Page 1

DOT MATRIX PRINTER MECHANISM
MP111MP-24G-A
MP115MP-24G-A
SPECIFICATION
AND
OPERATION MANUAL
Page 2

NOTICE
• All rights reserved. Reproduction of any part of this manual in any form whatsoever, without STAR’s
express permission is forbidden.
• The contents of this manual are subject to change without notice.
• All efforts have been made to ensure the accuracy of the contents of this manual at the time of going to
press. However, should any errors be detected, STAR would greatly appreciate being informed of them.
• The above notwithstanding, STAR can assume no responsibility for any errors in this manual.
Copyright 1999 Star Micronics Co., LTD.
Page 3

Contents
1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION ................................................................................................................ 1
2. CONSTRUCTION ................................................................................................................................ 2
2.1 Configuration ........................................................................................................................... 2
2.2 Principle of Operation.............................................................................................................. 2
3. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS .......................................................................................................... 5
3.1 Printing Specifications ............................................................................................................. 5
3.2 Paper Specifications................................................................................................................. 6
3.3 Ink Ribbon Specifications........................................................................................................ 7
3.4 Connector Specifications ......................................................................................................... 9
3.5 Print Timing ........................................................................................................................... 11
3.6 Timing Chart.......................................................................................................................... 12
3.7 Print Head Specifications....................................................................................................... 14
3.8 CR Motor Specifications........................................................................................................ 18
3.9 Paper Feed Motor Specifications ........................................................................................... 20
3.10 Ribbon Shift Solenoid (RS-SOL) Specifications................................................................... 21
3.11 Timing Signal Detector Specifications .................................................................................. 22
3.12 Home Position Detector (HP-sig) Specifications .................................................................. 23
3.13 Paper-out Detector (PE-sig) Specifications ........................................................................... 23
3.14 Ribbon Position Detector (RS-sig) Specifications (MP115MP only) ................................... 24
3.15 Dimension and Weight .......................................................................................................... 24
4. RELIABILITY SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................................................. 27
5. SETTING THE RIBBON CARTRIDGE ......................................................................................... 28
6. SETTING THE PAPER ..................................................................................................................... 29
6.1 Setting the Paper .................................................................................................................... 29
6.2 Removing the Paper............................................................................................................... 29
7. INSTALLATION ................................................................................................................................ 30
8. OPERATIONAL NOTES .................................................................................................................. 35
8.1 Power ON/OFF Note ............................................................................................................. 35
8.2 Carriage Motor Protection Method (Against Mechanical Errors) ......................................... 36
8.3 Other Notes ............................................................................................................................ 36
9. POWER SUPPLY CAPACITY .........................................................................................................37
9.1 24 V Line ............................................................................................................................... 37
9.2 5 V Line ................................................................................................................................. 37
10.OPTIONS............................................................................................................................................. 38
Page 4
1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
MP111MP-24G-A and MP115MP-24G-A are serial impact dot matrix printer mechanisms used to record
data and as electrical equipment such as for ECR.
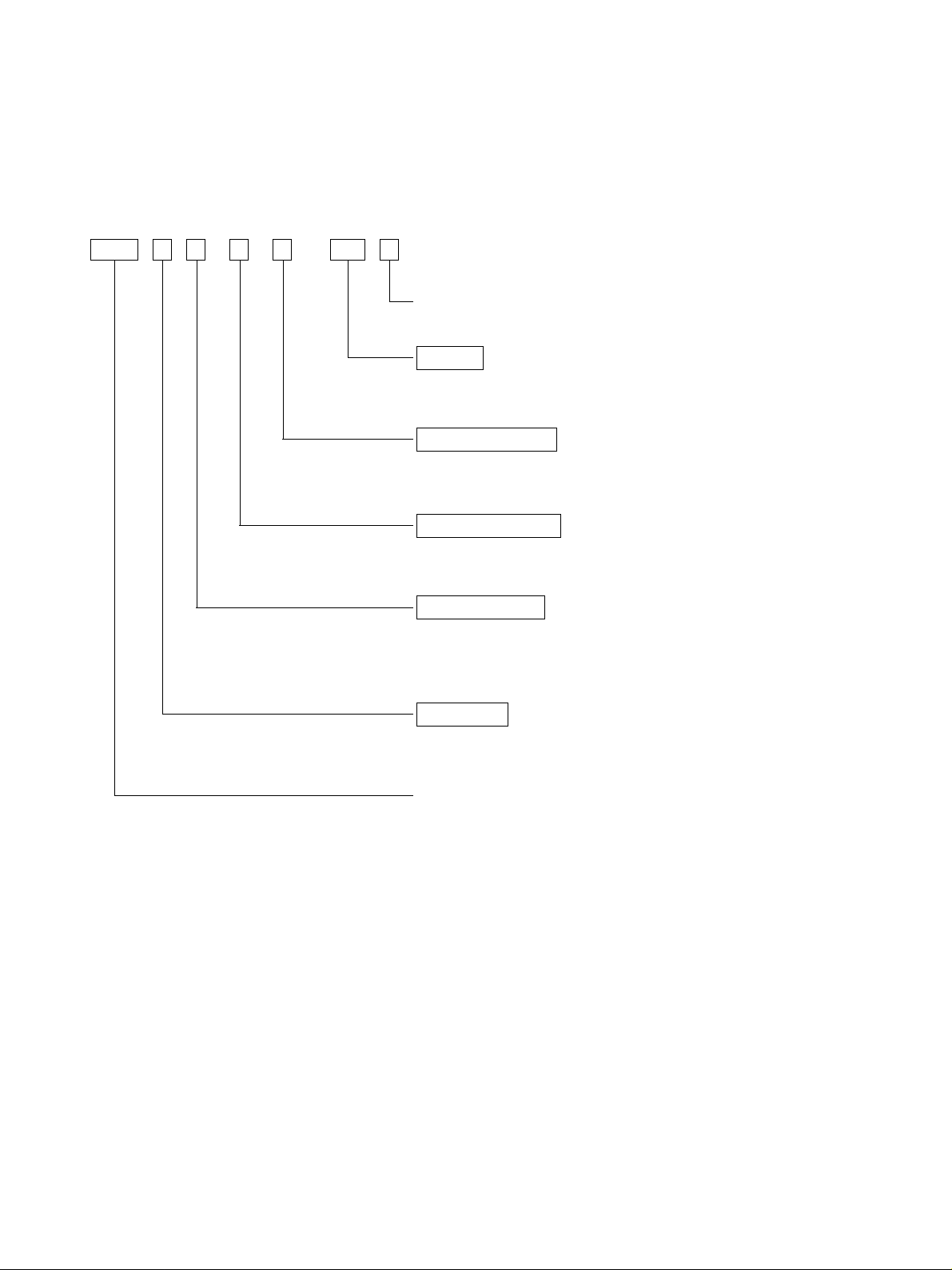
Model Name Notation
MP1 1 1 M P - 24 G - A
G: FG compatible
Voltage
24 : 24 VDC
Paper-out detector
P : Includes the paper-out detector
Paper feed method
M : Friction method and stepping motor
Mechanism type
1 : Monochromatic, 16.9 CPI, 32 columns per line
5 : 2 colors, 16.9 CPI, 32 columns per line
Printer type
1 : Type 1
MP100 Series printer mechanism
– 1 –
Page 5

2. CONSTRUCTION
2.1 Configuration
This printer mechanism is composed of the following components.
Printer mechanism Drive unit, gears, and carriage unit
Detectors Timing detector
Home position detector
Paper out detector
Paper feed mechanism
Ink ribbon wind mechanism
Print head unit
Frame unit
Other
You can also use 1.75 inch (45 mm) width roll paper by removing the paper guide B and attaching the optional
guide.
2.2 Principle of Operation
2.2.1 Drive
This printer mechanism moves the print head, feeds paper and feed ribbon with the motor.
2.2.2 Print head movement
The rotation of the motor is transmitted to drive shaft through the reduction gears. The carriage makes lateral
reciprocal movements along a groove that is carved on this drive shaft, consequently moving the print head.
2.2.3 Print timing
Printing is done when the timing signal is generated synchronized with the rotation of the motor, based on the
home position signal.
2.2.4 Ribbon feed
The ink ribbon is housed inside a ribbon cartridge in endless fashion. A ribbon feed roller is turned by the
rotation of the motor whereby the ink ribbon is wound up.
2.2.5 Paper feed
Paper feeding is done by the rotation of the stepping motor.
– 2 –
Page 6
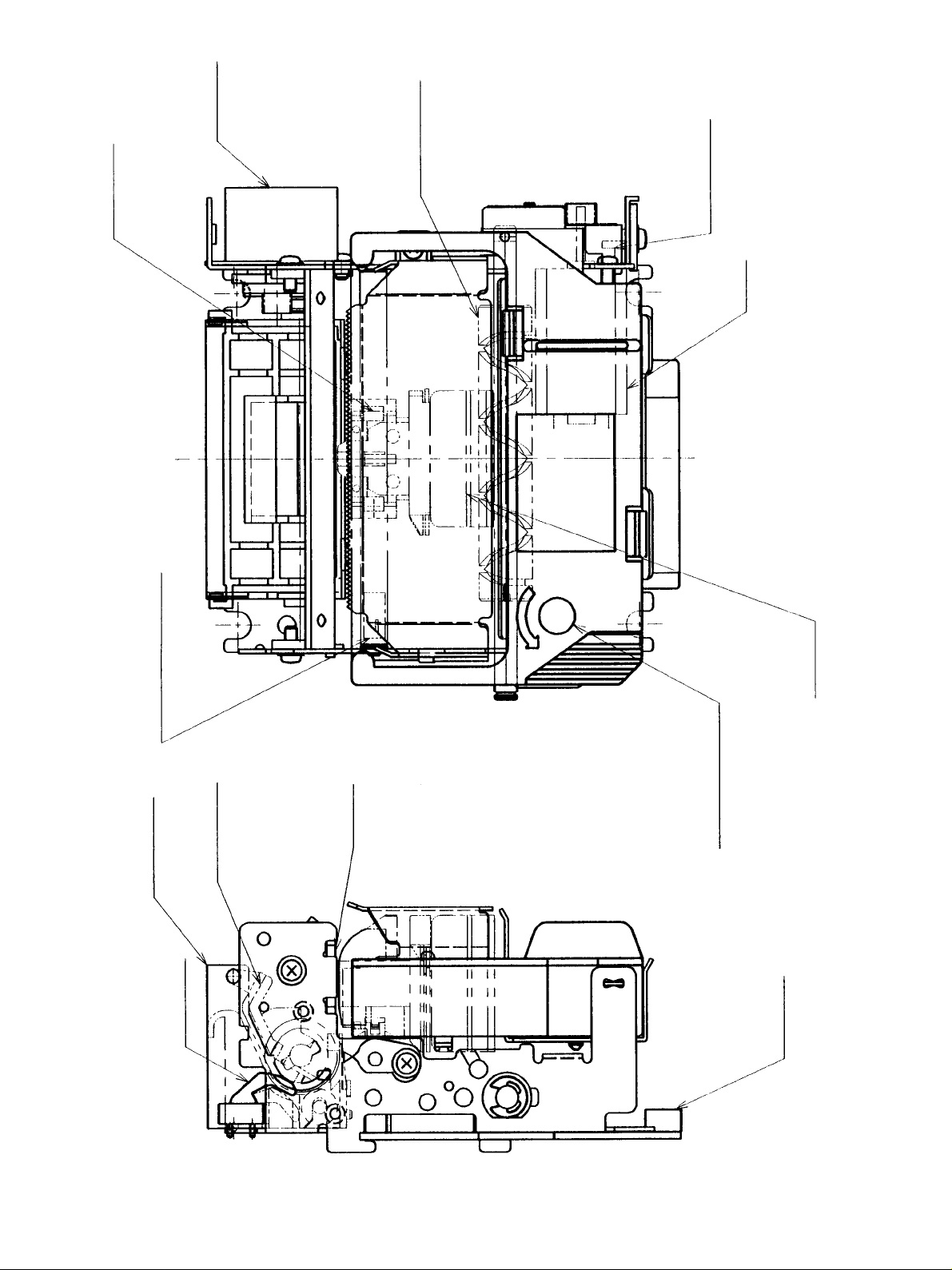
PF Motor
Drive Shaft
Carriage
Timing Detector
Motor
Home Position Detector
Paper Guide B
Paper Guide A
Paper-out
Detector
Platen
Ink Ribbon
Cassette
Print Head
Connector
Fig. 2-1 MP111MP External view
– 3 –
Page 7
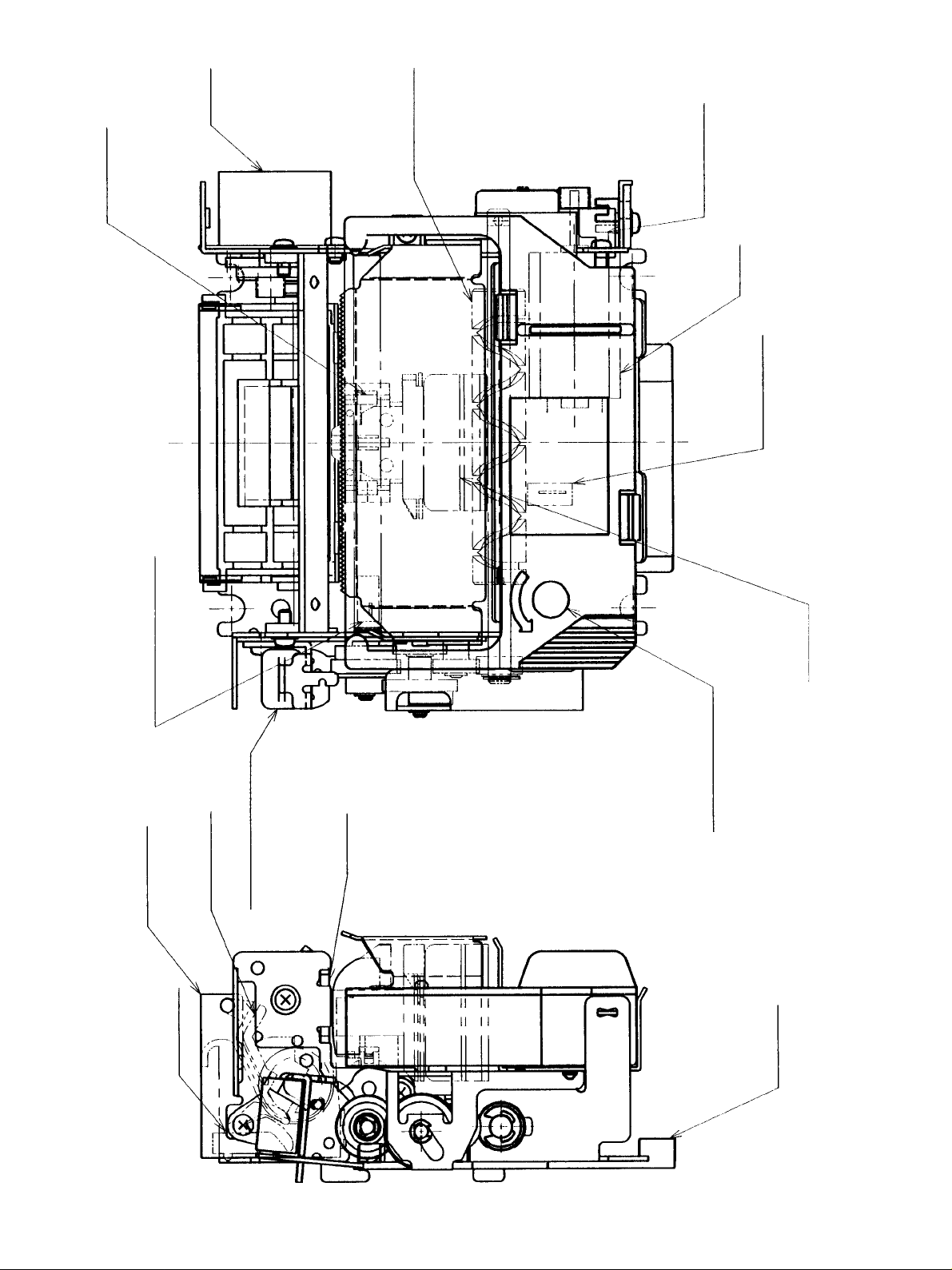
PF
Motor
Drive Shaft
Carriage
Timing Detector
Motor
Ribbon Position
Detector
Home Position Detector
Ribbon Solenoid
Paper Guide A
Paper-out
Paper Guide B
Detector
Print Head
Ink Ribbon Cassette
Platen
Connector
Fig. 2-2 MP115MP External view
– 4 –
Page 8
3. GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
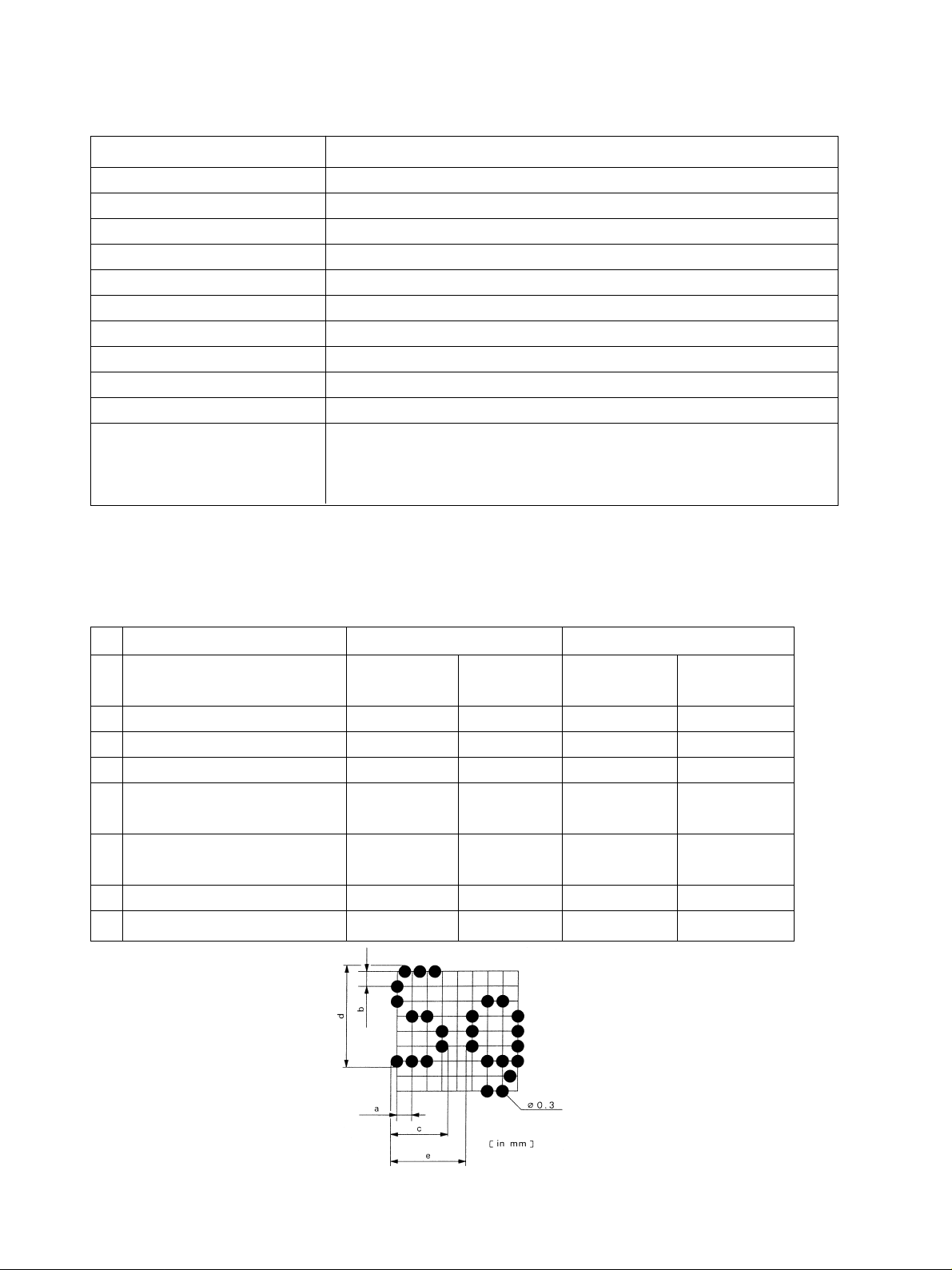
3.1 Printing Specifications
Item Specifications
Printing method Impact Dot Matrix
Printing configuration 7 x 9 (half dot) or 5 x 9
Printing direction Bidirectional (See note 1)
Printing speed Approximately 3.85 lines/second
Printing lines 32 lines (when using 7 x 9 half dots)
Character dimension Width 1.2 mm (when using 7 x 9 half dots) Height 2.42 mm
Dot spacing Horizontal 0.3 mm (with full dots) Vertical 0.353 mm
Printing area 48 mm
Paper feed speed Approximately 3.77 in./sec. (continuous feeding)
Wire diameter ø 0.3 mm
Line space 1/6, 1/8, 1/12, 1/72, 1/144 inches
Feed paper more than one line before printing graphics or vertically
expanded characters.
Note 1: When performing bidirectional printing, horizontal drift is likely to occur in unidirectional printing.
Details of Character Dimentions
1 Paper width 2.25 inches (57.5 mm) 1.75 inches (44.5 mm) Optional
2 Fonts configuration (H x V) 7 x 9 5 x 9 7 x 9 5 x 9
(half) (half)
3 CPI 16.9 14.1 16.9 14.1
4 Printing column count 32 26 24 20
5 Spacing e mm 1.5 1.8 1.5 1.8
6 Character dimensions c mm 1.2 1.5 1.2 1.5
d mm 2.42 2.42 2.42 2.42
7 Dot space a mm 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3
b mm 0.353 0.353 0.353 0.353
8 Total no. of dots 160 156 120 120
9 Printing area mm 48 46.8 36 36
Fig. 3-1 Character Size (7x 9 font)
– 5 –
Page 9
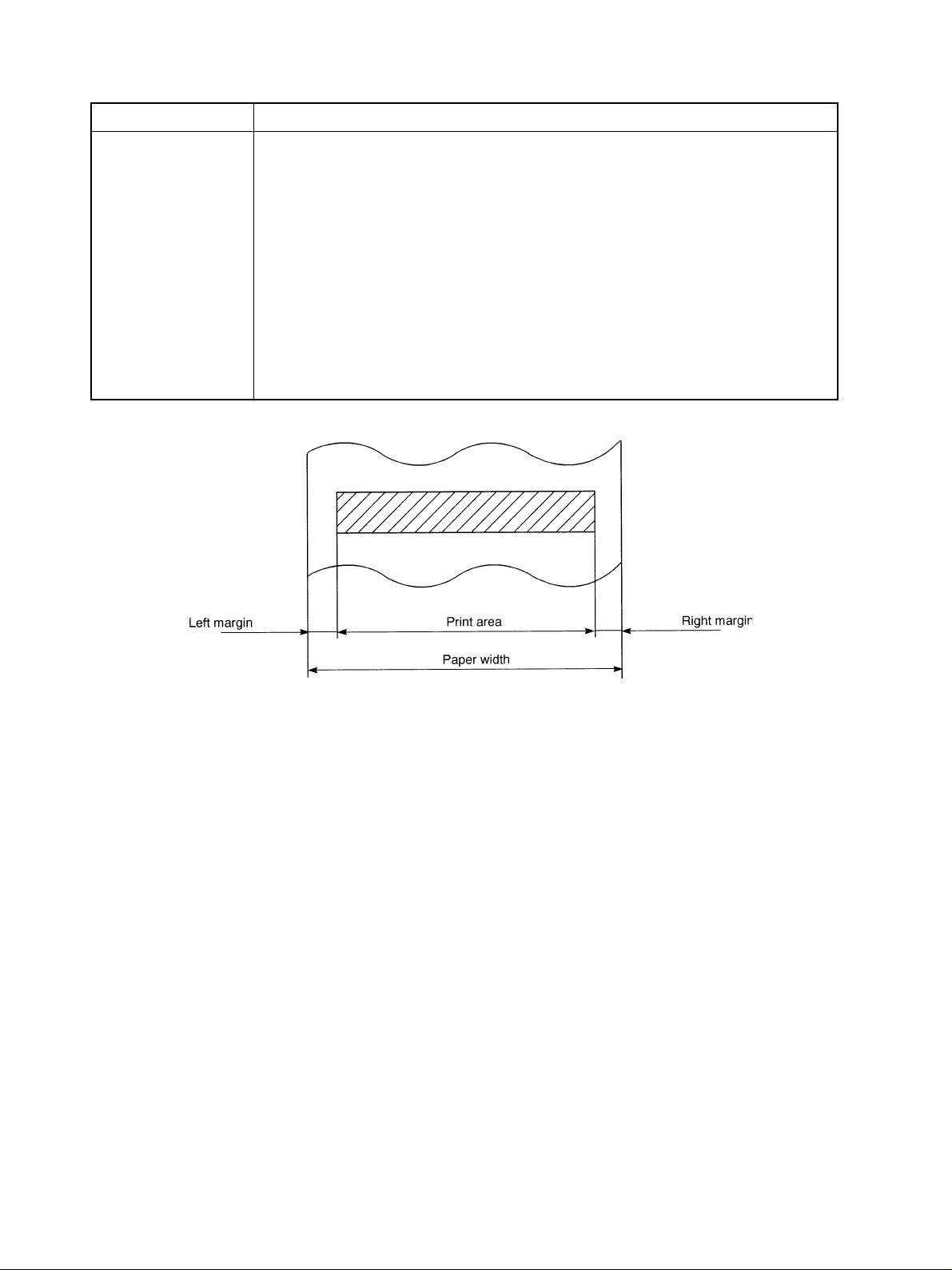
3.2 Paper Specifications
Item Specifications
Paper type Ordinary roll paper (1P) and carbonless roll paper (2P or 3P)
Paper width 57.5 ± 0.5 mm (2.25 inch). With options, 44.5 ±0.5 mm(1.75 inch) possible
Roll diameter Max. 85 mm (3.35 inch)
Thickness Single : 0.07 mm to 0.10 mm
Copies : Original + 1 copy
Total thickness max. 0.14 mm, with each sheet 0.05 to 0.08 mm thick
Original + 2 copies
Total thickness max. 0.2 mm, with each sheet 0.05 to 0.08 mm thick
Core diameter 12 ± 1 mm
Other No glue between the paper and the core diameter
Fig. 3-2 Paper spec. & Print area
– 6 –
Page 10
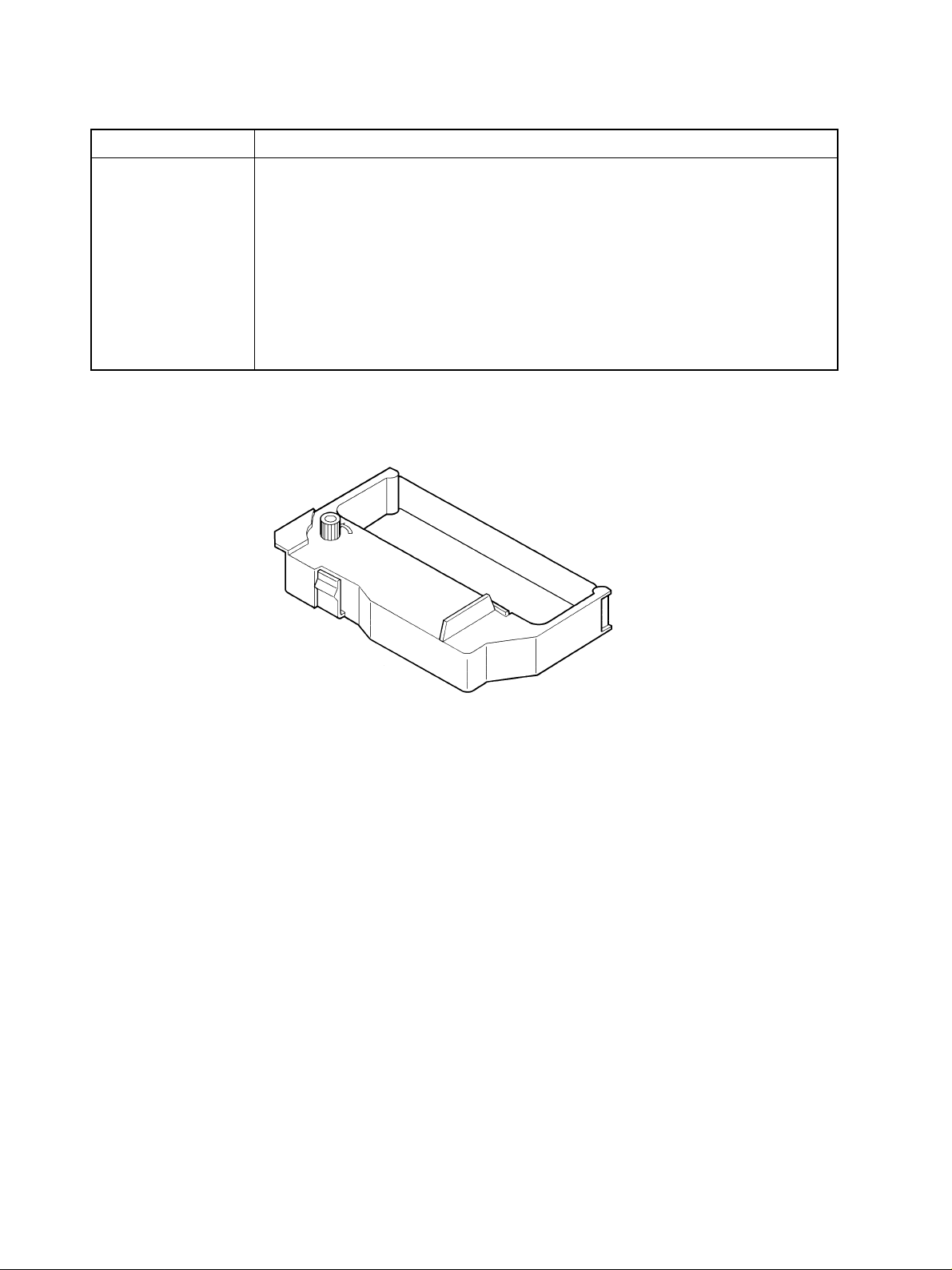
3.3 Ink Ribbon Specifications
1) MP111
Item Specifications
Type Dedicated cartridge
Color Purple (standard)
Ribbon material Nylon 66
Ribbon size Width: 13 mm
Model name Purple (standard): Ribbon cassette RC100 P
Black (optional): Ribbon cassette RC100 B
Ribbon life Purple: Approx. 1,500,000 characters
Black: Approx. 800,000 characters
Note: There is the possibility of damaging the printer by using ribbon cassettes that have not been speci-
fied. We do not offer warrantee for problems that occur from using the wrong ribbon cassette.
Fig. 3-3 Ink ribbon cartridge (RC100 P.B.)
– 7 –
Page 11
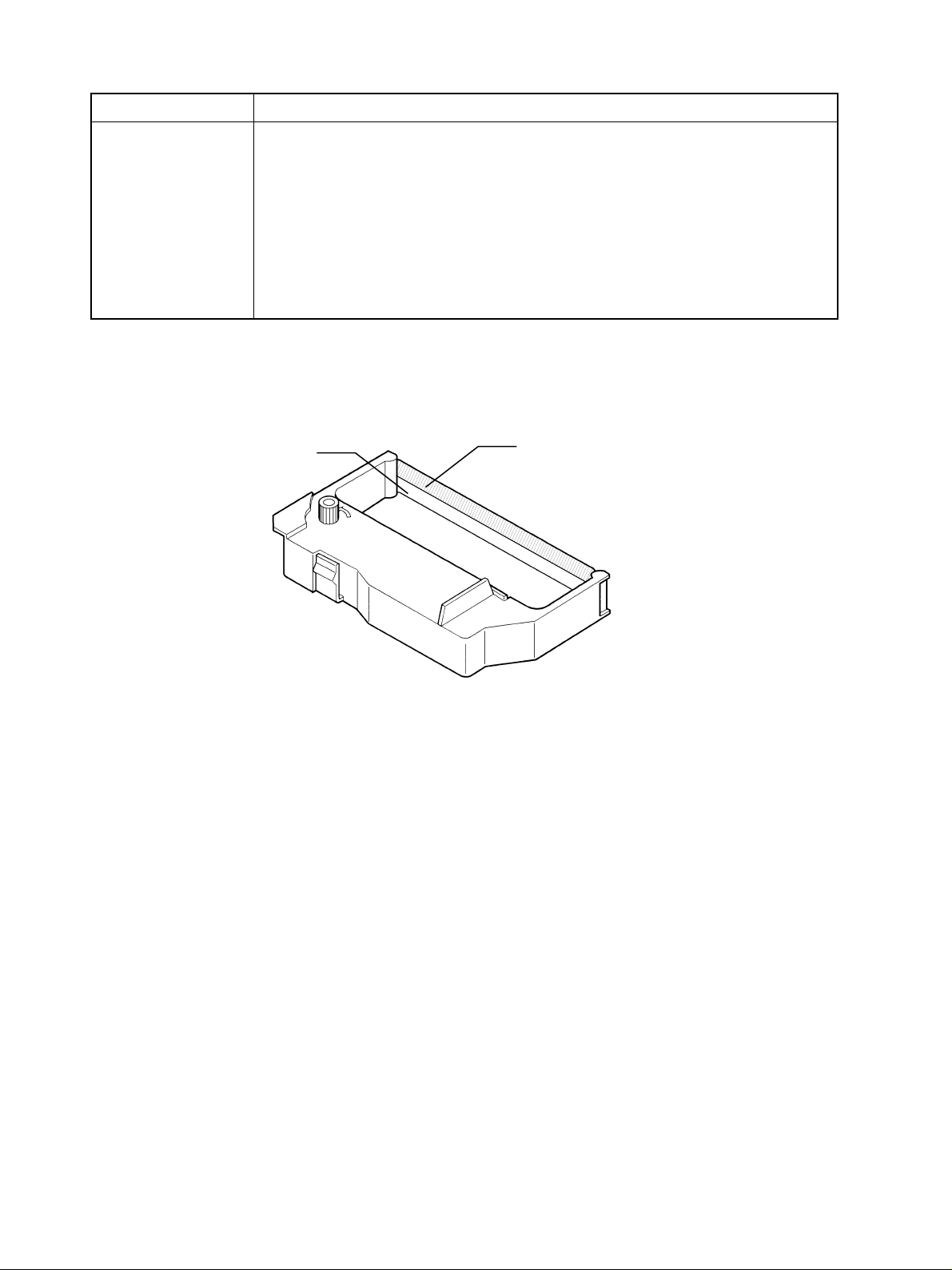
2) MP115
Item Specifications
Type Dedicated cartridge
Color Black and red
Ribbon material Nylon 66, (#40 denier)
Ribbon size Width: 13 mm
Model No. Black and red: Ribbon cassette RC100BR
Ribbon life Black: Approx. 400,000 characters
Red: Approx. 250,000 characters
Note: There is the possibility of damaging the printer by using ribbon cassettes that have not been speci-
fied. We do not offer warrantee for problems that occur from using the wrong ribbon cassette.
Red
Black
Fig. 3-4 Ink ribbon cartridge (RC100BR)
– 8 –
Page 12
3.4 Connector Specifications
Connector Type
NIPPON FCI
HLEM28R-1
Connection Drawing See next page
1 HD #6
2 HD CMN
3 HD #4
4 HD #5
5 HD #1
6 HD CMN
7 HD #2
8 HD #3
9 HD CMN
10 HD #7
11 HD #8
12 HD #9
13 LF-ø4
14 LF-CMN A, B
15 LF-ø2
16 LF-ø1
17 LF-ø3
18 RS-Sig (Ribbon shift) MP115M only
19 S-GND
20 PE-Sig
21 CR MOTOR (–)
22 HP-Sig
23 RS-SOL (Ribbon shift) MP115M only
24 T2-Sig
25 T1-Sig
26 +5V
27 NC
28 CR MOTOR (+) (CMN VH)
– 9 –
Page 13
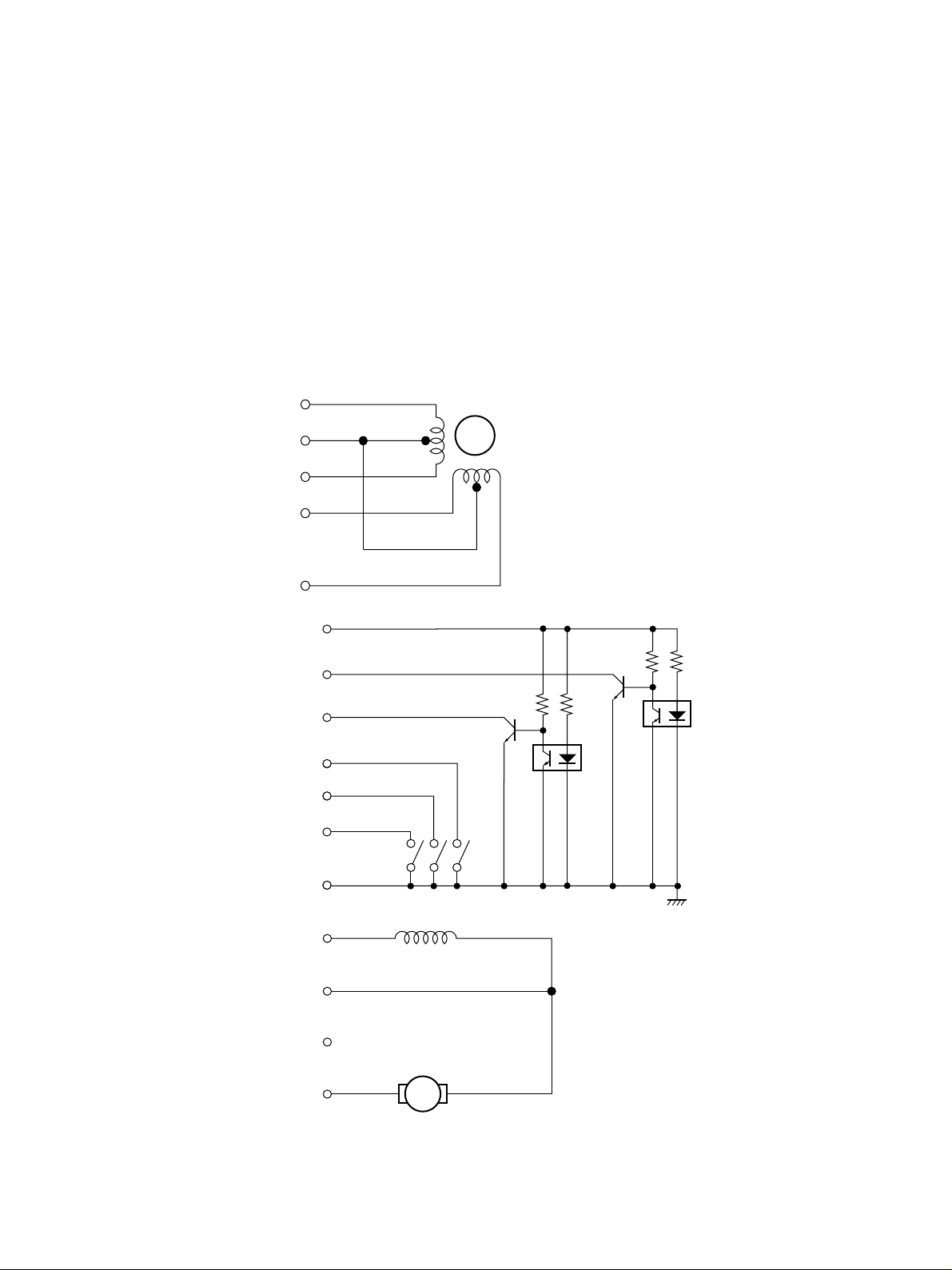
LF-ø1
16
LF-CMN A,B
LF-ø3
LF-ø2
LF-ø4
+5V 26
T1-sig 25
T2-sig 24
HP-sig 22
PE-sig 20
(RS-sig) *1 18
S-GND 19
14
17
15
13
M
(
RS-SOL) *1 23
)
CR MOTOR(+
(
CMN(VH
NC 27
CR MOTOR(-
))
28
)
21
M
*1 MP115MP only
Fig. 3-5 Connector connections
– 10 –
Page 14

3.5 Print Timing
This printer uses a timing signal of 1 as the total number of pulses to control the solenoid and motor. The
numbering of Tn of the timing signal 1 is found as shown below. The first timing signal 2 after the rise of the
home position signal is detected and the fall of the first timing signal 1 after the rise of timing signal 2 is set
as T-1. The subsequent timing signal falls are set as T0, T1 and T2.
You should be careful of the following points concerning this print timing.
There is a minimum of 2 pulses for the timing signal 1 for electrical cycles for the same pin. Therefore, you
cannot energize Tn, Tn+1 using the same pin.
7✕9 (half) font
Forward printing
Normal character
Rotated character
Backward printing
5✕9 font
T2
T4 T6 T8 T10 T12 T14 T16 T18 T20 T22 T312T314T316T318T320T322
T1 T3 T5 T7 T9
1st chara
135
T11
7
246
7531 7531 7311
642 642 642
32th chara
T754T752T750T748T746T744
T753T751T749T747T745T743
Note ) The electric cycles for identical 1 pins has 2 pulses or more.
There Tn, Tn+1 electricity is impossible
T13 T15 T17 T19 T21 T311T313T315T317T319T321
2nd chara
1357
32th chara
1357
246 246
31th chara
T742T740T738T736T734
T741T739T737T735T733
T444T442T440T438T436T434
1st chara
T443T441T439T437T435T433
Forward printing
Normal character
Rotated character
Backward printing
T2
T4 T6 T8 T10 T12 T14 T16 T18 T20 T22 T312T314
T1
T3 T5 T7 T9
1st chara
12345 12345
T754T752T750T748T746T744
T753T751T749T747T745T743
T11
T13 T15 T17 T19 T21 T311T313T315T317T319T321
2nd chara
1234
5
432
26th chara
T742T740T738T736T734
T741T739T737T735T733
T310 T316T318T320T322
T309
26th chara
5
4321
1st chara
T444T442T440T438T436T434
T446
T443T441
T445 T439T437T435T433
Fig. 3-6 Print Timing
– 11 –
Page 15

3.6 Timing Chart
(1) Printing Action
– 12 –
MOTOR
OFF
HIGH
HP-sig
LOW
HIGH
Fig. 3-7 Printing action
T2-sig
LOW
HIGH
T1-sig
LOW
PRINT
PF MOTOR
ON
T0 T2
T-1
T4
T1
T3 T322 T323 T754
Carriage reversal
area
(110 pulses)
TYP. 66.3 ms
Forward print area (322 pulses)
MIN. 64.3 ms
T433 T490
ON
1/6 Inch = 24 Steps
T1-sig: Type 1660 Hz, Max. 1710 Hz (Software and CPU should be designed at Max. 2000 Hz.)
Printing speed: T1-sig 1600 Hz = Approximately 3.84 lines/sec. 1710 Hz = 3.96 lines/sec.
Paper feed action must be carried out within the carriage reversal area.
After print
Motor OFF Timing
Backward print area
(322 pulses)
T755
Carriage reversal
area
(110 pulses)
TYP. 66.3 ms
MIN. 64.3 ms
T-1
T0 (T863)
T1
Forward print area
Page 16

(2) Ribbon Shift Operation (Only with 2 color printing on the MP115)
Release Action
MOTOR
TIMING SIG-1
RIBBON SHIFT
RIBBON SHIFT GEAR
ON
OFF
HIGH
LOW
ON
OFF
ROTATE
STOP
T1 T2T3
T30
18 Pulses
288 Pulses
Ribbon shift gear rotation:
18 x 6 x 32/12 = 288 pulses
Fig. 3-8 Release action
T336
– 13 –
Page 17

3.7 Print Head Specifications
(1) Basic Specifications
Item Specifications
Supply voltage 24 VDC ± 2.4 V
Response frequency Max. 900 Hz
Energized time See below
Coil resistance 14.7 ± 0.4 Ω (includes cable resistance)
Peak current 1.0 A/solenoid (for 24 VDC, 375 µs)
Timing Energizing is begun at the fall of the output signal of timing signal 1.
Energizing cycle shall be 2 pulses or more of timing signal 1.
Peak current 1.0 A 1.1 A
Condition 24 V 26.4 V
Typ. Max.
375 µs 340 µs
Transistor’s turn off delay time (td): 2 µs
Fig. 3-9 Current waveform
(µs)
415
395
375
Energizing Time
355
340
21.6 24 25.222.8 26.4 (V)
Voltage
Fig. 3-10 Head Energizing Time - Head Power Supply Voltage
– 14 –
Page 18

We employ a zener diode to control spike voltages that occur when the transistor is turned OFF. The following figure
shows and example of the drive circuit. With this circuit, we use a transistor equipped with a zener diode (zener voltage
60 + 10/-5V) between the base and collector.
TR1 2SD2041 (ROHM)
R1 1K Ω
R2 330Ω
HV (24 V)
VH 23V + TR1 for VCE (sat) = 24 V
Fig. 3-11 Example of Print Solenoid Drive Circuit
– 15 –
Page 19

(2) Pre-fire
This operation applies minute vibrations to the needle wire to allow for its smooth movement as printer warmup.
Pre-fire is performed under the following conditions. The energizing time is too short to allow for the printing
action to occur.
Operating time When power is turned ON. Number of times 32 Times
Frequency 900 Hz Power supply voltage DC24V ±2.4 V
Energizing time 175 ± 5 µs
(3) Print Duty
This print head is not equipped with a head temperature detector. Therefore, use the printer within the maximum printing ratio shown below. If you print exceeding this printing ratio, you can damage the printer.
Ambient Temperature 25°C
1140
Print Ratio N
(dot /sec)
Ambient Temperature 50°C
830
21.6 V 24.0 V 26.4 V
Fig. 3-12 Print duty
The figure above shows the print duty that is possible with continuous printing when each wire is used an
equivalent number of times. In this case, you can calculate the possible dot count for D per character using the
following numerical formula.
N (Print Ratio) x T (Print time per line includes the time of the paper feed [sec])
L (number of character per line)
[dot/chara]
– 16 –
Page 20

When you use the specific wires many times, make sure the maximum print ratio is not over the print duty shown in Fig.
3-13. Fig. 3-13 shows operation at 24.0V.
1200
1100
1000
900
800
700
Print Ratio N (dot/sec)
600
500
400
Temperature 25°C
500
380
12345678
Ambient
(1155)
1100
(1030)
950
(850)
750
(785)
(730)
680
(615)
550
Number of the specific wires
Fig. 3-13 Print duty (specific wires)
(1200)
890
(840)
Ambient
Temperature 50°C
– 17 –
Page 21

3.8 CR Motor Specifications
Item Specifications
Type DC motor
Supply voltage 24 VDC + 1.2 V
Start current Max. 1.6 A
Average current Approx. 0.15 A
Fig. 3-14 Current waveform of the motor
– 18 –
Page 22

Fig. 3-15 Motor drive circuit (example)
R1 10 KΩ TR1 2SA950
R2 3.3 KΩ TR2 2SC1740
R3 6.8 KΩ 1/6 W TR3 2SA1175
Notes: Adjust motor speed with VR
adjustment and T1 signal to
1660 Hz ± 30 Hz.
R4 2.2 KΩ TR4 2SD882
R5 1.2 KΩ TR5 2SB1359
R6 10 KΩ TR6 2SD1637
R7 20 KΩ IC1 SN74LS05
C1 0.47 µF (Film) IC2 M51971L (MITSUBISHI)
C2 0.033 µF (Film) VR 6.8 KΩ
C3 0.022 µF (Film)
3.8.1 FG Circuit
The motor control circuit with a Frequency Governor circuit maintains the printing speed at the settings. It is
mainly constructed of a Speed Control IC (IC2) and a Power Transistor TR6 shown in Fig. 3-15. It measures
the number of rotations of the Carriage Motor from the Timing Signal 1. This signal is then compared to the
standard signal to control the speed by controlling the voltage energizing the Carriage Motor.
3.8.2 Merits of the FG Circuit
The FG circuit maintains a stable output regardless of the environment where it is being used.
It maintains stability even at high speeds.
It protects the head because the speed is stable.
– 19 –
Page 23

3.9 Paper Feed Motor Specifications
Item Specifications
Type PM type stepping motor
Drive method 2-Phase excitation unipolar method
Terminal voltage 24 VDC ± 1.2 V (for drive), 4.2 VDC (when holding)
Peak current Max. 0.7 A
Average current About 0.28 A
Holding current About 0.08 A
Amount of paper feed
1/144 inch per 1 step
Feed method Forward feed only
Excitation signal a. When paper feed amount is less that 4 steps.
Set to 350 pps drive.
b. When paper feed amount is over 5 steps and less than 8 steps. Set the slow-
down area so that the final 2 steps become 300 pps and 200 pps. The other
areas are set to 350 pps drive.
c. When paper feed amount is over 9 steps and less than 18 steps. Set the inital
4 steps so that they become 350 pps (slow-up area). Set the slow-down area
so that the final 4 steps become 500 pps, 400 pps, 300 pps, and 200 pps.
The other areas are set to 550 pps drive.
d. When paper feed amount is over 19 steps.
Set the initial and final 4 steps so that they become 350 pps. The other areas
are set to 550 pps drive.
VH 24 V D1 DSM1D1 (HITACHI)
TA1 µPA1428AH (NEC)
R2 to R3
10 kΩ
TR1 2SB1359 Compatible D1 DSM1D1 (Hitachi)
TR2 2SC1740 Compatible IC SN74L04
15
13
Fig. 3-16 Drive circuit of paper feed motor (example)
– 20 –
Page 24

3.10 Ribbon Shift Solenoid (RS-SOL) Specifications
MP115MP only
Item Specifications
Supply voltage 24 VDC ± 1.2 V
Pulse width T1-sig 18 pulses (Approx. 12 ms)
Coil resistance Approx. 57.0 Ω
Average current Approx. 400 mA
Fig. 3-17 Current waveform of RS-SOL
TR1 2SD2010 (ROHM)
D1 DSM1D1
R1 1 kΩ
R2 330 Ω
VH 23 V + TR1 V
CE (sat.) = 24 V
Fig. 3-18 RS-SOL drive circuit (example)
– 21 –
Page 25

3.11 Timing Signal Detector Specifications
The timing signal detector is composed of a detection slit mounted on the motor shaft, a photo interruptor,
and waveform shaping circuit.
Timing signal 1 is generated 18 pulses and timing signal 2 is generated 1 pulse every time the motor rotates
by 1 turn.
PS Photo interruptor
ON1004R
(MATSUSHITA)
TR1 2SC1740
R1 4.7 kΩ
R2 56 kΩ
R3 150 Ω
C1 2200 PF
Fig. 3-19 Circuit of timing signal 1 (example)
PS Photo interruptor
ON1004R
(MATSUSHITA)
TR1 2SC1740
R1 4.7 kΩ
R2 56 kΩ
R3 150 Ω
C1 2200 PF
Fig. 3-20 Circuit of timing signal 2 (example)
– 22 –
Page 26

3.12 Home Position Detector (HP-sig) Specifications
The home position detector is composed of the mechanical switch. While the carriage is located at the left
end, the switch remains ON.
R1 10 kΩ
R2 15 kΩ
C1 0.022 µF
Fig. 3-21 Home position detector circuit (example)
In order to improve reliability, we recommend that the HP-sig is detected as described below.
(1) When the T1-sig is unstable when turning on the power, etc.
Detect the L level after having detected the H level of the HP-sig, and then, after having carried out 81
pulse counts for the T1-sig, detect the H level.
(2) When the T1-sig is decided during continuous operation of the motor
Detect the L level of the HP-sig, and then, after having counted 847 pulses of the T1-sig, detect the H
level.
3.13 Paper-out Detector (PE-sig) Specifications
The Paper-out Detector is composed of a mechanical switch. While the paper is set in the paper tray, the
switch remains ON.
R1 10 kΩ
R2 15 kΩ
C1 0.022 µF
Fig. 3-22 Paper-out detector circuit (example)
– 23 –
Page 27

3.14 Ribbon Position Detector (RS-sig) Specifications (MP115MP only)
The ribbon position is made up by a mechanical switch.
When the ribbon is at the position for printing of black characters, the switch is ON.
R1 10 kΩ
R2 15 kΩ
C1 0.022 µF
Fig. 3-23 Example of ribbon position detection circuit
In order to improve the reliability, we recommend that the RS-sig is detected while the motor is off.
3.15 Dimension and Weight
See Fig on the next page for external dimension of the printer mechanism.
Weight of printer mechanism: MP111MP, approx. 410 g (excludes the ribbon cartridge)
MP115MP, approx. 450 g (excludes the ribbon cartridge)
Weight of ink ribbon cartridge: approx. 24 g
– 24 –
Page 28

Paper Entrance
Paper Entrance
Connector
Position
Paper Entrance
Paper Entrance
Paper Entrance
Print Center
Print Area
Paper Guide Wdith
Paper Entrance
Figure 3-24 MP111MP External dimension (unit: mm)
– 25 –
Print Center
Page 29

Connector
Position
Paper Entrance
Paper Entrance
Paper Entrance
Paper Entrance
Paper Entrance
Print Center
Paper Guide Wdith
Paper Entrance
Print Area
Print Center
Figure 3-25 MP115MP External dimension (unit: mm)
– 26 –
Page 30

4. RELIABILITY SPECIFICATIONS
Item Specification Remarks
Printer reliability
4 million lines MCBF
Except print head life
Life
Operating
environment
Storage
environment
Vibration test
Shock test
Print head life
Temperature
Relative
humidity
Temperature
Relative
humidity
Approx. 70 million characters
0°C to 50°C
10 to 80% RH (at 40°C)
(no condensation)
-20°C to +70°C
5 to 95% RH (at 40°C)
(no condensation)
Vibration : 10 ~ 55 ~ 10 Hz
Amplitude : 1.54 mm (at regular range)
Sweep : one minute
Gravity : 0.3 ~ 9.3 G
Direction : X,Y and Z directions
Test time : Two hours in each direction
(Six hours in three directions)
Packing : With the least packing unit
Height : 85 cm
Order : 1 corner, 3 edges, and 6 sur-
faces
Packing : With the least packing unit
14 dots per character
Recommended ribbon:
Purple color ink ribbon cartridge (RC100 P)
After being left under this
environment for two hours,
the printer mechanism must
satisfy general specification.
After being left under this
environment 96 hours, and
under normal temperature
and humidity for two hours,
the printer mechanism must
satisfy general specification.
The printer must satisfy general specification after testing.
The printer must satisfy general specification after testing.
Insulation resistance
1 MΩ (100 VDC)
When you put the printer
mechanism to the quality
control test, use the printer
under the environment as
shown at the left.
– 27 –
Page 31

5. SETTING THE RIBBON CARTRIDGE
1. Turn the ribbon feed knob of ribbon cartridge in the direction of the arrow to remove slack in the ribbon.
2. Place the ribbon cartridge and press it to set in the Unit. When the ribbon cartridge is hard to set to the
proper position, turn the ribbon feed knob in the direction of the arrow.
Insert the ink ribbon between the print head and the platen.
3. Turn the ribbon feed knob of ribbon cartridge in the direction of the arrow to remove slack in the ribbon.
– 28 –
Page 32

6. SETTING THE PAPER
6.1 Setting the Paper
1. Cut straight the leading edge of the paper.
2. Insert the paper squarely into the paper guide.
3. Turn the paper feed motor to feed the paper.
4. When the paper comes out of the paper outlet, turn the feed motor off, and stop the paper feed.
6.2 Removing the Paper
1. Cut the paper behind the paper guide.
2. Turn the paper feed motor to remove the paper.
– 29 –
Page 33

7. INSTALLATION
1. At the time of mounting the printer mechanism into its housing cabinet, put cushion material, such as,
rubber foot, on the printer mechanism legs. If installed directly, reverberations occur producing noise.
We recommend that you use the following rubber foot.
Parts name : DAMPER RUBBER
SP2
Parts No. : 30290010
Fig. 7-1 Recommended Rubber foot
Parts name : SCREW 3.0
Parts No. : 30250010
Fig. 7-2 Recommended Set screw (unit: mm)
2. Set the play between the roll paper holder and paper thrust direction to within 2 mm, and ensure that the
roll paper holder doesn’t hold back the edge of paper.
3. Set the paper inserting angle to within 65°.
4. Edges around the paper insertion area should be rounded at R2 mm or more.
5. Set the paper feed load, at the printer’s paper inlet, to 30 g or less.
6. Take into account prevention of paper rewinding, when designing the case.
7. Allow needed space surrounding the printer. Fig. 7-3 shows an example of installation space.
8. Fig. 7-4 shows an example of installation.
9. Since this printer mechanism employs galvanized steel panels, the end surface doesn’t come plated.
– 30 –
Page 34

Mechanism Attachment
Position (4 Places)
Paper Entrance
Paper Exit
(Paper Tube
Inner Diameter
Roll Diameter
Paper Entrance
Paper Entrance
Sectional View of Paper Holder AA
Frame
Screw 3.0
Vibration Isolation
Rubber SP2
Chassis
Fig. 7-3 Installation space (example) (unit: mm)
– 31 –
Page 35

Mechanism Attachment
Position (4 Places)
Paper Entrance
Paper Exit
Roll Diameter
Paper Entrance
Paper Entrance
Roll Diameter
Frame
Screw 3.0
Vibration Isolation
Rubber SP2
Chassis
Sectional View of Paper Holder
Fig. 7-4 Printer installation (example) (unit: mm)
– 32 –
Page 36

Mechanism Attachment
Position (4 Places)
Roll Diameter
Paper Entrance
Paper Entrance
Paper Entrance
(Rib Height)
Paper Exit
Frame
Screw 3.0
Vibration Isolation
Rubber SP2
Chassis
Sectional View of Paper Holder
Fig. 7-5 Printer installation (Placing the roll paper without using the roller.)
– 33 –
Page 37

Be careful of the
soldered
side of the PCB.
(MP111MP)
(MP115MP)
Fig. 7-6 Printer installation
– 34 –
Page 38

8. OPERATIONAL NOTES
8.1 Power ON/OFF Note
If the 5 V power supply line for logic has not fully risen or fallen immediately after the power supply is
turned ON or OFF, the CPU or TTL in the logic circuit may misoperate. At such times, power is supplied to
the motor or solenoid, causing, in the worst case, burnt out solenoid or running of motor (misoperation),
unless the 24 V power supply line for motor drive is completely OFF. To avoid such misoperation, take into
account the following points.
8.1.1 Power supply ON/OFF timing rule
Supply 24 V line after the 5 V line has fully risen. Similarly, cut off the 5 V line after the 24 V line has fully
fallen.
Fig. 8-1 Power supply ON/OFF timing rule
8.1.2 Method of controlling the drive circuit
Fig. 8-2 Drive circuit controlling method
If the power supply ON/OFF timing rule cannot be followed, reset the print solenoid or motor drive circuit
with control signal. An example of this type of circuit is shown in Fig. 8-3. Turn OFF transistor TR1, while
the 5 V line has not completely risen, in order to inhibit power to the print solenoid. Then as soon as the 5 V
line has completely risen, turn ON TR1, permitting power to the print solenoid.
– 35 –
Page 39

TR1 2SD2041 (ROHM)
HRT Type
R1 1 kΩ
R2 330 Ω
VH 23 V+V
CE (Sat.) of
TR1=24 V
Fig. 8-3 Circuit to control drive circuit (example)
8.2 Carriage Motor Protection Method (Against Mechanical Errors)
If the carriage motor gets locked as a result of trapping foreign matter, etc. in the printer mechanism, a risk
of damaging the motor due to flow of excess current to it is generated. Therefore, it becomes necessary to
monitor the excess load status of printer mechanism, by detecting the cycle of timing signal 1 with timer,
etc. Once the cycle of timing signal 1 becomes as given below, stop power being supplied to the motor.
a. Print interval: 2.57 ms or more/450 µms or less
b. Outside print interval: 257 ms or more
8.3 Other Notes
1. Do not attempt to print when the paper or ribbon cartridge are not loaded in the printer mechanism as
this could damage the print head.
2. Do not store or use the printer mechanism at places of substantial dust, iron content, etc., or in oily
atmosphere.
3. Wipe off dust, dirt, etc. from the printer mechanism, using a soft brush. Or, wipe with a piece of cloth
dampened in alcohol.
4. Never inflict strong force on the printer mechanism. Otherwise, the frame or other parts may be distorted, rendering normal functioning impossible.
5. Avoid sudden changes in the ambient conditions like temperature, humidity, etc. even while they are
hold in prescribed limits. If sudden change occurs, allow about 30 minutes for acclimatizing, before
using the printer mechanism.
6. Never use the printer mechanism with condensation deposited onto it.
– 36 –
Page 40

9. POWER SUPPLY CAPACITY
9.1 24 V Line
Arrange for the following power supply, taking into account the voltage drop (about 1 V) of V
power transistor for driving print solenoid.
Power supply voltage 23V+1V = 24V ± 10 %
Similarly, arrange for 2.0 A or larger power supply capacity; and connect an electrolytic condenser of 4700
µF to 6800 µF/35 V to the power source.
9.2 5 V Line
Arrange for 5 V power supply for the detector (photo interruptor).
Voltage 5 V ± 5 %
Current consumption Approx. 60 mA
CE (sat) of the
– 37 –
Page 41

10. OPTIONS
You can also use 1.75 inch (44.5 mm) width roll paper by removing the paper guide B and attaching the
optional guide C.
(1) Removing the Paper Guide B
Spread the boss unit on both sides of the paper guide B and remove the the boss from the paper guide
A side. Rotate the paper guide B and remove it.
(2) Setting the Paper Guide C
When you remove the paper guide B, you can see the groove at the right side of the paper guide A.
Insert the paper guide C into that groove.
Fig. 10-1 Paper Guide Option
– 38 –
Page 42

HEAD OFFICE
ELECTRONIC PRODUCTS DIVISION
STAR MICRONICS CO., LTD.
536 Nanatsushinya, Shimizu,
Shizuoka, 424-0066 JAPAN
Tel : 0543-47-0112
Fax: 0543-48-5271
Please access the following URL
http://www.star-micronics.co.jp/service/sp_sup_e.htm
for the lastest revision of the manual.
OVERSEAS SUBSIDIARY COMPANIES
STAR MICRONICS AMERICA, INC.
70-D Ethel Road West,
Piscataway, NJ 08854 U.S.A.
Tel : 732-572-9512
Fax: 732-572-5095
Distributed by
STAR MICRONICS U.K. LTD
Star House, Peregrine Business
Park, Gomm Road, High Wycombe,
Bucks, HP13 7DL, U.K.
Tel : 01494-471111
Fax: 01494-473333
Printed in Japan, 80874315
 Loading...
Loading...