Sierra Profibus DP 600 Series, Profibus DP 760S, Profibus DP 640S, Profibus DP 700 Series, Profibus DP 780S-UHP Instruction Manual
Page 1

600/700 Series Profibus DP
Instruction Manual
Profibus DP Device Specification for Models:
640S, 760S, 780S, and 780S-UHP
Thermal Mass Flow Meters
Part Number: IM600/700 ProfibusDP Rev.V1
May 2013
Page 2

GLOBAL SUPPORT LOCATIONS: WE ARE HERE TO HELP!
CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS
5 Harris Court, Building L Monterey, CA 93940
Phone (831) 373-0200 (800) 866-0200 Fax (831) 373-4402
www.sierrainstruments.com
EUROPE HEADQUARTERS
Bijlmansweid 2 1934RE Egmond aan den Hoef
The Netherlands
Phone +31 72 5071400 Fax +31 72 5071401
ASIA HEADQUARTERS
Second Floor Building 5, Senpu Industrial Park
25 Hangdu Road Hangtou Town
Pu Dong New District, Shanghai, P.R. China
Postal Code 201316
Phone: + 8621 5879 8521 Fax: +8621 5879 8586
IMPORTANT CUSTOMER NOTICE- OXYGEN SERVICE
Sierra Instruments, Inc. is not liable for any damage or personal injury, whatsoever, resulting from the use of Sierra Instruments standard mass
flow meters for oxygen gas. You are responsible for determining if this mass flow meter is appropriate for your oxygen application. You
are responsible for cleaning the mass flow meter to the degree required for your oxygen flow application.
© COPYRIGHT SIERRA INSTRUMENTS 2012
No part of this publication may be copied or distributed, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into any
human or computer language, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, manual, or otherwise, or disclosed to third parties
without the express written permission of Sierra Instruments. The information contained in this manual is subject to change without
notice.
TRADEMARKS
SteelMass™, ChlorineTrak™, and FlatTrak™ are trademarks of Sierra Instruments, Inc. Other product and company names listed in this
manual are trademarks or trade names of their respective manufacturers.
Page 3
!
Warnings and Cautions
Warning!
nameplate for specific flow meter approvals before any hazardous location installation.
Warning!
manufacturer of the hot tap equipment and/or the contractor performing the hot tap is responsible for providing proof of such a
permit.
Warning!
Warning!
to a power source and to peripheral devices. Failure to do so could result in injury or death. All AC power connections must be in
accordance with published CE directives.
Warning!
sensors and/or damage to the electronics.
Warning!
Warning!
Agency approval for hazardous location installations varies between flow meter models. Consult the flow meter
Hot tapping must be performed by a trained professional. U.S. regulations often require a hot tap permit. The
All wiring procedures must be performed with the power off.
To avoid potential electric shock, follow National Electric Code safety practices or your local code when wiring this unit
Do not power the flow meter with the sensor remote (if applicable) wires disconnected. This could cause over-heating of the
Before attempting any flow meter repair, verify that the line is de-pressurized.
Always remove main power before disassembling any part of the mass flow meter.
Caution!
control system. Adjustments to the electronics will cause direct changes to flow control settings.
Before making adjustments to the device, verify the flow meter is not actively monitoring or reporting to any master
Caution!
as the main pipeline.
Caution!
You cannot add or subtract wire length without returning the meter to the factory for re-calibration.
Caution!
before installing the meter.
Caution!
Caution!
precautions to minimize the risk of damage:
All flow meter connections, isolation valves and fittings for hot tapping must have the same or higher pressure rating
Changing the length of cables or interchanging sensors or sensor wiring will affect the accuracy of the flow meter.
When using toxic or corrosive gases, purge the line with inert gas for a minimum of four hours at full gas flow
The AC wire insulation temperature rating must meet or exceed 80°C (176°F).
Printed circuit boards are sensitive to electrostatic discharge. To avoid damaging the board, follow these
before handling the assembly, discharge your body by touching a grounded, metal object
handle all cards by their edges unless otherwise required
when possible, use grounded electrostatic discharge wrist straps when handling sensitive components
Page 4
Warning!
Caution!
This statement appears with information that
is important to protect people and equipment
from damage. Pay very close attention to all
warnings that apply to your application.
This statement appears with information that is
important for protecting your equipment and
performance. Read and follow all cautions that
apply to your application.
!
Note and Safety Information
We use caution and warning statements throughout this book to draw your attention to
important information.
Receipt of System Components
When receiving a Sierra mass flow meter, carefully check the outside
packing
carton for
damage incurred in shipment. If the carton is damaged, notify the local carrier and submit a
report to the factory or distributor. Remove the packing slip and check that all ordered
components are present. Make sure any spare parts or accessories are not discarded with
the packing material. Do not return any equipment to the factory without first contacting
Sierra Customer Service
.
Technical Assistance
If you encounter a problem with your flow meter, review the configuration information for
each step of the installation, operation, and setup procedures. Verify that your settings
and adjustments are consistent with factory recommendations. Installation and
troubleshooting information can be found in the SteelMass™ 640S and FlatTrak™ 780S
(includes 760S and 780S-UHP) Series product manuals.
If the problem persists after following the troubleshooting procedures outlined in the 640S or
780S product manuals, contact Sierra Instruments by fax or by E-mail (see inside front
cover). For urgent phone support you may call (800) 866-0200 or (831) 373-0200 between
8:00 a.m. and 5:00 p.m. PST. In Europe, contact Sierra Instruments Europe at +31 20
6145810. In the Asia-Pacific region, contact Sierra Instruments Asia at +
When contacting Technical Support, make sure to include this information:
86-21-58798521.
The flow range, serial number, and Sierra order number (all marked on
the meter nameplate)
The software version (visible at start up)
The problem you are encountering and any corrective action taken
Application information (gas, pressure, temperature and piping configuration)
4
Page 5

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction ................................................................................................................... 6
Set Up Quick Step Plan ............................................................................................................................... 6
Chapter 2: Field bus installation .................................................................................................... 7
Fieldbus Connector ..................................................................................................................................... 7
Cable ........................................................................................................................................................... 7
Termination .................................................................................................................................................. 9
Status Leds .................................................................................................................................................. 9
Status LED: .................................................................................................................................................. 9
Slave Address ........................................................................................................................................... 10
Dip Switch ................................................................................................................................................... 10
Server Assigned Address ........................................................................................................................... 11
Set Address (126) ....................................................................................................................................... 11
Chapter 3: Configuration .............................................................................................................. 12
GSD File .................................................................................................................................................... 12
Cyclic Data Overview ................................................................................................................................ 12
Cyclic Data Explained ................................................................................................................................ 13
Syscon Software ........................................................................................................................................ 14
Import Device Description Files ................................................................................................................. 14
Configure A Slave ...................................................................................................................................... 15
Create A New Document And Insert A Master: ......................................................................................... 15
Auto Addressing ........................................................................................................................................ 16
Insert A Slave To The System. .................................................................................................................. 17
Download Configuration ............................................................................................................................ 18
Check The Configuration ........................................................................................................................... 20
Kepserverex 4.0 ........................................................................................................................................ 22
GSD File .................................................................................................................................................... 30
5
Page 6

Chapter 1: Introduction
This manual will explain how to add a Sierra flow meter to a Profibus DP network using the Profibus
DP interface. The interface allows access to all relevant data available in the flow meter.
Set Up Quick Step Plan
To successfully add the flow meter to a Profibus DP network you need the following:
Profibus network with a DP master
GSD file
Bitmap files
Connection cable
Power supply (for the flow meter)
Setup steps:
Load GSD
Copy bitmaps
Add slave device to system
Set slave configuration
Set slave station address
Download configuration
Test configuration
6
Page 7

Chapter 2: Field bus installation
PB-GND
3
PB-A (green)
PB-B (red)
EARTH
5
PB-5V
2
Fieldbus
Connector
All fieldbus connection for your Smart Meter is made on the right side:
Fieldbus Connector
The Profibus DP network is connected to the chassis female M12 connector (B-coded). The connector
has the following pin configuration:
(Front view)
The Profibus DP network can be connected with a special terminal block connection. This must be
requested at the time of ordering. The down side of this is the PB-5V and PB-GND will not be
available to power a terminator. You should also pull 2 Profibus cables to maintain the daisy chain
topography, to avoid spur lines.
7
Page 8
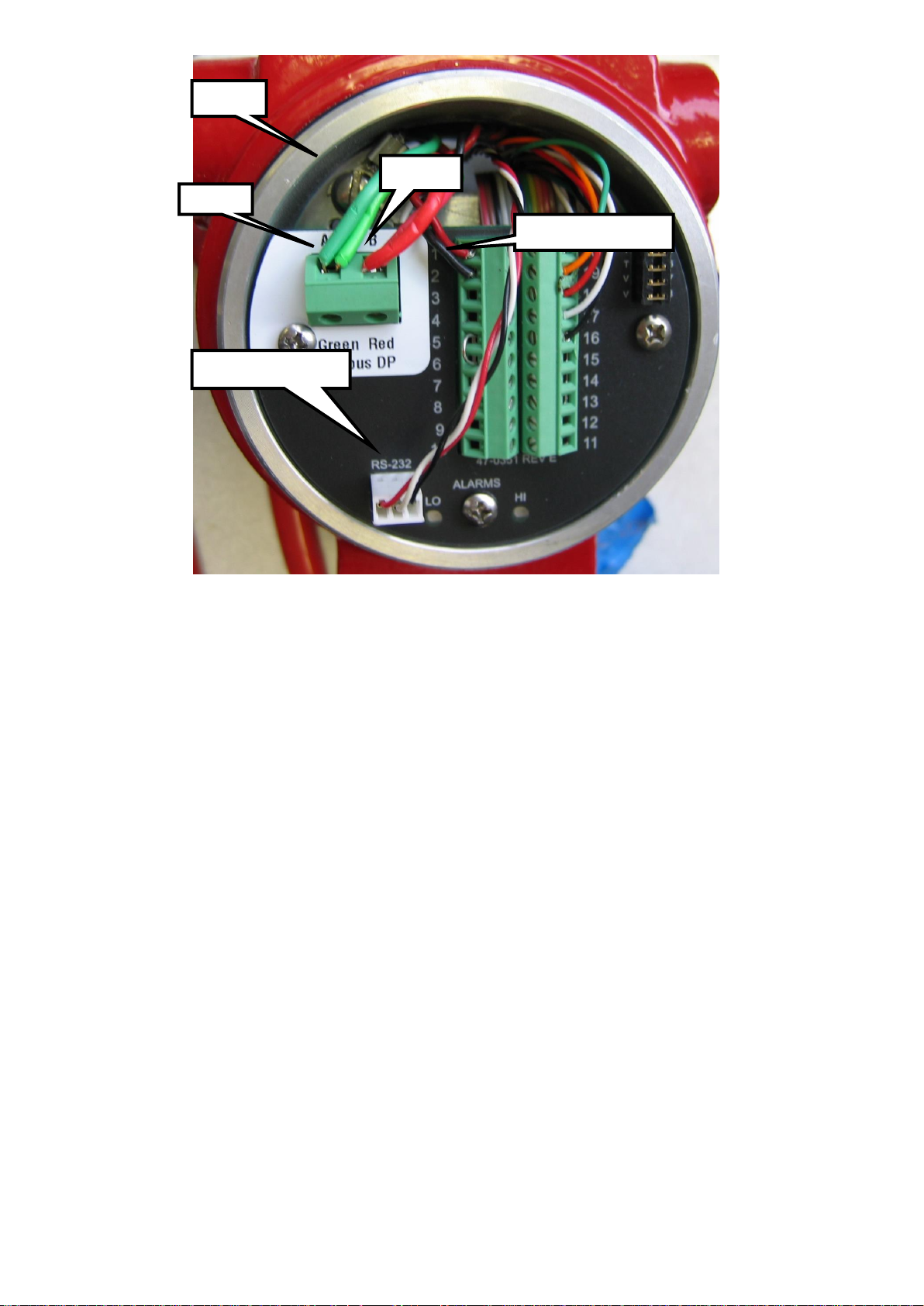
PB-A
PB-B
Earth
Meter DC Power
RS232 cable
Cable
Profibus cables are shielded twisted-pair copper cables which differ from each other in the type of
wire (fixed/flexible) and/or sheath. The two inner cores of a Profibus cable have green and red
insulation. The specifications in this chapter are primarily intended to provide a general introduction
and describe the cable properties to be considered (see also IEC 61784-5-3). A good cabling guide can
be found online at: http://verwertraining.com/wp-content/uploads/InstallationGuideV9_2.pdf .
The cable must conform to the following specifications:
Impedance: 150 Ohm (nominal) at frequencies from 3 to 20 MHz.
Cable capacitance: < 30 pF per meter.
Core diameter: > 0,34 mm², corresponds to AWG 22.
Cable type: twisted pair cable. 1x2 or 2x2 or 1x4 lines.
Resistance: < 110 Ohm per km.
Signal attenuation: max. 9 dB over total length of line section.
Shielding: CU shielding braid or shielding braid and shielding foil.
Max. Bus length: 200 m at 1500 Kbit/s, up to 1,2 km at 93,75 Kbit/s.
8
Page 9
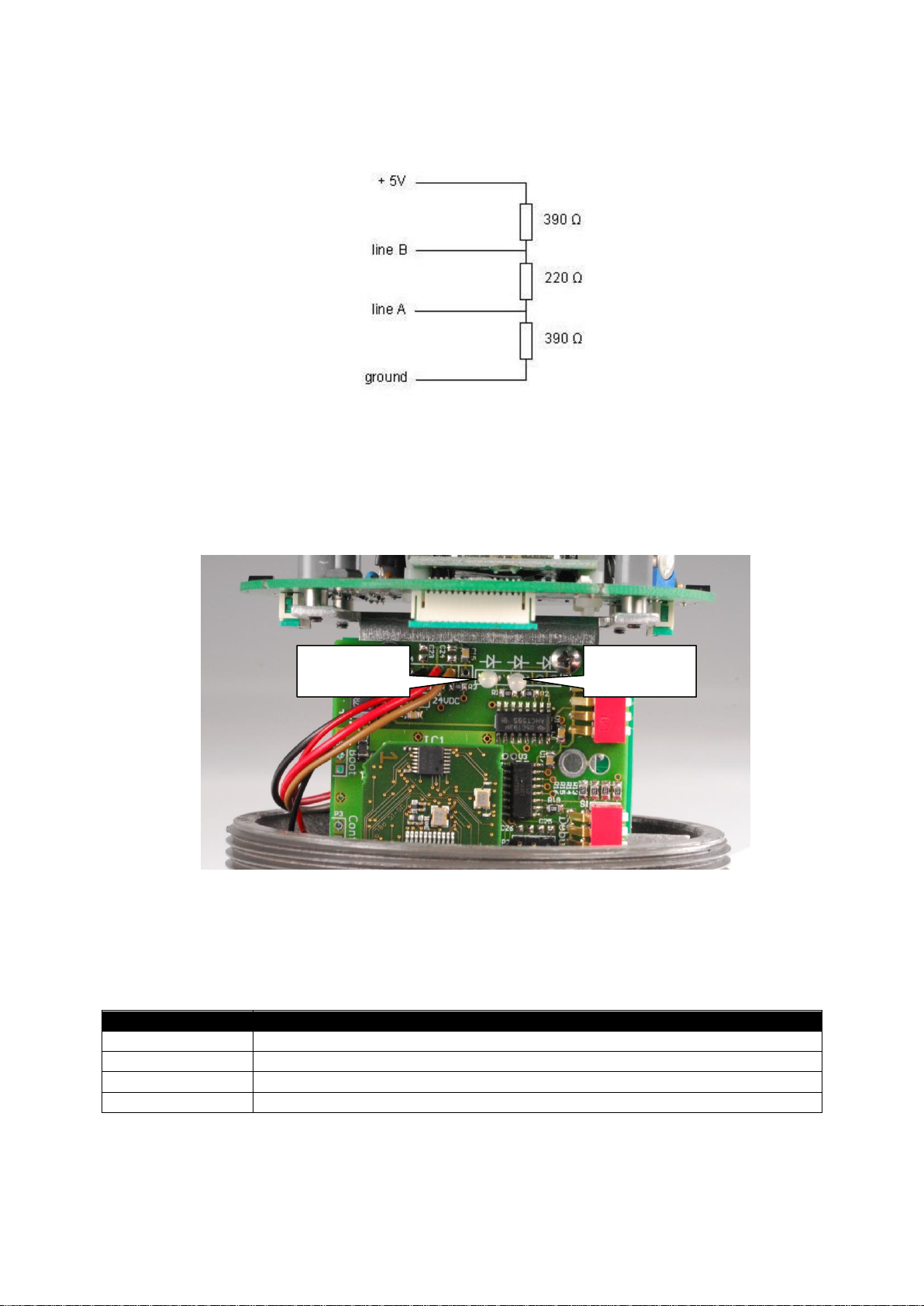
Termination
Status
Description
Flashing green/red
Initializing
Steady green
Device operational
Flashing red
Recoverable hardware failure
Steady red
Hardware failure – attention required
Status
LED
Network
LED
The Profibus physical layer is based on RS-485, and therefore termination resistors are needed at both
ends of the network. The image below shows how to connect the terminators:
Ready-made terminators are available for easy installation.
Status Leds
The interface has two multi-color LED’s mounted inside the enclosure to indicate the status. To access
the LED’s, remove the front cap.
The left LED shows the status of the interface, the right LED shows the network status.
Status LED:
Network LED:
9
Page 10

Status
Description
Off
Not online – waiting for configuration
Steady green
Data exchange
Flashing red
Connection lost
LSB
1 2 4 8
MSB
16 32 64 128
Slave Address
Once the interface is installed, the slave address of the interface can be set. Default instruments will be
delivered with slave address 126. This address has been agreed by the Profibus organization to be free
for installing new devices to the bus. Changing the station address is done in two ways, either through
a dip switch or through the master.
Dip Switch
The dip switches are located inside the meter. Remove the display cover to expose the switches:
The dip switch is binary encoded with the LSB (lowest bit) on the left side. The switch is only read
during power-up.
The switch becomes active when the slider is moved upwards. Here some examples of some addresses
(1 = on/up, 0 = off/down):
10
Page 11

Address
ID
Dip Switch
1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
1
1|0|0|0||0|0|0|0
14
0|1|1|1||0|0|0|0
60
0|0|1|1||1|1|0|0
125
1|0|1|1||1|1|1|0
Note: An address set with the dip switch has the highest priority and the slave address will use this
address when powering up!
Server Assigned Address
It is possible to change the address of the unit through the server. Perform the following steps to
change the address:
1. Assign a new address from the server
2. Set the dip switch to 128 (pin 8 on) or higher.
The assigned address will be used each time that the unit is powered.
Set Address (126)
It is possible to force the address of the unit to 126. Set the dip switch to zero and power cycle the unit.
The address is set to 126. The address can be changed by the server if needed. Do keep in mind that if
the dip switch remains set to zero, the address will be set to 126 at each power-up.
11
Page 12

Chapter 3: Configuration
Data
Address
Description
Size
(bytes)
Format
0
Flow
4
REAL
4
Totalizer
4
REAL
8
User full scale
4
REAL
12
Factory full scale
4
REAL
16
K-factor
4
REAL
20
Serial number
12
ASCII
32
Flow unit
5
ASCII
37
Totalizer unit
3
ASCII
40
Status
2
INT
42 bytes
GSD File
Each Profibus DP instrument comes with its own GSD-file. The GSD file can be obtained from the
documents and downloads page (http://www.sierrainstruments.com/products/downloads/profibus-dp ).
The GSD file contains the instrument specifications telling the master configuration software which
facilities/features the instrument offers to the Profibus system.
The GSD-file is a text-file containing:
Identification info:
o Model name: “SteelMass™ 640S - Profibus”
o Vendor name: “Sierra Instruments Inc.”
o Identification number: 0x013E
o Bitmap device: “640S_dev”
o Bitmap diagnostics: “640S_dia”
o Bitmap SF: “640S_spf”
(Bitmap files are used in configuration software to indicate instrument status)
Revision numbers
Hardware characteristics:
o VPC3+C dependable properties
Software characteristics:
o Supported features of Profibus: Freeze, Sync, auto baud rate detection
Maximum bus data lengths
Size of used data buffers
Modules with cyclic input / output variables for the instrument.
Cyclic Data Overview
The following table shows the cyclic input & output buffer supported by the device. Module 1 has 42
bytes in of process data in, and 12 bytes out. The actual data address will depend on preceding
devices on your bus. The matrix example below shows the actual data addresses, assuming the
640S/780S is the first device on your Profibus network.
Incoming Cyclic Data (Slave To Master Module 1)
12
Page 13

Data
Address
Description
Size
(bytes)
Format
0
Reset totalizer
4
REAL
4
User full scale
4
REAL
8
K-factor
4
REAL
12 bytes
Outgoing Cyclic Data (Master To Slave Module 1)
Cyclic Data Explained
Flow (R):
Data type: 32 bit floating point (LSB – MSB)
Description: The actual flow as measured by the instrument
Totalizer (R):
Data type: 32 bit floating point (LSB – MSB)
Description: Accumulated flow
User full scale (R):
Data type: 32 bit floating point (LSB – MSB))
Description: The user full scale value allows you to re-range the instrument. Any value between
50% and 100% of the factory full scale is allowed. The new value will also redefine the analog
outputs of the instrument (when used). The 20mA/5 VDC will represent the new full scale value.
Factory Full Scale (R):
Data type: 32 bit floating point (LSB – MSB)
Description: Factory full scale value of the instrument.
K-Factor (R):
Data type: 32 bit floating point (LSB – MSB)
Description: K-factor which can be used to adjust the flow reading
Serial Number (R):
Data type: 16 bits ASCII
Description: Serial number of the instrument (12 characters).
Flow Unit (R):
Data type: 16 bits ASCII
Description: Flow unit of the instrument (5 characters).
Totalizer Unit (R):
Data type: 16 bits ASCII
Description: Totalizer unit of the instrument (3 characters).
Status (R):
Data type: 16 bit integer
Description: Status indicates if the quality of the data in the registers (0 = bad, 1 = good).
Reset Totalizer (W):
Data type: 32 bit floating point (LSB – MSB)
Description: Accumulated flow
13
Page 14

K-Factor (W):
Data type: 32 bit floating point (LSB – MSB)
Description: K-factor which can be used to adjust the flow reading
User Full Scale (W):
Data type: 32 bit floating point (LSB – MSB))
Description: The user full scale value allows you to re-range the instrument. Any value between
50% and 100% of the factory full scale is allowed. The new value will also redefine the analog
outputs of the instrument (when used). The 20mA/5 VDC will represent the new full scale value.
Syscon Software
Sycon is a tool for the configuration of a Fieldbus network using a Hilscher CIF50-PB master. You
may be using different configuration software and hardware Master. However you will need to
accomplish the same functions. No specific slave DTMs of the equipment are available, which are
generated from the device description files, called generic slave DTMs.
Online diagnostic indicators and auto-scan function for the reading of network participants assist in the
commissioning of the network.
This guide will explain step by step how to configure the system to support various fieldbus slaves on
a Hilscher CIF50-PB master.
Before starting make sure that the necessary device description files (GSD & bit maps) are available in
your device catalog. These are available on our web site.
Import Device Description Files
In order to use a fieldbus device its properties need to be added to the server. This is done by
importing the device description files into Sycon.
Start Sycon and create a new document (File -> New)
A dialog window appears asking to select a fieldbus. For this example select Profibus:
The main window is loaded. Go to the file menu and select “Copy GSD”:
14
Page 15

Add master here
Locate the desired GSD file and load it. The GSD data is added to the Sycon library but it isn’t
available yet. Quit the program and restart it to make it available.
Configure A Slave
Create A New Document And Insert A Master:
Place the master at the top of the line. A dialog window appears where a master needs to be selected
from a list. The list shows every type of master supported by Sycon. Select the Profibus master which
has been installed on the PC:
15
Page 16

Leave the station address set to zero. Press the “Add” button and then the “OK” button.
A window pops up showing the driver linked to the selected master. Press “Yes” to use the hardware.
Note: The board ID number changes when extra PCI cards are added to the PC. Older configurations
must be checked before trying to run them.
Auto Addressing
The master needs to be set to auto addressing. Click on the master and from the file menu select
“Settings -> Master configuration”:
Make sure the “Auto addressing” is checked:
16
Page 17

Add slave here
Insert A Slave To The System.
File menu: Insert -> Slave. Place it below the master:
Set the slave filter to “Sierra Instruments Inc.”. Select the desired GSD file, press the “Add” button,
set the slave address and description to match the slave and press the “OK” button.
17
Page 18

Note: If no slave device appears in the window then the GSD file hasn’t been copied into Sycon.
Double click on the added slave in the main window. The slave configuration window appears:
Select the desired modules by double clicking on the module name. Press the “OK” button.
When done save the new configuration to disk (File -> save as).
Download Configuration
The configuration needs to be downloaded to the master (Online -> Download):
18
Page 19

A pop-up may appear warning you that the communication may stop:
Press “Yes” to continue. The data is downloaded to the master:
The system is ready to be used.
19
Page 20

Check The Configuration
To make sure things are working start the debug mode:
If everything is working correctly then the line between the master and the slave will be green and the
bit map shows a green check:
Double click on the slave to see the diagnostic status:
20
Page 21

Press the “OK” button and leave the debug mode (Online -> Stop Debug Mode).
Should the line be red (error) then double click the slave to find out what the problem is:
The diagnostic window gives an indication of a problem, wrong address here:
21
Page 22

In this case the slave is deactivated. Check the address of “Slave1” to see if it matches with the
physical address of the hardware slave.
Correct any error. If the slave address in the configuration is incorrect, adjust it and download the
configuration.
Kepserverex 4.0
You may be using different server software or a PLC. This example shows how to use the
KepserverEx 4.0 free demo software on a windows PC. For your convenience we put a copy on our
web site.
After you have installed the KepserverEx software start a new project.
Click to add a channel.
Give the channel a name. Click Next.
22
Page 23

Choose a Master, we are using a Hilscher CIF50 master. Click, Next.
The defaults will work, click Next.
Chose the board and type, click next.
23
Page 24

You’ll need to import the setup .pb file that we created earlier in Syscon. You may browse to the
location where you saved it. Click on the Browse button.
Browse the 640S flowmeter.pb you just created in Sycon. Once highlighted, click Open.
24
Page 25

You should see this warning.
You can review the summary of the new channel you just created.
You may now add your first slave device. Click on “Click to add a device”
25
Page 26

Give your new device a name.
Set the device ID. ID# 0 was already used for the master, so chose #1.
26
Page 27

The next 2 screens will be fine as default, click next. Choose the device type. Click next.
Review the new device summary, click next.
27
Page 28

Click Finish, you have now created a new device for your network.
You will now need create a Tag to access each piece of Cyclic data, as specified in chapter 3.2. Click
on “Click to add a static tag” and fill in the boxes as above.
The example above is for the flow:
28
Page 29

Flow (R):
Data type: 32 bit floating point (MSB – LSB) Should this be LSB-MSB?
Description: The actual flow as measured by the instrument
Because you only have one device on your network, and the Flow is “Instance ID1”, the Data Address
would be 0. If there were other save devices in your network you would need to add the last Address
of the previous device to the starting address of the new device.
Add a tag name. Address 0 with the data type, in this case IO D 0 S. (32 bit float, byte swapped). Add
a description. Set the Client access to Read Only. Click OK.
Kepserver has a very simple Quick Client that can be used to read and write to device tags. Click the
Hammer icon to start the quick client. When you highlight the profibus master.C100_1 tag, you can
read the flow data (4.756) and quality of the communications.
29
Page 30

GSD File
GSD File Text:
#Profibus_DP
;
; Sierra Instruments Inc.
;
; Version 1.0
;
; This GSD-File is intended for the Smart Meter 640S
; This Unit supports DPV0
;
; Outgoing Cyclic data (slave to master)
;
; Instance ID | Description | Size (bytes) | Format
;---------------+-----------------------+---------------+------; 1 | Flow | 4 | REAL
; 2 | Totalizer | 4 | REAL
; 3 | User full scale | 4 | REAL
; 4 | Factory full scale | 4 | REAL
; 5 | K-factor | 4 | REAL
; 6 | Serial Number | 12 | ASCII
; 7 | Flow unit | 5 | ASCII
; 8 | Totalizer unit | 3 | ASCII
; 9 | Status | 2 | INT
;
; Incoming Cyclic data (master to slave)
;
; Instance ID | Description | Size (bytes) | Format
;---------------+-----------------------+---------------+------; 10 | Reset totalizer | 4 | REAL
; 11 | User full scale | 4 | REAL
; 12 | K-factor | 4 | REAL
;
GSD_Revision = 4
;
Vendor_Name = "Sierra Instruments, Inc."
Model_Name = "Smart Meter 640S - Profibus"
Revision = "V1.0"
Ident_Number = 0x0e13
Protocol_Ident = 0
Station_Type = 0
FMS_supp = 0
Hardware_Release = "Revision H"
Software_Release = "V6.0"
;
9.6_supp = 1
19.2_supp = 1
45.45_supp = 1
93.75_supp = 1
187.5_supp = 1
500_supp = 1
1.5M_supp = 1
3M_supp = 1
6M_supp = 1
12M_supp = 1
;
30
Page 31

MaxTsdr_9.6 = 60
MaxTsdr_19.2 = 60
MaxTsdr_45.45 = 60
MaxTsdr_93.75 = 60
MaxTsdr_187.5 = 60
MaxTsdr_500 = 100
MaxTsdr_1.5M = 150
MaxTsdr_3M = 250
MaxTsdr_6M = 450
MaxTsdr_12M = 800
;
Redundancy = 0
Implementation_Type = "VPC3+C"
Bitmap_Device = "640S_De"
Bitmap_Diag = "640S_Di"
Bitmap_SF = "640S_Sf"
;
Freeze_Mode_supp = 1
Sync_Mode_supp = 1
Auto_Baud_supp = 1
Set_Slave_Add_supp = 1
Min_Slave_Intervall = 1
;
Modular_Station = 0
;
Fail_Safe = 0
Slave_Family = 0 ; General
Max_Diag_Data_Len = 6
;
DPV1_Slave = 1
C1_Read_Write_supp = 0
Max_Initiate_PDU_Length = 52
C2_Read_Write_supp = 1
C2_Max_Data_Len = 80
C2_Response_Timeout = 300
C2_Read_Write_required = 1
C2_Max_Count_Channels = 2
;
DPV1_Data_Types = 0
;
Max_User_Prm_Data_Len = 0
;
; <Module-Definition-List>
Module = "42 bytes in, 12 bytes out" 0xc0,0x8b,0xa9
1
EndModule
31
Page 32

GSD File Cert:
32
 Loading...
Loading...