Page 1

®
SUPER X5DMS-6GM
SUPER X5DMS-8GM
USER’S MANUAL
Revision 1.0b
SUPER
Page 2

The information in this User’s Manual has been carefully reviewed and is believed to be
accurate. The vendor assumes no responsibility for any inaccuracies that may be
contained in this document, makes no commitment to update or to keep current the
information in this manual, or to notify any person or organization of the updates.
Please Note: For the most up-to-date version of this manual, please
see our web site at www.supermicro.com.
SUPERMICRO COMPUTER reserves the right to make changes to the product described in
this manual at any time and without notice. This product, including software, if any, and
documentation may not, in whole or in part, be copied, photocopied, reproduced, translated
or reduced to any medium or machine without prior written consent.
IN NO EVENT WILL SUPERMICRO COMPUTER BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT,
SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE USE OR
INABILITY TO USE THIS PRODUCT OR DOCUMENTATION, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN PARTICULAR, THE VENDOR SHALL NOT HAVE
LIABILITY FOR ANY HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, OR DATA STORED OR USED WITH THE
PRODUCT, INCLUDING THE COSTS OF REPAIRING, REPLACING, INTEGRATING,
INSTALLING OR RECOVERING SUCH HARDWARE, SOFTWARE, OR DATA.
Any disputes arising between manufacturer and customer shall be governed by the laws of
Santa Clara County in the State of California, USA. The State of California, County of
Santa Clara shall be the exclusive venue for the resolution of any such disputes.
Supermicro's total liability for all claims will not exceed the price paid for the hardware
product.
Unless you request and receive written permission from SUPER MICRO COMPUTER, you
may not copy any part of this document.
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Other products and
companies referred to herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
companies or mark holders.
Copyright © 2003 by SUPER MICRO COMPUTER INC.
All rights reserved.
Printed in the United States of America
Page 3

iii
Preface
Preface
About This Manual
This manual is written for system integrators, PC technicians and
knowledgeable PC users. It provides information for the installation and use
of the SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM serverboard. The SUPER X5DMS6GM/X5DMS-8GM supports single or dual Intel® 603/604-pin XeonTM processors at up to 3.06 GHz at a 533/400 MHz front side bus. Please refer to the
support section of our web site (http://www.supermicro.com/
TechSupport.htm) for a complete listing of supported processors. This
product is intended to be professionally installed.
Manual Organization
Chapter 1 begins with a checklist of what should be included in your
mainboard box, describes the features, specifications and performance of
the motherboard and provides detailed information about the chipset.
Chapter 2 begins with instructions on handling static-sensitive devices.
Read this chapter when you want to install the processor and memory
modules and when mounting the mainboard in the chassis. Also refer to
this chapter to connect the floppy and hard disk drives, SCSI drives, the IDE
interfaces, the parallel and serial ports, the keyboard and mouse, the power
supply and various other connections, buttons and indicators.
If you encounter any problems, see Chapter 3, which describes troubleshooting procedures for the video, the memory and the setup configuration
stored in CMOS. For quick reference, a general FAQ [Frequently Asked
Questions] section is provided. Instructions are also included for contacting technical support. In addition, you can visit our web site (at
www.supermicro.com/techsupport.htm) for more detailed information.
Chapter 4 includes an introduction to PhoenixBIOS and provides detailed
information on running the CMOS Setup utility.
Appendix A gives information on PhoenixBIOS POST messages.
Appendix B provides PhoenixBIOS POST codes.
Page 4

iv
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
Preface
About This Manual ...................................................................................................... ii i
Manual Organization ................................................................................................... iii
Chapter 1: Introduction
1-1 Overview ......................................................................................................... 1-1
Checklist .................................................................................................... 1-1
Contacting Supermicro ............................................................................ 1-2
Super X5DMS-6GM Image ...................................................................... 1-3
Super X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM Layout ............................................. 1-4
Super X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM Quick Reference............................ 1-5
Motherboard Features ............................................................................. 1-6
Intel E7501 Chipset: System Block Diagram ........................................ 1-8
1-2 Chipset Overview........................................................................................... 1-9
1-3 Special Features............................................................................................. 1-9
ATI Graphics Controller .......................................................................... 1-9
Recovery from AC Power Loss ........................................................... 1-9
1-4 PC Health Monitoring.................................................................................... 1-10
1- 5 ACPI Features ............................................................................................... 1-11
1-6 Power Supply ............................................................................................... 1-12
1- 7 Super I/O......................................................................................................... 1-13
Chapter 2: Installation
2-1 Static-Sensitive Devices ............................................................................... 2-1
Precautions............................................................................................... 2-1
Unpacking.................................................................................................. 2-1
2-2 PGA Processor and Heatsink Installation .................................................. 2-2
2-3 Installing DIMMs............................................................................................... 2-5
2- 4 I/O Ports/Control Panel Connectors ............................................................. 2-6
2-5 Connecting Cables .......................................................................................... 2-8
ATX Power Connection .......................................................................... 2-8
PWR_SEC Connection ............................................................................. 2-8
Power LED ................................................................................................. 2-8
NMI Button .................................................................................................. 2-8
HDD LED .................................................................................................... 2-9
NIC1 LED ................................................................................................... 2-9
NIC2 LED ................................................................................................... 2-9
Overheat LED ........................................................................................... 2-9
Table of Contents
Page 5

Table of Contents
v
Power Fail Button ..................................................................................... 2-9
Reset Button ........................................................................................... 2-10
Power Button ......................................................................................... 2-10
Chassis Intrusion ................................................................................... 2-10
Universal Serial Bus (USB0/1) ............................................................ 2-10
Extra Universal Serial Bus Headers ................................................... 2-11
Serial Ports ............................................................................................. 2-11
LAN (Ethernet) Ports.............................................................................. 2-11
ATX PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Ports ................................................2-11
Fan Headers ........................................................................................... 2-12
Power LED/Speaker (JD1) ................................................................... 2-12
Third Power Supply Fail Header ..........................................................2-12
Keylock ..................................................................................................... 2-13
Wake-On-LAN ......................................................................................... 2-13
Wake-On-Ring ......................................................................................... 2-13
2- 6 Jumper Settings ............................................................................................ 2-14
Explanation of Jumpers ........................................................................ 2-14
CMOS Clear............................................................................................. 2-14
Main Power Override ............................................................................. 2-14
Mb LAN Enable/Disable......................................................................... 2-15
Gb LAN Enable/Disable......................................................................... 2-15
VGA Enable/Disable ............................................................................... 2-15
Third Supply Alarm Enable/Disable ...................................................... 2-15
SCSI Enable/Disable................................................................................ 2-16
SCSI Termination Enable/Disable..........................................................2-16
Watch Dog Enable/Disable .................................................................... 2-16
System Bus Speed ................................................................................. 2-17
2-7 Onboard Indicators ...................................................................................... 2-17
Gb LAN LEDs ..........................................................................................2-17
2- 8 Parallel Port, Floppy/Hard Disk Drive and SCSI Connections ............... 2-18
Parallel Port Connector ......................................................................... 2-18
Floppy Connector ................................................................................... 2-19
IDE Connectors ...................................................................................... 2-19
Ultra160/320 SCSI Connectors ............................................................. 2-20
2-9 Installing Software Drivers......................................................................... 2-21
Supero Doctor III ..................................................................................... 2-22
Page 6

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
vi
Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
3-1 Troubleshooting Procedures ........................................................................ 3-1
Before Power On .................................................................................... 3-1
No Power .................................................................................................. 3-1
No Video ................................................................................................... 3-1
Memory Errors .......................................................................................... 3-2
Losing the System’s Setup Configuration ........................................... 3-2
3-2 Technical Support Procedures .................................................................... 3-2
3-3 Frequently Asked Questions........................................................................ 3-3
3-4 Returning Merchandise for Service............................................................ 3-4
Chapter 4: BIOS
4- 1 Introduction....................................................................................................... 4-1
4- 2 Running Setup .................................................................................................. 4-2
4- 3 Main BIOS Setup.............................................................................................. 4-2
4-4 Advanced Setup.............................................................................................. 4-6
4-5 Security Setup...............................................................................................4-15
4-6 Power Setup ..................................................................................................4-17
4- 7 Boot Setup...................................................................................................... 4-19
4-8 PIR Setup ........................................................................................................4-20
4-9 Exit ................................................................................................................... 4-22
Appendices:
Appendix A: BIOS POST Messages ..................................................................... A-1
Appendix B: BIOS POST Codes .............................................................................B-1
Page 7

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-1
Introduction
Chapter 1
Introduction
1-1 Overview
Checklist
Congratulations on purchasing your computer motherboard from an acknowledged leader in the industry. Supermicro boards are designed with
the utmost attention to detail to provide you with the highest standards in
quality and performance.
Please check that the following items have all been included with your
motherboard. If anything listed here is damaged or missing, contact your
retailer.
One (1) Supermicro Mainboard
One (1) ribbon cable for IDE devices
One (1) floppy ribbon cable
One (1) I/O backpanel shield
One (1) USB ribbon cable (retail only)
One (1) COM Port w/cable (retail only)
One (1) Supermicro CD containing drivers and utilities
One (1) User's/BIOS Manual
Two (2) Pentium 4 Xeon active heatsinks (FAN-042, retail only)
Two (2) heatsink retention clips (SKT-095-604)
SCSI Accessories
One (1) 68-pin LVD SCSI cable (retail only)
One (1)SCSI CD ROM
One (1) SCSI manual
Page 8

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
1-2
Introduction
Contacting Supermicro
Headquarters
Address: SuperMicro Computer, Inc.
980 Rock Ave.
San Jose, CA 95131 U.S.A.
Tel: +1 (408) 503-8000
Fax: +1 (408) 503-8008
Email: marketing@supermicro.com (General Information)
support@supermicro.com (Technical Support)
Web Site: www.supermicro.com
Europe
Address: SuperMicro Computer B.V.
Het Sterrenbeeld 28, 5215 ML
's-Hertogenbosch, The Netherlands
Tel: +31 (0) 73-6400390
Fax: +31 (0) 73-6416525
Email: sales@supermicro.nl (General Information)
support@supermicro.nl (Technical Support)
rma@supermicro.nl (Customer Support)
Asia-Pacific
Address: SuperMicro, Taiwan
D5, 4F, No. 16 Chien-Ba Road
Chung-Ho 235, Taipei Hsien, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Tel: +886-(2) 8226-3990
Fax: +886-(2) 8226-3991
Web Site: www.supermicro.com.tw
Technical Support:
Email: support@supermicro.com.tw
Tel: 886-2-8228-1366, ext.132 or 139
Page 9

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-3
Introduction
Figure 1-1. SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM Image
Note: The only difference between the X5DMS-6GM and the X5DMS-8GM is
that the X5DMS-6GM uses Ultra 160 LVD SCSI, and the X5DMS-8GM uses
Ultra 320 LVD SCSI.
Page 10
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
1-4
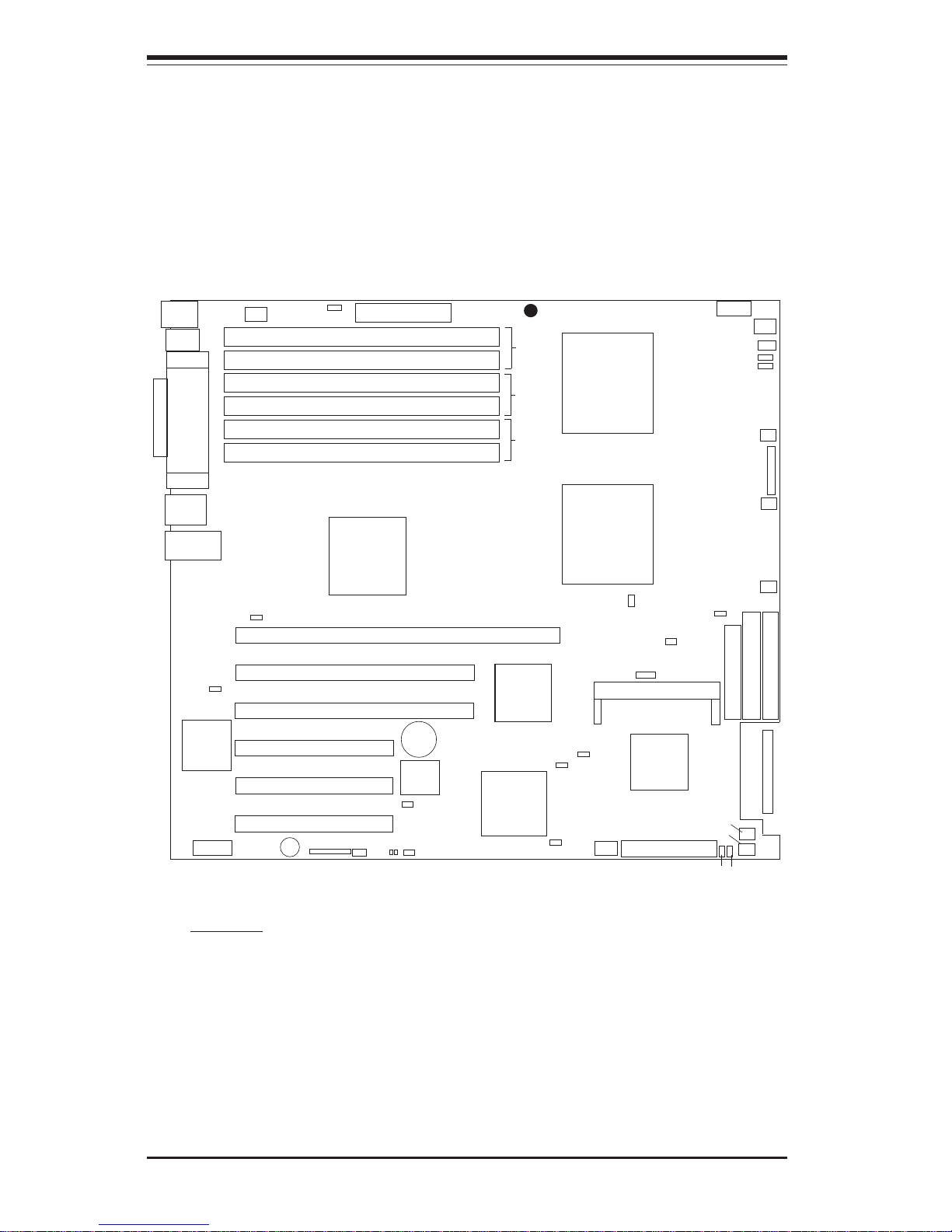
Introduction
Figure 1-2. SUPER X5DMS-6G/X5DMS-8GM Layout
(not drawn to scale)
1. The IPMI socket is an optional feature.
2. Jumpers not noted are for test purposes only.
3. The only difference between the X5DMS-6GM and the X5DMS-8GM is
that the X5DMS-6GM uses Ultra 160 LVD SCSI, and the X5DMS-8GM uses
Ultra 320 LVD SCSI. (*The X5DMS-8GM includes Adaptec's AIC-7902W in
place of the AIC-7899W.)
CPU1 CH FAN
CPU2 CH FAN
DIMM #3B
DIMM #3A
DIMM #2B
DIMM #2A
DIMM #1B
DIMM #1A
BANK 3
BANK 2
BANK 1
ATX PWR CONN
JF2
JP36
J15
CPU 2
Keyboard
Mouse
CPU 1
Rage
XL
JP9
JP39
JP7
IDE #2
IDE #1
FLOPPY
Ultra III LVD SCSI CH B
BIOS
Battery
P64H2
JP37
MCH
AIC-7899W
ICH3
IPMI
USB2/
FPUSB0/1
Speaker
64-bit 133 MHz PCI-X #6
64-bit 66 MHz PCI-X #5
64-bit 66 MHz PCI-X #4
33 MHz PCI #3
33 MHz PCI #2
33 MHz PCI #1
WOL
COM2
JA1
JA2
JD3
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/8GM
®
JP22
JP4
JP35
JPA2
JD1
JPA1
JP8
JP3
J9
USB 0/1
COM1
VGA
Parallel Port
Mb LAN
Gb LAN
JP40
CH FAN3
CH FAN4
CH FAN5
Ultra III LVD SCSI CH A
JBT1
J7
JOH1
JWOR1
CH FAN1
SMB
CH FAN2
JL1
Notes:
Page 11

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-5
Introduction
X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM Quick Reference
Jumper Description Default Setting
JBT1 CMOS Clear See Section 2-6
JPA1/JPA2 SCSI CH A/B Termination Open (Enabled)
JP3/JD3 Mb/Gb LAN Enable/Disable Pins 1-2 (Enabled)
JP4 VGA Enable/Disable Pins 1-2 (Enabled)
JP9 3rd P/S Fail Alarm En/Dis Open (Disabled)
JP22 SCSI Enable/Disable Pins 1-2 (Enabled)
JP37 Watch Dog Enable/Disable Open (Disabled)
JP39 Front Side Bus Speed Pins 1-2 (Auto)
JP40 Main Power Override Open (Normal)
Connector Description
ATX PWR CONN Primary ATX Power Connector
DIMM#1A-DIMM#3B Memory (RAM) Slots
COM1/COM2 COM1/COM2 Serial Port Connector
CPU/CHS/OH FAN CPU/Chassis/Overheat Fan Headers
Gb LAN Gb LAN (Ethernet) Port
IDE#1/IDE#2 IDE #1/#2 Hard Disk Drive Connectors
FPUSB0/1 Front Side USB0/1 Headers
J7 Parallel (Printer) Port
J9 PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse Ports
J15* Secondary ATX Power Connector
JA1/JA2 Ultra 160 LVD SCSI CH A(J1)/CH B(J2)
Connectors (*X5DMS-6GM)
(*JA1/J2) Ultra320 LVD SCSI CH A(J1)/CH B(J2)
Connectors (*X5DMS-8GM)
JD1 PWR LED Header / Speaker Header/Jumper
JF2 Front Control Panel Connector
JL1 Chassis Intrusion Header
JOH1 Overheat LED
JP7 Floppy Disk Drive Connector
JP8 Third Power Supply Fail Header
JP35 Keylock Switch Connector
JP36 3rd Power Supply Alarm Reset Switch
JWOR1 Wake-on-Ring Header
Mb LAN Mb LAN (Ethernet) Port
Speaker Onboard Speaker Header
USB2 USB2 Header
VGA VGA Display (Monitor) Port
WOL Wake-on-LAN Header
*
The Secondary 12v 8-pin power connector at J15 must also be
connected to your power supply.
Page 12

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
1-6
Introduction
Motherboard Features
CPU
• Single or dual Intel® 603/604-pin XeonTM processors at up to 3.06 GHz
at a 533/400 MHz front side (system) bus speed.
Note: Please refer to the support section of our web site for a complete listing of supported
processors (http://www.supermicro.com/TechSupport.htm).
Memory
• Six 184-pin DDR DIMM sockets supporting up to 12 GB of registered
ECC DDR-266/200 (PC2100/1600) DDR SDRAM (*When a 400 MHz FSB
CPU is used, DDR-266 will run at the speed of 200 MHz.)
Note: Interleaved memory; requires memory modules to be installed in
pairs. Do not mix memory sizes and speeds. See Section 2-3 for details.
Chipset
• Intel E7501 chipset
Expansion Slots
• One 64-bit, 133 MHz PCI-X
• Two 64-bit, 66 MHz PCI-X
• Three 32-bit, 33 MHz PCI
BIOS
• 4 Mb Phoenix® Flash ROM
• APM 1.2, DMI 2.1, PCI 2.2, ACPI 1.0, Plug and Play (PnP), SMBIOS 2.3
PC Health Monitoring
• Onboard voltage monitors for CPU cores, chipset voltage, 3.3V, +5V,
+12V and 3.3V standby
• Fan status monitor with firmware/software on/off control
• CPU/chassis temperature monitors
• CPU fan auto-off in sleep mode
• CPU slow-down on temperature overheat
• CPU overheat LED header
• Power-up mode control for recovery from AC power loss
• Auto-switching voltage regulator for CPU core
• Chassis intrusion detection
• System resource alert
Page 13

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-7
Introduction
ACPI/PC 98 Features (optional)
• Microsoft OnNow
• Slow blinking LED for suspend state indicator
• Main switch override mechanism
• External modem ring-on
Onboard I/O
• AIC-7899 for dual channel Ultra160 SCSI (*X5DMS-6GM)
• AIC-7902 for dual channel Ultra320 SCSI (*X5DMS-8GM)
• Zero channel RAID slot (green PCI-X slot)
• Riser card slot (brown PCI-X slot)
• Integrated ATI Rage XL graphics controller
• Intel 82545EM Gb Ethernet controller
• Intel 82551 10/100 Mb Ethernet controller
• 2 EIDE ATA100 bus master interfaces
• 1 floppy port interface (up to 2.88 MB)
• 2 Fast UART 16550A compatible serial ports
• 1 EPP/ECP Parallel Port (Enhanced Parallel Port/Extended Capabilities
Port)
• PS/2 mouse and PS/2 keyboard ports
• Two USB (Universal Serial Bus) ports, three USB headers (USB 1.1)
Other
• Internal/external modem ring-on
• Recovery from AC power loss control
• Wake-on-LAN (WOL)
• Console redirection
• IPMI (optional)
CD/Diskette Utilities
• BIOS flash upgrade utility
• Device drivers
Dimensions
• Extended ATX: 12" x 13.05" (304.8 x 331.5 mm)
Page 14

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
1-8
Introduction
Figure 1-5. Intel E7501 Chipset:
System Block Diagram
Note: This is a general block diagram. Please see the previous Motherboard
Features pages for details on the features of each motherboard.
PCI-X Slot 4, 5, SCSI
MCH
533/400 MHz System Bus
266/200 MHz Memory Bus
ATA 100
Ports
P64H2
Processor 1 Processor 0
2-Channel
DDR SDRAM
PCI-X Slot 6, Gb LAN
ICH3-S
USB 1.1
Ports
SMBus
Super IO
Mb LAN
Controller
ATI
Graphics
Page 15

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-9
Introduction
1-2 Chipset Overview
The Intel E7501 chipset is a high-performance chipset with a performance
and feature-set designed for mid-range, dual processor servers. The
E7501 chipset consists of four major components: the Memory Controller
Hub (MCH), the I/O Controller Hub 3 (ICH3), the PCI-X 64-bit Hub 2.0 (P64H2)
and the 82808AA Host Channel Adapter (VxB).
The MCH has four hub interfaces, one to communicate with the ICH3 and
three for high-speed I/O communications. The MCH employs a 144-bit wide
memory bus for a DDR-266 memory interface, which provides a total bandwidth of 3.2 GB/s. The ICH3 interface is a 266 MB/sec point-to-point connection using an 8-bit wide, 66 MHz base clock at a 4x data transfer rate.
The P64H2 interface is a 1 GB/s point-to-point connection using a 16-bit
wide, 66 MHz base clock at a 8x data transfer rate.
The ICH3 I/O Controller Hub provides various integrated functions, including
a two-channel UDMA100 bus master IDE controller, USB host controllers, a
System Management Bus controller and an AC'97 compliant interface.
The P64H2 PCI-X Hub provides a 16-bit connection to the MCH for highperformance IO capability and two 64-bit PCI-X interfaces.
1-3 Special Features
ATI Graphics Controller
The X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM has an integrated ATI video controller based
on the Rage XL graphics chip. The Rage XL fully supports sideband addressing and AGP texturing. This onboard graphics package can provide a
bandwidth of up to 512 MB/sec over a 32-bit graphics memory bus.
Recovery from AC Power Loss
BIOS provides a setting for you to determine how the system will respond
when AC power is lost and then restored to the system. You can choose
for the system to remain powered off (in which case you must hit the
power switch to turn it back on) or for it to automatically return to a poweron state. See the Power Lost Control setting in the Advanced BIOS Setup
section (Peripheral Device Configuration) to change this setting. The default setting is Always On.
Page 16

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
1-10
Introduction
1-4 PC Health Monitoring
This section describes the PC health monitoring features of the SUPER
X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM. The motherboard has an onboard System Hardware Monitor chip that supports PC health monitoring.
Onboard Voltage Monitors for the CPU Cores, Chipset
Voltage, +3.3V, +5V, +12V and +3.3V Standby
An onboard voltage monitor will scan these voltages continuously. Once a
voltage becomes unstable, a warning is given or an error message is sent
to the screen. Users can adjust the voltage thresholds to define the
sensitivity of the voltage monitor.
Fan Status Monitor with Firmware/Software On/Off Control
The PC health monitor can check the RPM status of the cooling fans. The
onboard 3-pin CPU and chassis fans are controlled by the power management functions. The thermal fan is controlled by the overheat detection
logic.
CPU Fan Auto-Off in Sleep Mode
The CPU fan activates when the power is turned on. It continues to operate
when the system enters Standby mode. When in sleep mode, the CPU will
not run at full power, thereby generating less heat.
CPU Overheat LED
JOH1 is a header used to connect to a CPU overheat LED. When the CPU
temperature becomes too high, both the overheat alarm and the warning
LED are activated.
System Resource Alert
This feature is available when used with Intel's LANDesk Client Manager
(optional). LDCM is used to notify the user of certain system events. For
example, if the system is running low on virtual memory and there is insufficient hard drive space for saving the data, you can be alerted of the
potential problem.
Page 17

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-11
Introduction
Auto-Switching Voltage Regulator for the CPU Core
The auto-switching voltage regulator for the CPU core can support up to
20A current and auto-sense voltage IDs ranging from 1.4V to 3.5V. This
will allow the regulator to run cooler and thus make the system more stable.
1-5 ACPI Features
ACPI stands for Advanced Configuration and Power Interface. The ACPI
specification defines a flexible and abstract hardware interface that provides a standard way to integrate power management features throughout
a PC system, including its hardware, operating system and application software. This enables the system to automatically turn on and off peripherals
such as CD-ROMs, network cards, hard disk drives and printers. This also
includes consumer devices connected to the PC such as VCRs, TVs, telephones and stereos.
In addition to enabling operating system-directed power management, ACPI
provides a generic system event mechanism for Plug and Play and an operating system-independent interface for configuration control. ACPI leverages the Plug and Play BIOS data structures while providing a processor
architecture-independent implementation that is compatible with both Windows 2000 and Windows NT 5.0.
Microsoft OnNow
The OnNow design initiative is a comprehensive, system-wide approach to
system and device power control. OnNow is a term for a PC that is always
on but appears to be off and responds immediately to user or other requests.
Slow Blinking LED for Suspend-State Indicator
When the CPU goes into a suspend state, the chassis power LED will start
blinking to indicate that the CPU is in suspend mode. When the user presses
any key, the CPU will wake-up and the LED will automatically stop blinking
and remain on.
Page 18

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
1-12
Introduction
Main Switch Override Mechanism
When an ATX power supply is used, the power button can function as a
system suspend button to make the system enter a SoftOff state. The
monitor will be suspended and the hard drive will spin down. Depressing
the power button again will cause the whole system to wake-up. During
the SoftOff state, the ATX power supply provides power to keep the required circuitry in the system alive. In case the system malfunctions and
you want to turn off the power, just depress and hold the power button for
4 seconds. This option can be set in the Power section of the BIOS Setup
routine.
External Modem Ring-On
Wake-up events can be triggered by a device such as the external modem
ringing when the system is in the SoftOff state. Note that external modem
ring-on can only be used with an ATX 2.01 (or above) compliant power
supply.
Wake-On-LAN (WOL)
Wake-On-LAN is defined as the ability of a management application to remotely power up a computer that is powered off. Remote PC setup, updates and asset tracking can occur after hours and on weekends so that
daily LAN traffic is kept to a minimum and users are not interrupted. The
motherboards have a 3-pin header (WOL) to connect to the 3-pin header on
a Network Interface Card (NIC) that has WOL capability. Note that WakeOn-LAN can only be used with an ATX 2.01 (or above) compliant power
supply.
1-6 Power Supply
As with all computer products, a stable power source is necessary for
proper and reliable operation. It is even more important for processors that
have high CPU clock rates.
The SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM accommodates ATX power supplies.
Although most power supplies generally meet the specifications required by
the CPU, some are inadequate. You should use one that will supply at least
400W of power and includes the additional +12V, 8-pin power connector an even higher wattage power supply is recommended for high-load configurations. Also your power supply must provide 1.5A, which is needed
for the LAN
Page 19

Chapter 1: Introduction
1-13
Introduction
port(s).
NOTE: Auxiliary 12v power (J15) is necessary to support Intel Xeon
CPUs. Failure to provide this extra power will result in the CPUs
becoming unstable after only a few minutes of operation. See
Section 2-5 for details on connecting the power supply cables.
It is strongly recommended that you use a high quality power supply that
meets ATX power supply Specification 2.02 or above. It must also be SSI
compliant (info at http://www.ssiforum.org/). Additionally, in areas where
noisy power transmission is present, you may choose to install a line filter
to shield the computer from noise. It is recommended that you also install a
power surge protector to help avoid problems caused by power surges.
1-7 Super I/O
The disk drive adapter functions of the Super I/O chip include a floppy disk
drive controller that is compatible with industry standard 82077/765, a data
separator, write pre-compensation circuitry, decode logic, data rate selection, a clock generator, drive interface control logic and interrupt and DMA
logic. The wide range of functions integrated onto the Super I/O greatly
reduces the number of components required for interfacing with floppy disk
drives. The Super I/O supports 360 K, 720 K, 1.2 M, 1.44 M or 2.88 M disk
drives and data transfer rates of 250 Kb/s, 500 Kb/s or 1 Mb/s.It also
provides two high-speed, 16550 compatible serial communication ports
(UARTs), one of which supports serial infrared communication. Each UART
includes a 16-byte send/receive FIFO, a programmable baud rate generator,
complete modem control capability and a processor interrupt system.
Each UART includes a 16-byte send/receive FIFO, a programmable baud
rate generator, complete modem control capability and a processor interrupt system. Both UARTs provide legacy speed with baud rate of up to
115.2 Kbps as well as an advanced speed with baud rates of 250 K, 500 K,
or 1 Mb/s, which support higher speed modems.
The Super I/O supports one PC-compatible printer port (SPP), Bi-directional
Printer Port (BPP) , Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) or Extended Capabilities
Port (ECP).
The Super I/O provides functions that comply with ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface), which includes support of legacy and ACPI
power management through an SMI or SCI function pin. It also features
auto power management to reduce power consumption.
Page 20

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
1-14
Introduction
The IRQs, DMAs and I/O space resources of the Super I/O can flexibly
adjust to meet ISA PnP requirements, which support ACPI and APM (Advanced Power Management).
Page 21

Chapter 2: Installation
2-1
Chapter 2
Installation
2-1 Static-Sensitive Devices
Electric-Static-Discharge (ESD) can damage electronic components. To prevent damage to your system board, it is important to handle it very carefully.
The following measures are generally sufficient to protect your equipment
from ESD.
Precautions
• Use a grounded wrist strap designed to prevent static discharge.
• Touch a grounded metal object before removing the board from the antistatic bag.
• Handle the board by its edges only; do not touch its components, peripheral chips, memory modules or gold contacts.
• When handling chips or modules, avoid touching their pins.
• Put the motherboard and peripherals back into their antistatic bags when
not in use.
• For grounding purposes, make sure your computer chassis provides excellent conductivity between the power supply, the case, the mounting
fasteners and the motherboard.
Unpacking
The motherboard is shipped in antistatic packaging to avoid static damage.
When unpacking the board, make sure the person handling it is static protected.
Page 22

2-2
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
IMPORTANT: Always connect the power cord last and always remove it
before adding, removing or changing any hardware components. Make
sure that you install the processor into the CPU socket before you install
the CPU heat sink.
2-2 PGA Processor and Heatsink Installation
1. Locate the following components, which are included in the shipping
package. The amounts shown are for each CPU.
Retention brackets
(2)
Clips (2)
Screws* (4)
*These screws are for mounting the
motherboard to the back panel of a
chassis that has four mounting holes
(as shown on right).
White pegs (4)
2. Insert the white pegs into the
black anchors. Do not force the
white pegs all the way in - only
about 1/3 of the way into the black
anchors.
3. Place a retention bracket in the
proper position and secure it by
pressing pegs into two of the retention
holes until you hear a *click*. The
clicking sound indicates that the peg is
locked and secured.
Two pegs in
position
One retention bracket in
position
Black anchors (4)
For chassis that do not have four
mounting holes, use the anchor/peg
assemblies:
Anchor/peg
assemblies
When handling the processor package, avoid placing direct
pressure on the label area of the fan. Also, do not place the
motherboard on a conductive surface, which can damage the
BIOS battery and prevent the system from booting up.
!
Page 23

Chapter 2: Installation
2-3
5. Lift the lever on the CPU socket:
lift the lever completely or you will
damage the CPU socket when
power is applied. (Install CPU1
first.)
Socket lever
6. Install the CPU in the socket. Make sure
that pin 1 of the CPU is seated on pin 1 of
the socket (both corners are marked with a
triangle). When using only one CPU, install it
into CPU socket #1 (CPU socket #2 is automatically disabled if only one CPU is used).
Pin 1
4. Secure the other retention
bracket into position by
repeating Step 3.
7. Press the lever down until
you hear it *click* into the
locked position.
8. Apply the proper amount of thermal
glue to the CPU die and place the
heatsink and fan on top of the CPU.
Heatsink
9. Secure the heatsink by locking the
retention clips into their proper
position.
10. Connect the three wires of
the CPU fan to the respective CPU
fan connector.
CPU fan
connector
CPU fan
wires
Retention clip
Fan
Page 24
2-4
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
Mounting the Motherboard in the Chassis
All motherboards have standard mounting holes to fit different types of
chassis. Make sure the location of all the mounting holes for both the
motherboard and the chassis match. Although a chassis may have both
plastic and metal mounting fasteners, metal ones are highly recommended
because they ground the motherboard to the chassis. Make sure the metal
standoffs click in or are screwed in tightly. Then use a screwdriver to
secure the motherboard onto the motherboard tray.
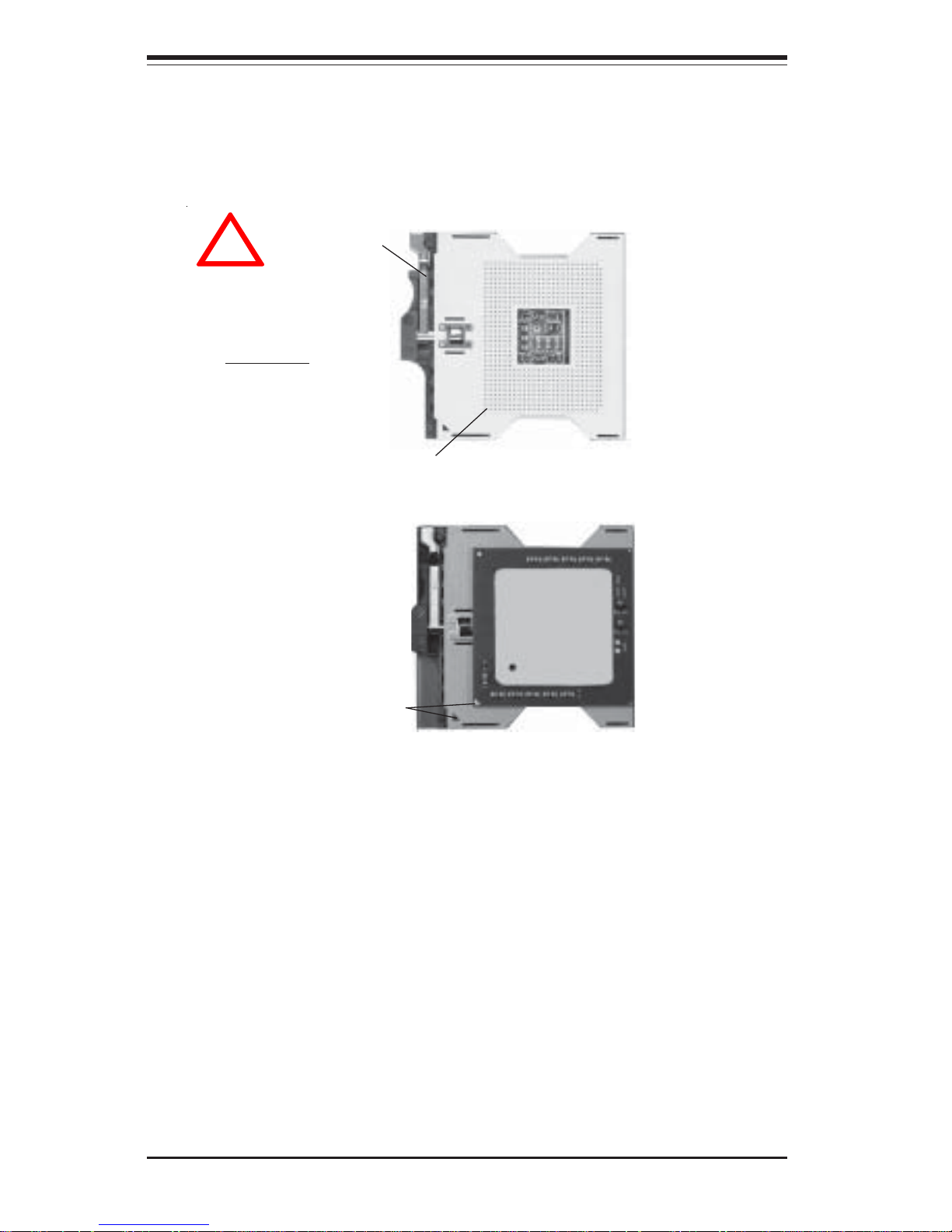
Figure 2-1. PGA604 Socket: Empty and with Processor Installed
Warning! Make
sure you lift the
lever completely
when installing the
CPU. If the lever is
only partly raised,
damage to the
socket or CPU may
result.
Pin 1
Lever
Processor
(installed)
Notched
Corner
!
Page 25

Chapter 2: Installation
2-5
Figure 2-2. Installing and Removing DIMMs
To Install: Insert module vertically and press down until it snaps into
place. Pay attention to the notches.
2-3 Installing DIMMs
Note: Check the Supermicro web site for recommended memory modules:
http://www.supermicro.com/TECHSUPPORT/FAQs/Memory_vendors.htm
CAUTION
Exercise extreme care when installing or removing DIMM
modules to prevent any possible damage. Also note that the
memory is interleaved to improve performance (see step 1).
DIMM Installation (See Figure 2-2)
1. Insert the desired number of DIMMs into the memory slots, starting with
Bank 1. The memory scheme is interleaved so you must install two
modules at a time, beginning with Bank 1, then Bank 2, then Bank 3.
2. Insert each DIMM module vertically into its slot. Pay attention to the
notch along the bottom of the module to prevent inserting the DIMM
module incorrectly.
3. Gently press down on the DIMM module until it snaps into place in the
slot. Repeat for all modules (see step 1 above).
Memory Support
The X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM can support up to 12 GB of ECC registered
DDR-266/200 (PC2100/1600) SDRAM memory. However, when a 400 FSB
CPU is used, DDR-266 will run at the speed of 200 MHz. PC100/133 SDRAM
is not supported.
Page 26

2-6
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
To Remove:
Use your thumbs to gently push near the edge of both ends of
the module. This should release it from the slot.
Parallel Port (Burgundy)
2-4 I/OPorts/Control Panel Connectors
The I/O ports are color coded in conformance with the PC 99 specification.
See Figure 2-3 below for the colors and locations of the various I/O ports.
Figure 2-3. I/O Port Locations and Definitions
Mouse
(Green)
Keyboard
(Purple)
USB Ports
COM1 Port
(Turquoise)
VGA (Monitor)
Port (Blue)
Mb LAN Gb LAN
Note: COM2 is a header located on the motherboard. See the motherboard
layout pages in Chapter 1 for location.
Page 27

Chapter 2: Installation
2-7
Front Control Panel
JF2 contains header pins for various buttons and indicators that are normally located on a control panel at the front of the chassis. These connectors are designed especially for use with Supermicro server chassis. See
Figure 2-4 for the descriptions of the various control panel buttons and LED
indicators. Refer to the following section for descriptions and pin definitions.
Figure 2-4. JF2 Header Pins
Power Button
Overheat LED
1
NIC1 LED
Re se t B utto n
2
Po w e r F a il L E D
NIC2 LED
HDD LED
Power LED
Reset
Pwr
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
Ground
Ground
1920
Vcc
X
Ground
NMI
X
JF2
Page 28

2-8
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
Power LED
The Power LED connection is located on pins 15 and 16 of JF2.
Refer to the table on the right for
pin definitions.
ATX Power Supply 24-pin Connector
Pin Definitions
Pin Number Definition
13 +3.3V
14 -12V
15 COM
16 PS_ON#
17 COM
18 COM
19 COM
20 Res(NC)
21 +5V
22 +5V
23 +5V
24 COM
Pin Number Definition
1 +3.3V
2 +3.3V
3 COM
4 +5V
5 COM
6 +5V
7 COM
8 PWR_O K
9 5VS B
10 +12V
11 +12V
12 +3.3V
2-5 Connecting Cables
ATX Power Connection
The X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM
power supply connector meets the
SSI (Superset ATX) 24-pin specification, however it also supports
a 20-pin power supply connector.
Make sure that the orientation of
the PS connector is correct.
Pins
1 thru 4
5 thru 8
Defin i tio n
Ground
+12v
8-Pin +12v Power Supply
Connector (J15)
PWR_SEC Connection
In addition to the Primary ATX
power connector (above), the
Secondary 12v 8-pin J15 connector must also be connected to
your power supply. See the table
on the right for pin definitions.
Pin
Number
15
16
Defin itio n
Vcc
Control
Power LED Pin
Definitions (J F 2)
NMI Button
The non-maskable interrupt button
header is located on pins 19 and
20 of JF2. Refer to the table on
the right for pin definitions.
Pin
Number
19
20
Defin itio n
Control
Ground
NMI Button Pin
Definitions (J F 2)
Page 29

Chapter 2: Installation
2-9
Overheat LED (OH)
Connect an LED to the OH connection on pins 7 and 8 of JF2 to provide advanced warning of chassis
overheating. Refer to the table on
the right for pin definitions.
NIC2 LED
The NIC2 (Network Interface Controller) LED connection is located
on pins 9 and 10 of JF2. Attach
the NIC2 LED cable to display network activity. Refer to the table
on the right for pin definitions.
Power Fail Button
The Power Fail Button connection
is located on pins 5 and 6 of JF2.
Refer to the table on the right for
pin definitions.
NIC1 LED
The NIC1 (Network Interface Controller) LED connection is located
on pins 11 and 12 of JF2. Attach
the NIC1 LED cable to display network activity. Refer to the table
on the right for pin definitions.
HDD LED
The HDD LED (for IDE Hard Disk
Drives) connection is located on
pins 13 and 14 of JF2. Attach the
IDE hard drive LED cable to these
pins to display disk activity. Refer
to the table on the right for pin
definitions.
HDD LED Pin
Definitions
(JF2)
Pin
Number
13
14
Defin i ti o n
Vcc
HD Active
NIC1 LED Pin
Definitions
(JF2)
Pin
Number
11
12
Defin i ti o n
Vcc
GND
Overheat (OH) LED
Pin Definitions
(JF2 )
Pin
Number
7
8
Defin i tio n
Vcc
GND
Power F a il Butto n
Pin Definitions
(JF2 )
Pin
Number
5
6
Defin i tio n
Vcc
GND
NIC2 LED Pin
Definitions
(JF2)
Pin
Number
9
10
Defin i ti o n
Vcc
GND
Page 30
2-10
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
Power Button
The Power Button connection is
located on pins 1 and 2 of JF2.
Momentarily contacting both pins
will power on/off the system. This
button can also be configured to
function as a suspend button (see
the Power Button Mode setting in
BIOS). To turn off the power
when set to suspend mode, depress the button for at least 4
seconds. Refer to the table on the
right for pin definitions.
Pin
Number
1
2
Defin i ti o n
PW _ON
Ground
Pow e r B utton
Connector
Pin Definitions
(JF2)
Universal Serial Bus
(USB0/1)
Two Universal Serial Bus ports
are located beside the PS/2 keyboard/mouse ports. USB0 is the
bottom connector and USB1 is the
top connector. See the table on
the right for pin definitions.
Universal Serial Bus Pin Definitions
Pin
Number Definition
1+5V
2P0 3P0+
4 Ground
5 N/A
Pin
Number Definition
1+5V
2P0 3P0+
4 Ground
5Key
USB0
USB1
Reset Button
The Reset Button connection is located on pins 3 and 4 of JF2. Attach it to the hardware reset
switch on the computer case.
Refer to the table on the right for
pin definitions.
Chassis Intrusion
A Chassis Intrusion header is located at JL1. Attach the appropriate cable to inform you of a chassis intrusion.
Pin
Number
3
4
Defin i tio n
Reset
Ground
Reset Pin
Definitions
(JF2 )
Page 31

Chapter 2: Installation
2-11
Extra Universal Serial Bus
Headers
Extra USB headers (FPUSB0/1 and
USB2) are included on the
motherboard. FPUSB0/1 were designed to provide front side USB
access. You will need a USB
cable (not included) for these
headers. Refer to the tables on
the right for pin definitions.
Pin
Number
2
4
6
8
10
Defin i ti o n
Power
-
+
Ground
Key
USB2 Pin
Definition s (J13)
Pin
Number
1
3
5
7
9
Defin i tio n
Power
-
+
Ground
Key
USB3 Pin
Definitions (J14)
ATX PS/2 Keyboard and
PS/2 Mouse Ports
The ATX PS/2 keyboard and the
PS/2 mouse are located on J9.
See the table on the right for pin
definitions. (The mouse port is
above the keyboard port. See Figure 2-3.)
PS/2 Keyboard
and Mouse Port
Pin Definitions
(J9)
Pin
Number
1
2
3
4
5
6
Defin itio n
Data
NC
Ground
VCC
Clock
NC
Serial Ports
The COM1 serial port is located
under the parallel port (see Figure
2-3). See the table on the right for
pin definitions. The COM2 connector is a header located near the
PCI-X #1 slot on the motherboard.
LAN (Ethernet) Ports
Two Ethernet ports are located
beside the VGA port on the IO
backplane. These ports accept
RJ45 type cables. See Figure 2-3
for port definitions.
Serial Port Pin Definitions
(COM 1 , C O M 2 )
Pin Number Definition
1 C D
2 R D
3 TD
4 DTR
5 Ground
Pin Number Definition
6 D S R
7 RTS
8 CTS
9 R I
10 NC
Note: Pin 10 is included on the header but not on
the port.
Page 32

2-12
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
Third Power Supply Fail
Header
Connect a cable from your power
supply to the JP8 header to provide warning of power supply failure. This warning signal is
passed through the PWR_LED pin
on JF2 to indicate of a power failure on the chassis. See the table
on the right for pin definitions.
Th ird Po w e r S u pply Fail H ea der
Pin Defini tion s (J P 8)
Pin
Number
1
2
3
4
Defi n itio n
P/S 1 Fail Signal
P/S 2 Fail Signal
P/S 3 Fail Signal
Res et (from M B)
Note: This feature is only available when using
redundant Supermicro power supplies.
Power LED/Speaker (JD1)
On the JDI header, pins 1-3 are for
the PWR LED and pins 4-7 are for
the speaker connection. See the
table on the right for speaker pin
definitions. Note: The speaker
connector pins are for use with an
external speaker. If you wish to
use the onboard speaker, you
should close pins 6-7 with a
jumper. (Note that the two pins
beside the PWR LED header is for
JP37 and not part of JD1 - see
silkscreen on motherboard.)
Speaker Connector Pin
Definitio ns (JD 1 )
Pin
Number
6
7
8
9
Function
+
Key
Defi n itio n
Red wire, Speaker data
No connection
Key
Speaker data
Fan Header Pin Definitions
Pin
Number
1
2
3
Defin i tion
Ground (black)
+12V (red)
Tachometer
Caution: These fan headers
are DC power.
Fan Headers
Your motherboard has several fan
headers designated CPU1 Chassis
Fan, CPU2 Chassis Fan, Chassis
Fan3, Chassis Fan4 and Chassis
Fan5. The first two attach to the
fans on the CPU heatsinks. See
the table on the right for pin definitions. Only the CPU1Chassis Fan,
CPU2 Chassis Fan and Chassis
Fan 3 are monitored by the hardware monitor logic (see BIOS).
Page 33

Chapter 2: Installation
2-13
Pin
Number
1
2
3
Defin itio n
+5V Standby
Ground
Wake-up
Wake-On-LAN Pin
Definitions (WOL)
Wake-On-LAN
The Wake-On-LAN header is designated WOL. See the table on the
right for pin definitions. You must
enable the LAN Wake-Up setting in
BIOS to use this feature. You
must also have a LAN card with a
Wake-on-LAN connector and
cable.
Wake-On-Ring
The Wake-On-Ring header is designated JWOR1. This function allows your computer to receive
and "wake-up" by an incoming call
to the modem when in suspend
state. See the table on the right
for pin definitions. You must have
a Wake-On-Ring card and cable to
use this feature.
Wake-on-Ring
Pin Definitions
(JWO R 1)
Pin
Number
1
2
Defin i ti o n
Ground
Wake-up
Keylock
The keyboard lock connection is located on JP35. Utilizing this header
allows you to inhibit any actions
made on the keyboard, effectively
"locking" it.
Page 34
2-14
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
2-6 Jumper Settings
Explanation of
Jumpers
To modify the operation of the
motherboard, jumpers can be
used to choose between
optional settings. Jumpers
create shorts between two pins
to change the function of the
connector. Pin 1 is identified
with a square solder pad on
the printed circuit board. See
the motherboard layout pages
for jumper locations.
Note: On two pin jumpers,
"Closed" means the jumper is
on and "Open" means the
jumper is off the pins.
Connector
Pins
Jumper
Cap
Setting
Pin 1-2 short
3 2 1
3 2 1
CMOS Clear
JBT1 is used to clear CMOS. Instead of pins, this jumper consists of contact pads to prevent accidentally clearing the contents of CMOS. To clear
CMOS, use a metal object such as a small screwdriver to touch both pads
at the same time to short the connection. Always remove the AC power
cord from the system before clearing CMOS.
Note: For an ATX power supply, you must completely shut down the system, remove the AC power cord and then short JBT1 to clear CMOS. Do
not use the PW_ON connector to clear CMOS.
Main Power Override
Instead of using the chassis
power on switch, you may close
jumper JP40 to apply power to the
system. This effectively disables
the power button from turning off
the system. See the table on the
right for jumper settings. The default setting is Open (normal).
Jumper
Position
Open
Closed
Defin itio n
Normal
Force Po we r O n
Power On
Jumper Settings
(JP40)
Page 35

Chapter 2: Installation
2-15
Mb LAN Enable/Disable
Change the setting of jumper JP3
to enable or disable the Mb LAN
port on the motherboard (see Figure 2-3 for location). Refer to the
table on the right for jumper settings. The default setting is Enabled.
Jumper
Position
Pins 1-2
Pins 2-3
Defin itio n
Enabled
Disabled
Mb LAN
Enable/D isa b le
Jump e r Setting s
(JP3)
Gb LAN Enable/Disable
Change the setting of jumper JD3
to enable or disable the Gb LAN
port on the motherboard. (see Figure 2-3 for location). Refer to the
table on the right for jumper settings. The default setting is Enabled.
Jumper
Position
Pins 1-2
Pins 2-3
Defin itio n
Enabled
Disabled
Gb LAN
Enable/D isa b le
Jump e r Setting s
(JD3)
VGA Enable/Disable
JP4 allows you to enable or disable
the VGA port. The default position
is on pins 1 and 2 to enable VGA.
See the table on the right for
jumper settings.
Jumper
Position
1-2
2-3
Defin itio n
Enabled
Disabled
VGA E n a b le/Disable
Jump e r Setting s
(JP4)
Third Power Supply Alarm
Enable/Disable
The system will notify you in the
event of a power supply failure.
This feature assumes that three
power supply units are installed in
the chassis, with one acting as a
backup. If you only have one or
two power supply units installed,
you should disable this (the default
setting) with JP9 to prevent false
alarms. See the table on the right
for jumper settings.
Jumper
Position
Open
Closed
Defin i tio n
Disabled
Enabled
Third Power Supply
Alarm Enable/Disable
Jumper Settings (JP9)
Page 36

2-16
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
SCSI Enable/Disable
The SCSI Termination jumper at
JP22 allows you to enable or disable the onboard SCSI controller.
The normal (default) position is on
pins 1-2 to enable SCSI termination. See the table on the right for
jumper settings.
Jumper
Position
Pins 1-2
Pins 2-3
Defin itio n
Enabled
Disabled
SCS I En a b le /D is a b le
Jump e r Setting s
(JP22)
SCSI Termination Enable/
Disable
Jumpers JPA1 and JPA2 allow you
to enable or disable termination for
the individual SCSI channels.
Jumper JPA1 controls SCSI channel
A and JPA2 controls SCSI channel
B. The normal (default) setting is
open to enable (terminate) both
SCSI channels. If you wish to connect external SCSI devices, you
should disable termination for the
channels you will be connecting
them to. See the table on the right
for jumper settings.
Jumper
Position
Open
Closed
Defin itio n
Enabled
Disabled
SCS I C ha n n e l T e rmination
Enable/Dis a b le
Jump e r Setting s
(JPA1, JPA 2)
Watch Dog Enable/Disable
Use JP37 to enable or disable the
Watch Dog feature. The default position is open to disable the Watch
Dog timer. The jumper must be used
in conjunction with the Watch Dog
enabled setting in BIOS (Advanced
Setup > I/O Device Configuration).
When enabled, Watch Dog can
reboot your PC if an application is
"hung up" or the system goes
down. See the table on the right
for jumper settings.
Jumper
Position
Open
Closed
Defin itio n
Disabled
Enabled
Watch Dog Timer Enable/
Disable Jumper Settings
(JP37)
Page 37

Chapter 2: Installation
2-17
System Bus Speed
JP39 allows you to select Auto or
400 MHz for your system (front
side) bus speed. The recommended
Auto setting will automatically determine the system bus speed of your
processor(s). See the table on the
right for jumper settings.
"Auto" is the recommended setting.
Jumper
Position
Pins 1-2
Pins 2-3
Open
Defin itio n
Auto
400 MHz
533 MHz
System Bus Speed
Jumper Settings (JP39)
2-7 Onboard Indicators
LAN (Ethernet) LEDs
The Gb and the Mb LAN (Ethernet)
ports both have two LEDs, which
are used to give connectivity status as shown below. The yellow
(left) LED flashes to indicate activity while the other (right) LED may
flash green or orange to indicate
the speed of the connection (there
is no orange indication on the Mb
port). See the tables below for
the functions associated with
these LEDs.
LED
Color
Off
Green
Orange
Definition
No Connection
100 MHz
1 GHz
LAN LED Indicator (Right)
LED
Color
Off
Yellow
Definition
Not Active
Active
LAN LED Indicator (Left)
Page 38

2-18
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
2-8 Parallel Port, Floppy/Hard Disk Drive and SCSI
Connections
Note the following when connecting the floppy and hard disk drive cables:
• The floppy disk drive cable has seven twisted wires.
• A red mark on a wire typically designates the location of pin 1.
• A single floppy disk drive ribbon cable has 34 wires and two connectors to
provide for two floppy disk drives. The connector with twisted wires always
connects to drive A, and the connector that does not have twisted wires
always connects to drive B.
Parallel Port Connector
The parallel (printer) port is located on J7. See the table on the
right for pin definitions.
Pin Number Function
1 Strobe 3 Data B it 0
5 Data B it 1
7 Data B it 2
9 Data B it 3
11 Data B it 4
13 Data B it 5
15 Data B it 6
17 Data B it 7
19 ACK
21 BU S Y
23 PE
25 S L C T
Pin Number Function
2 Auto Feed 4 Erro r 6 Init 8 SLCT IN 10 G ND
12 G ND
14 G ND
16 G ND
18 G ND
20 G ND
22 G ND
24 G ND
26 NC
Parallel (Printe r) P o rt Pin D e finitio ns
(J7)
Page 39
Chapter 2: Installation
2-19
IDE Connectors
There are no jumpers to
configure the onboard IDE#1
and #2 connectors. See the
table on the right for pin
definitions.
Pin Number Function
1 GN D
3 GN D
5 Ke y
7 GN D
9 GN D
11 GN D
13 GN D
15 GN D
17 GN D
19 GN D
21 GN D
23 GN D
25 GN D
27 GN D
29 GN D
31 GN D
33 GN D
Pin Number Function
2 FDHDIN
4 Re s e rv e d
6 FDE DIN
8 Index 10 Motor Enable
12 Drive S e l e ct B 14 Drive S e l e ct A 16 Motor Enable
18 DIR 20 ST E P 22 Wri te D a ta 24 Write Gate 26 Track 00 28 Write Protect 30 Read Data 32 Side 1 Select 34 Dis ke tte
Floppy Connector Pin Definitions (JP7)
Pin Number Function
1 R e s e t ID E
3 H o s t D a ta 7
5 H o s t D a ta 6
7 H o s t D a ta 5
9 H o s t D a ta 4
11 Ho st Data 3
13 Ho st Data 2
15 Ho st Data 1
17 Ho st Data 0
19 GND
21 DR Q3
23 I/O W rite 25 I/O Read 27 IOCHRDY
29 D A C K 3 31 IR Q14
33 Ad d r 1
35 Ad d r 0
37 C h i p S e le c t 0
39 A cti vi ty
Pin Number Function
2 GN D
4 Hos t Data 8
6 Hos t Data 9
8 Host D a ta 1 0
10 H o s t D a ta 1 1
12 H o s t D a ta 1 2
14 H o s t D a ta 1 3
16 H o s t D a ta 1 4
18 H o s t D a ta 1 5
20 Ke y
22 G N D
24 G N D
26 G N D
28 BAL E
30 G N D
32 IOC S 1 6 34 G N D
36 Add r 2
38 C h i p S e l e ct 1 40 G N D
IDE Connector Pin Definitions
(IDE#1, IDE#2)
Floppy Connector
The floppy connector is located
on JP7. See the table below for
pin definitions.
Page 40

2-20
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
Signal Names
+DB(12)
+DB(13)
+DB(14)
+DB(15)
+DB(P1)
+DB(0)
+DB(1)
+DB(2)
+DB(3)
+DB(4)
+DB(5)
+DB(6)
+DB(7)
+DB(P)
GROUND
DIFFSENS
TERMPWR
TERMPWR
RESERVED
GROUND
+ATN
GROUND
+BSY
+ACK
+RST
+MSG
+SEL
+C/D
+REQ
+I/O
+DB(8)
+DB(9)
+DB(10)
+DB(11)
Connector
Contact
Number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
Signal Names
-DB(1 2)
-DB(1 3)
-DB(1 4)
-DB(1 5)
-DB(P 1)
-DB(0 )
-DB(1 )
-DB(2 )
-DB(3 )
-DB(4 )
-DB(5 )
-DB(6 )
-DB(7 )
-DB(P )
GROUND
GROUND
TERMPWR
TERMPWR
RESERVED
GROUND
-ATN
GROUND
-BSY
-ACK
-RST
-MSG
-SEL
-C/D
-REQ
-I/O
-DB(8 )
-DB(9 )
-DB(1 0)
-DB(1 1)
Connector
Contact
Number
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
68-pin Ultra160 SCSI Connectors (JA1 and JA2)
Ultra160/320 SCSI Connectors
(Ultra160 SCSI: X5DMS-6GM, Ultra 320 SCSI: X5DMS-
8GM)
Refer to the table below for the pin definitions of the Ultra
160/320 SCSI connectors located at JA1 and JA2.
Page 41

Chapter 2: Installation
2-21
Figure 2-5. Driver/Tool Installation Display Screen
2-9 Installing Software Drivers
After all the hardware has been installed you must install the software
drivers. The necessary drivers are all included on the Supermicro CD that
came packaged with your motherboard. After inserting this CD into your
CDROM drive, the display shown in Figure 2-5 should appear. (If this display does not appear, click on the My Computer icon and then on the icon
representing your CDROM drive. Finally, double click on the S "Setup" icon.)
(*Note: Click the icons showing a hand writing on paper to view the readme
files for each item. Click the computer icons to the right of these items to
install each item (from top to the bottom) one at a time. After installing
each item, you must re-boot the system before moving on to the
next item on the list. You should install everything here except for the
SUPER Doctor utility and the LAN/SCSI driver diskettes, which are optional.
The bottom icon with a CD on it allows you to view the entire contents of
the CD. )
Page 42
2-22
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
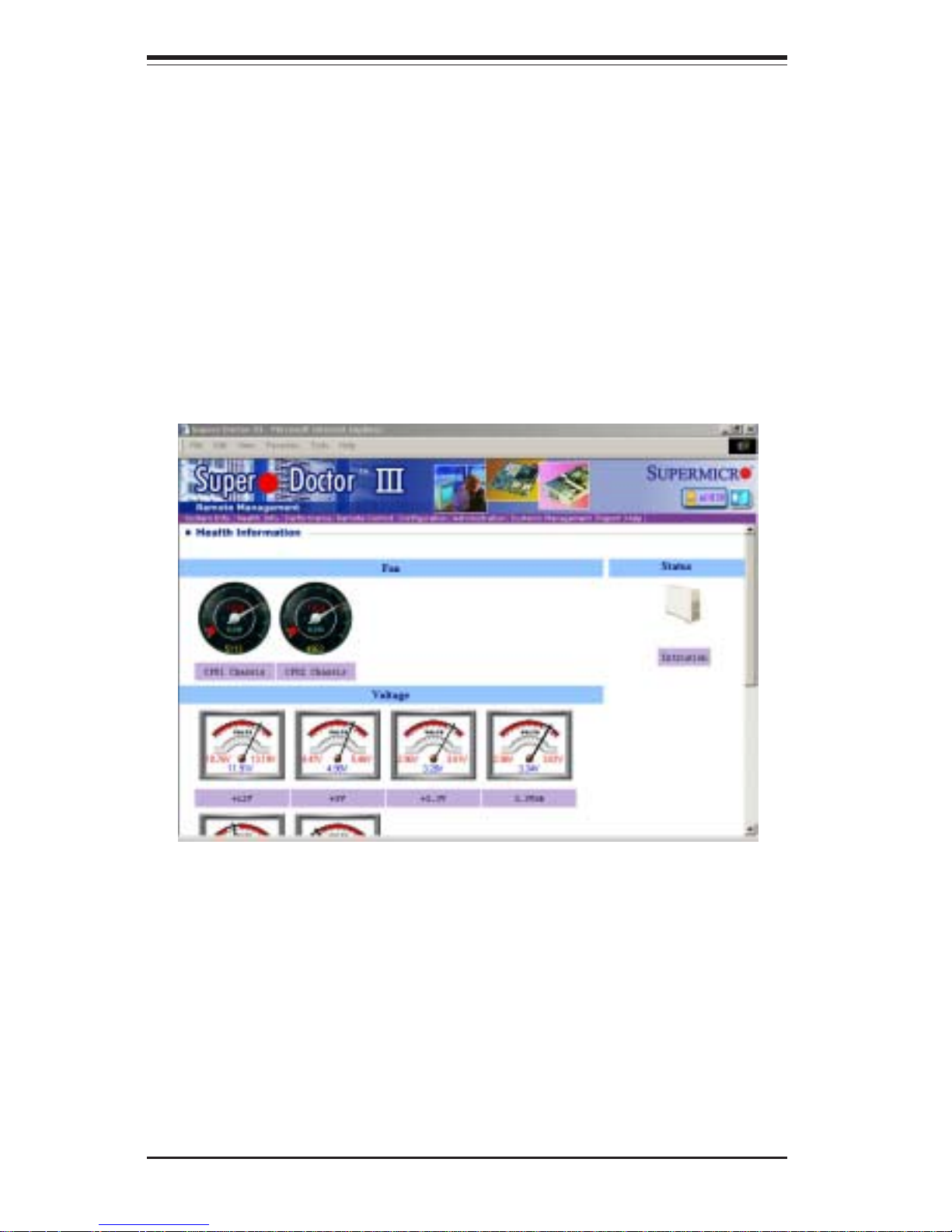
Supero Doctor III
The Supero Doctor III program is a Web base management tool that
supports remote management capability. It includes Remote and Local
Management tools. The local management is called SD III Client. The
Supero Doctor III program included on the CDROM that came with your
motherboard allows you to monitor the environment and operations of
your system. Supero Doctor III displays crucial system information such
as CPU temperature, system voltages and fan status. See the Figure
below for a display of the Supero Doctor III interface.
Supero Doctor III Interface Display Screen-I (Health Information)
Page 43

3-1
Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
Chapter 3
Troubleshooting
3-1 Troubleshooting Procedures
Use the following procedures to troubleshoot your system. If you have
followed all of the procedures below and still need assistance, refer to the
‘Technical Support Procedures’ and/or ‘Returning Merchandise for Service’
section(s) in this chapter.
Note: Always disconnect the power cord before adding, changing
or installing any hardware components.
Before Power On
1. Make sure no short circuits exist between the motherboard and chassis.
2. Disconnect all ribbon/wire cables from the motherboard, including those
for the keyboard and mouse.
3. Remove all add-on cards.
4. Install one CPU (making sure it is fully seated) and connect the chassis
speaker and the power LED to the motherboard. (Check all jumper
settings as well.)
No Power
1. Make sure no short circuits exist between the motherboard and the chassis.
2. Verify that all jumpers are set to their default positions.
3. Check that the 115V/230V switch on the power supply is properly set.
4. Turn the power switch on and off to test the system.
5. The battery on your motherboard may be old. Check to verify that it still
supplies ~3VDC. If it does not, replace it with a new one.
No Video
1. If the power is on but you have no video, remove all the add-on cards
and cables.
2. Use the speaker to determine if any beep codes exist. Refer to the
Appendix for details on beep codes.
Page 44

3-2
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
Losing the System’s Setup Configuration
1. Ensure that you are using a high quality power supply. A poor quality
power supply may cause the system to lose the CMOS setup information. Refer to Section 1-6 for details on recommended power supplies.
2. The battery on your motherboard may be old. Check to verify that it still
supplies ~3VDC. If it does not, replace it with a new one.
3. If the above steps do not fix the Setup Configuration problem, contact
your vendor for repairs.
3-2 Technical Support Procedures
Before contacting Technical Support, please take the following steps. Also,
note that as a motherboard manufacturer, SuperMicro does not sell directly
to end-users, so it is best to first check with your distributor or reseller for
troubleshooting services. They should know of any possible problem(s)
with the specific system configuration that was sold to you.
NOTE
If you are a system integrator, VAR or OEM, a POST diagnos-
tics card is recommended. For I/O port 80h codes, refer to
App. B.
Memory Errors
1. Make sure the DIMM modules are properly and fully installed.
2. Determine if different speeds of DIMMs have been installed and verify
that the BIOS setup is configured for the fastest speed of RAM used.
It is recommended to use the same RAM speed for all DIMMs in the
system.
3. Make sure you are using registered ECC DDR-266/200 (PC2100/1600)
type SDRAM. However, when a (*When a 400 MHz FSB CPU is used,
DDR-266 will run at the speed of 200 MHz.) EDO SDRAM and PC100/
133 SDRAM are not supported.
4. Check for bad DIMM modules or slots by swapping a single module between two slots and noting the results.
5. Make sure all memory modules are fully seated in their slots. As an
interleaved memory scheme is used, you must install two modules at a
time, beginning with Bank 1, then Bank 2, then Bank 3 (see Section 2-
3).
6. Check the power supply voltage 115V/230V switch.
Page 45

3-3
Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
1. Please go through the ‘Troubleshooting Procedures’ and 'Frequently
Asked Question' (FAQ) sections in this chapter or see the FAQs on our
web site (http://www.supermicro.com/techsupport.htm) before contacting Technical Support.
2. BIOS upgrades can be downloaded from our web site at
http://www.supermicro.com/techsupport/download.htm.
Note: Not all BIOS can be flashed depending on the modifications
to the boot block code.
3. If you still cannot resolve the problem, include the following information
when contacting Super Micro for technical support:
• Motherboard model and PCB revision number
• BIOS release date/version (this can be seen on the initial display when
your system first boots up)
•System configuration
An example of a Technical Support form is on our web site at
http://www.supermicro.com/techsupport/contact_support.htm.
4. Distributors: For immediate assistance, please have your account number
ready when placing a call to our technical support department. We can
be reached by e-mail at support@supermicro.com or by fax at:
(408) 503-8000, option 2.
3-3 Frequently Asked Questions
Question: What are the various types of memory that the X5DMS6GM/X5DMS-8GM motherboard can support?
Answer: The X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM has six DIMM slots that support
184-pin, registered ECC DDR-266/200 (PC2100/1600) DDR-SDRAM modules.
(*When a 400 MHz FSB CPU is used, DDR-266 will run at the speed of 200
MHz.) It is strongly recommended that you do not mix memory modules of
different speeds and sizes. Unbuffered SDRAM, non-ECC memory and
PC100/133 SDRAM modules are not supported.
Question: How do I update my BIOS?
Answer: It is recommended that you do not upgrade your BIOS if you are
experiencing no problems with your system. Updated BIOS files are located
on our web site at http://www.supermicro.com. Please check our BIOS
warning message and the info on how to update your BIOS on our web
Page 46

3-4
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
site. Also, check the current BIOS revision and make sure it is newer than
your BIOS before downloading. Select your motherboard model and download the BIOS file to your computer. Unzip the BIOS update file and you will
find the readme.txt (flash instructions), the flash.bat (BIOS flash utility) and
the BIOS image (xxxxxx.rom) files. Copy these files onto a bootable floppy
and reboot your system. It is not necessary to set BIOS boot block protection jumpers on the motherboard. Finally, follow the readme text that has
been included in the unzipped files.
Question: What's on the CD that came with my motherboard?
Answer: The supplied compact disc has quite a few drivers and programs
that will greatly enhance your system. We recommend that you review the
CD and install the applications you need. Applications on the CD include
chipset drivers for Windows and security and audio drivers.
Question: Why can't I turn off the power using the momentary
power on/off switch?
Answer: The instant power off function is controlled in BIOS by the Power
Button Mode setting. When the On/Off feature is enabled, the motherboard
will have instant off capabilities as long as the BIOS has control of the
system. When the Standby or Suspend feature is enabled or when the
BIOS is not in control such as during memory count (the first screen that
appears when the system is turned on), the momentary on/off switch must
be held for more than four seconds to shut down the system. This feature
is required to implement the ACPI features on the motherboard.
3-4 Returning Merchandise for Service
A receipt or copy of your invoice marked with the date of purchase is
required before any warranty service will be rendered. You can obtain
service by calling your vendor for a Returned Merchandise Authorization
(RMA) number. When returning to the manufacturer, the RMA number
should be prominently displayed on the outside of the shipping carton, and
mailed prepaid or hand-carried. Shipping and handling charges will be applied for all orders that must be mailed when service is complete.
Page 47

3-5
Chapter 3: Troubleshooting
This warranty only covers normal consumer use and does not cover damages incurred in shipping or from failure due to the alternation, misuse,
abuse or improper maintenance of products.
During the warranty period, contact your distributor first for any product
problems.
Page 48

3-6
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
Notes
Page 49

Chapter 4: BIOS
4-1
Chapter 4
BIOS
4-1 Introduction
This chapter describes the PhoenixBIOS™ Setup utility for the X5DMS-6GM/
X5DMS-8GM. The Phoenix ROM BIOS is stored in a flash chip and can be
easily upgraded using a floppy disk-based program.
Note: Due to periodic changes to the BIOS, some settings may have been
added or deleted and might not yet be recorded in this manual. Please refer
to the Manual Download area of the Supermicro web site
<http://www.supermicro.com> for any changes to BIOS that may not be
reflected in this manual.
System BIOS
The BIOS is the Basic Input Output System used in all IBM® PC, XT™, AT®,
and PS/2® compatible computers. The PhoenixBIOS flash chip stores the
system parameters, such type of disk drives, video displays, etc. in the
CMOS. The CMOS memory requires very little electrical power. When the
computer is turned off, a back-up battery provides power to the BIOS flash
chip, enabling it to retain system parameters. Each time the computer is
powered-on the computer is configured with the values stored in the BIOS
ROM by the system BIOS, which gains control at boot-up.
How To Change the Configuration Data
The CMOS information that determines the system parameters may be
changed by entering the BIOS Setup utility. This Setup utility can be accessed by pressing the <Delete> key at the appropriate time during system
boot, see below.
Starting the Setup Utility
Normally, the only visible POST (Power On Self Test) routine is the memory
test. As the memory is being tested, press the <Delete> key to enter the
main menu of the BIOS Setup utility. From the main menu, you can access
the other setup screens, such as the Security and Power menus. Beginning with Section 4-3, detailed descriptions are given for each parameter
setting in the Setup utility.
Page 50

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User's Manual
4-2
4-2 Running Setup
*Default settings are in bold text unless otherwise noted.
The BIOS setup options described in this section are selected by choosing the appropriate text from the main BIOS Setup screen. All displayed
text is described in this section, although the screen display is often all
you need to understand how to set the options (see on next page).
When you first power on the computer, the PhoenixBIOS™ is immediately
activated.
While the BIOS is in control, the Setup program can be activated in one of two
ways:
1. By pressing <Delete> immediately after turning the system on, or
2. When the message shown below appears briefly at the bottom of the
screen during the POST (Power On Self-Test), press the <Delete> key to
activate the main Setup menu:
Press the <Delete> key to enter Setup
4-3 Main BIOS Setup
All main Setup options are described in this section. The main BIOS Setup screen
is displayed below.
Use the Up/Down arrow keys to move among the different settings in each menu.
Use the Left/Right arrow keys to change the options for each setting.
Press the <Esc> key to exit the CMOS Setup Menu. The next section describes
in detail how to navigate through the menus.
Items that use submenus are indicated with the ! icon. With the item highlighted,
press the <Enter> key to access the submenu.
Page 51

Chapter 4: BIOS
4-3
Main BIOS Setup Menu
Main Setup Features
System Time
To set the system date and time, key in the correct information in the
appropriate fields. Then press the <Enter> key to save the data.
System Date
Using the arrow keys, highlight the month, day and year fields and enter
the correct data. Press the <Enter> key to save the data.
Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility
Main Advanced Security Power Boot Exit
System Time [16:19:20]
System Date [02/02/02]
Legacy Diskette A: [1.44/1.25 MB]
Legacy Diskette B: [Not Installed]
!
Primary Master
[120 GB]
!
Primary Slave
[None]
!
Secondary Master
[CD-ROM]
!
Secondary Slave
[None]
System Memory 256 MB
Extended Memory 3967 KB
Item Specific Help
F1 Help ↑↓ Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit ↔ Select Menu Enter Select!Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
Page 52

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User's Manual
4-4
Legacy Diskette A
This setting allows the user to set the type of floppy disk drive installed as
diskette A. The options are Disabled, 360Kb 5.25 in, 1.2MB 5.25 in, 720Kb
3.5 in, 1.44/1.25MB, 3.5 in and 2.88MB 3.5 in.
Legacy Diskette B
This setting allows the user to set the type of floppy disk drive installed as
diskette B. The options are Disabled, 360Kb 5.25 in, 1.2MB 5.25 in, 720Kb
3.5 in, 1.44/1.25MB, 3.5 in and 2.88MB 3.5 in.
!!
!!
!Primary Master/Primary Slave/Secondary Master/Secondary
Slave
These settings allow the user to set the parameters of the IDE Primary
Master/Slave and IDE Secondary Master/Slave slots. Hit <Enter> to activate
the following sub-menu screen for detailed options of these items. Set the
correct configurations accordingly. The items included in the sub-menu are:
Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility
Main Advanced Security Boot Exit
Type: [Auto]
Multi Sector Transfer: [16 Sectors]
LBA Mode Control: [Enabled]
32-bit I/O: [Enabled]
Transfer Mode: [Fast PIO 4]
Ultra DMA Mode: [Disabled]
SMART Monitoring: [Enabled]
Item Specific Help
F1 Help ↑↓ Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit ↔ Select Menu Enter Select!Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
Page 53

Chapter 4: BIOS
4-5
Type
Selects the type of IDE hard drive. The options are Auto (allows BIOS
to automatically determine the hard drive's capacity, number of heads,
etc.), a number from 1-39 to select a predetermined type of hard drive,
CD-ROM and ATAPI Removable.
Multi-Sector Transfers
Select the number of transfer sectors. Options are 2, 4, 6, 8 and 16
Sectors.
LBA Mode Control
This item determines whether Phoenix BIOS will access the IDE Primary
Master Device via LBA mode. The options are Enabled and Disabled.
32-bit I/O
Selects 32-bit I/O operation. Options are Enabled and Disabled.
Transfer Mode
Selects the transfer mode. Options are Standard, Fast PIO1, Fast PIO2,
Fast PIO3, Fast PIO4, FPIO3/DMA1 and FPIO4/DMA2.
Ultra DMA Mode
Selects Ultra DMA Mode. Options are Disabled, Mode 0, Mode 1, Mode
2, Mode 3, Mode 4 and Mode 5.
System Memory
This display informs you how much system memory is recognized as being
present in the system.
Extended Memory
This display informs you how much extended memory is recognized as
being present in the system.
Page 54
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User's Manual
4-6
4-4 Advanced Setup
Choose Advanced from the Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility main menu with the arrow
keys. You should see the following display. The items with a triangle beside
them have sub menus that can be accessed by highlighting the item and pressing
<Enter>. Options for PIR settings are displayed by highlighting the setting option
using the arrow keys and pressing <Enter>. All Advanced BIOS Setup options
are described in this section.
Quick Boot Mode
If enabled, this feature will speed up the POST (Power On Self Test) routine
after the computer is turned on. The settings are Enabled and Disabled. If
Disabled, the POST routine will run at normal speed.
Quiet Boot
This setting allows you to Enable or Disable the diagnostic screen during
boot-up.
Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility
Main Advanced Security Boot
Exit
Quick Boot Mode [Enabled]
Quiet Boot [Enabled]
!
PCI/PnP Configuration
!
I/O Device Configuration
!
Advanced Chipset Control
!
Advanced Processor Options
!
DMI Event Logging
!
Console Redirection
Item Specific Help
F1 Help ↑↓ Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit ↔ Select Menu Enter Select!Sub-Menu F10 Save and E xit
Page 55

Chapter 4: BIOS
4-7
!!
!!
!PCI/PnP Configuration
Access the submenu for this item to make changes to the PCI/PnP
configuration, as listed below.
Onboard LAN1 OPROM Configure
Enabling this setting allows you to boot your system from LAN 1. Options
are Enabled and Disabled.
Onboard LAN2 OPROM Configure
Enabling this setting allows you to boot your system from LAN 2. Options
are Enabled and Disabled.
Legacy USB Support
This setting allows you to enable support for Legacy USB devices. The
settings are Enabled and Disabled.
Installed OS
This setting allows you to select the operating system for your computer.
The settings are Other, Win95, Win98, WinMe and Win 2000.
NT4 Installation Workaround
This setting allows BIOS to provide a workaround for the absence of a
floppy drive during NT4 installation. Options are Enabled and Disabled.
Reset Configuration Data
Options are Yes and No. Choosing Yes will clear the Extended System
Configuration Data (ECSD).
Page 56

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User's Manual
4-8
!!
!!
!PCI Slot Configuration
PCI/PCIX Frequency (Slot 4-5)
This setting controls the bus speed of PCI-X slots # 4 and 5. Options
are 33 MHz, 66 MHz, 100 MHz, 133 MHz and Auto. Note that the
onboard SCSI limits the speed of these two slots to 66 MHz on the
P4DMS-6GM.
PCI/PCIX Frequency (Slot 6)
This setting controls the bus speed of PCI-X slots # 4 and 5. Options
are 33 MHz, 66 MHz, 100 MHz, 133 MHz and Auto.
!!
!!
!PCI Device, Slot 1
!!
!!
!PCI Device, Slot 2
!!
!!
!PCI Device, Slot 3
!!
!!
!PCI Device, Slot 4
!!
!!
!PCI Device, Slot 5
!!
!!
!PCI Device, Slot 6
Option ROM Scan
This setting (included in the submenu for the above six settings) will
initialize the selected device's expansion ROM when enabled.
Options are Enabled and Disabled.
Enable Master
This setting (included in the submenu for the above six settings) will
designate the selected device as the PCI bus master when enabled.
Options are Enabled and Disabled.
Page 57

Chapter 4: BIOS
4-9
Latency Timer
This setting (included in the submenu for the above six settings) sets
the minimum guaranteed time slice allotted to the bus master in units
of PCI bus clocks. Options are Default, 0020h, 0040h, 0060h,
0080h, 00A0h, 00C0h and 00E0h.
Large Disk Access Mode
This setting determines how large hard drives are to be accessed. The
options are DOS or Other (for Unix, Novellle NetWare and other operating
systems).
Local Bus IDE Adapter
Use this setting to enable the integrated local bus IDE adapter. Options
are Disable, Primary, Secondary and Both.
!!
!!
!I/O Device Configuration
Access the submenu to make changes to the following settings.
Power Loss Control
This setting allows you to choose how the system will react when power
returns after an unexpected loss of power. Options are Stay Off, Power
On and Last State.
Watch Dog
This setting is used to enable or disabled the Watch Dog Timer function.
It must be used in conjunction with the JP37 jumper (see Chapter 2 for
details). Options are Enabled and Disabled.
KBC Clock Input
Use this setting to select the keyboard clock rate. Options are 6 MHz, 8
MHz and 12 MHz.
Page 58

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User's Manual
4-10
Serial Port A
This setting allows you to assign control of serial port A. The options
are Enabled (user defined), Disabled, Auto (BIOS controlled) and OS
Controlled.
Base I/O Address
Select the base I/O address for serial port A. The options are 3F8,
2F8, 3E8 and 2E8.
Interrupt
Select the IRQ (interrupt request) for serial port A. Options are IRQ3
and IRQ4.
Serial Port B
This setting allows you to assign control of serial port B. The options
are Enabled (user defined), Disabled, Auto (BIOS controlled) and OS
Controlled.
Mode
Specify the type of device that will be connected to serial port B.
Options are Normal and IR (for an infrared device).
Base I/O Address
Select the base I/O address for serial port B. The options are 3F8,
2F8, 3E8 and 2E8.
Interrupt
Select the IRQ (interrupt request) for serial port B. Options are IRQ3
and IRQ4.
Parallel Port
This setting allows you to assign control of the parallel port. The options
are Enabled (user defined), Disabled and Auto (BIOS controlled).
Page 59

Chapter 4: BIOS
4-11
Base I/O Address
Select the base I/O address for the parallel port. The options are 378,
278 and 3BC.
Interrupt
Select the IRQ (interrupt request) for the parallel port. Options are
IRQ5 and IRQ7.
Mode
Specify the parallel port mode. Options are Output Only, Bi-directional,
EPP and ECP.
DMA Channel
Specify the DMA channel. Options are DMA1 and DMA3.
Floppy Disk Controller
This setting allows you to assign control of the floppy disk controller.
The options are Enabled (user defined), Disabled and Auto (BIOS
controlled).
Base I/O Address
Select the base I/O address for the parallel port. The options are
Primary and Secondary.
!!
!!
!Advanced Chipset Control
Access the submenu to make changes to the following settings.
Clock Spectrum Feature
This setting allows you to enable the clock spectrum feature. The options
for this setting are Disabled and Enabled.
Page 60

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User's Manual
4-12
SMART Device Monitoring
This setting lets you enable or disable SMART device monitoring, which
may predict IDE drive failure. The options are Enabled and Disabled.
ECC Configuration
This setting lets you enable or disable ECC (Error Correction and
Checking). The options are ECC and Disabled.
ECC Error Type
This setting lets you select which type of interrupt will be activated as a
result of an ECC error. The options are None, NMI (Non-Maskable
Interrupt), SMI (System Management Interrupt) and SCI (System Control
Interrupt.
SERR Signal Condition
This setting specifies the conditions required to qualify as an ECC error.
Options are None, Single Bit, Multiple Bit and Both.
!!
!!
!Advanced Processor Options
Access the submenu to make changes to the following settings.
CPU Speed
This is a display that indicates the speed of the installed processor.
Fast String Operations
This setting allows you to Enable or Disable fast string operations.
Compatible FPU Code
This setting allows you to Enable or Disable the compatible FPU code.
Page 61

Chapter 4: BIOS
4-13
Split Lock Operations
This setting allows you to Enable or Disable split lock operations.
Hyper-Threading
This setting allows you to Enable or Disable hyper-threading. Enabling
hyper-threading results in increased CPU performance.
!!
!!
!DMI Event Logging
Access the submenu to make changes to the following settings.
Event Log Validity
This is a display, not a setting, informing you of the event log validity.
Event Log Capacity
This is a display, not a setting, informing you of the event log capacity.
View DMI Event Log
Highlight this item and press <Enter> to view the contents of the event
log.
Event Logging
This setting allows you to Enable or Disable event logging.
ECC Event Logging
This setting allows you to Enable or Disable ECC event logging.
Mark DMI Events as Read
Highlight this item and press <Enter> to mark the DMI events as read.
Page 62

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User's Manual
4-14
Clear All DMI Event Logs
This setting will clear all DMI event logs when set to Yes. Options are
Yes and No.
!!
!!
!Console Redirection
Access the submenu to make changes to the following settings.
COM Port Address
Specifies to redirect the console to On-board COMA or On-board COMB.
This setting can also be Disabled.
BAUD Rate
Select the BAUD rate for console redirection.
Console Type
Choose from the available options to select the console type for console
redirection.
Flow Control
Choose from the available options to select the flow control for console
redirection.
Console Connection
Select the console connection: either Direct or Via Modem.
Continue CR after POST
Choose whether to continue with console redirection after the POST
routine. Options are On and Off.
# of Video Pages to Support
Choose the number of video pages to allocate for redirection when video
hardware is not available. Options are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8.
Page 63

Chapter 4: BIOS
4-15
4-5 Security
Choose Security from the Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility main menu with the arrow
keys. You should see the following display. Security setting options are
displayed by highlighting the setting using the arrow keys and pressing <Enter>.
All Security BIOS settings are described in this section.
Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility
Main Advanced Security Power Boot PIR
Exit
Supervisor Password Is: [Clear]
User Password Is: [Clear]
Set Supervisor Password: [Enter]
Set User Password: [Enter]
Password on Boot [Disabled]
Fixed Disk Boot Sector [Normal]
Item Specific Help
F1 Help ↑↓ Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit ↔ Select Menu Enter Select!Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
Supervisor Password Is:
This displays whether a supervisor password has been entered for the
system. Clear means such a password has not been used and Set means
a supervisor password has been entered for the system.
User Password Is:
This displays whether a user password has been entered for the system.
Clear means such a password has not been used and Set means a user
password has been entered for the system.
Page 64

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User's Manual
4-16
Set Supervisor Password
When the item "Set Supervisor Password" is highlighted, hit the <Enter> key.
When prompted, type the Supervisor's password in the dialogue box to set
or to change supervisor's password, which allows access to BIOS.
Set User Password
When the item "Set User Password" is highlighted, hit the <Enter> key.
When prompted, type the user's password in the dialogue box to set or to
change the user's password, which allows access to the system at bootup.
Password on Boot
This setting allows you to require a password to be entered when the
system boots up. Options are Enabled (password required) and Disabled
(password not required).
Fixed Disk Boot Sector
This setting may offer some protection against viruses when set to Write
Protect, which protects the boot sector on the hard drive from having a
virus written to it. The other option is Normal.
Page 65

Chapter 4: BIOS
4-17
4-6 Power
Choose Power from the Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility main menu with the arrow
keys. You should see the following display. Power setting options are displayed
by highlighting the setting using the arrow keys and pressing <Enter>. All Power
BIOS settings are described in this section.
ACPI Mode
Use the setting to determine if you want to employ ACPI (Advanced
Configuration and Power Interface) power management on your system.
Options are Yes and No.
Power Savings
This setting sets the degree of power saving for the system. The options
are Disabled, Customized, Maximum Power Savings and Maximum
Performance. Customized allows you to alter the other two modes.
Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility
Main Advanced Security Power Boot
Exit
ACPI Mode: [Yes]
Power Savings: [Customized]
Suspend Timeout: [Off]
Resume On Time: [Off]
Resume Time: [Off]
Resume On Modem Ring: [Off]
Item Specific Help
F1 Help ↑↓ Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit ↔ Select Menu Enter Select!Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
Page 66

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User's Manual
4-18
Suspend Timeout
Use this setting to specify the period of system inactivity to transpire before
entering the suspend state. Options are Off, 5 min, 10 min, 15 min, 20 min,
30 min, 40 min and 60 min.
Resume on Time
Select either Off or On, which will wake the system up at the time specified
in the next setting.
Resume Time
Use this setting to specify the time you want the system to wake up (the
above setting must be set to On). Enter the time with the number keys.
Resume On Modem Ring
When set to On, the system can be woken up when an incoming call is
detected on the modem. The settings are Select Off and On.
Page 67

Chapter 4: BIOS
4-19
4-7 Boot
Choose Boot from the Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility main menu with the arrow keys.
You should see the following display. Highlighting a setting with a + or - willl
expand or collapse that entry. See details on how to change the order and specs
of boot devices in the Item Specific Help window. All Boot BIOS settings are
described in this section.
+Removable Devices
Highlight and presss <Enter> to expand the field. See details on how to
change the order and specs of removable devices in the Item Specific Help
window.
CD-ROM Drive
See details on how to change the order and specs of removable devices in
the Item Specific Help window.
+Hard Drive
Highlight and presss <Enter> to expand the field. See details on how to
change the order and specs of hard drives in the Item Specific Help
window.
Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility
Main Advanced Security Power Boot PIR
Exit
+ Removable Devices
CD-ROM Drive
+ Hard Drive
Item Specific Help
F1 Help ↑↓ Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit ↔ Select Menu Enter Select!Sub-Menu F10 Save and E xit
Page 68
SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User's Manual
4-20
4-8 P I R
Choose PIR from the Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility main menu with the arrow keys.
You should see the following display. The items with a triangle beside them have
sub menus that can be accessed by highlighting the item and pressing <Enter>.
PIR stands for "Processor Info ROM", which allows BIOS to read certain
information from the processors. Options for PIR settings are displayed by
highlighting the setting option using the arrow keys and pressing <Enter>. All
PIR BIOS Setup options are described in this section.
Select the Processor's PIR
Selects the processor PIR. Options are A0h/A1h, A2h/A3h, A4h/A5h, A6h/
A7h, A8h/A8h, AAh/ABh, ACh/ADh and AEh/AFh. See the Item Specific
Help field for details.
Select the Thermal Unit
Selects the thermal unit. Options are 30h/31h, 32h/33h, 34h/35h, 52h/53h,
54h/55h, 56h/57h, 98h/99h, 9Ah/9Bh and 9Ch/9Dh. See the Item Specific
Help field for details.
Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility
Main Advanced Security Power Boot
PIR
Exit
Select the Processor’s PIR
Select the Thermal Unit
#
Processor Info ROM Data
#
Hardware Monitor Logic
Item Specific Help
F1 Help ↑↓ Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit ↔ Select Menu Enter Select!Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
Page 69

Chapter 4: BIOS
4-21
Header Info
Processor Data
Processor Core Data
L3 Cache Data
Package Data
Part Number Data
Thermal Reference Data
Feature Data
Other Data
OEM Data
!!
!!
!Hardware Monitor Logic
Highlight this and hit <Enter> to see monitor data for the following items:
CPU1 Temperature
CPU2 Temperature
System Temperature
CPU Fan1 Chassis Fan
CPU Fan2 Chassis Fan
Processor Vcore (V)
!!
!!
!Processor Info ROM Data
Highlight this and hit <Enter> to see PIR data on the following items:
Page 70

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User's Manual
4-22
3.3V Standby (V)
3.3V Vcc (V)
5V Vcc (V)
12V Vcc (V)
1.8V Vcc (V)
-12V Vcc (V)
4-9 Exit
Choose Exit from the Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility main menu with the arrow keys.
You should see the following display. All Exit BIOS settings are described in this
section.
Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility
Main Advanced Security Power Boot PIR
Exit
Exit Saving Changes
Exit Discarding Changes
Load Setup Defaults
Discard Changes
Save Changes
Item Specific Help
F1 Help ↑↓ Select Item -/+ Change Values F9 Setup Defaults
Esc Exit ↔ Select Menu Enter Select!Sub-Menu F10 Save and Exit
Page 71

Chapter 4: BIOS
4-23
Exit Saving Changes
Highlight this item and hit <Enter> to save any changes you made and to
exit the BIOS Setup utility.
Exit Discarding Changes
Highlight this item and hit <Enter> to exit the BIOS Setup utility without saving
any changes you may have made.
Load Setup Defaults
Highlight this item and hit <Enter> to load the default settings for all items in
the BIOS Setup. These are the safest settings to use.
Discard Changes
Highlight this item and hit <Enter> to discard (cancel) any changes you
made. You will remain in the Setup utility.
Save Changes
Highlight this item and hit <Enter> to save any changes you made. You will
remain in the Setup utility.
Page 72

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User's Manual
4-24
Notes
Page 73

A-1
Appendix A: BIOS POST Messages
Appendix A
BIOS POST Messages
During the Power-On Self-Test (POST), the BIOS will check for problems. If a problem
is found, the BIOS will activate an alarm or display a message. The following is a list
of such BIOS messages.
Failure Fixed Disk
Fixed disk is not working or not configured properly. Check to see if fixed disk is
attached properly. Run Setup. Find out if the fixed-disk type is correctly identified.
Stuck key
Stuck key on keyboard.
Keyboard error
Keyboard not working.
Keyboard Controller Failed
Keyboard controller failed test. May require replacing keyboard controller.
Keyboard locked - Unlock key switch
Unlock the system to proceed.
Monitor type does not match CMOS - Run SETUP
Monitor type not correctly identified in Setup
Shadow Ram Failed at offset: nnnn
Shadow RAM failed at offset nnnn of the 64k block at which the error
was detected.
System RAM Failed at offset: nnnn
System RAM failed at offset nnnn of in the 64k block at which the error
was detected.
Extended RAM Failed at offset: nnnn Extended memory not
working or not configured properly at offset nnnn.
System battery is dead - Replace and run SETUP
The CMOS clock battery indicator shows the battery is dead. Replace the
battery and run Setup to reconfigure the system.
Page 74

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
A-2
System CMOS checksum bad - Default configuration used
System CMOS has been corrupted or modified incorrectly, perhaps by an
application program that changes data stored in CMOS. The BIOS installed Default
Setup Values. If you do not want these values, enter Setup and enter your own
values. If the error persists, check the system battery or contact your dealer.
System timer error
The timer test failed. Requires repair of system board.
Real time clock error
Real-Time Clock fails BIOS hardware test. May require board repair.
Check date and time settings
BIOS found date or time out of range and reset the Real-Time Clock. May require
setting legal date (1991-2099).
Previous boot incomplete - Default configuration used
Previous POST did not complete successfully. POST loads default values and
offers to run Setup. If the failure was caused by incorrect values and they are
not corrected, the next boot will likely fail. On systems with control of wait
states, improper Setup settings can also terminate POST and cause this error on
the next boot. Run Setup and verify that the waitstate configuration is correct.
This error is cleared the next time the system is booted.
Memory Size found by POST differed from CMOS
Memory size found by POST differed from CMOS.
Diskette drive A error
Diskette drive B error
Drive A: or B: is present but fails the BIOS POST diskette tests. Check to see that
the drive is defined with the proper diskette type in Setup and that the diskette
drive is attached correctly.
Incorrect Drive A type - run SETUP
Type of floppy drive A: not correctly identified in Setup.
Incorrect Drive B type - run SETUP
Type of floppy drive B: not correctly identified in Setup.
Page 75

A-3
Appendix A: BIOS POST Messages
System cache error - Cache disabled
RAM cache failed and BIOS disabled the cache. On older boards, check the
cache jumpers. You may have to replace the cache. See your dealer. A disabled
cache slows system performance considerably.
CPU ID:
CPU socket number for Multi-Processor error.
EISA CMOS not writeable
ServerBIOS2 test error: Cannot write to EISA CMOS.
DMA Test Failed
ServerBIOS2 test error: Cannot write to extended DMA (Direct Memory
Access) registers.
Software NMI Failed
ServerBIOS2 test error: Cannot generate software NMI (Non-Maskable
Interrupt).
Fail-Safe Timer NMI Failed
ServerBIOS2 test error: Fail-Safe Timer takes too long.
device Address Conflict
Address conflict for specified device.
Allocation Error for: device
Run ISA or EISA Configuration Utility to resolve resource conflict for the
specified device.
CD ROM Drive
CD ROM Drive identified.
Entering SETUP ...
Starting Setup program
Failing Bits: nnnn
The hex number nnnn is a map of the bits at the RAM address which failed
the memory test. Each 1 (one) in the map indicates a failed bit. See errors
230, 231, or 232 above for offset address of the failure in System,
Extended, or Shadow memory.
Page 76

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
A-4
Fixed Disk n
Fixed disk n (0-3) identified.
Invalid System Configuration Data
Problem with NVRAM (CMOS) data.
I/O device IRQ conflict
I/O device IRQ conflict error.
PS/2 Mouse Boot Summary Screen:
PS/2 Mouse installed.
nnnn kB Extended RAM Passed
Where nnnn is the amount of RAM in kilobytes successfully tested.
nnnn Cache SRAM Passed
Where nnnn is the amount of system cache in kilobytes successfully tested.
nnnn kB Shadow RAM Passed
Where nnnn is the amount of shadow RAM in kilobytes successfully
tested.
nnnn kB System RAM Passed
Where nnnn is the amount of system RAM in kilobytes successfully tested.
One or more I2O Block Storage Devices were excluded from the Setup
Boot Menu
There was not enough room in the IPL table to display all installed I2O blockstorage devices.
Operating system not found
Operating system cannot be located on either drive A: or drive C:. Enter Setup
and see if fixed disk and drive A: are properly identified.
Parity Check 1 nnnn
Parity error found in the system bus. BIOS attempts to locate the address and
display it on the screen. If it cannot locate the address, it displays ????. Parity is
a method for checking errors in binary data. A parity error indicates that some
data has been corrupted.
Page 77

A-5
Appendix A: BIOS POST Messages
Parity Check 2 nnnn
Parity error found in the I/O bus. BIOS attempts to locate the address and display
it on the screen. If it cannot locate the address, it displays ????.
Press <F1> to resume, <F2> to Setup, <F3> for previous
Displayed after any recoverable error message. Press <F1> to start the boot
process or <F2> to enter Setup and change the settings. Press <F3> to display
the previous screen (usually an initialization error of an Option ROM, i.e., an
add-on card). Write down and follow the information shown on the screen.
Press <F2> to enter Setup
Optional message displayed during POST. Can be turned off in Setup.
PS/2 Mouse:
PS/2 mouse identified.
Run the I2O Configuration Utility
One or more unclaimed block storage devices have the Configuration Request bit
set in the LCT. Run an I2O Configuration Utility (e.g. the SAC utility).
System BIOS shadowed
System BIOS copied to shadow RAM.
UMB upper limit segment address: nnnn
Displays the address nnnn of the upper limit of Upper Memory Blocks,
indicating released segments of the BIOS which can be reclaimed by a virtual
memory manager.
Video BIOS shadowed
Video BIOS successfully copied to shadow RAM.
Page 78

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
A-6
Notes
Page 79

Appendix B: BIOS POST Codes
B-1
This section lists the POST (Power On Self Test) codes for the PhoenixBIOS. POST
codes are divided into two categories: recoverable and terminal.
Recoverable POST Errors
When a recoverable type of error occurs during POST, the BIOS will display
an POST code that describes the problem. BIOS may also issue one of the
following beep codes:
1 long and two short beeps - video configuration error
1 continuous long beep - no memory detected
Terminal POST Errors
If a terminal type of error occurs, BIOS will shut down the system. Before
doing so, BIOS will write the error to port 80h, attempt to initialize video and
write the error in the top left corner of the screen.
The following is a list of codes that may be written to port 80h.
Appendix B
BIOS POST Codes
POST Code Description
02h Verify Real Mode
03 h Disable Non-Maskable Interrupt (NMI)
04h Get CPU type
06h Initialize system hardware
07 h Disable shadow and execute code from the ROM.
08 h Initialize chipset with initial POST values
09h Set IN POST flag
0Ah Initialize CPU registers
0Bh Enable CPU cache
0C h Initialize caches to initial POST values
0Eh Initialize I/O component
0Fh Initialize the local bus IDE
10 h Initialize Power Management
11 h Load alternate registers with initial POST values
12 h Restore CPU control word during warm boot
13 h Initialize PCI Bus Mastering devices
14 h Initialize keyboard controller
16 h 1-2-2-3 BIOS ROM checksum
17 h Initialize cache before memory Auto size
Page 80

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
B-2
POST Code Description
18h 8254 timer initialization
1Ah 8237 DMA controller initialization
1Ch Reset Programmable Interrupt Controller
20 h 1-3-1-1 Test DRAM refresh
22 h 1-3-1-3 Test 8742 Keyboard Controller
24 h Set ES segment register to 4 GB
28h Auto size DRAM
29h Initialize POST Memory Manager
2Ah Clear 512 kB base RAM
2Ch 1-3-4-1 RAM failure on address line xxxx*
2Eh 1-3-4-3 RAM failure on data bits xxxx* of low byte of
memory bus
2Fh Enable cache before system BIOS shadow
32 h Test CPU bus-clock frequency
33 h Initialize Phoenix Dispatch Manager
36 h Warm start shut down
38 h Shadow system BIOS ROM
3Ah Auto size cache
3C h Advanced configuration of chipset registers
3D h Load alternate registers with CMOS values
41 h Initialize extended memory for RomPilot
42 h Initialize interrupt vectors
45 h POST device initialization
46 h 2-1-2-3 Check ROM copyright notice
47 h Initialize I20 support
48 h Check video configuration against CMOS
49 h Initialize PCI bus and devices
4Ah Initialize all video adapters in system
4Bh QuietBoot start (optional)
4Ch Shadow video BIOS ROM
4Eh Display BIOS copyright notice
4Fh Initialize MultiBoot
50 h Display CPU type and speed
51h Initialize EISA board
52 h Test keyboard
54h Set key click if enabled
55 h Enable USB devices
58 h 2-2-3-1 Test for unexpected interrupts
59 h Initialize POST display service
5Ah Display prompt “Press F2 to enter SETUP”
5Bh Disable CPU cache
Page 81

Appendix B: BIOS POST Codes
B-3
POST Code Description
5Ch Test RAM between 512 and 640 kB
60 h Test extended memory
62h Test extended memory address lines
64h Jump to UserPatch1
66h Configure advanced cache registers
67 h Initialize Multi Processor APIC
68 h Enable external and CPU caches
69h Setup System Management Mode (SMM) area
6Ah Display external L2 cache size
6Bh Load custom defaults (optional)
6Ch Display shadow-area message
6Eh Display possible high address for UMB recovery
70h Display error messages
72 h Check for configuration errors
76 h Check for keyboard errors
7C h Set up hardware interrupt vectors
7D h Initialize Intelligent System Monitoring
7Eh Initialize coprocessor if present
80 h Disable onboard Super I/O ports and IRQs
81 h Late POST device initialization
82 h Detect and install external RS232 ports
83 h Configure non-MCD IDE controllers
84 h Detect and install external parallel ports
85 h Initialize PC-compatible PnP ISA devices
86 h Re-initialize onboard I/O ports.
87h Configure Motherboard Configurable Devices
(optional)
88h Initialize BIOS Data Area
89 h Enable Non-Maskable Interrupts (NMIs)
8Ah Initialize Extended BIOS Data Area
8Bh Test and initialize PS/2 mouse
8C h Initialize floppy controller
8Fh Determine number of ATA drives (optional)
90h Initialize hard-disk controllers
91h Initialize local-bus hard-disk controllers
92h Jump to UserPatch2
93 h Build MPTABLE for multi-processor boards
95h Install CD ROM for boot
96 h Clear huge ES segment register
97 h Fix up Multi Processor table
98 h 1-2 Search for option ROMs. One long, two short
beeps on checksum failure
Page 82

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
B-4
POST Code Description
99h Check for SMART Drive (optional)
9Ah Shadow option ROMs
9C h Set up Power Management
9D h Initialize security engine (optional)
9Eh Enable hardware interrupts
9Fh Determine number of ATA and SCSI drives
A0h Set time of day
A2h Check key lock
A4h Initialize typematic rate
A8h Erase F2 prompt
AAh Scan for F2 key stroke
ACh Enter SETUP
AEh Clear Boot flag
B0h Check for errors
B1h Inform RomPilot about the end of POST.
B2h POST done - prepare to boot operating system
B4h 1 One short beep before boot
B5h Terminate QuietBoot (optional)
B6h Check password (optional)
B7h Initialize ACPI BIOS
B9h Prepare Boot
BA h Initialize SMBIOS
BBh Initialize PnP Option ROMs
BCh Clear parity checkers
BDh Display MultiBoot menu
BEh Clear screen (optional)
BFh Check virus and backup reminders
C0h Try to boot with INT 19
C1h Initialize POST Error Manager (PEM)
C2 h Initialize error logging
C3 h Initialize error display function
C4 h Initialize system error handler
C5 h PnPnd dual CMOS (optional)
C6 h Initialize note dock (optional)
C7 h Initialize note dock late
C8 h Force check (optional)
C9h Extended checksum (optional)
CAh Redirect Int 15h to enable remote keyboard
CBh Redirect Int 13h to Memory Technologies
Devices such as ROM, RAM, PCMCIA, and
serial disk
CC h Redirect Int 10h to enable remote serial video
Page 83

Appendix B: BIOS POST Codes
B-5
POST Code Description
CDh Re-map I/O and memory for PCMCIA
CEh Initialize digitizer and display message
D2h Unknown interrupt
The following are for boot block in Flash ROM
POST Code Description
E0h Initialize the chipset
E1h Initialize the bridge
E2h Initialize the CPU
E3h Initialize system timer
E4h Initialize system I/O
E5h Check force recovery boot
E6h Checksum BIOS ROM
E7h Go to BIOS
E8h Set Huge Segment
E9h Initialize Multi Processor
EAh Initialize OEM special code
EBh Initialize PIC and DMA
ECh Initialize Memory type
EDh Initialize Memory size
EEh Shadow Boot Block
EFh System memory test
F0h Initialize interrupt vectors
F1h Initialize Run Time Clock
F2h Initialize video
F3h Initialize System Management Manager
F4h Output one beep
F5h Clear Huge Segment
F6h Boot to Mini DOS
F7h Boot to Full DOS
* If the BIOS detects error 2C, 2E, or 30 (base 512K RAM error), it displays an additional
word-bitmap (xxxx) indicating the address line or bits that failed. For example, “2C
0002” means address line 1 (bit one set) has failed. “2E 1020" means data bits 12
and 5 (bits 12 and 5 set) have failed in the lower 16 bits. The BIOS also sends the
bitmap to the port-80 LED display. It first displays the checkpoint code, followed by
a delay, the high-order byte, another delay, and then the loworder byte of the error.
It repeats this sequence continuously.
Page 84

SUPER X5DMS-6GM/X5DMS-8GM User’s Manual
B-6
Notes
 Loading...
Loading...