Page 1

Advanced Server UNIX V4.0
Overview and Installation
Edition April 1999
Page 2

Comments… Suggestions… Corrections…
The User Documentati on Department woul d like to know your
opinion on this manual. Y our fe edback helps us to optimize our
documentation to suit your individual needs.
Fax forms for sending us your comments are included at the
back of the manual.
There you will also find the addresses of the relevant User
Documentation Department.
Copyright and Trademarks
Copyright © Siemens AG 1999.
All rights reserved.
Delivery subject to availability; right of technical modifications reserved.
All hardware and software names used are trademarks of their respective manufacturers
Information in this document is subject to change without notice. Companies, names, and data used in examples
herein are fictitiou s unless other wise note d. No part of this docum ent may be reproduced or transmitte d in any form
or by any means, electronic or mechanical, for any purpose, without the express written permission of AT&T and
Siemens AG.
© 1985-1998 AT&T. All rights reserved.
© 1985-1998 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
AT&T is a registered trademark of AT&T Corporation.
Microsoft, MS, MS-DOS, Windows, and Windows NT either are registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
Microsoft may have patents or pending patent applications, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property
rights covering subject matter in this document. The furnishing of this document does not give you any license to
these patents, trad em ark s, c op yri ghts , o r othe r in tel lec tua l property rights except as expressly p rov ide d in any written license agreement from Microsoft.
All other companies and product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders.
This manual is pri nted
on paper treated with
chlorine-free bleach.
Page 3

1Preface
Advanced Server for UNIX can be used to integrate personal computers, which are
operated under MS-DOS
®
OS/2 or OS/2® (referred to as OS/2 in this manual), Windows 95/98 and MS Windows
MS
®
operating systems, in local networks (LAN, Local Area Network and WAN, Wide Area
NT
Network). Advanced Server for UNIX allows the operation of various systems in a network.
Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0 (Advanced Server for UNIX in this manual) provides users
with server functions for the local network. It extends UNIX
Advanced Server for UNIX corresponds to Windows NT Server. The network server is
based on systems with the operating system UNIX. Cooperation with Microsoft
ensured that Advanced Server for UNIX is compatible with Windows NT Server.
The operating system is generally referred to as UNIX in this manual. This term is
i
used generically to include all UNIX operating systems on which Advanced Server
for UNIX is installed, for example Reliant UNIX.
Advanced Server for UNIX is also used in abbreviated form as AS/X, as well as
sometimes as AS/U or Advanced Server. All of these terms are synonymous for the
same product.
The description of the entire Advanced Server for UNIX product covers several manuals.
The “Concepts and Planning” manual provides information on the structure and function-
ality of Advanced Server for UNIX and describes, among other things, the differences in
comparison to LAN Manager/X.
This manual provides information on the enhancements that are implemented in Advanced
Server for UNIX; it supplements the information in the manual entitled “Concepts and
Planning”. The installation and configuration of Advanced Server for UNIX on the UNIX
system are also described in that manual.
®
(also running MS Windows or MS Windows for Workgroups),
®
to a network operating system.
®
has
The “API Reference” manual contains information on the API (Application Programming
Interface) with regard to syntax and functions. It is supplemented by online documentation
which is supplied with the package for the manual pages.
The “SNMP Service” manual contains information on the installation and configuration of
an extension for the SNMP agent (Simple Network Management Protocol), which among
other things allows network events to be determined centrally. This manual is part of the
LAN Manager/X V2.2 series of manuals.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 4

Preface Target Group
The “User's Guide for MS-DOS Clients” and “User's Guide for MS Windows Clients” are
aimed at users of the MS-DOS or Windows clients. They provide information on starting up
and closing down clients, and on shared directories and printers. They also provide references to the commands available for working with the client. The manuals “Installation
Guide for Clients”, “MS Network Client V2.2”, and “MS Network Client V3.0” describe how
to install these clients.
The manual “NetWare Connectivity” contains information on how your MS-DOS client can
work simultaneously with Advanced Server for UNIX or LAN Manager servers and with
NetWare
Connectivity.
®
servers. It also contains installation and configuration instructions for NetWare
1.1 Target group
This manual is intended for the system and network administrator, who is responsible for
installing, configuring, and operating Advanced Server for UNIX.
The network administrator is known as the administrator in this manual.
● The administrator requires the rights of the system administrator root and
i
must have an in-depth knowledge of the operating system and of the Advanced
Server for UNIX product. The tasks of the administrator and the system administrator are undertaken by one
person.
● In order to execute administrator commands using the net commands, you
simply need to log on with net logon Administrator <password>.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 5
Preface Summary of Contents
1.2 Summary of contents
Information that became available after this manual went to print is contained in the
i
SIreadmeM package which is supplied with Advanced Server for UNIX.
The chapter “Preface” provides users with an overview of the content and structure of this
manual.
The chapter “Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX” contains information on the supple-
ments and changes which you will require in addition to the information contained in the
“Concepts and Planning” manual.
The chapter “Advanced Server for UNIX architecture” contains an overview of the process
model and of internal and external Advanced Server for UNIX communication.
The chapter “Installing Advanced Server for UNIX” contains information on the hardware
and software requirements of your server system. It also provides instructions for transferring the Advanced Server for UNIX software onto the server system as well as all the
information required to configure the system and Advanced Server for UNIX software, and
to create a development environment for Advanced Server for UNIX applications.
The chapter “Configuring Advanced Server for UNIX” contains, among other things, the
steps necessary for configuring and for starting NetBIOS and Advanced Server for UNIX.
Y ou should consult the chapter “Administration guidelines” if you want to change the role of
the server, for example if you have installed and configured Advanced Server for UNIX.
Among other things, the chapter also describes how to enable a CD-ROM drive for
Advanced Server for UNIX.
The chapter “Tools for sp ec ial t asks” describes other tools offered by Advanced Server for
UNIX. These are generally only relevant when used with particular applications.
Another chapter is dedicated to “Installing Network and Administrative Client Software”.
The next chapter is about “Administering Advanced Server at the Command Prompt”.
Then a chapter describes in detail the WINS service: “Implement ing WINS”.
The chapter entitled “Troubleshooting” contains guidelines for resolving errors.
The chapter “Advanced Server for UNIX - directories and files” contains an overview of the
most important files and directories of Advanced Server for UNIX.
The following chapters describe in detail “Advanced Server Registry” and the “Lanman.ini
File”.
The “Glossary”, “Abbreviations”, and “Index” chapters are useful as a reference when
reading this manual.
The “Related publications” chapter lists additional useful documentation.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 6

Preface Changes since the last version
1.3 Changes since the last version of the manual
The documentation has been updated to conform to the software level of Advanced Server
for UNIX V4.0B.
For a list of differences between Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0B and the previons version,
please refer to the section “Compatibility” in the chapter “Introduction to Advanced Server
for UNIX”.
1.4 Notational conventions
The following notational conventions are used in this manual:
Convention Usage
Italics in the main body of text denote file, variable, and
program names, as well as commands and
options in continuous text
Bordered Courier indicates extracts from files
Courier denotes system output
Courier semi-bold denotes user input in a sample dialog
Key
Ê indicates tasks to be performed by the user
i
!
indicates a key or key combination
denotes important information that must be
heeded
denotes a warning that you must heed to avoid
loss of data or serious errors
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 7

2 Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX
This chapter contains supplementary and additional information on Advanced Server for
UNIX that is not contained in the manual entitled “Concepts and Planning”.
The following topics are dealt with:
● Shared resources and services
● Connection management
● Administration
● Application Programming Interface (API)
The section on “Client-server architecture” contai ns a sh or t de s cription of th e c lient-ser ve r
architecture. The section entitled “Shared resources” contains information on which
network resources of Advanced Server for UNIX can be shared.
The section entitled “Services” introduces the services provided by Advanced Server for
UNIX. The section “Connection management” explains the terms “sessions“ as well as
“connection”. This section also provides information on the security concept of Advanced
Server for UNIX. The manual entitled “Concepts and Planning” contains conceptional infor-
mation relating to this topic.
Finally, the section “Administration of Advanced Server for UNIX” prov id es inf or mati on on
remote administration.
Information on the programming interface and on compatibility can be found at the end of
this chapter.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 8

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Client-server architecture
2.1 Client-server architecture
One or more server systems and several clients (workstations) are connected in a network
(LAN, Local Area Network and WAN, Wide Area Network) with Advanced Server for UNIX.
The server systems provide services and resources in the local network. In contrast, the
clients utilize the services and resources of the server and generally do not provide any
services and resources themselves in the network.
Provided they are authorized, every client can access every server system in the local
network. Advanced Server for UNIX also supports so-called trust relationships between
domains, which permit the user to access resources in other domains.
2.2 Shared resources
The resources provided by a server system for the network are known as shared
resources. Shared resources are protected against unauthorized access (for more
detailed information, see section on “Security concept”).
Advanced Server for UNIX provides users with the following types of resources, which can
be shared by one or more users in the network:
● Shared directory
● Shared printer
● Interprocess communication resource IPC$
● Network-wide administration (Resource ADMIN$)
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 9
Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Shared resources
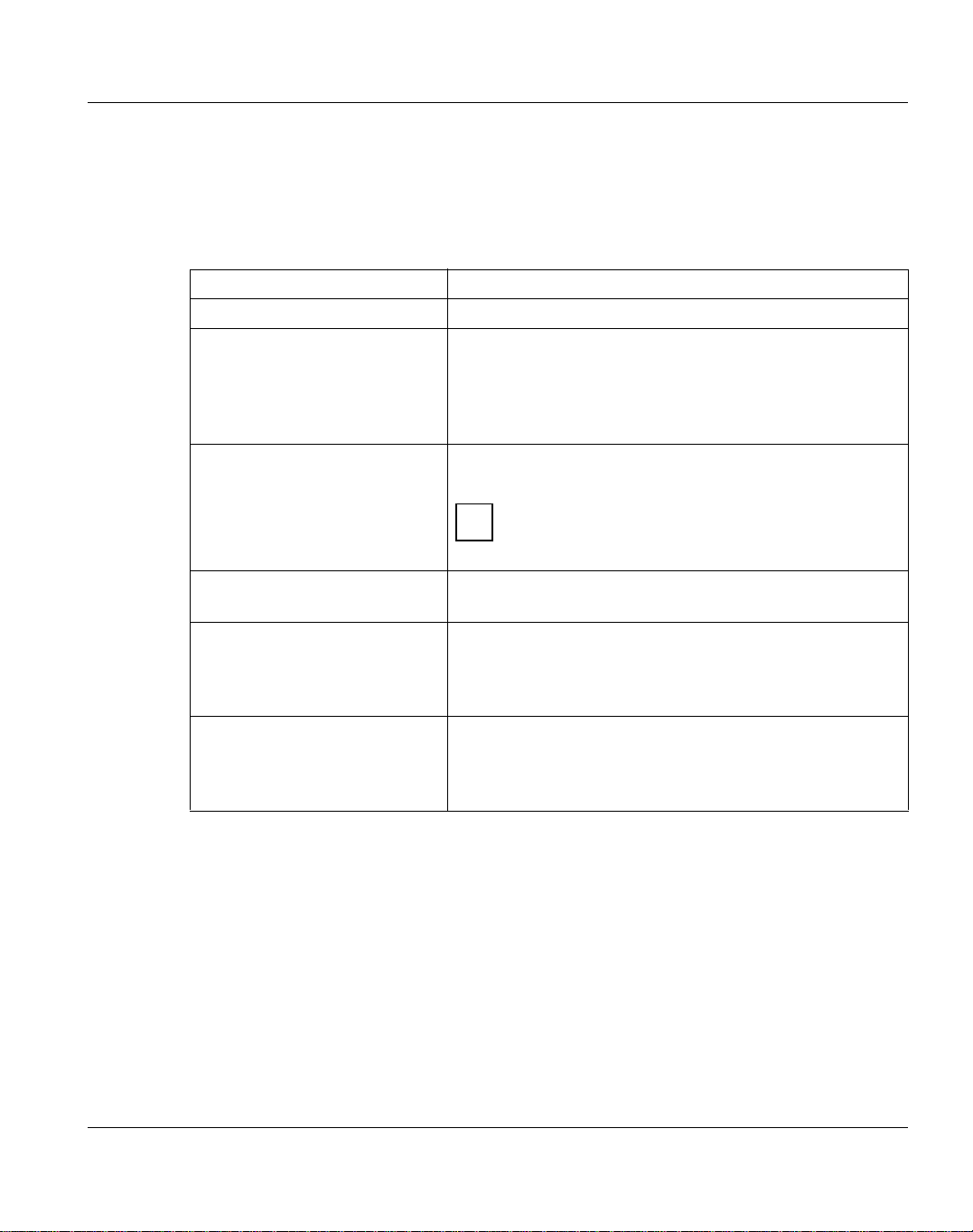
2.2.1 Names in the network
In the network, servers, domains, clients, users, and resources are assigned unique
names. The following table describes briefly the various types of names in the network.
Name Meaning
System name Name of the UNIX system
Computername, server name Each server and client in a network must have a unique
computername.
A proposed server name is derived from the system
name when it is being installed first (maximum 15
characters).
Username The administrator provides each user in a network with a
unique username for identification.
Users from other domains with which there is a
i
trust relationship are addressed with <domain
name>\<username>.
Sharename The administrator assigns a unique sharename to each
shared resource on a server.
Network name, UNC name The network name consists of the server’s computer
name and the sharename of one of this server’s
resources. A connection to a resource is established, for
example, with a network name.
Domain name The domain gets a domain name when you install the
primary domain controller. By default, it consists of the
first eleven characters of the system name plus the suffix
.dom (maximum 15 characters).
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 10
Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Shared resources
2.2.1.1 System name
Each UNIX system has a unique name in the network, which can be displayed using the
command uname -n and set as the network node name using the SYSADM utility program.
In order to avoid problems, it is strongly recommended that the system names you
!
assign are unique throughout the network. While the same system name may
appear several times in different DNS domains, even in the same network,
Advanced Server for UNIX uses the system name internally for generating names
which must always be unique.
2.2.1.2 Computername (server name)
Servers and clients must have a unique name in the network, known as the computername.
The computername of a server is also called server name.
A proposed server name is derived from the first 15 characters of the system name when
it is being installed first. The terms computername and server name are used synonymously in relation to the server.
It can be changed to any name (with a maximum of fifteen characters) during installation.
The server name is stored automatically in the lanman.ini file on the server. It is part of the
network name and may only be changed after the installation using special utility programs.
For further information please refer to the section entitled “Changing server attributes” in
the chapter entitled “Administration guidelines”.
● The server name consists of up to fifteen characters: letters from a to z,
i
i
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
numbers from 0 to 9 and the special characters -.~!#$%^&()_{}.
● In the previous Version 2.0, the server name for the LAN Manager/X server had
the suffix .serve. Please note that both LAN Manager/X Version 2.2 and
Advanced Server for UNIX up to version 4.0A10 propose the suffix .srv for a first
installation instead.
● Since Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0B, the default server name proposed
during the first installation is built from the system name without an extension.
● In order not to run into problems when upgrading to upcoming NT/AS/X-
versions in the future, all tools requesting a server name during installation or
reconfiguration offer the DNS-compatible host name (‘uname -n‘) as the default
server name. The extension .srv can still be used, but is not recommended and
no longer offered as a default. Installation/configuration scripts now inform the
administrator about DNS-incompatible server names.
Page 11

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Shared resources
2.2.1.3 Username
Every user of a client is assigned a username by the administrator, which is unique
throughout the network. Users are identified by their usernames in the network.
The username consists of three to fifteen characters: letters, numbers, spaces and
i
special characters without / \ * ’ " ‘!. Use a maximum of eight characters to achieve
unique mapping between UNIX names and Advanced Server for UNIX users. It is
not recommended to use umlauts or characters like the euro symbol in usernames.
2.2.1.4 Sharename
If a resource on a server is shared, it gets a sharename. The sharename identifies the
resource on the server. A sharename for a resource must appear only once on a server,
however the same sharename may be used several times on other servers in the network.
The sharename is part of the network name.
The sharename consists of up to twelve characters: letters (no umlauts), numbers,
i
and special characters. For MS-DOS clients, the sharename must comply with the
MS-DOS conventions.
Example
The command net share sf1=c:/u1/public is used by the administrator to share the directory
/u1/public as a resource for the network, sf1 is the sharename of this resource.
● The character string c: must always precede the resource pathname when
i
2.2.1.5 Network name
A client user sets up a connection to a shared resource using the network name. The
network name of a shared resource consists of the computername of a server and of the
sharename of the resource shared on this server.
Example
The command net use j: \\server1\sf1 is used by the client user to set up a connection to the
shared resource with the sharename sf1, which is located on the server with the
computername server1. The network name of the resource in this case is \\server1\sf1. Using
the command dir \\server1\sf1 or dir j: you can then display the contents of the shared
directory.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
sharing directories.
Page 12

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Shared resources
2.2.1.6 Domain name
A domain gets its domain name during installation of the primary domain controller. The
backup domain controllers are assigned during installation of a domain. The assignment of
a client to a domain is defined while it is being installed; it can be reconfigured later or, on
some clients, modified temporarily with the net logon command, for example.
The trust relationship concept means that it is easier to manage and use several domains.
(The manual entitled “Concepts and Planning” contains further information relating to this
topic.)
The default domain name consists of the first eleven characters of the system name plus
the suffix .dom, e.g. the domain name of the server server1 would be server 1.dom.
The domain name consists of up to fifteen characters: letters from a to z, numbers
i
from 0 to 9 and the special characters -.~!#$%^&()_{}.
The domain name may only be changed following installation using special utility programs.
Please refer here to the section entitled “Changing server attributes” in the chapter
“Administration guidelines”.
2.2.2 Mapping of file attributes through Advanced Server for UNIX
This section contains information on how Advanced Server for UNIX maps characters and
file attributes between the server and clients.
DOS
The following DOS attributes are mapped on the server by Advanced Server for UNIX:
● r (read only)
● d (directory)
● h (hidden)
● s (system)
● a (archive)
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 13

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Shared resources
The attributes r and d are mapped to the relating UNIX mechanisms. The attributes a, s and
h, as well as any possible combination of these are translated to Advanced Server for UNIX
by means of UNIX group names. The table below, for example, shows how the MS-DOS
file BSP.DAT with the attributes a and h and the MS-DOS file READONLY.BSP with the attri-
butes a, r and h are mapped under UNIX:
Permissions Owner Group Filename
rw-rwsr-- lmxadmin DOS-a-h bsp.dat
r--r-sr-- lmxadmin DOS-a-h readonly.bsp
OS/2
The extended file attributes of the HPFS (OS/2 extended attributes) contain additional information on OS/2 files such as long filenames or comments, for example. The UNIX file
system does not support all attributes, so Advanced Server for UNIX creates a hidden
shadow file for each file with extended attributes. This shadow file has the default name
.EA@<filename>. For example:
The autoexec.bat file has a shadow file with the name .EA@autoexec.bat.
The period (.) as the first character in the filename hides the file under UNIX. The
i
hidden files are not displayed with the ls command. To do this, use the ls -a
command.
You must try to ensure that these files are only handled under OS/2. If you delete or copy
the files under UNIX, you should also delete or copy the shadow file accordingly.
It is not possible to copy these files with their attributes from an Intel-based to a
!
RISC-based UNIX system using UNIX commands, as the internal formats do not
match. When the server system is changed, copy the files from the first server to an
OS/2 PC first and from this PC to the other server.
The shadow files of LAN Manager/X 2.2 are compatible with those of Advanced Server for
UNIX and can be continued to be used unchanged.
You should also be aware that with the current version of Advanced Server for UNIX, files
with extended attributes cannot be transferred via the replicator service and also cannot be
copied locally, for example, with lmshell.
The defa ult valu e of the EAF ilePrefix registry parameter has changed since Version 4.0A10
of Advanced Server for UNIX. Instead of .ea@, the value .EA@ is now used to ensure
compatibility with Advanced Server for UNIX V3.5.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 14

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Shared resources
Existing configurations are not modified during an upgrade installation. You should
therefore use either the Registry Editor or the regconfig command to set the value of the
EAFilePrefix parameter in the registry to .EA@ under the key
SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\AdvancedServer
\FileServiceParameters.
If you previously operated Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0A10 with the setting UseEAs=1,
you will now have to rename all hidden shadow files with the extended file attributes.
Use the following command to display all existing shadow files:
find / -type f -name ’.ea@*’ -print
The following shell script can be used to give all old shadow files the new prefix .EA@:
for eafile in ‘find / -type f -name ’.ea@*’ -print‘
do
newfile="‘echo $eafile | sed ’s/\.ea@/.EA@/’‘"
echo rename "$eafile" to "$newfile"
mv "$eafile" "$newfile"
done
Advanced Server for UNIX will only find the extended attributes of a file if the
!
associated hidden shadow file has the same prefix as is set in the current Advanced
Server for UNIX configuration instance. It would be best to change the file and
directory names and the registry parameters when the server is stopped and then
start the server again.
2.2.3 Share table (list of shared resources)
All shared resources are comprised in the share table. Every resource shared using the
command net share is entered in the share table. Every resource deleted using net share
/delete is removed from the share table.
Advanced Server for UNIX stores the share table in an internal format in the registry. The
share table is loaded automatically each time Advanced Server for UNIX is started. The
various types of shared resources are introduced in the following sections.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 15

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Shared resources
2.2.4 Shared directory
A shared directory is a file tree of a server system, which was shared for the usage in the
local network. Users can access the shared directory from a client using the sharename.
In this case, users work with the shared directory as they would with a local drive or
directory on t heir clients.
The security check is not taken into account in the following description in order to
i
avoid complexity.
The administrator is responsible for assigning a directory (for example with the server
named server1) to a sharename. The administrator links the local directory name
/u1/public1 to the sharename sf1 using the command: net share sf1=c:/u1/public1 , at the same
time sharing this resource for use in the local network.
● The directory must have been created beforehand, otherwise the administration
i
Access information is assigned to shared directories using net perms, which is stored in the
AS/X database (acl).
interface reports an error.
● The character string c: must always precede the resource pathname on the
Advanced Server for UNIX.
For example, using net perms c:/u1/public1 /grant group1:fullcontrol the group group1 is
assigned read, write, and execute permissions as well as the permission to create files and
directories, to change or delete attributes and to change the permissions for these directories.
● UNIX permissions have a higher priority than permissions assigned using net
i
perms. Thus, for example, the above dir ec to ry has no write authorization if the
permissions r-x-r-x-r-x are set up using UNIX. If problems arise, the UNIX
permissions can be set temporarily to rwxrwxrwx to establish whether the
missing UNIX permissions have caused the problem.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 16

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Shared resources
Authorized users can assign this shared directory to their clients. The network name of the
shared directory (in accordance with DOS naming conventions) \\server1\sf1 is linked on the
client to a local drive letter, e.g. j:, using the command net use j : \\server1\sf1.
The user may have to allow additional drive letters on the client in the configuration
i
file config.sys using the command lastdrive.
The client user can then access the shared directory using the drive letter j:. All attempts to
access files (copying files and directories, editing files etc.) made by the user on drive letter
j: are mapped on the file system of the server.
The shared directory can therefore be used by a user or a user group. If several users wish
to process a file at the same time, entire files or parts of files can be locked using file locks
for the duration of processing. Read and/or write locks are available.
Older MS-DOS versions or programs are not network-ready, in this case only one
i
user at a time can access a file.
Advanced Server for UNIX maps the interfaces available under the MS-DOS, OS/2,
Windows, Windows for Workgroups, Windows 95/98 and Windows NT operating systems
to UNIX mechanisms in order to manipulate files and directories.
For further information, please refer to the manual entitled “Concepts and Planning”.
2.2.5 Shared printer resource
As an administrator, it is possible to share the printer queues for the network. The
administrator can also check the status of the printer queue using the corresponding administration commands and can manipulate the print jobs (delete, for example).
The printout waits in the printer queue and is then printed on a printer connected to the
UNIX system or on a printer connected to a specially configured client (shared client
printer). For further information, please refer to the chapter entitled “Configuring Advanced
Server for UNIX”.
2.2.5.1 Printer spoolers
Interfaces for the following spoolers are available for Advanced Server for UNIX:
● Standard spooler (AT&T
● SPOOL V4.2 (and above) for all Reliant UNIX systems
Please refer to the section “Configuring printers on the UNIX system” for information on how
to configure the interface to the spooler.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
®
high performance interface)
Page 17
Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Shared resources
2.2.5.2 Shared client printer
It is also possible to route the output of the printer spooler to a printer which is connected
to a client (shared client printer). For further information, please refer to the manuals entitled
“MS Network Client V2.2” and “User's Guide for MS-DOS Clients”.
2.2.5.3 Printer server
The output of the printer spooler can also be routed to server and client systems that can
share a printer resource (e.g. Windows for Workgroups, Windows NT).
2.2.5.4 Sharing a printer
The administrator shares the printer queue on the server (with the computername server1).
For example, you can enable a printer group or class with the sharename sp1 using the
net share sp1 /print command.
For example, the user of the client with the computername cl3 links to a shared printer. To
do this, he/she assigns the network name \\server1\sp1 with lpt1 using the command (in the
MS-DOS naming conventions) net use lpt1: \\server1\sp1. The user can now work on lpt1: for
all print jobs as he/she would on a local printer.
● For Windows NT-Style Printing the sharing of a printer with UNIX commands is
i
no longer recommended.
For further information, please consult the manual entitled “Concepts and Planning”.
2.2.6 Interprocess communication resource, IPC$
Advanced Server for UNIX can be used to implement distributed applications: Application
processes on the server system exchange data over the network with application
processes on clients. The resource IPC$ enables this communication using LM named
pipes and mailslots.
Special functions also allow the administration of Advanced Server for UNIX using
programs. For additional information please refer to the manual “API Reference” and in the
manual pages for the API, which are supplied with Advanced Server for UNIX. The
following sections contain further information on interprocess communication.
The IPC$ resource is automatically shared.
i
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 18

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Shared resources
2.2.6.1 LM named pipes
Advanced Server for UNIX also provides LM named pipes. They are bidirectional communication channels for interprocess communication in the network. They differ from UNIX
named pipes.
The following example describes the basic procedure for setting up and clearing down an
LM named pipe: An application process with root authorization creates a named pipe on the
server. The client process on the client sets up a connection to the known named pipe over
the local network. Both processes can then exchange data using the LM named pipe. When
the data exchange has ended, the LM named pipe is deleted.
Advanced Server for UNIX must be running in order to use LM named pipes.
i
Example
The root-authorized process on the server server1 creates a LM named pipe with the name
srvp using the function DosMakeNmPipe (“/PIPE/srvp” , &reference,...) and waits using the
function DosConnectNmPipe (re ference) for a connection to be set up (_dos_open) to the client
process.
The client process – under MS-DOS, OS/2, Windows, Windows for Workgroups,
Windows NT or Windows 95/98 – opens the named pipe with
_dos_open ("\\\\server1\\PIPE\\srvp",&cfd,...), and data can now be exchanged between the
processes.
The character “\” must always be specified twice in a C program since the first “\” is
i
interpreted as an escape character.
®
The connection to the LM named pipe is set up using the resource IPC$. If a client process
on a client wishes to communicate with an application process on the server, this resource
is connected automatically.
If the LM named pipe is to be closed again after the data exchange, the client process closes this named pipe using _dos_close(cfd).
The server process can then clear down the connection using
DosDisconnectNmPipe(reference) and delete the named pipe using DosClose(reference).
Further information on LM named pipes can be found in the manual “API Reference” and
in the manual pages for the API.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 19

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Shared resources
2.2.6.2 Mailslots
Mailslots are unidirectional communication channels. They are created by an application
process on the server or by a client process on the client. In contrast to LM named pipes,
several processes can write to the same mailslot simultaneously but only the process that
created the mailslot can read from it.
Example
A reading process (on the server server1) creates a mailslot with the name ms. This program
waits for messages for the mailslot. The writing program sends a message to the network
name of the mailslot //server1/mailslot/ms.
The developer implements this in the program sources for client processes using the API
functions, in compliance with MS-DOS and OS/2 naming conventions:
In the reading program using DosMakeMailslot(\\\\mailslot\\ms, ..) and in the writing program
using DosWriteMailslot(\\\\server1\\mailslot\\ms, ,..).
The following calls are used in the processes on the server:
In the reading program using DosMakeMailslot(//mailslot/ms, ..) and in the writing program
using DosWriteMailslot(//server1/mailslot/ms, ,..).
2.2.7 Using the UNIX operating system from the PC
You can execute UNIX commands from the PC over the netrun service. For further infor-
mation, please consult “Chapter 5 - Enhanced Reference” in the manual “User's Guide for
MS-DOS Clients”.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 20
Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Services
2.3 Services
The following additional services can be configured in Advanced Server for UNIX:
Service Comments
Alerter
Auditing
Replicator
Netlogon
Timesource
SNMP Extension Daemon
Netrun
Browser
Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS)
The following sections briefly explain these services.
configurable
configurable
configurable
configured when server is installed
configurable
installed and configured with the asxsnmp
package
configurable
configured automatically
configurable
2.3.1 Alerter
This service sends alarm messages to certain client users. For example, alarm messages
are initiated if access permissions are violated when using shared resources and if
important limits are exceeded (maximum error rate when accessing networks and hard
disks and maximum number of logon attempts ) .
2.3.2 Auditing
Important activities in the network are recorded by this service. These include starting and
stopping the server, user sessions and utilization of shared resources by specifying the
username and time. This list can be displayed if required.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 21

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Services
2.3.3 Replicator
The Replicator service allows specific files and directories to be copied automatically from
the export server to one or more of the specifically configured import servers (server and
clients with the Replicator service).
The Replicator service on the export server monitors the export directory, containing the
designated files and directories. If a file in the export directory is changed or directories
and/or files are added or deleted, the Replicator service updates these directories and files
under the import directories.
2.3.4 Netlogon
The netlogon service connects a specified server to a domain. This simplifies the administrator’s duties: within a domain a user account only needs to be managed and maintained
on one server. User accounts can be maintained on each server using the single system
image (SSI), the accounts is thus centrally manag ed and dis trib ute d.
The netlogon service ensures that there is an identical copy of the user account on the
primary domain controller and the backup domain controllers of the domain. The netlogon
service also processes the logon procedures of the clients.
If you are using the Netlogon service, the servers in a domain have several roles:
Server role Task
Primary Domain Controller Maintains and distributes the master copy of
the user account database, handles “logon”
requests.
Backup Domain Controller Receives a copy of the user account
database, handles “logon” requests.
The netlogon service also provides connections to other domains with which a trust
relationship exis ts .
2.3.5 Timesource
This is a Advanced Server service which identifies a server as the time source for a domain.
Other servers can synchronize their clocks with the time source.
UNIX servers cannot synchronise their clocks using this service.
i
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 22

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Services
2.3.6 SNMP service
The SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) service is installed and configured with
the asxsnmp package. This daemon process is started and stopped automatically with
Advanced Server for UNIX. It provides a connection between Advanced Server for UNIX
and the SNMP agent. Please refer to the manual “SNMP Service” for further information. In
addition, the “Emanate Master Agent” (Slsnmpdm) can also be used with the “SINIX SNMP
Agent Adapter” (Slsnmpd).
2.3.7 Netrun service
The Netrun service enables you to run a UNIX program on Advanced Server for UNIX from
an OS/2 or an extended MS-DOS client.
The corresponding user interface is not available on Windows for Workgroups, Windows
95/98, and Windows NT.
2.3.8 Browser
The browser service extends the announce messages that normally occured in the LAN
Manager/X environment (every 60 seconds). This new mechanism consists of a system of
hierarch ically order ed br owser progr ams t hat ar e used for search ing do mains, serv ers and
resources within the network. The browser service function is provided in the Explorer/File
Manager and Windows Print Manager. Relevant shared resources on other servers and on
servers in other domains can be found using this system.
However, the browser service can only be used by a Windows NT server, a Windows NT
workstation, a Windows 95/98 client, or a Windows for Workgroups client. It is not available
on a Windows or MS-DOS client.
For further information in this regard, please refer to the “Concepts and Planning” manual.
2.3.9 Windows Internet Naming Service
The Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) is used to map computernames to IP
addresses. For further information please consult the chapter describing “Implementing
WINS”.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 23

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Connection management
2.4 Connection management
The following sections contain descriptions of a network connection between the server and
the client. The terms “session” and “network connection” are explained and the security
concept of Advanced Server for UNIX is introduced.
2.4.1 Sessions
A session is set up between a client and a server the first time when a connection from the
client to a server resource was successful. (N.B. Windows NT clients sometimes have two
sessions to the s am e se rv er) . Ev ery cl ie nt can h a ve se ve ral se ssio ns with seve ra l s erve rs.
● Sessions are also set up between the servers in a domain; likewise, local
i
sessions exist on the server. The command net session shows all current
sessions.
● The MAXCLIENTS parameter restricts the number of sessions that can exist
simultaneously. See also section “Parameters” in chapter “Lanman.ini File” in
this manual.
2.4.2 Connection to a resource
If the client user successfully connects to a resource first time from a server, a session is
automatically set up for this server (see above). However, if there is already a session with
this server then a new connection is set up to the required resource of this server using the
existing session.
A connection is explicitly cleared down from a client using the command net use and the
option /delete. On the other hand, if the session with a server is shut down then all connections to the shared resources of this server are closed.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 24
Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Administration
2.4.3 Security concept
In order to protect shared resources from unauthorized access, the user level security
concept is always used in Advanced Server for UNIX.
Users must legitimate using their username and password once in the domain to be able
to access the shared resources for which they are authorized.
Even after you have successfully logged onto a domain, you may need to carry out
i
further steps to be able to use the resource of a server in another domain:
● If you have a different password for the same user name in another domain, you
must enter this password.
● If you have a different user name in another domain, you must log off from the
previous domain and log onto the new domain or alternatively make the
connection with the resource as a different user.
● If there is a trust relationship between the two domains there is no need to
create the user account a second time. You can also access the resources in
the other domain if you are a legitimate user in your domain. For further information, please refer to the “Concepts and Planning” manual.
2.5 Administration of Advanced Server for UNIX
The administrator manages and controls the shared resources, users, and their permissions on the UNIX server.
Advanced Server for UNIX is managed via the graphical interface of the Windows NT
Server T ools. Using this administration program you can carry out your administration tasks
remotely, e.g. from a Windows NT system (server or client) or a Windows, Windows for
Workgroups or a Windows 95/98 client if these utilities are installed there.
The administration of Advanced Server at the command prompt is described in chapter
“Administering Advanced Server at the Command Prompt”.
Administration functions can also be carried out from programs via the programming
interface (API). For further information please refer to the manual “API Reference” and the
API manual pages.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 25
Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Programming interface (API)
2.5.1 Remote administration
You can execute remote administration from any of the following systems:
● Windows NT client and server
● Windows 95/98, Windows for Workgroups, or Windows client
● Extended MS-DOS client
● UNIX system running Advanced Server for UNIX
2.5.1.1 Remote administration under MS-DOS
The administration shell is started using the command
net admin \\<servername> [password] /command and thereafter commands are issued using
the command net <subcommand>.
The command exit or the key combination and can be used to exit the administration shell and return to the operating shell system.
2.5.1.2 Remote administration under Windows
Remote administration is possible from any system on which MS Windows, Windows for
Workgroups, Windows NT, or Windows 95/98 is installed. For this reason, the Windows NT
Server Tools are supplied with Advanced Server for UNIX. Special NT Server Tools have
been developed for the Windows client. Since they have the same functionality, a standard
administration interface is available to you on all clients and workstations.
2.6 Programming interface (API)
Advanced Server for UNIX provides a programming interface (application programming
interface (API)), which can be used to develop distributed applications in the network. The
API provides functions, for example, for the LM named pipes and mailslots. You can also
execute administration functions from your own programs.
With these functions, you can develop your own programs on the server operating system
which can exchange data with client processes. Advanced Server for UNIX itself uses the
API for administration tasks.
The API functions and changes since LAN Manager/X V2.2 are described in the manual
“API Reference” and in API manual pages. For information on how to install the manual
pages, please refer to the section “Installing the asxman package”.
CTRL
Z
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 26

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Compatibility
2.6.1 Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
Advanced Server for UNIX supports the Microsoft Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs). This
platform-independent mechanism is used for interprocess communication within a clientserver architecture.
The new functions of Advanced Server for UNIX are called up internally via RPC.
2.7 Compatibility
2.7.1 Client software
The functionality of Advanced Server for UNIX corresponds to the server part of Microsoft
Windows NT Server. The Advanced Server for UNIX product uses the SMB protocol
(Server Message Block) and is thus compatible with the following products:
● MS Networks 1.01 (not included in delivery package)
● MS Network Client MS-DOS V3.0 (included in delivery package)
● MS LAN Manager MS-DOS V1.1 (not included in delivery package)
● MS LAN Manager MS-DOS V2.0 (not included in delivery package)
● MS LAN Manager MS-DOS V2.1 (not included in delivery package)
● MS LAN Manager MS-DOS V2.2c (included in delivery package)
● MS LAN Manager OS/2 V1.1 (not included in delivery package)
● MS LAN Manager OS/2 V2.0 (not included in delivery package)
● MS LAN Manager OS/2 V2.1 (not included in delivery package)
● MS LAN Manager OS/2 V2.2 (not included in delivery package)
● MS Windows for Workgroups V3.1 (not included in delivery package)
● MS Windows for Workgroups V3.11 (not included in delivery package)
● MS Windows 95 (not included in delivery package)
● MS Windows 98 (not included in delivery package)
● MS Windows NT Version 3.1 and later, for administration Version 3.51 and later (not
included in delivery package)
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 27
Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Compatibility
● The RFC 1001/2 implementation (NetBIOS™ on TCP/IP) is the basis for
i
communication with the server system.
● The MS LAN Manager OS/2 products referred to above are only available for
OS/2 V1.x.
● If you are using the client with MS LAN Manager V2.0, you must set up the
TCP/IP communication software with the Siemens product LAN1 Vx.
● The product MS LAN Manager provides TCP/IP with Version 2.1 and later; with
this product you have the option (e.g. if you want to implement an emulation in
parallel) of incorporating the product LAN1 Vx.
● The product LAN1 is not supplied with Advanced Server for UNIX.
● The commands referred to, i.e. udir, uren, and uchmod, cannot be used on all
clients. In this case you should use the corresponding UNIX commands.
2.7.2 Role of the server
You can install Advanced Server for UNIX and LAN Manager/X in a domain with Windows
NT servers. Only one Advanced Server for UNIX or Windows NT server can be installed as
a primary domain controller in a single domain. LAN Manager/X servers cannot take on the
server role of primary domain controller.
The server roles of member server and standalone server have been omitted from
i
Advanced Server for UNIX.
2.7.3 Server hardware
Advanced Server for UNIX can be operated via any network with TCP/IP capability, e.g. via
Ethernet
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
®
or Token Ring™.
Page 28

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Compatibility
2.7.4 LAN Manager/X V1.1
Version 2.0 and later of LAN Manager/X or Advanced Server for UNIX are compatible with
Version 1.1 as regards the following:
● The environment variable $xLMX
● The environment variable $LM_HOMEDIR
● The file /etc/rclmx, in which the environment variables are set
● The automatic call of /etc/rclmx from the script /etc/profile
● The utilities
d
os2unix and unix2dos, which can be called under the system path and
under $xLMX/bin
● The programs net and lm, which can be called under
● The script lmx for starting and stopping the server (with the NetBIOS administration
$xLMX/bin
program) and the server status display.
Important changes to the previous version for Version 2.0 and later:
● The domain concept is supported.
● You can route the output of the printer spooler to a printer that is connected to a client
(shared client printer).
● The share table and usernames are saved in a different format (if required this data can
be converted manually for the new version).
● The MS-DOS notation must be used with the command net, for example options may
only be introduced with the character “/”.
● For shared directories, c: must always be specified with the command net share,
e.g. net share sf1=c:/u1/sf1.
● Programs which create LM named pipes must have root authorization.
● LAN Manager/X must be started when creating the LM named pipes.
● Remote systems can be administered from a client with the command net admin. For
this purpose, the server name must always be specified e.g.
net admin \\server1 /command
● The prefix net must always be set in the administration shell.
● The configuration file is now called
deviate from standard. The program
$xLMX/lanman.ini, and only contains values which
srvconfig should always be used for viewing or
modification functions. The chapter “Lanman.ini File“ contains a description of this.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 29

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Compatibility
2.7.5 LAN Manager/X V2.0
Version 2.2 and later of LAN Manager/X or Advanced Server for UNIX is compatible with
Version 2.0 as regards the following:
● The API of Version 2.0 is a subset of the API of Version 2.2.
Important changes to Version 2.0
● The API of Version 2.0 has been extended.
● The Targon/31 system is no longer supported.
● Y ou are now provided with a suggested name for the server name consisting of the first
nine characters of the host name and the suffix .srv instead of .serve (e.g. server1.srv).
● In order to start a UNIX program from the PC, you should now use the command netrun
(extended MS-DOS client) instead of uexec.
● In the case of an update installation, the configuration of Versions 2.0 and 2.2 can be
adopted.
● Server attributes such as server role, server name etc. can be changed afterwards with
a utility program.
● The servers and clients can be located in different subnets.
● You can save the entries for installation in a file and carry out the installation at a later
date. This file also makes it possible for you to carry out “automatic installation” – even
on other UNIX systems.
● Individual services can be started and stopped.
● The command net version shows which version of LAN Manager is installed on the
current system.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 30
Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Compatibility
2.7.6 LAN Manager/X V2.2
Advanced Server for UNIX since V3.5 is compatible with LAN Manager/X V2.2 as regards
the following:
● Advanced Server for UNIX supports the full functionality of LAN Manager/X V2.2.
● Interoperability is possible both with LAN Manager V2.x systems and with LAN
Manager V2.0 and V2.2 clients under MS-DOS, OS/2, Windows 3.1, and Windows 3.11
(Windows for Workgroups).
● The environment variable $xLMX and the lmx command are still available.
Important changes to Version 2.2
Advanced Server for UNIX has the following new or modified features and functions:
New and modified commands or procedures are explained in comparative tables
i
with comments in Appendix A of the manual “Concepts and Planning”. Please refer
to the tables for these descriptions.
● Like a Windows NT server, Advanced Server for UNIX can take on the server role of
primary domain controller in a domain.
● The server roles of “member server” and “standalone server” have been omitted. In an
upgrade, the member server is given the role of “backup domain controller” and the
standalone server is given the role of “primary domain controller”.
● The share level security concept is no longer supported. In the upgrade installation, the
server is given the server role of primary domain controller with the user level security
concept.
● Modified processing and defaults for acce ss permissions
● The environment variable $xASX exists in parallel to the environment variable $xLMX.
The new command asx (e.g. asx start) corresponds to the lmx command, which can still
be used.
● The Replicator service is no longer started automatically.
● Trust relationships can be set up between domains. These facilitate the use of
resources in other domains.
● Global and local groups as well as global and local user accounts are supported.
● Customizable user environments: A specific user environment is recorded by means
of defining a user profile or by allocating a logon script regardless of which client the
user logs on from.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 31

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Compatibility
● Administration: The primary administration tool for Advanced Server for UNIX are the
Windows NT Server Tools, which can be used from a Windows NT workstation or a
Windows NT server. They are also available under Windows 3.1, Windows for
Workgroups, and Windows 95/98.
The NT Server Tools replace the graphical user interface netadmin.
Administration tasks can still be carried out via the UNIX console.
● Monitoring: The network is monitored with the graphical monitoring tools Event Viewer,
Performance Monitor, and Server Manager which supplement the Alerter service.
● New security concept: Advanced Server for UNIX has a more extensive security
concept, which consists of user identification, user authentication, access control, and
access logging.
● Remote Procedure Calls (RPC): Advanced Server for UNIX supports the Microsoft
Remote Procedure Calls (RPCs).
● Browser service: This service is used by Windows applications like Explorer/File
Manager and Print Manager as well as by the net view command.
● Support for UNIX quotas (configurable).
● Name Space Mapping: Mapping of long file names to DOS 8.3 naming conventions.
● Mixed Case Support: Configurable support for uppercase in file and directory names.
● New utilities: accget, accadm, and userget.
● Interoperability with Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 95/98.
● Configuration of NetBIOS (For further information please refer to the section entitled
section “Configuring NetBIOS”).
● Migration tools: Advanced Server for UNIX has migration tools with which existing
user accounts, access lists etc. are converted.
● No licensing with key diskettes; no additional user extensions.
● Manual pages for the API; the NetAccessEnum function has been omitted from the API.
● Utilities for generating installation diskettes for clients.
● The net error and net audit commands are obsolete; the net access command as well as
the new net perms command can only be invoked with parameters.
● Version 3.0 of MS Network Client
● German language message texts in a separate package
● In the lanman.ini file a series of parameters have been omitted. After an upgrade instal-
lation, these parameter entries should be removed manually.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 32

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Compatibility
● The add_access, add_user and buildacc utilities have been omitted. Instead of lmxsetup
and lmxinfo, asxsetup and asxinfo are available.
● With Advanced Server for UNIX, the AT&T and SPOOL V4.x spoolers are supported.
2.7.7 Advanced Server for UNIX V3.5
Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0 is compatible with V3.5 except for the following:
● Intel systems are not longer supported (e.g. SINIX-L/-M/-Z and UnixWare).
● AS/X V4.0 needs at least SINIX / Reliant UNIX -N/-Y V5.43C00.
● AS/X V4.0 needs additional software installed on the SINIX / Reliant UNIX (see section
“Hardware and software requirements”).
Important changes to V3.5:
Advanced Server for UNIX has the following new or modified features:
● NT style printing is supported and gives the possibility to install printer drivers for
Windows 95/98 and Windows NT on the server. It is no longer neccesary to install the
printer driver on each client manually.
● A Windows NT compatible WINS-service is available with Advanced Server for UNIX
V4.0. This makes it much more easy to operate the server and clients in a routed
environment.
● Registry: Most of the Advanced Server for UNIX configuration is stored in a binary
Registry file. The configuration can now be done via the Windows Registry Editor.
● SMB Signatures: SMB signing provides a message authentication by placing a digital
security signature into each SMB, which is then verified by both the client and the
server. For more information about SMB signatures take a look at Microsoft Knowledge
Base.
● It is possible to select the language of builtin names (domain language) before the
initialization of the Advanced Server for UNIX databases takes place (e.g. the local
group “Administrators” becomes “Administratoren” and "builtin\guest" becomes a
"vordefiniert\Gast").
● New command net computer to display or modify the list of the computer accounts in the
domain database, net sid to translate Security Identifiers (SIDs) into account names and
vice versa.
● German language message texts are integrated in the asxserver package and can be
activated with a utility.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 33

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Compatibility
2.7.8 Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0A
Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0B has the following new or modified features:
● DNS-WINS-integration: new NetBIOS version to support the DNS-WINS- Integration of
Reliant UNIX V5.45. For a documentation of the DNS-WINS integration, please refer to
the manuals of the operating system.
● Compatible with SIthreads package (used for the WINS service).
● Compatible with Reliant UNIX V5.45.
● Integration with RMS (Reliant Monitor Software).
● Euro symbol support.
● All AS/X files are now located below the /var/opt/lanman directory.
● The joindomain command now supports additional command line options allowing non-
interactive mode operation.
● New utilities: printadm, repladm, userrights, promote
● Online manual pages for all AS/X commands, new manual pages for:
– new utilities: printadm, promote, repladm, userrights
– other utilities: accadm, accget, addclip r , addserver , a sxcheck, asxinfo, asxperf, asxpwexp,
asxregview , delclipr, delserver, setdomainlang, setlang, setspooler, userget
● asxregview enhancements.
● Improved asxinfo and asxcheck utilities.
● New /HOMEDIRDRIVE option for the ne t user command.
● New options -o and -M for acladm utility, new additional options -f and -n for acladm -C.
● New option -d for regconfig utility, support pathnames with "/" and "\".
● New option -q for blobadm utility to support low level blob file compression.
● Improved performance during the blob file grow process (used for all Advanced Server
databases).
● Improved installation of asxserver package.
● Default of servername without ".", that means .srv is omitted.
● The .srv extension for server names is no longer offered as the default. Warnings occur
if server names are incompatible with DNS names.
● Share table information moved to registry.
● lmshare command now supports printer driver fields.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 34

Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX Compatibility
● Updated description “Compression of the ACL Database”
● Updated description: “Moving directories with existing access permissions”
● New configuration option to spoolin print jobs with the User ID of the mapped UNIX user
instead of the User ID of "root".
● New registry parameters: ConnectTimeout, MaxMpxCt, NetPopup, SpoolinAsUnixUser,
DeletedPrintJobTimeOnQ
● New lanman.ini parameters: maxspoolfds, os2searchfix, ProductType
● The following registry parameters are no longer supported: ShareCacheCount
● Removed limit of 128 trust relationships.
● New range 0 - 2 for the value of the UseUnixLocks registry parameter.
● The limits of the NumCLIENT_SESSION and NumSERVER_SESSION registry parameters
are watched and resource shortages are reported.
● UnixQuotas registry parameter also used to restrict the user's disk space for non-root
users (if supported by the file system).
● Implemented Level II Oplocks to improve co-operation with NT clients.
● NetBIOS keep alive timeout is now configurable and changed from1 minute to 30
minutes to reduce the number of frames on the network.
● New NetBIOS tunables NBRFCMAXDGMS and NBRFCMAXFRAGS.
● NBRFCKALIVE tunable now used to set the keep alive timeout in minutes. Default
changed to 30 minutes.
● The time when a NetBIOS name conflict occured is also displayed when calling
nbrfcdiag -n.
● The tcp_nodelay functionality is no longer configured as a lanman.ini parameter. Now it
is configured at the NetBIOS daemon startup (-n option).
● NetBIOS daemon startup parameters now configured in a configuration file.
● NetBIOS diagnostic messages now written to syslog.
● Additionally, the IP address can be used with the -E and -D options of the nbconfig
command.
● New -a, -A and -q options for nbtstat utility.
● New NetBIOS findbrow utility on UNIX.
For a detailed description of the new options and commands, please refer to the description
of the commands in the online manual pages or in this manual.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 35

3 Advanced Server for UNIX architecture
This chapter contains descriptions of the architecture of Advanced Server for UNIX.
Communication takes place via TCP/IP (Transmission Transport Protocol/Internet
Protocol).
Processes required for the administration of NetBIOS are not considered here!
i
3.1 Process model
A series of processes are started in order to carry out specific tasks when Advanced Server
for UNIX is started. The following sections contain a short description of these processes
and their tasks.
The number of processes depends on the current configuration which is stored in the
lanman.ini file and in the Registry.
3.1.1 Communication between the processes
Data which is required by all Advanced Server for UNIX processes is stored in a shared
memory segment. This data includes, for example, the file and lock tables. Data that is not
required by all processes is retained by the control process and made available as required
by means of interprocess communication.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 36

Advanced Server for UNIX architecture Process model
3.1.2 Overview of the processes
The following table lists the daemon processes active when Advanced Server for UNIX has
been started in a maximum configuration.
Process Task
lmx.ctrl
lmx.srv
lmx.dmn
lmx.alerter
lmx.browser
lmx.repl
lmx.wins
lmx.ep
lmx.netrun
lmx.extd
lmx.nvalert
daemon process for connection setup and administrative tasks
daemon process (generated from the process lmx.ctrl) for processing
tasks from several workstations
daemon process for the service Netlogon, for synchronization
between different servers (Single System Image (SSI)), trust relationships
daemon process for alarm messages (Alerter service)
daemon process for Browser service
daemon process for the replicator service
daemon process for Windows Internet Naming Service
endpoint mapper for RPCs for WINS service
daemon process for the Netrun service
daemon process that works with the SNMP service
daemon process for the Net View Alerter service (not supported by
Siemens Advanced Server for UNIX)
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 37

Advanced Server for UNIX architecture Process model
The following diagram clarifies the cooperation between Advanced Server for UNIX
processes on a server started with the default configuration:
Shared memory
lmx.browser lmx.ctrl lmx.dmn
lmx.srv
1
PC PC
Advanced Server for UNIX processes
lmx.alerter
lmx.srv
n-1
lmx.srv
n
PC PC PC PC
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 38

Advanced Server for UNIX architecture Process model
The process lmx.ctrl
The process lmx.ctrl manages the individual server processes and undertakes those tasks
which cannot be directly allocated to a workstation. Several tasks are carried out within the
process which are not controlled by the operating system scheduler (as the process is) but
which assume control alternately. The individual tasks in the process lmx.ctrl are shown in
the following diagram:
Named
lmx.ctrl
pipe
service
pipeserv
task
task0
Server
requirements
New
client
The process lmx.ctrl
listener
task
lmx.srv
process 1
mcpwork
task
lmx.srv
process 2
mslot
task
lmx.srv
process 3
Mailslot
tasks
Message
datagrams
The task0 task queries events in the network or in the other processes and gives control of
one of the tasks described below to the lmx.ct rl process.
The
l
istener task reacts to incoming requests from the workstations and distributes the
connection requests to the existing server process
lmx.srv or, if necessary , generates a new
server process.
The
mslot task receives the mailslot requests and passes them on to the server. It also
processes the announce requests from other servers. This task transmits the mailslot
messages to the application processes on the server, which can then be read using the API
function DosReadMailslot. In addition, this task manages the server function autodisconnect.
mcpwork Task oversees all lmx.srv processes and answers administrative queries from
The
the workstations.
The
pipeserv Task coordinates transactions between server and client applications.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 39

Advanced Server for UNIX architecture Process model
The process lmx.srv
One or more lmx.srv processes process the requests of several workstations in the network.
Each lmx.srv process is started, as required, using the process lmx.ctrl. The relevant lmx.srv
process passes the print requests and their management on to the system spooler.
The maximum number of workstations to be operated in parallel can be configured for the
lmx.srv process in lanman.ini file and in the registry. The minimum and maximum number
depend on the parameters maxclients (in lanman.ini), MaxVCs (Regist ry) and VCDistribution
(Registry). The Registry parameters MinVCPerProc, MaxVCPerProc and VCDistribution
should be used to change the maximum number.
The process lmx.dmn
The daemon process lmx.d mn performs the service network logon security. It also synchronizes the in dividua l server s (single system image, SSI) and is used for trust relationships. This
process is started by the process lmx.ctrl when Advanced Server for UNIX is being
initialized.
The lmx.alerter process
This daemon process manages the alerter function. If not disabled, it is started automatically when AS/X is started.
The lmx.browser process
This process enables the Browser service. If not disabled, this process is started when
Advanced Server for UNIX is being initialized.
The process lmx.repl
The process lmx.repl establishes contact with other servers and imports or exports files from
and to these servers in order to ensure data consistency. This process is only started if it
has been configured.
The lmx.wins process
This process establishes the WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service) service. It is started
only when configured.
The lmx.ep process
This process works together with the lmx.wins process. It is started and stopped automatically with WINS.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 40

Advanced Server for UNIX architecture Process model
The lmx.netrun process
This process provides the Netrun service: UNIX programs can be executed on the server
from MS-DOS or OS/2 workstations using this process.
The process lmx.extd
The lmx.extd program is installed and configured with the installation of the software
package asxsnmp. This process sets up the connection between the SNMP service and
Advanced Server for UNIX; it informs the SNMP agent when Advanced Server for UNIX
starts and stops.
The lmx.nvalert process
This process is not supported by Siemens Advanced Server for UNIX.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 41

Advanced Server for UNIX architecture Network communication
3.2 Network communication
A workstation and an Advanced Server for UNIX communicate in the network using several
protocol layers. NetBIOS is implemented in accordance with RFC1001/2. This NetBIOS
implementation is based on the standard protocol TCP/IP. The following diagram illustrates
the way in which the individual modules work together in the communication process.
Advanced Server for UNIX
NB-LIB
TLI
RFC 1001/2
TCP/IP
TCP/IP application
Sockets
WAN driver
Communications
controller for WAN
HDLC, X.25, or
ISDN
Communication architecture of Advanced Server for UNIX
Token Ring driver
Communications
controller for Token Ring
LAN
Token Ring
Ethernet driver
Communications controller
for Ethernet
LAN
Ethernet
● This diagram is a simplified illustration of the communication architecture, other
i
products such as CMX, for example, may be required for communications
controllers.
● Depending on the UNIX system implemented
– there are different connection options
– communications controllers and card drivers are required
– several communications controllers can be implemented simultaneously.
The NetBIOS component of the operating system kernel is implemented in the streams
architecture. The library NB-Lib in Advanced Server for UNIX allows access to the NetBIOS
streams driver using the standard interface TLI. Access to TCP/IP takes place via the
NetBIOS streams driver. Parallel access to TCP/IP is possible via the socket interface.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 42

Advanced Server for UNIX architecture Local communication for UNIX systems
3.3 Local communication for UNIX systems
If a user is working on the server system as an Advanced Server for UNIX user, e.g.
administrator, then NetBIOS is used for a local session.
The programming interface to Advanced Server for UNIX, the application programming
interface (API), is implemented using local interprocess communication (LIPC). Advanced
Server for UNIX processes use the same interface. The requests are mapped to streams
pipes in the operating system kernel.
The following diagram shows that the Advanced Server for UNIX processes and the application processes access the same interface:
Application
Advanced Server for UNIX
LIPC LIPC
Named pipes of the operating system
API
Local communication
The named pipes of the operating system are used for data transport.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 43

4 Installing Advanced Server for UNIX
This chapter contains the information required to install Advanced Server for UNIX. System
administrator root rights are required for this purpose. In order to configure the server
system in accordance with individual requirements after the installation, please read the
chapter on “Configuring Advanced Server for UNIX”.
The Release Notice and most recent information that only became available after
i
this manual went to print, e.g. on the version specifications of required software
products and supported hardware, are contained in the SIreadmeM package, which
is supplied with Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0.
4.1 Advanced Server for UNIX delivery package
All of the software for Advanced Server for UNIX is contained on CD-ROM in package
format (PKG). An overview of this is given on the next page.
Advanced Server for UNIX Version 4.0 and later is only supplied on CD-ROM. Key
i
diskettes are no longer used for installation.
The following manuals are available for Advanced Server for UNIX, and they can be
obtained in various delivery units:
● This manual “Overview and Installation” (German and English)
● “Concepts and Planning” (German and English)
● “API Reference”
● “SNMP Service” (from the series of manuals on LAN Manager/X V2.2)
● “Installation Guide for Clients”
● “User's Guide for MS-DOS Clients”
● “User's Guide for MS Windows Clients”
● “NetWare Connectivity”
● “Installation Guide for Clients” (Supplement to Version 3.0 of MS Network Client)
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 44

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Hardware and software requirements
The following packages are included in the Advanced Server for UNIX delivery package:
● SIreadmeM Readme file and Release Notice in German and English
● nbrfc NetBIOS (RFC1001/2)
● asxserver Server
● asxtools Microsoft Windows NT Server Tools
● asxtoolsD Microsoft Windows NT Server Tools (German language)
● msclients Microsoft Client Software
● asxman Manual pages for Advanced Server for UNIX
● asxdocs Online documentation and Acrobat Reader
● asxsnmp Advanced Server for UNIX SNMP extension for TransView
Extensible Agent
● asxdebug This package is only intended for the Siemens Support Service.
4.2 Hardware and software requirements
Before installation users must check that the following hardware and software requirements
are met.
4.2.1 Hardware requirements
One of the following UNIX systems that is connected to a LAN is required for the installation
of Advanced Server for UNIX:
● RM200
● RM300
● RM400
● RM600-xxx
4.2.1.1 Main memory
At least 64 Mbytes of main memory is required, 128 Mbytes is recommended.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 45

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Hardware and software requirements
4.2.1.2 Hard disk storage
The file systems must have the following available disk space for Advanced Server for
UNIX at installation time:
File system Min. number in Mbytes Comment
/
/usr
/usr
/usr
/var
/opt
Any file system
Any file system
Any file system
Any file system
In addition, sufficient space must be reserved for the shared directories and the replicator
files and directories.
The server software is installed under the /var/opt/lanman directory . If a different file system
(e.g. /<new_dir>) is required, the following commands must be executed before installation:
6-10
<1
2
< 1
20
< 1
20
21
20
21
For the new kernel
For the asxserver package
For the asxman package
For the asxsnmp package
For the asxtools package
For the asxtoolsD package
For the msclients package
For the asxdocs package
mkdir /var/opt
mkdir /new_dir/lanman
ln -s /new_dir/lanman /var/opt/lanman
● The names of the file systems and the size of available memory can be viewed
i
!
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
using the df -v or dfspace command.
● The installation procedure also requires free disk space under the /var directory
during installation from CD-ROM.
● Likewise, please note that the Advanced Server for UNIX databases also
require free disk space under the /var directory (in large configurations approx.
50 Mbyte is not unusual).
Page 46

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Hardware and software requirements
4.2.2 Software requirements
The software listed below must be installed on the server system in order to run
Advanced Server for UNIX:
System software version
RM200
RM300
RM400
RM600-xxx
If you would like to use the “shared printer” resource with Advanced Server for UNIX, you
must configure one of the following spoolers before installing Advanced Server for UNIX:
Product name Meaning
AT&T spooler
SPOOL V4.2B or Xpri nt 5.0 (and lat er)
The following software package must be installed before installing Advanced Server for
UNIX:
Reliant UNIX-N V5.43C0 and later
Reliant UNIX-N V5.43C0 and later
Reliant UNIX-N V5.43C0 and later
Reliant UNIX-Y V5.43C0 and later
Standard spooler
Siemens Spooler package
Product name Meaning
CDS++RTS V1.0B00 (and later) Reliant UNIX C++ Runtime system
When the WINS Service is to be used then one of the following software packages must be
installed before installing Advanced Server for UNIX:
Product name Meaning
DCE-THR V2.0A20 (or later)
SIthreads
This package is only necessary if the machine should run the Advanced Server for
!
UNIX WINS service.
The “
SIthreads
operating system versions. This package replaces the previous version
“DCE-THR“. In this case, you should only use the “SIthreads“ package.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
“ package is included on the operating system CD with more recent
from the CD-SYS-MI from 8/97
delivered with the operating system
Page 47

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX The installation procedure
4.2.2.1 Dependencies
You can use Advanced Server for UNIX from clients if one of the client software products
described in section “Client softwar e” is installed on them.
4.3 The installation procedure
The softw are is insta lled from t he C D-ROM using the cdinst utility. cdinst invokes the pkgadd
program implicitly. You should proceed as follows:
1. Deinstall LAN Manager/X V2.0, V2.2, V3.5 or V4.0 if they exist.
2. Install the SIreadmeM package with the release information and important information
first.
3. Then install NetBIOS and restart the system.
4. The server software of Advanced Server for UNIX can be installed now. There are
different installation steps for the
– upgrade installation of Advanced Server for UNIX from previous versions
and the
– new installation of Advanced Server for UNIX.
5. You can now install the optional Advanced Server for UNIX software.
If you do not follow this sequence, installation cannot be carried out successfully for,
i
for instance, the server role backup domain controller.
During installation, you must specify the name of the device from which the software is to
be installed. The device name of the CD-ROM drive depends on the UNIX system used.
For further information, please refer to the UNIX reference manual “Commands – Volume
1 and 2“.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 48

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Deinstalling previous versions
4.4 Deinstalling previous versions
Before this version of Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0 is installed, the previous versions
must be deinstalled. You must follow the sequence for deinstallation described here in a
domain with a primary and one or more backup domain controllers.
● The LAN Manager/X server roles ’member server’ and ‘standalone server’ are
i
1. Stop the primary domain controller.
2. Deinstall LAN Manager/X or Advanced Server for UNIX.
3. Then install Advanced Server for UNIX as the primary domain controller.
If individual backup domain controllers are to continue being operated with the new
Advanced Server for UNIX version, carry out the following steps:
not supported by Advanced Server for UNIX.
● A member server should be handled in the same way as a backup domain
controller.
● A standalone server should be handled in the same way as a primary domain
controller.
● A LAN Manager/X server can never be the Primary Domain Controller in a
domain with NT servers or computers running Advanced Server for UNIX.
1. Stop the backup domain controller.
2. Deinstall LAN Manager/X or Advanced Server for UNIX.
3. Then install Advanced Server for UNIX as the backup domain controller.
The primary domain controller must be running.
i
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 49

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Deinstalling previous versions
4.4.1 Deinstalling LAN Manager/X V2.0 and V2.2
You can continue to use the existing server configuration for the new version.
● With Version 2.0 of LAN Manager/X the logon scripts of the LAN Manager/X
!
The following steps must be carried out before deinstalling LAN Manager/X V2.0:
Ê To back up the logon scripts, copy all files under the /var/opt/lanman/repl/export/scripts
directory (on the export server) or /var/opt/lanman/repl/import/scripts (on the import
server) to another directory in the file system – not to /var/opt/lanman.
If you do not want to modify the server roles and if you are using the replicator service,
you only need to back up the logon scripts for the export server.
Ê If you are working under Reliant UNIX-N, back up the /etc/default/inet file, to
/etc/default/inet.org for example, before executing the pkgrm nbrfc command.
When deinstalling, you have the option to back up the logon scripts for Version 2.2 and later
of LAN Manager/X.
user are not backed up automatically when the software is deleted.
● When the NetBIOS of Version 2.0 under Reliant UNIX-N is deinstalled, the
/etc/default/inet file is deleted illegally.
The following steps are required for deinstalling both versions:
Ê Delete LAN Manager/X V2.0 or LAN Manager/X V2.2 as documented.
Deinstall the server software and NetBIOS of Versions 2.0 or 2.2. During deinstallation
you are given the options of backing up the lanman.ini file, the user account etc. and to
continue using them for Version 4.0. For further information on deinstalling Version 3.5,
LAN Manager/X V2.0 or 2.2 please refer to the “Overview and Installation” manual for
the relevant version.
● The /var/opt/lanman/lanman.ini and /var/opt/lanman/datafiles/accounts.lmx files
i
Ê Install Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0 as described on the following pages.
The standard logon scripts netlogon.bat and netlogon.cmd are recreated during instal-
i
Ê If you deinstalled LAN Manager/X V2.0 beforehand, copy the backed up logon scripts
back to /var/opt/lanman/repl/export/scripts (on the export server) or to
/var/opt/lanman/repl/import/scripts (on the import server).
must be backed up for an upgrade from LAN Manager/X V2.0 or V2.2 to
Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0.
● If you want to install Version 4.0 after deinstalling Version 2.0 or 2.2 of NetBIOS,
you do not need to restart the system now.
lation of Advanced Server for UNIX.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 50

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Deinstalling previous versions
Ê If you deinstalled LAN Manager/X V2.0 under Reliant UNIX-N, copy the
/etc/default/inet.org file – backed up as described above – back to /etc/d efault/inet.
4.4.2 Deinstalling Advanced Server for UNIX V3.5
You can continue to use the existing server configuration for the new version.
You should proceed as follows:
Ê Stop Advanced Server for UNIX
Ê Check the databases. This will save time during the upgrade installation if the
databases are corrupt.
Call /var/opt/lanman/bin/acladm -C -y and /var/opt/lanman/bin/samcheck -r to check and
repair the acl database and the account databases.
Ê Remove Advanced Server for UNIX V3.5 as described in the manual for the respective
version.
Ê Deinstall the optional packages including optional Service Packs, the server software,
and NetBIOS. When you are deinstalling you will be offered the option of saving the
lanman.ini file, the user account etc. and using them for the new version. For further
information on deinstalling Advanced Server for UNIX please refer to the “Overview and
Installation” manual for the respective version to be deinstalled.
Ê If you want to install the new version after NetBIOS has been deinstalled, you do not
need to restart the system.
Special features of NetBIOS configuration:
The following applies only if you had previously installed a NetBIOS Version 3.5A.
The NetBIOS Version 3.5A /var/opt/nbrfc/nbrfc.cfg configuration file is copied to /tmp when
the nbrfc package is deleted, and can then be saved. The reinstallation of NetBIOS Version
3.5B and later is based on a new configuration file structure. It is not possible to automati-
cally retain the old interface configuration, but you can convert old NetBIOS name
mappings into the new configuration file structure.
The following options are available:
To ignore old name mappings:
Ê Install the nbrfc package without regard for the old nbrfc.cfg file. You will then find a new
configuration with the configuration files under /var/opt/nbrfc/conf. All network inter faces
found are configured automatically in the interfaces.cfg file.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 51

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Automatic installation with TransView SAX
To automatically convert old name mappings:
Ê Prior to installation, create the directory /var/opt/nbrfc, with owner root, group bin, and
permissions 755.
Ê Copy the saved nbrfc.cfg file to this directory.
Ê Install the new nbrfc package. If there is a name table available in the [NBRFC] section
of the old nb rfc.cfg file, it is transferred automatically to the names.cfg file.
To manually convert old name mappings:
Ê Install the nbrfc package.
Ê Copy the saved nbrfc.cfg file to the /var/opt/nbrfc directory.
Ê Us e the /var /opt/n b rfc/bin /mv_na mes command. If there is a name table available in the
[NBRFC] section of the old nbrfc.cfg file, it is transferred automatically to the names.cfg
file. Please refer to the description in section “/var/opt/nbrfc/bin/mv_names”.
In any case the network interface configuration must be compared visually with the
i
interface sections of the old nbrfc.cfg file. Please retain the new keyword "default".
For further information on the new configuration files, please refer to section “Configuring
NetBIOS”.
4.5 Automatic installation with TransView SAX
All packages of Advanced Server for UNIX can be distributed with TransView SAX and
installed automatically with a response file. Later versions of Advanced Server for UNIX can
also be installed with TransView SAX as delta products.
It is not possible to upgrade from LAN Manager/X with a delta installation.
i
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 52

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing from CD-ROM with cdinst
4.6 Installing from CD-ROM with cdinst
Advanced Server for UNIX is only supplied on CD-ROM. The first steps for installation with
the cdinst program are the same for all packages and are thus described here centrally. The
other installation steps for the individual packages are given at the end of this section.
Carry out the following steps in the specified sequence:
1. Log on as system administrator root and insert the CD into the drive of the system from
which you want to carry out the installation.
You can initiate the installation procedure from the UNIX command prompt.
2. Start the installation program with cdinst. The following dialog box is displayed:
1 Process Multi-Product CD-ROM
Server: local
CD-ROM device name: /dev/ios0/sdisk005s0
Remote pathname/
Local mountpoint: /cdrom0
Fill in the form and then press SAVE.
Ê Place the cursor on CD-ROM device name and select the device name for the CD-
ROM drive with (CHOICES). Then select (SAVE) to confirm your
F2 F3
input. A general message about the volume is then displayed.
Ê Acknowledge with (CONTINUE).
3. Mark the ASX set in the displayed list with the cursor and then press (MARK)
and (ENTER). The following message is then displayed:
F3
2
info
pkginfo
README
install
Move the cursor to the item you want and press ENTER to
select it.
F8
F2
- Display Detailed Product Information
- Display Detailed Information on Packages
- Display README Files
- Install Products
Ê Select info to display other information on the Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0
product, e.g. the name of the manufacturer, date of manufacture, version etc.
F6
(CANCEL) returns you to the displayed selection.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 53

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing from CD-ROM with cdinst
F6
Ê Select pkginfo to display more details on individual packages, e.g. number of files
or memory requirements. (CANCEL) returns you to the displayed selection.
F6
Ê Select README to display a list of the readme files for the Advanced Server for
UNIX product. (CANCEL) returns you to the displayed selection.
4. Select install and then press (MARK) and (ENTER) to begin installation
F2 F3
of the individual packages.
4 Install
Install:
Installation mode:
Installation default file name:
Path to response files:
Fill in the form and then press SAVE.
Package
dialog
default
/tmp/16632/response
In the Install selection field you can choose between Complete Produ ct, SIr ea dmeM, and
Package. To confirm your selection, press (CHOICES).
Do not select Complete Product. If you select this, installation will fail.
!
F2
Ê Select SIreadmeM or Package.
The selection field Installation mode provides a choice between automatic and dialog via
F2
(CHOICES).
Ê Select the installation mode dialog. For information on how to install the asxs erver,
asxtools, asxtoolsD, asxdocs, and msclients packages with the default configuration
without further input, please refer to the section “Installing with the default config-
uration”. The other packages do not require any further input during installation.
Ê Press (SAVE).
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
F3
Page 54

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing from CD-ROM with cdinst
5. If you select Package, the following selection is displayed (for contents of the packages,
please refer to section “Advanced Server for UNIX delivery package”):
5 4.0 Packages
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
SIreadmeM
nbrfc
asxserver
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
Mark the items you want and press ENTER to select them.
Ê Use the cursor to select the required package and press (MARK), then start
installation with (ENTER).
asxtools
asxtoolsD
msclients
asxman
asxdocs
asxsnmp
asxdebug
F2
F3
The pkgadd program is thus called implicitly.
Ê Carry out the other installation steps as they are described in the following
paragraphs.
Install the packages in the following (mandatory) sequence:
!
1. SIreadmeM
2. nbrfc: Once you have successfully installed the nbrfc package for NetBIOS,
reboot the system.
3. asxserver
6. The following packages are optional and can be installed in any sequence:
– asxdocs
– asxman
– asxtools
– asxtoolsD
– msclients
– asxsnmp
For further information on the optional packages, please refer to the section “Installing
optional packages”.
From this point on, the individual packages are installed via pkgadd.
i
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 55

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing the prerequisited packages
4.7 Installing the prerequisited packages
Install the following before the actual server software:
● SIreadmeM package
● NetBIOS
Please observe the specified installation sequence here.
i
4.7.1 Installing the SIreadmeM package
Install the SIreadmeM package first. The package contains README files in German and
English. These contain information that became available after this manual went to print.
Install the SIreadmeM with the following steps:
Ê Log on to the system console as system administrator root.
Ê Carry out the installation procedure as described in the section “Installing from CD-
ROM with cdinst”.
Ê Then, under AS/X select the package called SIreadmeM. The system now copies the
German files from the volume to /opt/readme/asx.D and the English files to
/opt/readme/asx.GB.
Please observe the information in these files for the next steps.
i
The README files are always located under this path. The manual page files are
numbered consecutively, e.g. the first file for Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0 is stored in
the path /opt/readme/asx.D/man400. Since the package is a general UNIX package which is
used by different products, the package cannot be removed again.
4.7.2 Installing NetBIOS
To be able to use the WINS Service functionality NetBIOS Version 4.0A00 or later
!
has to be installed. When installing the AS/X package asxserver a warning will
appear if the correct version is not present.
To be able to be use the DNS-WINS integration functionality that is provided with
!
Reliant UNIX V5.45, NetBIOS Version 4.0B or later has to be installed.
The Advanced Server for UNIX package nbrfc with NetBIOS must be installed first. As, in
certain cases, Advanced Server for UNIX establishes contact with o ther servers when
installing the server software, NetBIOS must be available in advance.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 56

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing the prerequisited packages
In the case of multiprocessor systems the parallel NetBIOS is installed automatically, which
increases performance.
Please deinstall the previous version of LAN Manager/X or Advanced Server for
!
UNIX.
A new UNIX kernel is generated during installation; the file mtune is modified here.
Now install NetBIOS, working through the following steps:
Ê Log on to the system console as system administrator root.
Ê Start installation with the cdinst command and carry out the first steps as described in
the section “Installing from CD-ROM with cdinst“.
Ê Select nbrfc for the NetBIOS software from the selection list for the packages.
● Do not under any circumstances select the option Complete Product if you are
!
installing using cdinst.
● The nbrfc package must be installed before the rest of the software.
The system will now copy the files from the data medium, set up NetBIOS for all network
controllers in the system automatically, and generate a new UNIX kernel. This process will
be displayed on the screen, though it may take a little time.
The configuration data is stored in the /var/opt/nbrfc/conf/interfaces.cfg file during installation.
If a file already exists, it will not be overwritten.
If you are installing a backup domain controller, the local machine will need to be able to
find the primary domain controller during installation of the asxserver package. Therefore, if
you are installing a backup domain controller and the primary controller of the domain you
want to join is located in a different subnet, you have to ensure that the domain name and
the server name can be resolved by the local NetBIOS. This can be accomplished in the
following ways:
To ensure that the primary domain controller can be found if WINS is not used:
Ê If the fil e names.cfg in the directory /var/opt/nbrfc/conf does not exist, create it by copying
the names.sam file in the same directory.
Ê Edit the names.cfg file and manually add two lines containing NetBIOS-name-to-IP-
address mappings:
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 57

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing the prerequisited packages
Example entries in nam e s. c fg :
# My primary domain controller
mypdc 144.145.101.10 UN
# The domain I want to join
mypdc.dom 144.145.101.10 UN #1b
Note that both the server name (“mypdc”) and the domain name (“mypdc.dom”)
i
must be given together with the server's IP address.
or (as an alternative):
Ê Edit the file
controller’s subnet in the appropriate interface section using the parameter
“brdcast_list=”:
Example entry in interfaces.cfg:
[et0]
# Subnet address of my primary domain controller:
If the
i
line!
To ensure that the primary domain controller can be found if this server is a WINS
client:
Ê Edit the file
For detailed information on configuring name resolution, refer to section “Configuring
NetBIOS Name Resolution”.
/var/opt/nbrfc/conf/interfaces.cfg and configure the IP address of the primary
active=yes
used_by_wins=yes
ip_addr=default
brdcast_addr=default
brdcast_list=144.145.101.255
netmask=default
brdcast_list line is commented out (default), do not forget to uncomment the
/var/opt/nbrfc/conf/wins.cfg and add the appropriate WINS server addresses.
In any case, you should now reboot the system before proceeding with the instal-
i
lation of the server so ftware.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 58

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
4.8 Installing server software (asxserver package)
The following software package has to be installed before installing Advanced
i
Server for UNIX:
Product name Meaning
CDS++RTS V1.0B00 (or later) Reliant UNIX C++ Runtime system
If you want to use the WINS service then one of the following packages has to be
i
installed before installing Advanced Server for UNIX:
Product name Meaning
DCE-THR V2.0A20 (or later)
SIthreads
This package is only necessary if the machine should run the Advanced Server for
!
UNIX WINS service.
from the CD-SYS-MI from 8/97
delivered with the operating system
The “
SIthreads
operating system versions. This package replaces the previous version
“DCE-THR“. In this case, you should only use the “SIthreads“ package.
“ package is included on the operating system CD with more recent
4.8.1 Preparing the installation
If the servers of the domain are distributed over several subnetworks, ensure that NetBIOS
can resolve the names. For details on configuring NetBIOS name resolution, please refer
to the section “Configuring NetBIOS Name Resolution”.
The individual installation steps depend on whether you are carrying out an upgrade installation from a previous version or a new installation. Furthermore, the installation requirements and steps differ depending on the server role required.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 59

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
In the case of an upgrade installation, as many configuration information as possible is
automatically incorporated from the previous version. Although it is possible to deinstall the
previous version with the option of saving only a part of the data, it is recommended to save
all configuration data.
Before you upgrade Advanced Server for UNIX, it is strongly recommended that
!
you back up the contents of the /var/opt/lanman directory after the deinstallation.
First a general description of the installation steps is given.
Afterwards, the following installations are described separately:
● Upgrade installation of a primary domain controller from Version 2.x
● Upgrade installation of a backup domain controller from Version 2.x
● Upgrade installation of a primary domain controller from Version 3.5 or 4.0
● Upgrade installation of a backup domain controller from Version 3.5 or 4.0
● New installation of a primary domain controller
● New installation of a backup domain controller
4.8.1.1 Installation steps
Before starting the installation, be prepared to answer the following questions.
Remember you can change your selections after the server installation process is
complete.
Stop the server
You are first asked if you want to stop the server if it is running.
This is for security reasons only , because the installatio n cannot continue if t he server is running.
The installation will abort if the server is running and you do not choose to stop the server.
Because this happens very early during installation, this question is asked every time
regardless of the actual system configuration.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 60

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Interactive or non-interactive installation
There are two ways to install Advanced Server for UNIX:
1. Select interactive if the required data is to be input during installation. This is the recommended installation mode for installations via cdinst.
2. Select non-interactive if the required data is to be input before installation, but if the
default configuration should not be used. The input entered before installation will be
stored in a response file that can be used for installations with no user interaction. This
installation mode is only used for special configurations and it is not described here.
You can start the non-interactive installation with a default configuration. With this installation type, no further input is required before and during installation. Using this method, the
server is always installed as a primary domain controller in it’s own domain. For further
information, please refer to the section “Installing with the default configuration”.
The steps for interactive installation are presented on the following pages.
Normally you will choose this installation.
Output language
The output language configuration is used to specify the output language of the UNIX
commands net and elfread and of the Windows Administrative Tool EventViewer.
The output l anguage does not affect the builtin names of Advanced Server for UNIX objects
as domain language does (see below).
The output language has to be specified during all installation types.
Please refer to the chapter entitled “Administration guidelines” for further information on
how to change the output language after installation.
Interface name of the spooler used by the server
Establish which spooler your system will use and specify this during installation.
Check whether the spooler you are going to specify has been configured in UNIX and is
started.
If the spooler has not been started during installation, you will receive a warning message.
The spooler has to be configured during all installation types.
During instal lation of th e server softwa re, the printe r devices lmxn ul and lmxnone are created
for inte rnal use.
These printer devices cannot be deleted and cannot be used for printing from the
i
UNIX shell.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 61

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Please refer to the chapter entitled “Administration guidelines” for further information on
how to change the spooler after installation.
Server name
Every Advanced Server for UNIX needs a unique server name.
During a new installation, the installation program constructs a server name from the
system name. The suggested name can be accepted or replaced by another name
consisting of up to 15 characters. Please refer to the chapter entitled “Introduction to
Advanced Server for UNIX” for information on the naming conventions for server names.
In order not to run into problems when upgrading to upcoming NT/AS/X-versions in the
future, all tools requesting a server name during installation or reconfiguration offer the
DNS-compatible host name (’uname -n’) as the default server name. The extension .srv can
still be used, but is not recommended and no longer offered as a default. Installation/configuration scripts now inform the administrator about DNS-incompatible server names.
During an upgrade installation, the server name is retained from the previous version, if
possible.
The server name must not be modified manually in the lanman.ini file or in the
!
Advanced Server Registry under any circumstances.
Please refer to the chapter entitled “Administration guidelines” for further infor-
mation on how to change the server name after installation.
Server role
During a new installation, the role of the server has to be specified.
In a domain there is exactly one primary domain controller. The primary domain controller
must be the first server that is installed in a domain. Other LM/X and AS/X servers can be
backup domain controller s.
If you do a new installation of a server as a primary domain controller in a domain that
already exists, the result will be two domains with the same name, neither of which will
operate properly.
Note that a LAN Manager/X server can never be a primary domain controller in a domain
with Windows NT servers or Advanced Server for UNIX servers. After the upgrade of the
primary domain controller, all other LAN Manager/X servers, Advanced Server for UNIX
servers and Windows NT servers can still be used without having adopted. Please plan
your upgrade order accordingly.
In the case of an upgrade installation, the server role is automatically incorporated from the
previous installation, if possible.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 62

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
LAN Manager/X servers offer four types of server roles: primary domain controller, backup
domain controller, member server and standalone server.
The server roles “member server” and “standalone server” are no longer supported with all
Advanced Server for UNIX versions.
The server role “member server” becomes backup domain controller, and the “standalone
server” becomes primary domain controller.
Please refer to the chapter entitled “Administration guidelines” for further information on
how to change the server role after installation.
Domain name
During installation, the server is automatically allocated to a domain. Please refer to the
chapter entitled “Introduction to Advanced Server for UNIX” for information on the naming
conventions for domain names.
In the case of an upgrade installation, the domain name is automatically incorporated from
the previous installation, if possible.
The domain name must not be modified manually in lanman.ini under any circum-
!
stances.
Please refer to the chapter entitled “Administration guidelines” for further infor-
mation on how to change the domain name after installation.
Name of the primary domain controller
If you wish to install a new backup domain controller, you will be asked to enter the server
name of the primary domain controller.
Name of the administrator
During the new installation of a primary domain controller, the builtin account Administrator
is created automatically.
During any installation of a primary domain controller, this account is used for all administration tasks during the installation.
For security reason, other administrative accounts may have been created on the primary
domain controller with different names. During the installation of a backup domain
controller, you will be asked to enter the name of an administrative account.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 63

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Administrator’s password
During the installation of a primary domain controller, the password for the builtin user
Administrator is set.
During the installation of a backup domain controller, you will be asked to enter the
password for an administrative account of the primary domain controller.
The password has to be entered twice to avoid errors. The passwords are not displayed on
the screen as they are typed.
Domain language
The term domain language is used whenever the language of builtin objects is referenced
(e.g. the object Everyone showed when domain language is set to ENGLISH corresponds to
Jeder in an environment with domain language set to GERMAN).
The domain language of a domain is always dependent on the domain language of the primary
domain controller of that domain.
In a domain with “mixed” language various problems can occur.
!
It is not recommended to do that!
With AS/X 3.5 it was not possible to change the domain language, english was always
used. So it could happen that AS/X 3.5 was an english backup domain controller in a
german Windows NT domain. You should use joindomain to “repair” your domain.
The domain language of a primary domain controller is evaluated when the databases of the
primary domain controller are initialized. Changing the domain language has no effect
without re-initializing those databases (re-initialization means loss of all created users and
groups).
The customer is recommended to use joindomain to do a new initialization of the database.
Everytime joindomain is going to create a new database, you can specify the domain
language.
To prevent the loss of user and group information the installation only asks for the domain
language if there are no existing databases or if the existing databases cannot be used.
(Keep in mind that during the preparation of an unattended installation the question is asked
to have the setting on the target machine.)
If you upgrade an Advanced Server for UNIX V3.5 (primary or backup domain controller),
the databases are upgraded from the older version, there is no new initialization to prevent
loss of exisiting users and groups.
That's why the domain language cannot be entered. The internal setting of the domain
language will be default ENGLISH.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 64

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
If you install an Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0 primary domain controller from scratch or
upgrade a LAN Manager/X to be an Advanced Server for UNIX primary domain controller,
you can select the domain language for the domain. All builtin objects are initialized using the
selected domain language.
If you install an Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0 backup domain controller from scratch or
upgrade a LAN Manager/X to be an Advanced Server for UNIX backup domain controller
you should select the same domain language as on the primary domain controller to prevent
trouble managing objects in that domain.
During an upgrade installation it could happen that a database cannot be upgraded
because it is too corrupt to repair. In this very special situation it must be re-initialized with
a new domain language.
To change the output language of commands see Output language.
Please refer to the chapter entitled “Administration guidelines“ for further information on
how to change the domain language after installation.
Windows NT-style Printing
One of the new features in Advanced Server for UNIX Version 4.0 is Windows NT-style
printing.
This feature means that you can manage Advanced Server for UNIX print operations in the
same way as Windows NT. Advanced Server computers can store printer drivers for
Windows NT and Windows 95/98 client computers on the server. Printer drivers are
downloaded automatically from the server to Windows 95/98 and Windows NT client
computers. These clients then can use the server’s printers without loading printer drivers
manually.
However, Windows NT-style Printing requires that the administrator updates each printer
share with the appropriate printer driver(s) before Windows NT client computers will be able
to use this server’s printers.
If you don’t disable Windows NT-style printing, your Windows NT client computers
!
will not be able to print until you administer each printer share that these clients will
use.
Only Windows NT client computers are affected. This is not required for Windows
95/98 or any other type of Microsoft network clients; they will continue to work as
before.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 65

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Start the server
You can start the server directly during the installation or manually after the installation.
Note that after having installed a new NetBIOS, the system must have been rebooted
before you can start the server.
The upgrade installation from Version 2.x needs a running server to convert the old
databases into the Advanced Server for UNIX databases automatically. Further information
can be found in the description of the upgrade installation from Version 2.x.
4.8.2 Upgrade installation of a primary domain controller from Version 2.x
For the upgrade installation of a primary domain controller, proceed as described below.
Data backed up from LAN Manager/X Version 2.x (e.g. user account) is taken over.
If the servers of the domain are distributed over several subnetworks, ensure that NetBIOS
can resolve the names. For details on configuring NetBIOS name resolution, please refer
to the section “Configuring NetBIOS Name Resolution”.
Ê Log on as system administrator root.
Ê Start the installation procedure as described in the section “Installing from CD-ROM
with cdinst”.
Ê Select the asxserver package under AS/X.
Ê Stop the server.
Ê Choose y to stop the server.
Interactive or non-interactive installation
Ê Choose interactive for interactive installation.
The following description applies for interactive installation.
The system now copies the files from the installation medium and sets up specific users
and user groups for Advanced Server for UNIX.
Output language
The system now displays the supported languages (ENGLISH and GERMAN) and outputs
the message
Please enter the language or press ENTER if it is "ENGLISH":
Ê Enter the output language.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 66

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Interface name of the spooler used by the server
The system now displays all configurable spoolers and outputs the message
Please enter the interface name or press ENTER if it is <spool interface>:
Ê Enter the interface name of the spooler.
Server name
The server name is incorporated from the previous version, if possible.
Server role
The server role is incorporated from the previous version, if possible.
Domain name
The domain name is incorporated from the previous version, if possible.
Name of the administrator
On a primary domain controller, the builtin administrative account Administrator is always
used. During an upgrade installation from Version 2.x, the account Admin is mapped to
Administrator automatically.
Administrator’s password
The password of the account Administrator has to be set manually.
Domain Language
The system now displays the supported languages (ENGLISH and GERMAN) and outputs
the message
Please enter the language or press ENTER if it is "ENGLISH":
Ê Enter the domain language.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 67

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Windows NT-style Printing
When there have been shared printers from a previous installation, you now have to decide
how to upgrade these printers.
The system displays some information and the message
You can choose to disable Windows NT-style printing and allow Windows NT
client computers to print without first administering each print share on
this server. You can enable this feature at any time in the future.
Do you want to disable Windows NT-style printing [y/n]?
Ê Enter your selection.
Start the server
To complete the upgrade installation, the saved LAN Manager/X datafiles must now be
adapted.
For this purpose, the primary domain controller must be started. The system provides you
with the option of starting the server immediately with the message
NOTICE: To upgrade the saved data from LM/X 2.x you have to start the server!
Do you want to start the Advanced Server [y/n]?
Ê Enter y to start the server during the installation, or n to start it manually after the instal-
lation.
Upgrade of the accounts database (lmxupgrade)
If you have started the server, the upgrade is executed automatically and the output of the
command lmxupgrade is written to the screen and the file
/var/opt/lanman/logs/lmxupgrade.log.
If the server is not started, the following message gives you information on how to upgrade
later:
Access Control Entries, user accounts and groups can be upgraded from the
LAN Manager 2.x accounts file (/var/opt/lanman/accounts.lm2).
Make sure the Advanced Server for UNIX is running and then manually run
lmxupgrade -UGA ... .
In this case, the administration files must be adjusted after Advanced Server for UNIX has
been started:
Ê start AS/X with asx start
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 68

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Ê call /var/opt/lanman/bin/lmxupgrade -YUGA
Watch the output of the command for files and directories which are not found for
upgrading access permissions
Note that the guest account will be set to state “inactive” during the upgrade.
4.8.3 Upgrade installation of a backup domain controller from Version 2.x
Ensure that the primary domain controller (Advanced Server for UNIX or Windows NT
server) of this domain has been started.
If the primary domain controller of the domain you want to join is located in a different
subnet, you have to ensure that the domain name and the server name of the primary
domain controller can be resolved by the local NetBIOS. Please refer to the section
“Installing NetBIOS” on how to accomplish this.
For the upgrade installation of a backup domain controller, proceed as follows.
Ê Log on as system administrator root.
Ê Start the installation procedure as described in the section “Installing from CD-ROM
with cdinst”.
Ê Select the asxserver package under AS/X.
Stop the server
Ê Choose y to stop the server.
Interactive or non-interactive installation
Ê Choose interactive for interactive installation.
The following description applies for interactive installation.
The system now copies the files from the installation medium and sets up specific users
and user groups for Advanced Server for UNIX.
Output language
The system now displays the supported languages (ENGLISH and GERMAN) and outputs
the message
Please enter the language or press ENTER if it is "ENGLISH":
Ê Enter the output language.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 69

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Interface name of the spooler used by the server
The system now displays all configurable spoolers and outputs the message
Please enter the interface name or press ENTER if it is <spool interface>:
Ê Enter the interface name of the spooler.
Server name
The server name is incorporated from the previous version, if possible.
Server role
The server role is incorporated from the previous version, if possible.
Domain name
The domain name is incorporated from the previous version, if possible.
Name of the primary domain controller
The name of the old primay domain controller must be confirmed here.
Enter the name of the primay domain controller
or press Enter to select ‘<old primary name>’:
Name of the administrator
The name of an administrative account on the primary domain controller must be entered
here.
Enter the name of an administrative account on ‘<primary name>’
or press Enter to select ‘administrator’:
Administrator’s password
Ê Enter the password for the administrator twice:
Enter the password for administrator:
Re-enter password:
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 70

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Domain Language
The system now displays the supported languages (ENGLISH and GERMAN) and outputs
the message
Please enter the language or press ENTER if it is "ENGLISH":
Ê Enter the domain language of the primary domain controller.
Windows NT-style Printing
When there have been shared printers from a previous installation, you now have to decide
how to upgrade these printers.
The system displays some information and the message
You can choose to disable Windows NT-style printing and allow Windows NT
client computers to print without first administering each print share on
this server. You can enable this feature at any time in the future.
Do you want to disable Windows NT-style printing [y/n]?
Ê Enter your selection.
Start the server
To complete the upgrade installation, the saved access permissions must be transferred
from the previous version. The account data (the users and groups) is transferred automatically from the primary domain controller. To do this, the backup domain controller must set
up a connection with the primary domain controller.
For this purpose, both the primary domain controller and the backup domain controller must
be started. The system provides you with the option of starting the server immediately with
the message
NOTICE: To upgrade the saved data from LM/X 2.x you have to start the server!
Do you want to start the Advanced Server [y/n]?
Ê Enter y to start the server during the installation, or n to start it manually after the instal-
lation.
Upgrade of the accounts database (lmxupgrade)
If you have started the server, the upgrade is executed automatically and the output of the
command lmxupgrade is written to the screen and the file
/var/opt/lanman/logs/lmxupgrade.log.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 71

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
If the server is not started, the following message gives you information on how to upgrade
later:
Access Control Entries can be upgraded from the LAN Manager 2.x accounts
file (/var/opt/lanman/datafiles/accounts.lm2) after the user accounts and
groups have been replicated to this backup controller.
You will need to manually run lmxupgrade -A ... after this has occurred.
In this case, the administration files must be adjusted after Advanced Server for UNIX has
been started.
Ê Start AS/X with asx start.
Ê Use the net user command to check whether the account data has already been trans-
ferred to this backup domain controller. If it has not been transferred, you can start the
transfer using the command net accounts /sync. If there are problems transferring the
account data, you may have to call /var/opt/lanman/bin/joindomain to re-establish the
connection again.
Ê If the account data has been updated on this backup domain controller, the access
permission s must be created for Advanced Server for UNIX. Call
/var/opt/lanman/bin/lmxupgrade -YA.
Watch the output of the command for files and directories which are not found for
upgrading access permissions.
4.8.4 Upgrade installation of a primary domain controller from
Version 3.5 or 4.0
T o upgrade a primary domain controller from a previous Advanced Server for UNIX version,
proceed as follows. In contrast to an upgrade installation from Version 2.x, the data can be
upgraded directly; no conversion has to be done.
Ê Log on as system administrator root.
Ê Start the installation procedure as described in the section “Installing from CD-ROM with
cdinst”.
Ê Select the asxserver package under AS/X.
Stop the server
Ê Choose y to stop the server.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 72

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Interactive or non-interactive installation
Ê Choose interactive for interactive installation.
The following description applies for interactive installation.
The system now copies the files from the installation medium and sets up specific users
and user groups for Advanced Server for UNIX.
Output language
The system now displays the supported languages (ENGLISH and GERMAN) and outputs
the message
Please enter the language or press ENTER if it is "ENGLISH":
Ê Enter the output language.
Interface name of the spooler used by the server
The system now displays all configurable spoolers and outputs the message
Please enter the interface name or press ENTER if it is <spool interface>:
Ê Enter the interface name of the spooler.
Server name
The server name is incorporated from the previous installation, if possible.
Server role
The server role is incorporated from the previous installation, if possible.
Domain name
The domain name is incorporated from the previous installation, if possible.
Administrator’s password
The password of the account Administrator is incorporated from the previous version.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 73

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Domain Language
The domain language is incorporated from the previous version, if the databases could be
successfully checked and taken over. In the event that a database is inconsistent, the installation repairs the database. If the database is too corrupt to repair, the installation is aborted
and you have to repair the database manually (e.g. restore the databases from a system
backup).
Note that if the previous version was an Advanced Server for UNIX Version 3.5, the domain
language will always be ENGLISH.
Changing the domain language after the installation is only possible with loss of all
!
user and group accounts. Use /var/opt/lanman/b in/joindomain to perform this task.
Windows NT-style Printing
When there have been shared printers from a previous installation, you now have to decide
how to upgrade these printers.
The system displays some information and the message
You can choose to disable Windows NT-style printing and allow Windows NT
client computers to print without first administering each print share on
this server.You can enable this feature at any time in the future.
Do you want to disable Windows NT-style printing [y/n]?
Ê Enter your selection.
Start the server
The installation is now complete.
The system offers you the option of starting the server immediately:
Do you want to start the Advanced Server [y/n]?
Ê Enter y (yes) or n (no).
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 74

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
4.8.5 Upgrade installation of a backup domain controller from
Version 3.5 or 4.0
T o upgrade a backup domain controller from a previous Advanced Server for UNIX version,
proceed as follows. In contrast to an upgrade installation from Version 2.x, the data can be
upgraded directly; no conversion has to be done. Normally the upgrade of a backup domain
controller does not differ from the upgrade of a primary domain controller.
However there is one known problem during the upgrade of an Advanced Server for UNIX
Version 3.5 that was a backup domain controller on a server with a german names for
builtin objects (either a german Windows NT Server or an Advanced Server for UNIX
Version 4.0 with a german domain languag e). In this case it can happen that the database is
reported corrupt. See the detailed description below.
If the primary domain controller of the domain you want to join is located in a different
subnet, you have to ensure that the domain name and the server name of the primary
domain controller can be resolved by the local NetBIOS. Please refer to the section
“Installing NetBIOS” on how to accomplish this. Although this name resolution is important
for the functionality of the backup domain controller, it is needed during the installation only
if the database is corrupt.
Ê Log on as system administrator root.
Ê Start the installation procedure as described in the section “Installing from CD-ROM
with cdinst”.
Ê Select the asxserver package under AS/X.
Stop the server
Ê Choose y to stop the server.
Interactive installation
Ê Choose interactive for interactive installation.
The following description applies for interactive installation.
The system now copies the files from the installation medium and sets up specific users
and user groups for Advanced Server for UNIX.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 75

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Output language
The system now displays the supported languages (ENGLISH and GERMAN) and outputs
the message
Please enter the language or press ENTER if it is „ENGLISH“:
Ê Enter the output language.
Interface name of the spooler used by the server
The system now displays all configurable spoolers and outputs the message
Please enter the interface name or press ENTER if it is <spool interface>:
Ê Enter the interface name of the spooler.
Checking the accounts database
During the installation, the accounts database from the previous version is checked. If some
corruption is detected, the accounts database is replicated from the primary domain
controller.
In this very special case, the server name, the administrator on the primary domain
controller, the administrator password and the domain language have to be entered.
Server name
The server name is incorporated from the previous installation, if possible.
Server role
The server role is incorporated from the previous installation, if possible.
Domain name
The domain name is incorporated from the previous installation, if possible.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 76

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Name of the primary domain controller
The name of the primary domain controller is incorporated from the previous installation, if
possible.
In the case of database corruption, the name of the primary domain controller has to be
entered:
Enter the name of the primary domain controller:
Ê Enter the name of the primary domain controller.
Name of the administrator
All user accounts are automatically taken over from the previous installation.
In the case of database corruption, the name of the administrator has to be entered:
Enter the name of an administrative account on ‘<primary name>’
or press Enter to select ‘administrator’:
Ê Enter the name of an administrative account.
Administrator’s password
The password of the account Administrator is incorporated from the previous version.
In the case of database corruption, the password of the administrative account has to be
entered here twice:
Enter the password for administrator:
Re-enter password:
Domain Language
The domain language is incorporated from the previous version, if the databases could be
successfully checked and taken over.
If the database is reported to be corrupt (e.g. due to the usage of mixed languages within
the domain), you have to enter the domain language of the primary domain controller here.
Normally you will change the domain language here to avoid the same problem in the
future.
The system now displays the supported languages (ENGLISH and GERMAN) and outputs
the message
Please enter the language or press ENTER if it is "ENGLISH":
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 77

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Ê Enter the domain language of the primary domain controller.
A new AS/X database is now created using the specified language and the account data is
replicated from the primary domain controller in the correct language.
Windows NT-style Printing
When there have been shared printers from a previous installation, you now have to decide
how to upgrade these printers.
The system displays some information and the message
You can choose to disable Windows NT-style printing and allow Windows NT
client computers to print without first administering each print share on
this server.You can enable this feature at any time in the future.
Do you want to disable Windows NT-style printing [y/n]?
Ê Enter your selection.
Start the server
The installation is now complete.
The system offers you the option of starting the server immediately:
Do you want to start the Advanced Server [y/n]?
Ê Enter y (yes) or n (no).
4.8.6 New installation of a primary domain controller
The following sections describe how Advanced Server for UNIX is installed as a primary
domain controller on a system on which neither LAN Manager/X nor Advanced Server for
UNIX was previously installed or on which the LAN Manager/X or Advanced Server for
UNIX installation has been fully deinstalled.
If the servers of the domain are distributed over several subnetworks, ensure that NetBIOS
can resolve the server names. For details on configuring NetBIOS name resolution, please
refer to the section “Configuring NetBIOS Name Resolution”.
To install a primary domain controller, proceed as follows.
Ê Log on as system administrator root.
Ê Start the installation procedure as described in the section “Installing from CD-ROM
with cdinst”.
Ê Select the asxserver package under AS/X.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 78

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Stop the server
Ê Choose y to stop the server.
Interactive or non-interactive installation
Ê Choose interactive for interactive installation.
The following description applies for interactive installation.
The system now copies the files from the installation medium and sets up specific users
and user groups for Advanced Server for UNIX.
Output language
The system now displays the supported languages (ENGLISH and GERMAN) and outputs
the message
Please enter the language or press ENTER if it is „ENGLISH“:
Ê Enter the output language.
Interface name of the spooler used by the server
The system now displays all configurable spoolers and outputs the message
Please enter the interface name or press ENTER if it is <spool interface>:
Ê Enter the interface name of the spooler.
Server name
The system generates a default server name from the system name and displays the
message
Enter the name of the server or press Enter to select <system name>:
Ê Enter the server name.
Server role
The message
Enter role (primary or backup) or press Enter to select ‘primary’:
is displayed.
Ê Enter the server role ‘primary’.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 79

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Domain name
The system suggests a domain name, which is formed from the system name and the
extension .dom.
The message
Enter the name of the domain or press Enter to select ‘<system name.dom>’:
is displayed.
Ê Enter the domain name.
Confirm choices
The server name, the server role and the domain name have to be confirmed now or can
be re-entered.
Administrator’s password
The password of the account Administrator has to be entered twice:
Enter the password for administrator:
Re-enter password:
Domain Language
The system now displays the supported languages (ENGLISH and GERMAN) and outputs
the message
Please enter the language or press ENTER if it is "ENGLISH":
Ê Enter the domain language.
A new AS/X database is now created using the specified language.
Start the server
The installation is now complete.
The system offers you the option of starting the server immediately:
Do you want to start the Advanced Server [y/n]?
Ê Enter y (yes) or n (no).
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 80

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
4.8.7 New installation of a backup domain controller
The following sections describe how Advanced Server for UNIX is installed as a backup
domain controller on a system on which neither LAN Manager/X nor Advanced Server for
UNIX was previously installed or on which the LAN Manager/X or Advanced Server for
UNIX installation has been fully deinstalled.
If the primary domain controller of the domain you want to join is located in a different
subnet, you have to ensure that the server name of the primary domain controller and the
domain name can be resolved by the local NetBIOS. Please refer to the section “Installing
NetBIOS” on how to accomplish this.
To install a backup domain controller, proceed as follows.
Ê Log on as system administrator root.
Ê Start the installation procedure as described in the section “Installing from CD-ROM
with cdinst”.
Ê Select the asxserver package under AS/X.
Stop the server
Ê Choose y to stop the server.
Interactive or non-interactive installation
Ê Choose interactive for interactive installation.
The following description applies for interactive installation.
The system now copies the files from the installation medium and sets up specific users
and user groups for Advanced Server for UNIX.
Output language
The system now displays the supported languages (ENGLISH and GERMAN) and outputs
the message
Please enter the language or press ENTER if it is "ENGLISH":
Ê Enter the output language.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 81

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Interface name of the spooler used by the server
The system now displays all configurable spoolers and outputs the message
Please enter the interface name or press ENTER if it is <spool interface>:
Ê Enter the interface name of the spooler.
Server name
The system generates a default server name from the system name and displays the
message
Enter the name of the server or press Enter to select <system name>:
Ê Enter the server name.
Server role
The message
Enter role (primary or backup) or press Enter to select ‘primary’:
is displayed.
Ê Enter the server role ‘backup’.
Name of the primary domain controller
The system displays the message
Enter the name of the primary domain controller:
Ê Enter the name of the primary domain controller.
The primary domain controller must be running and connected to the network.
Domain name
During the installation of a backup domain controller, the domain name is automatically
obtained from the primary domain controller.
Name of the administrator
The message is displayed:
Enter the name of an administrative account on ‘<primary name>’
or press Enter to select ‘administrator’:
Ê Enter the name of an administrative account.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 82

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Administrator’s password
The password of the administrative account has to be entered twice:
Enter the password for administrator:
Re-enter password:
Contacting the primary domain controller
The server now uses this information to establish contact with the primary domain controller
and, among other things, to get the domain name.
If the contact can be succcessfully established, continue with confirming the choices.
If the contact could not be established, an error message is displayed that describes the
problem, e.g.:
ERROR: Creation of remote account failed - Server Unavailable. The primary
domain controller ‘<primary name>’ is not running or is not connected to
this network.
Do you want to retry [y/n]?
Check whether
● it is possible to reach the primary domain controller using the ping command.
● the domain name and the name of the primary domain controller can be resolved
by the local NetBIOS. Refer to the section “Installing NetBIOS” on how to accomplish this.
● the local server name can be resolved by the NetBIOS of the primary domain
controller. If the primary domain controller is an Advanced Server for UNIX
computer, refer to the section “Configuring NetBIOS Name Resolution”. If the
primary domain controller is a Windows NT server system, please refer to the
Microsoft documentation.
● the primary domain controller has been started.
● the server name of the primary domain controller, the login name of the adminis-
trator and the password have been specified correctly.
If the problem can be fixed immediately, enter y to re-establish the connection to the primary
domain controller.
If the problem has to be fixed later, enter n. In this case, the installation will proceed, but the
server will become a primary domain controller (!) with a temporary domain name, so that
you can complete the configuration after the problem is fixed:
Ê Use the command /var/opt/lanman/bin/joindomain to change the role of the server to a
backup domain controller.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 83

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Confirm choices
The server name, the server role, the domain name and the name of the primary domain
controller have to be confirmed now or can be re-entered.
Domain Language
The system now displays the supported languages (ENGLISH and GERMAN) and outputs
the message
Please enter the language or press ENTER if it is "ENGLISH":
Ê Enter the domain language of the primary domain controller.
A new AS/X database is now created using the specified language.
Start the server
The installation is now complete.
The system offers you the option of starting the server immediately:
Do you want to start the Advanced Server [y/n]?
Ê Enter y (yes) or n (no).
4.8.8 After the installation
Automatic Start and Stop
During the package installation, the start and stop scripts of the server are placed into the
/etc/rc2.d and /etc/ rc0.d directories, so that Advanced Server for UNIX is automatically
started and stopped together with the UNIX system.
Advanced Server for UNIX environment variables
The first time you log on after installation, the following environment variables are present:
Environment variable Meaning
$xASX Installation path, under which the Advanced Server for UNIX
software is located (always:
$LM_HOMEDIR Object path, $xASX/bin
$xLMX Compatibility with the previous versions
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
/var/opt/lanman)
Page 84

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing server software (asxserver package)
Check whether these variables exist. If necessary, start the /etc/rclmx script with
i
. /etc/rclmx.
Windows NT-Style Printing
To enable Windows NT-style Printing after an upgrade installation, set the value of the
DisableUpLevelPrinting key to 0 in the Advanced Server for UNIX registry. Restart the server,
and then associate a printer driver with each printer share used by Windows NT clients (see
chapter “Setting Up Print Servers“ in the “Concepts and Planning“ manual for more information).
Upgrade of lanman.ini parameters
As a result of upgrading LAN Manager/X or Advanced Server for UNIX most of the values
in your previous lanman.ini configuration file are mapped to Advanced Server registry
keywords. Some lanman.ini file parameters are not incorporated into the registry but are
stored in a new lanman.ini file. A copy of your previous lanman.ini file is saved and renamed
lanman.old. For more information about the “Advanced Server Registry” and the
“Lanman.ini File” see the appropriate chapters.
Converting the german umlauts from previous versions (mapnames)
Starting with Version 3.5B, Advanced Server for UNIX uses a new character set.
As a result, some file and directory names with umlauts created with all LAN Manager/X
versions and with Advanced Server for UNIX Version 3.5A can no longer be displayed by
the client after an upgrade.
A utility is being shipped with Advanced Server for UNIX since Version 3.5B which renames
files and directory names containing german umlauts and adjusts their permissions so that
they correspond to the new character set.
The conversion has to be performed only once, if you already upgraded to Version 3.5B
before, this step is not necessary.
For further information on this topic please refer to the information in the chapter entitled
“Troubleshooting“: section “File names with umlauts are not visible after an upgrade”.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 85

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing optional packages
4.9 Installing optional packages
Installation of the packages asxdocs, asxman, asxtools, asxtoolsD, msclients, and asxsnmp is
optional. When you have finished installing Advanced Server for UNIX, you can install all
or some of these packages afterwards as required.
Each of these packages is installed as described in the section “Installing from CD-ROM
with cdinst”. During the installation of the packages asxdocs, asxtools, asxtoolsD and msclients,
a resource containing the associated software is shared automatically with a sharename
derived from the package name.
msclients
This package contains the following PC client software:
● Microsoft LAN Manager Client 2.2c
● Microsoft Network Client 3.0
● TCP/IP-32 for Windows for Workgroups 3.11
● Update for Windows for Workgroups 3.11
For information on generating client diskettes, please refer to the section “Installing from
CD-ROM with cdinst”.
asxtools and asxtoolsD
These packages contain the Windows NT Server Tools for the following platforms and are
available in German or English:
● Windows, Windows for Workgroups and Windows 95/98
● Windows NT Workstation 3.51 and 4.0
For information on memory requirements, please refer to the table in the section “Hard disk
storage ”.
asxman
This package contains UNIX manual pages for the API as well as for all Advanced Server
for UNIX commands. The manual “API Reference” contains as a supplement the data structures and an overview of the API functions. Please refer to the manual pages of this
package for more detailed information.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 86

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing optional packages
asxdocs
This package contains the manuals for Advanced Server for UNIX in PDF format as well as
a version of Acrobat Reader.
asxsnmp
This package contains the extensions for the SNMP Service. For further information, please
refer to the LAN Manager/X manual “SNMP Service”.
4.9.1 Installing the msclients package
Installation of the msclients package is optional. This package contains the following PC
client software:
● Microsoft LAN Manager Client 2.2c (MS-DOS)
● Microsoft Network Client 3.0 (MS-DOS)
● TCP/IP-32 for Windows for Workgroups 3.11
● Update for Windows for Workgroups 3.11
● The package comprises approximately 20 Mbytes. In order that it can be
i
installed in a file system that has sufficient free disk space, you can specify an
installation path during installation.
● To generate installation diskettes, it is sufficient to install this package on one
server only.
Now install the msclients package with the following steps:
Ê Log on as system administrator root.
Ê Establish which file system contains sufficient free disk space.
Ê Carry out the installation procedure as described in section “Installing from CD-ROM
with cdinst”.
Ê Select the package called msclients under AS/X.
Ê During installation, specify the name of the directory where you want to install the client
software. The system now copies the data from the volume to the specified directory.
A resource with the sharename msclient is shared automatically. This contains the
software for the client types mentioned above.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 87

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing optional packages
For information on generating the client diskettes, please refer to the section “Creating
Installation Disk ettes ” .
Please refer to the “readme.txt” file in the "update.wfw/disks/disk1" directory for information on how to install the update for Windows for Workgroups.
4.9.2 Installing the as xtools and asxtoolsD pack ages
Installation of the asxtools and asxtoolsD packages is optional. The asxtools package
contains the English software, while the asxtoolsD package contains the German software
for the Windows NT Server Tools for the following platforms:
● Windows, Windows for Workgroups
● Windows 95/98
● Windows NT Workstation Version 3.51
● Windows NT Workstation Version 4.0
● Both packages comprise approximately 20 Mbytes. In order that they can be
i
installed in a file system that has sufficient free disk space, you can specify an
installation path during installation.
● It is sufficient to install the required language variant of this package on only one
of the servers in a domain.
Now install the asxtools or asxtoolsD
package with the following steps:
Ê Log on as system administrator root.
Ê Establish which file system contains sufficient free disk space.
Ê Carry out the installation procedure as described in the section “Installing from CD-
ROM with cdinst”.
Ê Select the package called asxtools or asxtoolsD
under AS/X.
Ê During installation, specify the name of the directory where you want to install the
Windows NT Server Tools.
The system now copies the data from the volume to the specified directory . A resource
with the sharename astools or astoolsD
is shared automatically.
For information on installing the server tools from this directory on a PC client or a
Windows NT workstation, please refer to the section “Administrative Clients”.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 88

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing optional packages
4.9.3 Installing the asxman package
Installation of the asxman package is optional, but recommended. The package contains
UNIX manual pages for the API of Advanced Server for UNIX as well as for all Advanced
Server for UNIX commands. The manual “API Reference” contains the data structures and
an overview of the API functions as a supplement to this. Please refer to the manual pages
of this package for more detailed information.
Install the asxman package with the following steps:
Ê Log on as system administrator root.
Ê Carry out the installation procedure as described in the section “Installing from CD-
ROM with cdinst”.
Ê Select the asxman package under AS/X.
The system now copies the data from the volume to /usr/share/man/mrd/catman/asx.
4.9.4 Installing the asxdocs package
Installation of the asxdocs package is optional. In addition to the manuals for Advanced
Server for UNIX in PDF format, the package also contains an "Acrobat Reader" (English
language) for installation on a workstation.
Install the asxdocs package with the following steps:
Ê Log on as system administrator root.
Ê Carry out the installation procedure as described in the section “Installing from CD-
ROM with cdinst”.
Ê Select the asxdocs package under AS/X.
Ê During installation, specify the name of the directory where you want to install the
documentation files.
The system copies the files from the volume to the specified directory . If Advanced Server
for UNIX is already installed, a resource with the sharename asdocs is shared automatically.
The Acrobat Reader program (either ar16e30.exe for Windows 3.x or ar32e30.exe for
Windows 95/98 or Windows NT) which is stored in the acrobat directory, must be invoked
for installation on a workstation. The Acrobat Reader is then installed on the workstation
and can be used to read the PDF files.
The asxdocs package can be installed prior to installation of AS/X so that the documentation
can be accessed before Advanced Server for UNIX is installed. Both the Acrobat Reader
and the PDF files must then be transferred to a workstation by some other means (e.g. via
FTP).
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 89

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing optional packages
4.10 Installing with the default configuration
You can install the asxserver, asxtools, or asxtoolsD and msclients packages with a default
configuration without any further input.
The default parameters for all packages are listed at the end of this section.
i
Carry out the following steps in the given sequence:
1. Log on as system administrator root and insert the CD in the drive of the system, from
which you want to install the software.
2. Start the installation program with cdinst. The following dialog box is displayed:
1 Process Multi-Product CD-ROM
Server: local
CD-ROM device name: /dev/ios0/sdisk005s0
Remote pathname/
Local mountpoint: /cdrom0
Fill in the form and then press SAVE.
Ê Position the cursor on CD-ROM device name and select the device name for the CD-
ROM drive with (CHOICES). Then select (SAVE) in order to confirm
F2 F3
your entry. You are then given a general message about the volume.
Ê Acknowledge with (CONTINUE).
3. Use the cursor to mark the ASX set in the list displayed and then press (MARK)
and (ENTER). The following is displayed:
F3
2
info
pkginfo
README
install
Move the cursor to the item you want and press ENTER to
select it.
F8
F2
- Display Detailed Product Information
- Display Detailed Information on Packages
- Display README Files
- Install Products
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 90

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing optional packages
F2
4. Select install and then press (MARK) and (ENTER) in order to start
F2 F3
installation of the individual packages.
4 Install
Install:
Installation mode:
Installation default file name:
Path to response files:
Package
dialog
default
/tmp/16632/response
Fill in the form and then press SAVE.
In the Install selection field you can select between Complete Product, SIreadmeM, and
Package. Press (CHOICES) to make your selection.
Do not select Complete Product. The installation will fail with this selection.
!
Ê Select Package.
The Instal latio n mode selection field offers a choice between automatic and dialog. Press
F2
(CHOICES) to make your selection.
Ê Select automatic as the installation mode.
Ê Select the entry on CD-ROM under Path to response files using (CHOICES).
Ê Press (SAVE).
F3
F2
5. The following selection is displayed (for contents of the packages see the section
“Advanced Server for UNIX delivery package”):
5 Packages
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
AS/X 4.0<version>
SIreadmeM
nbrfc
asxserver
asxtools
asxtoolsD
msclients
asxman
asxdocs
asxsnmp
asxdebug
Mark the items you want and press ENTER to select them.
6. Use the cursor to select the required packages and press (MARK). Then start
the installation with (ENTER).
F3
F2
The installation is started implicitly with pkgadd.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 91

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing optional packages
Default parameters for the asxserver package:
R_INSTTYPE=’automatic’
R_PKGNAME=’Advanced Server 4.0 for UNIX’
R_VERSION=’4.0B0003’
R_LMXSPOOLER=’default’
R_AUTOSTART=’NO’
R_PASSWORD=’password’
R_LANG=’ENGLISH’
R_DOMAINLANG=’ENGLISH’
R_SAVEONREMOVAL=’YES’
R_MAPWARNTOERR=’NO’
SERVERNAME=’default’
DOMAIN=’default’
ROLE=’primary’
PRIMARY=’’
ADMIN_ACCT=’administrator’
STOPSERVER=’YES’
USE_DEFAULT_PASSWD=’NO’
ASK_ABOUT_PRINTER_UPGRADE=’NO’
ALWAYS_USE_UPLEVEL_PRINTING=’NO’
The entry default means that the value for the parameter is automatically formed on
i
the system.
In the case of an upgrade installation, as many configuration information as possible is
automatically incorporated from the previous version. Then the corresponding default
parameter is ignored.
The default response file gives the following answers. Please refer to section “Installation
steps” for more information.
Installation step:
Parameter:
Value:
Installation step:
Parameter:
Value:
Parameter:
Value
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Stop the server
STOPSERVER
YES
Interactive or non-interactive installation
R_INSTTYPE
automatic (non-interactive)
R_MAPWARNTOERR
NO
Page 92

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing optional packages
By default, warnings are mapped to state "OK" during the installation. If
i
R_MAPWARNTOERR is set to YES, the warnings are mapped to the state "ERROR".
Installation step:
Parameter:
Value:
Installation step:
Parameter:
Value:
Installation step:
Parameter:
Value:
Installation step:
Parameter:
Value:
Installation step:
Parameter:
Value:
Output language
R_LANG
ENGLISH
Interface of the spooler used by the server
R_LMXSPOOLER
default (the spooler configured in UNIX)
Server name
SERVERNAM E
default (system name)
Server role
ROLE
Domain name
Domain name
DOMAIN
default (system name with .dom)
Installation step:
Parameter:
Value:
Installation step:
Parameter:
Value:
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Name of the primary domain controller
PRIMARY
<empty>
Name of the administrator
ADMIN_ACCT
administrator
Page 93

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing optional packages
Installation step:
Parameter:
Value:
Parameter:
Value:
Installation step:
Parameter:
Value:
Installation step:
Parameter:
Value:
Parameter:
Value:
Installation step:
Parameter:
Value:
Administrator’s password
R_PASSWORD
password (has to be changed!)
USE_DEFAULT_PASSWD
Value:
Domain language
R_DOMAINLANG
ENGLISH
Windows NT-style Printing
ASK_ABOUT_PRINTER_UPGRADE
NO
ALWAYS_USE_UPLEVEL_PRINTING
NO
Start the server
R_AUTOSTART
NO
Installation step:
Parameter:
Value:
After an default installation of the asxserver package,deinstallation of the package
i
on the target system will also run without any interaction. The AS/X configuration
files will automatically be saved for an upgrade installation. If you want to remove
AS/X completely, you have to modify the variable R_SAVEONREMOVAL=NO in the
file /var/sadm/pkg/asxserver/pkginfo.
The parameters R_PKGNAME and R_VERSION are used for internal purposes.
The /var installation path is used for the asxtools package.
Default response file for the asxtools package:
NEXUS=’/var/opt/lanman/share s/ast ool s’
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Deinstalling the server
R_SAVEONREMOVAL
NO
Page 94

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing optional packages
RETURN
The /var installation path is used for the asxtoolsD package.
Default response file for the asxtoolsD package:
NEXUS=’/var/opt/lanman/shares/astools.deu’
The /var installation path is used for the msclients package.
Default response file for the msclients package:
MSCLIENT=’/var/opt/lanman/shares/msclient’
4.11 Deinstalling Advanced Server for UNIX V4.0
Deinstall the software in the following sequence:
● begin with the optional packages (including AS/X Service Packs from the field support)
● then the server
● followed by NetBIOS.
4.11.1 Deinstalling optional packages
To deinstall the <Package> package, carry out the following steps:
1. Log on as system administrator root.
2. Enter pkgrm <Package>.
Ê Confirm with . The software of the package is now deleted.
Ê Repeat the pkgrm <Package> command for all optional packages installed.
4.11.2 Deinstalling the server
Work through the following steps:
1. Log on as system administrator root
2. Stop the server using the asx stop command
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 95

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing optional packages
RETURN
3. Enter pkgrm asxserver
Ê Verify with the key. The server software is now deleted.
If the server software was installed with the default configuration, no further
i
prompts are issued during deinstallation. The configuration files are not
deinstalled in this case.
Ê At the prompt Would you like to retain any of these data
items [y/n]? you can enter y to save the configuration files for a subsequent
installation.
The files and directories of the users are not affected by your decision and will not be
deleted.
The system will ask you if you wish to save or delete the following data:
● User data in the public directories DOSUTIL, OS2UTIL, LIB and PRINTLOG, which was not
created when the server was installed.
● Customized print processor scripts.
● Information about shared printers (servers and workstations). Printers are either linked
directly to the server or to specific workstations (shared client printer). If you enter n
here, all data relating to the printer will be deleted.
● AS/X users and accounts.
● Configuration files and registry database.
● WINS database.
The logon scripts are saved automatically.
i
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 96

Installing Advanced Server for UNIX Installing optional packages
RETURN
4.11.3 Deinstalling NetBIOS
Work through the following steps:
1. Log on as system administrator root.
2. Enter pkgrm nbrfc.
Ê Verify with the key. NetBIOS is now deleted, and a new UNIX kernel is
generated. During this process you will receive a corresponding system wait
message.
The configuration files remain in the /var/opt/nbrfc/conf directory and can be saved from
there, or can be left there for a later reinstallation. In this case the reinstallation will use
the existing configuration.
3. Start the system with the newly generated UNIX kernel or, if necessary, install a new
NetBIOS and then start the system.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 97

5 Configuring Advanced Server for UNIX
This chapter contains the information required to configure Advanced Server for UNIX. You
must have root privilege to configure NetBIOS and Advanced Server for UNIX.
5.1 Configuring NetBIOS
The following section first gives a brief introduction to NetBIOS.
The remaining sections include the following type of information you need to configure
NetBIOS:
● The second section describes how to configure network interfaces so that they can be
used by NetBIOS.
● The 3rd section describes how to configure NetBIOS name resolution.
● If not stated otherwise all following descriptions imply that all NetBIOS tuning param-
eters use predefined values. The fourth sections will show how – in case of need – the
behavior of NetBIOS can be influenced by changing the tuning parameters.
In what follows the reader is assumed to be familiar with the basic concepts and terms of
TCP/IP networking (IP addresses, netmasks, subnets etc.).
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 98

Configuring Advanced Server for UNIX Configuring NetBIOS
5.1.1 Introduction to NetBIOS
An important part of Advanced Server for UNIX communication is not based directly on
TCP/IP protocols but uses NetBIOS.
In terms of the OSI Reference Model for a layered networking architecture, NetBIOS is a
level 5 pro tocol (“Sess ion Layer”). The session layer establishes a communications session
between processes running on different computers. Functions of the session layer include:
● Name Service: The Name Service allows application processes to register unique
NetBIOS names. It provides the means by which these names can be resolved to the
network layer.
● Session Service: The Session Service is responsible for establishing, monitoring, and
terminating a virtual-circuit session between two processes identified by their NetBIOS
names.
● Datagram Service: This service allows application processes identified by their
NetBIOS names to exchange datagrams (messages of limited length).
On Advanced Server computers, NetBIOS services are provided by two STREAMS drivers
which are linked to the UNIX kernel during NetBIOS installation.
NetBIOS Names
The NetBIOS name space is flat (that is, it is not hierarchical), so all names within a network
must be unique. NetBIOS names are 16 characters in length. Advanced Server for UNIX
as well as Microsoft networking components allow the first 15 characters of a NetBIOS
name to be specified by the user or administrator (usually a given name is converted to
uppercase letters and padded with spaces), but reserve the 16th character of the NetBIOS
name to indicate a resource type (00-FF hex). Names can be registered as unique (one
owner) or as group (multiple owner) names. In addition to this there is also the concept of
an internet group (with multiple owners and multiple addresses). Following are the important
NetBIOS names used in Advanced Server environments:
Unique names:
<computername>[ 0x0 0]
<computername>[ 0x0 3]
<computername>[ 0x2 0]
<username>[0x03]
<domain_name>[0x1D]
<domain_name>[0x 1B ]
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Workstation Service
Messenger Service
Server Service
Messenger Service
Master Browser
Domain Master Browser (PDC)
Page 99

Configuring Advanced Server for UNIX Configuring NetBIOS
Group names:
<domain_name>[0x00]
<domain_name>[0x1C]
<domain_name>[0x1E]
. . __MSBROWSE__ . [0x01]
Domain Name
Domain Controllers ("Domain Group"/"Internet Group")
Browser Service Elections
Master Browser
Information on the meaning of the various NetBIOS name extensions and their usage can
be found in the “Microsoft Windows NT Resource Kit Networking Guide”.
The two most important aspects of the NetBIOS name service are registration and resolution:
● Registration is the process used to register a unique name for each computer (node) on
the network. A computer typically registers itself when it starts.
● Resolution is the process used to determine the specific IP address for a certain
NetBIOS name.
An Advanced Server for UNIX computer can use one or more of the following methods to
ensure accurate name resolution in TCP/IP internetworks:
Broadcast name resolution
Broadcast name resolution is a NetBIOS over TCP/IP mode of operation defined in RFC
1001/1002 as b-node. This method relies on a computer making IP-level broadcasts to
register its name by announcing it on the network and to query a name by asking all other
computers in the broadcast area. Each computer in the broadcast area is responsible for
challenging attempts to register a duplicate name and for responding to name queries for
its registered name.
Broadcast name resolution has two major problems:
1. Broadcast messages typically do not pass IP routers, so computers that are on opposite
sides of a routers are not reachable.
2. In a large environment, it loads the network with broadcasts, which every computer
must handle.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
Page 100

Configuring Advanced Server for UNIX Configuring NetBIOS
names.cfg file
On Advanced Server for UNIX computers, a names.cfg file (residing in /var/opt/nbrfc/conf) can
be used to specify static mappings of NetBIOS names to IP addresses. These mappings
can be loaded into an internal name table. If a b-node attempt fails, the system looks in this
name table to find a name and then uses the associated address to cross the router. The
function of the names.cfg file is comparable to the LMHOSTS file known from the Microsoft
networking components, however the format differs.
Files with static mappings, like LMHOSTS or names.cfg files, allow NetBIOS name resolution
to span routers, thus solving the problem of b-node name resolution in routed environments. However, each computer must have the necessary list of static mappings, and all
lists must be consistent. This creates an administrative burden in maintaining and distributing the lists.
Windows Internet Name Service (WINS)
A computer can use WINS if at least one WINS server is available that contains a dynamic
database that maps computer names to IP addresses. WINS can be used in conjunction
with broadcast name resolution for an internetwork where other name resolution methods
are inadequate. As described in chapter “Implementing WINS”, WINS is a NetBIOS over
TCP/IP mode of operation defined in RFC 1001/1002 as p-node. When configured as a
WINS client, Advanced Server computers use a variant of p-node known as h-node.
WINS is designed to solve the problems that occur with name resolution in medium sized
and complex internetworks and is the preferred method for name resolution. For details on
the WINS service, consult the chapter “Implementing WINS”.
An Advanced Server for UNIX computer never uses DNS (the Internet Domain Name
Service) for NetBIOS name resolution purposes.
All name resolution methods depicted above can be combined with each other. How name
resolution is handled on an Advanced Server for UNIX computer is explained in more detail
in “Configuring NetBIOS Name Resolution”.
Product Manual U7613-J-Z815-6-76
 Loading...
Loading...