Sony KDL-46XBR10, KDL-52XBR10 Schematic
Training Manual
KDL52XBR10
EX2S/EX2WM Direct-View LCD Television Chassis
Circuit Description and Troubleshooting Guide
MODELS: KDL46XBR10
KDL52XBR10
Course : CTV-62

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 – Introduction ..................................................... 1
Overview .......................................................................... 1
Features .......................................................................... 1
Full HD 1080 Panel .............................................................. 1
240HZ Motionflow™ ............................................................ 1
Super Slim Design ............................................................... 1
Edge LED Backlighting ..................................................... 2
Enhanced Cross Media Bar (XMB) ...................................... 2
Internet Connectivity ............................................................ 2
USB2.0 Input ....................................................................... 2
HDMI 1.3 .............................................................................. 2
Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) ..................................... 2
xvYCC ..................................................................................... 2
Deep Color .............................................................................. 2
Bravia® Sync ....................................................................... 3
Advanced Contrast Enhancer (ACE) ................................... 3
Digital Media Port ................................................................ 3
Digital Media Extender (DMEX) ........................................... 3
Interactive Program Guide (IPG) ......................................... 3
Digital Living Network Alliance (DLNA) ................................ 3
Chapter 2 – Wireless Features ............................................ 4
Overview .......................................................................... 4
Millimeter Wave RF ......................................................... 4
Wireless HD Module ........................................................ 5
Wireless “Pairing” ................................................................ 7
Remote Control RF Module Replacement ....................... 7
Media Receiver .................................................................... 7
Wireless HD Module Replacement ................................ 10
Media Receiver .................................................................. 10
Wireless HD Module Pairing .............................................. 15
Troubleshooting ............................................................. 16
Remote Control RF Module ............................................... 16
Chapter 3 – Overall Circuit Description ........................... 19
Overview ........................................................................ 19
Overall Block Diagram ................................................... 19
Media Receiver .................................................................. 19
Monitor ............................................................................... 19
Circuit Board and Component Views ................................. 19
Chapter 4 – Media Receiver Circuit Description ............. 23
Overview ........................................................................ 23
Circuit descriptions ............................................................ 23
BUB Board ......................................................................... 23
Analog Sources ..................................................................... 23
Digital Sources ...................................................................... 23
Audio Output ......................................................................... 23
TV MICRO ............................................................................ 23
Power Supply ..................................................................... 25
Wireless Module ................................................................ 25
RF Remote ........................................................................ 25
H1B Board ......................................................................... 25
H3B Board ......................................................................... 25
H5B Board ......................................................................... 25
CTV-62 i

Table of Contents (continued)
Chapter 5 – Monitor Circuit Description .......................... 26
Overview ........................................................................ 26
Circuit descriptions ............................................................ 26
QTM Board ........................................................................ 26
BE Micro ............................................................................... 26
Video Data ............................................................................ 26
Audio Data ............................................................................ 26
Wireless Module ................................................................ 26
RF Remote Module ............................................................ 26
GD1 Board ......................................................................... 26
Reverse Panel Drive ...................................................... 28
Troubleshooting ............................................................. 29
Audio .................................................................................. 29
Video .................................................................................. 29
Chapter 6 – Power Supplies and Protection ................... 32
Overview ........................................................................ 32
Media Receiver Power ....................................................... 32
Protection ........................................................................... 32
Standby Power ...................................................................... 34
Primary Power ...................................................................... 34
LED Inverter .......................................................................... 34
Protection ........................................................................... 34
Troubleshooting ............................................................. 36
Backlight Troubleshooting .................................................. 39
With 6X Shutdown ................................................................ 39
With No Shutdown ................................................................ 39
CTV-62 ii

Chapter 1 – Introduction
Overview
The EX2S/EX2WM chassis is the top of the line model for the 2009 Sony
Bravia® LCD televisions. It has several new breakthrough features which
cause it to stand out from the other television models of the year.
2 models of televisions fall into this chassis category. They are the
KDL46XBR10 and KDL52XBR10 which are designed as monitor display
devices. A separate media receiver with an integrated NTSC/ATSC tuner
is used to connect all external devices to the LCD monitor. Transmission
of the video and audio content is accomplished by using a wireless
transmitter on the media receiver to a wireless receiver on the monitor.
The media receiver and monitor communicate with each other via a bidirectional wireless RF receiver/transmitter. The traditional backlighting
method utilizing fluorescent lamps has been replaced with an array of
LED’s along the bottom of the LCD panel assembly.
Features
Several new features are introduced in the EX2S/EX2WM chassis models
along with some carryovers from the previous year.
The customer has the option of changing the settings of the Motion
Enhancement and Motion Compensation circuits to smooth the “judder”
inherent with 24-frame film-based content or keep the judder for a film-like
experience.
Super Slim Design
The use of LED’s along the bottom edge of the LCD panel along with
new circuit board designs and mounting allows for the creation of an
exceptionally slim television. The depth of the panel varies from 15.8mm
(0.622”) at the top, 40.3mm (1.59”) at the rear cover and 57.3mm (2.26”)
at the bottom where the speakers are housed.
Full HD 1080 Panel
Both models have a 1920 X 1080 native resolution panel. All video signals
exit the video process circuits with resolution of 1080p 60HZ. The RGB
resolution is 10-bit to provide 1,024 levels of gray scale for improved
picture resolution.
240HZ Motionflow™
A frame-quadrupling circuit utilizing proprietary circuitry and algorithms is
able to capture and compare the movement from one frame to another. By
anticipating the location of a moving object, an additional frame is inserted
to increase the frame refresh rate from 60HZ to 240HZ. The result is an
exceptionally smooth picture during fast moving objects and scenes.
CTV-62 1

Chapter 1 - Introdcution
Edge LED Backlighting
High-intensity LED’s strategically placed along the bottom edge of the
LCD panel along and a wave guide diffuser plate tht disperses the light to
allow for a dramatic reduction of the depth of the television.
Bravia Wireless HD
All video and audio content is transmitted from the media receiver to
the monitor via a 60GHZ millimeter wave radio frequency which allows
adequate bandwidth for full 1080p un-compressed video content. This
frequency allows for minimal interference from other wireless devices in
the area.
Enhanced Cross Media Bar (XMB)
A new graphics user interface with rich 3-D graphics allows the user to
customize the setup of the television and to access various adjustments
and control of optional devices. Optional external devices can also be
detected and displayed. One example is when a USB storage device is
plugged into the USB2.0 side input that contains JPEG format photos.
The detection of the device will appear in the XMB graphics icons along
with thumbnail views of the photos stored on the device. The photos can
be viewed individually or be displayed as a slide show.
Internet Connectivity
Once available as an optional device to connect to the television, this
feature is now an integral part of the product. The rear of the media receiver
contains an Ethernet port to connect to a high speed network. Access to
online music and video through partnered websites is possible.
Personalized “widgets” are small applications that can be placed on the
screen and accessed with the touch of a button to bring up programming
such as weather, stocks and sports information.
USB2.0 Input
This feature was available in selected 2008 models and allowed the
viewing of JPEG formatted pictures and playback of MP3 audio files. The
media content has been expanded this year to allow playback of MPEG2
format video content.
HDMI 1.3
This new version of HDMI introduces several new enhancements and
features and the EXS/EX2WM chassis supports 3 of the new features.
Consumer Electronics Control (CEC)
A standardized protocol for the control of consumer electronics devices
allows for communication and control via the HDMI cable on products that
have this feature. Any brand of electronic equipment that is CEC compliant
can communicate with another to generate operational commands. The
Bravia Sync feature uses the CEC format to control other Sony devices
in the system.
xvYCC
The previous color bandwidth limitations applied for compatibility with
analog signals are no longer present with digital signals. This allows for
1.8 times more colors.
Deep Color
The previous HDMI specifications limited the RGB sample level to 24-bit.
Deep Color expands this up to 48-bit giving the ability to generate a color
depth of 2.8 trillion levels.
CTV-62 2

Chapter 1 - Introdcution
Bravia® Sync
By utilizing the CEC feature of HDMI 1.3, this feature allows the customer
to easily control the various Sony devices within their home entertainment
system provided that all of the other devices have this feature included.
Advanced Contrast Enhancer (ACE)
By monitoring the overall level of the video signal, the backlights are
dynamically controlled and reduced during low light level scenes to
enhance the contrast ratio.
Digital Media Port
This port allows for the hookup of optional devices that provide an interface
with digital media products such as MP3 players and video cameras.
Digital Media Extender (DMEX)
A USB 1.0 port is provided to supply a digital connection path to control
optional modules such as the BRAVIA DVD Link and BRAVIA Wireless
Link. Devices connected will automatically appear on the XMB menu.
Digital Living Network Alliance (DLNA)
An industry standard networking protocol has been developed by leading
manufacturers to allow other devices such as a compatible computer
to communicate with the television via an Ethernet connection to your
home network. This gives the ability to view photos, audio and movie
content directly from your computer via the network. Future plans include
the ability to download software updates for the television via the home
network.
Interactive Program Guide (IPG)
An interactive guide is included to provide continuously updated program
information at no charge to the customer. The guide (provided by TV
Guide) is part of the XMB graphics feature. Program material is updated
from the local PBS station when the television is off.
CTV-62 3

Chapter 2 – Wireless Features
Overview
One of the several new features found in the EX2S/EX2WM chassis is the
use of wireless transmission for audio and video content. There is also RF
remote controlling between the media receiver and the display panel.
While wireless RF transmission systems have been around since the
invention of radio, the transmission of full 1920 X 1080p uncompressed
video along with 5.1 channel audio has presented a challenge. Many
homes have other wireless devices in operation such as cordless phones
and wireless networks. Broadcasting uncompressed video and audio
information without any interruptions is a challenge when operating near
these frequencies.
Millimeter Wave RF
Access to a license exempt 7GHZ band falling between 57 and 64GHZ
was released by the FCC back in 2001. This extremely high frequency
and range allows for several significant advantages over Ultra Wideband
and 802.11 compliant transmissions. Table 2-1 illustrates the advantage
of using this frequency band.
Note the significant increase in bits-per-second when using the 60GHZ
band. Higher transmit power is allowed because 60GHZ is absorbed at
a greater rate by the oxygen in the air. This provides several advantages
such as reduction of interference from other devices, increased security
from detection by other devices and a reduction in interference from other
60GHZ devices.
Another advantage of this frequency spectrum is the directional nature
of the RF energy. 2 to 5GHZ radio frequencies tend to be more omnidirectional which is suitable for wireless telephones and computer
networking devices. The wireless transmitter used in the KDL46/52XBR10
models uses a dynamically steerable narrow beam which can be directed
to the transmit and receive antennas of the devices. The term used for
the device that transmits is “source” while the receiving device is referred
to as “sink”.
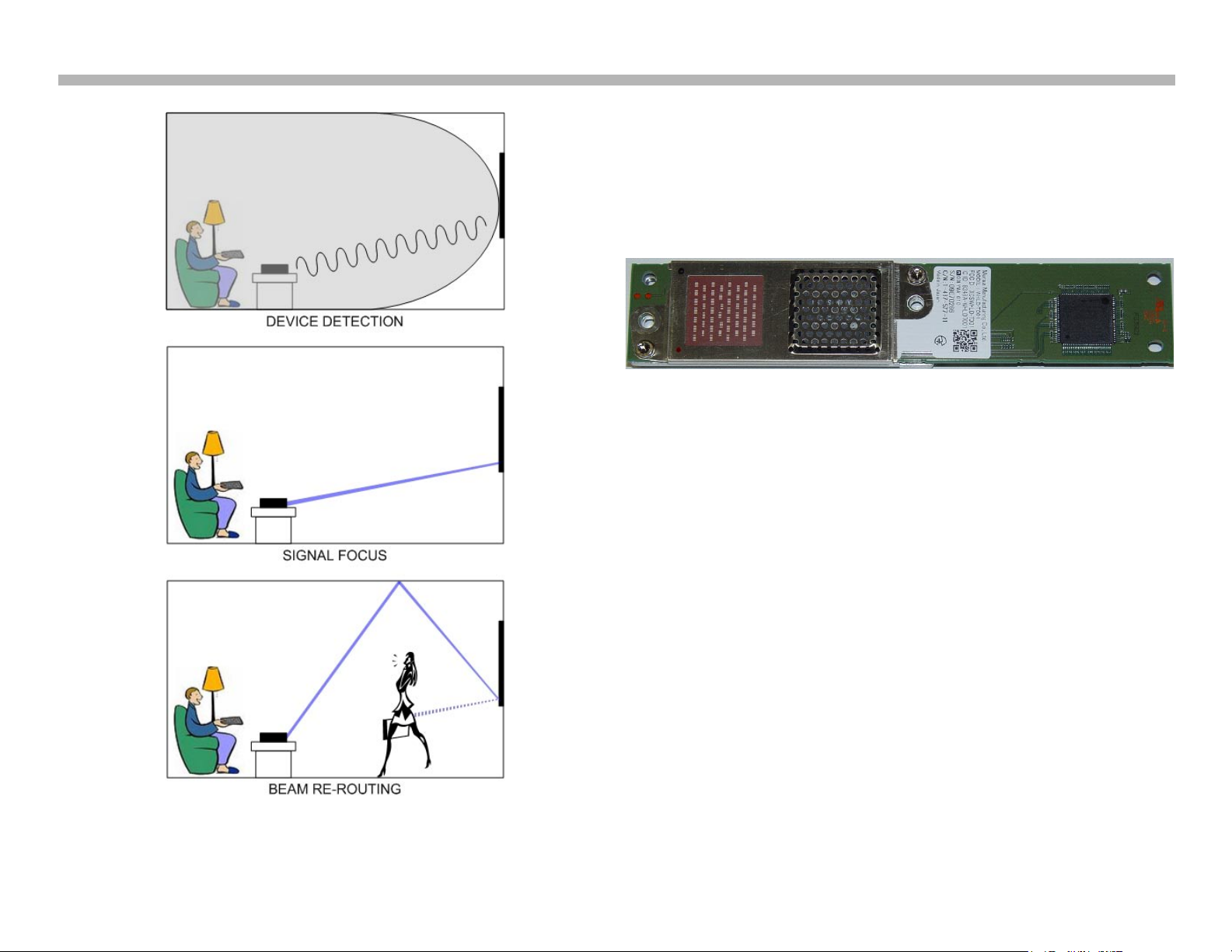
Since 60GHZ does not penetrate solid objects very well it is important
to maintain a line of sight between the source and sink device with the
narrow beam. The steerable antenna allows for this and can manipulate
the beam to bounce off of walls, ceilings and floors as needed. An example
of this feature is illustrated in Figure 2-1.
MAXIMUM
CHANNEL
UWB 520MHZ 0.4mW 80Mbs
802.11 40MHZ 160mW 1,100Mbs
60GHZ 2,500MHZ 8000mW 25,000Mbs
BANDWIDTH
TABLE 2-1
WIRELESS TRANSMISSION COMPARISONS
EFFECTIVE
TRANSMIT POWER
DATA
RATE
CTV-62 4
Chapter 2 - Wireless Features
Wireless HD Module
Figure 2-2 illustrates the wireless module used for the source (transmit)
side in the medial receiver unit. Audio and video information is received
via a LVDS connection to the processing circuits. The RF processor and
transmitter modulates the LVDS information to the RF carrier. The small
copper colored perforated plate is the steerable antenna system.
ANTENNA RF RX/TX
LVDS RX/TX
FIGURE 2-2
WIRELESS MODULE
Wireless Circuit Description
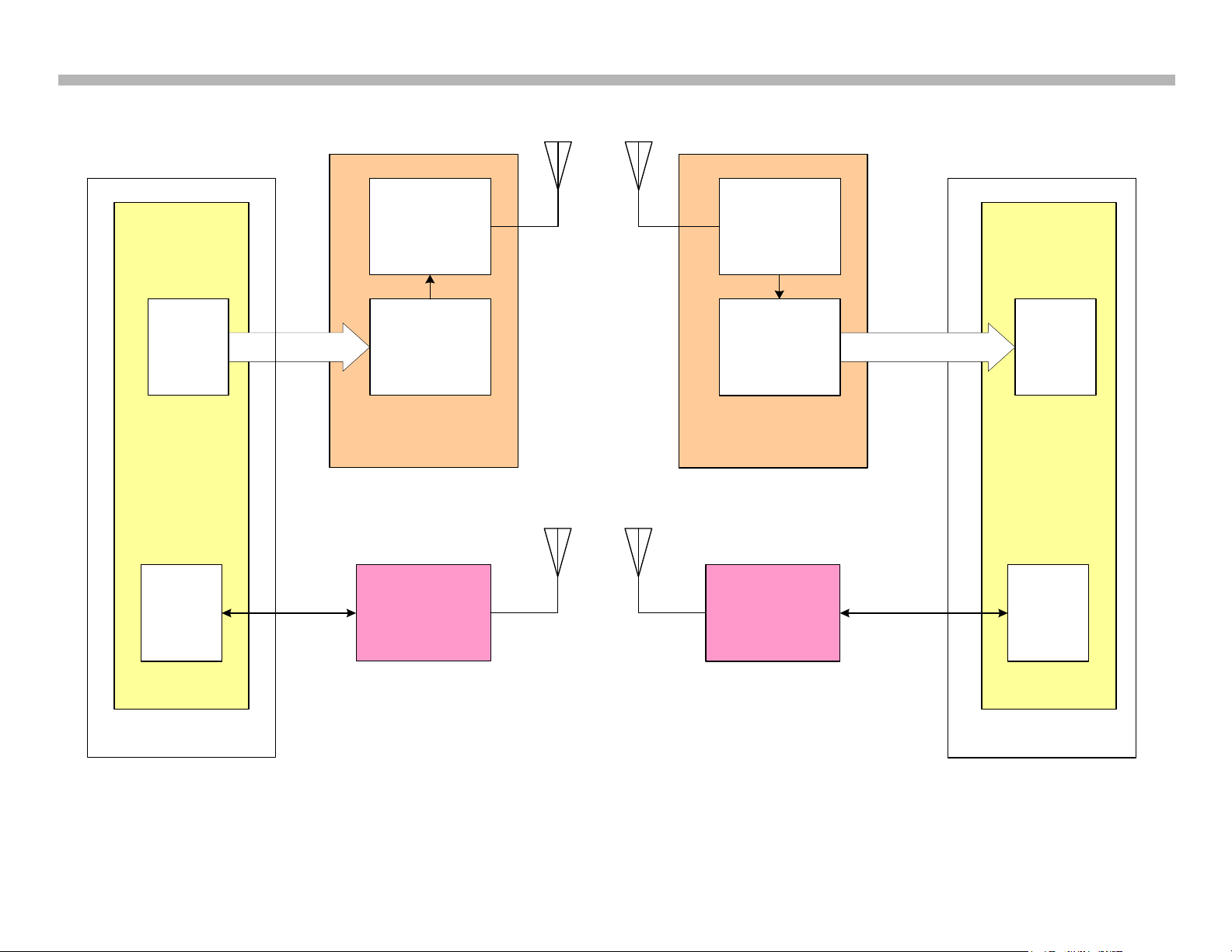
In Figure 2-3 a block diagram of the wireless systems used in this chassis
is shown. The media receiver functions as the source device and the
monitor as the sink device. The LVDS transmitter located on the BUB
board sends the necessary information to the wireless transmit module.
NOTE: Even though the only connection between the BUB board and
wireless module is a LVDS cable, some of the cable lines are used for
B+, ground, audio I2S information, and I2C communications. Most of the
LVDS lines carry the RGB video information.
The wireless sink module receives the information from the media receiver
and sends the information to the QTM board on the monitor as an LVDS
signal. Data, control and audio information is separated from the video
information and processed accordingly.
FIGURE 2-1
WIRELESS STEERING
CTV-62 5
Chapter 2 - Wireless Features
LVDS RX
TRAN SMITTER
LVDS TX
REC EIVER
LVDS RX
MEDIA RECEIVER MONITOR
BUB QTM
LVDS COMPONENTS
PANEL 12
V
GROUND
I²C DATA
TX
0~4 EVEN
TX
0-4 ODD
TX EVEN CLOCK
TX ODD CLOCK
I²S DATA AND CLOCK
SPDIF (NOT USED)
WIRELESS MODULE
(SOURCE)
WIRELESS MODULE
(SINK)
LVDS TX
RF REMOTE
MODULE
RF REMOTE
MODULE
SUB
MICRO
BE
MICRO
FIGURE 2-3
WIRELESS CIRCUITS BLOCK DIAGRAM
CTV-62 6

RF MODULE
SECURED BY 1
SCR EW AND CLIP
LIFT 2 RETAININ G C LIPS ON
BOTTOM TO R ELEASE FR ONT
PANEL AND POSITION AS SH OWN
Remote Control RF
The sub micro located on the BUB board of the media receiver sends
commands to the RF remote module via a UART bus. The same holds
true for the BE micro located on the QTM board on the monitor. Both
microprocessor and RF remote modules can send or receive data.
Wireless “Pairing”
In order to keep other devices using the same or similar wireless
frequencies from interfering with each other, both the wireless and RF
remote modules are paired together. The wireless modules are paired by
recognizing each other’s MAC address while the RF remote modules are
paired by handshaking an encryption code. If one or both of the wireless
or RF remote modules are changed, they must be paired once again.
This procedure is performed in the service menu and will be described in
further detail later in this chapter.
Remote Control RF Module Replacement
This section explains the removal procedure for the Wireless RF Module.
It is relatively simple for the media receiver and more time consuming for
the monitor.
Chapter 2 - Wireless Features
Media Receiver
Remove the top cover and front panel as illustrated in the service manual.
Position the front panel as illustrated in Figure 2-4. The RF remote module
is secured by 1 screw and retaining clip. Once the replacement module is
installed, perform the pairing procedure explained on Page 9.
FIGURE 2-4
MEDIA RECEIVER RF MODULE REMOVAL
CTV-62 7
Chapter 2 - Wireless Features
UNP LUG LED
POWER AN D
SPEAKER
CONN ECTOR
REMOVE
CABLES FROM
RETAINER S
REMOVE 2
SPEAKER
SCR EWS
LIFT SPEAKER
GRILL BY
GRABBING AT
BOTH ENDS
NOTE THE
RUB BER
SPEAKER
GROMMET
REMOVE 2
SMALL MACHINE
SCR EWS
REMOVE 1
LARGE MACHINE
SCR EW
REMOVE 3
LARGE HEAD
SELF
-TAP
SCR EWS
FLIP BRACKET OVER
AND REMOVE 1 SC REW
SECURING REMOTE RF
MODULE
Monitor
Remove the stand (if installed) and the rear cover of the monitor as
instructed in the service manual. The monitor must be laying face-down
on a flat cushioned surface. Loosen the wire harness and remove the left
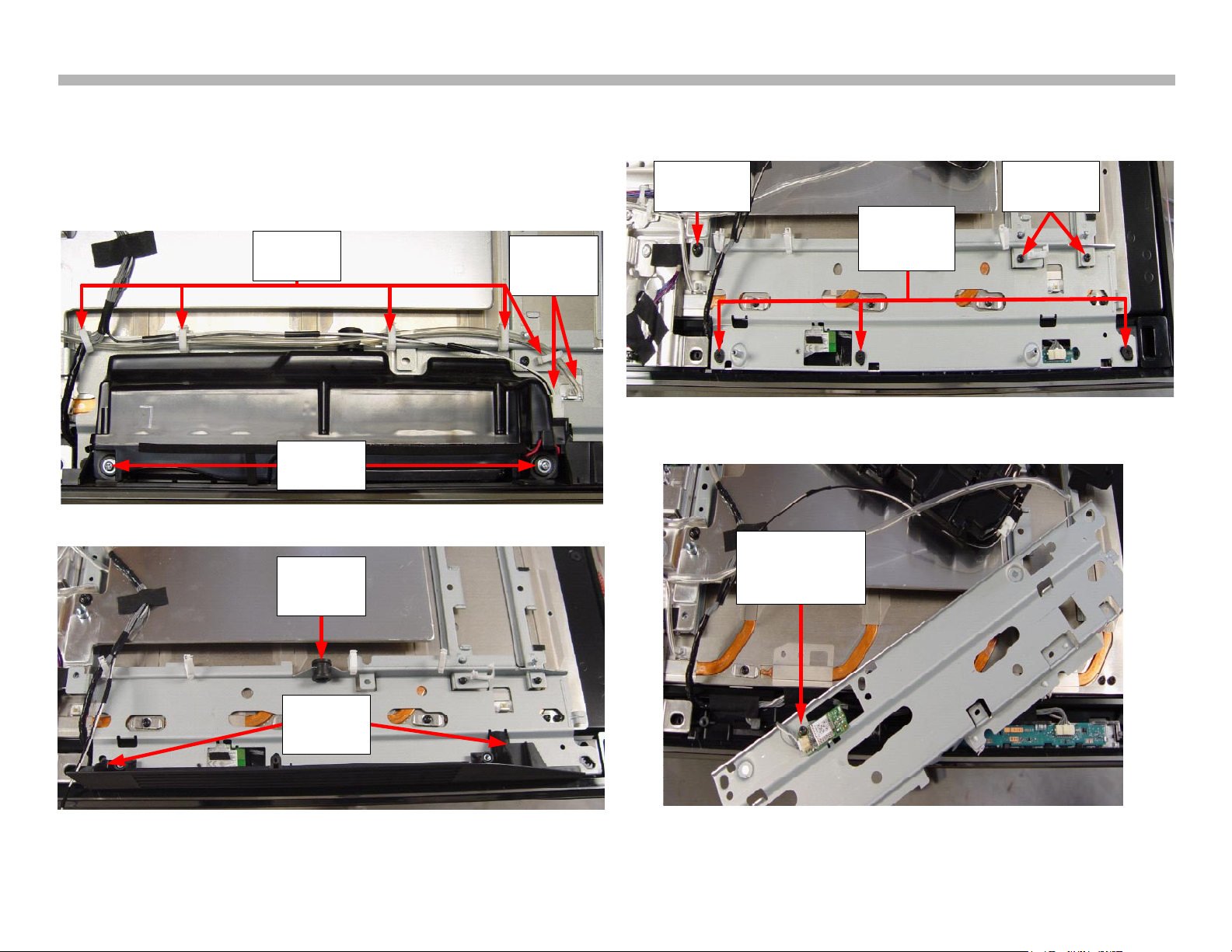
speaker assembly and grill as illustrated in Figure 2-5.
Following the illustration in Figure 2-6, remove the indicated screws
securing the bracket. Flip the bracket over to expose the RF module.
MONITOR RF MODULE REMOVAL (STEP 1)
CTV-62 8
FIGURE 2-5
FIGURE 2-6
MONITOR RF MODULE REMOVAL (STEP 2)
Chapter 2 - Wireless Features
PRESS “3” KEY TO
CHANGE DATA TO
“1”
PRESS “5” KEY
TO ENTER
GROUP 28,
ITEM 1
“EXECUTIN G” WILL
APPEAR
PRESS R F
SERVICE BU TTON
FOR AT LEAST 2
SECONDS
DONE!
FIGURE 2-7
RF REMOTE MODULE PAIRING
CTV-62 9
REMOVE 1 SCREW IN REAR AND 3 IN FRONT
RELEASE
LVDS CABLE
FROM TAPE
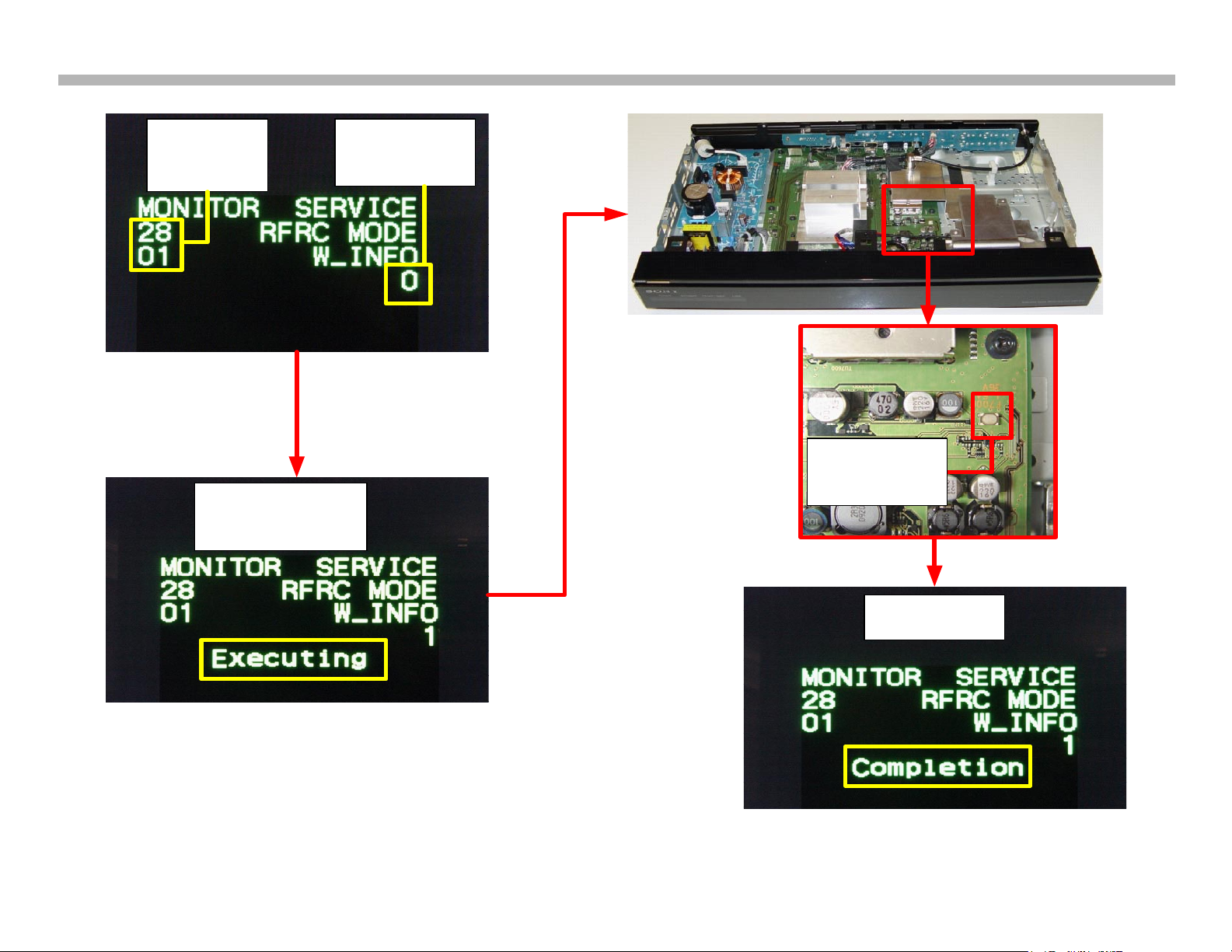
Remote Control RF Module Pairing
If one or both of the RF remote modules is replaced, they must be “paired”.
A unique encryption must be applied to prevent communication with
another television if it exists in the area. The top cover and plate must be
removed from the media receiver to gain access to the circuit boards.
Referring to Figure 2-7, place the television into service mode by pressing
“DISPLAY’, “5”, “VOL+” and “POWER”, in sequence, on the remote
commander while the monitor and media receiver are off. Be certain that
“MONITOR SERVICE” is displayed. If another page is present, press the
“JUMP” key to display the appropriate page. Press the “5” key to scroll to
group 28 “W_INFO”.
Change the data from “0” to “1” with the “3” key on the remote. The word
“Executing” will appear. Press the RF service button on the lower right
side of the BUB board for about 2 seconds. If successful, “completion” will
appear on the screen.
Wireless HD Module Replacement
Chapter 2 - Wireless Features
The Wireless HD Module unit in the media receiver (source) or in the
monitor (sink) can be replaced individually. If either is replaced, they must
be “paired” once again. The MAC address of the source module must be
recognized by the monitor.
Media Receiver
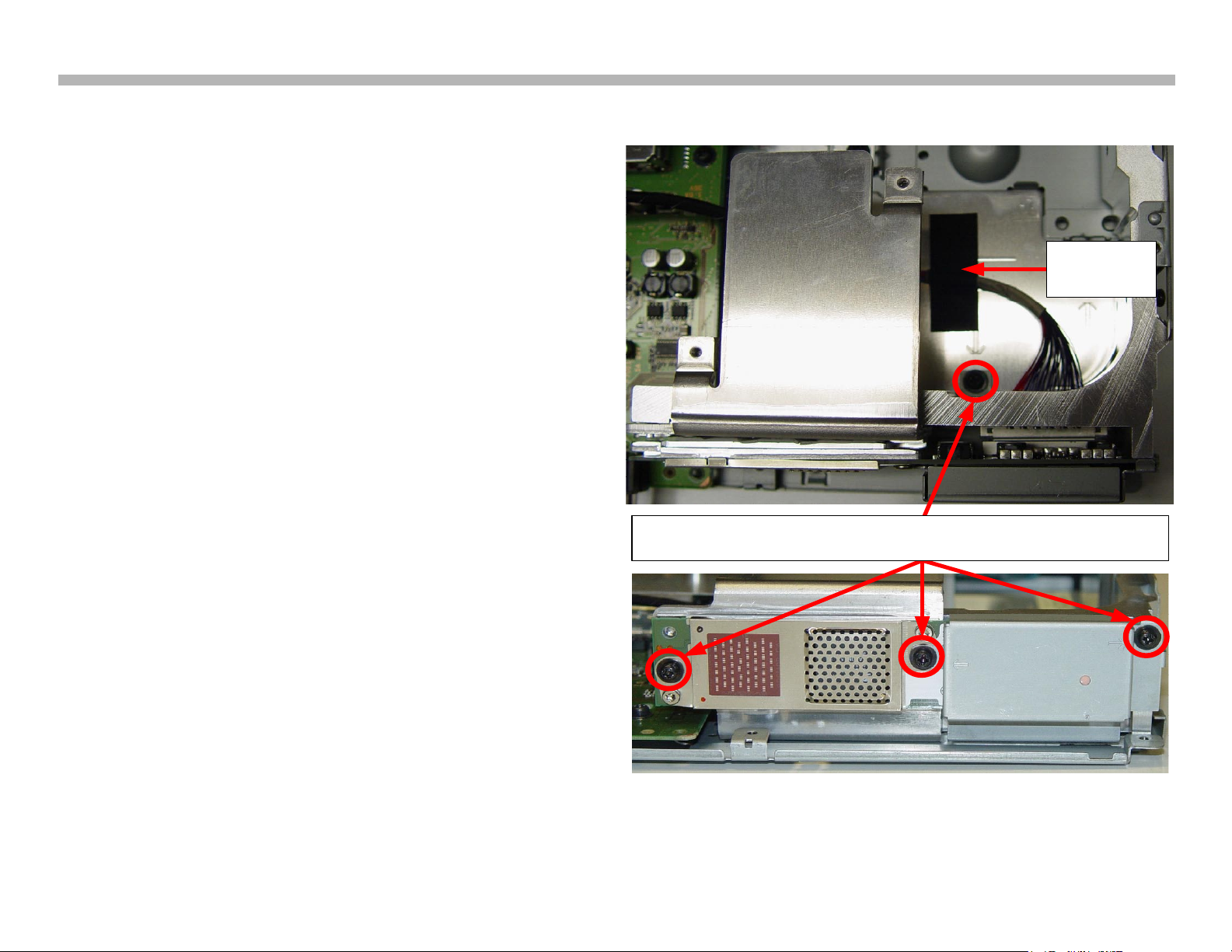
Replacement of the wireless module in the media receiver requires the
removal of the top cover and front panel. The wireless module is secured
with 1 screw in the rear and 3 in the front as illustrated in Figure 2-8. Lift
the cloth tape to release the LVDS cable.
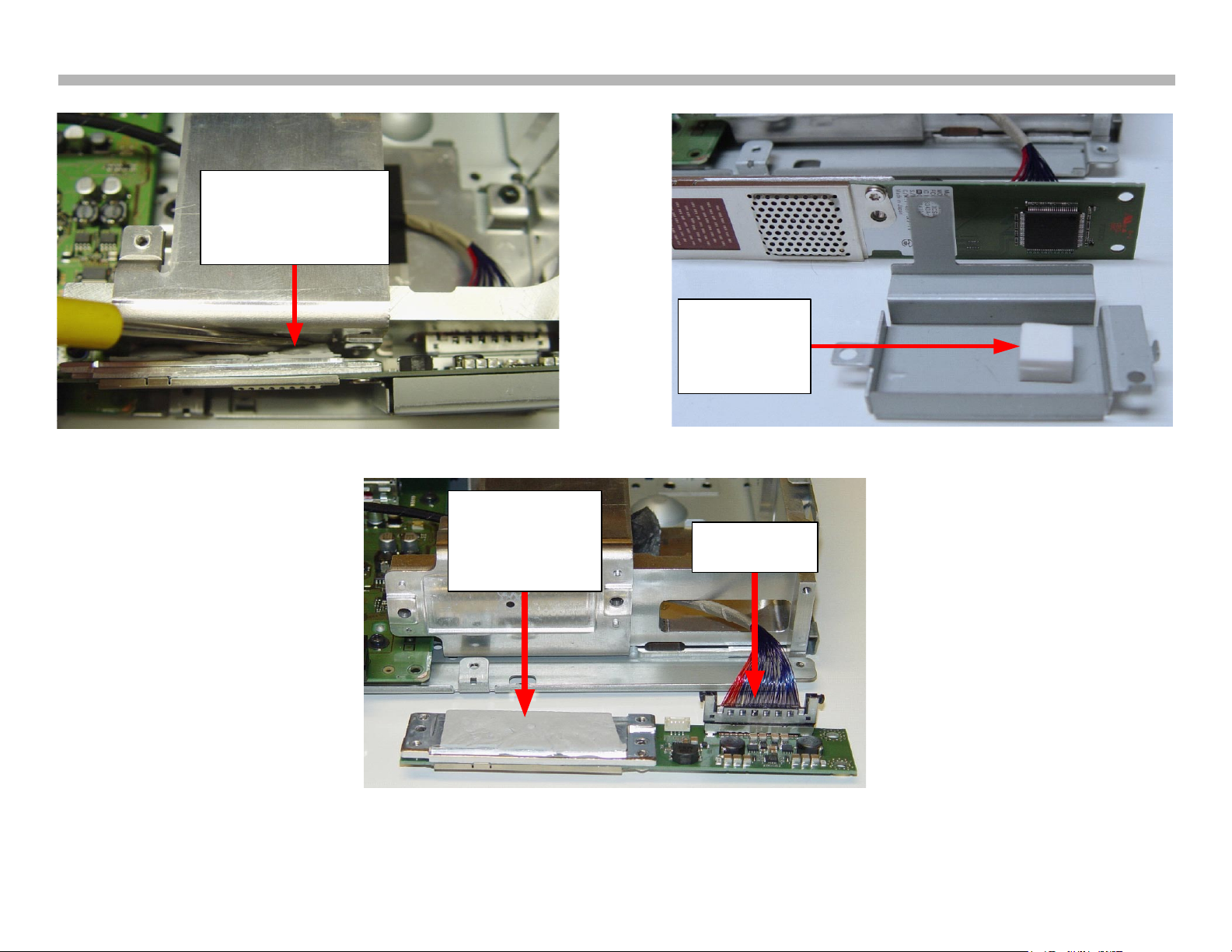
Referring to Figure 2-9, use a small flat-blade screwdriver or similar tool
to peel the heat transfer pad from the heat sink. The objective is to keep
the entire pad intact on the rear of the module. The front shield is easily
removed. Take note of the heat transfer pad. Unplug the LVDS connector
and transfer the heat transfer pad to the replacement module.
MEDIA RECEIVER WIRELESS MODULE REMOVAL (STEP 1)
CTV-62 10
FIGURE 2-8
USE FLAT TOOL TO
KEEP HEAT TRANSFER
PAD ATTACHED TO
WIRELESS MODULE
REMOVE
FRONT SHIELD.
NOTE HEAT
TRAN SFER PAD
HEAT TRANSFER
PAD MUST BE
PLACED ON
REPLACEMENT
MODULE
UNPLUG LVDS
CABLE
Chapter 2 - Wireless Features
FIGURE 2-9
MEDIA RECEIVER WIRELESS MODULE REMOVAL (STEP 2)
CTV-62 11
Chapter 2 - Wireless Features
REMOVE SIN GLE
MACH INE SCREW
SECU RING STAND
PLATE C OVER
REMOVE AC INLET
AS SHOWN BELOW
AND LIFT STAND
PLATE C OVER OFF
RELEASE CLAWS
ON BOTH SIDES
Monitor
If the stand is attached to the monitor, it must be removed. Lay the monitor
on a flat surface with sufficient padding. Remove the rear cover. Remove
the left speaker, grill and bracket as described earlier in this chapter for
removal of the RF module. Remove the 2 screws from the right speaker
but do not remove it.
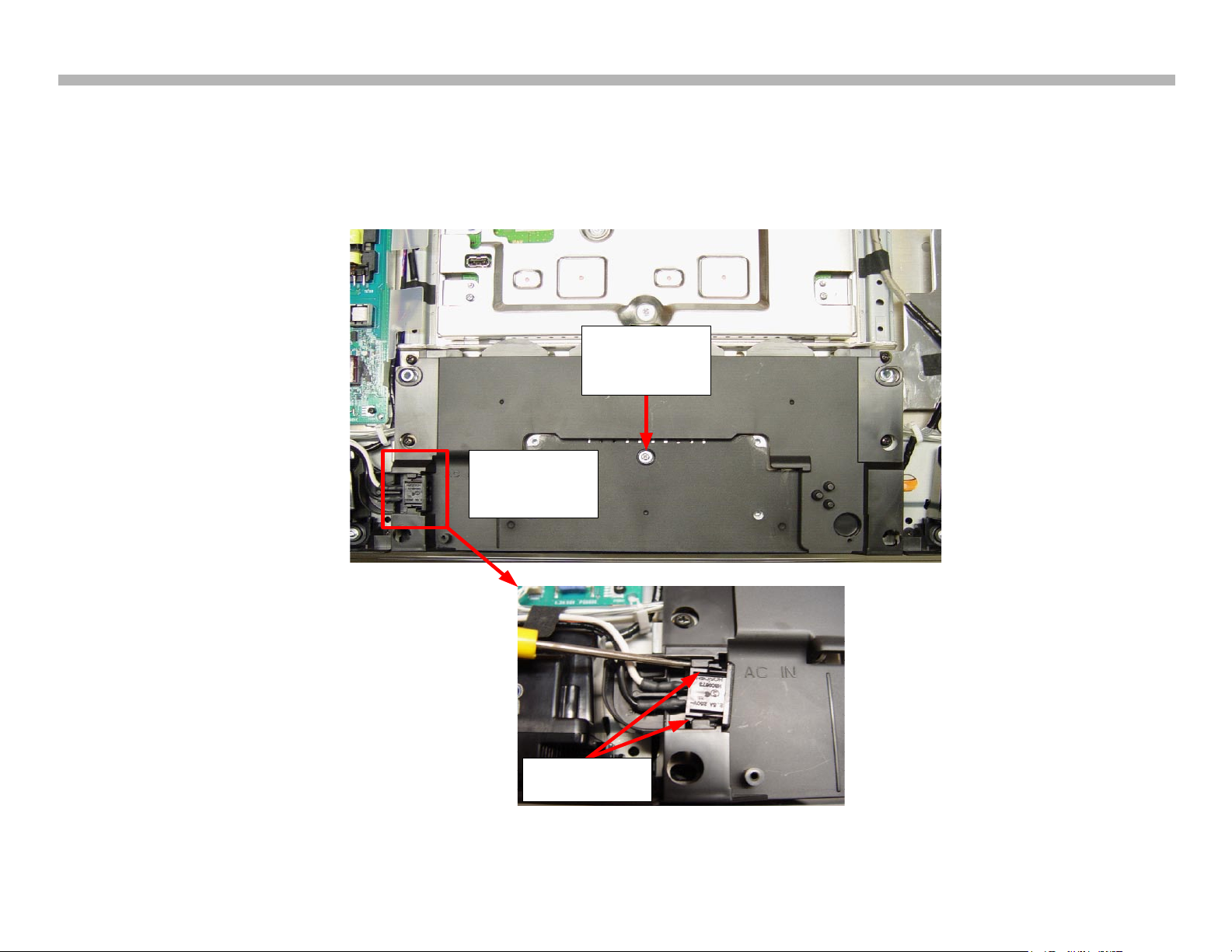
Referring to Figure 2-10, remove the AC inlet from the stand cover plate
by carefully prying the claws on both sides of the socket. Remove the
single machine screw and lift the cover plate off.
FIGURE 2-10
MONITOR WIRELESS MODULE REMOVAL (STEP 1)
CTV-62 12
 Loading...
Loading...