Page 1

FURNACE UTILIZATION AND
REPORTING SYSTEM
TRACKING AND REPORTING SOFTWARE
OPERATIONS MANUAL
Super Systems Inc.
7205 Edington Drive
Cincinnati, OH 45249
513-772-0060
Fax: 513-772-9466
www.supersystems.com
Page 2

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
Super Systems Inc.
Super Systems Europe
Super Systems México
Super Systems China
USA Office
Corporate Headquarters
7205 Edington Drive
Cincinnati, OH 45249
Phone: (513) 772-0060
http://www.supersystems.com
Sistemas Superiores Integrales S de RL de CV
Calle 3 Int.: 11.
Zona Ind. Benito Juarez
Querétaro, Qro. Méx.
C.P.: 76120
Phone: +52 (442) 210 2459
http://www.supersystems.com.mx
Units 3 & 4, 17 Reddicap Trading Estate,
Sutton Coldfield, West Midlands
B75 7BU
UNITED KINGDOM
Phone: +44 (0) 121 329 2627
http://www.supersystemseurope.com
No. 335 XianXia Road
Room 308
Shanghai, CHINA
200336
Phone: +86 21 5206 5701/2
http://www.supersystems.com
Super Systems Inc. Page 2 of 25
Page 3

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
Table of Contents
Introduction ........................................................................................................................................ 4
Setup and Use Diagram ..................................................................................................................... 5
Prerequisites ...................................................................................................................................... 6
Installation ......................................................................................................................................... 6
FURS Concepts .................................................................................................................................. 8
Data Point ....................................................................................................................................... 8
Additional Technical Details ...................................................................................................... 8
Data Point Group ............................................................................................................................ 9
Data Points, Data Point Groups, and Report Generation ............................................................ 10
Scripting (VBScript) ...................................................................................................................... 11
Report Templates ......................................................................................................................... 11
Configuration Screens ................................................................................................................. 11
If Using Load Data and Running FURS for the First Time .............................................................. 11
Using the Software........................................................................................................................... 13
Main Window ................................................................................................................................ 14
File Menu .................................................................................................................................. 14
View Menu ................................................................................................................................. 15
Settings Menu ........................................................................................................................... 15
Help Menu................................................................................................................................. 17
Language Menu ........................................................................................................................ 17
Data Point Setup Window ......................................................................................................... 17
Data Point Group Setup ............................................................................................................ 19
Report Generation .................................................................................................................... 22
Revision History ............................................................................................................................... 23
Appendix 1: Configuration File Settings (AppOptions.xml) ............................................................ 24
Super Systems Inc. Page 3 of 25
Page 4

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
Introduction
Part of the SSi SuperDATA suite of programs, the Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS)
provides powerful tools for analyzing and generating reports on utilization of furnace
equipment. FURS works seamlessly with SuperDATA, generating reports and visual graphs
based on log file data created by SuperDATA. The cost of fuel to run a furnace (or group of
furnaces) can be estimated based on log data and rates provided by the user. FURS allows for
customized scripting based on VBScript.
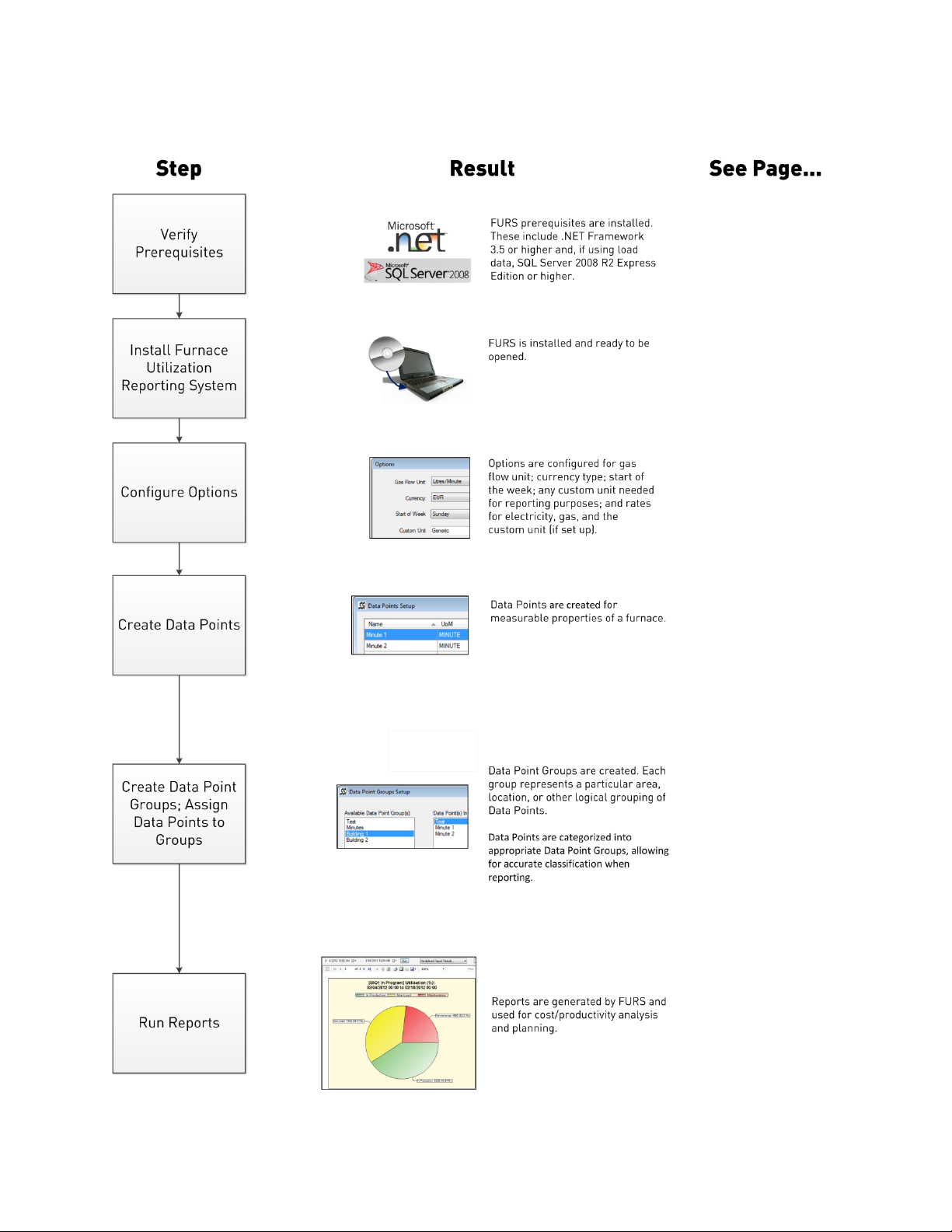
The setup diagram below shows the suggested procedure for installing, configuring, and using
FURS.
Super Systems Inc. Page 4 of 25
Page 5
Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
6 6 17
17
19
22
Setup and Use Diagram
Super Systems Inc. Page 5 of 25
Page 6
Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
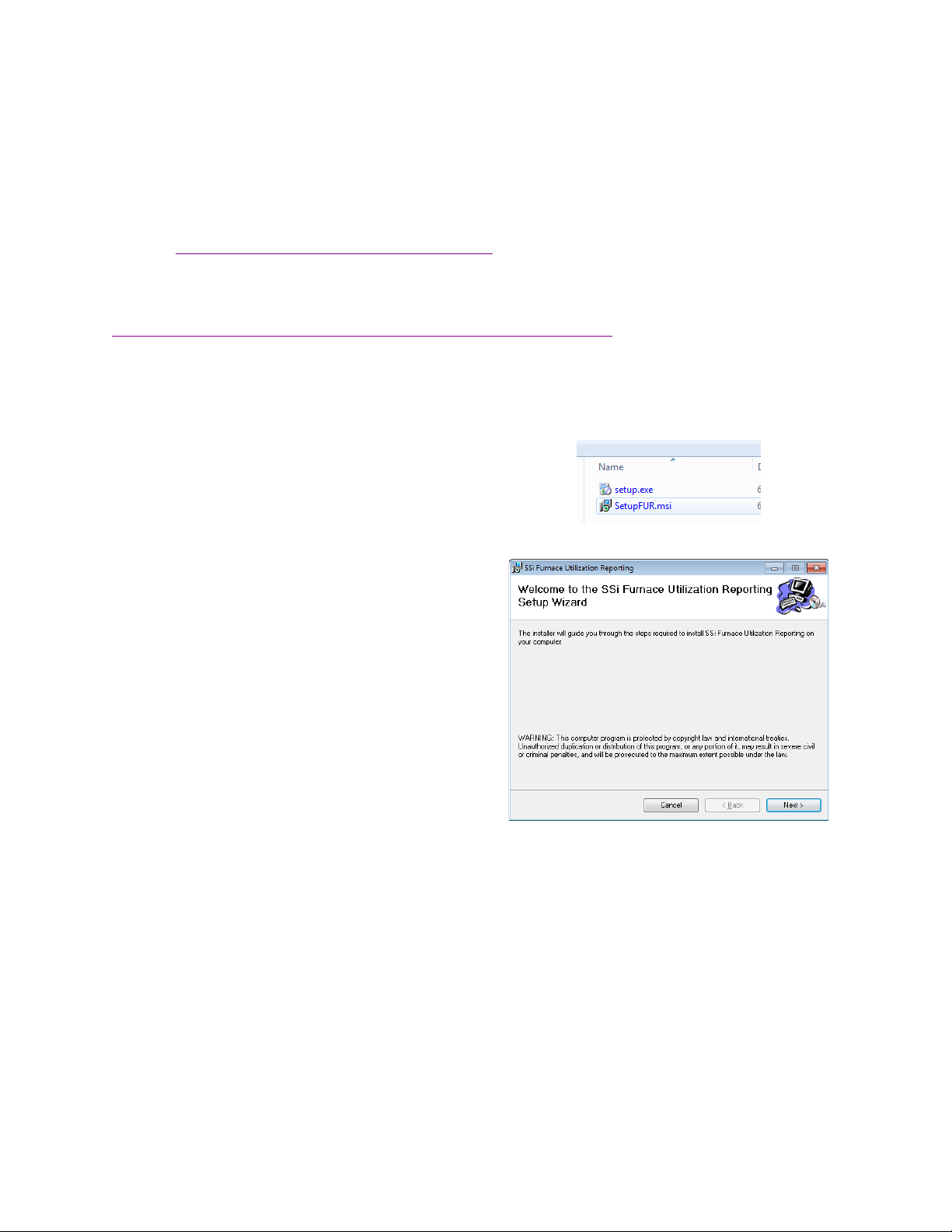
To install, open the “SetupFUR.msi” file. The
Setup Wizard
Prerequisites
FURS has some prerequisites in order to run properly. Windows XP or higher operating system
is required. Windows 7 or higher is recommended.
Microsoft .NET Framework 3.5 or higher is required to run FURS. The URL for .NET is as
follows: http://www.microsoft.com/net/downloads
.
Required for accessing load data (optional) from an SQL Server
: SQL Server 2008 R2 Express
Edition or higher. The URL for downloading SQL Server 2008 R2 Express Edition is as follows:
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=30438
. [Note: If load data is being
accessed, the <UseSQLEXPRUtilDB> option will be “true” in the AppOptions.xml file. See the
Appendix 1: Configuration File Settings (AppOptions.xml) section for more information.]
Installation
window will appear. Click “Next”
continue.
Super Systems Inc. Page 6 of 25
Page 7
Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
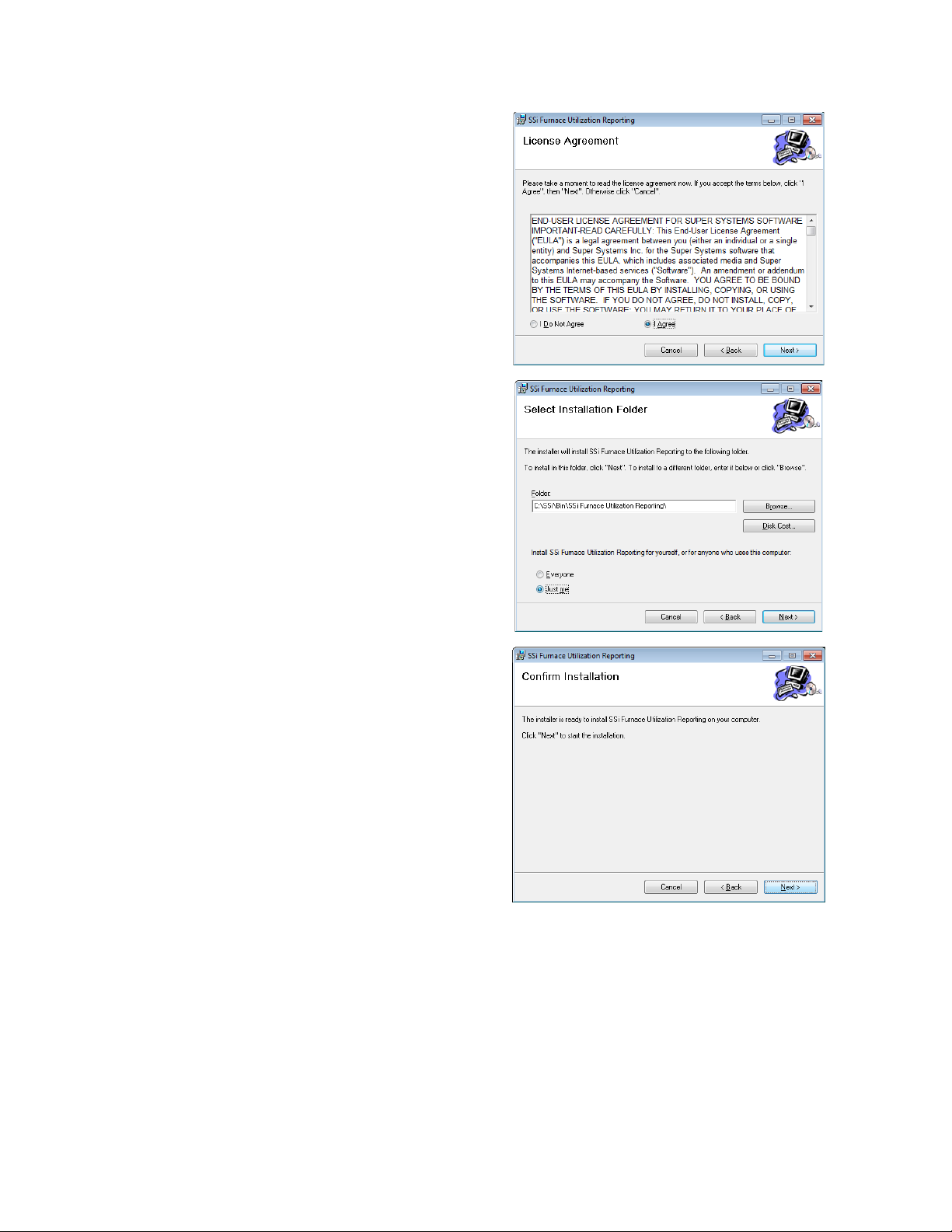
The License Agreement window will appear.
The next window will give you the options to
SUGGESTED:
A Confirm Installation window will appear. Click
Read the terms of the license and, if in
agreement, select “I Agree” and then click
“Next”.
change the installation folder for FURS, to
install FURS for the current user or for all users
of the computer, and to estimate the amount of
disk space that will be used when the program
is installed. Click “Next” to continue.
Record the folder name where
FURS is installed so that you can refer to it in
the future.
“Next” to continue.
Super Systems Inc. Page 7 of 25
Page 8
Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
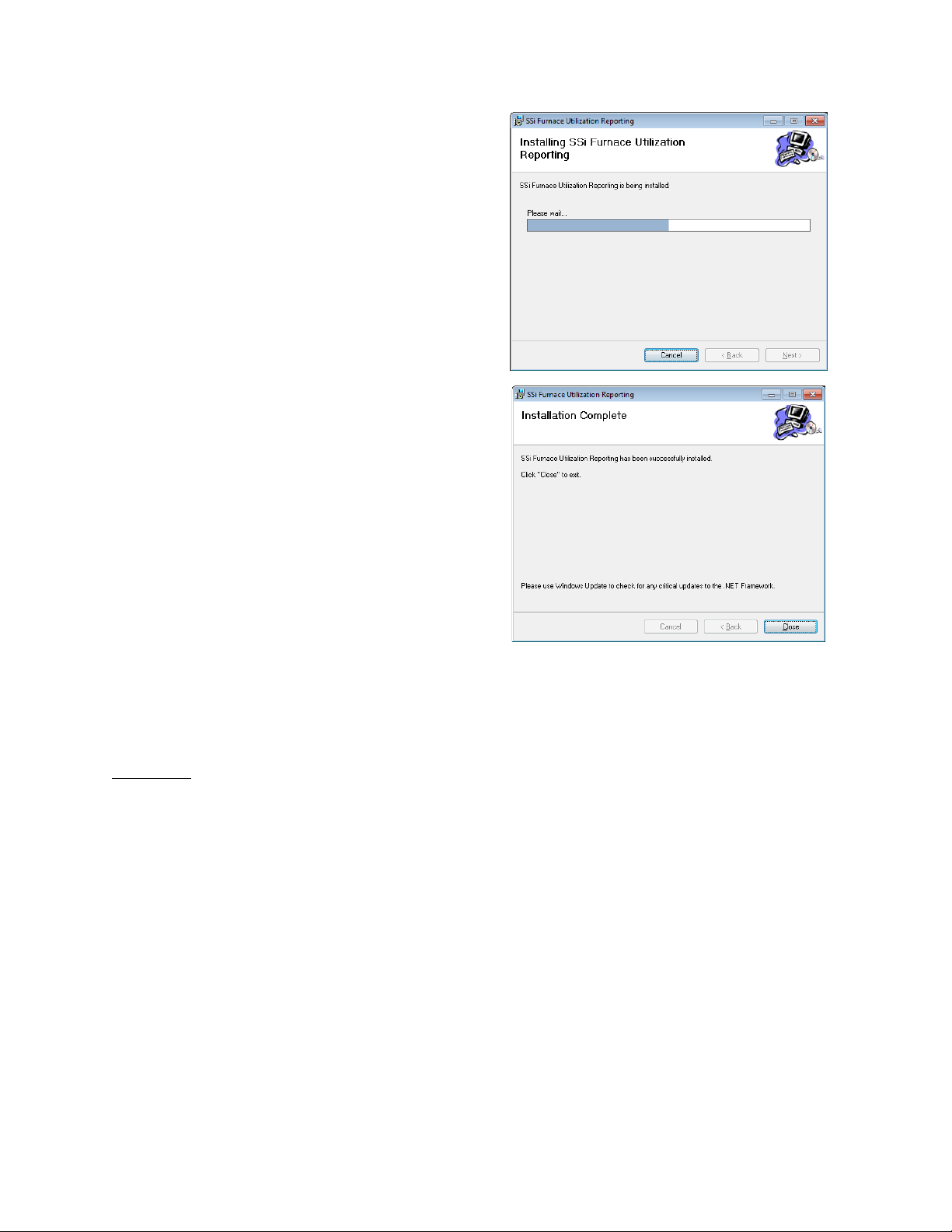
An installation status window will appear.
Once the installation process has finished, the
Installation Complete
If a window appears on screen asking if you want
to authorize changes being made to your
computer, simply choose “Yes”.
window will appear. Click
“Close” to close the window.
FURS Concepts
Before using FURS, it is helpful to have an understanding of the concepts used in the software.
Data Point
The main building block of a FURS report is a Data Point. A Data Point represents a measurable
property associated with a furnace. Examples might include fuel consumption, non-production
time, load time, or percentage of utilization during certain periods of the day. Data is gathered
from SDIO (the SuperDATA communications engine) and, for calculations that involve loads,
from an SQL database. Using scripting within the program, the user can then instruct FURS on
how to use that data to generate meaningful calculations on a furnace property. These
calculations are used to generate Data Points, which are then used to generate graphs, tables,
and reports within FURS.
Additional Technical Details
A data point represents a one-minute resolution data item which is calculated by using any
number of available “raw data points” as inputs. The VBScript language can be used on the
inputs to create the desired output.
Currently, data points with the following units of measurements are available in the
program:
Super Systems Inc. Page 8 of 25
Page 9

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
•
scfm
(Standard Cubic Feet per Minute)
m3m
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
A data point will have a script (in VBScript syntax) that tells the program how to generate usable
data from raw data. A simple script to determine a data point value follows:
In the above script, the data point value is simply the average value of the three raw data points:
c1s1.value, c2s2.value, and c3s3.value. The names of raw data points are predefined as
cxsy.value. Descriptions for the raw data points are available in the program.
Depending on the unit of measurement of the data point, available reports for the data point will
be determined automatically by the program. For example, a data point with a unit of
measurement of
Data Point Group
Once Data Points have been defined, they can be added to Data Point Groups. A Data Point
Group is a collection of data points typically organized by shared location, building, department,
type of furnace, or some other common trait. For example, a Data Point Group may be created
for “Batch Furnaces – Building 1” and may include Data Points such as:
• Production Time – Batch Furnace 1
• Production Time – Batch Furnace 2
• Production Time – Batch Furnace 3
• Non-Production Time – Batch Furnace 1
• Non-Production Time – Batch Furnace 2
• Non-Production Time – Batch Furnace 3
• Fuel Cost per Week – Batch Furnaces – Totalized
With FURS’s scripting abilities, the possibilities become very diverse as the availability of raw
data increases.
(Cubic Meter per Minute)
litres/minute
kwh
(Kilowatt Hour)
minute
USD
(US Dollar)
EUR
(Euro)
GBP
(British Pound Sterling)
result.value = (c1s1.value + c2s2.value + c3s3.value) / 3
scfm
will have a “Gas Usage” report available.
Super Systems Inc. Page 9 of 25
Page 10

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
Data Points, Data Point Groups, and Report Generation
The diagram below illustrates how FURS operates. First, the SuperDATA server acquires data on furnace operation from furnace instrumentation.
That data is shared with a computer running FURS using SDIO, the SuperDATA communications engine. Using the acquired data, FURS executes
one or more scripts. The results of the script calculations are then applied to Data Points within Data Point Groups. Using the organized data, FURS
can generate reports and graphs.
Super Systems Inc. Page 10 of 25
Page 11

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
Scripting (VBScript)
The purpose of a script is to allow the generation of reportable data from raw data. A script will
have an output and one or more raw data input(s). Programming logic would be used on raw
data points to generate the reportable output.
Below are the naming conventions for use in scripting:
• Script output shall always be referenced as:
• Script input(s) shall be referenced as: cxsy.value (where x is the channel number and y is
the slot number).
Examples of valid raw data points:
c1s1.value, c2s2.value, c10s2.value.
result.value
Possible Example:
A customer is interested in knowing how much time his furnace is in production based on the
following condition:
• Furnace temperature (identified by c1s1.value) is greater than 1400 degrees F.
• A recipe is running (when c2s2.value = 1)
The below script will be appropriate for this case:
if (c1s1.value > 1400 and c2s2.value = 1) then
result.value = 1
else
result.value = 0
end if
Report Templates
The program will allow saving all of its configuration parameters in a template to allow that
template to be reused later. Report templates will be saved in separated XML files to allow
greater portability. Report templates can be modified and saved. Multiple report templates can
be created but only one can be used at a time. The Save and Load template feature is accessible
under the File menu of the program.
Configuration Screens
All configuration information will be stored in the database of the program. The order of
configuring in this section is important and should be followed before reports can be generated.
The screens are captured on a new installation of the program so that a user can easily follow
after installing his program.
If Using Load Data and Running FURS for the First Time
Before running FURS for the first time on the computer where it is installed, follow these steps.
Doing so will help ensure that FURS starts and runs smoothly and that the program is able to
recognize where to obtain load data from.
1. Determine whether the load database will be:
a. Stored on the local machine or
b. Accessed from a server.
Super Systems Inc. Page 11 of 25
Page 12

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
2. In Windows Explorer, open the folder where FURS is installed. A common folder location
for FURS is “C:\SSi\Bin\SSi Furnace Utilization Reporting” (but this is not always the
case).
3. Open the file AppOptions.xml in a text editor (such as Notepad).
4. Find the tag for option UseSQLEXPRUtilDB. The open tag is <UseSQLEXPRUtilDB> and
true
the close tag is </UseSQLEXPRUtilDB>. The value for the option will be
or
false
.
Super Systems Inc. Page 12 of 25
Page 13

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
IMPORTANT!
If Using Load Data and Running FURS for the First Time before using this section.
5. The next actions you take will be based on whether the load database is stored locally or
accessed from a server.
a. If the load database will be stored on the local machine, make sure that
UseSQLEXPRUtilDB is
to the
b. If the load database will be accessed from a server, make sure that
UseSQLEXPRUtilDB is
SQLEXPRUtilDBConnString:
Save the AppOptions.xml file and close it. Proceed to the Using the Software section.
Using the Software
Using the Software section.
• Server (the location of the SQL Express server)
• Database (the name of the database)
• UserID (the login/user ID of a user with permissions needed to access the
• Password (the password for the user)
• Trusted_Connection (True or False—whether the SQL connection is trusted
database)
or not)
true
. Then save the AppOptions.xml file and close it. Proceed
false.
Then enter the following parameters for the
If you are running FURS for the first time on the computer where it is installed and intend to use
FURS to analyze load information, please refer to the section
Super Systems Inc. Page 13 of 25
Page 14

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
Option
Description
Save Template
This option allows you to save a template file with the .tfl extension.
and can be loaded into FURS in future instances.
Load Template
This option allows you to select a template file for FURS to load. Once
information will be loaded into the program.
Exit
This option closes FURS.
Main Window
This is the entry point and the main window of the program.
The menu section at the top of the window allows access to features of the program such as
save template, load template, data point setup, data point group setup, non-production time
setup, options, etc.
The left hand side panels allow users to select what object to report on and what report to
display on the right hand section of the window.
File Menu
The template file contains the Data Point and Data Point Group data
the template file is loaded, saved Data Point and Data Point Group
Super Systems Inc. Page 14 of 25
Page 15

View Menu
Option
Description
Show Left Panel
When this option is checked, the left menu is displayed. The left menu
available within FURS.
Option
Description
Data Points Setup…
This option brings up the Data Points Setup window. See the Data
Point Setup Window section on page 17 for more details.
Data Point Group
Setup…
This option brings up the Data Point Group Setup window. See the
Data Point Group Setup section on page 19 for more details.
Price Point Setup…
This option allows you to add price points for different gases used in
accessible from a drop-down list.
Settings Menu
Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
shows Data Points, Data Point Groups, and report types that are
heat treating processes. The gas is determined by the Gas Type field,
with the unit of measurement determined by the Units field. The Cost
per Unit is entered in the Cost field. Start and end dates for the price
point can be manually entered or selected from pre-defined periods
Super Systems Inc. Page 15 of 25
Page 16

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
Option
Description
Shift Setup…
This option gives you the ability to set up shifts in FURS. Times are
16:00).
Non Production Time
Using this option, you can enter specific periods of non-production
and enter notes on what the non-production time was used for.
entered in a 24-hour format (for example, 4:00 p.m. is entered as
Super Systems Inc. Page 16 of 25
Page 17

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
Option
Description
Options
Options allow you to configure units and rates used within FURS. Gas
whatever custom unit is set up.
Option
Description
Check for Updates
This option will check for updates to the FURS program. If updates
work.
Open Help File
This option will bring up the manual for FURS.
About
This option will bring up a window showing version details for FURS. It
Utilization features.
flow units can be standard cubic feet per minute (SCFM), cubic
meters per minute (M3M), or litres per minute. Currency can be US
Dollars (USD), Euro (EUR), or British pound sterling (GBP). The start
of the week can be set up as any of the seven days of the week. A
custom unit can be set up, along with rates for electricity, gas, and
Help Menu
are available, FURS will give you the option to have them downloaded
and installed. An Internet connection is needed for this option to
also provides the link to download the installation file for Realtime
Language Menu
The Language menu displays the available languages for the FURS interface. Two letters
denoting each available language are shown. For instance,
en
represents English.
Data Point Setup Window
To access this window, select Settings -> Data Points Setup… from the main window.
This window allows setting up data points for use in the program. The following figure shows
this window.
Super Systems Inc. Page 17 of 25
Page 18

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
Clicking Add… (Or Edit when applicable) in the above screen will bring up the screen below.
Note that the available raw data points are listed on the right side of the window.
Creating a data point using the above window is straightforward. A data point name, a unit of
measurement, and a script are the required information. A sample script is automatically
inserted as a hint. Once a data point is customized as needed, clicking OK will save it to the
Super Systems Inc. Page 18 of 25
Page 19

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
database. The newly created data point is now ready for reporting or for inclusion in data point
group(s).
In the above screen, a data point named “Furnace 1 In Production” will be created. The script of
this data point will yield a result of 1 (minute) for any minute that the value of c1s2.value is
greater than 1300°F. The right side grid of the window indicates that c1s2.value contains
temperature information.
Other features in this window:
• Select from saved scripts…: allows users to select from any saved script to use with
current data point.
• Save script to template: allows users to save current script to a text file to use later.
• Verify script…: allows users to check the current script for any errors so that
adjustments can be made. This feature also allows users to provide input(s) and verify
that the script generates the correct output.
• Update Snapshot: allows users to pick a time and see values of raw data points at that
time to get a perspective of the data.
Data Point Group Setup
To access this window, select Settings -> Data Point Group Setup… from the main
window.
This window allows adding/editing data point groups. Information needed to set up a data point
group includes a name and needed data points.
Clicking Add… in the above screen will bring up the screen below.
Super Systems Inc. Page 19 of 25
Page 20

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
Provide a name for the data point group.
After the data point group is added, data point(s) can be added to the group as shown in the
following screens.
Resulting main window after the data point group is added follows.
Super Systems Inc. Page 20 of 25
Page 21

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
Super Systems Inc. Page 21 of 25
Page 22

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
Report Generation
From here users can follow the instructions on screen (green text) to generate report(s).
Following is a sample report for the data point that was created earlier.
Super Systems Inc. Page 22 of 25
Page 23

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
Rev.
Description
Date
MCO #
New
New manual
A
Changes to manual to reflect interface
changes and functionality extensions
9/10/2014
2150
Revision History
Super Systems Inc. Page 23 of 25
Page 24

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
Appendix 1: Configuration File Settings (AppOptions.xml)
Each installation of the program comes with a configuration file named AppOptions.xml, which
controls how the program works.
The location of the file is the installation folder of the program. The default location for this file
is
C:\SSi\Bin\SSi Furnace Utilization Reporting.
This section will provide explanations for each setting in the file.
Below are the contents of the default AppOptions.xml file:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Options xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema">
<GasUsageUoM>SCFM</GasUsageUoM>
<Currency>USD</Currency>
<GasRate>0.0088</GasRate>
<ElectricityRate>0.11</ElectricityRate>
<UseSQLEXPRUtilDB>false</UseSQLEXPRUtilDB>
<SQLEXPRUtilDBConnString>Server=localhost\sqlexpress;Database=FurnaceUtil;User
ID=SSiUser;Password=ssississi;Trusted_Connection=False;</SQLEXPRUtilDBConnString>
<LoadDBConnString>Server=localhost\sqlexpress;Database=SSiLoads;User
ID=SSiUser;Password=ssississi;Trusted_Connection=False;</LoadDBConnString>
<LoadsTableName>Loads</LoadsTableName>
<LoadIDColName>LID</LoadIDColName>
<LoadFurnaceColName>Furnace</LoadFurnaceColName>
<LoadOperatorColName>Operator</LoadOperatorColName>
<LoadStartColName>DateTimeIN</LoadStartColName>
<LoadEndColName>DateTimeOUT</LoadEndColName>
</Options>
Explanations of settings:
• <GasUsageUoM>: Unit of Measurement for gas usage such as SCFM (Standard Cubic
Feet per Minute) or M3M, etc.
• <Currency>: Currency type for use with cost reports. Example values are USD, EUR, etc.
• <GasRate>: Gas price per one gas unit specified in the <GasUsageUoM> setting and in
the currency specified in the <Currency> setting.
• <ElectricityRate>: Electric price per KWH in the currency specified in the <Currency>
setting.
• <UseSQLEXPRUtilDB>: 1.) If set to true: To use a centralized Furnace Utilization SQL
database server specified in the <SQLEXPRUtilDBConnString> setting. 2.) If set to false:
To use the local SQL CE database on the local machine for all the configurations for the
program.
• <SQLEXPRUtilDBConnString>: Connection settings for the centralized Furnace
Utilization SQL database. This setting will only be used if <UseSQLEXPRUtilDB> is set to
true.
• <LoadDBConnString>: Connection settings for the Load Entry SQL database.
• <LoadsTableName>: Name of the Loads table within the Load Entry SQL database.
• <LoadIDColName>: Name of the LoadID column of the Loads table within the Load Entry
SQL database.
• <LoadFurnaceColName>: Name of the Furnace column of the Loads table within the
Load Entry SQL database.
Super Systems Inc. Page 24 of 25
Page 25

Furnace Utilization Reporting System (FURS) Operations Manual
• <LoadOperatorColName>: Name of the Operator column of the Loads table within the
Load Entry SQL database.
• <LoadStartColName>: Name of the TimeIn column of the Loads table within the Load
Entry SQL database.
• <LoadEndColName>: Name of the TimeOut column of the Loads table within the Load
Entry SQL database.
Super Systems Inc. Page 25 of 25
 Loading...
Loading...