Texas Instruments BQ3285EDSSTR, BQ3285EDSS, BQ3285LDSSTR, BQ3285LDSS Datasheet
bq3285ED/LD
Features
➤ ACPI-compliant
day-of-month alarm
➤ Direct clock/calendar replace-
ment for IBM
computers and other applications
➤ 2.7–5.5V operation (bq3285LD);
4.5–5.5V operation (bq3285ED)
➤ 242 bytes of general nonvolatile
storage
➤ Dedicated 32.768kHz output pin
➤ System wake-up capability—
alarm interrupt output active in
battery-backup mode
➤ Less than 0.55µA load under bat-
tery operation
➤ Selectable Intel or Motorola bus
timing
➤ 24-pin plastic SSOP
®
AT-compatible
Real-Time Clock(RTC
General Description
The CMOS bq3285ED/LD is a lowpower microprocessor peripheral providing a time-of-day clock and 100year calendar with alarm features
and battery operation. The architecture is based on the bq3285/7 RTC
with added features: low-voltage operation, 32.768kHz output, 128 additional bytes of CMOS, and a day-ofmonth alarm to be compliant with
the ACPIRTC specification.
A 32.768kHz output is available for
sustaining power-management activities. The bq3285ED/LD 32kHz
output is always on whenever V
valid. In VCCstandby mode, the
32kHz is active, and the bq3285LD
typically draws 100µA while the
bq3285ED typically draws 300µA.
Wake-up capability is provided by
an alarm interrupt, which is active
in battery-backup mode. In batterybackup mode, current drain is less
than 550nA.
CC
The bq3285ED/LD write-protects the
clock, calendar, and storage registers
during power failure. A backup
battery then maintains data and operates the clockand calendar.
The bq3285ED/LD is a fully compatible real-time clock for IBM ATcompatible computers and other applications. The only external components are a 32.768kHz crystal and a
backup battery.
The bq3285ED is intended for use in
5V systems. The bq3285LD is intended for use in 3V systems; the
bq3285LD, however, may also operate at 5V and then go into a 3V
is
power-down state, write-protecting
as if in a 3V system.
)
Pin Connections Pin Names
AD0–AD7Multiplexed address/
data input/output
MOT
X1
X2
AD
AD
AD
AD
AD
AD
AD
AD
V
SS
July 1997
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
24-Pin SSOP
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
V
32k
EXTRAM
RCL
BC
INT
RST
DS
V
R/W
AS
CS
PN3285ED/LD.eps
CC
SS
MOT Bus type select input
CS Chip select input
AS Address strobe input
DS Data strobe input
R/W Read/write input
INT Interrupt request output
RST Reset input
32K 32.768kHz output
EXTRAM Extended RAM enable
RCL RAM clear input
BC 3V backup cell input
X1–X2 Crystal inputs
V
CC
V
SS
Power supply
Ground
1
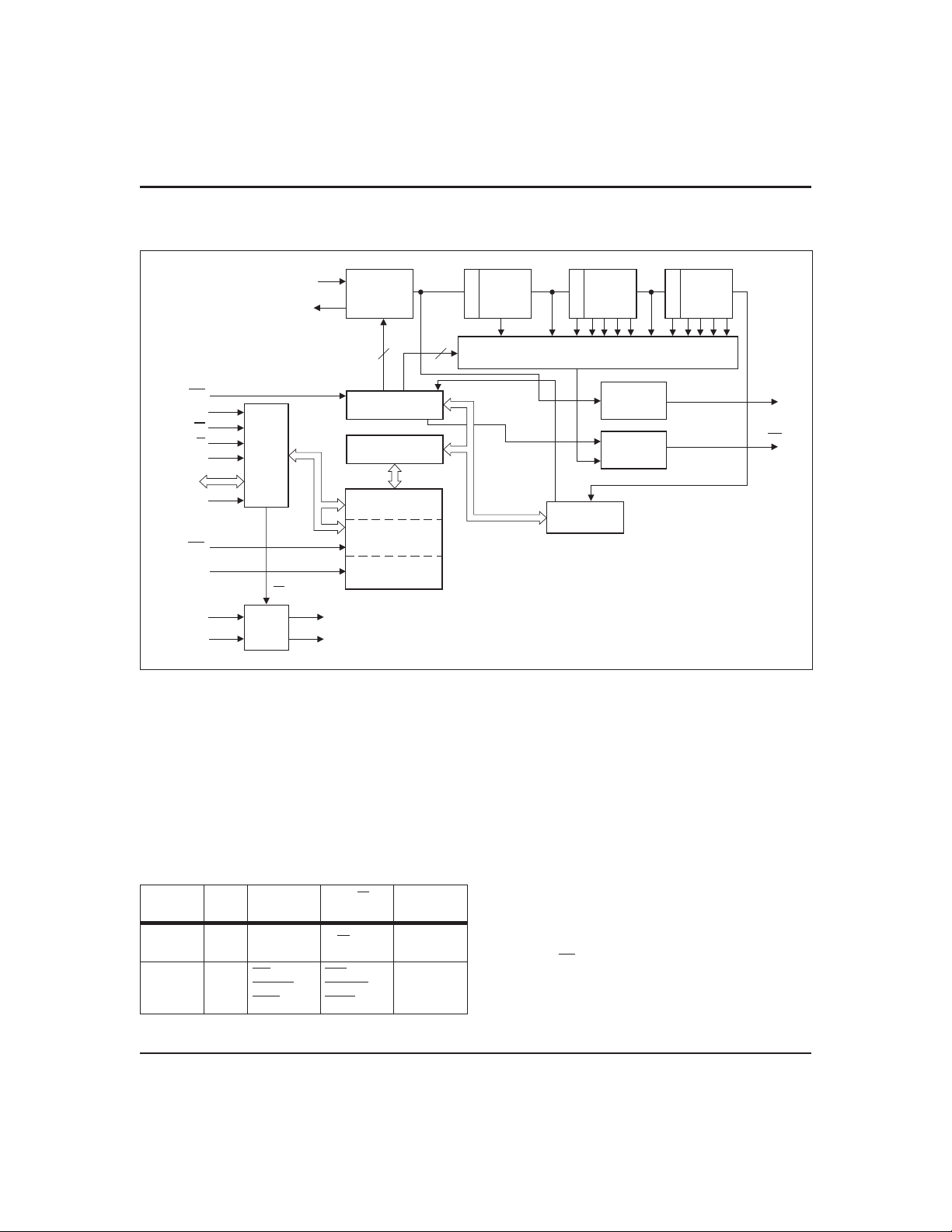
bq3285ED/LD
Block Diagram
X
1
X
2
TimeBase
Oscillator
÷ 8 ÷ 64 ÷ 64
RST
MOT
CS
R/W
AS
AD0–AD
DS
RCL
EXTRAM
V
CC
BC
µ
P
Bus
I/F
7
CS
Power-
Fail
Control
V
OUT
Write
Protect
Pin Descriptions
MOT Bus type select input
MOT selects bus timing for either Motorola
or Intel architecture. This pin should be
tied to VCCfor Motorola timing or to VSSfor
Intel timing (see Table 1). The setting
should not be changed during system operation. MOT is internally pulled low by a 30K
resistor.
Ω
Table 1. Bus Setup
Bus
Type
Motorola V
Intel V
MOT
LevelDSEquivalent
DS,E,or
CC
2
Φ
RD,
MEMR,or
SS
I/OR
EquivalentASEquivalent
R/W
WR,
MEMW,or
I/OW
3
Control/Status
Registers
Clock/Calendar, Alarm
and Control Bytes
User Buffer
(14 Bytes)
Storage Registers
(114 Bytes)
Storage Registers
(128 Bytes)
R/W
AS
ALE
4
16 1 MUX
:
Control/Calendar
Update
32K
Driver
Interupt
Generator
32K
INT
BD328501.eps
AD0–AD7Multiplexed address/data
input/output
The bq3285ED/LD bus cycle consists of two
phases: the address phase and the datatransfer phase. The address phase precedes the data-transfer phase. During the
address phase, an address placed on
AD0–AD7and EXTRAM is latched into the
bq3285ED/LD on the falling edge of the AS
signal. During the data-transfer phase of
the bus cycle, the AD0–AD7pins serve as a
bidirectional data bus.
AS Address strobe input
AS serves to demultiplex the address/data
bus. The falling edge of AS latches the address on AD0–AD7and EXTRAM. This demultiplexing process is independent of the
CS signal. For DIP and SOIC packages
with MOT = VSS, the AS input is provided a
signal similar to ALE in an Intel-based system.
July 1997
2

bq3285ED/LD
DS Data strobe input
When MOT = VCC, DS controls data transfer during a bq3285ED/LD bus cycle. During a read cycle, the bq3285ED/LD drives
the bus after the rising edge on DS. During
a write cycle, the falling edge on DS is used
to latch write data into the chip.
When MOT = VSS, the DS input is provided
a signal similar to RD, MEMR, or I/OR in
an Intel-based system. The falling edge on
DS is used to enable the outputs during a
read cycle.
R/W
CS Chip select input
INT Interrupt request output
32K 32.768 kHz output
EXTRAM Extended RAM enable
Read/write input
When MOT = VCC, the level on R/W identifies the direction of data transfer. A high
level on R/W indicates a read bus cycle,
whereas a low on this pin indicates a write
bus cycle.
When MOT = VSS, R/W is provided a signal
similar to WR, MEMW,or I/OW in an Intelbased system. The rising edge on R/W
latches data into the bq3285ED/LD.
CS should be driven low and held stable
during the data-transfer phase of a bus cycle accessing the bq3285ED/LD.
INT is an open-drain output. This allows
alarm INT to be valid in battery-backup
mode. To use this feature, connect INT
through a resistor to a power supply other
than VCC. INT is asserted low when any
event flag is set and the corresponding
event enable bit is also set. INT becomes
high-impedance whenever register C is read
(see the Control/Status Registers section).
32K provides a buffered 32.768 kHz output.
The frequency remains on and fixed at
32.768kHz as long as VCCis valid.
Enables 128 bytes of additional nonvolatile
SRAM. It is connected internally to a 30k
pull-down resistor. To access the RTC registers,EXTRAM must be low.
RCL
BC 3V backup cell input
RST Reset input
X1–X2 Crystal inputs
Ω
RAM clear input
A low level on the RCL pin causes the contents of each of the 242 storage bytes to be
set to FF(hex). The contents of the clock
and control registers are unaffected. This
pin should be used as a user-interface input
(pushbutton to ground) and not connected
to the output of any active component. RCL
input is only recognized when held low for
at least 125ms in the presence of VCC. Using RAM clear does not affect the battery
load. This pin is connected internally to a
30kΩpull-up resistor.
BC should be connected to a 3V backup cell
for RTC operation and storage register nonvolatility in the absence of system power.
When VCCslews down past VBC(3V typical), the integral control circuitry switches
the power source to BC. When VCCreturns
above VBC, the power source is switched to
VCC.
Upon power-up, a voltage within the V
range must be present on the BC pin for
the oscillator to start up.
The bq3285ED/LD is reset when RST is
pulled low. When reset, INT becomes high
impedance, and the bq3285ED/LD is not accessible. Table 4 in the Control/Status Registers section lists the register bits that are
cleared by a reset.
Reset may be disabled by connecting RST
to VCC. This allows the control bits to retain their states through powerdown/power-upcycles.
The X1–X2 inputs are provided for an external 32.768kHz quartz crystal, Daiwa
DT-26 or equivalent, with 6pF load capacitance. A trimming capacitor may be necessary for extremely precise time-base generation.
In the absence of a crystal, a 32.768kHz
waveformcan be fed into the X1 input.
BC
July 1997
3
bq3285ED/LD
Functional Description
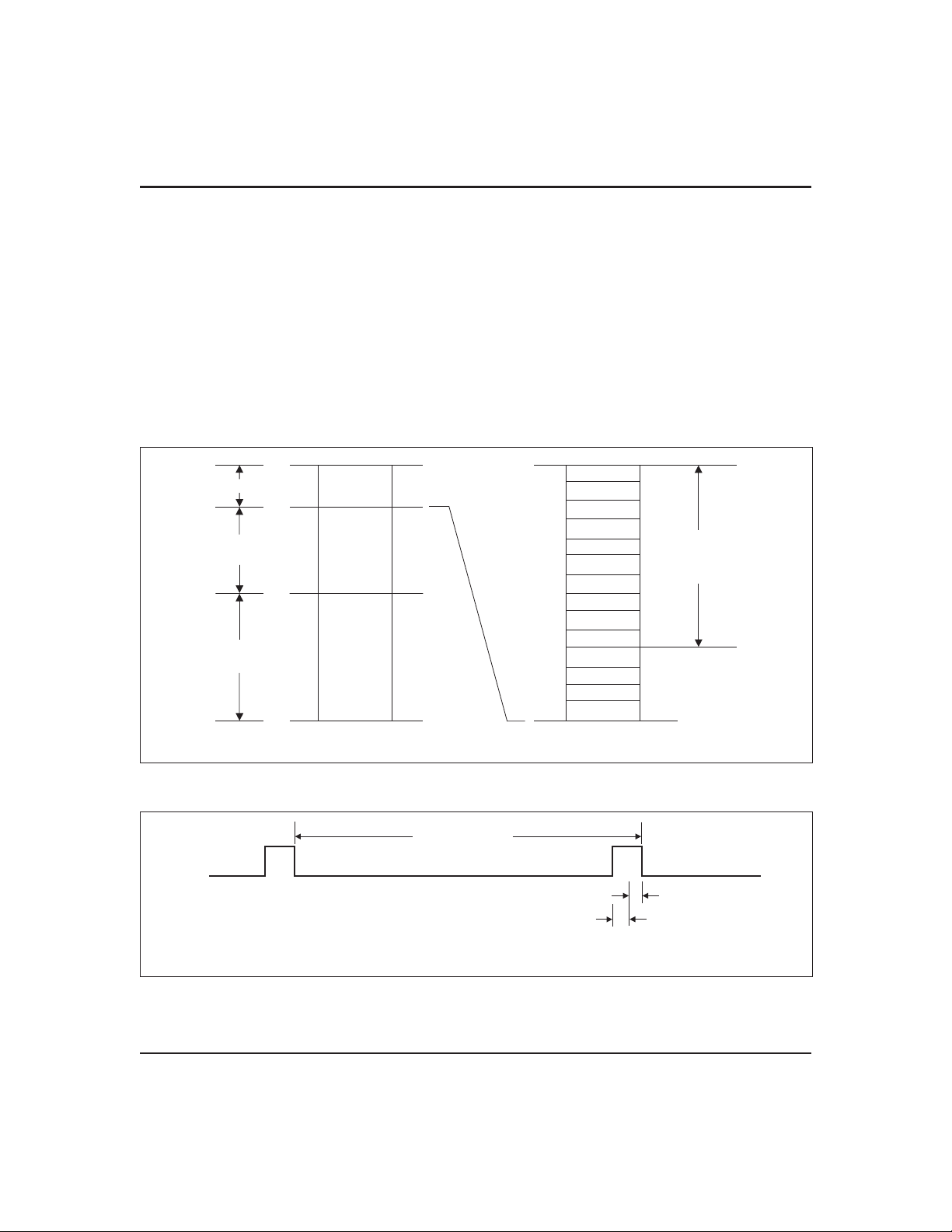
Address Map
The bq3285ED/LD provides 14 bytes of clock and control/status registers and 242 bytes of general nonvolatile
storage. Figure 1 illustrates the address map for the
bq3285ED/LD.
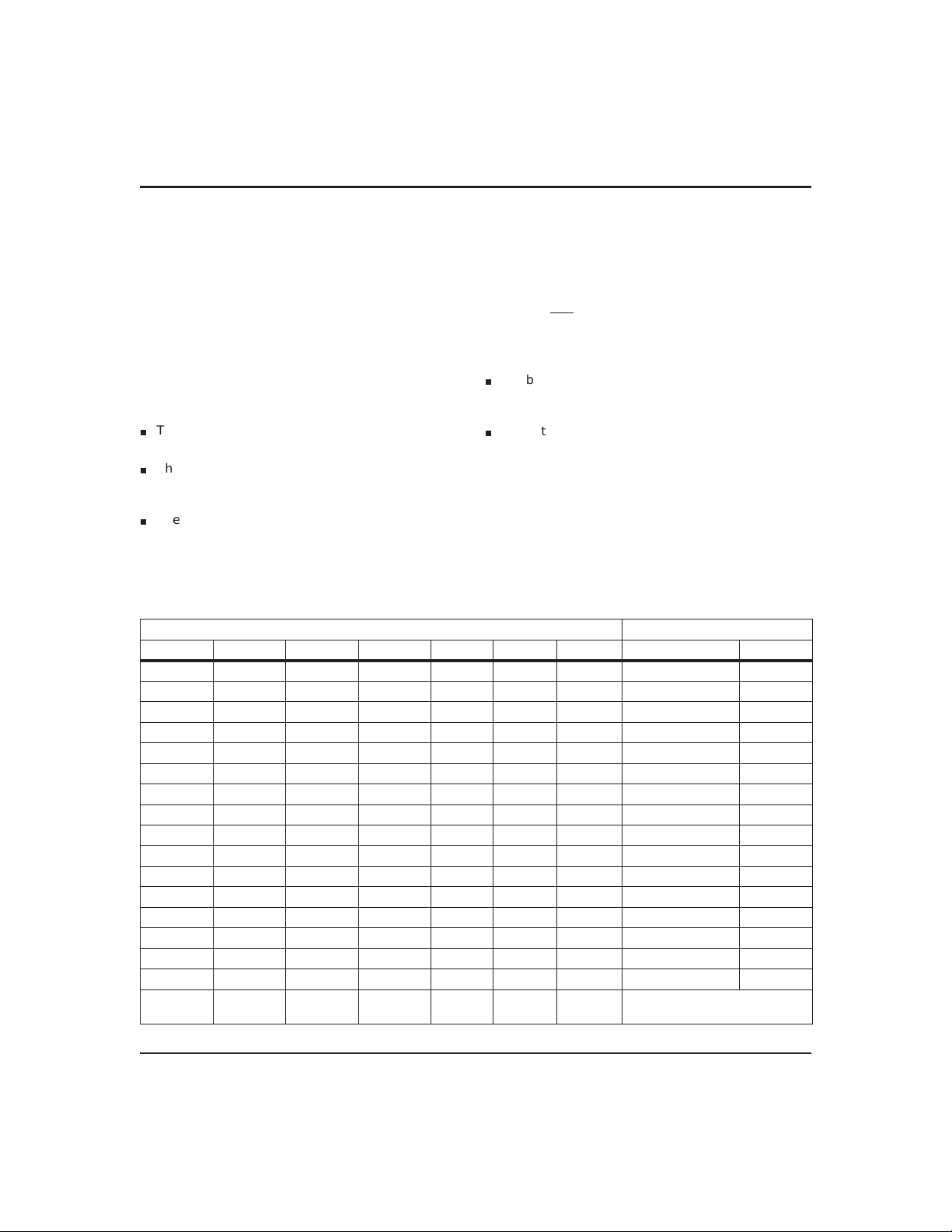
Update Period
The update period for the bq3285ED/LD is one second.
The bq3285ED/LD updates the contents of the clock and
calendar locations during the update cycle at the end of
16 Bytes
114
Bytes
128
Bytes
0
13
14
127
0
127
Clock and
Control Status
Registers
Storage
Registers
with
EXTRAM = 0
Storage
Registers
with
EXTRAM = 1
00
0D
0E
7F
00
7F
each update period (see Figure 2). The alarm flag bit
may also be set during the update cycle.
The bq3285ED/LD copies the local register updates into
the user buffer accessed by the host processor. When a 1
is written to the update transfer inhibit bit (UTI) in register B, the user copy of the clock and calendar bytes remains unchanged, while the local copy of the same bytes
continues to be updated every second.
The update-in-progress bit (UIP) in register A is set
time before the beginning of an update cycle (see
t
BUC
Figure 2). This bit is cleared and the update-complete
flag (UF) is set at the end of the update cycle.
0
1
Seconds Alarm
2
Minutes Alarm
3
4
Hours Alarm
5
6
Day of Week
7
Date of Month
8
9
10
11
12
Day of Month
13
Seconds
Minutes
Hours
Month
Year
Register A
Register B
Register C
Alarm
00
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
0A
0B
0C
0D
FG328501.eps
BCD
or
Binary
Format
UIP
Figure 1. Address Map
Update Period
(1 sec.)
t
BUC
Figure 2. Update Period Timing and UIP
4
t
UC
TD3285e1.eps
(Update Cycle)
July 1997
bq3285ED/LD
Programming the RTC
The time-of-day, alarm, and calendar bytes can be written in either the BCD or binary format (see Table 2).
These steps may be followed to program the time, alarm,
and calendar:
1. Modify the contents of register B:
a. Writea1totheUTIbittoprevent trans-
fers between RTC bytes and user buffer.
b. Write the appropriate value to thedata
format (DF) bit to select BCD or binary
format for all time, alarm, and calendar
bytes.
c. Write the appropriate valueto the hour
format (HF) bit.
2. Write new values to all thetime, alarm, and
calendar locations.
3. Clear the UTI bit to allowupdate transfers.
On the next update cycle, the RTC updates all 10 bytes
in the selected format.
Table 2. Time, Alarm, and Calendar Formats
Range
Address RTC Bytes
0 Seconds 0–59 00H–3BH 00H–59H
1 Seconds alarm 0–59 00H–3BH 00H–59H
Decimal Binary
Binary-Coded
Decimal
2 Minutes 0–59 00H–3BH 00H–59H
3 Minutes alarm 0–59 00H–3BH 00H–59H
4
Hours, 12-hour format 1–12
Hours, 24-hour format 0–23 00H–17H 00H–23H
Hours alarm, 12-hour format 1–12
5
Hours alarm, 24-hour format 0–23 00H–17H 00H–23H
6 Day of week (1=Sunday) 1–7 01H–07H 01H–07H
7 Day of month 1–31 01H–1FH 01H–31H
8 Month 1–12 01H–0CH 01H–12H
9 Year 0–99 00H–63H 00H–99H
D Day of month alarm 1–31 01H-1FH 01–31H
July 1997
01H–OCH AM;
81H–8CH PM
01H–OCH AM;
81H–8CH PM
5
01H–12H AM;
81H–92H PM
01H–12H AM;
81H–92H PM
bq3285ED/LD
32kHz Output
The bq3285ED/LD provides for a 32.768kHz output, and
the output is always active whenever VCCis valid (V
+t
). The bq3285ED/LD output is not affected by the
CSR
bit settings in Register A. Time-keeping aspects, however,still require setting OS0-OS2.
Interrupts
The bq3285ED/LD allows three individually selected interrupt events to generate an interrupt request. These
Each of the three interrupt events is enabled by an individual interrupt-enable bit in register B. When an event
occurs, its event flag bit in register C is set. If the corresponding event enable bit is also set, then an interrupt
PFD
request is generated. The interrupt request flag bit
(INTF) of register C is set with every interrupt request.
Reading register C clears all flag bits, including INTF,
and makes INT
high-impedance.
Two methods can be used to process bq3285ED/LD interrupt events:
Enable interrupt events and use the interrupt
n
request output to invoke an interrupt service routine.
three interrupt events are:
The periodic interrupt, programmable to occur once
n
every 122µs to 500ms.
The alarm interrupt, programmable to occur once per
n
second to once per day, is active in battery-backup
mode, providing a “wake-up” feature.
The update-ended interrupt, which occurs at the end
n
Do not enable the interrupts and use a polling
n
routine to periodically check the status of the flag
bits.
The individual interrupt sources are described in detail
in the following sections.
of each update cycle.
Table 3. Periodic Interrupt Rate
Register A Bits Periodic Interrupt
OSC2 OSC1 OSC0 RS3 RS2 RS1 RS0 Period Units
0100000None
0100001 3.90625 ms
0100010 7.8125 ms
0100011 122.070
0100100 244.141
0100101 488.281
0100110 976.5625
0100111 1.95315 ms
0101000 3.90625 ms
0101001 7.8125 ms
0101010 15.625 ms
0101011 31.25 ms
0101100 62.5 ms
0101101 125 ms
0101110 250 ms
0101111 500 ms
011XXXX
same as above defined
by RS3–RS0
µ
µ
µ
µ
s
s
s
s
July 1997
6
PeriodicInterrupt
If the periodic interrupt event is enabled by writing a 1
to the periodic interrupt enable bit (PIE) in register C,
an interrupt request is generated once every 122µsto
500ms. The period between interrupts is selected with
bits RS3-RS0 in register A (see Table3).
Alarm Interrupt
The alarm interrupt is active in battery-backup mode,
providing a “wake-up” capability. During each update
cycle, the RTC compares the day-of-the-month, hours,
minutes, and seconds bytes with the four corresponding
alarm bytes. If a match of all bytes is found, the alarm
interrupt event flag bit, AF in register C, is set to 1. If
the alarm event is enabled, an interrupt request is generated.
An alarm byte may be removed from the comparison by
setting it to a “don't care” state. The seconds, minutes,
and hours alarm bytes are set to a “don't care” state by
writinga1toeachofitstwomost-significant bits. The
day-of-the-month alarm byte is set to a “don’t care”state
by setting DA5–DA0, in register D, to all zeros. A “don't
care” state may be used to select the frequency of alarm
interrupt events as follows:
n
If none of the four alarm bytes is “don't care,” the
frequency is once per month, when day-of-the-month,
hours, minutes, and seconds match.
n
If only the day-of-the-month alarm byte is “don’t
care”, the frequency is once per day, when hours,
minutes, and seconds match.
n
If only the day-of-the-month and hour alarm byte is
“don't care,” the frequency is once per hour, when
minutes and seconds match.
n
If only the day-of-the-month, hour and minute alarm
bytes are “don't care,” the frequency is once per
minute, when seconds match.
bq3285ED/LD
If the day-of-the-month, hour, minute, and second
n
alarm bytes are “don't care,” the frequency is once
per second.
Update Cycle Interrupt
The update cycle ended flag bit (UF) in register C is set to
a 1 at the end of an update cycle. If the update interrupt
enable bit (UIE) of register B is 1, and the update transfer
inhibit bit (UTI) in register B is 0, then an interrupt request is generated at the end of each update cycle.
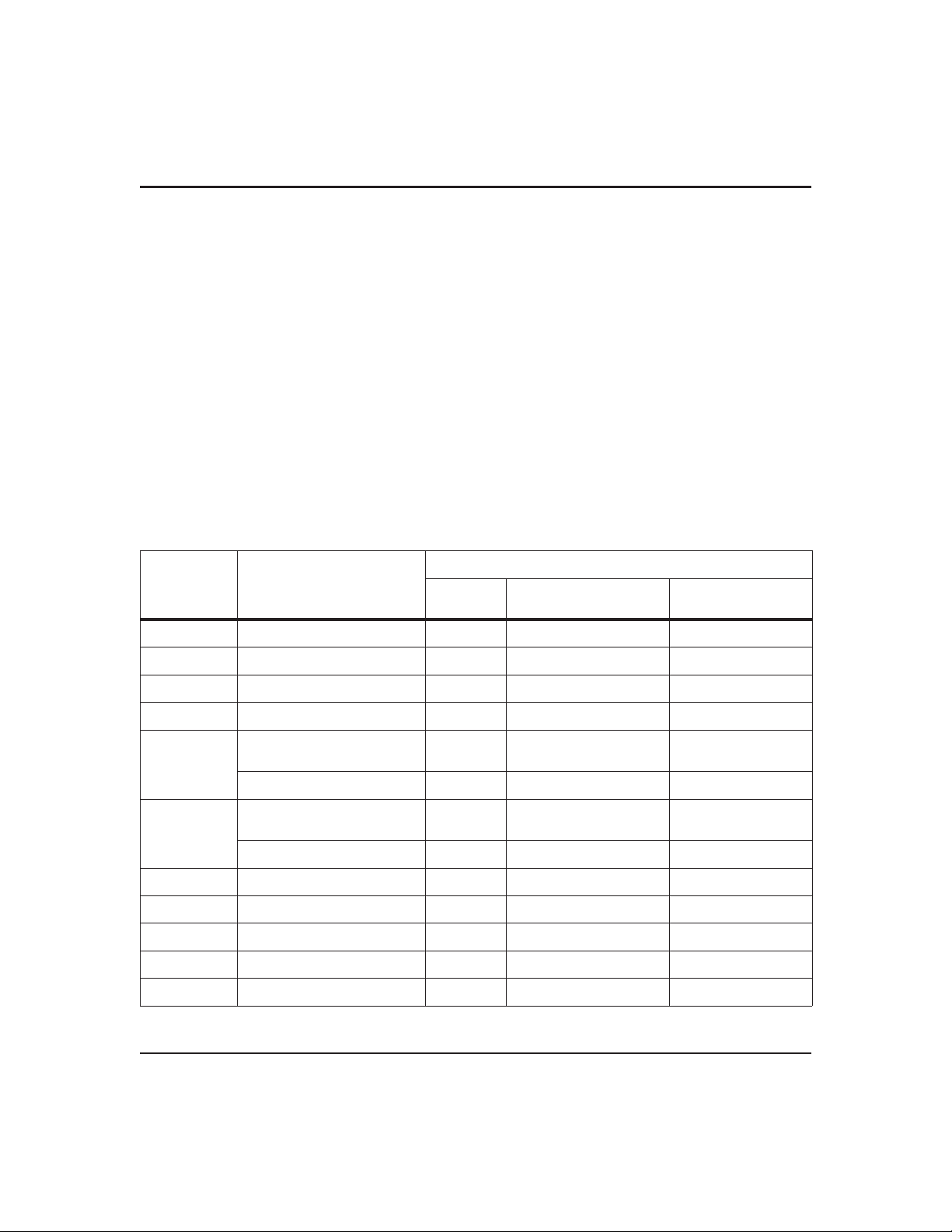
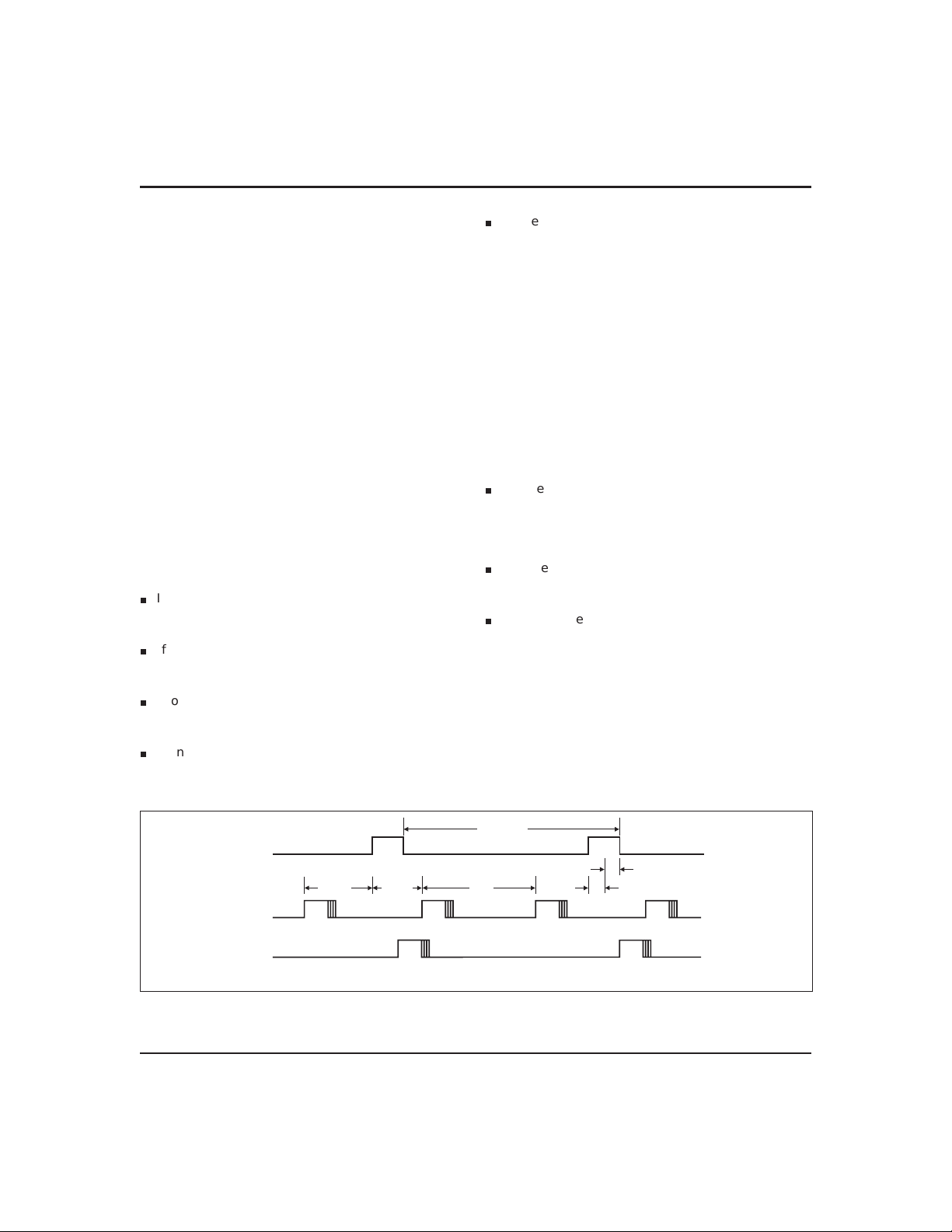
Accessing RTC bytes
The EXTRAM pin must be low to access the RTC registers. Time and calendar bytes read during an update
cycle may be in error. Three methods to access the time
and calendar bytes without ambiguity are:
Enable the update interrupt event to generate
n
interrupt requests at the end of the update cycle.
The interrupt handler has a maximum of 999ms to
access the clock bytes before the next update cycle
begins (see Figure 3).
Poll the update-in-progress bit (UIP) in register A. If
n
UIP = 0, the polling routine has a minimum of t
time to access the clock bytes (see Figure 3).
n
Use the periodic interrupt event to generate
interrupt requests every tPItime, such that UIP = 1
always occurs between the periodic interrupts. The
interrupt handler has a minimum of tPI/2+t
time to access the clock bytes (see Figure 3).
Oscillator Control
When power is first applied to the bq3285ED/LD and
VCCis above V
divider are turned on by writing a 010 pattern to bits 4
through 6 of register A. A pattern of 11X turns the oscillator on but keeps the frequency divider disabled.Any
, the internal oscillator and frequency
PFD
BUC
BUC
July 1997
1 Sec.
UIP
PF
UF
(tPl)/2 (tPl)/2 t
Pl
t
BUC
Figure 3. Update-Ended/Periodic Interrupt Relationship
7
t
UC
T3285L02.eps
bq3285ED/LD
other pattern to these bits keeps the oscillator off. A
pattern of 010 must be set for the bq3285ED/LD to keep
time in battery backup mode.
Power-Down/Power-Up Cycle
The bq3285ED and bq3285LD power-up/power-down cycles are different. The bq3285LD continuously monitors
VCCfor out-of-tolerance. During a power failure, when
VCCfalls below V
(2.53V typical), the bq3285LD write-
PFD
protects the clock and storage registers . The power source
is switched to BC when VCCis less than V
greater than V
is less than V
, or when VCCis less than VBCand V
PFD
. RTC operation and storage data are
PFD
PFD
and BC is
BC
sustained by a valid backup energy source. When VCCis
above V
tinues for t
The bq3285ED continuously monitors V
, the power source is VCC. Write-protection con-
PFD
time after VCCrises above V
CSR
PFD
CC
.
for out-oftolerance. During a power failure, when VCCfalls below
V
(4.17V typical), the bq3285ED write-protects the
PFD
clock and storage registers. When VCCis below VBC(3V
typical), the power source is switched to BC. RTC operation and storage data are sustained by a valid backup
energy source. When VCCis above VBC, the power
source is VCC. Write-protection continues for t
after VCCrises above V
PFD
.
CSR
time
Control/Status Registers
The four control/status registers of the bq3285ED/LD
are accessible regardless of the status of the update cycle (see Table4).
Register A
Register A Bits
76543210
UIP OS2 OS1 OS0 RS3 RS2 RS1 RS0
Register A programs:
The frequency of the periodic event rate.
n
Oscillator operation.
n
Time-keeping
n
Register A provides:
Status of the update cycle.
n
RS0–RS3 - Frequency Select
76543210
----RS3RS2RS1RS0
These bits select the periodic interrupt rate, as shown in
Table3.
OS0–OS2 - Oscillator Control
76543210
-OS2OS1OS0----
These three bits control the state of the oscillator and
divider stages. A pattern of 010 or 011 enables RTC operation by turning on the oscillator andenabling the frequency divider. This pattern must be set to turn the oscillator on and to ensure that the bq3285ED/LD keeps
time in battery-backup mode. A pattern of 11X turnsthe
oscillator on, but keeps the frequency divider disabled.
When 010 is written, the RTC begins its first update after 500ms.
Table 4. Control/Status Registers
Loc.
Reg.
(Hex) Read Write
A 0A Yes Yes
7 (MSB) 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 (LSB)
1
UIP na OS2 na OS1 na OS0 na RS3 na RS2 na RS1 na RS0 na
B 0B Yes Yes UTI na PIE 0 AIE 0 UIE 0 - 0 DF na HF na DSE na
C 0C Yes No INTF 0 PF 0 AF 0 UF 0 - 0 - na - 0 - 0
2
D 0D Yes Yes
VRT na - 0 DA5 na DA4 na DA3 na DA2 na DA1 na DA0 na
Notes: na = not affected.
1. Except bit 7.
2. Except bits 6 and 7.
Bit Name and State on Reset
8
July 1997
 Loading...
Loading...