Page 1
SERVICE MANUAL
No. 00ZUXA255USME
FACSIMILE
UX-A255U
MODEL
SELECTION CODE DESTINATION
UX-A255U
Chapters 1, 2, 3, 7 and 8 of this manual are omitted because they are partly common to the UX-P100U.
Please refer to previous service manual (00ZUXP100USME) for these chapters.
CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
[1] Specifications ............................................ 1-1
[2] Operation panel......................................... 1-2
[3] Refer to the service manual of UX-P100U.
[4] Refer to the service manual of UX-P100U.
[5] Quick setup guide ..................................... 1-3
[6] Quick reference guide ............................... 1-4
[7] Option imaging film specifications
(UX-5CR) ............................................1-4
CHAPTER 2. ADJUSTMENTS
[1] Adjustments............................................... 2-1
[2] Diagnostics and service soft switch .......... 2-2
[3] Refer to the service manual of UX-P100U.
[4] Refer to the service manual of UX-P100U.
CHAPTER 5. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
[1] Circuit description...................................... 5-1
[2] Circuit description of control PWB..............5-2
[3] Circuit description of TEL/LIU PWB ........ 5-10
[4] Circuit description of
power supply PWB............................5-13
[5] Circuit description of CIS unit...................5-13
CHAPTER 6. CIRCUIT SCHEMATICS AND
P ARTS LAYOUT
[1] Control PWB circuit ................................... 6-1
[2] TEL/LIU PWB circuit ................................. 6-9
[3] Power supply PWB circuit ...................... 6-14
[4] Operation panel PWB circuit ................... 6-16
[5] Interface PWB circuit............................... 6-18
UX-A255
U.S.A.
CHAPTER 3. MECHANISM BLOCKS
[1] Refer to the service manual of UX-P100U.
[2] Refer to the service manual of UX-P100U.
CHAPTER 4. DIAGRAMS
[1] Block diagram ............................................4-1
[2] Wiring diagram .......................................... 4-2
[3] Point-to-point diagram............................... 4-3
Parts marked with " " are important for maintaining the safety of the set. Be sure to replace these parts with specified ones for
maintaining the safety and performance of the set.
SHARP CORPORATION
CHAPTER 7. OPERATION FLOWCHART
[1] Refer to the service manual of UX-P100U.
[2] Refer to the service manual of UX-P100U.
CHAPTER 8. OTHERS
[1] Refer to the service manual of UX-P100U.
[2] Refer to the service manual of UX-P100U.
[3] Refer to the service manual of UX-P100U.
P ARTS GUIDE
This document has been published to be used
for after sales service only.
The contents are subject to change without notice.
Page 2
UX-A255U
CAUTION FOR BATTERY REPLACEMENT
(Danish) ADVARSEL !
Lithiumbatteri-Eksplosionsfare ved fejlagtig håndtering.
Udskiftning må kun ske med batteri af samme fabrikat og type.
Levér det brugte batteri tilbage til leverandoren.
(English) Caution !
Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or equivalent type
recommended by the equipment manufacturer.
Discard used batteries according to manufacturer’s
instructions.
(Finnish) VAROITUS
Paristo voi räjähtää, jos se on virheellisesti asennettu.
Vaihda paristo ainoastaan laitevalmistajan suosittelemaan
tyyppiin. Hävitä käytetty paristo valmistajan ohjeiden
mukaisesti.
(French) ATTENTION
Il y a danger d’explosion s’ il y a remplacement incorrect
de la batterie. Remplacer uniquement avec une batterie du
même type ou d’un type recommandé par le constructeur.
Mettre au rébut les batteries usagées conformément aux
instructions du fabricant.
(Swedish) VARNING
Explosionsfare vid felaktigt batteribyte.
Använd samma batterityp eller en ekvivalent
typ som rekommenderas av apparattillverkaren.
Kassera använt batteri enligt fabrikantens
instruktion.
(German) Achtung
Explosionsgefahr bei Verwendung inkorrekter Batterien.
Als Ersatzbatterien dürfen nur Batterien vom gleichen Typ oder
vom Hersteller empfohlene Batterien verwendet werden.
Entsorgung der gebrauchten Batterien nur nach den vom
Hersteller angegebenen Anweisungen.
Page 3

CHAPTER 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
[1] Specifications
UX-A255U
Automatic dialing: 30 numbers
Imaging film: Initial starter roll: (included with
machine): 32 ft. (10 m) (approx. 30
letter-size pages)
Replacement roll (not included):
UX-5CR 164 ft. (50 m) roll (one roll
yields approx. 150 letter-size pages)
Memory size* : 504 KB (approx. 30 average pages
with no voice messages recorded and
ECM turned off, or 20 minutes of voice
documents in memory)
Modem speed: 14,400 bps with automatic fallback to
lower speed
Transmission time* : Approx. 6 seconds
(only when ECM is on)
Resolution: Horizontal:
203 pels/inch (8 dots/mm)
Vertical:
Standard: 98 lines/inch
(3.85 lines/mm)
Fine/Halftone: 196 lines/inch
(7.7 lines/mm)
Super fine: 391 lines/inch
(15.4 lines/mm)
Automatic document feeder: 10 pages max. (letter/A4, 20 lb paper)
Recording system: Thermal transfer recording
Halftone (grayscale): 64 levels
Compression scheme: MH, MR, MMR
Display: 16-digit LCD display
Applicable telephone line: Public switched telephone network
Paper tray capacity: Letter: Approx. 50 sheets (20-lb. copier
paper at room temperature; maximum
stack height should not be higher than
the line on the tray)
Legal: 5 sheets
Recommended paper weight is 20-lb.
Copy Bond
Compatibility: ITU-T (CCITT) G3 mode
Input document size: Automatic feeding:
Width: 5.8 to 8.5"
(148 to 216 mm)
Length: 5.5 to 11"
(140 to 279 mm)
Manual feeding:
Width: 5.8 to 8.5"
(148 to 216 mm)
Length: 5.5 to 23.6"
(140 to 600 mm)
Effective scanning width: 8.3" (210 mm) max.
Effective printing width: 8.3" (210 mm) max.
Contrast control: Automatic/Dark selectable
Reception modes: TEL/FAX/TAD
Copy function: Single/Multi (99 copies/page)
Telephone function: Yes
(cannot be used if power fails)
Power requirements: 120 V AC, 60 Hz
Operating temperature: 41 - 95°F (5 - 35°C)
Humidity: Maximum: 85 % RH
Power consumption: Stand-by: 3.6 W
Maximum: 100 W
Dimensions (without Width: 12.9" (327 mm)
attachments): Depth: 7.6" (193 mm)
Height: 6.4" (163 mm)
Weight (without Approx. 6.2 lbs. (2.8 kg)
attachments):
* Based on ITU-T (CCITT) Test Chart #1 at standard resolution in Sharp
special mode, excluding time for protocol signals (i.e., ITU-T phase
C time only).
As a part of our policy of continuous improvement, SHARP reserves the right to make design and specification changes for product
improvement without prior notice. The performance specifications figures indicated are nominal values of production units. There may be some
deviation from these values in individual units.
1 – 1
Page 4
UX-A255U
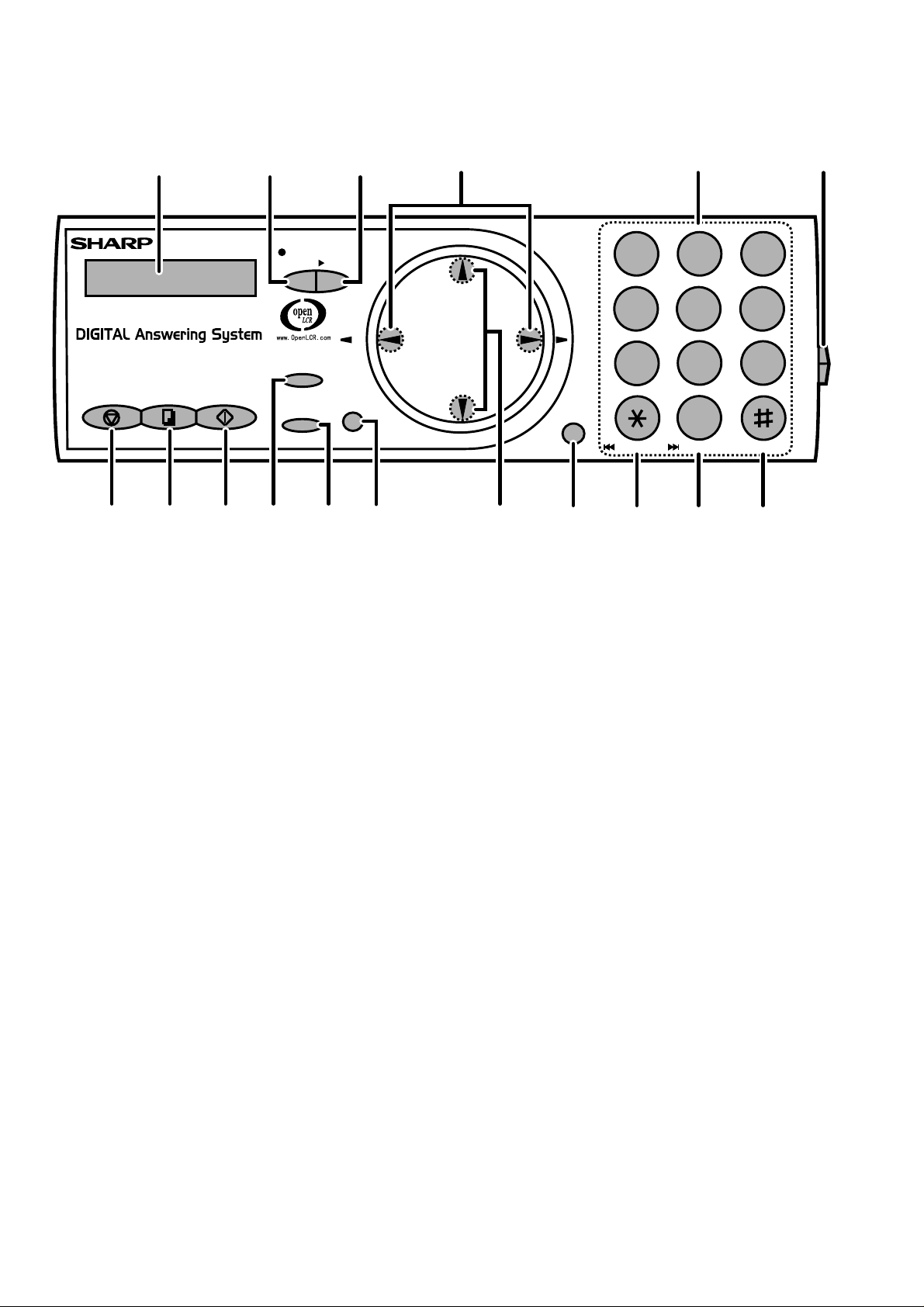
[2] Operation panel
1
STOP
1. Display
This displays messages and prompts to help you operate the
machine.
2. REC/MEMO key
Press this key to record an outgoing message, phone
conversation, or memo.
3. PLAY key
Press this key to play recorded messages.
4. Left and right arrow keys
Auto-dial numbers: When sending a fax or making a phone
call, press these keys to scroll through your auto-dial numbers,
the "REVIEW CALLS" list (only available if you have Caller
ID), and the last number dialed (redial).
FUNCTION key settings: Press the right arrow key after
scrolling with the up and down arrow keys to select a
FUNCTION key setting.
5. Number keys
Use these keys to dial numbers, and enter numbers and
letters when storing auto-dial numbers.
6. Panel release
Press this release to open the operation panel.
7. STOP key
Press this key to cancel operations before they are completed.
8. COPY/HELP key
When a document is in the feeder, press this key to make a
copy of a document. At any other time, press this key to print
out the Help List, a quick reference guide to the operation of
your fax machine.
9. START/MEMORY key
Press this key after dialing to begin fax transmission. Press
this key before dialing to send a fax through memory. The key
can also be pressed in the date and time display to show the
percentage of memory currently used.
7
COPY/HELP
START/MEMORY
8
2
TEL
9
FAX
TAD
REC/
MEMO
RESOLUTION/
RECEPTION MODE
FUNCTION
10 13
3
PLAY
Z A
REDIAL
OpenLCR
12
11
4
P
U
1
GHI
4
PQRS
7
SPEAKER
D
N
O
W
14
10. RESOLUTION / RECEPTION MODE key
When a document is in the feeder, press this key to adjust
the resolution for faxing or copying. At any other time, press
this key to select the reception mode (an arrow in the display
will point to the currently selected reception mode).
11. FUNCTION key
Press this key to followed by the arrow keys select special
functions and setting.
12. OpenLCR key
Press this key to register for OpenLCR service and receive
rate information to your fax.
13. UP and DOWN arrow keys
Enlarge/Reduce setting: When marking a copy of a
document, press these keys to select an enlarge/reduce
setting.
Volume setting: When a document is not in the feeder,
press these keys to change the handset volume when the
handset is lifted, the speaker volume when the SPEAKER
key has been pressed, or the ringer volume at any other time.
FUNCTION key setting: Press these keys after pressing the
FUNCTION key to scroll through the FUNCTION MODE
settings.
14. SPEAKER key
Press this key to listen to the line and fax tones through the
speaker when faxing a document.
Note: This is not a speakerphone. You must pick up the
handset to talk with the other party.
15. REPEAT key
Press this key while listening to a message to play it again.
16. SKIP key
Press this key while listening to a messgae to skip to the next
message.
17. DELETE key
Press this key to erase recorded messages.
REPEAT
15 16 17
5
ABC
2 3
JKL
5
TUV
8
0
SKIP
DEF
MNO
6
WXYZ
9
DELETE
6
1 – 2
Page 5
UX-A255U
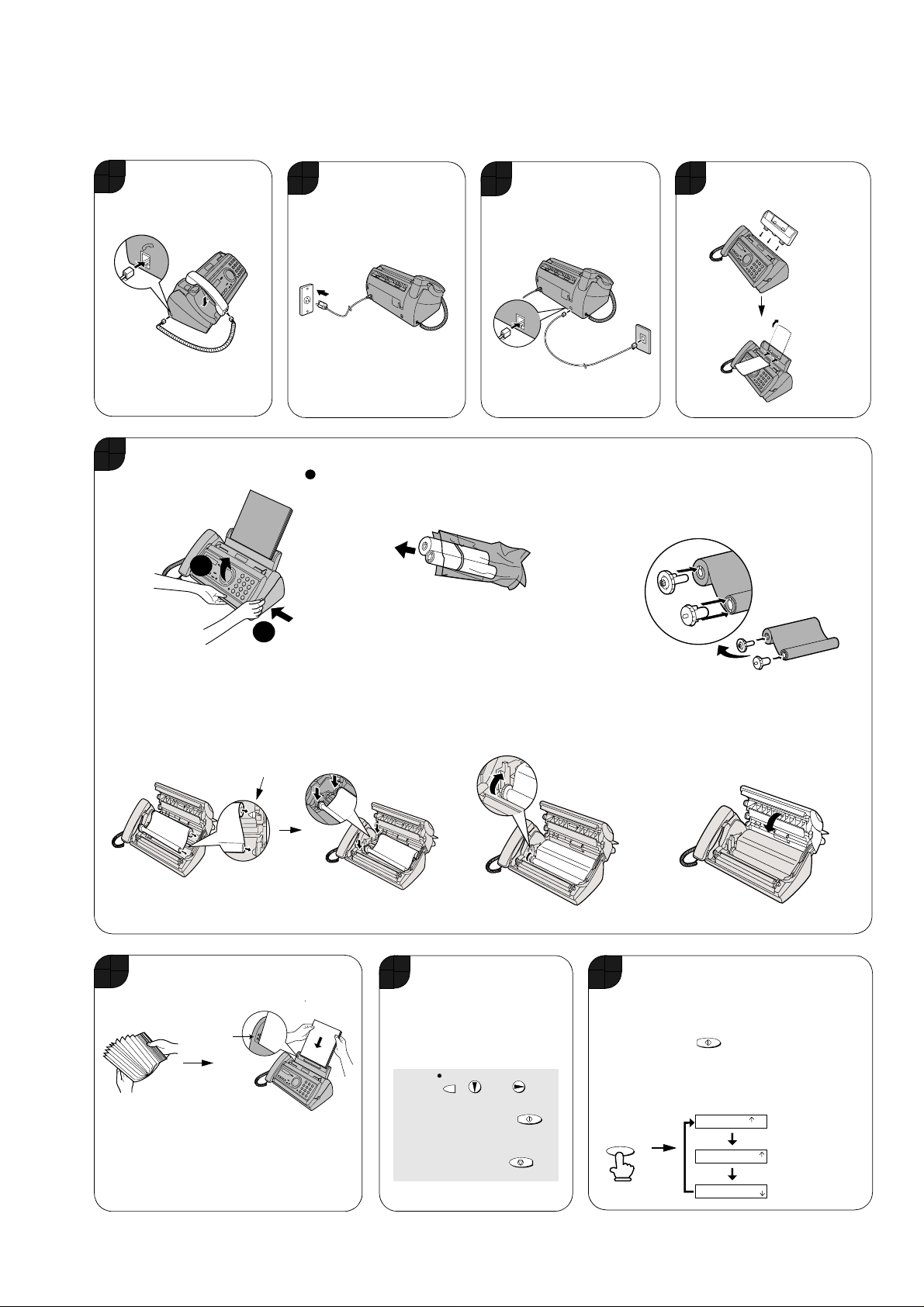
[5] Quick setup guide
Connect the handset
1
and place it on the
handset rest.
Load the imaging film.
5
1.Open the operation panel (press ).
Plug the power cord
2
into a 120 V grounded
outlet.
1
Note: To enter your name and fax number and set the date and time so that they
appear at the top of each fax you send, see pages 16 - 19 of your operation
manual.
Connect the telephone
3
line cord to the TEL.
LINE jack and a wall
telephone jack.
TEL
.
L
IN
E
2. Remove the imaging film from its packaging.
Cut the band that holds the rolls together.
Attach the paper tray
4
and document support.
3. Insert the green gears.
IMPORTANT: Do NOT discard the
green gears. They are not included
with replacement imaging film.
Note: If the
support does
not go in,
turn it over.
2
1
4. Insert the film into the print compartment.
Fit ends of
rolls onto hubs
Load paper.
6
The stack
should not
be higher
than this line.
• GENTLY LOAD PAPER INTO THE PAPER TRAY.
• DO NOT FORCE IT DOWN INTO THE FEED SLOT.
Note: If you loaded legal paper, see page 15 of the
operation manual to change the paper size setting
to LEGAL.
Insert the paper
print side down.
5. Rotate the front spool as shown
until the film is taut.
Record an outgoing message
7
(greeting) for TAD mode inviting
callers to leave a message.
(Note: "TAD" stands for
"Telephone Answering Device".)
REC/
1. Press , , and .
2. Lift the handset, press ,
MEMO
START/MEMORY
and speak into the handset.
3. When finished, press .
STOP
1 slot
Make sure
the gears fit
into the slots
in the ends of
the rolls.
2 slots
6. Close the operation panel (press
down on both sides to make sure it
clicks into place).
Select the reception mode for incoming faxes
8
and voice calls:
FAX mode: The machine automa tic ally
answers all calls and begins fax reception.
TEL mode: Lift the handset when the mach ine
rings. Press to begin fax reception.
START/MEMORY
TA D mode: Select this mode when you go out
to receive both voice messages and faxes.
(Note: To select TAD mode, you must first
record an outgoing message.)
TEL
FAX
TAD
The arrow in the
TEL
FAX
display points to
the selected
TAD
reception mode.
TEL
FAX
TAD
RESOLUTION/
RECEPTION MODE
JAN-01 10:30
JAN-01 10:30
JAN-01 10:30
1 – 3
Page 6
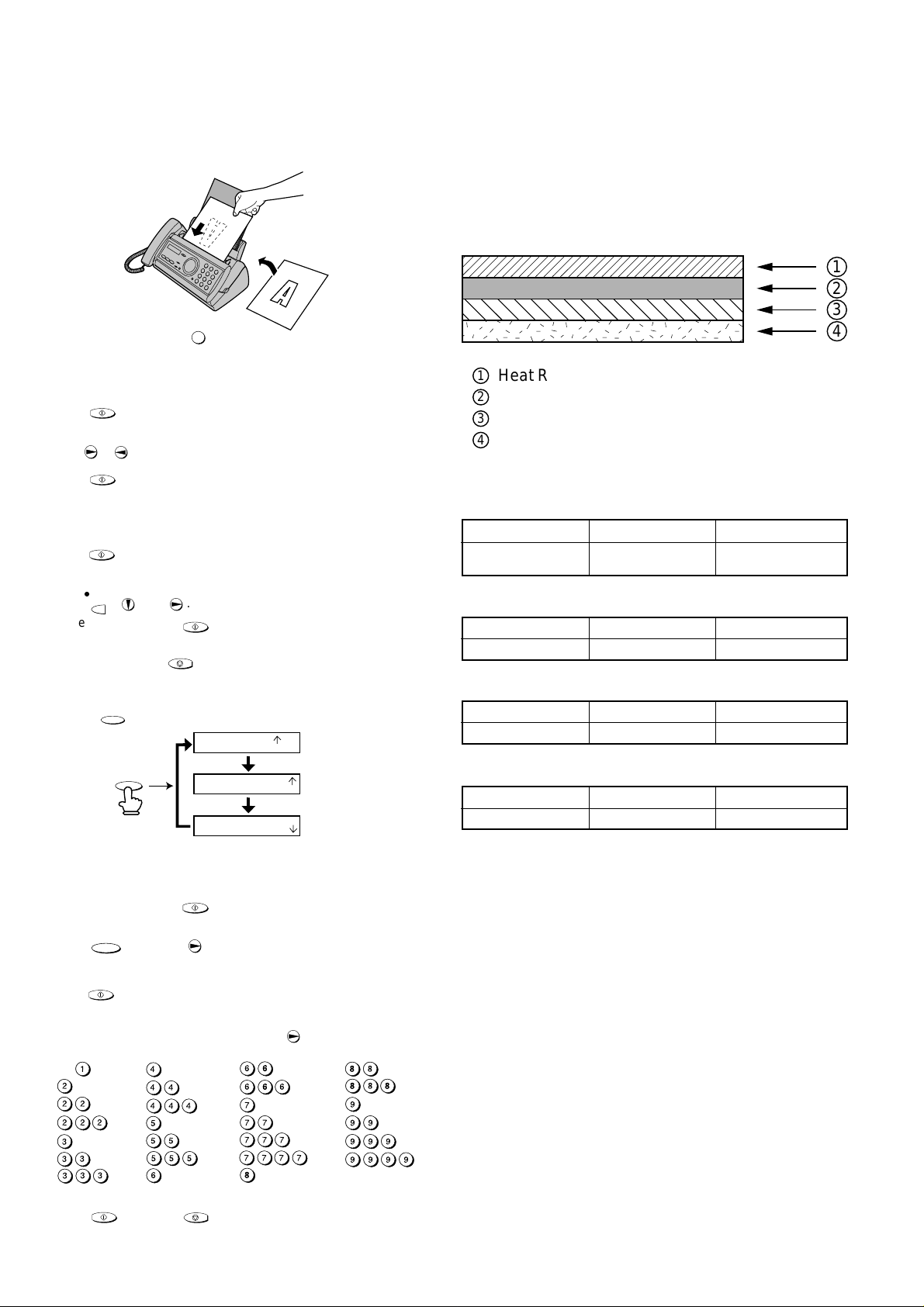
UX-A255U
SPEAKER
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
Heat Resistant Layer
Base Film
Matt Layer
Hot melt Ink Layer
[6] Quick reference guide
SENDING FAXES
Place your document (up to 10 pages) face down in the document feeder.
Normal Dialing
1. Lift the handset or press .
2. Dial the fax number.
3. Wait for the reception tone (if a person answers, ask them to press
their Start key).
4. Press .
Automatic Dialing
1. Press or until the desired destination appears in the display.
2. Press .
Direct Keypad Dialing
1. Dial the fax number.
2. Press .
RECORDING AN OUTGOING MESSAGE
1. Press , ,and .
2. Lift the handset, press ,and
3. When finished, press .
RECEIVING FAXES
Press the until the arrow in the display points to the desired
reception mode.
FAX mode: The fax machine automatically answers and receives the
incoming document.
TEL mode: Answer all calls (even faxes) by picking up the handset. To
begin fax reception, press .
STORING AUTO DIAL NUMBERS
1. Press once and twice.
2. Enter the full fax/phone number.
3. Press .
START/MEMORY
START/MEMORY
START/MEMORY
REC/
MEMO
speak into the handset.
RESOLUTION/
RECEPTION MODE
RESOLUTION/
RECEPTION MODE
FUNCTION
START/MEMORY
START/MEMORY
STOP
JAN-01 10:30
JAN-01 10:30
JAN-01 10:30
START/MEMORY
TEL
TEL
TEL
FAX
TAD
FAX
TAD
FAX
TAD
[7] Option imaging film specifications
(UX-5CR)
1. Structure
This article is composed of polyester film coated with heat-resistant layer,
matt layer and hot melt ink layer, leader film and paper core. Ink film
specification is "DNP standard ink film HC".
2. Details of compositions
2-1. Base film
Heading Requirements Measuring method
Material
Polyethylene terephthalate
2-2. Heat resistant layer
Heading Requirements Measuring method
Grade HR Mixer P-5 –
2-3. Matt layer
Heading Requirements Measuring method
Grade ML Sumi –
2-4. Hot melt ink layer
Heading Requirements Measuring method
Grade #507W –
–
4. Enter the name by pressing number keys. (To enter two letters in
succession that require the same key, press after entering the first
letter.)
SPACE =
A =
B =
C =
D =
E =
F =
5. Press and then .
G =
H =
I =
J =
K =
L =
M =
START/MEMORY
STOP
N =
O =
P =
Q =
R =
S =
T =
U =
V =
W =
X =
Y =
Z =
1 – 4
Page 7
UX-A255U
(step 1) Select "OPTION SETTING".
KEY : FUNCTION
DISPLAY: OPTION SETTING NUMBER OF RING
(step 2) Select "DIAL MODE".
KEY: Push until DIAL MODE is
indicated because the number of
's changes by the model.
DISPLAY: DIAL MODE 1=TONE, 2=PULSE
(step 3) Select, using "1" or "2".
KEY: 1
DISPLAY: TONE SELECTED
KEY: 2
DISPLAY: PULSE SELECTED
(step 4) End, using the "STOP" key.
KEY:
STOP
CHAPTER 2. ADJUSTMENTS
[1] Adjustments
General
Since the following adjustments and settings are provided for this model,
make adjustments and/or setup as necessary.
1. Adjustments of output voltage (FACTORY ONLY)
1. Install the power supply unit in the machine.
2. Set the recording paper and document.
3. When the document is loaded, power is supplied to the output lines.
Confirm that outputs are within the limits below.
Output voltage settings
POWER
SUPPLY
PWB
(BOTTOM SIDE)
CNPS
CNPW
CNPN
CNTH
CONTROL
PWB
(TOP SIDE)
Output Voltage limits
+5V 4.25V ~ 5.75V
+24V 23.3V ~ 24.7V
2. IC protectors replacement
ICPs (IC Protectors) are installed to protect the motor driver circuit.
ICPs protect various ICs and electronic circuits from an overcurrent condition.
The location of ICPs are shown below:
CNLIUA
FU100
CONTROL PWB
(BOTTOM SIDE)
(1)FU100 (KAB2402) is installed in order to protect IC’s from an over-
current generated in the motor drive circuit. If FU100 is open, replace it with a new one.
(BOTTOM SIDE)
CNLIUA
CNLIUA
CNPRG
CNMT
CNCSW
CNSP
Connector
Pin No.
1 +24V
2 +24V
3MG
4MG
5DG
6 Vreg(+5V)
CNPW
TEL/LIU PWB
CNCIS
No. CNPW
3. Settings
(1) Dial mode selector
DIAL mode (Soft Switch No. SW-B4 DATA No. 3)
4. Volume adjustment
Y ou can adjust the volume of the speaker , handset, and ringer using the
UP and DOWN arrow keys.
(1) Speaker
1. Press the SPEAKER key.
2. Press the UP or DOWN until the display shows the desired volume
level.
• Press SPEAKER key again to turn off the speaker.
(2) Handset
1. When talking through the handset, press UP or DOWN until the
display shows the desired volume level.
Display:
RECEIVER: HIGH
↔
RECEIVER: MIDDLE
↔
• Note: The volume reverts to
MIDDLE each time you
replace the handset.
RECEIVER: LOW
(3) Ringer
1. Press the UP or DOWN key. (Make sure SPEAKER key has not been
pressed, the handset is not lifted, and a document is not loaded in the
feeder.)
Display:
RINGER: HIGH
RINGER: MIDDLE
RINGER: LOW
RINGER OFF: OK?
2. If you selected RINGER OFF: OK?, press START/MEMORY key.
2 – 1
↔
↔
↔
• The ringer will ring once at the
selected level, then the date
and time will reappear in the
display.
Page 8
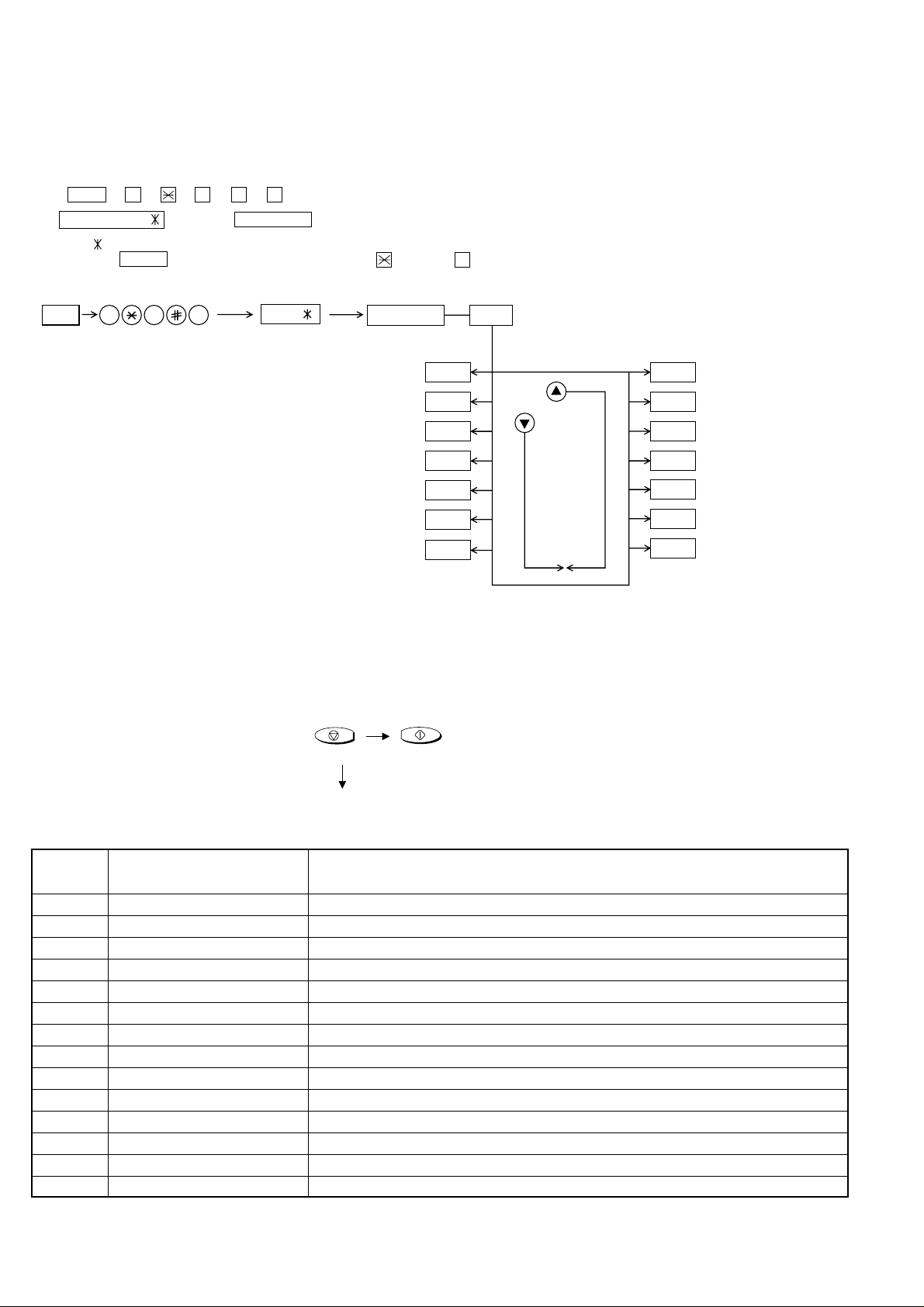
UX-A255U
[2] Diagnostics and service soft switch
1. Operating procedure
(1) Entering the diagnostic mode
Press FUNC → 9 → → 8 → # → 7 , and the following display will appear.
ROM Ver. TA18 After 2 sec: DIAG MODE
TA18
Then press the START key. Select the desired item with the key or the # key or select with the rapid key. Enter the mode with the START key.
(Diag•specifications)
FUNC
9 8 7
TA18
DIAG MODE
ROM & RAM check
Aging mode
Panel key test
Check pattern
If the diag mode cannot be set, repeat the diag mode operation, performing the following operation.
After the power is turned on and "WAIT A MOMENT" is indicated, press
the STOP key.
START
KEY
"Power ON"
STOP
KEY
+
Memory clear
(Work + Backup)
2. Diagnostic items
START
STARTSoft switch mode
START
START
START
START
STARTSignal send mode
STARTMemory clear
In relation with the process response (request from Production
Engineering) "WAIT A MOMENT" clock indication may appear depending
on STOP key timing. If the STOP key is held down, "MEMOR Y CLEAR?"
appears.
START
START
START
START
START
START
START
Flash memory clear
Flash memory check
Entry data receive
Entry data send
Auto feeder mode
All black print
Shading mode
ITEM No. Contents Function
1 SOFT SWITCH MODE Soft switches are displayed and changed. List can be output.
2 ROM & RAM CHECK ROM is sum-checked, and RAM is matched. Result list is output.
3 AGING MODE 10 sheets of check patterns are output every 5 minutes per sheet.
4 PANEL KEY TEST Panel keys are tested. Result list is output.
5 CHECK PATTERN Check pattern is output.
6 SIGNAL SEND MODE Various signals of FAX communication are output.
7 MEMORY CLEAR Back-up memory is cleared, and is set at delivery.
8 SHADING MODE Shading compensation is performed in this mode.
9 ALL BLACK PRINT To check the print head, whole dots are printed over the interval of 2 m.
10 AUTO FEEDER MODE Insertion and discharge of document are tested.
11 ENTRY DATA SEND Registered content is sent.
12 ENTRY DATA RECEIVE Registered content is received, and its list is output.
13 FLASH MEMORY CHECK Checks flash memory write/read.
14 FLASH MEMORY CLEAR Checks flash memory clearing.
2 – 2
Page 9
UX-A255U
3. Diagnostic items description
3. 1. Soft switch mode
Used to change the soft switch settings.
The soft switch which is stored internally is set by using the keys.
The available soft switches are SW-A1 to SW-N3.
The content of soft switches is shown in page 2-5 to 2-18.
The contents are set to factory default settings.
3. 2. ROM & RAM check
ROM executes the sum check, and RAM executes the matching test.
The result will be notified with the number of short sounds of the buzzer
as well as by printing the ROM & RAM check list.
Number of short sounds of buzzer 0 → No error
1 → ROM error
2 → RAM error (4 Kbyte SRAM or
512 Kbyte DRAM)
3. 3. Aging mode
If any document is present, copying will be executed sheet by sheet. If
no document is present, the check pattern will be printed sheet by sheet.
This operation will be executed at a rate of one sheet per 5minutes, and
will be ended at a total of 10 sheets.
3. 4. Panel key test
This mode is used to check whether each key operates properly. Press
the key on the operation panel, and the key will be displayed on the
display. Therefore, press all keys. At this time, finally press the STOP
key.
When the STOP key is pressed, the keys which are not judged as
"pressed" will be printed on the result list.
• LED part of the contact image sensor (CIS) is kept on during the term
from when "START" of the panel test mode to end with the ST OP key .
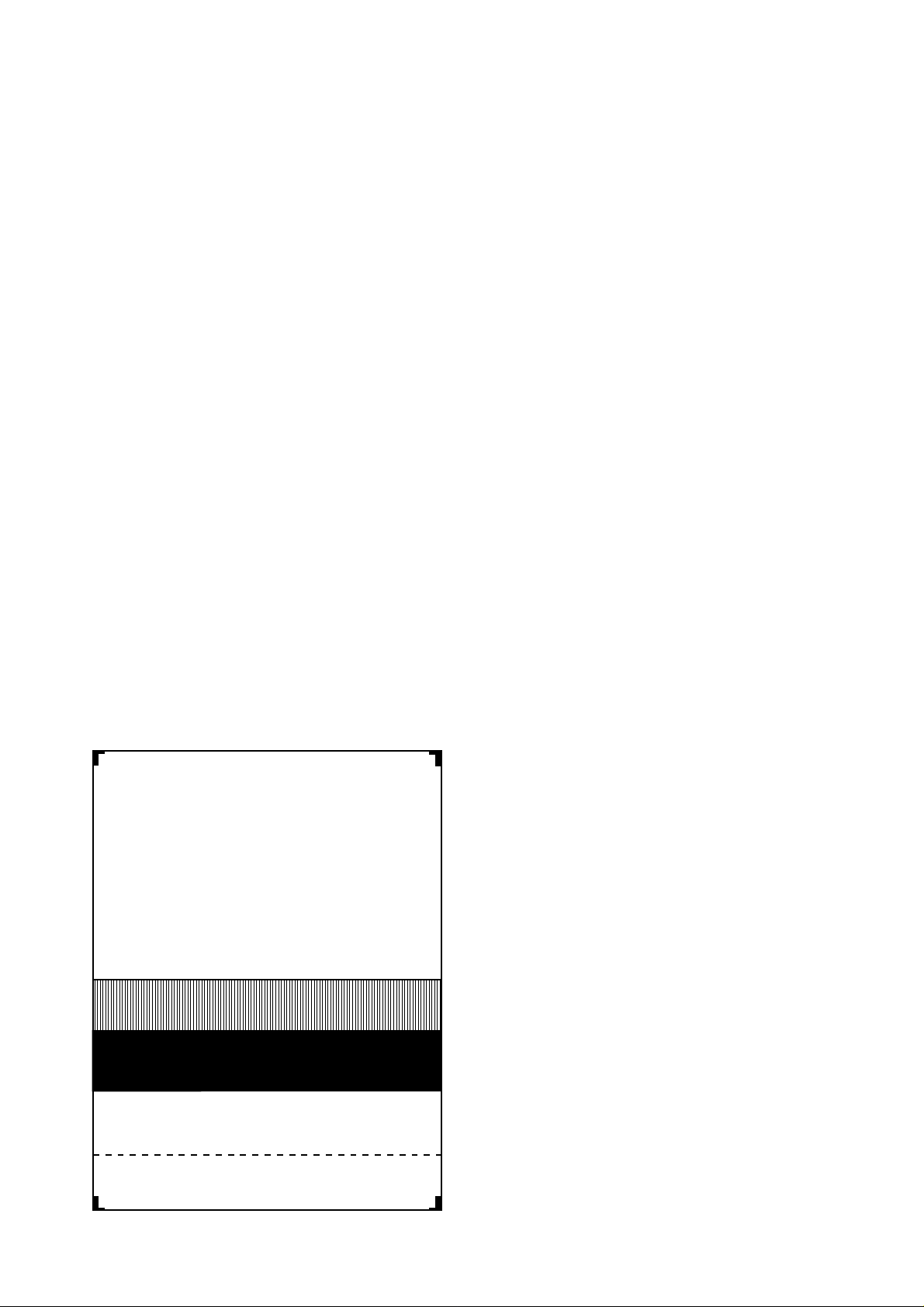
3. 5. Check pattern
This mode is used to check the state of the printing head. It is ended
with the following pattern printed on one printing sheet.
1
B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB
B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB
B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB
2
B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB
B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB
B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB
3
B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB
B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB
B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB
4
B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB
B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB
B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B B BB
1 DOT
2 DOTS
3 DOTS
4 DOTS
3. 6. Signal send mode
This mode is used to send various signals to the circuit during FAX communication. Every push of START key sends a signal in the following
sequence. Moreover, the signal sound is also output to the speaker when
the line monitor of the soft switch is on.
[1] No signals
[2] 144000BPS (V.33)
[3] 12000BPS (V.33)
[4] 144000BPS (V.17)
[5] 12000BPS (V.17)
[6] 9600BPS (V.17)
[7] 7200BPS (V.17)
[8] 9600BPS (V.29)
[9] 7200BPS (V.29)
[10] 4800BPS (V27ter)
[11] 2400BPS (V27ter)
[12] 300BPS (FLAG)
[13] 2100Hz (CED)
[14] 1100Hz (CNG)
3. 7. Memory clear
This mode is used to clear the backup memory and reset to the default
settings.
3. 8. Shading mode
The mode is used for the shading compensation. For reading, set up the
special original paper.
The compensation memorizes the reference data of white and black for
reading.
Moreover, the memorized data is not erased even if memory clear mode
is executed.
3. 9. All black print
This mode is used to check the state of the printing head and to intentionally overheat it. Whole dots are printed over the interval of 2 m. If it is
overheated or the printing sheet is jammed, press STOP key for the end.
3. 10. Auto feeder mode
In this mode, a document is inserted and discharged to check the auto
feed function.
After this mode is started, set a document, and the document feed will
be automatically tested.
3. 11. Entry data send
This mode is used to send the registered data to another machine and
make the other machine copy the registered content.
Before sending in this mode, it is necessary to set the other machine at
the entry data receive mode.
The following, information will be sent to the remote machine:
1. Telephone list data
2. Sender register data
3. Optional setting content
4. Soft switch content
5. Junk fax number list
6. Recording setting list data
2 – 3
Page 10
UX-A255U
3. 12. Entry data receive
In this mode, the registered data sent from the other machine is received and the received data is registered in the machine. When this mode
is used for receiving, the other machine must be in the entry data send
mode.
After receiving is completed, the following lists are printed.
1. Telephone list data
2. Sender register data (*)
3. Optional setting list (*)
4. Soft switch content
5. Junk fax number list (*)
6. Recording setting list data (*)
(*): Refer to SETUP LIST
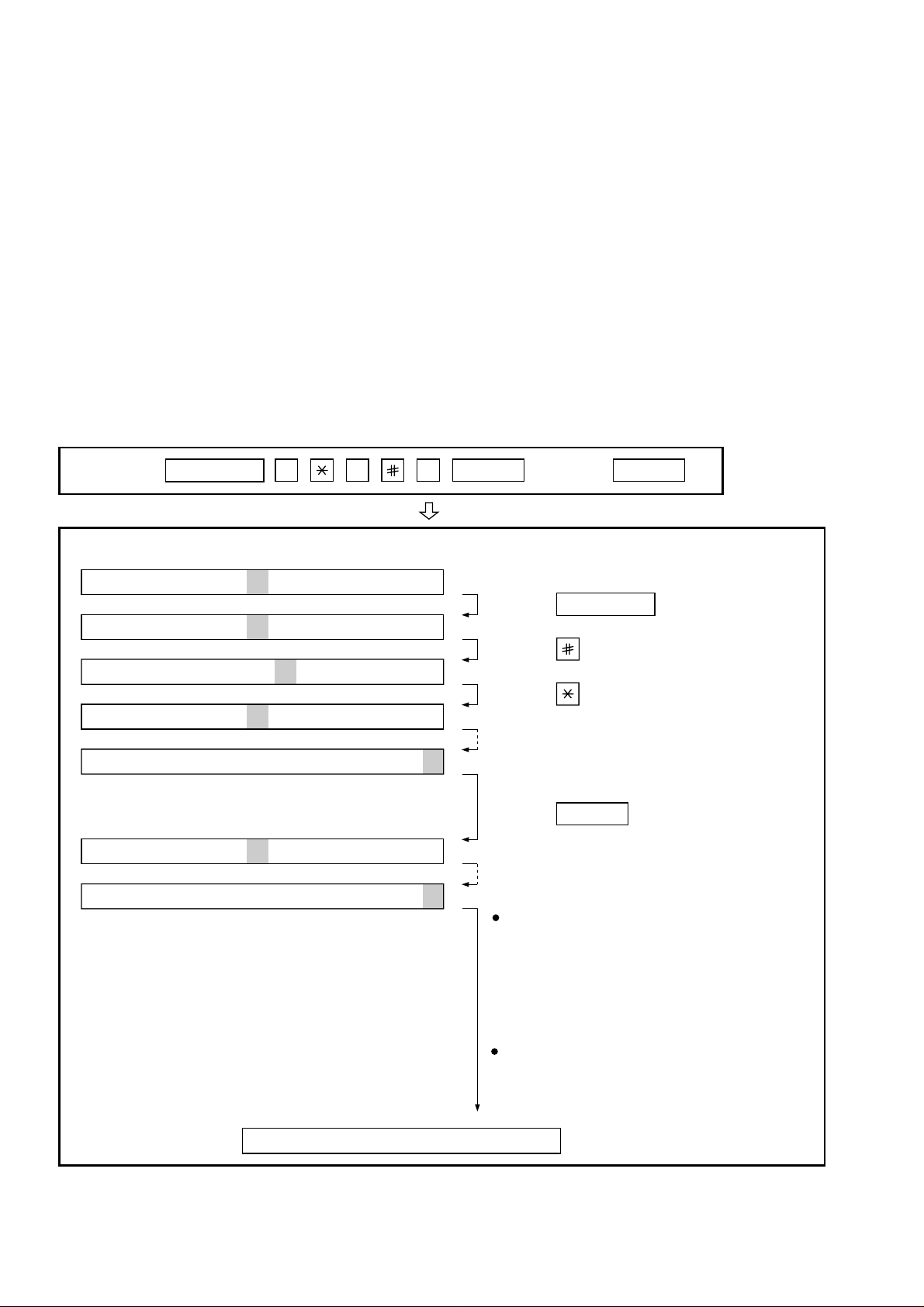
4. How to make soft switch setting
To enter the soft switch mode, press the following key entries in sequence.
Press
FUNCTION
9 8 7 START START
3. 13. Flash memory check
Data is written into and read from the flash memory to check data conformity. When the unit enters this mode, the check is started.
3. 14. Flash memory clear
Data in the flash memory is cleared (memory clear). When the unit enters this mode, the check is started.
*Operation of hardware and signal in the flash memory check mode and
flash memory clear mode, and the result of check.
The result is announced by the buzzer beeps. The result of check is
printed.
Beeps
0 → No error
1 → Memory error
DATA No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
S F T SW-A1 = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T SW-A1 = 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T SW-A1 = 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T SW-A1 = 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T SW-A1 = 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T SW-A2 = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T SW-N3 = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Press FUNCTION key.
Press key.
Press key.
Bit1 - 8 are set.
Press key during setting.
START
Soft SW-A2 - SW-N3 are set.
To finish the settings halfway between
SW-A1 and SW-N3, press the STOP
key. In this case, the setting being done
to the SW No. on display will be nullified
while settings done to the preceding
SW No. remain in effect.
When the COPY key is pressed, the
contents of soft switches are printed.
The soft switch mode is terminated.
2 – 4
Page 11
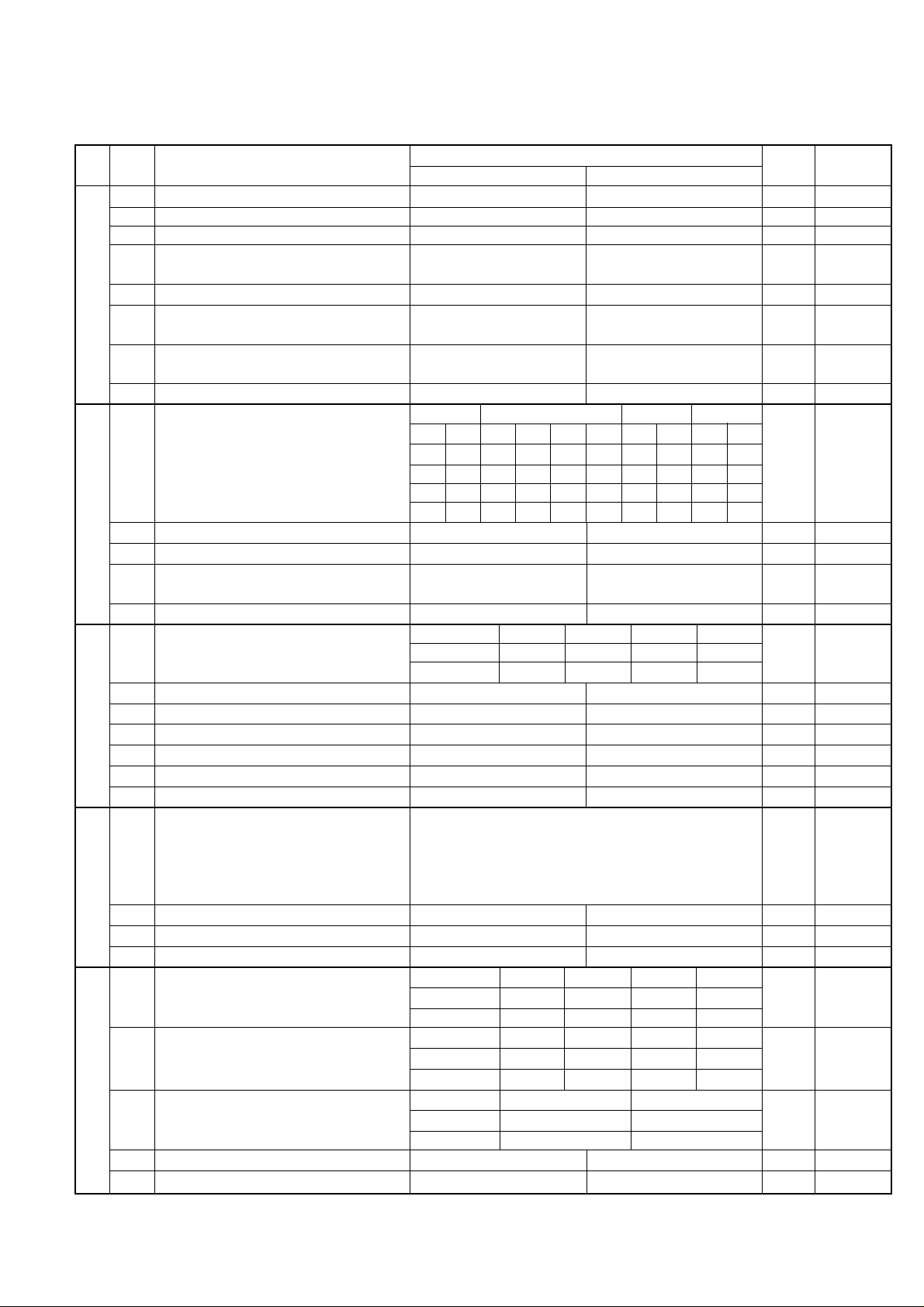
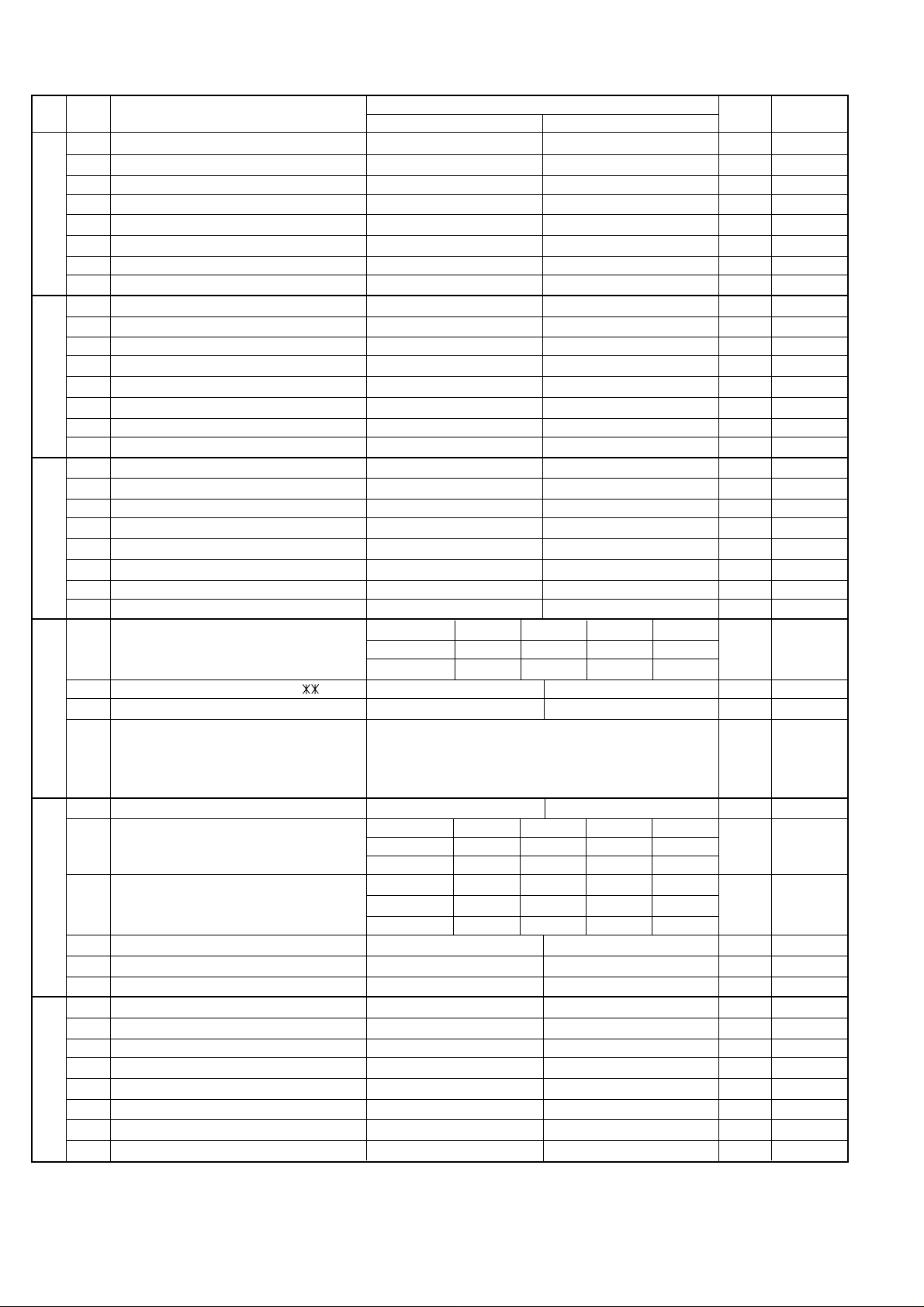
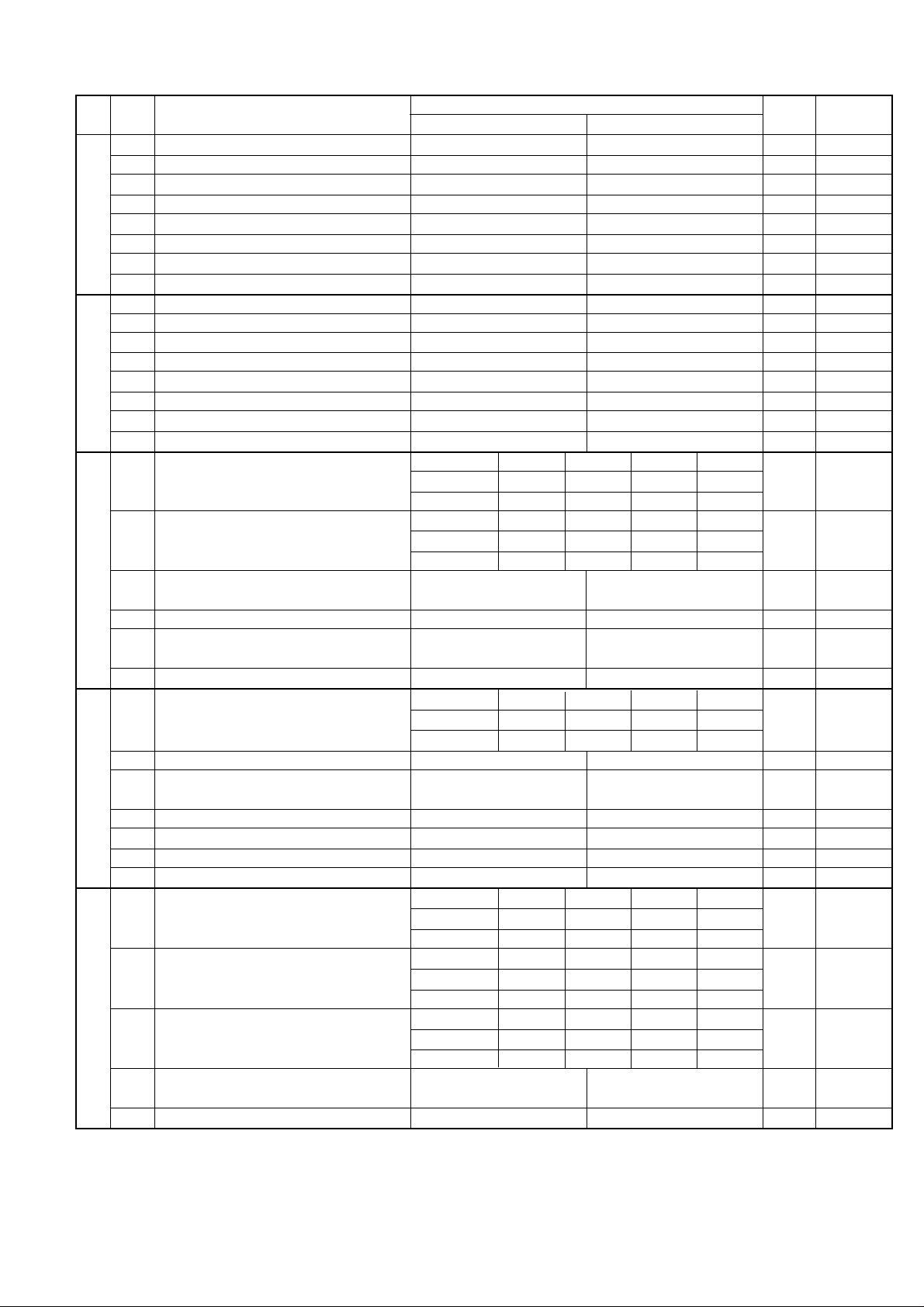
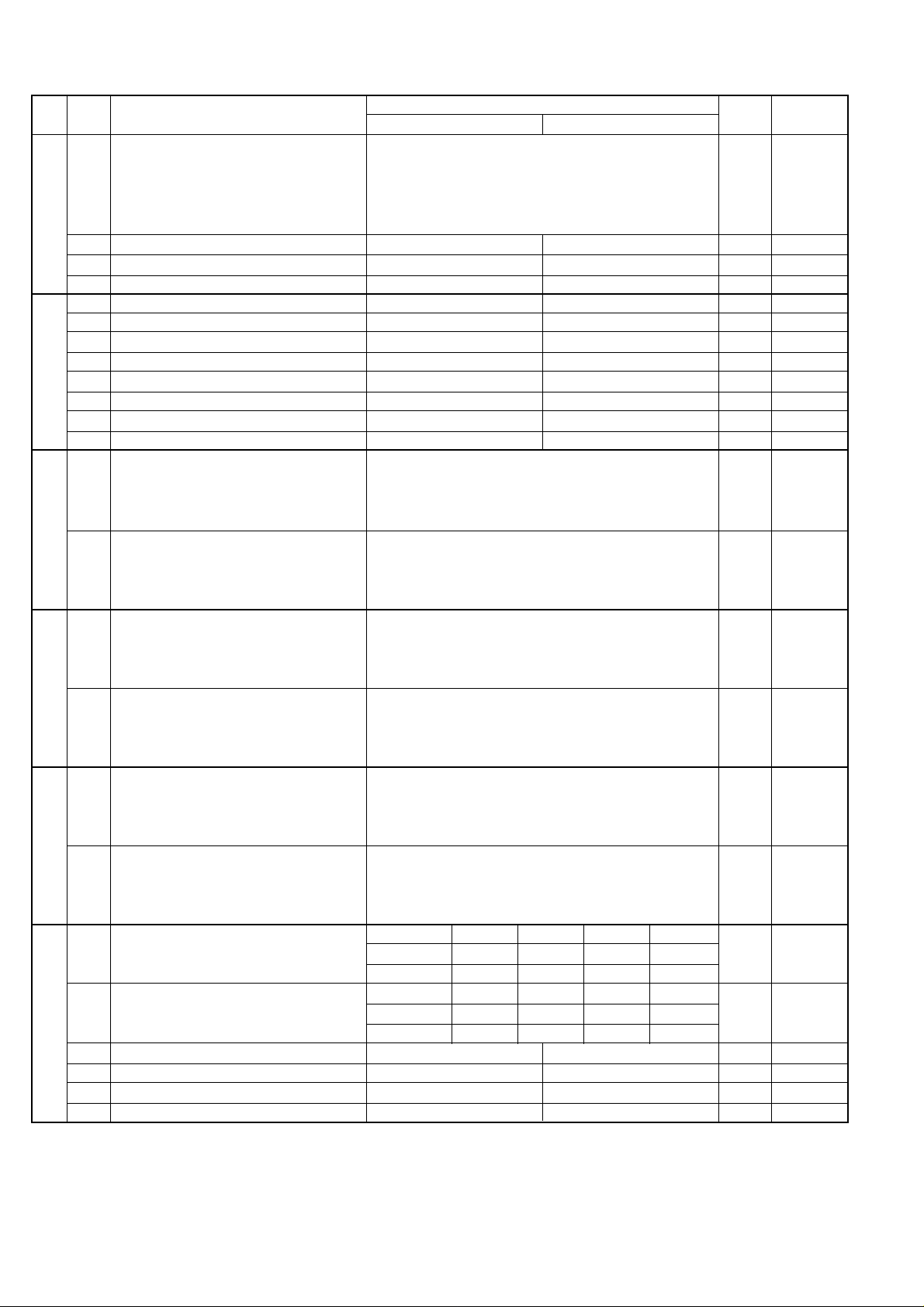
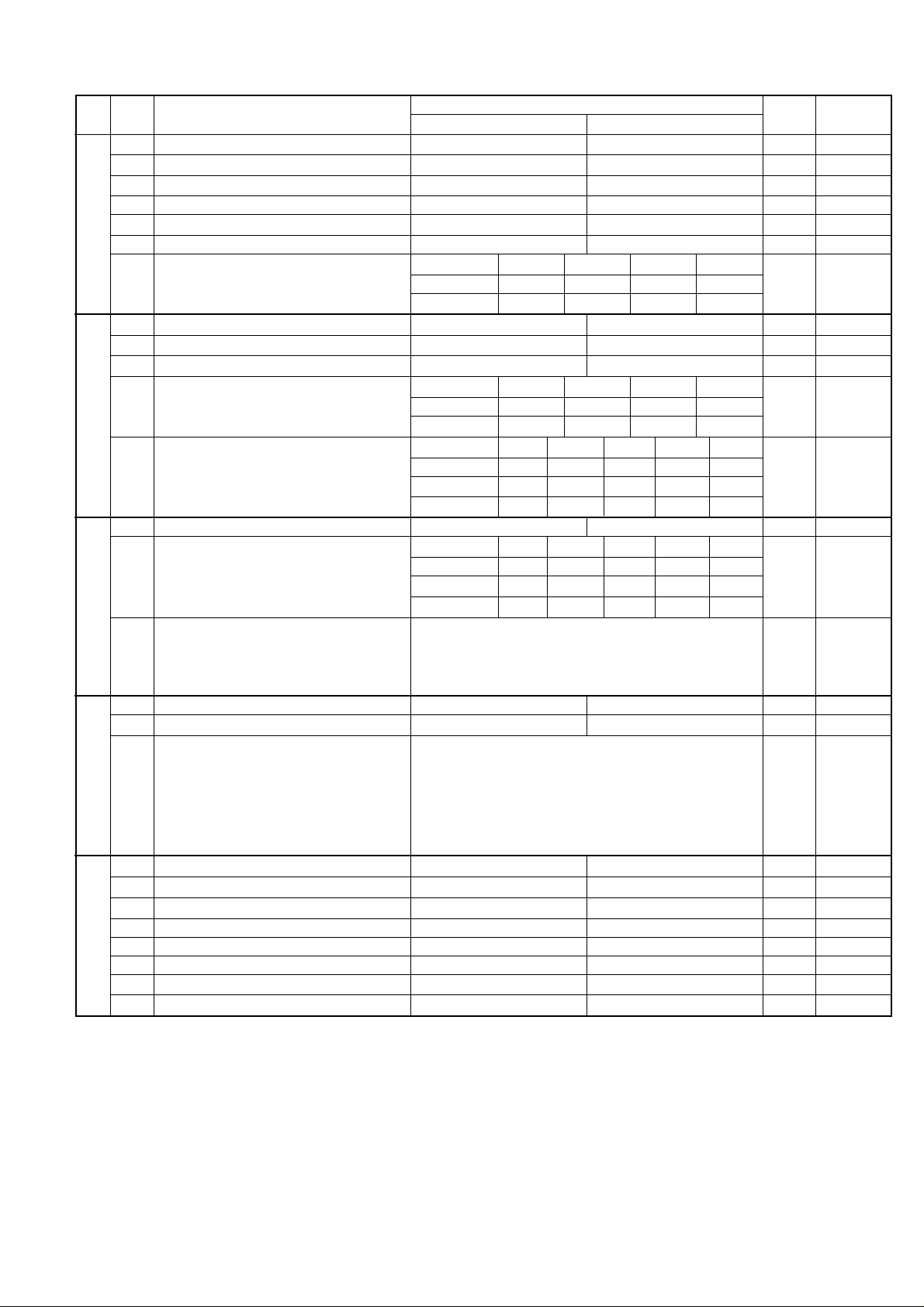
5. Soft switch description
• Soft switch
UX-A255U
SW
NO.
SW
A1
SW
A2
SW
A3
SW
l
A4
SW
l
A5
DATA
NO.
1 Protect from echo No Yes 0
2 Forced 4800 BPS reception Yes No 0
3 Footer print Yes No 0
4 Length limitation of copy/send/receive No limit Copy/send: 60cm 0
5 CSI transmission No transmitted Transmitted 0
l
6 DIS receive acknowledgement during G3 Twice NSF: Once 0
transmission DIS: Twice
7 Non-modulated carrier for V29 transmission Yes No 0
mode
8 EOL detect timer 25 s 13 s 0
Modem speed V.33 V.17 V.29 V.27 ter
1 0011110000 1
2 1100000000 0
3 0101010110 0
4 0000111100 0
l
5 Sender’s information transmit No Yes 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Communication error treatment in RTN No communication error Communication error 0
sending mode (reception)
8 CNG transmission No Yes 0
CED tone signal interval 1000ms 750ms 500ms 75ms
1 No. 1 1 1 0 0 0
2 No. 2 1 0 1 0 0
3 MR coding No Yes 0
l
4 ECM mode No Yes 0 OPTION
5 ECM MMR mode No Yes 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Signal transmission level Binary input 0
2 No. = 16 8 4 2 1 1
3 1 2 3 4 5 0
4 0 1 0 0 0 0
5 0
6 Protocol monitor (error print) Printed at com. error Not printed 0
7 Protocol monitor Yes No 0
8 Line monitor Yes No 0
Digital line equalization setting (Reception) 7.2km 3.6km 1.8km 0km
1 No. 1 11000
2 No. 2 10101
Digital line equalization setting 7.2km 3.6km 1.8km 0km
3 (Transmission) No. 3 11000
4 No. 4 10101
Digital cable equalizer setting (Reception 7.2km 0km
5 for Caller ID) No. 5 1 0 0
6 No. 6 1 0 0
7 Error criterion 10 ~ 20 % 5 ~ 10 % 0
8 Anti junk fax check Yes No 1
ITEM
14400 12000 14400 12000 9600 7200 9600 7200 4800 2400
Switch setting and function
10
Receive: 1m
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 5
Page 12
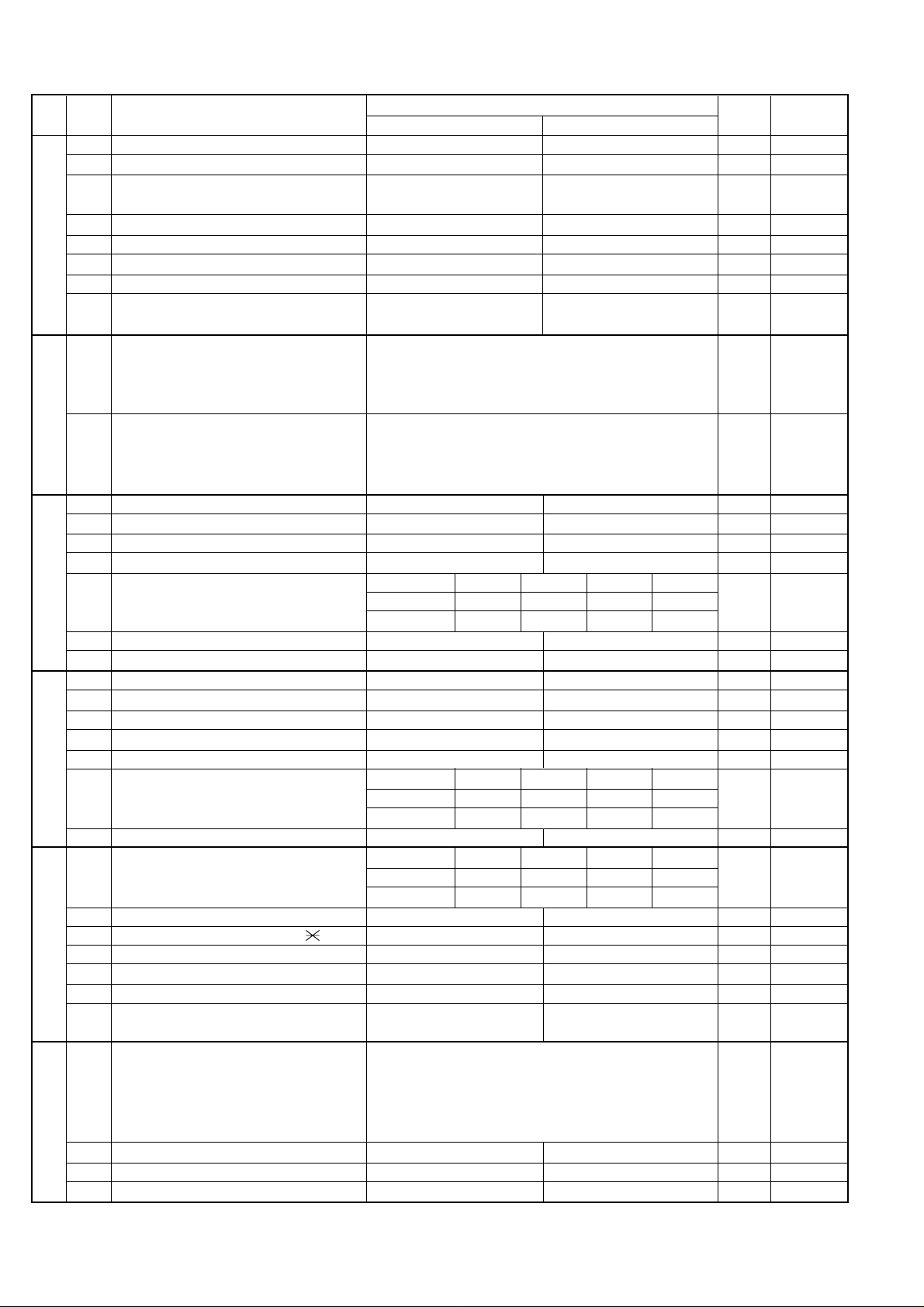
UX-A255U
SW
DA TA
NO.
NO.
1 Reserved 0
2 End Buzzer Yes No 1
3 Disconnect the line when DIS is received in No Yes 1
RX mode
SW
4 Equalizer freeze control (MODEM) On Off 0
l
5 Equalizer freeze control 7200 BPS only No Yes 0
A6
6 CNG transmission in manual TX mode Yes No 1
7 Reserved 0
8 Modem speed automatic fallback when RX Yes No 0
level is under -40dBm
1 Recall interval Binary input 0
2 No. = 8 4 2 1 1
3 1 2 3 4 0
SW
4 0 1 0 1 1
l
5 Recall times Binary input 0
B1
6 No. = 8 4 2 1 0
7 5 6 7 8 1
8 0 0 1 1 1
1 Dial pausing (sec/pause) 4 sec 2 sec 0
2 Dial tone detection (before auto dial) No Yes 1
3 Reserved 0
4 Busy tone detection (after auto dial) No Yes 0
SW
l
B2
SW
l
B3
SW
l
B4
SW
l
B5
Waiting time after dialing
5 No.5 00110
6 No.6 01010
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
Auto dial mode delay timer of before line
6 connect No.6 00110
7 No.7 01010
8 Reserved 0
Auto dial mode delay timer of after line
1 connect No.1 00110
2 No.2 01010
3 Dial mode Tone Pulse 1 OPTION
4 Pulse → Tone change function by key Enable Disable 1
5 Dial pulse make/break ratio (%) 40/60 33/67 1
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8
Recalling fixed only one time when dialing was
unsuccessful without detecting busy tone signal
1 DTMF signal transmission level (Low) Binary input 0
2 No. = 16 8 4 2 1 1
3 1 2 3 4 5 0
4 0 1 0 0 1 0
5 1
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
Yes No 1
Switch setting and function
10
45 seconds 55 seconds 90 seconds 140 seconds
0 second 1.5 seconds 3.0 seconds 4.5 seconds
1.7 seconds 3.0 seconds 3.6 seconds 4.0 seconds
setting
Initial
Remarks
2 – 6
Page 13
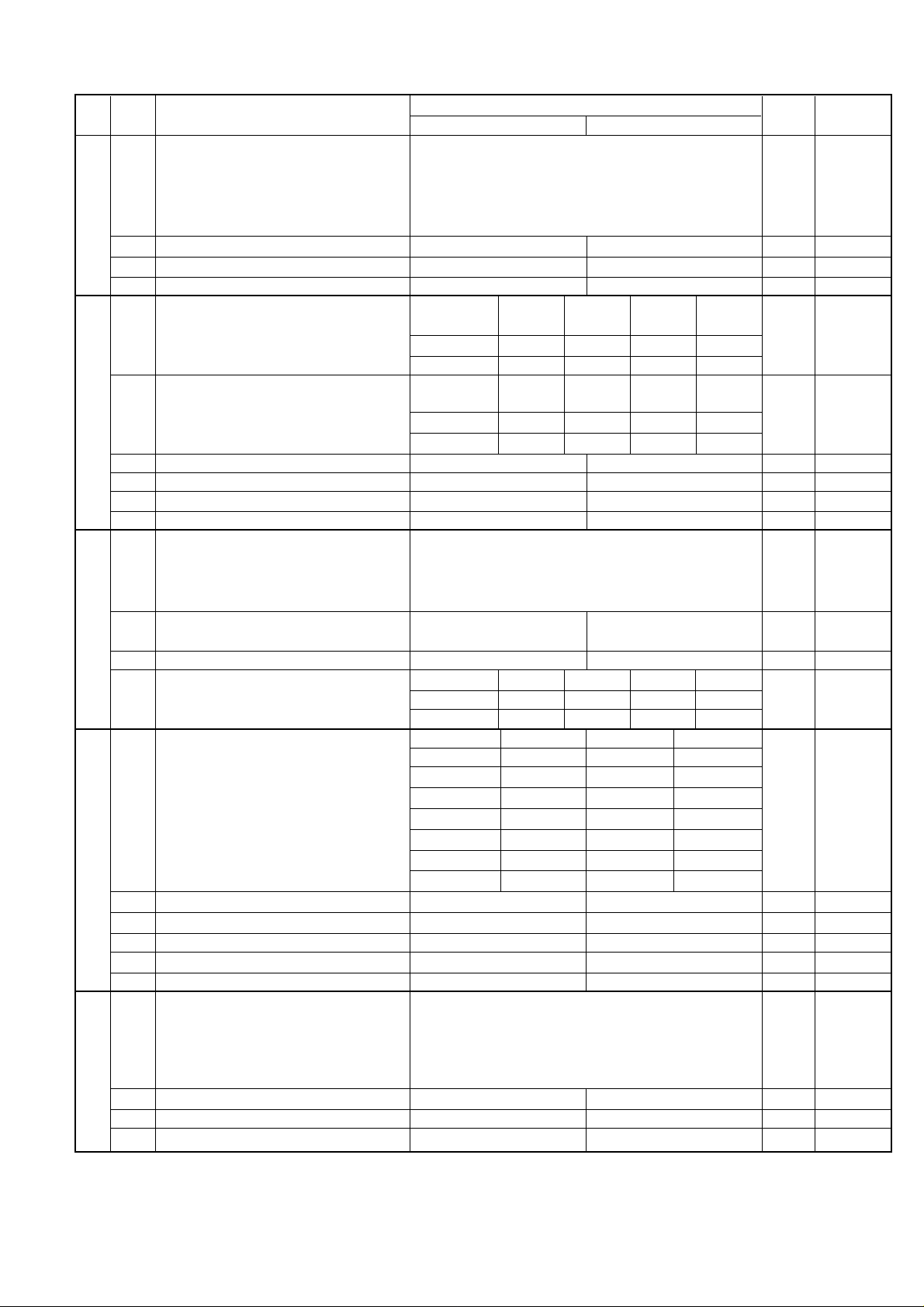
UX-A255U
SW
NO.
SW
B6
SW
C1
SW
D1
SW
D2
SW
D3
DAT A
NO.
1 DTMF signal transmission level (High) Binary input 0
2 No. = 16 8 4 2 1 0
3 1 2 3 4 5 1
4 0 0 1 0 1 0
l
5 1
6
Dial tone detection (LCR center call)
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
Reading slice (Binary) Factory Light Dark Darker in
1 No. 1 0 1 0 1 0
2 No. 2 0 0 1 1 0
Reading slice (Half tone) Factory Light Dark Darker in
l
3 No. 3 0 1 0 1 0
4 No. 4 0 0 1 1 0
5 Line density selection Fine Standard 0
6 Reserved 0
7 MTF correction in half tone mode No Yes 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Number of rings for auto receive Binary input 0 OPTION
2 No. = 8 4 2 1 1
3 1 2 3 4 0
4 0 1 0 0 0
5 Automatic switching manual to auto receive Reception after 5 rings No reception 0
l
l
l
mode
6 Reserved 0
Cl detect frequency
7 No.7 0 0 1 1 0
8 No.8 0 1 0 1 0
Distinctive ringing setting No. 1 No. 2 No. 3 OPTION
(PATTERN 4 and 5 are for CANADA only) OFF 0 0 0
1 PATTERN3 1 0 0 0
2 PATTERN4 1 0 1 0
3 PATTERN5 1 1 0 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Caller ID function Yes No 0 OPTION
6 Caller ID detect during CI off All times Only first 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Cl off detection timer (0-1550ms setting by Binary input 0
2 50ms step) No. = 16 8 4 2 1 1
3 1 2 3 4 5 1
4 0 1 1 1 0 1
5 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
No Yes 0
STANDARD 0 0 1
PATTERN1 0 1 0
PATTERN2 0 1 1
Switch setting and function
10
setting dark
setting dark
As PTT 11.5Hz 13.0Hz 20.0Hz
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 7
Page 14
UX-A255U
SW
DA TA
NO.
NO.
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
SW
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Reserved 0
E1
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
SW
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Reserved 0
E2
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
SW
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Reserved 0
E3
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
DTMF detection time 50ms 80ms 100ms 120ms
1 No. 1 0 0 1 1 0
2 No. 2 0 1 0 1 0
3 Protection of remote reception (5 ) detect Yes No 1
SW
4 Remote reception with GE telephone Compatible Not compatible 1
l
5 Remote operation code figure by external Binary input 0
F1
6 TEL (0~9) No. = 8 4 2 1 1
7 5 6 7 8 0
8 0 1 0 1 1
1 CNG detection in STAND-BY mode Yes No 1 OPTION
Number of CNG detect (AM mode) 1pulse 2pulses 3pulses 4pulses
2 No. 2 0 0 1 1 0
3 No. 3 0 1 0 1 1
SW
l
F2
SW
l
G1
Number of CNG detect (STAND-BY mode) 1pulse 2pulses 3pulses 4pulses
4 No. 4 0 0 1 1 0
5 No. 5 0 1 0 1 1
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
0
setting
Initial
Remarks
2 – 8
Page 15
UX-A255U
SW
NO.
SW
G2
SW
G3
SW
H1
SW
H2
SW
l
I1
DAT A
NO.
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
Busy tone detection ON/OFF time (Lower 150ms 200ms 250ms 350ms
1 duration) No. 1 0 0 1 1 0
2 No. 2 0 1 0 1 1
Busy tone detection ON/OFF time (Upper 650ms 900ms 1500ms 2700ms
3 duration) No. 3 0 0 1 1 0
4 No. 4 0 1 0 1 1
l
5 Busy tone detect continuation sound detect No Yes 0
during OGM
6 Busy tone detect continuation sound detect No Yes 0
7 Busy tone detect intermittent sound detect No Yes 0
during OGM
8 Busy tone detect intermittent sound detect No Yes 0
Busy tone detection pulse number 2pulses 4pulses 6pulses 10pulses
1 No. 1 0 0 1 1 0
2 No. 2 0 1 0 1 1
3 Fax switching when A.M. full Yes No 0 OPTION
4 Busy tone detect continuation sound detect 320Hz - 570Hz 320Hz - 460Hz 0
l
frequency
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 AM OGM announce only mode Yes No 0 OPTION
8 Busy tone continuous sound detect time 5s 10s 1
ICM recording time 4min 15s 30s 60s OPTION
1 No. 1 0 0 1 1 0
2 No. 2 0 1 0 1 0
A.M. quiet time 1 2s 3s 4s 5s
3 No. 3 0 0 1 1 0
4 No. 4 0 1 0 1 0
A.M. quiet time 2 0s 1s 2s 3s
5 No. 5 0 0 1 1 1
6 No. 6 0 1 0 1 0
7 Key input buzzer on/off switch (Two way On Off 0
recording mode)
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 9
Page 16
UX-A255U
SW
DA TA
NO.
NO.
1 A.M. quiet detect time Binary input 0
2 No. = 16 8 4 2 1 0
3 1 2 3 4 5 1
SW
4 00110 1
l
5 0
I2
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Max OGM record time 15s 60s 0
3 Two way record function Disable Enable 0
SW
4 Toll saver Disable Enable 0 OPTION
l
5 Reserved 0
I3
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Transfer dial recall No Yes 0
1 AGC maximum gain (line) Binary input 0
2 (10 ~ 25 dB) (1 dB step) No. = 8 4 2 1 1
3 1 2 3 4 0
SW
4 0101 1
l
5 AGC maximum gain (Mic) Binary input 0
I4
6 (10 ~ 25 dB) (1 dB step) No. = 8 4 2 1 1
7 5 6 7 8 1
8 0110 0
1 AGC eref access code (line) Binary input 1
2 (-0 ~ -30 dB) (2 dB step) No. = 8 4 2 1 0
3 1 2 3 4 1
SW
4 1011 1
l
5 AGC eref access code (Mic) Binary input 1
I5
6 (-0 ~ -30 dB) (2 dB step) No. = 8 4 2 1 1
7 5 6 7 8 0
8 1101 1
1 AGC again adaptation threshold (line) Binary input 1
2 No. = 8 4 2 1 1
3 1 2 3 4 1
SW
4 1111 1
l
5 AGC again adaptation threshold (Mic) Binary input 1
I6
6 No. = 8 4 2 1 1
7 5 6 7 8 1
8 1111 1
AGC slew rate (line) Slow Normal Little fast Fast
1 No. 1 0 0 1 1 0
2 No. 2 0 1 0 1 1
AGC slew rate (Mic) Slow Normal Little fast Fast
SW
3 No. 3 0 0 1 1 1
l
4 No. 4 0 1 0 1 1
I7
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
0
setting
Initial
Remarks
2 – 10
Page 17
UX-A255U
SW
NO.
SW
J1
SW
l
J2
SW
J3
SW
K1
SW
l
L1
DA TA
NO.
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Sender’s phone number setting Cannot change Change allowed 0
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Reserved 0
6 Summer time setting No Yes 1 OPTION
Ringer volume Off Low Middle High OPTION
7 No. 7 0 0 1 1 1
8 No. 8 0 1 0 1 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
Handset receiver volume Low Low Middle High OPTION
4 No. 4 0 0 1 1 1
5 No. 5 0 1 0 1 0
Speaker volume (5 stages)
6 No. 6 000010
7 No. 7 001101
8 No. 8 010100
1 Reserved 0
Communication results printout E/T/M
(Transaction report)
2
3 No. 3 001100
4 No. 4 010100
l
5 OGM/ICM output level to speaker Binary input 0
6 (0 dB ~ -15 dB) (1 dB step) No. = 8 4 2 1 0
7 5 6 7 8 1
800111
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 OGM/ICM output level Binary input 0
4 (0 dB ~ -32 dB) (1 dB step) No. = 32 16 8 4 2 1 0
l
5 3 45678 1
6 0 01001 0
7 0
8 1
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Cut off mode (COPY mode) Yes No 1 OPTION
6 A4 paper enable Enable Disable 0
7 LEGAL & LETTER paper enable Enable Disable 1
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
No. 2 000011
Switch setting and function
1
Very Low
Low Middle High
Send only
Always No print Err only OPTION
0
Very High
Initial
setting
Remarks
OPTION
2 – 11
Page 18
UX-A255U
SW
DA TA
NO.
NO.
Paper set size LETTER LEGAL A4 OPTION
1 No. 1 0 0 1 0
2 No. 2 0 1 0 0
3 Automatic reduce of receive Auto 100 % 1 OPTION
SW
l
L2
SW
l
M1
SW
l
M2
SW
l
N1
SW
l
N2
SW
l
N3
Print contrast Normal Lighter Light Dark Darker OPTION
4 No. 4 000011
5 No. 5 001100
6 No. 6 010100
7
Reception reduction ratio in case of memory ful
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 LCR short time Binary input 0 OPTION
2 No. = 32 16 8 4 2 1 0
3 1 2 3 4 5 6 0
4 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
5 1
6 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 LCR long time Binary input 0 OPTION
2 No. = 32 16 8 4 2 1 0
3 1 2 3 4 5 6 0
4 0 0 0 1 0 0 1
5 0
6 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 LCR Time Select Long Short 0 OPTION
2 Temporary release of caller ID withhold Yes No 1
3 Connect Japanese center Connect Japanese center Connect USA center 0
4 Open LCR debug mode Open LCR debug mode ON Open LCR debug mode OFF 0
Digital line equalization setting 0km 0km 7.2km 7.2km
5 (Open LCR downloading) No. 5 0 0 1 1 0
6 No. 6 0 1 0 1 0
7
Release code of Call ID withhold for tone or pulse line
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
100 % 93 % 0
Tone *82 Pulse 1182 1
Switch setting and function
1
0
setting
Initial
Remarks
2 – 12
Page 19
UX-A255U
• Soft switch function description
SW-A1 No. 1 Protect from echo
Used to protect from echo in reception.
SW-A1 No. 2 Forced 4800BPS reception
When line conditions warrant that receptions take place at 4800 BPS
repeatedly.
It may improve the success of receptions by setting at 4800BPS.
This improves the receiving document quality and reduces handshake
time due to fallback during training.
SW-A1 No. 3 Footer print
When set to "1", the date of reception, the sender machine No., and the
page No. are automatically recorded at the end of reception.
SW-A1 No. 4 Length limitation of copy/send/receive
Used to set the maximum page length.
To avoid possible paper jam, the page length is normally limited to 0.6
meter for copy or transmit, and 1 meters for receive.
It is possible to set it to "No limit" to transmit a long document, such as a
computer print form, etc. (In this case, the receiver must also be set to
no limit.)
SW-A1 No. 5 CSI transmission
(CSI TRANSMISSION) is a switch to set whether the machine sends or
does not send the signal (CSI signal) informing its own telephone No. to
the remote fax machine when information is received. When "nonsending"
is set, the telephone No. is not output on the remote transmitting machine if the remote transmitting machine has the function to display or
print the telephone No. of receiving machine, using this CSI signal.
SW-A1 No. 6 DIS receive acknowledgment during G3 transmission
Used to make a choice of whether reception of DIS (NSF) is acknowledged after receiving two DISs (NSFs) or receiving one DIS (two NSFs).
It may be useful for overseas communication to avoid an echo suppression problem, if set to 1.
SW-A1 No. 7 Non-modulated carrier for V29 transmission mode
Though transmission of a non-modulated carrier is not required for transmission by the V29 modem according to the CCITT recommendation, it
may be permitted to a send non-modulated carrier before the image
signal to avoid an echo suppression problem. It may be useful for overseas communication to avoid an echo suppression problem, if set to 1.
SW-A1 No. 8 EOL (End Of Line) detect timer
Used to make a choice of whether to use the 25-second or 13-second
timer for detection of EOL.
This is effective to override communication failures with some facsimile
models that have longer EOL detection.
SW-A2 No. 1 ~ No. 4 Modem speed
Used to set the initial modem speed. The default is 14400BPS.
It may be necessary to program it to a slower speed when frequent line
fallback is encountered, in order to save the time required for fallback
procedure.
SW-A2 No. 5 Sender’s information transmit
(SENDER’S INFORMATION TRANSMISSION) is a switch to set the
function to print the content of HEADER PRINT described in the passcode
list at the front end of receiver’s original when original is sent to the
remote machine.
If this switch is set to "NO", the HEADER PRINT is not output at the
receiving machine.
SW-A2 No. 6 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-A2 No. 7 Communication error treatment in RTN sending mode
(Reception)
Used to determine communication error treatment when RTN is sent by
occurrence of a received image error in G3 reception. When it is set to
"1", communication error is judged as no error.
SW-A2 No. 8 CNG transmission
When set to "0" , this model allows CNG transmission by pressing the
Start key in the key pad dialing mode. When set to "1", CNG transmission in the key pad dialing mode cannot be performed. In either case.
CNG transmission can be performed in the auto dial mode.
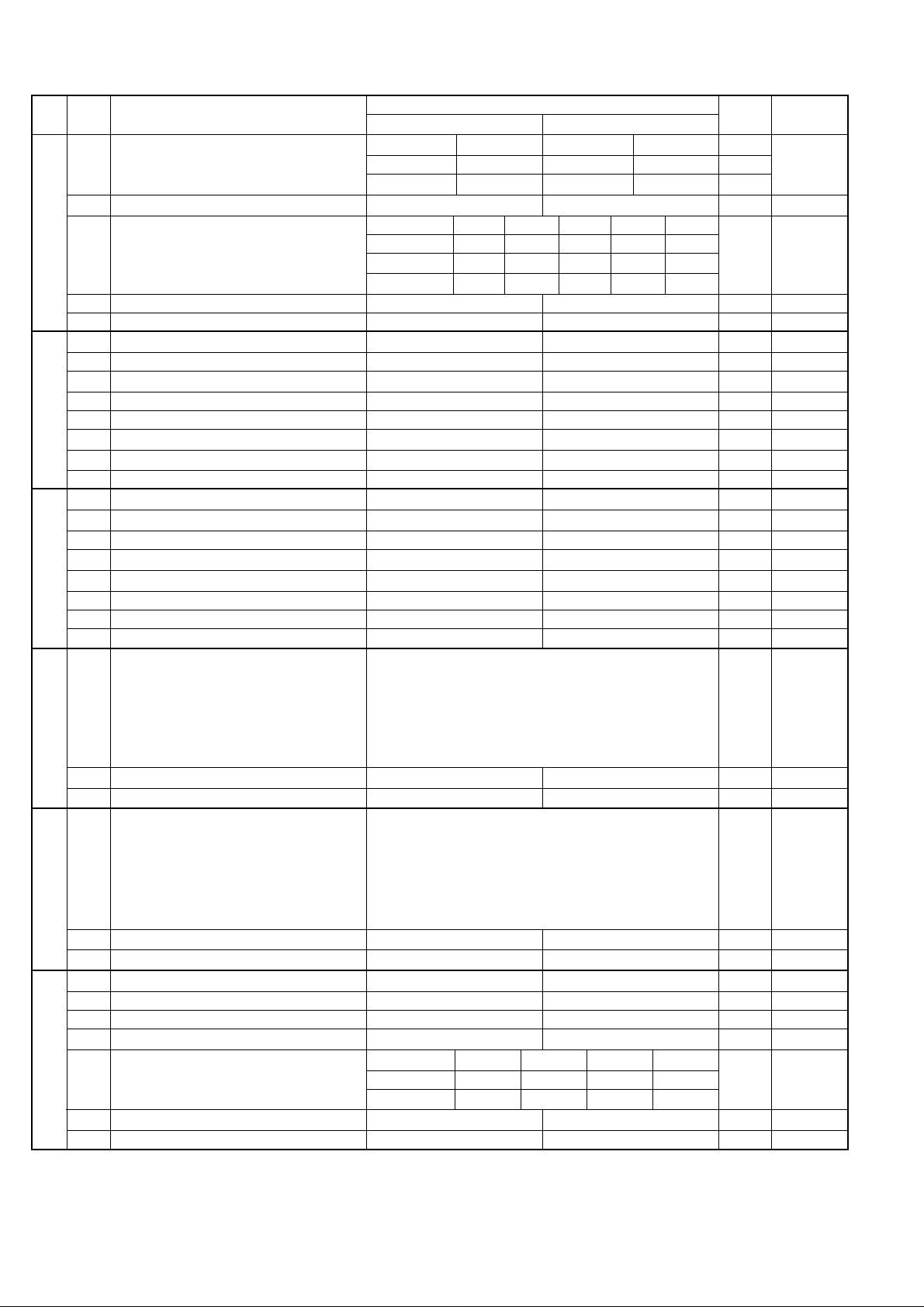
SW-A3 No. 1, No. 2 CED tone signal interval
For international communication, the 2100Hz CED tone may act as an
echo suppression switch, causing a communication problem.
Though SW-A3 No. 1 and No. 2 are normally set to 0, this selfing is used
to change the time between the CED tone signal to eliminate the communication caused by echo.
TX RX
CED
T
DIS
SW-A3 No. 3 MR Coding
MR Coding is enable.
SW-A3 No. 4 ECM mode
Used to determine ECM mode function. Refer to following table.
SW-A3 No.4 ECM MODE 0 0 1 1
SW-A3 No.5 ECM MMR MODE 0 1 0 1
Compression
method
(Depending on remote machine)
SW-A3 No. 5 ECM MMR mode
See SW-A3 No. 4.
SW-A3 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-A4 No. 1 ~ No. 5 Signal transmission level
Used to control the signal transmission level in the range of-0dB to31dB.
SW-A4 No. 6 Protocol monitor (Error print)
If set to "1", protocol is printed at communication error.
SW-A4 No. 7 Protocol monitor
Normally set to "0". If set to "1", communication can be checked, in case
of trouble, without using a G3 tester or other tools.
When communication FSK data transmission or reception is made, the
data is taken into the buffer. When communication is finished, the data is
analysed and printed out. When data is received with the line monitor
(SW-A4 No. 8) set to "1" the reception level is also printed out.
SW-A4 No. 8 Line monitor
Normally set to "0". If set to "1", the transmission speed and the reception level are displayed on the LCD. Used for line tests.
SW-A5 No. 1, No. 2 Digital line equalization setting (Reception)
Line equalization when reception is to be set according to the line characteristics.
Setting should be made according to distance between the telephone
and the telephone company central switching station.
SW-A5 No. 3, No. 4 Digital line equalization setting (Transmission)
Line equalization when transmitter is to be set according to the line
characteristics.
Setting should be made according to distance between the telephone
and the telephone company central switching station.
ECM MMR mode Yes No No No
ECM MH mode Yes Yes No No
MR Mode Yes Yes Yes Yes
2 – 13
Page 20
UX-A255U
SW-A5 No. 5, No. 6 Digital cable equalizer setting
(Reception for Caller ID)
Line equalization when reception for CALLER ID is to be set according
to the line characteristics.
Setting should be made according to distance between the telephone
and the telephone company central switching station.
SW-A5 No. 7 Error criterion
Used to select error criterion for sending back RTN when receiving image data.
SW-A5 No. 8 Anti junk fax check
When using the Anti junk fax function, set to "1".
SW-A6 No. 1 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-A6 No. 2 End buzzer
Setting this bit to 0 will disable the end buzzer (including the error buzzer/
on-hook buzzer).
SW-A6 No. 3 Disconnect the line when DIS is received in RX mode
Bit1= 0: When DIS signal is received during RX mode, the line is disconnected immediately.
Bit1= 1: When DIS signal is received during RX mode, the line is disconnected on the next tone.
SW-A6 No. 4 Equalizer freeze control (MODEM)
This switch is used to perform reception operation by fixing the equalizer control of modem for the line which is always in an unfavorable
state and picture cannot be received.
* Usually, the control is executed according to the state of line where
the equalizer setting is changed always.
SW-A6 No. 5 Equalizer freeze control 7200BPS only
Setting which specifies SW-A3 No. 6 control only in the condition of
7200BPS modem speed.
SW-A6 No. 6 CNG transmission in manual TX mode
When set to "1", fax transmit the CNG signal in case of manual transmission mode (User press the START key after waiting for the fax answering signal from handset or speaker).
SW-A6 No. 7 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-A6 No. 8 Modem speed automatic fallback when RX level is
under -40dBm
When set to "1", if fax signal level is under -40dBm during reception,
machine selects the slower modem speed automatically.
It is effective when noises occur on the received document due to the
long distance communications.
SW-B1 No. 1 ~ No. 4 Recall interval
Choice is made for a redial interval for speed and rapid dial calls.
Use a binary number to program this. If set to 0 accidentally, 1 will be
assumed.
SW-B1 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Recall times
Choice is made as to how many redials there should be.
SW-B2 No. 1 Dialing pause (sec/pause)
Pauses can be inserted between telephone numbers of direct dial connection. Selection of 4 sec or 2 sec pause is available.
SW-B2 No. 2 Dial tone detection (before auto dial)
Used to set YES/NO of dial tone detection in auto dialing.
SW-B2 No. 3 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-B2 No. 4 Busy tone detection (after auto dial)
Used to set busy tone detection in auto dialing.
SW-B2 No. 5, No. 6 Waiting time after dialing
This is time waiting for the opponent’s signals after dialing.
SW-B2 No. 7, No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-B3 No. 1 ~ No. 5 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-B3 No. 6, No. 7 Auto dial mode Delay timer of before line connect
Delay time between the dial key input and line connection under the
auto dial mode.
RAPID01 CML RELAY ON
DIALLING
No.6 No.7
0 0 0sec
0 1 1.5sec
1 0 3.0sec
1 1 4.5sec
SW-B3 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-B4 No. 1, No. 2 Auto dial mode Delay timer of after line connect
Delay time between the line connection and dial data output under the
auto dial mode.
RAPID01 CML RELAY ON
No.1 No.2
0 0 1.7sec
0 1 3.0sec
1 0 3.6sec
1 1 4.0sec
DIAL DATA
SW-B4 No. 3 Dial mode
When using the pulse dial, set to 1. When using the tone dial, set to 0.
SW-B4 No. 4 Pulse → Tone change function by key
When setting to 1, the mode is changed by pressing the key from the
pulse dial mode to the tone dial mode.
SW-B4 No. 5 Dial pulse make/break ratio (%)
When using the 33% make ratio pulse dial, set to "0".
When using the 40% make ratio pulse dial, set to "1".
SW-B4 No. 6, No. 7 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-B4 No. 8 Recalling fixed only one time when dialing was unsuccessful without detecting busy tone signal
When dialing results in failure since the busy tone cannot be detected,
recalling is fixed to one time.
Supplementary explanation
If time-out termination is made when dialing, only single recall is possible even if the setting time of recalls (SW-B1 No. 5 - No. 8) has been set
to some times. This soft switch is added in order to meet FCC regulations.
SW-B5 No. 1 ~ No. 5 DTMF signal transmission level (Low)
The transmission level of DTMF signal is adjusted. (lower frequency)
00000: 0dBm
↓
11111: -15.5dBm (-0.5dBm x 31)
SW-B5 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-B6 No. 1 ~ No. 5 DTMF signal transmission level (High)
The transmission level of DTMF signal is adjusted. (higher frequency)
00000: 0dBm
↓
11111: -15.5 dBm (-0.5dBm x 31)
2 – 14
Page 21
UX-A255U
SW-B6 No. 6 Dial tone detection (LCR center call)
Used to set YES/NO of dial tone detection (calling LCR center).
SW-B6 No. 7, No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-C1 No. 1, No. 2 Reading slice (Binary)
Used to determine the set value of reading density in standard/fine mode.
The standard setting is "00" (Factory setting is "00")
SW-C1 No. 3, No. 4 Reading slice (Half tone)
Used to determine the set value of reading density in half tone mode.
The standard setting is "00" (Factory setting is "00")
SW-C1 No. 5 Line density selection
Used to set the transmission mode which is automatically selected when
the Resolution key is not pressed. In the copy mode, however, the fine
mode is automatically selected unless the Resolution key is manually
set to another mode.
SW-C1 No. 6 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-C1 No. 7 MTF correction in half tone mode
This allows selection of MTF correction (dimness correction) in the half
tone mode.
When "NO" (=1) is selected, the whole image becomes soft and mild.
Clearness of characters will be reduced. Normally set to "YES" (=0).
SW-C1 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-D1 No. 1 ~ No. 4 Number of rings for auto receive
When the machine is set in the auto receive mode, the number of rings
before answering can be selected. It may be set from one to four rings
using a binary number. Since the facsimile telephone could be used as
an ordinary telephone if the handset is taken off the hook, it should be
programmed to the user ’s choice. If the soft switch was set to 1, direct
connection is made to the facsimile. If a facsimile calling beep was heard
when the handset is taken off the hook, press the START key and put
the handset on the hook to have the facsimile start receiving. If it was
set to 0 accidentally, receive ring is set to 1.
NOTE: If the machine is set to answer after a large number of rings, it
may not be able to receive faxes successfully. If you have difficulty receiving faxes, reduce the number of rings to a maximum
of 6.
SW-D1 No. 5 Automatic switching manual to auto receive mode
This soft switch is used to select whether the machine should switch to
the auto receive mode after 5 rings in the manual receive mode or remain in the same way as SW-D1 No. 1, No. 2, No. 3 and No. 4 "0"1"0"1"(5
rings).
SW-D1 No. 6 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-D1 No. 7, No. 8 CI detect frequency
Detection frequency of ring signal for auto reception is set.
When set to No. 6=0, No. 7=0, frequency is set to PTT recommendation.
When set to No. 6=0, No. 7=1, frequency is set to 11.5Hz or more.
When set to No. 6=1, No. 7=0, frequency is set to 13.0Hz or more.
When set to No. 6=1, No. 7=1, frequency is set to 20.0Hz or more.
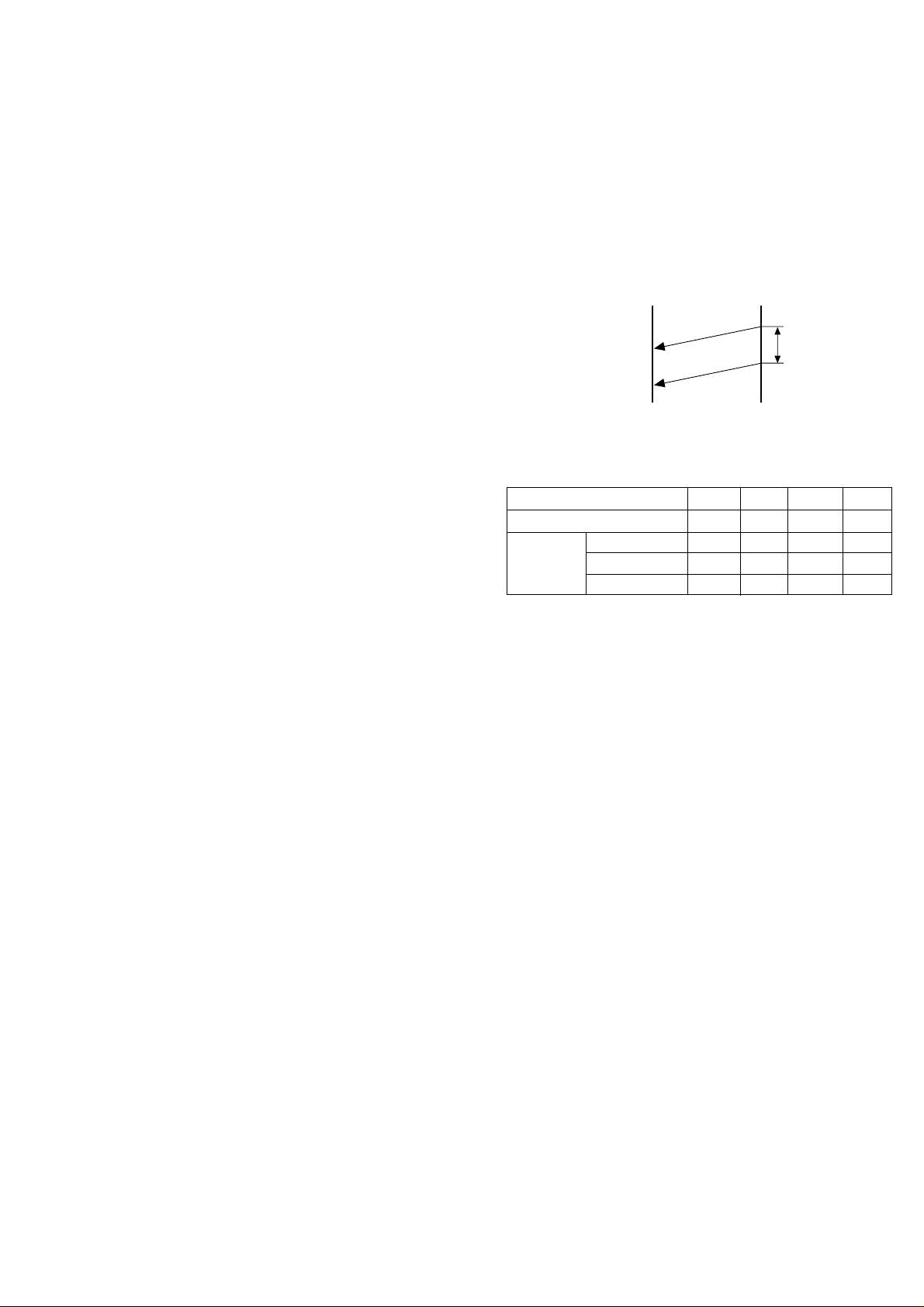
SW-D2 No. 1 ~ No. 3 Distinctive ringing setting (PATTERN 4 and 5
are for CANADA only)
This function allows reception of services offered by USA and Canada
telephone companies in which the customer contracts with the telephone
company to have up to 4 telephone numbers (USA) or 6 telephone numbers (Canada) established for one line.
Each telephone number is signalled by a different ringing pattern, and
the customer can allocate each number to a specific use.
<Example of use>
Phone Number Intended Ring Pattern
Purpose
Ring Pattern 555-1234 Voice Calls Standard
555-1235 Facsimile Calls Pattern 1
555-1236 Answering Pattern 2
Machine
555-1237 PC Modem Pattern 3
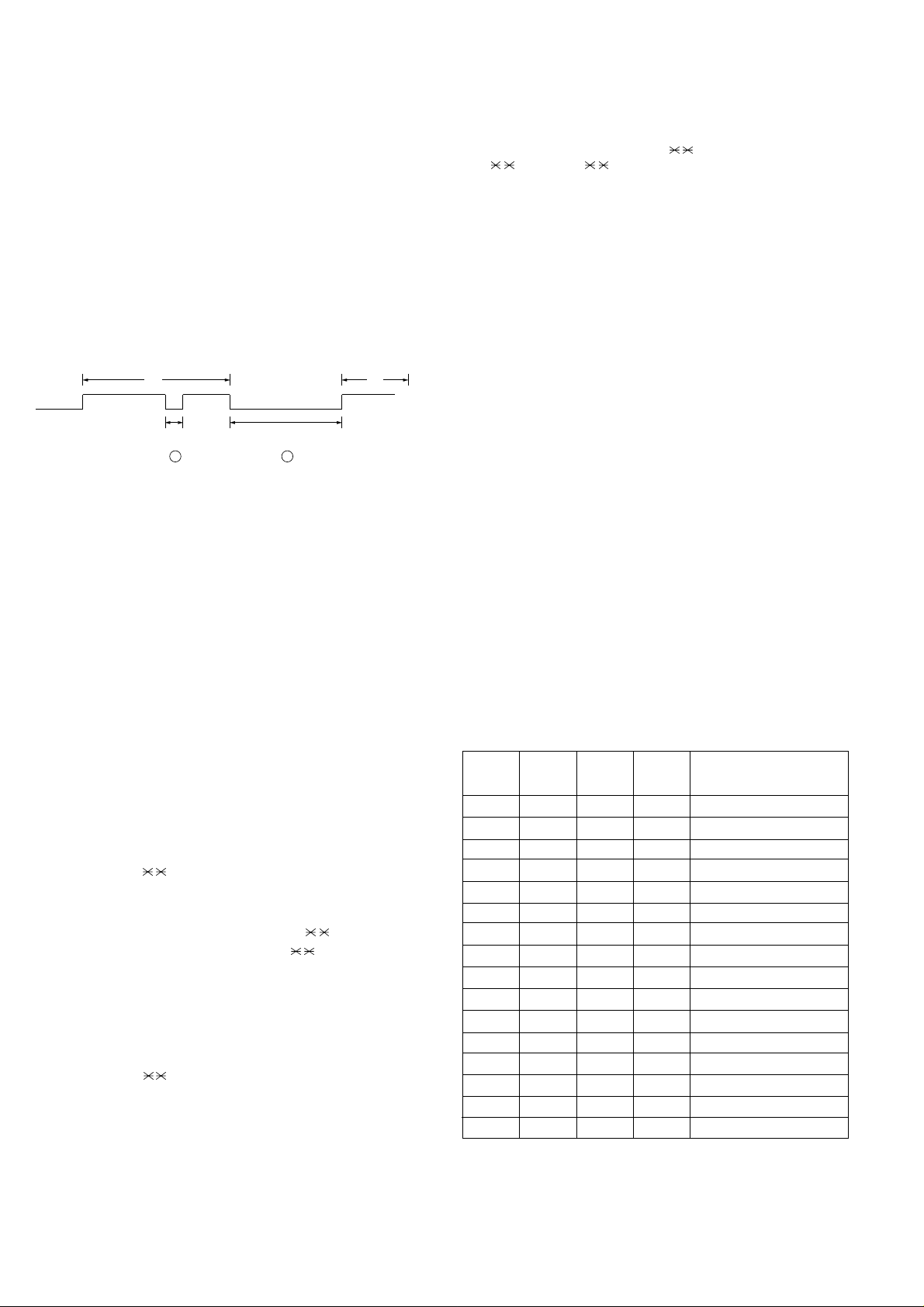
<Distinctive Ringing Timing Specifications>
1) USA
DISTINCTIVE RING → 1:RING P A TTERN 1 → 2:RING P A TTERN 2
↑↓
5:OFF SETTING ←
4:STANDARD RING
← 3:RING P A TTERN 3
2) Canada
DISTINCTIVE RING → 1:RING P A TTERN 1 → 2:RING P A TTERN 2
↑↓
7:OFF SETTING 3:RING P A TTERN 3
↑↓
6:
STANDARD RING←5:
RING P ATTERN 5 ← 4:RING PA TTERN 4
• Ring Pattern
STANDARD has 5 ring patterns, and DISTINCTIVE has 9 patterns.
Ring patterns 1~4 for USA, and 5~9 for Canada.
However, to make the setting procedure as easy as possible for the
user to understand these patterns are grouped as follows:
<Optional Setting>
1) RING PATTERN 1 RING PATTERN 1 for USA
RING PATTERN 4 for USA
RING PATTERN 5 for Canada
2) RING PATTERN 2 RING PATTERN 2 for USA
RING PATTERN 6 for Canada
3) RING PATTERN 3 RING PATTERN 3 for USA
RING PATTERN 7 for Canada
4) RING PATTERN 4 RING PATTERN 8 for Canada
5) RING PATTERN 5 RING PATTERN 9 for Canada
6) STANDARD RING
7) OFF SETTING
2S ring
STANDARD
RING
PATTERN 1
for USA
RING
PATTERN 2
for USA
RING
PATTERN 3
for USA
RING
PATTERN 4
for USA
RING
PATTERN 5
for CANADA
RING
PATTERN 6
for CANADA
RING
PATTERN 7
for CANADA
RING
PATTERN 8
for CANADA
RING
PATTERN 9
for CANADA
1.5S ring
1S ring
1.5S ring
0.8S
0.3S
0.2S
0.4S
0.2S 0.2S
0.25S
0.25S
2S ring
0.4S
1S
0.4S 0.8S
1S
1S 1S
0.5S
0.5S
0.25S
0.2S
0.2S
0.25S
0.2S
0.5S
0.8S
0.2S
1S
0.3S
0.5S
2S ring
3S ring
4S ring
0.5S
1S
1S 0.5S
0.5S
0.5S0.5S
0.25S
4S ring
4S ring
4S ring
4S ring
4S ring
4S ring
0.5S0.5S
1S
6S
2 – 15
Page 22
UX-A255U
SW-D2 No. 4 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-D2 No. 5 Caller ID function
Used for Caller ID function.
SW-D2 No. 6 Caller ID detect during CI off
Detection of caller ID signal is performed as follows:
0:First CI OFF only
1:All of CI OFF
SW-D2 No. 7, No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-D3 No. 1 ~ No. 5 CI off detection timer (0-1550ms setting by
50ms step)
Set the minimum time period of CI signal interruption.
(Example)
AB
400msec
1 2
011 10 (50ms ~ 14):
700ms (CI interruption>700ms:Judged as a CI OFF section)
The section 1 is not judged as a CI OFF section, the CI signal A
is counted as one signal.
The section 2 is judged as a CI OFF section, the CI signal B is
considered as the second signal.
00111 (50ms ~ 7):
350ms (CI interruption>350ms:Judged as a CI OFF section)
The section 1 is judged as a CI OFF section, and the CI signal A
is counted as two signals.
The section 2 is judged as a CI OFF section, and the CI signal B
is considered as the third signal.
SW-D3 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-E1 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-E2 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-E3 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-F1 No. 1, No. 2 DTMF detect time
Used to set detect time of DTMF (Dual Tone Multi Frequency) used in
remote reception (5 ).
The longer the detect time is, the less the error detection is caused by
noises.
SW-F1 No. 3 Protection of remote reception (5 ) detect
Used to set the function of remote reception (5 ). When set to "1",
the remote reception function is disabled.
SW-F1 No. 4 Remote reception with GE telephone
(Corresponding to TEL made by GE) P. B. X.
"1": Compatible with TEL mode by GE
"0": Not compatible
2000msec
• When sending (5 ) for remote reception with a GE manufactured
telephone remote reception may not take place because of special
specifications in their DTMF.
To overcome this, a soft SW is provided to change the modem setting to allow for remote reception.
• If this soft SW is set to "1", other telephone sets may be adversely
affected.
SW-F1 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Remote operation code figure by external TEL
(0 ~ 9)
Remote operation codes can be changed from 0 through 9. If set to
greater than 9, it defaults to 9. The "5 " is not changed.
Ex-7 (Default: 5 )
SW-F2 No. 1 CNG detection in STAND-BY mode
When setting to "1", the CNG signal detection function during standby
stops.
SW-F2 No. 2, No. 3 Number of CNG detect (AM mode)
Used for detection of CNG in 1 to 4 pulses.
SW-F2 No. 4, No. 5 Number of CNG detect (STAND-BY mode)
Used for detection of CNG in 1 to 4 pulses.
SW-F2 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-G1 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-G2 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-G3 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-H1 No. 1, No. 2 Busy tone detection ON/OFF time (Lower duration)
The initial value of detection is set according to electric condition.
The set value is changed according to the local switch board. (Erro-
neous detection of sound is reduced.)
Normally the upper limit is set to 900msec, and the lower limit to 200msec.
If erroneous detection is caused by sound, etc., adjust the detection
range.
The lower limit can be set in the range of 350msec to 150msec.
SW-H1 No. 3, No. 4 Busy tone detection ON/OFF time (Upper duration)
Similarly to SW-H1 No. 1, the set value can be varied.
The upper limit can be set in the range of 650msec to 2700msec.
SW-H1 SW-H1 SW-H1 SW-H1
No. 1 No. 2 No. 3 No. 4
0 0 0 0 150msec ~ 650msec
0 0 0 1 150msec ~ 900msec
0 0 1 0 150msec ~ 1500msec
0 0 1 1 150msec ~ 2700msec
0 1 0 0 200msec ~ 650msec
0 1 0 1 200msec ~ 900msec
0 1 1 0 200msec ~ 1500msec
0 1 1 1 200msec ~ 2700msec
1 0 0 0 250msec ~ 650msec
1 0 0 1 250msec ~ 900msec
1 0 1 0 250msec ~ 1500msec
1 0 1 1 250msec ~ 2700msec
1 1 0 0 350msec ~ 650msec
1 1 0 1 350msec ~ 900msec
1 1 1 0 350msec ~ 1500msec
1 1 1 1 350msec ~ 2700msec
Detection range
2 – 16
Page 23

UX-A255U
SW-H1 No. 5 Busy tone detect continuation sound detect during
OGM
Used to detect the continuous tone of specific frequency during OGM
output.
SW-H1 No. 6 Busy tone detect continuation sound detect
Used to select detection of the continuous sound of certain frequency.
SW-H1 No. 7 Busy tone detect intermittent sound detect during
OGM
Used to detect the intermittent tone of specific frequency during OGM
output.
SW-H1 No. 8 Busy tone detect intermittent sound detect
Used to select detection of the intermittent sound of certain frequency.
SW-H2 No. 1, No. 2 Busy tone detection pulse number
Used to set detection of Busy tone intermittent sounds.
SW-H2 No. 3 Fax switching when A.M. full
If the answering machine’s memory is full and there is no response, the
machine automatically switches to Fax reception.
SW-H2 No. 4 Busy tone detect continuation sound detect frequency
Set detecting frequency of busy tone continuation sound for 320 ~ 570
Hz of 320 ~ 460 Hz.
SW-H2 No. 5, No. 6 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-H2 No. 7 AM OGM announce only mode
If this switch is set to 1, the machine will not record ICM.
(disconnect the line after OGM output)
SW-H2 No. 8 Busy tone continuous sound detect time
Set detecting time busy tone continuous sound for 5 or 10 seconds.
SW-I1 No. 1, No. 2 ICM recording time
Used to select the incoming message recording time to 15sec/30sec/
60sec/4min.
SW-I1 No. 3, No. 4 A.M. quiet time 1
Used to select four kinds of no sound time (2 sec ~ 5 sec) after reception
in the T.A.D mode until OGM is output.
Reception
OGM output ICM recording
2 sec~ 5 sec ( SW-I1No. 3, No. 4)
SW-I1 No. 5, No. 6 A.M. quiet time 2
Used to select four kinds of no sound time (0 sec ~ 3 sec) after OGM
output the T.A.D mode until ICM recording is started.
Reception
OGM output ICM recording
0 sec~3 sec (SW-I1 No. 5, No. 6)
SW-I1 No. 7
Used to turn ON/OFF key input buzzer in the TWO-WA Y recording mode.
SW-I1 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-I2 No. 1 ~ No. 5 A.M. quiet detect time
Used to set no sound time (0 sec ~ 32 sec) during the T.A.D. mode
operation.
SW-I2 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-I3 No. 1 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-I3 No. 2 Max OGM record time
Used select the outgoing message recording time to 60sec or 15sec.
Key input buzzer on/off switch (Two way recording mode)
SW-I3 No. 3 Two way record function
If this switch is set to "1", the machine disables two way recording.
SW-I3 No. 4 Toll saver
Used to turn on the toll saver function. If it is off, the reception frequency
in the AM mode is indentical with that in the FAX mode.
SW-I3 No. 5 ~ No. 7 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-I3 No. 8 Transfer dial recall
If this switch is set to "1", machine disables redial in Transfer function.
SW-I4 No. 1 ~ No. 4 AGC maximum gain (Line)
(10 ~ 25dB) (1dB step)
The AGC Maximum Gain limits the gain applied by the AGC. Messages
with average energy below the AGC Energy Reference Level will have
their average energy level increased by no more than the AGC Maximum
Gain. The AGC Maximum Gain should average energy of the message
with the lowest average energy to the AGC Energy Reference Level.
SW-I4 No. 5 ~ No. 8 AGC maximum gain (Mic)
(10 ~ 25dB) (1dB step)
The AGC Maximum Gain limits the gain applied by the AGC. Messages
with average energy below the AGC Energy Reference Level will have
their average energy level increased by no more than the AGC Maximum
Gain. The AGC Maximum Gain should average energy of the message
with the lowest average energy to the AGC Energy Reference Level.
SW-I5 No. 1 ~ No. 4 AGC eref access code (Line)
(-0 ~ -30dB) (2dB step)
The AGC Energy Reference Level controls the playback level. Any
message having average speech energy above the energy reference
level has its playback level attenuated, and any level has its playback
level increased. If the playback level is too high (low), then decreasing
(increasing) the AGC Energy Reference Level will achieve the desired
level.
SW-I5 No. 5 ~ No. 8 AGC eref access code (Mic)
(-0 ~ -30dB) (2dB step)
The AGC Energy Reference Level controls the playback level. Any
message having average speech energy above the energy reference
level has its playback level attenuated, and any level has its playback
level increased. If the playback level is too high (low), then decreasing
(increasing) the AGC Energy Reference Level will achieve the desired
level.
SW-I6 No. 1 ~ No. 4 AGC gain adaptation threshold (Line)
The AGC adjusts the amount of gain applied to the incoming message
only when the average energy exceeds the AGC Gain Adaptation
Threshold. The AGC Gain Adaptation Threshold prevents message
background noise from corrupting the gain provided that the AGC Gain
Adaptation Threshold is greater than the background noise energy. In
the event that a message has background noise energy greater than
the AGC Gain Adaptation Threshold, the AGC Gain can be no greater
than the AGC Maximum Gain. Note that the AGC Gain Adaptation
Threshold must always be greater than the RPACS VOX Turn-On
Threshold.
SW-I6 No. 5 ~ No. 8 AGC gain adaptation threshold (Mic)
The AGC adjusts the amount of gain applied to the incoming message
only when the average energy exceeds the AGC Gain Adaptation
Threshold. The AGC Gain Adaptation Threshold prevents message
background noise from corrupting the gain provided that the AGC Gain
Adaptation Threshold is greater than the background noise energy. In
the event that a message has background noise energy greater than
the AGC Gain Adaptation Threshold, the AGC Gain can be no greater
than the AGC Maximum Gain. Note that the AGC Gain Adaptation
Threshold must always be greater than the RPACS VOX Turn-On
Threshold.
SW-I7 No. 1, No. 2 AGC slew rate (Line)
The AGC Slew Rate controls the convergence of the message playback
level to the desired playback level. A large slew rate will allow faster
convergence and a small slew rate will allow slower convergence.
2 – 17
Page 24

UX-A255U
SW-I7 No. 3, No. 4 AGC slew rate (Mic)
The AGC Slew Rate controls the convergence of the message playback
level to the desired playback level. A large slew rate will allow faster
convergence and a small slew rate will allow slower convergence.
SW-I7 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-J1 No. 1, No. 2 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-J1 No. 3 Sender’s phone number setting
Used to make a choice of whether the registered sender’s phone number
can be changed or not. If the switch is set to "1", new registration of the
sender’s phone number is disabled to prevent accidental wrong input.
SW-J1 No. 4, No. 5 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-J1 No. 6 Summer time setting
This is used to set YES/NO of automatic clock adjustment for daylight
saving time.
SW-J1 No. 7, No. 8 Ringer volume
Used to adjust ringing volume.
SW-J2 No. 1 ~ No. 3 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-J2 No. 4, No. 5 Handset receiver volume
Used to adjust the a handset receiver volume.
SW-J2 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Speaker volume (5 stages)
Used to adjust sound volume from a speaker.
SW-J3 No. 1 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-J3 No. 2 ~ No. 4 Communication result printout (Transaction
report)
Every communication, the result can be output. As usual, it is set to print
the timer sending communication error alone. If No. 2: 0 No. 3: 1 No. 4:
0 are set, printing is always on (printed even if it is normally ended).
000: Error, timer and memory sending/receiving
001: Sending
010: Continuous printing
011: Not printed
100: Communication error
SW-J3 No. 5 ~ No. 8 OGM/ICM output level to speaker
(0dB ~ -15dB) (1dB step)
Used to control OGM and ICM output level to speaker.
SW-K1 No.1, No. 2 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-K1 No. 3 ~ No. 8 OGM/ICM output level to Line
(0dB ~ -32dB) (1dB step)
Used to control OGM and ICM output level to Line.
SW-L1 No. 1 ~ No. 4 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-L1 No. 5 Cut off mode (COPY mode)
Whether the excessive part is printed on the next recording paper or
discarded is selected to copy a document which is longer than the recording paper.
SW-L1 No. 6 A4 Paper enable
The use of recording paper of A4 is enabled.
SW-L1 No. 7 LEGAL and LETTER paper enable
The use of recording paper of LEGAL and LETTER is enabled.
SW-L1 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-L2 No. 1, No. 2 Paper set size
At present size of the recording paper.
SW-L2 No. 3 Automatic reduce of receive
If set to 1, it is reduced automatically when receiving.
SW-L2 No. 4 ~ No. 6 Print contrast
Used for adjustment of print contrast.
SW-L2 No. 7 Reception reduction ratio in case of memory full
This model is designed so that the print is started according to the setting of SW-L2 No.3 when reception of one page is completed. However,
if the memory is filled with data before completion of reception of one
page, the print is started with the reduction ratio which is set with this
switch.
SW-L2 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-M1 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-M2 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-N1 No. 1 ~ No. 6 LCR short time
First time setting transmitting to the Open LCR center.
SW-N1 No. 7, No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-N2 No. 1 ~ No. 6 LCR long time
Second time setting transmitting to the Open LCR center.
SW-N2 No. 7, No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-N3 No. 1 LCR Time Select
Used to select LCR short time or LCR long time.
0:LCR short time is selected.
1:LCR long time is selected.
SW-N3 No. 2 T emporary release of caller ID withhold
Used to do temporary release of caller ID withhold.
0:Normal dialing.
1:Release of caller ID withhold before dialing.
SW-N3 No. 3 Connect Japanese center
Used to connect Japanese open LCR center.
0:Connect USA open LCR center.
1:Connect Japanese open LCR center.
SW-N3 No. 4 Open LCR debug mode
Used to debug open LCR function.
0:Normal mode.
1:debug mode.
SW-N3 No. 5, No.6 Digital line equalization setting (Open LCR
downloading)
Line equalization when Open LCR downloading is to be set according to
the line char-acteristics. Setting should be made according to distance
between the telephone and the telephone company central switching
station.
SW-N3 No. 7 Relese code of Caller ID withhold for tone or pulse
line.
Used to connect Open LCR server.
"0": *82 (for TONE)
"1": 1182 (for PULSE)
SW-N3 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
2 – 18
Page 25

CHAPTER 4. DIAGRAMS
DRAM
4Mbit
FLASH ROM
2Mbit
CPU I/F
TIMER
RTC
WATCHDOG
TIMER
CLOCK
32.768kHz
INTERRUPT
CONTROLLER
CIS I/F
VIDEO
PROCESSING
MOTOR I/F
SENSOR I/F
SIO
THERMAL
HEAD I/F
PANEL I/F
PM
OPERATION
PANEL
CPU
CONTROL PWB UNIT
1CHIP FAX ENGINE (SCE214V)
HANDSET
SPEAKER
+24V
OPERATION
PANEL
TEL/LIU
PWB UNIT
DRIVER
MOTOR
CONTACT
IMAGE
SENSOR
DOCUMENT
SENSOR
PIO
POWER SUPPLY
PWB UNIT
AMPLIFIER
FAX MODEM
DSP CORE
SURGE
PROTECT/
FILTER
CML TRANSFORMER
CI
VBT
STABILIZER
RECTIFIER
TRANSFORMER
RECTIFIER
DIODE
TRANS
SURGE
ABSORBER
FILTER
LINE
CLOCK
32.256MHz
LCD
FET
THERMAL
HEAD
P-IN
SENSOR
FILM
SENSOR
RECORDING PAPER
FRONT
SENSOR
SIO
S-RAM(32kbit)
IA(CX20438)
CNPRG
AMPLIFIER
REGULATOR
+3.3V
IMAGING
FILM
FLASH MEMORY
4Mbit
[1] Block diagram
UX-A255U
4 – 1
Page 26

UX-A255U
6
CAM SW
26
THERMAL HEAD
CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR
LCD UNIT
CNLCD
OPERATION
PANEL PWB
NUIT
14
CNPN-A
15
7
16
CNCSWCNMT
CNTH
CNCIS
CNPN CNSP
SPEAKER
CNLIUA
CNPW
14
6
CONTROL PWB UNIT
TEL/LIU
PWB UNIT
POWER SUPPLY
PWB UNIT
CNLIUA
CNPS
TEL LINE
CNLNJ
CNHJ
AC CORD
TX/RX MOTOR
2
HANDSET
4
16
INTERFACE
PWB
CNPN-A
CNPN
[2] Wiring diagram
4 – 2
Page 27
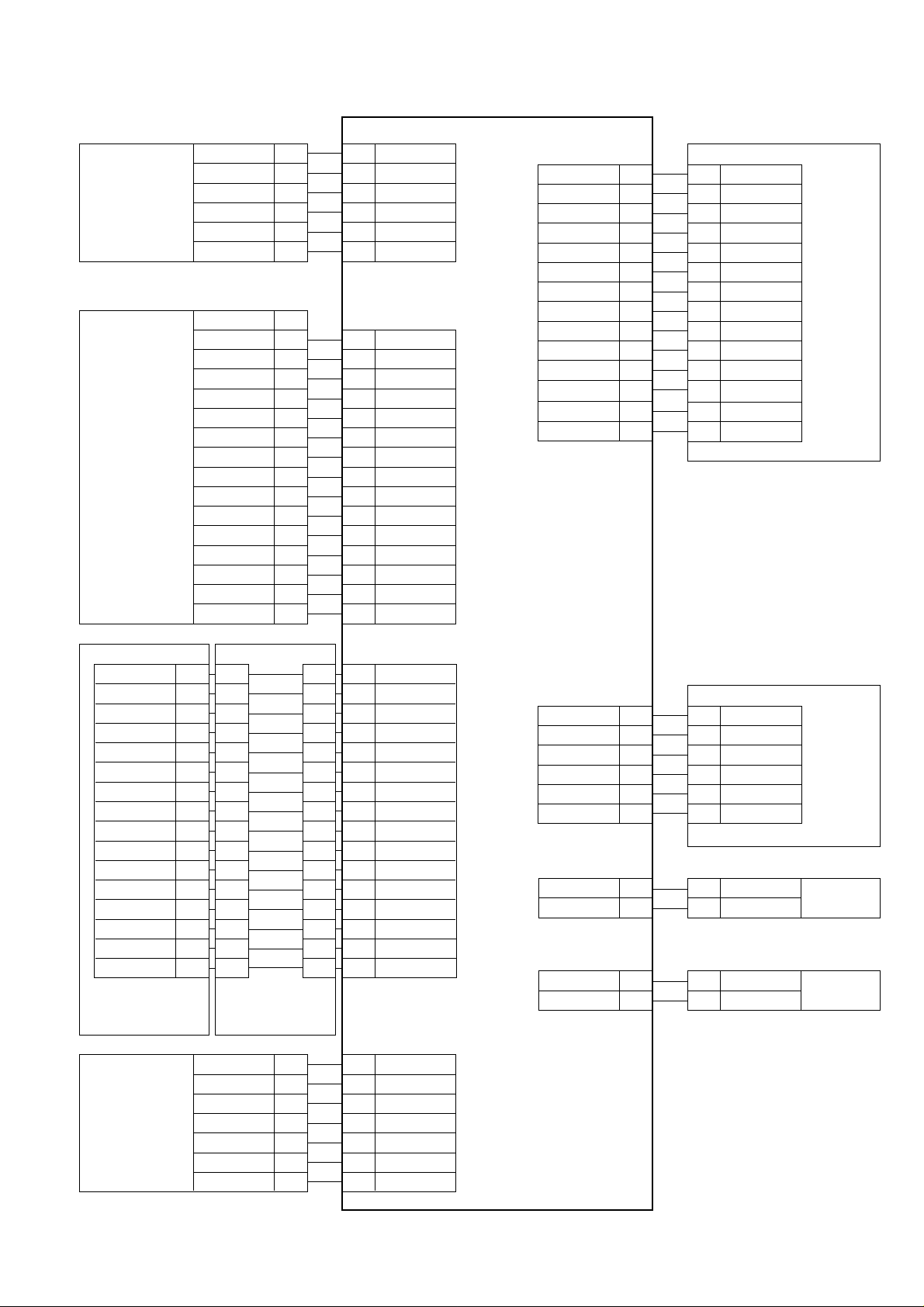
[3] Point-to-point diagram
TPBDTPAD-
TX/RX
MOTOR
THERMAL
HEAD
TPBD
TPAD
VMT
VMT
VTH
VTH
STRB1STRB2-
THI
RANK
THG
THG
THG
THVDD
STRB3STRB4LATCH-
PCLK
DATA
VTH
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
UX-A255U
CNMT
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
CNTH
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
TPBDTPAD-
TPBD
TPAD
VMT
VMT
VTH
STRB1STRB2-
THI
RANK
THG
THG
THG
THVDD
STRB3STRB4LATCH-
PCLK
DATA
VTH
RHSMAG
+24VL
MICMUTE
TELIN
TELMUTE
RXIN
TXOUT
CML
PIN
FILM
CI-
HS-
TELOUT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
CNLIUACNLIUA
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
RHS-
MAG
+24VL
MICMUTE
TELIN
TELMUTE
RXIN
TXOUT
CML
PIN
FILM
CI-
HS-
TELOUT
TEL/LIU
PWB
CNPN-A
KEN4A
KEN3A
KEN2A
KEN1A
DG
+3.3V
ORGSNS-
FRSNS-
E
SEN0
SEN1
SEN2
SEN3
SEN4
SEN5
SEN6
OPERATION
PANEL
PWB
CIS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
CNPN-A
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
INTERFACE
VO
VG
CISVDD
øT
CISCLK
GLED
+24V
PWB
CNPN
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
CNPN
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
ORGSNS8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
CNCIS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
KEN4A
KEN3A
KEN2A
KEN1A
DG
+3.3V
FRSNS-
E
SEN0
SEN1
SEN2
SEN3
SEN4
SEN5
SEN6
VO
VG
CISVDD
øT
CISCLK
GLED
+24V
CONTROL
PWB
+24V
+24V
MG
MG
DG
VREG
CSW-
DG
SP+
SP-
CNPW
1
2
3
4
5
6
CNCSW
1
2
CNSP
1
2
CNPS
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
2
1
2
+24V
+24V
MG
MG
DG
VREG
CSW-
DG
SP+
SP-
POWER
SUPPLY
PWB
CAM
SWITCH
SPEAKER
4 – 3
Page 28
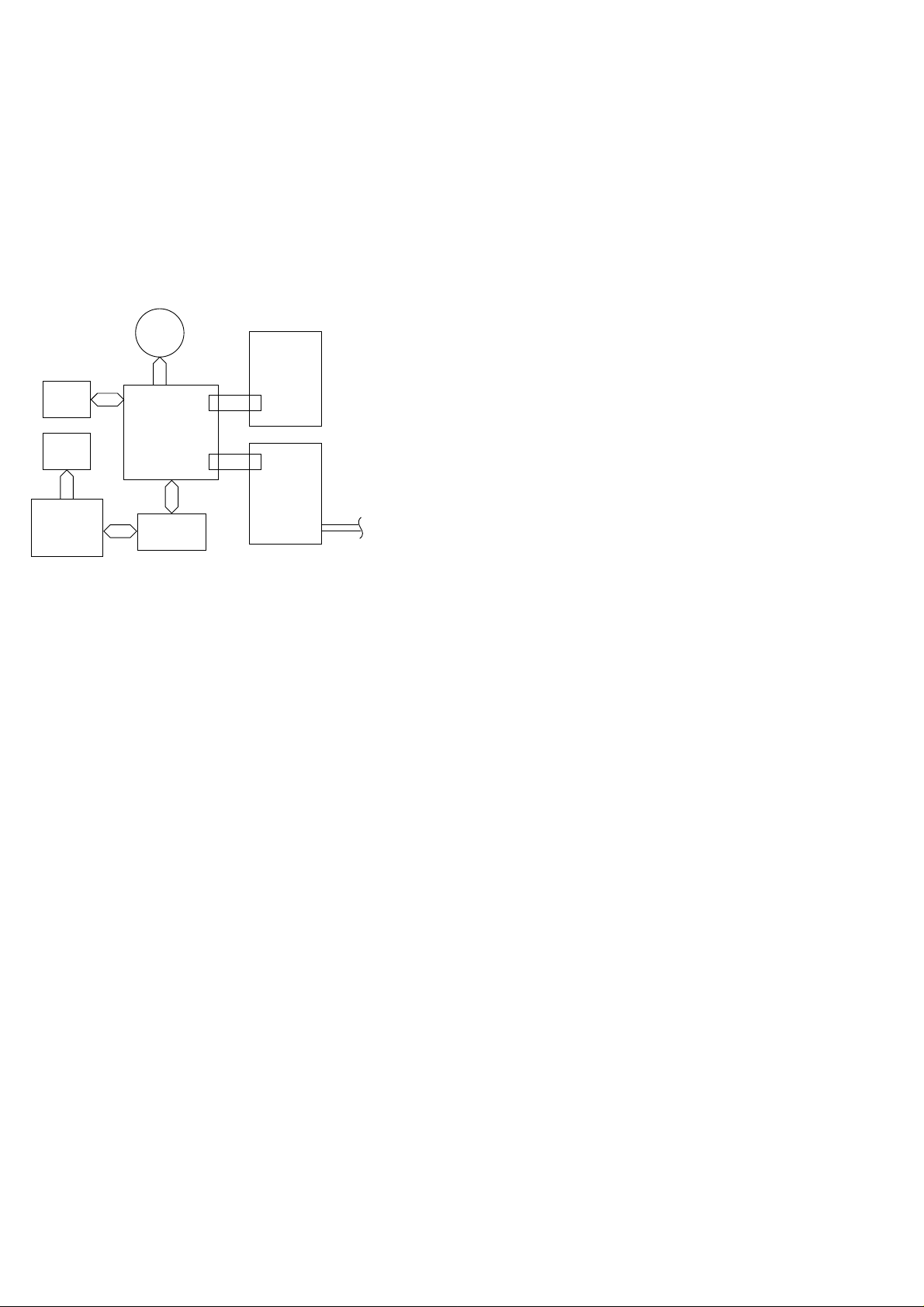
UX-A255U
CHAPTER 5. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
[1] Circuit description
1. General description
The compact design of the control PWB is obtained by using CONEXANT
fax engine in the main control section and high density printing of surface mounting parts. Each PWB is independent according to its function
as shown in Fig. 1.
2. PWB configuration
MOTOR
TEL/LIU
PWB
CIS
CONTROL
LCD
PWB
PANEL
PWB
1) Control PWB
The control PWB controls peripheral PWBs, mechanical parts, transmission, and performs overall control of the unit.
This machine employs a 1-chip modem (SCE214V) which is installed
on the control PWB.
2) TEL/LIU PWB
This PWB controls connection of the telephone line to the unit.
3) Power supply PWB
This PWB provides voltages of Vreg(+5V) and +24V to the other PWBs.
PWB
INTERFACE
PWB
POWER
SUPPLY
PWB
AC CORD
Fig. 1
3. Operational description
Operational descriptions are given below:
• Transmission operation
When a document is loaded in stand-by mode, the state of the document sensor is sensed via the 1 chip fax engine (SCE214V). With
depression of the START key in the off-hook state, transmission takes
place. Then, the procedure is sent out from the modem and the motor is rotated to move the document down to the scan line. In the
scan processor, the signal scanned by the CIS is sent to the internal
image processor and the AD converter to convert the analog signal
into binary data. This binary data is transferred from the scan processor to the image buffer within the RAM and encoded and stored in
the transmit buffer of the RAM. The data is then converted from parallel to serial form by the modem where the serial data is modulated
and sent onto the line.
• Receive operation
There are two ways of starting reception, manual and automatic.
Depression of the START key in the off-hook mode in the case of
manual receive mode, or CI signal detection by the LIU in the automatic receive mode.
First, the SCE214V controls the procedure signals from the modem
to be ready to receive data. When the program goes into phase C,
the serial data from the modem is converted to parallel form in the
modem interface of the 1 chip fax engine (SCE214V) which is stored
in the receive buffer of the RAM. The data in the receive buffer is
decoded software-wise to reproduce it as binary image data in the
image buffer. The data is DMA transferred to the recording processor
within the SCE214V which is then converted from parallel to serial
form to be sent to the thermal head. The data is printed line by line by
the SCE214V which is assigned to control the motor rotation and
strobe signal.
• Copy operation
T o make a copy on this facsimile, the COPY key is pressed when the
machine is in stand-by with a document on the document table and
the telephone set is in the on-hook state. First, depression of the
COPY key advances the document to the scan line. Similar to the
transmitting operation, the image signal from the CIS is converted to
a binary signal in the DMA mode via the 1 chip fax engine (SCE214V)
which is then sent to the image buffer of the RAM. Next, the data is
transferred to the recording processor in the DMA mode to send the
image data to the thermal head which is printed line by line. The
copying takes place as the operation is repeated.
4) Panel PWB
The panel PWB allows input of the operation keys.
5) LCD PWB
This PWB controls the LCD display.
6) Interface PWB
This PWB connect control PWB with panel PWB.
5 – 1
Page 29

UX-A255U
[2] Circuit description of control PWB
1. General description
Fig. 2 shows the functional blocks of the control PWB, which is composed of 4 blocks.
(1) SCE214V
IA(20438)
MEMORY(SRAM)
Fig. 2 Control PWB functional block diagram
2. Description of each block
(1) Main control block
The main control block is composed of CONEXANT 1 chip fax engine
(SCE214V), FLASH ROM (2Mbit), DRAM (4Mbit) and FLASH MEMORY
(4Mbit).
Devices are connected to the bus to control the whole unit.
1) SCE214V (IC3) : pin-176 QFP (FAX CONTROLLER)
1 chip fax engine has Internal Integrated Analog (20438) and Internal
memory (SRAM : 32kbit).
2) SST39VF020P (IC1): pin-32 TSOP (FLASH ROM)
FLASH of 2Mbit equipped with software for the main CPU.
3) MSM51V4800E (IC2): pin-28 SOJ (DRAM)
• Image memory for recording process.
• Memory for openLCR function.
4) K9F4008W0A (IC8): pin-44 TSOP (FLASH MEMORY)
A 512 k x 8bit NAND FLASH MEMORY to store the voice and image
data when using memory function.
(2) IC3 (SCE214V) Hardware description
A) CONTROL BLOCK
1) Integrated Controller (SCC)
The Controller contains an internal MC24 Processor with a 16-MB address space and dedicated circuitry optimized for facsimile image
processing and monitoring and for thermal or thermal transfer printer
support.
The CPU provides fast instruction (up to 10 MHz clock speed) execution and memory efficient input/output bit manipulation. The CPU connects to other internal functions over an 8-bit data bus and 24-bit address bus and dedicated control lines.
The 24-bit external address bus, 8-bit data bus, control, status and decoded chip select signals support connection to external ROM, SRAM,
DRAM, and FLASH memory.
2) DRAM Controller
The CX06835 includes a DRAM controller with signal and page mode
access support which supports fast, normal, or slow refresh time. DRAM
memory space is provided in one block up to 4 MB. A maximum of 4 MB
of DRAM is supported. This space has a programmble size and starting
address. Refresh is performed automatically and is supported in standby mode. CAS and RAS signal support is provided for one-DRAM banks
for both 4-bit and 8-bit organizations. Access speeds from 50ns to 70ns
can be supported.
3) DMA Channels
Six internal DMA channels support memory access for scanner, T.4/T.6,
and resolution conversion. DMA Channel 2 can be reprogrammed for
external access to thermal printing, thermal transfer, or plain paper inkjet
printing.
(2) FLASH
ROM
(3) DRAM
(4) FLASH
MEMORY
4) External RAM and ROM
Moveable and programmble size external SRAM memory of up to 1 MB,
DRAM memory of up to 4 MB, and ROM of up to 2 MB can be directly
connected to the SCE214V. By using an external address decoder, the
size of SRAM and/or ROM can be extened. The ROM stores all the
program object code.
5) Flash Memory Controller
The SCE214V includes a flash memory controller that supports NOR,
NAND, and Serial NAND-type flash memory. The supported size of NORtype memory is up to 1 MB and the supported size of NAND-type memory
is unlimited.
6) Stepper Motor Control
Eight outputs are provided to external current drivers: four to the scanner motor and four to the printer motor. The stepping patterns are programmable and selectable line times are supported. A timeout circuit
controls the power control of the motors. The printer or scanner motor
outputs can be programmed as GPOs for applications using single motor or paper printers.
7) T.4/T.6 Compressor/Decompressor
MH, MR and MMR compression and decompression are provided in
hardware. T .4 line lengths of up to 8192 pixels are supported. MMR and
Alternating Compression/Decompression (ACD) on a line by line basis
provide support for up to three independent compression and decompression processes.
8) Bi-level Resolution Conversion
One independent programmable bi-level 1D-resolution conversion block
is provided to perform expansion or reduction on the T.4 decompressed
data and scan image data. Image expansion can be programmed up to
200% and reduction down to 33%. Vertical line ORing and data output
bit order reversal is also provided.
9) Printer IF
The Printer Interface provides a standard connection between the
SCE214V and a thermal printhead to support thermal printing or thermal
transfer. The thermal printer interface consists of programmable data,
latch, clock, and up to four strobe signals. Programmable timing supports traditional thermal printers, as well as the latchless split mode printers, and line lengths of up to 2048 pixels. Line times from 5 ms to 40 ms
are supported.
The SCE214V includes a thermal ADC (TADC) function utilizing a D/A
converter and a comparator to monitor the printhead temperature. External terminating resistors must be supplied; the values are determined
by the specific printhead selected.
As an option, plain paper inkjet printing can be supported.
10) TPH Hardware Timer
The TPH hardware timer provides a 500 ms timer that can be re-triggered or reset.
11) Scanner and Video Control
Five programmable control and timing signals support common CCD
and CIS scanners. The video control function provides signals for controlling the scanner and for processing its video output. Three programmable control signals (START, CLK1n, and CLK2) provide timing related to line and pixel timing. These are programmable with regard to
start time, relative delay and pulse width.
Two video control output siganls (VIDCTL[1:0]) provide digital control
for external signal pre-processing circuitry. These signals provide a per
pixel period, or per line period, timing with programmable polarity control for each signal.
5 – 2
Page 30

UX-A255U
12) Video Processing
The CX06835 supports two modes of shading correction for scanner
data non-uniformity arising from uneven sensor output or uneven illumination. Corrections are provided on either an 8-pixel group or are applied separately to each pixel. Dark level correction and gamma correction are also provied.
Two-dimensional Error Diffusion/Dithering is performed on halftone images.
The CX06835 includes an 8 x 8 dither table, which is programmable and
stored internally (8-bit per table entry). The table is arranged in a matrix
of 8 rows by 8 columns. The video processing circuit provides mixedmode detection/processing and multi-level Resolution Conversion for
the scanner multi-level data. The conversion ratio of the multi-level Resolution Conversion is fixed to B4-A4 conversion.
13) Operator Panel Interface
Operation Panel functions are supported by the operator output bus
OPO[6:0], the operator input bus OP[3:0], and two control outputs
(LCDCS and LEDCTRL).
The CX06835 can directly interface to a 28-key keypad.
A 2-line LCD display module with 20 characters per line can be supported.
14) Synchronous Serial Interface (SSIF)
One or optionally two Synchronous only Serial Interfaces (SSIF) are
built into the CX06835, which allows it to communicate with external
peripherals. Each SSIF provides separate siganls for Data (SSTXD,
SSRXD), Clock (SSCLK), and Status (SSSTAT). Each SSIF is a duplex,
three-wire system. The SSIF may be configured to operate as either a
master or a slave interface. The bit rate, clock polarity, clock phase, and
data shifting order are programmable.
15) Synchronous/Asynchronous Serial Interface (SASIF)
One or optionally two Synchronous/Asynchronous Serial Interface
(SASIF) performs the following:
• Serial-parallel conversion of data received from a peripheral device.
• Parallel-to-serial conversion of data for transmission to a peripheral
device.
This interface consists of serial transmit data (SASTXD), serial receive
data (SASRXD), and a serial clock(SASCLK). The SASIF includes a
programmable bit rate generator for asynchronous and synchronous
operations. The data shifting order, data bit number, and the SASCLK
polarity are programmable.
The optional SASIF 2 has an additional pin called DSS_AVAIL. This
signal can be used to tristate the SASCLK2 and SASTXD2 signals.
16) Real Time Clock (RTC)
The CX06835 includes a battery backup real time clock. The RTC will
automatically maintain the proper date and time for 32 years. Leap year
compensation is included. A 32.768 kHz or 65.536 kHz crystal is required by the RTC.
17) Tone Generator (ALT_TONE)
The CX06835 provides a programmable tone generator output. The frequency of the tone generator is programmable from 400 Hz to 4 kHz. By
using a PWM programmable high frequency as a modulation frequency,
the output level can be made programmable.
18) Watchdog Timer
The Programmable Watchdog Timer is intended to guard against
firmware lockup on the part of either executive-controlled background
tasks or interrupt-driven tasks, and can only be enabled by a sequence
of events under control of the W atchdog Control Logic. Once the Watchdog Timer has been enabled, it can not be disabled unless a system
reset occurs.
19) Reset and Power Control
The RESETn I/O pin provides an internally generated reset output to
external circuits, or it can accept an externally generated reset signal.
This reset signal will not reset the RTC. Separate RTC battey power
inputs are provided for battery-backup functions. A BA TRSTn pin is provided, which resets the RTC circuits and other SCC circuits.
20) Power Up/Down Control
Power Up/Down detection is provided internally . The threshold voltages
are:
• Power Up detection level = 2.83V to 2.95V.
An internally generated power down signal controls internal switching
between primary and battey power. This control signal is also provied as
an output on the PWRDWNn pin. An externally generated power down
detector (optional) can be provided as an input on the PWRDWNn pin
by setting the INTPWRDWNEn pin.
21) Stand-by and Sleep Modes
Two power saving modes are provided to reduce the power consumption. In stand-by mode, the CPU is functional, but the modem clock is
turned off to save power. When this occurs, the modem may be activated by software under different conditions. In sleep mode, the clock is
cut off from both the modem and the CPU to increase the power savings.
The system can be activated by paper insertion, key pressing events,
and telephone ring detection.
22) Embedded Modem DSP
The embedded modem DSP is a synchronous 9600 bps half-duprex
modem with error detection and DTMF generation/reception. It provides
data transmission/reception from regular PSTN lines, PBX, or private
lines.
The modem can operate at any standard V.29 data speed up to 9600
bps as well as in V.21 and V.23 modes.
The modem is designed for use in Group 3 facsimile machines. It satisfies the requirements specified in ITU-T recommendations V .29, V.27ter,
V .21 Channel 2, and T.4 , and meets the signaling requirements of T .30.
It also performs HDLC framing according to T.30 at all speeds.
Note: For technical details, refer to the FM209/FM214 Designer’s Guide,
(document 1175).
23) Software and Firmware Support Features
Available software and embedded firmware provides the following:
• Modem support for speeds up to 9600 bps.
• ECM under conditional assembly.
• DRAM memory support under conditional assembly.
• MH, MR and MMR support.
• Page memory receiving.
• 5ms minimum scan line time.
• Conditional Error Diffusion or Dither table (8x8) support.
• Dark Level Correction support.
• Single motor support.
• 28-key operator panel support.
• Call progress support for Europe and U.S.A.
• Monochrome inkjet print engine support.
5 – 3
Page 31

UX-A255U
B) Modem block
1) Facsimile Modem
The modem can operate at 14400, 12000, 9600, 7200, 4800, 2400, or
300 bps, and can perform HDLC framing per T.30 at all rates. A programmable DTMF detector, three programmable tone detectors, V.21
Channel 2 FSK 7E flag detector, Caller ID demodulator and ring detector are provided.
2) Voice and Audio Codecs
The voice coder/decoder (codec) compresses voice at an average rate of
2.9 kbps which provides 24 minutes of stored voice messages in 4 Mbits
of memory. But for UX-A255U, a part of memory is used for other usages.
So the total recording time is shortened at about 20 minutes. This voice
codec allows the host controller to efficiently store and playback digital
incoming messages (ICMs), outgoing messages (OGMs).
The ADPCM audio codec compresses audio signals (music/voice) at 32
kbps or 24 kbps and the PCM audio codec records audio signals at 128
kbps or 64 kbps for highest fidelity coding and reproduction.
Selectable error correction coding allows storage in audio grade RAMs
(ARAMs). Echo cancellation techniques employed during playback
allow DTMF tone and Type II Caller ID CAS detection during voice/audio
codec operation to support user selectable features. The coder can record
messages from the PIA or SIA. The decoder can playback messages to
the PIA or both the PIA and SIA. Dual/signal tone transmission is available when the decoder is disabled.
3) V.23 Full-duplex Modem and Caller ID
Both full-duplex transmit and receive (with asymmetric 1200/75 bps connection) and half-duplex (1200 bps) asynchronous V.23 are supported,
as will as both serial and parallel interfaces to the modem. The V.23
algorithm includes an optional, programmable. receive compromise
equalizer which is active in both V .23 and Caller ID (V.23 Receive only)
modes.
Common applications for V.23 include France’s Minitel and Japan’s Lowest
Cost Routing.
4) Features
• Group 3 facsimile transmission/reception
- ITU-T V.17 and V.33
- ITU-T V.29, V.27 ter, T.30, V.21 Channel 2, T.4
- ITU-T V.17 and V.27 ter short train
- HDLC framing at all speeds
- Receive dynamic range: 0 dBm to -43 dBm
- Automatic adaptive equalization
- Fixed and programmable digital compromise equalization
- DTMF detect and tone detect
- ITU-T V.21 Channel 2 FSK 7E Flag Detect
- Ring detector
- Programmable transmits level
- Programmable single/dual tone transmission
• Voice codec
- 24 minutes of voice storage per 4 Mbit memory
- Near toll quality voice recording and playback
- Programmable AGCs
-
Programmable line/microphone input and line/speaker output filters
- Error correction coding allows ARAM usage
- DTMF detect, tone detect, and tone transmit
- Type II Caller ID CAS detection
- Pitch synchronized fast and slow playback
- Near-end echo cancellation
• ADPCM Audio codec
- High fidelity recording and playback of audio signals
- 32 kbps and 24 kbps
- Programmable AGCs
-
Programmable line/microphone input and line/speaker output filters
- DTMF detect, tone detect, and tone transmit
- Type II Caller ID CAS detection
- Near-end echo cancellation
• PCM audio codec
- 128 kbps and 64 kbps
- DTMF detect and tone detect
- Type II Caller ID CAS detection
- Near-end echo cancellation
• V.23 and Type I Caller ID
- Full-duplex modes:
TX = 75 bps. RX = 1200 bps
TX = 1200 bps. RX = 75 bps
- Half-duplex mode:
TX = RX = 1200 bps
- Serial and parallel data modes
- Programmable parallel data mode
- 5, 6, 7, or 8 data bits
- 1 or 2 Stop bits
- Mark, Space, Even, or Odd Parity
- Break function
- Transmitter squelch
- Compromise equalizer
• 3.3V/5V operation
5 – 4
Page 32

UX-A255U
5) Integrated Analog Control Resisters for 20438
The 20438 IA can be used as a Primary Integrated Analog (PIA) codec or as a Secondary Integrated Analog (SIA) codec, depending on the signal
connection with the SCE Controller ASIC device. In the SCE100 product, both the PIA and the SIA are packaged external to the SCE Controller device,
whereas in the SCE214V, the PIA is packaged with the SCE214V Controller and the SIA is external.
The 20438 IA provides gain, filtering, internal analog switching, and an internally sourced microphone bias output. The IA is controlled by three control
registers and an address register located in internal RAM space which are accessed via the modem interface memory. These registers provide individual controls for the IA’s inputs, outputs, gain settings, and switching.
The registers are located in internal DSP RAM. Each bit of each 8-bit IA control register has exactly the same meaning for the PIA and the SIA. The LSB
of each 16-bit address contents is used to control the PIA. The MSB of each 16-bit address contents is used to control the SIA.
The following table the PIA/SIA control register RAM access code.
Register SBRAMx BRx Crx IOx AREXx ADDx PIA Reg* SIA Reg*
IACR1 0 0 0 0 0 D0 0 1
IACR2 0 0 0 0 0 D4 0 1
IACR3 0 0 0 0 0 D5 0 1
IAADD 0 0 0 0 0 CE 0, 1 0, 1
NOTES: *Registers to use when x=1. When x=2, add 10h.
• For changes made to IACR1 tobe effective, the host must write to IAADD with a value of 0002h.
• For changes made to IACR2 tobe effective, the host must write to IAADD with a value of 0006h.
• For changes made to IACR3 tobe effective, the host must write to IAADD with a value of 0007h.
Configuration default values are shown below.
DEFAULT VALUE
CONFIGURATION IACR1 IACR2 IACR3
V.17/V.33 1D9Eh 0008h 0000h
V.29 1D9Eh 0008h 0000h
V.27ter 1D9Eh 0008h 0000h
V.21 Ch. 2 1D9Eh 0008h 0000h
V.23/Caller ID 1D9Eh 0008h 0000h
Tone Transmit/Detect 1D9Eh 0008h 0000h
V oice/Audio Codec 0D16h 0008h 0000h
Speakerphone 0D16h 0008h 0000h
The following signal flow block diagram is for a signal IA and it applies to both PIA and SIA.
MICP
MICM
LINEIN
LINE OUT
LINE IN ENABLE MIC ENABLE
GAIN
MIC/LINE SELECT
0, 20, 25, 30 dB(MIC IN)
0dB(LINE IN)
LINE OUT ENABLE
LINE
DRIVER
Mute, 0, -6, -12 dB
LPF ADC
(1,0)
(1,1)
LINE IN
SELECT
(0,0)
SOUT
0, +4 dB
SPKRP
SPKRM
SPEAKER
DRIVER
SPEAKER OUT ENABLE
Fig. 3 PIA/SIA Signal Flow Control
Loop
(1,1)
(1,0)
(0,1)
(0,0)
DAC
0, 6 dB
SIN
RT
5 – 5
Page 33

SCE214V (IC3) Terminal descriptions
Pin
No. Type Type
1 VDDPLL ———PLL Power
2 VSSPLL ———PLL GND
3 ROMCSn O — 13Xs —
4 SYNC/GPO[20] O — 13Xs —
5 WRn O — 13Xs —
6 RDn O — 13Xs —
7 DEBUGn I Hu ——
8 TSTCLK O — 13Xs —
9 VSS ———Digital GND
10 SXIN I Osc0 ——
11 SXOUT O — Osc0 —
12 OPO[0]/GPO[8]/SMPWRCTRL O — 13Xs —
13 OPO[1]/GPO[9]/PMPWRCTRL O — 13Xs —
14 OPO[2]/GPO[10]/RINGER OZ — 13Xs —
15 OPO[3]/GPO[11] O — 13Xs —
16 OPO[4]/GPO[12]/SSTXD1 O — 13Xs —
17 OPO[5]/GPO[13] O — 13Xs —
18 OPO[6]/GPO[14] O — 13Xs —
19 OPI[0]/GPIO[21]/SSRXD1 I/O Hu 13Xs —
20 OPI[1]/GPIO[22]/SSSTAT1 I/O Hu 13Xs —
21 OPI[2]/GPIO[23]/SSCLK1 I/O Hu 13Xs —
22 OPI[3]/GPIO[24] I/O Hu 13Xs —
23 LCDCS/GPO[17] O — 1XC —
24 VDD ———Digital Power
25 RASn O — 13Xs —
26 CAS[0]n O — 13Xs —
27 DWRn O — 13Xs —
28 VBAT ———RTC Battery Power
29 XIN I Osc1 ——
30 XOUT O — Osc1 —
31 WRPROTn O — 1XC —
32 TEST[1] I Hd ——
33 TEST[0] I Hd ——
34 BATRSTn I H ——
35 INTPWRDWNEn I H ——
36 PWRDWNn I/O H 13Xs —
37 N.C. ————
38 ADGA — VADG — PADC Analog GND
39 VREFn/CLREF I VR- — PADC
40 VIN I VA — PADC
41 ADGA — VADG — PADC Analog GND
42 ADVA — VADV — PADC Analog Power
43 ADXG — VXG — PADC
44 VREFp I VR — PADC
45 VSS ———VSS Digital GND
46 IVREFn O — VR- PADC
47 IVREFp O — VR+ PADC
48 VDD ———Digital Power
49 THADI I Analog — TADC
50 VSS ———Digital GND
51 GPIO[17]/DSPIRQn I/O Hu 13Xs —
52 GPIO[16]/IRQ[8] I/O Hu 13Xs —
53 GPIO[15]/CS[5]n I/O Hu 13Xs —
54 GPIO[13]/CS[3]n I/O Hu 13Xs —
55 GPIO[37]/IRQ15n/DSPCSn I Hu 13Xs —
56
57 STRB[0] O — 1XC —
58 STRB[1] O — 1XC —
59 STRB[2] O — 1XC —
60 STRB[3] O — 1XC —
61 PLAT O — 3XC —
62 PDAT O — 2XC —
63 PCLK/DMAACK O — 3XC —
GPIO[4]/CPCIN/TPHPWRCTRL/DMAREQ
Pin List I/O
I/O Hu 13Xs —
Input Output
UX-A255U
Pin Description
5 – 6
Page 34

UX-A255U
SCE214V (IC3) Terminal descriptions
Pin
No. Type Type
64 VDD ———Digital Power
65 GPIO[11]/BE/SERINP/SR4IN I/O Hu 13Xs —
66 GPIO[19]/RDY/SEROUT I/O Hu 13Xs —
67 START O — 2XC —
68 CLK1n/GPO[25] O — 13Xs —
69 CLK2/GPO[24] O — 13Xs —
70 GND ———IA GND
71 MCLK ID ——Main Clock from DSP
72 CTRLI ID d — Control Data from DSP
73 TESTC ID d — IA Test
74 SOUT OD — T Serial Data to DSP
75 SIN ID d — Serial Data to DSP
76 FSYNC I/OD d — Frame Sync Signal (IA)
77 POR IA d — Hardware Reset
78 GND ———IA GND
79 LINE_INP IA ——Analog Input to Line Pre-Amp.
80 MIC_INP IA ——Positive differential Analog Input to Microphone Pre-Amp.
81 MIC_INM IA ——Negative differential Analog Input to Microphone Pre-Amp.
82 MIC_BIAS OA ——2.2 V Nominal DC Bias Source for Electret Microphone
83 BG OA ——Analog reference Voltage Output
84 VC OA ——Analog Ground Bias Output
85 AVDD PWR ——IA Analog Power
86 GND ———IA GND
87 LINE_OUTP OA ——Line Driver Output
88 SPKR_OUTP OA ——Positive Speaker Driver Output
89 SPKR_OUTM OA ——Negative Speaker Driver Output
90 DVDD PWD ——IA Digital Power
91 MODE_0 ID u — Connect to VSS (IA Mode Selection)
92 ICLK I/OD ——IA Bit Clock Input/Output
93 VSS ———VSS Digital GND
94 FCSn[1]/VIDCTL[0]/GPO[23] O — 13Xs —
95 IARESET O — 13Xs DSP to EXTIA POR
96 IACLK O — 13Xs DSP to EXTIA MCLK
97 VDD ———Digital Power
98 IA1CLK I H — DSP from EXTIA ICLK
99 SR3IN/DSPIRQn I H — DSP from primary EXTIA SOUT/EXT. Modem IRQn
100 SR4OUT O — 13Xs DSP to primary EXTIA SIN
101 SR1IO O — 13Xs DSP to EXTIA CTRL1
102 SA1CLK I H — DSP from EXTIA FSYNC
103 GPIO[7]/SSRXD2/SASRXD2 I/O Hu 13Xs —
104 GPIO[6]/SSTXD2/SASTXD2 I/O Hu 13Xs —
105 GPIO[5]/SSCLK2/SASCLK2 I/O Hu 13Xs —
106 GPIO[10]/SSSTAT2/DSS_AVAIL I/O Hu 13Xs —
107 VSS ———Digital GND
108 RESETn I/O Hu 2XC —
109 GPIO[3]/SASCLK I/O Hu 13Xs —
110 GPIO[2]/SASRXD I/O Hu 13Xs —
111 GPIO[1]/SASTXD I/O Hu 13Xs —
112 GPIO[9]/FRDn I/O Hu 13Xs —
113 GPIO[8]/FWRn I/O Hu 13Xs —
114 A[0] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
115 A[1] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
116 A[2] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
117 A[3] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
118 A[4] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
119 VDD ———Digital power
120 A[5] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
121 A[6] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
122 A[7] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
123 A[8] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
124 A[9] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
125 A[10] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
126 A[11] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
Pin List I/O
Input Output
Pin Description
5 – 7
Page 35

SCE214V (IC3) Terminal descriptions
Pin
No. Type Type
127 A[12] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
128 A[13] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
129 A[14] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
130 A[15] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
131 A[16] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
132 VDD ———Digital Power
133 VSS ———Digital GND
134 A[17] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
135 A[18] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
136 A[19] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
137 A[20] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
138 A[21]/EYECLK I/O T u 13Xs CPU Address Bus
139 A[22]/EYESYNC I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
140 A[23]/EYEXY I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Address Bus
141 D[0] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Data Bus
142 D[1] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Data Bus
143 D[2] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Data Bus
144 D[3] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Data Bus
145 D[4] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Data Bus
146 D[5] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Data Bus
147 D[6] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Data Bus
148 D[7] I/O Tu 13Xs CPU Data Bus
149 GPIO[20]/ALTTONE I/O Hu 13Xs —
150 GPIO[26] I/O Hu 13Xs —
151 GPIO[27] I/O Hu 13Xs —
152 GPIO[28] I/O Hu 13Xs —
153 GPO[26] O — 13Xs —
154 GPO[27] O — 13Xs —
155 GPO[28] O — 13Xs —
156 GPO[29] O — 13Xs —
157 GPO[30]/SR3OUT O — 13Xs —
158 GPIO[29] I/O Hu 13Xs —
159 GPIO[31] I/O Hu 13Xs —
160 GPIO[32] I/O Hu 13Xs —
161 VDD ———Digital power
162 GPIO[34] I/O Hu 13Xs —
163 GPIO[35] I/O Hu 13Xs —
164 GPIO[36] I/O Hu 13Xs —
165 Vss ———Digital GND
166 VDD ———Digital Power
167 PM[0]/GPO[0] O — 13Xs —
168 PM[1]/GPO[1] O — 13Xs —
169 PM[2]/GPO[2] O — 13Xs —
170 PM[3]/GPO[3] O — 13Xs —
171 SM[0]/GPO[4] O — 13Xs —
172 SM[1]/GPO[5] O — 13Xs —
173 SM[2]/GPO[6] O — 13Xs —
174 SM[3]/GPO[7] O — 13Xs —
175 REGDMA/GPO[18]/CLKDIV[0] I/O T 13Xs —
176 WAITn/GPO[19]/CLKDIV[1] I/O T 13Xs —
Pin List I/O
Input Output
UX-A255U
Pin Description
5 – 8
Page 36
UX-A255U
(3) Panel control block
The following controls are performed by the SCE214V.
• Operation panel key scanning
• Operation panel LCD display
(4) Mechanism/recording control block
• Recording control block diagram (1)
OPERATOR
PANEL,
KEYPAD,
LEDS & LCD
PRINTER DATA
CONTROI &
SENSORS
PRINTER &
SCANNER
MOTOR DRIVERS
SCANNER
CONTROLS &
SENSORS
OPO[7:0]*
OPI[3:0]*
LEDCTL*
LCDCS*
STRB[3:0]
STRBPOL
THADI
PDAT
PCLK
PLAT
PM[3:0]*
SM[3:0]*
START
CLK2
CLK1
CLK1N
SCE214V
1-CHIP
FAX ENGINE
TEST[1:0]
BATRSTN
RESETN
TONE
ALTTONE
TSTCLK
REGDMA
WAITN
SYNC
PWRDWNN
INTPWRDWNEN
XIN
XOUT
SXIN
SXOUT
RTC
CRYSTAL
SYSCLK
CRYSTAL
INTERNAL
IA
RXIN
TXOUT
TELEPHONE
LINE
LINE
INTERFACE
SCANNER
VIDEO
PREPROCESSING
SERIAL SYNC
PORTS
(SSIF)
PURPOSE I/O
SYNC/ASYNC
SERIAL PORT
SASIF
VIDCTL[1:0]
VIN
VREFP
VREFN
IVREFP
IVREFN
SSCLK[2:1]*
SSTXD[2:1]*
SSRXD[2:1]*
SSSTAT[2:1]*
GPIOGENERAL
SASCLK*
SASTXD*
SASRXD*
A[23:0]
D[7:0]
RDN
WRN
ROMCSN
CS[5:0]N*
WRPROTN
FRDN*
FRWN*
FCLE*
FCSN[2:0]
DEBUGN
VDD
VDRAM
VBAT
VSS
ADVA
ADGA
Fig. 4
EXTERNAL BUS
NOTES: * ALTERNATIVE GPO, GPI OR GPIO LINES
**FOR SAMSUNG NAND-TYPE FLASH
RDN, ROMCSN
CAS[0,1]N, RASN, DWRN
CS3N,
CS4N**
FLASH MEMORY
(OPTION)
D7[7:0]
FLASH
ROM
DRAM
5 – 9
Page 37

[3] Circuit description of TEL/LIU PWB
(1) TEL/LIU block operational description
UX-A255U
1) Block diagram
LINE
HANDSET
CML
H
L
CI DETECTOR
PC1
RX
TX
Q101
Q102
TEL MUTE
(H:MUTE)
MIC MUTE
(H:MUTE)
IC102-B
IC102-A
SPEAKER
IC101-A
IC101-B
IC7
TXOUT
RXIN
TEL IN
SP MUTE
(H:MUTE)
CONTROL PWBTEL/LIU PWB
IC5
+24VL
DG
Q104
Q105
SIGTX
SIGRX
SPOUT
BZOUT1
DTMFMUTE
RCVOL
SP MUTE
TEL MUTE
CML
MIC MUTE
VOL-A
VOL-B
VOL-C
MODEM BLOCK
(20438 I/A)
SPKRP
MIC ENABLE
MICP
LINEIN
LINE
OUT
CI
MIC
/LINE
SELECT
LINE IN ENABLE
SP OUT ENABLE
0,20,25,30dB
LINE OUT ENABLE
MUTE,0,-6,-12dB
IC3 SCE214V
FAX CONTROLLER
RTLOOP
0,1
0,0
1,0
1,1
LPF
LINESEL
1,1
0,0
1,0
0,6dB
DAC
DAC
SIN
ADC
0,+4dB
SOUT
2) Circuit description
The TEL/LIU PWB is composed of the following 6 blocks.
1. Speech circuit section
2. Dial transmission section
3. Speaker amplifier section
4. Ringer circuit section
5. CI detection circuit
6. Signal/DTMF transmission level & receiving level
Fig. 5
3) Block description
1. Speech circuit section
• The receiver volume is an electronic volume type, this model is
switched in 3 steps.
2. Dial transmission section
• D.P. transmission: The CML relay is turned on and off for control in
the DP calling system. (Refer to the attached sheet.)
• DTMF transmission: It is formed in the modem, and is output.
3. Speaker amplifier section
• Ringer volume :It is controlled by the combination of the
attenuator value of the LINE DRIVER in the
modem and the ringer sending level sent from
the modem.
• Speaker volume :It is controlled by the attenuator value of the
IC5 and IC3 (VOL-A,B,C)
4. Ringer circuit section
• The ringer sound is formed in the tone of modem when CI signal is
detected. The amplifier circuit drives the speaker of the main body.
5 – 10
Page 38

UX-A255U
5. CI detection circuit
• CI is detected by the photo coupler which is integrated in series in
the primary side TEL circuit well proven in the existing unit.
6. Signal/DTMF transmission level & receiving level
•
Signal transmission level setting: ATT -8 dB Circuit output: -11 dBm.
• DTMF transmission level setting: HF -2.5 dBm LF -4.5 dBm
Thus, set the level.
4) Signal selection
The following signals are used to control the transmission line of TEL/
FAX signal. For details, refer to the signal selector matrix table.
[Control signals from output port]
Signal Name Description
CML Line connecting relay and DP generating relay
(The circuit is located H: Line make
in the TEL/LIU PWB.) L: Line break
SP MUTE Speaker tone mute control signal
(The circuit is located H: Muting (Power down mode)
in the TEL/LIU PWB.) L: Muting cancel (Normal operation)
TELMUTE H: Muting
RCVOL
DTMFMUTE
(The circuit is located
in the control PWB.)
Handset reception mute control signal
L: Muting cancel
Handset receiver volume control signal
Volume High Middle Low
RCVOL
DTMFMUTE L L H H
Note: The DTMF sending listed above is DTMF signal
sending in the handset OFF-HOOK mode.
LHH H
DTMF sending
VOLUME SETTING
Receiver volume setting Low 1 1
Middle 1 0
High 0 0
DTMF Transmission Fixed 1 1
volume setting (Receiver)
Key buzzer volume setting Fixed 1 1 1
Speaker volume setting Level1 0 1 1
Level2 0 0 1
Level3 1 1 0
Level4 0 1 0
Level5 1 0 0
Ringer volume setting Low 1 1 1
Middle 0 0 1
High 0 0 0
DTMF speaker volume Level1 1 0 1
setting Level2 1 0 1
Level3 1 0 1
Level4 1 0 1
Level5 1 0 1
OGM playback speaker Level1 0 0 1
volume setting Level2 1 1 0
Level3 0 1 0
Level4 1 0 0
Level5 0 0 0
ICM record speaker Level1 0 0 1
volume setting Level2 1 1 0
Level3 0 1 0
Level4 1 0 0
Level5 0 0 0
LINEOUT A RCVOL DTME VOL A VOL B VOL C
(HIGH) (LOW) MUTE
5 – 11
Page 39

[Signals for status recognition according to input signals]
Signal Name Function
RHS
H:The handset is in the on-hook state.
L: The handset is in the off-hook state.
CI Incoming call (CI) detection signal
[Other signals]
Signal Name Function
TEL IN Receiving signal from line or modem
SPOUT Speaker output signal
TXOUT
RXIN
Transmission (DTMF) analog signal output
from modem
Reception (DTMF, others) analog signal
into modem
TELOUT Voice input to MODEM from handset.
input
NO Signal Name (CNLIUA)
1 RHS2DG
3 +24VL
4 MICMUTE
5
TELIN
6 TELMUTE
7 RXIN
UX-A255U
NO Signal Name (CNLIUA)
8 TXOUT
9 CML
10 PIN
11 FILM
12
13 HS14 TELOUT
CI-
(Example: SENDING/RECEIVING)
TEL MUTE
(H:MUTE)
IC102-B
LINE
CML
HANDSET
H
L
CI DETECTOR
RX
TX
: FAX SENDING/RECEIVING
PC1
Q101
Q102
MIC MUTE
(H:MUTE)
IC102-A
IC101-A
IC101-B
SPEAKER
IC7
TXOUT
RXIN
TEL IN
SP MUTE
(H:MUTE)
CONTROL PWBTEL/LIU PWB
IC5
+24VL
DG
Q104
Q105
SIGTX
SIGRX
SPOUT
BZOUT1
DTMFMUTE
RCVOL
SP MUTE
TEL MUTE
CML
MIC MUTE
VOL-A
VOL-B
VOL-C
MODEM BLOCK
(20438 I/A)
SPKRP
MIC ENABLE
MICP
LINEIN
LINE
OUT
CI
MIC
/LINE
SELECT
LINE IN ENABLE
SP OUT ENABLE
0,20,25,30dB
LINE OUT ENABLE
MUTE,0,-6,-12dB
IC3 SCE214V
FAX CONTROLLER
RTLOOP
0,1
0,0
1,0
1,1
LPF
LINESEL
1,1
0,0
1,0
0,6dB
DAC
DAC
SIN
ADC
0,+4dB
SOUT
Fig. 6
5 – 12
Page 40

UX-A255U
[4] Circuit description of power supply PWB
1. Block diagram
2.5A/125V
AC IN
Noise
Filter
Circuit
Rectifying
Smoothing
Circuit
Fig. 7
Switching
Circuit
Control
Circuit
Photo Coupler
+24V
FUSE
4A/32V
VREG
(+5V)
2-1. Noise filter circuit
The input noise filter section is composed of L1 and C1, which reduces
normal mode noise from the AC line and common mode noise to the AC
line.
2-2. Rectifying/smoothing circuit
The AC input voltage is rectified by diode D1, 2, 3, 4 and smoothed by
capacitor C2 to supply DC voltage to the switching circuit section.
2-3. Switching circuit
This circuit includes MOS FET Q1 and the gate drive circuit, and components around Q1.
In this circuit, the DC voltage supplied from the rectifying/smoothing
section is converted into high Frequency pulses by ON/OFF repetition
of Q1.
[5] Circuit description of CIS unit
1. CIS
Cis is an image sensor which puts the original paper in close contact
with the full-size sensor for scanning, being a monochromatic type
with the pixel number of 1,728 dots and the main scanning density of
8 dots/mm.
It is composed of sensor, rod lens, LED light source, light-conductive
plate, control circuit and so on, and the reading line and focus are
previously adjusted as the unit.
Due to the full-size sensor, the focus distance is so short that the set
is changed from the light weight type to the compact type.
2-4. Control circuit
This circuit controls output voltage of +24V by adjusting ON period of
Q1, looking at signal from photo coupler PC1.
In this operation PC1 takes charge of important part.
The over current protection is performed by bringing Q1 to OFF state
through detection of voltage of T1 Subwiding.
The over voltage protection is performed by operating the over current
protection circuit through detection of Zener diode ZD4 and shortcircuiting of load.
2-5. VREG(+5V) circuit
DC voltage supplied by rectifying the output of transformer T1 with diode D8, C10.
2. Waveforms
The following clock is supplied from SCE214V of the control board,
and VO is output.
5ms
øT
2µs
CISCLK
Approx.3.3V
0V
5 – 13
VO
0.8V~2.9V
(White original paper)
Fig. 8
Page 41

CHAPTER 6. CIRCUIT SCHEMA TICS AND PARTS LAYOUT
A
A
B
B
C
C
D
D
E
E
F
F
G
G
H
H
I
I
6 6
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 2
1 1
STRB3-
STRB2-
STRB1-
PCLK
DATA
LATCH-
DG
DG
DG
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D7
DG
(2-4G)
(2-5A)
DG
!T
STRB4-
SEN3
SEN2
SEN1
E
SEN4
SEN0
DG DGDG
DG
D6
A0
A3
A13
A11
A15
(2-6A)
A8
A7
A18
A9
A16
A14
A17
A5
A4
A10
A12
A1
A6
A2
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG DG
DG
CISCLK
KEN1A
KEN4A
KEN2A
KEN3A
SEN6
SEN5
(2-4A)
(2-3A)
(2-3A)
(4-2D)
(5-2I)
(6-1E)
(5-5E)
(5-5E)
(5-5E)
(5-5E)
DG
DG
(5-6D)
N.M.
<G>
DG
DG
(2-4G)
(2-4G)
(6-2A)
(2-3F)
+3.3V
VBAT
+3.3V
+3.3V
C168
0.1u/50V
<D>
C166
1u/10V
C132
22p/50V
<L>
C104
R106
470
R132
1K
C138
0.1u/50V
C196
C1401u/10V
<K>
R175 270
C144
1u/10V
DG
C154
N.M.
C102
N.M.
<J>
C122
0.1u/50V
R105
470
C116
N.M.
C198
C129
0.1u/50V
R101
10K
IC 3
SCE214V(1/2)
FAX CONTROLLER
33
32
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
140
139
138
137
136
135
134
131
130
129
128
127
126
125
124
123
122
121
120
118
114
117
116
115
6
5
3
4
175
176
25
26
27
31
34
28
36
35
30
29
44
39
40
49
149
19
20
21
22
171
172
173
174
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
10
11
69
67
57
58
59
60
63
62
61
165
133
107
70
50
45
9
2
8
108
7
1
166
161
132
119
64
48
24
47
46
43
38,41
42
23
97
TEST0
TEST1
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
A23
A22
A21
A20
A19
A18
A17
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
A0
A3
A2
A1
RD
WR
ROMCS
SYNC
REGDMA/GPO18/CLKDIV0
WAIT/GPO19/CLKDIV1
RAS
CAS
DWR
WRPROT
BATRST
VBAT
PWRDWN
INTPWRDOWNE
XOUT
XIN
VREFp
VREFn/CLREF
VIN
THADI
ALTTONE (BZ)
OPI0
OPI1
OPI2
OPI3
SM0
SM1
SM2
SM3
OPO0
OPO1
OPO2
OPO3
OPO4
OPO5
OPO6
SXIN
SXOUT
CLK2
START
STRB0
STRB1
STRB2
STRB3
PCLK
PDAT
PLAT
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSSPLL
TSTCLK
RESET
DEBUGn
VDDPLL
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
IVREFp
IVREFn
ADXG
ADGA
ADVA
LCDCS
VDD
C121
0.1u/50V
<A>
C103
R130
1K
<! T>
<! T><! T>
<! T>
C147 1u/10V
C199
C113
100p
C111
R156
270
RA2
470
5
1
8
7
6
2
3
4
32.768KHz
X2
RA1
470
5
1
8
7
6
2
3
4
C145
1u/10V
C109
C141
0.1u/50V
C197
RA3
470
5
1
8
7
6
2
3
4
R134
220
R108
470
C123
0.1u/50V
R135
1K
C112
32.256MHz
X1
R128
220K
C174
R173 270
<BATRST>
R133
1M
C143
1u/10V
<M>
R155 270
C167
<F>
C115
100p
C170
1u/10V
C108
C131
22p/50V
C177
100p/50V x 7
C149
20p/50V
R104 0
C142
1u/10V
C194
<I>
C146
20p/50V
R116 270
<C>
C148
1u/10V
C130
0.1u/50V
R187
100
C118
N.M.
<H>
C119
0.1u/50V
C175
<CISCLK>
R118
1K
<E>
C200
1000p/50V x 3
C152
C176
<B>
R157
10M
C195
R117 150
C101
C110
100pF x 5
C107
WR-
THADI
BZOUT1
CNTH-10
CNTH-2
CNTH-12
CNCIS-5
CNTH-11
CNTH-3
CNPN-10
CNPN-12
CNPN-9
CNPN-13
A[18:0]
PWRDWN-
TPB-
TPA-
TPA
TPB
CNTH-14
CNTH-13
CNCIS-4
CNPN-14
CNPN-11
CNPN-2
CNPN-3
CNPN-4
CNPN-15
CNPN-16
CNPN-1
D[7:0]
RD-
CAS-
ROMCS-
VIN
DWR-
RAS-
RLYCONT
WP-
UX-A255U
Main control block
[1] Control PWB circuit 1/6
6 – 1
Page 42

UX-A255U
A
A
B
B
C
C
D
D
E
E
F
F
G
G
H
H
I
I
6 6
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 2
1 1
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D6
D7
D5
A0
A1
A3
A2
A4
A5
A7
A6
A8
A9
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
DG DG
(1-5I)
(1-6I)
(1-3I)
(1-4I)
(1-3I)
(1-3I)
(1-3I)
(1-4I)
D7
D4
D1
(3-2A)
(3-2A)
(3-2A)
(3-2A)
D5
D6
D2
DG
(3-2A)
D3
D0
(3-2A)
(1-6H)
DG
DG
+3.3V
+3.3V
+3.3V
+3.3V
+3.3V
+3.3V
IC8
K9F4008W0A
FLASH MEMORY
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
12
13
14
15
16
18
19
20
21
1
44
242526
27
11
30
29
28
17
31
32
33
34
35
40
41
42
43
23
38
37
36
39
VSS
CLE
ALE
WE-
WP-
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
I/O0
I/O1
I/O2
I/O3
VSS
VCC
I/O4
I/O5
I/O6
I/O7
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
GNDR/B-
RE-
CE-
VCC
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
IC1
SST39VF020P
FLASH ROM
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
3
2
31
1
12
4
5
11
10
6
30
32
7
21
22
23
25
26
27
28
29
8
24
9
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
CE
OE
WE
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
VDD
GND
N.C.(A18)
R125
10k
R112
10k
C100
0.1u/50V
IC2
MSM51V4800E
DRAM
1
7
8
9
14
15
22
23
28
2
3
4
5
24
25
26
27
10
11
12
13
16
17
18
19
20
6
21
VCC
WE
RAS
A9
VCC
GND
OE
CAS
GND
DQ0
DQ1
DQ2
DQ3
DQ4
DQ5
DQ6
DQ7
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
NC
NC
R115
N.M.
C126
0.1u/50V
R113
0
R114
N.M.
C210
N.M.
R199
N.M.
C135
0.1u/50V
C217
N.M.
DWR-
CAS-
ROMCS-
A[18:0]
D[7:0]
RD-
WR-
FRD-
FCLE
FCS-
FWR-
FALE
READY
RAS-
WP-
Memory block 2/6
6 – 2
Page 43

UX-A255U
A
A
B
B
C
C
D
D
E
E
F
F
G
G
H
H
I
I
6 6
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 2
1 1
DG
DG
DG
DG
(6-1C)
(6-6E)
(6-2E)
(6-4E)
DG
THRANK
DPON
DG
PIN
RHS-
HS-
CI-
DTMFMUTE
SIGMUTE
DG
(6-3E)
CML
SPMUTE
RCVOL
TELMUTE
(6-1A)
(6-3E)
DG
(6-1I)
DPMUTE
DG DG
DG
(4-5C)
(4-4C)
(4-6C)
(5-5E)
(4-3C)
(5-3D)
FLRXD
FLTXD
DG
<CS5A>
CI-
SRLTX
SRLRX
PARK
VOL C
VOL B
LEDON
VTHON
FRSNS
ORGSNS
DR/RBN
CSWI
FCS
FRD
FWR
FCLE
FALE
READY
VOL A
(2-2G)
(2-2G)
(2-3G)
(2-3G)
(2-3G)
(2-2G)
(6-1G)
(6-1G)
(6-1G)
(5-2D)
<CS5>
(6-2D)
MICMUTE
N.M.
(5-5E)
NOT MOUNTED
+3.3V
+3.3V
R129 1K
C128
+
C7
10u/50V
C127
R153
1K
L104
15
R186 270
R154
2.2K
R177
+
C6
10u/50V
C204
R189 270
R183 270
R178 470
C203
+
C4
10u/50V
C162
0.1u/50V
C163
0.1u/50V
C139
0.1u/50V
C164
0.1u/16V-K
R176
C165
0.1u/50V
C169
1000p/50V
C137
N.M.
C205
N.M.
R190 150
C209
R174 1K
C206
N.M.
C190
R191 150
RA4
270
5
1
8
7
6
2
3
4
IC3
SCE214V(2/2)
MODEM BLOCK
53
52
85
55
155
159
154
68
162
157
160
54
51
88
168
81
80
156
91
167
79
37
110
109
66
65
164
163
56
82
73
94
158
105
106
103
87
104
170
169
150
151
153
112
74
77
76
92
71
72
75
102
98
96
101
100
99
95
93
90
89
84
83
78
86
113
152
111
GPIO15 / CS5
GPIO16
AVDD (IIA)
GPIO37
GPO28
GPIO31
GPO27
GPO25
GPIO34
GPO30
GPIO32
GPIO13
GPIO17
SPKR_OUTP (IIA)
GPO1
MIC_INM (IIA)
MIC_INP (IIA)
GPO29
MCDE0
GPO0
LINE_INP (IIA)
N.C.
SASRXD
GPIO3
GPIO19
GPIO11
GPIO36
GPIO35
VTHON
MIC_BIAS (IIA)
TESTC
FCS
GPIO29
SASCLK2
DSS_PARK
SASRXD2
LINE_OUTP (IIA)
SASTXD2
VOL-C
VOL-B
VOL-A
READY
FALE
FRD
SOUT (IIA)
POR (IIA)
FSYNC (IIA)
ICLK (IIA)
MCLK (IIA)
CTRLI (IIA)
SIN (IIA)
SA1CLK
IA1CLK
IACLK
SR1IO
SR4OUT
SR3IN
IARESET
DVSS(IIA)
DVDD (IIA)
SPKR_OUTM (IIA)
AGND (IIA)
VREF (IIA)
AVSS2 (IIA)
AVSS1 (IIA)FWR
FCLE
SASTXD
C202
CNLIUA-15
CNLIUA-12
CNLIUA-13
CNLIUA-10
SPMUTE
RCVOL
SIGMUTE
DTMFMUTE
CNLIUA-6
CNLIUA-16
CNLIUA-9
SIGRX
ORGSNS-
CSWI
LEDON
VTHON
DR/RBN
FRSNS-
CNPRG-1
CNPRG-3
SIGTX
READY
FCLE
FALE
FRD-
FWR-
FCS-
VOLB
VOLC
VOLA
CNDSS-5
CNLIUA-1
TELOUT1
SPOUT
CNDSS-7
CNDSS-6
CNDSS-8
W-TONE
THLOOK
CNLIUA-4
CNTH-5
THCHK
FAX Modem block 3/6
6 – 3
Page 44

UX-A255U
A
A
B
B
C
C
D
D
E
E
F
F
G
G
H
H
I
I
6 6
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 2
1 1
CSW-
FRSNS-
ORGSNS-
DG
DG
MG
FG
VREG
DG
+24V
+24V
DG
DG
MG
MG
(3-3A)
(1-1G)
DG
DG
DG
(3-3A)
(3-3A)
(3-3A)
DG
FILM
DG
DG
DG
+3.3V
DG DG
DG
<TP22>
<FILM>
<TP104>
<TP113>
<+24V>
<TP140>
<TP139>
<TP19-132>
DG
+3.3V
+3.3V
VBAT
+24V
VREG
+3.3V
+3.3V
<+3.3V>
D100
HRW0202
A1
A2
K
C207
1000p/50V
C105
1000p/50V
D101
1SS355
A
K
L102
0
R179
270
BAT1
CR2032
+
C211
470p/50V
R103
270
REG1
814A33AUC-BCX
S-
5
1
2
3
4
Vin Vout
VSS
NCON/OFF
R166
20k
R127
51K
R102
270
R100
5.6K
R111
N.M.
R168
270
C106
1000p/50V
C171
100p/50V
R170
N.M.
+
C9
47u/25V
C193
0.1u/50V
R109
N.M.
+
C10
22u/50V
<VBT1>
+
C8
220u/6.3V
C159
1u/10V
<VBT>
R147
N.M.
C158
N.M.
C192
0.1u/50V
C157
N.M.
<DG>
<DG>
CSWi-
ORGSNSi-
PWRDWN-
CNPN-8
CNPW-6
CNPW-5
CNPW-1
CNPW-2
CNPW-3
CNPW-4
CNPN-5
CNCSW-2
CNPN-6
CNCSW-1
CNPN-7
CNLIUA-11
DR/RBN
CNPRG-2
FRSNSi-
CNDSS-1
CNDSS-2
CNDSS-3
CNDSS-4
CNLIUA-2
Sensor/Reset/Power supply block 4/6
6 – 4
Page 45

UX-A255U
A
A
B
B
C
C
D
D
E
E
F
F
G
G
H
H
I
I
6 6
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 2
1 1
VG
VG
VO
DG
VG
MG MG
VMT
VMT
TPAD
TPBD
TPAD-
TPBD-
THG
THG
THG
MG
VTH
VTH
DG
(1-2F)
(3-3A)
(3-3A)
(1-1F)
(1-1E)
(1-1E)
(1-1E)
DG
+24V
GLED
DG
(5-5I)
(5-3A)
VG
THG
THI
THVDD
THADI
DG
(1-2F)
DG
CISVDD
THG
THG
+24VL
(3-4A)
(5-3D)
(3-2B)
(5-5H)
DG
DYNA
ROHM
0Ω
N.M.
N.M. 0.01u/50V
300Ω (2W ) 1000p/50V
R1 R192 C124CIS Maker
<TP109>
<TP141>
<TP17>
<TP20>
<TP138>
<TP137>
<TP136>
<TP135>
<TP134>
<TP133>
<TP131>
CISVDD
+24V
+24V
+3.3V
+3.3V
+24V
CISVDD
R1 N.M.
R172
22K
C117
0.1u/50V
R149 100k
R192
0
C114
0.1u/50V
Q100
KTA1504GR
B
C
E
R152
20K
R150
470K
R171
120K
C1
220u/6.3V
IC6
KID65001AP
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
9
E
1B
2B
3B
4B
5B
6B
7B 7C
6C
5C
4C
3C
2C
1C
COM
Q102
KRC106
B
C
E
<VIN>
<VO>
FU100
KAB2402
ZD1
1N4748
<VG>
R163
0.1u/50V
D1
D2
D3
D4S1
S2
S3
G
Q108
SI4431DY
4
5
8
3
1
2
6
7
C161
N.M.
Q111
KRA102S
B
C
E
C160
1u/10V
R151 100k
C178
N.M.
ZD100
02CZ18-Y
R120
5.1K
R107
10K
+
C5
N.M.
+
C3
10u/50V
L103
0
L100
0
Q110
KRC102S
B
C
E
R119 0
C124
0.01u/50V
VIN
TPA
TPB
TPA-
TPB-
VTHON
CNCIS-1
CNCIS-3
CNCIS-2
CNMT-5
CNMT-6
CNMT-4
CNMT-3
CNMT-2
CNMT-1
CNTH-1
CNTH-15
CNTH-6
CNTH-7
CNTH-8
LEDON
CNCIS-6
LEDON-
LEDON-
CNTH-4
THADI
CNTH-9
CNLIUA-3
CNCIS-7
THCHK-
THCHK
THCHK-
THLOOK
+
NOTE:
This marks is satety-cirtical parts.
Video processing/Motor drive/Thermal block 5/6
6 – 5
Page 46

UX-A255U
A
A
B
B
C
C
D
D
E
E
F
F
G
G
H
H
I
I
6 6
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 2
1 1
DG
(3-5A)
NOT MOUNTED
DG DG
SIGRX
(3-2H)
SP-
SP+
DG
(3-5A)
TELOUT
DG
(1-1F)
(3-2H)
TELIN
DG
(3-5A)
(3-3H)
DG
RXIN
(3-1A)
DG
(3-1A)
DG DG
DG
INCOM
DG
DG
TXOUT
DG
(3-3H)
SIGTX
(3-5A)
DG
DG
DSSIN
DSSOUT
DG
DG
DG
DSSRX
DSSTX
(3-1A)
DG
NOT MOUNTED
NOT MOUNTED
NOT MOUNTED
NOT MOUNTED
NOT MOUNTED
(6-5A)
(6-2F)
(3-3A)
DG
(3-4A)
CML
(6-2A)
(1-3I)
(6-6C)
(3-5A)
(3-5A)
DG
NOT MOUNTED
NOT MOUNTED
IC12C
8
97
6
14
NOT MOUNTED
NOT MOUNTED
VREG
+3.3V
+3.3V
+3.3V
+3.3V
+3.3V
+3.3V
+3.3V
+3.3V
+3.3V
Q103
KRC102S
B
C
E
C188
0.1u/16V-K
R160
A
C
LV4051
X0
X1
X2
X3
X4
X5
X6
X7
X
B
VDD
GND
VEE
E-
IC5
16
7
11
10
9
6
3
13
14
15
12
1
5
2
4
8
R165
6.8K
C172
R121
150K
D102
1SS355
R197
IC12A
3
4
5
1
2
13
R137
20K
C212
0.1u/50V
Q104
KRC102S
B
C
E
Q112
B
C
E
R198
ZD101
N.M.
C189
1u/10V
R164
1M
C214
R184
R180 39K
R194
IC10A
4
5
3
9
7
6
8
16
IC10B
15
1
2
10
7
6
8
16
C2
47u/25V
1
2
C187
0.1u/16V-K
R143 39K
R181
R144 24K
C182
1u/10V-K
C183
IC11
2
1
5
3
4
C181 0
R140 470K
R138
N.M.
R142 200K
C216
R122
100K
C156
0.1u/50V
C186
0
C125
1u/10V
R146 91K
R193
0
C150
1u/10V
R203
R136
3K
R196
R201
C213
R145 6.2K
C185
R124 220K
R131
15K
IC12B
4
3
5
C215
R202
Q106
B
C
E
C184
R141 1.5M
C208
1u/10V-K
R195
0
R200
Q105
KRC102S
B
C
E
D103
1SS355
IC4
2
1
5
3
4
C133
0.01u/50V
C134 220p/50V
R139 220K
C151
4700p/50V
R167
4.7K
R182
C155
-
+
NJM2113
IC7
5
4
3
2
1
7
8
6
IC10C
14
12
13
11
7
6
8
16
C179
1u/10V-K
C180
CNLIUA-5
CNLIUA-14
SPOUT
DTMFMUTE
TELOUT1
CNSP-1
SIGRX
CNLIUA-7
VOLA
VOLB
VOLC
BZOUT1
RCVOL
CNDSS-11
SIGMUTE
SIGTX
CNLIUA-8
CNDSS-9
CNSP-2
CNDSS-13
W-TONE
SPMUTE
CNDSS-10
CNDSS-12
ICM
ICM
CNLIUA-9
TELOUT
RLYCONT
DTMFMUTE
RCVOL
TELOUT
6 – 6
Analog signal block 6/6
Page 47

Control PWB parts layout (Top side)
UX-A255U
6 – 7
Page 48

UX-A255U
Control PWB parts layout (Bottom side)
6 – 8
Page 49

UX-A255U
5
5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
D D
C C
B B
A A
JP6
R117
22K
PC3(1/2)
L6
VA1
RA-391P-V6-2
Q104
N.M.
Q 5
C124
1000P
R118
100
Q3
JP5
C9
JUMPER
C11
CML(2/3)
C10
0.82
JP22
N.M.
JP23
C6
C12
22/50
+
IN/OUT
L5
N.M.
L9
N.M.
ZD8
R115
R4
22K
(1/2W)
CML(1/3)
OUAZ-SH-124DZ
C15
+
R140
D4
1SS133
JP24
R145
REC1
–~
~
+
R143
R10
Q 4
AR2
ERZV5D471
C20
0.01
N.M.
R144
L7
N.M.
ZD6
JUMPER
JP25
L4
JP20
N.M.
R9
C122
T1
I2164
JP21
N.M.
PC1(1/2)
PC817X4
PC4(1/2)
AR1
ERZV5D471
L8
PC2(1/2)
A
R5
JP1
C125
ZD4
HZ27-A
JP4
Vref A
C118
DG
ARG
CNTLJ-3
CNLNJ-3
CNTLJ-2
CNLNJ-4
CNLNJ-1
CNLNJ-2
CNLNJ-6
CNLNJ-5
CNTLJ-4
CNTLJ-5
43
G
G
98
10
45
3
21
21
43
(2-5D)
L2
E
S
EX-T2
EX-T1
N.C.
E
S
L1
T1
T2
(2-5D)
NOTE:
These marks are all satety-cirtical parts.
D
S
D
S
ZD3
HZ2C1
ZD2
HZ2C1
ZD9
VA2
N.M.
N.M.
N.M.
N.M.
1/3
[2] TEL/LIU PWB circuit
6 – 9
Page 50

UX-A255U
(1-1D)
RXIN
RX+
TXOUT
RX–
(3-2A)
(3-2A)
TX+
(3-5D)
TX–
(1-1D)
MICMUTE
TELOUT
(3-2A)
TELIN
TELMUTE
5
5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
D D
C C
B B
A A
C142
0.1
DG1
R134
24K
C131
C135
ZD5
MTZJ10B
R121
3.6K
C136
N.M.
R133
22K
R137
3.3K
Vref B
HSDG
C134
DG1
C113
L1
C23
N.M.
+
C13
47/16
+
C115
8.2K
C103
220P
C102
1000P
Vref A
DG1
C133
C108
N.M.
R106
Q100
KTC3875GR
R136
39K
R103
0
Vref A
D2
N.M.
C140
L2
C116
C132
N.M.
R111
220K
C101
1000P
R109
8.2K
IC102
NJM2904M
–
+
C2
N.M.
+
C119
N.M.
(2-1B)
Vref A
Q102
KRC106S
C127
0
R126
Vref B
C22
N.M.
+
ZD7
MTZJ10B
Vref A
R104
3.3K
IC102
NJM2904M
–
+
C138
N.M.
IC101
NJM2904M
–
+
C129
N.M.
Q6
KRA102M
Vref A
Q106
N.M.
JP29
N.M.
C4
22/50
+
(2-3D)
JP30
N.M.
R107
1K
C1
22/50
+
JP31
C143
0
C112
2200P
N.M.
A
R132
0
IC101
NJM2904M
–
+
C144
1
C100
N.M.
IN/OUT
R120
3.3K
R125
1K
C145
1
R112
1.5K
C139
33P
R127
0
R110
13K
DG1
C106
N.M.
C105
N.M.
R124
620
R100
3.3K
Q101
KRC106S
E
D1
C137
820P
L3
N.M.
R105
150
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG DG
DG
DG
CNLIUA-8
CNHJ-3
CNLIUA-4
CNHJ-4
CNLIUA-7
CNHJ-1
CNHJ-2
CNLIUA-5
CNLIUA-6
CNLIUA-14
7
6
5
1
2
3
1
2
3
7
6
5
C
(3-2A)
(3-2A)
R131
R130
R122
82K
C130
33P
R142
8.2K
R135
15K
C117
220P
R102
16K
C109
1000P
R101
1K
C104
0.1
D
S
G
N.M.
N.M.
2/3
TEL/LIU PWB circuit
6 – 10
Page 51

5
5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
D D
C C
B B
A A
C114
C121
0.1
Vref B
+24VL
PH1
SG206
DG2
Q108
DG1
A
C8
100/50
+
C110
N.M.
REG1
NJM78L05A
+24VA
DG1
R2
100
C128
N.M.
C5
+
DG1
C141
R3
1.2K
(1W)
+24VL
C126
PC3(2/2)
Q105
Q107
ZD1
N.M.
+24VL
PC1(2/2)
PC817X4
R1
R119
C107
R128
IC102
NJM2904M
Q103
KRC106S
TP1
C123
0.1
D3
1SS133
Vref A
C111
0.1
PC2(2/2)
C3
+
IC101
NJM2904M
PC4(2/2)
N.M.
R116
DG1
CML(3/3)
OUAZ-SH-124DZ
Q109
N.M.
HSDG
PH2
SG206
Vref A
R123
Vref A
R129
+24VA
R113
0
TP2
C120
0.1
24VL
C14
22/50
+
SW1
HOOK SW
R108
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
CNLIUA-11
CNLIUA-13
CNLIUA-2
CNLIUA-9
CNLIUA-3
CNLIUA-17
CNLIUA-15
CNLIUA-12
CNLIUA-10
CNLIUA-16
CNLIUA-1
Vout
1
GND
2
Vin
3
21
43
84
21
84
43
3
1
2
RHS
+24VL
DG
PIN
DPON
HS
CML
(2-5D)
DPMUTE
FILM
(1-1D)
Ci
RLYCNT
(3-2A)
(3-2A)
N.M.
NOTE:
These marks are all satety-cirtical parts.
N.M.
N.M.
N.M.
N.M.
UX-A255U
3/3
6 – 11
TEL/LIU PWB circuit
Page 52

UX-A255U
TEL/LIU PWB parts layout (Top side)
6 – 12
Page 53

TEL/LIU PWB parts layout (Bottom side)
UX-A255U
6 – 13
Page 54

UX-A255U
D7
S3L20U
C13
1500P
T1
PTTN129-KTT
FB3
BP53RB052025050
FB2
WBRH-35608-T5
R27
6.8K
ZD4
HZ30CPTK
ZD8
MTZJT-72 5.6B
F3
4A/32V
C30
R16
10K
C12
0.1
R15
330K
R14
1K
R13
4.7K
PC1
PS2501-1L
(1/2)
R18
3.3K
Q4
2SC1740S
ZD5
RD6.2SB-T1
VR1
2.2K
R17
3.3K
C10
330/16
D8
ERA81-004
L2
RS908
R4
680
C4
1000P
ZD2
RD4.3SB2-T1
C6
0Ω
D5
1SS355TE
R6
PC1
PS2501-1L
(1/2)
C17
C5
0.015
R7
180
D6
12
3
1
5
4
11
14
15
R2
470K
R3
470K
Q1
FS7KM
C3
1000P
ZD1
RD27ESAB2
Q2
2SC4115S
Q3
2SC1741AS
R9
47
R10
0.12(1W)
R8
47K
C26
C27
CNAC
F1
2.5A/125V
C1
2.2
C7
0.01
C28
0.01
R1
2.2M(1/2W)
1
2
V1
S07K150GA
L1
19mH/0.5A
D2
ERA15-06
D4
ERA15-06
D3
ERA15-06
D1
ERA15-06
N.M.
CNPS
1
2
3
4
5
6
+24V
+24V
MG
(+24V GND)
MG
(+24V GND)
Vreg
(+5V)
DG
(Vreg GND)
C2
220/200
C8
330/35
C24
270P
R5
2.7K
N.M.
N.M.
A
A
B
B
C
C
D
D
E
E
F
F
G
G
H
H
I
I
6 6
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 2
1 1
N.M.
N.M.
R28
6.8K
R29
6.8K
1/1
[3] Power supply PWB circuit
6 – 14
Page 55
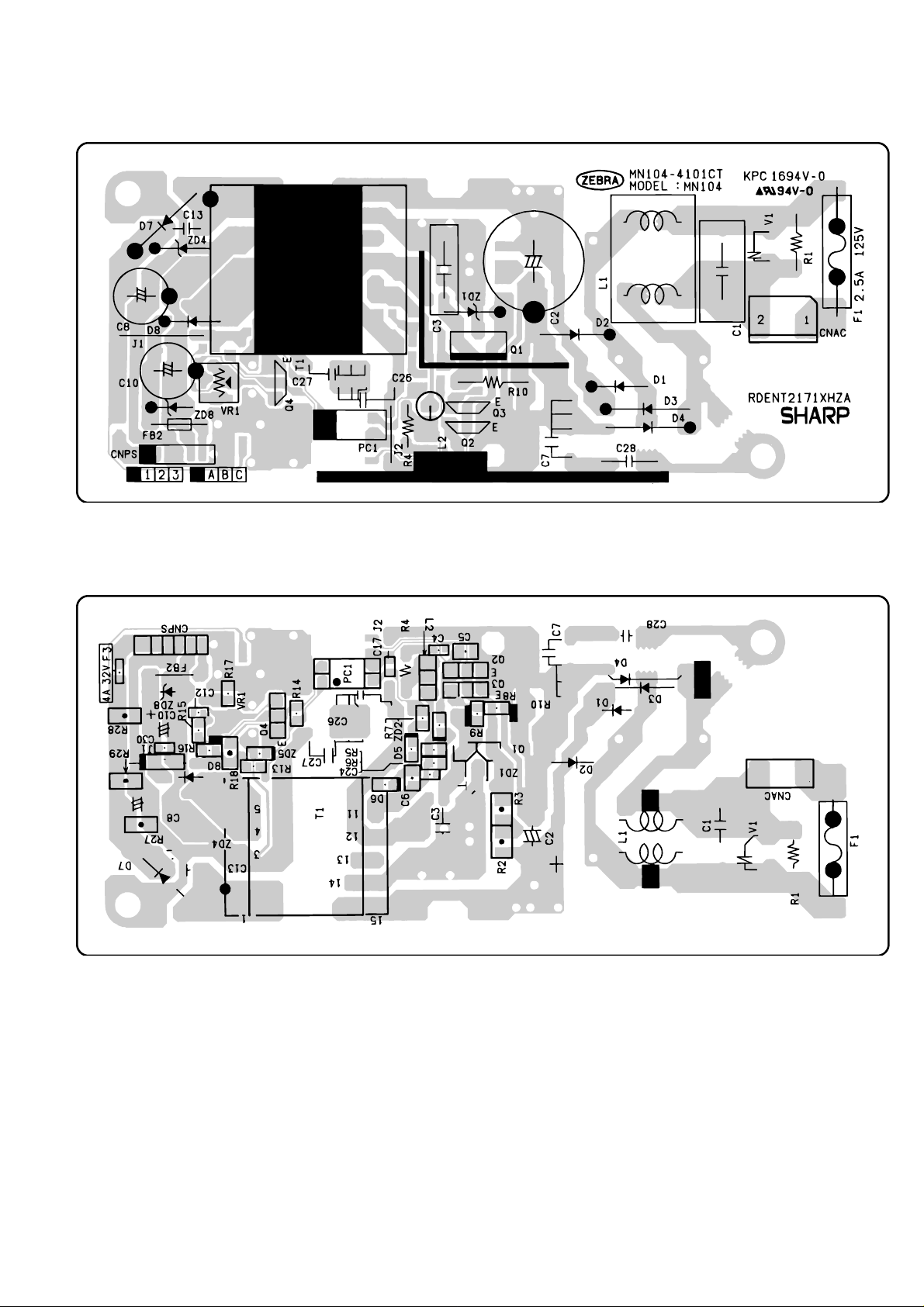
Power supply PWB parts layout (Top side)
UX-A255U
Power supply PWB parts layout (Bottom side)
6 – 15
Page 56

UX-A255U
5
5
4
4
3
3
2
2
1
1
D D
C C
B B
A A
D1
1SS133
5
0
SW2
8
START
SW1
R4
C2
22/50
+
UP
R1
1
DOWN
R5
4
A
R6
7
REC/MEMO
INTERCOM
R3
JP
D6
1SS133
C1
N.M.
REDIAL
D7
1SS133
N.M.
STOP
COPY
D3
1SS133
PLAY
D2
1SS133
D4
1SS133
3
FUNCTION
6
RESOLUTION
D5
1SS133
#
SPEAKER
9
2
OP LCR
R2
N.M.
DG
DGDG
DG
+3.3V
E
+3.3V
VO
+3.3V
DG
LD3
LD1
LD0
LD2
E
RS
R/W
ORGSNS
FRSNS
DG
KEN1A
SEN6
KEN2A
KEN3A
KEN4A
SEN0
SEN1
SEN2
SEN3
SEN4
SEN5
CNPN_A-10
CNPN_A-11
CNPN_A-13
CNPN_A-14
CNLCD-11
CNLCD-12
CNLCD-13
CNLCD-14
CNLCD-4
CNLCD-5
CNLCD-6
CNLCD-3
CNLCD-2
CNLCD-1
CNPN_A-3
CNPN_A-2
CNPN_A-1
CNPN_A-4
CNPN_A-15
CNPN_A-16
CNPN_A-9
CNPN_A-6
CNPN_A-5
CNPN_A-7
CNPN_A-8
CNPN_A-12
N.M.
2
6
11
14
4
12
8
LD2
N.C.
N.C.
LD0
E
1
3
5
7
9
10
13
N.C.
LD1
LD3
N.C.
R/W
DG
RS
VO
+3.3V
CNPN
2
6
11
14
4
12
16
8
SEN3
ORGSNS-
E
SEN1
+3.3V
1
3
5
7
9
10
13
15
SEN0
SEN2
SEN4
SEN5
SEN6
FRSNS-
DG
KEN4A
KEN1A
KEN2A
KEN3A
CNPN-A
NOTE:
These marks are all satety-cirtical parts.
1/1
Note: Since the parts of PWB cannot be supplied, change it as a unit.
[4] Operation Panel PWB circuit
6 – 16
Page 57

UX-A255U
Operation panel PWB parts layout
(Top side)
Operation panel PWB parts layout
(Bottom side)
Note: Since the parts of PWB cannot be supplied, change it as a unit.
6 – 17
Page 58
UX-A255U
A
A
B
B
C
C
D
D
E
E
D D
C C
B B
A A
2
6
11
14
4
12
16
8
SEN3
ORGSNS-
E
SEN1
+3.3V
1
3
5
7
9
10
13
15
SEN0
SEN2
SEN4
SEN5
SEN6
FRSNS-
DG
KEN4A
KEN1A
KEN2A
KEN3A
CNPN
2
6
11
14
4
12
16
8
SEN3
ORGSNS-
E
SEN1
+3.3V
1
3
5
7
9
10
13
15
SEN0
SEN2
SEN4
SEN5
SEN6
FRSNS-
DG
KEN4A
KEN1A
KEN2A
KEN3A
CNPN-A
SEN6
SEN0
SEN1
SEN2
SEN3
SEN4
SEN5
KEN1A
KEN2A
E
+3.3V
ORGSNS
FRSNS
DG
KEN4A
KEN3A
KEN4A
KEN3A
KEN2A
KEN1A
ORGSNS
FRSNS
E
SEN0
SEN1
SEN2
SEN3
SEN4
SEN5
SEN6
DG
+3.3V
CNPN-A-10
CNPN-A-11
CNPN-A-13
CNPN-A-14
CNPN-A-15
CNPN-A-16
CNPN-A-12
CNPN-A-3
CNPN-A-4
CNPN-A-9
CNPN-A-6
CNPN-A-5
CNPN-A-7
CNPN-A-8
CNPN-A-1
CNPN-A-2
CNPN-10
CNPN-11
CNPN-12
CNPN-3
CNPN-4
CNPN-9
CNPN-5
CNPN-7
CNPN-8
CNPN-1
CNPN-2
CNPN-13
CNPN-15
CNPN-16
CNPN-6
CNPN-14
1/1
Interface PWB parts layout
[5] Interface PWB circuit
6 – 18
Page 59

PARTS GUIDE
SELECTION CODE DESTINATION
UX-A255U
UX-A255U
UX-A255MODEL
U.S.A.
CONTENTS
1 Cabinet, etc.
2 Top cover/Sub frame
3 Upper cabinet/Document guide upper
4 Drive unit
5 Packing material & Accessories
6 Control PWB unit
7 TEL/LIU PWB unit
8 Power supply PWB unit
9 Operation panel PWB unit
10 Interface PWB unit
Index
Because parts marked with " " are indispensable for the machine safety maintenance and operation, it must be
replaced with the parts specific to the product specification.
Page 60

UX-A255U
[1] Cabinet,etc.
28
27
26
22
31
33
25
30
26
62
25
34
24
OPERATION
PANEL UNIT
63
23
32
16
B1
64
B2
DOCUMENT
GUIDE UPPER
TOP COVER/
SUB FRAME
41
B2
B2
46
49
B4
B1
65
42
55
39
45
38
39
40
44
7
43
B3
W1
59
35
29
29
B1
4
57
36
37
61
58
3
56
50
52
51
6
53
54
48
47
8
B1
17
B1
5
DRIVE
B1
60
UNIT
– 1 –
Page 61

UX-A255U
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
[1] Cabinet,etc.
3 CCNWN484AXH01 AL C Speaker ass’y
4 CLEVP2358XH01 AD C Hook switch lever ass’y
5 CROLR2481XH01 AQ C PO roller ass’y
6 DCEKC282RXHZZ BU N E Control PWB unit(Within ROM)
7 DCEKL364CXH01 BC N E TEL/LIU PWB unit
8 DCEKP337CXH01 AF E Interface PWB unit
16 QCNWN487AXHZZ AL C Panel cable
17 LBNDJ2006XHZZ AA C Band(100mm)
22 LBSHP2140XHZZ AC C Back bearing,left
23 LBSHP2143XHZZ AC C Back bearing,right
24 LFRM-2225XHSA AL C Scanner frame
25 MSPRC3295XHZZ AB C CIS spring
26 MSPRD3296XHZZ AB C PO pinch roller spring
27 NGERH2569XHZZ AC C Back gear
28 NGERH2570XHZZ AD C Reduction gear,21/37Z
29 NROLP2332XHZZ AD C PO pinch roller
30 NROLR2482XHZZ AR C Back roller
31 PGIDM2617XHZZ AD C CIS guide,left
32 PGIDM2618XHZZ AD C CIS guide,right
33 QCNWN485AXHZZ AG C CIS cable
34 RUNTZ2082XHZZ BR B CIS unit
35 GCABB2393XHSH AZ N D Lower cabinet
36 LHLDZ2227XHZZ AD C Ink ribbon spool 1
37 LHLDZ2228XHZZ AD C Ink ribbon spool 2
38 MSPRC3287XHZZ AB C Head spring A
39 MSPRC3288XHZZ AB C Head spring B
40 MSPRC3340XHZZ AD N C Head spring C
41 PCOVP2130XHZZ AE C Head cover
42 PGIDM2615XHZZ AD C Head guide,left
43 PGIDM2616XHZZ AD C Head guide,right
44 QCNWN486AXHZZ AM C Head cable
45 RHEDZ2065XHZZ BP B Thermal head
46 GCOVA2447XHSA AF D Front cover
47 GLEGG2078XHZZ AD C Rubber leg
48 LPLTM3178XHZZ AF C Bottom plate
49 LPLTP3177XHZZ AD C Stopper plate
50 MLEVP2357XHZZ AD C Film sensor lever
51 MLEVP2356XHZZ AD C P-IN sensor lever,lower
52 MSPRD3286XHZZ AB C Film sensor lever spring
53 MSPRD3285XHZZ AB C P-IN sensor lever spring,lower
54 MSPRD3291XHZZ AD C Speaker hold spring
55 MSPRD3292XHZZ AB C Head earth spring
56 MSPRP3297XHZZ AD C Earth spring
57 PCOVP2131XHSA AD C Interface PWB cover
58 PCOVP2132XHZZ AD C Control PWB cover
1 59 QACCD2054XHZZ AP B AC cord ass’y
60 QCNWN496AXHZZ AL C Interface cable
1 61 RDENT2171XHZA BG N E Power supply PWB unit
62 HPNLH2418XHSD AL N D Decoration panel
63 PBRS-2055XHZZ AN C Static brush
64 PSHEZ3687XHZZ AD C Earth sheet
65 MSPRD3341XHZZ AD N C Up spring
B1 XEBSD30P10000 AA C Screw(3x10)
B2 XEBSD30P12000 AA C Screw(3x12)
B3 LX-BZ2282XHZZ AB C Screw
B4 XEPSD30P08000 AA C Screw(3x8)
W1 XWHSN40-08100 AA C Washer
DESCRIPTION
– 2 –
Page 62

UX-A255U
[2] Top cover/Sub frame
27
25
16
28
15
26
30
1
B1
11
20
19
23
B2
4
24
29
3
2
NO.
[2] Top cover/Sub frame
1 GCOVA2448XHSA AG C Top cover
2 MSPRC3301XHZZ AB C Hopper spring
3 NGERP2318XHZZ AD C Pinion gear
4 PGIDM2619XHSA AF C Hopper guide,left
5 PGIDM2620XHSA AF C Hopper guide,right
6 LFRM-2227XHZZ AQ C Sub frame
7 LFRM-2232XHZZ AT C Sub frame plate
8 MLEVP2363XHZZ AD C P-IN sensor lever,upper
9 MSPRC3305XHZZ AB C Release lever spring
10 MSPRD3302XHZZ AB C P-IN sensor lever spring,upper
11 NGERH2580XHZZ AC C Reduction gear,15/22Z
12 NGERH2581XHZZ AC C Idler gear,25Z
13 NROLR2483XHZZ AL C Paper feed roller
14 NROLR2484XHZZ AL C PU roller
15 NSFTP2357XHZZ AG C Paper feed roller shaft
16 NSFTP2358XHZZ AG C PU roller shaft
17 PGIDM2621XHSA AF C Release lever
18 LHLDZ2224XHZZ AL C RP feed plate holder
19 LPLTG3181XHZZ AD C RP separate rubber
20 LPLTP3179XHZZ AD C RP separate base
21 LPLTP3180XHZZ AH C RP separate plate
22 LPLTP3182XHZZ AH C RP feed plate
23 MSPRC3299XHZZ AB C RP separate spring
24 MSPRC3300XHZZ AB C RP feed spring
25 LBSHP2141XHZZ AC C Platen bearing,left
26 LBSHP2142XHZZ AC C Platen bearing,right
27 NGERH2579XHZZ AD C Platen gear
28 NROLR2485XHZZ AQ C Platen roller
29 LBNDJ2006XHZZ AA C Band
30 MSPRC3335XHZZ AD C Paper feed roller spring
31 TLABH319DXHZZ AD D Imaging film set label
B1 LX-BZ2234XHZZ AD C Screw
B2 XEBSD30P10000 AA C Screw(3x10)
B3 LX-BZ2222XHZZ AC C Screw
PARTS CODE
B3
5
PRICE
RANK
22
NEW
MARK
24
21
22
18
B2
PART
RANK
B1
17
12
13
31
8
9
DESCRIPTION
B2
6
B2
14
10
7
B2
– 3 –
Page 63

[3] Upper cabinet/Document guide upper
UX-A255U
901
18
1
10
9
6
5
13
7
12
15
3
4
B1
8
17
11
2
14
16
NO.
[3] Upper cabinet/Document guide upper
1 GCASP2145XHSB AQ N D Panel case
2 JBTN-2339XHSA AF C 12 key
3 JBTN-2340XHSA AD C Start key
4 JBTN-2341XHSA AD C Function key
5 DCEKP336CXH04 AY N E Operation panel PWB unit
6 QSW-K0005AWZZ AC C Tact switch [SW]
1 7 QSW-M2246AXZZ AH C FRSNS sensor [SW1]
1 8 QSW-M2294XHZZ AE C ORGSNS sensor [SW2]
9 QCNWN487AXHZZ AL C Panel cable
10 RUNTZ2080XH01 BA E LCD unit
11 LPLTG2911XHZZ AE C Separate rubber
12 LPLTP3175XHZZ AD C Separate plate
13 LPLTP3176XHZZ AD C Feed plate
14 MSPRD3293XHZZ AB C Separate spring
15 MSPRT3294XHZZ AB C Feed spring
16 PGIDM2614XHSA AL C Document guide upper
17 PSHEP3660XHZZ AE C Separate rubber sheet
18 JBTN-2342XHSB AT N C TAD key
B1 XEBSD20P06000 AA C Screw(2x6)
901 DCEKP334CXH05 BF N E Operation panel unit
PARTS CODE
(Unit)
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
– 4 –
Page 64

UX-A255U
[4] Drive unit
1
22
B1
16
15
4
11
18
8
15
21
20
13
3
9
2
6
12
19
10
5
14
7
10
17
NO.
[4] Drive unit
1 CGERH2314XH04 AR C Slip gear ass’y
2 CLEVP2359XH01 AD C Planet gear lever ass’y A
3 CLEVP2360XH01 AD C Planet gear lever ass’y B
4 CLEVP2361XH01 AD C Planet gear lever ass’y C
5 CLEVP2362XH01 AD C Planet gear lever ass’y D
6 LFRM-2226XHZZ AQ C Drive unit frame
7 LPLTM3190XHZZ AG C Motor plate
8 MCAMP2028XHZZ AE C Cam
9 MSPRD3298XHZZ AE C Cam hold spring
10 NGERH2380XHZZ AC C Reduction gear,17/36Z
11 NGERH2409XHZZ AB C Idler gear,23Z
12 NGERH2571XHZZ AD C Slip gear
13 NGERH2572XHZZ AD C Reduction gear,25/63Z
14 NGERH2573XHZZ AD C Reduction gear,20/40Z
15 NGERH2574XHZZ AD C Reduction gear,15/30Z
16 NGERH2575XHZZ AD C Idler gear,40Z
17 NGERH2576XHZZ AD C Idler gear,21Z
18 NGERH2577XHZZ AD C Idler gear,20Z
19 NGERH2582XHZZ AC C Idler gear,15Z
20 QCNWN483AXHZZ AD C Cam switch cable
21 QSW-F2224SCZZ AE C Cam switch
22 RMOTS2175XHZZ AX B Motor
B1 XEBSD30P08000 AA C Screw(3x8)
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
– 5 –
DESCRIPTION
Page 65

[5] Packing material & Accessories
R
R
11
8
16
9
4
7
3
5
20
1
21
6
2
18
12
14
15
17
TAPE
AC CORD
TAPE
TAPE
(1)
(3)
(4)
(2)
UX-A255U
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
[5] Packing material & Accessories
1 DUNTK468BXHFW AS E Handset
1 2 QCNWG209BXHOW AH C Handset cord
3 LPLTP3184XHZZ AH C Paper tray extension
4 NGERH2568XHZZ AB C Imaging film gear
5 PRBNN2033SC10 AL S Imaging film(Initial starter film 10m)
1 6 QCNWG208BXHZZ AF C Telephone line cord
7 TCADZ3319XHZZ AT N D Setup guide
8 TCADZ3283XHZZ AD D Fax transmission sheet
9 TCADZ3282XHZZ AD D Open LCR information
11 TINSE4265XHTZ AT N D Operation manual
12 TLABM309DXHZZ AD N D Pop label
14 SPAKA465CXHZZ AF D Packing add.,left
15 SPAKA466CXHZZ AF D Packing add.,right
16 SPAKA467CXHZZ AD D Packing add.,accessories
17 CPAKC292DXH01 AV N D Packing case with label
18 SPAKP474CXHZZ AB D Vinyl cover
20 CPLTP3183XHR7 AN N C Paper tray ass’y
21 CGERH2566XH01 AG C Imaging film gear ass’y
– 6 –
DESCRIPTION
Page 66

UX-A255U
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[6] Control PWB unit
1 UBATL2049SCZZ AF B Battery(CR2032T23) [BAT1]
2 VCEAGA0JW227M AD C Capacitor(6.3WV 220µF) [C1]
3 VCEAGA1EW476M AA C Capacitor(25WV 47µF) [C2]
4 VCEAGA1HW106M AA C Capacitor(50WV 10µF) [C3]
5 VCEAGA1HW106M AA C Capacitor(50WV 10µF) [C4]
6 VCEAGA1HW106M AA C Capacitor(50WV 10µF) [C6]
7 VCEAGA1HW106M AA C Capacitor(50WV 10µF) [C7]
8 VCEAGA0JW227M AD C Capacitor(6.3WV 220µF) [C8]
9 VCEAGA1EW476M AA C Capacitor(25WV 47µF) [C9]
10 VCEAGA1HW226M AB C Capacitor(50WV 22µF) [C10]
11 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C100]
12 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C105]
13 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C106]
14 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C108]
15 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C109]
16 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C110]
17 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C111]
18 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C112]
19 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C113]
20 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C114]
21 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C115]
22 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C117]
23 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C119]
24 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C121]
25 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C122]
26 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C123]
27 VCKYCY1HB103K AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.01µF) [C124]
28 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C125]
29 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C126]
30 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C129]
31 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C130]
32 VCCCCY1HH220J AA C Capacitor(50WV 22PF) [C131]
33 VCCCCY1HH220J AA C Capacitor(50WV 22PF) [C132]
34 VCKYCY1HB103K AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.01µF) [C133]
35 VCCCCY1HH221J AA C Capacitor(50WV 220PF) [C134]
36 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C135]
37 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C138]
38 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C139]
39 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C140]
40 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C141]
41 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C142]
42 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C143]
43 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C144]
44 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C145]
45 VCCCCY1HH200J AA C Capacitor(50WV 20PF) [C146]
46 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C147]
47 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C148]
48 VCCCCY1HH200J AA C Capacitor(50WV 20PF) [C149]
49 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C150]
50 VCKYCY1HB472K AA C Capacitor(50WV 4700PF) [C151]
51 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C156]
52 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C159]
53 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C160]
54 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C162]
55 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C163]
56 VCKYCY1CB104K AB C Capacitor(16WV 0.1µF) [C164]
57 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C165]
58 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C166]
59 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C167]
60 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C168]
61 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C169]
62 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C170]
63 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C171]
64 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C176]
65 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C177]
66 VCKYCY1AB105K AB N C Capacitor(10WV 1.0µF) [C179]
67 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [C181]
68 VCKYCY1AB105K AB N C Capacitor(10WV 1.0µF) [C182]
69 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [C186]
70 VCKYCY1CB104K AB C Capacitor(16WV 0.1µF) [C187]
71 VCKYCY1CB104K AB C Capacitor(16WV 0.1µF) [C188]
72 VCKYCY1AF105Z AC C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C189]
73 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C192]
74 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C193]
75 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C194]
76 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C195]
77 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C196]
78 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C197]
79 VCCCCY1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C198]
80 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C199]
– 7 –
Page 67

UX-A255U
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[6] Control PWB unit
81 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C200]
82 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C207]
83 VCKYCY1AB105K AB N C Capacitor(10WV 1.0µF) [C208]
84 VCKYCY1HB471K AB C Capacitor(50WV 470PF) [C211]
85 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C212]
86 QCNCM7014SC0G AB C Connector(7pin) [CNCIS]
87 QCNCM7014SC0B AD C Connector(2pin) [CNCSW]
88 QCNCM2508SC1D AF N C Connector(14pin) [CNLIUA]
89 QCNCM7014SC0F AB C Connector(6pin) [CNMT]
90 QCNCM7014SC1F AD C Connector(16pin) [CNPN]
91 QCNCM7014SC0C AA C Connector(3pin) [CNPRG]
92 QCNCM2638SC0F AE C Connector(6pin) [CNPW]
93 QCNCM2401SC0B AA C Connector(2pin) [CNSP]
94 QCNCM7014SC1E AC C Connector(15pin) [CNTH]
95 VHDHRW0202B-1 AD B Diode(HRW0202B) [D100]
96 VHD1SS355//-1 AB B Diode(1SS355) [D101]
97 VHD1SS355//-1 AB B Diode(1SS355) [D102]
98 VHD1SS355//-1 AB B Diode(1SS355) [D103]
1 99 QFS-P2010SCZZ AD A IC protector(KAB2402) [FU100]
100 VHIF002/TA18A BN N B IC,EPROM(2MB)(TA18A) [IC1]
101 RH-IX2168SCZZ BB B IC(MSM51V4800E) [IC2]
102 VHISCE214V/-1 AF N B IC(SCE214V) [IC3]
103 RH-IX2270XHZZ AL N B IC(SN74LV4051ANSR) [IC5]
104 VHIKID65001AP AE B IC(KID65001AP) [IC6]
105 VHINJM2113M-1 AG B IC(NJM2113M) [IC7]
106 VHIKM29W040-1 AV B IC(K9F4008W0A) [IC8]
107 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [L100]
108 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [L102]
109 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [L103]
110 VRS-CY1JB150J AA C Resistor(1/16W 15Ω ±5%) [L104]
111 VSKTA1504GR-1 AC B Transistor(KTA1504G) [Q100]
112 VSKRC106S//-1 AD B Transistor(KRC106S) [Q102]
113 VSKRC102S//-1 AB B Transistor(KRC102S) [Q103]
114 VSKRC102S//-1 AB B Transistor(KRC102S) [Q104]
115 VSKRC102S//-1 AB B Transistor(KRC102S) [Q105]
116 VSSI4431DY+-1 AF B FET(SI4431DY) [Q108]
117 VSKRC102S//-1 AB B Transistor(KRC102S) [Q110]
118 VSKRA102S//-1 AD B Transistor(KRA102S) [Q111]
119 VRS-CY1JB562J AA C Resistor(1/16W 5.6KΩ ±5%) [R100]
120 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/16W 10KΩ ±5%) [R101]
121 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/16W 270Ω ±5%) [R102]
122 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/16W 270Ω ±5%) [R103]
123 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [R104]
124 VRS-CY1JB471J AA C Resistor(1/16W 470Ω ±5%) [R105]
125 VRS-CY1JB471J AA C Resistor(1/16W 470Ω ±5%) [R106]
126 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/16W 10KΩ ±5%) [R107]
127 VRS-CY1JB471J AA C Resistor(1/16W 470Ω ±5%) [R108]
128 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/16W 10KΩ ±5%) [R112]
129 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [R113]
130 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/16W 270Ω ±5%) [R116]
131 VRS-CY1JB151J AA C Resistor(1/16W 150Ω ±5%) [R117]
132 VRS-CY1JB102J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1KΩ ±5%) [R118]
133 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [R119]
134 VRS-CY1JB512J AA C Resistor(1/16W 5.1KΩ ±5%) [R120]
135 VRS-CY1JB154J AA C Resistor(1/16W 150KΩ ±5%) [R121]
136 VRS-CY1JB104J AA C Resistor(1/16W 100KΩ ±5%) [R122]
137 VRS-CY1JB224J AA C Resistor(1/16W 220KΩ ±5%) [R124]
138 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/16W 10KΩ ±5%) [R125]
139 VRS-CY1JB513J AA C Resistor(1/16W 51KΩ ±5%) [R127]
140 VRS-CY1JB224J AA C Resistor(1/16W 220KΩ ±5%) [R128]
141 VRS-CY1JB102J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1KΩ ±5%) [R129]
142 VRS-CY1JB102J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1KΩ ±5%) [R130]
143 VRS-CY1JB153J AA C Resistor(1/16W 15KΩ ±5%) [R131]
144 VRS-CY1JB102J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1KΩ ±5%) [R132]
145 VRS-CY1JB105J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1.0MΩ ±5%) [R133]
146 VRS-CY1JB221J AA C Resistor(1/16W 220Ω ±5%) [R134]
147 VRS-CY1JB102J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1KΩ ±5%) [R135]
148 VRS-CY1JB302J AA C Resistor(1/16W 3KΩ ±5%) [R136]
149 VRS-CY1JB203J AA C Resistor(1/16W 20KΩ ±5%) [R137]
150 VRS-CY1JB224J AA C Resistor(1/16W 220KΩ ±5%) [R139]
151 VRS-CY1JB474J AA C Resistor(1/16W 470KΩ ±5%) [R140]
152 VRS-CY1JB155J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1.5MΩ ±5%) [R141]
153 VRS-CY1JB204J AA C Resistor(1/16W 200KΩ ±5%) [R142]
154 VRS-CY1JB393J AA C Resistor(1/16W 39KΩ ±5%) [R143]
155 VRS-CY1JB243J AA C Resistor(1/16W 24KΩ ±5%) [R144]
156 VRS-CY1JB622J AA C Resistor(1/16W 6.2KΩ ±5%) [R145]
157 VRS-CY1JB913J AA C Resistor(1/16W 91KΩ ±5%) [R146]
158 VRS-CY1JB104J AA C Resistor(1/16W 100KΩ ±5%) [R149]
159 VRS-CY1JB474J AA C Resistor(1/16W 470KΩ ±5%) [R150]
160 VRS-CY1JB104J AA C Resistor(1/16W 100KΩ ±5%) [R151]
– 8 –
Page 68

UX-A255U
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[6] Control PWB unit
161 VRS-CY1JB203J AA C Resistor(1/16W 20KΩ ±5%) [R152]
162 VRS-CY1JB102J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1KΩ ±5%) [R153]
163 VRS-CY1JB222J AA C Resistor(1/16W 2.2KΩ ±5%) [R154]
164 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/16W 270Ω ±5%) [R155]
165 VRS-CY1JB103J AA C Resistor(1/16W 10KΩ ±5%) [R156]
166 VRS-CY1JB106J AA C Resistor(1/16W 10MΩ ±5%) [R157]
167 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [R163]
168 VRS-CY1JB105J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1.0MΩ ±5%) [R164]
169 VRS-CY1JB682J AA C Resistor(1/16W 6.8KΩ ±5%) [R165]
170 VRS-CY1JB203J AA C Resistor(1/16W 20KΩ ±5%) [R166]
171 VRS-CY1JB472J AA C Resistor(1/16W 4.7KΩ ±5%) [R167]
172 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/16W 270Ω ±5%) [R168]
173 VRS-CY1JB124J AA C Resistor(1/16W 120KΩ ±5%) [R171]
174 VRS-CY1JB223J AA C Resistor(1/16W 22KΩ ±5%) [R172]
175 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/16W 270Ω ±5%) [R173]
176 VRS-CY1JB102J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1KΩ ±5%) [R174]
177 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/16W 270Ω ±5%) [R175]
178 VRS-CY1JB471J AA C Resistor(1/16W 470Ω ±5%) [R178]
179 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/16W 270Ω ±5%) [R179]
180 VRS-CY1JB393J AA C Resistor(1/16W 39KΩ ±5%) [R180]
181 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/16W 270Ω ±5%) [R183]
182 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/16W 270Ω ±5%) [R186]
183 VRS-CY1JB101J AA C Resistor(1/16W 100Ω ±5%) [R187]
184 VRS-CY1JB271J AA C Resistor(1/16W 270Ω ±5%) [R189]
185 VRS-CY1JB151J AA C Resistor(1/16W 150Ω ±5%) [R190]
186 VRS-CY1JB151J AA C Resistor(1/16W 150Ω ±5%) [R191]
187 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [R192]
188 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [R193]
189 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [R195]
190 RR-TZ3018SCZZ AC C Block resistor(470Ωx4) [RA1]
191 RR-TZ3018SCZZ AC C Block resistor(470Ωx4) [RA2]
192 RR-TZ3018SCZZ AC C Block resistor(470Ωx4) [RA3]
193 RR-TZ3017SCZZ AC C Block resistor(270Ωx4) [RA4]
194 VHIS814A33AUC AH B IC(S-814A33AUC-BCX-T2) [REG1]
195 RCRSP2176SCZZ AG B Crystal(32.256MHz) [X1]
196 RCRSB0297AFZZ AD B Crystal(32.768kHz) [X2]
197 VHE1N4748A/-1 AC B Diode(1N4748A) [ZD1]
198 VHE02CZ180Y-1 AC B Zener diode(02CZ180Y) [ZD100]
901 DCEKC282RXHZZ BU N E Control PWB unit(Within ROM)
(Unit)
[7] TEL/LIU PWB unit
1 VHVERZV5D471/ AC B Varistor(ERZV5D471) [AR1]
2 VHVERZV5D471/ AC B Varistor(ERZV5D471) [AR2]
3 VCEAGA1HW226M AB C Capacitor(50WV 22µF) [C1]
4 VCEAGA1HW226M AB C Capacitor(50WV 22µF) [C4]
5 VCEAGA1HW107M AA C Capacitor(50WV 100µF) [C8]
6 RC-FZ3024SCZZ AG C Capacitor(250WV 0.82µF) [C10]
7 VCEAGA1HW226M AB C Capacitor(50WV 22µF) [C12]
8 VCEAGA1CW476M AB C Capacitor(16WV 47µF) [C13]
9 VCEAGA1HW226M AB C Capacitor(50WV 22µF) [C14]
10 VCKYPA1HB103K AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.01µF) [C20]
11 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C101]
12 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C102]
13 VCCCCY1HH221J AA C Capacitor(50WV 220PF) [C103]
14 VCKYCY1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C104]
15 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C109]
16 VCKYTV1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C111]
17 VCKYCY1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C112]
18 VRS-CY1JB822J AA C Resistor(1/16W 8.2KΩ ±5%) [C115]
19 VCCCCY1HH221J AA C Capacitor(50WV 220PF) [C117]
20 VCKYTV1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C120]
21 VCKYTV1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C121]
22 VCKYTV1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C123]
23 VCKYCY1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C124]
24 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [C127]
25 VCCCCY1HH330J AA C Capacitor(50WV 33PF) [C130]
26 VCKYCY1HB821K AA C Capacitor(50WV 820PF) [C137]
27 VCCCCY1HH330J AA C Capacitor(50WV 33PF) [C139]
28 VCKYCY1CB104K AB C Capacitor(16WV 0.1µF) [C142]
29 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [C143]
30 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C144]
31 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(10WV 1µF) [C145]
32 RRLYD3433XHZZ AH B Relay(OUAZ-SH-124DZ) [CML]
33 QJAKZ2079XH0D AD C Jack [CNHJ]
34 QCNCW715PAFZZ AG N C Connector(14pin) [CNLIUA]
35 QJAKZ2073SCFB AD C Jack [CNLNJ]
36 VHDDSS133//-1 AA B Diode(1SS133) [D3]
37 VHDDSS133//-1 AA B Diode(1SS133) [D4]
38 VHINJM2904M-2 AG B IC(NJM2904M) [IC101]
– 9 –
Page 69

UX-A255U
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[7] TEL/LIU PWB unit
39 VHINJM2904M-2 AG B IC(NJM2904M) [IC102]
40 VRS-HT3AA510J AA C Resistor(1W 51Ω ±5%) [JP21]
41 VHPPC817X4/-1 AC B Photo coupler(PC817X4) [PC1]
1 42 VHPSG206S//-1 AG B Photo transistor(SG206S) [PH1]
1 43 VHPSG206S//-1 AG B Photo transistor(SG206S) [PH2]
44 VSKRA102M//-3 AD B Transistor(KRA102M) [Q6]
45 VSKTC3875GR-1 AB B Transistor(KTC3875GR) [Q100]
46 VSKRC106S//-1 AD B Transistor(KRC106S) [Q101]
47 VSKRC106S//-1 AD B Transistor(KRC106S) [Q102]
48 VSKRC106S//-1 AD B Transistor(KRC106S) [Q103]
49 VRD-HT2EY101J AA C Resistor(1/4W 100Ω ±5%) [R2]
50 VRS-RE3AA122J AC C Resistor(1W 1.2KΩ ±5%) [R3]
51 VRD-HT2HY223J AA C Resistor(1/2W 22KΩ ±5%) [R4]
52 VRS-TS2AD332J AA C Resistor(1/10W 3.3KΩ ±5%) [R100]
53 VRS-CY1JB102J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1KΩ ±5%) [R101]
54 VRS-CY1JB163J AA C Resistor(1/16W 16KΩ ±5%) [R102]
55 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [R103]
56 VRS-CY1JB332J AA C Resistor(1/16W 3.3KΩ ±5%) [R104]
57 VRS-TS2AD151J AA C Resistor(1/10W 150Ω ±5%) [R105]
58 VRS-CY1JB102J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1KΩ ±5%) [R107]
59 VRS-CY1JB822J AA C Resistor(1/16W 8.2KΩ ±5%) [R109]
60 VRS-CY1JB133J AA C Resistor(1/16W 13KΩ ±5%) [R110]
61 VRS-CY1JB224J AA C Resistor(1/16W 220KΩ ±5%) [R111]
62 VRS-CY1JB152J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1.5KΩ ±5%) [R112]
63 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [R113]
64 VRS-TS2AD223J AA C Resistor(1/10W 22KΩ ±5%) [R117]
65 VRS-CY1JB102J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1KΩ ±5%) [R118]
66 VRS-CY1JB332J AA C Resistor(1/16W 3.3KΩ ±5%) [R120]
67 VRS-CY1JB362J AA C Resistor(1/16W 3.6KΩ ±5%) [R121]
68 VRS-TS2AD823J AA C Resistor(1/10W 82KΩ ±5%) [R122]
69 VRS-CY1JB621J AA C Resistor(1/16W 620Ω ±5%) [R124]
70 VRS-CY1JB102J AA C Resistor(1/16W 1KΩ ±5%) [R125]
71 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [R127]
72 VRS-CY1JB000J AA C Resistor(1/16W 0Ω ±5%) [R132]
73 VRS-CY1JB223J AA C Resistor(1/16W 22KΩ ±5%) [R133]
74 VRS-CY1JB243J AA C Resistor(1/16W 24KΩ ±5%) [R134]
75 VRS-CY1JB153J AA C Resistor(1/16W 15KΩ ±5%) [R135]
76 VRS-CY1JB393J AA C Resistor(1/16W 39KΩ ±5%) [R136]
77 VRS-CY1JB332J AA C Resistor(1/16W 3.3KΩ ±5%) [R137]
78 VRS-CY1JB822J AA C Resistor(1/16W 8.2KΩ ±5%) [R142]
79 VHINJM78L05A1 AD B IC(NJM78L05A) [REG1]
80 QSW-Z2317XHZZ AF C Hook switch [SW1]
1 81 RTRNI2164XHZZ AG B Transformer(I2164) [T1]
82 VHVRA391PV6-1 AE B Varistor(RA-391P-V6-2) [VA1]
83 VHEHZ2C1///-1 AA B Zener diode(HZ2C1) [ZD2]
84 VHEHZ2C1///-1 AA B Zener diode(HZ2C1) [ZD3]
85 VHEHZ27-1//-1 AB B Zener diode(HZ27) [ZD4]
86 VHEMTZJ100B-1 AC B Zener diode(MTZJ10B) [ZD5]
87 VHEMTZJ100B-1 AC B Zener diode(MTZJ10B) [ZD7]
901 DCEKL364CXH01 BC N E TEL/LIU PWB unit
(Unit)
[8] Power supply PWB unit
1 0CBUGFM224KR/ AF C Capacitor(275WV 2.2µF) [C1]
2 0CBUGA0291ZZ/ AC C Capacitor(200WV 220µF) [C2]
3 0CBUGCU102JC/ AF C Capacitor(1KWV 1000PF) [C3]
4 0CBUGXGCF102/ AD C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C4]
5 0CBUGXHWF153/ AF N C Capacitor(50WV 0.015µF) [C5]
6 0CBUEXCAP000/ AC C Resistor(1/8W 0Ω ±5%) [C6]
7 0CBUGCM103BH/ AD C Capacitor(125WV 0.01µF) [C7]
8 0CBUGA0315ZZ/ AL N C Capacitor(35WV 330µF) [C8]
9 0CBUGA0302ZZ/ AK N C Capacitor(16WV 330µF) [C10]
10 0CBUGXGFD104/ AD C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C12]
11 0CBUGCS152AC/ AD C Capacitor(500WV 1500PF) [C13]
12 0CBUGXGDF271/ AD C Capacitor(50WV 270PF) [C24]
13 0CBUGCM103GF/ AD N C Capacitor(125WV 0.01µF) [C28]
14 0CBPKZ0194ZZ/ AC C Base post ass’y(2pin) [CNAC]
15 0CBPCZ0307ZZ/ AD C Connector(6pin) [CNPS]
16 0CBUBC0125DK/ AD B Diode(ERA15-06) [D1]
17 0CBUBC0125DK/ AD B Diode(ERA15-06) [D2]
18 0CBUBC0125DK/ AD B Diode(ERA15-06) [D3]
19 0CBUBC0125DK/ AD B Diode(ERA15-06) [D4]
20 0CBUBY0020AK/ AD B Diode(1SS355TE) [D5]
21 0CBUBC0336AZ/ AL B Diode(S3L20U-4004P15) [D7]
22 0CBUBC0070AM/ AG N B Diode(ERA81-004) [D8]
23 0CBPJCSX2501/ AH A Current fuse(2.5A/125V) [F1]
24 0CBPZZ1008ZZ/ AH N A Circuit protect chip(4A/32V) [F3]
25 0CBBFZ80078E/ AD N C Beads core(WBRH-35608-T5) [FB2]
26 0CBBFZ89633Z/ AD C Beads inductor(BP53RB052025050) [FB3]
27 0CBUKZ0790ZZ/ AK C Filter(19mH/0.5A) [L1]
– 10 –
Page 70

UX-A255U
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[8] Power supply PWB unit
28 0CBUZZ0203ZZ/ AK C Inductor(RS908) [L2]
29 0CBLRZ6803ZP/ AQ C Heat sink [MT2]
30 0CBUDC0062MZ/ AG B Photo coupler(PS2501-1L) [PC1]
31 0CBUAG0225AZ/ AQ B FET(FS7KM) [Q1]
32 0CBUAC0255AM/ AD B Transistor(2SC4115S) [Q2]
33 0CBUAC0264AK/ AD B Transistor(2SC1741AS) [Q3]
34 0CBUAC0034EL/ AD B Transistor(2SC1740S) [Q4]
35 0CBUEEC225CF/ AC C Resistor(1/2W 2.2MΩ ±5%) [R1]
36 0CBUEXDAW474/ AC N C Resistor(1/4W 470KΩ ±5%) [R2]
37 0CBUEXDAW474/ AC N C Resistor(1/4W 470KΩ ±5%) [R3]
38 0CBUEEB681CT/ AC C Resistor(1/8W 680Ω ±5%) [R4]
39 0CBUEXCAP272/ AC C Resistor(1/8W 2.7KΩ ±5%) [R5]
40 0CBUEXCAP181/ AC C Resistor(1/8W 180Ω ±5%) [R7]
41 0CBUEXCAP473/ AC C Resistor(1/8W 47KΩ ±5%) [R8]
42 0CBUEXCAP470/ AC C Resistor(1/8W 47Ω ±5%) [R9]
43 0CBUEFDR12DB/ AE C Resistor(1W 0.12Ω ±5%) [R10]
44 0CBUEXCAP472/ AC C Resistor(1/8W 4.7KΩ ±5%) [R13]
45 0CBUEXCAP102/ AC C Resistor(1/8W 1KΩ ±5%) [R14]
46 0CBUEXCAP334/ AC C Resistor(1/8W 330KΩ ±5%) [R15]
47 0CBUEXCAP103/ AC C Resistor(1/8W 10KΩ ±5%) [R16]
48 0CBUEXCAP332/ AC C Resistor(1/8W 3.3KΩ ±5%) [R17]
49 0CBUEXJAV332/ AC N C Resistor(1/4W 3.3KΩ ±5%) [R18]
50 0CBUDXDAW682/ AC N C Resistor(1/4W 6.8KΩ ±5%) [R27]
51 0CBUDXDAW682/ AC N C Resistor(1/4W 6.8KΩ ±5%) [R28]
52 0CBUDXDAW682/ AC N C Resistor(1/4W 6.8KΩ ±5%) [R29]
53 0CB829655050/ BF N B Transformer(PTTN129-KTT) [T1]
54 0CBUEZ0666ZZ/ AD B Varistor(S07K150GA) [V1]
55 0CBUFBA222EQ/ AD B Variable resistor(2.2KΩ) [VR1]
56 0CBUBDBE270C/ AD B Zener diode(RD27ESAB2) [ZD1]
57 0CBUBXAD4R3C/ AD B Zener diode(RD4.3SB2-T1) [ZD2]
58 0CBUBDDA300A/ AD N B Zener diode(HZ30CPTK) [ZD4]
59 0CBUBXAD6R2C/ AD B Zener diode(RD6.2SB-T1) [ZD5]
60 0CBUBDBW5R6C/ AE N B Zener diode(MTZJT-72 5.6B) [ZD8]
1 901 RDENT2171XHZA BG N E Power supply PWB unit
(Unit)
[9] Operation panel PWB unit
1 2 QSW-M2246AXZZ AH C FRSNS sensor [SW1]
1 3 QSW-M2294XHZZ AE C ORGSNS sensor [SW2]
1 QSW-K0005AWZZ AC C Tact switch [SW]
(Unit)
901 DCEKP336CXH04 AY N E Operation panel PWB unit
[10] Interface PWB unit
1 QCNCM7014SC1F AD C Connector(16pin) [CNPN]
2 QCNCM7014SC1F AD C Connector(16pin) [CNPN-A]
901 DCEKP337CXH01 AF E Interface PWB unit
(Unit)
– 11 –
Page 71

I n d e x x
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
PARTS CODE No.
MSPRD3291XHZZ 1-54 AD C
MSPRD3292XHZZ 1-55 AB C
MSPRD3293XHZZ 3-14 AB C
MSPRD3296XHZZ 1-26 AB C
MSPRD3298XHZZ 4-9 AE C
MSPRD3302XHZZ 2-10 AB C
MSPRD3341XHZZ 1-65 AD N C
MSPRP3297XHZZ 1-56 AD C
MSPRT3294XHZZ 3-15 AB C
[N]
NGERH2380XHZZ 4-10 AC C
NGERH2409XHZZ 4-11 AB C
NGERH2568XHZZ 5-4 AB C
NGERH2569XHZZ 1-27 AC C
NGERH2570XHZZ 1-28 AD C
NGERH2571XHZZ 4-12 AD C
NGERH2572XHZZ 4-13 AD C
NGERH2573XHZZ 4-14 AD C
NGERH2574XHZZ 4-15 AD C
NGERH2575XHZZ 4-16 AD C
NGERH2576XHZZ 4-17 AD C
NGERH2577XHZZ 4-18 AD C
NGERH2579XHZZ 2-27 AD C
NGERH2580XHZZ 2-11 AC C
NGERH2581XHZZ 2-12 AC C
NGERH2582XHZZ 4-19 AC C
NGERP2318XHZZ 2-3 AD C
NROLP2332XHZZ 1-29 AD C
NROLR2482XHZZ 1-30 AR C
NROLR2483XHZZ 2-13 AL C
NROLR2484XHZZ 2-14 AL C
NROLR2485XHZZ 2-28 AQ C
NSFTP2357XHZZ 2-15 AG C
NSFTP2358XHZZ 2-16 AG C
[P]
PBRS-2055XHZZ 1-63 AN C
PCOVP2130XHZZ 1-41 AE C
PCOVP2131XHSA 1-57 AD C
PCOVP2132XHZZ 1-58 AD C
PGIDM2614XHSA 3-16 AL C
PGIDM2615XHZZ 1-42 AD C
PGIDM2616XHZZ 1-43 AD C
PGIDM2617XHZZ 1-31 AD C
PGIDM2618XHZZ 1-32 AD C
PGIDM2619XHSA 2-4 AF C
PGIDM2620XHSA 2-5 AF C
PGIDM2621XHSA 2-17 AF C
PRBNN2033SC10 5-5 AL S
PSHEP3660XHZZ 3-17 AE C
PSHEZ3687XHZZ 1-64 AD C
[Q]
QACCD2054XHZZ 1-59 AP B
QCNCM2401SC0B 6-93 AA C
QCNCM2508SC1D 6-88 AF N C
QCNCM2638SC0F 6-92 AE C
QCNCM7014SC0B 6-87 AD C
QCNCM7014SC0C 6-91 AA C
QCNCM7014SC0F 6-89 AB C
QCNCM7014SC0G 6-86 AB C
QCNCM7014SC1E 6-94 AC C
QCNCM7014SC1F 6-90 AD C
″ 10-1 AD C
″ 10-2 AD C
QCNCW715PAFZZ 7-34 AG N C
QCNWG208BXHZZ 5-6 AF C
QCNWG209BXHOW 5-2 AH C
QCNWN483AXHZZ 4-20 AD C
QCNWN485AXHZZ 1-33 AG C
QCNWN486AXHZZ 1-44 AM C
QCNWN487AXHZZ 1-16 AL C
″ 3-9 AL C
QCNWN496AXHZZ 1-60 AL C
QFS-P2010SCZZ 6-99 AD A
QJAKZ2073SCFB 7-35 AD C
QJAKZ2079XH0D 7-33 AD C
QSW-F2224SCZZ 4-21 AE C
QSW-K0005AWZZ 3-6 AC C
″ 9-1 AC C
QSW-M2246AXZZ 3-7 AH C
″ 9-2 AH C
PRICE
PARTS CODE No.
[C]
CCNWN484AXH01 1-3 AL C
CGERH2314XH04 4-1 AR C
CGERH2566XH01 5-21 AG C
CLEVP2358XH01 1-4 AD C
CLEVP2359XH01 4-2 AD C
CLEVP2360XH01 4-3 AD C
CLEVP2361XH01 4-4 AD C
CLEVP2362XH01 4-5 AD C
CPAKC292DXH01 5-17 AV N D
CPLTP3183XHR7 5-20 AN N C
CROLR2481XH01 1-5 AQ C
[D]
DCEKC282RXHZZ 1-6 BU N E
″ 6-901 BU N E
DCEKL364CXH01 1-7 BC N E
″ 7-901 BC N E
DCEKP334CXH05 3-901 BF N E
DCEKP336CXH04 3-5 AY N E
″ 9-901 AY N E
DCEKP337CXH01 1-8 AF E
″ 10-901 AF E
DUNTK468BXHFW 5-1 AS E
[G]
GCABB2393XHSH 1-35 AZ N D
GCASP2145XHSB 3-1 AQ N D
GCOVA2447XHSA 1-46 AF D
GCOVA2448XHSA 2-1 AG C
GLEGG2078XHZZ 1-47 AD C
[H]
HPNLH2418XHSD 1-62 AL N D
[J]
JBTN-2339XHSA 3-2 AF C
JBTN-2340XHSA 3-3 AD C
JBTN-2341XHSA 3-4 AD C
JBTN-2342XHSB 3-18 AT N C
[L]
LBNDJ2006XHZZ 1-17 AA C
″ 2-29 AA C
LBSHP2140XHZZ 1-22 AC C
LBSHP2141XHZZ 2-25 AC C
LBSHP2142XHZZ 2-26 AC C
LBSHP2143XHZZ 1-23 AC C
LFRM-2225XHSA 1-24 AL C
LFRM-2226XHZZ 4-6 AQ C
LFRM-2227XHZZ 2-6 AQ C
LFRM-2232XHZZ 2-7 AT C
LHLDZ2224XHZZ 2-18 AL C
LHLDZ2227XHZZ 1-36 AD C
LHLDZ2228XHZZ 1-37 AD C
LPLTG2911XHZZ 3-11 AE C
LPLTG3181XHZZ 2-19 AD C
LPLTM3178XHZZ 1-48 AF C
LPLTM3190XHZZ 4-7 AG C
LPLTP3175XHZZ 3-12 AD C
LPLTP3176XHZZ 3-13 AD C
LPLTP3177XHZZ 1-49 AD C
LPLTP3179XHZZ 2-20 AD C
LPLTP3180XHZZ 2-21 AH C
LPLTP3182XHZZ 2-22 AH C
LPLTP3184XHZZ 5-3 AH C
LX-BZ2222XHZZ 2-B3 AC C
LX-BZ2234XHZZ 2-B1 AD C
LX-BZ2282XHZZ 1-B3 AB C
[M]
MCAMP2028XHZZ 4-8 AE C
MLEVP2356XHZZ 1-51 AD C
MLEVP2357XHZZ 1-50 AD C
MLEVP2363XHZZ 2-8 AD C
MSPRC3287XHZZ 1-38 AB C
MSPRC3288XHZZ 1-39 AB C
MSPRC3295XHZZ 1-25 AB C
MSPRC3299XHZZ 2-23 AB C
MSPRC3300XHZZ 2-24 AB C
MSPRC3301XHZZ 2-2 AB C
MSPRC3305XHZZ 2-9 AB C
MSPRC3335XHZZ 2-30 AD C
MSPRC3340XHZZ 1-40 AD N C
MSPRD3285XHZZ 1-53 AB C
MSPRD3286XHZZ 1-52 AB C
No.
RANK
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
UX-A255U
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
PARTS CODE
QSW-M2294XHZZ 3-8 AE C
″ 9-3 AE C
QSW-Z2317XHZZ 7-80 AF C
[R]
RC-FZ3024SCZZ 7-6 AG C
RCRSB0297AFZZ 6-196 AD B
RCRSP2176SCZZ 6-195 AG B
RDENT2171XHZA 1-61 BG N E
″ 8-901 BG N E
RH-IX2168SCZZ 6-101 BB B
RH-IX2270XHZZ 6-103 AL N B
RHEDZ2065XHZZ 1-45 BP B
RMOTS2175XHZZ 4-22 AX B
RR-TZ3017SCZZ 6-193 AC C
RR-TZ3018SCZZ 6-190 AC C
″ 6-191 AC C
″ 6-192 AC C
RRLYD3433XHZZ 7-32 AH B
RTRNI2164XHZZ 7-81 AG B
RUNTZ2080XH01 3-10 BA E
RUNTZ2082XHZZ 1-34 BR B
[S]
SPAKA465CXHZZ 5-14 AF D
SPAKA466CXHZZ 5-15 AF D
SPAKA467CXHZZ 5-16 AD D
SPAKP474CXHZZ 5-18 AB D
[T]
TCADZ3282XHZZ 5-9 AD D
TCADZ3283XHZZ 5-8 AD D
TCADZ3319XHZZ 5-7 AT N D
TINSE4265XHTZ 5-11 AT N D
TLABH319DXHZZ 2-31 AD D
TLABM309DXHZZ 5-12 AD N D
[U]
UBATL2049SCZZ 6-1 AF B
[V]
VCCCCY1HH101J 6-14 AA C
″ 6-15 AA C
″ 6-16 AA C
″ 6-17 AA C
″ 6-18 AA C
″ 6-19 AA C
″ 6-21 AA C
″ 6-63 AA C
″ 6-64 AA C
″ 6-65 AA C
″ 6-75 AA C
″ 6-76 AA C
″ 6-77 AA C
″ 6-78 AA C
″ 6-79 AA C
VCCCCY1HH200J 6-45 AA C
″ 6-48 AA C
VCCCCY1HH220J 6-32 AA C
″ 6-33 AA C
VCCCCY1HH221J 6-35 AA C
″ 7-13 AA C
″ 7-19 AA C
VCCCCY1HH330J 7-25 AA C
″ 7-27 AA C
VCEAGA0JW227M 6-2 AD C
″ 6-8 AD C
VCEAGA1CW476M 7-8 AB C
VCEAGA1EW476M 6-3 AA C
″ 6-9 AA C
VCEAGA1HW106M 6-4 AA C
″ 6-5 AA C
″ 6-6 AA C
″ 6-7 AA C
VCEAGA1HW107M 7-5 AA C
VCEAGA1HW226M 6-10 AB C
″ 7-3 AB C
″ 7-4 AB C
″ 7-7 AB C
″ 7-9 AB C
VCKYCY1AB105K 6-66 AB N C
″ 6-68 AB N C
″ 6-83 AB N C
VCKYCY1AF105Z 6-28 AC C
″ 6-39 AC C
PRICE
RANK
– 12 –
Page 72

UX-A255U
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
PRICE
PARTS CODE
VCKYCY1AF105Z 6-41 AC C
″ 6-42 AC C
″ 6-43 AC C
″ 6-44 AC C
″ 6-46 AC C
″ 6-47 AC C
″ 6-49 AC C
″ 6-52 AC C
″ 6-53 AC C
″ 6-58 AC C
″ 6-62 AC C
″ 6-72 AC C
VCKYCY1CB104K 6-56 AB C
″ 6-70 AB C
″ 6-71 AB C
″ 7-28 AB C
VCKYCY1HB102K 6-12 AA C
″ 6-13 AA C
″ 6-59 AA C
″ 6-61 AA C
″ 6-80 AA C
″ 6-81 AA C
″ 6-82 AA C
″ 7-11 AA C
″ 7-12 AA C
″ 7-15 AA C
″ 7-23 AA C
VCKYCY1HB103K 6-27 AA C
″ 6-34 AA C
VCKYCY1HB222K 7-17 AA C
VCKYCY1HB471K 6-84 AB C
VCKYCY1HB472K 6-50 AA C
VCKYCY1HB821K 7-26 AA C
VCKYCY1HF104Z 6-11 AA C
″ 6-20 AA C
″ 6-22 AA C
″ 6-23 AA C
″ 6-24 AA C
″ 6-25 AA C
″ 6-26 AA C
″ 6-29 AA C
″ 6-30 AA C
″ 6-31 AA C
″ 6-36 AA C
″ 6-37 AA C
″ 6-38 AA C
″ 6-40 AA C
″ 6-51 AA C
″ 6-54 AA C
″ 6-55 AA C
″ 6-57 AA C
″ 6-60 AA C
″ 6-73 AA C
″ 6-74 AA C
″ 6-85 AA C
″ 6-167 AA C
″ 7-14 AA C
VCKYPA1HB103K 7-10 AA C
VCKYTV1CF105Z 7-30 AB C
″ 7-31 AB C
VCKYTV1HF104Z 7-16 AA C
″ 7-20 AA C
″ 7-21 AA C
″ 7-22 AA C
VHDDSS133//-1 7-36 AA B
″ 7-37 AA B
VHDHRW0202B-1 6-95 AD B
VHD1SS355//-1 6-96 AB B
″ 6-97 AB B
″ 6-98 AB B
VHEHZ2C1///-1 7-83 AA B
″ 7-84 AA B
VHEHZ27-1//-1 7-85 AB B
VHEMTZJ100B-1 7-86 AC B
″ 7-87 AC B
VHE02CZ180Y-1 6-198 AC B
VHE1N4748A/-1 6-197 AC B
VHIF002/TA18A 6-100 BN N B
VHIKID65001AP 6-104 AE B
VHIKM29W040-1 6-106 AV B
No.
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
PRICE
PARTS CODE
VHINJM2113M-1 6-105 AG B
VHINJM2904M-2 7-38 AG B
″ 7-39 AG B
VHINJM78L05A1 7-79 AD B
VHISCE214V/-1 6-102 AF N B
VHIS814A33AUC 6-194 AH B
VHPPC817X4/-1 7-41 AC B
VHPSG206S//-1 7-42 AG B
″ 7-43 AG B
VHVERZV5D471/ 7-1 AC B
″ 7-2 AC B
VHVRA391PV6-1 7-82 AE B
VRD-HT2EY101J 7-49 AA C
VRD-HT2HY223J 7-51 AA C
VRS-CY1JB000J 6-67 AA C
″ 6-69 AA C
″ 6-107 AA C
″ 6-108 AA C
″ 6-109 AA C
″ 6-123 AA C
″ 6-129 AA C
″ 6-133 AA C
″ 6-187 AA C
″ 6-188 AA C
″ 6-189 AA C
″ 7-24 AA C
″ 7-29 AA C
″ 7-55 AA C
″ 7-63 AA C
″ 7-71 AA C
″ 7-72 AA C
VRS-CY1JB101J 6-183 AA C
VRS-CY1JB102J 6-132 AA C
″ 6-141 AA C
″ 6-142 AA C
″ 6-144 AA C
″ 6-147 AA C
″ 6-162 AA C
″ 6-176 AA C
″ 7-53 AA C
″ 7-58 AA C
″ 7-65 AA C
″ 7-70 AA C
VRS-CY1JB103J 6-120 AA C
″ 6-126 AA C
″ 6-128 AA C
″ 6-138 AA C
″ 6-165 AA C
VRS-CY1JB104J 6-136 AA C
″ 6-158 AA C
″ 6-160 AA C
VRS-CY1JB105J 6-145 AA C
″ 6-168 AA C
VRS-CY1JB106J 6-166 AA C
VRS-CY1JB124J 6-173 AA C
VRS-CY1JB133J 7-60 AA C
VRS-CY1JB150J 6-110 AA C
VRS-CY1JB151J 6-131 AA C
″ 6-185 AA C
″ 6-186 AA C
VRS-CY1JB152J 7-62 AA C
VRS-CY1JB153J 6-143 AA C
″ 7-75 AA C
VRS-CY1JB154J 6-135 AA C
VRS-CY1JB155J 6-152 AA C
VRS-CY1JB163J 7-54 AA C
VRS-CY1JB203J 6-149 AA C
″ 6-161 AA C
″ 6-170 AA C
VRS-CY1JB204J 6-153 AA C
VRS-CY1JB221J 6-146 AA C
VRS-CY1JB222J 6-163 AA C
VRS-CY1JB223J 6-174 AA C
″ 7-73 AA C
VRS-CY1JB224J 6-137 AA C
″ 6-140 AA C
″ 6-150 AA C
″ 7-61 AA C
VRS-CY1JB243J 6-155 AA C
″ 7-74 AA C
No.
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
PRICE
PARTS CODE
VRS-CY1JB271J 6-121 AA C
″ 6-122 AA C
″ 6-130 AA C
″ 6-164 AA C
″ 6-172 AA C
″ 6-175 AA C
″ 6-177 AA C
″ 6-179 AA C
″ 6-181 AA C
″ 6-182 AA C
″ 6-184 AA C
VRS-CY1JB302J 6-148 AA C
VRS-CY1JB332J 7-56 AA C
″ 7-66 AA C
″ 7-77 AA C
VRS-CY1JB362J 7-67 AA C
VRS-CY1JB393J 6-154 AA C
″ 6-180 AA C
″ 7-76 AA C
VRS-CY1JB471J 6-124 AA C
″ 6-125 AA C
″ 6-127 AA C
″ 6-178 AA C
VRS-CY1JB472J 6-171 AA C
VRS-CY1JB474J 6-151 AA C
″ 6-159 AA C
VRS-CY1JB512J 6-134 AA C
VRS-CY1JB513J 6-139 AA C
VRS-CY1JB562J 6-119 AA C
VRS-CY1JB621J 7-69 AA C
VRS-CY1JB622J 6-156 AA C
VRS-CY1JB682J 6-169 AA C
VRS-CY1JB822J 7-18 AA C
″ 7-59 AA C
″ 7-78 AA C
VRS-CY1JB913J 6-157 AA C
VRS-HT3AA510J 7-40 AA C
VRS-RE3AA122J 7-50 AC C
VRS-TS2AD151J 7-57 AA C
VRS-TS2AD223J 7-64 AA C
VRS-TS2AD332J 7-52 AA C
VRS-TS2AD823J 7-68 AA C
VSKRA102M//-3 7-44 AD B
VSKRA102S//-1 6-118 AD B
VSKRC102S//-1 6-113 AB B
″ 6-114 AB B
″ 6-115 AB B
″ 6-117 AB B
VSKRC106S//-1 6-112 AD B
″ 7-46 AD B
″ 7-47 AD B
″ 7-48 AD B
VSKTA1504GR-1 6-111 AC B
VSKTC3875GR-1 7-45 AB B
VSSI4431DY+-1 6-116 AF B
[X]
XEBSD20P06000 3-B1 AA C
XEBSD30P08000 4-B1 AA C
XEBSD30P10000 1-B1 AA C
″ 2-B2 AA C
XEBSD30P12000 1-B2 AA C
XEPSD30P08000 1-B4 AA C
XWHSN40-08100 1-W1 AA C
[0]
0CBBFZ80078E/ 8-25 AD N C
0CBBFZ89633Z/ 8-26 AD C
0CBLRZ6803ZP/ 8-29 AQ C
0CBPCZ0307ZZ/ 8-15 AD C
0CBPJCSX2501/ 8-23 AH A
0CBPKZ0194ZZ/ 8-14 AC C
0CBPZZ1008ZZ/ 8-24 AH N A
0CBUAC0034EL/ 8-34 AD B
0CBUAC0255AM/ 8-32 AD B
0CBUAC0264AK/ 8-33 AD B
0CBUAG0225AZ/ 8-31 AQ B
0CBUBC0070AM/ 8-22 AG N B
0CBUBC0125DK/ 8-16 AD B
″ 8-17 AD B
″ 8-18 AD B
″ 8-19 AD B
No.
RANK
– 13 –
Page 73

UX-A255U
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
PARTS CODE No.
PRICE
PARTS CODE No.
0CBUBC0336AZ/ 8-21 AL B
0CBUBDBE270C/ 8-56 AD B
0CBUBDBW5R6C/ 8-60 AE N B
0CBUBDDA300A/ 8-58 AD N B
0CBUBXAD4R3C/ 8-57 AD B
0CBUBXAD6R2C/ 8-59 AD B
0CBUBY0020AK/ 8-20 AD B
0CBUDC0062MZ/ 8-30 AG B
0CBUDXDAW682/ 8-50 AC N C
″ 8-51 AC N C
″ 8-52 AC N C
0CBUEEB681CT/ 8-38 AC C
0CBUEEC225CF/ 8-35 AC C
0CBUEFDR12DB/ 8-43 AE C
0CBUEXCAP000/ 8-6 AC C
0CBUEXCAP102/ 8-45 AC C
0CBUEXCAP103/ 8-47 AC C
0CBUEXCAP181/ 8-40 AC C
0CBUEXCAP272/ 8-39 AC C
0CBUEXCAP332/ 8-48 AC C
0CBUEXCAP334/ 8-46 AC C
0CBUEXCAP470/ 8-42 AC C
0CBUEXCAP472/ 8-44 AC C
0CBUEXCAP473/ 8-41 AC C
0CBUEXDAW474/ 8-36 AC N C
″ 8-37 AC N C
0CBUEXJAV332/ 8-49 AC N C
0CBUEZ0666ZZ/ 8-54 AD B
0CBUFBA222EQ/ 8-55 AD B
0CBUGA0291ZZ/ 8-2 AC C
0CBUGA0302ZZ/ 8-9 AK N C
0CBUGA0315ZZ/ 8-8 AL N C
0CBUGCM103BH/ 8-7 AD C
0CBUGCM103GF/ 8-13 AD N C
0CBUGCS152AC/ 8-11 AD C
0CBUGCU102JC/ 8-3 AF C
0CBUGFM224KR/ 8-1 AF C
0CBUGXGCF102/ 8-4 AD C
0CBUGXGDF271/ 8-12 AD C
0CBUGXGFD104/ 8-10 AD C
0CBUGXHWF153/ 8-5 AF N C
0CBUKZ0790ZZ/ 8-27 AK C
0CBUZZ0203ZZ/ 8-28 AK C
0CB829655050/ 8-53 BF N B
No.
RANK
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
– 14 –
Page 74

UX-A255U
COPYRIGHT © 2001 BY SHARP CORPORATION
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
No part of this publication may be reproduced,
stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in
any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical,
photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without
prior written permission of the publisher.
SHARP CORPORATION
Communication Systems Group
Quality & Reliability Control Center
Higashihiroshima, Hiroshima 739-0192, Japan
Printed in U.S.A.
A0112-1124DS•IS•T
 Loading...
Loading...