Page 1
D
Low Supply Voltage Range 1.8 V – 3.6 V
D
Ultralow-Power Consumption
Low Operation Current,
1.3 µA at 4 kHz, 2.2 V
160 µA at 1 MHz, 2.2 V
D
Five Power Saving Modes:
(Standby Mode: 0.8 µA,
RAM Retention Off Mode: 0.1 µA)
D
Wake-Up From Standby Mode in 6 µs
D
16-Bit RISC Architecture, 125 ns
Instruction Cycle Time
D
Basic Clock Module Configurations:
– Various Internal Resistors
– Single External Resistor
– 32 kHz Crystal
– High Frequency Crystal
– Resonator
– External Clock Source
D
16-Bit Timer With Three Capture/Compare
Registers
D
Slope A/D Converter With External
Components
D
On-Chip Comparator for Analog Signal
Compare Function or Slope A/D
Conversion
description
D
Serial Onboard Programming
D
Programmable Code Protection by Security
Fuse (C11x1 Only)
D
Family Members Include:
MSP430C1 111: 2KB ROM,128B RAM
MSP430C1 121: 4KB ROM, 256B RAM
MSP430F1101: 1KB + 128B Flash Memory
MSP430F1121: 4KB + 256B Flash Memory
D
Available in a 20-Pin Plastic Small-Outline
Wide Body (SOWB) Package and 20-Pin
Plastic Thin Shrink Small-Outline Package
(TSSOP)
TEST
VCC
P2.5/R
osc
V
SS
XOUT
XIN
/NMI
RST
P2.0/ACLK
P2.1/INCLK
P2.2/CAOUT/TA0
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
(MTP{), 128B RAM
(MTP{), 256B RAM
DW OR PW PACKAGE
(TOP VIEW)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
P1.7/TA2/TDO/TDI
P1.6/TA1/TDI
P1.5/TA0/TMS
P1.4/SMCLK/TCK
P1.3/TA2
P1.2/TA1
P1.1/TA0
P1.0/TACLK
P2.4/CA1/TA2
P2.3/CA0/TA1
The T exas Instruments MSP430 series is an ultralow-power microcontroller family consisting of several devices
featuring different sets of modules targeted to various applications. The microcontroller is designed to be battery
operated for an extended-application lifetime. With 16-bit RISC architecture, 16 bit integrated registers on the
CPU, and a constant generator, the MSP430 achieves maximum code efficiency. The digitally-controlled
oscillator provides fast wake-up from all low-power modes to active mode in less than 6 ms.
Typical applications include sensor systems that capture analog signals, convert them to digital values, and then
process the data and display them or transmit them to a host system. Stand alone RF sensor front end is another
area of application. The I/O port inputs provide single slope A/D conversion capability on resistive sensors. The
MSP430x11x series is an ultralow-power mixed signal microcontroller with a built in 16-bit timer and fourteen
I/O pins. The MSP430x11x1 family adds a versatile analog comparator.
The flash memory provides added flexibility of in-system programming and data storage without significantly
increasing the current consumption of the device. The programming voltage is generated on-chip, thereby
alleviating the need for an additional supply , and even allowing for reprogramming of battery-operated systems.
Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of
Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet.
{
MTP = Multiple Time Programmable
PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date.
Products conform to specifications per the terms of Texas Instruments
standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include
testing of all parameters.
Copyright 2000, Texas Instruments Incorporated
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
1
Page 2
MSP430x11x1
40°C to 85°C
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
T
A
°
–
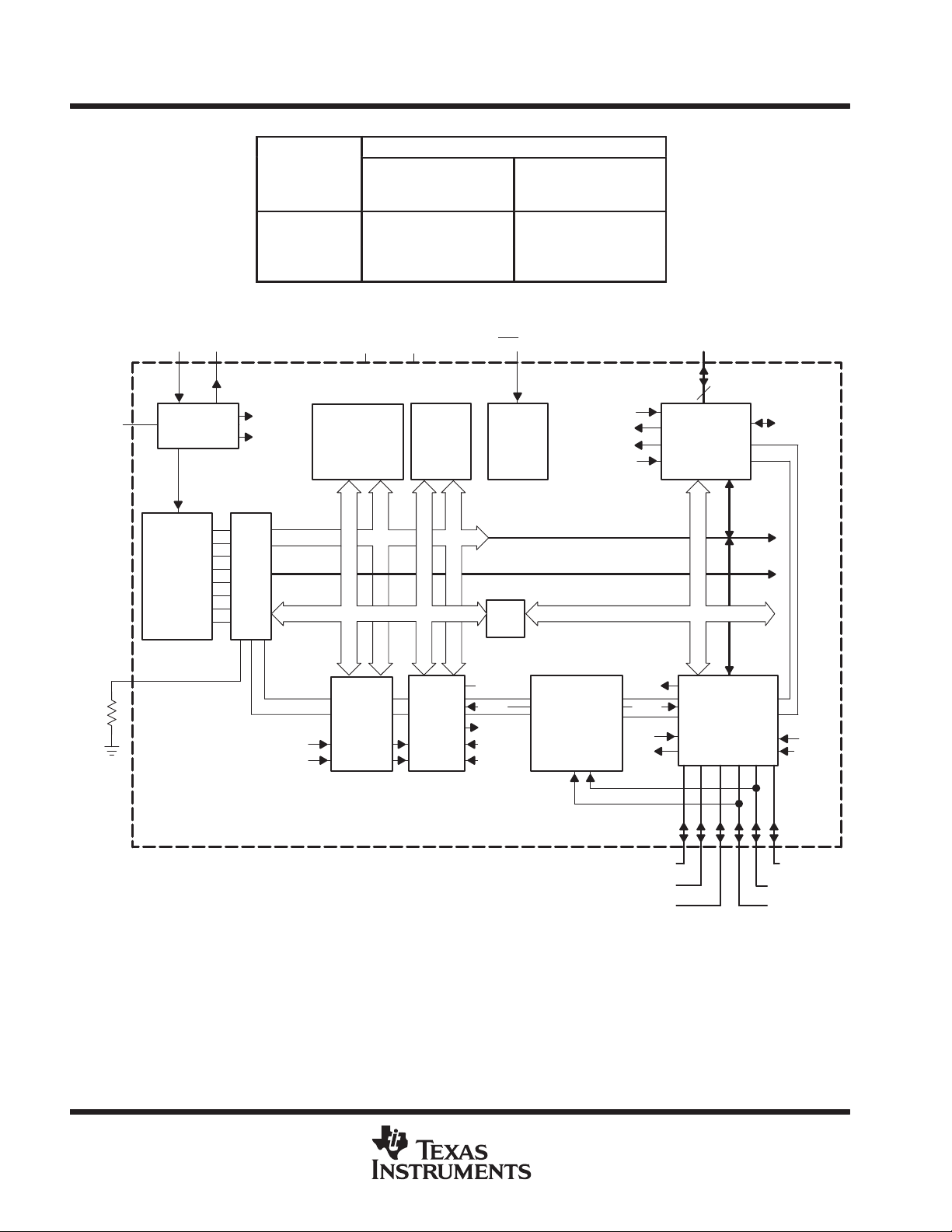
functional block diagram
°
AVAILABLE OPTIONS
PACKAGED DEVICES
PLASTIC
20-PIN SOWB
(DW)
MSP430C1111IDW
MSP430C1121IDW
MSP430F1101IDW
MSP430F1121IDW
PLASTIC
20-PIN TSSOP
(PW)
MSP430F1101IPW
MSP430F1121IPW
TEST
Rosc
†
XIN XOUT
Oscillator
System Clock
MCLK
CPU
Incl. 16 Reg.
Test
JTAG
ACLK
SMCLK
MAB, 16 Bit
MDB, 16 Bit
ACLK
SMCLK
V
CC
1/2/4 KB ROM/
Flash+126/256B
Flash INFO
’C’: ROM
’F’: Flash
Watchdog
Timer
15/16 Bit
V
SS
128/256B
RAM
Timer_A
3 CC
Register
CCR0/1/2
x = 0, 1, 2
RST/NMI P1.0–7
Power-on-
Reset
Bus
Conv.
TACLK or
INCLK
CCI1
Outx
CCIx
CCIx
Comparator-A
Input Multiplexer
RC Filtered O/P
Internal Vref
Analog Switch
Outx
CCIxA
TACLK
SMCLK
MAB, 4 Bit
MCB
MDB, 8 Bit
INCLK
Out0
CCI0
8 I/O’s, All With
CCI1
8
I/O Port P1
Interrupt
Capabililty
I/O Port P2
6 I/O’s All With
Interrupt
Capabililty
JTAG
ACLK
DCOR
†
2
A pulldown resistor of 30 kΩ is needed on F11x1.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
P2.0 / ACLK
P2.1 / INCLK
P2.2 / CAOUT/TA0
P2.5 / Rosc
P2.4 / CA1/TA2
P2.3 / CA0/TA1
Page 3
MSP430x11x1
TERMINAL
I/O
DESCRIPTION
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
Terminal Functions
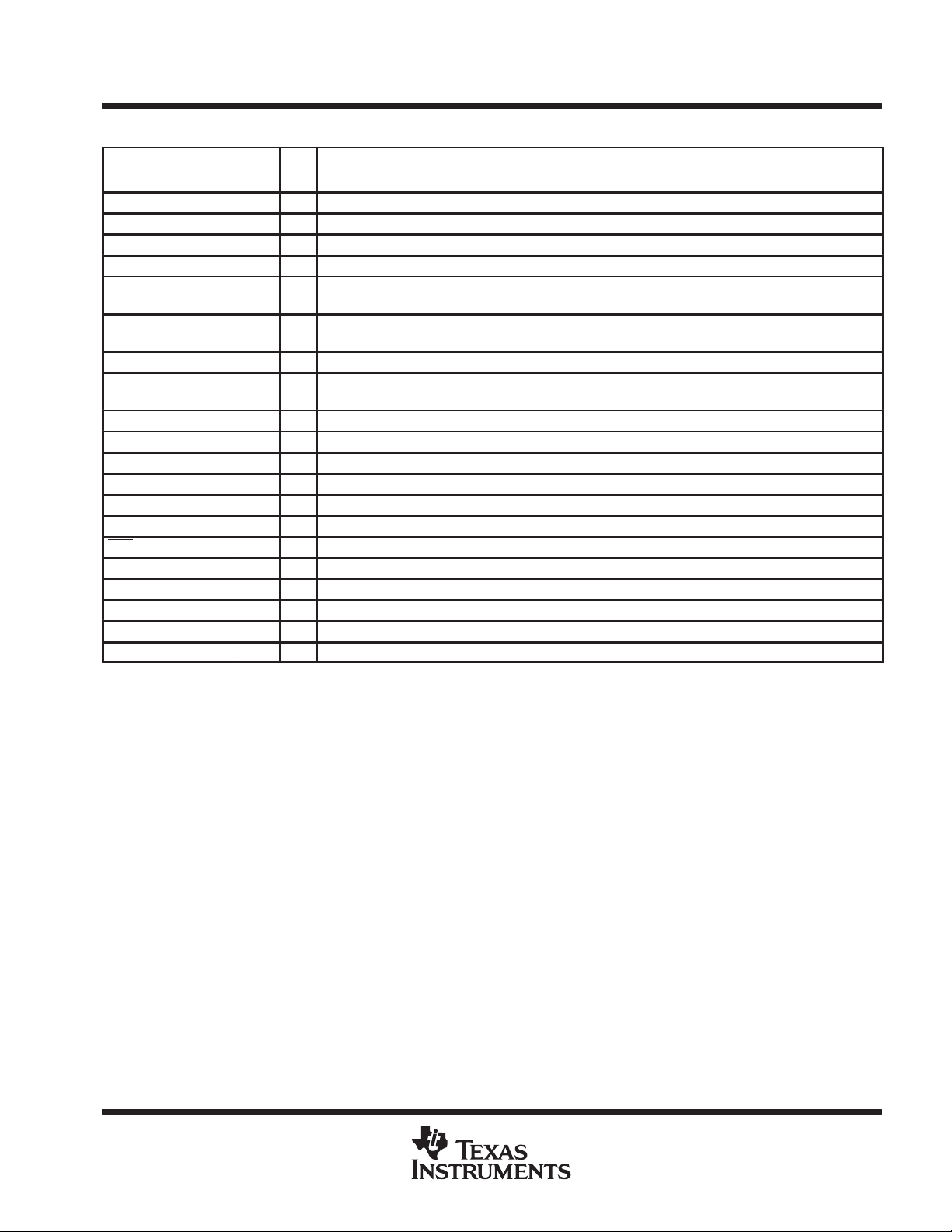
NAME NO.
P1.0/TACLK 13 I/O General-purpose digital I/O pin/Timer_A, clock signal TACLK input
P1.1/TA0 14 I/O General-purpose digital I/O pin/Timer_A, capture: CCI0A input, compare: Out0 output
P1.2/TA1 15 I/O General-purpose digital I/O pin/Timer_A, capture: CCI1A input, compare: Out1 output
P1.3/TA2 16 I/O General-purpose digital I/O pin/Timer_A, capture: CCI2A input, compare: Out2 output
P1.4/SMCLK/TCK 17 I/O General-purpose digital I/O pin/SMCLK signal output/test clock, input terminal for device programming
P1.5/TA0/TMS 18 I/O General-purpose digital I/O pin/Timer_A, compare: Out0 output/test mode select, input terminal for
P1.6/TA1/TDI 19 I/O General-purpose digital I/O pin/Timer_A, compare: Out1 output/test data input terminal
P1.7/TA2/TDO/TDI
P2.0/ACLK 8 I/O General-purpose digital I/O pin/ACLK output
P2.1/INCLK 9 I/O General-purpose digital I/O pin/Timer_A, clock signal at INCLK
P2.2/CAOUT/T A0 10 I/O General-purpose digital I/O pin/Timer_A, capture: CCI0B input/comparator_A, output
P2.3/CA0/T A1 11 I/O General-purpose digital I/O pin/Timer_A, compare: Out1 output/comparator_A, input
P2.4/CA1/T A2 12 I/O General-purpose digital I/O pin/Timer_A, compare: Out2 output/comparator_A, input
P2.5/R
osc
RST/NMI 7 I Reset or nonmaskable interrupt input
TEST 1 I Select of test mode for JTAG pins on Port1. Must be tied low with less than 30 kΩ (F11x1).
VCC 2 Supply voltage
V
SS
XIN 6 I Input terminal of crystal oscillator
XOUT 5 I/O Output terminal of crystal oscillator
†
TDO or TDI is selected via JTAG instruction.
†
20 I/O General-purpose digital I/O pin/Timer_A, compare: Out2 output/test data output terminal or data input
3 I/O General-purpose digital I/O pin/Input for external resistor that defines the DCO nominal frequency
4 Ground reference
and test
device programming and test
during programming
short-form description
processing unit
The processing unit is based on a consistent, and orthogonally-designed CPU and instruction set. This design
structure results in a RISC-like architecture, highly transparent to the application development, and noted for
its programming simplicity . All operations other than program-flow instructions are consequently performed as
register operations in conjunction with seven addressing modes for source, and four modes for destination
operands.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
3
Page 4
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
short-form description (continued)
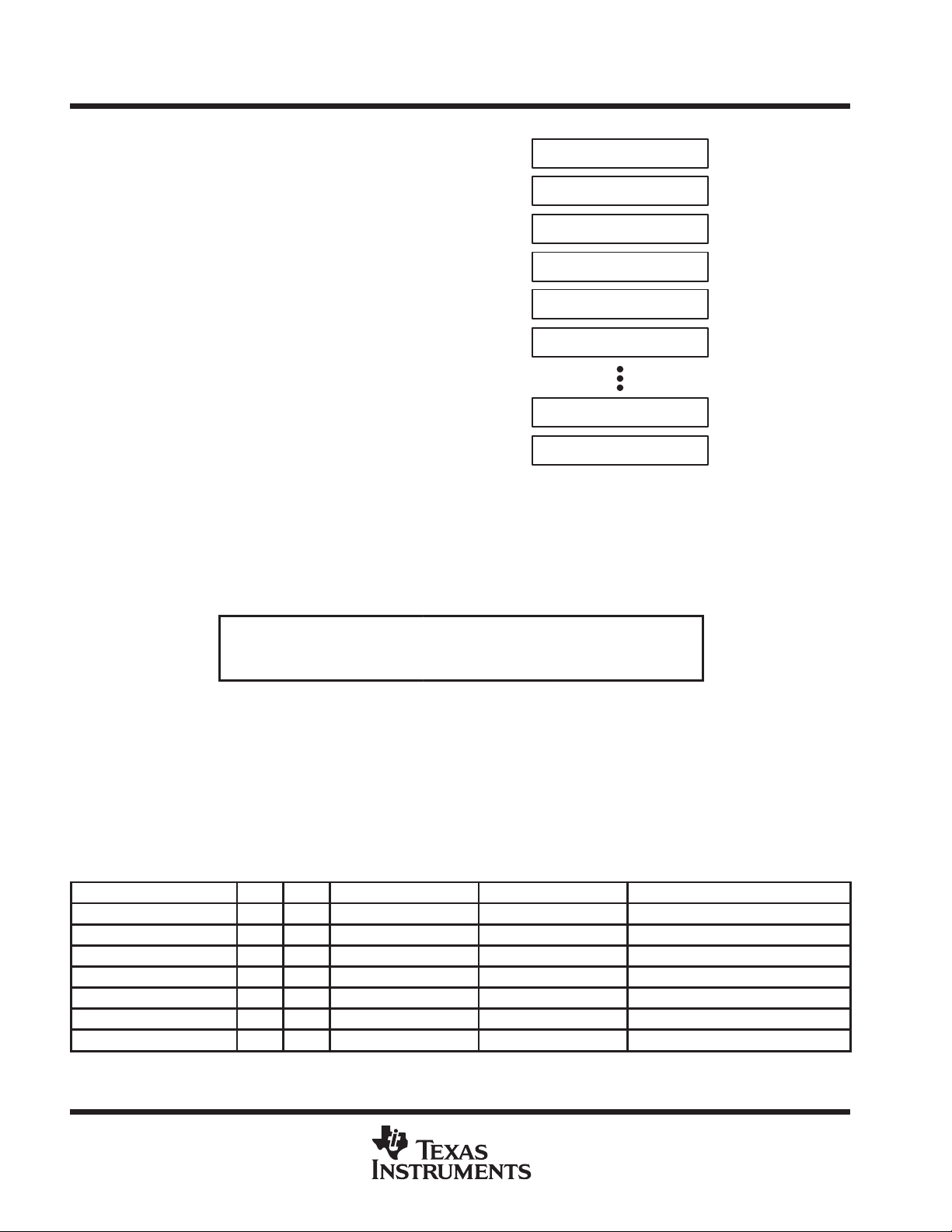
CPU
Program Counter
PC/R0
All sixteen registers are located inside the CPU,
Stack Pointer
SP/R1
providing reduced instruction execution time. This
reduces a register-register operation execution
Status Register
SR/CG1/R2
time to one cycle of the processor.
Constant Generator
CG2/R3
Four registers are reserved for special use as a
program counter, a stack pointer , a status register,
General-Purpose Register
R4
and a constant generator. The remaining twelve
registers are available as general-purpose
General-Purpose Register
R5
registers.
Peripherals are connected to the CPU using a
data address and control buses and can be
General-Purpose Register R14
handled easily with all instructions for memory
manipulation.
General-Purpose Register
R15
instruction set
The instructions set for this register-register architecture provides a powerful and easy-to-use assembly
language. The instruction set consists of 51 instructions with three formats and seven addressing modes.
T able 1 provides a summation and example of the three types of instruction formats; the addressing modes are
listed in Table 2.
Table 1. Instruction Word Formats
Dual operands, source-destination e.g. ADD R4, R5 R4 + R5 → R5
Single operands, destination only e.g. CALL R8 PC → (TOS), R8 → PC
Relative jump, un-/conditional e.g. JNE Jump-on equal bit = 0
Most instructions can operate on both word and byte data. Byte operations are identified by the suffix B.
Examples: Instructions for word operation Instructions for byte operation
MOV EDE,TONI MOV.B EDE,TONI
ADD #235h,&MEM ADD.B #35h,&MEM
PUSH R5 PUSH.B R5
SWPB R5 —
Table 2. Address Mode Descriptions
ADDRESS MODE s d SYNTAX EXAMPLE OPERATION
Register √ √ MOV Rs, Rd MOV R10, R11 R10 → R11
Indexed √ √ MOV X(Rn), Y(Rm) MOV 2(R5), 6(R6) M(2 + R5) → M(6 + R6)
Symbolic (PC relative) √ √ MOV EDE, TONI M(EDE) → M(TONI)
Absolute √ √ MOV &MEM, &TCDAT M(MEM) → M(TCDAT)
Indirect √ MOV @Rn, Y(Rm) MOV @R10, Tab(R6) M(R10) → M(Tab + R6)
Indirect autoincrement √ MOV @Rn+, RM MOV @R10+, R11 M(R10) → R11, R10 + 2 → R10
Immediate √ MOV #X, TONI MOV #45, TONI #45 → M(TONI)
NOTE: s = source d = destination Rs/Rd = source register/destination register Rn = register number
4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 5

MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
instruction set (continued)
Computed branches (BR) and subroutine calls (CALL) instructions use the same addressing modes as the other
instructions. These addressing modes provide
calls. The full use of this programming capability permits a program structure different from conventional 8- and
16-bit controllers. For example, numerous routines can easily be designed to deal with pointers and stacks
instead of using flag type programs for flow control.
indirect
operation modes and interrupts
The MSP430 operating modes support various advanced requirements for ultralow-power and ultralow energy
consumption. This is achieved by the intelligent management of the operations during the different module
operation modes and CPU states. The advanced requirements are fully supported during interrupt event
handling. An interrupt event awakens the system from each of the various operating modes and returns with
the
RETI
instruction to the mode that was selected before the interrupt event. The different requirements of the
CPU and modules, which are driven by system cost and current consumption objectives, necessitate the use
of different clock signals:
D
Auxiliary clock ACLK (from LFXT1CLK/crystal’s frequency), used by the peripheral modules
D
Main system clock MCLK, used by the CPU and system
D
Subsystem clock SMCLK, used by the peripheral modules
addressing, ideally suited for computed branches and
low-power consumption capabilities
The various operating modes are controlled by the software through controlling the operation of the internal
clock system. This clock system provides many combinations of hardware and software capabilities to run the
application with the lowest power consumption and with optimized system costs:
D
Use the internal clock (DCO) generator without any external components.
D
Select an external crystal or ceramic resonator for lowest frequency or cost.
D
Select and activate the proper clock signals (LFXT1CLK and/or DCOCLK) and clock pre-divider function.
D
Apply an external clock source.
Four of the control bits that influence the operation of the clock system and support fast turnon from low power
operating modes are located in the status register SR. The four bits that control the CPU and the system clock
generator are SCG1, SCG0, OscOff, and CPUOff:
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
5
Page 6

MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
status register R2
15 9 8 7 0
Reserved For Future
Enhancements
rw-0 rw-0 rw-0 rw-0 rw-0 rw-0 rw-0 rw-0 rw-0 rw-0
V SCG1 SCG0 OscOff
6543 21
CPUOff GIE N Z C
The bits CPUOff, SCG1, SCG0, and OscOff are the most important low-power control bits when the basic
function of the system clock generator is established. They are pushed onto the stack whenever an interrupt
is accepted and thereby saved so that the previous mode of operation can be retrieved after the interrupt
request. During execution of an interrupt handler routine, the bits can be manipulated via indirect access of the
data on the stack. That allows the program to resume execution in another power operating mode after the
return from interrupt (RETI).
SCG1: The clock signal SMCLK, used for peripherals, is enabled when bit SCG1 is reset or disabled if
the bit is set.
SCG0: The dc-generator is active when SCG0 is reset. The dc-generator can be deactivated only if the
SCG0 bit is set and the DCOCLK signal is not used for MCLK or SMCLK. The current consumed
by the dc-generator defines the basic frequency of the DCOCLK. It is a dc current.
The clock signal DCOCLK is deactivated if it is not used for MCLK or SMCLK or if the SCG0 bit
is set. There are two situations when the SCG0 bit cannot switch off the DCOCLK signal:
1. DCOCLK frequency is used for MCLK (CPUOff=0 and SELM.1=0).
2. DCOCLK frequency is used for SMCLK (SCG1=0 and SELS=0).
NOTE:
When the current is switched off (SCG0=1) the start of the DCOCLK is delayed slightly . The delay
is in the µs-range (see device parameters for details).
OscOff: The LFXT1 crystal oscillator is active when the OscOff bit is reset. The LFXT1 oscillator can only
be deactivated if the OscOff bit is set and it is not used for MCLK or SMCLK. The setup time to
start a crystal oscillation needs consideration when oscillator off option is used. Mask
programmable (ROM) devices can disable this feature so that the oscillator can never be switched
off by software.
CPUOff: The clock signal MCLK, used for the CPU, is active when the CPUOf f bit is reset or stopped if it
is set.
6
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 7
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
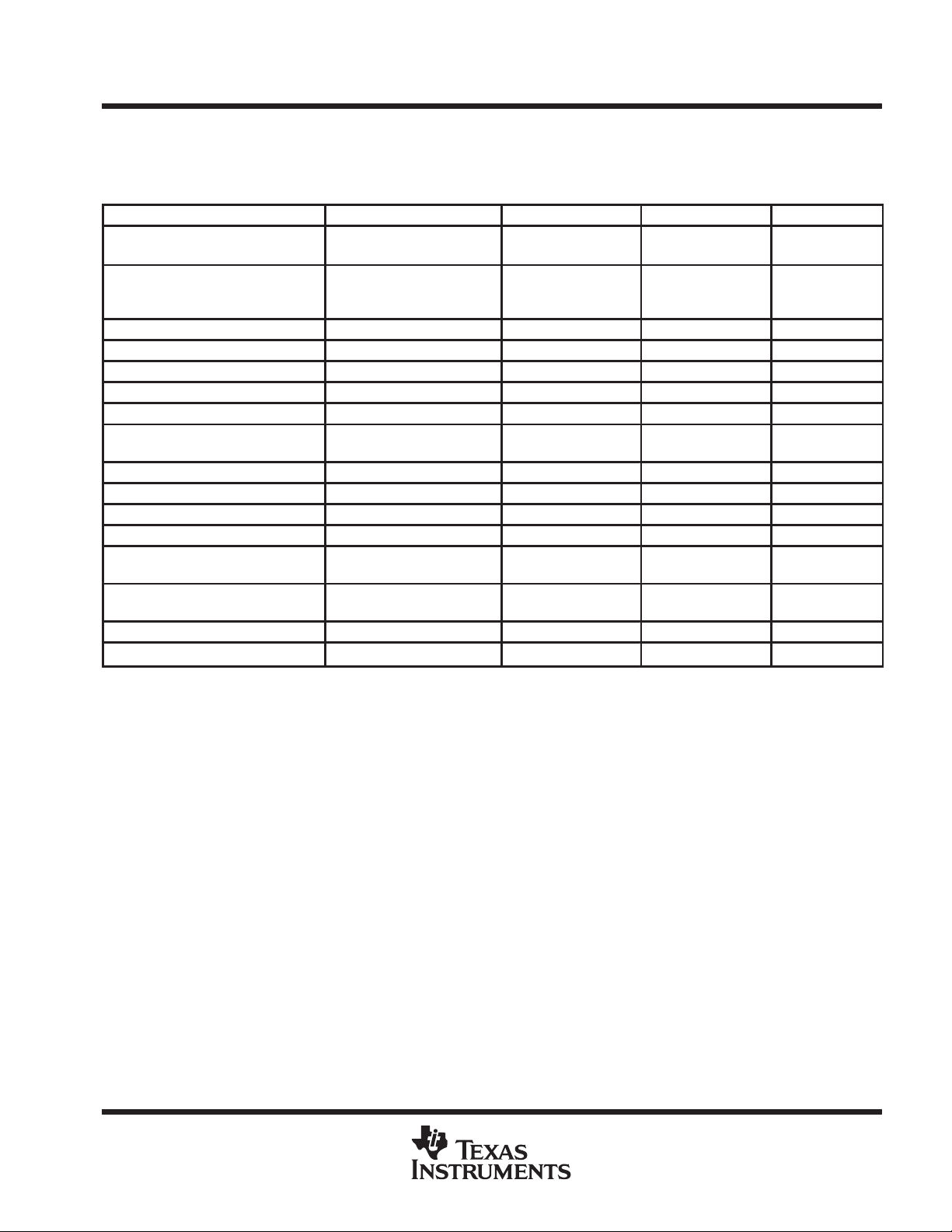
interrupt vector addresses
The interrupt vectors and the power-up starting address are located in the memory with an address range of
0FFFFh-0FFE0h. The vector contains the 16-bit address of the appropriate interrupt handler instruction
sequence.
INTERRUPT SOURCE INTERRUPT FLAG SYSTEM INTERRUPT WORD ADDRESS PRIORITY
Power-up, external reset, watchdog
NMI, oscillator fault, flash memory
access violation
Comparator_A CAIFG maskable 0FFF6h 11
Watchdog timer WDTIFG maskable 0FFF4h 10
Timer_A CCIFG0 (Note 2) maskable 0FFF2h 9
Timer_A
I/O Port P2 (eight flags – see Note 3)
I/O Port P1 (eight flags)
NOTES: 1. Multiple source flags
2. Interrupt flags are located in the module
3. There are eight Port P2 interrupt flags, but only six Port P2 I/O pins (P2.0–5) are implemented on the 11x1 devices.
4. (non)-maskable: the individual interrupt enable bit can disable an interrupt event, but the general interrupt enable cannot.
Nonmaskable: neither the individual nor the general interrupt enable bit will disable an interrupt event.
WDTIFG (Note1)
KEYV (Note 1)
NMIIFG (Notes 1 and 4)
OFIFG (Notes 1 and 4)
ACCVIFG (Notes 1 and 4)
CCIFG1, CCIFG2, TAIFG
(Notes 1 and 2)
P2IFG.0 to P2IFG.7
(Notes 1 and 2)
P1IFG.0 to P1IFG.7
(Notes 1 and 2)
Reset 0FFFEh 15, highest
(non)-maskable,
(non)-maskable,
(non)-maskable
maskable 0FFF0h 8
maskable 0FFE6h 3
maskable 0FFE4h 2
0FFFCh 14
0FFFAh 13
0FFF8h 12
0FFEEh 7
0FFECh 6
0FFEAh 5
0FFE8h 4
0FFE2h 1
0FFE0h 0, lowest
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
7
Page 8
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
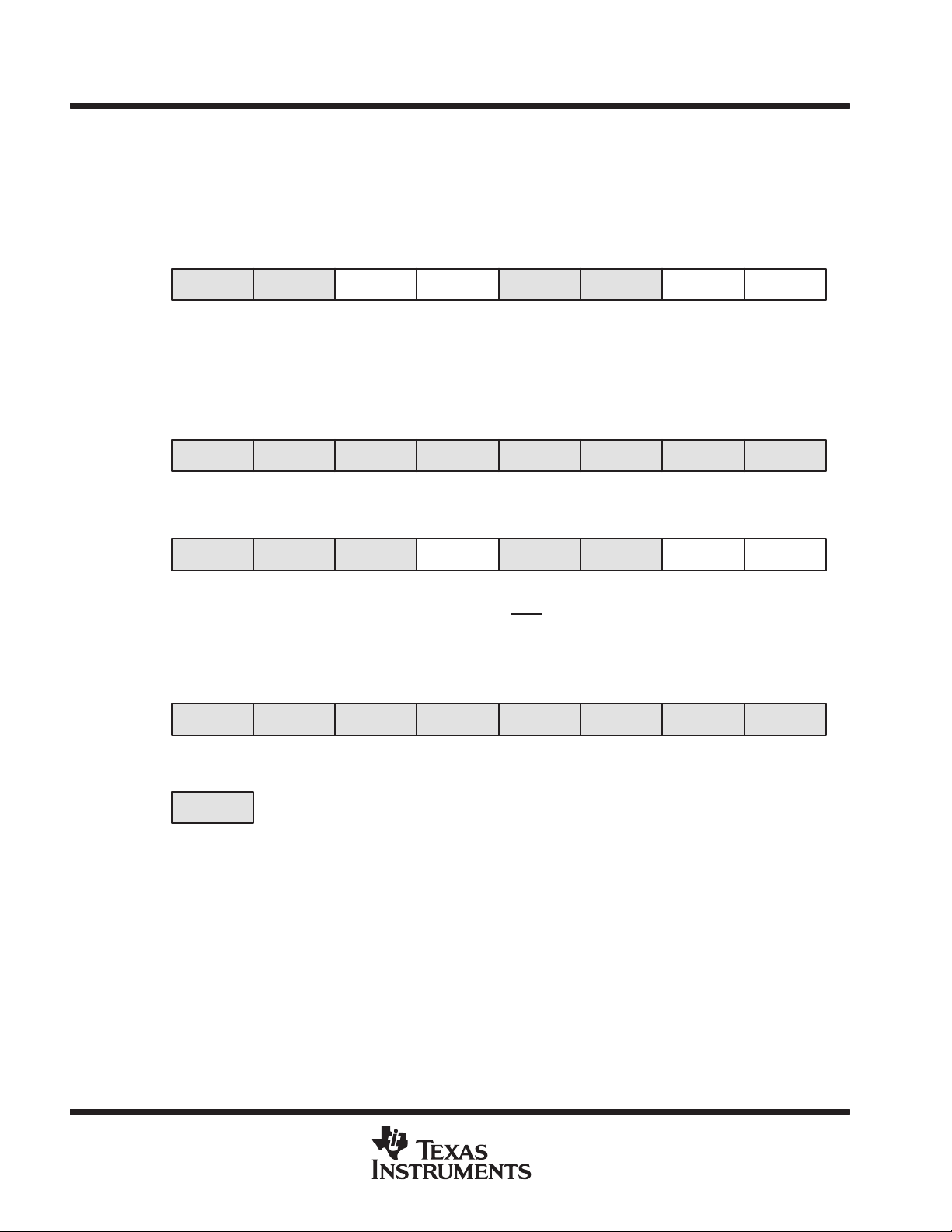
special function registers
Most interrupt and module enable bits are collected into the lowest address space. Special function register bits
that are not allocated to a functional purpose are not physically present in the device. Simple software access
is provided with this arrangement.
interrupt enable 1 and 2
Address
0h
7654 0
rw-0 rw-0 rw-0
WDTIE: Watchdog timer enable signal
OFIE: Oscillator fault enable signal
NMIIE: Nonmaskable interrupt enable signal
ACCVIE: Access violation at flash memory
Address
01h
7654 0321
interrupt flag register 1 and 2
Address
02h NMIIFG
7654 0
WDTIFG: Set on overflow or security key violation or
Reset on V
power-on or reset condition at RST/NMI-pin
CC
OFIFG: Flag set on oscillator fault
NMIIFG: Set via RST/NMI-pin
Address
03h
7654 0321
321
NMIIEACCVIE
321
rw-0 rw-1 rw-0
OFIE WDTIE
rw-0
OFIFG WDTIFG
8
Legend rw:
rw-0:
Bit can be read and written.
Bit can be read and written. It is reset by PUC
SFR bit is not present in device.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 9
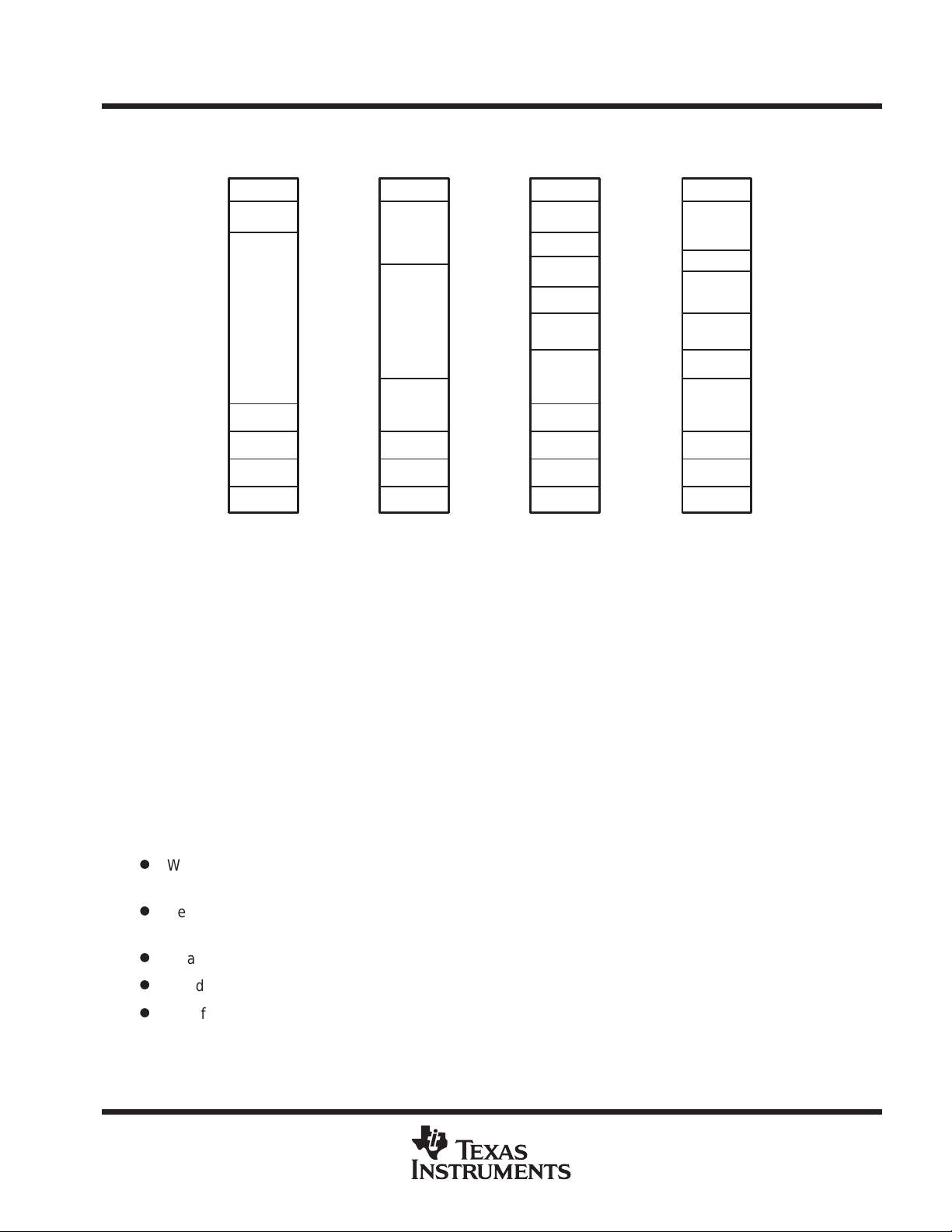
memory organization
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
FFFFh
FFE0h
FFDFh
F800h
027Fh
0200h
01FFh
0100h
00FFh
0010h
000Fh
0000h
MSP430C111 1
Int. Vector
2 KB ROM
128B RAM
16b Per.
8b Per.
SFR
FFFFh
FFE0h
FFDFh
F000h
02FFh
0200h
01FFh
0100h
00FFh
0010h
000Fh
0000h
MSP430C1121
Int. Vector
4 KB
ROM
256B RAM
16b Per.
8b Per.
SFR
FFFFh
FFE0h
FFDFh
FC00h
10FFh
1080h
0FFFh
0C00h
027Fh
0200h
01FFh
0100h
00FFh
0010h
000Fh
0000h
MSP430F1101
Int. Vector
1 KB Flash
Segment0,1
128B Flash
SegmentA
1 KB
Boot ROM
128B RAM
16b Per.
8b Per.
SFR
FFFFh
FFE0h
FFDFh
F000h
10FFh
1000h
0FFFh
0C00h
02FFh
0200h
01FFh
0100h
00FFh
0010h
000Fh
0000h
MSP430F1121
Int. Vector
4 KB
Flash
Segment0–7
2 × 128B
Flash
SegmentA,B
1 KB
Boot ROM
256B RAM
16b Per.
8b Per.
SFR
Main
Memory
Information
Memory
boot ROM containing bootstrap loader
The intention of the bootstrap loader is to download data into the flash memory module. V arious write, read, and
erase operations are needed for a proper download environment. The bootstrap loader is only available on F
devices.
functions of the bootstrap loader:
Definition of read: apply and transmit data of peripheral registers or memory to pin P1.1 (BSLTX)
write: read data from pin P2.2 (BSLRX) and write them into flash memory
unprotected functions
Mass erase, erase of the main memory (Segment0 to Segment7)
Access to the MSP430 via the bootstrap loader is protected. It must be enabled before any protected function
can be performed. The 256 bits in 0FFE0h to 0FFFFh provide the access key.
protected functions
All protected functions can be executed only if the access is enabled.
D
Write/program byte into flash memory; Parameters passed are start address and number of bytes (the
segment-write feature of the flash memory is not supported and not useful with the UART protocol).
D
Segment erase of Segment0 to Segment7 in the main memory and segment erase of SegmentA and
SegmentB in the information memory.
D
Read all data in main memory and information memory.
D
Read and write to all byte peripheral modules and RAM.
D
Modify PC and start program execution immediately.
NOTE:
Unauthorized readout of code and data is prevented by the user’s definition of the data in the
interrupt memory locations.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
9
Page 10
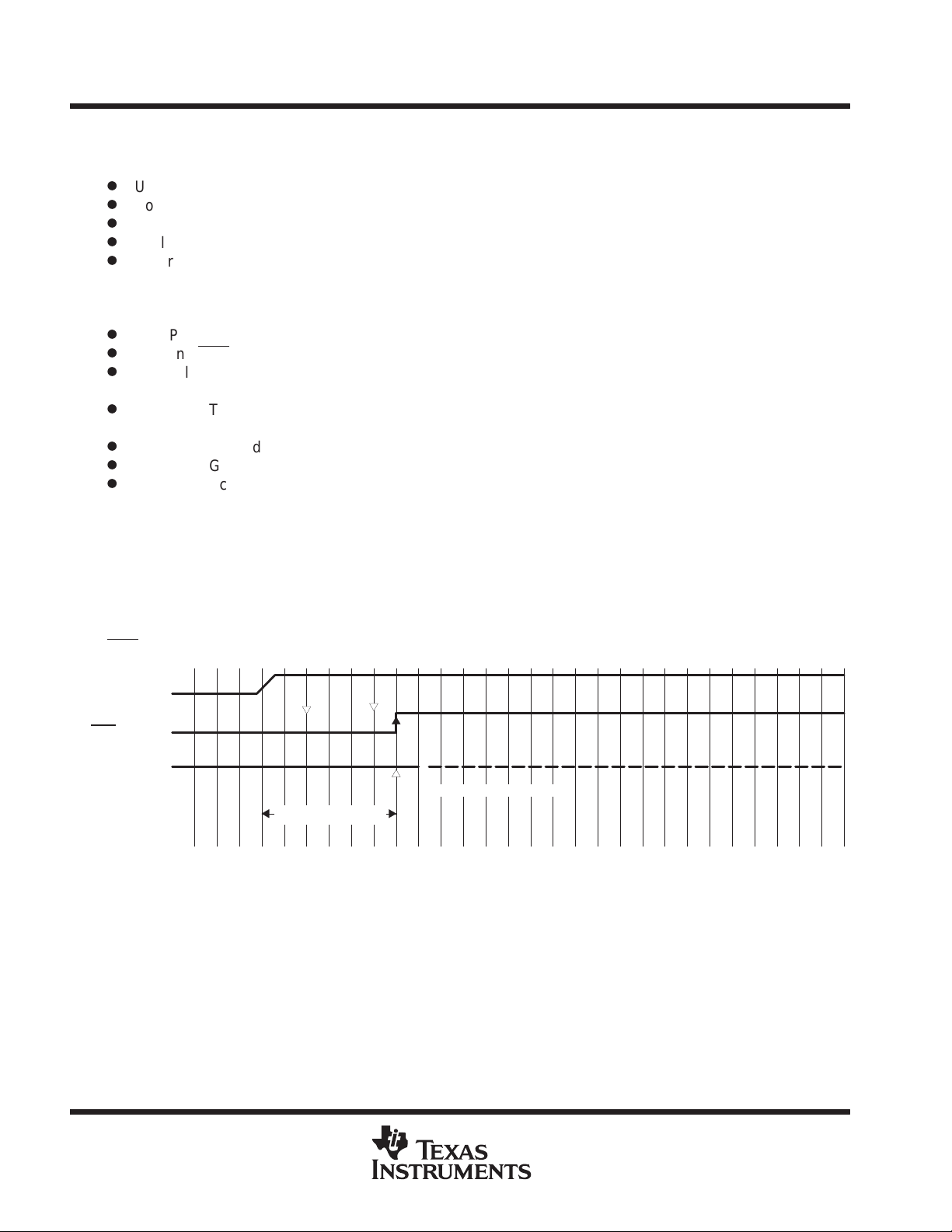
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
boot ROM containing bootstrap loader (continued)
features of the bootstrap loader are:
D
UART communication protocol, fixed to 9600 baud
D
Port pin P1.1 for transmit, P2.2 for receive
D
TI standard serial protocol definition
D
Implemented in flash memory version only
D
Program execution starts with the user vector at 0FFFEh or with the bootstrap loader (start vector is at
address 0C00h)
hardware resources used for serial input/output:
D
Pins P1.1 and P2.2 for serial data transmission
D
Test and RST/NMI to start program execution at the reset or bootstrap loader vector
D
Basic clock module: Rsel=5, DCO=4, MOD=0, DCOCLK for MCLK and SMCLK, clock divider for MCLK
and SMCLK at default: dividing by 1
D
Timer_A: Timer_A operates in continuous mode with MCLK source selected, input divider set to 1,
using CCR0, and polling of CCIFG0.
D
WDT: Watchdog timer is halted
D
Interrupt: GIE=0, NMIIE=0, OFIFG=0, ACCVIFG=0
D
Memory allocation and stack pointer:
If the stack pointer points to RAM addresses above 0220h, 6 bytes of the stack are allocated
plus RAM addresses 0200h to 0219h. Otherwise the stack pointer is set to 0220h and allocates
RAM from 0200h to 021Fh.
NOTE:
When writing RAM data via bootstrap loader, take care that the stack is outside the range
of the data being written.
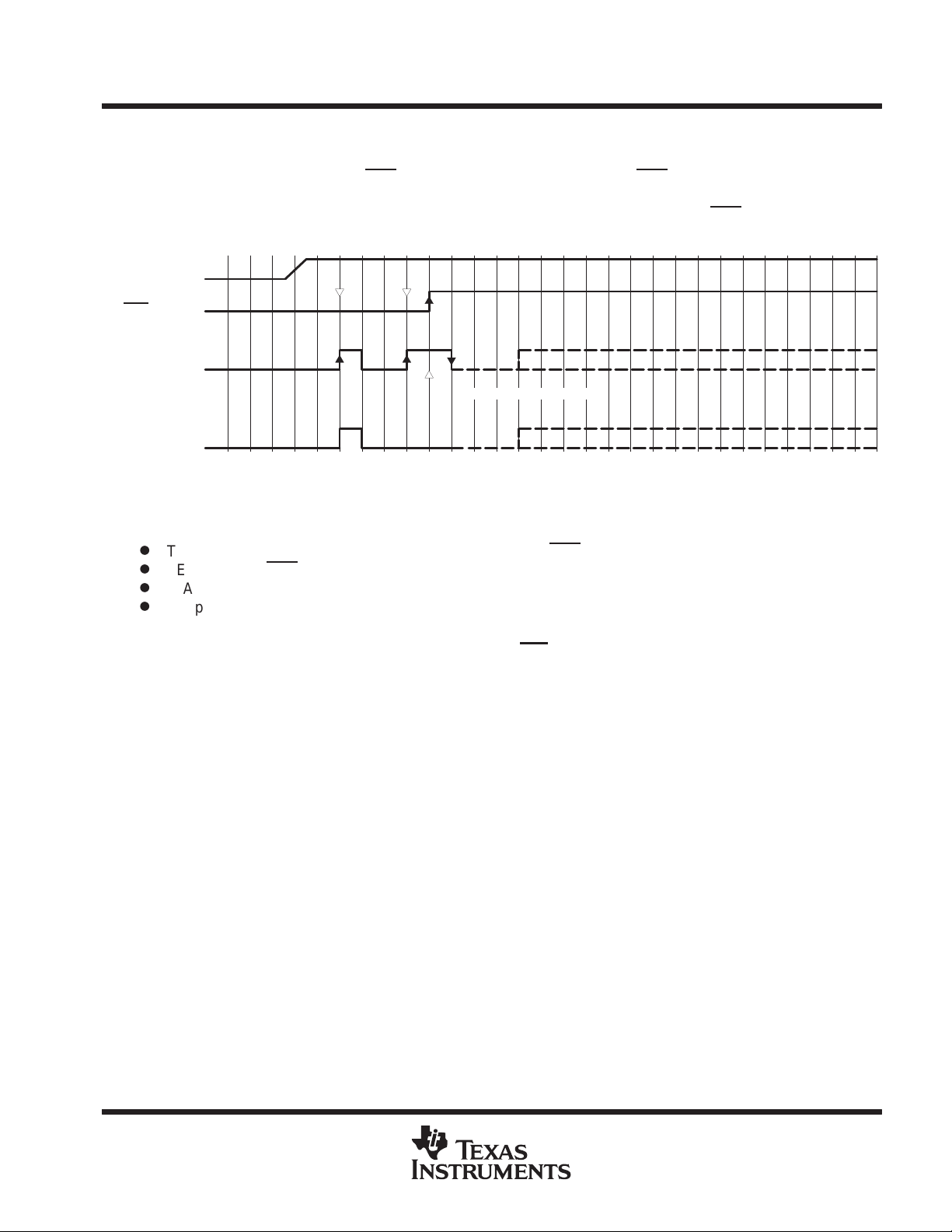
Program execution begins with the user’s reset vector at FFFEh (standard method) if TEST is held low while
RST
/NMI goes from low to high:
V
CC
RST/NMI PIN
TEST PIN
User Program Starts
Reset Condition
10
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 11
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
boot ROM containing bootstrap loader (continued)
Program execution begins with the bootstrap vector at 0C00h (boot ROM) if a minimum of two positive edges
have been applied to TEST while RST/NMI is low, and TEST is high when RST/NMI goes from low to high. The
TEST signal is normally used internally to switch pins P1.4, P1.5, P1.6, and P1.7 between their application
function and the JTAG function. If the second rising edge at TEST is applied while RST
internal TEST signal is held low and the pins remain in the application mode:
V
CC
RST/NMI PIN
TEST PIN
Bootstrap loader Starts
TEST
(Internal)
/NMI is held low, the
Test mode can be entered again after TEST is taken low and then back high.
The bootstrap loader will not be started (via the vector in address 0C00h), if:
D
There were less than two positive edges at TEST while RST/NMI is low
D
TEST is low if RST/NMI goes from low to high
D
JTAG has control over the MSP430 resources
D
Supply voltage VCC drops and a POR is executed
WARNING:
The bootstrap loader starts correctly only if the RST
to the NMI function, unpredictable program execution may result. However, a
bootstrap-load may be started using software and the bootstrap vector, for example the
instruction BR &0C00h.
/NMI pin is in reset mode. If it is switched
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
11
Page 12

MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
flash memory
The flash memory consists of 512-byte segments
in the main memory and 128-byte segments in the
information memory. See device memory maps
for specific device information.
Segment0 to Segment7 can be erased
individually, or altogether as a group.
SegmentA and SegmentB can be erased
individually, or as a group with segments 0–7.
The memory in SegmentA and SegmentB is also
called
Information Memory.
VPP is generated internally. VCC current
increases during programming.
During program/erase cycles, VCC must not drop
below the minimum specified for program/erase
operation.
Program and erase timings are controlled by the
flash timing generator—no software intervention
is needed. The input frequency of the flash timing
generator should be in the proper range and must
be applied until the write/program or erase
operation is completed.
0FFFFh
0FE00h
0FDFFh
0FC00h
0FBFFh
0FA00h
0F9FFh
0F800h
0F7FFh
0F600h
0F5FFh
0F400h
0F3FFh
0F200h
0F1FFh
0F000h
010FFh
01080h
0107Fh
01000h
NOTE: All segments not implemented on all devices.
Segment0 w/
Interrupt Vectors
Segment1
Segment2
Segment3
Segment4
Segment5
Segment6
Segment7
SegmentA
SegmentB
Flash Main Memory
Memory
Information
During program or erase, no code can be executed from flash memory and all interrupts must be disabled by
setting the GIE, NMIE, ACCVIE, and OFIE bits to zero. If a user program requires execution concurrent with
a flash program or erase operation, the program must be executed from memory other than the flash memory
(e.g., boot ROM, RAM). In the event a flash program or erase operation is initiated while the program counter
is pointing to the flash memory, the CPU will execute JMP $ instructions until the flash program or erase
operation is completed. Normal execution of the previously running software then resumes.
Unprogrammed, new devices may have some bytes programmed in the information memory (needed for test
during manufacturing). The user should perform an erase of the information memory prior to first use.
flash memory control register FCTL1
All control bits are reset during PUC. PUC is active after V
is applied, a reset condition is applied to the
CC
RST/NMI pin, the watchdog timer expires, a watchdog access violation occurs, or an improper flash operation
has been performed. A more detailed description of the control-bit functions is found in the flash memory module
description (refer to
MSP430x1xx User’s Guide
, literature number SLAU049). Any write to control register
FCTL1 during erase, mass erase, or write (programming) will end in an access violation with ACCVIFG=1.
Special conditions apply for segment-write mode. Refer to
MSP430x1xx User’s Guide
, literature number
SLAU049 for details.
12
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 13
flash memory control register FCTL1 (continued)
Read access is possible at any time without restrictions.
The control bits of control register FCTL1 are:
FCTL1
0128h
FCTL1 read:
FCTL1 write:
096h
0A5h
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
7
815
SEG
WRT
rw–0
WRT
rw–0
res.r0res.r0res.
MEras Erase res.
r0
0
r0rw-0rw–0
Erase 0128h, bit1,
Erase a segment
0:1:No segment erase will be started.
Erase of one segment is enabled. The segment to be erased is defined by a
dummy
write into any address within the segment. The erase bit is
automatically reset when the erase operation is completed.
MEras 0128h, bit2,
Mass Erase, main memory segments are erased together.
0:1:No segment erase will be started.
Erase of main memory segments is enabled. Erase starts when a dummy
write to any address in main memory is executed. The MEras bit is
automatically reset when the erase operation is completed.
WRT 0128h, bit6, Bit WRT must be set for a successful write execution.
If bit WRT is reset and write access to the flash memory is attempted, an
access violation occurs and ACVIFG is set.
SEGWRT 0128h, bit7,
Bit SEGWRT may be used to reduce total programming time.
Refer to
MSP430x1xx User’s Guide
, literature number SLAU049 for details.
0:1:No segment-write acceleration is selected.
Segment-write is used. This bit needs to be reset and set between segment
borders.
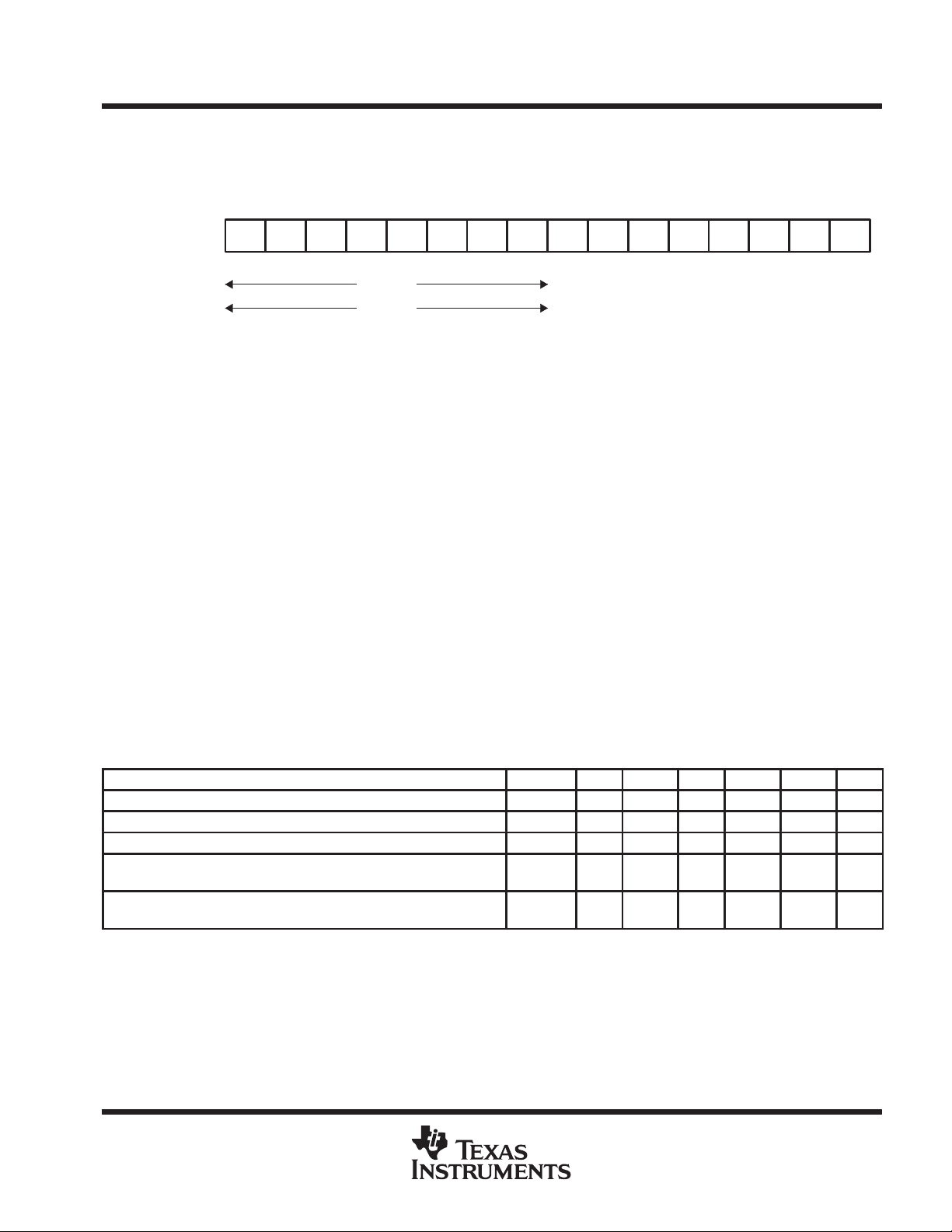
Table 3. Allowed Combinations of Control Bits Allowed for Flash Memory Access
FUNCTION PERFORMED SEGWRT WRT MEras Erase BUSY WAIT Lock
Write word or byte 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
Write word or byte in same segment, segment write mode 1 1 0 0 0 → 1 0 → 1 0
Erase one segment by writing to any address in the target segment 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
Erase all segments (0 to 7) but not the information memory
(segments A and B)
Erase all segments (0 to 7 and A and B) by writing to any address in
the flash memory module
NOTE: The table shows all valid combinations. Any other combination will result in an access violation.
0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 1 1 0 0 0
flash memory, timing generator, control register FCTL2
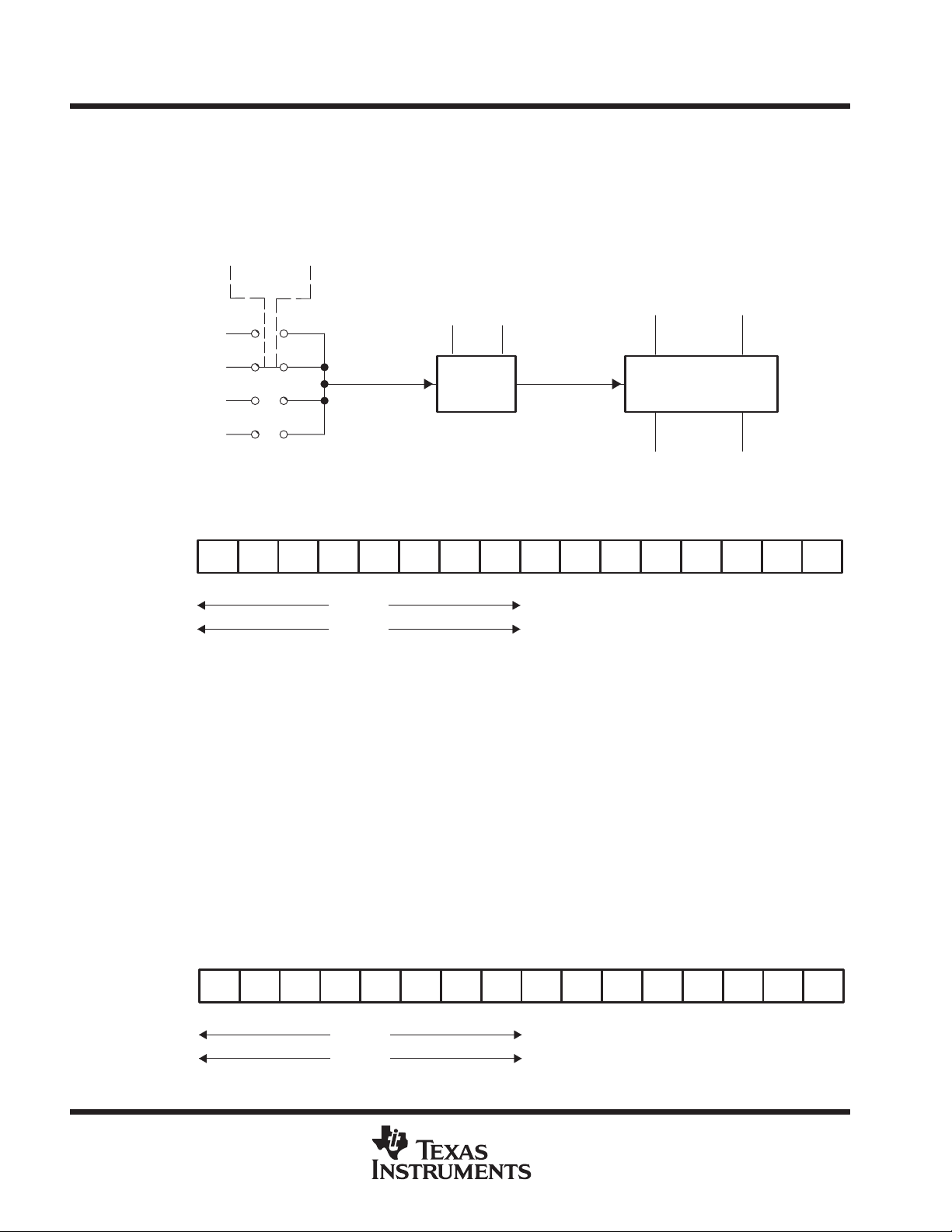
The timing generator (Figure 1) generates all the timing signals necessary for write, erase, and mass erase from
the selected clock source. One of three different clock sources may be selected by control bits SSEL0 and
SSEL1 in control register FCTL2. The selected clock source should be divided to meet the frequency
requirements specified in the recommended operating conditions.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
13
Page 14
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
flash memory, timing generator, control register FCTL2 (continued)
The flash timing generator is reset with PUC. It is also reset if the emergency exit bit EMEX is set.
Control register FCTL2 may not be written to if the BUSY bit is set; otherwise, an access violation will occur
(ACCVIFG=1).
Read access is possible at any time without restrictions.
SSEL1
SSEL0
Write ’1’ to
Reset
Flash Timing
Generator
ACLK
MCLK
SMCLK
SMCLK
0
1
2
3
FN5.......... FN0
Divider,
1 .. 64
f
X
PUC EMEX
BUSY WAIT
Figure 1. Flash Memory Timing Generator Diagram
8
FCTL2
012Ah
FCTL2 read:
FCTL2 write:
15
096h
0A5h
SSEL1
rw–0
7
SSEL0
rw–1
FN5 FN4 FN3
rw-0rw-0rw-0
FN2 FN1 FN0
The control bits are:
FN0–FN5 012Ah, bit0–5 These six bits define the division rate of the clock signal. The division
rate is 1 to 64, according to the digital value of FN5 to FN0 plus one.
0
rw-0rw-1rw–0
SSEL0, SSEL1 012Ah, bit6,7 Clock source select
0: ACLK
1: MCLK
2: SMCLK
3: SMCLK
The flash timing generator is reset with PUC. It is also reset if the EMEX bit is set.
flash memory control register FCTL3
There are no restrictions to modify this control register.
7
8
res.
res.r0EMEX Lock WAIT
r0
14
FCTL3
012Ch
FCTL3 read:
FCTL3 write:
15
096h
0A5h
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
0
ACCV
KEYV BUSY
IFG
rw-1rw-1rw-0
r(w)-0rw-(0)rw–0
Page 15

flash memory control register FCTL3 (continued)
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
BUSY 012Ch, bit0,
KEYV, 012Ch, bit1
ACCVIFG, 012Ch, bit2 Access violation interrupt flag
WAIT, 012CH, bit3
The BUSY bit shows if an access to the flash memory is allowed (BUSY=0), or
if an access violation occurs. The BUSY bit is read-only , but a write operation is
allowed. The BUSY bit should be tested before each write and erase cycle. The
flash timing-generator hardware immediately sets the BUSY bit after start of a
write, segment-write, erase, or
completed the operation, the BUSY bit is reset by the hardware.
No program code can be executed from the
program or erase cycle.
0: Flash memory is not busy.
1: Flash memory is busy, and remains in busy state if segment write function
is in
wait
mode.
Key violation
0: Key 0A5h (high byte) was not violated.
1: Key 0A5h (high byte) was violated. Violation occurs when a write access to
registers FCTL1, FCTL2, or FCTL3 is executed and the
equal to 0A5h. If the security key is violated, bit KEYV is set and a PUC is
performed.
The access-violation flag is set when any combination of control bits other than
those shown in Table 3 is attempted, or an instruction is fetched while a
segment-write operation is active.
Reading the control registers will not set the ACCVIFG bit.
NOTE: The respective interrupt-enable bit ACCVIE is located in the interrupt
enable register IE1 in the special function register. The software can set
the ACCVIFG bit. If set by software, an NMI is also executed.
In the segment-write mode, the WAIT bit indicates that data has been written and
the flash memory is prepared to receive the next data for programming. The
WAIT bit is read only, but a write to the WAIT bit is allowed.
0: The segment-write operation has began and programming is in progress.
1: The segment-write operation is active and data programming is complete.
mass
erase operation. If the timing generator has
busy
flash memory during the entire
high byte
is not
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
15
Page 16

MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
flash memory control register FCTL3 (continued)
LOCK 012Ch, bit4,
EMEX, 012Ch, bit5,
The lock bit may be set during any write, segment-erase, or
Any active sequence in progress is completed normally . In segment-write mode,
the SEGWRT bit is reset and the W AIT bit is set after the mode ends. The lock
bit is controlled by software or hardware. If an access violation occurs and the
ACCVIFG is set, the LOCK bit is set automatically.
0: Flash memory may be read, programmed, erased, or
1: Flash memory may be read but not programmed, erased, or
A current program, erase, or
The access-violation interrupt flag ACCVIFG is set when data are written to
the flash memory module while the lock bit is set.
Emergency exit. The emergency exit should only be used if the flash memory
write or erase operation is out of control.
0: No function.
1: Stops the active operation immediately, and shuts down all internal parts in
the flash memory controller. Current consumption immediately drops back
to the active mode. All bits in control register FCTL1 are reset. Since the
EMEX bit is automatically reset by hardware, the software always reads
EMEX as 0.
mass
-erase operation will complete normally .
mass
-erase request.
mass
erased.
mass
flash memory, interrupt and security key violation
One NMI vector is used for three NMI events: RST/NMI (NMIIFG), oscillator fault (OFIFG), and flash-memory
access violation (ACCVIFG). The software can determine the source of the interrupt request since all flags
remain set until they are reset by software. The enable flag(s) should be set simultaneously with one instruction
before the return-from-interrupt RETI instruction. This ensures that the stack remains under control. A pending
NMI interrupt request will not increase stack demand unnecessarily.
erased.
16
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 17

ACCV
FCTL1.1
S
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
ACCVIFG
IE1.5
PUC
RST/NMI
IFG1.4
PUC
IE1.4
PUC
OSCFault
IFG1.1
IE1.1
PUC
Clear
S
Clear
Clear
S
Clear
ACCVIE
NMIFG
NMIIE
OFIFG
OFIF
NMI_IRQA
Counter
NMITMSELNMIES
WDT
IFG1.0
POR
IRQA
TIMSEL
IE1.0
Flash Module
Flash Module
Flash Module
POR PUC
KEYV
System Reset
Generator
WDTQn EQU
S
Clear
Clear
WDTIFG
WDTIE
VCC
PUC
POR
NMIRS
PUC POR
IRQ
IRQA: Interrupt Request Accepted
Figure 2. Block Diagram of NMI Interrupt Sources
Watchdog Timer Module
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
PUC
17
Page 18

MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
peripherals
Peripherals are connected to the CPU through data, address, and control buses and can be handled easily with
memory manipulation instructions.
oscillator and system clock
Three clocks are used in the system—the system (master) clock MCLK, the subsystem (master) clock SMCLK,
and the auxiliary clock ACLK:
Main system clock MCLK, used by the CPU and the system
Subsystem clock SMCLK, used by the peripheral modules
Auxiliary clock ACLK, originated by LFXT1CLK (crystal frequency) and used by the peripheral modules
After a POR, the DCOCLK is used by default, the DCOR bit is reset, and the DCO is set to the nominal initial
frequency. Additionally, if LFXT1CLK fails as the source for MCLK, the DCOCLK is automatically selected to
ensure fail-safe operation.
SMCLK can be generated from LFXT1CLK or DCOCLK. ACLK is always generated from LFXT1CLK.
The crystal oscillator can be defined to operate with watch crystals (32768 Hz) or with higher-frequency ceramic
resonators or crystals. The crystal or ceramic resonator is connected across two terminals. No external
components are required for watch-crystal operation. If the high frequency XT1 mode is selected, external
capacitors from XIN to VSS and XOUT to VSS are required as specified by the crystal manufacturer.
The LFXT1 oscillator starts after applying VCC. If the OscOff bit is set to 1, the oscillator stops when it is not
used for MCLK. The clock signals ACLK and SMCLK may be used externally via port pins.
Different application requirements and system conditions dictate different system clock requirements, including:
High frequency for quick reaction to system hardware requests or events
Low frequency to minimize current consumption, EMI, etc.
Stable peripheral clock for timer applications, such as real-time clock (RTC)
Start-stop operation to be enabled with minimum delay
18
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 19

oscillator and system clock (continued)
OSCOff XTS
XIN
LFXT1CLK
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
DIVA
2
/1, /2, /4, /8
ACLKGEN
ACLK
Auxiliary Clock
XOUT
V
CC
P2.5/Rosc
P2.5
LFXT1 OSCILLATOR
0,1
V
CC
1
0
SCG0
sel
DC
Generator
DCGEN
DCOR
DCO MODR
Digital Controlled Oscillator (DCO)
+
Modulator (MOD)
The DCO-Generator is connected to pin P2.5/Rosc if DCOR control bit is set.
The port pin P2.5/Rosc is selected if DCOR control bit is reset (initial state).
DCOCLK
53
DCOMOD
SELM CPUOff
3
2
SELS SCG1
0
1
DIVM
22
/1, /2, /4, /8, Off
MCLKGEN
DIVS
2
/1, /2, /4, /8, Off
SMCLKGEN
MCLK
Main System Clock
SMCLK
Subsystem Clock
Figure 3. Clock Signals
Two clock sources, LFXT1CLK and DCOCLK, can be used to drive the MSP430 system. The LFXT1CLK is
generated from the LFXT1 crystal oscillator. The LFXT1 crystal oscillator can operate in three modes—low
frequency (LF), moderate frequency (XT1), and external input mode. The LFXT1 crystal oscillator may be
switched off when it is not in use.
DCOCLK is generated from the DCO. The nominal DCO frequency is defined by the dc generator and can be
set by one external resistor, or can be set to one of eight values with integrated resistors. Additional adjustments
and modulations of DCOCLK are possible by software manipulation of registers in the DCO module. DCOCLK
is stopped automatically when it is not used by the CPU or peripheral modules. The dc generator can be shut
down with the SCG0 bit to realize additional power savings when DCOCLK is not in use.
NOTE:
The system clock generator always starts with the DCOCLK selected for MCLK (CPU clock) to
ensure proper start of program execution. The software defines the final system clock generation
through control bit manipulation.
digital I/O
There are two eight-bit I/O ports, port P1 and port P2 – implemented (1 1x1 parts only have six port P2 I/O signals
available on external pins). Both ports, P1 and P2, have seven control registers to give maximum flexibility of
digital input/output to the application:
• All individual I/O bits are programmable independently.
• Any combination of input, output, and interrupt conditions is possible.
• Interrupt processing of external events is fully implemented for all eight bits of port P1 and for six bits of
port P2.
• Read/write access to all registers with all instructions
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
19
Page 20

MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
digital I/O (continued)
The seven registers are:
• Input register 8 bits at port P1/P2 contains information at the pins
• Output register 8 bits at port P1/P2 contains output information
• Direction register 8 bits at port P1/P2 controls direction
• Interrupt edge select 8 bits at port P1/P2 input signal change necessary for interrupt
• Interrupt flags 8 bits at port P1/P2 indicates if interrupt(s) are pending
• Interrupt enable 8 bits at port P1/P2 contains interrupt enable bits
• Selection (Port or Mod.) 8 bits at port P1/P2 determines if pin(s) have port or module function
All these registers contain eight bits. Two interrupt vectors are implemented: one commonly used for any
interrupt event on ports P1.0 to P1.7, and one commonly used for any interrupt event on ports P2.0 to P2.7.
NOTE:
Six bits of port P2, P2.0 to P2.5, are available on external pins – but all control and data bits for port
P2 are implemented.
watchdog timer
The primary function of the watchdog timer (WDT) module is to perform a controlled system restart after a
software problem has occurred. If the selected time interval expires, a system reset is generated. If this
watchdog function is not needed in an application, the module can work as an interval timer, which generates
an interrupt after the selected time interval.
The watchdog timer counter (WDTCNT) is a 16-bit up-counter which is not directly accessible by software. The
WDTCNT is controlled through the watchdog timer control register (WDTCTL), which is a 16-bit read/write
register. W riting to WDTCTL is, in both operating modes (watchdog or timer), only possible by using the correct
password in the high-byte. The low-byte stores data written to the WDTCTL. The high-byte must be the
password 05Ah. If any value other than 05Ah is written to the high-byte of the WDTCTL, a system reset PUC
is generated. When the password is read, its value is 069h. This minimizes accidental write operations to the
WDTCTL register. In addition to the watchdog timer control bits, there are two bits included in the WDTCTL
register that configure the NMI pin.
Timer_A (Three capture/compare registers)
The Timer_A module on 1 1x1 devices of fers one sixteen bit counter and three capture/compare registers. The
timer clock source can be selected to come from two external sources T ACLK (SSEL=0) or INCLK (SSEL=3),
or from two internal sources, the ACLK (SSEL=1) or SMCLK (SSEL=2). The clock source can be divided by
one, two, four, or eight. The timer can be fully controlled (in word mode) since it can be halted, read, and written.
It can be stopped, run continuously , counted up or up/down, using one compare block to determine the period.
The three capture/compare blocks are configured by the application to run in capture or compare mode.
The capture mode is primarily used to measure external or internal events using any combination of positive,
negative, or both edges of the signal. Capture mode can be started and stopped by software. Three different
external events T A0, TA1, and TA2 can be selected. At capture/compare register CCR2 the ACLK is the capture
signal if CCI2B is selected. Software capture is chosen if CCISx=2 or CCISx=3 (see Figure 4).
The compare mode is primarily used to generate timings for the software or application hardware, or to generate
pulse-width modulated output signals for various purposes like D/A conversion functions or motor control. An
individual output module is assigned to each of the three capture/compare registers. The output modules can
run independently of the compare function, or can be triggered in several ways.
20
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 21

Timer_A (3 capture/compare registers) (continued)
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
P1.0
P2.1
P1.1
P2.2
P1.2
CAOUT
TACLK
ACLK
SMCLK
INCLK
CCI0A
CCI0B
GND
V
CC
CCI1A
CCI1B
GND
V
CC
SSEL0SSEL1
0
1
2
3
ID1
CCIS00CCIS01
0
1
2
3
CCI0 CCM00
CCIS10CCIS11
0
1
2
3
CCI1 CCM10
32 kHz to 8 MHz
Timer Clock
Input
Divider
ID0
Capture
Mode
CCM01
Capture
Mode
CCM11
15
CLK
POR/CLR
Capture
Capture
Data
16-Bit Timer
Carry/Zero
0
RC
15
Capture/Compare
Register CCR0
15
15
Capture/Compare
Register CCR1
15
Mode
Control
MC1 MC0
Comparator 0
Comparator 1
16-Bit Timer
Equ0
Set_TAIFG
Capture/Compare Register CCR0Timer Bus
0
0
0
0
OM02 OM00OM01
Output Unit 0
EQU0
Capture/Compare Register CCR1
OM12 OM10OM11
Output Unit 1
EQU1
Out 0
Out 1
P1.1
P1.5
P1.2
P1.6
P2.3
Capture/Compare Register CCR2
0
0
OM22 OM20OM21
EQU2
Out 2
Output Unit 2
P1.3
ACLK
CCI2A
CCI2B
GND
V
CC
CCIS20CCIS21
0
1
2
3
CCI2 CCM20
Capture
CCM21
Mode
Capture
15
Capture/Compare
Register CCR2
15
Comparator 2
Figure 4. Timer_A, MSP430x11x1 Configuration
Two interrupt vectors are used by the Timer_A module. One individual vector is assigned to capture/compare
block CCR0, and one common interrupt vector is implemented for the timer and the other two capture/compare
blocks. The three interrupt events using the same vector are identified by an individual interrupt vector word.
The interrupt vector word is used to add an offset to the program counter to continue the interrupt handler
software at the corresponding program location. This simplifies the interrupt handler and gives each interrupt
event the same overhead of 5 cycles in the interrupt handler.
UART
Serial communication is implemented by using software and one capture/compare block. The hardware
supports the output of the serial-data stream, bit by bit, with the timing determined by the comparator/timer. The
data input uses the capture feature. The capture flag finds the start of a character, while the compare feature
latches the input-data stream, bit by bit. The software/hardware interface connects the mixed-signal controller
to external devices, systems, or networks.
P1.3
P1.7
P2.4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
21
Page 22
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
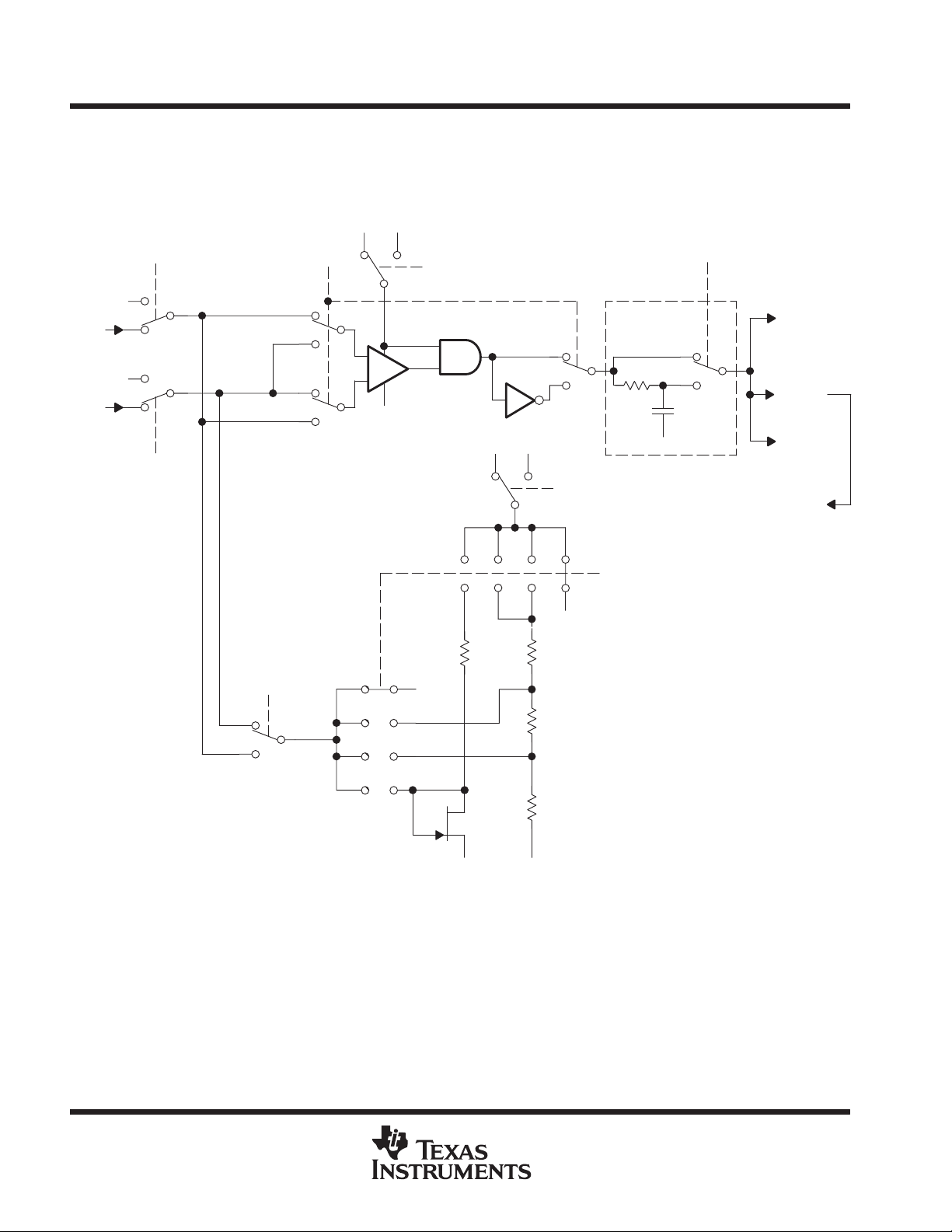
Comparator_A
The primary function of the comparator module is to support precision A/D slope conversion applications,
battery voltage supervision, and observation of external analog signals. The comparator is connected to port
pins P2.3/CA0 and to P2.4/CA1. It is controlled via twelve control bits in registers CACTL1 and CACTL2.
V
0 V
CC
1
P2.3/
CA0/
TA1
P2.4/
CA1/
TA2
P2CA0
0
1
0
1
P2CA1
CA0
CA1
CAEX
0
1
0
1
0
+
_
0 V
CAON
0 V
Low Pass Filter
0
1
V
CC
1
0
CAON
CAF
0
1
0 V
τ ≈ 2.0 µs
CAOUT/TA0
CCI1B
CAOUT
Set CAIFG
Flag
P2.2/
CARSEL
1
0
V
CAREF
0123
0
2
1
3
0 V 0 V
0.5 x V
0.25 x V
CC
CC
Figure 5. Block Diagram of Comparator_A
CAREF
22
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 23

MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
Comparator_A (continued)
The control bits are:
CAOUT, 05Ah, bit0, Comparator output
CAF, 05Ah, bit1, The comparator output is transparent or fed through a small filter
CA0, 05Ah, bit2, 0: Pin P2.3/CA0/TA1 is not connected to Comparator_A.
1: Pin P2.3/CA0/TA1 is connected to Comparator_A.
CA1, 05Ah, bit3, 0: Pin P2.4/CA1/TA2 is not connected to Comparator_A.
1: Pin P2.4/CA1/TA2 is connected to Comparator_A.
CACTL2.4
to
CATCTL2.7
CAIFG, 059h, bit0, Comparator_A interrupt flag
CAIE, 059h, bit1, Comparator_A interrupt enable
CAIES, 059h, bit2, Comparator_A interrupt edge select bit
CAON, 059h, bit3, The comparator is switched on.
CAREF, 059h, bit4,5, Comparator_A reference
CARSEL, 059h, bit6, An internal reference V
CAEX, 059h, bit7, The comparator inputs are exchanged, used to measure and compensate
05Ah, bit4,
05Ah, bit7,
Bits are implemented but do not control any hardware in this device.
0: The rising edge sets the Comparator_A interrupt flag CAIFG
1: The falling edge set the Comparator_A interrupt flag CAIFG
0: Internal reference is switched off, an external reference can be applied.
1: 0.25 × VCC reference selected.
2: 0.50 × VCC reference selected.
3: A diode reference selected.
, selected by CAREF bits, can be applied to
signal path CA0 or CA1. The signal V
CAREF
CAREF
is only driven by a voltage
source if the value of CAREF control bits is 1, 2, or 3.
the offset of the comparator.
MSP430x11x1
Eight additional bits are implemented into the Comparator_A module and enable the SW to switch off the input
buffer of port P2. A CMOS input buffer would dissipate supply current when the input is not near VSS or VCC.
Comparator_A port disable control bits CAPD0 to CAPD7 are initially reset, and the port input buffer is active.
The port input buffer is disabled if the appropriate control bit is set.
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
23
Page 24

MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
Comparator_A (continued)
0
CAIFG
rw-(0)
0
CAOUT
r-(0)
0
CAPD0
rw-(0)
CACTL1
059h
CACTL2
05Ah
CAPD
05Bh
7
CAEX
rw-(0)
7
CACTL
2.7
rw-(0)
7
rw-(0)
CA
RSEL
rw-(0)
CACTL
2.6
rw-(0)
rw-(0) rw-(0) rw-(0)
CA
REF1
rw-(0)
CACTL
2.5
rw-(0) rw-(0) rw-(0) rw-(0)
CA
REF0
rw-(0)
CACTL
2.4
CAPD4CAPD5CAPD6CAPD7
CAON
rw-(0)
CA1 CA0
CAPD3
rw-(0)
CAIES
rw-(0)
CAPD2
rw-(0)
CAIE
rw-(0)
CAF
rw-(0)
CAPD1
rw-(0)
NOTE:
Ensure that the comparator input terminals are connected to signal, power, or ground level.
Otherwise, floating levels may cause unexpected interrupts and current consumption may be
increased.
slope a/d conversion
The Comparator_A is well suited for use in single or multiple-slope conversions. The internal-reference levels
may be used to set a reference during timing measurement of charge or discharge operations. They can also
be used externally to bias analog circuitry.
Voltage, current, and resistive or capacitive sensor measurements are basic functions. The sensors sense
physical conditions like temperature, pressure, acceleration, etc.
24
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 25

peripheral file map
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
PERIPHERALS WITH WORD ACCESS
Timer_A Reserved
Flash Memory Flash control 3
Watchdog Watchdog/timer control WDTCTL 0120h
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Capture/compare register
Capture/compare register
Capture/compare register
Timer_A register
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Capture/compare control
Capture/compare control
Capture/compare control
Timer_A control
Timer_A interrupt vector
Flash control 2
Flash control 1
CCR2
CCR1
CCR0
TAR
CCTL2
CCTL1
CCTL0
TACTL
TAIV
FCTL3
FCTL2
FCTL1
017Eh
017Ch
017Ah
0178h
0176h
0174h
0172h
0170h
016Eh
016Ch
016Ah
0168h
0166h
0164h
0162h
0160h
012Eh
012Ch
012Ah
0128h
MSP430x11x1
PERIPHERALS WITH BYTE ACCESS
Comparator_A Comparator_A port disable
Comparator_A control2
Comparator_A control1
System Clock Basic clock sys. control2
Basic clock sys. control1
DCO clock freq. control
Port P2 Port P2 selection
Port P2 interrupt enable
Port P2 interrupt edge select
Port P2 interrupt flag
Port P2 direction
Port P2 output
Port P2 input
Port P1 Port P1 selection
Port P1 interrupt enable
Port P1 interrupt edge select
Port P1 interrupt flag
Port P1 direction
Port P1 output
Port P1 input
Special Function SFR interrupt flag2
SFR interrupt flag1
SFR interrupt enable2
SFR interrupt enable1
CAPD
CACTL2
CACTL1
BCSCTL2
BCSCTL1
DCOCTL
P2SEL
P2IE
P2IES
P2IFG
P2DIR
P2OUT
P2IN
P1SEL
P1IE
P1IES
P1IFG
P1DIR
P1OUT
P1IN
IFG2
IFG1
IE2
IE1
05Bh
05Ah
059h
058h
057h
056h
02Eh
02Dh
02Ch
02Bh
02Ah
029h
028h
026h
025h
024h
023h
022h
021h
020h
003h
002h
001h
000h
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
25
Page 26

MSP430x11x1
MSP430C11x1
1.8
3.6
Su ly voltage during rogram execution, V
CC
(see Note 5)
V
f
(LFXT1)
(see Note 6)
XT1 mode selected, XTS=1
kH
Input levels at XIN, XOUT
V
2.2 V/3 V
V
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
absolute maximum ratings
†
Voltage applied at VCC to VSS (MSP430C11x1) –0.3 V to 4.6 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Voltage applied at VCC to VSS (MSP430F11x1) –0.3 V to 4.1 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Voltage applied to any pin (referenced to V
) –0.3 V to VCC+0.3 V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SS
Diode current at any device terminal ±2 mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Storage temperature, T
Storage temperature, T
†
Stresses beyond those listed under “absolute maximum ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under “recommended operating conditions” is not
implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
NOTE: All voltages referenced to VSS.
(unprogrammed device) –55°C to 150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
stg
(programmed device) –40°C to 85°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
stg
recommended operating conditions
MIN NOM MAX UNITS
pp
Supply voltage during program/erase flash memory, V
Supply voltage, V
Operating free-air temperature range, T
LFXT1 crystal frequency,
Processor frequency f
Flash timing generator frequency, f
Cumulative program time, segment write, t
Low-level input voltage (TCK, TMS, TDI, RST/NMI), V
(excluding XIN, XOUT)
High-level input voltage (TCK, TMS, TDI, RST/NMI), V
(excluding XIN, XOUT)
p
NOTES: 5. The LFXT1 oscillator in LF-mode requires a resistor of 5.1 MΩ from XOUT to VSS when VCC <2.5 V.
The LFXT1 oscillator in XT1-mode accepts a ceramic resonator or a crystal frequency of 4 MHz at VCC ≥ 2.2 V.
The LFXT1 oscillator in XT1-mode accepts a ceramic resonator or a crystal frequency of 8 MHz at VCC ≥ 2.8 V.
6. The LFXT1 oscillator in LF-mode requires a watch crystal.
The LFXT1 oscillator in XT1-mode accepts a ceramic resonator or a crystal.
7. The cumulative program time must not be exceeded during a segment-write operation.
SS
p
(system)
CC
A
LF mode selected, XTS=0 Watch crystal 32768 Hz
(MCLK signal)
(FTG)
(see Note 7)
(CPT)
IL
IH
V
IL(XIN, XOUT)
V
IH(XIN, XOUT)
MSP430F11x1 1.8 3.6
MSP430F1 1x1 2.7 3.6 V
0 V
MSP430x11x1 –40 85 °C
Ceramic resonator 450 8000
Crystal 1000 8000
VCC = 1.8 V,
MSP430x1 1x1
VCC = 2.2 V,
MSP430x1 1x1
VCC = 3.6 V,
MSP430x1 1x1
MSP430F1 1x1 257 476 kHz
VCC = 2.7 V/3.6 V
MSP430F11x1
VCC = 2.2 V/3 V V
VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 0.8V
=
CC
dc 2
dc 5
dc 8
SS
CC
V
SS
0.8×V
CC
VSS+0.6 V
V
CC
0.2×V
CC
V
CC
MHz
3 ms
V
z
26
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 27

recommended operating conditions (continued)
MSP430x11x1 Devices
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
9
8
7
6
5
3
2
– Maximum Processor Frequency – MHzf
1
(system)
0
01 2344
NOTE: Minimum processor frequency is defined by system clock. Flash
program or erase operations require a minimum VCC of 2.7 V.
5 MHz at
2.2 V
2 MHz at
1.8 V
VCC – Supply Voltage – V
8 MHz at
3.6 V
Figure 6. Frequency vs Supply Voltage
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
27
Page 28

MSP430x11x1
f
(MCLK)
f
(SMCLK)
MHz
A
C11x1
A
A
I
Active mode
f
MCLK
f
(SMCLK)
MHz
A
F11x1
A
A
C11x1
f
(MCLK)
f
(SMCLK)
MHz
I
A
F11x1
f
(MCLK)
f
(SMCLK)
MHz
I
Low-power mode, (LPM2)
f
(MCLK)
f
(SMCLK)
MHz
A
I
()
f
(MCLK)
f
(SMCLK)
MHz
A
I
()
,
L
(LPM4)
f
(MCLK)
MHz,
()
(C11x1)
()
L
(LPM4)
()
(F11x1)
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
electrical characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (unless otherwise noted)
supply current (into VCC) excluding external current (f
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
TA = –40°C +85°C,
C11x1
(AM)
F11x1
(CPUOff)
(LPM2)
(LPM3)
(LPM3)
I
(LPM4)
I
(LPM4)
NOTE: All inputs are tied to 0 V or VCC. Outputs do not source or sink any current.
Low-power mode,
(LPM0)
p
Low-power mode, (LPM3)
(C11x1)
Low-power mode, (LPM3)
(F11x1)
ow-power mode,
ow-power mode,
f
TA = –40°C +85°C,
f
TA = –40°C +85°C,
f(ACLK)
TA = –40°C +85°C,
f
TA = –40°C +85°C,
f(ACLK)
TA = –40°C +85°C,
f(ACLK)
TA = –40°C +85°C,
f(ACLK)
TA = –40°C +85°C,
f(ACLK)
TA = –40°C 0.8 1.2
TA = 25°C
TA = 85°C
TA = –40°C
TA = 25°C
TA = 85°C 2.3 3.4
TA = –40°C
TA = 25°C
TA = 85°C
TA = –40°C 0.1 0.5
TA = 25°C
TA = 85°C 0.8 1.9
=
= 32,768 Hz
(ACLK)
= f
(MCLK)
(MCLK)
(SMCLK)
=
= 32,768 Hz
= f
(SMCLK)
= 0,
= 32,768 Hz
= 0,
= 32,768 Hz
=
= 32,768 Hz, SCG0 = 0
=
= 32,768 Hz, SCG0 = 1
= 1
f
f
(SMCLK)
f(ACLK)
(system)
= 1
= f
= f
= 0
= 0
,
= 4096 Hz
(ACLK)
,
= 4096 Hz
(ACLK)
= 1
= 1
= 0 MHz
0
= 0 Hz, SCG0 = 1
,
,
,
,
= 0 MHz,
= 1 MHz)
VCC = 2.2 V 160 200
VCC = 3 V 240 300
VCC = 2.2 V 1.3 2
VCC = 3 V 2.5 3.2
VCC = 2.2 V 200 250
VCC = 3 V 300 350
VCC = 2.2 V 1.6 3
VCC = 3 V 3 4.3
VCC = 2.2 V 30 40
VCC = 3 V 51 60
VCC = 2.2 V 32 45
VCC = 3 V 55 70
VCC = 2.2 V 11 14
VCC = 3 V 17 22
VCC = 2.2 V 1.2 1.7
VCC = 3 V 2 2.7
VCC = 2.2 V
VCC = 3 V
VCC = 2.2 V/3 V
VCC = 2.2 V/3 V
0.7 1
1.6 2.3
1.8 2.2
1.6 1.9
0.1 0.5
0.1 0.5
0.4 0.8
0.1 0.5
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
µ
µA
µA
µA
µA
current consumption of active mode versus system frequency, C version, F version
= I
I
AM
current consumption of active mode versus supply voltage, C version
IAM = I
current consumption of active mode versus supply voltage, F version
= I
I
AM
28
AM[1 MHz]
AM[3 V]
AM[3 V]
× f
system
[MHz]
+ 105 µA/V × (VCC–3 V)
+ 120 µA/V × (VCC–3 V)
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 29

MSP430x11x1
V
Positive-going input threshold voltage
V
V
Negative-going input threshold voltage
V
V
Input voltage hysteresis, (V
V
)
V
V
V
V
Port 1
(C11x1)
)
V
Port 1 (F11x1)
V
V
V
V
V
gg
V
V
V
V
V
V
Port 1
(C11x1
)
V
F11x1)
V
CC
V
I
High-impedance leakage current
nA
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
Schmitt-trigger inputs Port P1 to Port P2; P1.0 to P1.7, P2.0 to P2.5
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
IT+
IT–
hys
p
p
p
–
IT+
IT–
electrical characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
outputs Port 1 to P2; P1.0 to P1.7, P2.0 to P2.5
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
High-level output voltage
OH
OH
OL
NOTES: 8. The maximum total current, I
and Port 2
Port 1 (F11x1
High-level output voltage
Port 2 (F11x1)
Low-level output voltage
and Port 2
F11x1
drop specified.
9. The maximum total current, I
drop specified.
10. One output loaded at a time.
,
I
(OHmax)
I
(OHmax)
I
(OHmax)
I
(OHmax)
I
(OHmax)
I
(OHmax)
I
(OHmax)
I
(OHmax)
I
(OLmax)
I
(OLmax)
I
(OLmax)
I
(OLmax)
OHmax
OHmax
= –1.5 mA
= –6 mA
= –1.5 mA
= –6 mA
= –1 mA
= –3.4 mA
= –1 mA
= –3.4 mA
= 1.5 mA
= 6 mA
= 1.5 mA
= 6 mA
and I
OLmax
and I
OLmax
= 2.2
CC
= 3
CC
= 2.2
CC
= 3
CC
= 2.2
CC
= 3
, for all outputs combined, should not exceed ±12 mA to hold the maximum voltage
, for all outputs combined, should not exceed ±48 mA to hold the maximum voltage
VCC = 2.2 V 1.1 1.3
VCC = 3 V 1.5 1.8
VCC = 2.2 V 0.4 0.9
VCC = 3 V .90 1.2
VCC = 2.2 V 0.3 1
VCC = 3 V 0.5 1.4
See Note 8 VCC–0.25 V
See Note 9 VCC–0.6 V
See Note 8 VCC–0.25 V
See Note 9 VCC–0.6 V
See Note 10 VCC–0.25 V
See Note 10 VCC–0.6 V
See Note 10 VCC–0.25 V
See Note 10 VCC–0.6 V
See Note 8 V
See Note 9 V
See Note 8 V
See Note 9 V
SS
SS
SS
SS
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
CC
VSS+0.25
VSS+0.6
VSS+0.25
VSS+0.6
leakage current
lkg(Px.x)
NOTES: 1 1. The leakage current is measured with VSS or VCC applied to the corresponding pin(s), unless otherwise noted.
12. The leakage of the digital port pins is measured individually. The port pin must be selected for input and there must be no optional
pullup or pulldown resistor.
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Port P1: P1.x, 0 ≤ ×≤ 7
p
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
(see Notes 11, 12)
Port P2: P2.x, 0 ≤ ×≤ 5
(see Notes 11, 12)
VCC = 2.2 V/3 V,
VCC = 2.2 V/3 V,
±50
±50
29
Page 30

MSP430x11x1
yg
V
CC
V/3 V
Port P1, P2: P1.x to P2.x
()
ns
()
ns
f
Input frequenc
Internal TA0, TA1, TA2, t
t
MH
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
electrical characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
optional resistors, individually programmable with ROM code (see Note 13)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
R
(opt1)
R
(opt2)
R
(opt3)
R
(opt4)
R
(opt5)
R
(opt6)
R
(opt7)
R
(opt8)
R
(opt9)
R
(opt10)
NOTE 13: Optional resistors R
Resistors, individually programmable with ROM code, all port pins,
values applicable for pulldown and pullup
for pulldown or pullup are not available in standard flash memory device MSP430F11x1.
optx
inputs Px.x, TAx
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS VCC MIN TYP MAX UNIT
t
(int)
t
(cap)
NOTES: 14. The external signal sets the interrupt flag every time the minimum t
External interrupt timing
Timer_A, capture timing TA0, TA1, TA2. (see Note 15)
trigger signals shorter than t
cycles.
15. The external capture signal triggers the capture event every time when the minimum t
capture may be triggered with capture signals even shorter than t
a correct capture of the 16-bit timer value and to ensure the flag is set.
External trigger signal for the interrupt flag,
(see Note 14)
. Both the cycle and timing specifications must be met to ensure the flag is set. t
int
,
cap
= 2.2
2.2 V/3 V 1.5 cycle
2.2 V 62
3 V 50
2.2 V/3 V 1.5 cycle
2.2 V 62
3 V 50
cycle and time parameters are met. It may be set even with
int
. Both the cycle and timing specifications must be met to ensure
cap
2.5 5 10 kΩ
3.8 7.7 15 kΩ
7.6 15 31 kΩ
11.5 23 46 kΩ
23 45 90 kΩ
46 90 180 kΩ
70 140 280 kΩ
115 230 460 kΩ
160 320 640 kΩ
205 420 830 kΩ
is measured in MCLK
int
cycles and time parameters are met. A
internal signals TAx, SMCLK at Timer_A
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS VCC MIN TYP MAX UNIT
(IN)
f
(TAint)
p
Timer_A clock frequency Internally, SMCLK signal applied 2.2 V/3 V dc f
y
=
H
L
2.2 V 8
3 V 10
System
z
30
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 31

MSP430x11x1
P1.4/SMCLK
2.2 V/3 V
P2.0/ACLK
C
L
F
I
CAON=1
CARSEL=0
CAREF=0
A
(
(Refladder/
CAREF=1/2/3
load at
A
V
No load at P2.3/CA0/TA1 and
mV
A
ns
t
A
s
Overdrive 10 mV, without filter:
ns
(res onse HL)
A
s
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
electrical characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
outputs P1.x, P2.x, TAx
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS VCC MIN TYP MAX UNIT
f
(P20)
f
(TAx)
t
(Xdc)
t
(TAdc)
NOTE 16: The limits of the system clock MCLK has to be met. MCLK and SMCLK can have different frequencies.
Output frequency
Duty cycle of O/P
frequency
P2.0/ACLK, CL = 20 pF 2.2 V/3 V f
TA0, TA1, TA2, CL = 20 pF
Internal clock source, SMCLK signal applied (see Note 16)
f
CL = 20 pF
= 20
=
TA0, TA1, TA2, CL = 20 pF, Duty cycle = 50% 2.2 V/3 V 0 ±50 ns
,
,
p
f
f
f
f
f
f
SMCLK
SMCLK
SMCLK
SMCLK
= f
P20
= f
P20
= f
P20
= f
LFXT1
= f
LFXT1
= f
LFXT1/n
= f
DCOCLK
LFXT1
LFXT1
LFXT1/n
= f
= f
= f
= f
XT1
LF
XT1
LF
2.2 V/3 V dc f
40% 60%
35% 65%
50%–
15 ns
2.2 V/3 V
2.2 V/3 V
50%–
15 ns
40% 60%
30% 70%
50%
50%
50%
System
MHz
System
50%+
15 ns
50%+
15 ns
Comparator_A (see Note 17)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
(DD)
I
Refladder/
RefDiode)
V
(IC)
V
(Ref025)
See Figure 5
V
(Ref050)
See Figure 5
(RefVT)
V
(offset)
V
hys
(response LH)
Common-mode input
voltage
Voltage @ 0.25 VCCnode
V
CC
Voltage @ 0.5VCCnode
V
CC
Offset voltage See Note 18 VCC = 2.2 V/3 V –30 30 mV
Input hysteresis CAON=1 VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 0 0.7 1.4 mV
,
CAON=1, CARSEL=0,
P2.3/CA0/T A1 and P2.4/CA1/TA2
CAON =1 VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 0 VCC–1 V
PCA0=1, CARSEL=1, CAREF=1,
No load at P2.3/CA0/TA1 and
P2.4/CA1/T A2, See Figure 5
PCA0=1, CARSEL=1, CAREF=2,
No load at P2.3/CA0/TA1 and
P2.4/CA1/T A2, See Figure 5
PCA0=1, CARSEL=1, CAREF=3,
P2.4/CA1/TA2
TA = 25°C, Overdrive 10 mV, Without filter: CAF=0
TA = 25°C, Overdrive 10 mV, With
filter: CAF=1
TA = 25°C,
,
, No
VCC = 2.2 V 25 40
VCC = 3 V 45 60
VCC = 2.2 V 30 50
VCC = 3 V 45 71
VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 0.23 0.24 0.25
VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 0.47 0.48 0.5
VCC = 2.2 V 430 550 645
VCC = 3 V 450 565 660
VCC = 2.2 V 160 210 300
VCC = 3 V 90 150 200
VCC = 2.2 V 1.6 1.9 3.4
VCC = 3 V 1.1 1.5 2.6
VCC = 2.2 V 160 210 300
µ
µ
µ
t
p
NOTES: 17. The leakage current for the Comparator_A terminals is identical to I
18. The input offset voltage can be cancelled by using the CAEX bit to invert the Comparator_A inputs on successive measurements.
The two successive measurements are then summed together.
CAF=0
TA = 25°C,
Overdrive 10 mV , with filter: CAF=1
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
VCC = 3 V 90 150 200
VCC = 2.2 V 1.6 1.9 3.4
VCC = 3 V 1.1 1.5 2.6
lkg(Px.x)
specification.
µ
31
Page 32

MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
electrical characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
700
Mean –6 Sigma
(RefVT)
V
650
600
550
500
Mean –4 Sigma
Mean
Mean +4 Sigma
Mean +6 Sigma
450
–45 –25 –5 15 35 55 75
Temperature [°C]
Figure 7. V
700
650
600
(RefVT)
V
550
500
450
–45 –25 –5 15 35 55 75
(RefVT)
vs Temperature, VCC = 3 V, C1121
Temperature [°C]
95
Mean –6 Sigma
Mean –4 Sigma
Mean
Mean +4 Sigma
Mean +6 Sigma
95
32
Figure 8. V
(RefVT)
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
vs Temperature, VCC = 2.2 V, C1121
Page 33

MSP430x11x1
()
V
CC
V/3 V
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
electrical characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
V
0 V
CC
1
0
CAON
CAF
V+
V–
Low Pass Filter
+
_
0
1
0
1
τ ≈ 2.0 µs
Figure 9. Block Diagram of Comparator_A Module
V
CAOUT
V–
400 mV
V+
Overdrive
t
(response)
Figure 10. Overdrive Definition
To Internal
Modules
CAOUT
Set CAIFG
Flag
PUC/POR
t
(POR_delay)
V
(POR)
V
(min)
t
(reset)
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
150 250 µs
TA = –40°C 1.4 1.8 V
POR
PUC/POR Reset is accepted internally 2 µs
TA = 25°C
TA = 85°C
= 2.2
1.1 1.5 V
0.8 1.2 V
0 0.4 V
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
33
Page 34

MSP430x11x1
C
Input capacitance
pF
C
(XOUT)
Out ut ca acitance
F
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
electrical characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
V
VCC
V
(POR)
V
(min)
POR
No POR
Figure 11. Power-On Reset (POR) vs Supply Voltage
2.0
1.8
1.8
1.6
1.4
1.4
1.2
1.0
V POR [V]
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
–40 –20 0 20 40 60 80
Temperature [°C]
1.5
1.1
25°C
Max
Min
POR
t
1.2
0.8
Figure 12. V
vs Temperature
(POR)
crystal oscillator,LFXT1
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
XTS=0; LF mode selected.
p
(XIN)
NOTE 19: Requires external capacitors at both terminals. Values are specified by crystal manufacturers.
p
p
p
VCC = 2.2 V / 3 V
XTS=1; XT1 mode selected.
VCC = 2.2 V / 3 V (Note 19)
XTS=0; LF mode selected.
VCC = 2.2 V / 3 V
XTS=1; XT1 mode selected.
VCC = 2.2 V / 3 V (Note 19)
12
p
2
12
p
2
RAM
PARAMETER MIN NOM MAX UNIT
V
(RAMh)
NOTE 20: This parameter defines the minimum supply voltage VCC when the data in the program memory RAM remains unchanged. No program
CPU halted (see Note 20) 1.6 V
execution should happen during this supply voltage condition.
34
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 35
MSP430x11x1
f
R
DCO
MOD
DCOR
T
25°C
MH
f
R
DCO
MOD
DCOR
T
25°C
MH
f
R
DCO
MOD
DCOR
T
25°C
MH
f
R
DCO
MOD
DCOR
T
25°C
MH
f
R
DCO
MOD
DCOR
T
25°C
MH
f
R
DCO
MOD
DCOR
T
25°C
MH
f
R
DCO
MOD
DCOR
T
25°C
MH
f
R
7
DCO
MOD
DCOR
T
25°C
MH
f
(DCO77)
R
l
DCO
MOD
DCOR
T
A
25°C
MHz
f
R
DCO
MOD
DCOR
T
25°C
V
V/3 V
DCO40
DCO40
DCO40
MH
ratio
D
sel
%/°C
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
electrical characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
DCO
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
(DCO03)
(DCO13)
(DCO23)
(DCO33)
(DCO43)
(DCO53)
(DCO63)
(DCO73)
(DCO47)
S
(Rsel)
S
(DCO)
t
D
V
NOTE 21: These parameters are not production tested.
= 0,
sel
= 1,
sel
= 2,
sel
= 3,
sel
= 4,
sel
= 5,
sel
= 6,
sel
=
sel
= 7,
se
= 4,
sel
SR = f
Rsel+1/fRsel
S
= f
DCO
Temperature drift, R
(see Note 21)
Drift with VCC variation, R
(see Note 21)
= 3,
= 3,
= 3,
= 3,
= 3,
= 3,
= 3,
,
= 3,
= 7,
= 7,
DCO+1/fDCO
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 4, DCO = 3, MOD = 0
sel
= 4, DCO = 3, MOD = 0
sel
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
= 0,
°
=
A
°
=
A
°
=
A
°
=
A
°
=
A
°
=
A
°
=
A
°
=
A
°
=
°
=
A
VCC = 2.2 V 0.08 0.12 0.15
VCC = 3 V 0.08 0.13 0.16
VCC = 2.2 V 0.14 0.19 0.23
VCC = 3 V 0.14 0.18 0.22
VCC = 2.2 V 0.22 0.30 0.36
VCC = 3 V 0.22 0.28 0.34
VCC = 2.2 V 0.37 0.49 0.59
VCC = 3 V 0.37 0.47 0.56
VCC = 2.2 V 0.61 0.77 0.93
VCC = 3 V 0.61 0.75 0.9
VCC = 2.2 V 1 1.2 1.5
VCC = 3 V 1 1.3 1.5
VCC = 2.2 V 1.6 1.9 2.2
VCC = 3 V 1.69 2 2.29
VCC = 2.2 V 2.4 2.9 3.4
VCC = 3 V 2.7 3.2 3.65
VCC = 2.2 V 4 4.5 4.9
VCC = 3 V 4.4 4.9 5.4
F
= 2.2
CC
VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 1.35 1.65 2
VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 1.07 1.12 1.16
VCC = 2.2 V –0.31 –0.36 –0.40
VCC = 3 V –0.33 –0.38 –0.43
VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 0 5 10 %/V
DCO40FDCO40FDCO40
x1.7
x2.1
x2.5
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
z
°
f
(DCOx7)
f
(DCOx0)
Frequency Variance
Max
Min
Max
Min
2.2 V 3 V
V
CC
1
DCOCLK
f
01234567
DCO Steps
Figure 13. DCO Characteristics
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
35
Page 36

MSP430x11x1
ns
()
Delay time (see Note 22)
()
f
TCK frequenc
JTAG/test (see Note 25)
MH
t
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
electrical characteristics over recommended ranges of supply voltage and operating free-air
temperature (unless otherwise noted) (continued)
principle characteristics of the DCO
D
Individual devices have a minimum and maximum operation frequency. The specified parameters for
f
DCOx0
D
The DCO control bits DCO0, DCO1 and DCO2 have a step size as defined in parameter S
D
The modulation control bits MOD0 to MOD4 select how often f
cycles. f
D
The ranges selected by R
wake-up from lower power modes (LPMx)
t
(LPM0)
t
(LPM2)
t
(LPM3)
t
(LPM4)
NOTE 22: Parameter applicable only if DCOCLK is used for MCLK.
to f
DCO
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
are valid for all devices.
DCOx7
DCO+1
is used within the period of 32 DCOCLK
is used for the remaining cycles. The frequency is an average = f
Sel4
to R
Sel5
, R
to R
Sel5
VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 100
VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 100
f
(MCLK)
f
(MCLK)
f
(MCLK)
f
(MCLK)
f
(MCLK)
f
(MCLK)
, and R
Sel6
= 1 MHz, VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 6
= 2 MHz, VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 6
= 3 MHz, VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 6
= 1 MHz, VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 6
= 2 MHz, VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 6
= 3 MHz, VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 6
Sel6
to R
Sel7
MOD/32
× (2
DCO
are overlapping.
DCO
.
).
µs
µs
JT AG/programming
PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
(TCK)
V
(FB)
I
(FB)
t
(FB)
I
(DD-PGM)
I
(DD-ERASE)
(retention)
NOTES: 23. The power source to blow the fuse is applied to TDI pin.
24. Once the JTAG fuse is blown, no further access to the MSP430 JTAG/test feature is possible. The JT AG block is switched to bypass
25. f
26. Duration of the program/erase cycle is determined by f
Fuse blow voltage, C versions (see Notes 23 and 24) VCC = 2.2 V/3 V 3.5 3.9 V
Supply current on TDI during fuse blow (see Note 24) (C11x1) 100 mA
Time to blow the fuse (see Note 24) (C11x1) 1 ms
Current during program cycle (see Note 26)
Current during erase cycle (see Note 26)
Write/erase cycles MSP430F1 1x1 10
Data retention TJ = 25°C MSP430F11x1 100 Year
mode.
may be restricted to meet the timing requirements of the module selected.
(TCK)
t
(word write)
t
(segment write, byte 0)
t
(segment write, byte 1 – 63)
t
(mass erase)
t
(page erase)
y,
= 35 x 1/f
= 5297 x 1/f
= 4819 x 1/f
(FTG)
= 30 × 1/f
= 20 × 1/f
(FTG)
(FTG)
(FTG)
(FTG)
VCC = 2.2 V dc 5
VCC = 3 V dc 10
VCC = 2.7 V/3.6 V,
MSP430F11x1
VCC = 2.7 V/3.6 V,
MSP430F11x1
applied to the flash timing controller. It can be calculated as follows:
(FTG)
4
10
3 5 mA
3 5 mA
5
z
36
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 37

APPLICATION INFORMATION
input/output schematic
Port P1, P1.0 to P1.3, input/output with Schmitt-trigger
P1SEL.x
P1DIR.x
Direction Control
From Module
P1OUT.x
Module X OUT
P1IN.x
EN
0
1
0
1
Pad Logic
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
V
CC
(See Note 27)
(See Note 28)
P1.0 – P1.3
(See Note 28)
(See Note 27)
GND
Module X IN
P1IRQ.x
NOTE: x = Bit/identifier, 0 to 3 for port P1
Direction
PnSel.x PnDIR.x
P1Sel.0 P1DIR.0 P1DIR.0 P1OUT.0 VSS P1IN.0 TACLK
P1Sel.1 P1DIR.1 P1DIR.1 P1OUT.1 Out0 signal
P1Sel.2 P1DIR.2 P1DIR.2 P1OUT.2 Out1 signal
P1Sel.3 P1DIR.3 P1DIR.3 P1OUT.3 Out2 signal
†
Signal from or to Timer_A
NOTES: 27. Optional selection of pullup or pulldown resistors with ROM (masked) versions.
28. Fuses for optional pullup and pulldown resistors can only be programmed at the factory (ROM versions only).
control from
module
D
P1IE.x
P1IFG.x
PnOUT.x Module X OUT PnIN.x Module X IN PnIE.x PnIFG.x PnIES.x
EN
Q
Set
Interrupt
Flag
Interrupt
Edge
Select
P1IES.x
P1SEL.x
†
P1IN.1 CCI0A
†
P1IN.2 CCI1A
†
P1IN.3 CCI2A
†
†
†
†
P1IE.0 P1IFG.0 P1IES.0
P1IE.1 P1IFG.1 P1IES.1
P1IE.2 P1IFG.2 P1IES.2
P1IE.3 P1IFG.3 P1IES.3
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
37
Page 38

MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Port P1, P1.4 to P1.7, input/output with Schmitt-trigger and in-system access features
V
P1SEL.x
P1DIR.x
Direction Control
From Module
P1OUT.x
Module X OUT
P1IN.x
Module X IN
P1IRQ.x
EN
D
P1IE.x
P1IFG.x
0
1
0
0
1
1
Q
Interrupt
Flag
EN
Set
Pad Logic
Interrupt
Edge
Select
P1IES.x
P1SEL.x
TST
Control By JTAG
CC
See Note 27
GND
Bus Keeper
See Note 28
See Note 28
See Note 27
TST
Fuse
Fuse
Blow
TST
Control
P1.4–P1.7
60 kΩ
Typical
GND
NOTE: Fuse not implemented
in F11x1
TEST
P1.x
TDO
Controlled By JTAG
P1.7/TDI/TDO
Controlled by JTAG
P1.x
P1.6/TDI
P1.x
P1.5/TMS
NOTE: The test pin should be protected from potential EMI
and ESD voltage spikes. This may require a smaller
external pulldown resistor in some applications.
TDI
TMS
TST
TST
x = Bit identifier, 4 to 7 for port P1
During programming activity and during blowing
the fuse, the pin TDO/TDI is used to apply the test
input for JTAG circuitry.
TCK
TST
P1.x
P1.4/TCK
Direction
PnSel.x PnDIR.x
control from
PnOUT.x Module X OUT PnIN.x Module X IN PnIE.x PnIFG.x PnIES.x
module
P1Sel.4 P1DIR.4 P1DIR.4 P1OUT.4 SMCLK P1IN.4 unused P1IE.4 P1IFG.4 P1IES.4
P1Sel.5 P1DIR.5 P1DIR.5 P1OUT.5 Out0 signal
P1Sel.6 P1DIR.6 P1DIR.6 P1OUT.6 Out1 signal
P1Sel.7 P1DIR.7 P1DIR.7 P1OUT.7 Out2 signal
†
Signal from or to Timer_A
†
P1IN.5 unused P1IE.5 P1IFG.5 P1IES.5
†
P1IN.6 unused P1IE.6 P1IFG.6 P1IES.6
†
P1IN.7 unused P1IE.7 P1IFG.7 P1IES.7
NOTES: 27. Optional selection of pullup or pulldown resistors with ROM (masked) versions.
28. Fuses for optional pullup and pulldown resistors can only be programmed at the factory (ROM versions only).
38
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 39

APPLICATION INFORMATION
Port P2, P2.0 to P2.2, input/output with Schmitt-trigger
P2SEL.x
P2DIR.x
Direction Control
From Module
P2OUT.x
Module X OUT
0
1
0
1
0: Input
1: Output
Pad Logic
MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
V
CC
See Note 27
See Note 28
P2.0 – P2.2
See Note 28
See Note 27
GND
Bus Keeper
P2IN.x
EN
Module X IN
P2IRQ.x
NOTE: x = Bit Identifier, 0 to 2 for port P2
Direction
PnSel.x PnDIR.x
P2Sel.0 P2DIR.0 P2DIR.0 P2OUT.0 ACLK P2IN.0 unused P2IE.0 P2IFG.0 P1IES.0
P2Sel.1 P2DIR.1 P2DIR.1 P2OUT.1 VSS P2IN.1 INCLK
P2Sel.2 P2DIR.2 P2DIR.2 P2OUT.2 CAOUT P2IN.2 CCI0B
†
Signal from or to Timer_A
NOTES: 27. Optional selection of pullup or pulldown resistors with ROM (masked) versions.
28. Fuses for optional pullup and pulldown resistors can only be programmed at the factory (ROM versions only).
control from
module
D
CAPD.X
P2IE.x
P2IFG.x
PnOUT.x Module X OUT PnIN.x Module X IN PnIE.x PnIFG.x PnIES.x
EN
Q
Set
Interrupt
Flag
Interrupt
Edge
Select
P2IES.x
P2SEL.x
†
†
P2IE.1 P2IFG.1 P1IES.1
P2IE.2 P2IFG.2 P1IES.2
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
39
Page 40

MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Port P2, P2.3 to P2.4, input/output with Schmitt-trigger
P2SEL.3
P2DIR.3
Direction Control
From Module
P2OUT.3
Module X
OUT
0
1
0
1
0: Input
1: Output
Pad Logic
V
CC
See Note 27
See Note 28
See Note 28
See Note 27
P2.3
P2IN.3
Module X IN
P2IRQ.3
P2IRQ.4
Module X IN
P2IN.4
Module X OUT
P2OUT.4
Direction Control
From Module
P2DIR.4
P2SEL.4
CCI1B
EN
D
P2IE.3
P2IFG.3
P2IFG.4
P2IE.4
D
EN
EN
Q
Set
Interrupt
Flag
Interrupt
Flag
Set
Q
EN
1
0
1
0
Interrupt
Edge
Select
P2IES.3 P2SEL.3
P2SEL.4
P2IES.4
Interrupt
Edge
Select
Pad Logic
1: Output
0: Input
Bus Keeper
Comparator_A
CAF
0 V
CAREF
Bus Keeper
GND
CAPD.3
CAREF CAEXP2CA
+
_
Reference Block
CAPD.4
V
CC
See Note 27
See Note 28
See Note 28
See Note 27
GND
P2.4
APPLICATION INFORMATION
PnSel.x PnDIR.x Direction
control from module
P2Sel.3 P2DIR.3 P2DIR.3 P2OUT.3 Out1 signal
P2Sel.4 P2DIR.4 P2DIR.4 P2OUT.4 Out2 signal
†
Signal from Timer_A
NOTES: 27. Optional selection of pullup or pulldown resistors with ROM (masked) versions.
28. Fuses for optional pullup and pulldown resistors can only be programmed at the factory (ROM versions only).
40
PnOUT.x Module X OUT PnIN.x Module X IN PnIE.x PnIFG.x PnIES.x
†
P2IN.3 unused P2IE.3 P2IFG.3 P1IES.3
†
P2IN.4 unused P2IE.4 P2IFG.4 P1IES.4
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 41

MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
Port P2, P2.5, input/output with Schmitt-trigger and R
P2SEL.5
P2DIR.5
Direction Control
From Module
P2OUT.5
Module X OUT
P2IN.5
Module X IN
P2IRQ.5
EN
D
P2IE.5
P2IFG.5
0
0
1
1
Q
0
1
EN
Set
0: Input
1: Output
Interrupt
Edge
Select
function for the Basic Clock module
OSC
V
CC
Pad Logic
Bus Keeper
V
CC
See Note 27
See Note 28
See Note 28
See Note 27
GND
Internal to
Basic Clock
Module
P2.5
1
0
Interrupt
Flag
NOTE: DCOR: Control bit from Basic Clock Module if it is set, P2.5 Is disconnected from P2.5 pad
Direction
PnSel.x PnDIR.x
P2Sel.5 P2DIR.5 P2DIR.5 P2OUT.5 VSS P2IN.5 unused P2IE.5 P2IFG.5 P2IES.5
NOTES: 27. Optional selection of pullup or pulldown resistors with ROM (masked) versions.
28. Fuses for optional pullup and pulldown resistors can only be programmed at the factory (ROM versions only).
control from
module
PnOUT.x Module X OUT PnIN.x Module X IN PnIE.x PnIFG.x PnIES.x
P2IES.5
P2SEL.5
DCOR
CAPD.5
DC
Generator
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
41
Page 42

MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Port P2, unbonded bits P2.6 and P2.7
P2SEL.x
P2DIR.x
Direction Control
From Module
P2OUT.x
Module X OUT
0
1
0
0
1
1
0: Input
1: Output
P2IN.x
EN
Module X IN
P2IRQ.x
NOTE: x = Bit/identifier, 6 to 7 for port P2 without external pins
Direction
P2Sel.x
P2Sel.6 P2DIR.6 P2DIR.6 P2OUT.6 VSS P2IN.6 unused P2IE.6 P2IFG.6 P2IES.6
P2Sel.7 P2DIR.7 P2DIR.7 P2OUT.7 VSS P2IN.7 unused P2IE.7 P2IFG.7 P2IES.7
NOTE: A good use of the unbonded bits 6 and 7 of port P2 is to use the interrupt flags. The interrupt flags can not be influenced from any signal
P2DIR.x
other than from software. They work then as a soft interrupt.
control from
module
D
P2IE.x
P2IFG.x
P2OUT.x Module X OUT P2IN.x Module X IN P2IE.x P2IFG.x P2IES.x
EN
Q
Set
Interrupt
Flag
Interrupt
Edge
Select
P2IES.x
P2SEL.x
Node Is Reset With PUC
Bus Keeper
PUC
JTAG fuse check mode
MSP430 devices that have the fuse on the TEST terminal have a fuse check mode that tests the continuity of
the fuse the first time the JT AG port is accessed after a power-on reset (POR). When activated, a fuse check
current can flow from the TEST pin to ground if the fuse is not burned. Care must be taken to avoid accidentally
activating the fuse check mode and increasing overall system power consumption.
When the TEST pin is taken back low after a test or programming session, the fuse check mode and sense
currents are terminated.
42
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 43

MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
MECHANICAL DATA
DW (R-PDSO-G**) PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE PACKAGE
16 PIN SHOWN
0.050 (1,27)
16
1
0.020 (0,51)
0.014 (0,35)
9
0.299 (7,59)
0.293 (7,45)
8
A
0.010 (0,25)
0.419 (10,65)
0.400 (10,15)
M
0.010 (0,25) NOM
0°–8°
Gage Plane
0.010 (0,25)
0.050 (1,27)
0.016 (0,40)
0.104 (2,65) MAX
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters).
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusion not to exceed 0.006 (0,15).
D. Falls within JEDEC MS-013
0.012 (0,30)
0.004 (0,10)
PINS **
DIM
A MAX
A MIN
Seating Plane
0.004 (0,10)
16
0.410
(10,41)
0.400
(10,16)
20
0.510
(12,95)
0.500
(12,70)
24
0.610
(15,49)
0.600
(15,24)
4040000/D 02/98
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
43
Page 44

MSP430x11x1
MIXED SIGNAL MICROCONTROLLER
SLAS241C – SEPTEMBER 1999 – REVISED JUNE 2000
MECHANICAL DATA
PW (R-PDSO-G**) PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE PACKAGE
14 PINS SHOWN
0,65
1,20 MAX
14
0,30
0,19
8
4,50
4,30
PINS **
7
Seating Plane
0,15
0,05
8
1
A
DIM
6,60
6,20
14
0,10
M
0,10
0,15 NOM
0°–8°
2016
Gage Plane
24
0,25
0,75
0,50
28
A MAX
A MIN
NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters.
B. This drawing is subject to change without notice.
C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusion not to exceed 0,15.
D. Falls within JEDEC MO-153
3,10
2,90
5,10
4,90
5,10
4,90
6,60
6,40
7,90
7,70
9,80
9,60
4040064/F 01/97
44
POST OFFICE BOX 655303 • DALLAS, TEXAS 75265
Page 45

IMPORTANT NOTICE
T exas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue
any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information
to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold
subject to the terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment, including those
pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation of liability.
TI warrants performance of its semiconductor products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in
accordance with TI’s standard warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are utilized to the extent
TI deems necessary to support this warranty . Specific testing of all parameters of each device is not necessarily
performed, except those mandated by government requirements.
Customers are responsible for their applications using TI components.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer’s applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards must be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. TI does not warrant or represent
that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other
intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any combination, machine, or process in which such
semiconductor products or services might be or are used. TI’s publication of information regarding any third
party’s products or services does not constitute TI’s approval, warranty or endorsement thereof.
Copyright 2000, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...