Page 1

COMBINATION PRINTER
SCP700 SERIES
Programmer’s Manual
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter 1: Outline ....................................................................................... 1
Chapter 2: DIP Switch Settings ................................................................. 2
Accessing the DIP switches ....................................................... 2
Available DIP switch settings .................................................... 3
Chapter 3: Memory Switch Settings .......................................................... 6
Chapter 4: Control Panel Operations ....................................................... 7
Indicator lights ........................................................................... 7
Buttons ....................................................................................... 8
Producing a test print ................................................................. 8
Adjusting the slip printer’s dot alignment ................................. 9
Hexadecimal dump .................................................................. 11
Errors ....................................................................................... 11
Chapter 5: Standard Serial Interface ...................................................... 13
Standard serial interface pins and signal names ...................... 14
Interface connections ............................................................... 15
Data protocol ............................................................................ 16
Chapter 6: Optional Interface .................................................................. 19
Optional serial interface ........................................................... 19
Optional serial interface pins and signal names ....................... 20
Interface connections ............................................................... 21
Data protocol ............................................................................ 21
Optional parallel interface ....................................................... 22
Optional parallel interface pins and signal names ................... 23
Chapter 7: Peripheral Unit Driver Circuit ............................................. 25
Modular plug ............................................................................ 25
Drive circuit ............................................................................. 26
Chapter 8: Automatic Cutter ................................................................... 27
Chapter 9: Control Codes ......................................................................... 28
Appendix: Character Code Tables .......................................................... 77
Page 3

1
Chapter 1: Outline
The SCP700 Series combines both a quick, quiet and highly reliable thermal
receipt printer with an impact dot slip printer, enabling printing on single or
multiple sheets of slip paper of an unspecified size.
The thermal printer enables receipt printing without a thermal ribbon and makes
paper insertion extremely easy.
The biggest advantage of combining the two printer mechanisms into one unit
is that less space, only one power supply and only one port are necessary,
compared with using a slip printer which is separate from a thermal receipt
printer, each requiring space and a power supply.
Thermal printing on receipt paper is quiet and fast.
For improvement purposes, the descriptions and specifications in this
manual are subject to change without notice.
Page 4

2
Chapter 2: DIP Switch Settings
The printer’s DIP switches let you change communications parameters, thermal
printing density, interface type, input buffer size, and emulation. This chapter
explains the settings you can make and tells you how to actually change DIP
switch settings.
Accessing the DIP switches
The DIP switches are located inside the printer, underneath the document table.
Use the following procedure to remove the document table so you can operate
the DIP switches.
Make sure that the printer is turned off and unplugged from its wall outlet.
❏
Open the printer cover.
❏
Use a Phillips head screwdriver to remove the two screws that secure the
❏
document table in place.
Page 5
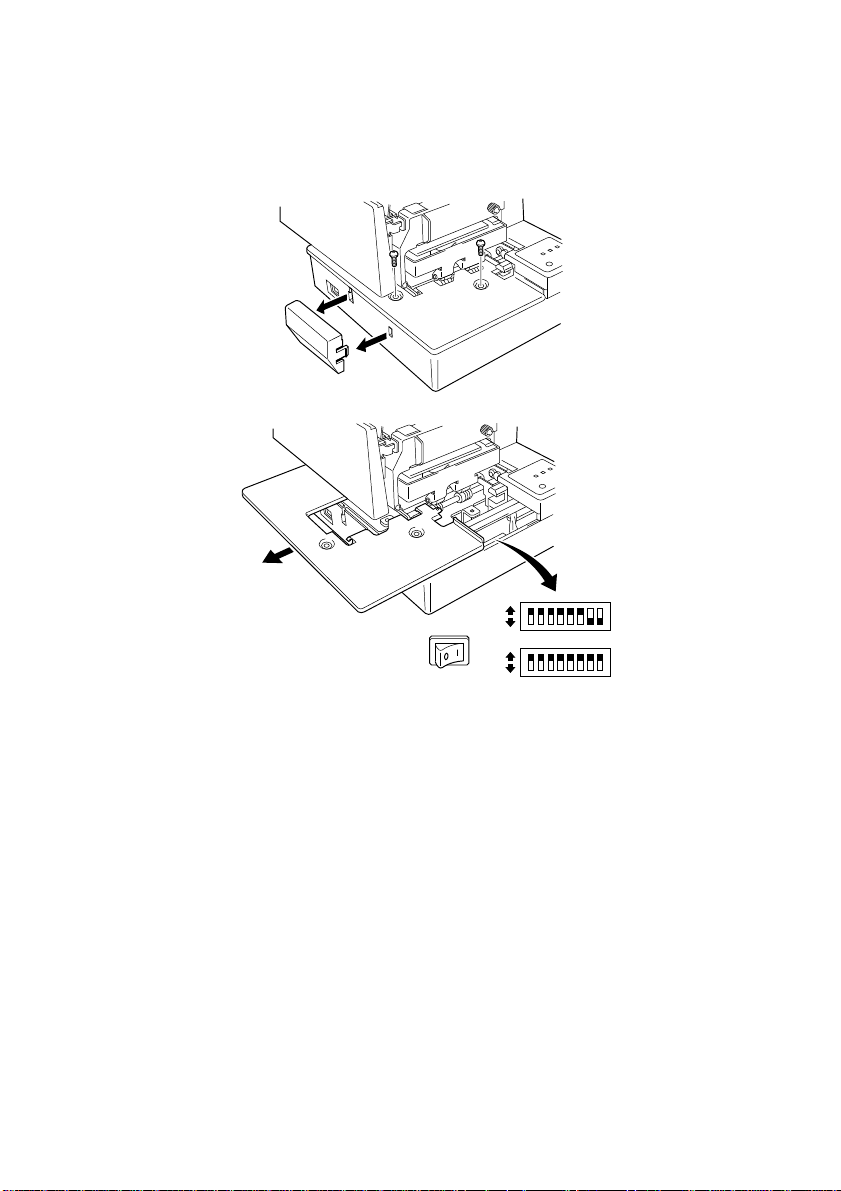
3
Carefully work the document table loose and slide it to the left of the
❏
printer out of the way. It is not necessary to remove the document table
complete, just move it enough so you can get at the DIP switches inside.
❏
After the document table is opened sufficiently, use a thin flat-blade
screwdriver or some other similar object to change DIP switch settings.
❏
Carefully return the document table to its original position and secure it in
place with the two screws.
Available DIP switch settings
There are two DIP switches inside the printer, named DIP Switch 1 and DIP
Switch 2. DIP Switch 1 controls data communication parameters, while DIP
Switch 2 controls other settings.
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Page 6
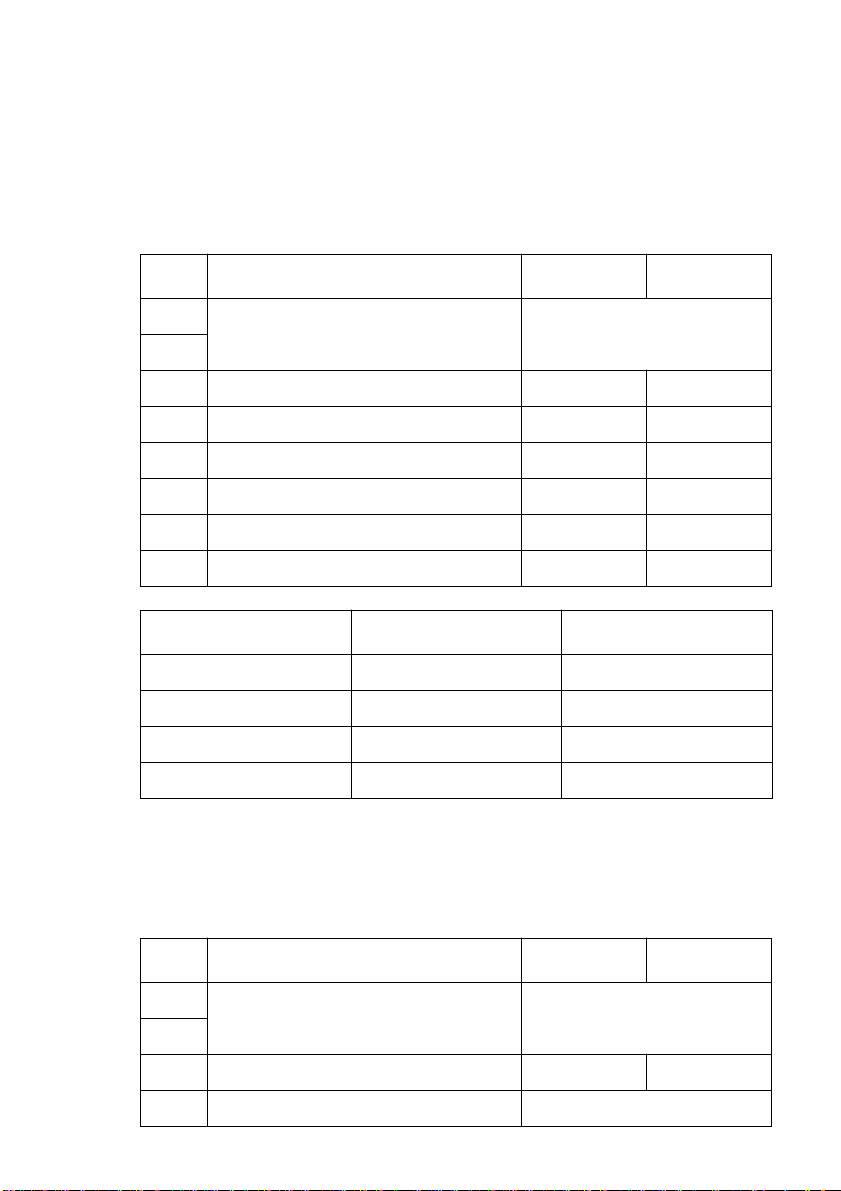
4
DIP Switch 1
The following table shows all the possible settings for DIP Switch 1. This
switch sets the transmission parameters of the Standard Serial Interface. All
switch settings, except for 1-7 and 1-8, are ON when the printer is shipped from
the factory.
Switch Parameter ON OFF
1-1
1-2
1-3 Data Length 8 bits 7 bits
1-4 Parity Check Disabled Enabled
1-5 Parity Selection Odd Even
1-6 Handshake DTR/mode XON/XOFF mode
1-7 Serial I/F Pin 6 Reset Signal Active Inactive
1-8 Serial I/F Pin8 Reset Signal Active Inactive
DIP Switch 2
The following table shows all the possible settings for DIP Switch 2. The
factory default setting for this switch is all ON.
Baud Rate See table below
Baud Rate Switch 1-1 Switch 1-2
2400BPS OFF OFF
4800BPS ON OFF
9600BPS ON ON
19200BPS OFF ON
Switch Parameter ON OFF
2-1
2-2
2-3 Input Buffer Size 4 KB 45 bytes
2-4 Always ON
Thermal Print Density See table below
Page 7
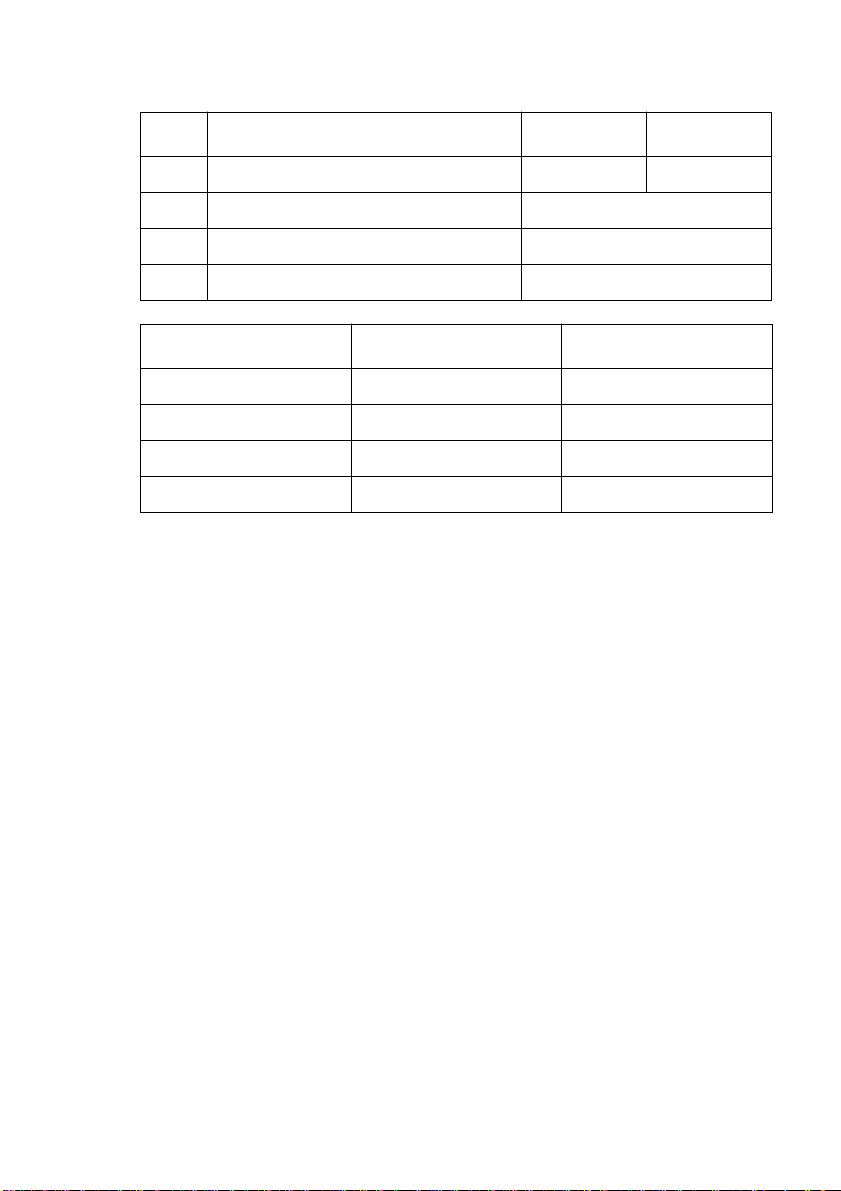
Switch Parameter ON OFF
2-5 Interface Standard Option
2-6 Always ON
2-7 Not Used
2-8 Not Used
Thermal Print Density Switch 2-1 Switch 2-2
Light OFF OFF
Standard ON ON
Heavy ON OFF
Very Heavy OFF ON
5
Page 8
6
Chapter 3: Memory Switch Settings
Each memory switch is a 16-bit word store in EEPROM. For details on the
functions and settings of memory switches, refer to “Chapter 9”.
The table below shows the factory settings for the memory switches.
Memory Switch Hexadecimal Code
0 0000
1 0000
2 0000
3 0000
4 0000
5 0000
Page 9

Chapter 4: Control Panel Operations
The control panel gives you some push-button control over the printer’s receipt
and slip printer operations. It also includes indicator lights, which tell you the
current status of the printer at a glance.
RECEIPT SLIP POWER
7
Indicator lights
The following table describes the meaning of indicator lights when it is on, off,
or flashing.
Indicator Light On Off Flashing (slow) Flashing (fast)
POWER
SLIP
RECEIPT
* All indicators flash to indicate a non-recoverable error.
RECEIPT
Power on Power off
Slip paper
released
Receipt printer
ready
Slip paper
engaged
Receipt printer
not ready
SLIP/RESUME
Dot adjustment
mode
Request
slip paper
Out of receipt
paper/Near end
Automatic
recovery Error
Slip printer error
Receipt printer
error
Page 10
8
Buttons
The following table describes the function of the two control buttons of the
control panel.
Button Description
RECEIPT
SLIP/RESUME
Producing a test print
The following procedure can be used at any time to test the receipt printer and
the slip printer.
Turn on the printer and insert a piece of paper into the slip printer. Also
❏
make sure that roll paper is loaded for the receipt printer.
Note:
If you want to produce a test print on the receipt printer only, simply don’t
insert paper into the slip printer.
❏
Turn off printer power.
❏
While holding down the RECEIPT button, turn printer back on. Keep
RECEIPT depressed for a few moments until the printer beeps and the
receipt printer test print starts.
After the receipt test print is complete, the slip printer will produce a test
print on the paper you inserted in the first step of this procedure. The slip
printer test will continue until it reaches the end of the paper.
Press to feed the thermal paper. Holding down this button feeds paper
at high speed.
1. Press this button to release or engage slip paper from the slip
printer. (Switching from releasing to engaging is only possible if
slip paper is inserted.)
2. Press this button to clear the errors of the slip printer and receipt
printer.
Note:
The slip printer momentarily releases the slip paper when you turn printer
power back on. If you are using a lar g e piece of paper, it may fall out of the slip
printer when this happens, causing the slip printer test to be skipped. Because
of this, it is a good idea to keep hold of the paper in the slip printer when you
turn power back on.
Page 11

Adjusting the slip printer’s dot alignment
You may never have to use the procedure described in this section, but after you
have been using your printer for some time you may find that the dots of some
graphics do not align correctly. For example, what should look like:
may come out looking like one of the following:
or like this
This is caused when mechanical parts of the printer get out of alignment. This
happens only rarely and you may never experience it at all throughout the life
of the printer. If you do have problems, use the following procedure to correct it.
Execute the test print
❏
When the slip printer produce the test print, hold down the control panel’s
❏
RECEIPT and SLIP/RESUME buttons, to enter the Dot Alignment
Adjust Mode. The POWER indicator flashes slowly to indicate this mode.
Entering the Dot Alignment Adjust Mode causes seven blocks of characters to
be printed as shown below. An asterisk to the left of the blocks indicates which
setting is currently selected. Use the RECEIPT button to specify which block
has the best aligned characters. Press RECEIPT once to specify the first block,
twice to specify the second block, and so on up to seven times to specify the
seventh block. Pressing the RECEIPT button more than seven times specifies
the seventh block, no matter how many times it is pressed.
9
Page 12

10
Note:
To exit this mode, press the SLIP/RESUME button. The dot alignment adjust
mode setting is stored in the memory, a pattern using the selected setting,
followed by “Adjust Completed” is printed, and the printer ejects the slip paper.
If you press the
after entering the Dot Alignment Adjust Mode, the printer assumes that you do
not want make any settings, so it prints the message “Adjust Complete!” and
exits the mode.
If a paper feed error occurs during this mode, the printer ejects the paper and
this mode is cancelled.
SLIP/RESUME
button without pressing the
RECEIPT
button
Page 13
Hexadecimal dump
This procedure prints in hexadecimal format all codes (character codes and
control codes) that are sent to the printer by the computer. The printer does not
execute any control codes (such as 0A - linefeed), it just prints them out. The
hexadecimal dump is useful when you are writing programs for printer control.
Make sure that roll paper is loaded in the receipt printer.
❏
Turn off the printer.
❏
While holding down the control panel’s SLIP/RESUME button, turn the
❏
printer back on to enter this mode. The printer beeps once to indicate in this
mode.
The printer will now print out the hexadecimal values of any data that is
❏
subsequently sent to it from your computer. The last line buffer should be
flushed by pressing the RECEIPT button.
To exit this mode, turn the printer off.
❏
Errors
There are three types of errors: automatic recovery errors that clear
automatically after some condition is attained, recoverable errors that require
some action by you before they clear, and non-recoverable errors that require
servicing by an authorized dealer. If a slip printer error occurs, the SLIP
indicator flashes quickly. If a receipt printer error occurs, the RECEIPT
indicator flashes quickly.
11
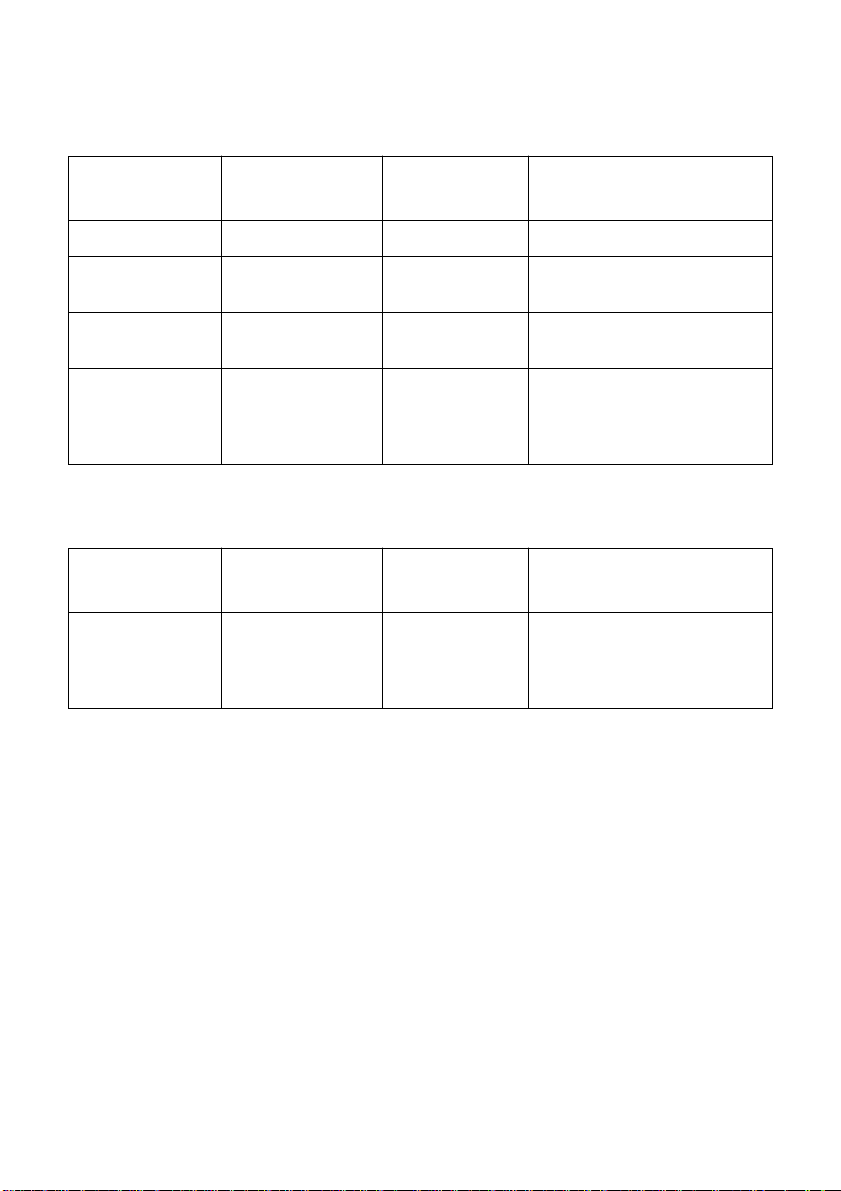
Automatic Recovery Error
Error Name Cause
Head Temperature Error Abnormal thermal head
temperature
POWER
Flashing Pattern
Fast Recovery occurs automatically after
head temperature returns to normal.
Recovery
Page 14
12
Receipt Printer Recoverable Errors
Error Name Cause
Paper Out Error No roll paper Slow Insert paper and press SLIP/RESUME.
Head Up Error Raised receipt printer
head
Near End Roll paper near end Slow Press SLIP/RESUME to resume
Cutter Error Error during roll paper
cutting
RECEIPT
Flashing Pattern
Fast Lower head and press SLIP/RESUME.
printing.
Fast If the blade is in the home position,
press SLIP/RESUME to continue
printing. If the blade is not in the home
position, this is a non-recoverable error.
Recovery
Slip Printer Recoverable Errors
Error Name Cause
Slip printer mechanism
error
• Carriage motor lock
• Timing signal defect
• Abnormal home
position check
SLIP
Flashing Pattern
Fast Correct the problem and press SLIP/
RESUME.
Recovery
Non-recoverable Errors
First try turning the printer off and then on again. If the error persists or if a nonrecoverable error is indicated by all indicators flashing, contact your nearest
authorized dealer.
Page 15
Chapter 5: Standard Serial Interface
This chapter provides detailed specifications for the printer’s standard serial
❏
interface (Connector Type: D-sub 9-pin).
Set the transmission parameters with DIP Switch 1.
Transmission type............Asynchronous serial interface
Baud rate (bps).................2400, 4800, 9600, or 19200
(Selected by DIP switch)
Word format
Start bit:................1
Data bits: ..............7 or 8 (Selected by DIP switch)
Parity:...................Odd, Even, or None
(Selected by DIP switch)
Stop bit:................1
Signal polarities
RS-232C...............Mark = Logic “1” (–3V to –15V)
Space = Logic “0” (+3V to +15V)
Handshaking ....................DTR or XON/XOFF mode (Selected by DIP switch)
13
Mark [1]
b0 b1 b2 b3 b4 b5 b6 (b7)
Space [0]
ABCD
Input (RXD, DSR)
Printer Host computer
Output (DTR, FAULT, TXD, RTS)
Printer Host computer
75188 or equivalent
A: Start bit
B: Data bits
C: Vertical parity bit
D: Stop bit
Page 16
14
r
u
Standard serial interface pins and signal names
Receipt printer head-up error
Receipt printer auto cutter erro
Receipt printer thermistor error
Cover open error
Slip printer mechanical error
1: Error
Receipt paper empty error (incl
1: Empty
Buffer empty
Pin
Signal
No.
1 FG — Frame Ground
2 RXD IN Receive data
3 TXD OUT Transmission data
4 DTR OUT Data terminal ready signal. This signal changes to SPACE when the printer is ready to
5 SG — Signal ground
Direction Function
Name
receive data.
6 DSR IN Signal line that indicates if the host computer can receive data.
SPACE: host can receive
MARK: host cannot receive
The status of this signal is not confirmed.
This signal can be specified as an internal reset signal using Switch 7 of DIP Switch 1
(page 4). MARK of 1ms or longer activates the reset.
7 RTS OUT Same as DTR (Pin 4).
8 INIT IN This signal can be specified as an internal reset signal using Switch 8 of DIP Switch 1
(page 4). SPACE of 1ms or longer activates the reset.
9 N/C — Not connected
Page 17
Interface connections
Refer to the interface specifications for the host computer for details on
❏
connecting to its interface connector. The following illustration shows a
typical connection configuration.
RS-232C
Printer side
(D-sub 9 pin)
15
IBM PC side
(D-sub 25 pin)
F-GND
RXD
TXD
DTR
S-GND
RTS
INIT
N/C
F-GND
RXD
TXD
DTR
S-GND
RTS
INIT
N/C
1
2
3
4
5
6DSR
7
8
9
Printer side
(D-sub 9 pin)
1
2
3
4
5
6DSR
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
20
IBM PC side
(D-sub 9 pin)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
F-GND
TXD
RXD
RTS
CTS
DSR
S-GND
DCD
DTR
DCD
RXD
TXD
DTR
S-GND
DSR
RTS
CTS
RI
Page 18
16
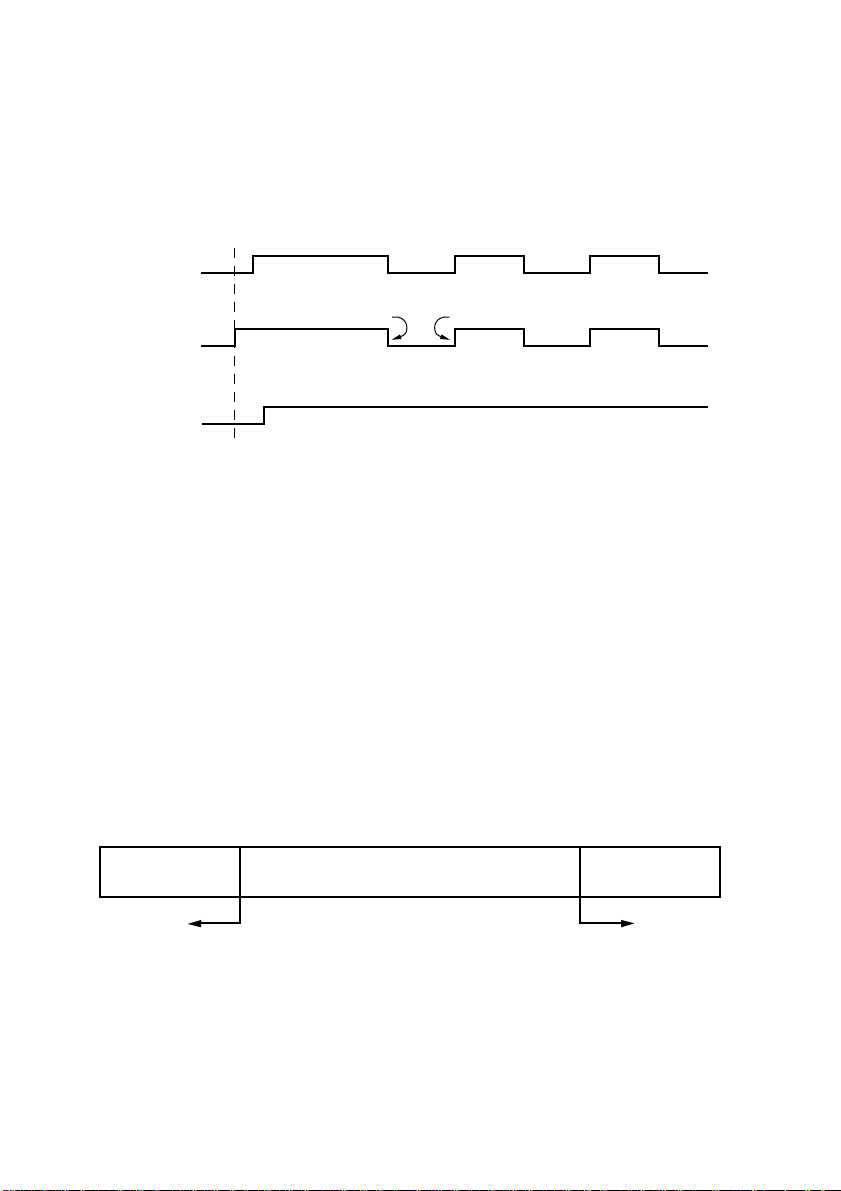
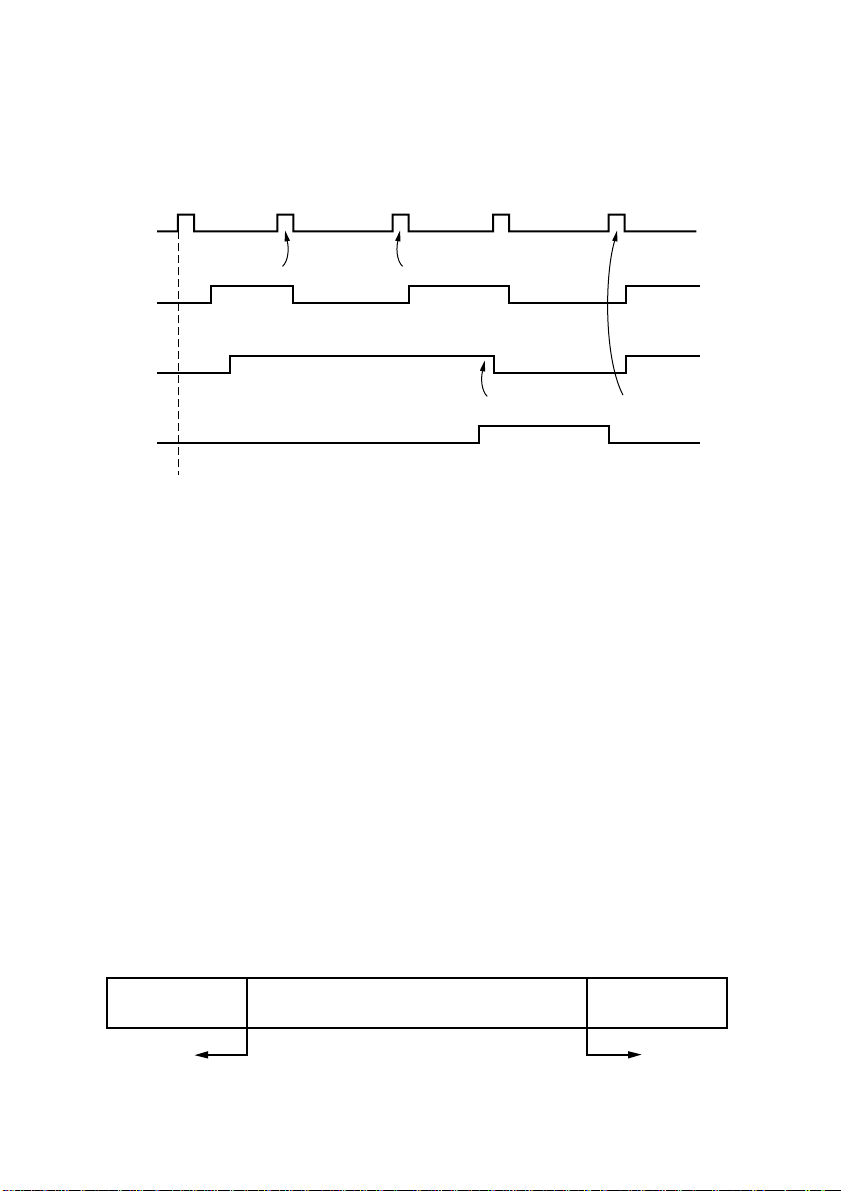
Data protocol
DTR mode
❏
This mode is accessed when the DIP switch 1-6 is set to ON.
Signals are controlled using the DTR line as a BUSY flag.
RXD
DTR
Printing
Power ON
Data Data Data
Buffer full Buffer empty
Immediately after power on (provided that no error occurs), the printer sets DTR
to “SPACE” to indicate that it is ready to receive data. When the host detects
that DTR is in “SPACE” condition, it begins sending text data over the RXD
line.
When the printer’s remaining buffer space falls to *256 bytes or less, the printer
sets DTR to “MARK.” The host responds by halting the data transfer. However,
note that the printer remains capable of receiving data until the buffer becomes
full.
Available buffer space increases as the printer prints the buffered data. When
the printer has cleared all but the last *256 bytes of data, it sets DTR back to
“SPACE” to indicate that it is ready to receive more data.
Data buffer full Nearly full
*256 bytes
remaining
Nearly empty Empty
*256 bytes
DTR
“MARK”
* 16 bytes when the buffer size is set to 45 bytes
DTR
“SPACE”
Page 19
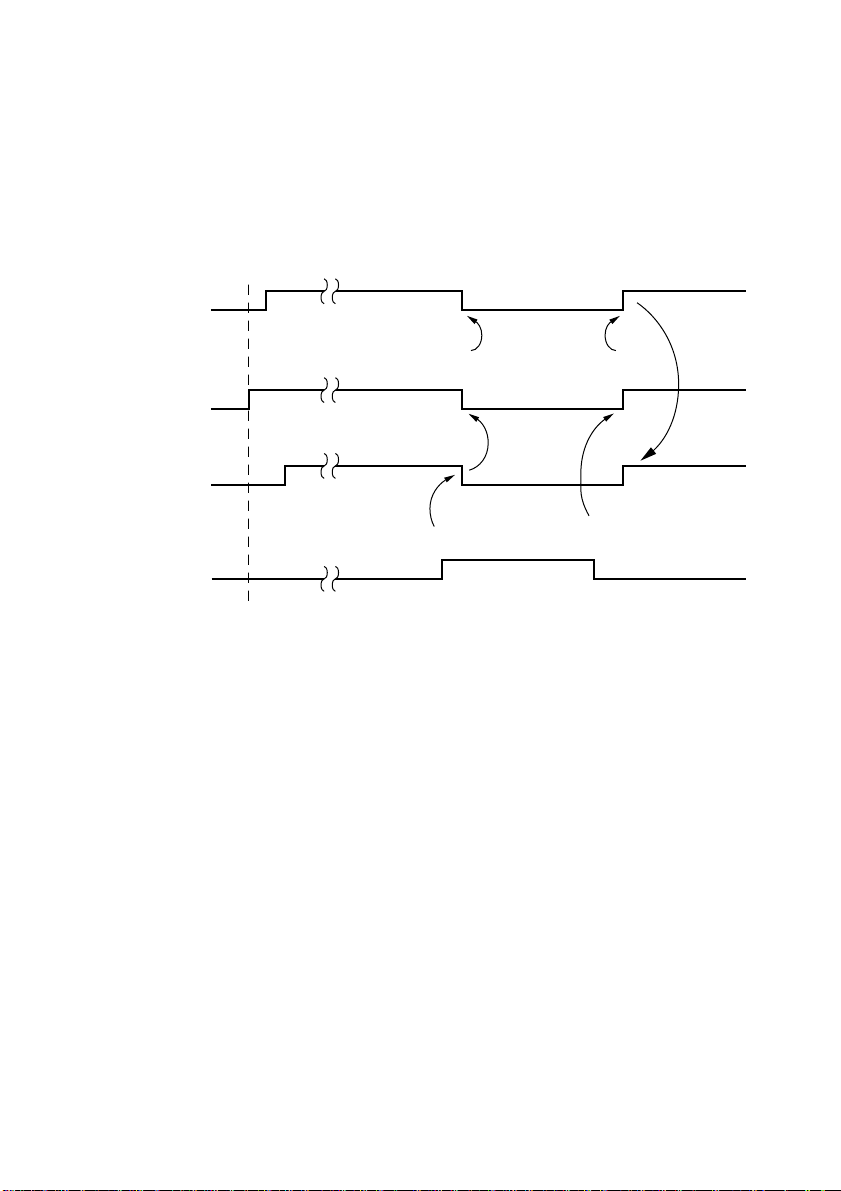
17
Error Condition
Upon detecting an error, the printer immediately sets DTR to “MARK” and
goes off-line. If the printer recovers from the error, DTR is set to “SPACE” and
the printer goes back on-line.
When paper is out
RXD
OFF LINE ON LINE
DTR
Printing
Printer error
Power ON
Error
Recovery
Page 20
18
❏ X-ON/X-OFF mode
This mode is accessed when DIP switch 1-6 is set to OFF.
X–ON X–OFF X–ON X–OFF X–ON
TXD
Bufferfull Bufferempty
RXD
Printing
Printer error
Power ON
The output timing conditions for X-ON and X-OFF are set using Memory Switch
4-C. If memory switch 4-C is set to 0 (factory setting), 1 byte is output for the XON signal when switching from Off-line (Printer Busy) to On-line (Printer
Ready), while 1 byte is output for the X-OFF signal when switching from On-line
(Printer Ready) to Off-line (Printer Busy). If Memory Switch 4-C is set to 1, the
X-ON signals are output every three seconds.
Immediately after power on (provided that no error occurs), the printer informs
the host that it is ready to receive data by outputting the X-ON signal (control code
DC1; valve = 11H) over the TXD line. If necessary the printer repeats the signal
every three seconds until the host begins sending text data over the RXD line.
When the printer’s remaining buffer space falls to *256 bytes or less, the printer
begins to output X-OFF signals (DC3, value = 13H) over the TXD line. The host
responds by halting the data transfer. Note that the printer remains capable of
receiving data until the buffer becomes full. If Memory Switch 4-C is set to 1,
the X-OFF signal is output each time 1 byte of data is received.
Available buffer space increases as the printer prints the buffered data. When the
printer has cleared all but the last *256 bytes of data, it again outputs the X-ON signal.
Data buffer full Nearly full
*256 bytes
remaining
Printer outputs
X-OFF.
* 16 bytes when the buffer size is set to 45 bytes
Data Data Data
Error Recovery
Nearly empty Empty
*256 bytes
Pinter outputs
X-ON.
Page 21

Chapter 6: Optional Interface
Optional serial interface
Use a thin flat-blade screwdriver or some other similar object to change DIP
switch settings on the optional serial interface board.
ON
19
OFF
12345678
The following table shows all the possible settings for the DIP switches. All
switch settings, except for 1-7 and 1-8, are ON when the printer is shipped from
the factory.
Switch Parameter ON OFF
1
2
3 Data Length 8 bits 7 bits
4 Parity Check Disabled Enabled
5 Parity Selection Odd Even
6 Handshake DTR/DSR XON/XOFF
7 Serial I/F Pin 6 Reset Signal Active Inactive
8 Serial I/F Pin 25 Reset Signal Active Inactive
Baud Rate Switch 1 Switch 2
Baud Rate See table below
2400BPS OFF OFF
4800BPS ON OFF
9600BPS ON ON
19200BPS OFF ON
Page 22

20
Optional serial interface pins and signal names
13
25
Pin
Signal
No.
1 FG — Frame Ground
2 TXD OUT Transmission data
3 RXD IN Receive data
4 RTS OUT Data terminal ready signal. This signal changes to SPACE when the printer is ready to
6 DSR IN Signal line that indicates if the host computer can receive data.
7 SG — Signal ground
20 DTR OUT Same as RTS (Pin 4).
25 INIT IN This signal can be specified as an internal reset signal using of DIP Switch 8 (page 19).
Direction Function
Name
receive data.
SPACE: host can receive
MARK: host cannot receive
The status of this signal is not confirmed.
This signal can be specified as an internal reset signal using of DIP Switch 7 (page 19).
MARK of 1ms or longer activates the reset.
SPACE of 1ms or longer activates the reset.
1
14
Page 23
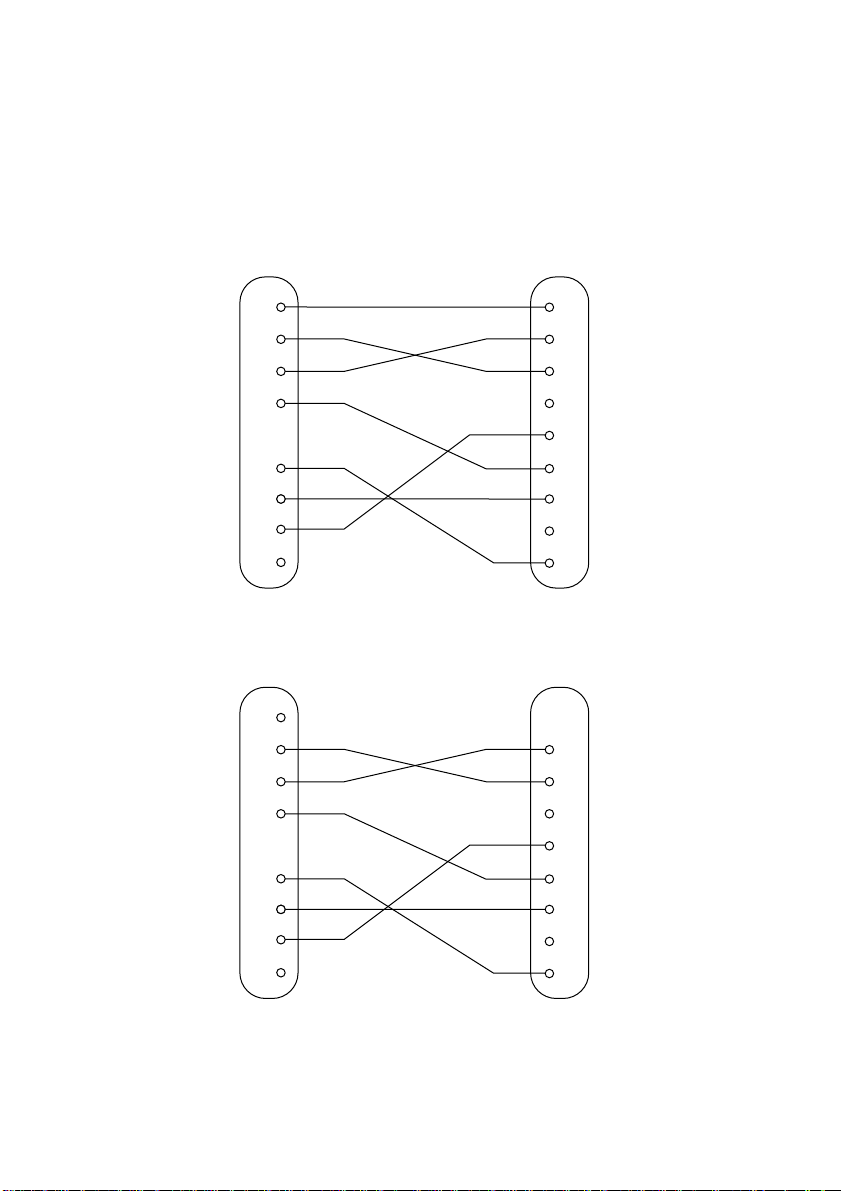
Interface connections
Refer to the interface specifications for the host computer for details on
❏
connecting to is its interface connector. The following illustration shows a
typical connection configuration.
21
F-GND
TXD
RXD
RTS
DSR
S-GND
DTR
INIT
F-GND
TXD
RXD
RTS
DSR
S-GND
DTR
INIT
Printer side
(D-sub 25 pin)
1
2
3
4
6
7
20
25
Printer side
(D-sub 25 pin)
1
2
3
4
6
7
20
25
IBM PC side
(D-sub 25 pin)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
20
IBM PC side
(D-sub 9 pin)
3
2
7
8
6
5
1
4
F-GND
TXD
RXD
RTS
CTS
DSR
S-GND
DCD
DTR
F-GND
TXD
RXD
RTS
CTS
DSR
S-GND
DCD
DTR
Data protocol
The specifications for the DTR and X-ON/X-OFF modes are the same as
❏
for the Standard Serial Interface.
Page 24
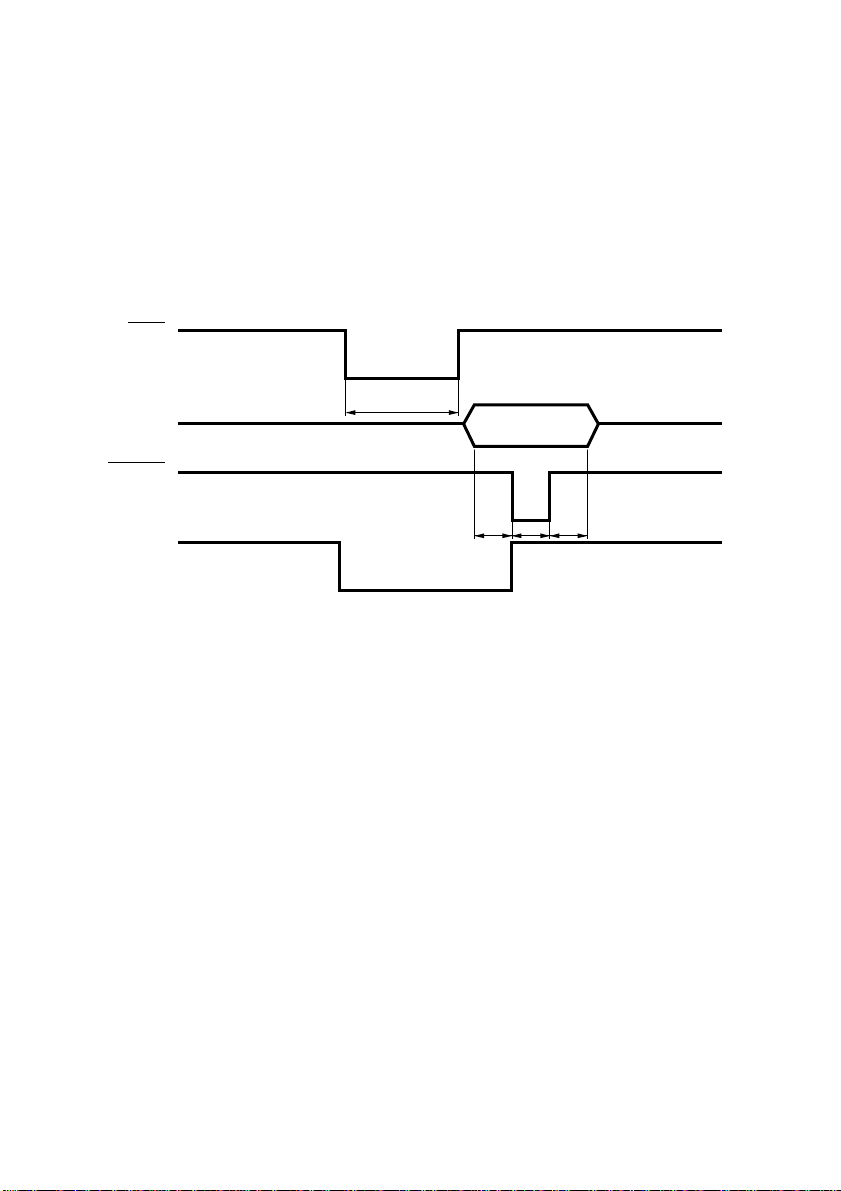
22
Optional parallel interface
Interface: Conforms with Centronics parallel interface standard
Data transfer speed: 1000 ~ 5000 CPS
Synchronization: External strobe pulse
Handshaking: Using ACK and BUSY
Logic level: TTL-level compatible
A C K
DATA
STROBE
Approx. 9ms
BUSY
TTT
T: At least 0.5ms
Page 25
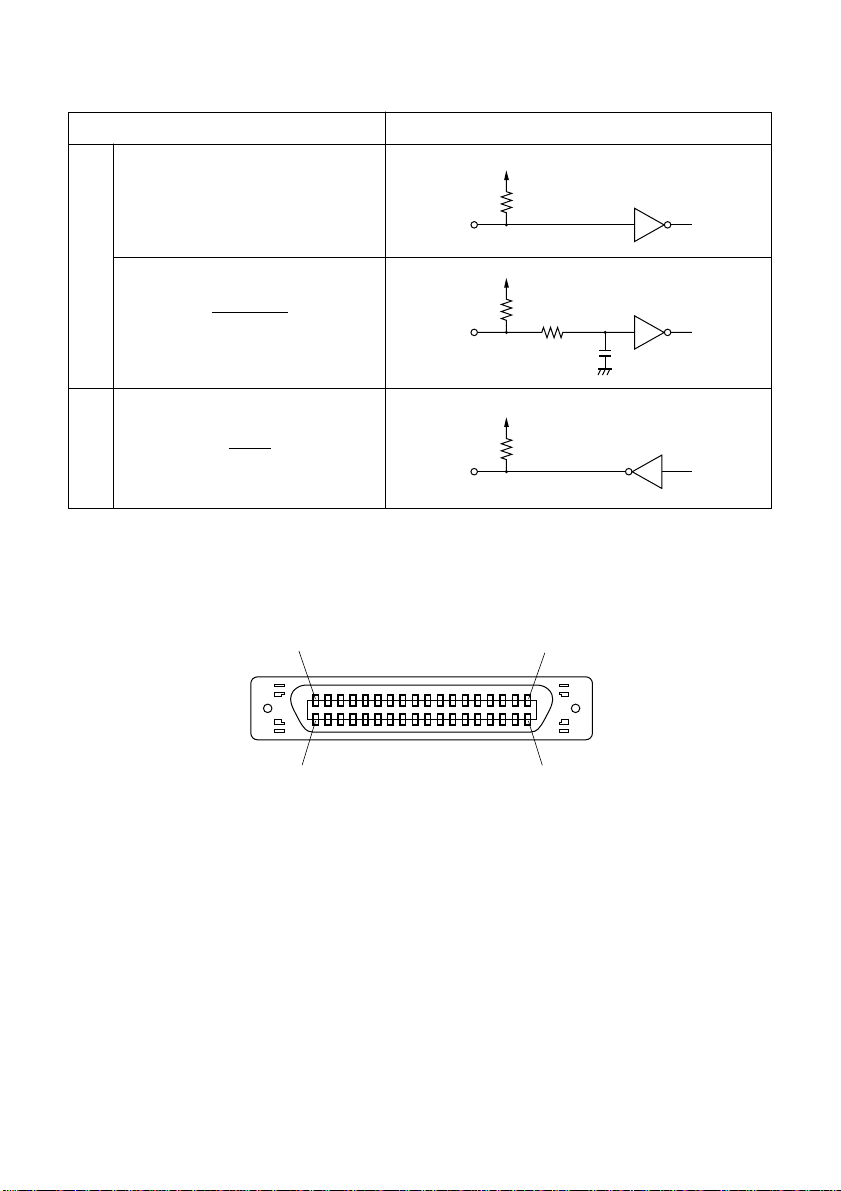
Signal Name Sample Circuit
23
DATA 1
4.7kW
DATA 8
Input
STROBE
1kW
100W
1000pF
1.8kW
BUSY
Output
ACK
Optional parallel interface pins and signal names
(18) (1)
74LS-equivalent
74LS-equivalent
74LS-equivalent
(36) (19)
Page 26
24
Pin
No.
Signal Name Direction Function
1 STROBE IN
2 - 9 DATA 1 - 8 IN
10 ACK OUT 9µs LOW pulse to acknowledge receipt of data
11 BUSY OUT Printer is ready to receive data when LOW. HIGH indicates one of the following
12 PAPER OUT OUT Normally LOW, this signal goes HIGH when the printer is out of paper.
13 SELECTED OUT HIGH when the printer is on line
14 — IN This signal is not checked by printer.
15 N/C — Not connected
16 SIGNAL GND — Signal ground
17 CHASSIS GND — Chassis ground (isolated from logic ground)
18 +5VDC — +5V DC (max. 50mA)
19 - 30 GND — Twisted pair return signal ground level
31 RESET
Signals when data is ready to be read. Signal goes from HIGH to LOW (for at
least 0.5 µs) when data is available.
Information on the first eight bits of parallel data. Each signal is HIGH for logical 1
and LOW for logical 0.
conditions.
• Data being entered
• Printer off line
• Error condition
IN LOW when printer is reset to power-on defaults
32
33 EXT GND — External ground
34 - 35 N/C — Not connected
36 — IN This signal is not checked by printer.
ERROR
OUT Normally HIGH, this signal goes LOW to signal that printing is disabled due to an
error condition.
Page 27

Chapter 7: Peripheral Unit Driver Circuit
The main logic board of this printer includes a circuit for driving peripheral
units, such as cash drawers. A modular connector for connection of the
peripheral unit is located on the back of the printer. To connect to the drive
circuit, connect the peripheral unit to the modular connector using a cable
supplied by you that meets the following specifications.
• Use a cable with a modular plug like that one shown in the figure below.
Important!
Never connect any other type of plug to the peripheral unit connector.
Modular plug
Modular plug: MOLEX 90075-0007,
AMP641337, or JAPAN BURNDY B-66-4
16
Shield
Wire lead
25
Ferrite core
1 loop
Page 28

26
Drive circuit
The recommended drive unit is shown below.
[Drive output 24V, max. 1.0A]
F.G
M-GND
M-GND
TR3
TR1
TR2
+5V
+24V
R2
D1
7824
D2
R1
Printer side User side
1
2
3
4
5
6
With shield
L1
L2
Peripheral
unit 2
Frame
ground
Peripheral
unit 1
R3
4.7kΩ
1/4W
Compulsion
switch
Notes
• Peripheral Units 1 and 2 cannot be driven simultaneously.
• For continuous driving, do not use drive duty above 20%.
• Compulsion switch status is available as status data.
• Minimum resistance for coils L1 and L2 is 24Ω.
• Absolute maximum ratings for diodes D1 and D2 (Ta = 25°C) are:
Average Rectified Current Io = 1A
Maximum forward surge current (60Hz, 1-cycle sine wave) I
FSM
= 40A
• Absolute maximum rating for transistors TR1 and TR2 (Ta = 25°C) are:
Collector current Ic = 2A
Page 29

Chapter 8: Automatic Cutter
1 The cutter operates in response to data commands. To enable cutter
operation, set Memory Switch #2-8 to indicate that the cutter is installed.
2 NEVER place fingers or metal objects in the cutter area.
3 If a jam occurs in the cutter area, switch off the power, use tweezers to
remove the jammed paper, then switch the power back on. The printer will
return the blade to the home position.
4 Never clean the cutter blade with alcohol or any other solvent, as this may
remove the blade’s lubrication and shorten the blade life.
27
Page 30

28
Chapter 9: Control Codes
Print Station Selection
Control codes Hexadecimal codes Function
<ESC> “+” “A” 0
<ESC> “+” “A” <0>
<ESC> “+” “A” 3
<ESC> “+” “A” <3>
1B 2B 41 30
1B 2B 41 00
1B 2B 41 33
1B 2B 41 03
Select receipt printer
Select slip printer
Character Selection
Control codes Hexadecimal codes Function
<ESC> “R” n 1B 52 n
<ESC> “/” “1”
<ESC> “/” <1>
<ESC> “/” “0”
<ESC> “/” <0>
<ESC> “b” n1 n2 n3 n4
d1 ... <RS>
<ESC> “M” 1B 4D
<ESC> “p” 1B 70 Select 14-dot pitch printing
<ESC> “P” 1B 50
<ESC> “:” 1B 3A
<ESC> <SP> n 1B 20 n Set character spacing
<SO> 0E
<DC4> 14
<ESC> “W” n 1B 57 n
<ESC> <SO> 1B 0E
1B 2F 31
1B 2F 01
1B 2F 30
1B 2F 00
1B 62 n1 n2 n3 n4
d1 ... 1E
Select international character
set
Select slash zero
Select normal zero
Select bar code printing
Select 12-dot pitch printing
Select 7 × 9 (half dot) font
Select 15-dot pitch printing
Select 5 × 9 (2 pulses = 1 dot)
font
Select 16-dot pitch printing
Select 5 × 9 (3 pulses = 1 dot)
font
Set the printing magnified
double in character width.
Resets the printing
magnified in character width.
Set the magnification rate in
character width.
Sets the printing magnified
double in character height.
Receiptprinter
Slip
printer
C
C
Receiptprinter
Slip
printer
CC
CC33
CC33
C
C
C 38
C
C
C 38
C
C 38
CC38
CC39
CC39
CC39
C
Page
33
33
Page
33
34
38
38
38
38
39
Page 31

29
Control codes Hexadecimal codes Function
<ESC> <DC4> 1B 14
<ESC> “h” n 1B 68 n
<ESC> “i” n1 n2 1B 69 n1 n2
<ESC> “–” “1”
<ESC> “–” <1>
<ESC> “–” “0”
<ESC> “–” <0>
<ESC> “_” “1”
<ESC> “_” <1>
<ESC> “_” “0”
<ESC> “_” <0>
<ESC> “4” 1B 34 Select highlight printing
<ESC> “5” 1B 35 Cancel highlight printing
<SI> 0F Inverted printing
<DC2> 12 Cancel inverted printing
<ESC> “E” 1B 45 Select emphasized printing
<ESC> “F” 1B 46 Cancel emphasized printing
1B 2D 31
1B 2D 01
1B 2D 30
1B 2D 00
1B 5F 31
1B 5F 01
1B 5F 30
1B 5F 00
Resets the printing
magnified in character height.
Sets the magnification rate in
character height.
Sets the magnification rates
in character width and height.
Select underlining
Cancel underlining
Select upperlining
Cancel upperlining
Page Formatting (Line Mode)
Receiptprinter
Slip
printer
C
CC40
C
C
C
CC40
CC41
CC41
CC41
CC41
CC41
CC41
CC42
CC42
Page
39
40
40
Control codes Hexadecimal codes Function
<ESC> “C” n 1B 43 n Set page length in lines
<ESC> “C” <0> n 1B 43 00 n Set page length in inches
<ESC> “N” n 1B 4E n Set bottom margin
<ESC> “O” 1B 4F Cancel bottom margin
<ESC> “1” n 1B 6C n Set left margin
<ESC> “Q” n 1B 51 n Set right margin
Print Position Control
Control codes Hexadecimal codes Function
<LF> 0A Line feed
<CR> 0D Carriage Return
<ESC> “a” n 1B 61 n Feed paper n lines
Receiptprinter
Slip
printer
C 43
C 43
C 43
C 43
CC44
CC44
Receiptprinter
Slip
printer
CC45
CC45
CC45
Page
Page
Page 32

30
Control codes Hexadecimal codes Function
<FF> 0C Form feed
<HT> 09 Horizontal tab
<VT> 0B Vertical tab
<ESC> “z” “1”
<ESC> “z” <1>
<ESC> “0” 1B 30
<ESC> “J” n 1B 4A n
<ESC> “j” n 1B 6A n
<ESC> “B” n1 n2 ... <0> 1B 42 n1 n2 ... 00 Set vertical tab stops
<ESC> “D” n1 n2 ... <0> 1B 44 n1 n2 ... 00 Set horizontal tab stops
1B 7A 31
1B 7A 01
Set line spacing to 4 mm
Set line spacing to 1/6-inch
Set line spacing to 3 mm
Set line spacing to 1/8-inch
One time n/4 mm feed
One time n/72-inch feed
One time n/4 mm backfeed
One time n/72-inch backfeed
Dot Graphics Printing
Control codes Hexadecimal codes Function
<ESC> “K” n <0>
m1 m2 ...
<ESC> “L” n1 n2
m1 m2 ...
<ESC> “k” n <0> m1 ... 1B 6B n 00 m1 ... Print fine density graphics
<ESC> “X” n1n2 m1 ... 1B 58 n1n2 m1... Print fine density graphics
1B 4B n 00 m1 m2
...
1B 4C n1 n2 m1 m2
...
Print normal density graphics
Print high density graphics
Receiptprinter
Slip
printer
C 45
CC45
C 46
C 46
C 46
C 46
C 46
C 46
C 46
C
C 47
C 47
CC48
Receiptprinter
Slip
printer
CC49
CC52
C
C
Page
47
Page
54
57
Download Graphics Printing
Control codes Hexadecimal codes Function
<ESC> “&” “1” “1”
n m1 m2 ... m48
<ESC> “&” <1> <1>
n m1 m2 ... m48
<ESC> “&” <0> n1 n2 1B 26 00 n1 n2
<ESC> “&” “1” “0” n 1B 26 31 30 n
<ESC> “&” <1> <0> n 1B 26 01 00 n
1B 26 31 31 n
m1 m2 ... m48
1B 26 01 01
n m1 m2 ... m48
Define download character
(12 × 24 dot font)
Define download character
(7 × 9, 5 × 9 dot font)
Delete a download character
(12 × 24 dot font)
Receiptprinter
Slip
printer
C 58
C 59
C
Page
61
Page 33

31
Control codes Hexadecimal codes Function
<ESC> “%” “1”
<ESC> “%” <1>
<ESC> “%” “0”
<ESC> “%” <0>
1B 25 31
1B 25 01
1B 25 30
1B 25 00
Enable download character
set
Disable download character
set
Peripheral Device Control
Control codes Hexadecimal codes Function
<ESC> <BEL> n1 n2 1B 07 n1 n2
<BEL> 07 Control peripheral device #1
<FS> 1C
<EM> 19
<SUB> 1A
Define drive pulse width for
peripheral device #1
Control peripheral device #1
immediately
Control peripheral device #2
immediately
Control peripheral device #2
immediately
Auto Cutter Control
Control codes Hexadecimal codes Function
<ESC> “d” “0”
<ESC> “d” <0>
<ESC> “d” “1”
<ESC> “d” <1>
1B 64 30
1B 64 00
1B 64 31
1B 64 01
Full-cut command to the auto
cutter
Partial-cut command to the
auto cutter
Receiptprinter
Slip
printer
CC61
CC61
Receiptprinter
Slip
printer
CC62
CC62
CC62
CC62
CC62
Receiptprinter
Slip
printer
C 62
C 62
Page
Page
Page
Slip Printer Control
Control codes Hexadecimal codes Function
<ESC> <SI> n 1B 0F n Setting slip sensor
<ESC> <FF> n 1B 0C n Slip function
<ESC> <VT> m n 1B 0B m n
<EOT> 04 Slip status enquiry
Set the paper eject direction/
length
Receiptprinter
Slip
printer
C 63
C 63
C 64
C 64
Page
Page 34

32
Page Mode
Control codes Hexadecimal codes Function
<ESC> “n” 1B 6E Select page mode
<ESC> “!” 1B 21 Select line mode
<ESC> “*” ... 1B 2A ...
<ESC> “T” n 1B 54 n
<FF> 0C Print in page mode
Setting print area in page
mode
Setting print direction in page
mode
Other Commands
Control codes Hexadecimal codes Function
<CAN> 18
<DC3> 13 Deselect printer
<DC1> 11 Set select mode
<RS> 1E Beep the buzzer
<ESC> “#N, n1 n2 n3 n4”
<LF> <NUL>
<ESC> “@” 1B 40 Initialize printer
<ENQ> 05 Enquiry
<ESC> “?” <LF> <NUL> 1B 3F 0A 00
1B 23 N 2C n1 n2 n3 n4
0A 00
Cancel printer buffer &
Initialize printer
Set memory switch
Reset printer hardware and
produce a test print.
Receiptprinter
Slip
printer
C 65
C 67
C 68
C 69
C 70
Receiptprinter
Slip
printer
CC71
CC71
CC71
CC71
CC72
CC74
CC74
CC75
Page
Page
Page 35

Printer Station Selection
33
CODE
FUNCTION
Character Selection
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “+” “A” n
Print Station Selection
n = 0, “0” : Selects the receipt printer
This command is only valid when it entered at the beginning of a
line. Be sure to add <LF> in the data immediately before this code.
<ESC> “R” n
Select international character set
Selects an international character set according to the value of n, as
shown below:
0 n 12, “0” n “9”, “A” n “C”
n = 0, “0” : U.S.A. 1, “1” : France 2, “2” : Germany
Although the international character set can also be selected using a
memory switch, the control code setting is given priority.
1B 2G 41 n
3, “3” : Selects the slip printer
1B 52 n
≤ ≤ ≤ ≤ ≤ ≤
3, “3” : England 4, “4” : Denmark Ι 5, “5” : Sweden
6, “6” : Italy 7, “7” : Spain Ι 8, “8” : Japan
9, “9” : Norway 10, “A” : Denmark 2 11, “B” : Spain 2
12, “C” : Latin America
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “/” n
1B 2F n
Select zero style
Causes subsequent zero characters to be printed with a slash when n
is 1, and without a slash when n is 0.
The valve of n can be set to 0(00H) or “0”(30H), or 1(0H) or
“1”(31H).
The default may differ depending on the memory switch setting.
Page 36

34
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “b” n1 n2 n3 n4 d1 ... dk <RS>
1B 62 n1 n2 n3 n4 d1 ... dk 1E
Select bar code printing
Prints bar code according to the value of n1, as shown below:
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
n1: Type of bar code
0 UPC-E
1 UPC-A
2 JAN/EAN-8
3 JAN/EAN-13
4 CODE 39
5 ITF
6 CODE 128
7 CODE 93
8 NW-7
The value of n1 can be set to 0(00H) or 8(08H) or “0”(30H) to
“8”(38H).
n2: Printing character below bar code or line feed
1 Character below bar code is not printed, Line feed is
performed after execution of command.
2 Character below bar code is printed, Line feed is
performed after execution of command.
3 Character below bar code is not printed, Line feed is
not performed after execution of command.
4 Character below bar code is printed, Line feed is not
performed after execution of command.
The value of n2 can be set to 1(01H) to 4(04H) or “1”(31H) to
“4”(34H).
n3: Mode of bar code
UPC-E, UPC-A, JAN/EAN-8, JAN/EAN-13, CODE 128,
CODE 93
1 Minimum module 2 dots
2 Minimum module 3 dots
3 Minimum module 4 dots
Page 37

35
CODE 39, NW-7, ITF
CODE 39, NW-7 ITF
1 Narrow : wide 2:6 dots 2:5 dots
2 Narrow : wide 3:9 dots 4:10 dots
3 Narrow : wide 4:12 dots 6:15 dots
4 Narrow : wide 2:5 dots 2:4 dots
5 Narrow : wide 3:8 dots 4:8 dots
6 Narrow : wide 4:10 dots 6:12 dots
7 Narrow : wide 2:4 dots 2:6 dots
8 Narrow : wide 3:6 dots 3:9 dots
9 Narrow : wide 4:8 dots 4:12 dots
When the value of n3 is UPC-E, UPC-A, JAN/EAN-8, JAN/EAN13, CODE 128 or CODE 93, 1(01H) to 3(03H) or “1”(31H) to
“3”(33H) can be set. When the value of n3 is CODE39, NW-7 or
ITF, 1(01H) to 9(09H) or “1”(31H) to “9”(39H) can be set.
n4: Height of bar code
Can be up to 255 dots (31.9 mm).
If the bar code height is larger than the line feed amount, the line
feed amount is automatically multiplied by an integer.
d1...dk: Bar code data
UPC-E/UPC-A: K = 11 (or 12)
The check digit at the 12th digit is automatically added,
and ignored even if it is specified.
JAN/EAN-8: K = 7 (or 8)
The check digit at the 8th digit is automatically added, and
ignored even if it is specified.
JAN/EAN-13: K = 12 (or 13)
The check digit at the 13th digit is automatically added,
and ignored even if it is specified.
CODE39: The value of k is optional, and the maximum
value also differs according to the modes (21
digits maximum in mode 7).
The start/stop code (“*”) is automatically added.
Page 38

36
ITF The value of k is optional, and the maximum
value also differs according to the modes (40
digits maximum in mode 4).
If the data is number of an odd digits, 0 is
automatically added at the beginning of the data.
CODE 128: The value of k is optional, and the maximum
value also differs according to the modes and the
types of character number (51 digits maximum
in mode 1).
The check character is automatically added.
CODE 93: The value of k is optional, and the maximum
value also differs according to the modes and the
types of character (30 digits maximum in mode
1).
The check characters (C and K) are
automatically added.
NW-7: The value of k is optional, and the maximum
value also differs according to the modes and the
types of character number (29 digits maximum
in mode 7).
The start/stop code is also contained in the data
(it is not automatically added).
The bar code printing start position is at the upper end of the
current line.
If the bar code is positioned beyond the right margin, neither the
bar code nor the character below the bar code will be printed.
Data of CODE 128 and CODE 93
When <LF> is used in a command, some kinds of control code
cannot be sent by the host PC. The control code should be sent
as the data as shown below:
• When sending the following data, express as a set of two
characters.
Express “% (25H)” as “%0 (25H30H)”.
Add “40H-5FH” after “%” for the control codes (00H-1FH).
Express the control code (7FH) as “%5(25H35H)”.
Add “1 - 4 (31H - 34H)” after “%” for the function code.
Add “6 - 8 (36H - 38H)” after “%” for the start code.
Page 39

3) 2-character codes
37
Control codes
CODE FORMAT
NUL 00H %@ 25H 40H
SOH 01H %A 25H 41H
STX 02H %B 25H 42H
ETX 03H %C 25H 43H
EOT 04H %D 25H 44H
ENQ 05H %E 25H 45H
ACK 06H %F 25H 46H
BEL 07H %G 25H 47H
BS 08H %H 25H 48H
HT 09H %I 25H 49H
LF 0AH %J 25H 4AH
VT 0BH %K 25H 4BH
FF 0CH %L 25H 4CH
CR 0DH %M 25H 4DH
SO 0EH %N 25H 4EH
SI 0FH %O 25H 4FH
DLE 10H %P 25H 50H
DC1 11H %Q 25H 51H
DC2 12H %R 25H 52H
DC3 13H %S 25H 53H
DC4 14H %T 25H 54H
NAK 15H %U 25H 55H
SYN 16H %V 25H 56H
ETB 17H %W 25H 57H
CAN 18H %X 25H 58H
EM 19H %Y 25H 59H
SUB 1AH %Z 25H 5AH
ESC 1BH %[ 25H 5BH
FC 1CH %¥ 25H 5CH
GS 1DH %] 25H 5DH
RS 1EH %^ 25H 5EH
US 1FH %_ 25H 5FH
DEL 7FH %5 25H 35H
Special code
CODE FORMAT
% 25H %0 25H 30H
Function codes
CODE FORMAT
FNC1 %1 25H 31H ✩
FNC2 %2 25H 32H ✩
FNC3 %3 25H 33H ✩
FNC4 %4 25H 34H ✩
Start codes
CODE FORMAT
START A %6 25H 36H ✩
START B %7 25H 37H ✩
START C %8 25H 38H ✩
✩ For CODE 128 only.
Page 40

38
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “M”
1B 4D
Receipt printer: Select 12-dot pitch printing
Prints in a 12 × 24 dot font with no spacing between
characters.
Slip printer : Select 7 × 9 (half dot) font
<ESC> “p”
1B 70
Select 14-dot pitch printing
Prints in a 12 × 24 dot font with 2-dot spacing between characters.
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
<ESC> “P”
1B 50
Receipt printer: Select 15-dot pitch printing
Prints in a 12 × 24 dot font with 3-dot spacing
between characters.
Slip printer : Select 5 × 9 (2 pulses = 1 dot) font
<ESC> “:”
1B 3A
Receipt printer: Select 16-dot pitch printing
Prints in a 12 × 24 dot font with 4-dot spacing
between characters.
Slip printer : Select 5 × 9 (3 pulses = 1 dot) font
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> <SP> n
1B 20 n
Set character spacing
Sets the spacing between characters according to the value of n.
The value of n can be set from 0 through 15, or from “0” through “9”
and “A” through “F”.
The default value of n is 0.
Page 41

39
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<SO>
0E
Sets the printing magnified double in character width.
Prints the subsequent data including a character spacing set by
<ESC><SP> n, magnified double in character width.
<DC4>
14
Resets the printing magnified in character width.
Resets the printing magnified in character width set by <SO>,
<ESC> “W” n and <ESC> “i”n1n2.
<ESC> “W” n
1B 57 n
Set the magnification rate in character width
Prints the subsequent data with a character width magnified by a rate
specified by the value of n.
Receipt printer: n= 0, “0”: Reset magnification (same as <DC4>)
1, “1”: Double magnification (same as <SO>)
2, “2”: Triple magnification
3, “3”: Quadruple magnification
4, “4”: Quintuple magnification
5, “5”: Sextuple magnification
Slip printer: n= 0, “0”: Reset magnification (same as <DC4>)
1, “1”: Double magnification (same as <SO>)
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> <SO>
1B 0E
Sets the printing magnified double in character height.
Prints the subsequent data magnified double in character height.
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
<ESC> <DC4>
1B 14
Resets the printing magnified in character height set by
<ESC><SO>, <ESC>“h”n and <ESC> “i” n1n2.
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
Page 42

40
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “h” n
1B 68 n
Set the magnification rate in character height
Prints the subsequent data with a character height magnified by a rate
specified by the value of n.
Receipt printer: n= 0, “0”: Reset magnification (same as
<ESC><DC4>)
1, “1”: Double magnification (same as
<ESC><SO>)
2, “2”: Triple magnification
3, “3”: Quadruple magnification
4, “4”: Quintuple magnification
5, “5”: Sextuple magnification
Slip printer: n= 0, “0”: Reset magnification (same as <DC4>)
1, “1”: Double magnification (same as <SO>)
<ESC> “i” n1 n2
1B 69 n 1 n2
Sets the magnification rates in character width and height
Prints the subsequent data in the size specified by n1 and n2. The
value of n1 indicates the height magnification and the value of n2
indicates the width magnification.
Receipt printer: n1 (n2)= 0, “0”: Normal height (or width) size
1, “1”: Double height (or width) size
2, “2”: Triple height (or width) size
3, “3”: Quadruple height (or width) size
4, “4”: Quintuple height (or width) size
5, “5”: Sextuple height (or width) size
The value of n is between 0(00H) and 5(05H) or “0” (30H) and “5”
(35H). This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “–” n
1B 2D n
Underlining
When the value of n is 1, underlines the subsequent data including a
character spacing set by <ESC><SP> n.
The part to be skipped by the horizontal tab setting and the block
graphic characters are not underlined.
Resets the underline mode when the value of n is 0.
The value of n can be set to 0(00H) or “0”(30H), or 1(01H) or
“1”(31H).
Page 43

41
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “_” n
1B 5F n
Upperlining
When the value of n is 1, over lines the subsequent data including a
character spacing set by <ESC><SP> n.
The part to be skipped by the horizontal tab setting and the block
graphic characters are not upper lined.
Resets the upper line mode when the value of n is 0.
The value of n can be set to 0(00H) or “0”(30H), or 1(01H) or
“1”(31H).
<ESC> “4”
1B 34
Select highlight printing
Prints the subsequent data including a character spacing set by
<ESC><SP> n reversed.
The part to be skipped by the horizontal tab setting is not reversed.
<ESC> “5”
1B 35
Cancel highlight printing
Cancels highlight printing
<SI>
0F
Inverted printing
Causes subsequent characters to be inverted.
Enter this command at the beginning of the line. If this code is
entered at any other position, it will be invalid. Therefore, it is not
possible to mix correct and inverted printing in one line.
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<DC2>
12
Cancel inverted printing
Cancels inverted printing
Enter this code at the beginning of the line.
Page 44

42
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “E”
1B 45
Select emphasized printing
Causes subsequent characters to be emphasized.
<ESC> “F”
1B 46
Cancel emphasized printing
Cancels emphasized printing.
Page 45

Page Formatting (Line Mode)
43
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “C” n
1B 43 n
Set page length in lines
Sets the page length using the current line spacing, where n is
between 1 and 127.
Changing the line spacing later does not alter the physical page
length.
The current line becomes the top of the page.
Resets the bottom margin.
Default page length is 42 lines.
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
<ESC> “C” <0> n
1B 43 00 n
Set page length in inches
Sets the page length to n × 24 mm, where n is between 1 and 22.
The current line becomes the top of the page.
Resets the bottom margin
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
<ESC> “N” n
1B 4E n
Set bottom margin
Sets the bottom margin to n lines at the current line spacing, where n
is between 0 and 255.
Bottom margin is reset when you change the page length.
Setting is invalid if the printing area on one page is 36 mm or less.
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “O”
1B 4F
Cancel bottom margin
Cancels the bottom margin.
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
Page 46

44
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “1” n
1B 6C n
Set left margin at column n at the current character pitch.
The left margin does not move if the character pitch is changed later.
If this function is set in the middle of a line, it will become valid
starting with the following line. When the power is turned on, the left
edge is set as the left margin.
Receipt printer: The setting is invalid if the print area for one line
would be 36 mm or less.
The value of n is between 0 and 255.
Slip printer : The left margin must be at least 18 dots to the left of
the right margin and within the limits below. If the
size of one character and its spacing is larger than
the print area defined by the margins, printing is not
possible and “?” is printed, instead of the character.
The value of n is between 0 and the value of the
right margin - 2.
<ESC> “Q” n
1B 51 n
Set right margin
Set right margin at column n at the current character pitch.
The right margin does not move if the character pitch is changed
later.
If this function is set in the middle of a line, it will become valid
starting with the following line. When the power is turned on, the
right edge is set as the right margin.
Receipt printer: The setting is invalid if the print area for one line
would be 36 mm or less. The value of n is between
0 and 255.
Slip printer : The right margin must be within the limits below
and set so that the allowable print area is more than
18 dots. If the size of one character and its spacing
is larger than the print area defined by the margins,
printing is not possible and “?” is printed, instead of
the character.
The value of n is between 2 and the value of the
maximum number of print columns.
Page 47

Print Position Control
45
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<LF>
0A
Line feed
Prints the current line and feeds the paper to the next line.
<CR>
0D
Carriage return
The <CR> code is valid for both the receipt and slip printers only if
memory switch 3-1 is set to 1. (The factory setting is 0.)
If the <CR> code is valid:
Receipt printer : Functions in the same way as an <LF> code.
Slip printer : The function of the <CR> code changes according to
the setting of memory switch 5-8.
When memory switch 5-8 is set to 0 (factory
setting): Functions in the same way as an <LF>
code (CRLF).
When memory switch 5-8 is set to 1: Executed only
when printing. The paper is not fed (CR).
<ESC> “a” n
1B 61 n
Feed paper n lines
Prints the current line and feeds the paper n lines (where n is between
1 and 127).
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<FF>
0C
From feed
Feeds the paper to the top of the next page, according to the page
length set by <ESC> “C”n or <ESC>”C”<0>n.
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
<HT>
09
Horizontal tab
Moves the print position to the next horizontal tab stop. Ignored if
there is no next horizontal tab stop on the current line.
Page 48

46
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<VT>
0B
Vertical tab
Prints the current line and feeds the paper to the next vertical tab stop
and moves the print position to the left margin.
Performs paper feed if no vertical tabs are set or if the current line is
at or below the last vertical tab stop.
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
<ESC> “z” “1” or <ESC> “z” <1>
1B 7A 31 or 1B 7A 01
Receipt printer: Set line spacing to 4 mm
Sets the distance that the paper advances in
subsequent line feeds to 4 mm.
Slip printer : Set line spacing to 1/6 inch
Sets the distance that the paper advances in
subsequent line feeds to 1/6 inch.
<ESC> “0”
1B 30
Receipt printer: Set line spacing to 3 mm
Sets the distance that the paper advances in
subsequent line feeds to 3 mm.
Slip printer : Set line spacing to 1/8 inch
Sets the distance that the paper advances in
subsequent line feeds to 1/8 inch.
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “J” n
1B 4A n
Receipt printer: One time n/4-mm feed
Performs a line feed of n/4 mm only once after
printing the data in the line buffer. The space setting
for lines do not change. The value of n is between 1
and 255.
Slip printer : One time n/72-inch feed
Performs a line feed of n/72-inch only once after
printing the data in the line buffer. The space setting
for lines do not change. The value of n is between 1
and 255.
Page 49

47
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “j” n
1B 6A n
Receipt printer: One time n/4-mm backfeed
Feeds the paper back n/4 mm only once after
printing the data in the line buffer. The space setting
for lines do not change. This command can also
feed the paper back to a previous page; however,
the position in the line on the previous page is
determined by the page length control.
The value of n is between 1 and 255.
Slip printer : One time n/72-inch backfeed
Performs a line feed of n/72-inch only once after
printing the data in the line buffer. The space setting
for lines do not change. The value of n is between 1
and 255.
<ESC> “B” n1 n2 ... <0>
1B 42 n1 n2 ... 00
Set vertical tab stops
Cancels all current vertical tab stops and sets new vertical tab stops
at lines n1, n2, etc., where n1, n2, etc. are numbers between 0 and
255. A maximum of 16 vertical tab stops can be set.
The tab stops must be specified in ascending order; any violation of
ascending order terminates the tab stop list. Standard termination is
by the <0> control code.
The vertical tab stops are set in terms of the current line spacing and
do not move if the line spacing is changed later.
With <ESC> “B” <0>, all vertical tab stops are cancelled. This
command is only valid with the receipt printer. When the power is
turned on, no vertical tabs are set.
Page 50

48
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “D” n1 n2 ... <0>
1B 44 n1 n2 ... 00
Set horizontal tab stops
Cancels all current horizontal tab stops and sets new tab stops at
columns n1, n2, etc. at the current character pitch, where n1, n2, etc.
are numbers between 1 and 255. A maximum of 16 horizontal tab
stops can be set.
The tab stops must be specified in ascending order; any violation of
ascending order terminates the tab stop list. Standard termination is
by the <0> control code.
With <ESC> “D” <0>, all horizontal tab stops are cancelled. The left
edge of the paper is always the reference point for the horizontal tab
positions, regardless of the left margin setting. When the power is
turned on, no horizontal tabs are set.
Page 51

Dot Graphics Printing
49
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “K” n <0> m1 m2 ...
1B 4B n 00 m1 m2 ...
Print normal density graphics
Receipt printer: Prints a 3 (horizontal) × 3 (vertical) dot bit image for
each dot of entered data. Data extending beyond the
right margin is ignored. The relationship between
the entered data and the actual printing is shown
below. The value of n is between 1 and 192.
DOT Position
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
23
MSB
D8
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
Image data LSB
Page 52

50
Slip printer: Prints a bit image of the number of dots specified by n. After printing the bit
image, the printer automatically returns to the character mode. The
relationship between the pins on the print head and the data is shown below.
Image data
Dot Position
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
(Not Used)
MSB LSB
8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
D
The value of n is between 1 and 210.
A maximum of 210 data bytes can printed in one line. Any data exceeding
210 bytes is ignored. Only uni-directional printing is possible.
Page 53

51
EXAMPLE
We will create the design below using a bit image.
First, since the volume of data is 30, n1 = (1E)
H. If the data m1 ~ m30
is converted to hexadecimal, it appears as shown below.
Data Binary
m1 00000001 01 m11 00111110 3E m21 00111110 3E
m2 00011110 1E m12 00000010 02 m22 00101110 2E
m3 00111110 3E m13 00000010 02 m23 00101110 2E
m4 01011111 5F m14 00111110 3E m24 00111110 3E
m5 00011111 1F m15 00111110 3E m25 00101111 2F
m6 01011110 5E m16 00101111 2F m26 00101111 2F
m7 00011110 1E m17 00101111 2F m27 00111110 3E
m8 00111111 3F m18 00111110 3E m28 00111110 3E
m9 00101111 2F m19 00101110 2E m29 00000010 02
m10 00111110 3E m20 00101110 2E m30 00000010 02
Hexa-
decimal
Data Binary
Hexa-
decimal
Data Binary
decimal
Hexa-
Printing Sample
Page 54

52
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “L” n1 n2 m1 m2 ...
1B 4C n1 n2 m1 m2 ...
Print high density graphics
Receipt printer: Prints a 1 (horizontal) × 3 (vertical) dot bit image
for each dot of entered data. Data extending beyond
the right margin is ignored. The relationship
between the entered data and the actual printing is
shown below. The value of n1 + n2 × 256 is
between 1 and 576.
DOT Position
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
MSB
D8
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
Image data LSB
Page 55

53
Slip printer: Prints a high density bit image of the number of dots specified by n1 and n2.
The value of n1 + 256 × n2 is between 1 and 420.
A maximum of 420 data bytes can printed in one line. Any data exceeding
420 bytes is ignored.
After printing the bit image, the printer automatically returns to the character
mode. The relationship between the pins on the print head and the data is the
same as those shown for the previous bit image code <ESC> “K”.
While printing a high density bit image, the horizontally adjacent dots
cannot be printed.
EXAMPLE
We will create the design below using a bit image.
Printing Sample
First, since the volume of data is 30, n1 = (1E)
H. If the data m1 ~ m30
is converted to hexadecimal, it appears as shown below.
Data Binary
m1 00000001 01 m11 00111110 3E m21 00111110 3E
m2 00011110 1E m12 00000010 02 m22 00101110 2E
m3 00111110 3E m13 00000010 02 m23 00101110 2E
m4 01011111 5F m14 00111110 3E m24 00111110 3E
m5 00011111 1F m15 00111110 3E m25 00101111 2F
m6 01011110 5E m16 00101111 2F m26 00101111 2F
m7 00011110 1E m17 00101111 2F m27 00111110 3E
m8 00111111 3F m18 00111110 3E m28 00111110 3E
m9 00101111 2F m19 00101110 2E m29 00000010 02
m10 00111110 3E m20 00101110 2E m30 00000010 02
Hexa-
decimal
Data Binary
Hexa-
decimal
Data Binary
Hexa-
decimal
Horizontal density is three times that of the bit image for <ESC>“k”.
(Compare the print samples.)
Page 56

54
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “k” n <0> m1 m2 ...
1B 6B n 00 m1 m2 ...
Print fine density graphics
Prints a 1 (horizontal) × 1 (vertical) dot bit image for each dot of
entered data. Data extending beyond the right margin is ignored. The
relationship between the entered data and the actual printing is
shown below. The value of n is between 1 and 72.
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
Page 57

Relationship between image data and print dots
Dot position
55
Image data
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
Page 58

56
EXAMPLE Printing Sample
Data Binary
d1 00000000 00 d2 00000000 00
d3 00011111 1F d4 11111000 F8
d5 00111111 3F d6 11111100 FC
d7 01110111 77 d8 01110111 EE
d9 11111000 F8 d10 00011111 1F
d11 11111000 F8 d12 00011111 1F
d13 11111000 F8 d14 00011111 1F
d15 00001111 0F d16 11110000 F0
d17 00011111 1F d18 11111000 F8
d19 00011111 1F d20 11111000 F8
d21 00111110 3E d22 01111100 7C
d23 00111000 38 d24 00011100 1C
d25 01111001 79 d26 10011110 9E
d27 01110011 73 d28 11001110 CE
d29 01110011 73 d30 11001110 CE
d31 11111001 F9 d32 10011111 9F
d33 11111000 F8 d34 00011111 1F
d35 11111110 FE d36 01111111 7F
d37 11111111 FF d38 11111111 FF
d39 11111111 FF d40 11111111 FF
d41 00000000 00 d42 00000000 00
d43 00000000 00 d44 00000000 00
d45 00000000 00 d46 00000000 00
d47 00000000 00 d48 00000000 00
Hexa-
decimal
Data Binary
Hexa-
decimal
Page 59

57
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
MSB
Dot
Position
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
<ESC> “X” n1 n2 m1 m2 ...
1B 5 n1 n2 m1 m2 ...
Print fine density graphics
Prints a bit image of the input data using horizontal and vertical
resolutions of 8 dots/mm.
Data extending past the right margin is ignored.
The relationship between the input data and the actual printing is
shown below.
≤ ≤
1 n1 + n2 × 256 576
d1•••
LSB
MSB LSB
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
d2•••
MSB LSB
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
d3•••
Page 60

58
Download Graphics Printing
CODE
CODE
HEX
HEX
FUNCTION
EXAMPLE
<ESC> “&” <1> <1> nm1m2... m48
<ESC> “&” “1” “1” nm1m2... m48
1B 26 01 01 nm1 m2... m48
1B 26 31 31 nm1 m2... m48
Define download character
Defines one new character and stores it in RAM for later use.
n is the character code of the character defined and must be between
21H and 7F4.
If the maximum of 32 external characters have already been stored,
the oldest stored external character are deleted so that new external
character can be stored.
The character matrix is 12 dots wide and 24 dots high.
Relationship between the character pattern and the character data is
shown below.
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
Page 61

59
CODE
Data Binary
m1 00011000 18 m2 00000000 00
m3 00111000 38 m4 00000000 00
m5 01111000 78 m6 00000000 00
m7 00011000 18 m8 00000000 00
m9 00011000 18 m10 00000000 00
m11 00011000 18 m12 01100000 60
m13 00011000 18 m14 11000000 C0
m15 00011001 19 m16 10000000 80
m17 00011011 1B m18 00000000 00
m19 00000110 06 m20 00000000 00
m21 00001100 0C m22 00000000 00
m23 00011011 1B m24 11000000 C0
m25 00110111 37 m26 11100000 E0
m27 01100110 66 m28 01100000 60
m29 00000000 00 m30 01100000 60
m31 00000000 00 m32 11000000 C0
m33 00000001 01 m34 10000000 80
m35 00000011 03 m36 00000000 00
m37 00000111 07 m38 11100000 E0
m39 00000111 07 m40 11100000 E0
m41 00000000 00 m42 00000000 00
m43 00000000 00 m44 00000000 00
m45 00000000 00 m46 00000000 00
m47 00000000 00 m48 00000000 00
Hexa-
decimal
Data Binary
Hexa-
decimal
When the 7 × 9 (half dot) character size (default setting) is set:
<ESC> “&” <0> n1 n2 [m0 m1 m2 m3 m4 m5 m6 m7]
n2 – n1 + 1
(1B)H (26)H (00)H n1 n2 [m0 m1 m2 m3 m4 m5 m6 m7] n2 – n1 + 1
When the 5 × 9 dot character size is set:
<ESC> “&” <0> n1 n2 [m0 m1 m2 m3 m4 m5] n2 – n1 + 1
(1B)H (26)H (00)H n1 n2 [m0 m1 m2 m3 m4 m5] n2 – n1 + 1
Page 62

60
FUNCTION
Pin No.
1
(Not used)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
EXAMPLE
Define download character (7 × 9 (half dot) font or 5 × 9 dot font)
Defines download characters
Up to 10 download characters can be defined and the defined
character patterns can be stored in the printer’s RAM.
The values of n1 and n2 are between (21)
H and (7F)H with n1 less
than or equal to n2 and the value of m0 is either (00)H or (80)H.
Defining of download characters begins with character code n1 and
completes with n2. When only one character is defined, n1 = n2.
m0 indicates the relationship between the character pattern and print
head.
m1 m2.... Indicate the character pattern
This command is only valid with the slip printer.
When m0=(00)H
MSB
D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
LSB
Pin No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
(Not used)
When m0=(80)H
MSB
D8 D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1
When the 7 × 9 (half dot) character size (default setting) is set, the
horizontally adjacent dots cannot be printed.
LSB
Printing possible Printing not possible
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
m2 m4 m6
m3 m5 m7
m1
D8
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
m2 m4 m6
m3 m5 m7
m1
Over lapping
horizontally
Over lapping
horizontally
Page 63

61
CODE
CODE
HEX
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “&” <1> <0> n
<ESC> “&” “1” “0” n
1B 26 01 00 n
1B 26 31 30 n
Delete a download character (12 × 24 dot font)
Deletes the download character which was assigned the value n.
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
<ESC> “%” “1” or <ESC> “%” <1>
1B 25 31 or 1B 25 01
Enable download character set
Enables the download character set.
<ESC> “%” “0” or <ESC> “%” <0>
1B 25 30 or 1B 25 00
Disable download character set
Disables the selected download character set and returns to the builtin ROM character set.
Page 64

62
Peripheral Device Control
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> <BEL> n1 n2
1B 07 n1 n2
Define drive pulse width for peripheral device #1
Defines the drive pulse width for peripheral devices requiring other
than standard 200 ms pulse time and delay time.
n1 indicates the energizing time and n2 indicates the delay time,
using 10ms units.
<BEL>
07
Control peripheral device #1
Executes drive pulse for peripheral device #1.
<FS>
1C
Control peripheral device #1 immediately
Executes drive pulse for peripheral device #1 immediately.
<EM>
19
Control peripheral device #2 immediately
Drives peripheral device #2. The drive pulse width and delay time
are fixed at 200 ms.
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<SUB>
1A
Control peripheral device #2 immediately
Drives peripheral device #2. The drive pulse width and delay time
are fixed at 200 ms.
Page 65

Auto Cutter Control
63
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “d” “0” or <ESC> “d” <0>
1B 64 30 or 1B 64 00
Full-cut command to the auto cutter
Cuts the receipt paper fully.
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
<ESC> “d” “1” or <ESC> “d” <1>
1B 64 31 or 1B 64 01
Partial-cut command to the auto cutter
Cuts the receipt paper partially.
This command is only valid with the receipt printer.
Page 66

64
Slip Printer Control
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> <SI> n
(1B)H (0F)H n
Setting slip sensor
Sets the slip printer TOF/BOF sensor according to the value of n.
TOF Sensor BOF Sensor
n = 00, “0” : Valid Valid
01, “1” : Valid Invalid
02, “2” : Invalid Valid
03, “3” : Invalid Invalid
The default value of n is 0.
This command is only valid with the slip printer.
<ESC> <FF> n
(1B)H (0C)H n
Slip function
After printing the data in the line buffer, operates the slip printer
according to the value of n.
n = 00, “0” : Operates the clamp
01, “1” : Releases the paper
02, “2” : Releases the paper and waits until it is removed
03, “3” : Feeds the paper backward (backfeed) until it
moves past the TOF sensor, then releases the
paper. (See NOTE below.)
04, “4” : Feeds the paper into the printer (operational feed)
until it moves past the BOF sensor, then releases
the paper.
05, “5” : Feeds the paper according to the direction and
length set by <ESC> <VT> m n (the paper is not
released)
(NOTE) When the slip paper is attached to duplicates, a paper jam
may occur if the paper is always fed backward. Therefore,
the paper should not be ejected with n=3. To feed slip paper
attached to duplicates backward, use <ESC> <VT> to set
the eject length to about half of the paper length, then eject
the paper using <ESC> <FF> 5.
This command is only valid with the slip printer.
Page 67

65
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> <VT> mn
(1B)H (0B)H mn
Set the paper eject direction/length
Sets the length of the ejection operation performed using <ESC>
<FF> 5 in line mode.
The value of m determines the ejection direction.
When m= “+”: the ejection direction is into the printer (operational
feed), and the ejection length is n lines (at the current
carriage return)
When m= “-”: the ejection direction is backward (backfeed), and
the ejection length is n lines (at the current carriage
return)
When m= 0 : the ejection direction is backward (backfeed), and
the ejection length is n inches
The default value of n is 0.
This command is only valid with the slip printer.
<EOT>
(04)H
Slip status enquiry
Sends slip printer status information to the host computer.
Status b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
10
Constantly
set at “1”
Constantly
set at “0”
TOF sensor 1: No paper
BOF sensor 1: No paper
Slip printer mechanical error 1: Error
Slip release/clamp 1: Clamp
0: Release
This command is only valid with the slip printer.
Page 68

66
Page Mode
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “n”
(1B)H (6E)H
Select page mode
Switches from line mode (default) to page mode.
This code is only valid when it is entered at the beginning of the line.
The page mode is suitable even though data is printed in the
rotational direction specified by <ESC> “T” n and in the page
coordinate range specified by <ESC> “*” •••, and though paper with
a horizontal length of a check, etc. is rotated 90 or 270 and printing
is carried out in all modes.
In page mode, since OR is applied to the data in the print area,
characters and bit images can be printed overlapping each other and
each character can be rotated and oriented independently.
In page mode, if printing data and a command such as <CR> or
<LF> are sent in the same way as in line mode, there is an automatic
rotation to the printer side.
All printing of data in the print area is performed according to <LF>.
After printing according to <FF>, the printer returns to line mode. In
addition, if <ESC> “!”, <ESC> “@” or <CAN> are specified,
printing is not performed and the printer leaves page mode and
returns to line mode.
While returning to line mode, the data in the printer buffer, the area
coordinates and the rotation directions are all cleared.
This command is only valid with the slip printer.
The following restrictions exist in page mode.
1) In page mode, half-dot characters cannot be printed since
printing is carried out in normal dot units.
When entering page mode, the ANK font is automatically set to
a 5 × 9 (2 pulses = 1 dot) font.
Since the 7 × 9 font and 5 × 9 (3 pulses = 1 dot) font commands
cannot be executed in page mode, they are executed after the
printer returns to line mode.
High density printing of graphics is ignored.
Page 69

67
2) Paper feed command
In paper mode, the paper feed command and carriage return are
executed in units of dots. A 1/72-inch (0.353-mm) paper feed is
considered 1 dot. Since a 1-dot pitch in the horizontal direction
is 0.30 mm and a 1-dot pitch in the vertical direction is 0.353
mm, the paper amount that is fed while printing using a 90 or
270 rotation is less when compared with a 0 or 150 rotation.
As a result, when printing using a 90 or 270 rotation, execute a
test print, check the horizontal and vertical dot alignment, then
adjust the alignment as necessary.
3) The following commands are not executed in page mode, but
are stored and executed when the printer returns to line mode.
Select 7 × 9 (half dot) font <ESC> “M”
Select 5 × 9 (3 pulses = 1 dot) font <ESC> “:”
Inverted printing/Cancel inverted
printing
Select highlight printing/Cancel
highlight printing
Underlining <ESC> “-” n
Upperlining <ESC> “_” n
Select print direction <ESC> “U” n
Select emphasized printing/Cancel
emphasized printing
Select left margin <ESC> “1” n
Select right margn <ESC> “Q” n
<SI>/<DC2>
<ESC> “4”/<ESC> “5”
<ESC> “E”/<ESC> “F”
Page 70

68
4) The following commands are ignored in page mode.
One time backfeed <ESC> “j” n
Print high density graphics <ESC> “L” •••
Slip function <ESC> <FF> n
Select print station <ESC> “+” “A” n
STX-ETX mode <STX> ••• <ETX>
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “!”
(1B)H (21)H
Select line mode (default)
If this command is specified while in page mode, printing is not
carried out and the printer returns to line mode.
This command is only valid with the slip printer.
Page 71

69
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “*” X
L XH YL YH dXL dXH dYL dYH
1B 2A XL XH YL YH dXL dXH dYL dYH
Setting print area in page mode
The coordinates of the current position at the moment that page
mode is entered are (0,0). The starting point of the print area is
defined by XL, XH, YL and YH. In addition, the length DX in the X
direction is specified by dXL and dXH, and the length DY in the Y
direction is specified by dYL and dYH.
Current position (0,0)
DX
(X0,Y0)
Paper feed direction
Print areaDY
Starting point X
0 = XL + (XH × 256) dots
Starting point Y0 = YL + (YH × 256) dots
Length in horizontal direction DX = dXL + (dXH × 256) dots
Length in vertical direction DY = dYL + (dYH × 256) dots
The values of XL, YL, dXL and dYL are between 0 and 255, and the
values of XH, YH, dXH and dYH are between 0 and 1.
However, dXL = dXH = 0 and dYL = dYH = 0 are not included.
In addition, since the maximum range in the X direction (XO + DX)
is 210 dots and the maximum range in the Y direction (YO + DY) is
720 dots, each parameter should be specified to satisfy these ranges.
When the power is turned on, XL = XH = YL = YH = 0 (XO,YO =
0,0)
dXL = 210, dXH = 0 (DX = 210) and
dYL = 64, dYH = 2 (DY = 576).
This command is stored, even in line mode, and the position at the
time that page mode is entered is used as the standard point (0,0).
Since the bottom of the character is used as the baseline, a minimum
print area of 8 dots are necessary in the character height direction to
print data in the page. (When printing a magnified character height,
the paper must be fed before printing.)
This command is only valid with the slip printer.
Page 72

70
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “T” n
(1B)H (54)H n
Setting print direction in page mode
Sets the direction in which the printing will be executed in page
mode according to the value of n.
This command is only valid in line mode.
Value of n Mode
0 or “0” 0 rotation mode (uni-directional printing)
1 or “1” 270 rotation mode (uni-directional printing)
2 or “2” 180 rotation mode (uni-directional printing)
3 or “3” 90 rotation mode (uni-directional printing)
The default value of n is 0.
<Rotation direction examples>
n = 1 n = 1 or 4 n = 2 n = 3
0° rotation 270° rotation 180° rotation 90° rotation
12345•••
ABCDE•••
ABCDE•••
12345•••
ABCDE•••
12345•••
12345•••
ABCDE•••
This command is only valid with the slip printer.
Page 73

71
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<FF>
(0C)H
Print in page mode (only valid when in page mode)
This command can only activate the slip printer. In page mode, all
page data in the page area is printed, then the printer returns to line
mode. After all the page data is printed, the data in the page, the page
print area and the print direction are all initialized.
In addition, this command has no function in line mode.
Page 74

72
Other Commands
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<CAN>
(18)
Cancel printer buffer & Initialize printer
Clears the line buffer, and initializes the commands set already.
Does not affect the external equipment drive conditions set by the
code <ESC> <BEL> n1 n2. (This is the same during a mechanical
error.)
(Line buffer means the print data expansion area.)
If <CAN> is specified in page mode while printing using the slip
printer, printing is not carried out and the printer returns to line mode
from page mode.
In addition, <CAN> initializes the print station selection. If the slip
printer was selected, the receipt printer will be re-selected.
This command cannot recover from errors or return to the on-line
status from off-line.
<DC3>
13
Deselect printer
Deselects the printer. The printer disregards all subsequent
characters and commands except <DC1>, which activates the
printer.
<DC1>
(11)H
Set select mode
When the printer receives a <DC1> code, the deselect mode is
canceled and data following this code is input to the buffer.
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<RS>
1E
Beep the buzzer
Sounds a brief beep tone.
Page 75

73
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC “# N , n1n2n3n4” <LF> <NUL>
1B 23 N 2C n1n2n3n4 0A 00
Set the memory switch. In order to enable changed memory switch
setting, turn the printer OFF and ON again or send printer reset
command (<ESC> “?”<LF><NUL>”) to the printer. Changed
memory switch settings are stored in EEPROM and these setting will
be stored as long as the time when they are changed again.
N :Memory switch number (“0”, “1”, “2”, “3”, “4”, “5”)
n1n2n3n4 :Mode settings (For details see below)
1) N=0
n1 :Always “0”
n2 :Always “0”
n3 :Always “0”
(Default)
Parameter Setting “0” “4”
n4 Receipt FF command Form Feed Paper Feed,
Cut & Back
2) N=1
n1 :Always “0”
n2 :Always “0”
(Default)
Parameter Setting “0” “1”
n3 Zero style Normal zero Slashed zero
n4 International character
set
See below
n4 Country n4 Country n4 Country n4 Country
“0” USA “3” UK “6” Italy “9” Norway
“1” France “4” Denmark #1 “7” Spain #1 “A” Denmark #2
“2” Germany “5” Sweden “8” Japan “B” Spain #2
n4 Country
“C” Latin America
Page 76

74
3) N=2
n3 :Always “0”
(Default)
Parameter Setting 0 1
n1 Receipt printer ESC d
command
Receipt printer
n2 Receipt printer cutter Valid Invalid
n3 Cover Open Invalid Valid
n4 Receipt printer paper
near end
Cut Paper feed,
& Cut
Invalid Valid
4) N=3
n1 :Always “0”
(Default)
Parameter Setting 0123
n2 Character table Normal IBM Katakana IBM
n3 Receipt printer printer
column
n4 CR code Invalid Invalid Valid Valid
Receipt printer line feed
(mm)
48 38 – –
4343
5) N=4
n2 :Always “0”
n3 :Always “0”
n4 :Always “0”
(Default)
Parameter Setting 0 1
n1 X on/X off Timing When
Toggled
every 3 sec
6) N=5
n1 :Always “0”
n3 :Always “0”
(Default)
Parameter Setting 0123
n2 When slip printer <CR>
code is valid
n4 Slip printer automatic
clamp
Slip printer automatic
starting print positioning
Print +
line feed
(CRLF)
Valid Valid Invalid Invalid
Valid Invalid Valid Invalid
print
(CR)
––
Page 77

75
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “@”
1B 40
Initialize printer
Reinitializes the printer. Clears the print buffer and returns settings
to their power-up values.
Does not clear the input buffer, downloaded characters, or conditions
for peripheral devices.
In addition, this command initializes the print station selection. If the
slip printer was selected, the receipt printer will be re-selected.
If this command is specified in page mode while printing using the
slip printer, printing is not carried out and the printer returns to line
mode from page mode.
This command cannot recover from errors or return to the on-line
status from off-line.
<ENQ>
05
Enquiry
Causes the printer to transmit a status byte.
Page 78

76
Status byte
Status
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
0
Constantly
set at “0”
Vertical parity error
1: Error
Framing error
1: Error
Receipt printer head-up error
Receipt printer auto cutter error
Receipt printer thermistor error
Cover open error
Slip printer mechanical error
1: Error
Receipt paper empty error (including near end)
1: Empty
Buffer empty
1: Empty
Buffer overflow
1: Overflow
Compulsion switch
1: High level (Switch is set to ON.)
CODE
HEX
FUNCTION
<ESC> “?” <LF> <NUL>
1B 3F 0A 00
Reset the printer hardware.
Resets the printer hardware and produces a test print
Page 79

Appendix : Character Code Tables
77
Page 80

78
(Character table: Normal)
Page 81

(Character table: katakana)
79
Page 82

80
(Character table: IBM)
Page 83

International Character Set
81
Page 84

HEAD OFFICE
STAR MICRONICS CO., LTD.
536 Nanatsushinnya, Shimizu, Shizuoka, 424 Japan
Tel: 0543-47-0112, Fax: 0543-48-5271
OVERSEAS SUBSIDIARY COMPANIES
STAR MICRONICS AMERICA, INC.
70-D Ethel Road West, Piscataway, NJ 08854 U.S.A
Tel: 908-572-9512, Fax: 908-572-5095
STAR MICRONICS DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Westerbachstraße 59, D-60489 Frankfurt, Germany
Tel: 069-789990, Fax: 069-781006
STAR MICRONICS U.K. LTD.
Star House, Peregrine Business Park, Gomm Road,
High Wycombe, Bucks, HP 13 7DL, U.K.
Tel: 01494-471111, Fax: 01494-473333
Printed in Japan, 80872035
 Loading...
Loading...