Toshiba AR-B1376, 386SX, AR-B1375 User Manual

AR-B1375/AR-B1376
Half Size All-In-One
386SX CPU CARD
User’ s Guide
Edition: 1.51
Book Number: AR-B1375/AR-B1376-05.0517


AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
Table of Contents
0. PREFACE...............................................................................................................................................................0-3
0.1 COPYRIGHT NOTICE AND DISCLAIMER............................................................................................................................ 0-3
0.2 WELCOME TO THE AR-B1375/AR-B1376 CPU BOARD ..................................................................................................... 0-3
0.3 BEFORE YOU USE THIS GUIDE.......................................................................................................................................... 0-3
0.4 RETURNING YOUR BOARD FOR SERVICE ....................................................................................................................... 0-3
0.5 TECHNICAL SUPPORT AND USER COMMENTS ............................................................................................................... 0-3
0.6 ORGANIZATION .................................................................................................................................................................... 0-4
0.7 STATIC ELECTRICITY PRECAUTIONS ............................................................................................................................... 0-4
1. OVERVIEW.............................................................................................................................................................1-1
1.1 INTRODUCTION.................................................................................................................................................................... 1-1
1.2 PACKING LIST....................................................................................................................................................................... 1-1
1.3 FEATURES ............................................................................................................................................................................ 1-2
2. SYSTEM CONTROLLER .......................................................................................................................................2-1
2.1 MICROPROCESSOR ............................................................................................................................................................ 2-1
2.2 DMA CONTROLLER.............................................................................................................................................................. 2-1
2.3 KEYBOARD CONTROLLER.................................................................................................................................................. 2-2
2.4 INTERRUPT CONTROLLER ................................................................................................................................................. 2-2
2.4.1 I/O Port Address Map..................................................................................................................................................... 2-3
2.4.2 I/O Channel Pin Assignment (Bus1) .............................................................................................................................. 2-3
2.5 REAL-TIME CLOCK AND NON-VOLATILE RAM.................................................................................................................. 2-5
2.6 TIMER .................................................................................................................................................................................... 2-5
2.7 SERIAL PORT........................................................................................................................................................................ 2-6
2.8 PARALLEL PORT .................................................................................................................................................................. 2-8
3. SETTING UP THE SYSTEM...................................................................................................................................3-1
3.1 OVERVIEW ............................................................................................................................................................................ 3-1
3.2 SYSTEM SETTING ................................................................................................................................................................ 3-2
3.2.1 Keyboard Connector ...................................................................................................................................................... 3-2
3.2.2 PC/104 Connector.......................................................................................................................................................... 3-3
3.2.3 Hard Disk (IDE) Connector (CN4).................................................................................................................................. 3-5
3.2.4 FDD Port Connector (CN5)............................................................................................................................................ 3-6
3.2.5 Parallel Port Connector (CN6) ....................................................................................................................................... 3-6
3.2.6 Serial Port....................................................................................................................................................................... 3-7
3.2.7 Reset Header (J1).......................................................................................................................................................... 3-8
3.2.8 LED Header.................................................................................................................................................................... 3-8
3.2.9 Power Connector (J3) .................................................................................................................................................... 3-9
3.2.10 External Speaker Header (J5).................................................................................................................................... 3-9
3.2.11 External Battery.......................................................................................................................................................... 3-9
3 . 2 . 12 C P U B a s e Cl o c k S e l e c t ( J P 1 ).............................................................................................................................................. 3-10
3.2.13 DRAM Configuration ................................................................................................................................................ 3-10
4. CRT/LCD FLAT PANEL DISPLAY ........................................................................................................................4-1
4.1 CONNECTING THE CRT MONITOR..................................................................................................................................... 4-1
4.1.1 VGA Setting (JP5).......................................................................................................................................................... 4-1
4.1.2 CRT Connector (CN13).................................................................................................................................................. 4-2
4.2 LCD FLAT PANEL DISPLAY ................................................................................................................................................. 4-2
4.2.1 Inverter Board Description ............................................................................................................................................. 4-3
4.2.2 LCD Connector............................................................................................................................................................... 4-3
4.3 SUPPORTED LCD PANEL .................................................................................................................................................... 4-4
5. INSTALLATION......................................................................................................................................................5-1
5.1 OVERVIEW ............................................................................................................................................................................ 5-1
5.2 UTILITY DISKETTE ............................................................................................................................................................... 5-1
5.2.1 VGA Driver..................................................................................................................................................................... 5-2
5.2.2 SSD Utility...................................................................................................................................................................... 5-3
5.3 WRITE PROTECT FUNCTION .............................................................................................................................................. 5-5
5.3.1 Hardware Write Protect.................................................................................................................................................. 5-6
5.3.2 Software Write Protect ................................................................................................................................................... 5-6
5.3.3 Enable the Software Write Protect................................................................................................................................. 5-6
5.3.4 Disable the Software Write Protect ................................................................................................................................ 5-6
5.4 WATCHDOG TIMER.............................................................................................................................................................. 5-7
5.4.1 Watchdog Timer Setting................................................................................................................................................. 5-7
5.4.2 Watchdog Timer Enabled............................................................................................................................................... 5-8
5.4.3 Watchdog Timer Trigger................................................................................................................................................. 5-8
5.4.4 Watchdog Timer Disabled.............................................................................................................................................. 5-8
6. SOLID STATE DISK...............................................................................................................................................6-1
6.1 OVERVIEW ............................................................................................................................................................................ 6-1
0-1

AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
6.2 SWITCH SETTING................................................................................................................................................................. 6-1
6.2.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................................................ 6-2
6.2.2 I/O Port Address Select (SW1-1) ................................................................................................................................... 6-2
6.2.3 SSD Firmware Address Select (SW1-2) ........................................................................................................................ 6-2
6.2.4 SSD Drive Number (SW1-3 & SW1-4)........................................................................................................................... 6-3
6.2.5 ROM Type Select (SW1-5 & SW1-6)............................................................................................................................. 6-4
6.3 JUMPER SETTING ................................................................................................................................................................ 6-5
6.4 ROM DISK INSTALLATION ................................................................................................................................................... 6-6
6.4.1 UV EPROM (27Cxxx)..................................................................................................................................................... 6-6
6.4.2 Large Page 5V FLASH Disk........................................................................................................................................... 6-7
6.4.3 Small Page 5V FLASH ROM Disk ................................................................................................................................. 6-9
6.4.4 RAM Disk ..................................................................................................................................................................... 6-10
6.4.5 Combination of ROM and RAM Disk............................................................................................................................ 6-11
7. BIOS CONSOLE ....................................................................................................................................................7-1
7.1 BIOS SETUP OVERVIEW ..................................................................................................................................................... 7-1
7.2 STANDARD CMOS SETUP................................................................................................................................................... 7-2
7.3 ADVANCED CMOS SETUP................................................................................................................................................... 7-3
7.4 ADVANCED CHIPSET SETUP.............................................................................................................................................. 7-5
7.5 PASSWORD SETTING.......................................................................................................................................................... 7-6
7.5.1 Setting Password ........................................................................................................................................................... 7-6
7.5.2 Password Checking........................................................................................................................................................ 7-6
7.6 LOAD DEFAULT SETTING.................................................................................................................................................... 7-6
7.6.1 Auto Configuration with Optimal Setting ........................................................................................................................ 7-6
7.6.2 Auto Configuration with Fail Safe Setting....................................................................................................................... 7-7
7.7 BIOS EXIT.............................................................................................................................................................................. 7-7
7.7.1 Save Settings and Exit................................................................................................................................................... 7-7
7.7.2 Exit Without Saving........................................................................................................................................................ 7-7
7.8 BIOS UPDATE ....................................................................................................................................................................... 7-7
8. SPECIFICATIONS & SSD TYPES SUPPORTED..................................................................................................8-1
8.1 SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................................................................................................................. 8-1
8.2 SSD TYPES SUPPORTED.................................................................................................................................................... 8-1
9. USING MEMORY BANKS......................................................................................................................................9-1
10. PLACEMENT & DIMENSIONS.........................................................................................................................10-1
10.1 PLACEMENT ................................................................................................................................................................... 10-1
10.2 DIMENSIONS................................................................................................................................................................... 10-2
11. PROGRAMMING RS-485 & INDEX..................................................................................................................11-1
11.1 PROGRAMMING RS-485 ................................................................................................................................................ 11-1
11.2 INDEX .............................................................................................................................................................................. 11-3
0-2

AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
0.PREFACE
0.1 COPYRIGHT NOTICE AND DISCLAIMER
September 1997
This document is copyrighted, 1997, by Acrosser Technology Co., Ltd. All rights are reserved. No part of this
manual may be reproduced, copied, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any language in
any form or by any means, such as electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, manual or other means
without prior written permission of original manufacturer.
Acrosser Technology assumes no responsibility or warranty with respect to the contents in this manual and
specifically disclaims any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Furthermore,
Acrosser Technology reserves the right to make improvements to the products described in this manual at any
times without notice. Such revisions will be posted on the Internet (WWW.ACROSSER.COM
Possession, use, or copying of the software described in this publication is authorized only pursuant to a valid
written license from Acrosser or an authorized sub licensor.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
(C) Copyright Acrosser Technology Co., Ltd., 1997. All rights Reserved.
Acrosser, ALI, AMI, PC/AT, WIN31, WIN 95, Windows NT, NEC, HITACHI, ORION, SHARP, FUJITSU, SONY, AKM,
INTEL, MITSUBISHI, NS, SGS-THOMSON, TI, TOSHIBA, AMD…are registered trademarks.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective holders.
This document was produced with Adobe Acrobat 3.01.
) as soon as possible.
0.2 WELCOME TO THE AR-B1375/AR-B1376 CPU BOARD
This guide introduces the Acrosser AR-B1375/AR-B1376 CPU board.
The information provided in this manual describes this card’s functions, and features. It also helps you start, set
up and operate your AR-B1375/AR-B1376. General system information can also be found in this publication.
0.3 BEFORE YOU USE THIS GUIDE
Please refer to the Chapter 3, “Setting Up the System” in this guide, if you have not already installed ARB1375/AR-B1376,. Check the packing list before you install and make sure the accessories in the package.
The AR-B1375 & AR-B1376 diskette provides the newest information regarding the CPU card. Please refer to
the README.DOC file of the enclosed utility diskette. It contains the modification and hardware & software
information, and it has updated to product functions that may not be mentioned here..
0.4 RETURNING YOUR BOARD FOR SERVICE
If your board requires any services, contact the distributor or sales representative from whom you purchased the
product for service information. If you need to ship your board to us for service, be sure it is packed in a protective
carton. We recommend that you keep the original shipping container for this purpose.
You can help assure efficient servicing for your product by following these guidelines:
1. Include your name, address, telephone and facsimile number where you may be reached during the day.
2. A description of the system configuration and/or software at the time is malfunction.
3. A brief description of problem occurred.
0.5 TECHNICAL SUPPORT AND USER COMMENTS
User’s comments are always welcome as they assist us in improving the quality of our products and the
readability of our publications. They create a very important part of the input used for product enhancement and
revision.
We may use and distribute any of the information you provide in any way appropriate without incurring any
obligation. You may, of course, continue to use the information you provide.
If you have any suggestions for improving particular sections or if you find any errors, please send your
comments to Acrosser Technology Co., Ltd. or your local sales representative and indicate the manual title and
book number.
Internet electronic mail to: webmaster@acrosser.com
0-3

AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
0.6 ORGANIZATION
This information for users covers the following topics (see the Table of Contents for a detailed listing):
z Chapter 1, “Overview,” provides an overview of the system features and packing list.
z Chapter 2, “System Controller,” describes the major structure.
z Chapter 3, “Setting Up the System,” describes how to adjust the jumper, and the connectors setting.
z Chapter 4, “CRT/LCD Flat Panel Display”, describes the configuration and installation procedure using
LCD and CRT display.
z Chapter 5, “Installation,” describes the utility diskette using, solid-state disk’s writing protect function, and
the watchdog timer.
z Chapter 6, “Solid State Disk,” describes the various type SSD’s installation steps.
z Chapter 7, “BIOS Console,” providing the BIOS options setting.
z Chapter 8, Specifications & SSD Types Supported
z Chapter 9, Using Memory Banks
z Chapter 10, Placement & Dimensions
z Chapter 11, Programming RS-485 & Index
0.7 STATIC ELECTRICITY PRECAUTIONS
Before removing the board from its anti-static bag, read this section about static electricity precautions.
Static electricity is a constant danger to computer systems. The charge that can build up in your body may be
more than sufficient to damage integrated circuits on any PC board. It is, therefore, important to observe basic
precautions whenever you use or handle computer components. Although areas with humid climates are much
less prone to static build-up, it is always best to safeguard against accidents may result in expensive repairs. The
following measures should generally be sufficient to protect your equipment from static discharge:
• Touch a grounded metal object to discharge the static electricity in your body (or ideally, wear a grounded
wrist strap).
• When unpacking and handling the board or other system component, place all materials on an antic static
surface.
• Be careful not to touch the components on the board, especially the “golden finger” connectors on the bottom
of every board.
0-4

AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
1. OVERVIEW
This chapter provides an overview of your system features and capabilities. The following topics are covered:
z Introduction
z Packing List
z Features
1.1 INTRODUCTION
The AR-B1375 and AR-B1376 are new generation half size, 386 ISA card. This card offers much greater performance
than the older cards such as support for 32MB’s of DRAM using two 72-pin SIMMs, one RS-232C/485 and one RS-232C
port and 3/1.5MB solid state disk capacity for ROM, FLASH and SRAM.
The unit also comes with a programmable watchdog timer and other typical interfaces. These 386 CPU cards are excellent
for embedded systems, MMI’s, workstations, medical applications or POS/POI systems. As well, an RS-232C/485 port
provided remote control. RS-485 has not been offered until recently on 386 cards.
Especially the AR-B1376 with on board VGA, offers the most exciting possibilities yet to the industry. The on board
VGA/LCD controller brings about a whole new dimension of industrial computing. No longer do you have to worry about
adding an extra card to your system. Negating the need of a separate VGA card saves space. The VGA/LCD unit comes
with 1MB of V-RAM on board and uses the C&T 65545 Chipset, to support a wide range of LCD Panels.
1.2 PACKING LIST
The accessories are included with the system. Before you begin installing your AR-B1375 or AR-B1376 board,
take a moment to make sure that the following items have been included inside the AR-B1375 or AR-B1376
package.
z The quick setup manual
z 1 AR-B1375 or AR-B1376 all-in-one single CPU board
z 1 Hard disk drive interface cable
z 1 Floppy disk drive interface cable
z 1 Parallel port interface cable
z 1 RS-232C interface cable
z 2 Software utility CD (AR-B1375 has not the VGA function, and only encloses one SSD utility
diskette).
1-1

AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
1.3 FEATURES
The system provides a number of special features that enhance its reliability, ensure its availability, and improve its
expansion capabilities, as well as its hardware structure.
z 80386SX-33/40 MHz CPU
z ISA and PC/104 extension bus
z Up to 32MB DRAM system
z On-board CRT and LCD panel display (AR-B1375 doesn’t provide this function)
z Supports IDE hard disk drives
z Supports floppy disk drives
z Supports 1 bi-directional parallel port
z Supports 2 serial ports (RS-232C and RS-485)
z PC/AT compatible keyboard
z Up to 3MB solid state disk
z Programmable watchdog timer
z Flash BIOS
z Built-in status LEDs indicator
z Signal 5V power requirement
z Multi-layer PCB for noise reduction
z Dimensions: 185mmX122mm
1-2
AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
2. SYSTEM CONTROLLER
This chapter describes the major structure of the AR-B1375 and AR-B1376 CPU board. The following topics are
covered:
z Microprocessor
z DMA Controller
z Keyboard Controller
z Interrupt Controller
z Real-Time Clock and Non-Volatile RAM
z Timer
z Serial Port
z Parallel Port
2.1 MICROPROCESSOR
The AR-B1375 and AR-B1376 use the ALI M6117 CPU, it is designed to perform like Intel’s 386SX system with
deep green features.
The 386SX core is the same as M1386SX of Acer Labs. Inc. and 100% object code c ompatible with the I ntel
386S X microprocessor. System manufacturers can provide 386 CPU based systems optimized for both cost and
size. Instruction pipelining and high bus bandwidth ensure short average instruction execution times and high
system throughput. Furthermore, it can keep the state internally from charge leakage while external clock to the
core is stopped without storing the data in registers. The power consumption here is almost zero when clock stops.
The internal structure of this core is 32-bit data and address bus with very low supply current. Real mode as well
as Protected mode are available and can run MS-DOS, MS-Windows, OS/2 and UNIX.
2.2 DMA CONTROLLER
The equivalent of two 8237A DMA controllers are implemented in the AR-B1375/AR-B1376 board. Each controller
is a four-channel DMA device that will generate the memory addresses and control signals necessary to transfer
information directly between a peripheral device and memory. This allows high speeding information transfer with less
CPU intervention. The two DMA controllers are internally cascaded to provide four DMA channels for transfers to
8-bit peripherals (DMA1) and three channels for transfers to 16-bit peripherals (DMA2). DMA2 channel 0 provides
the cascade interconnection between the two DMA devices, thereby maintaining IBM PC/AT compatibility.
Following is the system information of DMA channels:
DMA Controller 1 DMA Controller 2
Channel 0: Spare Channel 4: Cascade for controller 1
Channel 1: IBM SDLC Channel 5: Spare
Channel 2: Diskette adapter Channel 6: Spare
Channel 3: Spare Channel 7: Spare
Table 2-1 DMA Channel Controller
2-1

AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
2
2.3 KEYBOARD CONTROLLER
The 8042 processor is programmed to support the keyboard serial interface. The keyboard controller receives
serial data from the keyboard, checks its parity, translates scan codes, and presents it to the system as a byte data
in its output buffer. The controller can interrupt the system when data is placed in its output buffer, or wait for the
system to poll its status register to determine when data is available.
Data can be written to the keyboard by writing data to the output buffer of the keyboard controller.
Each byte of data is sent to the keyboard controller in series with an odd parity bit automatically inserted. The
keyboard controller is required to acknowledge all data transmissions. Therefore, another byte of data will not be
sent to keyboard controller until acknowledgment is received for the previous byte sent. The “output buffer full”
interruption may be used for both send and receive routines.
2.4 INTERRUPT CONTROLLER
The equivalent of two 8259 Programmable Interrupt Controllers (PIC) are included on the AR-B1375/AR-B1376
board. They accept requests from peripherals, resolve priorities on pending interrupts in service, issue interrupt
requests to the CPU, and provide vectors which are used as acceptance indices by the CPU to determine which
interrupt service routine to execute.
Following is the system information of interrupt levels:
InInterrupt Level
Description
NMI
CTRL1
IRQ 0
IRQ 1
Parity check
CTRL2
System timer interrupt from timer 8254
Keyboard output buffer full
IRQ 2
IRQ8 : Real time clock
IRQ9 : Rerouting to INT 0Ah from hardware IRQ
IRQ10 : Spare
IRQ11 : Spare
IRQ12 : Spare
IRQ13 : Math. coprocessor
IRQ14 : Hard disk adapter
IRQ15 : Reserved for watchdog
IRQ 3
IRQ 4
IRQ 5
IRQ 6
IRQ 7
Serial port 2
Serial port 1
Parallel port 2
Floppy disk adapter
Parallel port 1
Figure 2-1 Interrupt Controller
2-2
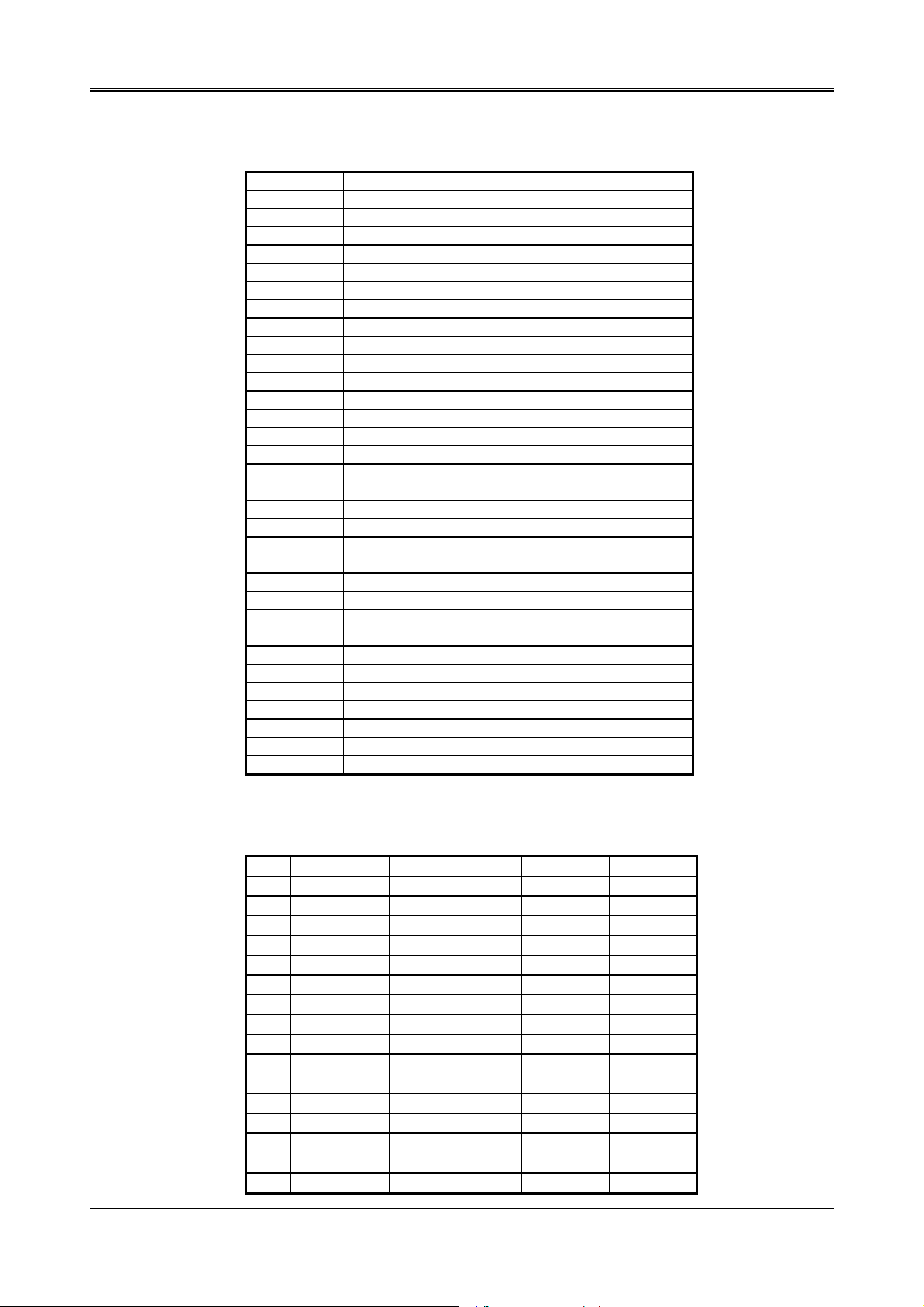
2.4.1 I/O Port Address Map
Hex Range Device
000-01F DMA controller 1
020-021 Interrupt controller 1
022-023 ALI M6117
040-04F Timer 1
050-05F Timer 2
060-06F 8042 keyboard/controller
070-071 Real-time clock (RTC), non-maskable interrupt (NMI)
080-09F DMA page registers
0A0-0A1 Interrupt controller 2
0C0-0DF DMA controller 2
0F0 Clear Math Co-processor
0F1 Reset Math Co-processor
0F8-0FF Math Co-processor
170-178 Fixed disk 1
1F0-1F8 Fixed disk 0
201 Game port
208-20A EMS register 0
218-21A EMS register 1
278-27F Parallel printer port 2 (LPT 2)
2E8-2EF Serial port 4 (COM 4)
2F8-2FF Serial port 2 (COM 2)
300-31F Prototype card/streaming type adapter
320-33F LAN adapter
378-37F Parallel printer port 1 (LPT 1)
380-38F SDLC, bisynchronous
3A0-3AF Bisynchronous
3B0-3BF Monochrome display and printer port 3 (LPT 3)
3C0-3CF EGA/VGA adapter
3D0-3DF Color/graphics monitor adapter
3E8-3EF Serial port 3 (COM 3)
3F0-3F7 Diskette controller
3F8-3FF Serial port 1 (COM 1)
Table 2-2 I/O Port Address Map
AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
2.4.2 I/O Channel Pin Assignment (Bus 1)
I/O Pin Signal Name Input/Output I/O Pin Signal Name Input/Output
A1 -IOCHCK Input B1 GND Ground
A2 SD7 Input/Output B2 RSTDRV Output
A3 SD6 Input/Output B3 +5V Power
A4 SD5 Input/Output B4 IRQ9 Input
A5 SD4 Input/Output B5 -5V Power
A6 SD3 Input/Output B6 DRQ2 Input
A7 SD2 Input/Output B7 -12V Power
A8 SD1 Input/Output B8 -ZWS Input
A9 SD0 Input/Output B9 +12V Power
A10 IOCHRDY Input B10 GND Ground
A11 AEN Output B11 -SMEMW Output
A12 SA19 Input/Output B12 -SMEMR Output
A13 SA18 Input/Output B13 -IOW Input/Output
A14 SA17 Input/Output B14 -IOR Input/Output
A15 SA16 Input/Output B15 -DACK3 Output
A16 SA15 Input/Output B16 DRQ3 Input
2-3
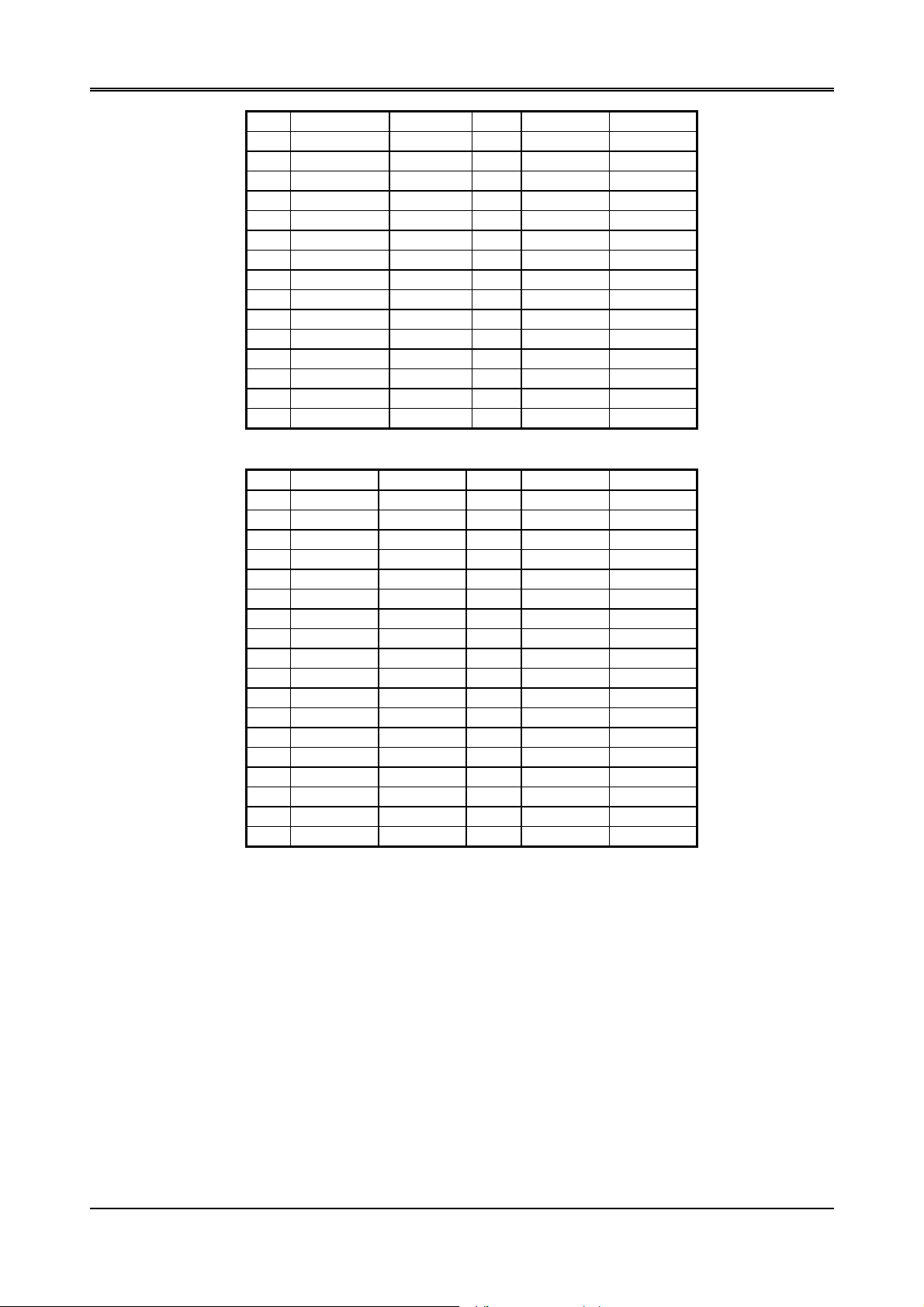
AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
I/O Pin Signal Name Input/Output I/O Pin Signal Name Input/Output
A17 SA14 Input/Output B17 -DACK1 Output
A18 SA13 Input/Output B18 DRQ1 Input
A19 SA12 Input/Output B19 -REFRESH Input/Output
A20 SA11 Input/Output B20 BUSCLK Output
A21 SA10 Input/Output B21 IRQ7 Input
A22 SA9 Input/Output B22 IRQ6 Input
A23 SA8 Input/Output B23 IRQ5 Input
A24 SA7 Input/Output B24 IRQ4 Input
A25 SA6 Input/Output B25 IRQ3 Input
A26 SA5 Input/Output B26 -DACK2 Output
A27 SA4 Input/Output B27 TC Output
A28 SA3 Input/Output B28 BALE Output
A29 SA2 Input/Output B29 +5V Power
A30 SA1 Input/Output B30 OSC Output
A31 SA0 Input/Output B31 GND Ground
Table 2-3 I/O Channel Pin Assignments
I/O Pin Signal Name Input/Output I/O Pin Signal Name Input/Output
C1 -SBHE Input/Output D1 -MEMCS16 Input
C2 LA23 Input/Output D2 -IOCS16 Input
C3 LA22 Input/Output D3 IRQ10 Input
C4 LA21 Input/Output D4 IRQ11 Input
C5 LA20 Input/Output D5 IRQ12 Input
C6 LA19 Input/Output D6 IRQ15 Input
C7 LA18 Input/Output D7 IRQ14 Input
C8 LA17 Input/Output D8 -DACK0 Output
C9 -MRD16 Input/Output D9 DRQ0 Input
C10 -MWR16 Input/Output D10 -DACK5 Output
C11 SD8 Input/Output D11 DRQ5 Input
C12 SD9 Input/Output D12 -DACK6 Output
C13 SD10 Input/Output D13 DRQ6 Input
C14 SD11 Input/Output D14 -DACK7 Output
C15 SD12 Input/Output D15 DRQ7 Input
C16 SD13 Input/Output D16 +5V Power
C17 SD14 Input/Output D17 -MASTER Input
C18 SD15 Input/Output D18 GND Ground
Table 2-4 I/O Channel Pin Assignments
2-4
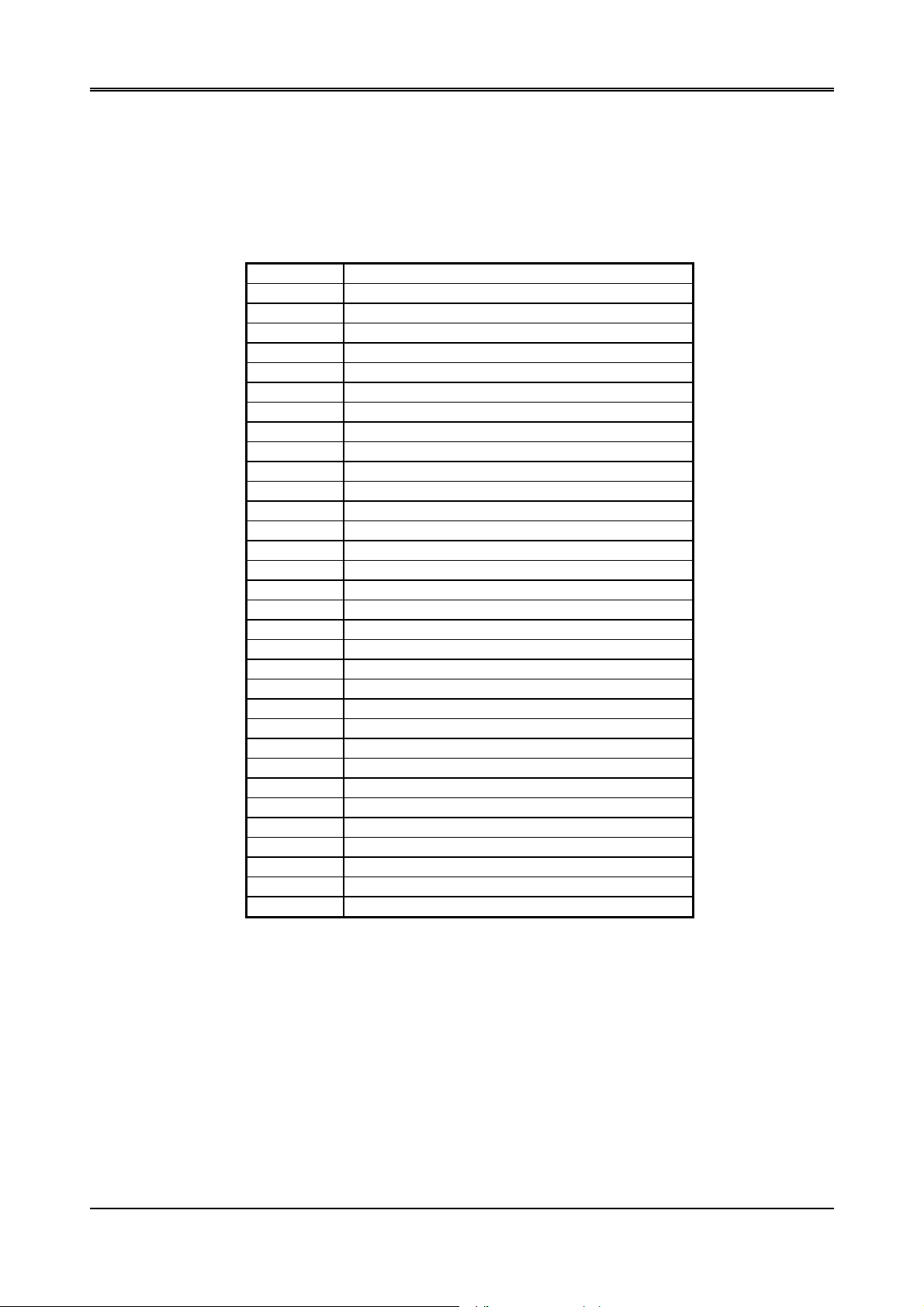
AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
2.5 REAL-TIME CLOCK AND NON-VOLATILE RAM
The AR-B1375/AR-B1376 contains a real-time clock compartment that maintains the date and time in addition to
storing configuration information about the computer system. It contains 14 bytes of clock and control registers
and 114 bytes of general purpose RAM. Because of the use of CMOS technology, it consumes very little power
and can be maintained for long period of time using an internal Lithium battery. The contents of each byte in the
CMOS RAM are listed as follows:
Address Description
00 Seconds
01 Second alarm
02 Minutes
03 Minute alarm
04 Hours
05 Hour alarm
06 Day of week
07 Date of month
08 Month
09 Year
0A Status register A
0B Status register B
0C Status register C
0D Status register D
0E Diagnostic status byte
0F Shutdown status byte
10 Diskette drive type byte, drive A and B
11 Fixed disk type byte, drive C
12 Fixed disk type byte, drive D
13 Reserved
14 Equipment byte
15 Low base memory byte
16 High base memory byte
17 Low expansion memory byte
18 High expansion memory byte
19-2D Reserved
2E-2F 2-byte CMOS checksum
30 Low actual expansion memory byte
31 High actual expansion memory byte
32 Date century byte
33 Information flags (set during power on)
34-7F Reserved for system BIOS
Table 2-5 Real-Time Clock & Non-Volatile RAM
2.6 TIMER
The AR-B1375/AR-B1376 provides three programmable timers, each with a timing frequency of 1.19 MHz.
Timer 0 The output of this timer is tied to interrupt request 0. (IRQ 0)
Timer 1 This timer is used to trigger memory refresh cycles.
Timer 2 This timer provides the speaker tone.
Application programs can load different counts into this timer to generate various sound frequencies.
2-5
AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
2.7 SERIAL PORT
The ACEs (Asynchronous Communication Elements ACE1 to ACE4) are used to convert parallel data to a serial
format on the transmit side and convert serial data to parallel on the receiver side. The serial format, in order of
transmission and reception, is a start bit, followed by five to eight data bits, a parity bit (if programmed) and one,
one and half (five-bit format only) or two stop bits. The ACEs are capable of handling divisors of 1 to 65535, and
produce a 16x clock for driving the internal transmitter logic.
Provisions are also included to use this 16x clock to drive the receiver logic. Also included in the ACE a completed
MODEM control capability, and a processor interrupt system that may be software tailored to the computing time
required handle the communications link.
The following table is summary of each ACE accessible register
DLAB Port Address Register
Receiver buffer (read) 0 base + 0
Transmitter holding register (write)
0 base + 1 Interrupt enable
X base + 2 Interrupt identification (read only)
X base + 3 Line control
X base + 4 MODEM control
X base + 5 Line status
X base + 6 MODEM status
X base + 7 Scratched register
1 base + 0 Divisor latch (least significant byte)
1 base + 1 Divisor latch (most significant byte)
Table 2-6 ACE Accessible Registers
(1) Receiver Buffer Register (RBR)
Bit 0-7: Received data byte (Read Only)
(2) Transmitter Holding Register (THR)
Bit 0-7: Transmitter holding data byte (Write Only)
(3) Interrupt Enable Register (IER)
Bit 0: Enable Received Data Available Interrupt (ERBFI)
Bit 1: Enable Transmitter Holding Empty Interrupt (ETBEI)
Bit 2: Enable Receiver Line Status Interrupt (ELSI)
Bit 3: Enable MODEM Status Interrupt (EDSSI)
Bit 4: Must be 0
Bit 5: Must be 0
Bit 6: Must be 0
Bit 7: Must be 0
(4) Interrupt Identification Register (IIR)
Bit 0: “0” if Interrupt Pending
Bit 1: Interrupt ID Bit 0
Bit 2: Interrupt ID Bit 1
Bit 3: Must be 0
Bit 4: Must be 0
Bit 5: Must be 0
Bit 6: Must be 0
Bit 7: Must be 0
2-6

(5) Line Control Register (LCR)
Bit 0: Word Length Select Bit 0 (WLS0)
Bit 1: Word Length Select Bit 1 (WLS1)
WLS1 WLS0 Word Length
0 0 5 Bits
0 1 6 Bits
1 0 7 Bits
1 1 8 Bits
Bit 2: Number of Stop Bit (STB)
Bit 3: Parity Enable (PEN)
Bit 4: Even Parity Select (EPS)
Bit 5: Stick Parity
Bit 6: Set Break
Bit 7: Divisor Latch Access Bit (DLAB)
(6) MODEM Control Register (MCR)
Bit 0: Data Terminal Ready (DTR)
Bit 1: Request to Send (RTS)
Bit 2: Out 1 (OUT 1)
Bit 3: Out 2 (OUT 2)
Bit 4: Loop
Bit 5: Must be 0
Bit 6: Must be 0
Bit 7: Must be 0
(7) Line Status Register (LSR)
Bit 0: Data Ready (DR)
Bit 1: Overrun Error (OR)
Bit 2: Parity Error (PE)
Bit 3: Framing Error (FE)
Bit 4: Break Interrupt (BI)
Bit 5: Transmitter Holding Register Empty (THRE)
Bit 6: Transmitter Shift Register Empty (TSRE)
Bit 7: Must be 0
(8) MODEM Status Register (MSR)
Bit 0: Delta Clear to Send (DCTS)
Bit 1: Delta Data Set Ready (DDSR)
Bit 2: Training Edge Ring Indicator (TERI)
Bit 3: Delta Receive Line Signal Detect (DSLSD)
Bit 4: Clear to Send (CTS)
Bit 5: Data Set Ready (DSR)
Bit 6: Ring Indicator (RI)
Bit 7: Received Line Signal Detect (RSLD)
AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
2-7
AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
(9) Divisor Latch (LS, MS)
LS MS
Bit 0: Bit 0 Bit 8
Bit 1: Bit 1 Bit 9
Bit 2: Bit 2 Bit 10
Bit 3: Bit 3 Bit 11
Bit 4: Bit 4 Bit 12
Bit 5: Bit 5 Bit 13
Bit 6: Bit 6 Bit 14
Bit 7: Bit 7 Bit 15
Desired
Baud Rate
50 2304 --75 1536 ---
110 1047 0.026
134.5 857 0.058
150 768 --300 384 --600 192 ---
1200 96 --1800 64 --2000 58 0.69
2400 48 --3600 32 --4800 24 --7200 16 ---
9600 12 --14400 8 --19200 6 --28800 4 --38400 3 --57600 2 ---
Table 2-7 Serial Port Divisor Latch
Divisor Used to
Generate 16x Clock
Present Error Difference
Between Desired and Actual
2.8 PARALLEL PORT
(1) Register Address
Port Address Read/Write Register
base + 0 Write Output data
base + 0 Read Input data
base + 1 Read Printer status buffer
base + 2 Write Printer control latch
Table 2-8 Registers’ Address
(2) Printer Interface Logic
The parallel portion of the SMC37C669 makes the attachment of various devices that accept eight bits of parallel
data at standard TTL level.
(3) Data Swapper
The system microprocessor can read the contents of the printer’s Data Latch through the Data Swapper by reading
the Data Swapper address.
2-8
AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
(4) Printer Status Buffer
The system microprocessor can read the printer status by reading the address of the Printer Status Buffer. The bit
definitions are described as follows:
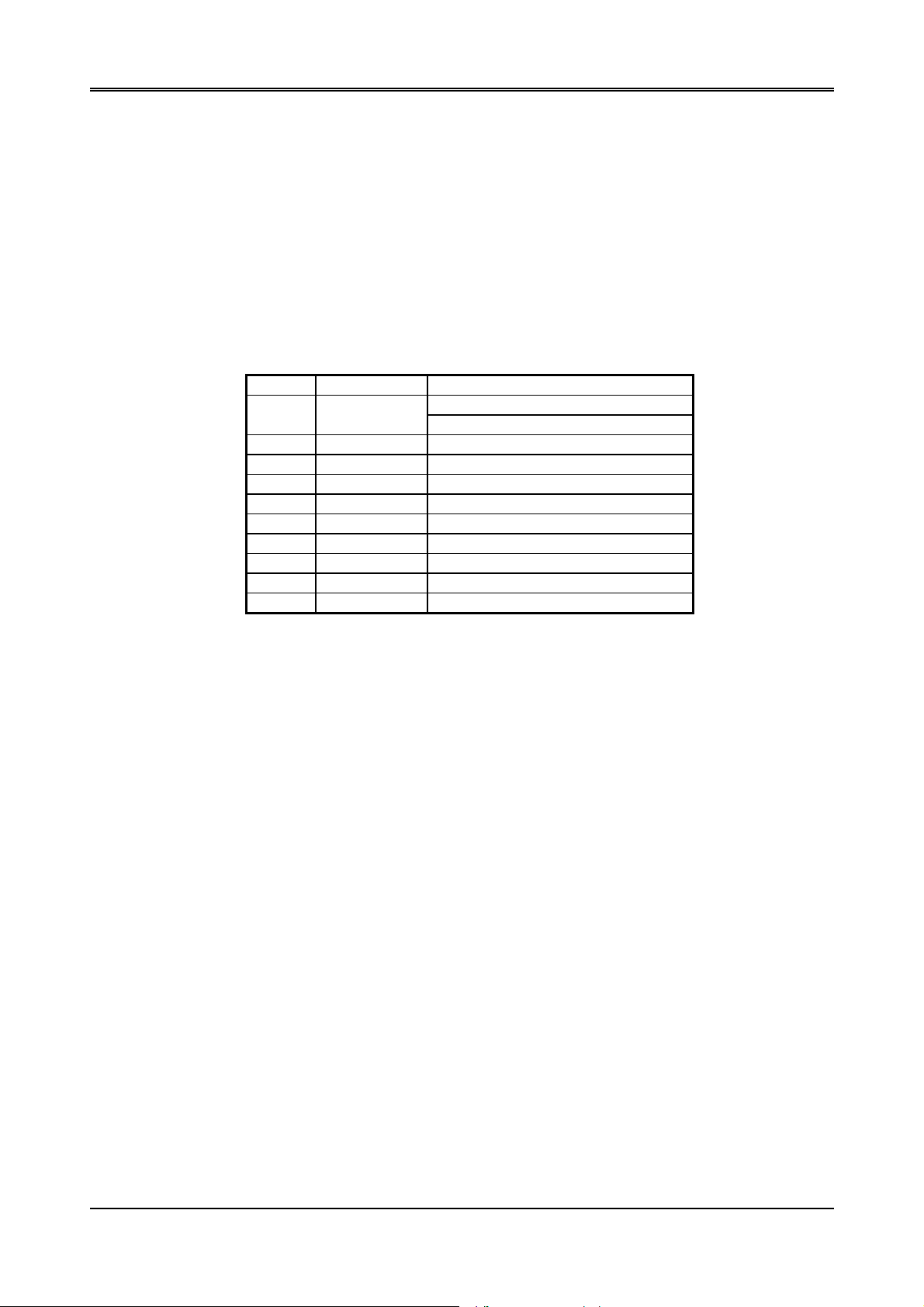
12345670
XXX
-ERROR
SLCT
PE
-ACK
-BUSY
Figure 2-2 Printer Status Buffer
NOTE: X presents not used.
Bit 7: This signal may become active during data entry, when the printer is off-line during printing, or when the
print head is changing position or in an error state. When Bit 7 is active, the printer is busy and cannot
accept data.
Bit 6: This bit represents the current state of the printer’s ACK signal. A0 means the printer has received the
character and is ready to accept another. Normally, this signal will be active for approximately 5
microseconds before receiving a BUSY message stops.
Bit 5: A1 means the printer has detected the end of the paper.
Bit 4: A1 means the printer is selected.
Bit 3: A0 means the printer has encountered an error condition.
(5) Printer Control Latch & Printer Control Swapper
The system microprocessor can read the contents of the printer control latch by reading the address of printer
control swapper. Bit definitions are as follows:
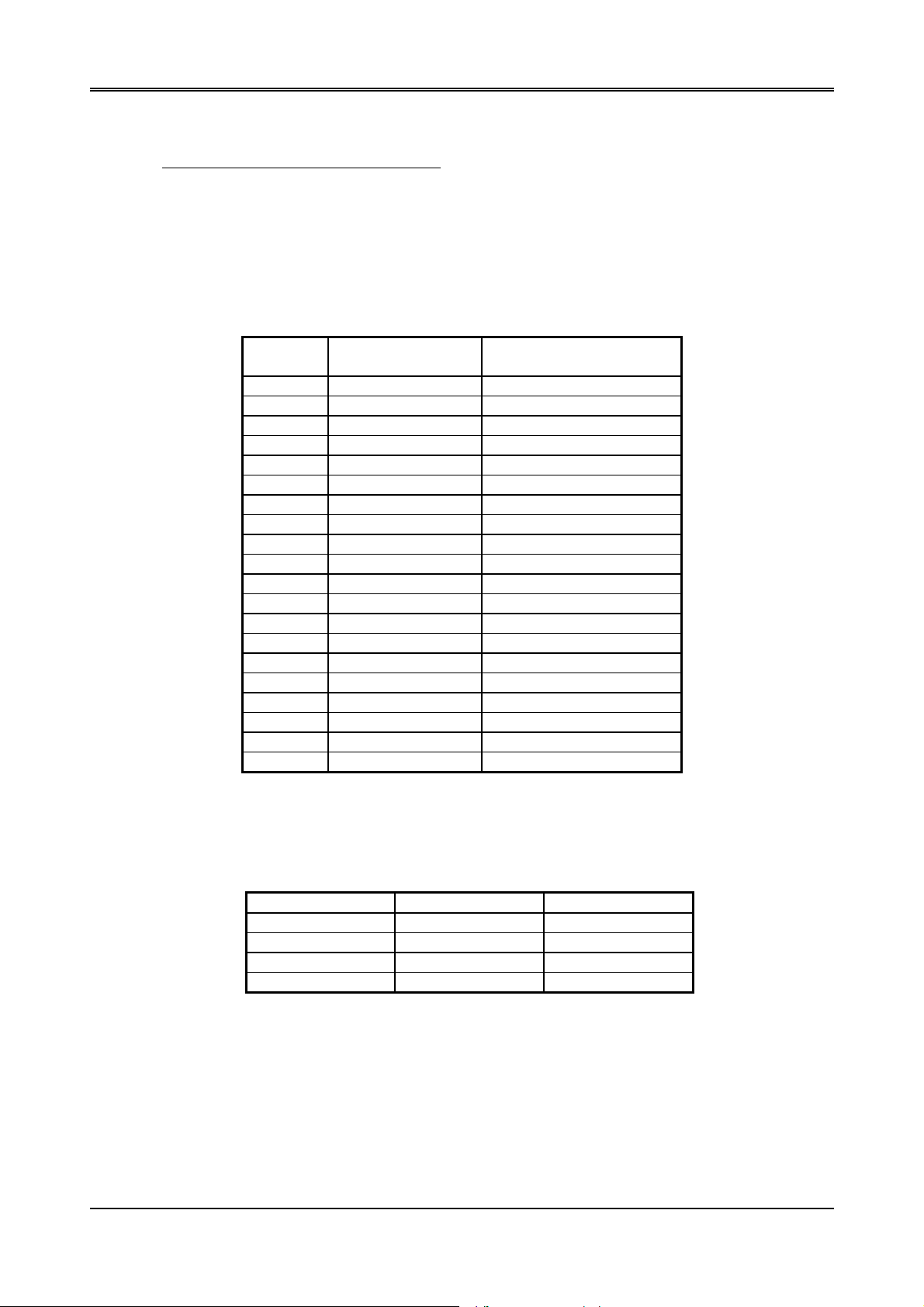
XX
12345670
STROBE
AUTO FD XT
INIT
SLDC IN
IRQ ENABLE
DIR(write only)
Figure 2-3 Bit’s Definition
NOTE: X presents not used.
Bit 5: Direction control bit. When logic 1, the output buffers in the parallel port are disabled allowing data driven
from external sources to be read; when logic 0, they work as a printer port. This bit is write only.
Bit 4: A1 in this position allows an interrupt to occur when ACK changes from low state to high state.
Bit 3: A1 in this bit position selects the printer.
Bit 2: A0 starts the printer (50 microseconds pulse, minimum).
Bit 1: A1 causes the printer to line-feed after a line is printed.
Bit 0: A0.5 microsecond minimum highly active pulse clocks data into the printer. Valid data must be present for
a minimum of 0.5 microseconds before and after the strobe pulse.
2-9

AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
3. SETTING UP THE SYSTEM
This section describes pin assignments for system’s external connectors and the jumpers setting.
z Overview
z System Setting
3.1 OVERVIEW
The AR-B1375 and AR-B1376 are all-in-one half size, Pentium single CPU board. This section provides
hardware’s jumpers setting, the connectors’ locations, and the pin assignment.
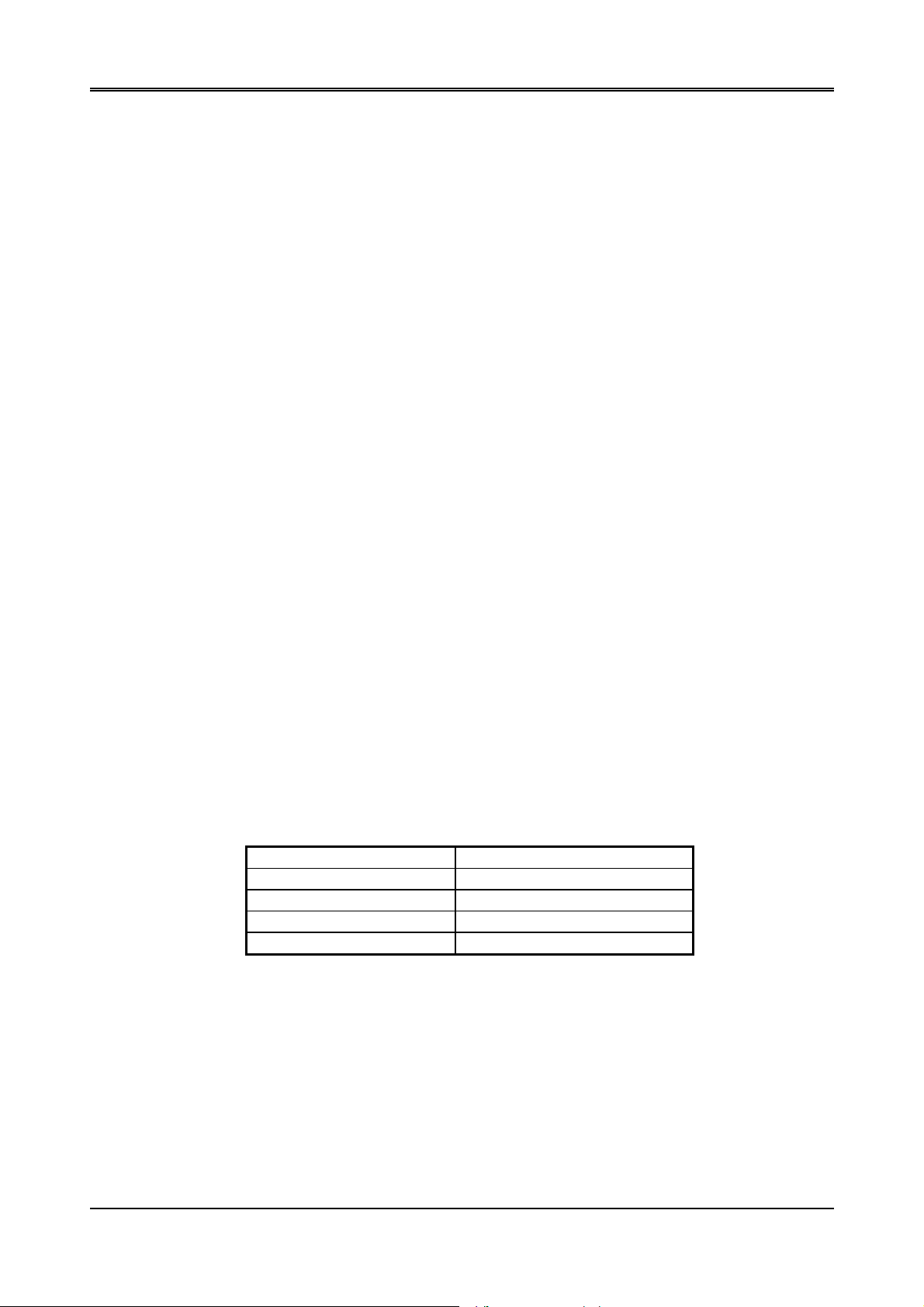
CAUTION: The CPU board doesn’t support the type DRAM SIMM of two-sided, it only supports single side DRAM
SIMM.
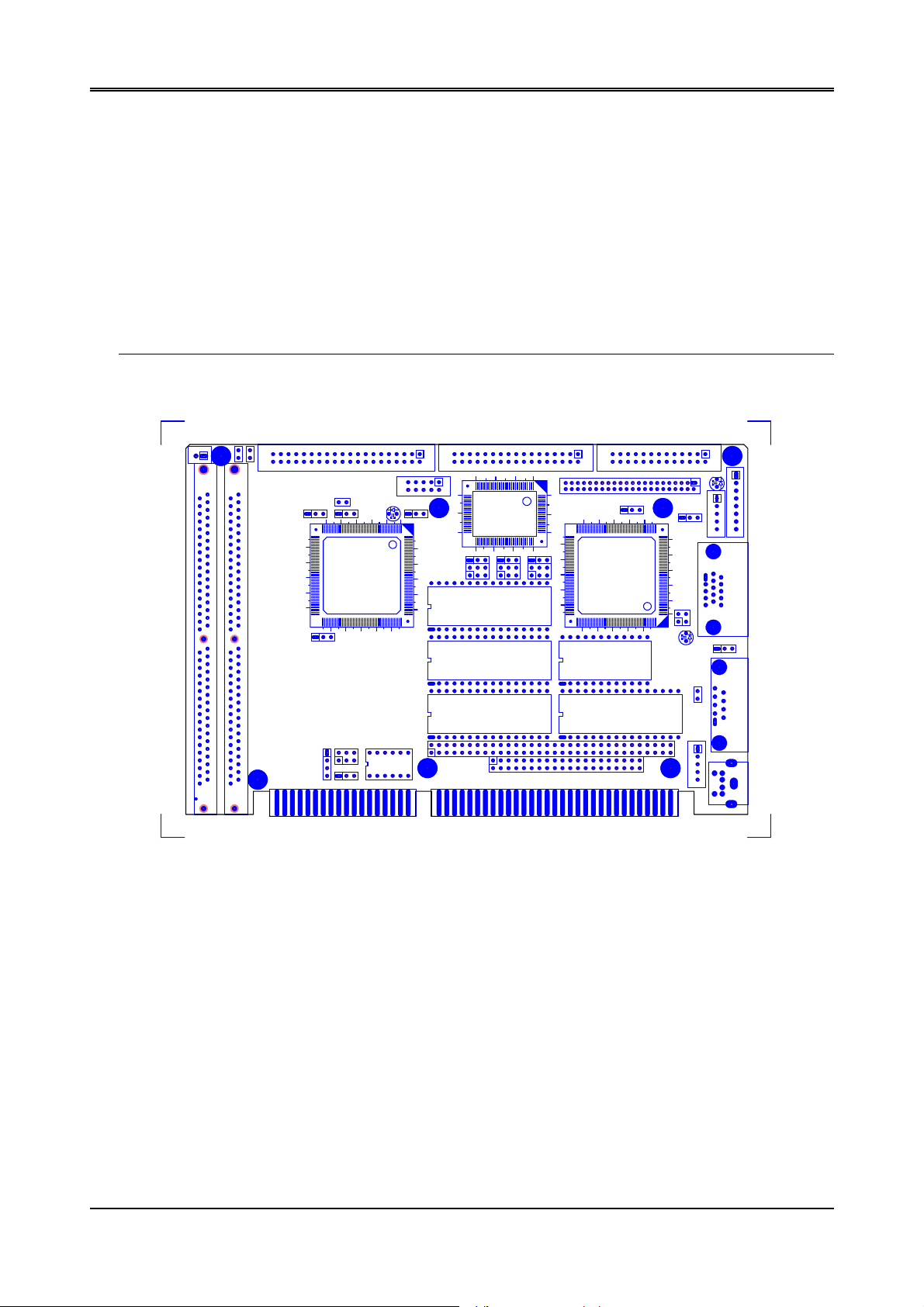
J11
1
H9
J8J1
S
S
I
I
M
M
M
M
2
1
H11H10
BUS2
1
CN4
CN7
JP7
JP4
11
J9
LED2
J6
1
U3
4
0
1
5
0
1
1
JP3
JP1
SW1
CN2
J5
JP2
2
1
1
1
1
1
3
P2
P1
P5
P3
P4
H5
P6
0
5
1
ABC ABC ABC
1
2
M1
3
U31
U32
U33
H8
CN1
BUS1
CN5
1
0
0
1
CN8
U12
8
1
5
11
22
33
105
M3
M2
MEM1
MEM2
MEM3
CN6
H4
1
2
H6
1
LED1
CN9
J2
1
JP6
4
0
1
J3
U34
DB1
1
DB2
U10
U11
2
1
1
LED3
JP5
J7
J10
J4
C
N
1
H7
CN3
Figure 3-1 AR-B1376 Jumpers & Connectors Placement
3-1
AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
3.2 SYSTEM SETTING
Jumper pins allow you to set specific system parameters. Set them by changing the pin location of jumper blocks.
(A jumper block is a small plastic-encased conductor [shorting plug] that slips over the pins.) To change a jumper
setting, remove the jumper from its current location with your fingers or small needle-nosed pliers. Place the
jumper over the two pins designated for the desired setting. Press the jumper evenly onto the pins. Be careful not
to bend the pins.
We will show the locations of the AR-B1375 and AR-B1376 jumper pins, and the factory-default setting.
CAUTION: Do not touch any electronic component unless you are safely grounded. Wear a grounded wrist strap
or touch an exposed metal part of the system unit chassis. The static discharges from your fingers can
permanently damage electronic components.
3.2.1 Keyboard Connector
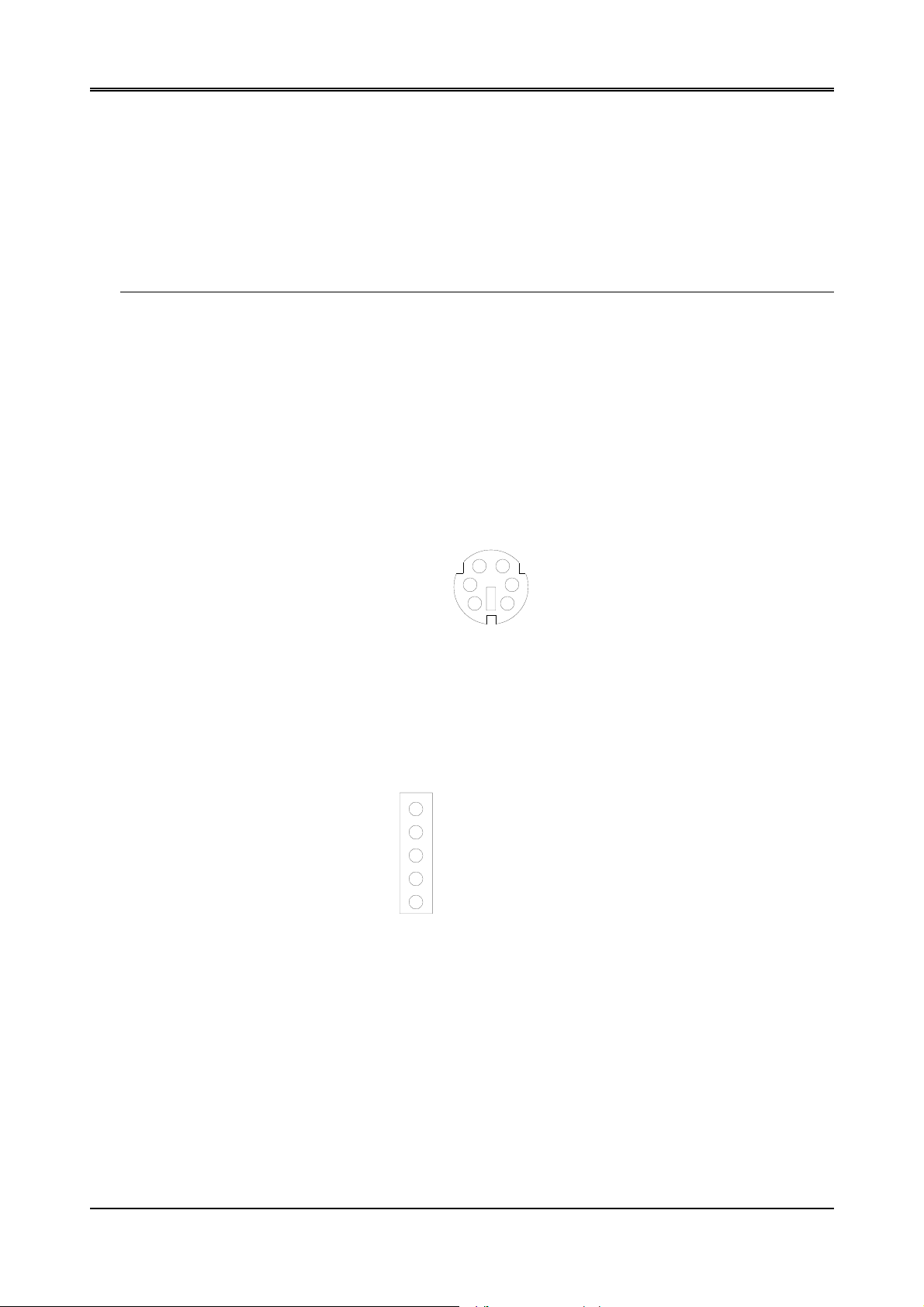
(1) 6-Pin Mini DIN Keyboard Connector (CN3)
CN3 is a Mini-DIN 6-pin connector. This keyboard connector is PS/2 type keyboard connector. This connector is
also for a standard IBM-compatible keyboard with the keyboard adapter cable.
CN3
1 DATA
1
2 N.C.
3 GND
4 VCC
3
5
2
4
6
5 CLOCK
6 N.C.
Figure 3-2 CN3: 6-Pin Mini Din Keyboard Connector
(2) AUX. Keyboard Connector (J4)
We can use a PC/AT compatible keyboard to connecting the provided adapter cable between J4 and the keyboard.
The pin assignments of J4 connector are as follows:
Front View
1 CLOCK
2 DATA
3 N.C.
4 GND
5 VCC
3-2
J4
Figure 3-3 J4: AUX. Keyboard Connector
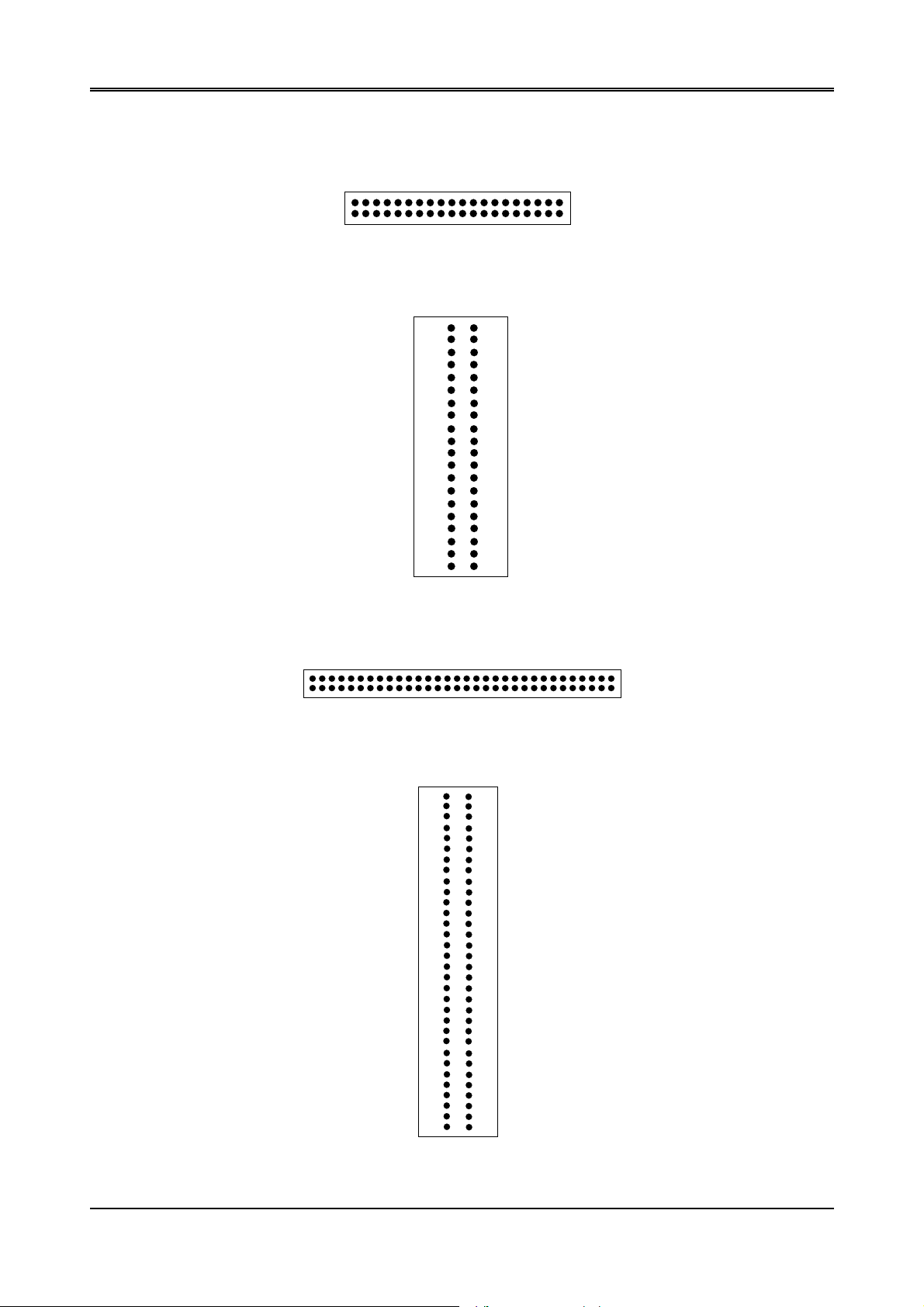
3.2.2 PC/104 Connector
R
(1) 40-Pin PC/104 Connector Bus C & D (CN1)
Figure 3-4 CN1: 40-Pin PC/104 Connector Bus C & D
Figure 3-5 CN1: 40-Pin PC/104 Connector Bus C & D
(2) 64-Pin PC/104 Connector Bus A & B (CN2)
2
1
2
GND ---
-SBHE --LA23 --LA22 --LA21 --LA20 --LA19 --LA18 --LA17 ---
-MEMR ---
-MEMW --SD8 --SD9 ---
SD10 --SD11 --SD12 --SD13 --SD14 --SD15 ---
Not Used ---
40 Pin PC/104 Connector
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
C6
C7
C8
C9
C10
C11
C12
C13
C14
C15
C16
C17
C18
C19
C20
CN1
1
2
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
D16
D17
D18
D19
D20
--- GND
--- -MEM16
--- -IO16
--- IRQ10
--- IRQ11
--- IRQ12
--- IRQ15
--- IRQ14
--- -DACK0
--- DRQ0
--- -DACK5
--- DRQ5
--- -DACK6
--- DRQ6
--- -DACK7
--- DRQ7
--- +5 VDC
--- -MASTE
--- GND
--- GND
AR-B1375/AR-B1376 User’s Guide
39
40
64
1
64-Pin PC/104 Connector
63
Figure 3-6 CN2: 64 Pin PC/104 Connector Bus A & B
CN2
-IOCHCK --SD7 --SD6 --SD5 --SD4 --SD3 --SD2 --SD1 --SD0 ---
IOCHRDY---
AEN ---
SA19 --SA18 --SA17 --SA16 --SA15 --SA14 --SA13 --SA12 --SA11 --SA10 ---
SA9 --SA8 --SA7 --SA6 --SA5 --SA4 --SA3 --SA2 --SA1 --SA0 ---
GND ---
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
A20
A21
A22
A23
A24
A25
A26
A27
A28
A29
A30
A31
A32
12
B1
B2
B3
B4
B5
B6
B7
B8
B9
B10
B11
B12
B13
B14
B15
B16
B17
B18
B19
B20
B21
B22
B23
B24
B25
B26
B27
B28
B29
B30
B31
B32
--- GND
--- RSTDRV
--- +5 VDC
--- IRQ9
--- -5 VDC
--- DRQ2
--- -12 VDC
--- -ZWS
--- +12 VDC
--- Not Used
--- -SMEMW
--- -SMEMR
--- -IOW
--- -IOR
--- -DACK3
--- DRQ3
--- -DACK1
--- DRQ1
--- -REFRSH
--- BUSCLK
--- IRQ7
--- IRQ6
--- IRQ5
--- IRQ4
--- IRQ3
--- -DACK2
--- TC
--- BALE
--- +5 VDC
--- OSC
--- GND
--- GND
Figure 3-7 CN2: 64-Pin PC/104 Connector Bus A & B
3-3
 Loading...
Loading...