Page 1

T60H677.02 WLAN 802.11b/g
User Manual
Page 2

Chapter 1 About the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device............................................. 3
1-1 Introduction .......................................................................................................... 3
1-2 Using a Wireless Local Area Network.................................................................3
1-3 Features and Requirements................................................................................... 4
Chapter 2 Network Configuring and Planning............................................................5
2-1 Ad-Hoc Network............................................................... ................................ .... 5
2-2 Access Point (Infrastructure) Network... ..................................... .........................6
Chapter 3 Atheros Client Utility Installation...............................................................7
3-1 Atheros Client Utility Installation.........................................................................7
Chapter 4 Atheros Client Utility (ACU) Configuration............................................ 10
4-1 Atheros Client Utility icon.................................................................................. 10
4-2 Current Status Tab .............................................................................................. 11
4-3 Profile Management ...........................................................................................13
4-3-1 Create or Modify a Profile ...................................................................... 14
4-3-2 Security Settings in Profile Management................................................ 16
4-3-3 Advance d settings in Profile Mana gement.............................................. 20
4-4 Diagnostic Tab.................................................................................................... 21
4-5 Action Menu.......................................................................................................22
4-5-1 Enable/Disable Radio............................ ...................................... ............ 22
4-5-2 Enable/Disable Tray Icon...................................................................... ..22
Chapter 5 Wireless Configuration using Windows XP..................................................... 23
5-1 Configuring Your Wireless Networking Settings............................................... 23
5-2 Advanced Wireless Settings............................................ ............................. ....... 23
5-3 Disabling the Radio............................. ................................... .. ..........................24
5-4 Help and Support Information............................................................................ 24
Appendix A - Atheros Client Utility Uninstall Process .................................................... 25
Appendix B - Glossary...................................................................................................... 28
Appendix C – Wireless Notice.......................................................................................... 29
Page 3

Chapter 1 About the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device
1-1 Introduction
The AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device allows you to access Wireless Local Area Networks
(WLANs), share a local printer and files with others in your network, access the Internet, and roam
about the office—wirelessly. This wireless Local Area Network solution is designed for both large
and small businesses, and it is scalable so that you can add users and new network features as your
networking needs grow.
The AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device is a 2.4Ghz WLAN technology that will operate with at a
maximum data rate of 11Mbps with 802.11b and maximum data rate of 54Mbps with 802.11g
wireless networks. The AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device will a u tomatically detect and
seamlessly roam between both 802.11b and 802.11g wireless networks.
1-2 Using a Wireless Local Area Network
A wireless LAN provides the same functionality of a wired network, but it eliminates the need to
install networking cables and other networking equipment. Not only is a wireless LAN easier to
deploy, but it also allows for mobility through “roaming.” For example the AMBIT WLAN
802.11b/g device can roam from a conference room to an office without being disconnected from
the network.
Page 4

1-3 Features and Requirements
The AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device includes the following features:
Wireless Features
• Support for the IEEE 802.11b standard
• Support for the IEEE 802.11 g standard
• Operates within the 2.4-GHz band
• Maximum data rate of up to 11 Mbps (802.11b)
• Maximum data rate of up to 54 Mbps (802.11g)
Interoperability
• WiFi certified at 2.4GHz to ensure wireless interoperability with other WiFi (802.11b)
certified devices.
Security
• Cisco Client Extension compatibility (including LEAP)
• Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) encryption, operating with 64bit, 128bit or 152 bit
encryption
• AES-CCM Encryption support
• Support for Windows 802.1X supplicants
Page 5
Chapter 2 Network Configuring and Planning
A wireless LAN can be configured for two different modes of operation. While each method has its
advantages, one may be better suited for your needs. Review the following configurations to
determine which mode is best for you.
• Ad-Hoc Network
• Access Point (Infrastructure) Network
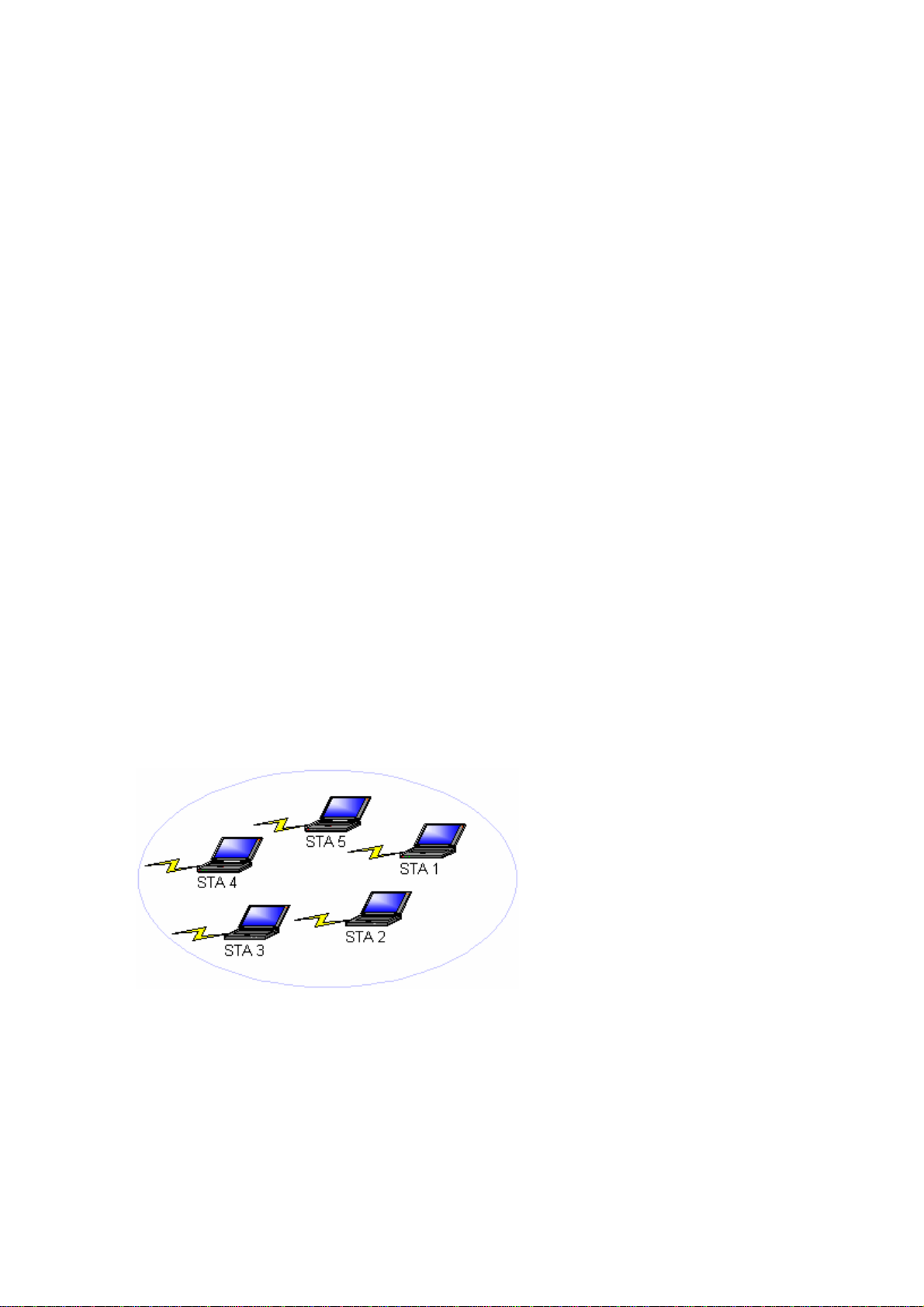
2-1 Ad-Hoc Network
An Ad-Hoc network is the simplest to deploy and is ideal for small offices. Ad-Hoc wireless
networks can be comprised of two or more wireless client configured to communicate with one
another. All Ad-hoc clients communicate directly with each other without using an access point
(AP). As a user on t his type of network, you a re able to quickly buil d up a wireles s network in or der
to share files with other employees, print to a shared office printer, and access the Internet through
a single shared connection.
Ad-hoc networking is cost effective, because no other devices components are needed (access
points, hubs or routers) in order to setup a network. However, with peer-to-peer Ad-Hoc
networking, your computer is only able to communicate with other nearby wireless clients.
Characteristics
Networked computers send data directly to each other
Advantages
• Simple setup
Cost efficiency
•
Disadvantages
Communication is limited to nearby wireless clients
Figure 2-1
Page 6
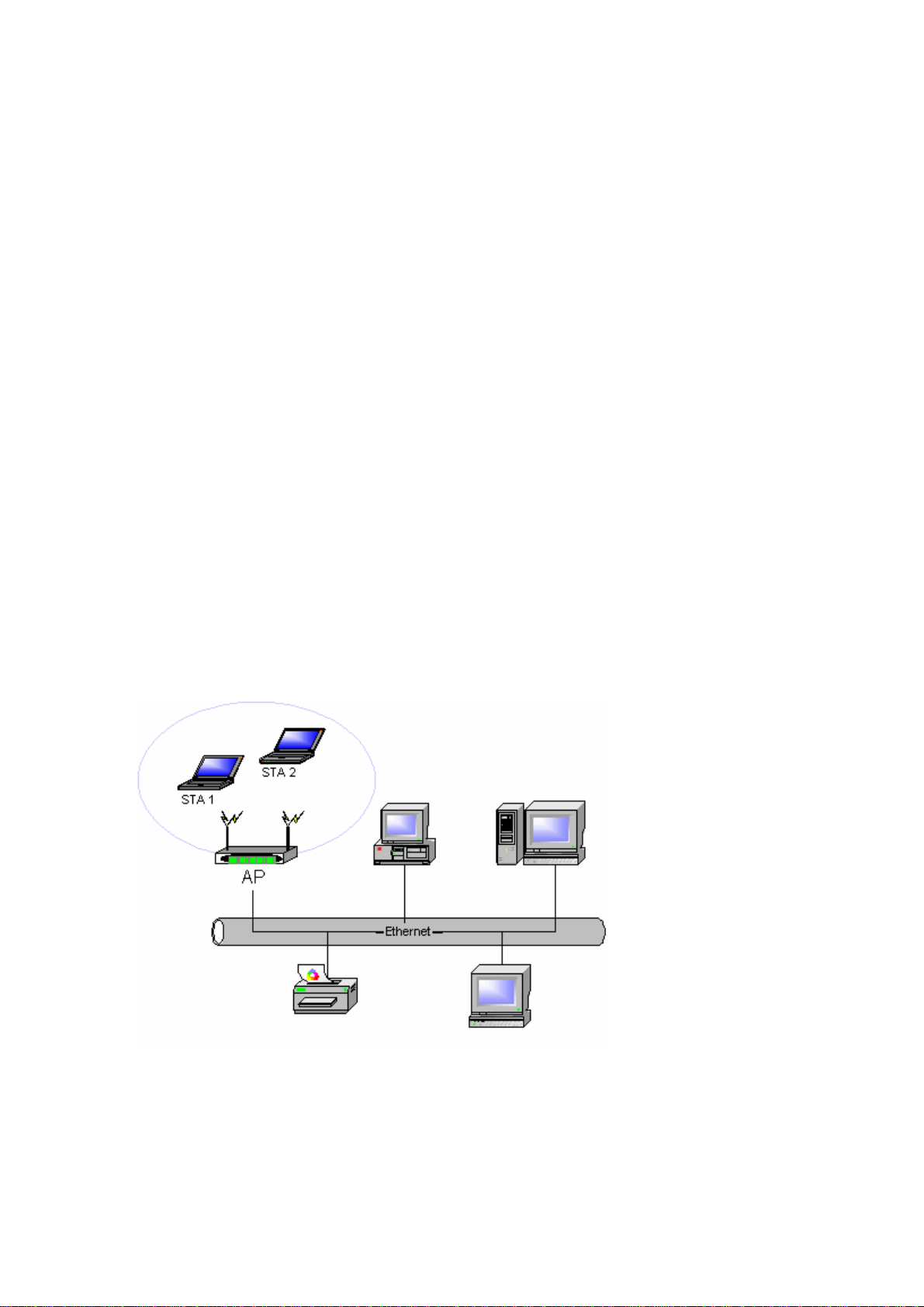
2-2 Access Point (Infrastructure) Network
An Access Point network is also referred to as an “Infrastructure” network. The key difference
between a wireless access point network and an Ad-Hoc network is the addition of one extra
element—the Access Point. The Access Point serves as the focal point for all data traffic on your
wireless network, optimally managing all wireless data transactions.
Additionally, the wireless Infrastructure can provide access to an existing wired LAN. This link
allows computers on the infrastructure wireless LAN to access the other wired LAN’s resources
and tools, including Internet access, email delivery, file transfer, and printer sharing.
Characteristics
Networked computers communicate with each other through a dedicated Access Point. All
data transmitted between the computers on this wireless LAN passes through the access point.
Advantages
• Extended range: The access point extends the range of the wireless LAN. Each wireless
client computer can communicate with other computers equipped with wireless devices
that are within the range of the access point.
• Roaming: As you move throughout the building, the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device
will automatically search for an access point to use, ensuring continuous communication
with the wireless network.
• Network connectivity: An access point can provide wireless LAN access to an existing
wired network by bridging the two networks together. This gives users of the wireless LAN
access to corporate email, Internet, shared printers and files.
Disadvantages
Because this network mode offers more features, it requires additional components and setup
time to deploy
.
Figure 2-2
Page 7
Chapter 3 Atheros Client Utility Installation
Note for Windows XP Users: The Windows XP operating system has a built-i n featur e
known as “Wireless Zero Configuration” which has the capability to configure and control
the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device (See Chapter 5). Installing the Wireless LAN Client
utility will disable this Windows XP feature. For most W indows XP users, it is
recommended that they do not install the Atheros Client Utility . Installation of the Atheros
Client utility is only needed if your wireless LAN network requires Cisco Client Extension
or if you want to use Atheros Client Utility instead of Wi ndows XP Wireless Zero
configuration services.
3-1 Atheros Client Utility Installation
1. Begin installation by starting the software setup program according to the step described
below…
• Windows 2000 – Double click the desktop icon labeled “Software Setup”.
• Windows XP - Choose Start\Programs\Software Setup
2. Click Next on the Software Setup “Welcome” dialog box.
Figure 3-1
Page 8
3. Scroll down and check the Box labeled, “Atheros Client Utility”.
4. Click on the Next button.
Figure 3-2
Figure 3-3
Page 9
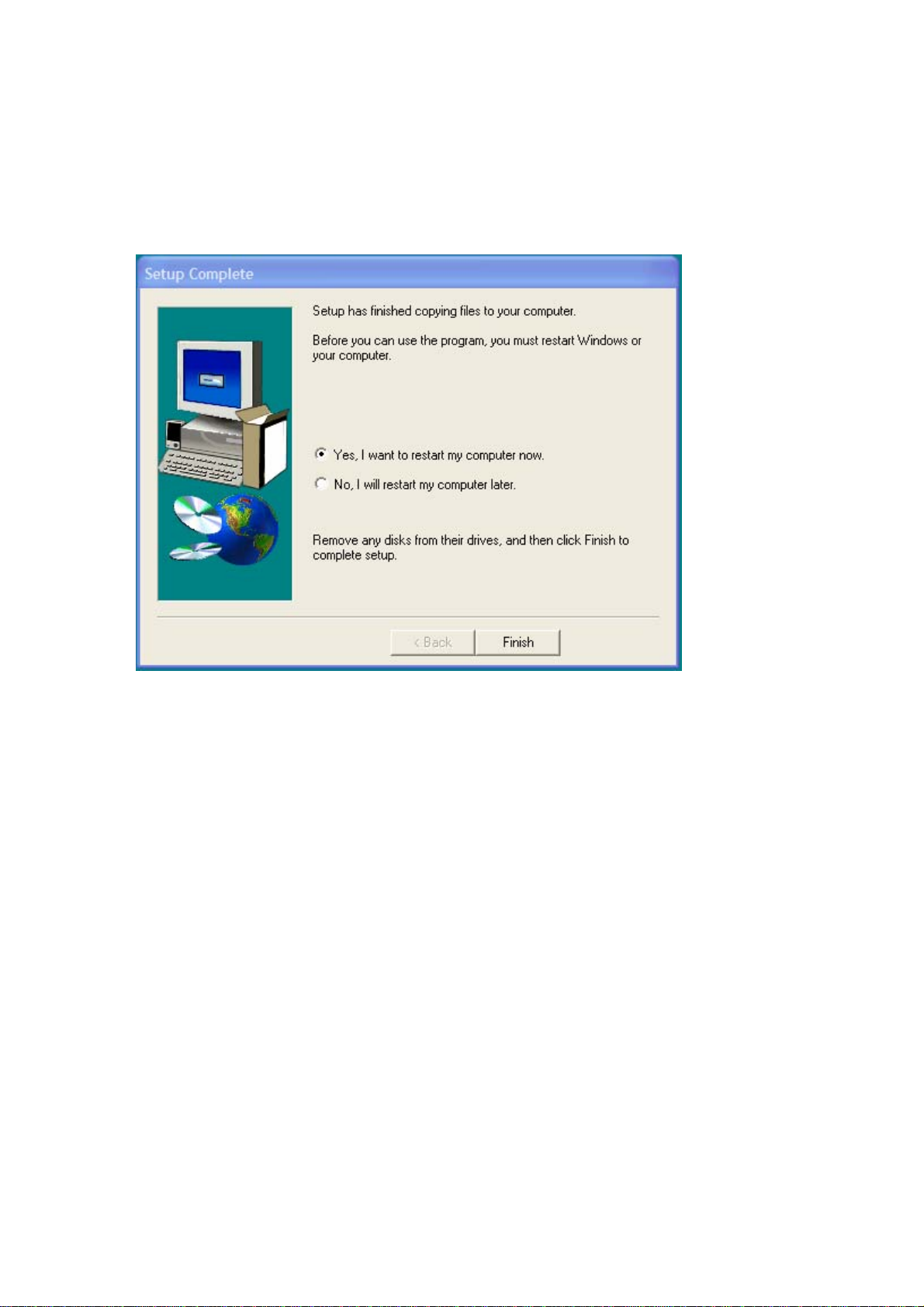
5. Congratulations! Atheros Client Utility has been installed successfully.
Please click ‘Finish’ to go to the next step.
Figure 3-4
6. The Atheros Client Utility will automatically be loaded each time your computer started. To
access the utility click on Atheros Client Utility icon in the system tray (Uninstall information
can be found in Appendix A)
Page 10

Chapter 4 Atheros Client Utility (ACU) Configuration
The following sections des cribe the A theros Clie nt Utilit y (ACU). The ACU p rovides
quick access and friendly interface to configure the Wireless LAN settings. If you are
using Windows XP and have not installed the Atheros Client Utility, information on
configuring your AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device using Windows XP Zero
Configuration feature can be found in Chapter 5.
4-1 Atheros Client Utility icon
The Atheros Client Utility icon will appear in the system tray each time your computer is
restarted.
The Atheros Client Utility icon will display the current status of the wireless connection.
The following are the various states that can be displayed by the icon…
• Radio Disabled indicates that the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g radio has been
• Yellow bars, then the signal strength is very small and the wireless connection is at
• Green bars indicate good or excellent signal strength is being received.
See Figure 4-1 shows the various states of the Atheros Client Utility icon.
To utilize the utility, double click on the ACU icon.
Figure 4-1
disabled through either Hardware or Software
its limit of range
Figure 4-2
Page 11

4-2 Current Status Tab
The current status tab displays the following information about your wireless connection.
• Profile Name –
• Network T ype – The current type of wireless network that is either Access Point or
Ad-hoc.
• Wireless Mode – The current wireless mode is the frequency and data rate that has
been selected.
• Current Channel – Specifies the current channel that the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g
is connected to or scanning on.
• Link Status – The link can be either connected or disconnected to an Access point
or other wireless client.
• Encryption Type – Describes whether or not the wireless traffic is encrypting
• IP Address –The current IP address of the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/ g
The current name of the selected configuration profile.
Figure 4-3
Page 12

The Advanced button provides more detailed information regarding your wireless
connection.
• Transmit Power Level – Provides current setting of Radio output power
• Network Name (SSID) – The wireless network name (SSID) that the device is
currently connected with
• Power Save Mode – The type of Power Savings that is configured on the device
• Frequency – The current frequency that the Wireless device is connected or
scanning on.
• Transmit Rate – The transmit rate (Mbps) for the current connection for the
wireless driver.
• Receive Rate –The receive rate (Mbps) for the current connection for the driver.
Figure 4-4
Page 13

4-3 Profile Management
The Profile Management tab allows the user to configure several different user defined
profiles. Each profile can be configured to match the appropriate settings of a unique
wireless network.
The Profile box lists all the configured profiles. The Details dialog describes th e basic
settings (SSID, Network Type, Security Mode) of the highlighted profile. The active
profile will be displayed with the wireless icon next to it. To make a profile active,
highlight the profile and click on the Activate button. By setting a Profile active, you
configure the wireless device to search for wireless networks t hat match up to those
specific profile wirel ess settings .
Figure 4-5
The Available networks button allows the user to vi ew a list of all avail able wireless
network that are within range of the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g . Each wireless network
entry displays the SSID, encryption settings, signal strength level, channel and wireless
mode information. You can create a new profile utilizing Available networks button by
highlighting the wireless network you want to create a profile for and clicking on the
Activate button.
Page 14

Figure 4-6
4-3-1 Create or Modify a Profile
1. From the Profile Management tab Click on the New or Modify button
2. The Network Configuration Settings dialog box will appear
3. In the Profile Name box, type in a unique name that describes the wireless network
you are configuring the settings to connect to.
4. In the SSID boxes type in the SSID that matches up with the wireless network you
are trying to configure the profile to connect with. There are three SSID selections
(SSID1, SSID2, SSID3) available; this feature allows you to configure a single
profile to match up to 3 different SSID’s.
Page 15

Figure 4-7
5. Select the Security Tab to manage the security settings associated with this profile
Figure 4-8
Page 16

6. Choose the security setting that is required on the wireless network. Once the
appropriate security mode is chosen the button next to the selection will enable you
to include any additional information required by that security mode.
4-3-2 Security Settings in Profile Management
The Security Tab allows you to configure the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device to match the
security settings of the Wireless LAN netwo rk.
Select the appropriate security mode…
• Pre-Shared Keys – This mode is commonly referred to as WEP encryption, and
allows for setting of all four WEP keys. The pre-shared key selection also allows for
setting of a unique key, which is used with higher forms of encryption such as AES.
• LEAP – This is CCX compliant feature that allows for authentication with Cisco
access points. This mode should only be used if your Wireless LAN requires LEAP
authentication
• Externally Managed 802.1X Keys – This security mode allows for dynamic
switching of encryption keys using 802.1X authentication. This mode should only be
used if your Wireless LAN requires 802.1X authentication.
• Disabled – Use this mode when there is no security authentication or encryption is
currently enabled on your Wireless LAN network.
Page 17

Figure 4-9
Setting Pre-Shared Keys
Pre-Shared keys can be defined using the “Define Pre-Shared Keys” box
Figure 4-10
Page 18

Key Entry Method – Determines the entry method for an encryption key:
• Hexadecimal (0-9, A-F)
• ASCII text (any keyboard characters, A-Z, 0-9).
PreUser Key – Defines the un ique e ncryptio n key for network c onfigura tion se curit y . The Pre
User key is used with many authentication mechanism and encryption
Shared Keys – Determines a set of shared encryption keys (First, Second, Third, Fourth) used
for wireless encryption and security. At least one Shared Key field must be populated to enable
security using a shared key. If more then one key is defined then Click on the radio button to
select a key as the default encryption key.
Key Length – The options for Key Length are
• 64 bit encryption (10 digits)
• 128 bit encryption (26 digits)
• 152 bit encryption (32 digits)
The number of available characters allowed to be entered in the encryption key field will
automatically be determined by the Key length setting.
Setting LEAP authentication
LEAP authentication is a part of CCX compatibility and allows you to configure the AMBIT
WLAN 802.11b/g device to match the work with a Wireless LAN that incorporates LEAP
authentication. This mode should only be used if your Wireless LAN requires LEAP
authentication.
To configure the LEAP settings for a particular profile select LEAP in the security mode and
click on the Define LEAP settings button to configure the settings described below.
• Username – The username that is used to log in to the LEAP network
• Password – The password used to log in to the LEAP network. This password is
encrypted using the same encryption as the encryption keys.
Page 19

Figure 4-11
Figure 4-12
Page 20

4-3-3 Advanced settings in Profile Management
The advanced tab provide more complex wireless settings and these settings should only be
modified if there is a specific requirement on your wireless network.
a. Power Save Mode - allows the user to minimize power utilized by the AMBIT
WLAN 802.11b/g device. Note: Setting Power Save Mode to enabled (Normal or
Maximum) may cause the user to experience an extended connection delay of up
to one minute.
b. Network Type - allows the user to config ure the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g
device as either an Ad-hoc or Access point type network
c. 802.11b Preamble - allows setting the preamble support to match up with the
specified wireless network.
d. Transmit Power Level - allows the user to modify the po wer output of the radio.
Setting. Note: Setting this to any other value except 100% will decrease range of
your AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device.
Figure 4-13
Page 21

Wireless Mode Setting
The wireless Mode settings allow the user to specify which wireless frequency and data rate the
wireless network is operating at. If all selections are chosen, the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g
device will automatically search all frequencies and data rates for wireless networks that match
up to the profile settings.
Wireless Mode when starting Ad-Hoc setting
The “Wireless Mode when starting ad-hoc setting” allows the user to determine the type of
ad-hoc network to be started. Note: This setting will only take effect if there are no other
ad-hoc networks with the same SSID currently operating within range. If existing ad-hoc
networks with the same SSID are currently operating, then the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g
device will connect using the frequency and data rate provided by the exiting ad-hoc network.
4-4 Diagnostic Tab
The diagnostic TAB displays the current data statistics for both receive and transmit.
Additional statistics and driver information can be displayed using the appropriate labeled
buttons.
Figure 4-14
Page 22

4-5 Action Menu
The Action menu allows for enabling and disabling both the wireless radio and/or system tray
icon.
Figure 4-15
4-5-1 Enable/Disable Radio
There may be situations when the user wants to disable the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device’s
radio, so that the wireless device cannot send or receive any wireless traffic. If a user is in an
environment where there are no wireless networks, the user may turn off the radio in order to
minimize power consumption of the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device.
In the ACTION menu of the ACU there is an Enable Radio/Disable Radio selection. The choice
provided in the menu will toggle the current state of the radio.
• Enable Radio: The Radio is currently OFF (Disabled), and the “Enable Radio”
selection will turn ON the Radio of the wireless device.
• Disable Radio: The Radio is currently ON (Enabled), and the “Disable Radio”
selection will turn OFF the Radio of the wireless device
The AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device radio also may be disabled through an external button
located on your platform, please review your platform user’s guide for additional information about
the wireless enable/disable button
4-5-2 Enable/Disable Tray Icon
In the ACTION menu of the ACU t here is an Enable T ray Icon/Disable tray Icon selection. The
choice provided in the menu will toggle the curren t s tate o f the System tray Icon.
• Disable T ray Icon: This will remove the tray icon from you system tray. The system
tray icon appears in the system tray again after system is restarted or if the Atheros
Client utility is opened again through Start\Programs\Atheros\ACU.
• Enable T ray Icon: This will allow for the system tray icon to once again be placed in
the system tray.
Page 23

Chapter 5 Wireless Configuration using Windows XP
5-1 Configuring Your Wireless Networking Settings
The Windows XP operating system has a built-in feature known as “Wireless Zero
Configuration” which has the capability to configure and control this Wireless LAN device.
To configure your device with this feature follow the steps below…
1. From the Start menu, select Control Panel.
2. Click Network and Internet Connections.
3. Click Network Connections.
4. Right-click the network connection associated with your AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device,
and select Properties.
5. Click on the Wireless Networks tab.
6. Click on the link Setting Up Wireless Network Configuration.
When the Help and Support Center window appears, you can access information regarding wireless
Network configuration. To access configuration information of your adapter, follow the on-screen
instructions.
5-2 Advanced Wireless Settings
AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device has several advanced settings which may need to be
The
configured depending on your wireless network. It i s recommended that these setting s
remain unchanged unless there is a specific need that requires modifying these settings.
1. From the Start menu, select Control Panel.
2. Click Network and Internet Connections.
3. Click Network Connections.
4. Right-click the connection for your AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device, and select Properties.
5. From the General tab, click the Configure button.
6. Click on the Advanced TAB
7. Modify the wireless settings as required
Page 24

5-3 Disabling the Radio
There may be situations when the user wants to disable the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device
radio, so that the wireless device cannot send or receive any wireless traffic. If a user is in an
environment where there are no wireless networks, the user may turn off the radio in order to
minimize power consumption of the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device. Follow the steps
outlined in the Section 5-2 above labeled “Advanced Wireless settings” and choose the Radio
ON/OFF selection.
• Select OFF – To turn OFF radio of the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device
Select ON – To turn ON the radio of the AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device
•
The AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device radio may also be disabled through an external button
located on your platform, please review your platform users guide for additional information about
the wireless enable/disable button
5-4 Help and Support Information
Configuration information and troubleshooting in Windows XP is available in
Microsoft’s Help and Support Center on Windows XP systems. Links to the appropriate Microsoft
Web sites are also available here.
To access this information:
1. From the Start menu, select Control Panel.
2. Click Network and Internet Connections.
3. Click Network Connections.
4. Right-click the connection for your AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device, and select Properties.
5. From the General tab, click the Configure button.
6. From the General tab, click the Troubleshoot button.
When the Help and Support Center window appears, you can access information regarding the
Network adapter. To access configuration information of your adapter, follow the on-screen
Instructions. For the network adapter to function in a wireless LAN, you must change the settings at
Least once.
Page 25

Appendix A - Atheros Client Utility Uninstall Process
Follow the steps below to remove the Atheros Client Utility:
1. Access the Control Panel from the Start menu
2. Click on the ‘Add/Remove Programs’ in the ‘Control Panel’.
3. Select ‘Atheros Client Utility’ and click ‘Change/Remove’ button, the dialog as below displays.
Figure A-1
Figure A-2
Page 26

4. Select ‘Remove’ and then click the ‘Next’ button to perform the un-installation. Click ‘OK’
button if you really want to remove the Atheros Client Utility.
Figure A-3
5. Wait for the un-installation to do its work. Click ‘Finish’ to complete the un-Installation.
Figure A-4
Figure A-5
Page 27

Figure A-6
Page 28

Appendix B - Glossary
ACU - Atheros Client Utility (ACU) is the utility that allows for configuration of the
AMBIT WLAN 802.11b/g device
Access Point - An internetworking device that seamlessly connects wired and wireless networks
together.
Ad Hoc - A peer- to-peer wireless network without Access Point. A group of wireless clients
consistent an independent wireless LAN.
Backbone - The core infrastructure of a network, the portion of the network that transports
information from one central location to another central location. The informatio n is then
off-loaded onto a local system.
BSS - Basic Service Set. An Access Point associated with several wireless stations.
ESS - Extended Service Set. More than one BSS can be configured as an Extended Service Set. An
ESS is basically a roaming domain.
ESSID –Extended Service Set Identifier. The length of the ESSID information is between 0 and 32
octets. A 0 length identifier indicates the broadcast SSID.
Ethernet - A popular local area data communications network, originally developed by Xerox
Corp., which accepts transmission from computers and terminals. Ethernet operates on 10/100
Mbps transmission rate over shielded coaxial cable or over shielded twisted pair telephone wire.
Infrastructure - An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an infrastructure configuration.
Roaming - A function that allows one to travel w ith a mobile end system (wireless LAN mobile
station, for example) through the territory of a domain (an ESS, for example) while continuously
connecting to the infrastructure.
SSID – Service Set Identifier (SSID) is the network name used by the Wireless LAN . The length of
the SSID information is between 0 and 32 octets.
WEP –Wired Equivalent Privacy. The optional cryptographic confidentiality algorithm specified
by IEEE 802.11 used to provide data confidentiality that is subjectively equivalent to the
confidentiality of a wired local area network (LAN) medium that does not employ cryptographic
techniques to enhance privacy.
Page 29

Appendix C – Wireless Notice
U.S. Regulatory Wireless Notice
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
The FCC requires the user to be notified that any changes or modifications made to device that are
not expressly approved by the Sony Corporation may void the user's authority to operate the
equipment.
This product emits radio frequency energy, but the radiated output power of this device is far below the FCC
radio frequency exposure limits. Nevertheless, the device should be used in such a manner that the potential
for human contact with the antenna during normal operation is minimized.
Warning: Exposure to Radio Frequency Radiation
!
The radiated output power of this device is far below the FCC radio frequency exposure limits.
Nevertheless, the device should be used in such a manner that the potential for human contact
during normal operation is minimized. In order to avoid the possibility of exceeding the FCC
radio frequency exposure limits, human proximity to the antenna should not be less than 1.5cm
(0.6 inches) during normal operation.
Canadian Regulatory Wireless Notice
Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device m ay not cause i nterference, and (2) this
device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired operation of the device.
European Union Notice
XXXX
Products bearing the CE marking comply with the R&TTE Directive (1999/5/EC), EMC Directive
(89/336/EEC) and the Low Voltage Directive (73/23/EEC) issued by the Commission of the European
Community.
Compliance with these directives implies conformity to the following European Norms (in parentheses are
the equivalent international standards and regulations):
• EN 55022 (CISPR 22) – Electromagnetic Interference
• EN55024 (IEC61000-4-2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 11) – Electromagnetic Immunity
• EN61000-3-2 (IEC61000-3-2) – Power Line Harmonics
Page 30

• EN61000-3-3 (IEC61000-3-3) – Power Line Flicker
• EN 60950 (IEC 60950) – Product Safety
• EN 300 328-2 – Technical requirements for radio equipment
• EN 301 489-1, -17 – General EMC requirements for radio equipment
This product may be used in the following EU and EFTA countries: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland,
Germany, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal,
Sweden, Switzerland and United Kingdom. Products not marked with “Not for use in France” may be used
in France.
Japanese Regulatory Wireless Notice
2. 4 DS-OF 4
Note: In Japan 5GHz is for indoor use only
Brazilian Regulatory Wireless Notice
Este equipamento opera em caráter secundário, isto é, não tem direito a proteção contra
interferência prejudicial, mesmo de estações do mesmo tipo, e não pode causar
interferência a sistemas operando em caráter primário.
 Loading...
Loading...