Page 1

User's Guide
SLAU336–March 2011
DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM
Contents
1 Introduction .................................................................................................................. 2
1.1 Overview ............................................................................................................ 2
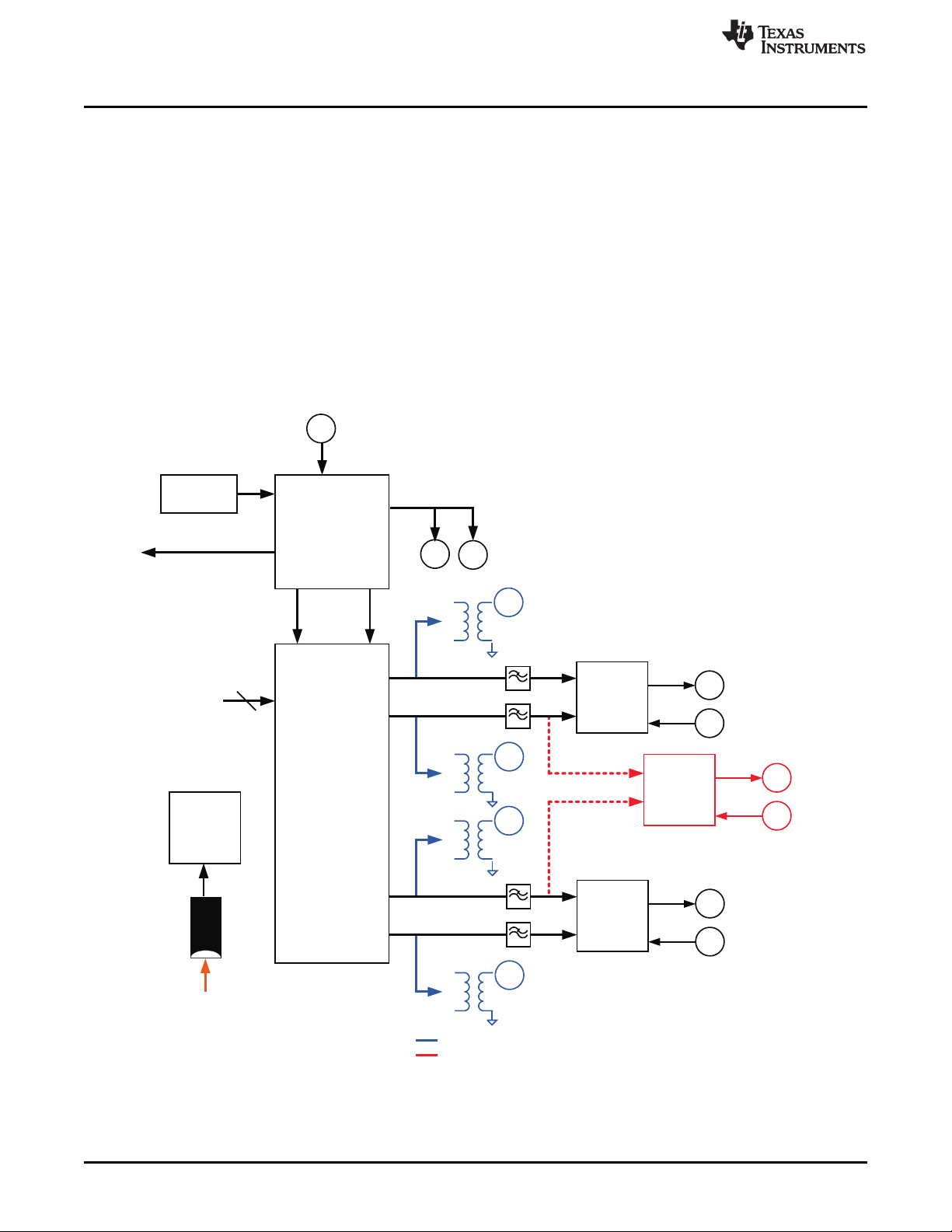
1.2 EVM Block Diagram ............................................................................................... 2
2 Software Control ............................................................................................................ 3
2.1 Installation Instructions ............................................................................................ 3
2.2 Software Operation ................................................................................................ 3
3 Basic Test Procedure ....................................................................................................... 8
3.1 Test Block Diagram ................................................................................................ 8
3.2 Test Set-Up Connection ........................................................................................... 9
3.3 TSW3100 Quick Start Operation ................................................................................. 9
3.4 DAC348x Software Quick Start Guide ......................................................................... 10
4 Optional Configuration .................................................................................................... 12
4.1 Configuring and Testing the DAC3484 Transformer Coupled Output ..................................... 12
4.2 Using the DAC3482 or Configuring DAC3484 in DAC3482 mode ......................................... 15
List of Figures
1 DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM Block Diagram ............................................................................... 2
2 Input Control Options....................................................................................................... 3
3 PLL Configuration........................................................................................................... 4
4 Digital Block Options ....................................................................................................... 5
5 Output Control Options..................................................................................................... 6
6 CDCE62005 Tab Configured for 4x Interpolation....................................................................... 7
7 Test Set-up Block Diagram................................................................................................ 8
8 TSW3100 CommsSignalPattern (WCDMA) Programming GUI..................................................... 10
9 DAC3484 + TRF3703-15 WCDMA Output ............................................................................ 11
10 DAC3484 + TRF3703-15 WCDMA Output ............................................................................ 12
11 Locations of DAC348x to Transformer Output Jumper Locations .................................................. 13
12 DAC3484 Transformer Coupled Output at 60MHz IF ................................................................ 14
13 DAC3484 Transformer Coupled Output at 30MHz IF ................................................................ 15
14 Locations of the DAC3482 to TRF3703-15 Interface Jumpers...................................................... 16
15 TSW3100 GUI Configuration for Generating a WCDMA Signal for DAC3482.................................... 17
SLAU336–March 2011 DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
1
Page 2
19.2MHz
TCXO
CDCE62005
DAC348X
DATA
DATA _CLK
FRAME
SYNC
PARITY
(LVDS DC Coupled)
DAC_CLK
(LVPECLAC
Coupled)
OSTR_CLK
(LVPECLAC
Coupled)
J20 RF
J19 LO
FPGA CLK
TSW3100
LVPECL DC coupled
TRF3703-15
Default TRF3703-15
Output
J7
J6
+
_
_
+
J10
Ext. CLK Output
6 V Only
J6
Power
Supply
Circuits
J21 RF
J22 LO
TRF3703-15
Default TRF3703-15
Output
J3
J2
+
_
_
+
J11
A
B
C
D
J9
Ext. CLK Input
1.5 Vrms Single Ended
1.25GHz Max
Primary Reference
(LVPECLAC coupled )
19.2 MHz Reference
LVCMOS Level
Secondary Reference for
CDCE62005 PLL Mode
Y4
Y3
Y1
Y2
PRI
SEC
J23 RF
J24 LO
TRF3703-15
Optional DAC Output
Optional TRF3703-15 Output for DAC3482 Dual DAC Mode
Introduction
1 Introduction
1.1 Overview
This document is intended to serve as a basic user’s guide for the DAC3484/2 EVM Revision D. The EVM
provides a basic platform to evaluate the DAC3484 and DAC3482, which are a family of 1.25GSPS, up to
16x interpolation, 16-bit high speed digital-to-analog converters. The DAC3484 is a quad-channel DAC,
and the DAC3482 is a dual-channel DAC.
The EVM includes the CDCE62005 clocking source which provides the clocks required for the DAC and
the pattern generator. The on-board TRF3703-15 modulators provide on-board IF-to-RF upconversion for
basic transmitter evaluation. This EVM is ideally suited for mating with the TSW3100 pattern generation
card for evaluating WCDMA, LTE, or other high performance modulation schemes.
1.2 EVM Block Diagram
Figure 1 shows the configuration of the EVM with the TSW3100 used for pattern generation.
www.ti.com
Figure 1. DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM Block Diagram
2
DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM SLAU336–March 2011
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 3
www.ti.com
2 Software Control
2.1 Installation Instructions
• Open the folder named DAC348x_Installer_vxpx (xpx represents the latest version)
• Run Setup.exe
• Follow the on-screen instructions
• Once installed, launch by clicking on the DAC348x_GUI_vxpx program in Start>Texas Instruments
DACs
• When plugging in the USB cable for the first time, you will be prompted to install the USB drivers.
– When a pop-up screen opens, select “Continue Downloading”.
– Follow the on screen instructions to install the USB drivers
– If needed, you can access the drivers directly in the install directory
2.2 Software Operation
The software allows programming control of the DAC device and the CDC device. The front panel
provides a tab for full programming of each device. The GUI tabs provide more convenient and simplified
interface to the most used registers of each device.
Each device, including the DAC3484, DAC3482, and DAC34H84, has its own custom control interface.
Select the device option from the top left-hand corner. The DAC3484 EVM Software Control is described
in this section.
Software Control
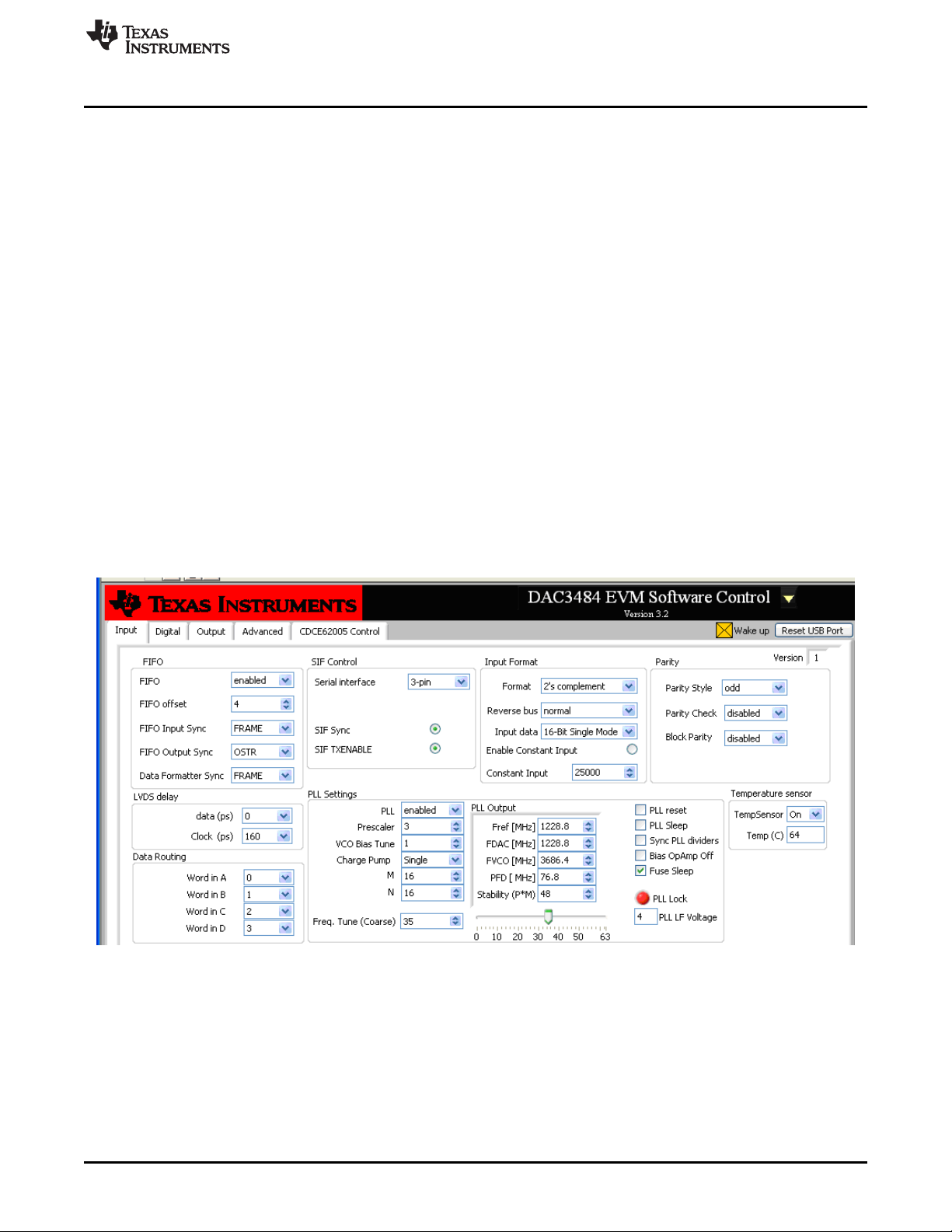
2.2.1 Input Control Options
Figure 2. Input Control Options
SLAU336–March 2011 DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
3
Page 4
Software Control
• FIFO: allows the configuration of the FIFO and FIFO sync sources.
• LVDS delay: provides internal delay of either the LVDS DATA or LVDS DATACLK to help meet the
input setup/hold time.
• Data Routing: provides flexible routing of the A, B, C, and D sample input data to the appropriate
digital path.
Note: the DAC3482 does not support this mode
• SIF Control: provides control of the Serial Interface (3-wires or 4-wires) and Serial Interface Sync (SIF
Sync).
• Input Format: provides control of the input data format (i.e., 2’s complement or offset binary).
• Parity: provides configuration of the parity input.
• PLL Settings: provides configuration of the on-chip PLL circuitry.
• Temperature Sensor: provides temperature monitoring of DAC3484/2 die temperature.
2.2.1.1 LVDS Delay Settings
The TSW3100 pattern generator sends out LVDS DATA and DATACLK as edge-aligned signal. The
following options can be implemented to meet the minimum setup and hold time of DAC348x data
latching:
• Set the on-chip LVDS DATACLOCK delay. Typical setting of 160ps or more will help meet the timing
requirement for most of the TSW3100 + DAC348x EVM setup. This LVDS DATACLOCK delay does
not account for additional PCB trace-to-trace delay variation, only the internal DATACLK delay.
• Modify the external LVDS DATACLK PCB trace delay: Additional trace length on the bottom side of the
PCB can be added to the LVDS DATACLK PCB trace length. Set SJP9, SJP10, SJP11, and SJP12 to
2-3 position for approximately 220ps of trace delay.
www.ti.com
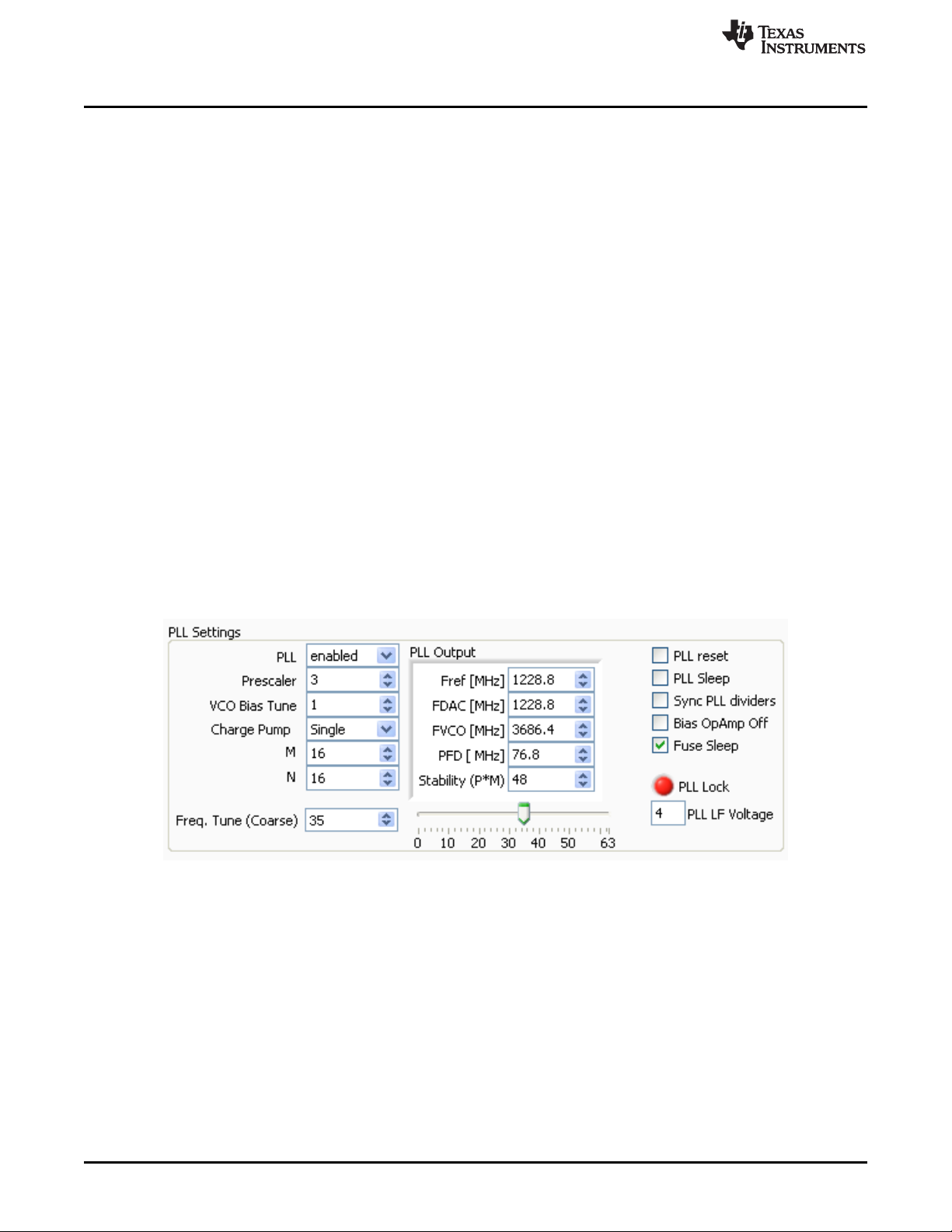
2.2.1.2 PLL Settings
Follow the steps below to configure the PLL.
• Enable PLL
• Uncheck PLL reset and PLL sleep
• Set M and N ratio such that F
• Set the prescaler such that the F
• Set VCO Bias Tune to “1”
• Charge Pump setting
– If stability (P×M) is less than 120, then set to “Single
– If stability (P×M) is greater than 120, then set to “Double” or install external loop filter
• Adjust the Freq. Tune (coarse tune) accordingly.
Figure 3. PLL Configuration
= (M)/(N)×Fref
DAC
×prescaler is within 3.3GHz and 4.0GHz
DAC
4
DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM SLAU336–March 2011
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 5

www.ti.com
2.2.2 Digital Block Options
Software Control
Figure 4. Digital Block Options
● Interpolation: allows control of the data rate versus DAC sampling rate ratio (i.e. data rate ×
interpolation = DAC sampling rate).
● Digital Mixer: allows control of the coarse mixer function.
Note: If fine mixer (NCO) is used, the “Enable Mixer” button must be checked, and the coarse
mixer must be bypassed. See NCO section for detail.
● Inverse sinx/x filter: allows compensation of the sinx/x attenuation of the DAC output.
Note: If inverse sinx/x filter is used, the input data digital full-scale must be backed off accordingly
to avoid digital saturation.
● Clock Receiver Sleep: allows the DAC clock receiver to be in sleep mode. The DAC has minimum
power consumption in this mode.
● Clock Divider Sync: allows the syncing of the internal divided-down clocks using either Frame,
Sync, or OSTR signal. Enable the divider sync as part of the initialization procedure or
resynchronization procedure.
● Group Delay: allows adjustment of group delay for each I/Q channel. This is useful for wideband
sideband suppression.
● Offset Adjustment: allows adjustment of DC offset to minimize the LO feed-through of the modulator
output. This section requires sync for proper operation. The sync options are listed below:
O REGWR: auto-sync from SIF register write.
O OSTR: sync from the external LVPECL OSTR signal. Clock divider sync must be enabled with
OSTR set as sync source
O SYNC: sync from the external LVDS SYNC signal.
O SIF SYNC: sync from SIF Sync. Uncheck and check the SIF Sync button for sync event.
● QMC Adjustment: allows adjustment of the gain and phase of the I/Q channel to minimize sideband
power of the modulator output.
O REGWR: auto-sync from SIF register write.
O OSTR: sync from the external LVPECL OSTR signal. Clock divider sync must be enabled with
OSTR set as sync source
O SYNC: sync from the external LVDS SYNC signal.
O SIF SYNC: sync from SIF Sync. Uncheck and check the SIF Sync button for sync event.
SLAU336–March 2011 DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
5
Page 6
Software Control
● NCO: allows fine mixing of the I/Q signal. The procedure to adjust the NCO mixing frequency are
listed below:
1. Enter the DAC sampling frequency in Fsample.
2. Enter the desired mixing frequency in both NCO freq_AB and NCO freq_CD.
3. Press Update freq
4. Sync the NCO block from the following options:
● REGWR: auto-sync from SIF register write. Writing to either Phase OffsetAB or Phase
OffsetCD can create a sync event.
● OSTR: sync from the external LVPECL OSTR signal. Clock divider sync must be enabled
with OSTR set as sync source. Refer to the datasheet for OSTR period requirement.
● SYNC: sync from the external SYNC signal
● SIF SYNC: sync from SIF Sync. Uncheck and check the SIF Sync button for sync
event.
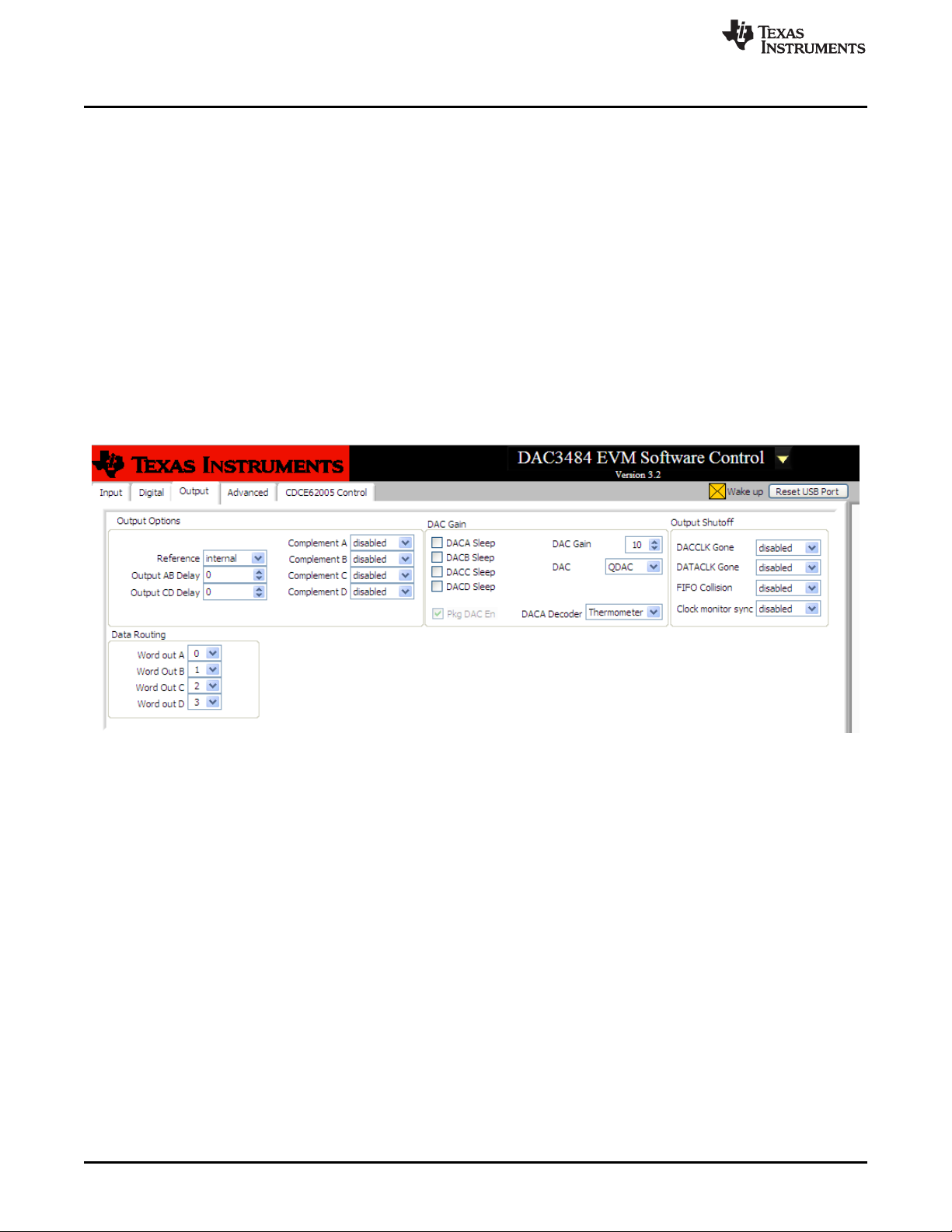
2.2.3 Output Control Options
www.ti.com
Figure 5. Output Control Options
● Output Options: allows the configuration of reference, output polarity, and output delay
● Data Routing: provides flexible routing of the A, B, C, and D digital path to the desired output
channels.
Note: The DAC3482 does not support this mode.
● DAC Gain: configures the full-scale DAC current and DAC3484/DAC3482 mode. With Rbiaj resistor
set at 1.28kΩ:
O DAC Gain = 15 for 30mA full-scale current.
O DAC Gain = 10 for 20mA full-scale current (default).
O DAC3484 = QDAC
O DAC3482 = DDAC
● This allows the DAC3484 to be configured as DAC3482 (see Using DAC3484 as DAC3482
section for detail)
● DAC Sel = Enable inner outputs of Ch. B and Ch. C as the DAC3482 output.
● DAC Sel = Enable outer outputs of Ch. A and Ch. D as the DAC3482 output. Outer
channels are grounded for the DAC3482 device.
● Output Shutoff On: allows outputs to shut-off when DACCLK GONE, DATACLK GONE, or FIFO
COLLISION alarm event occurs.
6
DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM SLAU336–March 2011
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Submit Documentation Feedback
Page 7

www.ti.com
2.2.4 CDCE62005
Software Control
Figure 6. CDCE62005 Tab Configured for 4x Interpolation
Clock frequency control is determined by register values in the CDCE62005 Control tab. Please refer to
the CDCE62005 datasheet for detailed explanations of the register configuration to change the clock
frequency.
The following CDCE62005 outputs are critical to proper operation of the DAC348x:
● Y1: DAC348x FIFO OSTR clock. The clock rate for this should be at least F
/Interpolation/8 for
DAC
DAC3484 mode and DAC3482 mode.
O The whole OSTR clock equation needs to take account of both the Y1 CDCE62005 clock
divider ratio and the additional CDCP1803 divide-by-2 clock divider.
O This OSTR signal can be a slower periodic signal or a pulse depending on the application.
O Note: The FIFO OSTR clock should be disabled when the DAC348x is configured in PLL
mode.
● Y2: DAC348x DAC sampling clock. If the DAC348x is configured for internal PLL mode, this will
be the reference clock input for the PLL block.
● Y3: TSW3100 FPGA clock. The clock rate for this should be F
mode and F
/interpolation/4 for DAC3482 mode.
DAC
/interpolation/2 for DAC3484
DAC
SLAU336–March 2011 DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
7
Page 8

PC
+5V
+6 V
Ethernet
USB
J13
J9
DAC348X
J14
J18
TSW3100
Pattern
Generator
J74
J13
Cross-over
Ethernet Cable
USB Mini-B
Cable
RF
LO
Spectrum
Analyzer
Signal
Generator
(LO Source)
Signal
Generator
(CLK Source)
J9
Basic Test Procedure
2.2.5 Register Control
● Send All: Sends the register configuration to all devices
● Read All: Reads register configuration from DAC348x device
● Load Regs: Load a register file for all devices. Sample configuration files for common frequency
plans are located in the install directory.
O Select Load Regs button.
O Double click on the data folder.
O Double click on the desired register file.
O Click on Send All to ensure all of the values are loaded properly.
● Save Regs: Saves the register configuration for all devices
2.2.6 Miscellaneous Settings
● Reset USB: Toggle this button if the USB port is not responding. This generates a new USB handle
address
O Note: It is recommended that the board be reset after every power cycle and the “reset usb”
button on the GUI be clicked.
● Exit: Stops the program
www.ti.com
3 Basic Test Procedure
This section outlines the basic test procedure for testing the EVM.
3.1 Test Block Diagram
The test set-up for general testing of the DAC348x with the TSW3100 pattern generation card is shown in
Figure 7.
8
DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM SLAU336–March 2011
Figure 7. Test Set-up Block Diagram
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 9

www.ti.com
3.2 Test Set-Up Connection
● TSW3100 Pattern Generator
1. Connect 5V power supply to J9, 5V_IN jack of the TSW3100 EVM.
2. Connect the PC’s Ethernet port to J13, Ethernet port of the TSW3100. The cable should be a
standard cross-over Cat5e Ethernet cable.
● DAC3484 EVM
1. Connect J13 connector of DAC348x EVM to J74 connector of TSW3100 EVM
2. Connect 6V to the J18, Power In jack of the DAC3484 EVM.
3. Connect PC’s USB port to J14 USB port of the DAC3484 EVM. The cable should be a
standard A to mini-B connector cable.
4. Provide a 1.5Vrms, 1.25GHz max Clock at J9, CLKIN SMA port of DAC3484 EVM.
5. Provide 12dBm max, 350MHz to 4GHz LO source at J19 or J22 port of the DAC3484 EVM.
This is to provide the LO source to the TRF3703-15 modulators.
6. Connect the RF output port of J20 or J21 to the spectrum analyzer.
● DAC3482 EVM
1. Repeat steps 1 to 4 of DAC3484 EVM connection
2. Provide 12dBm max, 350MHz to 4GHz LO source at J24 port of the DAC3484 EVM. This is to
provide the LO source to the TRF3703-15 modulators.
3. Connect the RF output port of J23 to the spectrum analyzer.
● DAC3484/2 EVM jumpers: make sure the following jumpers are at their default setting
1. JP6 on pin {1,2}
2. JP4 on pin {2,3}
3. JP5 on pin {1,2}
4. JP2 on pin {1,2}
5. JP3 on pin {2,3}
6. JP1 and JP8 should be installed
7. JP12 normally can be set in {1-2} position. If -5V supply is used to bias the DAC to modulator
interface, then J12 needs to be in {2-3} position prior to the 6V power supply connection. Once
the 6V power supply is connected, then J12 can be in {1-2} position to start the -5V sequence.
Basic Test Procedure
3.3 TSW3100 Quick Start Operation
Reference the TSW3100 User’s Guide for more detailed explanations of the TSW3100 set-up and
operation. This document assumes the TSW3100 software is installed and functioning properly. The
DAC348x needs TSW3100 operating software version 2.5 or higher with TSW3100 board Rev D (or
higher).
CommsSignalPattern Setup from Default Configuration (WCDMA)
• Change Interpolation value to DAC Clock Rate / Interpolation / 3.84 (i.e. 1228.8 / 4/ 3.84 = 80)
• Enter desired Offset Frequency (i.e. 30 MHz) for each desired carrier
• Select the 16b QDAC output button
• Check the “LOAD and Run” box
• Press the green “Create” button
SLAU336–March 2011 DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
9
Page 10

Basic Test Procedure
www.ti.com
Figure 8. TSW3100 CommsSignalPattern (WCDMA) Programming GUI
3.4 DAC348x Software Quick Start Guide
• Provide the clock input 1228.8 MHz at 1.5Vrms at J9 SMA connector of the DAC3484 EVM.
• Provide the LO source of 1.9GHz (12dBm max) at either J19 or J22 SMA connector of the DAC3484
EVM.
– Provide the LO source to J24 SMA connector for the DAC3482 EVM
• Turn on power to the board and press the reset button on the EVM
• Press the “Reset USB Port” button in GUI and verify USB communication.
• Switch to the INPUT tab of GUI
• Click “LOAD REGS”, browse to the installation folder and load example file
DAC3484_FDAC_1228p8MHz_4xint_NCO_30MHz_QMCon.txt. This file contains settings for 4x
interpolation with the DAC3484 running at 1228.8MSPS. Load this file and wait a couple of seconds for
the settings to go into effect.
• Verify the spectrum using the Spectrum Analyzer at the two RF outputs of the DAC EVM (J20 and
J21).
• (Toggle the SIF SYNC button to sync the appropriate digital blocks, if example file with NCO
setting is used)
10
DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM SLAU336–March 2011
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 11

www.ti.com
Basic Test Procedure
(Baseband = 30MHz, NCO = 30MHz with NCO Gain disabled, QMC Gain = 1446, LO = 1900MHz)
Figure 9. DAC3484 + TRF3703-15 WCDMA Output
SLAU336–March 2011 DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
11
Page 12

Optional Configuration
www.ti.com
(Baseband = 30MHz, NCO disabled, QMC Gain = 1024, LO = 1930MHz)
Figure 10. DAC3484 + TRF3703-15 WCDMA Output
4 Optional Configuration
4.1 Configuring and Testing the DAC3484 Transformer Coupled Output
• Eight 0 Ohm resistors must be moved to configure the output of the DAC3484 to be 4:1 transformer
coupled
• remove these resistors (Horizontal position): R19, R26, R33, R27, R35, R97, R76, R98.
• Install the following resistors (Vertical position): R162, R163, R17, R161, R8, R11, R1, R3. See Figure
11 below for detail.
12
DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM SLAU336–March 2011
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 13

www.ti.com
Optional Configuration
Figure 11. Locations of DAC348x to Transformer Output Jumper Locations
• Provide the clock input 1228.8 MHz at 1.5Vrms at J9 SMA connector of the DAC3484 EVM
• Turn on power to the board and press the reset button on the EVM
• Press the “Reset USB Port” button in GUI and verify USB communication.
• Switch to the INPUT tab of GUI
• Click “LOAD REGS”, browse to the installation folder and load example file
DAC3484_FDAC_1228p8MHz_4xint_NCO_30MHz_QMCon.txt. This file contains settings for 4x
interpolation with the DAC3484 running at 1228.8MSPS. Load this file and wait a couple of seconds for
the settings to go into effect.
• Verify the spectrum using the Spectrum Analyzer at the four DAC outputs of the DAC EVM (J7, J6, J3,
and J2).
• (Toggle the SIF SYNC button to sync the appropriate digital blocks, if example file with NCO
setting is used)
SLAU336–March 2011 DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
13
Page 14

Optional Configuration
www.ti.com
(baseband = 30MHz, NCO = 30MHz with NCO Gain disabled, QMC Gain = 1446)
Figure 12. DAC3484 Transformer Coupled Output at 60MHz IF
14
DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM SLAU336–March 2011
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 15

www.ti.com
Optional Configuration
(baseband = 30MHz, NCO disabled, QMC Gain = 1024)
Figure 13. DAC3484 Transformer Coupled Output at 30MHz IF
4.2 Using the DAC3482 or Configuring DAC3484 in DAC3482 mode
The DAC3484 EVM can also be used to evaluate the performance of DAC3482, or configure the
DAC3484 in Dual-DAC mode instead of the Quad-DAC mode. For DAC3482 or DAC3484 in Dual-DAC
mode, only the Inner Channels (B and C) are functional and the other two channels (A and D) are
disabled. The software can be configured as DAC3482 interface by selecting DAC3482 EVM Software
Control from the upper left-hand corner of the pull-down menu.
The DAC3484 EVM needs to be configured differently for the DAC3482 mode with the TRF3703-15
modulator. The inner DACs need to be routed to the third TRF3703-15 modulator in the middle.
To enable the DAC3482 Dual DAC with the TRF3703-15 interface, do the following board
modifications:
1. Remove R136, R278, R277, and R279 zero ohm jumpers
2. Install R137, R138, R246, R261
Refer to Figure 14 for locations of these zero ohm jumpers.
SLAU336–March 2011 DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
15
Page 16

Optional Configuration
www.ti.com
16
Figure 14. Locations of the DAC3482 to TRF3703-15 Interface Jumpers
The pattern generation is different for DAC3484 EVM when it is used as a Quad-DAC, compared to when
it is used as a Dual-DAC. Figure 15 shows a screen shot of TSW3100 GUI for generating a
communication signal for DAC3482. LVDS output option is selected. The setting displayed generates a
single carrier WCDMA signal at an IF of 30MHz for a DAC3482 running at 1228.8MHz with 4x
interpolation enabled.
DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM SLAU336–March 2011
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 17

www.ti.com
Optional Configuration
Figure 15. TSW3100 GUI Configuration for Generating a WCDMA Signal for DAC3482
SLAU336–March 2011 DAC3484/DAC3482 EVM
Submit Documentation Feedback
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
17
Page 18

Evaluation Board/Kit Important Notice
Texas Instruments (TI) provides the enclosed product(s) under the following conditions:
This evaluation board/kit is intended for use for ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT, DEMONSTRATION, OR EVALUATION
PURPOSES ONLY and is not considered by TI to be a finished end-product fit for general consumer use. Persons handling the
product(s) must have electronics training and observe good engineering practice standards. As such, the goods being provided are
not intended to be complete in terms of required design-, marketing-, and/or manufacturing-related protective considerations,
including product safety and environmental measures typically found in end products that incorporate such semiconductor
components or circuit boards. This evaluation board/kit does not fall within the scope of the European Union directives regarding
electromagnetic compatibility, restricted substances (RoHS), recycling (WEEE), FCC, CE or UL, and therefore may not meet the
technical requirements of these directives or other related directives.
Should this evaluation board/kit not meet the specifications indicated in the User’s Guide, the board/kit may be returned within 30
days from the date of delivery for a full refund. THE FOREGOING WARRANTY IS THE EXCLUSIVE WARRANTY MADE BY
SELLER TO BUYER AND IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED, IMPLIED, OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING
ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
The user assumes all responsibility and liability for proper and safe handling of the goods. Further, the user indemnifies TI from all
claims arising from the handling or use of the goods. Due to the open construction of the product, it is the user’s responsibility to
take any and all appropriate precautions with regard to electrostatic discharge.
EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT OF THE INDEMNITY SET FORTH ABOVE, NEITHER PARTY SHALL BE LIABLE TO THE OTHER
FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES.
TI currently deals with a variety of customers for products, and therefore our arrangement with the user is not exclusive.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance, customer product design, software performance, or infringement of
patents or services described herein.
Please read the User’s Guide and, specifically, the Warnings and Restrictions notice in the User’s Guide prior to handling the
product. This notice contains important safety information about temperatures and voltages. For additional information on TI’s
environmental and/or safety programs, please contact the TI application engineer or visit www.ti.com/esh.
No license is granted under any patent right or other intellectual property right of TI covering or relating to any machine, process, or
combination in which such TI products or services might be or are used.
FCC Warning
This evaluation board/kit is intended for use for ENGINEERING DEVELOPMENT, DEMONSTRATION, OR EVALUATION
PURPOSES ONLY and is not considered by TI to be a finished end-product fit for general consumer use. It generates, uses, and
can radiate radio frequency energy and has not been tested for compliance with the limits of computing devices pursuant to part 15
of FCC rules, which are designed to provide reasonable protection against radio frequency interference. Operation of this
equipment in other environments may cause interference with radio communications, in which case the user at his own expense
will be required to take whatever measures may be required to correct this interference.
EVM Warnings and Restrictions
It is important to operate this EVM within the input voltage range of 5.5 V to 7.0V and the output voltage range of 0 V to 3.3 V .
Exceeding the specified input range may cause unexpected operation and/or irreversible damage to the EVM. If there are
questions concerning the input range, please contact a TI field representative prior to connecting the input power.
Applying loads outside of the specified output range may result in unintended operation and/or possible permanent damage to the
EVM. Please consult the EVM User's Guide prior to connecting any load to the EVM output. If there is uncertainty as to the load
specification, please contact a TI field representative.
During normal operation, some circuit components may have case temperatures greater than 55° C. The EVM is designed to
operate properly with certain components above 55° C as long as the input and output ranges are maintained. These components
include but are not limited to linear regulators, switching transistors, pass transistors, and current sense resistors. These types of
devices can be identified using the EVM schematic located in the EVM User's Guide. When placing measurement probes near
these devices during operation, please be aware that these devices may be very warm to the touch.
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
Page 19

IMPORTANT NOTICE
Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements,
and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should
obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All products are
sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
TI warrants performance of its hardware products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance with TI’s standard
warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where
mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed.
TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or customer product design. Customers are responsible for their products and
applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with customer products and applications, customers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards.
TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any TI patent right, copyright, mask work right,
or other TI intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI products or services are used. Information
published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license from TI to use such products or services or a
warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual
property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI.
Reproduction of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied
by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. Reproduction of this information with alteration is an unfair and deceptive
business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional
restrictions.
Resale of TI products or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that product or service voids all
express and any implied warranties for the associated TI product or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not
responsible or liable for any such statements.
TI products are not authorized for use in safety-critical applications (such as life support) where a failure of the TI product would reasonably
be expected to cause severe personal injury or death, unless officers of the parties have executed an agreement specifically governing
such use. Buyers represent that they have all necessary expertise in the safety and regulatory ramifications of their applications, and
acknowledge and agree that they are solely responsible for all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning their products
and any use of TI products in such safety-critical applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support that may be
provided by TI. Further, Buyers must fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of TI products in
such safety-critical applications.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments unless the TI products are
specifically designated by TI as military-grade or "enhanced plastic." Only products designated by TI as military-grade meet military
specifications. Buyers acknowledge and agree that any such use of TI products which TI has not designated as military-grade is solely at
the Buyer's risk, and that they are solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in connection with such use.
TI products are neither designed nor intended for use in automotive applications or environments unless the specific TI products are
designated by TI as compliant with ISO/TS 16949 requirements. Buyers acknowledge and agree that, if they use any non-designated
products in automotive applications, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet such requirements.
Following are URLs where you can obtain information on other Texas Instruments products and application solutions:
Products Applications
Audio www.ti.com/audio Communications and Telecom www.ti.com/communications
Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Computers and Peripherals www.ti.com/computers
Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Consumer Electronics www.ti.com/consumer-apps
DLP® Products www.dlp.com Energy and Lighting www.ti.com/energy
DSP dsp.ti.com Industrial www.ti.com/industrial
Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Medical www.ti.com/medical
Interface interface.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security
Logic logic.ti.com Space, Avionics and Defense www.ti.com/space-avionics-defense
Power Mgmt power.ti.com Transportation and www.ti.com/automotive
Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Video and Imaging www.ti.com/video
RFID www.ti-rfid.com Wireless www.ti.com/wireless-apps
RF/IF and ZigBee® Solutions www.ti.com/lprf
TI E2E Community Home Page e2e.ti.com
Automotive
Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265
Copyright © 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
 Loading...
Loading...