
Features
SPIMD20
■ Advanced brushless motor control in a single
module easy to piggyback to the motor
■ Extremely compact dimensions: 165x60x26
mm, <0.5 kg weight
■ Up to 2 kW power with 800 Vdc supply, on
100°C motor surface, can withstand peak of
current up to 40 A
■ Can operate on a motor surface temperature
up to 100°C
■ Integrated drive with real time connectivity via
Ethernet-based fieldbus (i.e. EtherCAT
CANopen
■ Safe torque off to disable IGBT drivers via
®
DS402
hardware
■ CAN bus hand-shaking channel
■ RS232 interface for programming
■ 2 Mb Flash memory aboard; also support
removable Flash memory card.
■ Supports position feedback both with resolver
or digital encoder EnDat 2.2
■ Motor current sensing with shunt sensors (2
phases)
■ Vibration analysis and thermal sensing
■ IP65 compliant
■ Safe architecture to apply to most popular
safety standards IEC61800-5-1
■ EMI: IEC61800 - 3 / A11 and UL508C
■ Up to 800 V
V
DC
RoHS compliant
■
supply, auxiliary supply 18-48
DC
®
) and
SPIMD20
Integrated motor drive
Datasheet — production data
This Shuttle version of the IMD is suitable for
direct integration to the permanent magnet
synchronous motor (i.e. 6 Nm torque) thanks to
the reduced dimensions 165x60x26 mm. The
Shuttle Drive™ is designed to operate on a motor
with a surface temperature up to 100 °C. The IMD
performs all motor driving required functions
including speed, position and current loop
execution, plus connectivity. Connection to the
master is performed via real time ethernet
fieldbus, including but not limited to EtherCAT
per IEC61158. However, the IMD is an open and
flexible platform to execute any other
communication standard with the aboard FPGA
(Altera Cyclone III type) and the two
microprocessors STM32F103 series. A basic
software package is available with SPIMD20. This
software package includes PWM driving, current
loop and speed loop execution; all the above
being synchronized to the fieldbus.
Table 1. Device summary
Order code
SPIMD20
®
as
Description
SPIMD20 is an integrated motor drive with real
time connectivity enabling brushless motor
manufacturers to create a proprietary motion
control system based on a general purpose brick.
July 2012 Doc ID 17527 Rev 3 1/20
This is information on a product in full production.
www.st.com
20

Contents SPIMD20
Contents
1 Main features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.1 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.2 Safe torque off diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 General specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.1 Ambient conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.2 Vibrations and shocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3 Pin out description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
4 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.1 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.2 Electrical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.2.1 Power supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.2.2 Power stage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5 Mechanical dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1 Mechanical data (dimensions in mm) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
5.1.1 Technical specifications for surface coupling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.2 The basic software package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.3 Safety characteristics and connection requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.4 Installation and user's manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.5 Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
6 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2/20 Doc ID 17527 Rev 3

SPIMD20 Main features
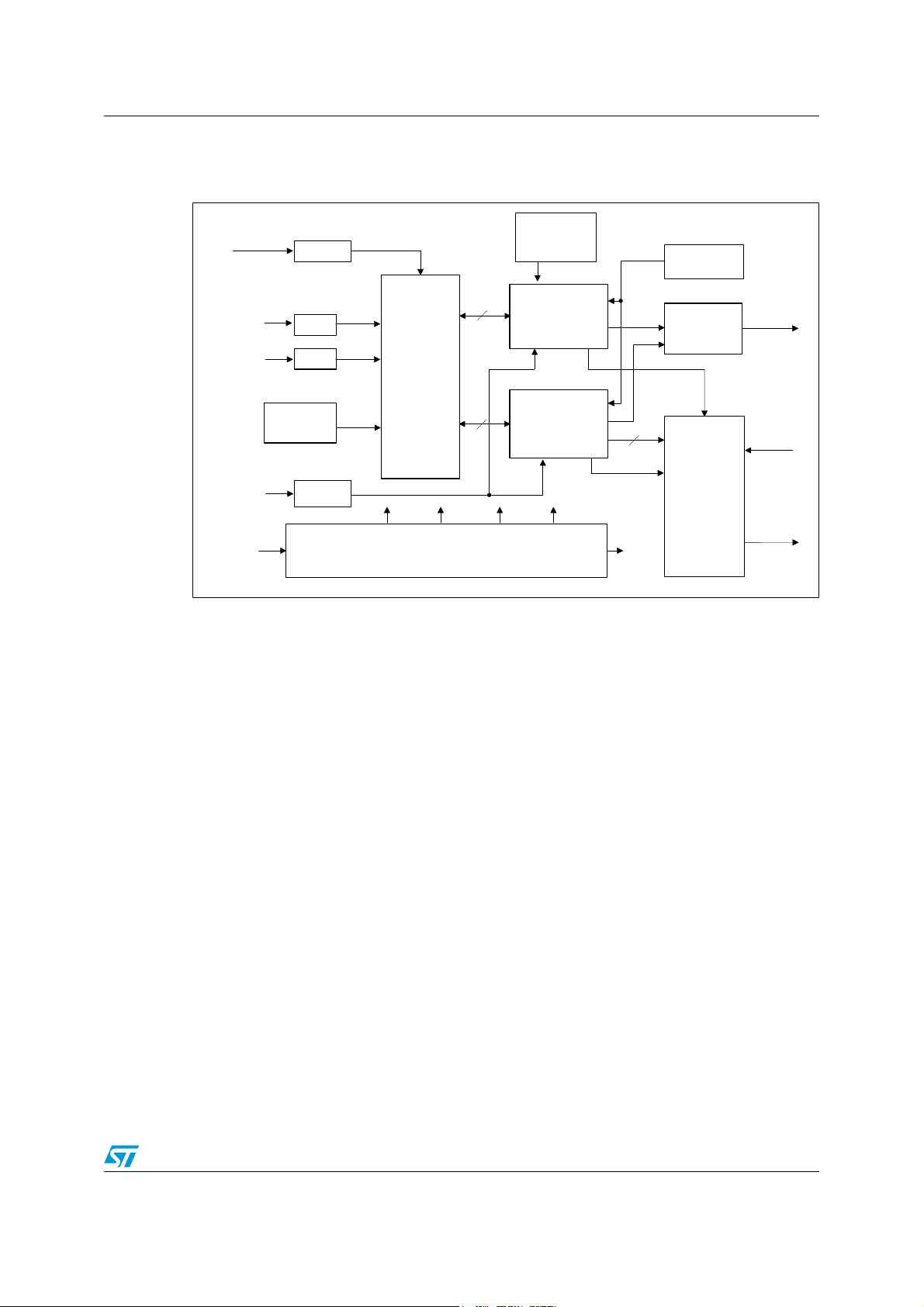
1 Main features
The SPIMD20 is the top level performing power drive system designed by
STMicroelectronics in cooperation with ROBOX S.p.A. Coming in a very compact size and
operating at very high temperature, the SPIMD20 is ideal for direct installation on a
permanent magnet synchronous motor or nearby the motor.
The advantages of this system architecture are many, among them:
● SPIMD20 directly assembled to the motor permits a strong wiring reduction. The
SPIMD20 just needs a DC power supply, a DC auxiliary supply, a fieldbus. All these
connections can jump from one device to the other. The electrical cabinet will therefore
result very compact.
● The distributed architecture allows faster designing and faster commissioning.
● The DC power supply shared between many SPIMD20s permits to realize sensible
energy saving in a lot of applications.
● The fieldbus, Ethernet real-time, permits to make profit of all the advantages of flexible
automation such as: recipes, fast switching among different previously saved menus,
in-line behaviour optimization, centralized diagnostic and data logging. CANopen is
optionally available in the development roadmap.
● A high performance FPGA Altera Cyclon III is available in the SPIMD20 to configure,
among others, the Ethernet real-time bus according to your needs or preferences. The
basic pack includes EtherCAT.
● Position read-out can be realized using the very popular resolver or other more
performing devices such as EnDat 2.2 which are interfaced through the high
performance FPGA. Different position transducers can be connected using their IP’s.
● PWM driving is organized for operation at 4-8-16-32 kHz. All the devices connected to
the same master are synchronized to the driving fieldbus. The synchronization involves
position, speed, current loops and the PWM.
● A MEMS accelerometer permits to analyze the vibrations: abnormal behavior can be
detected before a fatal crash occur
● An SPI channel is available to support a compact flash or similar device in order to
store parameters, programs or other tools depending on the application.
Doc ID 17527 Rev 3 3/20

Main features SPIMD20
● A basic software package is available with the SPIMD20. This software package
includes:
– torque speed position control
– PWM driving 4-8-16-32 kHz
– current loop closure 4-8-16 kHz (PI)
– speed loop closure 1-2 kHz (PI)
– position loop closure 1-2 kHz (P)
– torque, speed, feed forward inputs provided
– low pass or/and notch filters provided
– All the above are synchronized to the fieldbus
– Position transducers: resolver or encoder EnDat 2.2
– EtherCat connectivity (CoE DSP402)
– CANopen (DS301, DSP402) is also in the development roadmap
● Two powerful development environments are available:
– IAR’s Embedded WorkBench to work at source code level (C, C++)
– Robox’s RDE to work at system level, permitting debugging and performance
optimization under real operating conditions.
A third one, QUARTUS II Altera development environment, should be used to implement
other real time Ethernet standards or other digital transducers into the FPGA.
4/20 Doc ID 17527 Rev 3
SPIMD20 Main features
)3*$
3RZHU6XSSO\
3RZHU
6WDJH
'5,9(
SURFHVVRU
),(/'%86
SURFHVVRU
)ODVK
0HPRU\
5HVROYHU
+ROGLQJ
%UDNH
(1&2'(5
(Q'DW
&$1%XV
3+<
3+<
&$1%XV
0,,
0,,
)LHOGEXV
&$1%XV
ELW
ELW
(QDEOH8SSHU
%UXVKOHVV
0RWRU
9'&
+ROGLQJ
%UDNH
)LHOGEXV
(WKHUQHW
+DQG
6KDNLQJ
%XV
9'&
1.1 Block diagram
Figure 1. Block diagram
Doc ID 17527 Rev 3 5/20
Main features SPIMD20
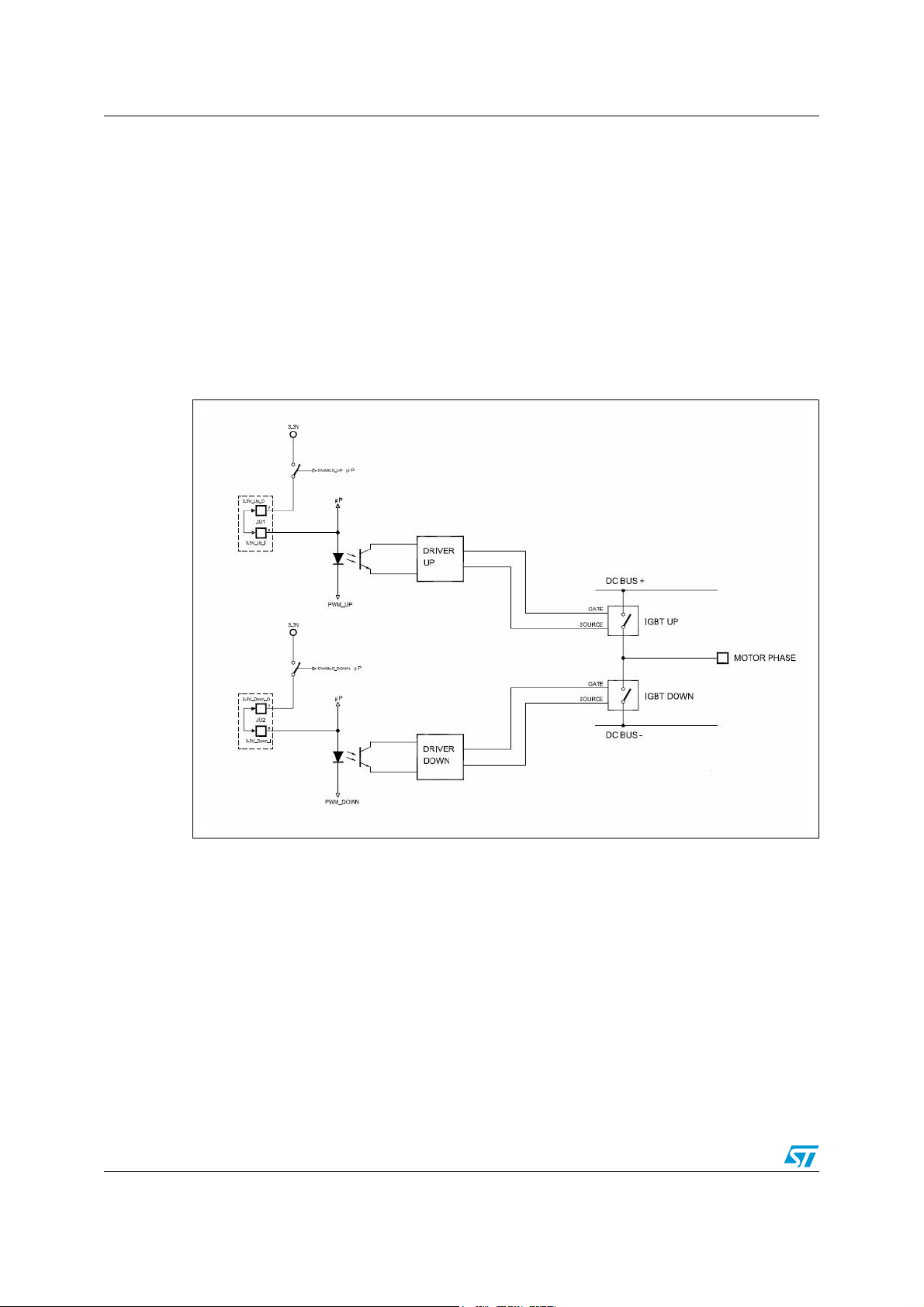
1.2 Safe torque off diagram
The module is equipped with four pins, available at JU1 and JU2 connectors, aimed to
disable the IGBT drivers via hardware.
The schematic architecture is showed in Figure 2.
Once the pins 7 of JU1 and JU2 are respectively let opened versus the pins 8 of JU1 and
JU2, the IGBT drivers are disabled.
If the pin 7 is shorted with the pin 8 on both the connectors JU1 and JU2, the module is
properly working.
The current flowing on those connections is less than 5 mA.
Figure 2. Safe torque off diagram
6/20 Doc ID 17527 Rev 3

SPIMD20 General specifications
2 General specifications
2.1 Ambient conditions
Table 2. Ambient conditions
operation (Ambient) 0 … +40°C
operation (Motor) 0 … +100°C
Temperature
Relative humidity
Altitude 4000mt
Protection degree IP 65 & IP 67
1. Without ice and condensation
operation (Bottom Heatsink) 0 … +100°C
operation (Top Heatsink) 0 … +70°C
storage -30 … +70°C
transportation -25 … +70°C
operation
storage
transportation
2.2 Vibrations and shocks
Table 3. Vibrations and shocks
Description Test conditions Value Unit
Vibration sine: amplitude
peak-peak
10…57Hz conforming to EN/IEC 60068-2-36 0.15 +/-15% mm
5 … 95%
5 … 95%
5 … 95%
(1)
(1)
(1)
Vibration sine: acceleration 57…150Hz conforming to EN/IEC 60068-2-6 1 +/-15% g
Vibration noise (random)
IEC 68-2-36
Vibration sine according to
EN 60068-2-6 and
EN 60068-2-37
Frequency 20 … 150 Hz
Spectral acceleration density, amplitude 0,005 ±3dB g2/Hz
10 … 2000Hz amplitude peak-peak 0.75 mm
Acceleration at 10 … 2000Hz 5 g
Doc ID 17527 Rev 3 7/20

Pin out description SPIMD20
3 Pin out description
Table 4. Pin description JU1/JU2
Name JU1 JU2 Type Description
PS_AUX+
PS_AUX-
POW_OK - 2 INP-48V Input power OK, PS_AUX- referred
IO_24V 5 -
IO_GND 6 -
INP1 - 5 INP-24V
INP2 - 6 INP-24V
3.3V_UP_O 7 -
3.3V_UP_I 8 -
3.3V_DOWN_O - 7
3.3V_DOWN_I - 8
ETH1_TXD+ 9 -
ETH1_TXD- 10 -
ETH1_RXD+ 11 -
11
2-
33
44
Power in
Power out 24Vdc digital inputs feeding
Safe torque off
Ethernet CH1 ethernet 10/100 IEEE 802.3
Auxiliary input voltage
18 to 48Vdc
Dig. inputs, 24Vdc, IO_GND referred
Disable the IGBT drivers via hardware. If the pin 7 is shorted with the
pin 8 on both the connectors JU1 and JU2, the module is properly
working
ETH1_RXD- 12 -
ETH2_TXD+ 13 -
ETH2_TXD- 14 -
ETH2_RXD+ 15 -
ETH2_RXD- 16 -
CANH - 9
CAN_GND - 11
SB_GND - 12
SB- - 14
HBR_RLS# - 15 INP-OD-3V3 Holding brake release
PB# - 16 INP-OD-3V3 User push-button
EXT_FLASH# - 17 INP-OD-3V3
Ethernet CH2 ethernet 10/100 IEEE 802.3
CanBus Fieldbus CANCANL - 10
CanBus Service busSB+ - 13
Connect to GND to enable boot from external flash memory (type
M25P16). External flash have to be connected to CRD_pins. (see
next page) leave pin EXT_FLASH floating to enable boot from
internal flash memory.
8/20 Doc ID 17527 Rev 3

SPIMD20 Pin out description
Table 4. Pin description JU1/JU2 (continued)
Name JU1 JU2 Type Description
LED1# 17 - OUT-LO-3V3
LED2# 18 - OUT-LO-3V3
WS_SDA - 18 BIDIR-3V3
WS_SCL 19 - OUT-3V3
JTMS 20 - INP-3V3
JTCK 21 - INP-3V3
JTDI 22 - INP-3V3
JTDO 23 - OUT-3V3
JTRST# 24 - INP-LO-3V3
JRESET# 25 - INP-OD-3V3
IO3# - 19 BIDIR-OD-3V3
IO4# - 20 BIDIR-OD-3V3
3V3 - 21
Power out 3.3V power supply for outputs, LED and I
GND - 22
CRD_CS# - 23 OUT-LO-3V3
CRD_CLK - 24 OUT-3V3
CRD_DI - 25 OUT-3V3
CRD_DO - 26 INP-3V3
User Led
2
C line for WorkStation connection
I
JTAG software debug port
TTL digital I/O, GND referred
External decoupling required
3.3V external flash.
SPI Interface 50mA max.
2
C - 100mA max
CRD_VCC - 27
CRD_GND - 28
RS232_GND 26 -
RS232_TXD 28 -
● INP-48 V: 48 V digital input, active high
● INP-24 V: 24 V digital input, active high
● INP-3V3: 3.3 V digital input, active high
● INP-LO-3V3: 3.3 V digital input, active low
● INP-OD-3V3: 3.3 V dig. input (Internal pull-up) to be connected to open-drain output
● OUT-3V3: 3.3 V digital output, push-pull active high
● OUT-LO-3V3: 3.3 V digital output, push-pull active low
● BIDIR-3V3: 3.3 V digital input/output
● BIDIR-OD-3V3: 3.3 V digital input/output (Internal Pull-up) to be connected to open-
drain output
Power out
RS232 RS232 full duplex connectionRS232_RXD 27 -
Doc ID 17527 Rev 3 9/20

Pin out description SPIMD20
Table 5. Pin description JU3
Name Pin Type Description
DC_BUS-
Power in 800VDC BusBar-
2
- 3 - Position not loaded
4
1
DC_BUS+
Power in 800VDC BusBar+
5
- 6 - Position not loaded
FE
7
8
Table 6. Pin description JM3
Functional
Earth
Connected to chassis and shield/FE pins of
JU1, JU2, JM3,JM7, JM9, JM10 and JM11 connectors
Name Pin Type Description
TMOT- 1 Analog
TMOT+ 2 Analog
Connection to PTC motor thermal probe
(KTY84-130)
-3 -N.C.
SHIELD 4 - Connected to PE pins on JU3
Table 7. Pin description JM7
Name Pin Type Description
PE 1 - Connected to PE pins on JU3
DC_BUS- 2 Power 800VDC BusBar capacitor connection
PE 3 - Connected to PE pins on JU3
DC_BUS+ 4 Power 800VDC BusBar capacitor connection
Table 8. Pin description JM9
Name Pin Type Description
1-
PE
Connected to PE pins on JU32
3
MOTOR_U 4 Motor Motor U phase
MOTOR_V 5 Motor Motor V phase
MOTOR_W 6 Motor Motor W phase
10/20 Doc ID 17527 Rev 3

SPIMD20 Pin out description
Table 9. Pin description JM10
Name Pin Type Description
SHIELD 1 - Connected to PE pins on JU3
-2 --
HBR+ 3 Brake
HBR- 4 Brake
24VDC holding brake connection
Current max 500mA
Table 10. Pin description JM11
Name Pin Type Description
SHIELD
ENC_GND 2
ENC_5V 9
ENC_CLK- 3
ENC_CLK+ 10
ENC_DAT- 4
ENC_DAT+ 11
RES_EXC- 5
RES_EXC+ 12
RES_SIN- 6
RES_SIN+ 13
RES_COS- 7
RES_COS+ 14
1
8
- Connected to PE pins on JU3
Power out
RS422
RS485
Analog
Analog
Analog
5V, 200mA max Encoder EnDat 2.2
Resolver
Doc ID 17527 Rev 3 11/20

Electrical characteristics SPIMD20
4 Electrical characteristics
4.1 Absolute maximum ratings
Table 11. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
DC_BUS_MAX MAX DC BusBar supply voltage (JU3 pin 1, 2, 4, 5) 850 V
DC_BUS_MIN MIN DC BusBar supply voltage (JU3 pin 1, 2, 4, 5) 40 V
Pw_MAX Max continuous power (Output current = 6A rms MAX) 2000 W
I_OUT_MAX Max output current (RMS) 6 A
I_OUT Max output current peak (200ms on 1.5s period) 17 A
PS_AUX DC auxiliary supply voltage (JU1 pin 1-4 JU2 pin 1, 3, 4) 50 V
IO_24V DC logic supply voltage (JU1 pin 5, 6) 28 V
Tstg Storage temperature range -30 … +70 °C
4.2 Electrical data
4.2.1 Power supply
Table 12. Power supply
Val u e
Symbol Parameter Test conditions
Min Typ Max
DC_AUX DC auxiliary supply voltage Power In ( JU1/JU2 pin 1-2 ) 18 24 48 V
Vin ( JU1/JU2 pin 1-2 ) = 18V, BRAKE
DC auxiliary current BRAKE
DC_AUX_
MAX_CUR
DC_Brake 24 V DC Brake connection Current max 500mA ( JM10 pin 3-4 ) 21.6 24 26.4 V
CRD_VCC
3V3 I
connected
DC auxiliary current without
BRAKE
Analogue supply for
external Flash
2
C power supply
connected
Vin ( JU1/JU2 pin 1-2 ) = 48V, BRAKE
connected
Vin ( JU1/JU2 pin 1-2 ) = 18V, without BRAKE 0.6 A
Vin ( JU1/JU2 pin 1-2 ) = 48V, without BRAKE 0.3 A
SPI max current 50mA ( JU2 pin 27 ) 3.2 3.3 3.4 V
DC for Outputs, I2C & LEDs 100mA max JU2
pin 21
3.2 3.3 3.4 V
1.6 A
0.8 A
Unit
IO_24V 24 Vdc digital inputs feeding 100mA max JU1 pin 5-6 21.6 24 26.4 V
12/20 Doc ID 17527 Rev 3

SPIMD20 Electrical characteristics
!-V
4.2.2 Power stage
Figure 3. Equivalent circuit Figure 4. Test circuit for inductive load
Table 13. IGBT
switching
Symbol Parameter Test conditions
= 15V, IC= 30A
V
V
CE(sat)
I
CES
I
GES
t
d(on)
t
d(off)
E
on
E
C
C
C
1. Eon is the turn-on losses when a typical diode is used in the test circuit in Figure 6.
Collector-emitter saturation voltage
Collector cut-off current (VGE = 0)
Gate-emitter leakage current (VCE = 0) VGE =± 20V - ± 100 nA
Tu r n- on d el a y t i me
Current rise time - 38 ns
t
r
Turn-off delay time - 420 ns
t
Current fall time - 360 ns
f
(1)
Turn-on switching losses - 4.7 mJ
Turn-off switching losses - 9.3 mJ
off
Input capacitance VCE = 25V, f = 1MHz, VGE=0 - 2577 pF
ies
Output capacitance - 196 pF
oes
Reverse transfer capacitance - 39.5 pF
res
Q
Total gate charge VCE = 960V, IC= 20A,VGE=15V - 126 nC
g
GE
V
= 15V, IC= 30A,
GE
=125 °C
T
j
=1200V
V
CE
=1200V, Tj=125 °C
V
CE
V
= 960V, IC = 30A
CC
= 10Ω, VGE= 15V,
R
G
T
= 125°C see Figure 6
j
Val ue
Min Typ Max
2.8
3.85
2.7
-
-
50010µA
- 45 ns
Unit
V
mA
Doc ID 17527 Rev 3 13/20

Electrical characteristics SPIMD20
Table 14. Diodes
Val ue
Symbol Parameter Test conditions
Unit
Min Typ Max
I
= 8A Tj = 25°C - 2.2
(1)
V
Forward voltage drop
F
I
1. Pulse test: tp = 380 µs, δ < 2 %
To evaluate the conduction losses use the following equation: P = 1.5 x I
Reverse recovery current
RM
Reverse recovery time
t
rr
F
= 8A Tj = 125°C - 1.3 2.0
I
F
= 8A, dIF/dt = -200A/μs,
I
F
= 600V, Tj = 125°C
V
R
IF = 1A, dIF/dt = -100A/µs,
V
= 30V, Tj = 25°C
R
+ 0.05 IF ² (RMS)
F(AV)
-1421A
-5070ns
V
Table 15. Thermal resistance
Value
Symbol Parameter Test conditions
Min TypMax
Unit
R
R
R
th(CH)
th(j-c)
th(j-c)
Thermal resistance
IGBT - - 0.42 °C/W
Diode - - 0.52 °C/W
Module with heatsink compound - - TBD °C/W
14/20 Doc ID 17527 Rev 3

SPIMD20 Mechanical dimensions
AM02500v1
5 Mechanical dimensions
5.1 Mechanical data (dimensions in mm)
Figure 5. Mechanical data (dimensions in mm)
Doc ID 17527 Rev 3 15/20

Mechanical dimensions SPIMD20
Figure 6. Mechanical data (dimensions in mm) continued
16/20 Doc ID 17527 Rev 3

SPIMD20 Mechanical dimensions
5.1.1 Technical specifications for surface coupling
IMD module can be coupled with a plane surface finished with characteristics detailed
below:
Table 16. Technical specifications for surface coupling
Parameter Value
Roughness 3.2 Ra
Planarity 0.1 mm
Max coupling torque on fixing screws 3 N/m
5.2 The basic software package
A basic software package is available on request, at source level. This software package is
written in C language (not C++) by Robox and is supplied AS IS.
The comments are in English. It was developed using the IAR’s Embedded WorkBench
development tool.
In the design workspace each processor, the fieldbus processor and the drive processor,
has its own project. The interface between them is defined in some common files.
The fieldbus processor main tasks are:
● building up of the whole system at power on
● communication handling with the external master fieldbus according to the EtherCat
CoE profile (Ecat sync mode or Distributed clock mode)
● information exchange with the drive processor through the dual port ram implemented
into the FPGA
● handling of the I
● holding brake management
2
C port to get application parameters
The drive processor main tasks are:
● PWM driving performed at the same frequency of the current loop or at double
frequency (4-8-16-32 kHz).
● current loop closure (4-8-16 kHz). The control algorithm is PI
● speed loop closure (1-2 kHz). The control algorithm is PI
● position loop closure (1-2 kHz). The control algorithm is P
The system is able to work in torque control or in speed control or in position control.
The feed forward inputs are provided for the two inner loops. The PWM driving, and the
loops closure, are synchronized to the external master fieldbus sync event.
● DC bus reading
An optically coupled reading of the DC bus voltage allows its monitoring. Moreover the
gains of the current loop are independent from the DC bus level.
● Filtering:
3 optional 2nd order filter stages (LowPass/Notch) can be activated on
SpeedReference
Doc ID 17527 Rev 3 17/20

Mechanical dimensions SPIMD20
3 optional 2nd order filter stages (LowPass/Notch) can be activated on
TorqueReference.
Triple sampling on the resolver reading is provided
● Position or time capture on the two digital inputs
● Self tuning
a complete self tuning procedure is available. It includes:
– motor characteristics (correct wiring, number of motor and transducer poles)
– current loop gains
– speed loop gains
– EnDat offset position read-out and storage in the e2prom
– resolver adjustment (amplitude, sample phase, position offset and alarm
threshold)
● Self test
built-in self test allowing to generate square or synusoidal waveforms on the speed or
torque reference with adjustable frequency, amplitude, offset and TT cycle.
A complete library to access all the involved peripherals is included.
The EtherCAT
request.
®
entries manual of the basic software package is available at Robox on
5.3 Safety characteristics and connection requirements
The IMD module is designed to comply with the IEC61800-5-1 norms, applicable to the D.C.
drive systems connected to the line voltage up to 800 V D.C.
The earthing connections are intended as TN or TT having the voltage between phase and
Earth 300 V r.m.s. maximum.
In case this voltage is higher than 300 V r.m.s. the user shall provide the system with
protective device (varistor, voltage discharger, etc.) in order to reduce the impulse voltage to
2500 V max.
The P.E. connections, available at JU3 pins 7, 8 and/or JM9 pins 1, 2, 3 shall be connected
to the protective bonding before supplying the system.
Please note that Earth leakage current is > 3.5 mA. Automatic disconnection of thesupply in
case of discontinuity of the protective conductor must be provided.
5.4 Installation and user's manual
For installation on a system or motor please ask end user.
Specifications for surface coupling can be find in this document section Section 5.1.1.
5.5 Maintenance
The IMD module doesn't require maintenance. In case of failure module is not repairable
and have to be replaced.
18/20 Doc ID 17527 Rev 3

SPIMD20 Revision history
6 Revision history
Table 17. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
31-May-2010 1 First release
26-Jan-2011 2
25-Jul-2012 3 Updated Table 5 on page 10 and Table 11 on page 12.
Updated coverpage, Table 4 on page 8
Added Section 1.2 on page 6
Doc ID 17527 Rev 3 19/20

SPIMD20
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY TWO AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVES, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2012 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
20/20 Doc ID 17527 Rev 3
 Loading...
Loading...