Texas Instruments TPS62200DBV, TPS62201DBV, TPS62202DBV, TPS62203DBV, TPS62204DBV Schematic [ru]
...
www.ti.com
V
I
GND
ENSWFB
C1
4.7 µF
L1
10 µH
C2
10 µF
TPS62202
V
I
2.5 V − 6 V
V
O
1.8 V / 300 mA
1
5
2
3
4
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
85
90
95
100
0.010 0.100 1
10 100 1000
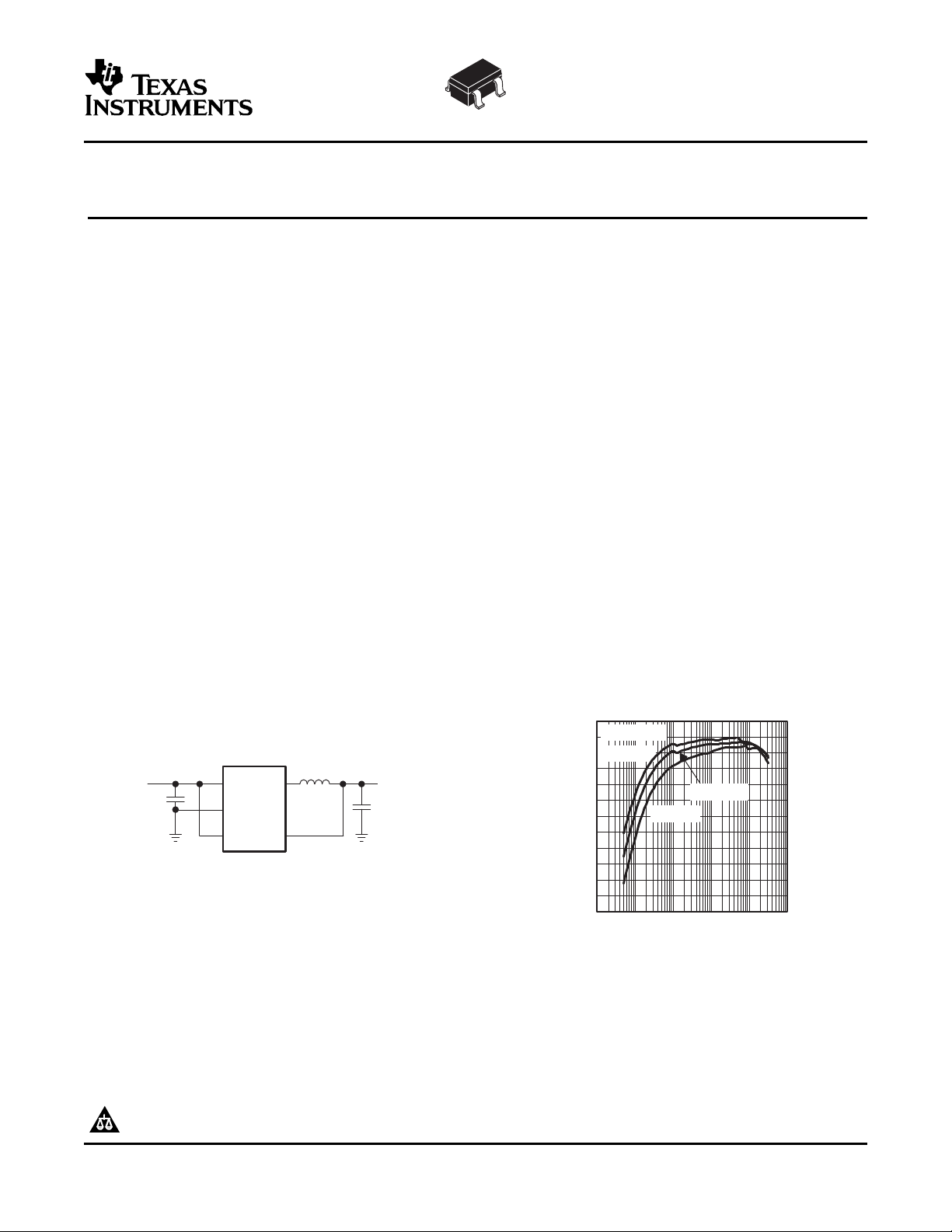
Efficiency − %
EFFICIENCY
vs
LOAD CURRENT
IL −Load Current − mA
VO = 1.8 V
VI = 2.7 V
VI = 3.7 V
VI = 5 V
HIGH-EFFICIENCY, SOT23
STEP-DOWN, DC-DC CONVERTER
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
FEATURES
• High Efficiency Synchronous Step-Down
Converter With up to 95% Efficiency
• 2.5-V to 6-V Input Voltage Range
• Adjustable Output Voltage Range From 0.7 V
to V
I
• Fixed Output Voltage Options Available
• Up to 300 mA Output Current
• 1-MHz Fixed Frequency PWM Operation
• Highest Efficiency Over Wide Load Current
Range Due to Power Save Mode
• 15-µA Typical Quiescent Current
• Soft Start
• 100% Duty Cycle Low-Dropout Operation
• Dynamic Output-Voltage Positioning
• Available in a 5-Pin SOT23 Package
APPLICATIONS
• PDAs and Pocket PC
• Cellular Phones, Smart Phones
• Low Power DSP Supply
• Digital Cameras
• Portable Media Players
• Portable Equipment
DESCRIPTION
The TPS6220x devices are a family of high-efficiency
synchronous step-down converters ideally suited for
portable systems powered by 1-cell Li-Ion or 3-cell
NiMH/NiCd batteries. The devices are also suitable
to operate from a standard 3.3-V or 5-V voltage rail.
With an output voltage range of 6 V down to 0.7 V
and up to 300 mA output current, the devices are
ideal to power low voltage DSPs and processors
used in PDAs, pocket PCs, and smart phones.
Under nominal load current, the devices operate with
a fixed switching frequency of typically 1 MHz. At
light load currents, the part enters the power save
mode operation; the switching frequency is reduced
and the quiescent current is typically only 15 µA;
therefore, it achieves the highest efficiency over the
entire load current range. The TPS6220x needs only
three small external components. Together with the
SOT23 package, a minimum system solution size is
achieved. An advanced fast response voltage mode
control scheme achieves superior line and load
regulation with small ceramic input and output
capacitors.
Figure 1. Typical Application
(Fixed Output Voltage Version)
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas
Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not
necessarily include testing of all parameters.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas
Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
Copyright © 2002–2006, Texas Instruments Incorporated
www.ti.com
3
2
4
5
DBV PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
1
V
I
GND
EN
SW
FB
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Texas Instruments recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with
appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degradation to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits may be
more susceptible to damage because very small parametric changes could cause the device not to meet its published
specifications.
ORDERING INFORMATION
T
A
-40°C to 85°C
(1) The DBV package is available in tape and reel. Add R suffix (DBVR) to order quantities of 3000 parts.
Add T suffix (DBVT) to order quantities of 250 parts
OUTPUT VOLTAGE SOT23 PACKAGE SYMBOL
Adjustable TPS62200DBV PHKI
1.2 V TPS62207DBV PJGI
1.5 V TPS62201DBV PHLI
1.6 V TPS62204DBV PHSI
1.8 V TPS62202DBV PHMI
1.875 V TPS62208DBV ALW
2.5 V TPS62205DBV PHTI
3.3 V TPS62203DBV PHNI
(1)
Terminal Functions
TERMINAL
NAME NO.
EN 3 I
FB 4 I used. For the adjustable version an external resistor divider is connected to this pin. The internal voltage divider
GND 2 Ground
SW 5 I/O Connect the inductor to this pin. This pin is the switch pin and is connected to the internal MOSFET switches.
V
I
I/O DESCRIPTION
This is the enable pin of the device. Pulling this pin to ground forces the device into shutdown mode. Pulling this
pin to Vin enables the device. This pin must not be left floating and must be terminated.
This is the feedback pin of the device. Connect this pin directly to the output if the fixed output voltage version is
is disabled for the adjustable version.
1 I Supply voltage pin
2
Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
_
+
_
+
_
+
_
+
_
+
REF
REF
Load Comparator
Skip Comparator
Current Limit Comparator
P-Channel
Power MOSFET
Driver
Shoot-Through
Logic
Control
Logic
Soft Start
1 MHz
Oscillator
Comparator
S
R
N-Channel
Power MOSFET
Comparator High
Comparator Low
Comparator Low 2
V
(COMP)
Sawtooth
Generator
V
I
Undervoltage
Lockout
Bias Supply
_
+
Comparator High
Comparator Low
Comparator Low 2
Compensation
V
REF
= 0.5 V
R2
See Note
R1
V
I
EN
SW
FB GND
Gm
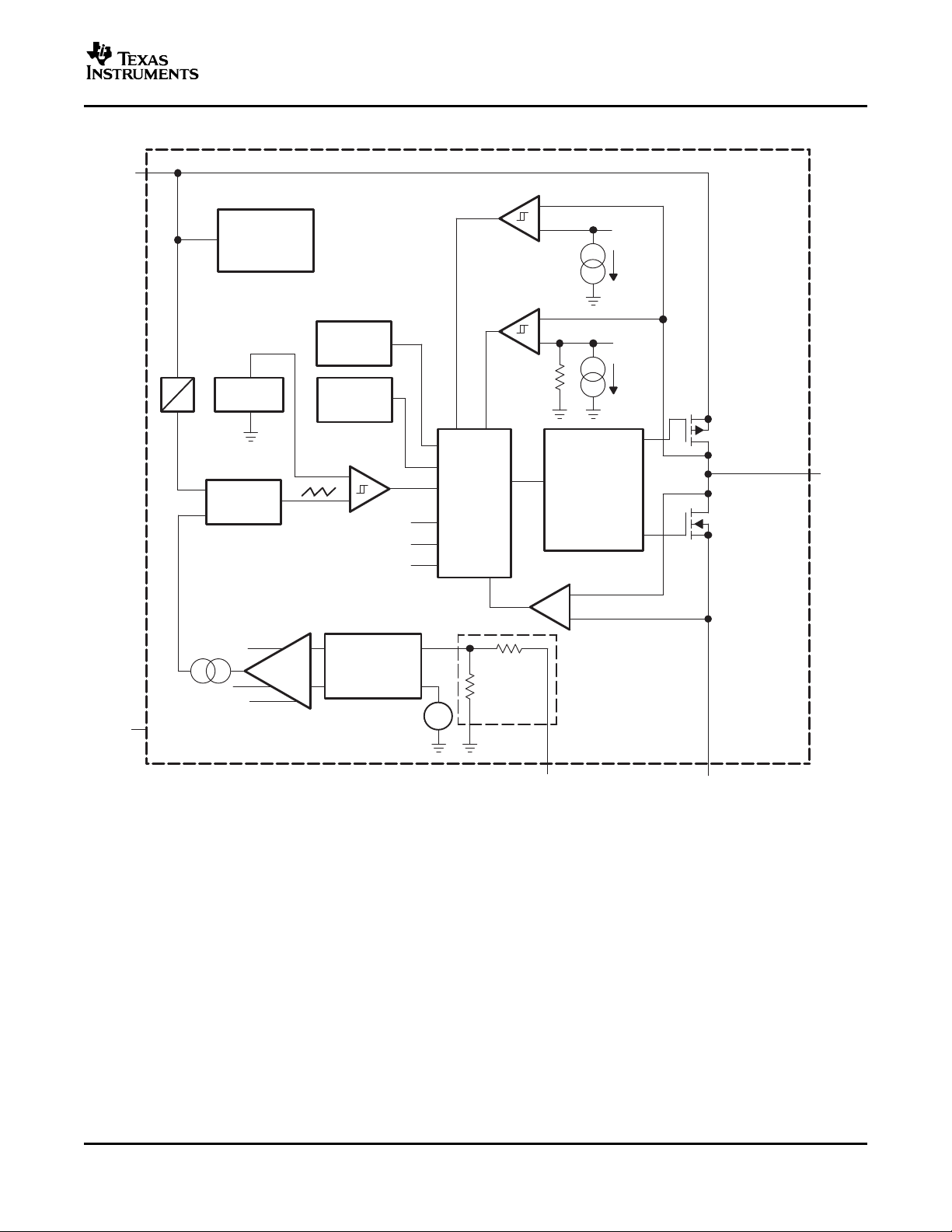
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
For the adjustable version (TPS62200) the internal feedback divider is disabled and the FB pin is directly connected
OPERATION
The TPS6220x is a synchronous step-down converter operating with typically 1-MHz fixed frequency pulse width
modulation (PWM) at moderate to heavy load currents and in power save mode operating with pulse frequency
modulation (PFM) at light load currents.
During PWM operation the converter uses a unique fast response, voltage mode, controller scheme with input
voltage feed forward. This achieves good line and load regulation and allows the use of small ceramic input and
to the internal GM amplifier
output capacitors. At the beginning of each clock cycle initiated by the clock signal (S), the P-channel MOSFET
switch is turned on, and the inductor current ramps up until the comparator trips and the control logic turns off
the switch. The current limit comparator also turns off the switch in case the current limit of the P-channel switch
is exceeded. Then the N-channel rectifier switch is turned on and the inductor current ramps down. The next
cycle is initiated by the clock signal again turning off the N-channel rectifier and turning on the P-channel switch.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION
Submit Documentation Feedback
3
www.ti.com
I
skip
v 66 mA )
Vin
160 W
I
peak
+ 66 mA )
Vin
80 W
PFM Mode at Light Load
Comparator High
Comparator Low
Comparator Low 2
PWM Mode at Medium to Full Load
1.6%
0.8%
V
O
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
DETAILED DESCRIPTION (continued)
The GM amplifier and input voltage determines the rise time of the Sawtooth generator; therefore any change in
input voltage or output voltage directly controls the duty cycle of the converter. This gives a very good line and
load transient regulation.
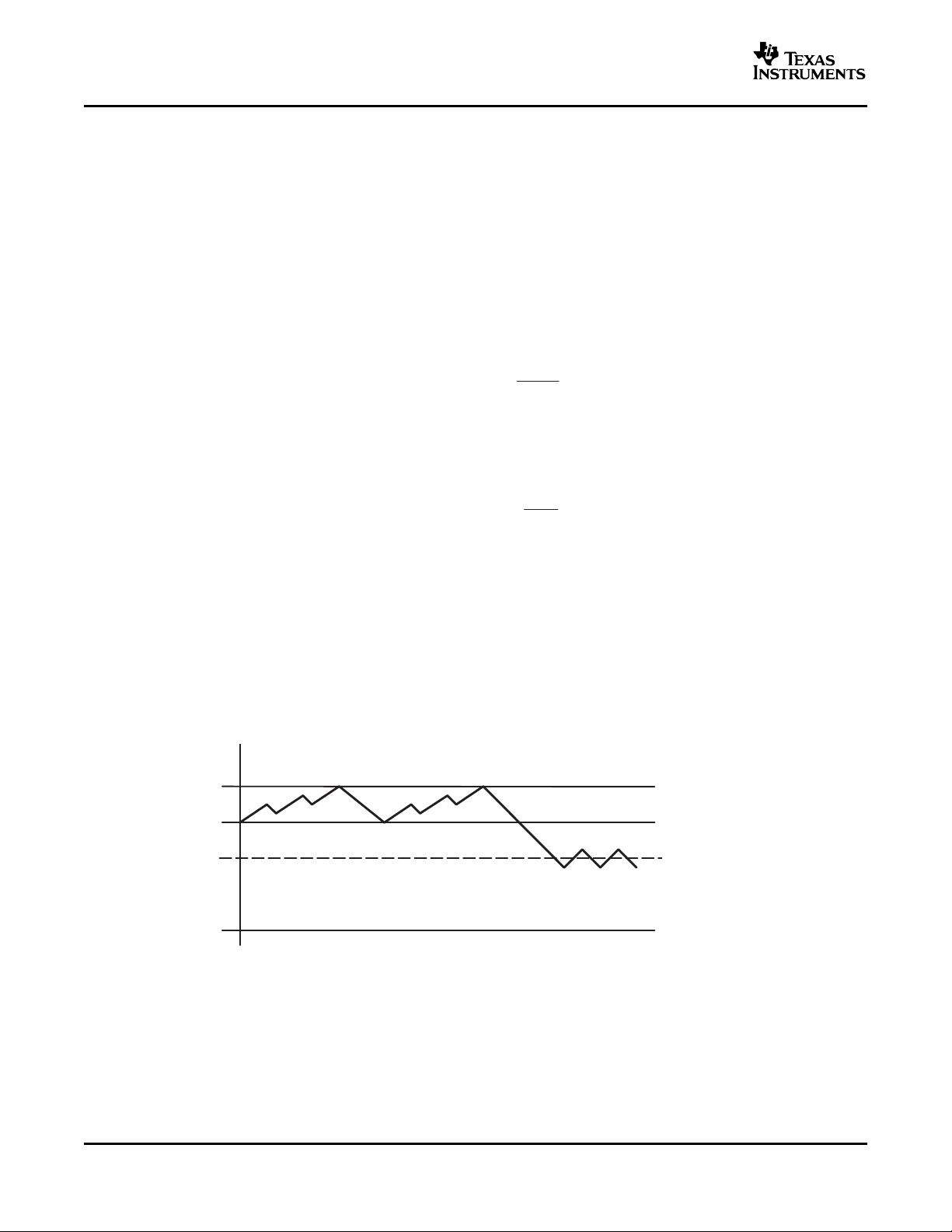
POWER SAVE MODE OPERATION
As the load current decreases, the converter enters the power save mode operation. During power save mode,
the converter operates with reduced switching frequency in PFM mode and with a minimum quiescent current to
maintain high efficiency.
Two conditions allow the converter to enter the power save mode operation. One is when the converter detects
the discontinuous conduction mode. The other is when the peak switch current in the P-channel switch goes
below the skip current limit. The typical skip current limit can be calculated as
During the power save mode the output voltage is monitored with the comparator by the thresholds comp low
and comp high. As the output voltage falls below the comp low threshold set to typically 0.8% above Vout
nominal, the P-channel switch turns on. The P-channel switch is turned off as the peak switch current is
reached. The typical peak switch current can be calculated:
The N-channel rectifier is turned on and the inductor current ramps down. As the inductor current approaches
zero the N-channel rectifier is turned off and the P-channel switch is turned on again, starting the next pulse.
The converter continues these pulses until the comp high threshold (set to typically 1.6% above Vout nominal) is
reached. The converter enters a sleep mode, reducing the quiescent current to a minimum. The converter
wakes up again as the output voltage falls below the comp low threshold again. This control method reduces the
quiescent current typically to 15 µA and reduces the switching frequency to a minimum, thereby achieving the
high converter efficiency. Setting the skip current thresholds to typically 0.8% and 1.6% above the nominal
output voltage at light load current results in a dynamic output voltage achieving lower absolute voltage drops
during heavy load transient changes. This allows the converter to operate with a small output capacitor of just 10
µF and still have a low absolute voltage drop during heavy load transient changes. Refer to Figure 2 for detailed
operation of the power save mode.
Figure 2. Power Save Mode Thresholds and Dynamic Voltage Positioning
The converter enters the fixed frequency PWM mode again as soon as the output voltage falls below the comp
low 2 threshold.
4
Submit Documentation Feedback

www.ti.com
Vin
min
+ Vout
max
) Iout
max
ǒ
rds(ON)
max
) R
L
Ǔ
Iout
max
= maximum output current plus inductor ripple current
rds(ON)
max
= maximum P-channel switch rds(ON)
RL = DC resistance of the inductor
Vout
max
= nominal output voltage plus maximum output voltage tolerance
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
DETAILED DESCRIPTION (continued)
DYNAMIC VOLTAGE POSITIONING
As described in the power save mode operation sections and as detailed in Figure 2 , the output voltage is
typically 0.8% above the nominal output voltage at light load currents, as the device is in power save mode. This
gives additional headroom for the voltage drop during a load transient from light load to full load. During a load
transient from full load to light load, the voltage overshoot is also minimized due to active regulation turning on
the N-channel rectifier switch.
SOFT START
The TPS6220x has an internal soft start circuit that limits the inrush current during start-up. This prevents
possible voltage drops of the input voltage in case a battery or a high impedance power source is connected to
the input of the TPS6220x.
The soft start is implemented as a digital circuit increasing the switch current in steps of typically 60 mA,120 mA,
240 mA and then the typical switch current limit of 480 mA. Therefore the start-up time mainly depends on the
output capacitor and load current. Typical start-up time with 10 µF output capacitor and 200 mA load current is
800 µs.
LOW DROPOUT OPERATION 100% DUTY CYCLE
The TPS6220x offers a low input to output voltage difference, while still maintaining operation with the 100%
duty cycle mode. In this mode, the P-channel switch is constantly turned on. This is particularly useful in battery
powered applications to achieve longest operation time by taking full advantage of the whole battery voltage
range. The minimum input voltage to maintain regulation, depending on the load current and output voltage, can
be calculated as
ENABLE
Pulling the enable low forces the part into shutdown, with a shutdown quiescent current of typically 0.1 µA. In
this mode, the P-channel switch and N-channel rectifier are turned off, the internal resistor feedback divider is
disconnected, and the whole device is in shutdown mode. If an output voltage, which could be an external
voltage source or super cap, is present during shutdown, the reverse leakage current is specified under
electrical characteristics. For proper operation the enable pin must be terminated and must not be left floating.
Pulling the enable high starts up the TPS6220x with the soft start as previously described.
UNDERVOLTAGE LOCKOUT
The undervoltage lockout circuit prevents the device from misoperation at low input voltages. It prevents the
converter from turning on the switch or rectifier MOSFET under undefined conditions.
Submit Documentation Feedback
5

www.ti.com
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
over operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)
Supply voltages, V
Voltages on pins SW, EN, FB
Continuous power dissipation, P
Operating junction temperature range, T
Storage temperature, T
Lead temperature (soldering, 10 sec) 260°C
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under "absolute maximum ratings" may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings
only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under "recommended operating
conditions" is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltage values are with respect to network ground terminal.
(2)
I
(2)
D
J
stg
DISSIPATION RATING TABLE
PACKAGE R
DBV 250°/W 400 mW 220 mW 160 mW
θ JA
(1)
-0.3 V to 7.0 V
-0.3 V to V
See Dissipation Rating Table
-40°C to 150°C
-65°C to 150°C
TA≤ 25°C TA= 70°C TA= 85°C
POWER RATING POWER RATING POWER RATING
UNIT
+0.3 V
CC
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
MIN NOM MAX UNIT
Supply voltage, V
I
Output voltage range for adjustable output voltage version, V
Output current, I
Inductor, L
Input capacitor, C
Output capacitor, C
Operating ambient temperature, T
Operating junction temperature, T
O
(1)
(1)
I
(1)
O
A
J
O
2.5 6.0 V
0.7 V
4.7 10 µH
4.7 µF
10 µF
40 85 °C
40 125 °C
(1) See the application section for further information.
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
VI= 3.6 V, VO= 1.8 V, IO= 200 mA, EN = VIN, TA= -40 °C to 85 °C, typical values are at TA= 25 °C (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
SUPPLY CURRENT
V
I
I
Q
ENABLE
V
(EN)
I
(EN)
POWER SWITCH
rds(ON)
I
lkg_(P)
Input voltage range 2.5 6.0 V
Operating quiescent current IO= 0 mA, Device is not switching 15 30 µA
Shutdown supply current EN = GND 0.1 1 µA
Undervoltage lockout threshold 1.5 2.0 V
EN high level input voltage 1.3 V
EN low level input voltage 0.4 V
EN input bias current EN = GND or VIN 0.01 0.1 µA
P-channel MOSFET on-resistance m Ω
N-channel MOSFET on-resistance m Ω
P-channel leakage current V
VIN= V
VIN= V
VIN= V
VIN= V
DS
= 3.6 V 530 690
GS
= 2.5 V 670 850
GS
= 3.6 V 430 540
GS
= 2.5 V 530 660
GS
= 6.0 V 0.1 1 µA
300 mA
V
I
6
Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (continued)
VI= 3.6 V, VO= 1.8 V, IO= 200 mA, EN = VIN, TA= -40 °C to 85 °C, typical values are at TA= 25 °C (unless otherwise noted)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
I
lkg_(N)
I
(LIM)
OSCILLATOR
f
S
OUTPUT
V
O
V
ref
V
O
I
lkg
I
lkg
N-channel leakage current V
= 6.0 V 0.1 1 µA
DS
P-channel current limit 2.5 V < Vin < 6.0 V 380 480 670 mA
Switching frequency 650 1000 1500 kHz
Adjustable output voltage
range
TPS62200 0.7 V
Reference voltage 0.5 V
Feedback voltage
(1)
TPS62200 VI= 3.6 V to 6.0 V, IO= 0 mA 0% 3%
Adjustable VI= 3.6 V to 6.0 V, 0 mA ≤ IO≤ 300 mA -3% 3%
TPS62207 VI= 2.5 V to 6.0 V, IO= 0 mA 0% 3%
1.2 V VI= 2.5 V to 6.0 V, 0 mA ≤ IO≤ 300 mA -3% 3%
TPS62201 VI= 2.5 V to 6.0 V, IO= 0 mA 0% 3%
1.5 V VI= 2.5 V to 6.0 V, 0 mA ≤ IO≤ 300 mA -3% 3%
TPS62204 VI= 2.5 V to 6.0 V, IO= 0 mA 0% 3%
1.6 V VI= 2.5 V to 6.0 V, 0 mA ≤ IO≤ 300 mA -3% 3%
Fixed output voltage
(1)
TPS62202 VI= 2.5 V to 6.0 V, IO= 0 mA 0% 3%
1.8 V VI= 2.5 V to 6.0 V, 0 mA ≤ IO≤ 300 mA -3% 3%
TPS62208 VI= 2.5 V to 6.0 V, IO= 0 mA 0% 3%
1.875 V VI= 2.5 V to 6.0 V, 0 mA ≤ IO≤ 300 mA -3% 3%
TPS62205 VI= 2.7 V to 6.0 V, IO= 0 mA 0% 3%
2.5 V VI= 2.7 V to 6.0 V, 0 mA ≤ IO≤ 300 mA -3% 3%
TPS62203 VI= 3.6 V to 6.0 V, IO= 0 mA 0% 3%
3.3 V VI= 3.6 V to 6.0 V, 0 mA ≤ IO≤ 300 mA -3% 3%
Line regulation VI= 2.5 V to 6.0 V, IO= 10 mA 0.26 %/V
Load regulation IO= 100 mA to 300 mA 0.0014 %/mA
Leakage current into SW pin Vin > Vout, 0 V ≤ Vsw ≤ Vin 0.1 1 µA
(Rev) Reverse leakage current into pin SW Vin = open, EN = GND, V
= 6.0 V 0.1 1 µA
SW
V
IN
(1) For output voltages ≤ 1.2 V a 22 µF output capacitor value is required to achieve a maximum output voltage accuracy of 3% while
operating in power save mode (PFM mode)
Submit Documentation Feedback
7

www.ti.com
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
85
90
95
100
0.010 0.100 1
10 100 1000
VO = 3.3 V
VI = 3.7 V
VI = 5 V
Efficency − %
IL − Load Current − mA
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
85
90
95
100
0.010 0.100 1
10 100 1000
Efficiency − %
IL −Load Current − mA
VO = 1.8 V
VI = 2.7 V
VI = 3.7 V
VI = 5 V
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
Table of Graphs
η Efficiency
I
Q
f
s
V
o
rds(on)
No load quiescent current vs Input voltage 7
Switching frequency vs Temperature 8
Output voltage vs Output current 9
rds(on) - P-channel switch, vs Input voltage 10
rds(on) - N-Channel rectifier switch vs Input voltage 11
Line transient response 12
Load transient response 13
Power save mode operation 14
Start-up 15
EFFICIENCY EFFICIENCY
LOAD CURRENT LOAD CURRENT
TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS
FIGURES
vs Load current 3,4,5
vs Input voltage 6
vs vs
8
Figure 3. Figure 4.
Submit Documentation Feedback

www.ti.com
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
85
90
95
100
0.010 0.100 1
10 100 1000
VO = 1.5 V
VI = 2.7 V
VI = 5 V
Efficency − %
IL − Load Current − mA
VI = 3.7V
70
75
80
85
90
95
100
2.50 3 3.50 4 4.50 5 5.50 6
VO = 1.8 V
IL = 150 mA
IL = 1 mA
IL = 300 mA
Efficiency − %
VI − Input Voltage − V
0
5
10
15
20
25
2.50 3 3.50 4 4.50 5 5.50 6
TA = 85°C
TA = 25°C
TA = −40°C
N0 Load Quiescent Current −
VI − Input Voltage − V
Aµ
1025
1030
1035
1040
1045
1050
1055
1060
1065
1070
1075
1080
−40 −30 −20 −10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
f − Frequency − kHz
TA − Temperature − °C
VI = 3.6 V
VI = 6 V
VI = 2.5 V
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
EFFICIENCY EFFICIENCY
vs vs
LOAD CURRENT INPUT VOLTAGE
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
Figure 5. Figure 6.
NO LOAD QUIESCENT CURRENT FREQUENCY
INPUT VOLTAGE TEMPERATURE
Figure 7. Figure 8.
vs vs
Submit Documentation Feedback
9

www.ti.com
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6
TA = 85°C
TA = 25°C
TA = −40°C
VI − Input Voltage − V
r
ds(on)
Ω− P-Channel Switch −
1.70
1.72
1.74
1.76
1.78
1.80
1.82
1.84
1.86
1.88
1.90
0 50 100 150 200 250 300
− Outrput Voltage − VV
O
IO − Output Current − mA
PFM Mode
PWM Mode
V
O
20 mV/div
V
I
3.6 V to 4.6 V
200 µs/div
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6
TA = 85°C
TA = 25°C
TA = −40°C
VI − Input Voltage − V
rDS
(on)
ΩN-Channel Switch —
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
OUTPUT VOLTAGE rds(on) P-CHANNEL SWITCH
OUTPUT CURRENT INPUT VOLTAGE
rds(on) P-CHANNEL SWITCH LINE TRANSIENT RESPONSE
vs vs
Figure 9. Figure 10.
vs
INPUT VOLTAGE
10
Figure 11. Figure 12.
Submit Documentation Feedback

www.ti.com
V
O
50 mV/div
I
O
3 mA to 270 mA
100 µs/div
V
SW
5 V/div
I
L
100 mA/div
V
O
20 mV/div
2 µs/div
VO = 1.8 V/200 mA
Enable
2 V/div
I
L
50 mA/div
V
O
1 V/div
100 µs/div
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
LOAD TRANSIENT RESPONSE POWER SAVE MODE OPERATION
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
Figure 13. Figure 14.
START-UP
Figure 15.
Submit Documentation Feedback
11
www.ti.com
V
out
+ 0.5 V ǒ1 )
R1
R2
Ǔ
C1 +
1
2 p 10 kHz R1
C2 +
R1
R2
C1
V
I
GND
EN
SW
FB
C3
4.7 µF
L1
10 µH
C4
10 µF
TPS62200
V
I
2.5 V − 6 V
V
O
1.8 V / 300 mA
R1
470k
R2
180k
C1
33 pF
C2
100 pF
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
APPLICATION INFORMATION
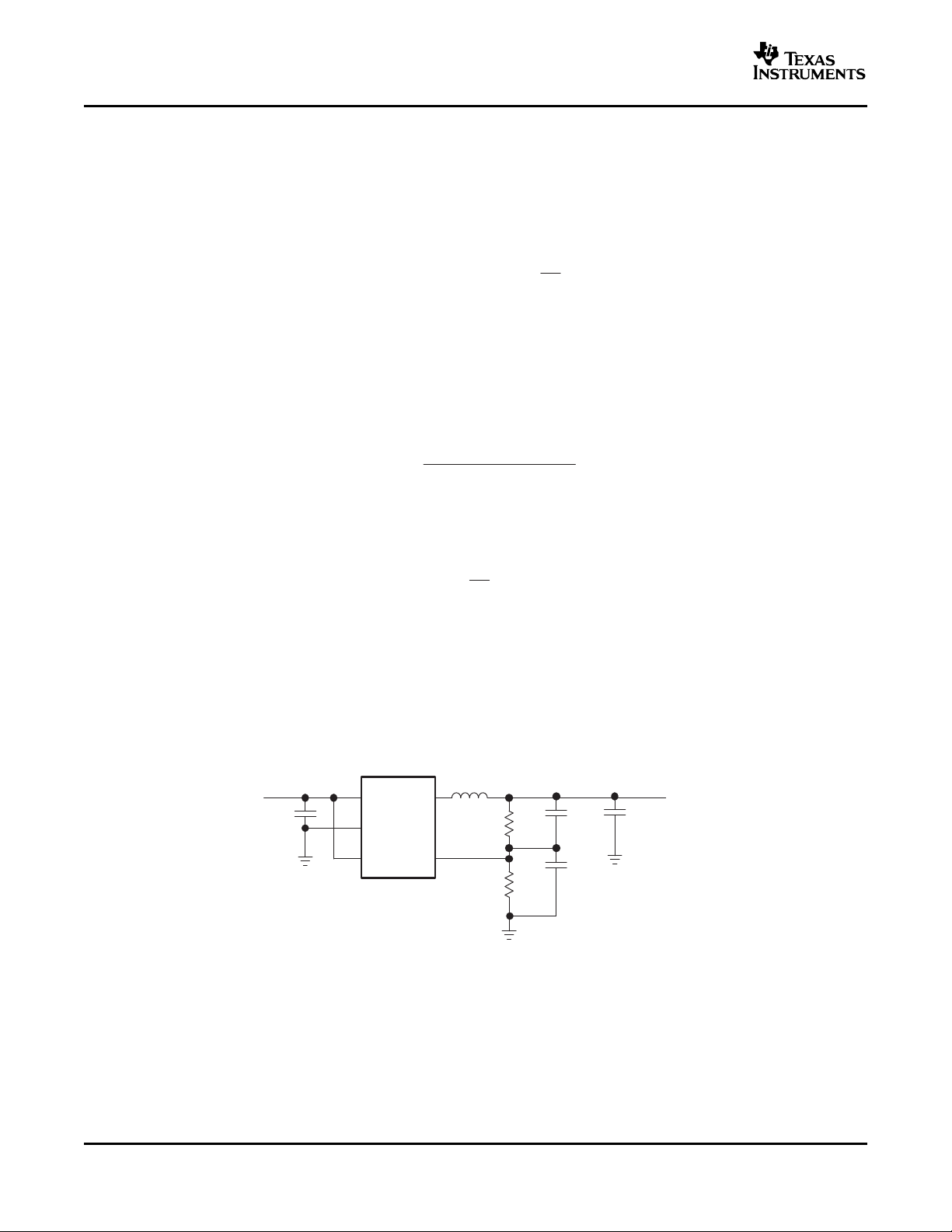
ADJUSTABLE OUTPUT VOLTAGE VERSION
When the adjustable output voltage version TPS62200 is used, the output voltage is set by the external resistor
divider. See Figure 16 .
The output voltage is calculated as
• R1 + R2 ≤ 1 M Ω and internal reference voltage V(ref)typ = 0.5 V
R1 + R2 should not be greater than 1 M Ω for reasons of stability. To keep the operating quiescent current to a
minimum, the feedback resistor divider should have high impedance with R1+R2 ≤ 1 M Ω . Because of the high
impedance and the low reference voltage of V
minimized. Using a capacitive divider C1 and C2 across the feedback resistors minimizes the noise at the
feedback without degrading the line or load transient performance.
C1 and C2 should be selected as
= 0.5 V, the noise on the feedback pin (FB) needs to be
ref
• R1 = upper resistor of voltage divider
• C1 = upper capacitor of voltage divider
For C1 a value should be chosen that comes closest to the calculated result.
• R2 = lower resistor of voltage divider
• C2 = lower capacitor of voltage divider
For C2 the selected capacitor value should always be selected larger than the calculated result. For example, in
Figure 16 for C2, 100 pF are selected for a calculated result of C2 = 86.17 pF.
If quiescent current is not a key design parameter, C1 and C2 can be omitted, and a low-impedance feedback
divider must be used with R1+R2 <100 k Ω . This design reduces the noise available on the feedback pin (FB) as
well, but increases the overall quiescent current during operation.
INDUCTOR SELECTION
The TPS6220x device is optimized to operate with a typical inductor value of 10 µH.
For high efficiencies, the inductor should have a low dc resistance to minimize conduction losses. Although the
inductor core material has less effect on efficiency than its dc resistance, an appropriate inductor core material
must be used.
12
Figure 16. Typical Application Circuit for the Adjustable Output Voltage
Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
DIL+ Vout
1–
Vout
Vin
L f
I
Lmax
+ I
outmax
)
DI
L
2
f = switching frequency (1 MHz typical, 650 kHz minimal)
L = inductor valfue
∆IL = peak-to-peak inductor ripple current
I
Lmax
= maximum inducator current
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
APPLICATION INFORMATION (continued)
The inductor value determines the inductor ripple current. The larger the inductor value, the smaller the inductor
ripple current, and the lower the conduction losses of the converter. On the other hand, larger inductor values
cause a slower load transient response. Usually the inductor ripple current, as calculated below, is around 20%
of the average output current.
In order to avoid saturation of the inductor, the inductor should be rated at least for the maximum output current
of the converter plus the inductor ripple current that is calculated as
The highest inductor current occurs at maximum Vin.
A more conservative approach is to select the inductor current rating just for the maximum switch current of
670 mA. Refer to Table 1 for inductor recommendations.
Table 1. Recommended Inductors
INDUCTOR VALUE COMPONENT SUPPLIER COMMENTS
10 µH Sumida CDRH5D28-100 High efficiency
10 µH Sumida CDRH5D18-100
10 µH Sumida CDRH4D28-100
10 µH Coilcraft DO1608-103
6.8 µH Sumida CDRH3D16-6R8 Smallest solution
10 µH Sumida CDRH4D18-100
10 µH Sumida CR32-100
10 µH Sumida CR43-100
10 µH Murata LQH4C100K04
INPUT CAPACITOR SELECTION
Because the buck converter has a pulsating input current, a low ESR input capacitor is required. This results in
the best input voltage filtering and minimizing the interference with other circuits caused by high input voltage
spikes. Also the input capacitor must be sufficiently large to stabilize the input voltage during heavy load
transients. For good input voltage filtering, usually a 4.7 µF input capacitor is sufficient. It can be increased
without any limit for better input-voltage filtering. If ceramic output capacitors are used, the capacitor RMS ripple
current rating always meets the application requirements.
Ceramic capacitors show a good performance because of the low ESR value, and they are less sensitive
against voltage transients and spikes compared to tantalum capacitors.
Place the input capacitor as close as possible to the input pin of the device for best performance (refer to
Table 2 for recommended components).
OUTPUT CAPACITOR SELECTION
The advanced fast response voltage mode control scheme of the TPS6220x allows the use of tiny ceramic
capacitors with a value of 10 µF without having large output voltage under and overshoots during heavy load
transients.
Ceramic capacitors with low ESR values have the lowest output voltage ripple and are therefore recommended.
If required, tantalum capacitors may be used as well (refer to Table 2 for recommended components).
Submit Documentation Feedback
13

www.ti.com
DVout + Vout
1–
Vout
Vin
L f
ǒ
1
8 Cout f
) ESR
Ǔ
V
I
GND
EN
SW
FB
C1
4.7 µF
L1
10 µH
C2
10 µF
TPS62200
V
I
2.5 V − 6 V
V
O
1.8 V / 300 mA
R1
R2
Cff
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
At nominal load current the device operates in PWM mode and the overall output voltage ripple is the sum of the
voltage spike caused by the output capacitor ESR plus the voltage ripple caused by charging and discharging
the output capacitor:
where the highest output voltage ripple occurs at the highest input voltage Vin.
At light load currents, the device operates in power save mode, and the output voltage ripple is independent of
the output capacitor value. The output voltage ripple is set by the internal comparator thresholds. The typical
output voltage ripple is 1% of the output voltage Vo.
Table 2. Recommended Capacitors
CAPACITOR VALUE CASE SIZE COMPONENT SUPPLIER COMMENTS
4.7 µF 0805 Taiyo Yuden JMK212BY475MG Ceramic
10 µF 0805 Taiyo Yuden JMK212BJ106MG Ceramic
10 µF 1206 Taiyo Yuden JMK316BJ106KL Ceramic
22 µF 1210 Taiyo Yuden JMK325BJ226MM Ceramic
TDK C12012X5ROJ106K Ceramic
TDK C3216X5ROJ106M
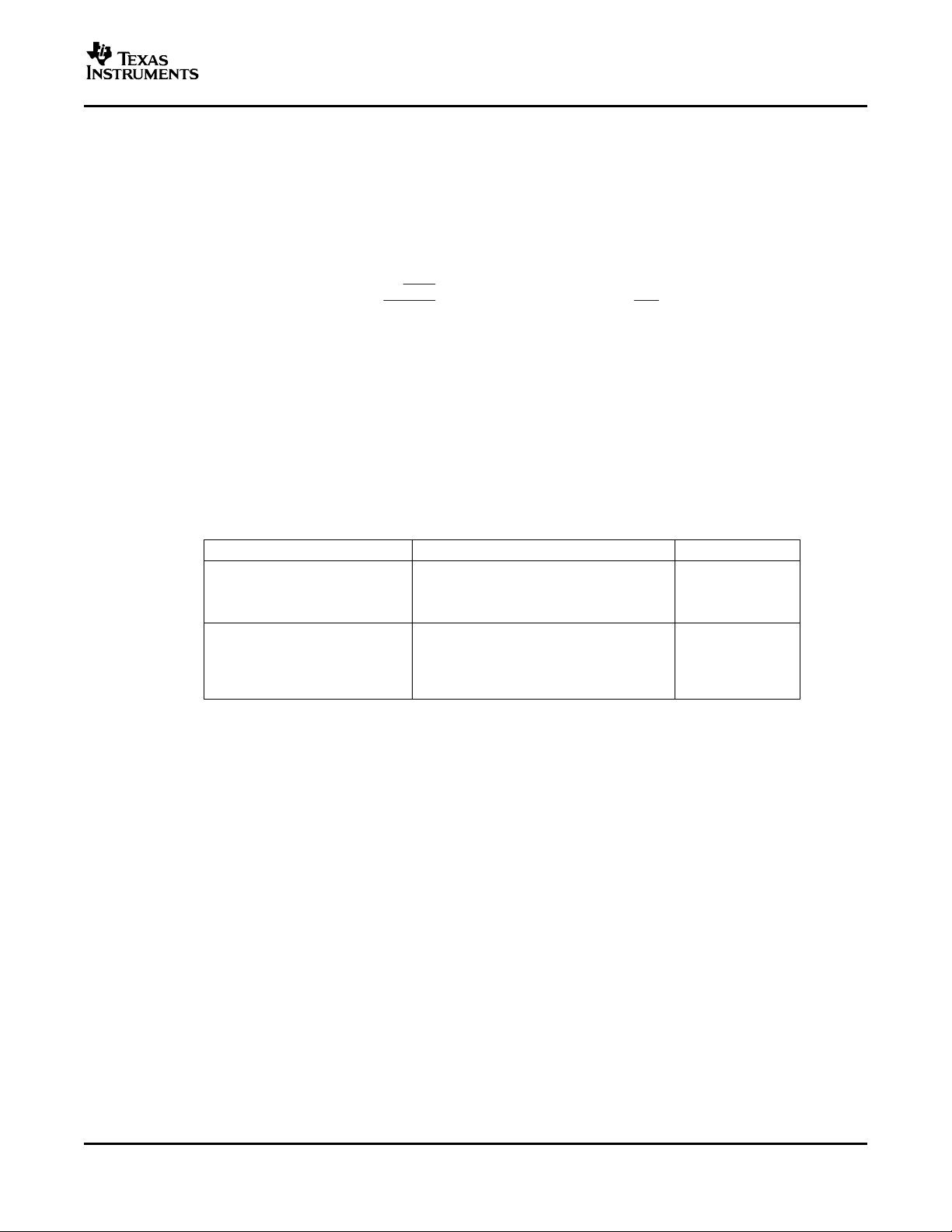
LAYOUT CONSIDERATIONS
For all switching power supplies, the layout is an important step in the design, especially at high peak currents
and switching frequencies. If the layout is not carefully done, the regulator shows stability problems as well as
EMI problems.
Therefore use wide and short traces for the main current paths, as indicated in bold in Figure 17 . The input
capacitor, as well as the inductor and output capacitor, should be placed as close as possible to the IC pins
The feedback resistor network must be routed away from the inductor and switch node to minimize noise and
magnetic interference. To further minimize noise from coupling into the feedback network and feedback pin, the
ground plane or ground traces must be used for shielding. This becomes very important especially at high
switching frequencies of 1 MHz.
Figure 17. Layout Diagram
14
Submit Documentation Feedback
www.ti.com
TYPICAL APPLICATIONS
V
I
GND
EN
SW
FB
C1
4.7 µF
L1
10 µH
C2
10 µF
TPS62202
V
I
2.5 V to 6 V
V
O
1.8 V/300 mA
1
2
3
5
4
V
I
GND
EN
SW
FB
C1
4.7 µF
L1
4.7 µH
C2
22 µF
TPS62202
V
I
2.5 V to 6 V
V
O
1.8 V/300 mA
1
2
3
5
4
V
I
GND
EN
SW
FB
C3
4.7 µF
L1
10 µH
C4
10 µF
TPS62200
V
I
2.5 V to 6 V
V
O
1.5 V/300 mA
R1
360 kΩ
R2
180 kΩ
C1
47 pF
C2
100 pF
1
2
3
5
4
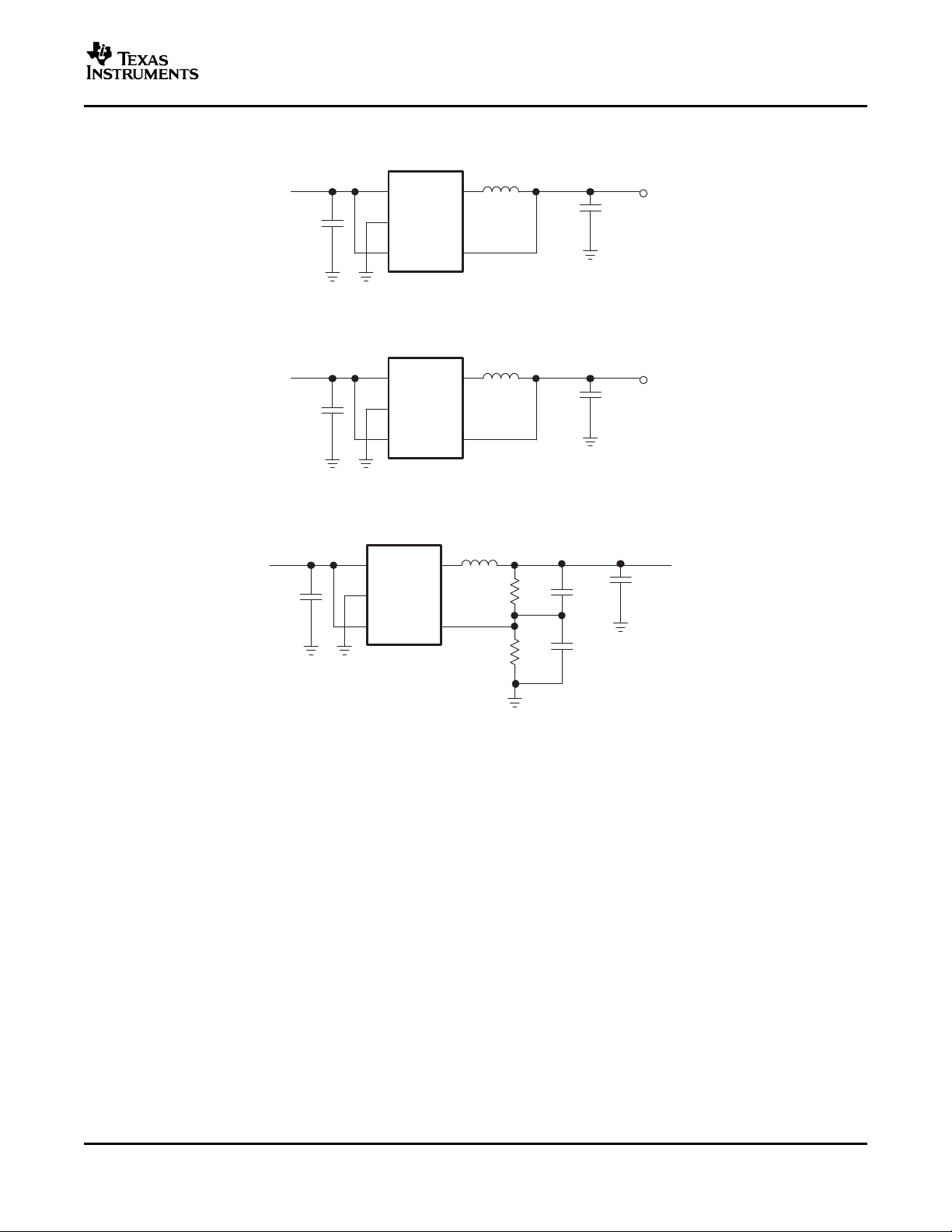
Figure 18. Li-Ion to 1.8 V Fixed Output Voltage Version
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
Figure 19. 1.8 V Fixed Output Voltage version Using 4.7µH Inductor
Figure 20. Adjustable Output Voltage Version Set to 1.5 V
Submit Documentation Feedback
15

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
TPS62200DBVR ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
TPS62200DBVRG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
TPS62200DBVT ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
TPS62200DBVTG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
TPS62201DBVR ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
TPS62201DBVRG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
TPS62201DBVT ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
TPS62201DBVTG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
TPS62202DBVR ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
TPS62202DBVRG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
TPS62202DBVT ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
TPS62202DBVTG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
TPS62203DBVR ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
TPS62203DBVRG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
TPS62203DBVT ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
TPS62203DBVTG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
TPS62204DBVR ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
TPS62204DBVRG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
TPS62204DBVT ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
TPS62204DBVTG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
TPS62205DBVR ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
TPS62205DBVRG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
TPS62205DBVT ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
TPS62205DBVTG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
TPS62207DBVR ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
(1)
Package
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
no Sb/Br)
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
5-Feb-2007
(3)
Addendum-Page 1

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
Orderable Device Status
(1)
Package
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
(2)
TPS62207DBVRG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
5-Feb-2007
(3)
no Sb/Br)
TPS62207DBVT ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
no Sb/Br)
TPS62207DBVTG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
no Sb/Br)
TPS62208DBVR ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
no Sb/Br)
TPS62208DBVRG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 Green (RoHS &
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
no Sb/Br)
TPS62208DBVT ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
no Sb/Br)
TPS62208DBVTG4 ACTIVE SOT-23 DBV 5 250 Green (RoHS &
CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM
no Sb/Br)
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in
a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS), Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt), or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check
http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements
for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered
at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt): This component has a RoHS exemption for either 1) lead-based flip-chip solder bumps used between the die and
package, or 2) lead-based die adhesive used between the die and leadframe. The component is otherwise considered Pb-Free (RoHS
compatible) as defined above.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame
retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous material)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder
temperature.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is
provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the
accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take
reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on
incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited
information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI
to Customer on an annual basis.
Addendum-Page 2
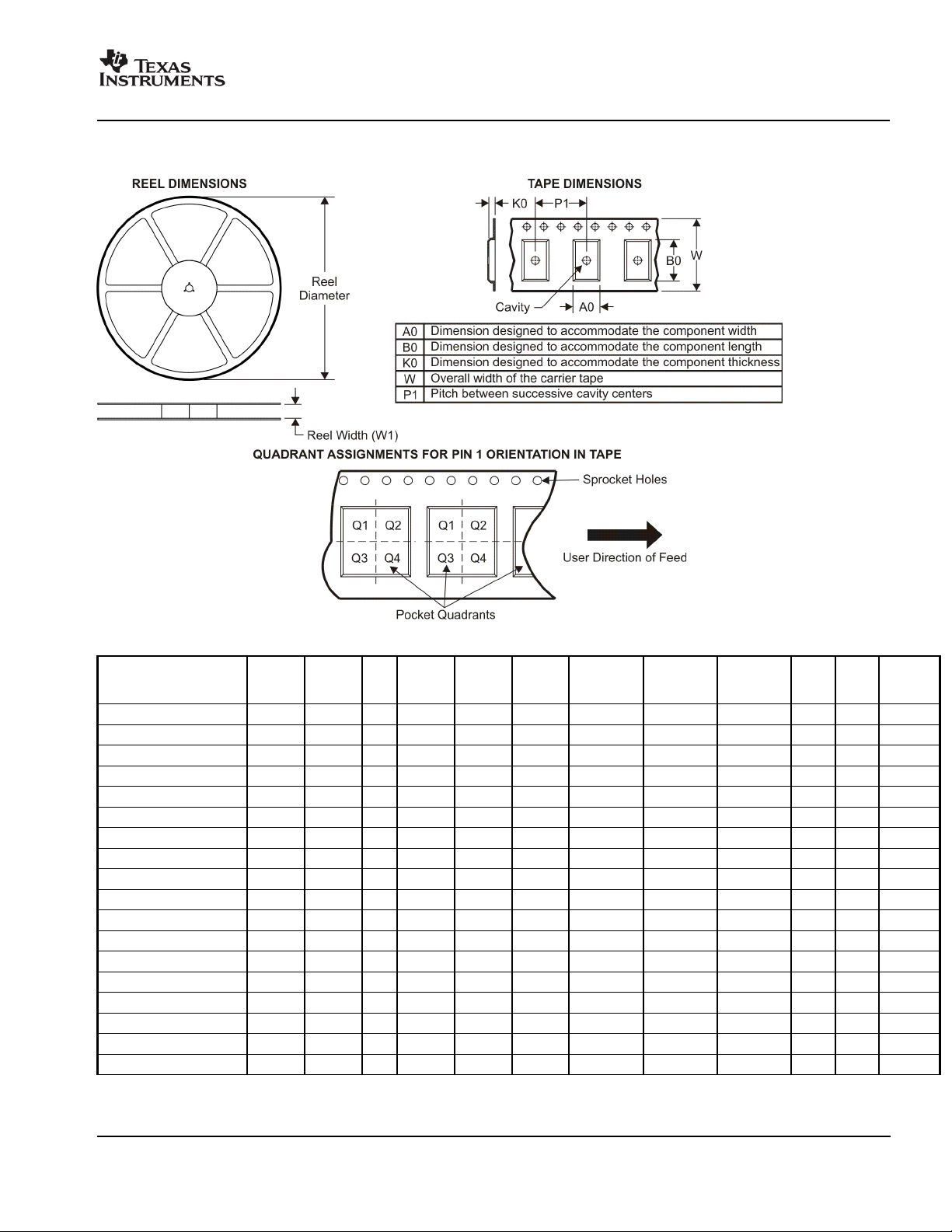
PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com
TAPE AND REEL INFORMATION
11-Mar-2008
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package
Type
TPS62200DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62200DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62201DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62201DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62202DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62202DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62203DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62203DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62204DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62204DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62205DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62205DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62207DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 180.0 9.0 3.15 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62207DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62207DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62207DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 180.0 9.0 3.15 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62208DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
TPS62208DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 179.0 8.4 3.2 3.2 1.4 4.0 8.0 Q3
Package
Drawing
Pins SPQ Reel
Diameter
(mm)
Reel
Width
W1 (mm)
A0 (mm) B0 (mm) K0 (mm) P1
(mm)W(mm)
Pin1
Quadrant
Pack Materials-Page 1

PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION
www.ti.com
11-Mar-2008
*All dimensions are nominal
Device Package Type Package Drawing Pins SPQ Length (mm) Width (mm) Height (mm)
TPS62200DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62200DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62201DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62201DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62202DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62202DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62203DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62203DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62204DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62204DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62205DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62205DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62207DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 182.0 182.0 20.0
TPS62207DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62207DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62207DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 182.0 182.0 20.0
TPS62208DBVR SOT-23 DBV 5 3000 195.0 200.0 45.0
TPS62208DBVT SOT-23 DBV 5 250 195.0 200.0 45.0
Pack Materials-Page 2


IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements,
and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should
obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are
sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard
warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where
mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products and applications, customers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask work right,
or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a
warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual
property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied
by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive
business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional
restrictions.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all
express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not
responsible or liable for any such statements.
TI products are not authorized for use in safety-critical applications (such as life support) where a failure of the TI product would reasonably
be expected to cause severe personal injury or death, unless officers of the parties have executed an agreement specifically governing
such use. Buyers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their applications, and
acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning their products
and any use of TI products in such safety-critical applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support that may be
provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in
such safety-critical applications.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI products are
specifically designated by TI as military-grade or "enhanced plastic." Only products designated by TI as military-grade meet military
specifications. Buyers acknowledge and agree that any such use of TI products which TI has not designated as military-grade is solely at
the Buyer's risk, and that they are solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in automotive applications or environments unless the specific TI products are
designated by TI as compliant with ISO/TS 16949 requirements. Buyers acknowledge and agree that, if they use any non-designated
products in automotive applications, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet such requirements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Interface interface.ti.com Medical www.ti.com/medical
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
RFID www.ti-rfid.com Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
RF/IF and ZigBee® Solutions www.ti.com/lprf Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2008, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless

 Loading...
Loading...