Page 1

FILE NO.SVM-05053-1
SERVICE MANUAL
HI WALL TYPE (INDOOR UNIT)
RAV-SM562KRT-E
RAV-SM802KRT-E
R410A
Rev. Mar, 2006
Page 2

CONTENTS
1. SPECIFICATIONS................................................................................................ 2
2. CONSTRUCTION VIEWS (EXTERNAL VIEWS) ................................................. 4
3. SYSTEMATIC REFRIGERATING CYCLE DIAGRAM ......................................... 5
4. WIRING DIAGRAM .............................................................................................. 6
5. SPECIFICATIONS OF ELECTRICAL PARTS ..................................................... 7
6. REFRIGERANT R410A ....................................................................................... 8
7. INDOOR UNIT CONTROL ................................................................................. 16
8. TROUBLESHOOTING ....................................................................................... 27
9. HOW TO REPLACEMENT OF SERVICE INDOOR P.C. BOARD....................... 50
10. SETUP AT LOCAL SITE AND O THERS ........................................................... 54
11. ADDRESS SETUP ............................................................................................. 71
12. EXPLODED VIEWS AND PARTS LIST.............................................................. 76
NOTE :
This Service Manual describes explanation for the Under Ceiling type indoor unit.
For the combined outdoor unit, refer to the following Service Manual.
Outdoor unit Model name SVM to be referred
RAV-SMXX0AT-E A03-007
RAV-SPXXXAT-E A03-014
RAV-SMXX1AT-E A05-001
– 1 –
Page 3
1-1. High-Wall Type (Indoor Unit)
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Model name
Standard capacity (Note 1) (kW)
Heating low temp. capacity (Note 1) (kW)
Energy consumption effect ratio (Cooling)
Power supply
Running current (A)
Electrical
characteristics
Appearance
Power consumption (kW)
(Low temp.) (kW)
Power factor (%)
Main unit
Ceiling Panel
(Sold separately)
Main unit Width (mm)
Model
Panel color
Height (mm)
RAV-SM562KRT-E RAV-SM802KRT-E
Cooling Heating Average Cooling Heating Average
5.1 5.6 6.7 8
(1.5 – 5.6) (1.5 – 6.3) (2.2 – 8.0) (2.2–9.0)
4.9 5.8
2.93 [D] 3.29 [C] 3.11 2.46 [E] 3.00 [D] 3.24
1 phase 230V (220 – 240V) 50Hz
8.33–7.63 8.138–7.46 13.15–12.05 12.91–11.84
1.74 1.7 2.72 2.67
1.95 2.21
95 95 94 94
Pure white
——
——
298
998
Outer
dimension
Ceiling panel
(Sold separately)
Total weight
Heat exchanger
Soundproof/Heat-insulating material
Fan unit Standard air flow High (Mid./Low) (m³/h)
Air filter
Controller (Sold separately)
Connecting
pipe
Main unit (kg)
Ceiling panel
Fan
Motor (W)
Gas side (mm)
Liquid side (mm)
Drain port (Nominal dia.)
Depth (mm)
Height (mm)
Width (mm)
Depth (mm)
221
——
——
——
12
——
Finned tubu
Inflammable polyethylene foam Foamed polyethylen
Turbo fan
840 1110
30
Attached main unit
Wired remote controller RBC-AMT21E
Ø12.7 (1/2”) Ø15.9 (5/8”)
Ø6.4 (1/4”) Ø9.5 (3/8”)
25 (Polyvinyl chloride tube)
Sound level High (Mid./Low) (Note 2) (dB•A)
45 41 36 45 41 36
Note 1 : The cooling capacities and electrical characteristics are measured under the conditions speciied by JIS B 8616 based
on the reference piping. The reference piping consists of 3 m of main piping and 2 m of branch piping connected with 0
meter height.
Note 2 : The sound level is measured in an anechoic chamber in accordance with JIS B8616. Normally, the values measured in
the actual operating environment become larger than the indicated values due to the effects of external sound.
Note : Rated conditions Cooling : Indoor air temperature 27°C DB/19°C WB, Outdoor air temperature 35°C DB
Heating : Indoor air temperature 20°C DB, Outdoor air temperature 7°C DB/6°C WB
– 2 –
Page 4
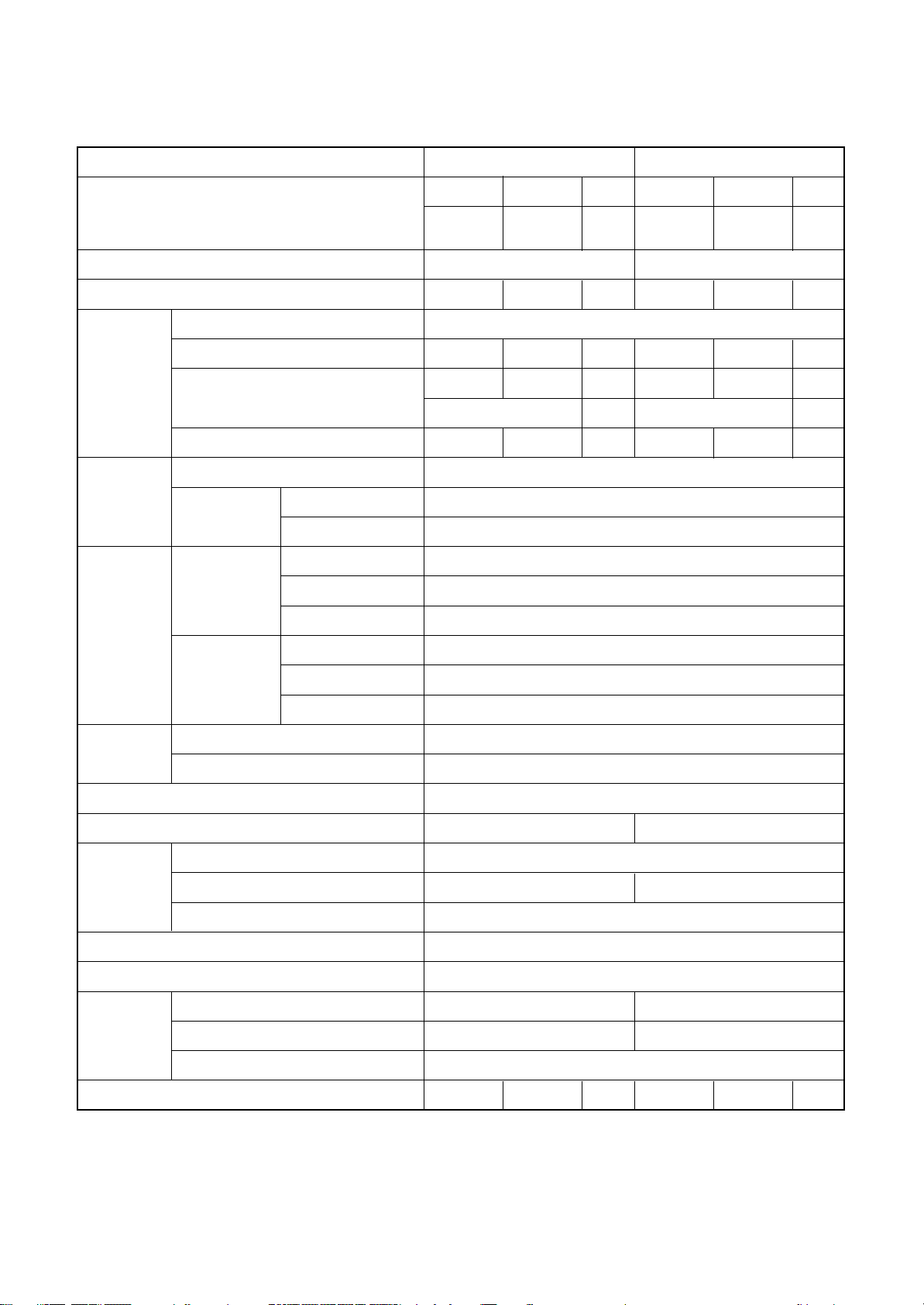
Operation characteristic curve
<Cooling> <Heating>
14
12
RAV-SM802KRT-E
10
8
6
Current (A)
4
2
0
0201540 60 70 80 100
RAV-SM562KRT-E
• Conditions
Indoor : DB27 C/WB19°C
Outdoor : DB35°C
Air flow : High
Pipe length : 7.5m
230V
Compressor speed (rps)
16
14
12
10
8
Current (A)
6
4
2
0
15
020
RAV-SM802KRT-E
RAV-SM562KRT-E
• Conditions
Indoor : DB20°C
Outdoor : DB7 C/WB6°C
Air flow : High
Pipe length : 7.5m
230V
40 60 80 90 100
Compressor speed (rps)
•Capacity variation ratioaccor ding to temperature
<Cooling> <Heating>
105
100
95
90
120
110
100
90
80
85
70
80
60
75
70
Capacity ratio (%)
65
60
55
• Conditions
Indoor : DB27 C/WB19°C
Indoor air flow : High
Pipe length : 7.5m
50
32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43
50
40
Capacity ratio (%)
30
20
10
0
-14-12-10-8-6-4-20246810
Outsoor temp. (°C)
• Conditions
Indoor : DB20°C
Indoor air flow : High
Pipe length : 7.5m
Outsoor temp. (°C)
– 3 –
Page 5
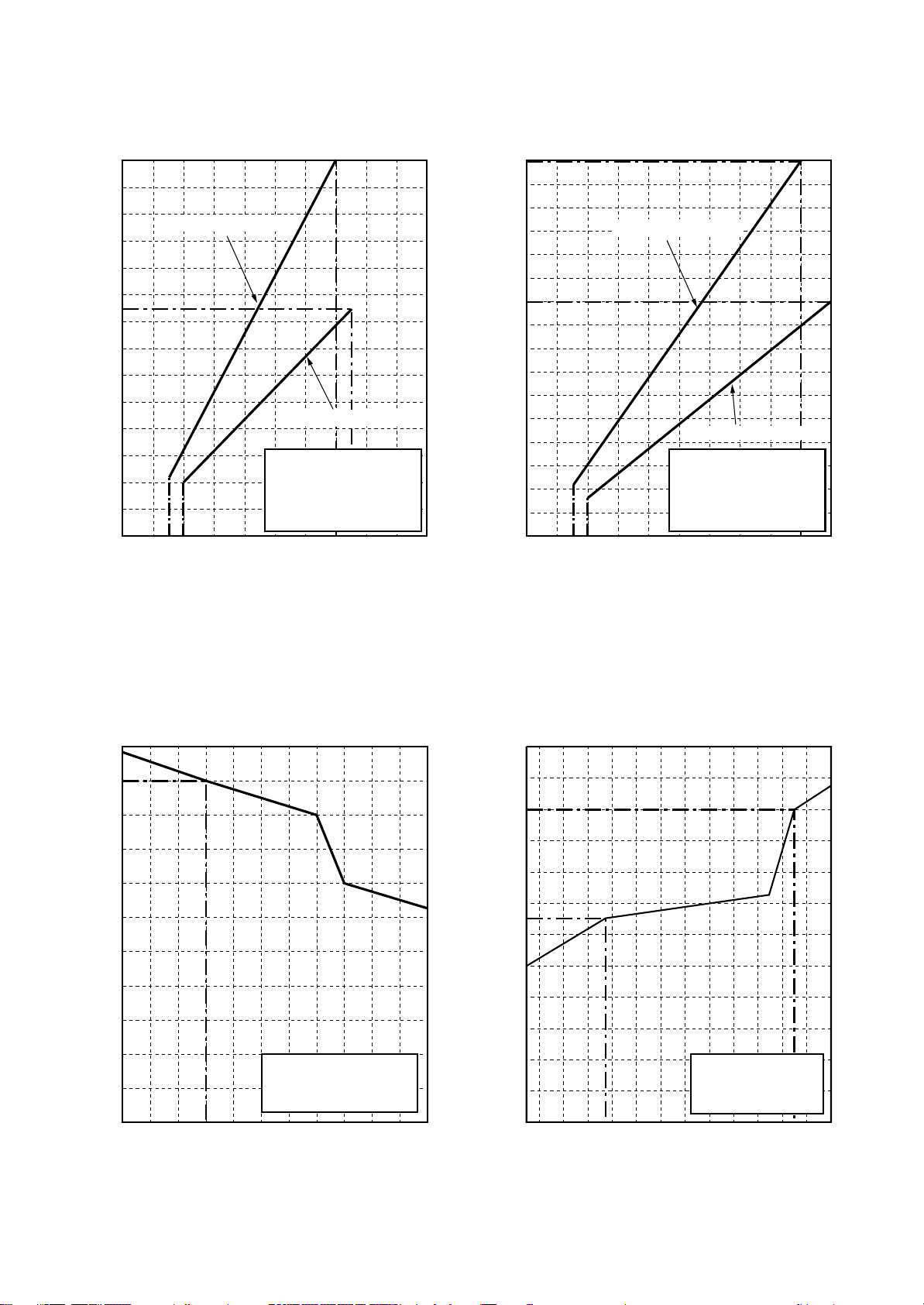
2. CONSTRUCTION VIEWS (EXTERNAL VIEWS)
High-Wall Type
RAV-SM562KRT-E/RAV-SM802KRT-E
75
7
51
Knock out system
Back body
Front panel
Grille inlet
298
Air inlet
Air outlet
998
75
56
220
Knock out system
50
50
75
8
Connection pipe (0.39 m)
(For SM802 : Flare ∅15.88)
(For SM562 : Flare ∅12.7)
55 or more
Outline of indoor unit
298
Minimum distance
to ceiling
∅65
100
20
48
998
763.5
450
Installation
Plate outline
Drain hose (0.54 m)
Connection pipe (0.49 m)
(Flare ∅6.35)
20
10
100
57
Wireless remote control
(For stud bolt ∅6)
(For stud bolt ∅8 -∅10)
29
41
55
5555
∅6
40
5
160
18
48
– 4 –
Page 6
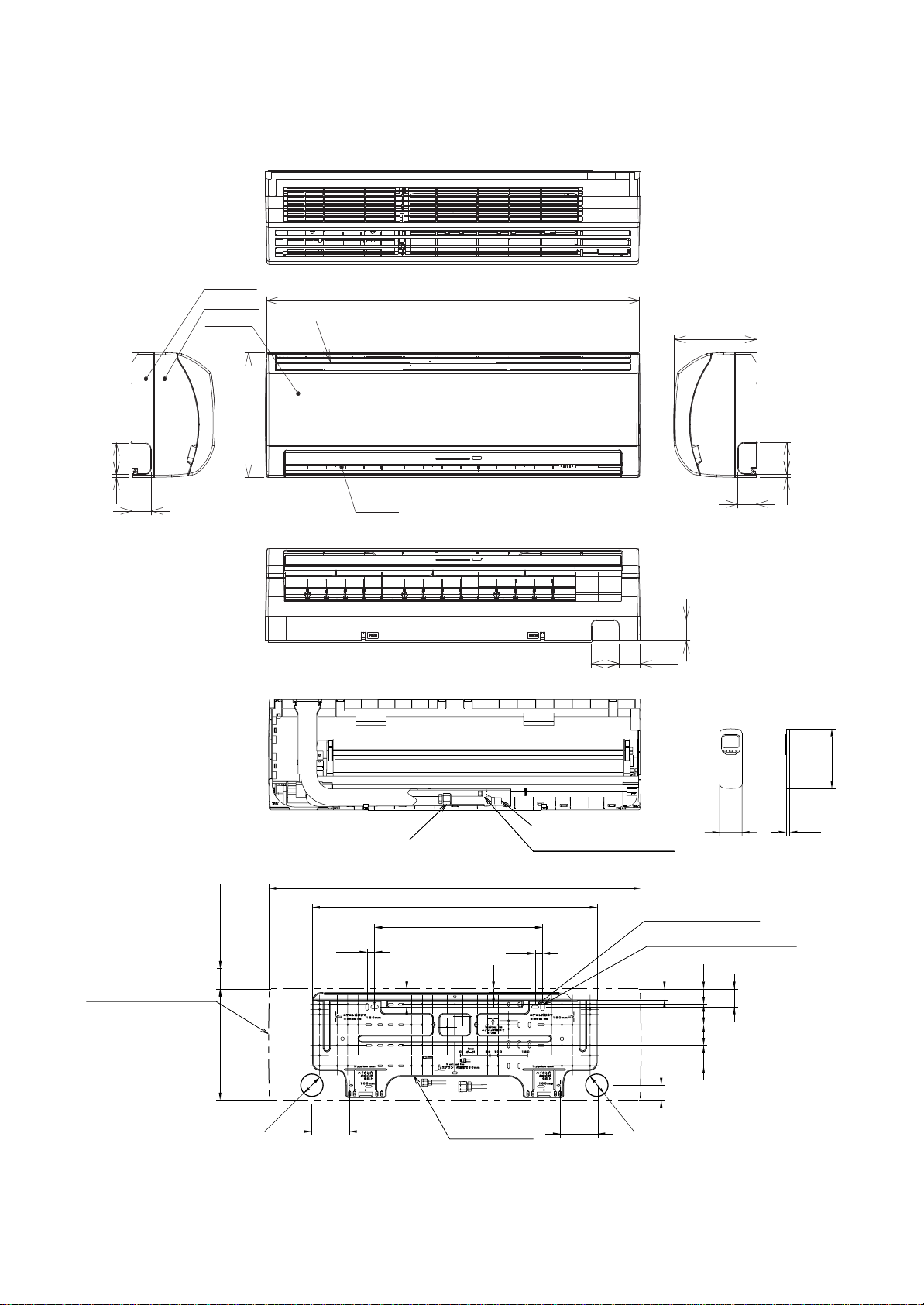
3. SYSTEMATIC REFRIGERATING CYCLE DIAGRAM
3-1. Hi Wall type
RAV-SM562KRT-E/SM802KRT-E
Outer diameter of refrig erant pipeModel
RAV-SM
562KRT-E
802KRT-E
Gas side ØA Liquid side ØB
12.7 mm 6.4 mm
15.9 mm
9.5 mm
Indoor unit
TCJ
sensor
Air heat exchanger
TC sensor
Refrigerant pipe
at gas side
Outer dia. ØA
Pd PsPacked valve
Packed valve
Outer dia. ØA
Refrigerant pipe
at liquid side
Outer dia. ØB
Outer dia. ØB
Outdoor unit
NOTE :
The refrigerating cycle differs according to the combined outdoor units.
For the cycle diagram, cycle pressure, etc., refer to the following Service Manual.
RAV-SMXXX0AT-E : A03-007
RAV-SPXXXXAT-E : A03-014
RAV-SMXXX1AT-E : A05-001
– 5 –
Cooling
Heating
Page 7
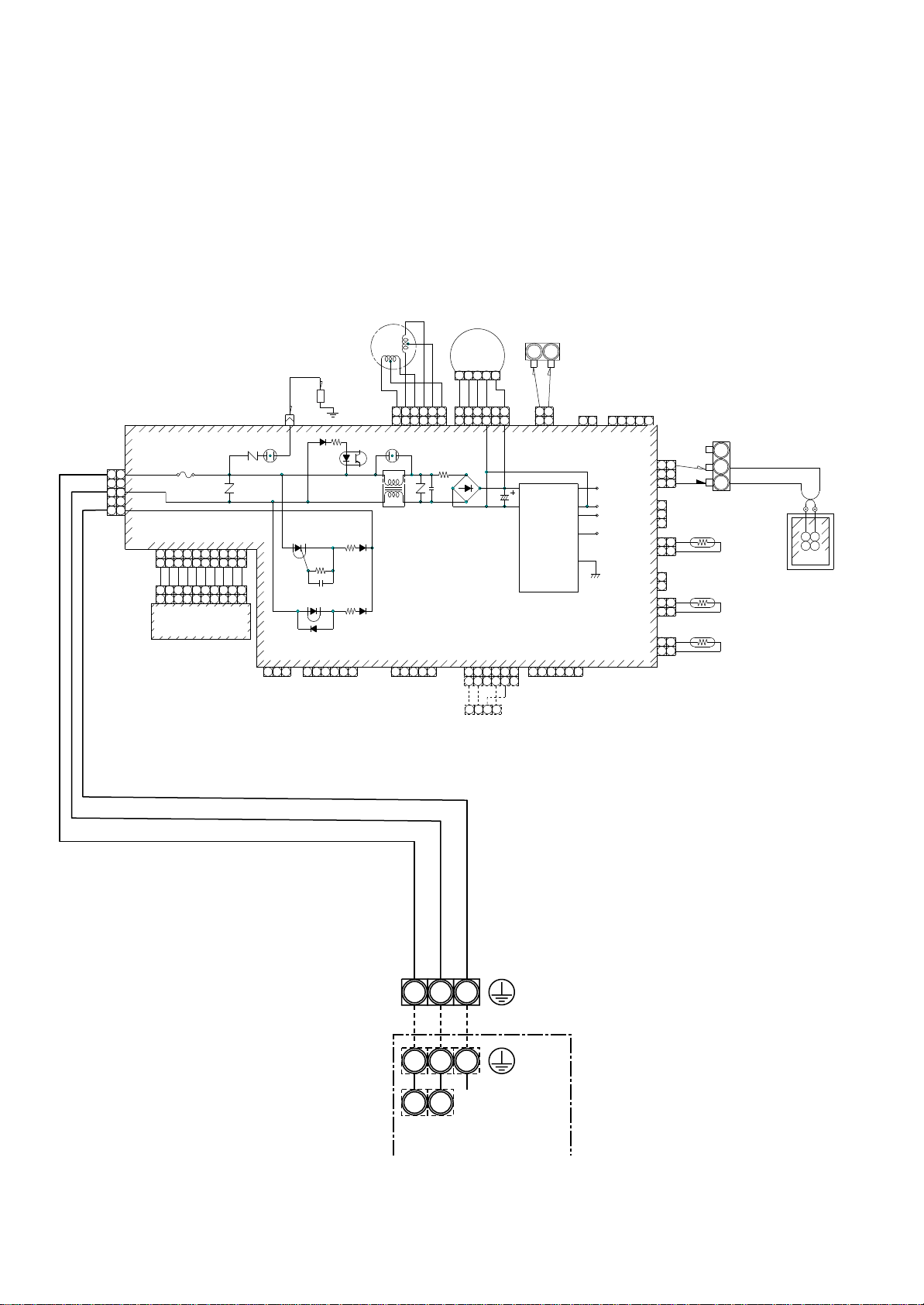
4-1. Hi Wall type (Indoor unit)
RAV-SM562KRT-E/SM802KRT-E
LOUVER
MOTOR
BLK
F
S
CN22
F301 FUSE
T3.15A 250V〜
1
1
3
3
5
5
CN67
(BLK)
CN213(WHI)
9
5 876
6 7 85
BLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLU
BLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLU
6 7 85
5 876
BLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLU
BLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLU
10
10
9
WHI
BLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLU
BLU
9
10
9
10
CN80
(GRN)
1 2 3
CN82
(BLU)
1
42 3
1
32 4
BLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLU
BLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLU
BLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLU
BLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLUBLU
1
32 4
1
42 3
INFRARED RAYS RECEIVE
AND INDICATION PARTS
(MCC−819)
PNL/EMG
4. WIRING DIAGRAM
TERMINAL
2 145 3
RED
BLK
1
34
1
CN61
(YEL)
53 4 621
53 4 62
3 42
BLOCK
U3
U4
BLU
BLU
112
2
CN40
(BLU)
POWER
SUPPLY
CIRCUIT
CN60
(WHI)
2 5431 6
OPTION
FAN
MOTOR
YEL
WHI
BRW
RED
ORN
BLU
YEL
PNK
BLU
13 2
123
CN210
(WHI)
5566
4 3
6 5
4
56
4
CN33
(WHI)
(MCC−1510)
ControlP.Cboard
forindoorunit
CN81
(BLK)
6321 4 5
4 51 2 3
1
1
HA
BUS
EMG
1 2
CN44
(BRW)
DC15V
DC 0V
DC12V
DC7V
21 543
CN50
(WHI)
3
CN41
2
1
(BLU)
1
CN100
2
(BRW)
3
1
CN101
(BLU)
1
CN103
2
(GRN)
1
CN102
2
(YEL)
1
CN104
2
(WHI)
3
2
1
212
1
2
1
2
BLK
BLK
BLK
BLK
BLK
BLK
BLK
BLK
TERMINAL
BLOCK
B
A
HEAT
EXCHANGER
SENSOR
(TC)
HEAT
EXCHANGER
SENSOR
(TCJ)
THERMO
SENSOR
(TA)
WHI
BLK
1
2
1
2
CN1(WHI)
WIERDREMOTE
CONTROLLER
NOTE
: Fan motor
FM
: Indoor temp. sensor
TA
: Temp. sensor
TC
: Temp. sensor
TCJ
: Louver motor
LM
WHI BLK
RED
321
321
Serial
NL
signal
Single phase 220V, 50Hz
– 6 –
Indoor unit
earth screw
Outdoor unit
earth screw
Color
Identification
BLACK
:
BLK
BLUE
:
BLU
RED
:
RED
GRAY
:
GRY
PINK
:
PNK
GREEN
:
GRN
WHITE
:
WHI
BROWN
:
BRW
ORANGE
:
ORN
YELLOW
:
YEL
Page 8
5. SPECIFICATIONS OF ELECTRICAL PARTS
5-1. Indoor Unit
High-Wall Type
RAV-SM562KRT-E/RAV-SM802KRT-E
No.
1
Fan motor (for indoor)
2
Grille motor
3
Thermo. sensor (TA-sensor)
4
Heat exchanger sensor (TC-sensor)
5
Heat exchanger sensor (TCJ-sensor)
Parts name
Type
ICF340-30-X
MF-340-30-X
MP35EA12
268 mm
Ø6 mm, 400 mm
Ø6 mm, 400 mm
Specifications
Output (Rated) 30 W, 220–240 V
10 kW at 25°C
10 kW at 25°C
– 7 –
Page 9

6. REFRIGERANT R410A
This air conditioner adopts the new refrigerant HFC
(R410A) which does not damage the ozone layer.
The working pressure of the new refrigerant R410A
is 1.6 times higher than conventional refrigerant
(R22). The refrigerating oil is also changed in
accordance with change of refrigerant, so be careful
that water, dust, and existing refrigerant or refrigerating oil are not entered in the refrigerant cycle of the
air conditioner using the new refrigerant during
installation work or servicing time.
The next section describes the precautions for air
conditioner using the new refrigerant. Conforming to
contents of the next section together with the
general cautions included in this manual, perform
the correct and safe work.
6-1. Safety During Installation/Servicing
As R410A's pressure is about 1.6 times higher than
that of R22, improper installation/servicing may
cause a serious trouble. By using tools and materials exclusive for R410A, it is necessary to carry out
installation/servicing safely while taking the following
precautions into consideration.
(1) Never use refrigerant other than R410A in an air
conditioner which is designed to operate with
R410A.
If other refrigerant than R410A is mixed, pressure in the refrigeration cycle becomes abnormally high, and it may cause personal injury, etc.
by a rupture.
(2) Confirm the used refrigerant name, and use
tools and materials exclusive for the refrigerant
R410A.
The refrigerant name R410A is indicated on the
visible place of the outdoor unit of the air conditioner using R410A as refrigerant. To prevent
mischarging, the diameter of the service port
differs from that of R22.
(3) If a refrigeration gas leakage occurs during
installation/servicing, be sure to ventilate fully.
If the refrigerant gas comes into contact with fire,
a poisonous gas may occur.
(4) When installing or removing an air conditioner,
do not allow air or moisture to remain in the
refrigeration cycle. Otherwise, pressure in the
refrigeration cycle may become abnormally high
so that a rupture or personal injury may be
caused.
(5) After completion of installation work, check to
make sure that there is no refrigeration gas
leakage.
If the refrigerant gas leaks into the room, coming
into contact with fire in the fan-driven heater,
space heater, etc., a poisonous gas may occur.
(6) When an air conditioning system charged with a
large volume of refrigerant is installed in a small
room, it is necessary to exercise care so that,
even when refrigerant leaks, its concentration
does not exceed the marginal level.
If the refrigerant gas leakage occurs and its
concentration exceeds the marginal level, an
oxygen starvation accident may result.
(7) Be sure to carry out installation or removal
according to the installation manual.
Improper installation may cause refrigeration
trouble, water leakage, electric shock, fire, etc.
(8) Unauthorized modifications to the air conditioner
may be dangerous. If a breakdown occurs
please call a qualified air conditioner technician
or electrician.
Improper repairÕs may result in water leakage,
electric shock and fire, etc.
6-2. Refrigerant Piping Installation
6-2-1. Piping Materials and Joints Used
For the refrigerant piping installation, copper pipes
and joints are mainly used. Copper pipes and joints
suitable for the refrigerant must be chosen and
installed. Furthermore, it is necessary to use clean
copper pipes and joints whose interior surfaces are
less affected by contaminants.
(1) Copper Pipes
It is necessary to use seamless copper pipes
which are made of either copper or copper alloy
and it is desirable that the amount of residual oil
is less than 40 mg/10 m. Do not use copper
pipes having a collapsed, deformed or discolored portion (especially on the interior surface).
Otherwise, the expansion valve or capillary tube
may become blocked with contaminants.
As an air conditioner using R410A incurs
pressure higher than when using R22, it is
necessary to choose adequate materials.
Thicknesses of copper pipes used with R410A
are as shown in Table 6-2-1. Never use copper
pipes thinner than 0.8 mm even when it is
available on the market.
– 8 –
Page 10
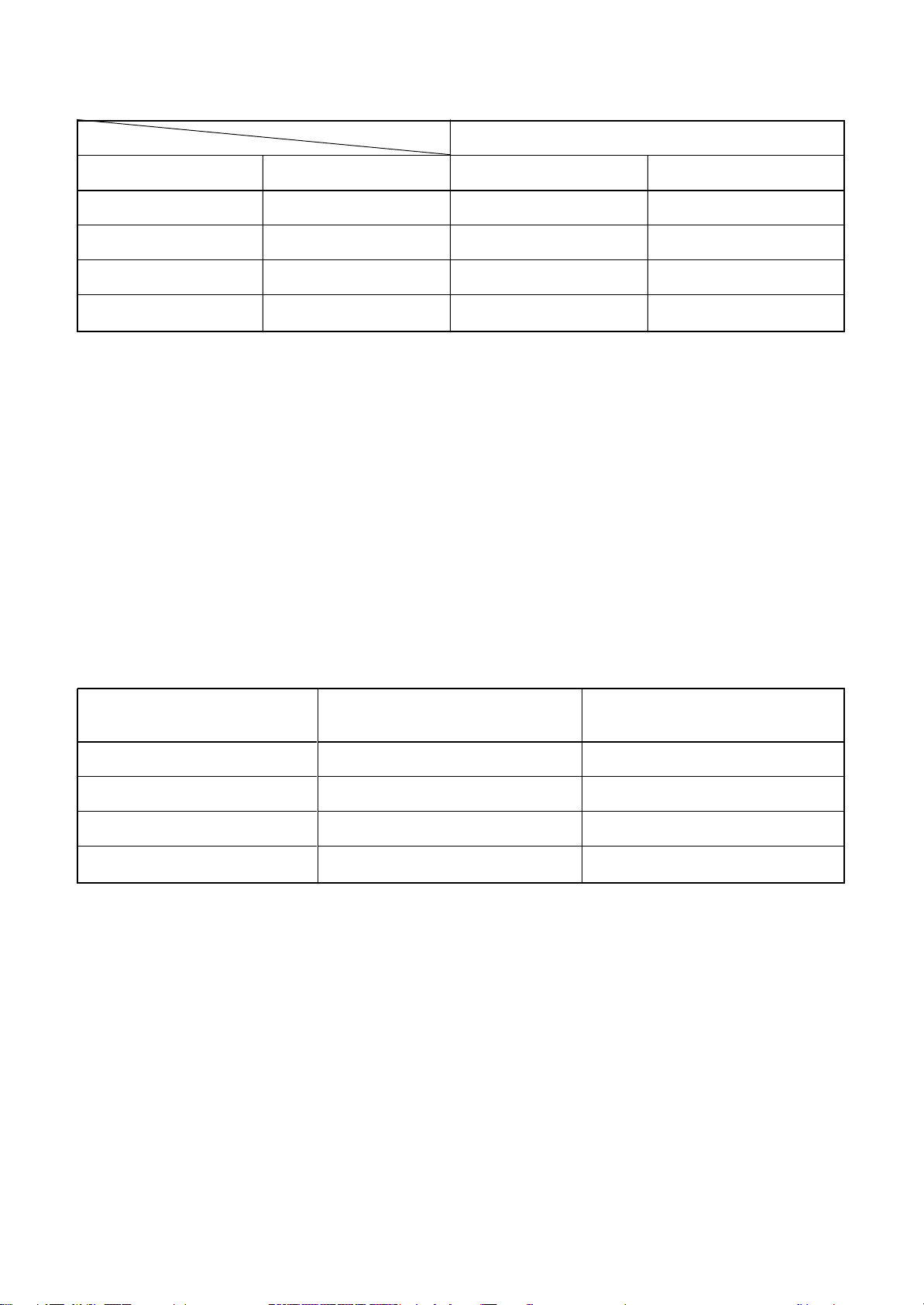
Table 6-2-1 Thicknesses of annealed copper pipes
Thickness (mm)
Nominal diameter
1/4
3/8
1/2
5/8
(2) Joints
For copper pipes, flare joints or socket joints are
used. Prior to use, be sure to remove all contaminants.
a) Flare Joints
Flare joints used to connect the copper pipes
cannot be used for pipings whose outer
diameter exceeds 20 mm. In such a case,
socket joints can be used.
Sizes of flare pipe ends, flare joint ends and
flare nuts are as shown in Tables 6-2-3 to 62-6 below.
Outer diameter (mm)
6.35
9.52
12.70
15.88
R410A R22
0.80 0.80
0.80 0.80
0.80 0.80
1.00 1.00
b) Socket Joints
Socket joints are such that they are brazed
for connections, and used mainly for thick
pipings whose diameter is larger than 20 mm.
Thicknesses of socket joints are as shown in
Table 6-2-2.
Table 6-2-2 Minimum thicknesses of socket joints
Nominal diameter
1/4
3/8
1/2
5/8
Reference outer diameter of
copper pipe jointed (mm)
6-2-2. Processing of Piping Materials
When performing the refrigerant piping installation,
care should be taken to ensure that water or dust
does not enter the pipe interior, that no other oil
other than lubricating oils used in the installed air
conditioner is used, and that refrigerant does not
leak. When using lubricating oils in the piping
processing, use such lubricating oils whose water
content has been removed. When stored, be sure to
seal the container with an airtight cap or any other
cover.
6.35
9.52
12.70
15.88
Minimum joint thickness
(mm)
0.50
0.60
0.70
0.80
(1) Flare Processing Procedures and Precautions
a) Cutting the Pipe
By means of a pipe cutter, slowly cut the pipe
so that it is not deformed.
b) Removing Burrs and Chips
If the flared section has chips or burrs,
refrigerant leakage may occur. Carefully
remove all burrs and clean the cut surface
before installation.
– 9 –
Page 11
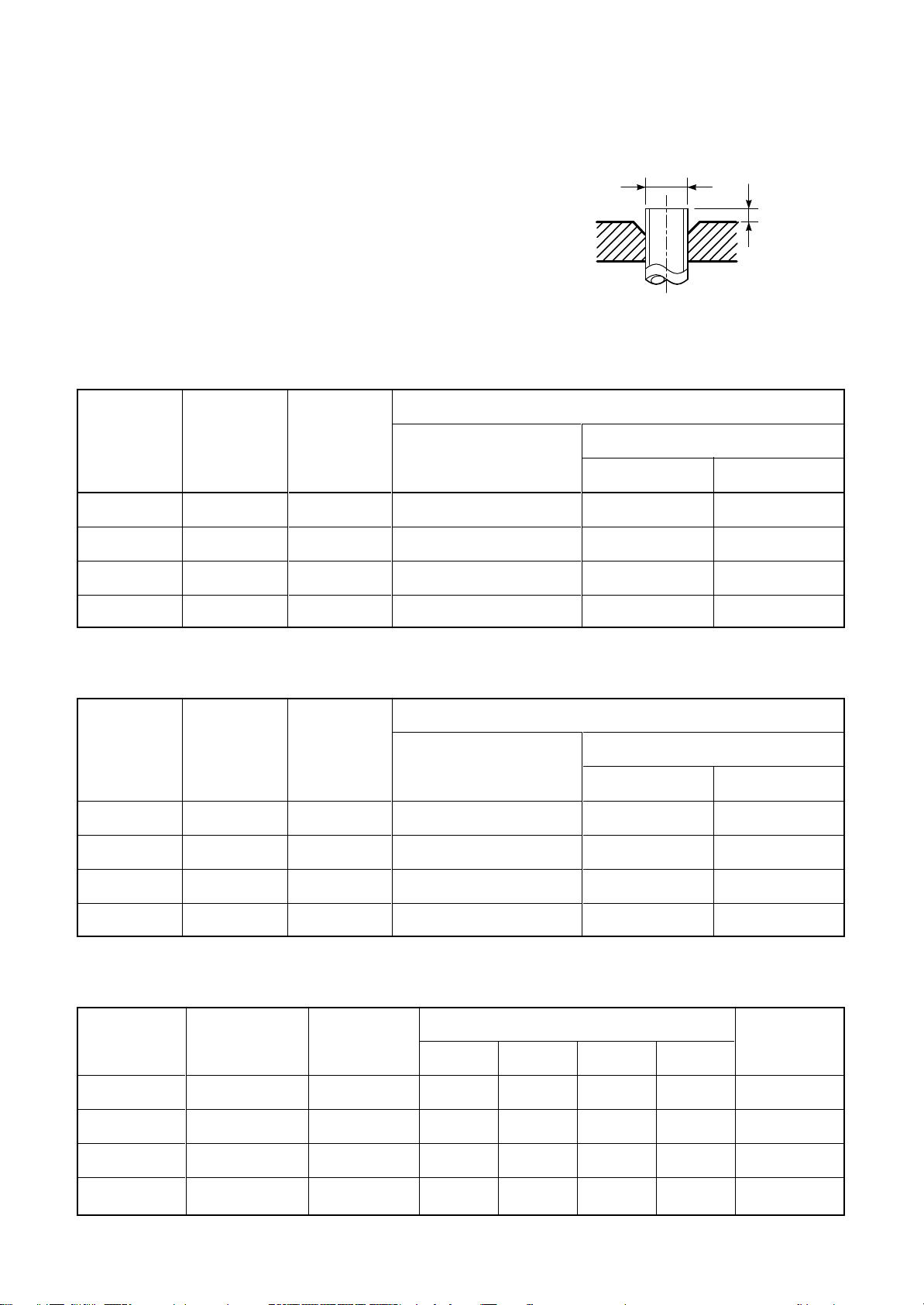
c) Insertion of Flare Nut
d) Flare Processing
Make certain that a clamp bar and copper
pipe have been cleaned.
By means of the clamp bar, perform the flare
processing correctly.
Use either a flare tool for R410A or conventional flare tool.
Table 6-2-3 Dimensions related to flare processing for R410A
Flare processing dimensions differ according
to the type of flare tool. When using a conventional flare tool, be sure to secure "dimension A" by using a gauge for size adjustment.
ØD
A
Fig. 6-2-1 Flare processing dimensions
Nominal
diameter
1/4
3/8
1/2
5/8
Nominal
diameter
1/4
3/8
Outer
diameter
(mm)
6.35
9.52
12.70
15.88
Thickness
(mm)
0.8
0.8
0.8
1.0
Flare tool for
R410A clutch type
0 to 0.5
0 to 0.5
0 to 0.5
0 to 0.5
Table 6-2-4 Dimensions related to flare processing for R22
Outer
diameter
(mm)
6.35
9.52
Thickness
(mm)
0.8
0.8
Flare tool for
R22 clutch type
0 to 0.5
0 to 0.5
A (mm)
Conventional flare tool
Clutch type Wing nut type
1.0 to 1.5 1.5 to 2.0
1.0 to 1.5 1.5 to 2.0
1.0 to 1.5 2.0 to 2.5
1.0 to 1.5 2.0 to 2.5
A (mm)
Conventional flare tool
Clutch type Wing nut type
0.5 to 1.0 1.0 to 1.5
0.5 to 1.0 1.0 to 1.5
1/2
5/8
Nominal
diameter
1/4
3/8
1/2
5/8
12.70
15.88
Table 6-2-5 Flare and flare nut dimensions for R410A
Outer diameter
(mm)
6.35
9.52
12.70
15,88
0.8
1.0
Thickness
(mm)
0.8
0.8
0.8
1.0
0 to 0.5
0 to 0.5
0.5 to 1.0 1.5 to 2.0
0.5 to 1.0 1.5 to 2.0
Dimension (mm)
ABCD
9.1 9.2 6.5 13
13.2 13.5 9.7 20
16.6 16.0 12.9 23
19.7 19.0 16.0 25
– 10 –
Flare nut
width (mm)
17
22
26
29
Page 12
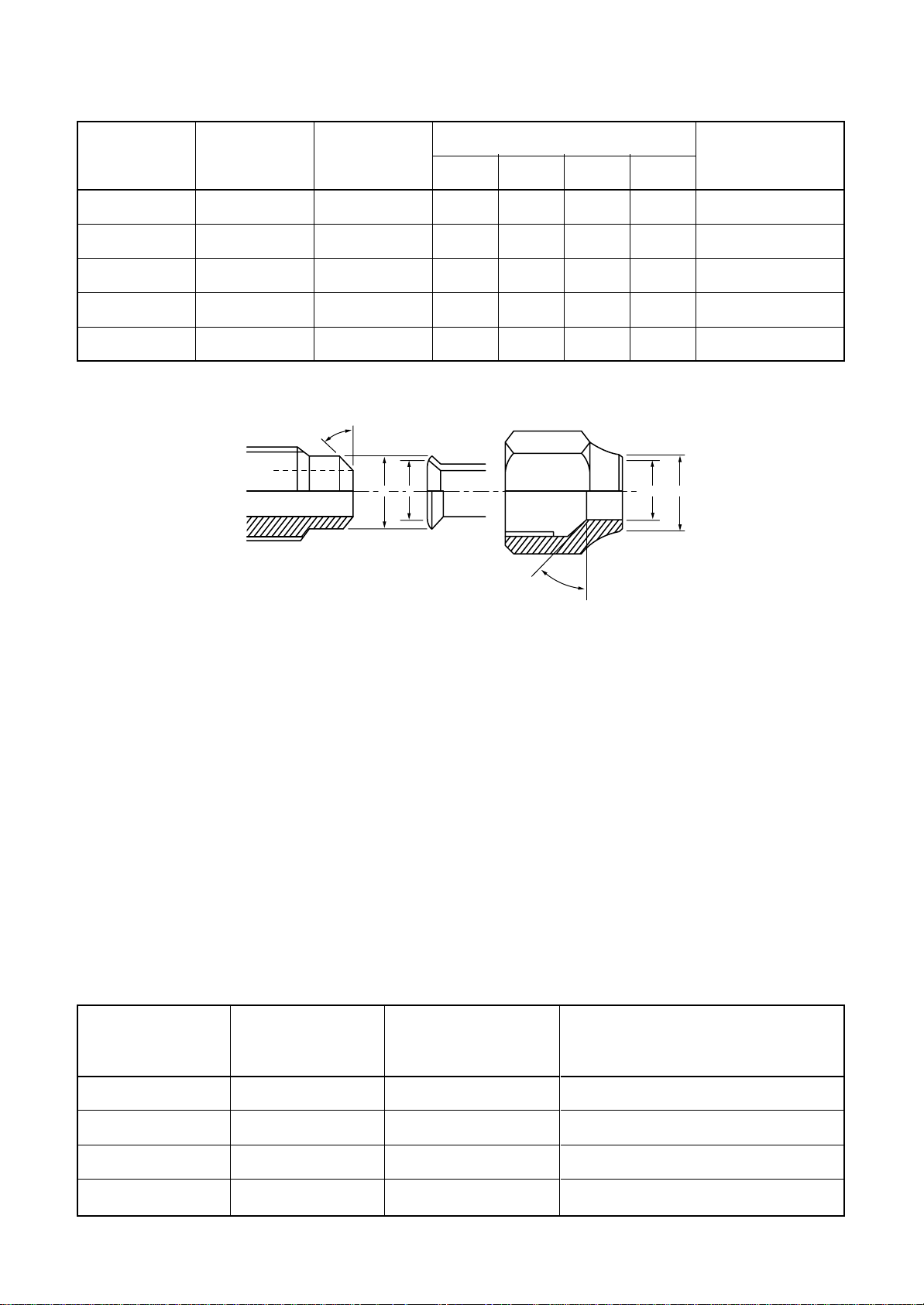
Table 6-2-6 Flare and flare nut dimensions for R22
Nominal Outer diameter Thickness
diameter (mm) (mm)
1/4 6.35 0.8
3/8 9.52 0.8
1/2 12.70 0.8
5/8 15.88 1.0
3/4 19.05 1.0
°
to 46
°
45
B A
Dimension (mm)
ABCD
9.0 9.2 6.5 13
13.0 13.5 9.7 20
16.2 16.0 12.9 20
19.4 19.0 16.0 23
23.3 24.0 19.2 34
D
C
43
°
to 45
°
Flare nut width
(mm)
17
22
24
27
36
Fig. 6-2-2 Relations between flare nut and flare seal surface
(2) Flare Connecting Procedures and Precautions
a) Make sure that the flare and union portions
do not have any scar or dust, etc.
b) Correctly align the processed flare surface
with the union axis.
c) Tighten the flare with designated torque by
means of a torque wrench. The tightening
torque for R410A is the same as that for
conventional R22. Incidentally, when the
torque is weak, the gas leakage may occur.
Table 6-2-7 Tightening torque of flare for R410A [Reference values]
Nominal Outer diameter Tightening torque
diameter (mm) N.m (kgf.cm)
1/4 6.35 14 to 18 (140 to 180)
When it is strong, the flare nut may crack and
may be made non-removable. When choosing
the tightening torque, comply with values
designated by manufacturers. Table 6-2-7
shows reference values.
NOTE:
When applying oil to the flare surface, be sure to use
oil designated by the manufacturer. If any other oil is
used, the lubricating oils may deteriorate and cause
the compressor to burn out.
Tightening torque of torque
wrenches available on the market
N.m (kgf.cm)
16 (160), 18 (180)
3/8 9.52 33 to 42 (330 to 420)
1/2 12.70 50 to 62 (500 to 620)
5/8 15.88 63 to 77 (630 to 770)
– 11 –
42 (420)
55 (550)
65 (650)
Page 13
6-3. Tools
6-3-1. Required Tools
The service port diameter of packed valve of the outdoor unit in the air conditioner using R410A is changed to
prevent mixing of other refrigerant. To reinforce the pressure-resisting strength, flare processing dimensions and
opposite side dimension of flare nut (For Ø12.7 copper pipe) of the refrigerant piping are lengthened.
The used refrigerating oil is changed, and mixing of oil may cause a trouble such as generation of sludge,
clogging of capillary, etc. Accordingly, the tools to be used are classified into the following three types.
(1) Tools exclusive for R410A (Those which cannot be used for conventional refrigerant (R22))
(2) Tools exclusive for R410A, but can be also used for conventional refrigerant (R22)
(3) Tools commonly used for R410A and for conventional refrigerant (R22)
The table below shows the tools exclusive for R410A and their interchangeability.
Tools exclusive for R410A (The following tools for R410A are required.)
Tools whose specifications are changed for R410A and their interchangeability
No. Used tool
Flare tool
1
Copper pipe gauge for
adjusting projection
2
margin
3
Torque wrench
Gauge manifold
4
Charge hose
5
Vacuum pump adapter
6
Electronic balance for
7
refrigerant charging
Refrigerant cylinder
8
Leakage detector
9
Charging cylinder
10
Usage
Pipe flaring
Flaring by conventional
flare tool
Connection of flare nut
Evacuating, refrigerant
charge, run check, etc.
Vacuum evacuating
Refrigerant charge
Refrigerant charge
Gas leakage check
Refrigerant charge
air conditioner installation
Existence of Whether convennew equipment tional equipment
for R410A can be used
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
Ye s
(Note 2)
R410A
(Note 1)
*
(Note 1)
*
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Conventional air
conditioner installation
Whether new equipment
can be used with
conventional refrigerant
(Note 1)
*
X
X
X
X
(Note 1) When flaring is carried out for R410A using the conventional flare tools, adjustment of projection
margin is necessary. For this adjustment, a copper pipe gauge, etc. are necessary.
(Note 2) Charging cylinder for R410A is being currently developed.
General tools (Conventional tools can be used.)
In addition to the above exclusive tools, the following equipments which serve also for R22 are necessary
as the general tools.
(1) Vacuum pump
Use vacuum pump by
attaching vacuum pump adapter.
(2) Torque wrench
(3) Pipe cutter
(4) Reamer
(5) Pipe bender
(6) Level vial
(7) Screwdriver (+, - )
(8) Spanner or Monkey wrench
(9) Hole core drill (Ø65)
(10) Hexagon wrench
(Opposite side 4mm)
(11) Tape measure
(12) Metal saw
Also prepare the following equipments for other installation method and run check.
(1) Clamp meter
(2) Thermometer
(3) Insulation resistance tester
(4) Electroscope
– 12 –
Page 14
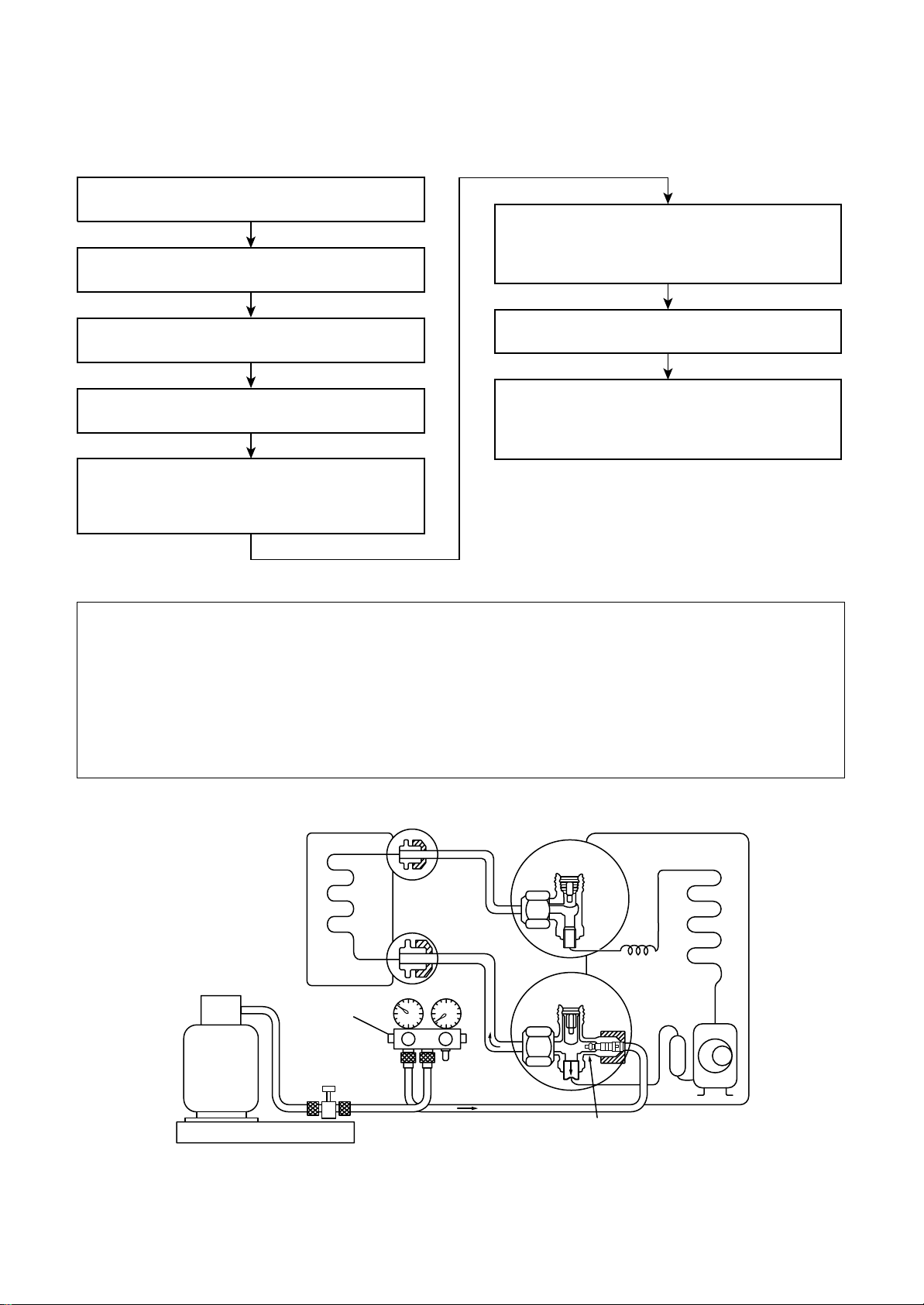
6-4. Recharging of Refrigerant
When it is necessary to recharge refrigerant, charge the specified amount of new refrigerant according to the
following steps.
Recover the refrigerant, and check no refrigerant
remains in the equipment.
Connect the charge hose to packed valve service
port at the outdoor unit's gas side.
When the compound gauge's pointer has indicated
- 0.1 Mpa (- 76 cmHg), place the handle Low in the
fully closed position, and turn off the vacuum pump's
power switch.
Connect the charge hose of the vacuum pump
adapter.
Open fully both packed valves at liquid and gas
sides.
Place the handle of the gauge manifold Low in the
fully opened position, and turn on the vacuum pump's
power switch. Then, evacuating the refrigerant in the
cycle.
Never charge refrigerant exceeding the specified amount.
1.
If the specified amount of refrigerant cannot be charged, charge refrigerant bit by bit in COOL mode.
2.
Do not carry out additional charging.
3.
Keep the status as it is for 1 to 2 minutes, and ensure
that the compound gauge's pointer does not return.
Set the refrigerant cylinder to the electronic balance,
connect the connecting hose to the cylinder and the
connecting port of the electronic balance, and charge
liquid refrigerant.
(For refrigerant charging, see the figure below.)
When additional charging is carried out if refrigerant leaks, the refrigerant composition changes in the
refrigeration cycle, that is characteristics of the air conditioner changes, refrigerant exceeding the
specified amount is charged, and working pressure in the refrigeration cycle becomes abnormally high
pressure, and may cause a rupture or personal injury.
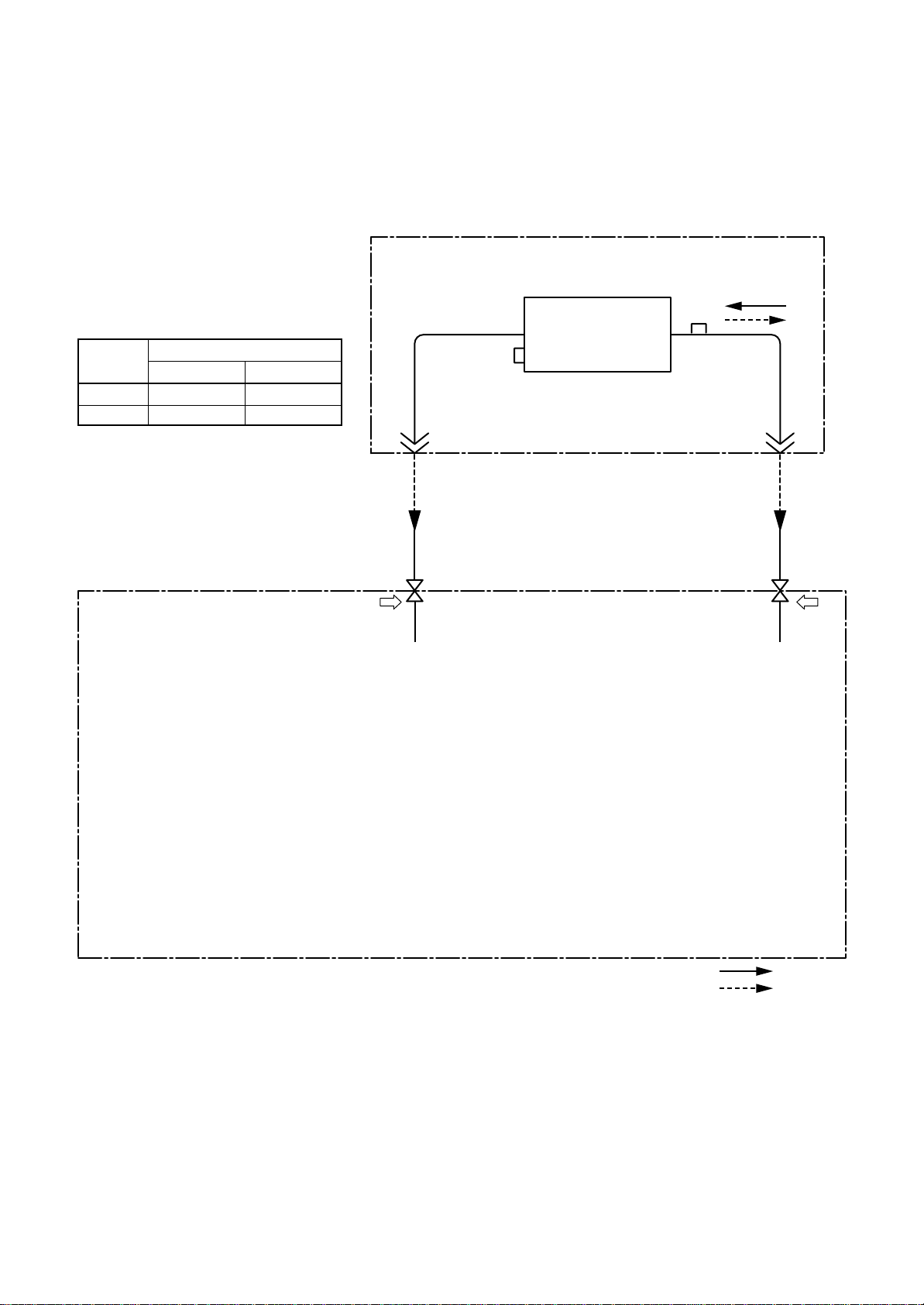
(INDOOR unit)
Refrigerant cylinder
(With siphon pipe)
Check valve
Open/Close valve
for charging
Electronic balance for refrigerant charging
Fig. 6-4-1 Configuration of refrigerant charging
(Liquid side)
(Gas side)
– 13 –
(OUTDOOR unit)
Opened
Closed
Service port
Page 15
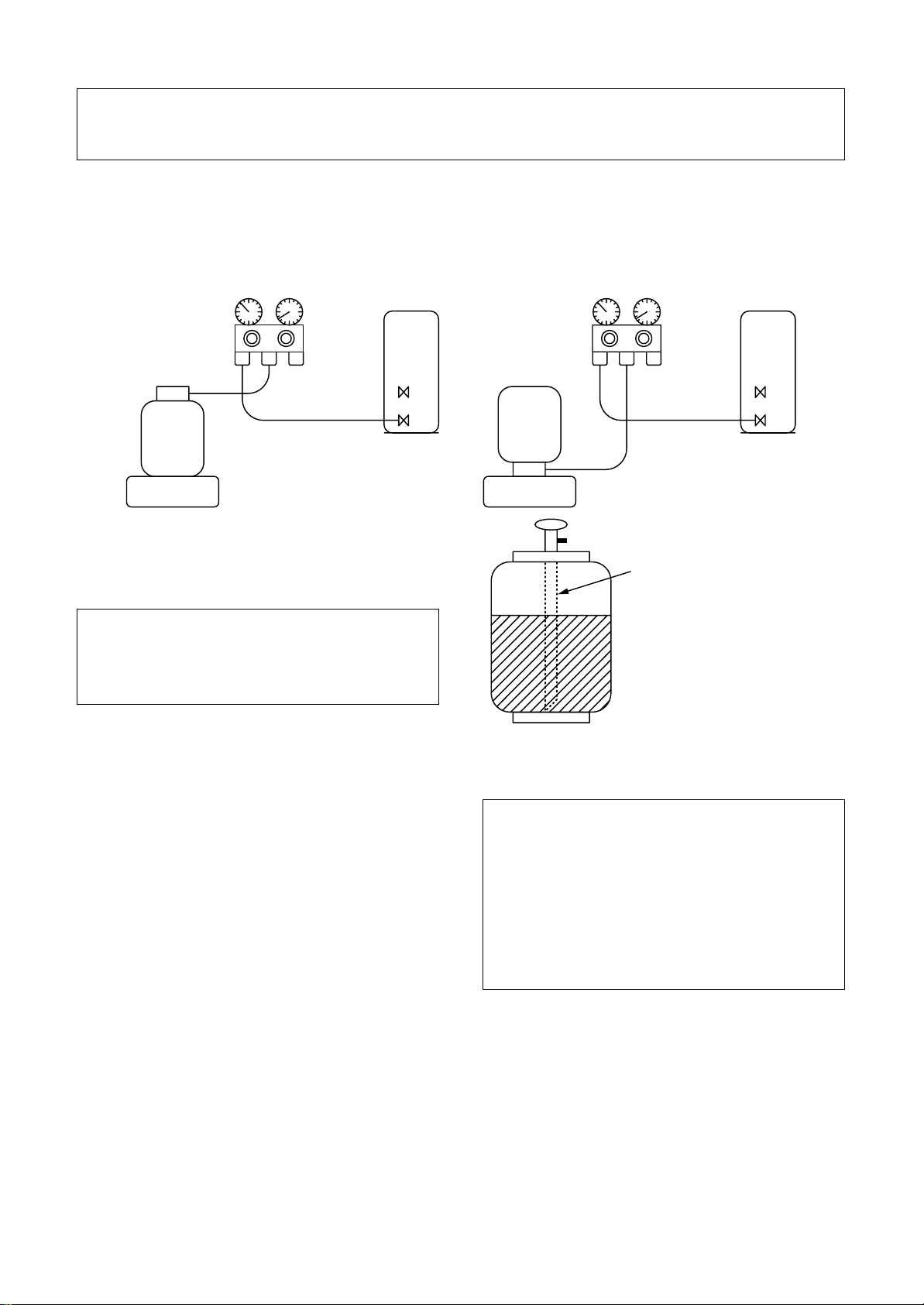
Be sure to make setting so that liquid can be charged.
When using a cylinder equipped with a siphon, liquid can be charged without turning it upside down.
It is necessary for charging refrigerant under condition of liquid because R410A is mixed type of refrigerant.
Accordingly, when charging refrigerant from the refrigerant cylinder to the equipment, charge it turning the
cylinder upside down if cylinder is not equipped with siphon.
[ Cylinder with siphon ] [ Cylinder without siphon ]
Gauge manifold
OUTDOOR unit
Refrigerant
cylinder
Gauge manifold
OUTDOOR unit
cylinder
Refrigerant
Electronic
balance
R410A refrigerant is HFC mixed refrigerant.
Therefore, if it is charged with gas, the composition of the charged refrigerant changes and the
characteristics of the equipment varies.
6-5. Brazing of Pipes
6-5-1. Materials for Brazing
(1) Silver brazing filler
Silver brazing filler is an alloy mainly composed
of silver and copper. It is used to join iron,
copper or copper alloy, and is relatively expensive though it excels in solderability.
(2) Phosphor bronze brazing filler
Phosphor bronze brazing filler is generally used
to join copper or copper alloy.
(3) Low temperature brazing filler
Low temperature brazing filler is generally called
solder, and is an alloy of tin and lead. Since it is
weak in adhesive strength, do not use it for
refrigerant pipes.
Fig. 6-4-2
Electronic
balance
Siphon
Phosphor bronze brazing filler tends to react
1.
with sulfur and produce a fragile compound
water solution, which may cause a gas
leakage. Therefore, use any other type of
brazing filler at a hot spring resort, etc., and
coat the surface with a paint.
2.
When performing brazing again at time of
servicing, use the same type of brazing filler.
6-5-2. Flux
(1) Reason why flux is necessary
1.By removing the oxide film and any foreign
matter on the metal surface, it assists the flow
of brazing filler.
2.In the brazing process, it prevents the metal
surface from being oxidized.
3.By reducing the brazing filler's surface tension,
the brazing filler adheres better to the treated
metal.
– 14 –
Page 16
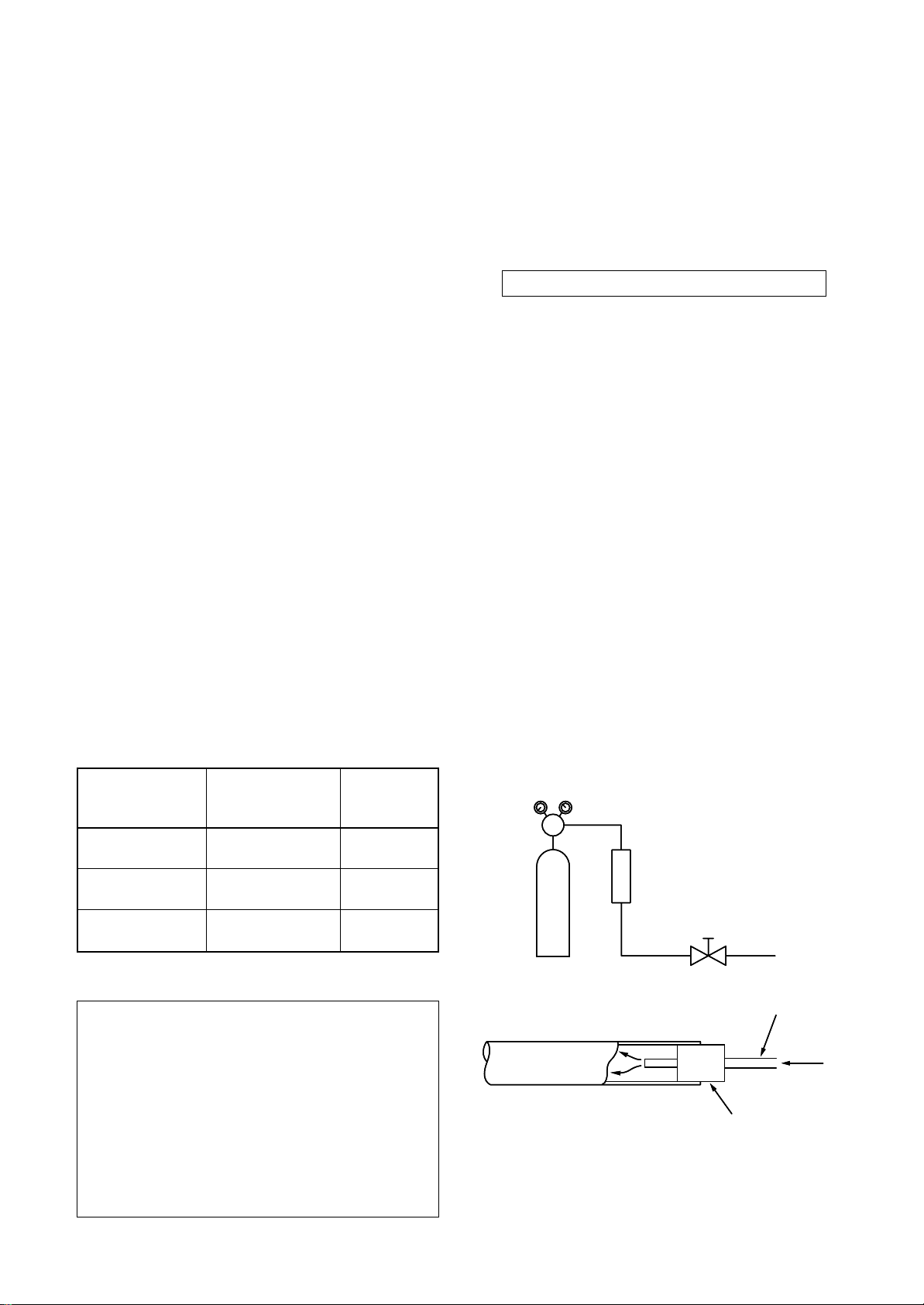
(2) Characteristics required for flux
Nitrogen gas
cylinder
Pipe
Flow meter
M
Stop valve
From Nitrogen cylinder
Nitrogen
gas
Rubber plug
Nitrogen gas
cylinder
Pipe
Flow meter
M
Stop valve
From Nitrogen cylinder
Nitrogen
gas
Rubber plug
1.Activated temperature of flux coincides with
the brazing temperature.
2.Due to a wide effective temperature range, flux
is hard to carbonize.
3.It is easy to remove slag after brazing.
4.The corrosive action to the treated metal and
brazing filler is minimum.
5.It excels in coating performance and is harmless to the human body.
As the flux works in a complicated manner as
described above, it is necessary to select an
adequate type of flux according to the type and
shape of treated metal, type of brazing filler and
brazing method, etc.
(3) Types of flux
Noncorrosive flux
Generally, it is a compound of borax and boric
acid.
It is effective in case where the brazing temperature is higher than 800°C.
Activated flux
Most of fluxes generally used for silver brazing
are this type.
It features an increased oxide film removing
capability due to the addition of compounds
such as potassium fluoride, potassium chloride
and sodium fluoride to the borax-boric acid
compound.
(4) Piping materials for brazing and used braz-
ing filler/flux
6-5-3. Brazing
As brazing work requires sophisticated techniques,
experiences based upon a theoretical knowledge, it
must be performed by a person qualified.
In order to prevent the oxide film from occurring in
the pipe interior during brazing, it is effective to
proceed with brazing while letting dry Nitrogen gas
(N2) flow.
Never use gas other than Nitrogen gas.
(1) Brazing method to prevent oxidation
1.
Attach a reducing valve and a flow-meter to
the Nitrogen gas cylinder.
2.
Use a copper pipe to direct the piping material, and attach a flow-meter to the cylinder.
Apply a seal onto the clearance between the
3.
piping material and inserted copper pipe for
Nitrogen in order to prevent backflow of the
Nitrogen gas.
4.
When the Nitrogen gas is flowing, be sure to
keep the piping end open.
5.
Adjust the flow rate of Nitrogen gas so that it
is lower than 0.05 m³/Hr or 0.02 MPa (0.2kgf/
cm²) by means of the reducing valve.
6.
After performing the steps above, keep the
Nitrogen gas flowing until the pipe cools
down to a certain extent (temperature at
which pipes are touchable with hands).
Remove the flux completely after brazing.
7.
Copper - Copper
Copper - Iron
1.
2.
3.
4.
Piping
material
Iron - Iron
Used brazing
filler
Phosphor copper
Silver
Silver
Used
flux
Do not use
Paste flux
Vapor flux
Do not enter flux into the refrigeration cycle.
When chlorine contained in the flux remains
within the pipe, the lubricating oil deteriorates.
Therefore, use a flux which does not contain
chlorine.
When adding water to the flux, use water
which does not contain chlorine (e.g. distilled
water or ion-exchange water).
Remove the flux after brazing.
Fig. 6-5-1 Prevention of oxidation during brazing
– 15 –
Page 17
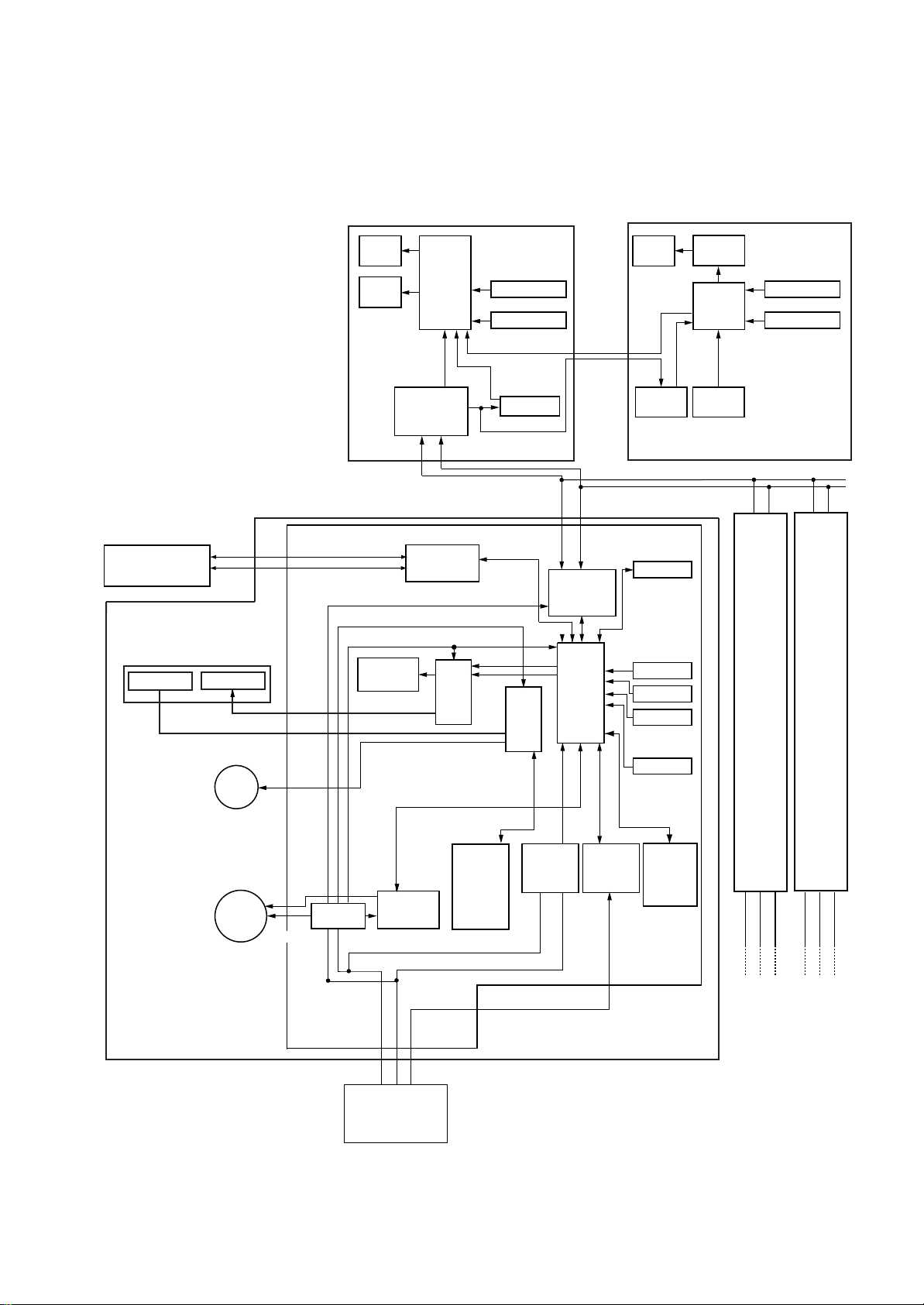
7-1. Indoor Control Circuit
7. INDOOR UNIT CONTROL
Max. 8 units are connectable.*1
*1 When group and twin combination.
main remote controller shal be connected
follower indoor unit
*2 Weekly timer is not connectable to the
sub remote controller.
Indoor unit
#1 Header unit
Indoor control P.C. board (MCC-1510)
Central control
remote controller
(Sold separatrly)
Reciver and Display P.C board
(MCC-819)
Reciver unit
Display LED
U3
U4
Main (Sub) master remote controller
(Wired)
Display
LCD
Display
LED
DC20V
DC12V
DC5V
Buzzer
CPU
Remote
controller
communication
circuit
Central control
communication
circuit
Driver
Function setup
Key switch
CN2 CN1
DC5V
Power circuit
Sold separatrly Sold separatrly
AB
Remote
controller
communication
circuit
CPU
Driver
H8/3039
Weekly timer
Display
LCD
2
*
Powe r
circuit
EEPROM
TA sensor
TC sensor
TCJ sensor
LCD
driver
CPU
DC5V
Secondary
battery
Follower unit
AB
#2
Same as
the left
Function setup
Key switch
#3
AB
Same as
the left
Louver
motor
Indoor
fan
motor
DC280V
Power
circuit
DC15V
Outdoor unit
Fan motor
control
circuit
123
3
12
Outside
output
Run
Warning
Ready
Thermo. ON
Cool
Heat
Fan
AC
synchronous
signal input
circuit
Serial
send/
receive
circuit
HA
Wireless
remote
signal
Setting
(A/B)
123
Outdoor
unit
123
Outdoor
unit
– 16 –
Page 18
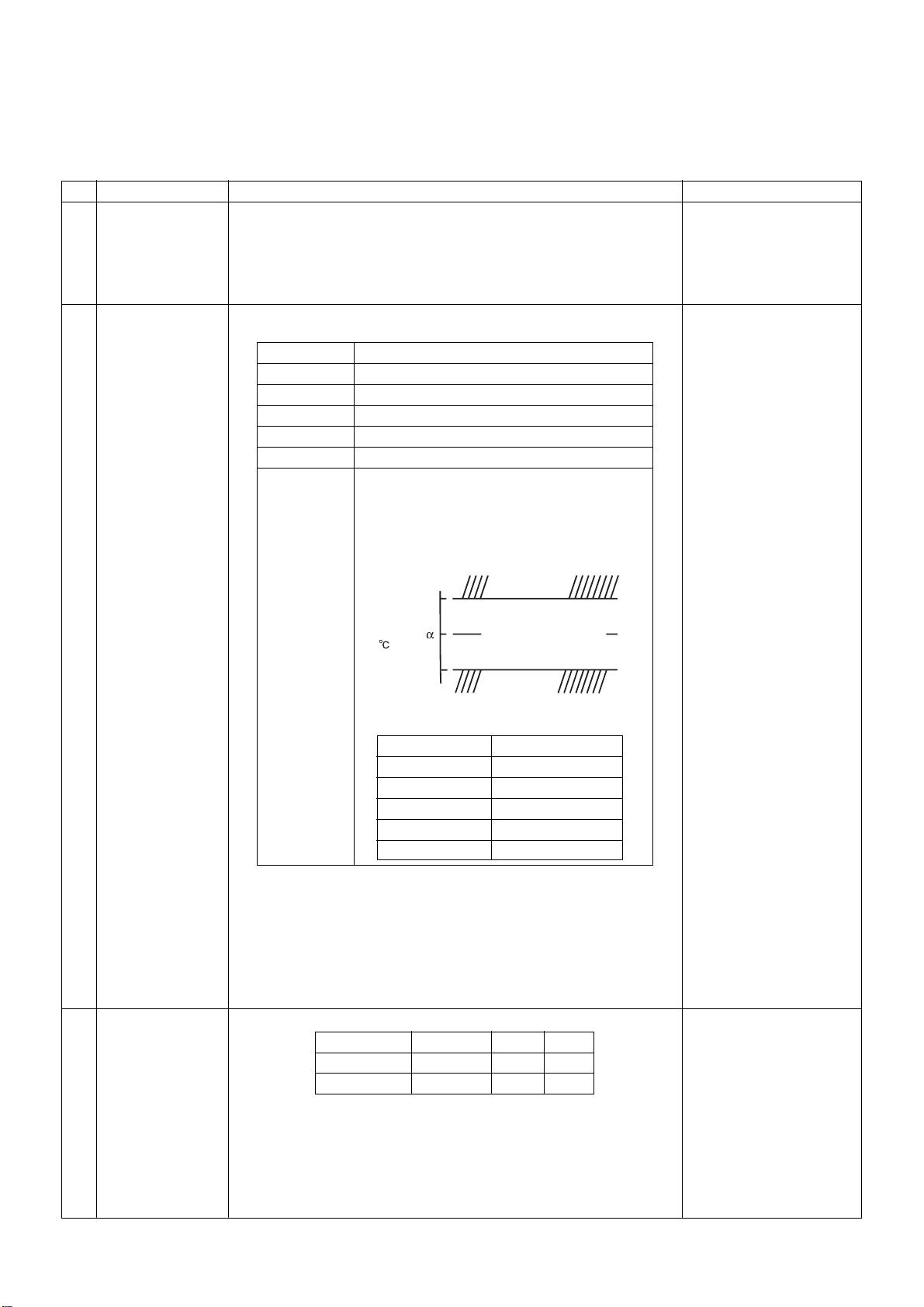
INDOOR UNIT CONTROL CIRCUIT (Continued)
7-2. Control Specifications
NO.
1
Control at
power-on reset
Operation mode
2
switching
Item
Overview of specifications
(1) Identification of outdoor unit
Identifies outdoor unit at power-on reset, and switches control
according to the identification result.
(2)
Setting of indoor unit fan speed and adjustment of air flow direction
Switches indoor unit fan speed, setting of air flow direction
adjustment, etc. based on EEPROM data.
(1) Switches operation mode according to mode select instruction
from remote controller.
R/C instructions
OFF
FAN
COOL
DRY
HEAT
AUTO
Turns OFF air conditioner
“Fan only” operation
Cooling operation
Dehumidifying operation
Heating operation
• Selects COOL or HEAT mode
Outline of control
automatically according to Ta, Ts, and To.
• The first operation is as follows according
to Ta. (COOL thermo sensor continues
OFF (FAN mode with set fan speed) within
the range of Ts +α-1<Ta< Ts +α+1.)
COOL
operation
FAN mode with
set fan speed
Ta
( )
+1.0
Ts+
Remarks
The “PREPARING” lamp
lights during initial setting
(model recognition) after
power-on reset.
Fan speed, adjustment of
air flow direction
Ta : Room temperature
Ts : Set temperature
To : Outside air temperature
Room temperature
3
control
-1.0
HEAT
operation
• α is corrected according to outside air
temperature.
Outside air temp. Corrected value (α)
No To 0 K
>
To
24°C -1 K
=
>
24>To
18°C 0 K
=
To<18°C +1 K
Abnormal To 0 K
(2) Operation instruction permission mode
HEAT and AUTO modes are not available for COOL only models.
When instruction is issued from wireless remote controller in the
HEAT or AUTO mode, it is indicated by a reception sound “pi, pi”
and by alternate blinking of “TIMER” and “PREPARING” lamps. To
cancel this alternate blinking, issue an instruction of mode other
than HEAT or AUTO.
(1) Adjustment range Remote controller set temperature (°C)
COOL/DRY HEAT AUTO
Wired type 18 - 29 18 - 29 18 - 29
Wireless type 17 - 30 17 - 30 17 - 30
* When use of remote controller sensor is set (with DN32), even
when sensor value is within the above range in HEAT or AUTO
mode, the thermo sensor turns OFF when Ta sensor value
exceeds 35 °C.
k=deg
– 17 –
Page 19
NO.
Room temperature
3
control
Capacity auto
4
control
(GA control)
Item
Overview of specifications
(2) The set temperature for HEAT operation can be corrected by code
No. 06.
Set data 0246
Correction of set temp. +0°C +2°C +4°C +6°C
Factory setting
Set data 2
* When use of remote controller sensor is set (with DN32), no
correction is performed.
(1) Issues instruction of operating frequency to outdoor unit according
to the difference between Ta and Ts.
(2) COOL operation
Calculates room temp. difference between Ta and Ts as well as
room temp. variation every 90 seconds to find correction value of
specified operating frequency and to correct the current operating
frequency.
Ta(n)–Ts(n) : Room temp. difference n : Number of detection times
Ta(n-1)–Ta(n) : Room temp. variation n–1 : Number of detection times
(90 seconds before)
(3) HEAT operation
Calculates room temp. difference between Ta and Ts as well as
room temp. variation every 60 seconds to find correction value of
specified operating frequency and to correct the current operating
frequency.
Ts(n)–Ts(n) : Room temp. difference n : Number of detection times
Ta(n)–Ta(n_1) : Room temp. variation n–1 : Number of detection times
(60 seconds before)
(4) DRY operation
The frequency correction control is the same as that for COOL
operation.
However, the maximum frequency is limited to S6 or so.
Note) When LOW fan speed is set, the maximum frequency is
limited to SB or so.
Remarks
Heat intake temperature
shift
(When unit’s temperature
sensor is used)
COOL/HEAT/
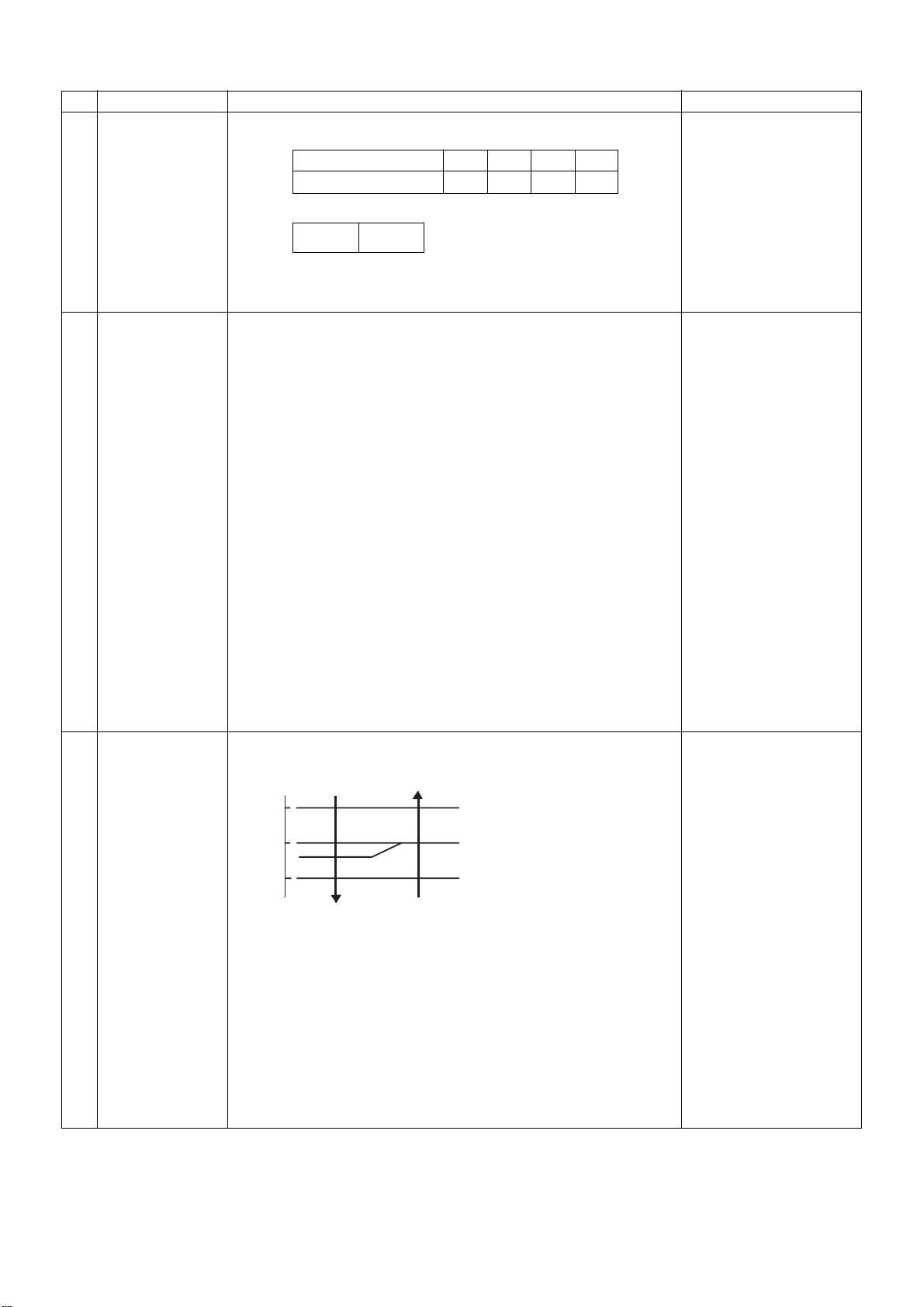
5
AUTO control
(1) Switching between COOL and HEAT is determined based on the
following control.
Ta
(˚C)
+1.5
Tsc
or
Tsh
COOL
(COOL ON)
(COOL OFF)
-1.5
After 10 minutes pass from
thermo sensor OFF,
operation mode changes
from HEAT (thermo sensor
OFF) to COOL if Ta exceeds
Tsh +1.5.
( ) shows an example of
HEAT
COOL ON/OFF.
After 10 minutes pass from
thermo sensor OFF,
operation mode changes
from COOL (thermo sensor
OFF) to HEAT if Ta lowers
below Tsc -1.5.
(2) The GA control after determination of operation mode follows the
description in No. 4.
(3) The room temperature control and temperature correction follow
the descriptions in No. 3 and No. 15.
Tsc : COOL set temp.
Tshc : HEAT set temp. +
room temp. control/
correction
– 18 –
Page 20
INDOOR UNIT CONTROL CIRCUIT (Continued)
NO.
6
Fan speed control
Item
Overview of specifications
(1) A fan speed HH (quick high), H (high), L (low) or AUTO is selected
according to the instruction from remote controller for FAN mode
operation.
(2) Fan speed is switched according to the difference between Ta and
Ts in the AUTO mode.
[Cooling]
Ta (˚C)
+3.0
+2.5
+2.0
+1.5
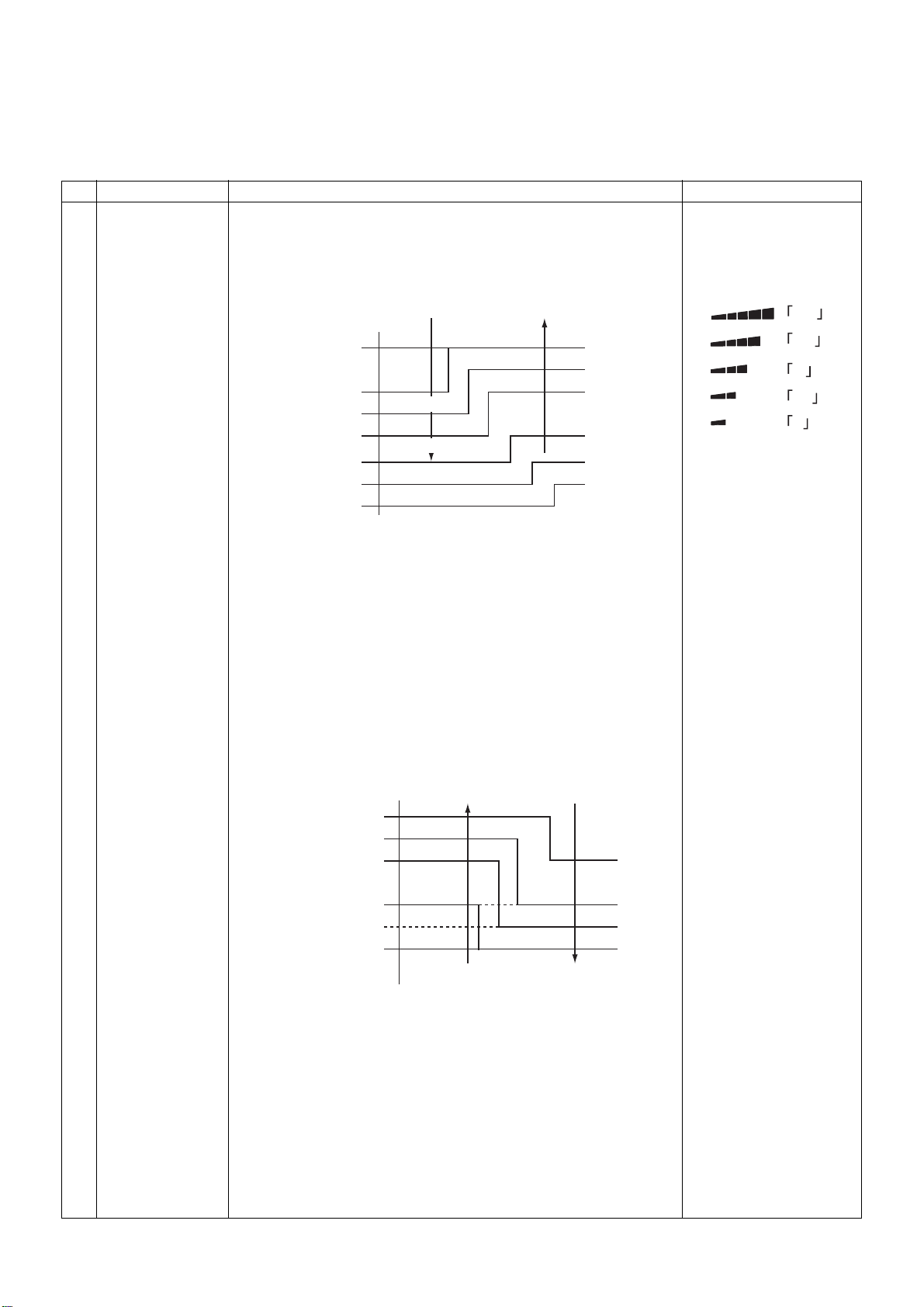
+1.0
+0.5
Tsc
-0.5
HH
(HH)
H+(HH)
H(HH)
L+(H+)
L(H)
L(H)
L(L+)
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
• The fan speed control is the same for temperature setting by remote
controller or the unit.
• Once fan speed is changed, it remains unchanged for 3 minutes
unless different fan speed is selected by instruction.
• At the beginning of cooling, a falling gradient (higher fan speed) is
selected.
• When the temperature difference between Ta and Ts is on a
threshold line, fan speed does not change.
• ( ): Auto cooling
Remarks
HH>H+>H>
L+>L>UL
Wireless type allows HH,
H+, H, L+, L, and AUTO.
HH
H+
H
L+
L
[Heating]
Ta (˚C)
(-0.5)
(0)
(+0.5)
(+1.0)
(+1.5)
(+2.0)
-1.0
Tsh
+1.0
+2.0
+3.0
+4.0
L( L+)
L+(H)
H(H+)
H+
(HH)
HH
(HH)
E
D
C
B
A
( ): Temperature setting by remote controller
Other than ( ): Temperature setting by unit
• Once fan speed is changed, it remains unchanged for one minute
unless different fan speed is selected by instruction.
• At the beginning of heating, a rising gradient (higher fan speed) is
selected.
• When the temperature difference between Ta and Ts is on a
threshold line, fan speed does not change.
• ( ): Auto heating
• Fan speed is switched to a higher level when Tc reaches 60 °C.
Tc : Indoor unit heat
exchange sensor
temp.
– 19 –
Page 21
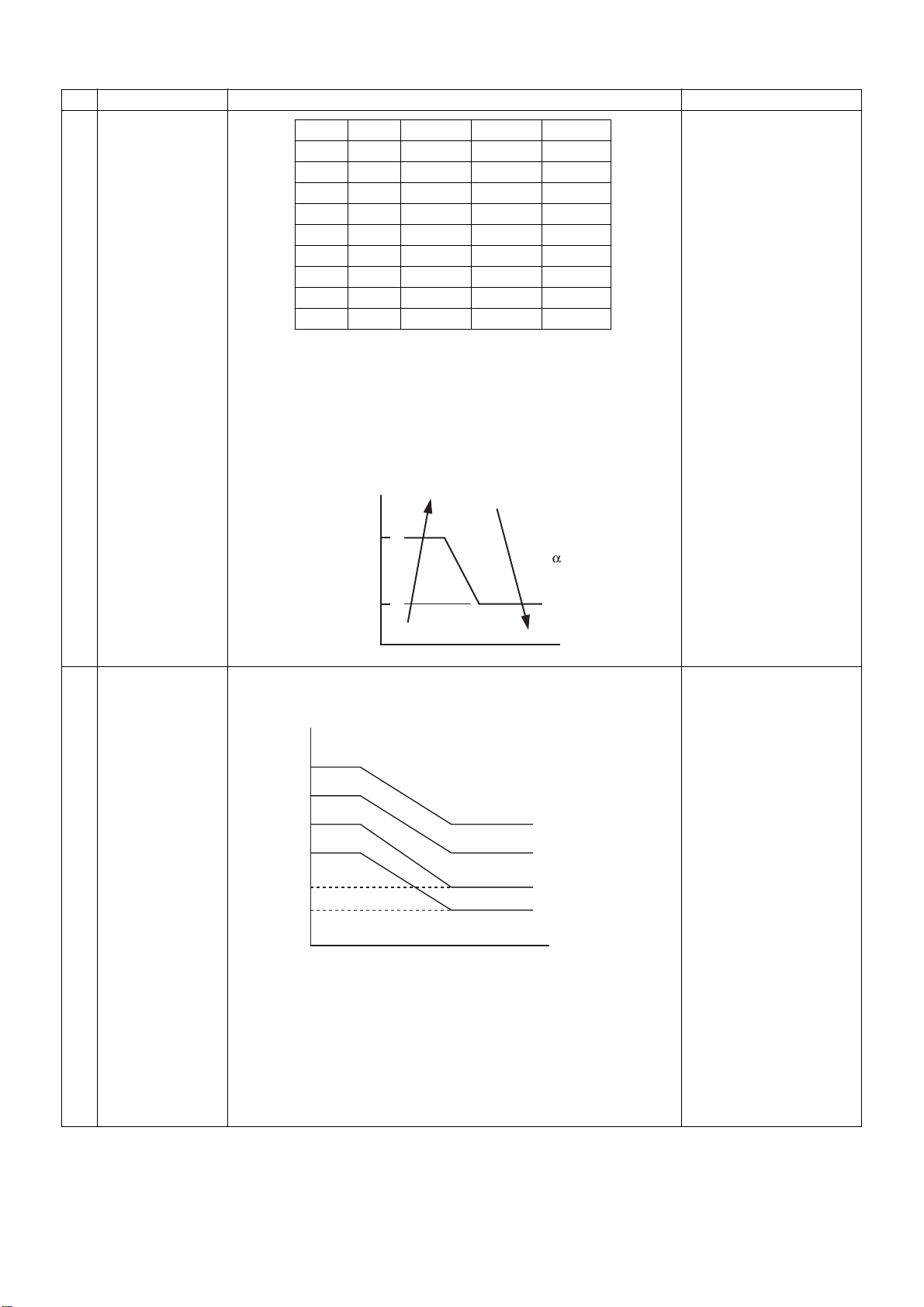
NO.
6
Fan speed control
Item
COOL
HH
H+
H
L+
L
UL
Overview of specifications
HEAT
HH
AP40-56
1220
AP63
1180
H+
H
1140
1120
1060
L+
L
1060
990
940
UL
500
1360
1300
1240
1200
1120
1120
1020
970
500
Remarks
AP71-80
1480
1340
1320
1300
1200
1200
1100
1040
500
7
Cool air prevention
control
(3) When thermo sensor turns OFF during heating, the fan speed
mode becomes UL (weak).
(4) When Ta is 25 °C or above at the beginning of HEAT operation or
when canceling defrost mode, H or HH mode continues for one
minute from the time when Tc enters zone E shown in the figure in
No.7 below.
(5) The HH fan speed for auto cooling/heating is set to a speed higher
than that for normal cooling/heating. However, it varies depending
on the temperature difference of Tc during auto heating.
Tc
(˚C)
47
HH+
42
HH
(1) Performs indoor unit fan control in the HEAT mode according to
the Tc (or Tcj) sensor detect temperature. The maximum speed is
limited as shown below.
Tc
Tcj
(˚C)
36
34
32
30
24
20
HH
H
L
UL
OFF
Shifts Tc control value by +6 °C
during defrosting. However, zone
B is regarded as zone C after 6
minutes pass from the startup of
compressor.
Zone E
Zone D
Zone C
Zone B
Zone A
“HEAT PREPARING”
indication
Fan speed select setting
by remote controller takes
precedence in zones D
and E.
“HEAT PREPARING” is
indicated in zones A and
B.
– 20 –
Page 22
INDOOR UNIT CONTROL CIRCUIT (Continued)
NO.
8
Freezing
prevention control
(low-temp.
release)
9
High-temp. release
control
Item
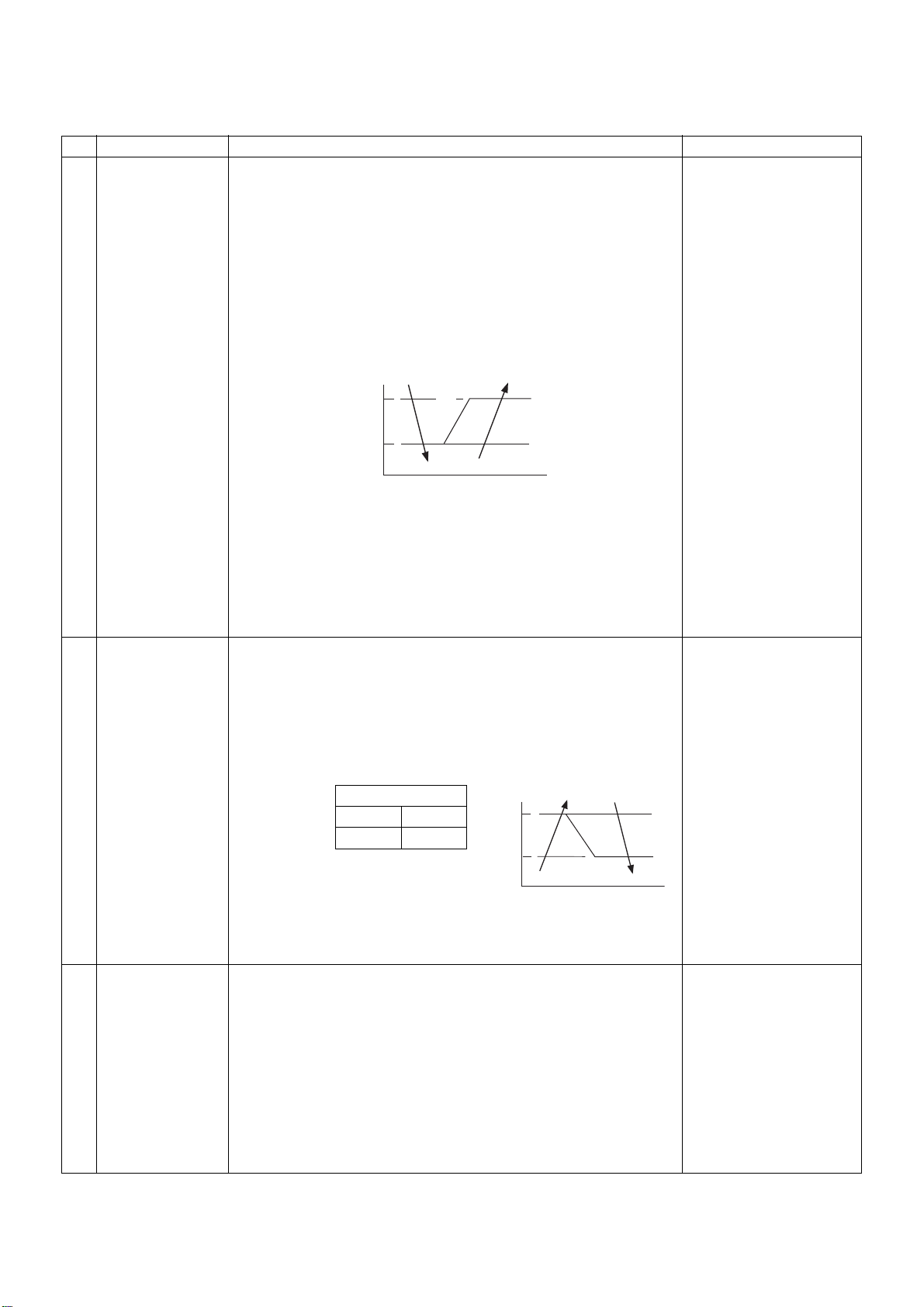
Overview of specifications
(1) Performs the following operation control in the COOL or DRY
mode according to the Tc (or Tcj) sensor detect temperature.
When zone J in the figure below is detected for 6 minutes, the
specified operating frequency is decreased from the actual
operating frequency, and the specified operating frequency is
changed every 30 seconds in zone J.
Timer count stops and is maintained in zone K.
Timer count is cleared to restore normal operation when zone I is
detected.
If the specified operating frequency becomes SO due to
continuation of zone J, return temperature A is raised from 5 to
12 °C, and operation with L fan speed continues until zone I is
detected.
Tc(˚C)
I5
2
J
A
K
If 4-way valve cannot be switched during heating and the following
conditions become true, freezing prevention control is performed.
(However, zone J entering control temperature is changed from 2
to -5 °C.)
[Conditions]
The following A or B becomes true after 5 minutes pass from
operation start.
<
A Tcn
B Tcn<Tc(n–1)–1 and Tcn
Tc(n–1)–5
=
<
Ta<5°C
=
(1) Performs the following operation control in the HEAT mode
according to the Tc (or Tcj) sensor detect temperature.
•
When zone M is detected, the specified operating frequency is
decreased from the actual operating frequency, and the specified
operating frequency is changed every 30 seconds in zone M.
• The specified operating frequency is maintained in zone N.
• When zone L is detected, the specified operating frequency is
returned by approx. 6 Hz every 60 seconds.
Factory setting
Control temp. (°C)
AB
Tc
Tcj
(˚C)
A
56 (54) 52 (52)
B
L
Remarks
Tcj : Indoor unit heat
exchange sensor
temp.
Tcn :
Tc after 5 minutes
from operation start
Tc (n-1):
Tc at operation start
This control is disabled for
twin follower indoor units.
M
N
Note) At the beginning of operation or when Tc (or Tcj) lowers below
30 °C after operation start, values (54) and (52) in the table are
used as control temperature.
10 Runs indoor unit fan in L (low) mode for about 30 seconds after HEAT
Residual heat
removal
operation stops to remove residual heat.
– 21 –
Even when the thermo is
set to OFF, the control is
implemented in the same
way.
Page 23
NO.
11
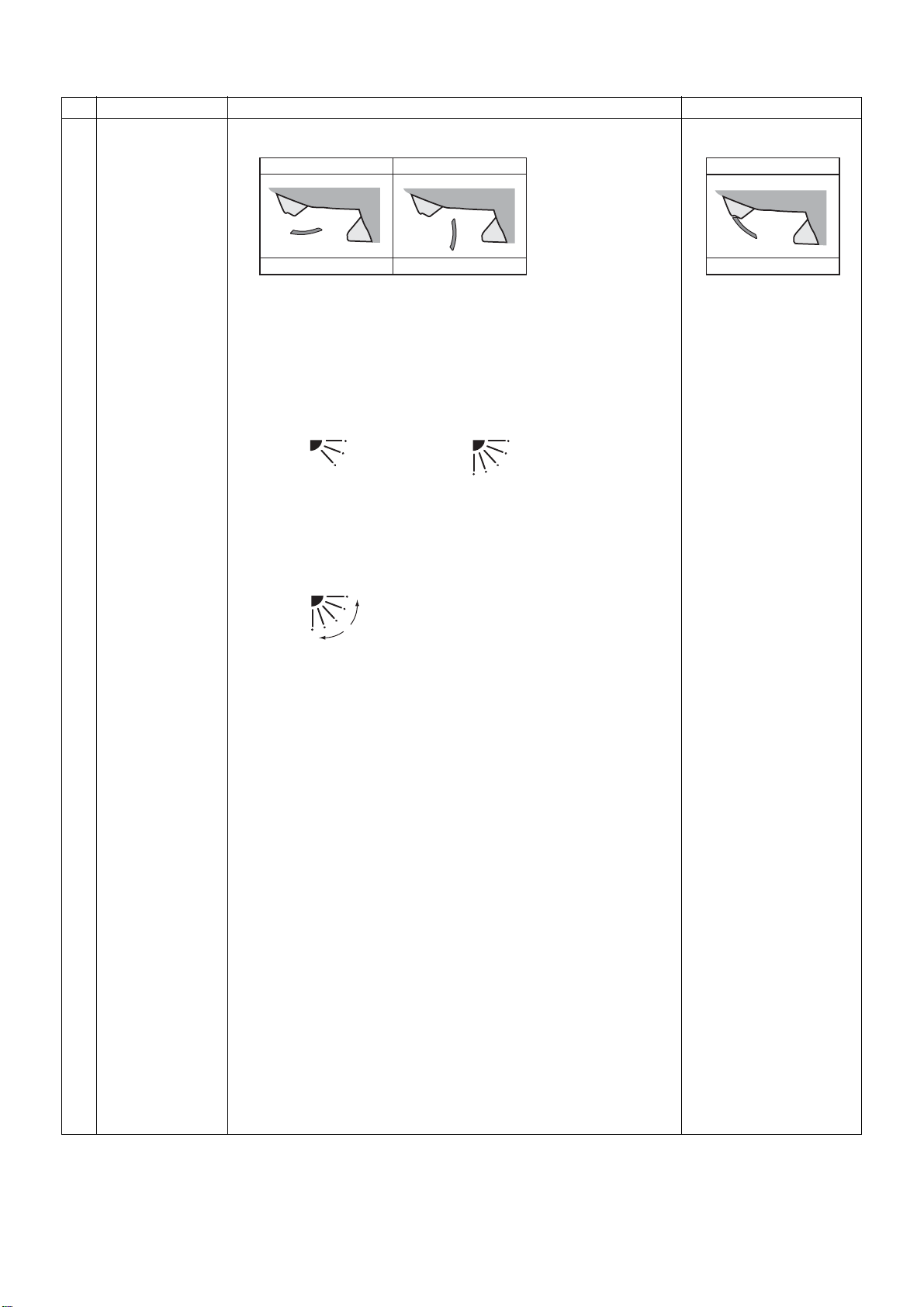
Item
Flap control
Overview of specifications
(1) During the first operation after power on, flap position is controlled
automatically according to operation mode (COOL/HEAT).
Cooling Heating
Remarks
Louver angle: 0 °C (full
close)
Full close
45°
103°
(2) When louver position is controlled by remote controller, the unit’s
microcomputer memorizes the position for use in the next
operation.
* The memorized louver position is cleared when power is turned
off, and returns to the state of (1) above.
(3) Flap position setting
• Flap position can be set within the range below.
COOL/DRY HEAT/FAN
• Flap position can be set collectively or individually in the group
twin or triple operation mode. (Wireless remote controller allows
individual setting only.)
(4) Swing setting
• Flap moves within the range below.
All operation modes
• Flap swing range can be set collectively or individually in the
group twin or triple operation mode. (Setting by wireless remote
controller is disabled when the main remote controller is used.)
(5) When air conditioner operation stops, flap closes automatically. It
keeps its position in the event of an alarm.
(6) Flap tilts upward automatically during preparation for heating.
(7) In the twin or triple operation mode selected by wireless remote
controller, swing setting interlocks with the header indoor unit. If
this setting is transmitted from a follower indoor unit, operation
does not change with a reception sound “pi, pi, pi” if operation
mode differs between header unit and follower unit.
0°
Alarm : A code number
(except F08 and
L31) appears on
the remote
controller and the
indoor unit stops.
– 22 –
Page 24
INDOOR UNIT CONTROL CIRCUIT (Continued)
NO.
12
Item
HA control
Overview of specifications
(1) When connected to a remote control system (tele-control or
remote on/off interface), operation ON/OFF can be controlled by
the HA signal input.
(2) Outputs operation ON/OFF status to the HA output terminal.
(3) HA signal input/output specifications conform to the JEMA
standard.
Remarks
A connector (separately
available) is required
when using the HA
terminal CH61 for remote
ON/OFF control.
When group operation is
in use, connect the
connector to either header
or follower indoor unit.
13
Filter sign
indication
(unavailable for
wireless type)
(1) Transmits filter replacement signal to remote controller for
indication on the LCD when accumulated operation hours of
indoor unit fan exceeds the specified time (150 hours).
(2) Clears accumulation timer upon receiving the filter reset signal
from remote controller. At this time, when the specified time has
already passed, the accumulated time is reset and the filter sign
disappears from the LCD.
“FILTER” lamp ON
– 23 –
Page 25

NO.
14
15 (1) Power-saving operation is available in the AUTO mode.
16
Item
Central control
mode switching
Power-saving
control
Maximum
frequency limit
control
(1) The scope of operation by remote controller on the indoor unit
side can be switched by the setting of remote controller.
(2) Scope of operation by remote controller on the indoor unit side
[Individual] : All settings and ON/OFF operations are available.
[Central 1] : ON/OFF operations are disabled.
[Central 2] : ON/OFF operations, operation mode selection, and
[Central 3] : Operation mode selection and temperature setting
[Central 4] : Operation mode selection is disabled.
(2) The set temperature is corrected using various sensor data within
the range where comfort is maintained.
(3) By using various sensor data including room temp. Ta, outside air
temp. To, fan speed, and indoor unit heat exchange sensor temp.
Tc, 20-minute data is averaged to calculate a set temperature
correction value.
(4) The set temperature is corrected every 20 minutes with the
following shift range.
Cooling : +1.5 to -1.0K
Heating : -1.5 to +1.0K
(1) This control is performed when AUTO mode is selected.
(2) COOL mode: When To is under 28 °C, the control is as follows.
Ta(˚C)
+4
+3
Tsc
Overview of specifications
temperature setting are disabled.
are disabled.
Normal control
Maximum frequency is
limited to the rating of cooling.
Remarks
No indication
“CENTRAL CONTROL”
lamp ON
“CENTRAL CONTROL”
lamp ON
“CENTRAL CONTROL”
lamp ON
“CENTRAL CONTROL”
lamp ON
When wired remote
controller is not used,
operation range is the
same as above though
lamp indication remains
unchanged.
If an unavailable operation
mode is transmitted from
wireless remote controller,
it is indicated with a
reception sound “pi, pi, pi,
pi, pi”.
(3) HEAT mode: When To is over 15 °C, the control is as follows.
Ta(˚C)
Tsh
-3
-4
Normal control
Maximum frequency is limited
to the rating of heating.
– 24 –
Page 26

INDOOR UNIT CONTROL CIRCUIT (Continued)
7-3. P. C. Board of Indoor Unit
MCC-1510
HA (T10)
CN61, DC12V
Option output
CN60, DC12V
CHK
CN71, DC5V
DISP
CN72, DC5V
External alarm input
CN80, DC12V
EXCT
CN73, DC5V
R/C power LED
D203
TA sensor
CN104, DC5V
Remote controller
CN41, DC20V
TC sensor TCJ sensor
CN101, DC5V CN102, DC5V D02
Microcomputer
run LED
EEPROM
IC10 CN67, AC200V
Indoor unit - outdoor unit wire
Optional power supply
CN309, AC200V
Central control
CN40, DC
Terminating resistor
provided/not provided
Remote controller A/B
selection
SW01
5V
FAN DRIVE
CN32, DC12V
Indication output/wireless receptionDC fan input/outputLouver
CN213, DC5VCN210CN33, DC12V
– 25 –
Page 27

7-4. Optional Onboard Connector Specifications
Description
Factory setting OFF: No terminating resistor ON for one unit when performing
central control by custom air conditioner only.
Factory setting OFF: Remote controller A
Specification
OFF: No terminating resistor
ON: Terminating resistor provided
OFF: R/C A, ON: R/C B
Bit 1
Pin No.
Connector No.
Bit 2
SW01
.
Single operation setting is performed with VENT button on the remote controller
(DN=31)
Factory setting: Interlocking with indoor unit operation ON/OFF
*
HA ON/OFF input (J01: input/no input=pulse (factory setting) / static input
changeover)
Enables/disables operation OFF by remote controller using the R/C prohibition
input.
ON during operation (answerback of HA)
DC12V
A
CN32
ON/OFF input
Output
B
A
CN61
OV (COM)
R/C prohibition input
Operation ON output
B
C
DEFABCDEFAB
ON during alarm
ON while outdoor unit is defrosting
DC12V (COM)
Alarm output
DC12V (COM)
Defrost output
CN60
ON when thermo sensor is ON (compressor ON)
ON in cooling mode (COOL/DRY/auto cooling)
ON in heating mode (HEAT/auto heating)
ON while indoor unit fan is ON
Factory setting: External alarm input setting (DN: 2A=2)
Indicates alarm code “L30” when an alarm continues for one minute and
performs forcible operation OFF.
(DN: 2A=1) Performs option alarm input control (indication of unit protection
attached externally).
* Remote control performs setting of option alarm input controller.
Used for checking indoor unit operation. (Outputs specified operations such as indoor
Thermo sensor ON output
COOL output
HEAT output
FAN output
DC12V (COM)
DC12V (COM)
Filter/option/external alarm input
C
CN80
Check mode input
ABA
CN71
unit fan speed H, without communication with outdoor unit or remote controller.)
DISP mode enables communication only between indoor unit and remote
controller. (at power on)
Timer short-circuited (always)
Turns OFF indoor unit thermo sensor forcibly.
OV
Display mode inputOVDemand input
B
CN72
OV
A
B
CN73
Function
Terminating resistor
Remote controller A/B
Ventilation output
HA
Option output
– 26 –
External
alarm input
CHK Operation
check
DISP DISP mode
EXCT Demand
Page 28

9
8. Troubleshooting
1. Guide to Troubleshooting
[Wired Remote Controller Type]
(1) Before starting troubleshooting
(a) Necessary tools/measuring equipment
• Phillips screwdrivers, flat-blade screwdrivers, wrenches, pliers, nipper, etc.
• Multimeter, thermometer, pressure gauge, etc.
(b) Precheck
A The following operations are normal.
1) Compressor does not work.
• Is 3-minute delay operation functioning? (for 3 minutes after compressor OFF)
• Is thermo sensor OFF?
• Is FAN mode or TIMER mode operation going?
• Is water overflow alarm detected?
• Is high outside air temperature operation control working during heating?
2) Indoor unit fan does not work.
• Is cool air prevention control working during heating?
3) Outdoor unit fan does not work or its fan speed changes.
• Is high-temp. release operation control working during heating?
• Is low outside air temperature operation control working during cooling?
• Is defrosting operation going?
4) Operation ON/OFF by remote controller is disabled.
• Is any remote controller or external control working?
• Is auto address setting in progress?
(At t he first power on or when indoor unit address is changed, operation control is disabled for
about 5 minutes after power on.)
B Are all cables/wiring set in the initial state?
C Are indoor unit and remote controller connected correctly?
(2) Troubleshooting procedure
When an error occurs, check the unit in the following procedure.
Error Check indication of check code Check faulty location and parts
(Note) Other than the check items in the table, malfunction or wrong diagnosis of microcomputer
due to effect of power or external noise is considered. If there is any source of noise, shield
the remote controller wiring.
→→
[Wireless Remote Controller Type]
(1) Before starting troubleshooting
(a) Necessary tools/measuring equipment
• Phillips screwdrivers, flat-blade screwdrivers, wrenches, pliers, nipper, etc.
• Multimeter, thermometer, pressure gauge, etc.
(b) Precheck
A The following operations are normal.
1) Compressor does not work.
• Is 3-minute delay operation functioning? (for 3 minutes after compressor OFF)
• Is thermo sensor OFF?
• Is FAN mode or TIMER mode operation going?
• Is high outside air temperature operation control working during heating?
2) Indoor unit fan does not work.
• Is cool air prevention control working during heating?
– 27 –
Page 29

3) Outdoor unit fan does not work or its fan speed changes.
• Is high-temp. release operation control working during heating?
• Is low outside air temperature operation control working during cooling?
• Is defrosting operation going?
4) Operation ON/OFF by remote controller is disabled.
• Is forcible operation OFF mode set?
• Is any remote controller or external control working?
• Is auto address setting in progress?
(At the first power on or when indoor unit address is changed, operation control is disabled for
about 5 minutes after power on.)
B Are all cables/wiring set in the initial state?
C Are indoor unit and receiver unit connected correctly?
(2) Troubleshooting procedure
When an error occurs, check the unit in the following procedure.
Error Check indication of lamps Check faulty location and parts
→→
(Note) Other than the check items in the table, malfunction or wrong diagnosis of microcomputer
due to effect of power or external noise is considered. If there is any source of noise, shield
the signal lines.
(a) Outline of judgment
The following describes the primary judgment of locating faulty unit (indoor unit or outdoor unit). (In
the case of group control operation, the header unit also indicates errors of follower unit by lamp.)
Judging from lamp status of indoor unit
The indoor unit monitors the operating status of air conditioner. When the protection circuit is
activated, the indoor unit indicates the following self-diagnosis contents.
: OFF : ON : Blinking (0.5 seconds interval)
Lamp indication
TIMER PREPARINGOPERATION
All OFF
TIMER PREPARINGOPERATION
Blinking
TIMER PREPARINGOPERATION
Check code
–
E01
E02
E03
E08
E09
E18
E04
Power OFF
Poor connection/contact between receiver/indication unit and
indoor unit control board
Reception error
Transmission error
Communication error
Duplication of indoor unit No.
Duplication of remote controller header
Poor connection/contact between indoor units or indoor unit
power OFF
(Communication error between header and follower indoor
units or between twin header and follower indoor units)
Wrong connection or poor contact between indoor unit and
outdoor unit
(Communication error between indoor and outdoor units)
Possible causes
Wired remote
controller
Wrong connection or
poor contact between
wired remote controller
and indoor unit
Invalid setting
Blinking
TIMER PREPARINGOPERATION
Alternate blinking
P12
Failure of indoor unit DC fan (Protection device of indoor unit is
activated.)
– 28 –
Page 30

Troubleshooting (Continued)
Outline of judgment (Contenued)
Lamp indication Check code
TIMER PREPARINGOPERATION
Alternate blinking
TIMER PREPARINGOPERATION
Alternate blinking
TIMER PREPARINGOPERATION
Alternate blinking
TIMER PREPARINGOPERATION
P03
P04
P19
P22
P26
P29
P31
F01
F02
F10
F04
F06
F08
F29
Possible causes
Abnormal outdoor unit discharge
temperature
Outdoor u
nit high-pressure system error
(*) Protection device
of outdoor unit is
activated.
Four-way valve system error (judged by indoor unit)
Outdoor unit: Malfunction of fan
Outdoor unit: Inverter Idc activated
Outdoor unit: Position detect error
Protection device of
outdoor unit is activated.
Header and follower indoor units in the group are not running
due to the following alarm.
(Alarm code: E03, L03, L07, L08)
Heat exchange sensor (TCJ) error
Heat exchange sensor (TC) error
Indoor unit sensor error
Room temperature sensor (TA) error
Discharge temperature sensor (TD) error
Temperature sensor (TE, TS) error
Outside air temperature sensor (TO) error
(*) Outdoor unit
sensor error
Failure of indoor unit EEPROM
Simultaneous blinking
TIMER PREPARINGOPERATION
Blinking
TIMER PREPARINGOPERATION
Simultaneous blinking
H01
H02
H03
H06
L03
L07
L08
L09
Compressor breakdown
Compressor locking
Current detect circuit error
Outdoor unit low-pressure system error
Duplication of header indoor unit
Group connection indoor unit for
→
individual indoor unit
Group address not set
No setting (indoor unit capacity)
(*) Outdoor unit
Auto address
*If group configuration
or address at power on
is invalid, the unit
enters address setting
mode automatically.
TIMER PREPARINGOPERATION
L20
L29
L30
L31
Duplication of indoor unit collective address
Other errors of outdoor unit (*)
External interlock error
Phase sequence error
Simultaneous blinking
(*) Check code detected by outdoor unit is a typical example. It varies with outdoor unit of combination.
For details, see the Service Guide of applicable outdoor unit.
compressor
system error
Others
– 29 –
Page 31

Others (Excluding check code)
Lamp indication Check code
TIMER PREPARINGOPERATION
Simultaneous blinking
TIMER PREPARINGOPERATION
Alternate blinking
–
–
Trial operation in progress
Invalid setting
(Auto cooling/heating setting for auto cooling/heating
unavailable unit or heating setting for cool only unit)
Possible causes
Error mode detected by remote controller or central controller
Diagnosis function
Check code
No
indication
(remote
controller
disabled)
E01
*2
E02
E09
L20
Central
controller
L20
–
*3
Central
controller
(Transmission)
C05
(Reception)
C06
–
Central
controller
P30/b7
*2
No check code can be indicated by wired remote controller. (Normal operation of air conditioner cannot be controlled by wired remote controller.)
Check codes are indicated by the lamps for wireless models.
*3 This is an error related to communication of remote controller (A, B) or central control system (TCC-LINK U3, U4).
Remote controller indicates E01, E02, E03, E09, E18 or no code according to situation.
Possible causes
No communication with
header indoor unit
Remote controller is not
connected correctly.
Indoor unit is not powered
on.
Auto address setting is not
completed.
No communication with
header indoor unit
Disconnection between
remote controller and header
indoor unit (detected by R/C)
Signal transmission error
to indoor unit (detected by
R/C)
Multiple remote controller
headers (detected by R/C)
Duplication of indoor unit
collective address during
communication of central
control system
(detected by indoor unit/
central controller)
Failure of central control
communication circuit
(detected by central
controller)
Failure of indoor unit group
follower unit.
Air conditioner status
OFF
OFF (auto reset)
*Operation
continues under
central control
OFF (auto reset)
*Operation
continues under
central control
OFF (Follower R/C
continues
operation)
OFF (auto reset)
Operation
continues (following
R/C)
Continue/OFF
(depending on
situation)
Conditions
–
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Judgment and action
Failure of remote controller power
supply or indoor unit EEPROM
1.Check remote controller wires.
2.Check remote controller.
3.Check indoor unit power wiring.
4.Check indoor unit P. C. board.
5.Check indoor unit EEPROM and
insertion into socket.
Auto address repetition occurs.
...
Remote controller signal reception error
1.Check remote controller wires.
2.Check remote controller.
3.Check indoor unit power wiring.
4.Check indoor unit P. C. board.
Remote controller transmission error
1.
Check remote controller transmitter.
... Replace remote controller.
1.
Check for multiple remote
controller headers.
... One header only, others are
follower R/C.
1.Check central control network
address setting.
1.Check communication line,
wrong connection, and indoor
unit power supply.
2.Check communication circuit
(U3, U4, XY terminals).
3.Check central controller
(including central control R/C).
4.Check terminating resistors
(TCC-LINK).
Check the unit's check code with
remote controller
– 30 –
Page 32

Troubleshooting (Continued)
Check Code Table (Indoor Unit)
Operation
continuation
A/C operation
Auto
reset
–
Operation
continuation
Auto
reset
–
A/C operation
–
–
A/C operation
Operation
Auto
continuation
reset
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
Description of failures
No signal from remote controller (no communication with central controller system)
When indoor unit – out door unit serial communication is abnormal
When same address as mine is detected
When communication between main motor microcomputers is abnormal
When communication between header and follower indoor units is disabled
When open-circuit or short-circuit of TCJ is detected
When open-circuit or short-circuit of TC is detected
Main faulty location
Indoor unit – R/C communication error
Indoor unit – out door unit serial communication error
Duplication of indoor unit address
Communication error between indoor unit MCUs
Communication error between header and follower indoor units
Indoor unit heat exchange sensor TCJ
Indoor unit heat exchange sensor TC
When open-circuit or short-circuit of TA is detected
Failure of EEPROM (Other errors are also detected in some cases.
Auto address repeated with no other errors.)
When multiple header units exist in the group
When there is at least one group connection indoor unit in individual indoor unit
When indoor group address is not set
Indoor unit room temp. sensor TA
Indoor unit other boards
Duplication of indoor group header unit setting
Group line in individual indoor unit
Indoor group address not set
Indoor unit capacity is not set.
Duplicated central control refrigerant line address is set.
Alarm stop by external alarm input (CN80)
When indoor unit AC fan alarm is detected (Fan motor thermal relay is activated.)
When float switch is turned on
When indoor unit DC fan alarm (overcurrent, locking, etc.) is detected
When an alarm is detected during heating due to temperature drop of
heat exchange sensor
Follower units in the group are disabled due to alarm (E03/L03/L07/L08) of header unit
Indoor unit capacity not set
Duplication of central control refrigerant line address
External alarm input into indoor unit (interlock)
Indoor unit AC fan
Indoor unit water overflow
Indoor unit DC fan
Four-way valve system
Other indoor unit errors
Description of failures
When signals cannot be received from indoor unit or when header R/C is
not set (including two R/Cs)
When signal transmission to indoor unit is disabled
When two remote controllers are set as header by double R/C control
(Header unit stops alarm, and follower continues operation.)
Main faulty location
No header R/C, R/C reception error
R/C transmission error
Duplication of header R/C
:When this alarm is detected before checking group configuration and address at power on, the unit enters auto address setting mode automatically.
:When this alarm is detected before checking group configuration and address at power on, the unit enters auto address setting mode automatically.
Description of failures
When transmission of central control signals is disabled or when there
are multiple central controllers with same address (AI-NET)
Main faulty location
Central control system transmission error
When signal transmission to indoor unit is disabled
A device connected to general equipment control interface (for TCC-
LINK/AI-NET only) is abnormal.
Group follower unit is abnormal. (R/C indicates unit No. and details.)
Central control system reception error
General equipment control I/F total alarm
Group follower unit error
Lamp indication
ON, Blinking, OFF, Alternate: Two LEDs blink alternately, Simultaneous: Two LEDs blink simultaneously
Check code
(Detected by indoor unit)
Blinking
Block indication
OPERATION TIMER PREPARING
E03
E04
E08
and remote controller
TCC-LINK central control
E10
E18
Alternate
F01
Alternate
F02
Alternate
Simultaneous
F10
F29
Simultaneous
Simultaneous
Simultaneous
L03
L07
L08
Simultaneous
Simultaneous
Simultaneous
L09
L20
L30
Alternate
P01
Alternate
Alternate
P10
P12
– 31 –
Alternate
P19
Alternate
Lamp indication
P31
Check code
(Detected by remote controller)
Blinking
Block indication
OPERATION TIMER PREPARING
E01
E02
Remote controller
E09
Blinking
Block indication
Lamp indication
OPERATION TIMER PREPARING
control
Check code
TCC-LINK central
(Detected by central controller)
–
(when R/C is used together)
No indication
C05
C06
C12
Depends on alarm No. above
P30
Note: Check code varies in some cases depending on the unit which detects errors even if its content is the same.
Check codes detected by R/C or central controller are not always related to air conditioner operation. This table does not include check codes detected by outdoor unit or thermal storage unit.
Page 33

Check Code Table (Outdoor Unit)
Operation
continuation
A/C operation
Auto
reset
Description of failures
Lamp indication
ON, Blinking, OFF, Alternate: Two LEDs blink alternately, Simultaneous: Two LEDs blink simultaneously
Typical error of thermal storage unit (Details are checked by R/C.)
When open-circuit or short-circuit of TD is detected
Main faulty location
Thermal storage unit error
Outdoor unit heat discharge sensor TD error
Blinking
Simultaneous
Alternate
Block indication
OPERATION TIMER PREPARING
When open-circuit or short-circuit of TE,TS is detected
When open-circuit or short-circuit of TO is detected
Short-circuit current Idc after direct current excitation is detected when
reaching minimum frequency in current release control.
When compressor locking is detected
Outdoor unit temp. sensor TE, TS error
Outdoor unit outside air temp. sensor TO error
Compressor breakdown
Compressor locking
Alternate
Alternate
Other outdoor unit errors 1) MCU communication error between PDU and
CDB, 2) IGBT heatsink temp. detect error
When phase sequence of 3-phase current is abnormal (thermo sensor
OFF operation continued) or other errors
When discharge temperature release control detects an error
When abnormal current is detected by AC-CT or when phase loss is
detected
Ps pressure sensor error. Low-pressure protection circuit is activated.
Current detect circuit error
Low-pressure system error
Other outdoor unit errors
Phase sequence error or others
Simultaneous
Simultaneous
When high-pressure switch or IOL is activated or when high-pressure
Abnormal outdoor unit discharge temperature
High-pressure system error
Alternate
Alternate
release control by TE detects an error
When outdoor unit fan drive circuit error (overcurrent, locking, etc.) is
detected
When short-circuit prevention control for compressor drive circuit devices
(G,Tr, IGBT) is activated
When compressor motor position error is detected
Outdoor unit fan alarm
Inverter Idc activated
Position detect error
Alternate
Alternate
Alternate
C15
Check code
and remote controller
TCC-LINK central control
(Main errors detected by outdoor unit)
F04
F06
F08
H01
H02
H03
H06
L29
L31
P03
P04
– 32 –
P22
P26
P29
applicable outdoor unit.
Note: The above check codes are typical examples. They vary with outdoor unit (including thermal storage unit) of combination. For details, see the Service Guide of
Page 34

Troubleshooting (Continued)
Check Code Table
Failure mode detected by indoor unit
Check code
E03
E04
E08
L03
L07
L08
L09
L30
P12
P19
P31
F01
F02
F10
F29
E18
Diagnosis function
Possible causes
No signal reception from remote
controller
Serial signal from outdoor unit does
not reach indoor unit.
• Wrong wire connection
• Failure of outdoor unit serial
transmitter
• Failure of indoor unit serial
receiver
Duplication of indoor unit address
Duplication of header indoor unit
Group line in individual indoor unit
Indoor unit group address not set
Indoor unit capacity not set
External interlock alarm input
Failure of indoor unit DC fan
Failure of 4-way valve system
• Indoor unit heat exchange
temperature lowers after HEAT
operation starts.
Indoor unit OFF during alarming to
other indoor units
Improper mounting, disconnection
or short-circuit of indoor unit heat
exchange sensor TCJ
Improper mounting, disconnection
or short-circuit of indoor unit heat
exchange sensor TC
Improper mounting, disconnection
or short-circuit of indoor unit room
temp. sensor TA
Failure of indoor unit EEPROM
• EEPROM access error
Communication error between
header and follower indoor units
Air conditioner status
OFF
(auto reset)
OFF
(auto reset)
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
(auto reset)
OFF
(follower units)
(auto reset)
OFF
(auto reset)
OFF
(auto reset)
OFF
(auto reset)
OFF
(auto reset)
OFF
(auto reset)
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Conditions
Judgment and action
1.Check remote controller wiring.
• No indication on remote controller
LCD (disconnection)
•
Central controller [C06] check code
1.
When outdoor unit does not work at all
• Check wires, correct wrong
connection.
•
Check outdoor unit boards and wiring
2.When outdoor unit works normally
Check boards (indoor unit receiver,
outdoor unit transmitter)
1.Check remote controller connection
(group/individual) change after
power on.
* If group configuration or address is
not correct, the unit enters auto
address setting mode automatically
for address re-setting.
1.Set indoor unit capacity (DN=11)
1.Check external devices.
2.Check indoor unit boards.
1. Position detect error
2.Overcurrent protection circuit
operation of indoor unit fan driver
3. Indoor unit fan lock
4. Check indoor unit boards.
1.Check 4-way valve.
2.Check 2-way valve/check valve.
3.
Check indoor unit heat exchanger (TC/TCJ)
4.Check indoor unit boards.
1.Judging follower unit when header
unit is E03, L03, L07 or L08
2.Check indoor unit boards.
1.Check TCJ.
2.Check indoor unit boards.
1.Check TC.
2.Check indoor unit boards.
1.Check TA.
2.Check indoor unit boards.
1.Check indoor unit EEPROM and
insertion into socket.
2.Check indoor unit boards.
1.Check remote controller wiring.
2.Check indoor unit power wiring.
3.Check indoor unit boards.
.
.
– 33 –
Page 35

Failure mode detected by outdoor unit (Representative codes)
• The check code used varies depending on the combination with the outdoor unit.
Diagnosis function
Check code Possible causes
H01
H02
H03
H06*1
L29
L31*1
P03
P04
P22
P26
P29
F04
F06
F08
*1 ROA-P*** is not detected by 1HS models.
Fan continues rotating in a failure mode detected by outdoor unit because there is no communication between outdoor unit
and follower indoor unit in twin group.
Compressor breakdown
• Compressor stops due to
operating frequency decrease.
Compressor does not work.
• Overcurrent protection circuit is
activated after a certain time from
compressor startup.
Failure of current detect circuit
• Large AC current even during
compressor OFF
• Phase loss in power supply
Low-pressure switch ON
(applicable models)
COOL : 30 seconds
HEAT : 10 minutes
Other outdoor unit errors
• CDB-IPDU communication error
(connector disconnection)
• Abnormal heatsink temperature
(over specified value)
Phase detection protection circuit
activated (normal models)
Abnormal discharge temperature
(over specified value)
Failure of high-pressure protection circuit
(Temperature over specified value
detected by TE sensor)
High-pressure switch (normal models)
Failure of outdoor unit DC fan
Inverter overcurrent protection
circuit activated (short time)
Main circuit short voltage operation
Failure of IPDU position detect
circuit
Improper mounting, disconnection
or short-circuit of outdoor unit temp.
sensor TD
Improper mounting, disconnection
or short-circuit of outdoor unit temp.
sensor TE, TS
Improper mounting, disconnection
or short-circuit of outdoor unit
outside air temp. sensor TO
Air conditioner status
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
Operation
continued
(compressor
OFF)
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
Operation
continued
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Indicated when an
error is detected
Conditions
1.
Check power voltages (200±20 VAC).
2.Freezing cycle overload operation
3.
Check current detect circuit on the AC side
1.Failure of compressor (lock, etc.)
... Replace the compressor.
2.
Improper compressor wiring (phase loss)
3.Lost-phase operation of power
supply (3-phase models)
Operation stops soon when restarted
1.
... Check IPDU.
2.
Lost-phase operation of power supply
Check 3-phase power voltages and wiring.
1.Check freezing cycle (gas
leakage).
2.Check low-pressure switch circuit.
3.Check outdoor unit CDB board.
1.Check CDB/IPDU wiring.
2.Freezing cycle overload operation
1.Check phase sequence, reverse
phase, and phase loss.
2.Check outdoor unit boards.
3.Check high-pressure switch.
4.
Check high-pressure switch circuit wiring.
1.
Check freezing cycle (gas leakage).
2.
Failure of electronic expansion valve
3.Check piping sensor (Td).
1.Freezing cycle overload operation
2.Check outdoor unit TE sensor.
3.Check outdoor unit CDB board.
4.
Check high-pressure switch and circuit.
1.Position detect error
2.Overcurrent protection circuit
operation of outdoor unit fan driver
3.Outdoor unit fan lock
4.Check outdoor unit CDB board.
1.
Operation stops soon when restarted.
... Compressor partial short-circuit
2.Check IPDU for improper wiring.
1.The circuit is activated even after
compressor’s 3P connector is
disconnected. ...Replace IPDU.
1.Check TD.
2.Check outdoor unit CDB board.
1.Check TE, TS.
2.Check outdoor unit CDB board.
1.Check TO.
2.Check outdoor unit CDB board.
Judgment and action
.
.
– 34 –
Page 36

Troubleshooting (Continued)
2.
Troubleshooting by Remote Controller Check Indication
Main Remote Controller (RBC-AMT31E)
(1) Checking
When an error occurs in the air conditioner, a
check code and an indoor unit number appear
on the LCD of remote controller.
Check code is displayed only during
operation.
If indication disappears, check errors following
Check code
“Checking Error Log” below.
(2) Checking Error Log
When an error occurs in the air conditioner, error log can be checked following the steps below. Up to 4
errors are memorized.
Error log can be checked in both operation ON and OFF states.
Step Operation
Press [SET] and [TEST] at the same time for 4 seconds or more. The LCD indication changes as shown below.
Indication of “SERVICE CHECK” shows that the unit is in the error log mode.
• Code No. “01” (order of error log) is displayed.
A
• A check code is displayed.
• The address of faulty indoor unit is displayed in the UNIT No. area.
Faulty indoor unit
No.
Each pressing of TEMP. ∆/∇ buttons displays stored error log sequentially.
Check code “01” shows the latest error, and “04” shows the oldest.
B
Note
Do not press [CL] as this button clears entire error log of indoor unit.
C
After checking the error log, press [TEST] to return to the normal indication.
Numbers appearing on the LCD
<Seven-segment display>
Hexadecimal number
– 35 –
Page 37

TCC-LINK Central Control Remote Controller (TCB-SC642TLE)
(1) Checking
When an error occurs in the air conditioner, a
check code and an indoor unit number appear on
the LCD of remote controller.
Check code is displayed only during operation.
If indication disappears, check errors following
“Checking Error Log” below.
Indication of unit number
UNIT No.
R.C. No.
Indication of alarm
CHECK
Alternate blinking
(2) Checking Error Log
When an error occurs in the air conditioner, error log can be checked following the steps below. Up to 4
errors are memorized.
Error log can be checked in both operation ON and OFF states.
A Press [SET] and [TEST] at the same time for 4 seconds or more.
B Indication of “SERVICE CHECK” and UNIT No. “01” appear.
C When selecting a group number (blinking), a unit number and the latest error log, if any, are displayed
alternately.
* Temperature setting is disabled at this time.
Indication of unit number
UNIT No.
Alternate blinking
R.C. No.
Indication of alarm
CHECK
D To check other errors, choose a code (01 to 04) with TEMP. ∆/∇ buttons.
E To check error log of another group, choose a group number with
/ buttons.
Do not press [CL] as this button clears entire error log of the selected group.
F Press [TEST] to finish the service check.
– 36 –
Page 38

Troubleshooting (Continued)
3. Troubleshooting for Each Check Code
Check code
[E01]
(New code)
Are R/C wires
A/B correct?
Improper harness
connection from
I/U terminal block?
Group control
operation?
YES
NO
YES
Check code name
I/U - R/C communication error
(detected by R/C)
NO
YES
NO
Possible causes
AImproper R/C wire connection
BFailure of I/U power supply
CFailure of I/U board
DInvalid R/C address setting
EFailure of R/C board
Correct R/C wires.
Correct connector connection.
Check circuit wiring.
Are all indoor
units powered ON?
YES
Is R/C powered ON?A/B
terminals: Approx. 18VDC
YES
Is “no header”
set by double R/C?
NO
NO
NO
YES
Check I/U power connection
(power off and on).
Check I/U boards.
→ Replace defective board.
Correct one header/one follower.
(R/C address connector)
Check R/C board.
→ Replace it if necessary.
– 37 –
Page 39

Check code
Check code name
Possible causes
[E02]
(New code)
R/C transmission error
Signal transmission to indoor unit is
disabled.
* Not indicated on the central controller and outdoor unit 7-segment.
Com. cable between
R/C and I/U connected
properly?
YES
Failure of R/C
transmitter → Replace R/C.
Check code
[E03]
(New code)
Indoor unit (I/U) detects this error when it cannot receive signals from remote controller (R/C).
Check communication wiring of R/C A and B.
This code E03 is not displayed on the R/C because of communication error.
This code is displayed on the TCC-LINK central controller.
NO
Check code name
I/U - R/C communication error
(detected by I/U)
Possible causes
No communication from R/C and communication adapter.
Correct communication cable.
– 38 –
Page 40

Troubleshooting (Continued)
Check code
[E04]
(New code)
Does O/U work?
YES
Check code name
I/U - O/U communication error
(detected by I/U)
NO NO
Is group address set correctly?
Are 1/2/3 wires normal?
Are connectors from I/U and
O/U connected normally?
Is I/U switch SW02
setting correct? Bit 1, 2: OFF
AImproper connector connection between I/U and O/U
BImproper wire connection between I/U and O/U
CFailure of I/U or O/U board
DCase thermo sensor ON
EInvalid I/U board switch setting
YES
YES
YES
YES
Possible causes
NO
NO
NO
Check code “14”.
Correct wires.
Correct connector connection.
Correct switch setting on
MCC-1510 board.
Check I/U boards.
® Replace defective board.
Does voltage between
I/U terminal 2 and 3 fluctuate?
(0-140 VDC)
* Measure within
YES
Is 280VDC
applied across IPDU main
circuit capacitor?
YES
Is 280VDC supplied to
CDB? (CN03)
YES
Is 7VDC supplied
to CDB? Is CN06-CN800
connection normal?
YES
Is case thermo sensor
connected? (CN500)
YES
Is case thermo sensor working?
YES
Check and correct refrigerant volume.
20 seconds
from power on.
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
NO
Check MCC-1510 board.
→ Replace it if necessary.
Black
C
White
B
A
Terminal block
Replace IPDU.
Replace IPDU.
Replace IPDU.
Correct connector connection.
Correct connector connection.
Check MCC-1510 board.
→ Replace it if necessary.
Check CDB. → Replace it if
necessary.
– 39 –
Page 41

Check code
Check code name
Possible causes
[E09]
(New code)
Are 2 headers set
by double R/C?
NO
Check code
[E18]
(New code)
Are A/B wires
normal?
Improper harness
connection from I/U terminal
block?
Communication error between header
YES
Duplication of R/C header
YES
Check code name
and follower I/U
NO
YES
R/C header setting is duplicated.
Correct one header/one follower.
(R/C address connector)
Check R/C board.
→ Replace it if necessary.
Possible causes
A Improper wire connection between I/U
B Improper wire connection between I/U and O/U
C Failure of I/U board
D Invalid I/U board switch setting
Correct R/C wire connection.
Correct connector connection.
Check circuit wiring.
NO
Is I/U switch SW02
setting correct?
Bit 1, 2: OFF
YES
Group control operation?
YES
Are all indoor
units powered ON?
YES
Twin or triple control?
YES
Improper signal
connection between I/U
and O/U?
NO
NO
NO
NO
YES
Correct switch setting on
MCC-1510 board.
Check I/U power connection
(power off and on).
Correct signal wire connection
between I/U and O/U.
NO
Check MCC-1510 board.
→ Replace it if necessary.
– 40 –
Page 42

Troubleshooting (Continued)
Check code
[F01]
(New code)
Is TCJ connector
CN102 connected
normally?
YES
Is TCJ resistor
characteristic
normal?
* See I/U temp. sensor characteristics-2.
YES
Check I/U main board.
→ Replace it if necessary.
Check code name
I/U sensor TCJ error
NO
NO
Possible causes
I/U sensor TCJ error
Correct connector connection.
Replace sensor TCJ.
Check code
[F02]
(New code)
Is TC connector
CN101 connected
normally?
YES
Is TC resistor
characteristic
normal?
* See I/U temp. sensor characteristics-2.
YES
Check I/U boards.
→ Replace defective board.
Check code name
I/U sensor TC error
NO
NO
Possible causes
Sensor TC open or short-circuit
Correct connector connection.
Replace sensor TC.
– 41 –
Page 43

Check code
Check code name
Possible causes
[F10]
(New code)
Is TA connector
CN104 connected
normally?
YES
Is TA resistor
characteristic
normal?
YES
Check MCC-1510 board.
Replace it if necessary.
Check code
I/U sensor TA error
Sensor TA open or short-circuit
NO
NO
* See I/U temp. sensor characteristics-1.
Check code name
Correct connector connection.
Replace sensor TA.
Possible causes
[F29]
Other indoor unit errors
Failure of I/U board
(New code)
This is an error of non-volatile EEPROM IC10 on the indoor unit board, which occurs during
operation. Replace the service board.
* If EEPROM is not mounted at power on or if no data can be read/written from/in the EEPROM,
auto address mode is repeated. At this time, the AI-NET central controller indicates code “97”.
(About 3 minutes) (About 1 minutes)
(Power on)
“SETTING” appears
on the R/C.
“SETTING” disappears.
(Repeated)
LED (D02) on the I/U
board blinks for about
10 seconds (1Hz).
Reboot
(reset)
– 42 –
Page 44

Troubleshooting (Continued)
Check code
[F31]
(New code)
Is O/U free from
power fluctuation?
YES
Check CDB board.
Check code name
O/U EEPROM error
NO
AFailure of O/U power supply (voltage, noise, etc.)
BFailure of O/U CDB board.
Check code
[E08][L03][L07][L08]
(New code/old code)
E08: I/U number duplicated
L03: Multiple header I/U under group control
L07: One or more group address “individual” under group control
L08: I/U group address not set (99)
Possible causes
Check power voltage.
Improve power lines.
Check external noise.
When any of these codes is detected at power on, the unit enters auto address setting mode
automatically. (No code is indicated.)
However, if any of these codes is detected in the auto address setting mode, a check code is
displayed in some cases.
Check code
[L09]
(New code)
Is indoor unit
capacity set?
YES
Check code name
Indoor unit capacity not set
NO
Indoor unit capacity not set
Possible causes
Set I/U capacity data. (DN=11)
Check MCC-1510 board.
→ Replace it if necessary.
– 43 –
Page 45

Check code
Check code name
Possible causes
[L20]
(New code)
Are U3/U4
communication
cables connected
normally?
When a unit
connected to U3/U4
is in a group, is it set
to header unit?
Check and correct I/U address,
central control address.
Duplication of central control address
YES
YES
NO
NO
Central control address is duplicated.
Correct cable connection.
Set the connected unit to
header unit.
Check code
[L30]
(New code)
Is external device
connected to CN80?
YES
Is external device
working normally?
YES
Check possible error
causes.
Check code name
I/U external interlock
NO
NO
Possible causes
When an external alarm is input
Check I/U boards.
→ Replace defective board.
Check external device.
→ Replace it if necessary.
– 44 –
Page 46

Troubleshooting (Continued)
Check code
[P12]
(New code)
Turn OFF the breaker.
Turn it ON 10 seconds
after.
Does fan stop with
operation OFF?
YES
Start cooling with LOW
fan speed.
Does fan rotate?
YES
Change fan speed to HH.
Does fan speed
increase?
YES
Fan motor is normal.
Check code name
Malfunction of I/U fan motor
Is min.1VDC present
NO
between CN210 pin
E and C ?
YES
Is min. 280VDC present
NO
between CN210 pin
A and C ?
YES
Is min. 15VDC present
between CN210 pin
D and C with
motor connected?
YES
Operate I/U (except
heating) by R/C. Is min.
1VDC present between
CN210 pin
C
?(Measure within
E
and
15 seconds.)
NO
YES
Does cross flow fan
rotate normally by hand?
YES
Rotate the fan by hand with
operation OFF. Is 0 to
15VDC (rev return signal)
generated between CN210
pin
F
and C ?
YES
A Failure of fan motor connector
B Failure of fan motor
C Failure of I/U board
D Failure of cross flow fan shaft
NO
NO
Stop operation and turn OFF
NO
breaker. Disconnect CN210,
turn ON breaker again, and
then stop operation using R/C.
Is min. 280VDC present
between CN210 pin
D
and C ?
YES
Stop operation and unplug
NO
AC cord. Disconnect
CN210, plug in AC cable
again, and then stop
operation using R/C.
NO
Operate I/U (except
heating) by R/C. Is min.
1VDC present between
CN210 pin
C
? (Measure within
15 seconds.)
YES
NO
E
and
Possible causes
NO
NO
Replace I/U fan
motor.
Replace I/U MCC-
1510 board.
Repair cross flow
fan shaft.
– 45 –
Page 47

Check code
Check code name
Possible causes
[P12]
(New code)
Check the fan motor output DC voltage on the I/U board.
Check voltage on the motor connector CN210 pin C (GND,
black) and pin E (+V line, yellow) while fan is rotating.
1.0VDC or
Failure of I/U
MCC-1510 board
Malfunction of I/U fan motor
When AC cord is plugged
in, I/U fan starts rotating.
higher
Below 1.0VDC
Failure of I/U fan
motor
A Failure of fan motor connector
B Failure of fan motor
C Failure of I/U board
D Failure of cross flow fan shaft
Yello w
Black
P. C. board
(Blue)
(Yellow)
(White)
(Black)
(Red)
– 46 –
Page 48

Troubleshooting (Continued)
Check code
[P31]
(New code)
When header unit detects E03, L03, L07 or L08 during group operation, “P31” is indicated on follower units in the group and
their operation stops. No code or alarm log is displayed on the R/C.
Check code name
Other I/U errors
(Group follower I/U error)
When an error occurs with other units in the group
Possible causes
– 47 –
Page 49

Check code
Check code name
Possible causes
[C05], [C06]
(Central controller)
Is I/U
powered ON?
YES
Is harness from I/U
terminal block
connected properly?
YES
Can I/U be
operated by R/C
individually?
YES
Are U3/U4 com.
cables. normal?
*1
YES
TCC-LINK central control
TCC-LINK central control communication error
communication error
NO
NO
NO
NO
* Check wrong connection, disconnection, and
shield wire’s contact with com. cable.
Power ON.
Correct connector connection.
Correct com. cable.
When a unit
connected to U3/U4
is in a group, is it
set to header
unit?
YES
Free from noise?
YES
Can other units
controlled by
central R/C? Is I/U
operating status
reflected?
YES
Is the code [C05]?
NO
Is I/U onboard fuse
F03 normal?
NO
NO
NO
YES
NO
Set the connected unit to
header unit.
Remove noise source.
Check central controller.
→ Replace it if necessary.
Confirm normal connection of
com. cable. Change connector
connection CN40 to CN44
(EMG) on I/U board.
YES
Check I/U boards. → Replace
defective board.
– 48 –
Page 50

Troubleshooting (Continued)
Relationship Between Temperature Sensor Resistance and Temperature
20
Characteristic-1
40
Sensor TA
Resistance
[k ]
10
0
10 20 30 40
Temperature
200
Resistance
[k ] [k ]
(10°C or lower)
Characteristic-3
50
[˚C]
Resistance
[k ]
30
20
10
0
0
-10
20
Characteristic-2
Sensor TC, TCJ
10 20 30 40
Temperature
Sensor TE, TO, TS
Resistance
(10°C or higher)
[˚C]
60 70
50
100
200
Resistance
[k ]
(50°C or lower)
100
10
0
Characteristic-4
10 20 30 40
0
Temperature
[˚C]
60 70-10
50
Sensor TD
0
20
Resistance
[k ]
(50°C or lower)
10
0
50
Temperature
100
[˚C]
0
– 49 –
Page 51

9. HOW TO REPLACE SERVICE BOARD OF INDOOR UNIT
Requirements When Replacing Service Board of Indoor Unit
The non-volatile EEPROM (IC10) on the board of indoor unit stores important data such as model-specific type and capacity
code (written during factory shipping) as well as system/indoor unit/group addresses set automatically/manually (written during
installation). Therefore, observe the following procedure when replacing indoor unit service boards.
After installation of indoor unit, check whether the settings are correct by checking indoor unit number and group header/
follower unit setting, and also check cycle through a trial operation.
[Replacement Procedures]
Case 1
When it is possible to power ON indoor unit before replacement and when wired R/C can read settings
Reading EEPROM Data *1 (see page 51)
Replacing Service Board and Power ON *2 (see page 51)
Writing Setting Data in EEPROM *3 (see page 52)
Power ON reset (for all indoor units connected to R/C in group control mode)
Case 2
When it is impossible to power ON indoor unit before replacement or when wired R/C is disabled
due to failure of power supply circuit (board failure)
Replacing EEPROM (For layout of components and replacement, see page 49.)
Remove the EEPROM on the board, and replace it with the EEPROM on the service board.
Replacing Service Board and Power ON *2 (see page 51)
Reading EEPROM Data *1 (see page 51)
If data cannot be read, go to Case 3.
Replacing EEPROM (For layout of components and replacement, see page 49.)
Replace EEPROM again. (Mount the original EEPROM on the service board.)
Replacing Service Board and Power ON *2 (see page 51)
Writing Setting Data in EEPROM *3 (see page 52)
Power ON reset (for all indoor units connected to R/C in group control mode)
Case 3
When the EEPROM before replacement is defective, and the settings cannot be read
Replacing Service Board and Power ON *2 (see page 51)
Writing Setting Data in EEPROM (using customer information) *3 (see page 52)
Power ON reset (for all indoor units connected to R/C in group control mode)
– 50 –
Page 52

HOW TO REPLACE SERVICE BOARD OF INDOOR UNIT (Continued)
*1 Reading EEPROM Data
(Read EEPROM data that was updated at site in addition to factory setting.)
1
1) Press
, , and on the R/C simultaneously for 4 seconds or more.
* In the group control mode, the header unit number is displayed first.
At this time, code (DN)
is displayed, and the fan of the selected indoor unit runs, its flap swings,
and the OPERATION, TIMER, and PREPARING lamps blink.
(see page 52)
2) Each pressing of
indicates indoor unit number in the group sequentially.
2
Specify indoor unit number whose board is to be replaced.
3) Each pressing of TEMP.
buttons increments or decrements DN.
3
4) Change DN from to first. (Setting of filter sign ON time)
Write down the setting data displayed.
5) Change DN with TEMP.
buttons, and write down the setting data displayed.
6) Repeat step 5) in the same way, and write down the important setting data shown in the table
(page 49).
* DN =
7) After writing down setting data, press
to . DN does not always shift sequentially.
to return the operation mode to normal OFF.
6
(It takes about one minute until R/C operation is enabled.)
Essential DN codes
DN
11
12
13
14
Description
Indoor unit capacity
Refrigerant line address
Indoor unit address
Group address
(1) Indoor unit capacity is necessary for fan speed setting.
(2) If refrigerant line address, indoor unit address or group
address differs from that before replacement, the unit enters
auto address setting mode, which requires manual re-setting
for group operation including twin or triple operation.
*2 Replacing Service Board and Power ON
1) Replace the board with a service board.
Reflect the jumper wire (cut) setting and switch setting on the board in the service board. For switch
setting and component layout, see page 53.
2) Power ON the indoor unit in either way of the following according to system configuration.
a) Single (individual) operation
Power ON the indoor unit with no operation.
i) Go to *3 when auto address setting mode ends (about 5 minutes).
(Refrigerant line address=1, indoor unit address=1, and group address=0 are set automatically.)
ii) Press
address setting mode, and then go to *3. (UNIT No.
, , and on the R/C simultaneously for 4 seconds or more (1) to cancel auto
is indicated.)
b) Group operation (including twin/triple/double twin)
Power ON the indoor unit whose service board is replaced in either way of the following.
i) Power ON the indoor unit only whose service board is replaced in the same way as a) i) and ii)
above.
There must be remote controller connection. If not, operation *3 is disabled.
ii) Power ON multiple indoor units including the unit whose service board is replaced.
• Twin, triple, double twin: One system only
• Group control: All indoor units
Go to *3 when auto address setting mode ends (about 5 minutes).
* Header indoor unit may change depending on auto address setting. The refrigerant line address and
indoor unit address of the indoor unit whose service board is replaced are automatically set to an
address that is not used in other units. It is recommended that you take a memo beforehand that to
which refrigerant system the indoor unit belongs and that the indoor unit is header or follower unit in
the group.
– 51 –
Page 53

*3 Writing Setting Data in EEPROM
(The data of the EEPROM on the service board is the factory setting data.)
1) Press
* In the group control mode, the header unit number is displayed first.
(If auto address setting mode is canceled in 2-2) a) ii) above, UNIT No.
At this time, code (DN)
and the OPERATION, TIMER, and PREPARING lamps blink.
, , and on the R/C simultaneously for 4 seconds or more.
is displayed, and the fan of the selected indoor unit runs, its flap swings,
1
(see page 52)
is indicated.)
2) Each pressing of
indicates indoor unit number in the group sequentially.
Specify indoor unit number whose board is replaced.
(This operation is disabled if UNIT No. is
3) Each pressing of TEMP.
.)
buttons increments or decrements DN.
4) Set the indoor unit capacity first.
The factory setting data is written in the EEPROM.
i) Change DN to
ii) Set the indoor unit capacity with TIME
with TEMP. buttons.
buttons. 4 (for
example, “0012” for 80 class) ... See the table (page 53).
iii) Press
iv) Press
Indication on the LCD shows normal operation.
to return the operation mode to normal OFF.
6
(It takes about one minute until R/C operation is enabled.)
5) Write the data set after installation (such as address) in the EEPROM.
Repeat steps 1) and 2) above.
6) Specify DN
with TEMP. buttons. (Setting of filter
sign ON time)
7) Check the displayed data comparing the content written down in *1
(page 49).
i) If the data is incorrect, change it with TIME
data of the memo, and then press
Indication on the LCD shows
buttons to the
normal operation.
ii) No operation is required for the same data.
2
3
<Remote Controller>
RBC-AMT21E
SETTING
5
6
1
4
32
8) Change DN with TEMP.
buttons.
In the same way as above, check the displayed data comparing the
content of the memo.
If the data is incorrect, change it to the data of the memo.
9) Repeat steps 7) and 8) above.
10) When the setting is completed, press
mode to normal OFF.
6
to return the operation
(It takes about one minute until R/C operation is enabled.)
* DN =
updated and
restored with
to . DN does not always shift sequentially. Even if data is
button is pressed by mistake, the previous data can be
button unless DN is changed.
RBC-AMT31E
3 5
6 2
4
1
– 52 –
Page 54

HOW TO REPLACE SERVICE BOARD OF INDOOR UNIT (Continued)
Example of Setting Contents to be Written Down (Code Table)
DN
Filter sign ON time
01
02
Filter contamination level
Central control address
03
06
HEAT intake temp. shift
PREPARING indication selection
0C
0F
COOL only
Type
10
11
Indoor unit capacity
Refrigerant line address
12
13
Indoor unit address
Group address
14
1E
Temp. range at COOL/HEAT auto switching control
Auto restart after power failure
28
2A
Option/alarm input (CN80) selection
Thermo output (T10-C) selection
2b
2E
HA terminal (T10-A) selection
Ventilation fan (single operation)
31
32
Sensor selection
Timer setting (wired R/C)
60
69
Flap setting for cooling
Correction of feeling of strong heating
8b
Item
Memo
Must be set to 0008
Factory setting
0001: 150 hours
0000: Average
0099: Not determined
0002: +2°C
0000: Normal
0000: Heat pump type air conditioner
0008: Wall type
Depends on capacity type
0099: Not determined
0099: Not determined
0099: Not determined
0003: 3°C (Ts±1.5)
0000: Not provided
0002: External alarm input
0000: Thermo output ON
0000: Operation input
0000: Disabled
0000: Unit sensor
0000: Available
0000: Normal
0000: Not provided
Onboard Component Layout
<MCC-1510>
SW01
ON
2
1
IC10
DIP switch setting
SW01
SW02
*1: Set to the state before replacement
Bit 1
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 2
Terminating resistor (for central control)
Selection of R/C A or B
Selection of custom or multiple
Not used
Setting
SW02
1
2
J01
ON
Indoor unit capacity
Code “11”
Setting data
0000*
0006
0007
DIP switches
(SW01, SW02)
0008
0009
0010
0011
0012
* Default value of EEPROM on the
EEPROM (IC10)
Mount EEPROM aligning its notch with
the notch of IC socket.
IC socket Notch EEPROM
AIK-AP**1H
*1
*1
OFF
OFF
service board
Factory setting
OFF (no resistor)
OFF (A is selected)
OFF (custom models)
OFF
Model
Invalid
40 type
45
50
56
63
71
80
Notch
– 53 –
Page 55

11
10. ON-SITE SETTING AND OTHERS
1. Indoor Unit
1.1 Trial Operation Setting by Remote Controller only.
The lamps on the unit blink during trial operation.
<Wired remote controller>
1
Press on the R/C for 4 seconds. When “TRIAL OPERATION” appears on the LCD, press .
• “TRIAL OPERATION” appears on the LCD during trial operation.
• Trial operation disables temperature control, but allows fan speed control.
• An instruction of fixed frequency is issued for cooling and heating of trial operation.
• Alarm detection is performed as usual.
The trial operation mode must be used for its original purpose only, because it stresses the air conditioner.
2
Choose COOL or HEAT mode only for trial operation.
• (Note) Outdoor unit does not run about 3 minutes after power on or operation stop.
3
Repress after trial operation and confirm that “TRIAL OPERATION” disappears from the LCD.
Wired remote controller has 60-minute timer reset function to prevent continuous trial operation.
Checking wiring and piping of indoor/outdoor units
1. Open the front panel of the indoor unit.
2. Press [TEMPORARY] button for 10 seconds. The unit enters forcible cooling mode with a sound
“pi”. COOL operation starts forcibly about 3 minutes later. Check whether cool air is discharged. If
COOL operation does not start, recheck the wiring.
3. Repress [TEMPORARY] for about one second to stop trial operation. The vertical airflow flap
closes and the operation stops.
Checking signal transmission from R/C
1. Press [ON/OFF] on the R/C to check for normal operation using R/C.
• To enter AUTO mode, press [TEMPORARY] once
for about one second.
For forcible cooling, press [TEMPORARY] for 10
seconds or more.
• COOL operation specified by R/C may not start
depending on temperature conditions.
Use forcible cooling operation to check wiring and
piping of indoor/outdoor units.
[TEMPORARY]
button
– 54 –
Page 56

ON-SITE SETTING AND OTHERS (Continued)
1.2 Forcible Defrost Setting by Remote Controller (wired R/C only)
Preliminary operation
1
Press , , and at the same time for 4 seconds or more in the OFF mode.
In the group control mode, the header unit number is displayed first.
2
Each pressing of indicates indoor unit number in the group sequentially.
Choose the main indoor unit (connected to the outdoor unit) for which forcible defrosting is to be
performed.
The fan and flap of the selected indoor unit start working.
3
Specify DN “8C” with buttons.
4
Set data 0001 with buttons. (Factory setting: 0000)
5
Press Indication on the LCD shows normal operation.
6
Press to return the operation mode to normal OFF.
Execution procedure
• Press
• Choose HEAT operation mode.
• After a while, a forcible defrosting signal is transmitted to the outdoor unit. Upon receiving the signal, the
outdoor unit starts defrosting. It takes up to 12 minutes.
• On completion of defrosting, the indoor unit restart HEAT operation.
on the R/C.
To reexecute defrosting, repeat steps from step
1
above.
Once forcible defrosting is performed, the above setting for forcible defrosting is reset.
1.3 Indication of Onboard LEDs
1. D02 (red)
Lights up by the control of main microcomputer when the indoor unit is powered on.
Blinks at intervals of one second (0.5-second on and off) when EEPROM is not mounted or write
error occurs.
Blinks at intervals of 10 seconds (5-second on and off) in the DISP mode. (CN72 short-circuited at
power on)
Blinks at intervals of 2 seconds (1-second on and off): Applicable unit in the EEPROM setting
(address, function selection, etc.) mode
2. D203 (red)
Lights up by hardware control when power is supplied to remote controller.
– 55 –
Page 57

1.4 JRA Capacity Measurement Mode (wired R/C only)
Preliminary operation
1
Press , , and at the same time for 4 seconds or more in the OFF mode.
In the group control mode, the header unit number is displayed first.
2
Each pressing of indicates indoor unit number in the group sequentially.
Choose the main indoor unit (connected to the outdoor unit) for which this control is to be performed.
The fan and flap of the selected indoor unit start working.
3
Specify DN “91” with buttons.
4
Set the following data with buttons. (Factory setting: 0000)
Data
Rating
Middle
5
Press Indication on the LCD shows normal operation.
6
Press to return the operation mode to normal OFF.
Execution procedure
• Press
0001
0002
Use this mode to measure JRA capacity.
Use this mode under the conditions of JIS B8615-1
Perform the settings in the table by remote
controller
.
Cooling rating
.
Heating rating
Cooling middle
Heating middle
on the R/C.
Operation
Cooling
Heating
Auto Cooling
Auto Cooling
Fan speed
Quick high
Quick high
Auto
Auto
Setting temp.
18°C
29°C
23°C
24°C
Flap position
Horizontal angle
Horizontal angle
Horizontal angle
Horizontal angle
To reexecute JRA capacity measurement, repeat steps from step
Once this measurement is completed, the above setting is reset.
1.5 Function Select Setting (wired R/C only)
Perform the following steps in the operation OFF mode.
1
Press , , and at the same time for 4 seconds or more in
the OFF mode.
In the group control mode, the header unit number is displayed
first.
2
Each pressing of indicates indoor unit number in the group
sequentially.
Choose the main indoor unit (connected to the outdoor unit) this
function is to be performed.
The fan and flap of the selected indoor unit start working.
Specify DN with buttons.
3
Operation procedure
4
Set the setting data with buttons.
1
above.
3 5
6 2
1 2 3 4 5 6
4
1
END
5
Press Indication on the LCD shows normal operation.
2
• To change the selected indoor unit, go to
• To change the item to be set, go to
6
Press to return the operation mode to normal OFF.
3
.
.
– 56 –
Page 58

ON-SITE SETTING AND OTHERS (Continued)
Function Select Code (DN) Table
DN
Filter sign ON time
01
Filter contamination level
02
03
Central control address
06
HEAT intake temp. shift
OC
PREPARING indication selection
OF
COOL only
10
Type
11
Indoor unit capacity
12
Refrigerant line address
13
Indoor unit address
14
Group address
1E
Temp. range at COOL/HEAT auto
switching control
28
Auto restart after power failure
2A
Option/alarm input (CN80)
selection
2b
Thermo output (T10-3) selection
2E
HA terminal (T10-1) selection
31
Ventilation fan (single operation)
32
Sensor selection
60
Timer setting (wired R/C)
69
Flap setting for cooling
8b
Correction of feeling of strong
heating
Item
Description
0000: None 0001: 150H
0002: 2500H 0003: 5000H
0004: 10000H 0005: Clogging sensor used
0000: Average 0001: Heavy
(half of standard time)
0001: No. 1 - 0064: No. 64
0099: Not determined
0000: No shift 0001: +1 °C
0002: +2 °C - 0010: +10 °C
(Up to +6 recommended)
0000:
PREPARING indicated
0000: Heat pump 0001: COOL only
0000: (Ceiling panel 1) 0001 (ceiling panel 4) -
0000: Not determined 0001 - 0034
0001: No. 1 - 0030: No. 30
0001: No. 1 - 0064: No. 64
0000: Individual 0001: Group header
0002: Group follower
0000: 0deg - 0010: 10deg
(Switching at set temperature ±(data)/2)
0000: Not provided 0001: Provided
0000: Filter input 0001: Alarm input
External alarm input
0002:
0000:
I/U thermo sensor ON
0000: Normal (JEMA) 0001: Card input
0002: Fire alarm input
0000: Disabled 0001: Enabled
0000: Unit sensor TA 0001: R/C sensor
0000: Available 0001: Unavailable
0000: Normal 0001: Down allowed
0000: Not provided 0001: Provided
0001: No indication
(No “AUTO”, “HEAT”
indication)
0037
0001: O/U compressor ON
output
Factory setting
0001: 150H
0000: Average
0099: Not determined
0002: +2 °C
0000: PREPARING
indicated
0000: Heat pump
0008: Wall type
Depends on capacity
type
0099: Not determined
0099: Not determined
0099: Not determined
0033: 3deg (Ts ± 1.5)
0000: Not provided
0002: External alarm
input
0000: I/U thermo
sensor ON
0000: Normal
(HA terminal)
0000: Disabled
0000: Unit sensor
0000: Available
0000: Normal
0000: Not provided
– 57 –
Page 59

1.6 Wiring and Setting for Remote Controller
Double R/C control (when controlling by two remote controller switches)
This control is provided to control one or more indoor units by two remote controllers. Up to 2 remote
controllers can be installed.
No setting is required when using in combination with a wireless remote controller .
Controlling one indoor unit by 2
remote controllers
R/C switch
(header)
AB
A B
Indoor unit
1 2 3
R/C switch
(follower)
OptionOption
AB
R/C wiring (on-site arrangement)
R/C wiring terminals
1 2 3
Outdoor unit
Setting
This control is provided to control one or more indoor units by two remote controllers.
Up to 2 remote controllers can be installed.
Remote controller (back, inside)
<Wired remote controller>
Setting to use a wired remote controller
as follower R/C:
Change the setting of DIP switch on the
back of R/C switch to “R/C follower” as
shown in the figure.
21
R/C follower
R/C header
21
21
DIP switch
– 58 –
Page 60

ON-SITE SETTING AND OTHERS (Continued)
1.7 Monitoring Function of Remote Controller Switch
■■
■Calling indication of sensor temperature
■■
<Description>
Calls the service monitor mode from the remote controller to
monitor sensor temperatures of the remote controller, indoor units,
and outdoor unit.
<Procedure>
1
Press and on the R/C simultaneously for 4 seconds or more
to call the service monitor mode.
“Service monitor” lights up and the header indoor unit number is
displayed first, and then temperature of code “
2
Choose a sensor number (code) you want to monitor with
buttons.
The following table lists sensor numbers.
Code
Room temp. under control *1
00
01
Room temp. (R/C)
Indoor unit intake temp.
02
03
Indoor unit coil temp. TCJ
Indoor unit coil temp. TC
04
Indoor unit data
05
Indoor unit coil temp. TC1
Data
Code
60
Heat exchange temp. TE
61
Outside air temp. TO
62
Discharge temp. TD
63
Intake temp. TS
64
Outdoor unit data
–
65
Heatsink temp. THS
” is displayed.
Data
4 3
2
Operation procedure
1 2 3 4
1
Returns to normal indication.
*1 Header indoor unit only under group control
3
Choose an indoor unit you want to monitor with button to monitor sensor temperatures of indoor
units and outdoor unit in the same control group.
4
Press to return to the normal indication.
– 59 –
Page 61

■■
■Calling error log
■■
<Description>
Calls past errors.
<Procedure>
1
Press and on the R/C simultaneously for 4 seconds or more
to call the service check mode.
“Service check” lights up and code is displayed first to display
the latest error.
The faulty indoor unit number and error content are displayed.
2
To monitor other errors, change error log number (code) with
buttons.
Code
(latest) → Code (oldest)
Note) Up to 4 errors are memorized in the error log.
3
Press to return to the normal indication.
3
2
Returns to normal indication.
Operation procedure
1
<REQUIREMENT>
Do not press as this button clears entire error log of indoor unit.
1 2 3
– 60 –
Page 62

ON-SITE SETTING AND OTHERS (Continued)
<Group Control Operation>
Group control allows operation control of up to 8 indoor units using one remote controller. It includes twin,
triple, and double twin controls with one outdoor unit.
The indoor unit connected to outdoor unit controls room temperature according to the R/C setting.
<An example of system>
O/U O/U
I/U I/U
1-1 2-1 3-1 3-2 4-1 7-1
R/C
Header
O/U O/U
I/U I/U
I/U
O/U
I/U
8 units maximum
(1) Scope of R/C indication
The indoor unit setting range (operation mode/fan speed/temperature) set in the header unit is
reflected in the remote controller.
A Do not set a concealed duct high static pressure type (AID-P***1H) for header unit.
• If the type is set as header unit, settings are as follows.
Operation mode: [Auto cooling/heating], [HEAT], [COOL] or [FAN] without [DRY]
Fan speed : [HH]
• In the DRY operation mode, FAN mode is not available for duct models.
B Do not set a “COOL only” model for header unit.
• [Auto cooling/heating] and [HEAT] operation modes are not available.
(2) HA
Both indoor and outdoor units are compatible with the remote control HA.
Operation ON/OFF control for entire group is available.
A Multiple HA inputs in one group are not allowed.
(3) Address setting
If there is no serial data communication between indoor and outdoor units at power on, the indoor unit
is regarded as twin follower unit. (Each time of power on)
... Recognition of twin header (main)/follower (sub) is carried out at each power on, and the result is
not stored in the non-volatile memory.
When performing auto address setting, power on the indoor units in a control group within 3 minutes.
... If powered on after 3 minutes when auto address judgment is completed, the unit is rebooted
and reenters auto address setting mode.
A Connect 3 wires between indoor and outdoor units properly.
B Check refrigerant line address, indoor unit address, and group address of each unit.
Regarding twin, triple, and double twin, in particular, check for one refrigerant line address for all
units.
C An indoor unit number (refrigerant line address/group address), once it is set, is retained in
principle unless it is not used for any other unit.
– 61 –
Page 63

Indoor Unit Power ON Sequence
<Auto address judgment>
*
Checking group
Power ON
<By power supply unit>
Incorrect
configuration
Correct
* Correct group configuration means
A No duplication of indoor unit address
B No invalid indoor unit address
C Individual units and header/follower units
are not mixed
D Only one individual unit
E One header and one or more follower units
in a group
System start
• Indoor units that are not supplied with power
are in waiting mode continuously.
→System start resets the waiting mode.
• Rebooted if power is supplied halfway
3 minutes
passed
Y
Auto address start
N
<Initial communication>
O/U model identification (10 seconds) (I/U)
Twin header/follower unit identification (I/U)
Group configuration/flap information (R/C)
R/C operation enabled (50 seconds after power on)
<Periodic communication>
Between indoor units (30-second cycle) (Header/follower)
Within same piping (30-second cycle) (Twin main/sub)
(Communication starts as soon as above status changes.)
<<Notes on trial operation>>
•
Check for normal connections of power
cable, I/U-O/U serial wiring, and group wiring
•
Power ON all indoor units within 3 minutes
•
R/C operation available time (after power on)
1)
When address is correct: Approx. 50 seconds
2)
When auto address is used: Approx. 4-5 minutes
(Repeated)
(About one minute to end)
• The indoor unit powered on after auto address judgment under group control is rebooted (system reset), unless it does not
receive data from the header unit or periodic communication within same piping within 120 seconds after power on.
→The sequence restarts from auto address judgment (checking group configuration).
• If the previous address fixed and the header unit is powered on and is rebooted, the refrigerant line address of indoor units
remains unchanged, but the header unit address may change.
– 62 –
Page 64

ON-SITE SETTING AND OTHERS (Continued)
3. Connections for Central Control
3.1 Connections for TCC-LINK Central Control
3.1.1 Functions
Connect an indoor unit to the TCC-LINK central controller.
3.1.2 Connection Diagram
Central controller
TCC-LINK
Number of units : 64
Communication length : 2km
CN41
Terminal block
(A/B)
Remote controller
Indoor unit
CN40
Terminal block
(U3/U4)
3.1.3 TCC-LINK Connections
How to make connections
The terminal block for TCC-LINK central control is located at the lower right of the indoor unit.
For details, see the installation manual of applicable central control remote control system.
When using the terminal block, detach the front panel following the description on how to replace main
components in this manual.
Electric parts box
Terminal block
Cord clamp
U4
U3
Terminal block for central control wiring (lower right part without front panel)
– 63 –
Page 65

3.1.4 Wiring Specifications
Number of wires
2
Size
Up to 1000m: 1.25mm2 stranded wires
Up to 2000m: 2.0mm2 stranded wires
Specification
MVVS
• A 2-wire non-polarity cable is used.
• The cable length depends on each central control system.
When used in a system including multiple air conditioners, the length includes the length of all wires
between indoor and outdoor units on the side of multiple air conditioners.
• Use 2-wire shield cable (MVVS) to protect from noise.
• Joint shield wire between indoor units by closed-end terminating, and leave its end open with insulation
processing.
Make one-point grounding at the indoor unit side. Set the terminating resistors.
(Central control for custom indoor units only)
N
A Joint shield wire between indoor units by closed-end terminating.
o
B Leave the end of the shield wire open with insulation processing.
t
123
e
C Make one-point grounding at the indoor unit side.
s
123
Note A
123
Central controller
U1 U2
Note B
Outdoor
unit
Indoor
unit
U3 U4
Header
123
AB
R/C R/C R/C
U3 U4
123
AB
(Group operation)
Follower
123
AB
– 64 –
Page 66

ON-SITE SETTING AND OTHERS (Continued)
3.1.5 Setting Onboard Switches
Setting of terminating resistors is necessary for central control of custom indoor units only.
• Use SW01 to set terminating resistors.
• Set terminating resistors for the indoor unit only with the smallest refrigerant line address.
Central controller Central controller
U1U3U2
U1U3U2
U4
U4
Refrigerant system 1 Refrigerant system 2 Refrigerant system 3
Outdoor
unit
123
Indoor
unit
U3 U4
123
AB
R/C R/C R/C
Refrigerant line address
SW01 bit 1
Central controller: Up to 10 units
123
U3 U4
TCC-LINK adapter (option)
Required for custom
indoor units other
than wall type
Header
123
AB
R/C wiring
Group operation (up to 8 indoor units)
1
ON
2
OFF
123
123
AB
Follower
3
OFF
Remarks Bit 1 ON Factory setting Factory setting
– 65 –
Page 67

3.1.6 Onboard Switch Setting Procedure
1. Detach the front panel.
2. Remove the drain guide, ground line, sensor TCJ, sensor TC, and motor leads.
3. Remove the screws to detach the electric parts box.
Sensor TCJ insertion position
(Insert the sensor drawn from above electric parts.)
Sensor TC insertion position
(Insert the sensor drawn from under electric parts.)
Fan motor connector insertion position
Louver motor connector insertion position
Electric parts box screw
4. Detach the electric parts cover, and set SW01 bit 1 to ON.
Do not touch bit 2 as it is for other setting.
DB301
C302
L301
CN67
C301
CN102
CN101
CN22
B
CN40
L41
CN213
IC01
BZ01
MCC-1510
T301
ON
21
SW01
L201
CN104
21
ON
SW02
1 : ON
1 : OFF
2 : OFF2 : OFF
ON
12ON12
After setting
Factory
setting
change
5. Install the removed parts by reversing steps 1 to 4.
(Insert the sensors and motor leads firmly into their correct positions.)
– 66 –
Page 68

ON-SITE SETTING AND OTHERS
3.1.7 Setting Addresses
Overview
To connect custom air conditioners to the TCC-LINK central control system for central control/monitoring,
addresses of connected indoor units must be set in the following procedure.
Connections/wiring
completed
System power ON
Auto address setting The system performs automatically after power on.
Manual setting/change of refrigerant
line addresses
Is group control (including twin/triple/
double twin) going?
YES
Are all indoor units with central control
function header unit (group address=1)?
NO
Re-set indoor units with central control function to header
unit, and other indoor units to follower unit.
* Refer to 11 ADDRESS SETTING.
Central control address number
setting
* Refer to the manual of the central control system.
Change refrigerant line address.
If auto address setting failed, set refrigerant line address manually.
* Refer to 11 ADDRESS SETTING.
NO
YES
END
– 67 –
Page 69

(1) Manual setting/change of indoor unit refrigerant line addresses
[In the case of 29 refrigerant systems or less (when multiple air conditioners are included,
their number of refrigerant systems is also included)]
Refrigerant address “1” is assigned to all indoor units except for group control by the auto address
setting after system power on. Therefore, change refrigerant line address of each refrigerant system
using the wired remote controller.
Central
controller
Refrigerant
system 1
O/U O/U O/U O/U O/U
I/U I/U I/U I/U I/UI/U
R/C R/C R/C R/C
Refrigerant line
address
Indoor unit
address
Group address
Refrigerant line
address
Indoor unit
address
Group address
1
1
0
1
1
0
Refrigerant
system 2
1
1
0
2
1
0
Refrigerant
system 3
1
1
1
3
1
1
1
2
2
3
2
2
Refrigerant
system 4
1
1
1
4
1
1
Refrigerant
system 5
2
1
2
5
1
2
An example after auto address
setting
After changing refrigerant line
address manually
* For changing/setting refrigerant line addresses by wired remote controller, refer to 11 ADDRESS
SETTING.
* Refrigerant line address must be unique for each refrigerant system.
To perform central control in combination of multiple and custom air conditioners, set refrigerant
line addresses different from those of multiple air conditioners.
– 68 –
Page 70

ON-SITE SETTING AND OTHERS
(2) Manual setting/change of indoor unit refrigerant line addresses
[In the case of 30 refrigerant systems or more (when multiple air conditioners are included,
their number of refrigerant systems is also included)]
Regarding refrigerant systems up to No. 29, manual setting/change is the same as that on the
previous page.
• Refrigerant address “1” is assigned to all indoor units except for group control by the auto address
setting after system power on. Therefore, change refrigerant line address of each refrigerant
system using the wired remote controller.
• Also change indoor unit addresses so as to avoid duplication of indoor unit numbers.
Central
controller
Refrigerant
system 30
O/U O/U O/U O/U O/U
I/U I/U I/U I/U I/UI/U
R/C R/C R/C R/C
Refrigerant line
address
Indoor unit
address
Group address
Refrigerant line
address
Indoor unit
address
Group address
* For changing/setting refrigerant line addresses by wired remote controller, refer to
1
1
0
1
1
0
Refrigerant
system 31
1
1
0
2
1
0
Refrigerant
system 32
1
1
1
3
1
1
1
2
2
3
2
2
Refrigerant
system 33
1
1
1
4
1
1
Refrigerant
system 34
2
1
2
5
1
2
An example after auto address
setting
After changing refrigerant line
address manually
11
ADDRESS
SETTING.
* Change refrigerant line address of all indoor units connected directly to the central controller to
“30”.
These indoor units are under twin or triple control, also change the refrigerant line address of
follower indoor units to “30”.
* Change indoor unit addresses so that they are not duplicated.
– 69 –
Page 71

3.1.8 Central Control Address Number Setting
To connect an indoor unit to the central control remote controller, an address number for central control
must be set.
An address number for central control is indicated as the refrigerant line number of the remote
controller.
1. Setting by Remote Controller on Indoor Unit Side
<Procedure> Perform the following steps in the operation OFF
mode.
1
Press and on the R/C simultaneously for 4 seconds
or more.
When group control is going, UNIT No.
is displayed first,
and all indoor units in the group are selected. At this time, the
fans of all the selected indoor units start running. (Fig. 1)
Maintain this state without pressing
.
For individual remote controllers without group control, a
refrigerant line address and an indoor unit address are
indicated.
2
Specify code with buttons.
3
Choose setting data with buttons.
Table 1 shows setting data.
4
Press Indication on the LCD shows normal operation.
• To change an item for setting, return to
.
2
(Fig. 1)
2
5
Tab l e 1
Setting data
0001
0002
0003
.....
0064
0099
4
3
1
Address No. for central control
1
2
3
.....
64
Not set (factory setting)
5
Press to return to the normal indication.
– 70 –
Page 72

11. ADDRESS SETTING
1. Address Setting
Address Setting Procedure
When twin or triple operation is selected with one indoor unit and one outdoor unit or when one outdoor is
connected to each indoor unit even with multiple refrigerant systems in group operation, auto address
setting is completed during the power on process of outdoor unit.
Remote controller operation is disabled during the auto address setting process (4 to 5 minutes).
O/U refrigerant line address/I/U
address/group address setting
Connections/wiring
completed
Do you set I/U
address freely?
(manually)
Y
Connect com. cable between
R/C and I/U temporarily one
to one.
Power ON outdoor unit.
N
One refrigerant
system?
Power ON outdoor unit
N
Y
(To auto address
setting mode)
Auto address setting
ends within 4 to 5
minutes.
N
N
N
Is group control going?
Y
Multiple units for
twin/triple operation?
Y
Auto address setting
first, then corrected?
Y
Power ON outdoor unit.
(Corrected to an address/group
Set address for each
I/U individually
END
manually after address setting)
• Unless the following addresses are stored in the EEPROM (IC10) on the indoor unit board, trial
operation is disabled. (Undefined data is stored at factory shipping.)
Setting data range
Refrigerant line address
Indoor unit address
Group address
Code
12
13
14
Factory setting data
0099
0099
0099
0001 (unit No. 1) to 0030 (unit No. 30)
0001 (unit No. 1) to 0064 (unit No. 64)
Maximum I/U address in the same refrigerant system (double twin=4)
0000 : Individual (indoor units without group control)
0001 : Header (one indoor unit in the group)
0002 : Follower (indoor units in the group except header unit)
– 71 –
Page 73

2. Address Setting and Group/Twin/Triple Control
<Definition of terms>
Indoor unit No. : N-n=O/U refrigerant line address N (30 max.) -I/U address n (64 max.)
Group address : 0=Individual (without group control)
1=Header unit under group control
2=Follower units under group control
Header indoor unit (=1) : A representative unit of multiple indoor units in group operation, which performs
communication between R/C and follower I/U. (* It does not mean an indoor unit
that communicates with O/U.)
Operation mode and setting temperature range (except flap air flow control) of
header unit are reflected on the LCD of remote controller.
Follower indoor unit (=2) : Indoor units except header unit in group operation.
It does not control communication with remote controller in principle (except
response to alarm/service data request).
Main unit :
(Representative)
(Twin header)
Sub indoor unit : Indoor units except the main indoor unit in a twin, triple or double twin system.
(Sub unit)
(Twin follower)
[1] System Configuration
a)Single b)Twin
In a minimal configuration of refrigerant cycle such as twin, triple or double twin, an indoor
unit which communicates with O/U among those with same refrigerant line address.
Communicates with sub indoor units and with O/U (instructions to compressor)
on behalf of cycle control.
Communicates with the main indoor unit with the same refrigerant line address,
and provides control in synchronization with the main indoor unit. It does not
communicate with O/U (no detection of serial signal alarm).
Outdoor unit
Indoor unit
1:1
individual
R/C
(H/M)
1-2
H/M
1-1
F/S
1-4
F/S
c) Single group operation
2-1
F/M
1-1
F/M
• Each indoor unit controls outdoor unit individually.
4-1
H/M
3-1
F/M
8-1
F/M
d) Multiple single/twin/triple group operation (manual address setting)
2-1
F/M
1-1
F/M
1-2
F/S
1-3
F/S
3-3
H/M
3-4
F/S
3-2
F/S
1-3
F/S
3-1
F/S
H : Header indoor unit
F : Follower indoor unit
M: Main indoor unit
S : Sub indoor unit
• Main indoor unit : Receives data (thermo status, etc.) from sub indoor units with same refrigerant line
address, and controls O/U compressor referring to the self thermo status. Transmits
this instruction to sub units.
• Sub indoor unit : Receives data from the main indoor unit with same refrigerant line address and serial
interface with O/U, and performs thermo operation in synchronization with the main
unit. Sends self thermo ON/OFF request to the main unit.
(Example) 1-1 main unit communicates with 1-2 and 1-3 sub units without being
affected by indoor units with refrigerant line address 2 or 3.
– 72 –
Page 74

[2] Examples of Auto Address Setting from No Address Setting
1) Standard (one outdoor unit)
a) Single
1-1
individual
(H/M)
2) Group operation (multiple O/U = multiple indoor units with serial communication interface, no twin)
b) Twin
(1-1) (1-2)
1-2
H/M
*** Turn ON the power. Address setting is completed automatically. ***
1-1
F/S
2-1
F/M
1-1
F/M
3-1
H/M
*** Turn ON the power. Address setting is completed automatically. ***
3) Multiple group operation
A (single) B (triple) C (double)
2-1
F/M
1-1
F/M
2-1
F/S
3-3
H/S
8-1
F/M
8 indoor units maximum
3-1
F/M
Change sub unit addresses at the same time manually
2-2
F/S
*** Address change required ***
from remote controller.
1-2
F/S
3-2
F/S
2-1 1-1 1-2 1-3 3-1 3-2 3-3 3-4
– 73 –
H : Header indoor unit
F : Follower indoor unit
M: Main indoor unit
S : Sub indoor unit
Page 75

3. Address Setting
When determining indoor unit addresses with wiring completed without piping
construction
(Manual setting by remote controller)
<Address setting procedure>
Connect a remote controller to the
indoor unit whose address you want to
set one to one.
Turn ON the power.
1
Press , , and on the R/C
simultaneously for 4 seconds or more.
Wiring example of 2 refrigerant systems
(Solid line: wiring, broken line: refrigerant piping)
O/U
(Power cable only) (Power cable only)
I/U
I/U I/U I/U I/U
Refrigerant line
address
Indoor unit address
Group address
→ 1
→ 1
→ 1
1
1
2
3
2
2
O/U
Refrigerant
line address
2
2
1
2
2
2
Indoor unit
address
→
2
Set code with buttons.
3
Set a refrigerant line address with
buttons.
4
Press Indication on the LCD shows
normal operation.
→
5
Set code with buttons.
For systems like this example, connect a wired remote controller
independently without connecting R/C wires, and then set these addresses.
Group address
Individual: 0000
Header unit: 0001
Follower unit: 0002
in case of group control
Group
address
5 63
2 4
8 9
7
10
End
11
Operation procedure
1 2 3 4
8 9 10 11
1
5 6 7
End
6
Set indoor unit addresses with
buttons.
7
Press Indication on the LCD shows
normal operation.
→
8
Set code with buttons.
9
Set indoor unit addresses with
buttons as follows:
Individual=
, header unit= ,
follower unit=
10
Press Indication on the LCD shows
normal operation.
11
Press .
Indoor unit address setting is completed.
The operation mode returns to normal
OFF.
– 74 –
Page 76

ADDRESS SETTING (Continued)
■■
■Checking location of indoor unit number
■■
(1) To find the address of indoor unit whose location is clear
In case of independent operation (1:1 connection of wired R/C
and I/U)
Perform the procedure during operation of indoor unit.
<Procedure>
1
When the indoor unit is not working, press on
the R/C.
2
Press .
UNIT No.
seconds.
The displayed number shows the refrigerant line address and
indoor unit address.
When other indoor units are connected to the same remote
controller (group control), their unit numbers are displayed in
order each time
appears on the LCD and disappears in several
is pressed.
2 1
Operation procedure
1 2
(2) To find the location of indoor unit from its address
When checking indoor unit number in the group.
Perform the procedure while the indoor unit is not working.
This procedure stops operation of all indoor units in the group.
<Procedure>
Indoor unit numbers appear one by one and the fan and flap of
the displayed unit run.
1
Press and on the R/C simultaneously for 4 seconds
or more.
• UNIT No. appears.
• The fan and flap of all indoor units in the group run.
2
Each pressing of on the R/C displays unit numbers in
the group sequentially.
• The header unit address appears first.
• The fan and flap of a selected indoor unit run.
3
Press to finish the procedure. Operation of all the indoor
units in the group turns OFF.
2
3
End Operation procedure
1
1 2 3
End
– 75 –
Page 77

12. EXPLODED VIEWS AND PARTS LIST
High-Wall Type
RAV-SM562KRT-E/RAV-SM802KRT-E
202
203
201
227
229
230
221
217
208
228
213
222
219
210
220
215
232214
218
216
211
209
231
226
224
212
223
207
204
Location Part
No. No. No. No.
201 43T00409 FRONT PANEL ASSY 217 43T19322 FIX-P-SENSOR
202 43T09375 GRILLE ASSY 218 43T49323 SPRING
203 43T80306
204 43T80312
207 43T03010 BODY; RIGHT 221 43T49038 PLATE; EVA-SEAL
208 43T03011 BODY; LEFT 222 43T49037 HOLDER; PLATE EVA-SEAL
209 43T03012 HIDE; CLAW 223 43T79007 GUIDE DRAIN
210 43T09345 LOUVER-H 224 43T39016 FIX FOR MOTOR
211 43T70001 HOSE ASSY; DRAIN 226 43T21368 MOTOR FAN
212 43T21367 MOTOR;STEPPING 227 43T20315 FAN; CROSS FLOW
213 43T44373 REFRIGERATION ASSEMBLY 228 43T22307 M-B-BEARING
213 43T44374 REFRIGERATION ASSEMBLY 230 43T03336 BACK BODY ASSY
216 43T49021 PIPE; SHIELD 232 43T82306 PLATE; INSTALLATION
AIR FILTER (L) 219 43T49324 PLATE; EVA-SEAL
AIR FILTER (R) 220 43T49039 HOLDER; PLATE EVA-SEAL
(FOR RAV-SM562KRT-E) 229 43T39015 BASE; BEARING
(FOR RAV-SM802KRT-E) 231 43T07022 HOLDER; PIPE
Description
236
233
Location Part
234 43T69495 WIRELESS REMOCON
235 43T83003 HOLDER; REMOTE CONTROLLER
236 43T62029 COVER; TERMINAL
Description
234
235
– 76 –
Page 78

RAV-SM562KRT-E/RAV-SM802KRT-E
Location Part Location Part
No. No. No. No.
401 43T60047 TERMINAL 407 43T60361 FUSE
402 43160508 TERMINAL 408 43T09343 E-PARTS BASE
403 43T60321 TERMINAL 409 43T69536 PC BOARD
404 43T50308 SENSOR HEAT EXCHANGER 410 43T69500 DISPLAY UNIT
405 43T50306 TEMPERATURE SENSOR 411 43T09344 CORD CLAMP
406 43T69320 TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Description Description
– 77 –
Page 79

TOSHIBA CARRIER (THAILAND) CO.,LTD.
144/9 MOO 5, BANGKADI INDUSTRIAL PARK, TIVANON ROAD, TAMBOL BANGKADI,
AMPHUR MUANG, PATHUMTHANI 12000, THAILAND.
 Loading...
Loading...