y
C903 AF500035 0CK103CK51A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.01UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP B(Y
C904 AF500035 0CK103CK51A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.01UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP B(Y
C905 AF500035 0CK103CK51A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.01UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP B(Y
C906 AF500035 0CK103CK51A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.01UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP B(Y
C911 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C912 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C913 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C914 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C915 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C916 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C918 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C919 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C921 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C922 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
C961 AF500036 0CK104CK56A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 1608 50V 10% R/TP X7R
R81 AF500039 0CK225DFK4A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "2.2UF 2012 16V 20%,-20% F(Y5"
R83 AF500039 0CK225DFK4A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" "2.2UF 2012 16V 20%,-20% F(Y5"
C121 AF500001 0CC100CK41A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(T" 10PF 1608 50V 5% R/TP NP0
C122 AF500001 0CC100CK41A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(T" 10PF 1608 50V 5% R/TP NP0
C43 AF500002 0CC102CK41A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(T" 1000PF 1608 50V 5% R/TP NP0
C47 AF500003 0CC220CK41A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(T" 22PF 1608 50V 5% R/TP NP0
C48 AF500003 0CC220CK41A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(T" 22PF 1608 50V 5% R/TP NP0
C56 AF500004 0CC221CK41A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(T" 220PF 1608 50V 5% R/TP NP0
C57 AF500004 0CC221CK41A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(T" 220PF 1608 50V 5% R/TP NP0
C58 AF500004 0CC221CK41A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(T" 220PF 1608 50V 5% R/TP NP0
C74 AF500002 0CC102CK41A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(T" 1000PF 1608 50V 5% R/TP NP0
C83 AF500002 0CC102CK41A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(T" 1000PF 1608 50V 5% R/TP NP0
C85 AF500002 0CC102CK41A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(T" 1000PF 1608 50V 5% R/TP NP0
C86 AF500002 0CC102CK41A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(T" 1000PF 1608 50V 5% R/TP NP0
C88 AF500005 0CC390CK41A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(T" 39PF 1608 50V 5% R/TP NP0
C89 AF500005 0CC390CK41A "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(T" 39PF 1608 50V 5% R/TP NP0
C1106 AF500016 0CE477BD618 "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 470UF KME TYPE 10V 20% FL TP
C1124 AF500016 0CE477BD618 "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 470UF KME TYPE 10V 20% FL TP
C1 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C108 AF500015 0CE476WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 47UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD) S
C1102 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C1103 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C1105 AF500034 0CH8476F691 "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 47UF 16V 20% 105STD (CYL) R/
C1109 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
- 29 -
Page 30

*S *AL LOC. NO.
TOSHIBAPART NO.
LG PART NO. DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
REMARKS
C111 AF500013 0CE475WJ6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 4.7UF MVK 35V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C1118 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C112 AF500013 0CE475WJ6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 4.7UF MVK 35V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C1130 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C1132 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C1134 AF500010 0CE227WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 220UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C1135 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C1137 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C119 AF500033 0CH8106F691 "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 10UF 16V 20% 105STD (CYL) R/
C120 AF500033 0CH8106F691 "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 10UF 16V 20% 105STD (CYL) R/
C1216 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C1218 AF500011 0CE337WH6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 330UF MVK 25V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C1219 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C1221 AF500014 0CE476VH6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 47UF MV 25V 20% R/TP(SMD) SM
C1223 AF500019 0CE477WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 470UF MVK 16V 20% SMD R/TP(S
C1225 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C1250 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C1251 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C1266 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C17 AF500013 0CE475WJ6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 4.7UF MVK 35V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C5 AF500013 0CE475WJ6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 4.7UF MVK 35V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C55 AF500012 0CE475VK6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 4.7UF MV 50V 20% R/TP(SMD) S
C563 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C60 AF500012 0CE475VK6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 4.7UF MV 50V 20% R/TP(SMD) S
C852 AF500034 0CH8476F691 "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 47UF 16V 20% 105STD (CYL) R/
C856 AF500034 0CH8476F691 "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 47UF 16V 20% 105STD (CYL) R/
C859 AF500034 0CH8476F691 "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 47UF 16V 20% 105STD (CYL) R/
C864 AF500034 0CH8476F691 "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 47UF 16V 20% 105STD (CYL) R/
C868 AF500034 0CH8476F691 "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 47UF 16V 20% 105STD (CYL) R/
C87 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
C873 AF500034 0CH8476F691 "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 47UF 16V 20% 105STD (CYL) R/
C876 AF500033 0CH8106F691 "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 10UF 16V 20% 105STD (CYL) R/
C888 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
D100 AF500046 0DRFC00288A "DIODE,RECTIFIERS" SS14 FAIR CHILD R/TP SMA 20D101 AF500046 0DRFC00288A "DIODE,RECTIFIERS" SS14 FAIR CHILD R/TP SMA 20D1200 AF500045 0DR340009AA "DIODE,RECTIFIERS" MBRS340 TP FAIRCHILD NON 40V
D1150 AF500047 0DRGS00199A "DIODE,RECTIFIERS" UF4001 GENERAL SEMICONDUCTOR
D104 AF500048 0DS181009AA "DIODE,SWITCHING" KDS181 TP KEC SOT-23 80V 3
D103 AF500048 0DS181009AA "DIODE,SWITCHING" KDS181 TP KEC SOT-23 80V 3
D107 AF500049 0DS226009AA "DIODE,SWITCHING" KDS226 TP KEC SOT-23 80V 30
ZD104 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
ZD105 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
ZD201 AF500051 0DZ510009EE "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 5.1B TP ROHM-K SOD323
ZD202 AF500051 0DZ510009EE "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 5.1B TP ROHM-K SOD323
ZD203 AF500051 0DZ510009EE "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 5.1B TP ROHM-K SOD323
ZD204 AF500051 0DZ510009EE "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 5.1B TP ROHM-K SOD323
ZD205 AF500051 0DZ510009EE "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 5.1B TP ROHM-K SOD323
ZD207 AF500051 0DZ510009EE "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 5.1B TP ROHM-K SOD323
ZD208 AF500051 0DZ510009EE "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 5.1B TP ROHM-K SOD323
ZD209 AF500051 0DZ510009EE "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 5.1B TP ROHM-K SOD323
ZD211 AF500051 0DZ510009EE "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 5.1B TP ROHM-K SOD323
ZD1200 AF500051 0DZ510009EE "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 5.1B TP ROHM-K SOD323
ZD1201 AF500051 0DZ510009EE "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 5.1B TP ROHM-K SOD323
ZD200 AF500051 0DZ510009EE "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 5.1B TP ROHM-K SOD323
ZD206 AF500051 0DZ510009EE "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 5.1B TP ROHM-K SOD323
D1151 AF500050 0DZ330009DF "DIODE,ZENERS" MTZJ33B TP ROHM-K DO34 0.5W
- 30 -
DIODEs
Page 31

*S *AL LOC. NO.
TOSHIBAPART NO.
LG PART NO. DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
REMARKS
IC905 AF500071 0IZZTSA024A "IC,DRAWING" T17LC10D FLASH ROM ASSY
IC3 AF500053 0IKE702700D "IC,KEC" "KIA7027AF 3, SOT-89 TP RESET"
IC200 AF500064 0IMMRSG036A "IC,MEMORIES" "M24C02-WMN6T SGS-THOMSON 8P,"
IC4 AF500054 0IMCRAL006A "IC,MEMORIES" AT24C16AN-10SI-2.7 ATMEL 8P
IC903 AF500054 0IMCRAL006A "IC,MEMORIES" AT24C16AN-10SI-2.7 ATMEL 8P
IC100 AF500060 0IMCRMZ002A "IC,MICRO CONTROLLER" MP7720 MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
IC101 AF500060 0IMCRMZ002A "IC,MICRO CONTROLLER" MP7720 MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
IC1103 AF500062 0IMCRNS007C "IC,MICRO CONTROLLER" LMS1587CS-ADJ NATIONAL SEMIC
IC1106 AF500062 0IMCRNS007C "IC,MICRO CONTROLLER" LMS1587CS-ADJ NATIONAL SEMIC
IC1114 AF500063 0IMCRNS007E "IC,MICRO CONTROLLER" LMS1587CS-3.3 NATIONAL SEMIC
IC1202 AF500061 0IMCRNS007A "IC,MICRO CONTROLLER" LM2940S 8V NATIONAL SEMICOND
IC1203 AF500059 0IMCRMZ001A "IC,MICRO CONTROLLER" MP1583DN MONOLITHIC POWER SY
IC851 AF500058 0IMCRMI006A "IC,MICRO CONTROLLER" "M52758FP MITSUBISHI 36PIN, R"
IC202 AF500065 0IMO140662A "IC,MOTOROLA" "MC14066BDR2 14P,SOIC TP BILA"
IC1 AF500068 0IPRPMN003C "IC,PERIPHERALS" VCT49XYF C7(NTSC+PAL) MICRON
IC800 AF500069 0IPRPNP001A "IC,PERIPHERALS" "SM5301BS(ATSC DTV) NPC 28P,H"
IC901 AF500067 0IPRPGN015A "IC,PERIPHERALS" "GM2221-BC GENESIS 208P,QFP T"
IC1108 AF500057 0IMCRKE010A "IC,POWER MANAGEMENT" KIA7812AF KEC 2P DPACK R/TP
IC1111 AF500055 0IMCRFA015A "IC,POWER MANAGEMENT" KA7805R FAIRCHILD 2P D-PAK R
IC1112 AF500057 0IMCRKE010A "IC,POWER MANAGEMENT" KIA7812AF KEC 2P DPACK R/TP
IC1115 AF500066 0IPMGFA061A "IC,POWER MANAGEMENT" "FAN1587AD33X FAIRCHILD 3P,DP"
IC1201 AF500066 0IPMGFA061A "IC,POWER MANAGEMENT" "FAN1587AD33X FAIRCHILD 3P,DP"
IC1110 AF500070 0ISS780800J "IC,SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS" "KA78M08R 3P,D-PAK TP VOL. RE"
IC1113 AF500070 0ISS780800J "IC,SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS" "KA78M08R 3P,D-PAK TP VOL. RE"
IC1200 AF500056 0IMCRFA021A "IC,STANDARD LOGIC" 74VHCU04MX FAIRCHILD 14P SOP
L104 AF500201 6140TBZ045A "COIL,CHOKE" "38.5UH(DIP), 6A, P7.5, DR8.3"
L105 AF500201 6140TBZ045A "COIL,CHOKE" "38.5UH(DIP), 6A, P7.5, DR8.3"
L1150 AF500138 150-985B "COIL,CHOKE" DR8*11 2.4MH 0.16MM 270.5T
L1209 AF500164 6140VR0008B "COIL,ENERGY RECOVERY" SLF12575T-150M3R2 15UH SMD
L1100 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L1101 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L1103 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
L1104 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
L1105 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L1106 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L1107 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L1205 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L1206 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L1207 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L1208 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L1210 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L1232 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
L1233 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
L1234 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
L200 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
L202 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
L203 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
L204 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
L206 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
L800 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L853 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L900 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L901 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L902 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L903 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
- 31 -
COIL & CORE & INDUCTOR
IC
Page 32

*S *AL LOC. NO.
TOSHIBAPART NO.
LG PART NO. DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
REMARKS
L906 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L908 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L1102 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L201 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L205 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
L10 AF500074 0LC1032101A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 10UH 10% 3216 R/TC FI-C3216L1003 AF500074 0LC1032101A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 10UH 10% 3216 R/TC FI-C3216L1220 AF500196 0LC2000005F "INDUCTOR,CHIP" F1-C2012-562-KJT CERATECH R/
L1221 AF500196 0LC2000005F "INDUCTOR,CHIP" F1-C2012-562-KJT CERATECH R/
L1222 AF500196 0LC2000005F "INDUCTOR,CHIP" F1-C2012-562-KJT CERATECH R/
L1223 AF500196 0LC2000005F "INDUCTOR,CHIP" F1-C2012-562-KJT CERATECH R/
L15 AF500074 0LC1032101A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 10UH 10% 3216 R/TC FI-C3216L2 AF500074 0LC1032101A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 10UH 10% 3216 R/TC FI-C3216L1001 AF500073 0LC1020101A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 1UH 10% 2012 R/TC FI-B2012-1
L1200 AF500073 0LC1020101A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 1UH 10% 2012 R/TC FI-B2012-1
L1201 AF500072 0LC0233002A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 3.3UH CERATECH R/TP
L1202 AF500072 0LC0233002A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 3.3UH CERATECH R/TP
L1203 AF500072 0LC0233002A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 3.3UH CERATECH R/TP
L8 AF500074 0LC1032101A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 10UH 10% 3216 R/TC FI-C3216-
IC902 AF500133 0TF492509AA FET SI4925DY TP TEMIC 30V 6.1A
IC1104 AF500133 0TF492509AA FET SI4925DY TP TEMIC 30V 6.1A
IC1107 AF500133 0TF492509AA FET SI4925DY TP TEMIC 30V 6.1A
Q1150 AF500135 0TR322809AB TRANSISTOR KTC3228-Y(KTC2383) TP KEC TO
Q1201 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1202 AF500134 0TR150400BA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SA1504S(ASY) BK KEC Q1204 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1209 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1210 AF500134 0TR150400BA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SA1504S(ASY) BK KEC Q1212 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q603 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q100 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1000 AF500137 0TR388109AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" KTC3881 CHIP TP KEC - Q101 AF500134 0TR150400BA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SA1504S(ASY) BK KEC Q1100 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1151 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q12 AF500134 0TR150400BA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SA1504S(ASY) BK KEC Q1200 AF500134 0TR150400BA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SA1504S(ASY) BK KEC Q1203 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1205 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1206 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1207 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1208 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1211 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1213 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1214 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1215 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1216 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q13 AF500134 0TR150400BA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SA1504S(ASY) BK KEC Q14 AF500134 0TR150400BA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SA1504S(ASY) BK KEC Q15 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q2 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q3 AF500134 0TR150400BA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SA1504S(ASY) BK KEC -
R101 AF500087 0RH1500D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 150 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1010 AF500101 0RH6801D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 6.8K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R102 AF500079 0RH0682D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 68 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
- 32 -
FET & TRANSISTOR
RESISTORs
Page 33

*S *AL LOC. NO.
TOSHIBAPART NO.
LG PART NO. DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
REMARKS
R107 AF500085 0RH1003D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1149 AF500090 0RH2200D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 220 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1151 AF500096 0RH4700D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 470 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1153 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1202 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1205 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1206 AF500088 0RH2000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 200 OHM 1 / 10 W 5% D R/TP
R1207 AF500100 0RH6201D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 6.2K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1220 AF500101 0RH6801D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 6.8K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1223 AF500091 0RH2700D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 270 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1224 AF500091 0RH2700D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 270 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1227 AF500081 0RH0822D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 82 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1229 AF500090 0RH2200D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 220 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1241 AF500101 0RH6801D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 6.8K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1243 AF500091 0RH2700D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 270 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1244 AF500091 0RH2700D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 270 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1247 AF500081 0RH0822D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 82 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R126 AF500097 0RH4701D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 4.7K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1265 AF500078 0RH0472D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 47 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1266 AF500078 0RH0472D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 47 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1280 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R132 AF500085 0RH1003D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R133 AF500085 0RH1003D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R134 AF500085 0RH1003D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R135 AF500085 0RH1003D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R140 AF500077 0RH0392D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 39 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R141 AF500077 0RH0392D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 39 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R142 AF500077 0RH0392D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 39 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R143 AF500077 0RH0392D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 39 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R144 AF500077 0RH0392D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 39 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R145 AF500077 0RH0392D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 39 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R146 AF500077 0RH0392D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 39 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R147 AF500077 0RH0392D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 39 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R211 AF500080 0RH0752D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 75 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R212 AF500080 0RH0752D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 75 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R213 AF500080 0RH0752D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 75 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R214 AF500098 0RH4703D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 470K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R215 AF500093 0RH3301D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 3.3K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R216 AF500093 0RH3301D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 3.3K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R217 AF500098 0RH4703D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 470K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R57 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R59 AF500086 0RH1201D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 1.2K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R907 AF500093 0RH3301D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 3.3K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R908 AF500081 0RH0822D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 82 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R910 AF500081 0RH0822D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 82 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R912 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R915 AF500094 0RH3600D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" CHIP 360-J 1/10 W
R930 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R931 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R934 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R935 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R953 AF500093 0RH3301D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 3.3K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R97 AF500087 0RH1500D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 150 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R979 AF500093 0RH3301D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 3.3K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R98 AF500079 0RH0682D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 68 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R981 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R989 AF500102 0RH8200D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 820 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
- 33 -
Page 34

*S *AL LOC. NO.
TOSHIBAPART NO.
LG PART NO. DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
REMARKS
R999 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R136 AF500103 0RH8202D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 82K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R137 AF500103 0RH8202D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 82K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
C932 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
C933 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R1011 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R106 AF500083 0RH1001D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 1K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R108 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R1106 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1152 AF500083 0RH1001D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 1K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R1203 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R1208 AF500089 0RH2002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 20K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1209 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1221 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1222 AF500083 0RH1001D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 1K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R1225 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1226 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1230 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1231 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1233 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1235 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1236 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1237 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1240 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1242 AF500083 0RH1001D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 1K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R1245 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1246 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1251 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1253 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1255 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1256 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1257 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R128 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R129 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R202 AF500076 0RH0222D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 22 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R205 AF500076 0RH0222D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 22 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R207 AF500083 0RH1001D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 1K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R208 AF500076 0RH0222D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 22 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R209 AF500076 0RH0222D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 22 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R210 AF500076 0RH0222D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 22 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R219 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R26 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R27 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R35 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R7 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R903 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R913 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R914 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R917 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R938 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R954 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R961 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R964 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R993 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R1 AF500114 0RJ1002D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R10 AF500123 0RJ3301D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 3.3K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1001 AF500108 0RJ0562D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 56 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
- 34 -
Page 35

*S *AL LOC. NO.
TOSHIBAPART NO.
LG PART NO. DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
REMARKS
R1002 AF500117 0RJ1501D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 1.5K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1003 AF500127 0RJ8200D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 820 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1004 AF500122 0RJ3000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 300 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1005 AF500109 0RJ0682D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 68 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1014 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R11 AF500123 0RJ3301D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 3.3K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1105 AF500113 0RJ1001D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 1K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1107 AF500125 0RJ4701D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 4.7K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1150 AF500105 0RJ0102D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1201 AF500125 0RJ4701D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 4.7K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1204 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1228 AF500118 0RJ2200D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 220 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1232 AF500110 0RJ0822D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 82 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1234 AF500110 0RJ0822D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 82 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1238 AF500120 0RJ2700D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 270 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1239 AF500120 0RJ2700D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 270 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R124 AF500116 0RJ1500D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 150 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R125 AF500125 0RJ4701D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 4.7K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1250 AF500114 0RJ1002D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1252 AF500110 0RJ0822D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 82 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1254 AF500110 0RJ0822D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 82 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1258 AF500120 0RJ2700D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 270 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1259 AF500120 0RJ2700D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 270 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1260 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1261 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1267 AF500126 0RJ5101D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 5.1K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1268 AF500126 0RJ5101D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 5.1K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R127 AF500121 0RJ2701D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 2.7K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1275 AF500104 0RJ0000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1281 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1282 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R1284 AF500104 0RJ0000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R130 AF500115 0RJ1202D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 12K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R131 AF500115 0RJ1202D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 12K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R138 AF500114 0RJ1002D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R139 AF500114 0RJ1002D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R15 AF500110 0RJ0822D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 82 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R16 AF500118 0RJ2200D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 220 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R17 AF500110 0RJ0822D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 82 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R18 AF500118 0RJ2200D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 220 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R19 AF500110 0RJ0822D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 82 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R2 AF500199 0RJ2002D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 20000 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/T
R20 AF500118 0RJ2200D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 220 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R203 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R206 AF500113 0RJ1001D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 1K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R21 AF500106 0RJ0222D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 22 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R218 AF500114 0RJ1002D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R22 AF500116 0RJ1500D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 150 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R221 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R224 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R225 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R226 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R227 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R229 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R23 AF500121 0RJ2701D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 2.7K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R24 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R240 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
- 35 -
Page 36

*S *AL LOC. NO.
TOSHIBAPART NO.
LG PART NO. DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
REMARKS
R25 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R3 AF500124 0RJ4700D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 470 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R34 AF500104 0RJ0000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R4 AF500198 0RJ1800D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 180 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R41 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R42 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R45 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R46 AF500113 0RJ1001D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 1K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R5 AF500109 0RJ0682D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 68 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R50 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R51 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R52 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R53 AF500116 0RJ1500D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 150 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R54 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R55 AF500116 0RJ1500D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 150 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R56 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R60 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R62 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R64 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R66 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R68 AF500104 0RJ0000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R69 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R70 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R72 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R73 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R74 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R75 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R76 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R77 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R78 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R8 AF500104 0RJ0000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R80 AF500119 0RJ2202D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 22K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R817 AF500104 0RJ0000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R818 AF500127 0RJ8200D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 820 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R822 AF500114 0RJ1002D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R835 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R838 AF500104 0RJ0000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R85 AF500125 0RJ4701D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 4.7K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R86 AF500125 0RJ4701D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 4.7K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R901 AF500107 0RJ0472D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 47 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R902 AF500107 0RJ0472D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 47 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R904 AF500107 0RJ0472D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 47 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R909 AF500110 0RJ0822D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 82 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R911 AF500125 0RJ4701D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 4.7K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R932 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R936 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R942 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R943 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R944 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R945 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R946 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R947 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R96 AF500123 0RJ3301D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 3.3K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R980 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R982 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R983 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R984 AF500111 0RJ1000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
- 36 -
Page 37

*S *AL LOC. NO.
TOSHIBAPART NO.
LG PART NO. DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
REMARKS
R985 AF500104 0RJ0000D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R991 AF500123 0RJ3301D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 3.3K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
R992 AF500123 0RJ3301D677 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 3.3K OHM 1/10 W 5% 1608 R/TP
Z1000 AF500202 6200QL3001Z "FILTER(CIRC),SAW" B39361-X6966-D100 EPCOS ST
X11 AF500166 6202VDT002E "RESONATOR,CRYSTAL" SX-1SMD SUNNY RADIAL 2025000
X900 AF500165 6202VDT002B "RESONATOR,CRYSTAL" SX-1 SUNNY SC14.3MHZ +/- 30
IC905 AF500203 6620F00017A "SOCKET(CIRC),IC" CCSD-32T-SM WOOYOUNG 32P PLC
TU1000 AF500204 6700VS0003D TUNER TAEW-G052P LGIT MULTI VS RCA
R2200 AF500128 0RN1000F409 "RESISTOR,FIXED METAL FILM" 100OHM 1/6 W 1% TA52
R2201 AF500132 0RN7500F409 "RESISTOR,FIXED METAL FILM" 750 1/6W 1% TA52
R2202 AF500129 0RN1801F409 "RESISTOR,FIXED METAL FILM" 1.80K 1/6W 1% TA52
R2203 AF500130 0RN3301F409 "RESISTOR,FIXED METAL FILM" 3.30K 1/6W 1% TA52
R2204 AF500131 0RN6201F409 "RESISTOR,FIXED METAL FILM" 6.20K 1/6W 1% TA52
R2205 AF500128 0RN1000F409 "RESISTOR,FIXED METAL FILM" 100OHM 1/6 W 1% TA52
R2206 AF500132 0RN7500F409 "RESISTOR,FIXED METAL FILM" 750 1/6W 1% TA52
R2207 AF500129 0RN1801F409 "RESISTOR,FIXED METAL FILM" 1.80K 1/6W 1% TA52
R2208 AF500130 0RN3301F409 "RESISTOR,FIXED METAL FILM" 3.30K 1/6W 1% TA52
R2209 AF500131 0RN6201F409 "RESISTOR,FIXED METAL FILM" 6.20K 1/6W 1% TA52
SW2200 AF500200 140-058E "SWITCH,TACT" SKHV10910B LGEC NON 12V 20A
SW2201 AF500200 140-058E "SWITCH,TACT" SKHV10910B LGEC NON 12V 20A
SW2202 AF500200 140-058E "SWITCH,TACT" SKHV10910B LGEC NON 12V 20A
SW2203 AF500200 140-058E "SWITCH,TACT" SKHV10910B LGEC NON 12V 20A
SW2204 AF500200 140-058E "SWITCH,TACT" SKHV10910B LGEC NON 12V 20A
SW2205 AF500200 140-058E "SWITCH,TACT" SKHV10910B LGEC NON 12V 20A
SW2206 AF500200 140-058E "SWITCH,TACT" SKHV10910B LGEC NON 12V 20A
SW2207 AF500200 140-058E "SWITCH,TACT" SKHV10910B LGEC NON 12V 20A
SW2208 AF500200 140-058E "SWITCH,TACT" SKHV10910B LGEC NON 12V 20A
SW2209 AF500200 140-058E "SWITCH,TACT" SKHV10910B LGEC NON 12V 20A
C1215 AF500029 0CH6151K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 150PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C41 AF500021 0CH3104K566 "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 50V 10% X7R 2012 R/TP
L1200 AF500168 6210TCE001G "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HH-1M3216-501 CERATEC 3216MM
L1201 AF500196 0LC2000005F "INDUCTOR,CHIP" F1-C2012-562-KJT CERATECH R/
L1202 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
L1203 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
L1206 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
L1207 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
L1208 AF500196 0LC2000005F "INDUCTOR,CHIP" F1-C2012-562-KJT CERATECH R/
Q1200 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1201 AF500134 0TR150400BA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SA1504S(ASY) BK KEC Q1203 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1204 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC R1202 AF500080 0RH0752D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 75 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1217 AF500080 0RH0752D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 75 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1218 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R1219 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R1220 AF500080 0RH0752D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 75 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1230 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
R1231 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R1232 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
R1233 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R1234 AF500197 0RH0562D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 56 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1235 AF500101 0RH6801D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 6.8K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1236 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1237 AF500083 0RH1001D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 1K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
- 37 -
OTHERs
CONTROL BOARD
REAR JACK
Page 38

- 38 -
IR LED & P/SW
SIDE
*S *AL LOC. NO.
TOSHIBAPART NO.
LG PART NO. DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
REMARKS
R1238 AF500078 0RH0472D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 47 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1239 AF500091 0RH2700D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 270 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1240 AF500091 0RH2700D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 270 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1244 AF500090 0RH2200D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 220 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1245 AF500090 0RH2200D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 220 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1247 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1250 AF500091 0RH2700D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 270 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1253 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
ZD1200 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
ZD1201 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
ZD1202 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
ZD1203 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
ZD1206 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
ZD1207 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
C1216 AF500031 0CH6331K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 330PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C1217 AF500014 0CE476VH6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 47UF MV 25V 20% R/TP(SMD) SM
C1218 AF500014 0CE476VH6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 47UF MV 25V 20% R/TP(SMD) SM
C1219 AF500007 0CE107WF6DC "CAPACITOR,FIXED ELECTROLY" 100UF MVK 16V 20% R/TP(SMD)
Q1202 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1205 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1206 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q1207 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC R1241 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1242 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1243 AF500081 0RH0822D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 82 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1246 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1248 AF500099 0RH5101D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 5.1K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1252 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1255 AF500091 0RH2700D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 270 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R1257 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
R1258 AF500084 0RH1002D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 10K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00%
C1303 AF500017 0CE477BF638 "CAPACITOR,AL.ELECTROLYTIC" 470UF KME TYPE 16V M FM5 TP
C2101 AF500021 0CH3104K566 "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 0.1UF 50V 10% X7R 2012 R/TP
L2101 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
Q2101 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q2102 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC Q2103 AF500136 0TR387500AA "TRANSISTOR,BIPOLARS" CHIP 2SC3875S(ALY) BK KEC R2101 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R2102 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R2103 AF500083 0RH1001D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 1K OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
R2104 AF500092 0RH3000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 300 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R2105 AF500090 0RH2200D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 220 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R2106 AF500082 0RH1000D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 100 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R2111 AF500095 0RH4301D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 4.3K 1/10W 5 TA
R2113 AF500075 0RH0000D622 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 0 OHM 1 / 10 W 2012 5.00% D
LED2100 AF500044 0DLLT0089AA LED LITEON LTL-1BEDJ-0C2 TP GREE
C2300 AF500020 0CH3103K516 "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 10000PF 50V 10% B(Y5P) 2012
C2301 AF500020 0CH3103K516 "CAPACITOR,FIXED CERAMIC(H" 10000PF 50V 10% B(Y5P) 2012
C2302 AF500032 0CH6471K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 470F 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C2303 AF500032 0CH6471K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 470F 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C2305 AF500031 0CH6331K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 330PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C2306 AF500031 0CH6331K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 330PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C2307 AF500031 0CH6331K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 330PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
C2308 AF500031 0CH6331K416 "CAPACITOR,CHIP[CERAMIC LD" 330PF 50V J NP0 2012 R/TP
L2300 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
Page 39

*S *AL LOC. NO.
TOSHIBAPART NO.
LG PART NO. DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
REMARKS
L2301 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
L2302 AF500167 6210TCE001A "CORE (CIRC),BEAD" HB-1S2012-080JT CERATEC 2012
L2303 AF500074 0LC1032101A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 10UH 10% 3216 R/TC FI-C3216L2304 AF500074 0LC1032101A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 10UH 10% 3216 R/TC FI-C3216L2305 AF500072 0LC0233002A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 3.3UH CERATECH R/TP
L2306 AF500072 0LC0233002A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 3.3UH CERATECH R/TP
L2307 AF500072 0LC0233002A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 3.3UH CERATECH R/TP
L2308 AF500072 0LC0233002A "INDUCTOR,CHIP" 3.3UH CERATECH R/TP
R2300 AF500112 0RJ1000H680 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/2 W 5% 5025 R/TP
R2301 AF500112 0RJ1000H680 "RESISTOR,METAL GLAZED(CHI" 100 OHM 1/2 W 5% 5025 R/TP
R2302 AF500080 0RH0752D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 75 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R2303 AF500080 0RH0752D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 75 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R2304 AF500080 0RH0752D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 75 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R2305 AF500098 0RH4703D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 470K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R2306 AF500098 0RH4703D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 470K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R2307 AF500078 0RH0472D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 47 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R2308 AF500099 0RH5101D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 5.1K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R2309 AF500099 0RH5101D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 5.1K 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R2310 AF500080 0RH0752D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 75 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
R2311 AF500080 0RH0752D622 "RESISTOR,CHIP" 75 1/10W 5 D.R/TP
ZD2302 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
ZD2303 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
ZD2304 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
ZD2305 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
ZD2306 AF500052 0DZ620009HB "DIODE,ZENER" UDZ S 6.2B TP ROHM SOD323 20
SW2500 AF500173 6600VM1001A "SWITCH,PUSH" SDKLA1 ALPS UL/CSA 250V 5A V
- 39 -
POWER JACK
Page 40

- 40 -
Page 41

- 41 -
Page 42

 Loading...
Loading...