Toshiba RAV-SM801BT-E, RAV-SM1400AT-E, RAV-SM1100AT-E, RAV-SM561BT-E, RAV-SM1401BT-E User Manual
...
SERVICE MANUAL
RAV-SM561BT-E/RAV-SM560AT-E
FILE NO. A03-007
SPLIT TYPE
RAV-SM801BT-E/RAV-SM800AT-E
RAV-SM1101BT-E/RAV-SM1100AT-E
RAV-SM1401BT-E/RAV-SM1400AT-E
R410A
PRINTED IN JAPAN, Feb.,2004 ToMo

CONTENTS
1. SPECIFICATIONS................................................................................................ 1
2. AIR DUCTING WORK..........................................................................................7
3. CONSTRUCTION VIEWS (EXTERNAL VIEWS) ................................................. 9
4. SYSTEMATIC REFRIGERATING CYCLE DIAGRAM .......................................13
5. WIRING DIAGRAM ............................................................................................ 17
6. SPECIFICATIONS OF ELECTRICAL PAR T S ................................................... 21
7. REFRIGERANT R410A ..................................................................................... 23
8. INDOOR UNIT CONTROL ................................................................................. 31
9. OUTDOOR CONTROL ...................................................................................... 40
10. TROUBLESHOOTING ....................................................................................... 47
11. REPLACEMENT OF SERVICE INDOOR P.C. BOARD ..................................... 70
12. SETUP AT LOCAL SITE AND OTHERS ........................................................... 74
13. ADDRESS SETUP ............................................................................................. 84
14. DETACHMENTS................................................................................................. 88
15. EXPLODED VIEWS AND PARTS LIST ........................................................... 114

1-1. Indoor Unit
Concealed Duct Type
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Model name
Standard capacity (Note 1) (kW)
Heating low temp. capacity (Note 1) (kW)
Energy consumption effect ratio (Cooling)
Power supply
Running current (A)
Electrical
characteristics
Appearance
Outer
dimension
Power consumption (kW)
(Low temp.) (kW)
Power factor (%)
Main unit
Ceiling Panel
(Sold separately)
Main unit Width (mm)
Ceiling panel
(Sold separately)
Model
Panel color
Height (mm)
Depth (mm)
Height (mm)
Width (mm)
Depth (mm)
RAV-SM561BT-E RAV-SM801BT-E
Cooling Heating Average Cooling Heating Average
5.0 5.6 7.1 8.0
(1.5 – 5.6) (1.5 – 6.3) (2.2 – 8.0) (2.2 – 9.0)
4.6 6.2
2.81 [C] 3.27 [C] 3.04 2.81 [C] 3.32 [C] 3.07
1 phase 230V (220 – 240V) 50Hz
8.99–8.24 8.18–7.50 12.25–11.21 11.65–10.68
1.78 1.71 2.53 2.41
1.98 2.86
95 95 94 94
Zinc hot dipping steel plate
——
——
320 320
700 1000
800 800
——
——
——
Total weight
Heat exchanger
Soundproof/Heat-insulating material
Fan unit Standard air flow High (Mid./Low) (m³/h)
Air filter
Controller (Sold separately)
Connecting
pipe
Sound level High (Mid./Low) (Note 2) (dB•A)
Main unit (kg)
Ceiling panel
Fan
Motor (W)
Gas side (mm)
Liquid side (mm)
Drain port (Nominal dia.)
42 39 36 43 40 37
30 39
——
Finned tubu
Inflammable polyethylene foam
Multi-blade fan
840 1140
120 120
Attached main unit
RBC-AMT21E
Ø12.7 (1/2”) Ø15.9 (5/8”)
Ø6.4 (1/4”) Ø9.5 (3/8”)
25 (Polyvinyl chloride tube)
Note 1 : The cooling capacities and electrical characteristics are measured under the conditions specified by JIS B 8616 based
on the reference piping 7.5m.
Note 2 : The sound level is measured in an anechoic chamber in accordance with JIS B8616. Normally, the values measured in
the actual operating environment become larger than the indicated values due to the effects of external sound.
Note : Rated conditions Cooling : Indoor air temperature 27°C DB/19°C WB, Outdoor air temperature 35°C DB
Heating : Indoor air temperature 20°C DB, Outdoor air temperature 7°C DB/6°C WB
1
Model name
Standard capacity (Note 1) (kW)
RAV-SM1101BT-E RAV-SM1401BT-E
Cooling Heating Average Cooling Heating Averag e
10.0 11.2 12.5 14.0
(2.2 – 11.2) (2.2 – 12.5) (3.0 – 13.2) (3.0 – 16.0)
Heating low temp. capacity (Note 1) (kW)
Energy consumption effect ratio (Cooling)
Power supply
Running current (A)
Electrical
characteristics
Appearance
Outer
dimension
Power consumption (kW)
(Low temp.) (kW)
Power factor (%)
Main unit
Ceiling Panel
(Sold separately)
Main unit Width (mm)
Ceiling panel
(Sold separately)
Model
Panel color
Height (mm)
Depth (mm)
Height (mm)
Width (mm)
Depth (mm)
8.7 11.8
2.81 [C] 3.57 [B] 3.19 2.83 [C] 3.47 [B] 3.15
1 phase 230V (220 – 240V) 50Hz
16.5–15.1 14.6–13.4 20.7–19.0 18.9–17.3
3.56 3.14 4.42 4.03
3.50 4.18
98 98 97 97
Zinc hot dipping steel plate
——
——
320
1340
800
——
——
——
Total weight
Heat exchanger
Soundproof/Heat-insulating material
Fan unit Standard air flow High (Mid./Low) (m³/h)
Air filter
Controller (Sold separately)
Connecting
pipe
Sound level High (Mid./Low) (Note 2) (dB•A)
Main unit (kg)
Ceiling panel
Fan
Motor (W)
Gas side (mm)
Liquid side (mm)
Drain port (Nominal dia.)
42 39 36 44 41 38
54 54
——
Finned tubu
Inflammable polyethylene foam
Multi-blade fan
1620 1980
120 120
Attached main unit
RBC-AMT21E
Ø15.9 (5/8”)
Ø9.5 (3/8”)
25 (Polyvinyl chloride tube)
Note 1 : The cooling capacities and electrical characteristics are measured under the conditions specified by JIS B 8616 based
on the reference piping 7.5m.
Note 2 : The sound level is measured in an anechoic chamber in accordance with JIS B8616. Normally, the values measured in
the actual operating environment become larger than the indicated values due to the effects of external sound.
Note : Rated conditions Cooling : Indoor air temperature 27°C DB/19°C WB, Outdoor air temperature 35°C DB
Heating : Indoor air temperature 20°C DB, Outdoor air temperature 7°C DB/6°C WB
2
1-2. Outdoor Unit
Model name
Appearance
Power supply
Type
Compressor Motor (kW)
Pole
Refrigerant charged (kg)
Refrigerant control
Standard length
Max. total length (m)
Pipe Over 20m
Outdoor lower (m)
Outdoor higher (m)
Outer
dimension
Height difference
Height (mm)
Width (mm)
Depth (mm)
RAV-SM560AT-E RAV-SM800AT-E
Silky shade (Muncel 1Y8.5/0.5)
1 phase 230V (220 – 240V) 50Hz
(Power exclusive to outdoor is required.)
Hermetic compressor
1.1 1.6
8 poles
R410A 0.9 R410A 1.5
Pulse motor valve
20 (without additional charge)
30 50
Add 20g/m (Max. 200g) Add 40g/m (Max. 1200g)
30
50
595 795
780 780
270 270
Total weight (kg)
Heat exchanger
Fan
Fan unit Standard air flow High (m³/h)
Motor (W)
Connecting
pipe
Protection device
Sound level High (Mid./Low)
(Note 2) (Cooling/Heating)
Gas side (mm)
Liquid side (mm)
(dB•A)
35 55
Finned tube
Propeller fan
2400 3400
43 63
Ø12.7 (1/2”) Ø15.9 (5/8”)
Ø6.4 (1/4”) Ø9.5 (3/8”)
Discharge temp. sensor
Over-current sensor
Compressor thermo.
46/48 45/50
Note 1 : The cooling capacities and electrical characteristics are measured under the conditions specified by JIS B 8616 based
on the reference piping 7.5m.
Note 2 : The sound level is measured in an anechoic chamber in accordance with JIS B8616. Normally, the values measured in
the actual operating environment become larger than the indicated values due to the effects of external sound.
Note : Rated conditions Cooling : Indoor air temperature 27°C DB/19°C WB, Outdoor air temperature 35°C DB
Heating : Indoor air temperature 20°C DB, Outdoor air temperature 7°C DB/6°C WB
3
Model name
RAV-SM1100AT-E RAV-SM1400AT-E
Appearance
Power supply
Type
Compressor Motor (kW)
Pole
Refrigerant charged (kg)
Refrigerant control
Standard length
Max. total length (m)
Pipe Over 20m
Height difference
Height (mm)
Outer
dimension
Total weight (kg)
Width (mm)
Depth (mm)
Outdoor lower (m)
Outdoor higher (m)
Silky shade (Muncel 1Y8.5/0.5)
1 phase 230V (220 – 240V) 50Hz
(Power exclusive to outdoor is required.)
Hermetic compressor
2.0 3.75
8 poles
R410A 2.1 R410A 2.3
Pulse motor valve
20 (without additional charge)
50
Add 40g/m (Max. 1200g)
15
30
1340
900
320
75 85
Heat exchanger
Fan
Fan unit Standard air flow High (m³/h)
Motor (W)
Connecting
pipe
Protection device
Sound level High (Mid./Low)
(Note 2) (Cooling/Heating)
Gas side (mm)
Liquid side (mm)
(dB•A)
6800 7500
63 + 43 63 + 63
53/54 53/54
Finned tube
2 Propeller fans
Ø15.9 (5/8”)
Ø9.5 (3/8”)
Discharge temp. sensor
Over-current sensor
Compressor thermo.
Note 1 : The cooling capacities and electrical characteristics are measured under the conditions specified by JIS B 8616 based
on the reference piping 7.5m.
Note 2 : The sound level is measured in an anechoic chamber in accordance with JIS B8616. Normally, the values measured in
the actual operating environment become larger than the indicated values due to the effects of external sound.
Note : Rated conditions Cooling : Indoor air temperature 27°C DB/19°C WB, Outdoor air temperature 35°C DB
Heating : Indoor air temperature 20°C DB, Outdoor air temperature 7°C DB/6°C WB
4
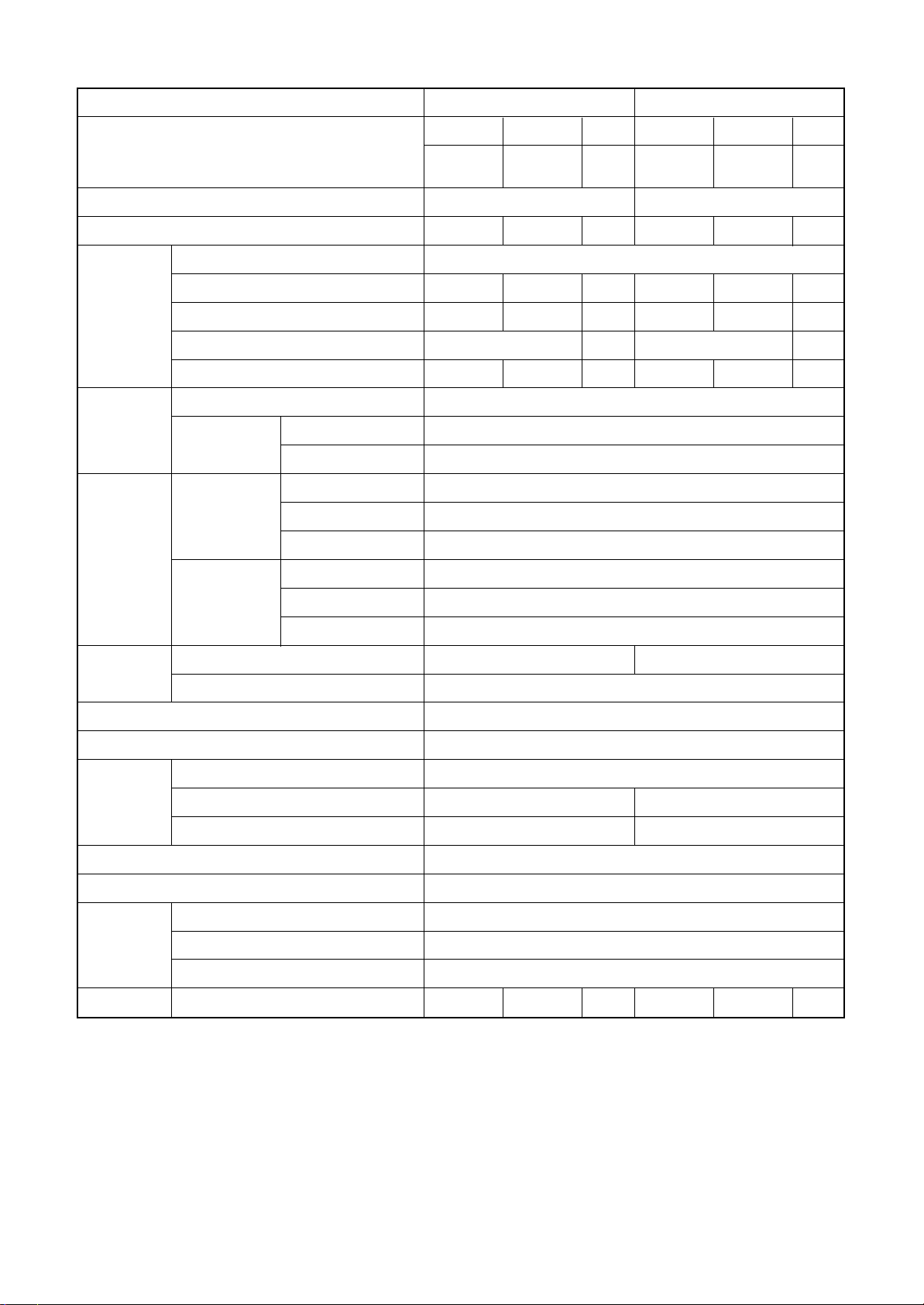
1-3. Operation Characteristic Curve
RAV-SM561BT-E / SM801BT-E
<Cooling> <Heating>
14
12
RAV-SM801BT-E
10
8
6
Current (A)
4
2
0
15
020
RAV-SM561BT-E
• Conditions
Indoor : DB27˚C/WB19˚C
Outdoor : DB35˚C
Air flow : High
Pipe length : 7.5m
220V
40 60 70 80 100
Compressor speed (rps)
16
14
12
10
8
Current (A)
6
4
2
0
15
020
RAV-SM801BT-E
RAV-SM561BT-E
• Conditions
Indoor : DB20˚C
Outdoor : DB7˚C/WB6˚C
Air flow : High
Pipe length : 7.5m
220V
40 60 80 90 100
Compressor speed (rps)
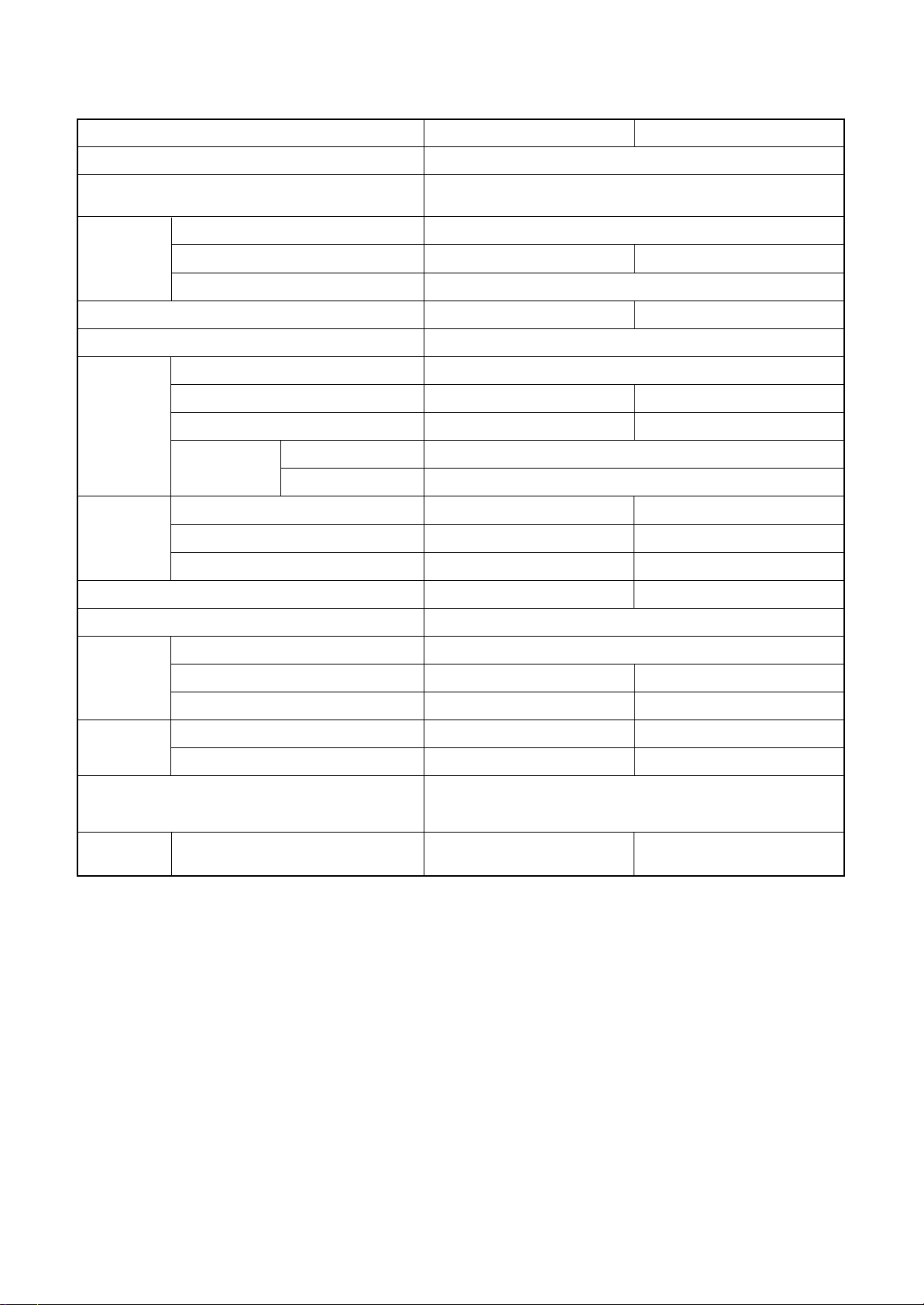
RAV-SM1101BT-E
<Cooling> <Heating>
20
18
16
14
12
10
Current (A)
8
6
4
2
0
0 204060
RAV-SM1100UT-ERAV-SM1101BT-E
• Conditions
Indoor : DB27˚C/WB19˚C
Outdoor : DB35˚C
Air flow : High
Pipe length : 7.5m
230V
80 100 120
20
18
16
14
12
10
Current (A)
8
6
4
2
0
0204060
RAV-SM1100UT-ERAV-SM1101BT-E
• Conditions
Indoor : DB20˚C
Outdoor : DB7˚C/WB6˚C
Air flow : High
Pipe length : 7.5m
230V
80 100 120
Compressor speed (rps)
Compressor speed (rps)
5
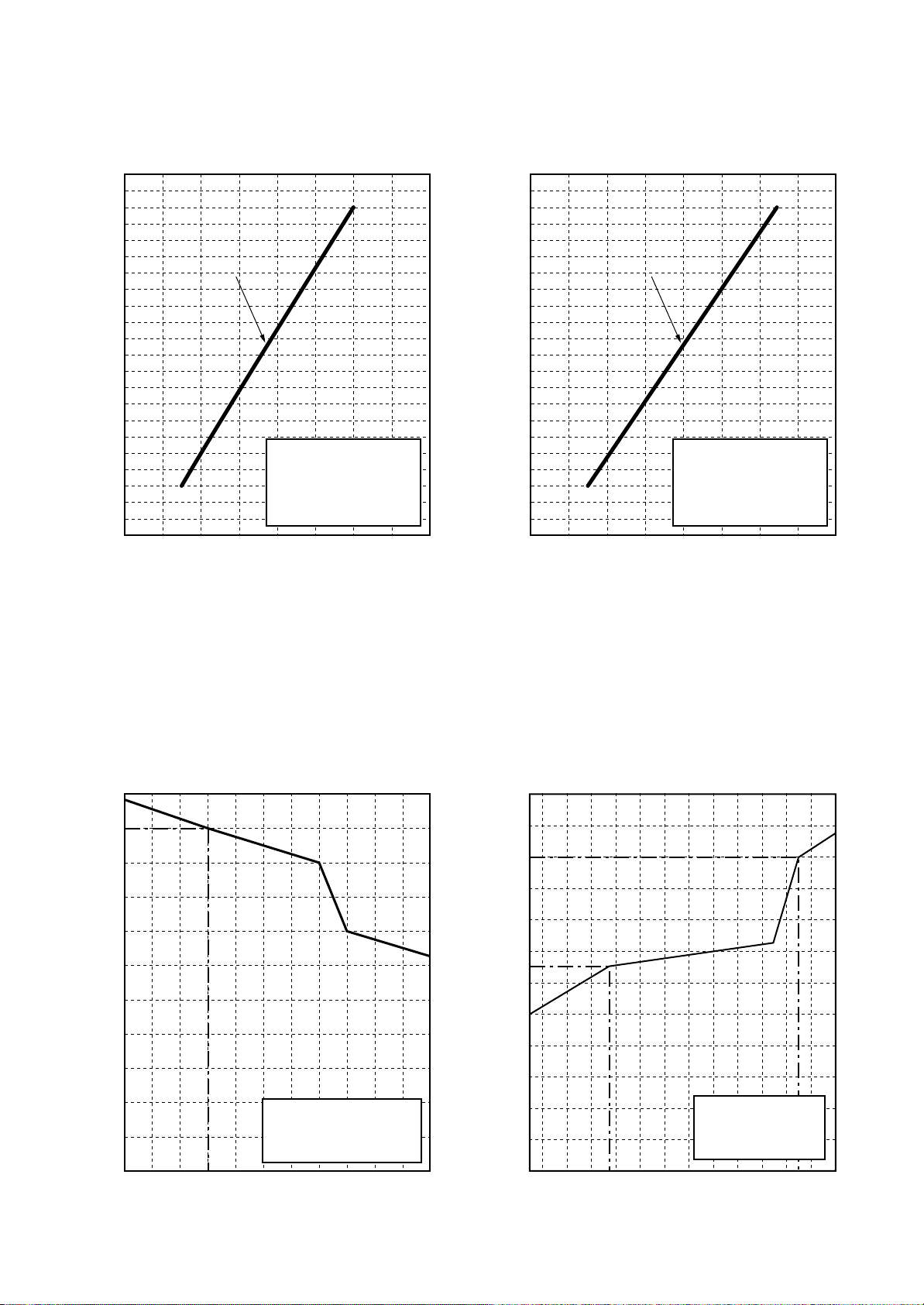
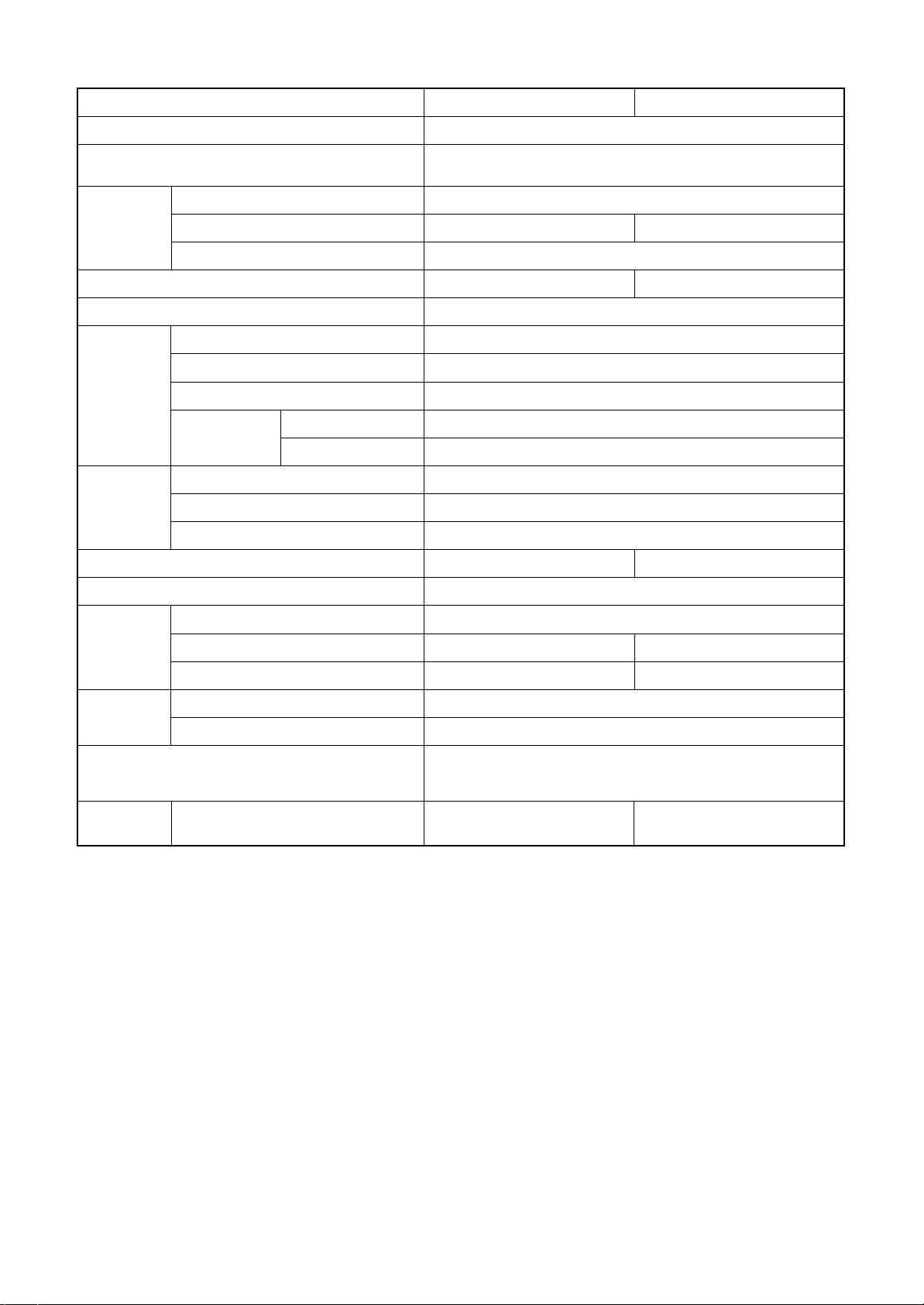
RAV-SM1401BT-E
<Cooling> <Heating>
22
20
18
16
RAV-SM1400UT-E
14
12
10
Current (A)
8
6
• Conditions
4
2
0
020406080
Indoor : DB27˚C/WB19˚C
Outdoor : DB35˚C
Air flow : High
Pipe length : 7.5m
230V
Compressor speed (rps)
22
20
18
16
RAV-SM1400UT-ERAV-SM1401BT-E RAV-SM1401BT-E
14
12
10
Current (A)
8
6
• Conditions
4
2
0
020406080
Indoor : DB20˚C
Outdoor : DB7˚C/WB6˚C
Air flow : High
Pipe length : 7.5m
230V
Compressor speed (rps)
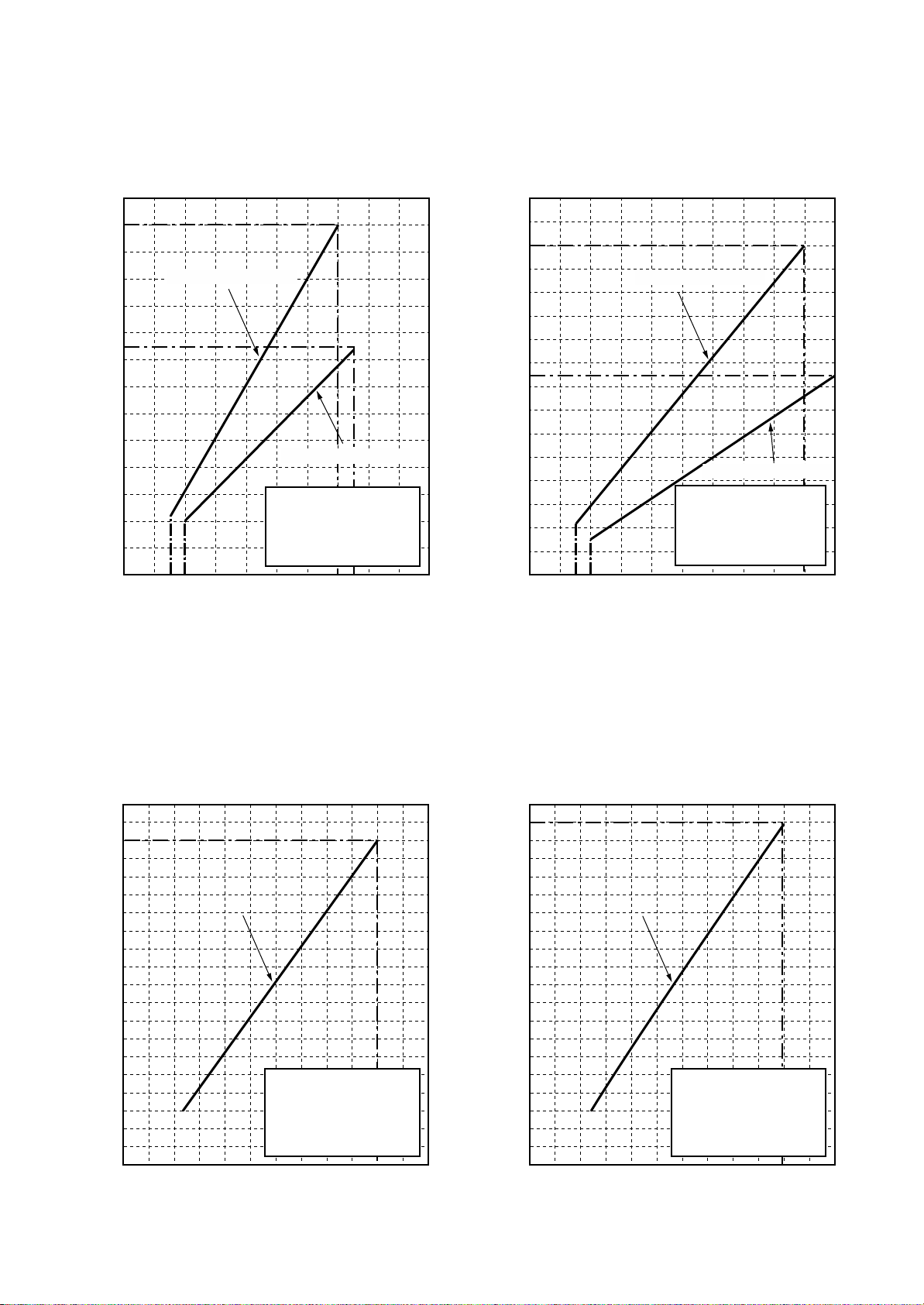
1-4. Capacity Variation Ratio According to Temperature
<Cooling> <Heating>
105
100
95
90
85
80
75
70
Capacity ratio (%)
65
60
55
• Conditions
Indoor : DB27˚C/WB19˚C
Indoor air flow : High
Pipe length : 7.5m
50
32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43
Outsoor temp. (˚C)
120
110
100
90
80
70
60
50
Capacity ratio (%)
40
30
20
10
0
-14 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 8 10
• Conditions
Indoor : DB20˚C
Indoor air flow : High
Pipe length : 7.5m
Outsoor temp. (˚C)
6
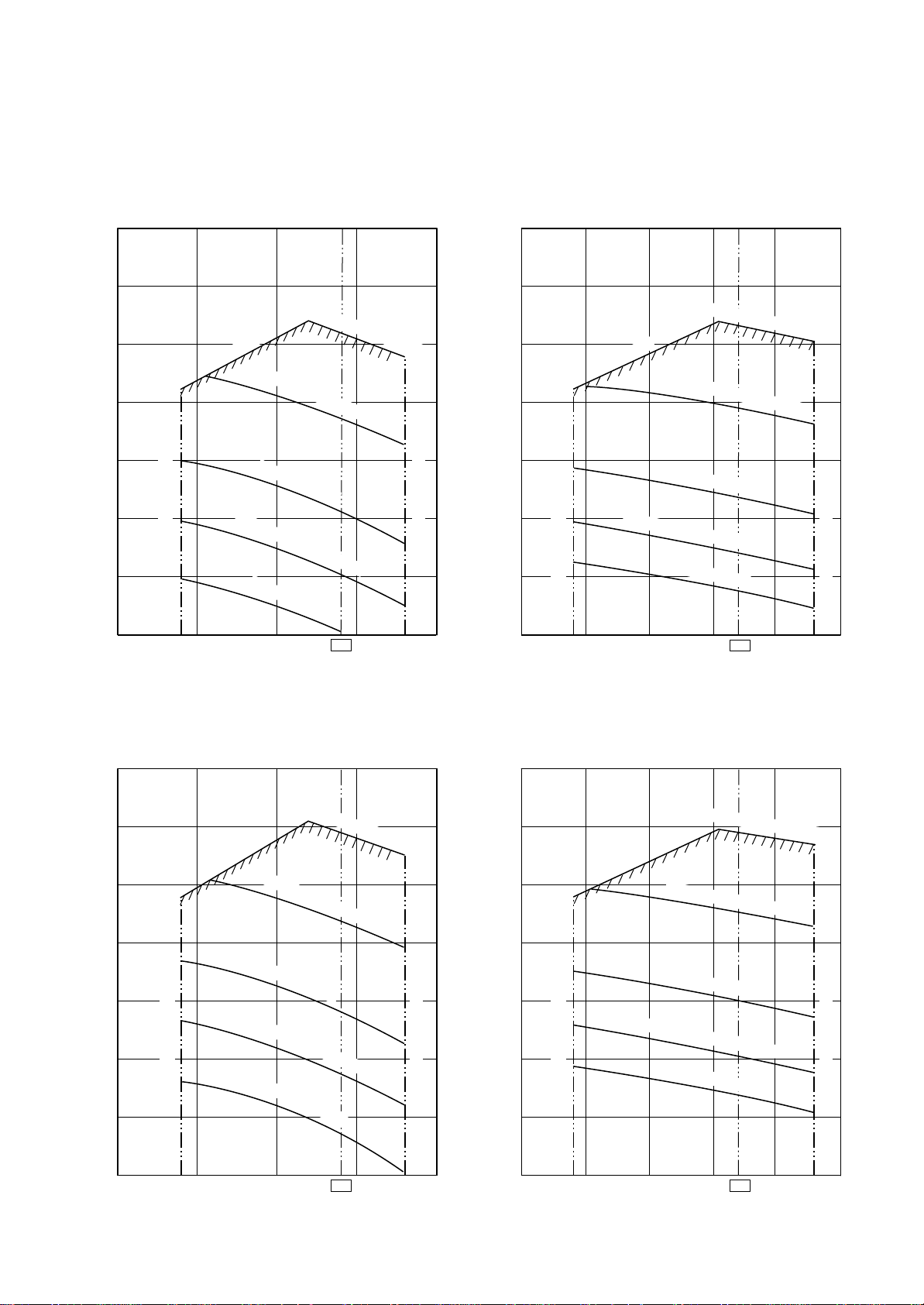
2. AIR DUCTING WORK
2-1. Static Pressure Characteristics of Each Model
Fig. 1 RAV-SM561BT-E (Round duct)
140
120
100
Usable limit
80
60
Static pressure (Pa)
40
Air volume limit (Min.)
20
Standard air volume 780m³/h
High static pressure 2H tap
High static pressure 1H tap
Standard H tap
Low static pressure H tap
Standard L tap
140
120
100
Static pressure (Pa)
Air volume limit (Max.)
Fig. 3 RAV-SM801BT-E (Round duct)
Standard air volume 1140m³/h
High static pressure 2H tap
Usable limit
80
60
40
20
Air volume limit (Min.)
High static pressure 1H tap
Standard H tap
Low static pressure H tap
Standard L tap
Air volume limit (Max.)
0
500 700 780 900
Air volume m³/h
Fig. 2 RAV-SM561BT-E (Square duct)
140
120
108
100
80
60
Usable limit
Static pressure (Pa)
40
Air volume limit (Min.)
20
Standard air volume 780m³/h
High static pressure 2H tap
High static pressure 1H tap
Standard H tap
Low static pressure H tap
Standard L tap
Static pressure (Pa)
Air volume limit (Max.)
0
800
1000
Air volume m³/h
Fig. 4 RAV-SM801BT-E (Square duct)
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
Usable lim
Air volume limit (Min.)
Standard air volume 1140m³/h
High static pressure 2H tap
it
High static pressure 1H tap
Standard H tap
Low static pressure H tap
Standard L tap
12001140 1300
Air volume limit (Max.)
0
500 700 780 900
Air volume m³/h
0
800
1000
12001140 1300
Air volume m³/h
7
0
Fig. 5 RAV-SM1101BT-E (Round duct)
Fig. 7 RAV-SM1401BT-E (Round duct)
140
120
Standard air volume 1620m³/h
140
120
Standard air volume 1980m³/h
High static pressure 2H tap
High static pressure 2H tap
100
100
Usable limit
High static pressure 1H tap
80
60
Standard H tap
Static pressure (Pa)
40
Air volume limit (Min.)
20
0
1200
Low static pressure H tap
Standard L tap
1620
Air volume limit (Max.)
2000
80
60
Static pressure (Pa)
40
20
0
1200 1800
Air volume m³/h
Usable limit
Air volume limit (Min.)
High static pressure 1H tap
Standard H tap
Low static pressure H tap
Standard L tap
1980
Air volume m³/h
Air volume limit (Max.)
2200 2400
Fig. 6 RAV-SM1101BT-E (Square duct)
140
120
Usable limit
100
80
60
Static pressure (Pa)
40
Air volume limit (Min.)
20
Low static pressure H tap
Standard air volume 1620m³/h
High static pressure 2H tap
High static pressure 1H tap
Standard H tap
Standard L tap
Air volume limit (Max.)
Fig. 8 RAV-SM1401BT-E (Square duct)
140
120
100
80
60
Usable limit
Static pressure (Pa)
40
Air volume limit (Min.)
20
Standard air volume 1980m³/h
High static pressure 2H tap
High static pressure 1H tap
Standard H tap
Low static pressure H tap
Standard L tap
Air volume limit (Max.)
0
1200
1620
Air volume m³/h
2000
0
1200 1800
1980
2200 240
Air volume hm³/h
8
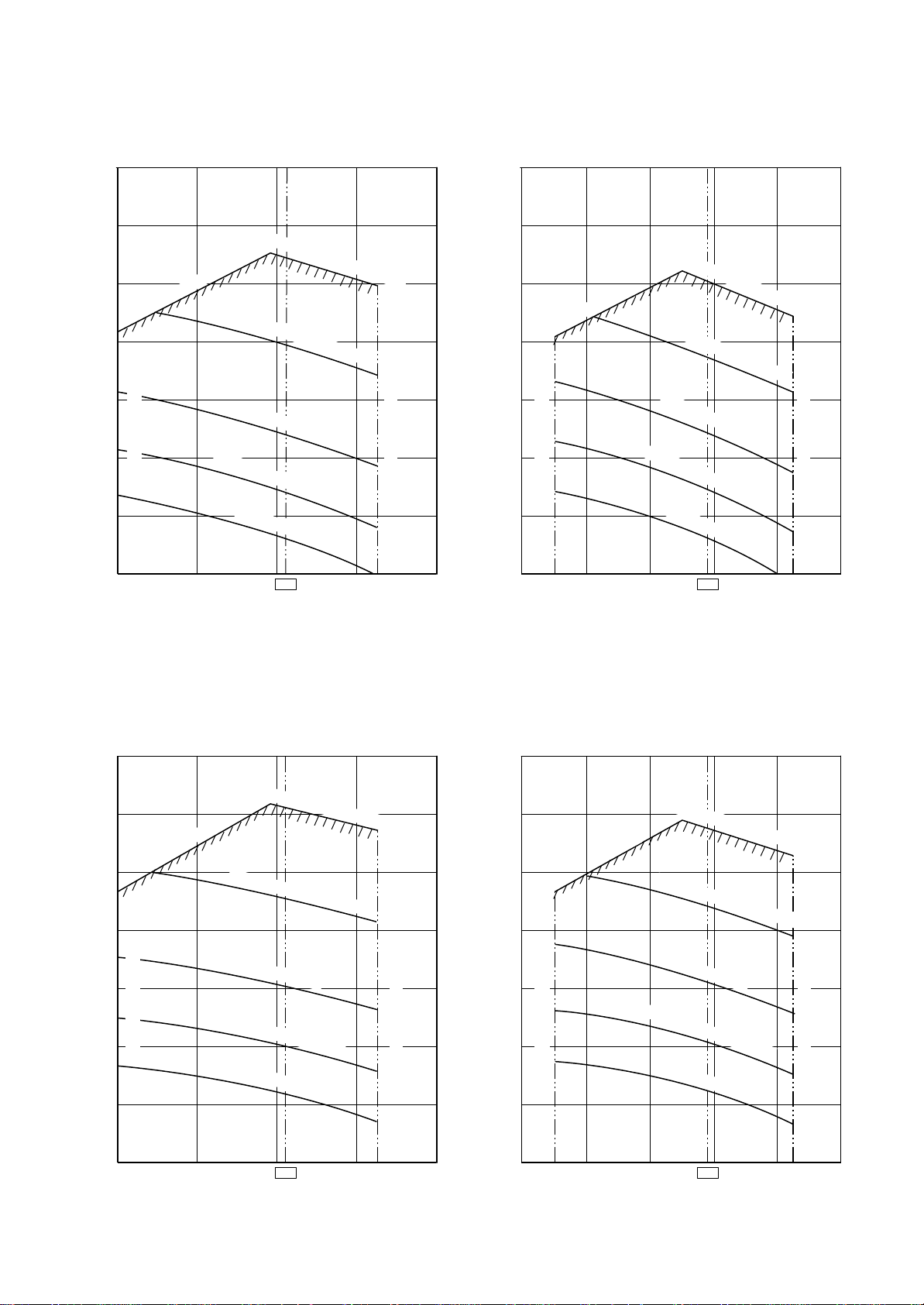
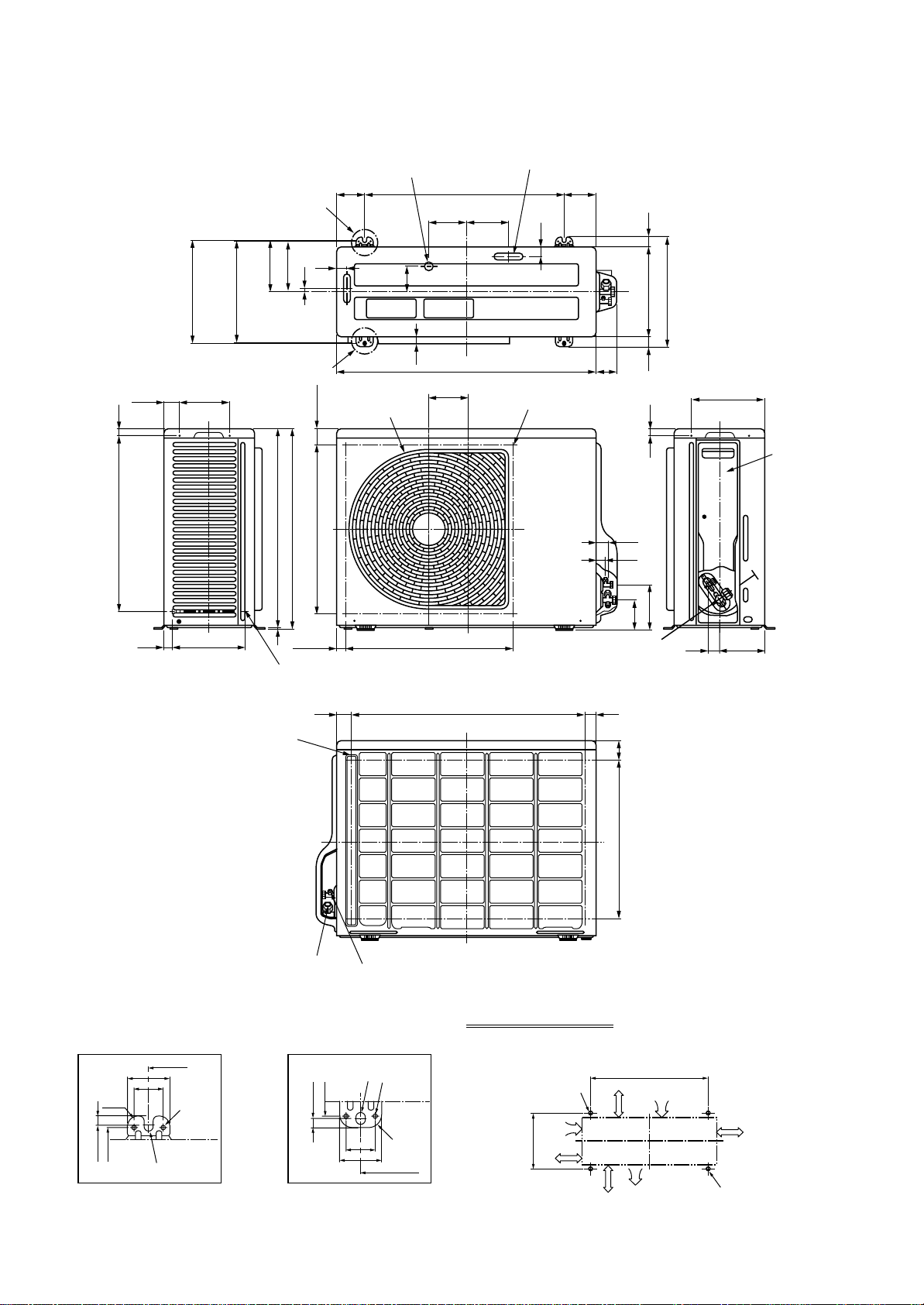
3. CONSTRUCTION VIEWS (EXTERNAL VIEWS)
3-1. Indoor Unit
3-1-1. Concealed Duct Type
RAV-SM561BT-E / SM801BT-E / SM1101BT-E / SM1401BT-E
129
110
Knock-out hole Ø125
(Air take-in port)
6-Ø4 T apping screw
undersized hole Ø160
Discharge port flange
N-Ø200
60 to 260
9
Suction port canvas
(Separate sold)
Refrigerant pipe connecting port
(Gas side ØF)
Hanging bolt pitch B
Main unit dimension A
J = M x K H
C
Ceiling open size D
Panel external dimension E
Hanging bolt
4-M10 screw
(Arranged locally)
44
49
Refrigerant pipe
connecting port
(Liquid side ØG)
Drain pipe connecting port
for vinyl chloride pipe
(Inner dia. 32, VP. 25)
75
Main unit dimension 800
Hanging bolt pitch 700
50
131
50
Ø26 Power supply,
remote controller
cable take-out port
638
498
393
41
196
243
Panel C.L
410
Ceiling open size
470
Panel external
dimension 500
5941
174
Suction port
flange
(Separate sold)
Suction port
panel
(Separate sold)
320
• Dimension
RAV-SM561BT
RAV-SM801BT
RAV-SM1101, 1401BT
ABCDEFGHJ KMN
700 766 690 750 780 12.7 6.4 252 280 280 1 2
1000 1066 990 1050 1080 15.9 9.5 252 580 290 2 3
1350 1416 1340 1400 1430 15.9 9.5 252 930 310 2 4
NOTE :
For maintenance of the equipment,
be sure to install a check port A at
the position as shown below.
Plane view of main unit
(Pipe side)
Discharge side
Check port A
300
100
450
9
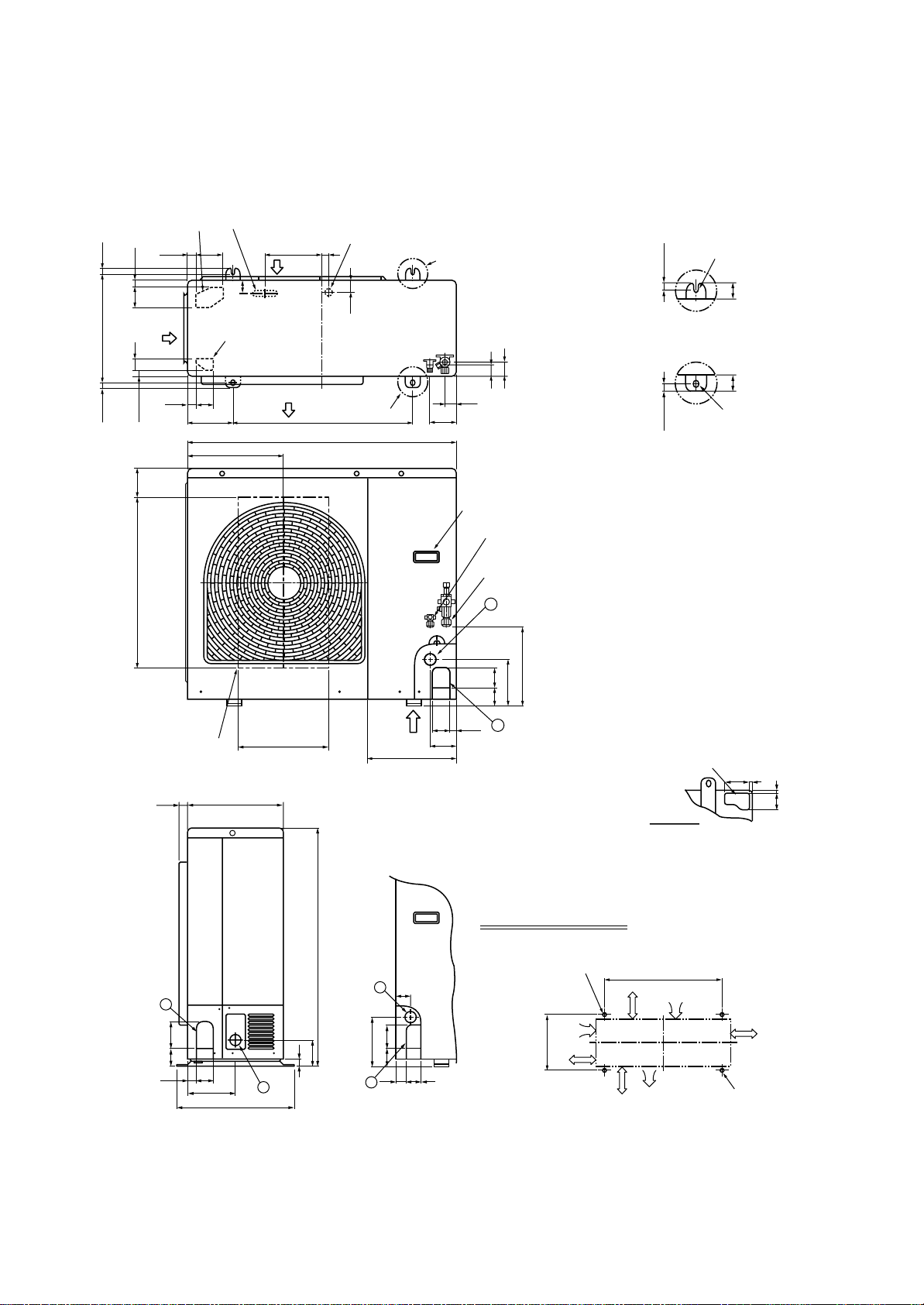
3-2. Outdoor Unit
RAV-SM560AT-E
49.5
521 21
25 220
308
302
Ø6 Hole pitch
for anchor bolt)
(Long hole pitch
147
Drain hole (Ø25)
83
A legs
150
11
30
76
153
B legs
Discharge guard
(49.3)
598
593
500 (Fan center dividing)
500 (Fan center dividing)
Protective net mounting hole
(2-Ø4 Embossing)
Drain hole (2-Ø20 x 88 long hole)
600
115.3 125
30
21
780
115.3
Discharge guide mounting hole
(4-Ø4 Embossing)
97
2927031
330
21
31
23
132
90.6
Charge port
216
Valve cover
31 134
43 707 30
Protective net mounting hole
(4-Ø4 Embossing)
Refrigerant pipe connecting port
(Ø12.7 Flare at gas side)
600
52
36
R15
302
308 11
Ø11 x 14 U-shape hole
Details of A legs Details of B legs
2-Ø6 hole
Product
external line
Ø11 x 14 Ushape holes
308
302
11
36
52
Refrigerant pipe connecting port
(Ø6.4 Flare at liquid side)
Space required for service
2-Ø6 hole
Product
external
line
R15
600
2-Ø11 x 14 U-shape holes
(For Ø8–Ø10 Anchor bolt)
150
or more
365
500
or more
60
475
Suction port
150
or more
Discharge
port
600
300
or more
Discharge
port
(Minimum
distance up to wall)
2-Ø11 x 14 long hole
(For Ø8–Ø10 Anchor bolt)
10
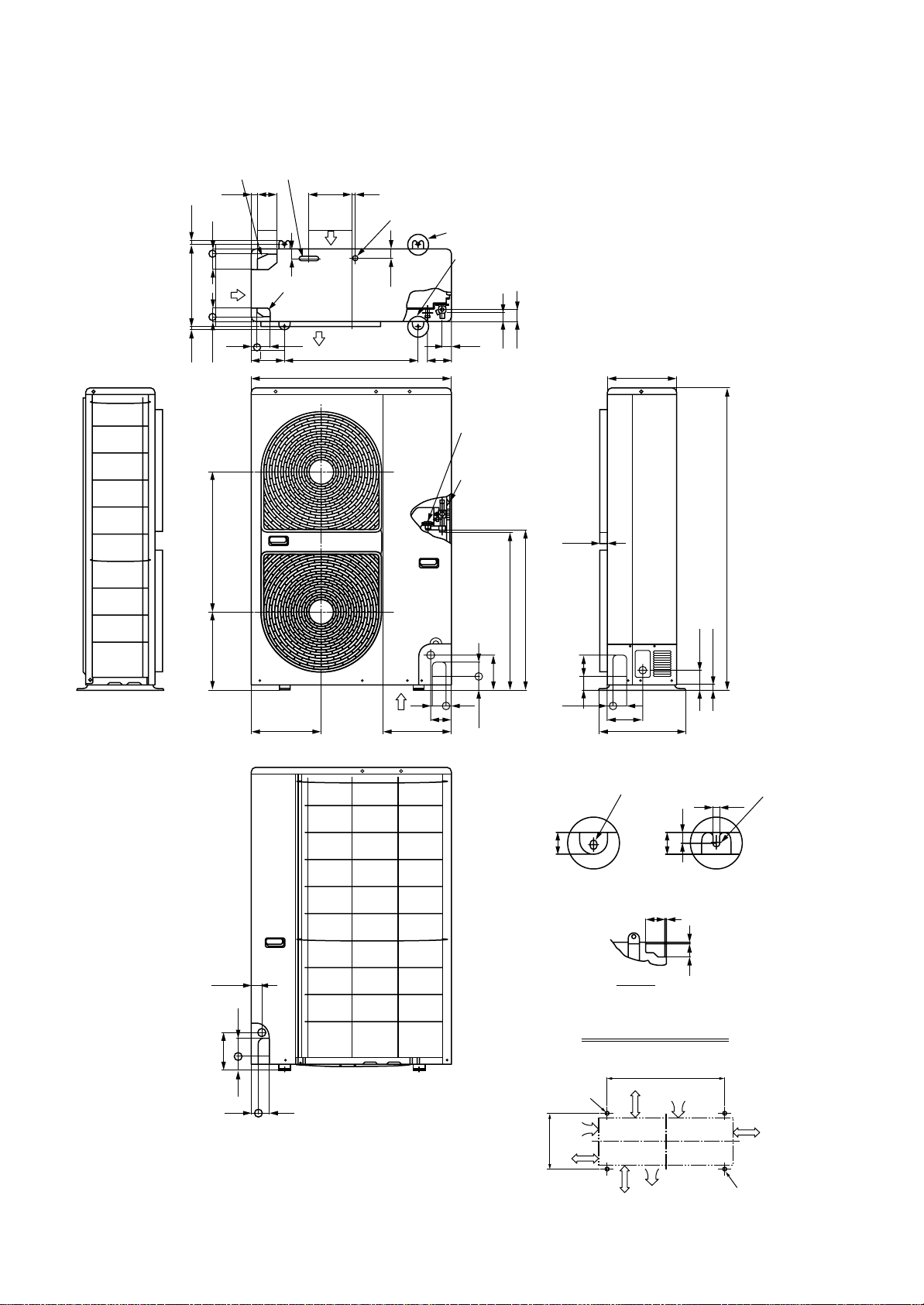
RAV-SM800AT-E
Knockout
(For draining)
21
Suction
port
365 17.517.5
40 70
(Long hole pitch
for anchor bolt)
21
565 101
Drain hole (Ø20 x 88 Burring hole)
29 90 191 20
Suction
port
43
Knockout
(For draining)
6026
Discharge
port
300150
900
314
Drain hole (Ø25 Burring hole)
Part B
40
39
Part A
43
95
Handles
(Both sides)
Refrigerant pipe connecting port
(Ø9.5 Flare at liquid side)
Refrigerant pipe connecting port
(Ø15.9 Flare at gas side)
2
47
Installation bolt hole
(Ø12 x 17 U-shape holes)
17.5
4040
Details of B part
Details of A part
17.5
Installation bolt hole
(Ø12 x 17 U-shape holes)
Discharge guide
mounting hole
(4-Ø4 Embossing)
1
60 90
58
27
161
32028
400
264
6760
154
2760
300
Z
307
96
1
Knockout for lower piping
86 7
7
58
Z views
Space required for service
795
2
46
25
85
2
165
60 80
30 45
1
2-Ø12 x 17 U-shape holes
(For Ø8–Ø10 Anchor bolt)
150
or more
365
500
or more
Suction port
150
or more
Discharge
port
600
150
or more
Discharge
port
(Minimum
distance up to wall)
2-Ø12 x 17 long hole
(For Ø8–Ø10 Anchor bolt)
11
RAV-SM1100AT-E / SM1400AT-E
Knockout (Drain)
70 21
Suction
port
365 17.517.5
21 40
350 625
Drain hole (Ø20 x 88)
9029
191 20
Suction
port
Drain hole (Ø25)
B legs
A legs
43
Knockout (Drain)
Discharge port
60 4326
50
600
40
108
40
54
900
Refrigerant pipe
connecting port
(Ø9.5 Flare at liquid side)
Refrigerant pipe
connecting port
(Ø15.9 Flare at gas side)
28
706
715
67
154
60 27
z
95
314 307 400
60
60 90
27
161
58
320
89
1340
25
46
8060
165
32 45
Mounting bolt hole
(Ø12 x 17 Long hole)
40
Details of A legs Details of B legs
2-Ø12 x 17 U-shape holes
(For Ø8–Ø10 Anchor bolt)
150
or more
365
Mounting bolt hole
(Ø12 x 17 U-shape hole)
20
40
86 7
Z view
58 7
Space required for service
600
Suction port
150
or more
Discharge
port
500
or more
Discharge
port
2-Ø12 x 17 long hole
(For Ø8–Ø10 Anchor bolt)
12
150
or more
(Minimum
distance up to wall)
12
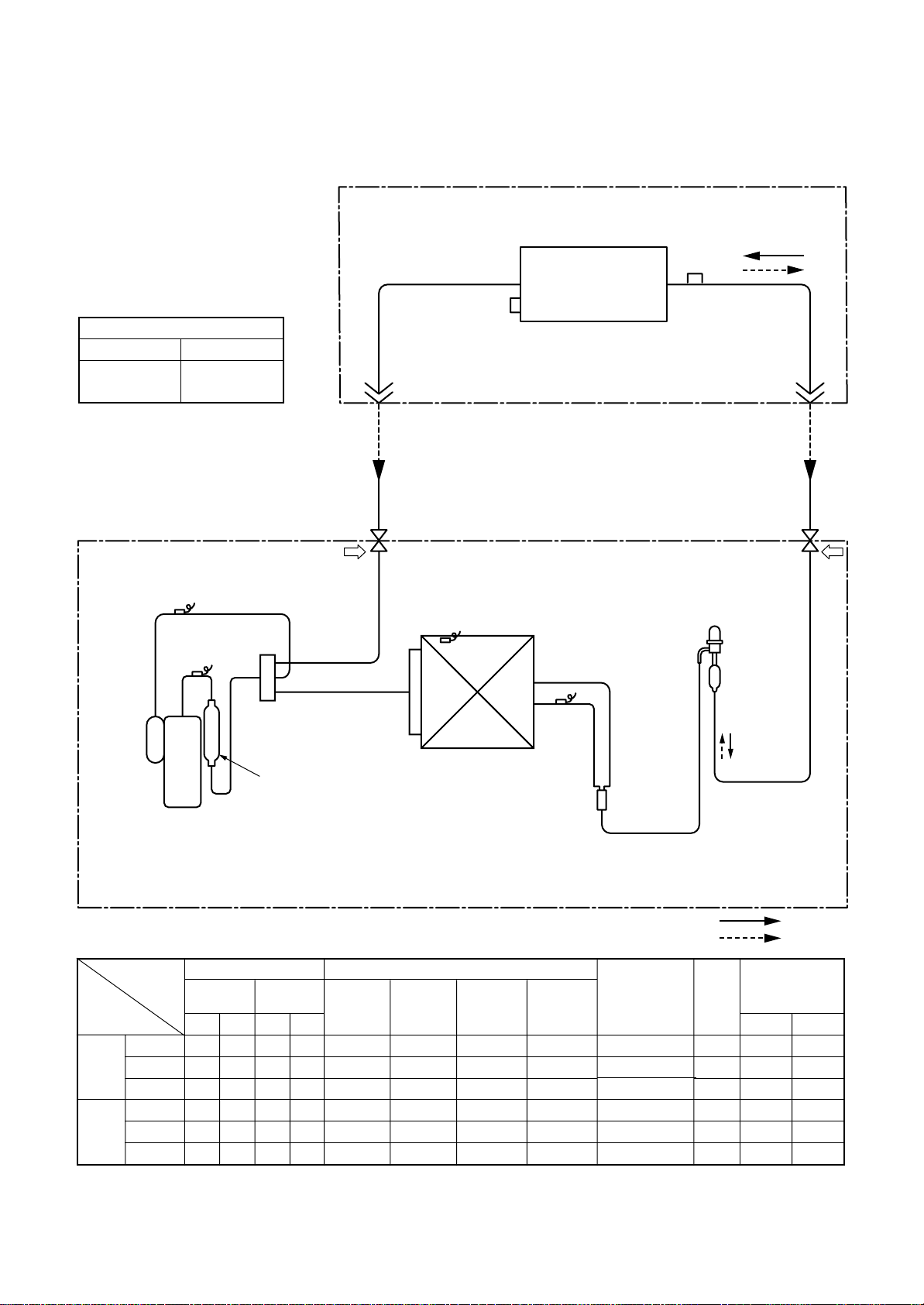
4. SYSTEMATIC REFRIGERATING CYCLE DIAGRAM
4-1. Indoor Unit/Outdoor Unit
RAV-SM561BT-E
Outer diameter of refrigerant pipe
Gas side ØA Liquid side ØB
12.7mm 6.4mm
Indoor unit
TCJ
sensor
Air heat exchanger
TC sensor
TS sensor
TD sensor
Rotary compressor
(DA130A1F-23F)
4-way valve
(VT7101D)
Muffler
Ø19 × L160
Refrigerant pipe
at gas side
Outer dia. ØA
Pd PsPacked valve
Packed valve
Outer dia. ØA
Outdoor unit
Refrigerant pipe
at liquid side
Outer dia. ØB
Outer dia. ØB
PMV
(SKV-18D26)
TO sensor
Strainer
TE
sensor
Heat exchanger
Ø8 multiple thread
ripple 1 row 22 stages
FP1.3 flat fin
Distributor
Max.
30m
R410A 0.9 kg
Cooling
Heating
Pressure
(MPa) (kg/cm²G)
Pd Ps Pd Ps
Standard
Cooling Overload
Low load
Standard
Heating Overload
Low load
4 poles are provided to this compressor.
*
3.1 0.9 31.9 8.9
3.6 1.0 37.1 10.4
0.9 0.7 9.1 7.1
2.3 0.6 23.6 6.2
3.3 1.2 33.2 11.8
1.7 0.2 16.4 1.8
Discharge Suction
Pipe surface temperature (°C)
Indoor heat
exchanger exchanger
(TD) (TS) (TC) (TE)
85 15 10 50
93 20 15 57
20735
71 1 39 3
78 20 54 19
110 –20 26 –22
Outdoor heat
Compressor
revolutions per
second (rps)
*
74
72
28
84
47
110
Indoor
fan
HIGH
HIGH
LOW
HIGH
LOW
HIGH
Indoor/Outdoor
temp. conditions
(DB/WB) (°C)
Indoor Outdoor
27/19 35/–
32/24 43/–
18/15.5 –5/–
20/– 7/6
30.– 24/18
15/––20/
The compressor frequency (Hz) measured with a clamp meter is 2 times of revolutions (rps) of the compressor.
13
(70%)
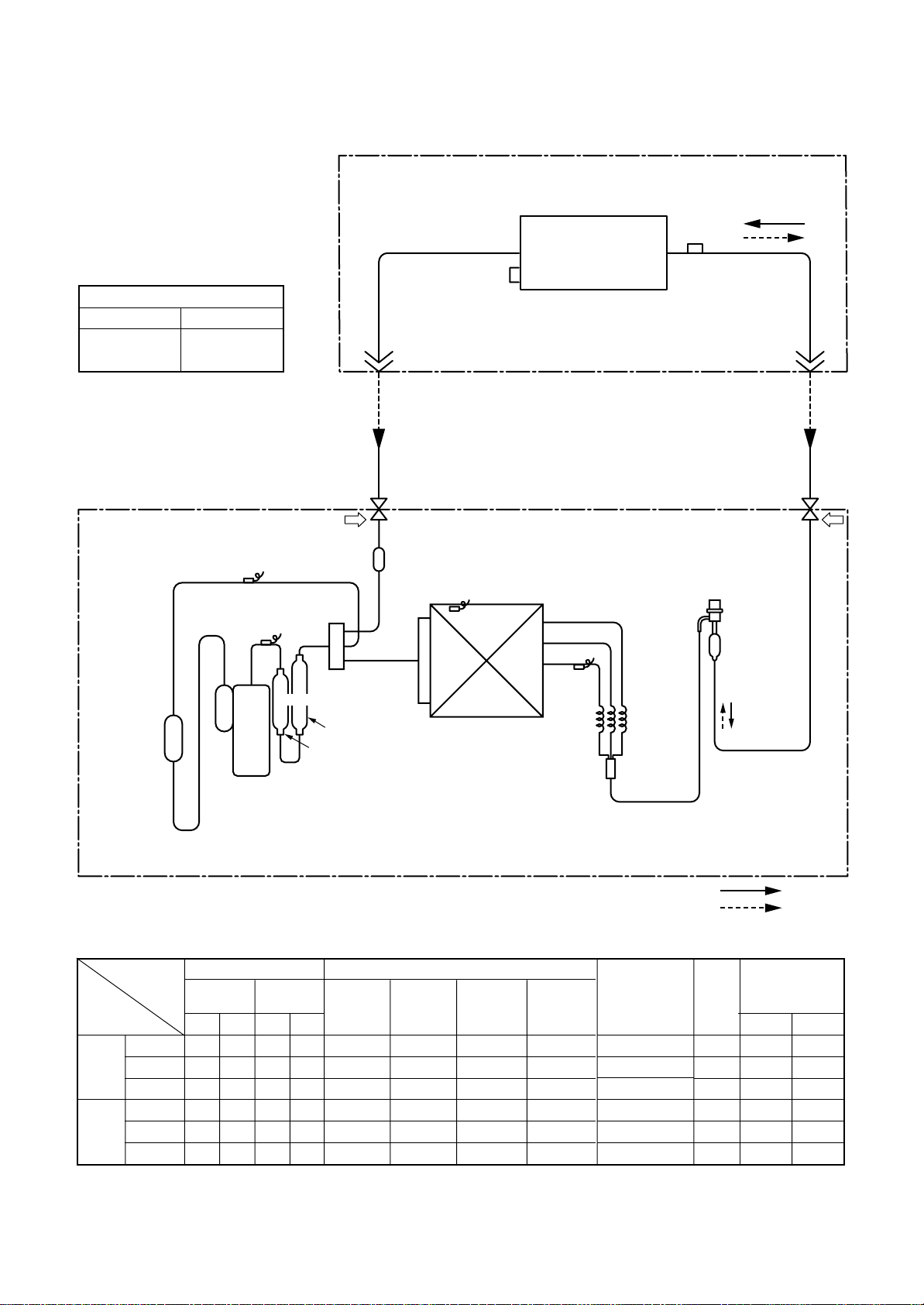
RAV-SM801BT-E
Outer diameter of refrigerant pipe
Gas side ØA Liquid side ØB
15.9mm 9.5mm
Indoor unit
TCJ
sensor
Air heat exchanger
TC sensor
Accumulator
(1500cc)
TS sensor
TD sensor
Muffler
Ø25 × L160
Rotary compressor
(DA220A2F-20L)
Refrigerant pipe
at gas side
Outer dia. ØA
Pd Ps
Packed valve
Outer dia. ØA
Outdoor unit
Strainer
Refrigerant pipe
at liquid side
Outer dia. ØB
Packed valve
Outer dia. ØB
Modulating (PMV)
(SKV-18D26)
TO sensor
Strainer
4-way valve
(STF-0213Z)
TE
sensor
Capillary
Ø3×Ø2×
Ø25 × L210
Heat exchanger Ø8
L530
1 row 30 stages
FP1.3 flat fin
Max.
50m
R410A 1.5 kg
Cooling
Heating
Pressure
(MPa) (kg/cm²G)
Pd Ps Pd Ps
Standard
Cooling Overload
Low load
Standard
Heating Overload
Low load
4 poles are provided to this compressor.
*
3.3 0.9 33.4 8.8
3.7 1.1 37.8 11.4
1.0 0.8 10.0 7.9
2.5 0.6 25.8 6.3
3.4 1.1 34.7 11.5
2.0 0.2 20.3 2.3
Discharge Suction
Pipe surface temperature (°C)
Indoor heat Outdoor heat
exchanger exchanger
(TD) (TS) (TC) (TE)
86 11 9 44
90 21 18 54
19448
67 6 42 2
85 23 55 16
89 –16 34 –18
Compressor
revolutions per
second (rps)
*
64
52
27
65
31
90
Indoor
fan
HIGH
HIGH
LOW
HIGH
LOW
HIGH
Indoor/Outdoor
temp. conditions
(DB/WB) (°C)
Indoor Outdoor
27/19 35/–
32/24 43/–
18/15.5 –5/–
20/– 7/6
30.– 24/18
15/––20/
The compressor frequency (Hz) measured with a clamp meter is 2 times of revolutions (rps) of the compressor.
14
(70%)
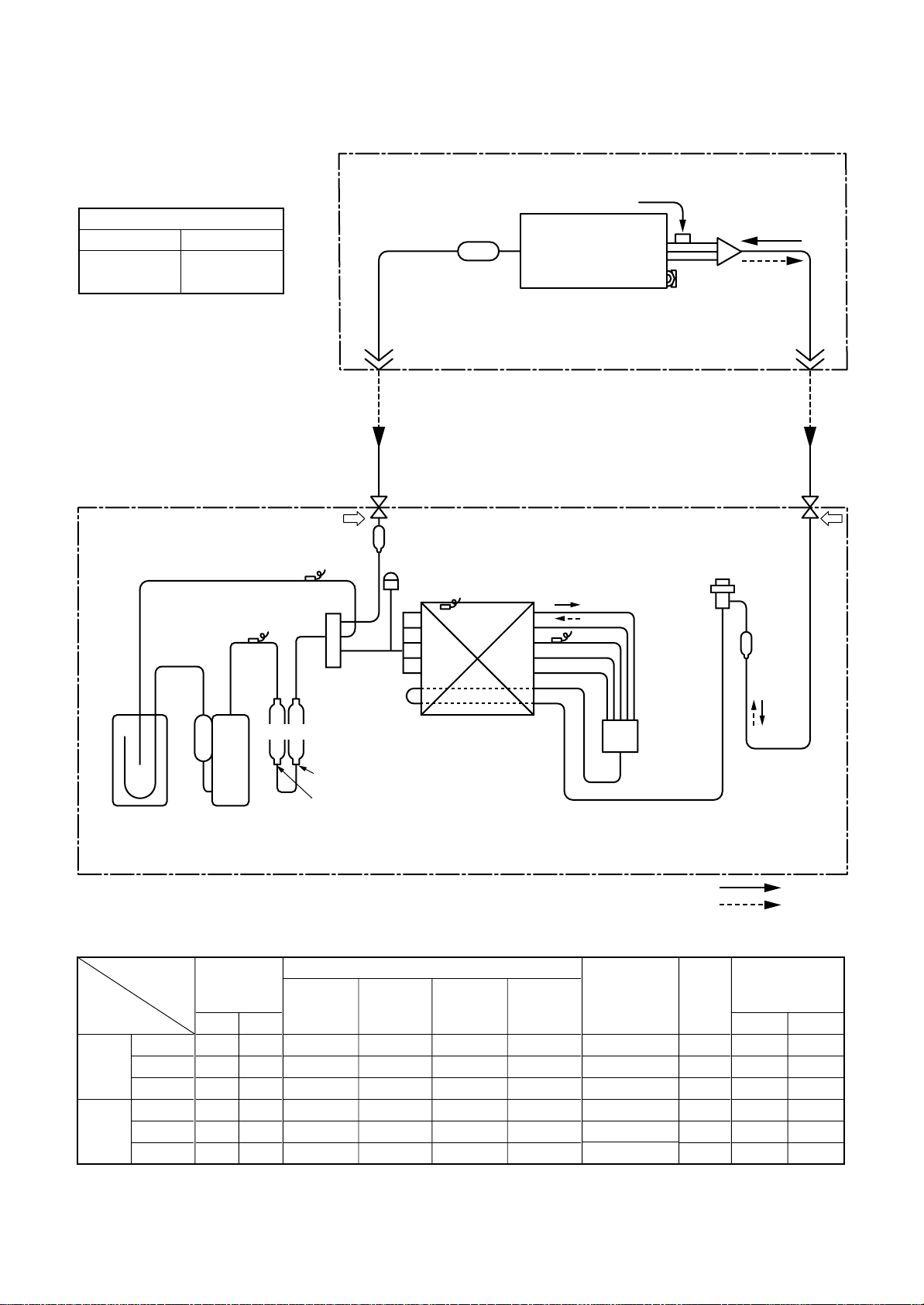
RAV-SM1001BT-E
Outer diameter of refrigerant pipe
Gas side ØA Liquid side ØB
15.9mm 9.5mm
Strainer
Indoor unit
TCJ sensor
Air heat exchanger
Distributor
(Strainer incorporated)
TC sensor
Accumulator
(2500cc)
(DA220A2F – 20L)
TD sensor
Rotary
compressor
TS sensor
(STF-0213Z)
Muffler
4-way valve
Ø25 × L210
Ø25 × L180
Refrigerant pipe
at gas side
Outer dia. ØA
Ball valve
Outer dia. ØA
Strainer
Check joint
TO sensor
Heat exchanger Ø8
1 row 52 stages
FP1.3 flat fin
Outdoor unit
TE sensor
Refrigerant pipe
at liquid side
Outer dia. ØB
Max.
50m
Packed valve
Outer dia. ØB
PMV
(UKV-25D22)
Strainer
Distributor
R410A 2.1kg
Cooling
Heating
Pressure
(MPa)
Pd Ps
Standard
Cooling Overload
Low load
Standard
Heating Overload
Low load
4 poles are provided to this compressor.
*
3.3 0.9
3.0 1.0
1.0 0.8
2.5 0.6
3.3 1.1
1.8 0.2
Discharge Suction
(TD) (TS) (TC) (TE)
88 10 8 38
88 14 14 46
30 8 8 3
90 4 50 2
83 17 54 13
80 –23 29 –20
Pipe surface temperature (°C)
Indoor heat
exchanger exchanger
Outdoor heat
Compressor
revolutions per
second (rps)
*
92
74
27
86
52
100
Indoor
fan
HIGH
HIGH
LOW
HIGH
LOW
HIGH
Indoor/Outdoor
temp. conditions
(DB/WB) (°C)
Indoor Outdoor
27/19 35/–
32/24 43/–
18/15.5 –5/–
20/– 7/6
30.– 24/18
15/––20/
The compressor frequency (Hz) measured with a clamp meter is 2 times of revolutions (rps) of the compressor.
15
(70%)

RAV-SM1401BT-E
Outer diameter of refrigerant pipe
Gas side ØA Liquid side ØB
15.9mm 9.5mm
Strainer
Indoor unit
TCJ sensor
Air heat exchanger
Distributor
(Strainer incorporated)
TC sensor
Accumulator
(2500cc)
(DA420A3F – 21M)
TD sensor
Rotary
compressor
TS sensor
(STF-0213Z)
Muffler
4-way valve
Ø25 × L210
Ø25 × L180
Refrigerant pipe
at gas side
Outer dia. ØA
Ball valve
Outer dia. ØA
Strainer
Check joint
TO sensor
Heat exchanger Ø8
1 row 52 stages
FP1.3 flat fin
Outdoor unit
TE sensor
Refrigerant pipe
at liquid side
Outer dia. ØB
Max.
50m
Packed valve
Outer dia. ØB
PMV
(UKV-25D22)
Strainer
Distributor
R410A 2.3kg
Cooling
Heating
Pressure
(MPa)
Pd Ps
Standard
Cooling Overload
Low load
Standard
Heating Overload
Low load
4 poles are provided to this compressor.
*
3.3 0.9
3.5 1.0
1.7 0.8
3.0 0.6
3.4 1.1
2.0 0.2
Discharge Suction
(TD) (TS) (TC) (TE)
84 11 10 40
87 7 15 54
44 8 4 8
79 2 44 2
78 21 54 17
82 –21 36 –18
Pipe surface temperature (°C)
Indoor heat
exchanger exchanger
Outdoor heat
Compressor
revolutions per
second (rps)
*
56
54
27
60
24
73
Indoor
fan
HIGH
HIGH
LOW
HIGH
LOW
HIGH
Indoor/Outdoor
temp. conditions
(DB/WB) (°C)
Indoor Outdoor
27/19 35/–
32/24 43/–
18/15.5 –5/–
20/– 7/6
30.– 24/18
15/––20/
The compressor frequency (Hz) measured with a clamp meter is 2 times of revolutions (rps) of the compressor.
16
(70%)
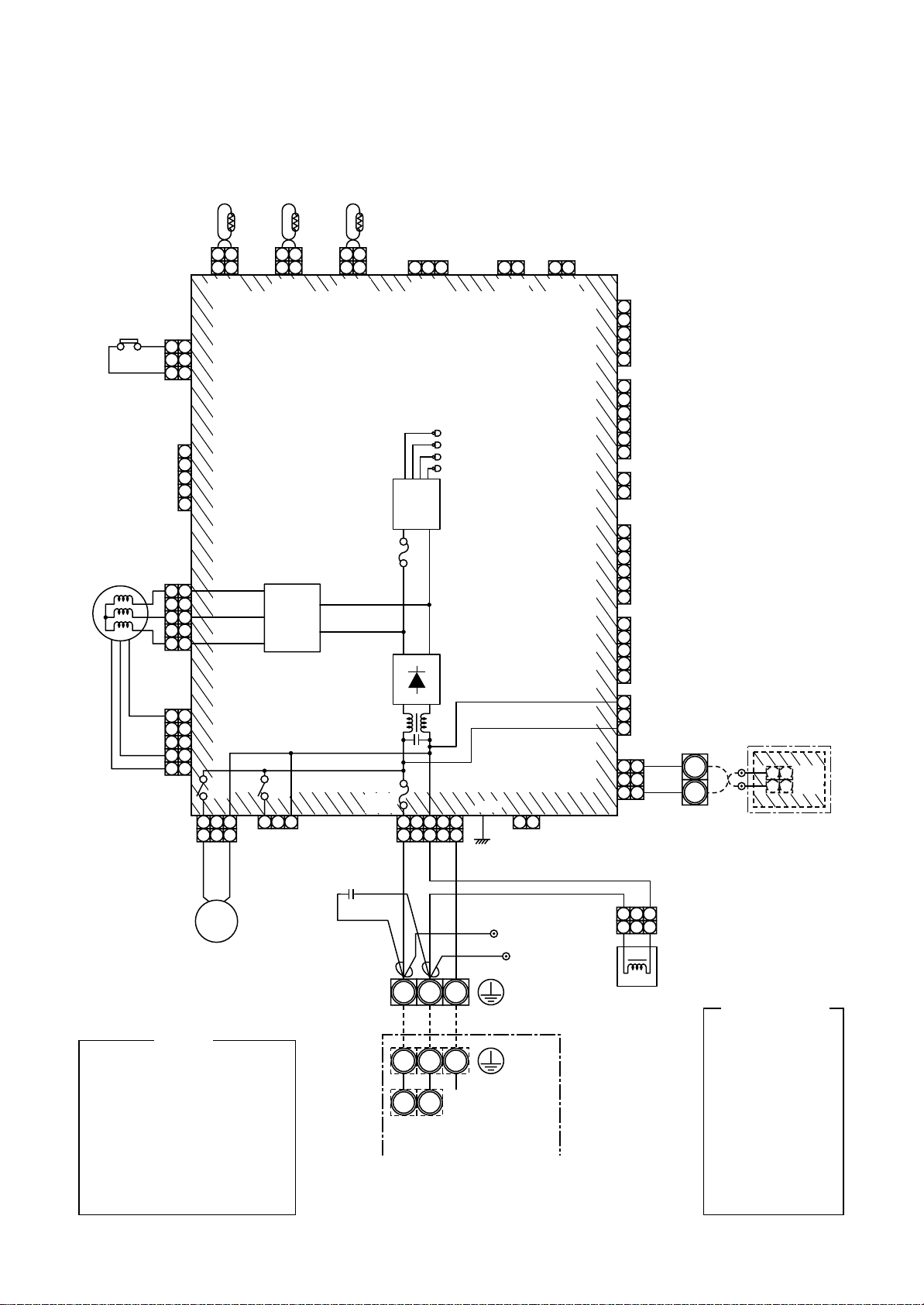
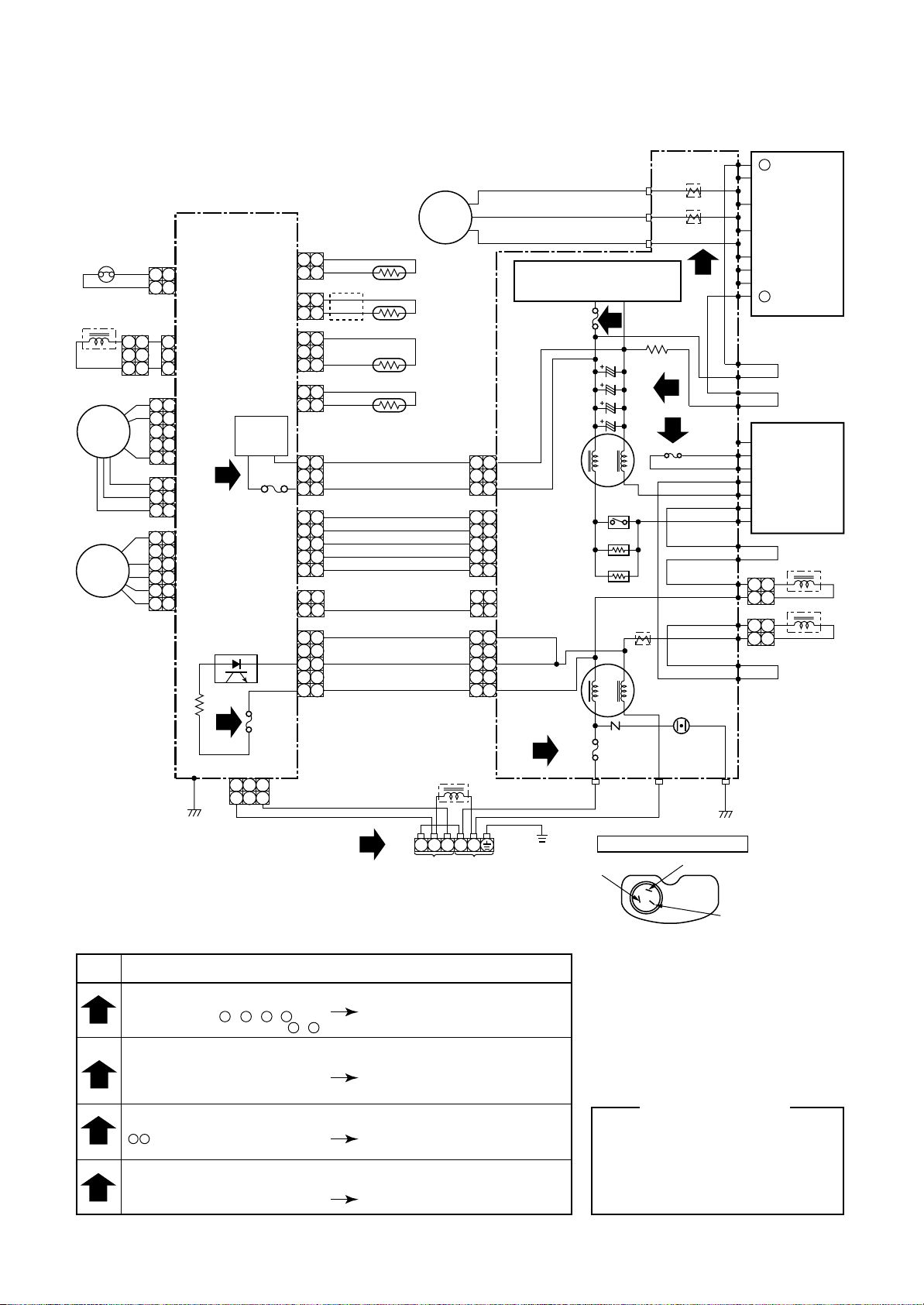
5. WIRING DIAGRAM
5-1. Indoor Unit
RAV-SM561BT-E / SM801BT-E / SM1101BT-E / SM1401BT-E
FM
FS
CN34
(RED)
3 3
2 2
1 1
CN33
(WHI)
CN333
(WHI)
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 2
1 1
CN334
(WHI)
1 1
2 2
3 3
4 4
5 5
CN68
(BLU)
5
4
3
2
1
TA
1 2
1 2
CN104
(YEL)
1 2
1 2
CN102
(RED)
Control P.C. Board for
Motor
drive
circuit
RY
302
1 233 1 2 3
1 2
RY
303
CN304
(GRY)
TCJ
1 2
1 2
CN101
(BLK)
TC
MCC-1402
Indoor Unit
Fuse
F302
T3.15A
250V~
Fuse
F301
250V~
T6.3A
CN67
(BLK)
RED
Capacitor
1 2 3
CN80
(GRN)
DC20V
DC15V
DC12V
DC7V
Power
supply
circuit
+ –
~~
1 233
1 2
WHI BLK
5
445
P301
BLK
(EXCT)
1 2
CN73
(RED)
CN66
(WHI)
1 2
1 2
CN70
(WHI)
5
4
CN620
3
(BLU)
2
1
6
5
CN60
4
(WHI)
3
2
1
CN32
2
(WHI)
1
(FAN DRIVE)
6
5
4
CN61
(YEL)
3
2
1
5
4
CN50
3
(WHI)
2
1
3
CN309
2
(YEL)
1
BLK
3
3
2 2
BLK
1 1
CN41
(BLU)
BLK
B
A
WHI
2 2
1 1
CN1
(WHI)
Wired Remote
Controller
FM
TA
TC
TCJ
DP
FS
RY302
DP
NOTE
: Fan motor
: Indoor temp. sensor
: Temp. sensor
: Temp. sensor
: Drain pump motor
: Float switch
: Drain control relay
RED
WHI
321
Indoor unit
earth screw
321
Outdoor unit
earth screw
Serial
NL
signal
Single phase 220V, 50Hz
17
Closed-end
connector
1 233
1 2
Reactor
Color
Identification
BLACK
:
BLK
BLUE
:
BLU
RED
:
RED
GRAY
:
GRY
PINK
:
PNK
GREEN
:
GRN
WHITE
:
WHI
BROWN
:
BRW
ORANGE
:
ORN
YELLOW
:
YEL
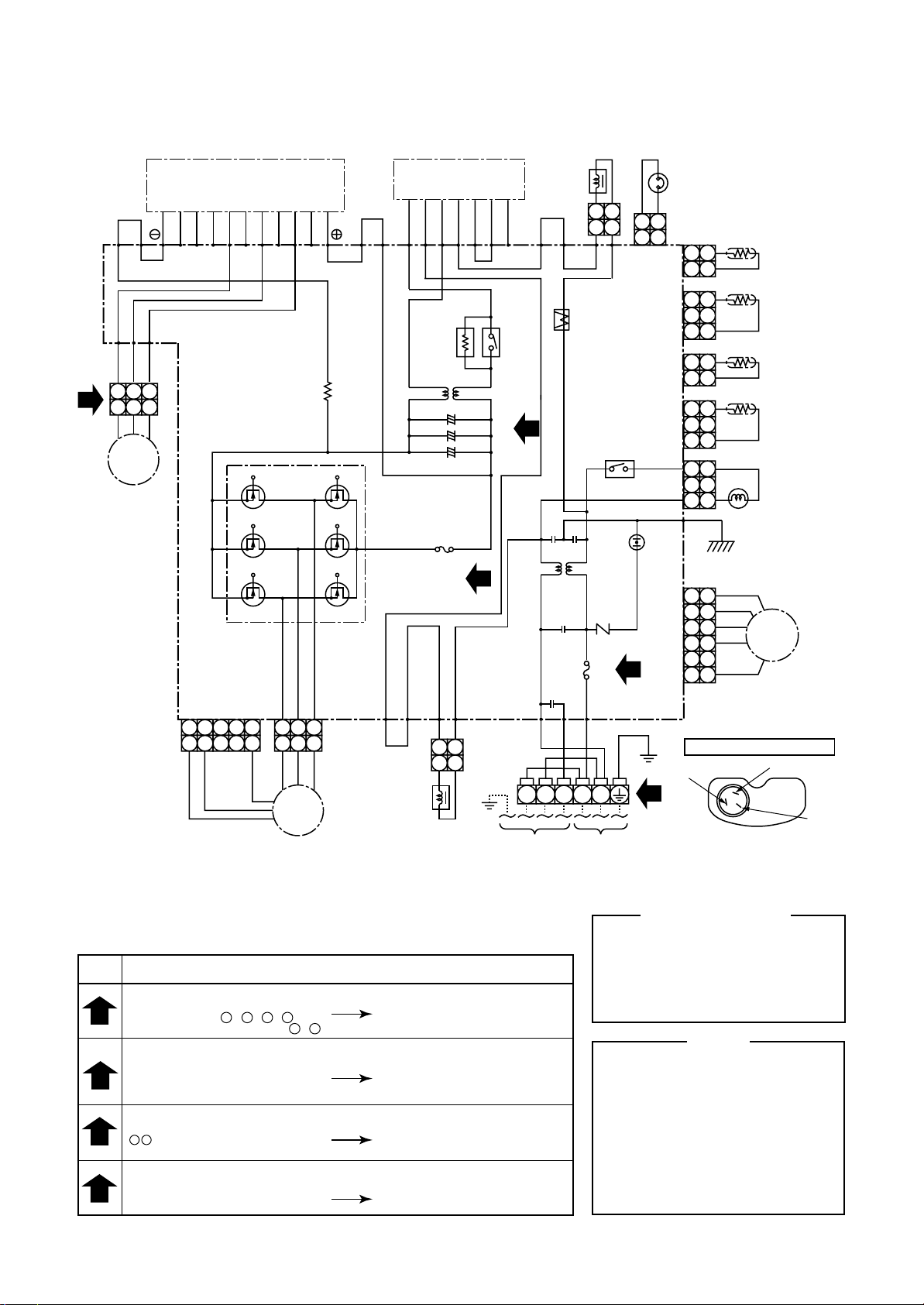
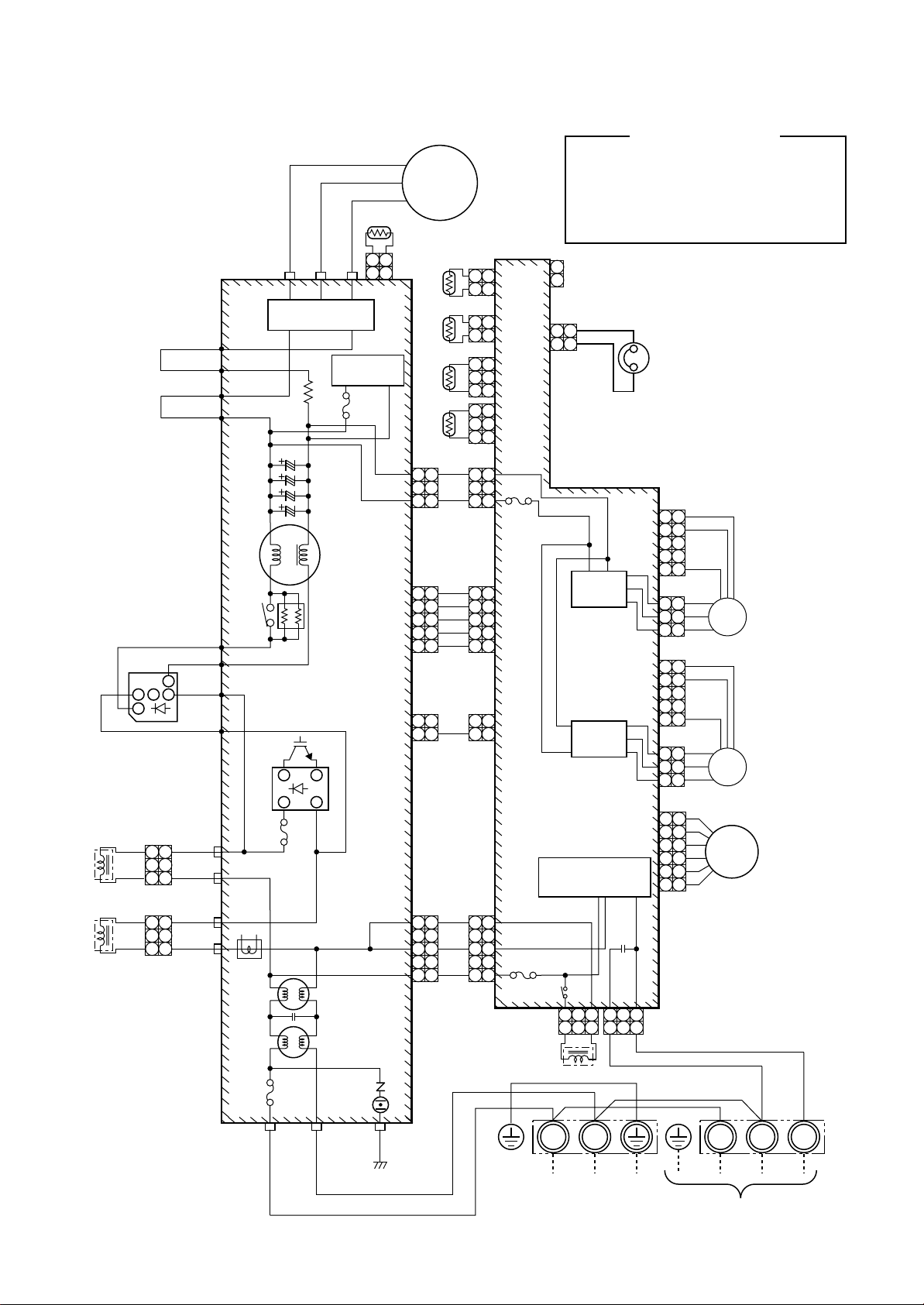
5-2. Outdoor Unit
RAV-SM560AT-E
Q200
BLU
P17 P18
P21
P22
P23
RED
WHI
BLK
2 1
4
233 1
CM
COMPRESSOR
CN301
IGBT MODULE
BZBYBXEWBWEVBVEUBU
P.C. BOARD
(MCC-813)
5
5
GRY
4 3
PNK
2 1
YEL
3
3
BLK
2 1
2 1
WHI
RED
2 1
4 3
FM
FAN MOTOR
Q300
CN300
BRW
P19P20
P14
PUR
REACTOR
DB01
CONVERTER
MODULE
~
~
–
+
ELECTRONIC
STARTER
–
–
–
F04
FUSE
T3. 15A
250V~
P13
P12
2 1
2 1
+
+
+
P11
C12
C13
C14
2
GEA
P10
POWER
RELAY
3
P02
1
TO
INDOOR
UNIT
REACTOR
ORN
P09
P08 P07
CT
FUSE
T25A
250V~
P03
ORN
WHI
2
3
L
POWER
SUPPLY
220V
50Hz
2 1
2 1
RELAY
VARISTOR
F01
P01
BLK
N
~
CN500
2 1
2 1
CN600
CN601
CN602
CN603
CN701
P06
SURGE
ABSORBER
2
WHITE (S)
1
THERMOSTAT
FOR
COMPRESSOR
TE
11
22
TD
11
22
33
TO
11
22
TS
11
22
33
11
22
33
COIL FOR
11
22
33
44
55
66
BLK
YEL
RED
ORN
RED
GRY
4-WAY VALVE
PMV
PULSE
MODULATING
VALVE
BLACK (C)
RED (R)
BLK
CN703
TERMINAL OF COMPRESSOR
The sign in ( ) is displayed
in the terminal cover
Check
items
1
2
3
4
SIMPLE CHECK POINTS FOR DIAGNOSING FAULTS
Diagnosis result
TERMINAL BLOCK
There is no supply voltage
(AC220V) between L - N , 1 - 2
There is no voltage (DC15 to 25V) 2 - 3
FUSE
T25A 250V to fuse (F01) blown
T3.15A 250V to fuse (F04) blown
ELECTROLYTIC CAPACITOR VOLTAGE (C12, C13, C14)
DC320V not available between
+ – terminal of electrolytic capacitor
INVERTER OUTPUT (Inverter and compressor connector out of position)
(Please confirm within six minutes after instructing in the drive.)
Voltage between each line of in v erter side
connector pins are not equal.
Power supply and connecting
cable check
Converter module (DB01) and
electrolytic capacitor (C12 to C14) check
IGBT module (Q200) check
Fan motor check
T25A fuse (F01) check
P.C. board and converter
module (DB01) check
IGBT module and
P.C. board check
18
Color Identification
BLK
BLU
RED
GRY
PNK
GRN
BLACK
:
BLUE
:
RED
:
GRAY
:
PINK
:
GREEN
:
WHI
BRW
ORN
YEL
PUR
NOTE
: Compressor
CM
: Pulse modulating valve
PMV
: Fan motor
FM
: Heat exchanger Temp. Sensor
TE
: Discharge Temp. Sensor
TD
: Outdoor Temp. Sensor
TO
: Suction Temp. Sensor
TS
: Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor
IGBT
: Converter module
DB01
: Curreut Transformer
CT
: Fan motor driver module
Q300
:
WHITE
:
BROWN
:
ORANGE
:
YELLOW
:
PURPLE
RAV-SM800AT-E
THERMOST AT
FOR
COMPRESSOR
ORN
212
ORN
4-WA Y V ALVE COIL
313
1
FAN MOTOR
5
4
FM
1
3
2
1
6
5
PMV
SUB
P.C. BO ARD
(MCC-1398)
4
3
2
1
SIMPLE CHECK POINTS FOR DIAGNOSING FAULTS
CN500
1
3
CN700
1
5
4
CN300
3
232
1
3
CN301
2
1
6
5
4
CN702
3
2
1
PHOTO COUPLER
CN02
2
2
Fan
circuit
CN302
F300
FUSE
T5A
CN800
2 31
2 31
COMPRESSOR
212
CN604
CN605
CN600
CN601
CN04
CN01
F01
FUSE
T3.15A
1
212
GRN
1
3
2
131
212
1
313
1
5 5 5 5
4 4 4 4
3 3 3 3
212
1
212
1
5 5 5 5
4 4 4 4
3 3 3 3
212
1
GRY
WHI
BLU
YEL
BLK
WHI
BLU
RED
PNK
ORN
BLK
WHI
RED
RED
1
CM
TE
TS
TD
TO
REACTOR
TO
INDOOR
UNIT
313
212
212
212
L N2 31
POWER
SUPPL Y
220V
50Hz
RED
WHI
BLK
POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT
(FOR P.C. BOARD)
F04
FUSE
3.15A
CN04
1
CN06
P.C. BO ARD
1
(MCC-1359)
CN05
1
1
CN13
F01
FUSE
2
25A
~
WHITE(S)
+
BU
EU
BV
EV
BW
EW
BX
BY
BZ
CN09
CN10
CN11
T03
CT
T04
CT
4
–
2
P20
P10
P11
P13
P12
P09
P08
P15
P14
CN03
BLKWHIRED
P19
P18
P17
G
E
A
~
–
~
+
REACTOR
212
REACTOR
212
RED(R)
C13
3
C12
C11
C10
POWER
RELA Y
RY01
R05
R06
T02
CT
VARIST OR
CN02CN01
TERMINAL OF COMPRESSOR
F02
2
FUSE
15A
SURGE
ABSORBER
BLACK(C)
IGBT
MODULE
Q200
YEL
BLU
CONVERTER
MODULE
DB01
ORN
1
1
BRN
The sign in ( )
is displayed
in the terminal
cover
Check
items
1
2
3
4
Diagnosis result
TERMINAL BLOCK
There is no supply voltage
(AC220V) between L - N , 1 - 2
There is no voltage (DC15 to 25V) 2 - 3
FUSE
25A fuse (F01) blown, 15A fuse (F02) blown
3.15A fuse (F04) blown,
T5A fuse (F300) blown (SUB P.C. board)
T3.15A fuse (F01) blown (SUB P.C. board)
ELECTROLYTIC CAPACITOR VOLTAGE (C10, C11, C12, C13)
DC320V not available between
+ – terminal of electrolytic capacitor
INVERTER OUTPUT (CN09, CN10, CN11)
(Please confirm within six minutes after instructing in the drive.)
Voltage between each line of in v erterside
connector pins are not equal.
Connecting cable check
Converter module (DB01) and electrolytic
capacitor (C10 to C13) check
IGBT module (Q200) check, Fan motor check
SUB P.C. board chec k
25A fuse (F01) check
P.C. board and coverter
module (DB01) check
IGBT module and
P.C. board check
19
Color Identification
BLACK
:
BLK
BLU
RED
GRY
PNK
GRN
BLUE
:
RED
:
GRAY
:
PINK
:
GREEN
:
WHI
BRN
ORN
YEL
PUR
:
WHITE
:
BROWN
:
ORANGE
:
YELLOW
:
PURPLE
RAV-SM1100AT-E / RAV-SM1400AT-E
RED
ORN
REACTOR
REACTOR
~
+
3 3
212
3 3
212
BLU
YEL
~
1
1
BLK
–
~
GRY
GRY
BRN
WHI
WHI
RED
CN09 CN10 CN11
IGBT MODULE
P18
P17
P20
P19
RY01
P29
P28
P24
P21
+
~
F02
P13
P12
P09
P08
FUSE
250V~
T25A
T02 CT
T25A
250V~
F01
FUSE
CN01 CN02 CN03
WHI
BLK
TH
212
SWITCHING
REGURATOR
F04
250V~
FUSE
T3.15A
P.C. BOARD
(MCC-1438)
–
~
COMPRESSOR
CM
CN600
1
TO
TE
TS
TD
3 3
212
CN04 CN03
5 5 5 5
4 4 4 4
3 3 3 3
212
CN06
22
121
CN05 CN04
5 5 5 5
4 4 4 4
3 3 3 3
212
CN13 CN01
BLK
1
1
1
BLU
YEL
BLK
WHI
BLU
RED
PNK
CN800
ORN
BLK
WHI
RED
212
212
3 3
212
3 3
212
3 3
212
212
2
1
212
CN606
2
T5A
1
2
2
1
1
CN500
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
CN601
CN604
CN605
CN600
250V~
FUSE
F300
SUB P.C. BOARD
(MCC-1398)
SERIAL
COMMUNICATION
CIRCUIT
T3.15A
250V~
F01 FUSE
1
RY700
4-WAY
VALVE
BLK
BLU
RED
GRY
PNK
GRN
ORN
ORN
FUN
CIRCUIT
FUN
CIRCUIT
2 31
2 31
GRN/YEL
Color Identification
BLACK
:
BLUE
:
RED
:
GRAY
:
PINK
:
GREEN
:
2 31
2 31
WHI
CN02CN700
GRY
WHI
BRN
ORN
YEL
PUR
GRN/YEL : GREEN&YELLO W
THERMOSTAT
CN300
5 5
4 4
3 3
212
1
CN301
3 3
212
CN302
5 5
4 4
3 3
212
CN303
3 3
212
CN702
6
5
4
3
2
1
FM01 FAN MOTOR
1
1
FM02 FAN MOTOR
1
6
5
4
PMV
3
2
1
WHI
:
WHITE
:
BROWN
:
ORANGE
:
YELLOW
:
PURPLE
RED
GRYWHI
321NL
WHI
RED
20
POWER SUPPLY
220V
50Hz
~
TO INDOOR UNIT
6. SPECIFICATIONS OF ELECTRICAL PARTS
6-1. Indoor Unit
RAV-SM561BT-E / SM801BT-E / SM1101BT-E / SM1401BT-E
No.
1
Fan motor (SM801BT-E)
Fan motor
2
(SM561BT-E/SM1101BT-E/SM1401BT-E)
3
Thermo. sensor (TA-sensor)
4
Heat exchanger sensor (TCJ-sensor)
5
Heat exchanger sensor (TC-sensor)
6
Float switch
7
Drain pump motor
8
Reactor
6-2. Outdoor Unit
RAV-SM560AT-E
No.
1
Fan motor
2
Compressor
3
Reactor
4
Outdoor temp. sensor (To-sensor)
5
Heat exchanger sensor (Te-sensor)
6
Suction temp. sensor (Ts-sensor)
7
Discharge temp. sensor (Td-sensor)
8
Fuse (Switching power (Protect))
9
Fuse (Inverter, input (Current protect)
10
4-way valve solenoid coil
11
Compressor thermo. (Protection)
Parts name
Parts name
Type
ICF-280-120-1
ICF-280-120-2
258 mm
Ø6 mm, 1200 mm
Ø6 mm, 1200 mm
FS-0218-106
ADP-1406
CH-43-2Z-K
Type
ICF-140-43-1
DA130A1F-23F
CH-57
—
—
—
—
STF-0108G
US-622
Specifications
Output (Rated) 120 W, 220–240 V
Output (Rated) 120 W, 220–240 V
10 kΩ at 25°C
10 kΩ at 25°C
10 kΩ at 25°C
10 mH, 1 A
Specifications
Output (Rated) 40 W
3 phase, 4P, 1100 W
10 mH, 16A
10 kΩ at 25°C
10 kΩ at 25°C
10 kΩ at 25°C
50 kΩ at 25°C
T3.15 A, AC 250 V
25 A, AC 250 V
ON : 90 ± 5°C, OFF : 125 ± 4°C
RAV-SM800AT-E
No.
1
Fan motor
2
Compressor
3
Reactor
4
Outdoor temp. sensor (To-sensor)
5
Heat exchanger sensor (Te-sensor)
6
Suction temp. sensor (Ts-sensor)
7
Discharge temp. sensor (Td-sensor)
8
Fuse (Switching power (Protect))
9
Fuse (Inverter, input (Current protect))
10
4-way valve solenoid coil
11
Compressor thermo. (Protection)
Parts name
Type
ICF-140-63-1 or ICF-140-63-2
DA220A2F-20L
CH-47
—
—
—
—
DKV-M0ZS743B0
US-622
21
Specifications
Output (Rated) 63 W
3 phase, 4P, 1600 W
8 mH, 16 A
10 kΩ at 25°C
10 kΩ at 25°C
10 kΩ at 25°C
50 kΩ at 25°C
T3.15 A, AC 250 V
25 A, AC 250 V
ON : 90 ± 5°C, OFF : 125 ± 4°C
RAV-SM1100AT-E
No.
1
Fan motor
2
Compressor
3
Reactor
4
Outdoor temp. sensor (To-sensor)
5
Heat exchanger sensor (Te-sensor)
6
Suction temp. sensor (Ts-sensor)
7
Discharge temp. sensor (Td-sensor)
8
Fuse (Switching power (Protect))
9
Fuse (Inverter, input (Current protect)
10
4-way valve solenoid coil
11
Compressor thermo. (Protection)
RAV-SM1400AT-E
No.
1
Fan motor
2
Compressor
Parts name
Parts name
Type
ICF-140-63-2
ICF-140-43-2
DA220A2F-20L
CH-56
—
—
—
—
VHV-01AJ502E1
US-622
Type
ICF-140-63-2
DA420A3F-21M
Specifications
Output (Rated) 63 W
Output (Rated) 43 W
3 phase, 4P, 2000 W
6 mH, 18.5 A
10 kΩ at 25°C
10 kΩ at 25°C
10 kΩ at 25°C
50 kΩ at 25°C
T3.15 A, AC 250 V
25 A, AC 250 V
AC 220 – 240 V
ON : 90 ± 5°C, OFF : 125 ± 4°C
Specifications
Output (Rated) 63 W
3 phase, 4P, 3500 W
3
Reactor
4
Outdoor temp. sensor (To-sensor)
5
Heat exchanger sensor (Te-sensor)
6
Suction temp. sensor (Ts-sensor)
7
Discharge temp. sensor (Td-sensor)
8
Fuse (Switching power (Protect))
9
Fuse (Inverter, input (Current protect))
10
4-way valve solenoid coil
11
Compressor thermo. (Protection)
CH-56
—
—
—
—
VHV-01AJ502E1
US-622
6 mH, 18.5 A
10 kΩ at 25°C
10 kΩ at 25°C
10 kΩ at 25°C
50 kΩ at 25°C
T3.15 A, AC 250 V
25 A, AC 250 V
AC 220 V
ON : 90 ± 5°C, OFF : 125 ± 4°C
22

7. REFRIGERANT R410A
This air conditioner adopts the new refrigerant HFC
(R410A) which does not damage the ozone layer.
The working pressure of the new refrigerant R410A
is 1.6 times higher than conventional refrigerant
(R22). The refrigerating oil is also changed in
accordance with change of refrigerant, so be careful
that water, dust, and existing refrigerant or refrigerating oil are not entered in the refrigerant cycle of the
air conditioner using the new refrigerant during
installation work or servicing time.
The next section describes the precautions for air
conditioner using the new refrigerant. Conforming to
contents of the next section together with the
general cautions included in this manual, perform
the correct and safe work.
7-1. Safety During Installation/Servicing
As R410A’s pressure is about 1.6 times higher than
that of R22, improper installation/servicing may
cause a serious trouble. By using tools and materials exclusiv e for R410A, it is necessary to carry out
installation/servicing safely while taking the following
precautions into consideration.
(1) Never use refrigerant other than R410A in an air
conditioner which is designed to operate with
R410A.
If other refrigerant than R410A is mixed, pressure in the refrigeration cycle becomes abnormally high, and it may cause personal injury, etc.
by a rupture.
(2) Confirm the used refrigerant name, and use
tools and materials exclusiv e for the refrigerant
R410A.
The refrigerant name R410A is indicated on the
visible place of the outdoor unit of the air conditioner using R410A as refrigerant. To prevent
mischarging, the diameter of the service port
differs from that of R22.
(3) If a refrigeration gas leakage occurs during
installation/servicing, be sure to ventilate fully.
If the refrigerant gas comes into contact with fire,
a poisonous gas may occur.
(4) When installing or removing an air conditioner,
do not allow air or moisture to remain in the
refrigeration cycle. Otherwise, pressure in the
refrigeration cycle may become abnormally high
so that a rupture or personal injury may be
caused.
(5) After completion of installation work, check to
make sure that there is no refrigeration gas
leakage.
If the refrigerant gas leaks into the room, coming
into contact with fire in the fan-driven heater,
space heater, etc., a poisonous gas may occur.
(6) When an air conditioning system charged with a
large volume of refrigerant is installed in a small
room, it is necessary to exercise care so that,
even when refrigerant leaks , its concentration
does not exceed the marginal level.
If the refrigerant gas leakage occurs and its
concentration exceeds the marginal level, an
oxygen starvation accident may result.
(7) Be sure to carry out installation or removal
according to the installation manual.
Improper installation may cause refrigeration
trouble, water leakage, electric shock, fire, etc.
(8) Unauthorized modifications to the air conditioner
may be dangerous. If a breakdown occurs
please call a qualified air conditioner technician
or electrician.
Improper repair’s may result in water leakage,
electric shock and fire, etc.
7-2. Refrigerant Piping Installation
7-2-1. Piping Materials and Joints Used
For the refrigerant piping installation, copper pipes
and joints are mainly used. Copper pipes and joints
suitable for the refrigerant must be chosen and
installed. Furthermore, it is necessary to use clean
copper pipes and joints whose interior surfaces are
less affected by contaminants.
(1) Copper Pipes
It is necessary to use seamless copper pipes
which are made of either copper or copper alloy
and it is desirable that the amount of residual oil
is less than 40 mg/10 m. Do not use copper
pipes having a collapsed, deformed or discolored portion (especially on the interior surface).
Otherwise, the expansion valve or capillary tube
may become blocked with contaminants.
As an air conditioner using R410A incurs
pressure higher than when using R22, it is
necessary to choose adequate materials.
Thicknesses of copper pipes used with R410A
are as shown in Table 7-2-1. Never use copper
pipes thinner than 0.8 mm even when it is
available on the market.
23
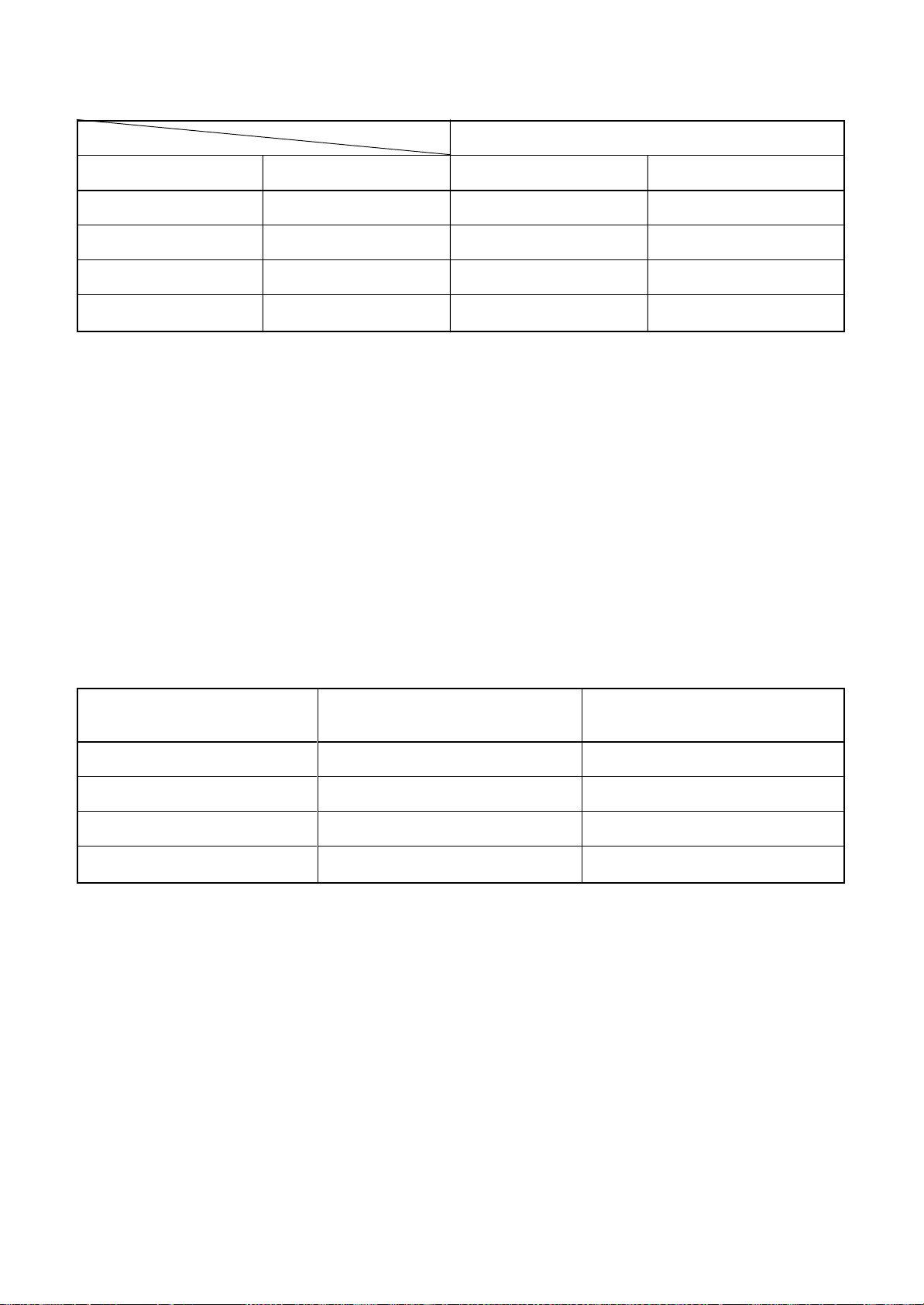
Table 7-2-1 Thicknesses of annealed copper pipes
Thickness (mm)
Nominal diameter
1/4
3/8
1/2
5/8
(2) Joints
For copper pipes, flare joints or socket joints are
used. Prior to use, be sure to remove all contaminants.
a) Flare Joints
Flare joints used to connect the copper pipes
cannot be used for pipings whose outer
diameter exceeds 20 mm. In such a case,
socket joints can be used.
Sizes of flare pipe ends, flare joint ends and
flare nuts are as shown in Tables 7-2-3 to 72-6 below .
Outer diameter (mm)
6.35
9.52
12.70
15.88
R410A R22
0.80 0.80
0.80 0.80
0.80 0.80
1.00 1.00
b) Socket Joints
Socket joints are such that they are brazed
for connections, and used mainly f or thick
pipings whose diameter is larger than 20 mm.
Thicknesses of socket joints are as shown in
Table 7-2-2.
Table 7-2-2 Minimum thicknesses of socket joints
Nominal diameter
1/4
3/8
1/2
5/8
Reference outer diameter of
copper pipe jointed (mm)
7-2-2. Processing of Piping Materials
When performing the refrigerant piping installation,
care should be taken to ensure that water or dust
does not enter the pipe interior, that no other oil
other than lubricating oils used in the installed air
conditioner is used, and that refrigerant does not
leak. When using lubricating oils in the piping
processing, use such lubricating oils whose water
content has been removed. When stored, be sure to
seal the container with an airtight cap or any other
cover.
6.35
9.52
12.70
15.88
Minimum joint thickness
(mm)
0.50
0.60
0.70
0.80
(1) Flare Processing Procedures and Precautions
a) Cutting the Pipe
By means of a pipe cutter, slowly cut the pipe
so that it is not deformed.
b) Removing Burrs and Chips
If the flared section has chips or burrs,
refrigerant leakage may occur. Carefully
remove all b urrs and clean the cut surface
before installation.
24
c) Insertion of Flare Nut
d) Flare Processing
Make certain that a clamp bar and copper
pipe have been cleaned.
By means of the clamp bar, perform the flare
processing correctly.
Use either a flare tool for R410A or conventional flare tool.
Table 7-2-3 Dimensions related to flare processing for R410A
Flare processing dimensions differ according
to the type of flare tool. When using a conventional flare tool, be sure to secure “dimen-
sion A” by using a gauge for size adjustment.
ØD
A
Fig. 7-2-1 Flare processing dimensions
Nominal
diameter
1/4
3/8
1/2
5/8
Nominal
diameter
1/4
3/8
Outer
diameter
(mm)
6.35
9.52
12.70
15.88
Thickness
(mm)
0.8
0.8
0.8
1.0
Flare tool for
R410A clutch type
0 to 0.5
0 to 0.5
0 to 0.5
0 to 0.5
Table 7-2-4 Dimensions related to flare processing for R22
Outer
diameter
(mm)
6.35
9.52
Thickness
(mm)
0.8
0.8
Flare tool for
R22 clutch type
0 to 0.5
0 to 0.5
A (mm)
Conventional flare tool
Clutch type Wing nut type
1.0 to 1.5 1.5 to 2.0
1.0 to 1.5 1.5 to 2.0
1.0 to 1.5 2.0 to 2.5
1.0 to 1.5 2.0 to 2.5
A (mm)
Conventional flare tool
Clutch type Wing nut type
0.5 to 1.0 1.0 to 1.5
0.5 to 1.0 1.0 to 1.5
1/2
5/8
Nominal
diameter
1/4
3/8
1/2
5/8
12.70
15.88
Table 7-2-5 Flare and flare nut dimensions for R410A
Outer diameter
(mm)
6.35
9.52
12.70
15,88
0.8
1.0
Thickness
(mm)
0.8
0.8
0.8
1.0
0 to 0.5
0 to 0.5
0.5 to 1.0 1.5 to 2.0
0.5 to 1.0 1.5 to 2.0
Dimension (mm)
ABCD
9.1 9.2 6.5 13
13.2 13.5 9.7 20
16.6 16.0 12.9 23
19.7 19.0 16.0 25
25
Flare nut
width (mm)
17
22
26
29

Table 7-2-6 Flare and flare nut dimensions for R22
Nominal Outer diameter Thickness
diameter (mm) (mm)
1/4 6.35 0.8
3/8 9.52 0.8
1/2 12.70 0.8
5/8 15.88 1.0
3/4 19.05 1.0
45˚to 46˚
B A
Dimension (mm)
ABCD
9.0 9.2 6.5 13
13.0 13.5 9.7 20
16.2 16.0 12.9 20
19.4 19.0 16.0 23
23.3 24.0 19.2 34
C
43˚to 45˚
Flare nut width
(mm)
17
22
24
27
36
D
Fig. 7-2-2 Relations between flare nut and flare seal surface
(2) Flare Connecting Procedures and Precautions
a) Make sure that the flare and union portions
do not have any scar or dust, etc.
b) Correctly align the processed flare surface
with the union axis.
c) Tighten the flare with designated torque by
means of a torque wrench. The tightening
torque for R410A is the same as that for
conventional R22. Incidentally, when the
torque is weak, the gas leakage may occur.
Table 7-2-7 Tightening torque of flare for R410A [Reference values]
Nominal Outer diameter Tightening torque
diameter (mm) N•m (kgf•cm)
1/4 6.35 14 to 18 (140 to 180)
When it is strong, the flare nut may crack and
may be made non-removable. When choosing
the tightening torque, comply with values
designated by manufacturers. Table 7-2-7
shows reference v alues.
NOTE:
When applying oil to the flare surface, be sure to use
oil designated by the manufacturer. If any other oil is
used, the lubricating oils may deteriorate and cause
the compressor to burn out.
Tightening torque of torque
wrenches available on the market
N•m (kgf•cm)
16 (160), 18 (180)
3/8 9.52 33 to 42 (330 to 420)
1/2 12.70 50 to 62 (500 to 620)
5/8 15.88 63 to 77 (630 to 770)
26
42 (420)
55 (550)
65 (650)

7-3. Tools
7-3-1. Required T ools
The service port diameter of packed v alve of the outdoor unit in the air conditioner using R410A is changed to
prevent mixing of other refrigerant. To reinforce the pressure-resisting strength, flare processing dimensions and
opposite side dimension of flare nut (For Ø12.7 copper pipe) of the refrigerant piping are lengthened.
The used refrigerating oil is changed, and mixing of oil may cause a trouble such as generation of sludge,
clogging of capillary, etc. Accordingly, the tools to be used are classified into the following three types.
(1) Tools e xclusive for R410A (Those which cannot be used for conventional refrigerant (R22))
(2) Tools exclusive for R410A, but can be also used for conventional refrigerant (R22)
(3) Tools commonly used for R410A and for conventional refrigerant (R22)
The table below shows the tools exclusive for R410A and their interchangeability.
Tools exclusive for R410A (The following tools for R410A are required.)
Tools whose specifications are changed for R410A and their interchangeability
No. Used tool
Flare tool
Copper pipe gauge for
adjusting projection
margin
Torque wrench
Gauge manifold
Charge hose
Vacuum pump adapter
Electronic balance for
refrigerant charging
Refrigerant cylinder
Leakage detector
Charging cylinder
Usage
Pipe flaring
Flaring by conventional
flare tool
Connection of flare nut
Evacuating, refrigerant
charge, run check, etc.
Vacuum evacuating
Refrigerant charge
Refrigerant charge
Gas leakage check
Refrigerant charge
air conditioner installation
Existence of Whether convennew equipment tional equipment
for R410A can be used
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
(Note 2)
R410A
(Note 1)
*
(Note 1)
*
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Conventional air
conditioner installation
Whether new equipment
can be used with
conventional refrigerant
¡
(Note 1)
*
X
X
¡
¡
X
¡
X
(Note 1) When flaring is carried out for R410A using the conventional flare tools, adjustment of projection
margin is necessary. For this adjustment, a copper pipe gauge , etc. are necessary.
(Note 2) Charging cylinder for R410A is being currently dev e loped.
General tools (Conventional tools can be used.)
In addition to the above exclusive tools, the following equipments which serve also for R22 are necessary
as the general tools.
(1) Vacuum pump
Use vacuum pump by
attaching vacuum pump adapter.
(2) Torque wrench
(3) Pipe cutter
(4) Reamer
(5) Pipe bender
(6) Level vial
(7) Screwdriver (+, –)
(8) Spanner or Monkey wrench
(9) Hole core drill (Ø65)
(10) Hexagon wrench
(Opposite side 4mm)
(11) Tape measure
(12) Metal saw
Also prepare the following equipments for other installation method and run check.
(1) Clamp meter
(2) Thermometer
(3) Insulation resistance tester
(4) Electroscope
27
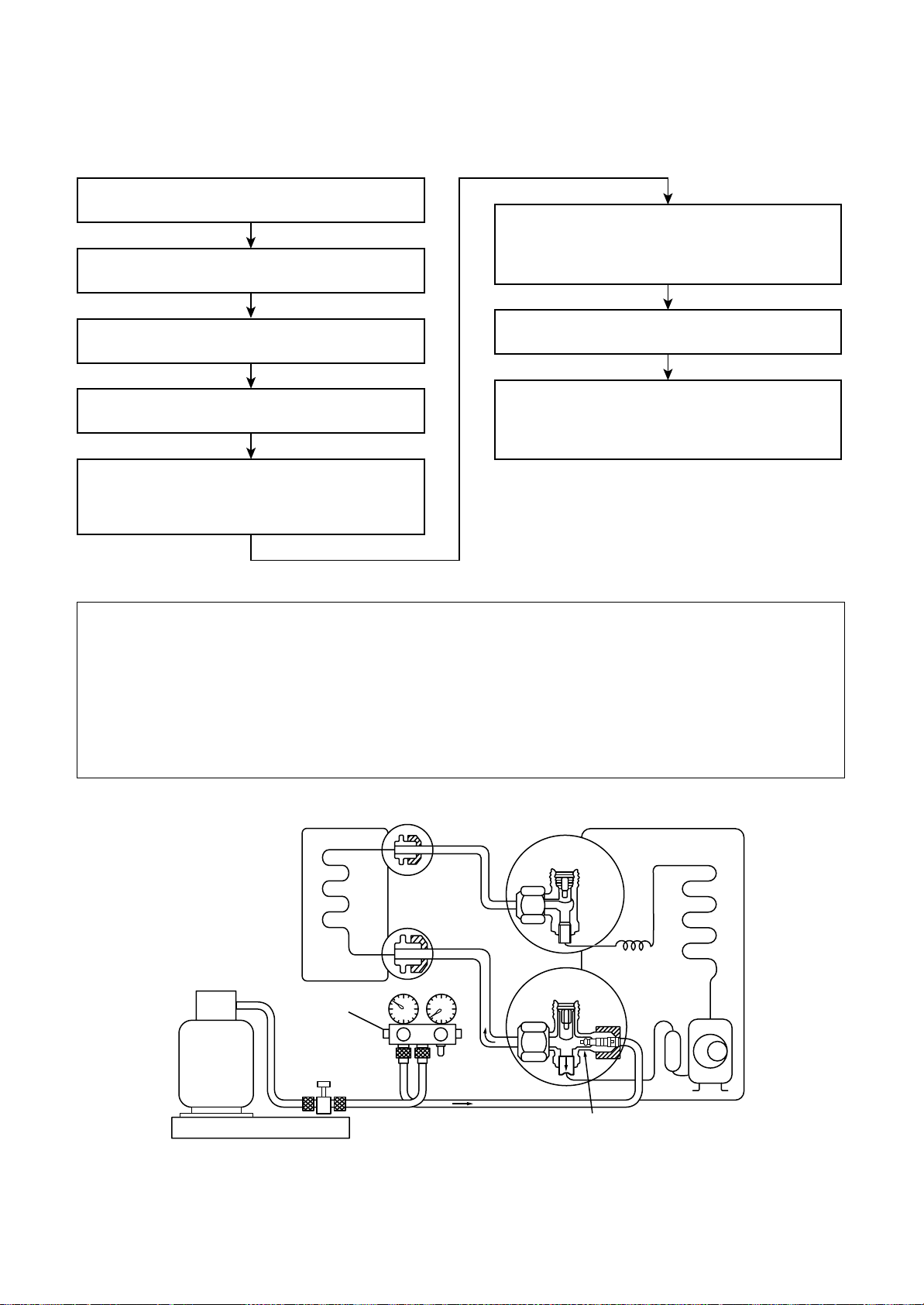
7-4. Recharging of Refrigerant
When it is necessary to recharge refrigerant, charge the specified amount of new refrigerant according to the
following steps .
Recover the refrigerant, and check no refrigerant
remains in the equipment.
Connect the charge hose to packed valve service
port at the outdoor unit’s gas side.
When the compound gauge’s pointer has indicated
–0.1 Mpa (–76 cmHg), place the handle Low in the
fully closed position, and turn off the vacuum pump’s
power switch.
Connect the charge hose of the vacuum pump
adapter.
Open fully both packed valves at liquid and gas
sides.
Place the handle of the gauge manifold Low in the
fully opened position, and turn on the vacuum pump’s
power switch. Then, evacuating the refrigerant in the
cycle.
Nev er charge refrigerant exceeding the specified amount.
If the specified amount of refrigerant cannot be charged, charge refrigerant bit by bit in COOL mode.
Do not carry out additional charging.
Keep the status as it is for 1 to 2 minutes, and ensure
that the compound gauge’s pointer does not return.
Set the refrigerant cylinder to the electronic balance,
connect the connecting hose to the cylinder and the
connecting port of the electronic balance, and charge
liquid refrigerant.
(For refrigerant charging, see the figure below.)
When additional charging is carried out if refrigerant leaks, the refrigerant composition changes in the
refrigeration cycle, that is characteristics of the air conditioner changes, refrigerant exceeding the
specified amount is charged, and working pressure in the refrigeration cycle becomes abnormally high
pressure, and may cause a rupture or personal injury.
(INDOOR unit)
Refrigerant cylinder
(With siphon pipe)
Check valve
Open/Close valve
for charging
Electronic balance for refrigerant charging
Fig. 7-4-1 Configuration of refrigerant charging
(Liquid side)
(Gas side)
28
(OUTDOOR unit)
Opened
Closed
Service port
 Loading...
Loading...