Page 1

Multiplexer User's Guide
Siemens Cellular Engines
Version: 06
DocID: Mux_guide_v06
User’s Guide
Page 2

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
Document Name:
Version:
Date:
DocId:
Status:
Multiplexer User's Guide
06
June 30, 2004
Mux_guide_v06
Confidential / Released
General notes
Product
The documentation and/or Product are provided for testing, evaluation, integration and information
purposes. The documentation and/or Product are provided on an “as is” basis only and may contain
deficiencies or inadequacies. The Documentation and/or Product are provided without warranty of any
kind, express or implied. To the maximum extent permitted by applicable law, Siemens further
disclaims all warranties, including without limitation any implied warranties of merchantability,
completeness, fitness for a particular purpose and non-infringement of third-party rights. The entire risk
arising out of the use or performance of the Product and documentation remains with Recipient. This
Product is not intended for use in life support appliances, devices or systems where a malfunction of
the product can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Applications incorporating the
described product must be designed to be in accordance with the technical specifications provided in
these guidelines. Failure to comply with any of the required procedures can result in malfunctions or
serious discrepancies in results. Furthermore, all safety instructions regarding the use of mobile
technical systems, including GSM products, which also apply to cellular phones must be followed.
Siemens or its suppliers shall, regardless of any legal theory upon which the claim is based, not be
liable for any consequential, incidental, direct, indirect, punitive or other damages whatsoever
(including, without limitation, damages for loss of business profits, business interruption, loss of
business information or data, or other pecuniary loss) arising out the use of or inability to use the
Documentation and/or Product, even if Siemens has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
The foregoing limitations of liability shall not apply in case of mandatory liability, e.g. under the German
Product Liability Act, in case of intent, gross negligence, injury of life, body or health, or breach of a
condition which goes to the root of the contract. However, Claims for Damages arising from a breach of
a condition which goes to the root of the contract shall be limited to the foreseeable damage which is
intrinsic to the contract, unless caused by intent or gross negligence or based on liability for injury of
life, body or health. The above provision does not imply a change on the burden of proof to the
detriment of the Recipient. Subject to change without notice at any time. The interpretation of this
general note shall be governed and construed according to German law without reference to any other
substantive law.
Copyright notice
Transmittal, reproduction, dissemination and/or editing of this document as well as utilization of its
contents and communication thereof to others without express authorization are prohibited. Offenders
will be held liable for payment of damages. All rights created by patent grant or registration of a utility
model or design patent are reserved.
Copyright © Siemens AG 2004
Trademark notice
MS Windows
is deemed accepted by Recipient and is provided without interface to Recipient’s products.
is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Mux_guide_v06 Page 2 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 3

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
Contents
0 Document history..........................................................................................................5
1 Introduction ...................................................................................................................6
1.1 Supported products and related documents..........................................................7
1.2 References ............................................................................................................7
1.3 Term and abbreviations .........................................................................................8
2 Multiplexer protocol – an overview .............................................................................9
2.1 Product concept and architecture ..........................................................................9
2.2 Virtual channels and AT commands ....................................................................10
3 Integrating multiplexer into the customer application ............................................ 11
3.1 Characteristics .....................................................................................................11
3.1.1 Basic requirements ................................................................................11
3.1.2 Restrictions ............................................................................................11
3.1.3 Dependencies between multiplexer channels and restrictions of use ...12
3.1.4 Functions without channel dependencies..............................................12
3.1.5 Timing conditions...................................................................................13
3.1.6 Operation of a second physical serial interface ASC1 (if applicable) ....13
3.2 Multiplexer control and signaling lines .................................................................14
3.2.1 Flow control............................................................................................14
3.2.2 Escape sequence ..................................................................................16
3.3 Power saving .......................................................................................................16
3.4 Bandwidth of logical channels .............................................................................16
4 Structure of the multiplexer protocol........................................................................17
4.1 Introduction of the multiplexer protocol................................................................17
4.2 Data link layer ......................................................................................................17
4.2.1 Flag sequence .......................................................................................18
4.2.2 Address field ..........................................................................................18
4.2.3 Control field............................................................................................ 19
4.2.4 Length indicator .....................................................................................20
4.2.5 Information field .....................................................................................20
4.2.6 Frame checking sequence field (FCS)...................................................20
4.3 State diagrams.....................................................................................................21
4.3.1 Start-up procedure.................................................................................25
4.3.2 DLC establishment.................................................................................25
4.3.3 Information transfer................................................................................ 25
4.3.4 DLC release...........................................................................................26
4.3.5 Close-down procedure........................................................................... 26
4.3.6 Multiplexer control channel ....................................................................26
4.3.7 Multiplexer close down (CLD) ................................................................ 27
4.3.8 Test command (Test).............................................................................27
4.3.9 Modem status command (MSC) ............................................................28
4.3.10 Power saving control (PSC)...................................................................30
4.3.11 Non-supported command response (NSC)............................................31
4.4 Example: Establishing logical channels without parameter negotiation ..............32
Mux_guide_v06 Page 3 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 4

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
5 Multiplexer protocol version control.........................................................................33
5.1 Introduction ..........................................................................................................33
5.2 Multiplexer protocol versions ...............................................................................34
5.3 Implementing version control...............................................................................35
5.3.1 Troubleshooting .....................................................................................35
5.3.2 Coding of “TestCommand” message .....................................................36
5.3.3 Example of “TestCommand” message ..................................................36
s
mo b i l e
Figures
Figure 1: Multiplexer architecture .............................................................................................9
Figure 2: Logical flow control and RTS/CTS signaling behind the decoder ........................... 15
Figure 3: Data link layer ......................................................................................................... 17
Figure 4: Relationship between the customer µC and the GSM engine µC........................... 22
Figure 5: MPI – Startup, DLC establishment and information transfer................................... 23
Figure 6: MP - DLC release and close down.......................................................................... 24
Figure 7: DLC establishment.................................................................................................. 25
Figure 8: Information transfer ................................................................................................. 25
Figure 9: DLC release ............................................................................................................ 26
Figure 10: Multiplexer control channel ...................................................................................26
Figure 11: Modem status command (MSC) ...........................................................................28
Figure 12: Power Saving Control (PSC)................................................................................. 30
Figure 13: Establishing the multiplexer control channel and the logical channel ................... 32
Figure 14: MSC as used in version 3 ..................................................................................... 34
Tables
Table 1: Comparison of multiplexer channels ........................................................................ 10
Table 2: Address field.............................................................................................................18
Table 3: Assignment of the DLCI ...........................................................................................18
Table 4: Use of the command/response bit............................................................................ 18
Table 5: Coding of the control field......................................................................................... 19
Table 6: Version differences for MSC ....................................................................................34
Table 7: IEI coding .................................................................................................................36
Table 8: Coding of “TestCommand” (Example)...................................................................... 36
Mux_guide_v06 Page 4 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 5
Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
0 Document history
This chapter reports modifications and improvements over previous versions of this
document.
Preceding document: “Multiplexer User's Guide” Version 05
New document: “Multiplexer User's Guide” Version 06
Chapter What is new
1.1 Added further supported products.
3.1.1 Added note about closing Multiplexer.
3.1.2 Added note about maximum frame size N1.
4.2.4 Second byte for frame size greater than 127 bytes is not supported.
4.3.5 Corrected description of Close-down procedure.
5 Corrected description of multiplexer version control.
5.3.3 Corrected example.
Preceding document: “Multiplexer User's Guide” Version 04
New document: “Multiplexer User's Guide” Version 05
Chapter What is new
1.1 Added further supported products.
3.1.4 Modified remark on AT&W.
3.1.6 Added chapter “Operation of a second physical serial interface ASC1 (if applicable)”
Preceding document: “Multiplexer User's Guide” Version 03
New document: “Multiplexer User's Guide” Version 04
Chapter What is new
1.1 Added further supported products.
3 - 3.4 Restructured and revised all chapters.
3.1.2, 3.3,
4.3.10
To control SLEEP mode use PSC messages rather than entering AT+CFUN=<n>
Mux_guide_v06 Page 5 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 6

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
1 Introduction
Siemens GSM engines support the basic option of the multiplexer according to the
ETSI TS 101 369, GSM 07.10 Multiplexer Protocol. This allows a mobile to run a triple
session over a serial link interface. Outside the GSM engine, on the application side of the
serial interface, another multiplexer must be integrated in order to demultiplex the signal and
distribute it on the three virtual channels. The external multiplexer needs to be provided by
the customer.
This document describes how to use the multiplexer and then explains how to design an
external multiplexer and integrate it into an application on top of a Siemens GSM engine.
Multiplexer protocol sources (WinMux2k), provided by Siemens AG, can be obtained on
request from your local distributor. For more detailed information please refer to [5].
Mux_guide_v06 Page 6 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 7

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
1.1 Supported products and related documents
Supported products
• AC43
• AC45
• MC35i
• MC35i Terminal
• MC39i
• MC45
• MC46
• MC388
• MC5x
• TC35i
• TC35i Terminal
• TC45
• XT55
Related documents
[1] Hardware Interface Description supplied with your GSM engine
[2] AT Command-Set supplied with your GSM engine
[3] Release Notes supplied with your GSM engine
[4] Remote-SAT User's Guide
[5] Multiplexer Driver Developer’s Guide for Windows 2000 and Windows XP
[6] Multiplexer Driver Installation Guide for Windows 2000 and Windows XP
For further documents regarding your GSM engine please refer to the latest Release Notes
supplied with the module.
To visit the Siemens Website you can use the following link:
http://www.siemens.com/wm
1.2 References
[1] Digital Cellular Telecommunications Systems (Phase 2+); Terminal Equipment to
Mobile Station (TE-MS) "Multiplexer Protocol"; ETSI TS 101 369 V7.1.0 (1999-11),
GSM 07.10 Version 7.1.0, Release 199
Mux_guide_v06 Page 7 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 8

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
1.3 Term and abbreviations
Abbreviation Description
CSD Circuit Switched Data
CTS Clear to Send
DCD Data Carrier Detect
DLCI Data Link Control Identifier
DSB Developer Support Box
DSR Data Set Ready
DTR Data Terminal Ready
FC Flow Control
FFC Flat Flex Cable
GPRS General Packet Radio Service
s
mo b i l e
GSM Global System of Mobile Communication
IEI Information Element Identifier
IP Internet Protocol
MO Mobile originated
MP Multiplexer Protocol
MS Mobile Station
MSDN Microsoft Developer Network
MT Mobile terminated
MUX Multiplexer
OS Operating System
PC Personal Computer
PSC Power saving control
RTS Request to Send
TE Terminal Equipment
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter
Mux_guide_v06 Page 8 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 9
Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
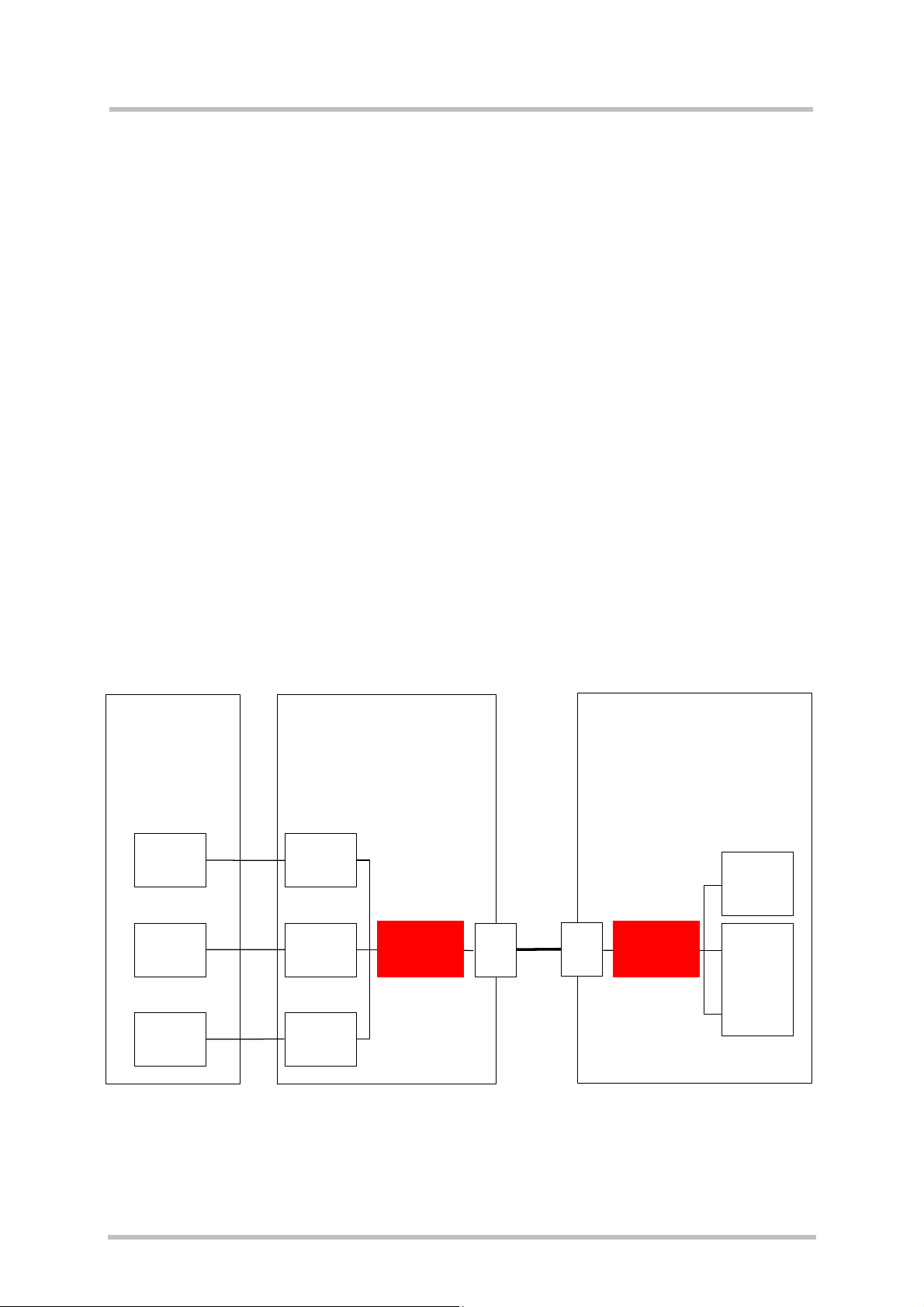
2 Multiplexer protocol – an overview
2.1 Product concept and architecture
The multiplexer mode enables one serial interface to transmit data to three different customer applications. This is achieved by providing three virtual channels using a
multiplexer (Mux).
This is especially advantageous when a fax/data/GPRS call is ongoing. Using the multiplexer
features, e.g. controlling the module or using the SMS service can be done via the additional
channels without disturbing the data flow; access to the second UART is not necessary.
Furthermore, several accesses to the module can be created with the multiplexer. This is of
great advantage when several independent electronic devices or interfaces are used.
To access the three virtual interfaces, both the GSM engine and the customer application
must contain Mux components which communicate over the multiplexer protocol.
In multiplexer mode, AT commands and data are encapsulated into packets. Each packet
has a channel identification and may vary in length.
Note:
All statements regarding GPRS are valid only for Siemens wireless products capable of
GPRS.
Terminal programs
or internal programs
integrated in customer application
platform
Terminal 1
Terminal 2
Terminal 3
User application
Channel 1
Channel 2
Channel 3
MUX
conforming
to GSM 07.10
Figure 1: Multiplexer architecture
Serial
MP
I/O
Serial
I/O
GSM engine
MUX
conforming
to GSM 07.10
Data/Fax/
1
GPRS
supported
2
Data/Fax
not
supported
3
Mux_guide_v06 Page 9 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 10

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
2.2 Virtual channels and AT commands
Please note that a cellular engine designed for multiplex operation does not include three
different devices. Only one single air interface (RF part) is available.
As mentioned before the multiplexer enables one serial interface to run three sessions
simultaneously. All incoming or outgoing calls are connected to the device.
Channel 1 supports the full range of functions, which is available without multiplexer tool.
Channel 2 and 3 are connected to a different AT interpreter and support a subset of the
functional range of channel 1, for more details refer to Table 1.
Table 1: Comparison of multiplexer channels
Channel 1
Channel 2, 3
! indicates that the functionality is available on the channel
--- indicates that the functionality is not available on the channel
1)
except for AT commands related to data and fax calls
2)
only two channels can be used parallel to transmit GPRS data
Voice calls
incoming
outgoing
! ! !
!
Data / fax calls
incoming
outgoing
-
SMS
incoming
outgoing
!
GPRS
connection
!2)
!2)
Phonebook
management
! !
!
AT
commands
!1)
Examples
• While a data call is in progress on channel 1, you can send a short message on channel
2 and edit the phonebook on channel 3.
• When receiving a fax on channel 1, you are able to check the battery capacity using the
appropriate AT command on channel 2 or 3.
Note
Due to the technical requirements of multiplexer mode, data and fax calls can only be set up
on logical channel 1 while GPRS connections can be established on every channel. Several
AT commands have a different behavior on channels 2 and 3. Additional information
regarding restrictions and interferences between the channels can be found in chapter 3.1
and in [2].
Mux_guide_v06 Page 10 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 11

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
3 Integrating multiplexer into the customer application
When designing a multiplexer application, you can create your own sources or take
advantage of the sources delivered upon request by Siemens. The Siemens sources are
packed in a *.zip file which includes a driver for Windows 2000 and Windows XP. See [5] for
a detailed description.
3.1 Characteristics
After establishing the multiplexer mode according to the multiplexer protocol, three logical
channels are available. Please keep the following restrictions and requirements in mind:
3.1.1 Basic requirements
• The GSM engine supports the basic option and UIH Framing according to GSM 07.10.
• Character
If you wish to use multiplexer mode with TC35i modules, be sure not to change this
setting.
• Hardware flow control AT\Q3 is recommended for use with multiplexer mode. If used, it
needs to be set before multiplexer mode is entered.
• Several customer software applications may be able to change the selected settings.
These settings will be stored in the non-volatile memory and used whenever the module
is powered up again. In this case the multiplexer fails to start. To avoid this, it is recommended to re-synchronize all settings before using the multiplexer mode again.
• Before closing the multiplexer make sure that there is no ongoing activity on one of the
channels. For example, check that voice, CSD or GPRS connections have ended and
wait until all pending AT command responses are received.
framing must be configured for 8 data bits, no parity and 1 stop bit.
3.1.2 Restrictions
If the GSM engine is operated in multiplexer mode, the following restrictions apply:
• MO and MT circuit-switched data and fax calls can only be set up on channel 1.
• It is not recommended to use AT+CFUN=<n> for selecting one of the SLEEP modes. For
products supporting Multiplexer Protocol version 3, the best approach to properly control
SLEEP mode in this case is to issue the PSC messages described in Chapter 4.3.10.
The multiplexer cannot be started if one of the following features is activated, nor can these
features be used when multiplexer is active:
• Multiplex mode cannot be started while autobauding (AT+IPR=0) is enabled.
• The multiplexer is not available in charge-only mode and in alarm mode.
• XON/OFF flow control is not supported in multiplexer mode.
The maximum frame size N1 (defined in GSM 07.10) is fixed to 98 bytes and cannot be
changed. The maximum frame size is the same for sending and receiving. See also Chapter
4 in this manual and GSM 07.10.
Mux_guide_v06 Page 11 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 12

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
3.1.3 Dependencies between multiplexer channels and restrictions of use
When using the following functions, be aware of possible dependencies between the
different channels. One way of avoiding problems may be to dedicate certain
commands/features to one of the channels or to assure that the application avoids conflicts.
• Call control: A voice call can be initiated, answered or ended on each channel. See AT
commands like ATD, ATA or ATH.
Please note that ATH terminates each voice, circuit switched data or fax call regardless
on which logical channel ATH was executed, for details see [2].
• Phonebook access: If you wish to write the same phonebook entry on two different
channels at the same time, please note that the last entry will be stored permanently. All
other data will be deleted.
• SMS read, write and delete.
• Time settings: Though the AT commands AT+CALA and AT+CCLK can be used on
either channel, the same time setting applies to all three channels. It is only the alarm
message <text> which may be specific to each channel. The URC “+CALA” will be issued
only on the channel where the last alarm setting was made. For details see [2].
• Device locks set with AT+CLCK.
• SIM card access.
• RF settings.
Example:
• An ongoing fax call has been established on channel 1. When answering an incoming
voice call on channel 2 or 3 and terminating it, the held fax call will be ended as well.
3.1.4 Functions without channel dependencies
The following functions or events may be ongoing independently on different channels:
• Unsolicited Result Codes (URCs) will generally be transmitted to all logical channels. For
example, an incoming voice call is indicated by the URC “RING” on all three channels.
Incoming data calls are indicated on channel 1 only.
• Device information can be queried on a single channel.
• Signal quality and cell information can be retrieved on a single channel.
• Further commands that can be used separately on one channel without impact on the
remaining channels: ATZ, AT&F, AT&V, AT+CEER, AT+CMEE.
• User profile: AT&W stores the current setting of each channel to the user profile, no
matter on which of the three channels the command is executed.
Example:
• The battery capacity can be queried from channel 2 or 3 while a voice, fax or data call is
made on channel 1.
Mux_guide_v06 Page 12 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 13

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
3.1.5 Timing conditions
Switching on the multiplexer with AT+CMUX=0 causes a 5s timer to start. If the multiplexer
control channel is not established within this time, the module returns to “normal AT
command mode” without multiplexer. This prevents the module from being blocked if, for
example, AT+CMUX=0 is sent from an application that does not support the multiplexer
protocol.
Fax is based on a protocol, which needs to respect timings between the application and the
module as well as between the module and the selected terminal equipment (TE). Hence,
heavy parallel traffic load in the module can lead to mistiming. This may result in malfunction
in both directions. Please consider the following recommendations:
Using the multiplexer it is not possible to define bandwidth and delay time per channel.
Therefore, the customer application should take care that the channels 2 and 3 are not
heavily loaded when faxing on channel 1.
Example 1: Checking the field strength every 2 seconds does not harm, sending an SMS
every 10 seconds may lead to problems.
Example 2: Reading a complete phone book, may cause problems if a fax transmission is
ongoing at the same time.
When switching on the module after a firmware update we recommend to wait 5 seconds
before entering the first AT command.
3.1.6 Operation of a second physical serial interface ASC1 (if applicable)
This chapter applies only to Siemens GSM modules equipped with a second physical serial
interface (referred to as ASC1). If your product has only one physical serial interface (ASC0)
you can skip this chapter.
ASC1 is disabled when the multiplexer is enabled on the first serial interface ASC0. Yet, both
ASC1 and the multiplexer channel 2 are using the same parameters, and thus, the same
user defined profile (if any). As a result, a user profile stored on multiplexer channel 2 takes
effect on ASC1 after closing the multiplexer and starting up ASC1. Likewise, a user profile
stored on ASC1 will be loaded on multiplexer channel 2.
This may be a problem when ASC1 is not connected, but flow control (for example AT\Q1 or
AT\Q3) is stored to the user profile on the multiplexer channel 2. In this case, flow control
takes effect on ASC1, when the multiplexer is switched off. If then for example a large
amount of URCs is generated, their transmission might be stopped due to the flow control.
To avoid this problem we recommend that you do not activate flow control on multiplexer
channel 2 when you set up a user profile with AT&W.
Mux_guide_v06 Page 13 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 14

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
3.2 Multiplexer control and signaling lines
The following chapter covers all information you need to develop and set up a virtual driver.
Differences and restrictions in comparison to the unframed module are pointed out.
3.2.1 Flow control
Logical flow control
The internal logical flow control (FC-BIT in MSC message, see Chapter 4.3.9) represents the
existing flow control to the module. For example, if a data call is initiated and the customer
application transmits data to the module on this channel, the module will stop the data
transmission from time to time. This happens because the module operates with a bandwidth
of 9k6 on air, but the customer application uses a larger width. In this case the module sends
a MSC message with FC-BIT set. After all data stored in the internal buffer have been sent,
the module will send a second MSC message with FC-BIT reset. As already pointed out, the
logical flow control operates like RTS/CTS but with FC-BIT on every channel. The RTS/CTS
are not used for flow control because the traffic on the logical channels may cause a
temporary loss of bandwidth on another channel. This behavior has no impact on the
handshake V.24 lines.
RTS/CTS on the physical channels
Hardware flow control (AT\Q3) is recommended for use with multiplexer. For power saving it
is indispensable. The setting AT\Q3 needs to be made before switching on the multiplexer.
The customer application decodes and encodes the data. To prevent loss of data, the
application must be able process the information about internal flow control (MSC) regulated
by the module. Flow control information is transmitted within the data flow and contains
messages whether or not the channel is allowed to send. See chapter 4.3.9 for MSC.
As of Multiplexer Protocol version 2, the customer application must set RTS (in the direction
to the module) on channel 1. RTS shall not be switched off to prevent loss of data (control
data cannot be sent in this case). If flow control is needed, it is recommended to use logical
flow control on every channel.
Mux_guide_v06 Page 14 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 15

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
RTS/CTS on the logical channels
The customer application needs to regulate the data flow according to the logical flow
control. The implementation of the WinMux2k is a good example. It maps the 3 decoded
channels to 3 serial interfaces as well as the logical flow control information (FC-BIT in MSC
message) directly on the RTS/CTS-control lines.
In this case CTS superposes the STOP information (data sending disabled) sent by the
module to control the data transmission from the customer application to the module. If RTS
is reset, a STOP is transmitted to the module to control the data transmission from the
module to the customer application. Figure 2 illustrates the data flow.
COM M
COM N
COM P
RTS/CTS
RTS/CTS
RTS/CTS
TE
Customer application
(WinMux2k)
Figure 2: Logical flow control and RTS/CTS signaling behind the decoder
Controller
(maps RTS/CTS of
the unframed
channels to log. FC)
Multiplexer
Protocol
GSM 07.10
Flow control between the applications
ser
IO
HW flow control
logical flow control (FC)
ser
IO
MS
Module
Multiplexer
Protocol
GSM 07.10
CSD
Channel 1:
RTS/CTS
Channel 2,3:
RTS
(/CTS)
AT
Interface
RING/DCD
Unlike all other lines DCD and RING are transmitted additionally on the UART directly by the
module. These signals are logical ORs from the three logical channel status lines. However,
the customer application must carefully decide how to handle these lines and ensure, that no
conflicts occur between the different channels. E.g. in some situations it may be advisable to
display RING on channel 1 only.
Please keep in mind that a call can be accepted on one channel only. Therefore some kind
of mutual locking mechanism must be used.
Mux_guide_v06 Page 15 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 16

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
3.2.2 Escape sequence
When the multiplexer protocol is active only coded data is transmitted over the UART. The
coding includes a header and a checksum. Therefore, the direct parsing of this sequence is
not possible. An escape might be undetected because the decoded time relations may be
disturbed.
The following transmission path for the ESC signal has been implemented:
• DTR is transported within the logical channel. To terminate a call, the normal way of
using DTR is available. Please keep in mind that the multiplexer cannot transport this
signal in real time. Please use a certain gap time between signaling with DTR.
• It is possible to detect “+++” on the customer multiplex application and transport this
information via the MSC signal to the module (see Chapter 4.3.9).
• As an alternative, ATH may be sent on one of the other channels, for more detailed
information please refer to [2].
3.3 Power saving
SLEEP mode reduces the functionality of the module to a minimum and, thus, minimizes the
current consumption to the lowest level. SLEEP mode can be set with the AT+CFUN
command which provides the choice of the functionality levels <fun>=0, 1, 5, 6, 7 or 8. For
further details on power saving see [1] and [2].
If the module is in multiplexer mode, it is not recommended to activate SLEEP mode with
AT+CFUN=<n>. For products supporting Multiplexer Protocol version 3, the best approach to
properly control SLEEP mode in this case is to issue the PSC messages described in
Chapter 4.3.10.
3.4 Bandwidth of logical channels
Please take into account that a data transmission, e.g. on channel 1, causes a transmission
delay on the remaining channels (see chapter 3.1). The multiplexer mode according to the
GSM 07.10 multiplexer protocol encapsulates data and AT commands into packets which
may vary in length. Therefore a header including protocol information located at the
beginning of the protocol data unit has to be transmitted. To summarize, if the module is set
to 115200 bps and an incoming GPRS call requires 5 kByte per second, the two other
channels have to operate within the range of the remaining 5 kByte per second.
If three large data transmissions are running simultaneously, the available bandwidth will be
shared equally among all channels. In such a case if channel 2 and 3 were used for data
transmissions, e.g. editing the phonebook, both channels would need to share a bandwidth
of approximately 3 kByte per second.
Mux_guide_v06 Page 16 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 17

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
4 Structure of the multiplexer protocol
4.1 Introduction of the multiplexer protocol
The supported multiplexer protocol conforms to the GSM 07.10 Multiplexer Protocol. The
non-error recovery mode was implemented with the basic option.
The frames have a start and a stop byte. A checksum is calculated to protect the transferred
data. Frame repetition is not enabled.
Data and fax calls are transferred in the logical channel DLCI = 1 (DLCI: Data Link
Connection Identifier). The remaining DLCIs are in AT command mode; two GPRS
connections can be established simultaneously on every channel.
The multiplexer protocol must be started and the logical channels opened in compliance with
specified procedures.
This chapter also discusses the following issues:
• Opening logical channels without parameter negotiation
• Opening logical channels with parameter negotiation
• Closing of logical channels
4.2 Data link layer
The following sections
Flag
1 Octet
Address
1 Octet
show the detailed structure of
a data link frame.
Figure 3: Data link layer
Control
1 Octet
EA C/R
DLCI: Data Link Connection Identifier
C/R: Command / Response
EA: extension bit; EA = 1
Length
1 or 2 Octets
Frame type:
SABM Set Asynchronous Balanced Mode
UA Unnumbered Acknowledgement
DM Disconnected Mode
DISC Disconnect
UIH Unnumbered Information with Header check
UI Unnumbered Information
P/F-Bit Poll- /Final - Bit
Information
n Octets
Length: Length Information
EA: extension bit;
EA = 1 -> 1 octet length information
EA = 0 -> >2 octets length information
DLCI
FCS
1 Octet
LengthEA
Flag
1 Octet
0xF9
Checksum for address,
control and length
fields, also for the
information field in the
case of UI frames FCS.
0xF9
Mux_guide_v06 Page 17 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 18

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
4.2.1 Flag sequence
A flag sequence is a specific bit pattern (usually 11111001; hexadecimal: 0xF9) used to mark
the beginning and the end of a frame of data.
Each frame begins and ends with a flag sequence. Only one flag sequence occurs between
any two frames. If two successive flag sequences do occur, the frame is regarded as being
empty and is discarded.
The flag sequence is used for the synchronization of frames.
4.2.2 Address field
Data link connection identifier is a frame relay term defining a 10-bit field of the address field.
The DLCI identifies the data link and its service parameters, including the frame size.
The values for the Data Link Connection Identifier (DLCI) are dynamically defined apart from
DLCI = 0.
Table 2: Address field
EA C/R
DLCI
DLCI: Data Link Connection Identifier
C/R: Command / Response
EA: extension bit; EA = 1
Table 3: Assignment of the DLCI
DLCI number (decimal) Priority
Multiplexer control channel
(see chapter 4.3.6)
AT commands, data, fax, GPRS
AT commands, GPRS
0
1
2,3
0
highest priority
7
7
The command/response bit identifies the frame as a command or response. A command
contains the address of the data link connection to which the command is sent. A response
contains the address of the data link connection sending the frame.
Table 4: Use of the command/response bit
Command/Response Direction C/R
Command
(SABM, DISC)
Customer µC → GSM engine
GSM engine → Customer µC
1
0
Response
(UA, DM)
Customer µC → GSM engine
GSM engine → Customer µC
0
1
Every command expects a response. No provision is made to repeat the command if no
response is received.
Mux_guide_v06 Page 18 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 19

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
4.2.3 Control field
The control field contains control information to define the frame.
Table 5: Coding of the control field
Frame Type 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
SABM
(set asynchronous
balanced mode)
UA
(unnumbered
acknowledgement)
DM
(disconnected mode)
DISC
(disconnect)
UIH
(unnumbered information
with header check)
1 1 1 1 P/F 1 0 0
1 1 0 0 P/F 1 1 0
1 1 1 1 P/F 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 P/F 0 1 0
1 1 1 1 P/F 1 1 1
P/F: Poll/Final bit
Commands: P = 1, Responses: F = 1
For each DLCI, only one frame with P = 1 may ever be expected.
Mux_guide_v06 Page 19 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 20

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
4.2.4 Length indicator
The length indicator specifies the length of the following information field. As the maximum
frame size N1 is 98 bytes and cannot be changed the E/A bit is always 1. The setting E/A = 0
defined in GSM 07.10 for a frame size greater than 127 bytes is not supported. See also
Chapter 3.1.2 for details on the maximum frame size.
st
1
octet:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
E/A L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 L7
nd
2
octet (not supported by Siemens wireless modules):
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
L8 L9 L10 L11 L12 L13 L14 L15
E/A = 1: only one octet for the Length Indicator
E/A = 0: two octets for the Length Indicator
4.2.5 Information field
The information field contains the data and has an octet structure. The field only exists for
UIH frames (unnumbered information with header check).
To transfer information fields, the P/F bit is set to 0; a response is not necessarily expected.
4.2.6 Frame checking sequence field (FCS)
The Frame Checking Sequence (FCS) is computed with the address, control and length
fields. It is a field added to the end of a frame that contains transmission error-checking
information. This field contains a value which is calculated by the source computer. The
receiving computer performs the same calculation. If the receiving computer’s calculation
does not match the result sent by the source computer, the packet is judged corrupt and
discarded. An FCS calculation is made for each packet.
Mux_guide_v06 Page 20 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 21

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
4.3 State diagrams
The multiplexer protocol is based on two state machines (see Figure 4). One state machine
initiates the setup of the logical channels, the other one responds to the requests.
The GSM engine can only respond to requests. A higher level for controlling the state
machines is not implemented.
The procedure for setting up the two state machines – the one for the customer µC and the
one for the GSM engine – is shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6.
Executing the AT command AT+CMUX=0 starts the switchover from AT command mode to
the multiplexer protocol and parameterizes the multiplexer control channel DLCI = 0. Both
state machines are entering the DISCONNECTED state and immediately have the option of
setting up the multiplexer control channel DLCI = 0 and other logical channels.
The logical channels are then set up (DLC establishment). If the DLC has been established
successfully the state machine for that particular channel changes to CONNECTED. If the
request is unsuccessful the logical channel cannot be established and the state machine
remains in DISCONNECTED on this particular channel.
Information can be transferred over all channels in CONNECTED. Control commands can be
transferred in the multiplexer control channel DLCI = 0; the other channels transfer data.
The parameters for all logical channels DLCI = 1...4 in DISCONNECTED can be set for the
requested logical channels by parameter negotiation.
Disconnecting individual channels (DLC release) causes the state machine for those
channels to revert to DISCONNECTED. Release of the multiplexer control channel DLCI = 0
corresponds to a CLOSE DOWN. The CLOSE DOWN command switches back.
Mux_guide_v06 Page 21 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 22

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
Master state machine
Customer µC
s
mo b i l e
GSM engine µC
Slave state machine
DLC Release
DLC Establishment
Inform atio n
Transfer
CLOSED-
DOWN
Start Up
DIS-
CONNECTED
CONNECTED
Close Down
DLC
parameter
negotiation
CLOSED-
DOWN
Close Down
Start Up
DIS-
CONNECTED-
NEGOTIATION
Close Down
DLC Release
DLC Establishment
Inform ation
Transfer
DIS-
CONNECTED
CONNECTED
Figure 4: Relationship between the customer µC and the GSM engine µC
Close Down
DLC
parameter
negotiation
Close Down
DIS-
CONNECTED-
NEGOTIATION
Close Down
Mux_guide_v06 Page 22 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 23

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
Serial
interface
Customer
µC
Closed Down Closed Down
RequestStartUp
Conf irmSt artUp
RequestSABM
Conf irmDM
RequestSABM
IndicationStartUp
ResponseStartUp
IndicationSABM
ResponseDM
IndicationSABM
GSM engine
µC
DisconnectedDisconnected
DisconnectedDisconnected
Start Up
"AT+CMUX"
DLC not created
DLC Establishment,
Conf irmUA
Connected
RequestUIH
IndicationUIH
ResponseUA
Connected
Indicati onUIH
ConnectedConnected
RequestUIH
ConnectedConnected
Figure 5: MPI – Startup, DLC establishment and information transfer
DLC created
DLC Establishment,
Transfer
Information
Mux_guide_v06 Page 23 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 24

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
Customer µC GSM engine µC
Connected Connected
s
mo b i l e
Serial interface
Disconnected/
Disconnected
Negotiation/
Connected
RequestDISC
Conf irmUA
RequestCloseDown
ConfirmCloseDown
IndicationDISC
Respons eUA
DLC Release
DisconnectedDisconnected
Disconnected/
Disconnected
Negotiati on/
Connected
IndicationCloseDown
ResponseCloseDown
Close Down
Closed Down
Closed Down
Figure 6: MP - DLC release and close down
Mux_guide_v06 Page 24 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 25

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
4.3.1 Start-up procedure
The only approach to activate the multiplexer protocol is entering the appropriate AT
command AT+CMUX=0. This enables the multiplexer control channel. The next step is to set
up the multiplexer control channel as described in Chapter 4.3.2.
4.3.2 DLC establishment
The multiplexer control channel must be set up as the first channel followed by all other
DLCIs. To do so, a SABM frame (see Chapter 4.2.3) must be sent to the GSM engine.
The module responds either with a UA frame if the DLCI was set up, or with a DM frame if
the DLCI was not set up.
No provision is made for repeating the request if a response is not received.
The state machine requesting the multiplexer control channel DLCI = 0 is the "initiating
station", while the other is called the "responding station".
SABM: P = 1
Address Field = DLCI of channel to be established
Customer
µC
UA: F = 1, DLCI is being established
DM: F = 1, not ready, DLCI is not established
Address Field = DLCI of requested channel
Figure 7: DLC establishment
GSM
engine
4.3.3 Information transfer
A response is not essential for every command – for example, an unsolicited result code
does not require a response.
UIH: P = 0, C/R = 1
Customer
GSM engine
µC
(Responder)
(Initiator)
UIH: P = 0, C/R = 0
Figure 8: Information transfer
Mux_guide_v06 Page 25 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 26

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
4.3.4 DLC release
No provision is made to repeat the request if no response is received.
DISC: P = 1
Customer
s
mo b i l e
GSM
µC
UA: F = 1
DM: F = 1 responding station is
already disconnected
Figure 9: DLC release
engine
4.3.5 Close-down procedure
To close down the multiplexer follow these two steps:
• First, disconnect all DLCIs by sending the DLCI Release command within the multiplexer
control channel frame (as described in section 4.3.6).
• Finally, close down the multiplexer control channel (DLCI = 0) by sending the multiplexer
close down command CLD (see section 4.3.7). After this, both the “initiating station” and
the “responding station” revert to AT command mode.
Before closing the multiplexer make sure that there is no ongoing activity on one of the
channels. For example, check that voice, CSD or GPRS connections have ended and wait
until all pending AT command responses are received.
4.3.6 Multiplexer control channel
DLCI = 0
Type
1 Octet
The commands are sent as information in the multiplexer control channel frame.
Type field:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
EA C/R T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6
EA bit: Extension bit.
In the last octet of the sequence the EA bit = 1, otherwise = 0.
If there is only on octet, EA bit = 1 is set.
C/R bit: Indicates whether the sequence is a command or a response.
T-bits: Coding of the command type.
Length
n Octets
Value 1
1 Octet
Value 2
1 Octet
Information Field
Figure 10: Multiplexer control channel
.....
Value n
1 Octet
Mux_guide_v06 Page 26 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 27

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
Length field:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
EA L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 L7
EA bit: Extension bit.
In the last octet of the sequence the EA bit = 1, otherwise = 0.
If there is only one octet, EA bit = 1 is set.
L-bits: Number of value octets; the following L1 is the LSB, L7 the MSB.
Multiple commands can be sent in a single frame only.
s
mo b i l e
4.3.7 Multiplexer close down (CLD)
Type field:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
1 C/R 0 0 0 0 1 1
Length byte = 0, no value octet
4.3.8 Test command (Test)
The test command is intended to test the connection between MS and TE.
Type field:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
1 C/R 0 0 0 1 0 0
The length byte indicates the number of test bytes sent in the value bytes. The responding
station should answer with exactly the same bit sequence. The test command is used for the
version control. For more detailed information see Chapter 5.
Mux_guide_v06 Page 27 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 28

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
4.3.9 Modem status command (MSC)
The Modem Status Command is used for software flow control.
Command
1 octet
Command:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
1 C/R 0 0 0 1 1 1
C/R bit: Indicates whether the sequence is a command or a response.
Length: Length = 2 , EA-Bit = 1
DLCI:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
Length
1 octet
DLCI
1 octet
Figure 11: Modem status command (MSC)
V.24 signals
1 octet
Break Signals
(optional)
1 octet
1 1 DLCI
V.24 signals:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
1 FC RTC RTR reserved 0 reserved 0 RING DCD
FC bit: Flow control, included in all multiplexer versions
FC = 1: no frames are accepted
The following bits for V24 status lines as described in this chapter are included in multiplexer
protocol version 3 only. However, if you wish to use the advantages of this version it is
absolutely necessary to switch on the version 3, otherwise version 1 will be used, see
Chapter 5.2.
Direction host application" module (for request only) MUX V3:
RTC: mapped to DTR
RTR: mapped to RTS
Bit 5, 6, 7, 8 are not valid.
Direction module " host application (for request only) MUX V3:
RTC: mapped to DSR
RTR: mapped to CTS
RING: mapped to RING
DCD: mapped to DCD
Bit 5, 6 are not valid
Mux_guide_v06 Page 28 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 29

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
Note:
The mappings are valid for version 3 and an MSC request only. Descriptions of all other
versions are available in Chapter 5.
The response to any MSC must be always the same data already sent.
Please keep in mind that it is impossible to remap any response bits.
Remember that the bits described above are valid in Mux version 3 only, switched on by a
version control handshake (see Chapter 5). More detailed information on older multiplexer
versions are available in Chapter 5.2.
Break signal (optional):
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
1 Not supported
Usually the break signal octet carries information about a break condition detected from the
host application in the data stream for the DLC.
Note:
This command supports no parameters. Instead we use this optional parameter to transport
the escape sequence detection from the host to the module. If the customer application
detects an escape sequence (usually +++), it sends this optional octet with bit 1 set to 1. The
module calls its original escape sequence.
s
mo b i l e
Mux_guide_v06 Page 29 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 30

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
4.3.10 Power saving control (PSC)
The power saving control message uses the following type field octet:
Type:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
1 C/R 0 0 0 0 1 0
C/R bit: Indicates whether the sequence is a command or a response.
Length: The length byte contains the value 0 (no value octet) or 1 (one value octet).
Value octet (Length=1)
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
P1 P2 P3 P4 0 0 0 0
The P-bits are defining the parameter value.
In commands:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Description
0 0 0 0 Switches to the same mode as without a
1 0 0 0 Switches into full functionality mode, like
0 1 0 0 Switches into NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode,
1 1 0 0 Switches into CYCLIC SLEEP mode, like
0 0 1 0 Switches into CYCLIC SLEEP mode, like
1 0 1 0 Switches off, like AT^SMSO
Figure 12: Power Saving Control (PSC)
value octet
AT+CFUN=1
like AT+CFUN=0
AT+CFUN=5
AT+CFUN=6
0 1 1 0 Resets, like AT+CFUN=1,1
1 1 1 0 Switches into CYCLIC SLEEP mode, like
AT+CFUN=7
0 0 0 1 Switches into CYCLIC SLEEP mode, like
AT+CFUN=8
All wake up events and details of the CYCLIC and NON-CYCLIC SLEEP mode are specified
in [2].
In responses:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Description
0 0 0 0 Failure
1 0 0 0 Success
Mux_guide_v06 Page 30 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 31

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
No Value octet (Length=0)
Switches into SLEEP mode, like AT+CFUN=0
Note:
According to the GSM 07.10 standard PSC supports no value octets. The optional value
octet was added to increase flexibility.
Developed as a substitute to the AT+CFUN command, PSC messages are recommended to
control the various SLEEP modes and to reset the mobile. Be sure not to enter any PSC
messages until after all responses to AT commands have been received and, in the case of
a received URC, the logical ring line has been activated for 1 second and deactivated again.
Please note that the behavior of the logical ring line is identical with the behavior of the
physical RING0 line described in [1].
s
mo b i l e
4.3.11 Non-supported command response (NSC)
This response is sent whenever a command type is not supported by the receiving entity.
Type field:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
1 C/R 0 0 1 0 0 0
C/R bit: Indicates whether the sequence is a command or a response.
Value octet:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
EA C/R Command type of the non-supported command
C/R bit: Returns the same value as in the received, non-supported command
Frames not recognized by the receiving entity are responded by a NSC-frame.
Mux_guide_v06 Page 31 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 32

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
4.4 Example: Establishing logical channels without parameter
negotiation
• Send AT+CMUX=0; wait for the response
• Send Request SABM for DLCI = 0; wait for the response
• Send Request SABM for all requested DLCIs; wait for the response
As a result the multiplexer is established and information / data can be transmitted
(⇒ ready for Information Transfer).
Serial
interface
Customer
µC
Closed Down Closed Down
Disconnected
DLCI = 0
Connected
DLCI = 0
RequestStartUp
ConfirmStartUp
RequestSABM
DLCI = 0
ConfirmUA
DLCI = 0
IndicationStartUp
ResponseStartUp
IndicationSABM
DLCI = 0
ResponseUA
DLCI = 0
GSM engine µC
DisconnectedDisconnected
Disconnected
DLCI = 0
Connected
DLCI = 0
Start Up
"AT+CMUX"
Create DLCI = 0
DLC Establishment,
Disconnected
DLCI = 1
Connected
DLCI = 1
RequestSABM
DLCI = 1
ConfirmUA
DLCI = 1
IndicationSABM
DLCI = 1
ResponseUA
DLCI = 1
Disconnected
DLCI = 1
Connected
DLCI = 1
Create DLCI = 1
DLC Establishment,
Figure 13: Establishing the multiplexer control channel and the logical channel
Mux_guide_v06 Page 32 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 33

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
5 Multiplexer protocol version control
5.1 Introduction
The multiplexer protocol offers a version control to ensure that TE and MS support the same
extent of functionality and to maintain upward and downward compatibility when later
firmware versions of the GSM engines are released. The implementation of version control is
a subset of the GSM 07.10 standards.
When the multiplexer is started, the MS and the application negotiate which MP version to
use. If TE and MS do not support the same multiplexer protocol, the lower version will be
agreed upon. If no version check is done the TE reverts, due to lack of version information, to
multiplexer version 1. This means that both sides only agree on version 1, even though they
may have the same and even higher version.
The TE and MS multiplexer version numbers can be traced on the serial interface.
They appear as follows:
• TE version (e.g. version 1):
• MS version (e.g. version 2):
In multiplexer protocol sources delivered by Siemens AG version control is integrated. When
designing an application based on other sources take care to implement the version check
as well, especially if you wish to upgrade to later firmware releases. It is strongly
recommended to implement the latest multiplexer version available.
TEMUXVERSION0001
MSMUXVERSION0002
Mux_guide_v06 Page 33 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 34

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
5.2 Multiplexer protocol versions
This section summarizes the differences of the existing multiplexer protocol versions.
1. No version check
• No break signal is sent
2. First version including the version check
• Additional features: Transparent signals DTR and RTS, escape sequence +++
transportable via MSC
3. Advanced version integrated in all modules listed in Chapter 1.1
• All features of version 2
• Transparent signals DSR, CTS, RING and DCD
• Send MSC request from module to host after version check on every channel to
signal the initial state
Modem status command (MSC):
Command
1 octet
Command:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
1 C/R 0 0 0 1 1 1
Length
1 octet
DLCI
1 octet
V.24 signals
1 octet
Break Signals
(optional)
1 octet
Figure 14: MSC as used in version 3
Version specific differences in handling the modem status command MSC are explained in
Table 6.
V.24 signals:
Bit 1 Bit 2 Bit 3 Bit 4 Bit 5 Bit 6 Bit 7 Bit 8
1 FC RTC RTR reserved 0 reserved 0 RING DCD
Table 6: Version differences for MSC
Version
number
1 1 1
2 DTR RTS Not used
3 DTR RTS DSR CTS RING DCD
RTC RTR
Host application ⇒ Module
If 0 is indicated, all calls are terminated
RTC RTR RING DCD
Module ⇒ Host application
Not used
Mux_guide_v06 Page 34 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 35

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
5.3 Implementing version control
The TE initiates the version check by sending the Test command via the multiplexer control
channel DLCI 0 (with TEMUX_Version).
As specified in the GSM recommendation 07.10 (chapter 5.4.6.3.4) the opposite entity shall
respond with exactly the same value bytes.
The MS shall return the Test command response with the same contents for the verification
pattern. Hereafter the MS shall send a Test command message (with MSMUX_Version) to
the TE, and the TE shall respond with the same contents. After sending the response a
version compare is made on both sides. As a result, both sides shall agree upon the same
multiplexer protocol version.
5.3.1 Troubleshooting
When the MS realizes the implemented software but the TE does not respond correctly, the
following errors might occur:
• The “Request Test” message is not sent from the TE:
No version check takes place. No retransmission for “Request Test“ message is
triggered. The multiplexer starts with protocol version 1 because no version information
was exchanged between TE and MS.
• The “Response Test” message is not sent from the TE:
No timer has been implemented for the non responding cases. If the response message
is not received as expected, the multiplexer stays in the state
DLC_CONNECTEDWAIT4RESPONSE until another multiplexing related action takes
place.
However, it is possible to send test commands with “any contents” (except for test messages
with the specific IEI for the version check). If a test command with “any contents” is sent, it
has to be sent back to the originator with the same contents.
Mux_guide_v06 Page 35 of 36 30.06.2004
Page 36

Multiplexer User's Guide
Confidential / Released
s
mo b i l e
5.3.2 Coding of “TestCommand” message
The coding of the multiplexer stack version is used specifically for SIEMENS equipment and
is not defined in ETSI standards. The IEI values defined for the verification pattern of the
“TestCommand” message are indicated in Table 7. See GSM recommendation 07.10,
Section 5.4.6.3.4).
Table 7: IEI coding
IEI coding Information element name
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 TEMUX_VERSION
0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 MSMUX_VERSION
Other values reserved for future use
For easier analysis of multiplexer traces the message shall be sent in the following format:
(1.) Version IEI
(2.) TEMUXVERSION/MSMUXVERSION (send as ASCII)
(3.) Version Number (1...999 send as ASCII)
The message part after the Version IEI is coded with ASCII characters. This allows to read
the version information from the trace file.
The version number must have a value between 1-999. If not all digits of the version number
are used only the used digits are coded as ASCII sign(s). Digits that are not used are sent as
zero string in the test message.
5.3.3 Example of “TestCommand” message
An example for coding a “TestCommand” message is illustrated in Table 8.
Table 8: Coding of “TestCommand” (Example)
Information element name
0x
F9 START Flag
Address Field DLCI=0,C/R=0,EA=0
03
Control Field UIH Frame, P/F=0
EF
Length LENGTH=18, EA=1
25
Type Field TestCommand, C/R=1, EA=1
23
Length Length=16, EA=1
21
04 TEMUX_VERSION
54 T
45 E
4D M
55 U
58 X
56 V
45 E
52 R
53 S
49 I
4F O
4E N
Version number = 999
39
39
39
FCS (is calculated)
XX
F9 END Flag
Mux_guide_v06 Page 36 of 36 30.06.2004
 Loading...
Loading...