Page 1
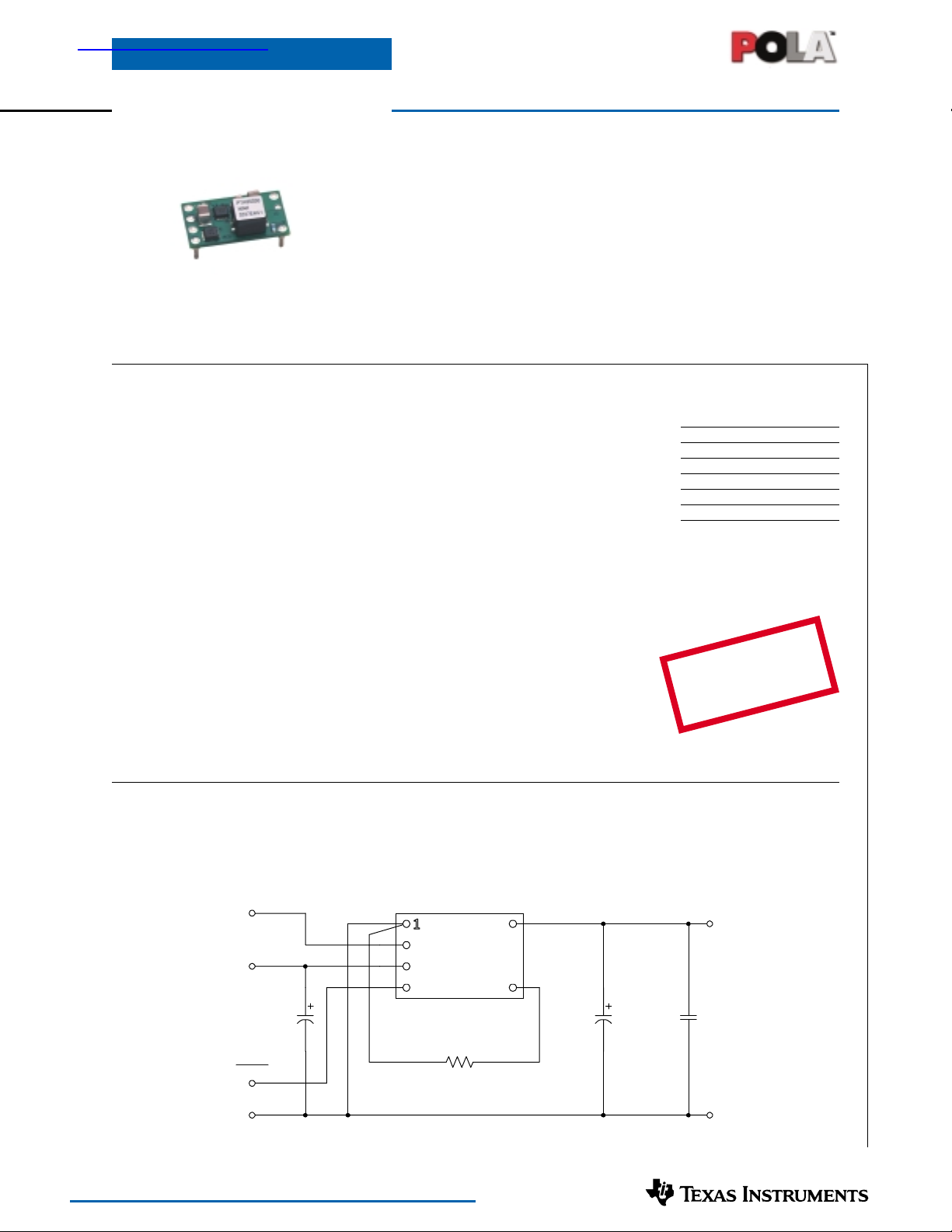
Auto-Track™
Sequencing
查询PTH03050W供应商
PTH05050W —5-V Input
6-A, 5-V Input Non-Isolated
Wide-Output Adjust Power Module
NOMINAL SIZE = 0.87 in x 0.5 in
(22,1 mm x 12,57 mm)
Description
The PTH05050 is one of the smallest
non-isolated power modules from Texas
Instruments that features Auto-Track™.
Auto-Track simplifies supply voltage
sequencing in power systems by enabling
modules to track each other, or any other
external voltage, during power up and
power down.
Although small in size (0.87 in × 0.5 in),
these modules are rated for up to 6 A of
output current, and are an ideal choice in
applications where space, performance,
and a power-up sequencing capability are
important attributes.
The product provides high-performance
step-down conversion from a 5-V input
bus voltage. The output voltage of the
PTH05050W can be set to any voltage
Features
• Up to 6-A Output Current
• 5-V Input Voltage
• Wide-Output Voltage Adjust
(0.8 V to 3.6 V)
• Efficiencies up to 95 %
• 135 W/in³ Power Density
• On/Off Inhibit
• Pre-Bias Startup
• Under-Voltage Lockout
• Operating Temp: –40 to +85 °C
over the range, 0.8 V to 3.6 V, using a
single resistor.
Other operating features include an
on/off inhibit, output voltage adjust (trim),
and output over-current protection. For
high efficiency these parts employ a
synchronous rectifier output stage, but a
pre-bias hold-off capability ensures that
the output will not sink current during
startup.
Target applications include telecom,
industrial, and general purpose circuits,
including low-power dual-voltage systems
that use a DSP, microprocessor, ASIC, or
FPGA.
Package options include both through-
hole and surface mount configurations.
• Auto-Track™ Sequencing
• Output Over-Current Protection
• IPC Lead Free 2
• Safety Agency Approvals:
• Point-of-Load Alliance (POLA)
SLTS213C – MAY 2003 – REVISED MAY 2004
(Non-Latching, Auto-Reset)
UL 1950, CSA 22.2 950, EN60950
VDE (Pending)
Compatible
Pin Configuration
Pin Function
1 GND
2 Track
3V
in
4 Inhibit *
5Vo Adjust
6V
out
* Denotes negative logic:
Open = Normal operation
Ground = Function active
Standard Application
Track
V
IN
C
IN
100 µF
(Required)
Inhibit
GND
For technical support and further information, visit http://power.ti.com
1
2
3
4
PTH05050W
(Top View)
R
SET
1 %, 0.1 W
(Required)
6
5
Co
1
100 µF
Electrolytic
(Optional)
R
= Required to set the output voltage to a value
set
higher than 0.8 V. (See spec. table for values)
Cin= Required 100 µF
Co1= Optional 100 µF capacitor
Co2= Optional 10 µF ceramic capacitor for reduced
output ripple.
V
OUT
Co
2
10 µF
Ceramic
(Optional)
GND
Page 2

PTH05050W —5-V Input
6-A, 5-V Input Non-Isolated
Wide-Output Adjust Power Module
Ordering Information
Output Voltage
Code Voltage
W 0.8 V – 3.6 V (Adjust)
Notes: (1) Add “T” to end of part number for tape and reel on SMD packages only.
(2) Reference the applicable package reference drawing for the dimensions and PC board layout
(3) “Standard” option specifies 63/37, Sn/Pb pin solder material.
(PTH05050Hxx)
Package Options
Code Description Pkg Ref.
AH Horiz. T/H (EUU)
AS SMD, Standard
(PTH05050xHH)
Pin Descriptions
Vin: The positive input voltage power node to the mod-
ule, which is referenced to common GND.
Vout: The regulated positive power output with respect
to the GND node.
GND: This is the common ground connection for the
Vin and Vout power connections. It is also the 0 VDC
reference for the control inputs.
Vo Adjust: A 1 % 0.1 W resistor must be directly connected
between this pin and GND to set the output voltage to
a value higher than 0.8 V. The temperature stability of the
resistor should be 100 ppm/°C (or better). The set point
range for the output voltage is from 0.8 V to 3.6 V. The
resistor value required for a given output voltage may be
calculated from the following formula. If this is pin is
left open circuit, the output voltage will default to its
lowest value. For further information on output voltage
adjustment consult the related application note.
R
set
= 10 kΩ ·
The specification table gives the preferred resistor values
for a number of standard output voltages.
0.8 V
V
– 0.8 V
out
– 2.49 kΩ
SLTS213C – MAY 2003 – REVISED MAY 2004
(1)
(2)
(3)
(EUV)
Inhibit: The Inhibit pin is an open-collector/drain negative
logic input that is referenced to GND. Applying a lowlevel ground signal to this input disables the module’s
output and turns off the output voltage. When the Inhibit
control is active, the input current drawn by the regulator is significantly reduced. If the Inhibit pin is left
open-circuit, the module will produce an output whenever a valid input source is applied.
Track: This is an analog control input that enables the
output voltage to follow an external voltage. This pin
becomes active typically 20 ms after the input voltage
has been applied, and allows direct control of the output
voltage from 0 V up to the nominal set-point voltage.
Within this range the output will follow the voltage at
the Track pin on a volt-for-volt basis. When the control
voltage is raised above this range, the module regulates
at its set-point voltage. The feature allows the output
voltage to rise simultaneously with other modules powered from the same input bus. If unused, the input should
be connected to V
. Note: Due to the under-voltage lockout
in
feature, the output of the module cannot follow its own input
voltage during power up. For more information, consult the
related application note.
For technical support and further information, visit http://power.ti.com
Page 3
PTH05050W —5-V Input
6-A, 5-V Input Non-Isolated
Wide-Output Adjust Power Module
SLTS213C – MAY 2003 – REVISED MAY 2004
Environmental & Absolute Maximum Ratings (Voltages are with respect to GND)
Characteristics Symbols Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Track Input Voltage V
Operating Temperature Range T
Solder Reflow Temperature T
Storage Temperature T
Mechanical Shock Per Mil-STD-883D, Method 2002.3
Mechanical Vibration Mil-STD-883D, Method 2007.2
track
a
reflow
s
Over Vin Range –40
Surface temperature of module body or pins 235
— –40 — 125 °C
1 msec, ½ Sine, mounted
20-2000 Hz
Weight — — 2.9 — grams
Flammability — Meets UL 94V-O
Notes: (i) For operation below 0 °C the external capacitors m ust bave stable characteristics. use either a low ESR tantalum, Os-Con, or ceramic capacitor.
(ii) During reflow of SMD package version do not elevate peak temperature of the module, pins or internal components above the stated maximum.
Specifications (Unless otherwise stated, T
=25 °C, Vin =5 V, Vo =3.3 V, Cin =100 µF, Co1 =0 µF, Co2 =0µF, and Io =Iomax)
a
Characteristics Symbols Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Output Current I
Input Voltage Range V
o
in
0.8 V ≤ Vo ≤ 3.6 V, 85°C, natural convection 0 — 6
Over Io range 4.5 — 5.5 V
Set-Point Voltage Tolerance Vo tol — — ±2
Temperature Variation ∆Reg
Line Regulation ∆Reg
Load Regulation ∆Reg
Total Output Variation ∆Reg
temp
line
load
tot
Efficiency η I
Vo Ripple (pk-pk) V
r
–40 °C <Ta < +85 °C — ±0.5 — %V
Over Vin range — ±10 — mV
Over Io range — ±12 — mV
Includes set-point, line, load,
–40 °C ≤ Ta ≤ +85 °C
=4 A R
o
= 698 Ω Vo = 3.3 V — 95 —
SET
= 2.21 kΩ Vo = 2.5 V — 93 —
R
SET
= 4.12 kΩ Vo = 2.0 V — 91 —
R
SET
= 5.49 kΩ Vo = 1.8 V — 90 —
R
SET
= 8.87 kΩ Vo = 1.5 V — 89 —
R
SET
= 17.4 kΩ Vo = 1.2 V — 87 —
R
SET
R
= 36.5 kΩ Vo = 1.0 V — 85 —
SET
20 MHz bandwidth, Co2 =10 µF ceramic — 20
Over-Current Threshold Io trip Reset, followed by auto-recovery — 12 — A
Transient Response 1 A/µs load step, 50 to 100 % I
t
tr
∆V
tr
Co
=100 µF
1
max,
o
Recovery Time — 70 — µSec
Vo over/undershoot — 100 — mV
Track Input Current (pin 2) IIL track Pin to GND — — –130
Track Slew Rate Capability dV
Under-Voltage Lockout UVLO V
Inhibit Control (pin4) Referenced to GND
Input High Voltage V
Input Low Voltage
Input Low Current
V
I
IL
track
IH
IL
inhibit
/dt C
≤ C
(max) — — 1 V/ms
out
out
increasing — 4.3 4.45
in
Vin decreasing 3.4 3.7 —
Pin to GND — –130 — µA
Input Standby Current Iin inh Inhibit (pin 4) to GND, Track (pin 2) open — 10 — mA
Switching Frequency ƒ
External Input Capacitance C
s
in
External Output Capacitance Co1, Co
Over Vin and Io ranges 550 600 650 kHz
Capacitance value non-ceramic 0 100
2
ceramic 0 — 300
Equiv. series resistance (non-ceramic) 4
Reliability MTBF Per Bellcore TR-332
Notes:
(1) No derating is required when the module is soldered directly to a 4-layer PCB with 1 oz. copper.
(2) The set-point voltage tolerance is affected by the tolerance and stability ofR
with 100 ppm/°C or better temperature stability.
(3) The pk-pk output ripple voltage is measured with an external 10 µF ceramic capacitor. See the standard application schematic.
(4) This control pin has an internal pull-up to the input voltage Vin. If it is left open-circuit the module will operate when input power is applied. A small
low-leakage (<100 nA) MOSFET is recommended for control. For further information, consult the related application note.
(5) A 100 µF input capacitor is required for proper operation. The capacitor must be rated for a minimum of 300 mA rms of ripple current.
(6) An external output capacitor is not required for basic operation. Adding 100 µF of distributed capacitance at the load will improve the transient response.
(7) This is the calculated maximum. The minimum ESR limitation will often result in a lower value. Consult the application notes for further guidance.
(8) This is the typcial ESR for all the electrolytic (non-ceramic) output capacitance. Use 7 m
50 % stress, Ta =40 °C, ground benign
. The stated limit is unconditionally met if R
SET
Ω
as the minimum when using max-ESR values to calculate.
–0.3 — Vin + 0.3 V
(i)
— 85 °C
(ii)
— 500 — G’s
—20— G’s
PTH05050W
(1)
(2)
——±3
(3)
Vin –0.5 — Open
–0.2 — 0.6
(5)
100
——µF
(6)
(8)
——mΩ
(2)
— mVpp
(4)
(4)
(7)
3,300
6 ——10
has a tolerance of 1 %
SET
°C
A
%V
%V
%
µA
V
V
µF
6
o
o
o
Hrs
For technical support and further information, visit http://power.ti.com
Page 4
PTH05050W —5-V Input
Typical Characteristics
6-A, 5-V Input Non-Isolated
Wide-Output Adjust Power Module
Characteristic Data; Vin =5 V (See Note A)
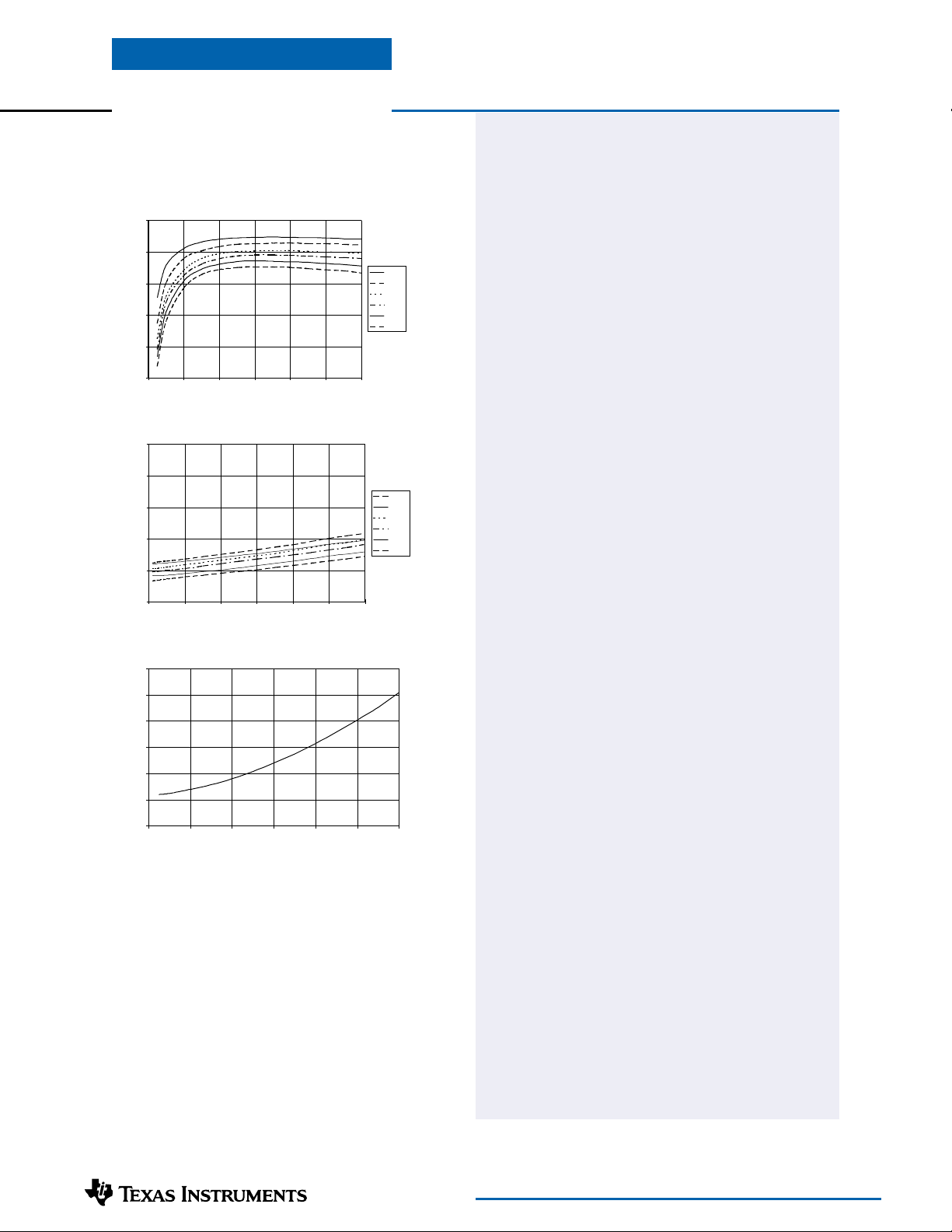
Efficiency vs Load Current
100
90
80
70
Efficiency - %
60
50
0123456
Output Ripple vs Load Current (See Note 3 to Table)
50
40
30
20
Ripple - mV
10
Iout - Amps
SLTS213C – MAY 2003 – REVISED MAY 2004
V
OUT
3.3 V
2.5 V
1.8 V
1.5 V
1.2 V
1.0 V
V
OUT
2.5 V
3.3 V
1.8 V
1.5 V
1.2 V
1.0 V
0
0123456
Power Dissipation vs Load Current
1.50
1.25
1.00
0.75
Pd - Watts
0.50
0.25
0.00
0123456
Iout - Amps
Iout - Amps
Note A: Characteristic data has been developed from actual products tested at 25°C. This data is considered typical data for the Converter.
For technical support and further information, visit http://power.ti.com
Page 5

Application Notes
PTH03050W & PTH05050W
Capacitor Recommendations for the PTH03050 &
PTH05050 Series of Power Modules
Input Capacitor
The recommended input capacitor(s) is determined by
the 100 µF
minimum ripple current rating.
Ripple current, less than 100 mΩ equivalent series resis-
tance (ESR), and temperature are the major considerations
when selecting input capacitors. Unlike polymer tantalum,
regular tantalum capacitors have a recommended mini-
mum voltage rating of 2 × (maximum DC voltage + AC
ripple). This is standard practice to ensure reliability.
For improved ripple reduction on the input bus, ceramic
capacitors may be used to complement electrolytic types
and achieve the minimum required capacitance.
Output Capacitors (Optional)
For applications with load transients (sudden changes in
load current), regulator response will benefit from an
external output capacitance. The recommended output
capacitance of 100 µF will allow the module to meet its
transient response specification (see product data sheet).
For most applications, a high quality computer-grade
aluminum electrolytic capacitor is adequate. These capacitors provide decoupling over the frequency range, 2 kHz
to 150 kHz, and are suitable when ambient temperatures
above 0 °C. For operation below 0 °C tantalum, ceramic
or Os-Con type capacitors are recommended. When using
one or more non-ceramic capacitors, the calculated equiva-
lent ESR should be no lower than 4 mΩ (7 mΩ using the
manufacturer’s maximum ESR for a single capacitor). A
list of preferred low-ESR type capacitors are identified
in Table 1-1.
Ceramic Capacitors
Above 150 kHz the performance of aluminum electrolytic
capacitors becomes less effective. To further improve the
reflected input ripple current or the output transient
response, multilayer ceramic capacitors can also be added.
Ceramic capacitors have very low ESR and their resonant
frequency is higher than the bandwidth of the regulator.
When used on the output their combined ESR is not
critical as long as the total value of ceramic capacitance
does not exceed 300 µF. Also, to prevent the formation of
local resonances, do not place more than five identical ceramic capacitors in parallel with values of 10 µF or greater.
Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum type capacitors can be used at both the input
and output, and are recommended for applications where
the ambient operating temperature can be less than 0 °C.
The AVX TPS, Sprague 593D/594/595 and Kemet T495/
[1]
minimum capacitance and 300 mArms
T510 capacitor series are suggested over many other
tantalum types due to their higher rated surge, power
dissipation, and ripple current capability. As a caution
many general purpose tantalum capacitors have considerably higher ESR, reduced power dissipation and lower
ripple current capability. These capacitors are also less
reliable as they have reduced power dissipation and surge
current ratings. Tantalum capacitors that do not have a
stated ESR or surge current rating are not recommended
for power applications.
When specifying Os-Con and polymer tantalum capacitors
for the output, the minimum ESR limit will be encountered well before the maximum capacitance value is
reached.
Capacitor Table
Table 1-1 identifies the characteristics of capacitors from a
number of vendors with acceptable ESR and ripple current
(rms) ratings. The recommended number of capacitors
required at both the input and output buses is identified
for each capacitor type.
This is not an extensive capacitor list. Capacitors from other
vendors are available with comparable specifications. Those
listed are for guidance. The RMS ripple current rating and
ESR (at 100kHz) are critical parameters necessary to insure
both optimum regulator performance and long capacitor life.
Designing for Very Fast Load Transients
The transient response of the DC/DC converter has been
characterized using a load transient with a di/dt of 1 A/µs.
The typical voltage deviation for this load transient is
given in the data sheet specification table using the
optional value of output capacitance. As the di/dt of a
transient is increased, the response of a converter’s regulation circuit ultimately depends on its output capacitor
decoupling network. This is an inherent limitation with
any DC/DC converter once the speed of the transient
exceeds its bandwidth capability. If the target application
specifies a higher di/dt or lower voltage deviation, the
requirement can only be met with additional output
capacitor decoupling. In these cases special attention
must be paid to the type, value and ESR of the capacitors
selected.
If the transient performance requirements exceed that
specified in the data sheet, or the total amount of load
capacitance is above 3,000 µF, the selection of output
capacitors becomes more important. For further guidance
consult the separate application note, “Selecting Output
Capacitors for PTH Products in High-Performance Applications.”
For technical support and further information, visit http://power.ti.com
Page 6

Application Notes
PTH03050W & PTH05050W
Table 1-1: Input/Output Capacitors
epyT,rodneVroticapaC
)elytS(seireS
cinosanaP
)laidaR(CF
)DMS(KF
oynaS
,XVAmulatnaT
SPT)DMS(V01
temeK
,D595mulatnaT)DMS(
)DMS(munimulA,CF
)DMS(munimulA-yloP,AW
munimulA,cinosanaP
noC–imehCdetinU
)laidaR(noc-sO,SF
)DMS(mulA-yloP,AXP
)DMS(munimulA,ZVM
)laidaR(.mulA-yloP,SP
munimulA,nocihciN
)laidaR(,MP
)DMS(munimulA,GW
)DMS(mulatnaT,55F
)DMS(noc-sO,PVS
)laidaR(noc-sO,PS
)DMS(remyloPpacsoPEPT
)DMS(mulA-yloP,025T
)DMS(mulatnaT,594T
)DMS(.mulA-yloP-007A
eugarpS-yahsiV
)DMS(mulatnaT,D495
)laidaR(noc-sO,AS49
)DMS(R5XcimareC,temeKV61
gnikroW
egatloV)Fµ(eulaV
V52
V01
V61
V61
V01
V01
V61
V01
V53
V52
V01
V01
V61
V01
V01
V01
V01
V3.6
V01
V01
V01
V3.6
022Fµ
033Fµ
021Fµ
022Fµ
001Fµ
001Fµ
021Fµ
001Fµ
01
74
Fµ001
Fµ021
Fµ001
Fµ001
Fµ051
Fµ001
µ022F
Fµ001
Fµ022
Fµ001
Fµ001
Fµ051
Fµ021
Fµ001
003.0 Ω
530.0 Ω
051.0 Ω
061.0 Ω
040.0 Ω
720.0 Ω
071.0 Ω
420.0 Ω
051.0 Ω
061.0 Ω
550.0 Ω
040.0 Ω
520.0 Ω
520.0 Ω
01.00Ω
001.0 Ω
080.0 Ω
001.0 Ω
810.0 Ω
090.0 Ω
041.0 Ω
200.0 Ω
200.0 Ω
scitsiretcarahCroticapaCytitnauQ
)RSE(.xaM
zHk001ta
Ω030.0
elppiR.xaM
C°58ta
)smrI(tnerruC
Am054
Am0082
Am555
Am006
Am0012
Am0342
Am054
Am0244
Am076
Am064
Am0002
Am0052>
Am0082>
Am0042>
Am0901>
Am4141>
× W3.4 × H1.4
Am0021
Am0011>
Am0092
Am0011
Am0001>
× W0.6 × H1.4
Am0762
—esac0121
8× 01
3.8 × 9.6
01 × 2.01
8× 2.01
3.6 × 8.9
8× 7.6
8× 01
8× 5.11
01 × 01
01 × 5.11
7.7 × 3.4
7×8
3.6 × 8.9
3.7 × 7.5
L3.7 × W7.5
× H0.4
8× 5.01
eziSlacisyhP
)mm(
L3.7
L3.7
mm5223
tupnI
suB
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
tuptuO
suB
1
≤5
1
1
≤5
≤4
1
≤4
1
1
1
≤5
≤4
≤4
≤5
≤5
1
1
≤3
1
1
≤4
≤5
]1[
≤5
M001SF01
M021PVS01
M001SPS61
rebmuNrodneV
P101E1CFVEE
P121A1AWFEE
122C1CFUEE
P133C1KFVEE
PT08HM121CV01AXP
PT01HM122CV52ZVM
11HM072SP01
SG1RNM101V1GWU
HPM151E1MPU
NM701A155F
LM022EPT01
0010R010M701DSPT
0010R010M722VSPT
SA010M701D025T
SA010M701X594T
TA600M701D007A
T2C0100X751D495
T2D0100X721D595
PBE0100X701AS49
CAP4M601C0121C
CAP9K674C0121C
cimareC,ataruMR5X)DMS(V3.6
V3.6
V61
V61
cimareC,KDTR5X)DMS(V3.6
V3.6
V61
V61
001
74
22
01
001
74
22
01
200.0 Ω —esac0121
200.0 Ω —esac0121
1
mm5223
mm5223
]1[
2
5
]2[
1
1
]1[
2
5
]2[
1
[1] Total capacitance of 94 µF is acceptable based on the combined ripple current rating.
[2] Small ceramic capacitors may be used to complement electrolytic types at the input to reduce high-frequency ripple current.
For technical support and further information, visit http://power.ti.com
3≤
≤5
≤5
≤5
3≤
≤5
≤5
≤5
M701J06RE23MRG
M674J06RE23MRG
K622C16RE23MRG
K601C16RD23MRG
TM701J0R5X5223C
TM674J0R5X5223C
TM622C1R5X5223C
TM601C1R5X5223C
Page 7

Application Notes
PTH03050W & PTH05050W
Adjusting the Output Voltage of the PTH03050W &
PTH05050W Wide-Output Adjust Power Modules
The Vo Adjust control (pin 5) sets the output voltage to a
value higher than 0.8 V. The adjustment range of the
PT03050W (3.3-V input) is from 0.8 V to 2.5 V 1, and
the PTH05050W (5-V input) from 0.8 V to 3.6 V. The
adjustment method requires the addition of a single
external resistor, R
, that must be connected directly
set
between the Vo Adjust and GND pins 2. Table 2-1 gives
the preferred value of the external resistor for a number
of standard voltages, along with the actual output voltage that this resistance value provides.
For other output voltages the value of the required resistor
can either be calculated using the following formula, or
simply selected from the range of values given in Table 2-2.
Figure 2-1 shows the placement of the required resistor.
R
set
= 10 kΩ ·
Table 2-1; Preferred Values of R
V
(Standard) R
out
1
3.3 V
2.5 V 2.21 kΩ 2.502 V
2 V 4.12 kΩ 2.010 V
1.8 V 5.49 kΩ 1.803 V
1.5 V 8.87 kΩ 1.504 V
1.2 V 17.4 kΩ 1.202 V
1 V 36.5 kΩ 1.005 V
0.8 V Open 0.8 V
Figure 2-1; Vo Adjust Resistor Placement
V
IN
+
C
IN
100 µF
V
IN
(Required)
0.8 V
V
– 0.8 V
out
for Standard Output Voltages
set
(Pref’d Value) V
set
698 Ω 3.309V
2
Track
PTH03050W
GNDInhibit
4
GND
15
– 2.49 kΩ
(Actual)
out
63
V
O
R
SET
1 %
0.1 W
+
C
100 µF
(Optional)
OUT
V
OUT
Table 2-2; Output Voltage Set-Point Resistor Values
Va Req’dR
0.800 Open
0.825 318 kΩ
0.850 158 kΩ
0.875 104 kΩ
0.900 77.5 kΩ
0.925 61.5 kΩ
0.950 50.8 kΩ
0.975 43.2 kΩ
1.000 37.5 kΩ
1.025 33.1 kΩ
1.050 29.5 kΩ
1.075 26.6 kΩ
1.100 24.2 kΩ
1.125 22.1 kΩ
1.150 20.4 kΩ
1.175 18.8 kΩ
1.200 17.5 kΩ
1.225 16.3 kΩ
1.250 15.3 kΩ
1.275 14.4 kΩ
1.300 13.5 kΩ
1.325 12.7 kΩ
1.350 12.1 kΩ
1.375 11.4 kΩ
1.400 10.8 kΩ
1.425 10.3 kΩ
1.450 9.82 kΩ
1.475 9.36 kΩ
1.50 8.94 kΩ
1.55 8.18 kΩ
1.60 7.51 kΩ
1.65 6.92 kΩ
1.70 6.4 kΩ
1.75 5.93 kΩ
1.80 5.51 kΩ
1.85 5.13 kΩ
1.90 4.78 kΩ
1.95 4.47 kΩ
set
Va Req’dR
2.00 4.18 kΩ
2.05 3.91 kΩ
2.10 3.66 kΩ
2.15 3.44 kΩ
2.20 3.22 kΩ
2.25 3.03 kΩ
2.30 2.84 kΩ
2.35 2.67 kΩ
2.40 2.51 kΩ
2.45 2.36 kΩ
2.50 2.22 kΩ
2.55 2.08 kΩ
2.60 1.95 kΩ
2.65 1.83 kΩ
2.70 1.72 kΩ
2.75 1.61 kΩ
2.80 1.51 kΩ
2.85 1.41 kΩ
2.90 1.32 kΩ
2.95 1.23 kΩ
3.00 1.15 kΩ
3.05 1.07 kΩ
3.10 988 Ω
3.15 914 Ω
3.20 843 Ω
3.25 775 Ω
3.30 710 Ω
3.35 647 Ω
3.40 587 Ω
3.45 529 Ω
3.50 473 Ω
3.55 419 Ω
3.60 367 Ω
set
Notes:
1. Modules that operate from a 3.3-V input bus should
not be adjusted higher than 2.5 V.
2. A 0.05-W resistor may be used. The tolerance should
be 1%, with temperature stability of 100 ppm/°C (or
better). Place the resistor as close to the regulator as
possible. Connect the resistor directly between pins 5
and 1 using dedicated PCB traces.
3. Never connect capacitors from V
. Any capacitance added to the Vo Adjust pin will affect
V
out
Adjust to either GND or
o
the stability of the regulator.
For technical support and further information, visit http://power.ti.com
Page 8

Application Notes
PTH/PTV Series of Wide-Output Adjust
Power Modules (3.3/5-V Input)
Features of the PTH Family of Non-Isolated
Wide Output Adjust Power Modules
POLA™ Compatibility
The PTH/PTV family of non-isolated, wide-output adjust
power modules from Texas Instruments are optimized
for applications that require a flexible, high performance
module that is small in size. Each of these products are
POLA™ compatible. POLA-compatible products are
produced by a number of manufacturers, and offer customers advanced, non-isolated modules with the same
footprint and form factor. POLA parts are also asssured
to be interoperable, thereby providing customers with true
second- source availability.
From the basic, “Just Plug it In” functionality of the 6-A
modules, to the 30-A rated feature-rich PTHxx030, these
products were designed to be very flexible, yet simple to
use. The features vary with each product. Table 3-1 provides a quick reference to the features by product series
and input bus voltage.
Table 3-1; Operating Features by Series and Input Bus Voltage
Series Input Bus I
3.3 V 6 A
PTHxx050
PTHxx060
PTHxx010
PTVxx010
PTHxx020
PTVxx020
PTHxx030
5 V 6 A
12 V 6 A
3.3 V / 5 V 10 A
12 V 8 A
3.3 V / 5 V 15 A
12 V 12 A
5 V 8 A
12 V 8 A
3.3 V / 5 V 22 A
12 V 18 A
5 V 18 A
12 V 16 A
3.3 V / 5 V 30 A
12 V 26 A
OUT
For simple point-of-use applications, the PTHxx050
provides operating features such as an on/off inhibit,
output voltage trim, pre-bias startup, and over-current
protection. The PTHxx060 (10 A), and PTHxx010 (15/12 A)
include an output voltage sense, and margin up/down
controls. Then the higher output current, PTHxx020
and PTHxx030 products incorporate over-temperature
shutdown protection.
On/Off Inhibit
Adjust (Trim)
Over-Current
Pre-Bias Startup
Auto-Track™
Output Sense
Margin Up/Down
•••••
•••••
•••••
•••••••
•••••••
•••••••
•••••••
••••• •
••••• •
••••••••
••••••••
••••• ••
••••• ••
••••••••
••••••••
The PTVxx010 and PTVxx020 are similar parts offered
in a vertical, single in-line pin (SIP) profile, at slightly
lower current ratings.
All of the products referenced in Table 3-1 include AutoTrack™. This feature was specifically designed to simplify
the task of sequencing the supply voltages in a power
system. This and other features are described in the following sections.
Soft-Start Power Up
The Auto-Track feature allows the power-up of multiple
modules to be directly controlled from their Track pin.
However in a stand-alone configuration, or when the
Auto-Track feature is not being used, the Track pin should
be directly connected to the input voltage, Vin (see Figure 3-1).
Figure 3–1
Adjust
7104
5
62
V
O
R
, 698Ω
SET
0.1 W, 1 %
98
Track
Up Dn Sense
5 V
+
Thermal Shutdown
GND
C
IN
1,000 µF
V
IN
PTH05020W
GNDInhibit
1
3
When the Track pin is connected to the input voltage the
Auto-Track function is permanently disengaged. This
allows the module to power up entirely under the control
of its internal soft-start circuitry. When power up is under
soft-start control, the output voltage rises to the set-point
at a quicker and more linear rate.
Figure 3–2
HORIZ SCALE: 5 ms/Div
+
Vin (1 V/Div)
Vout (1 V/Div)
Iin (5 A/Div)
C
OUT
330 µF
3.3 V
GND
For technical support and further information visit http://power.ti.com
Page 9

Application Notes
PTH/PTV Series of Wide-Output Adjust
Power Modules (3.3/5-V Input)
From the moment a valid input voltage is applied, the
soft-start control introduces a short time delay (typically
5 ms-10 ms) before allowing the output voltage to rise.
The output then progressively rises to the module’s setpoint voltage. Figure 3-2 shows the soft-start power-up
characteristic of the 22-A output product (PTH05020W),
operating from a 5-V input bus and configured for a 3.3-V
output. The waveforms were measured with a 5-A resistive
load, with Auto-Track disabled. The initial rise in input
current when the input voltage first starts to rise is the
charge current drawn by the input capacitors. Power-up
is complete within 15 ms.
Over-Current Protection
For protection against load faults, all modules incorporate
output over-current protection. Applying a load that
exceeds the regulator’s over-current threshold will cause
the regulated output to shut down. Following shutdown
a module will periodically attempt to recover by initiating
a soft-start power-up. This is described as a “hiccup” mode
of operation, whereby the module continues in a cycle of
successive shutdown and power up until the load fault is
removed. During this period, the average current flowing
into the fault is significantly reduced. Once the fault is
removed, the module automatically recovers and returns
to normal operation.
Over-Temperature Protection
The PTHxx020 and PTHxx030 series of products have
over-temperature protection. These products have an
on-board temperature sensor that protects the module’s
internal circuitry against excessively high temperatures.
A rise in the internal temperature may be the result of a
drop in airflow, or a high ambient temperature. If the
internal temperature exceeds the OTP threshold, the
module’s Inhibit control is automatically pulled low. This
turns the output off. The output voltage will drop as the
external output capacitors are discharged by the load
circuit. The recovery is automatic, and begins with a
soft-start power up. It occurs when the the sensed temperature decreases by about 10 °C below the trip point.
Note: The over-temperature protection is a last resort mechanism to prevent thermal stress to the regulator. Operation at
or close to the thermal shutdown temperature is not recommended and will reduce the long-term reliability of the module.
Always operate the regulator within the specified Safe Operating
Area (SOA) limits for the worst-case conditions of ambient
temperature and airflow.
Output On/Off Inhibit
For applications requiring output voltage on/off control,
each series of the PTH family incorporates an output
Inhibit control pin. The inhibit feature can be used wherever there is a requirement for the output voltage from
the regulator to be turned off.
The power modules function normally when the Inhibit
pin is left open-circuit, providing a regulated output
whenever a valid source voltage is connected to V
in
with
respect to GND.
Figure 3-3 shows the typical application of the inhibit
function. Note the discrete transistor (Q
). The Inhibit
1
control has its own internal pull-up to Vin potential. The
input is not compatible with TTL logic devices. An opencollector (or open-drain) discrete transistor is recommended
for control.
Figure 3–3
Sense
V
o
9
10
V
IN
C
1,000 µF
1 =Inhibit
GND GND
+
IN
Q
BSS138
3
1
8
PTH05020W
1
7
R
SET
5
4
62
C
OUT
330 µF
V
OUT
+
Turning Q1 on applies a low voltage to the Inhibit control
and disables the output of the module. If Q1 is then turned
off, the module will execute a soft-start power-up. A
regulated output voltage is produced within 20 msec.
Figure 3-4 shows the typical rise in both the output voltage and input current, following the turn-off of Q1. The
turn off of Q1 corresponds to the rise in the waveform,
Q1 Vds. The waveforms were measured with a 5-A load.
Figure 3–4
Vo (2V/Div)
Iin (2A/Div)
Q1Vds (5V/Div)
HORIZ SCALE: 10ms/Div
L
O
A
D
For technical support and further information visit http://power.ti.com
Page 10

Application Notes
PTH/PTV Series of Wide-Output Adjust
Power Modules (3.3/5-V Input)
Auto-Track™ Function
The Auto-Track function is unique to the PTH/PTV
family, and is available with the all POLA-compatible
products. Auto-Track was designed to simplify the amount
of circuitry required to make the output voltage from each
module power up and power down in sequence. The
sequencing of two or more supply voltages during power
up is a common requirement for complex mixed-signal
applications, that use dual-voltage VLSI ICs such as DSPs,
micro-processors, and ASICs.
How Auto-Track Works
Auto-Track works by forcing the module’s output voltage
to follow a voltage presented at the Track control pin. This
control range is limited to between 0 V and the module’s
set-point voltage. Once the track-pin voltage is raised
above the set-point voltage, the module’s output remains
at its set-point
regulator is at 1 V, the regulated output will be 1 V. But
if the voltage at the Track pin rises to 3 V, the regulated
output will not go higher than 2.5 V.
When under track control, the regulated output from
the module follows the voltage at its Track pin on a voltfor-volt basis. By connecting the Track pin of a number
of these modules together, the output voltages will follow a common signal during power-up and power-down.
The control signal can be an externally generated master
ramp waveform, or the output voltage from another power
supply circuit
porates an internal RC charge circuit. This operates off
the module’s input voltage to provide a suitable rising
voltage ramp waveform.
Typical Application
The basic implementation of Auto-Track allows for
simultaneous voltage sequencing of a number of AutoTrack compliant modules. Connecting the Track control
pins of two or more modules forces the Track control of
all modules to follow the same collective RC ramp waveform, and allows them to be controlled through a single
transistor or switch; Q1 in Figure 3-5.
To initiate a power-up sequence the Track control must
first pulled to ground potential. This should be done at
or before input power is applied to the modules, and then
held for at least 10 ms thereafter. This brief period gives
the modules time to complete their internal soft-start
initialization, which enables them to produce an output
voltage.
Applying a logic-level high signal to the circuit’s On/Off
Control turns Q
Track control. After completing their internal soft-start
intialization, the output of all modules will remain at zero
volts while Q1 is on. 10 ms after a valid input voltage has
been applied to all modules, Q1 can be turned off. This
allows the track control voltage to automatically rise
toward to the modules' input voltage. During this period
the output voltage of each module will rise in unison with
1
. As an example, if the Track pin of a 2.5-V
3
. For convenience the Track control incor-
on and applies a ground signal to the
1
other modules, to its respective set-point voltage.
Figure 3-6 shows the output voltage waveforms from the
circuit of Figure 3-5 after the On/Off Control is set from a
high to a low-level voltage. The waveforms, Vo
and Vo
1
represent the output voltages from the two power modules, U1 (3.3 V) and U2 (1.8 V) respectively. Vo1 and Vo
are shown rising together to produce the desired simultaneous power-up characteristic.
The same circuit also provides a power-down sequence.
Power down is the reverse of power up, and is accomplished by lowering the track control voltage back to zero
volts. The important constraint is that a valid input voltage
must be maintained until the power down is complete. It
also requires that Q
be turned off relatively slowly. This
1
is so that the Track control voltage does not fall faster than
Auto-Track's slew rate capability, which is 1 V/ms. The
components R1 and C1 in Figure 3-5 limit the rate at
which Q1 can pull down the Track control voltage. The
values of 100 k-ohm and 0.1 µF correlate to a decay rate
of about 0.17 V/ms.
The power-down sequence is initiated with a low-to-high
transition at the On/Off Control input to the circuit.
Figure 3-7 shows the power-down waveforms. As the
Track control voltage falls below the nominal set-point
voltage of each power module, then its output voltage
decays with all the other modules under Auto-Track
control.
Notes on Use of Auto-Track™
1. The Track pin voltage must be allowed to rise above
the module’s set-point voltage before the module can
regulate at its adjusted set-point voltage.
2. The Auto-Track function will track almost any voltage
ramp during power up, and is compatible with ramp
speeds of up to 1 V/ms.
3. The absolute maximum voltage that may be applied to the
Track pin is V
4. The module will not follow a voltage at its Track control
input until it has completed its soft-start initialization.
This takes about 10 ms from the time that the module
has sensed that a valid voltage has been applied its input.
During this period, it is recommended that the Track
pin be held at ground potential.
5. The module is capable of both sinking and sourcing
current when following a voltage at its Track pin.
Therefore startup into an output prebias is not supported
during Auto-Track control.
not necessary when all supply voltages rise simultaneously
under the control of Auto-Track.
6. The Auto-Track function can be disabled by connecting
the Track pin to the input voltage (V
disabled, the output voltage will rise at a quicker and
more linear rate after input power is applied.
.
in
Note: A pre-bias holdoff is
). With Auto-Track
in
2
2
For technical support and further information visit http://power.ti.com
Page 11

Application Notes
PTH/PTV Series of Wide-Output Adjust
Power Modules (3.3/5-V Input)
Figure 3–5; Sequenced Power Up & Power Down Using Auto-Track
+5 V
On/Off Control
1 = Power Down
0 = Power Up
0 V
R1
100 k
C1
0.1 µF
Q1
BSS138
U1
V
+
C
IN
U2
V
+
C
IN
98
10
PTH05020W
IN
GNDInhibit
3
1
10
98
PTH05010W
IN
GNDInhibit
1
3
Track
Track
5
=3.3 V
Vo
62
V
O
1
+
R
698
4
C
2
5
OUT
Vo2 =1.8 V
62
V
O
7
+
R
3
5k49
4
C
OUT
7
Figure 3–6; Simultaneous Power Up with Auto-Track Control
Vo1 (1 V/Div)
Vo2 (1 V/Div)
HORIZ SCALE: 10 ms/Div
On/Off Input
(5 V/Div)
Figure 3–7; Simultaneous Power Down with Auto-Track Control
Vo1 (1 V/Div)
Vo2 (1 V/Div)
On/Off Input
(5 V/Div)
HORIZ SCALE: 10 ms/Div
For technical support and further information visit http://power.ti.com
Page 12

Application Notes
(
)
PTH/PTV Series of Wide-Output Adjust
Power Modules (3.3/5-V Input)
Margin Up/Down Controls
The PTHxx060, PTHxx010, PTHxx020, and PTHxx030
products incorporate Margin Up and Margin Down control inputs. These controls allow the output voltage to be
momentarily adjusted 1, either up or down, by a nominal
5%. This provides a convenient method for dynamically
testing the operation of the load circuit over its supply
margin or range. It can also be used to verify the function
of supply voltage supervisors. The ±5% change is applied
to the adjusted output voltage, as set by the external resistor, R
at the Vo Adjust pin.
set
The 5% adjustment is made by pulling the appropriate
margin control input directly to the GND terminal
2
A low-leakage open-drain device, such as an n-channel
MOSFET or p-channel JFET is recommended for this
3
purpose
. Adjustments of less than 5% can also be accommodated by adding series resistors to the control inputs.
The value of the resistor can be selected from Table 3-2,
or calculated using the following formula.
Up/Down Adjust Resistance Calculation
To reduce the margin adjustment to a value less than 5%,
series resistors are required (See RD and RU in Figure 3-8).
For the same amount of adjustment, the resistor value
calculated for RU and RD will be the same. The formulas
is as follows.
RU or RD=
Where ∆% = The desired amount of margin adjust in
499
∆%
percent.
– 99.8 kΩ
Notes:
1. The Margin Up* and Margin Dn* controls were not
intended to be activated simultaneously. If they are
their affects on the output voltage may not completely
cancel, resulting in the possibility of a slightly higher
error in the output voltage set point.
2. The ground reference should be a direct connection to
the module GND at pin 7 (pin 1 for the PTHxx050).
This will produce a more accurate adjustment at the
load circuit terminals. The transistors Q
1
be located close to the regulator.
.
3. The Margin Up and Margin Dn control inputs are not
compatible with devices that source voltage. This includes
TTL logic. These are analog inputs and should only be
controlled with a true open-drain device (preferably
a discrete MOSFET transistor). The device selected
should have low off-state leakage current. Each input
sources 8 µA when grounded, and has an open-circuit
voltage of 0.8 V.
Table 3-2; Margin Up/Down Resistor Values
% Adjust RU / R
5 0.0 kΩ
4 24.9 kΩ
3 66.5 kΩ
2 150.0 kΩ
1 397.0 kΩ
D
and Q2 should
Figure 3–8; Margin Up/Down Application Schematic
V
IN
RDR
+
C
in
Q
MargDn
MargUp
GND
1
1
2
U
Q
2
10 9 8
PTH05010W
Top View
543
R
SET
0.1 W, 1 %
7
6
+V
o
0V
+V
OUT
+
C
out
GND
L
O
A
D
For technical support and further information visit http://power.ti.com
Page 13

Application Notes
PTH/PTV Series of Wide-Output Adjust
Power Modules (3.3/5-V Input)
Pre-Bias Startup Capability
A pre-bias startup condition occurs as a result of an external
voltage being present at the output of a power module prior
to its output becoming active. This often occurs in complex digital systems when current from another power
source is backfed through a dual-supply logic component,
such as an FPGA or ASIC. Another path might be via
clamp diodes as part of a dual-supply power-up sequencing
arrangement. A prebias can cause problems with power
modules that incorporate synchronous rectifiers. This is
because under most operating conditions, these types of
modules can sink as well as source output current.
The PTH/PTV family of power modules incorporate
synchronous rectifiers, but will not sink current during
1
startup
to ensure satisfactory operation of this function, certain
conditions must be maintained.
application demonstrating the pre-bias startup capability.
The start-up waveforms are shown in Figure 3-10. Note
that the output current from the PTH03010W (Io) shows
negligible current until its output voltage rises above
that backfed through diodes D1 and D2.
Note: The pre-bias start-up feature is not compatible with
Auto-Track. When the module is under Auto-Track control,
it will sink current if the output voltage is below that of a
back-feeding source. To ensure a pre-bias hold-off one of two
approaches must be followed when input power is applied to
the module. The Auto-Track function must either be disabled 3,
or the module’s output held off (for at least 50 ms) using the
Inhibit pin. Either approach ensures that the Track pin voltage is above the set-point voltage at start up.
, or whenever the Inhibit pin is held low. However,
2
Figure 3-9 shows an
Notes
1. Startup includes the short delay (approx. 10 ms) prior
to the output voltage rising, followed by the rise of the
output voltage under the module’s internal soft-start
control. Startup is complete when the output voltage
has risen to either the set-point voltage or the voltage
at the Track pin, whichever is lowest.
2. To ensure that the regulator does not sink current when
power is first applied (even with a ground signal applied
to the Inhibit control pin), the input voltage
be greater than the output voltage
must always
throughout the
power-up and power-down sequence.
3. The Auto-Track function can be disabled at power up
by immediately applying a voltage to the module’s Track
pin that is greater than its set-point voltage. This can
be easily accomplished by connecting the Track pin to
.
V
in
Figure 3–10; Pre-Bias Startup Waveforms
Vin (1 V/Div)
Vo (1 V/Div)
Io (5 A/Div)
Figure 3–9; Application Circuit Demonstrating Pre-Bias Startup
V
= 3.3 V
IN
10
98
Track
V
PTH03010W
IN
GNDInhibit
1
3
+
C
IN
330 µF
HORIZ SCALE: 5 ms/Div
5
Sense
62
V
O
Vadj
4
7
R
2
2k21
+
C
330 µF
Vo = 2.5 V
+
I
o
VCORE
OUT
VCCIO
ASIC
For technical support and further information visit http://power.ti.com
Page 14

Application Notes
PTH/PTV Series of Wide-Output Adjust
Power Modules (3.3/5-V Input)
Remote Sense
Products with this feature incorporate an output voltage
sense pin, V
regulation performance of the module by allowing it to
compensate for any ‘IR’ voltage drop between itself and
the load. An IR drop is caused by the high output current
flowing through the small amount of pin and trace resistance. To use this feature simply connect the V
to the V
standard application). If not used, the Vo Sense pin can
be left open-circuit. An internal low-value resistor (15-Ω
or less) is connected between the Vo Sense and V
ensures the output voltage remains in regulation.
With the sense pin connected, the difference between
the voltage measured directly between the V
pins, and that measured from Vo Sense to GND, is the
amount of IR drop being compensated by the regulator.
This should be limited to a maximum of 0.3 V.
Note: The remote sense feature is not designed to compensate
for the forward drop of non-linear or frequency dependent
components that may be placed in series with the converter
output. Examples include OR-ing diodes, filter inductors,
ferrite beads, and fuses. When these components are enclosed
by the remote sense connection they are effectively placed
inside the regulation control loop, which can adversely affect
the stability of the regulator.
Sense. A remote sense improves the load
o
Sense pin
node, close to the load circuit (see data sheet
out
o
. This
out
and GND
out
For technical support and further information visit http://power.ti.com
Page 15

PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM
www.ti.com
7-Sep-2005
PACKAGING INFORMATION
Orderable Device Status
PTH05050WAD ACTIVE DIP MOD
(1)
Package
Type
Package
Drawing
Pins Package
Qty
Eco Plan
EUU 6 56 TBD Call TI Call TI
ULE
PTH05050WAH ACTIVE DIP MOD
EUU 6 56 TBD Call TI Level-1-235C-UNLIM
ULE
PTH05050WAS ACTIVE DIP MOD
EUV 6 56 TBD Call TI Level-1-235C-UNLIM
ULE
PTH05050WAST ACTIVE DIP MOD
EUV 6 250 TBD CallTI Level-1-235C-UNLIM
ULE
PTH05050WAZ ACTIVE DIP MOD
EUV 6 56 Pb-Free
ULE
PTH05050WAZT ACTIVE DIP MOD
EUV 6 250 Pb-Free
ULE
(1)
The marketing status values are defined as follows:
ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs.
LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect.
NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in
a new design.
PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available.
OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device.
(RoHS)
(RoHS)
(2)
Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp
Call TI Level-3-260C-168 HR
Call TI Level-3-260C-168 HR
(3)
(2)
Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS) or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check
http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability information and additional product content details.
TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined.
Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements
for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered
at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes.
Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame
retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous material)
(3)
MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder
temperature.
Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is
provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the
accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take
reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on
incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited
information may not be available for release.
In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI
to Customer on an annual basis.
Addendum-Page 1
Page 16

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications,
enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue
any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing
orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are sold subject to TI’s terms
and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI
deems necessary to support this warranty . Except where mandated by government requirements, testing of all
parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for
their products and applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products
and applications, customers should provide adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right,
copyright, mask work right, or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process
in which TI products or services are used. Information published by TI regarding third-party products or services
does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof.
Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property
of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without
alteration and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction
of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for
such altered documentation.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that
product or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and
is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application
solutions:
Products Applications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Audio www.ti.com/audio
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Automotive www.ti.com/automotive
DSP dsp.ti.com Broadband www.ti.com/broadband
Interface interface.ti.com Digital Control www.ti.com/digitalcontrol
Logic logic.ti.com Military www.ti.com/military
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Optical Networking www.ti.com/opticalnetwork
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Telephony www.ti.com/telephony
Video & Imaging www.ti.com/video
Wireless www.ti.com/wireless
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments
Post Office Box 655303 Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright 2005, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...