Page 1

SERVICE MANUAL
No. 00ZFO50A//SME
FACSIMILE
FO-50
MODEL FO-70
FO-50A
FO-70A
Illustration: FO-50
CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
[1] Specifications ............................................ 1-1
[2] Operation panel......................................... 1-2
[3] Transmittable documents .......................... 1-3
[4] Installation ................................................. 1-4
[5] Quick reference guide ............................... 1-9
CHAPTER 2. ADJUSTMENTS
[1] Adjustments .............................................. 2-1
[2] Diagnostics and service soft switch .......... 2-2
[3] Troubleshooting ...................................... 2-18
[4] Error code table....................................... 2-19
CHAPTER 3. MECHANISM BLOCKS
[1] General description ................................... 3-1
[2] Disassembly and assembly
procedures ....................................... 3-3
CHAPTER 4. DIAGRAMS
[1] Block diagram ............................................4-1
[2] Wiring diagram .......................................... 4-2
[3] Point-to-point diagram ............................... 4-3
Non Cutter model Cutter model
FO-50 FO-70
CHAPTER 5. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
[1] Circuit description ..................................... 5-1
[2] Circuit description of control PWB ............ 5-2
[3] Circuit description of TEL/LIU PWB .......... 5-9
[4] Circuit description of
power supply PWB............................5-12
[5] Circuit description of CIS unit...................5-12
CHAPTER 6. CIRCUIT SCHEMATICS AND
PARTS LAYOUT
[1] Control PWB circuit ................................... 6-1
[2] TEL/LIU PWB circuit.................................. 6-9
[3] Power supply PWB circuit ...................... 6-13
[4] Operation panel PWB circuit ................... 6-15
CHAPTER 7. OPERATION FLOWCHART
[1] Protocol ..................................................... 7-1
[2] Power on sequence................................... 7-2
CHAPTER 8. OTHERS
[1] Service tools ............................................. 8-1
[2] IC signal name .......................................... 8-4
PARTS GUIDE
Parts marked with " " is important for maintaining the safety of the set. Be sure to replace these parts with specified ones for
maintaining the safety and performance of the set.
This document has been published to be used
SHARP CORPORATION
for after sales service only.
The contents are subject to change without notice.
Page 2
FO-50A
FO-70A
CAUTION FOR BATTERY REPLACEMENT
(Danish) ADVARSEL !
Lithiumbatteri-Eksplosionsfare ved fejlagtig håndtering.
Udskiftning må kun ske med batteri af samme fabrikat og type.
Levér det brugte batteri tilbage til leverandoren.
(English) Caution !
Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or equivalent type
recommended by the equipment manufacturer.
Discard used batteries according to manufacturer’s
instructions.
(Finnish) VAROITUS
Paristo voi räjähtää, jos se on virheellisesti asennettu.
Vaihda paristo ainoastaan laitevalmistajan suosittelemaan
tyyppiin. Hävitä käytetty paristo valmistajan ohjeiden
mukaisesti.
(French) ATTENTION
Il y a danger d’explosion s’ il y a remplacement incorrect
de la batterie. Remplacer uniquement avec une batterie du
même type ou d’un type recommandé par le constructeur.
Mettre au rébut les batteries usagées conformément aux
instructions du fabricant.
(Swedish) VARNING
Explosionsfare vid felaktigt batteribyte.
Använd samma batterityp eller en ekvivalent
typ som rekommenderas av apparattillverkaren.
Kassera använt batteri enligt fabrikantens
instruktion.
(German) Achtung
Explosionsgefahr bei Verwendung inkorrekter Batterien.
Als Ersatzbatterien dürfen nur Batterien vom gleichen Typ oder
vom Hersteller empfohlene Batterien verwendet werden.
Entsorgung der gebrauchten Batterien nur nach den vom
Hersteller angegebenen Anweisungen.
Page 3

CHAPTER 1. GENERAL DESCRIPTION
[1] Specifications
FO-50A
FO-70A
Automatic dialing: Rapid Key Dialing: 5 numbers
Speed Dialing: 35 numbers
Fax(thermal) paper: Initial starter roll (included with machine):
10 m
Recommended replacement roll:
FO-20PRw, 30m
Paper cutting method: FO-50: Tear off by hand
FO-70: Automatic cutter
Modem speed: 9600 bps with automatic fallback to lower
speeds
Transmission time* : Approx. 15 seconds
Resolution: Horizontal: 8 dots/mm
Vertical:
Standard: 3.85 lines/mm
Fine/Halftone: 7.7 lines/mm
Super fine: 15.4 lines/mm
Automatic document feeder: 5 pages max. (80 g/cm2 paper)
Halftone (grayscale): 64 levels
Display: 16-digit LCD display
Compression scheme: MR, MH, Sharp (H2)
Applicable telephone line: Public switched telephone network
Compatibility: ITU-T (CCITT) G3 mode
Input document size: Automatic feeding:
Width: 148 to 216 mm
Length: 140 to 297 mm
Manual feeding:
Width: 148 to 216 mm
Length: 140 to 600 mm
Effective scanning width: 210 mm max.
Effective printing width: 210 mm max.
Contrast control: Automatic/Dark selectable
Reception modes: Fax, Tel, Fax/Tel, A.M.
Copy function: Yes
Telephone function: Yes (cannot be used if power fails)
Power requirements: 230-240 V AC, 50 Hz
Operating temperature: 5 - 35°C
Humidity: Maximum: 85 % RH
Power consumption: Standby: 2.3 W
Maximum: 115 W
Dimensions: Width: 304 mm
Depth: 236 mm
Height: 122 mm
Weight: Approx. 2.6 kg
* Based on ITU-T (CCITT) Test Chart #1 at standard resolution in Sharp
special mode, excluding time for protocol signals (i.e., ITU-T phase C
time only).
Note: The facsimile machine is Year 2000 compliant.
As a part of our policy of continuous improvement, SHARP reserves the right to make design and specification changes for procduct
improvement without prior notice. The performance specifications figures indicated are nominal values of production units. There may be some
deviation from these values in individual units.
1 – 1
Page 4
FO-50A
FO-70A
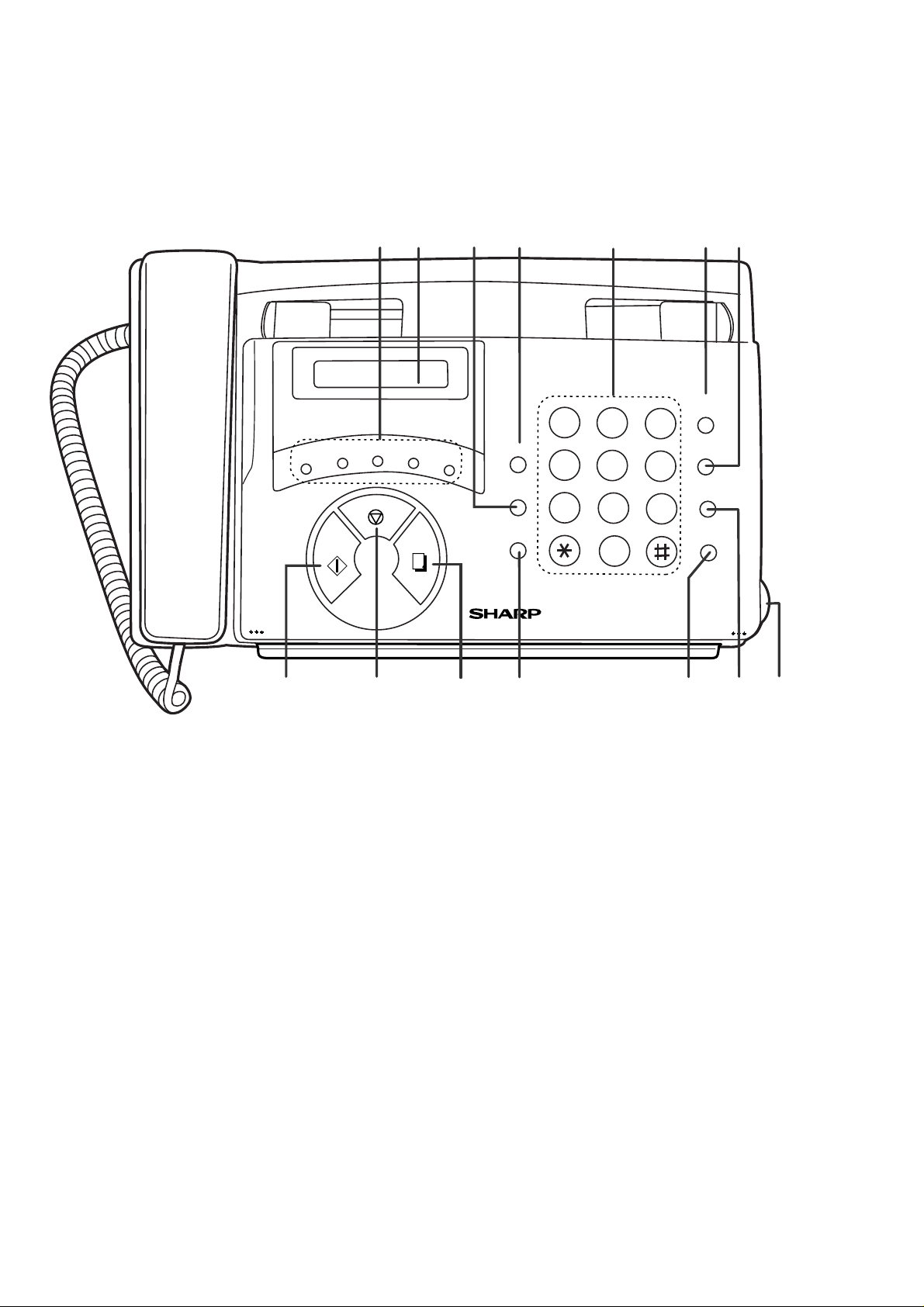
[2] Operation panel
GHI
PQRS
ABC
JKL
TUV
START
SPEED
DIAL
REDIAL
HOLD/
SEARCH
SPEAKER
7
1 4 5 62 3
RECEPTION
RESOLUTION FUNCTION
1
GHI
VOLUME
01
02
03
04
PQRS
FUNCTION
7
06
05
RESOLUTION/
RECEPTION MODE
08
07
09
10/POLL
ABC
DEF
2
23
JKL
TUV
MNO
COPY/HELP
WXYZ
8
START
0
STOP
654
9
TEL FAX
A.M.
TEL/FAX A.M.
SPEED DIAL
D
REDIAL
HOLD/SEARCH
SPEAKER
MODE
DOWN VOLUME UP
E/
POLL
COPY/
HELP
TEL FAX
DEF
C
B
A
MNO
STOP
WXYZ
8
1. Rapid Dial keys
Press one of these keys to dial a fax number automatically.
2. Display
This displays messages and prompts during operation and
programming.
3. FUNCTION key
Press this key to select various special functions.
4. VOLUME keys
Press this keys to adjust the volume of the speaker when
the SPEAKER key has been pressed, the volume of the
ringer at all other times.
5. Number keys
Use these keys to dial numbers, and enter numbers and
letters when storing auto-dial numbers.
6. SPEED DIAL key
Press this key to dial a fax or voice number using an
abbreviated 2-digit Speed Dial number.
7. REDIAL key
Press this key to automatically redial the last number
dialed.
8. START key
Press this key to begin transmission when using Speed
Dialing, Direct Keypad Dialing, or Normal Dialing.
9. STOP key
Press this key to cancel operation before it is completed.
11109
12
1314
10. COPY/HELP key
When a document is in the feeder, press this key to make
a copy of a document. At any other time, press this key to
print out the Help List, a quick reference guide to the
opeation of your fax machine.
11. RESOLUTION/RECEPTION MODE key
When a document is in the feeder, press this key to adjust
the resolution for faxing or copying. At any other time,
press this key to select the reception mode (an arrow in the
display will point to the currently selected reception mode).
12. SPEAKER key
Press this key to listen the line and fax tones through the
speaker when faxing a document.
Note: This is not a speakerphone. You must pick up the
handset to talk with the other party.
13. HOLD/SEARCH key
Press this key to search for an auto-dial number, or, during a
phone conversation, press this key to put the other party on
hold.
14. Panel release
Grasp this finger hold and pull toward you to open the
operation panel.
1 – 2
Page 5
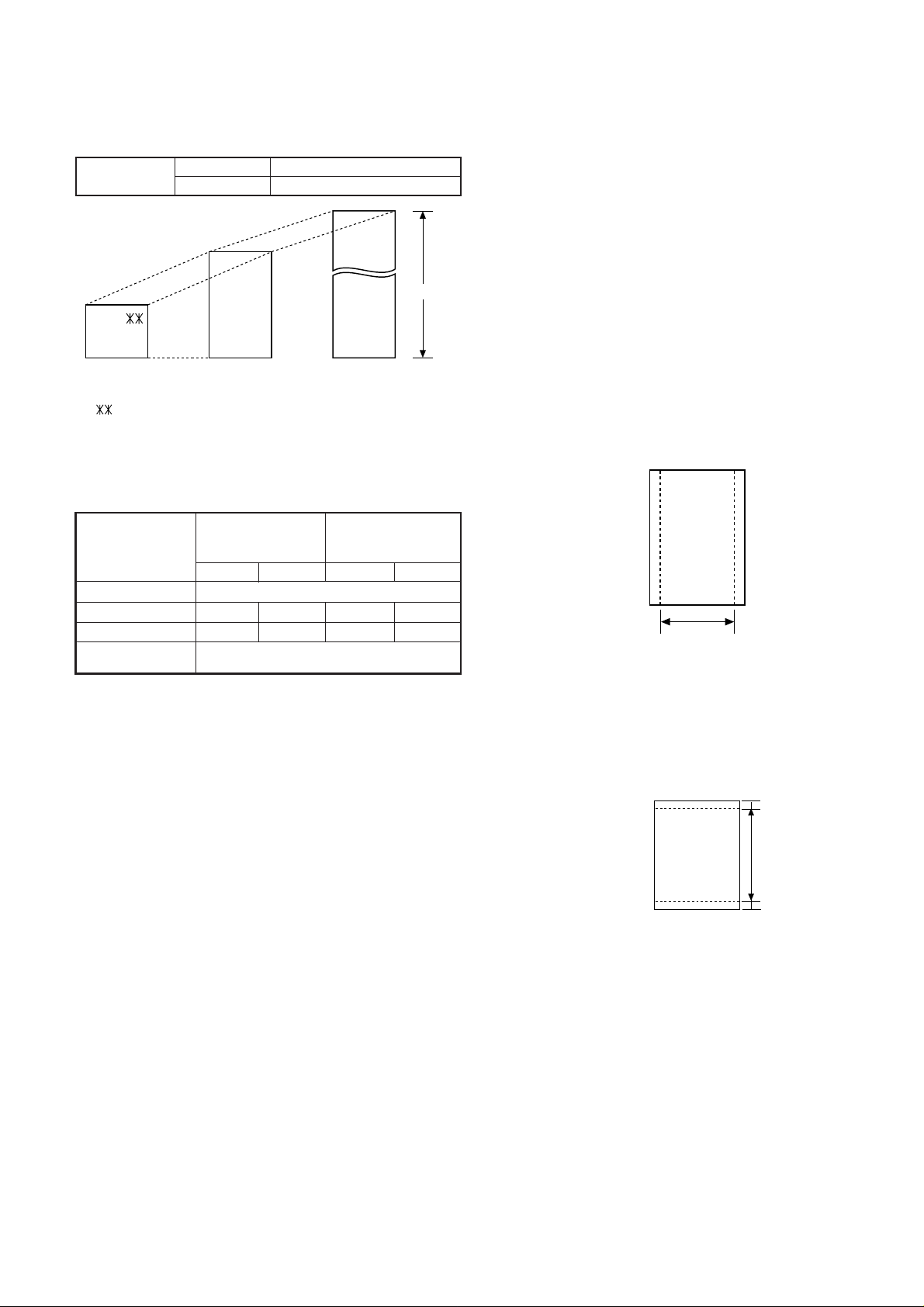
[3] T ransmittable documents
[
]
[
]
5mm
5mm
Readable length
1. Document Sizes
Normal size
(Min.)
140mm
148mm 216mm
Use document carrier sheet for smaller documents.
* With special sizes, only one sheet can be fed into the machine at a
time. Insert next page into feeder as current page is being scanned.
2. Paper Thickness & Weight
width 148 – 216 mm
length 140 – 297 mm
(Max.)
(Max.)
A4 size
297mm
216mm
Normal size
Special size
600mm
FO-50A
FO-70A
5. Automatic Document Feeder Capacity
Number of pages that can be placed into the feeder at anytime is as
follows:
Normal size: max. ADF 5 sheets
Special size: single sheet only (manual feed)
NOTES: • When you need to send or copy more pages than the feeder
limit, place additional pages in feeder when last page in
feeder is being scanned.
• Place additional pages carefully and gently in feeder.
If force is used, double-feeding or a document jam may
result.
6. Readable Width & Length
The readable width and length of a document are slightly smaller than
the actual document size.
Note that characters or graphics outside the effective document scanning range will not be read.
• Readable width
210mm, max.
4x6 series
(788mm x 1091mm x
1000mm sheets)
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
Feeder capacity 10 sheets, max.
Paper weight 45kg 69.2kg 52g/m
Paper thickness (ref.)
Paper size 148mm x 140mm ~
0.06mm 0.09mm 0.06mm 0.09mm
A4 (210mm x 297mm), Letter (216mm x 279mm)
Square
meter series
2
80g/m
3. Document Types
• Normal paper
Documents handwritten in pencil (No. 2 lead or softer), fountain
pen, ball-point pen, or felt-tipped pen can be transmitted.
Documents of normal contrast duplicated by a copying machine
can also be transmitted.
• Diazo copy (blue print)
Diazo copy documents of a normal contrast may be transmitted.
• Carbon copy
A carbon copy may be transmitted if its contrast is normal.
4. Cautions on Transmitting Documents
• Documents written in yellow, greenish y ellow, or light b lue ink cannot
be transmitted.
• Ink, glue, and correcting fluid on documents must be dry before
the documents can be transmitted.
• All clips, staples and pins must be removed from documents before transmission.
• Patched (taped) documents should be copied first on a copier and
then the copies used for transmission.
• All documents should be fanned before insertion into the feeder to
prevent possible double feeds.
2
Readable width
• Readable length
This is the length of the document sent minus 5mm from the top and
bottom edges.
1 – 3
Page 6
FO-50A
FO-70A
7. Use of Document Carrier Sheet
A document carrier sheet must be used for the following documents.
• Those with tears.
• Those smaller than size 148mm (W) x 140mm (L).
• Carbon-backed documents
TELEPHONE JACK
A standard telephone jack must be located near the machine.
This is the telephone jack commonly used in most homes and offices.
• Plugging the f ax machine into a jack which is not an jac k may result in
damage to the machine or your telephone system. If you do not know
what kind of jack you have , or need to hav e one installed, contact the
telephone company.
Make print straight
across paper
E.G.
Place the document
carrier in the document
feeder with the clear film
side down
Direction of insertion
NOTE: To transmit a carbon-backed document, insert a white sheet of
paper between the carbon back of the document and the document carrier.
• Those containing an easily separable writing substance (e.g., trac-
ing paper written on with a soft, heavy lead pencil).
NOTES: • When using the document carrier, carefully read the in-
structions written on the back.
• If the document carrier is dirty, clean it with a soft, moist
cloth, and then dry it before using for transmission.
• Do not place more than one document in the carrier at a
time.
[4] Installation
1. Site selection
T ak e the follo wing points into consideration when selecting a site for this
model.
ENVIRONMENT
• The machine must be installed on a level surface.
• Keep the machine away from air conditioners, heaters, direct sun-
light, and dust.
• Provide easy access to the front, back, and sides of the machine. In
particular, keep the area in front of the machine clear , or the original
document may jam as it comes out after scanning.
• The temperature should be between 5° and 35°C.
• The humidity should be between 30% and 85% (without conden-
sation).
ELECTRICITY
230-240 V, 50 Hz, grounded (3-prong) AC outlet is required.
Caution!
• Connection to a power source other than that specified will cause
damage to the equipment and is not covered under the warranty.
• If your area experiences a high incidence of lightning or power surges,
we recommend that you install a surge protector for the power and
telephone lines. Surge protectors can be purchased at most telephone
specialty stores.
If the machine is moved from a cold to a warm place...
Condensation may from on the reading glass if machine is mov ed from
a cold to a warm place, this will prevent proper scanning of documents
for transmission. Turn on the power and wait approximately 2 hours before using machine.
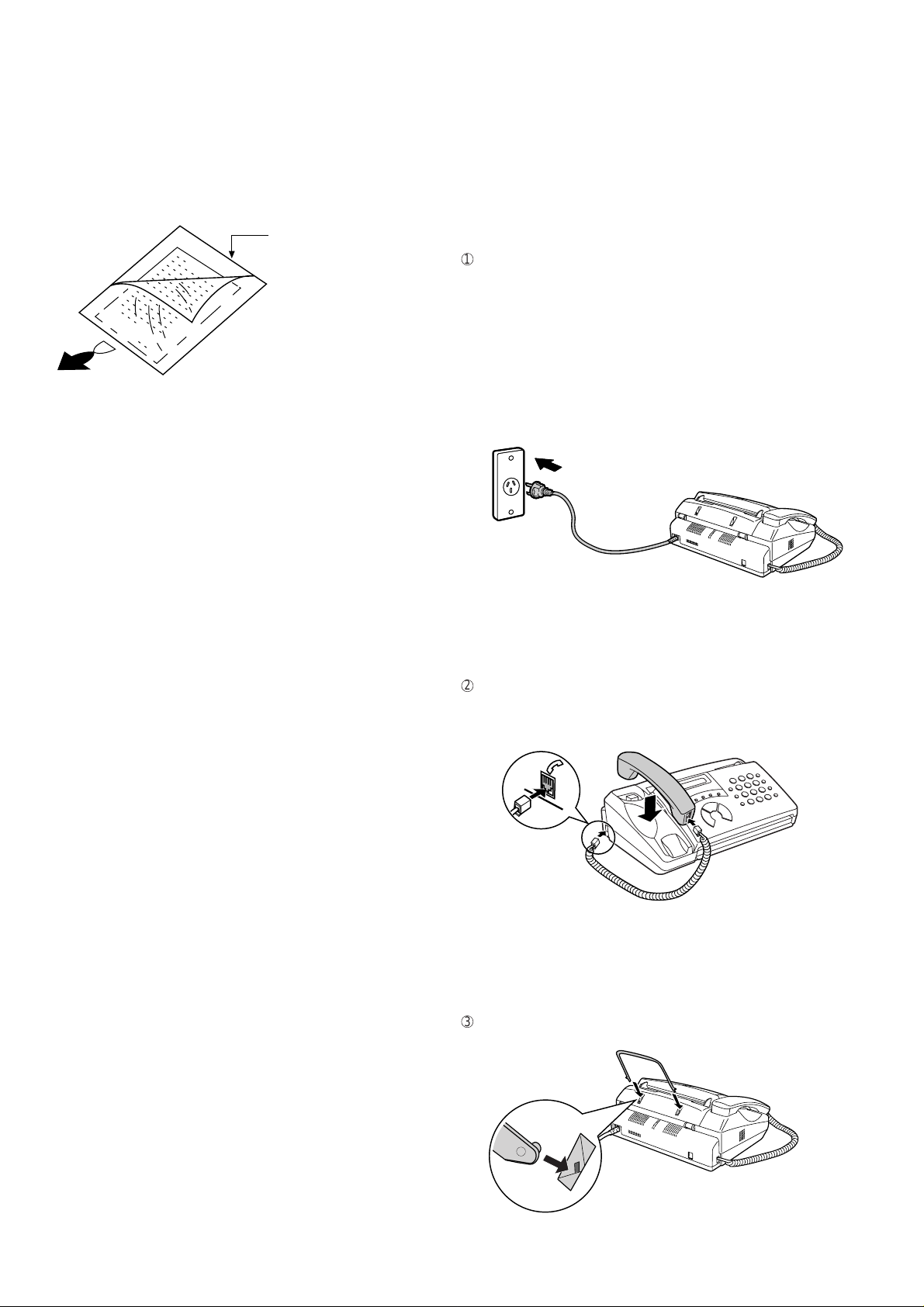
2. Assembly and connections
1
Plug the power cord into a 230-240 V, 50 Hz, earthed (3-prong) AC
outlet.
Caution:
When disconnecting the fax, unplug the telephone line cord before
unplugging the power lead.
• The mains outlet (socket-outlet) should be installed near the equip-
ment and be easily accessable.
• The machine does not have a power on/off s witch, so the power is
turned on and off by simply plugging in or unplugging the power
cord.
Note: If your area experiences a high incidence of lightning or power
surges, we recommend that you install surge protectors f or the power
and telephone lines. Surge protectors can be purchased at most telephone specialty stores.
2
Connect the handset as shown and place it on the handset rest.
• The ends of the handset cord are identical, so they will go into
either jack.
Make sure the handset cord
goes into the jack marked
with a handset symbol on the
side of the machine!
Use the handset to make ordinary
phone calls, or to transmit and receive
faxes manually.
3
Attach the original document support as shown below.
1 – 4
Page 7
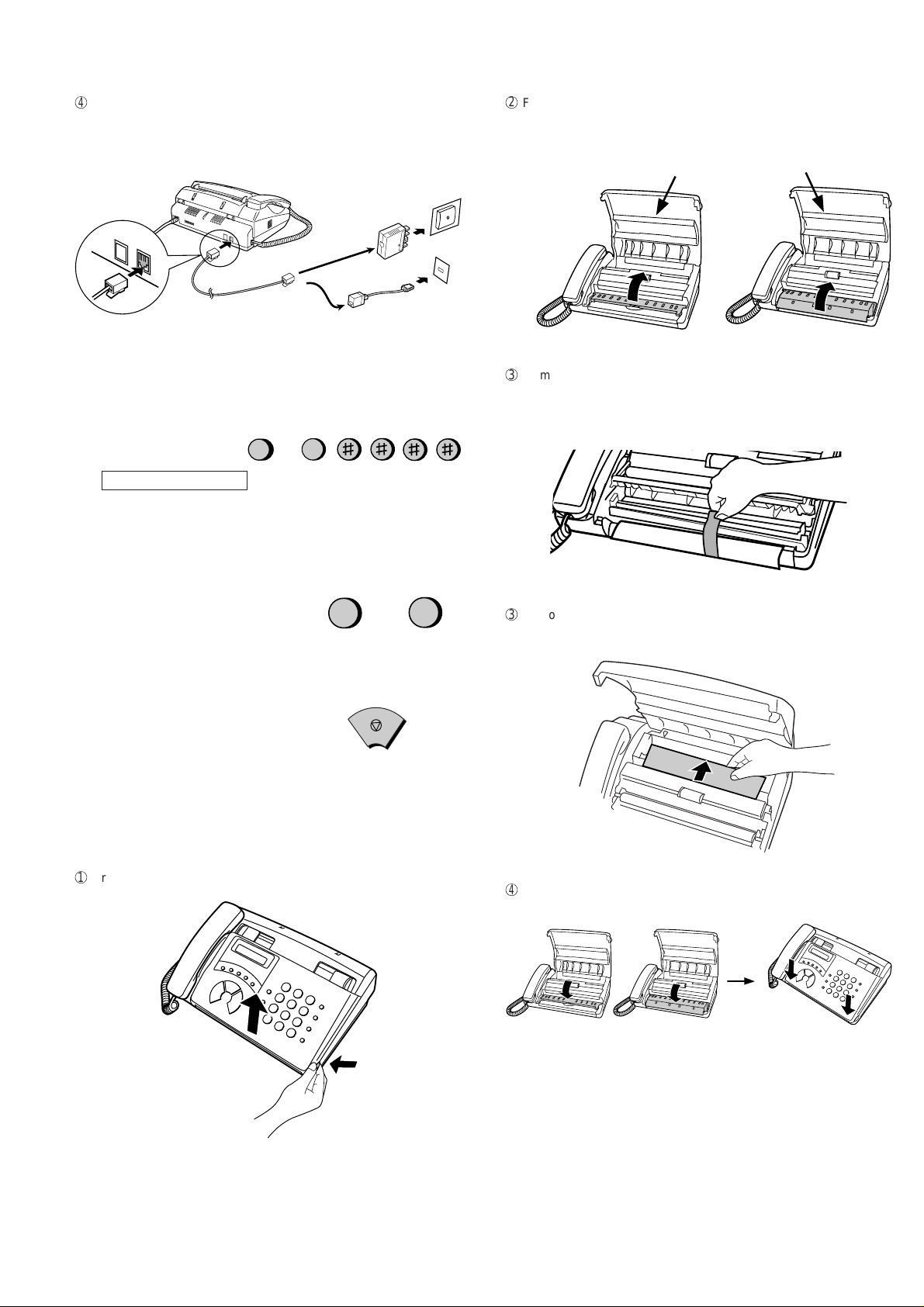
4
FO-50
FO-70
Note: Do not peel off or
bend this strip of film.
Insert one end of the telephone line cord into the adapter. Insert the
other end of the line cord into the socket on the back of the f ax marked
TEL. LINE. Plug the adapter into the telephone socket on the w all.
For Australia
TEL.
SET
TEL.
LINE
For New Zealand
Note: The f ax machine is set for tone dialing. If you are on a pulse dial
line, you must set the fax machine for pulse dialing.
Press the keys on the operation panel as follows:
FO-50A
FO-70A
2
Flip up the front paper guide.
3
Remove the tape and packing paper from the cutter unit.
(FO-70)
1. Press these keys:
The display will show:
DIAL MODE
2. Press 1 to select tone
dialing, or 2 to select pulse
dialing.
3. Press the STOP key to return to the date
and time display.
Note: For all units installed in New Zealand, select 1 f or tone dialing.
The pulse setting 2 will not operate correctly and must not be used.
FUNCTION
4
TONE
1
or
STOP
PULSE
2
3. Removing the packing paper
1
Grasp the finger hold and open the operation panel.
3
Remove the packing paper.
(FO-50)
4
Flip down the front paper guide and then close the operation panel.
1 – 5
FO-50
FO-70
Page 8
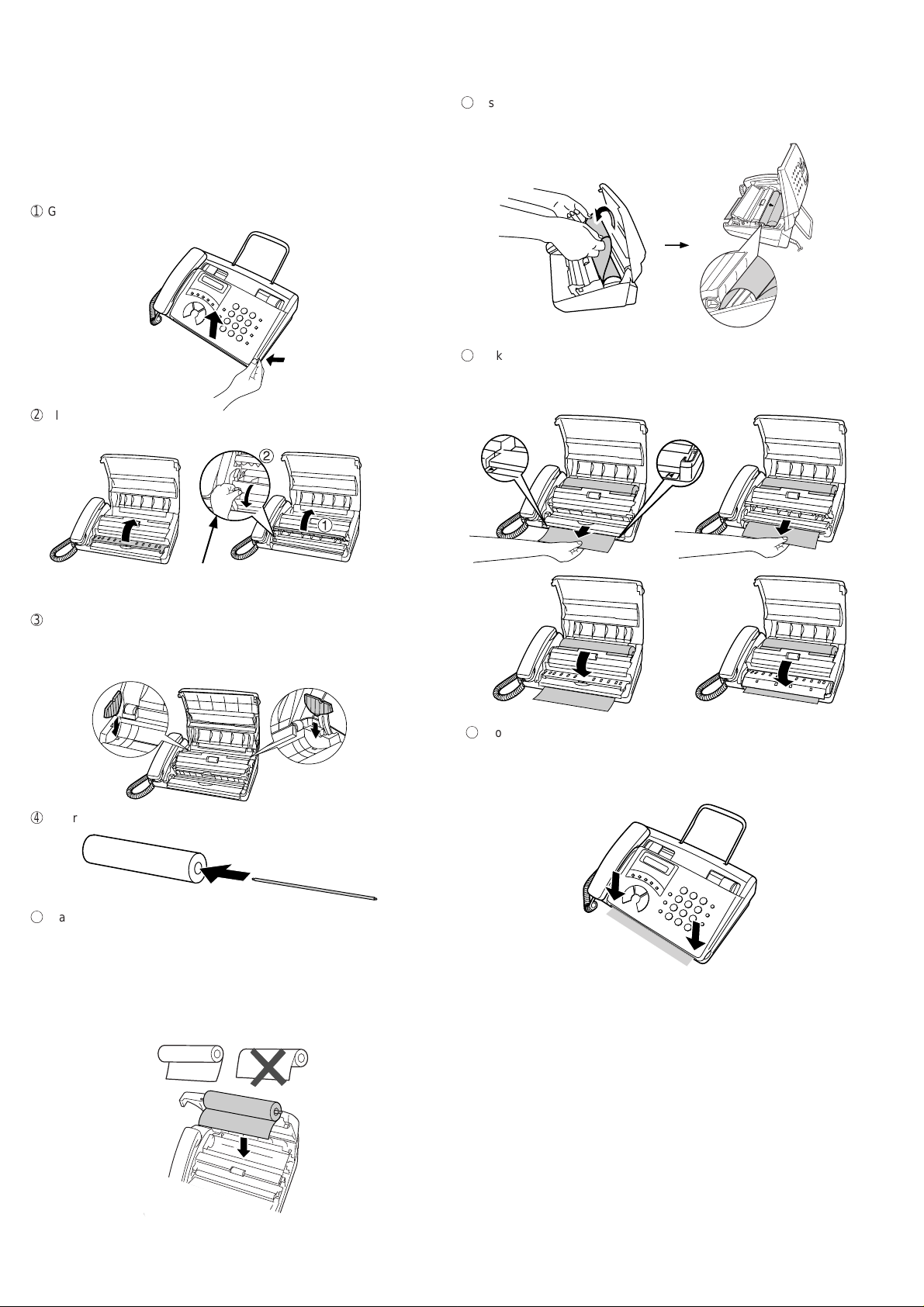
FO-50A
FO-70A
4. Loading the fax paper (FO-20PRw)
• Your f ax machine prints incoming fax es on a special kind of paper
called fax paper.
• The fax machine’s print head creates text and images by applying
heat to the fax paper.
1
Grasp the finger hold as shown and pull up to open the operation
panel.
6
Insert the leading edge of the paper into the slot as shown. Continue
to push the paper through the slot until it comes out the opening in
the front of the machine.
7
Make sure the paper comes out straight, and then flip down the pa-
per guide.
2
Flip up the front paper guide.
FO-50
3
If you are loading paper that is 210 mm in width, place the paper roll
shims on each side of the paper compartment. (Note that Sharp recommended paper, including the initial roll, is 216 mm in width.)
• The ribbed side of the shims should face in (toward each other).
4
Unwrap the roll of thermal paper and insert the paper shaft.
FO-70
Press the knob to make sure the
front side of the metal guide is down.
FO-50
8
Close the operation panel, making sure it clicks into place.
• A short length of the paper will be cut off. (FO-70)
• A short length of the paper will feed out.
Grasp the paper by the edge and pull upward to tear it off. (FO-50)
FO-70
5
Place the roll of fax paper in the compartment, making sure the ends
of the rod fit into the notches on each side of the compartment.
♦ Important: The roll must be placed so the leading edge of the
paper unrolls as shown. (The paper is only coated on one side for
printing. If the roll is placed backwards, the paper will come out
blank after printing.)
YES
NO!
Click!
1 – 6
Page 9
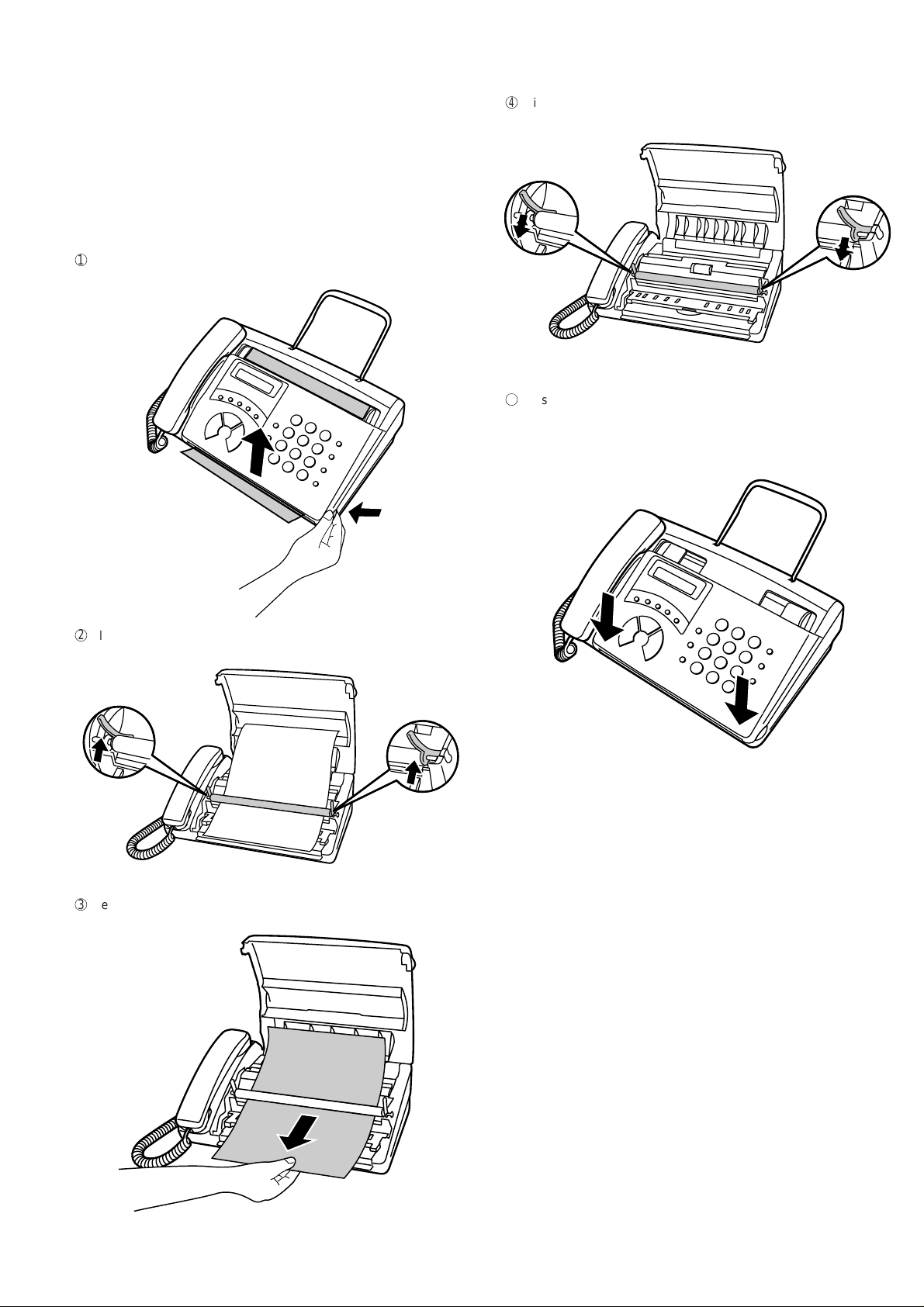
5. Clearing a jammed document
If the original document doesn’t feed properly during transmission or
copying, or DOCUMENT JAMMED appears in the display, first try pressing the STAR T ke y . If the document doesn’t feed out, open the operation
panel and remove it.
Important:
Do not try to remove a document without first releasing it as explained
below.
This may damage the feeder mechanism.
1
Grasp the finger hold and pull up to open the operation panel.
4
Flip down the green levers on each side of the white roller.
5
Close the operation panel, making sure it clicks into place.
• Press down on both front corners of the panel to make sure it
clicks into place.
FO-50A
FO-70A
2
Flip up the green levers on each side of the white roller.
3
Remove the document.
1 – 7
Page 10
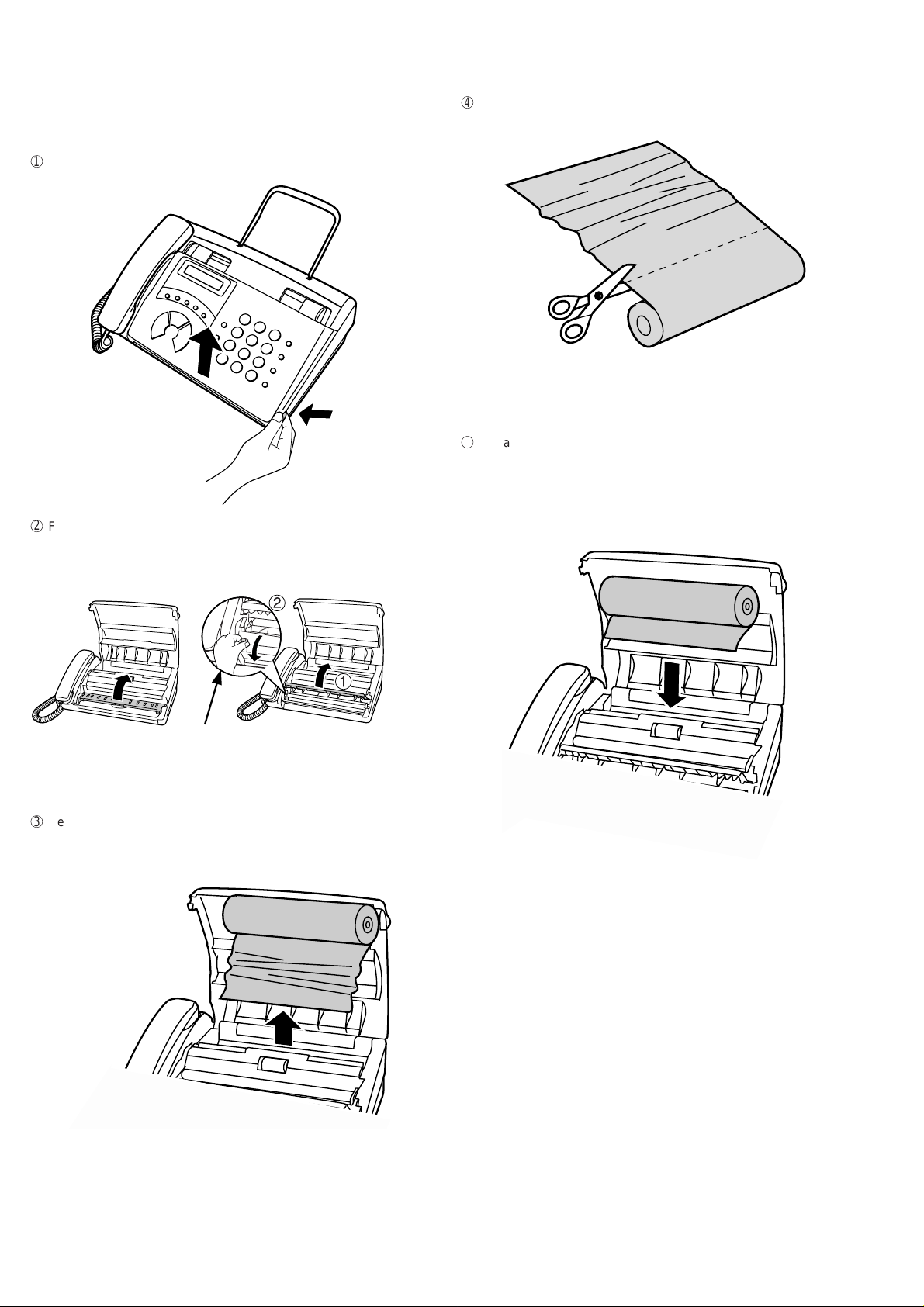
FO-50A
FO-70A
6. Clearing jammed paper
If the fax paper jams, PAPER JAMMED will appear in the display.
Follow the steps below to clear the jam.
1
Grasp the finger hold and pull up to open the operation panel.
2
Flip up the front paper guide.
4
Cut off the wrinkled part of the paper.
5
Reload the paper.
• Jammed paper is often caused by improper loading. Be sure to
carefully follow the instructions for paper loading given in Loading
the Fax Paper.
FO-50
FO-70
Press the knob to make sure the
front side of the metal guide is down.
3
Remove the paper roll.
• Remove any cut pieces of paper from the paper compartment.
(FO-70 only)
1 – 8
Page 11
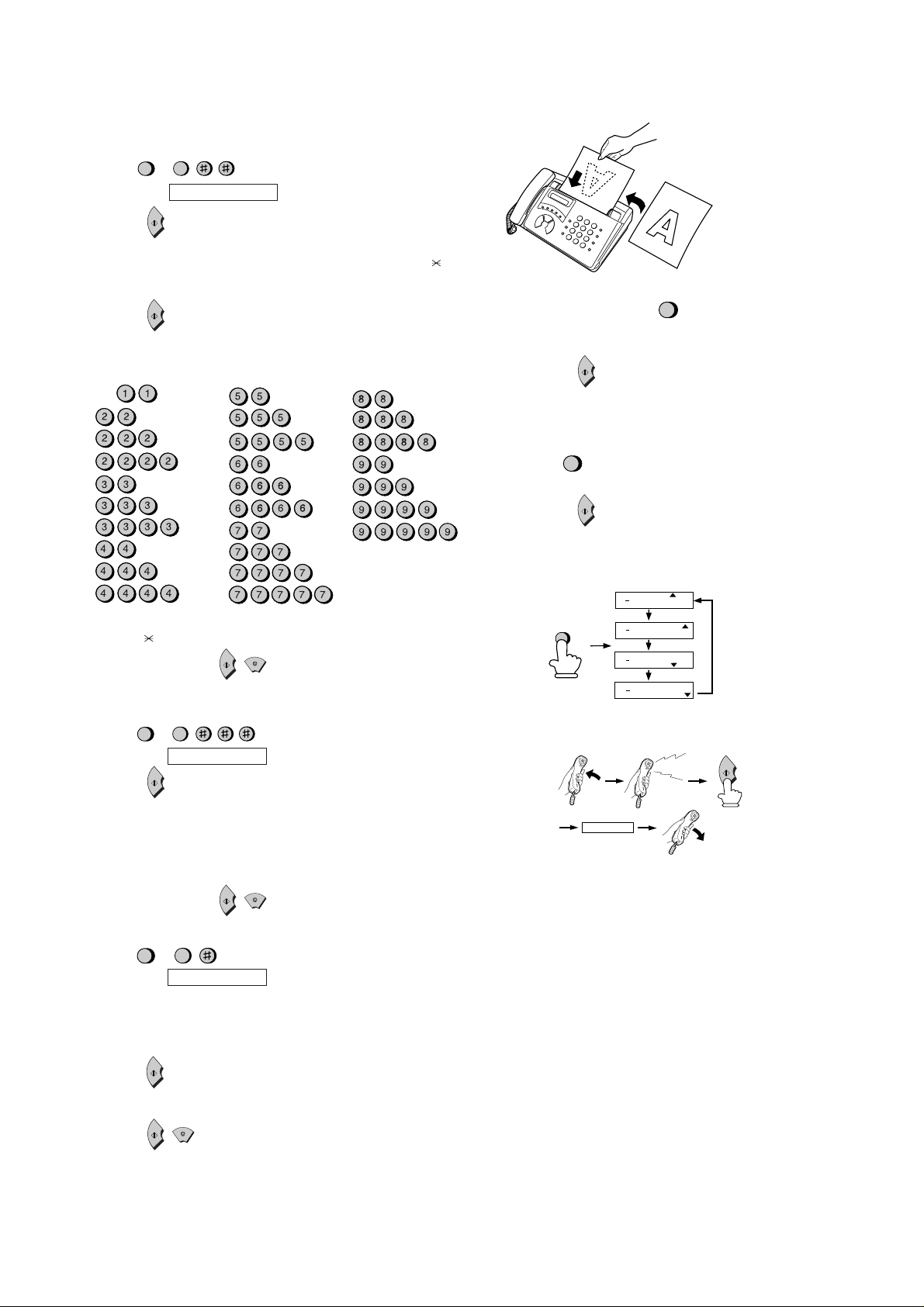
[5] Quick reference guide
RESOLUTION/
RECEPTION MODE
FAX
TEL
FAX
TEL
05 NOV 10:30
A.M.
TEL/FAX
A.M.
TEL/FAX
05 NOV 10:30
FAX
TEL
FAX
TEL
05 NOV 10:30
A.M.
TEL/FAX
A.M.
TEL/FAX
05 NOV 10:30
ENTERING YOUR NAME AND NUMBER
1. Press:
2. Press:
3. Enter your fax number (max. of 20 digits) by pressing the number keys.
• T o insert a space between digits, press the # k ey . T o enter "+", press the
• If you make a mistak e, press the SPEED DIAL k ey to backspace and clear the
4. Press:
5. Enter your name by pressing the appropriate number keys as shown below.
• T o enter two letters in succession that require the same k ey , press the SPEAKER
SPACE =
A =
B =
C =
D =
E =
F =
G =
H =
I =
FUNCTION
3
Display shows: OWN NUMBER SET
START
mistake.
START
key after entering the first letter.
J =
K =
L =
M =
N =
O =
P =
Q =
R =
S =
key.
T =
U =
V =
W =
X =
Y =
Z =
FO-50A
FO-70A
SENDING FAXES
Place your document (up to 5 pages)
face down in the document feeder.
Normal Dialing
1. Lift the handset or press
2. Dial the fax number.
3. Wait for the reception tone (if a person answers, ask them to press their Start
key).
4. Press:
START
Rapid Key Dialing
Press the appropriate Rapid Key. Transmission will begin automatically.
Speed Dialing
SPEED
1. Press:
DIAL
2. Enter 2-digit Speed Dial number.
3. Press:
START
RECEIVING FAXES
Press the RESOLUTION/RECEPTION MODE key until the arrow in the display
points to the desired reception mode (make sure the document feeder is empty).
SPEAKER
• To change case, press the REDIAL key.
Press # or
6. When finished, press:
to scroll through symbols and special characters.
START
STOP
SETTING THE DATE AND TIME
1. Press:
2. Press:
3. Enter two digits for the Day (01 through 31).
4. Enter two digits for the Month (01 through 12).
5. Enter four digits for the Year (Ex: 1999).
6. Enter two digits for the Hour (01 through 23).
7. Enter two digits for the Minute (00 through 59).
8. When finished, press:
FUNCTION
3
Display shows: DATE & TIME SET
START
START
STOP
STORING AND CLEARING AUTO DIAL NUMBERS
1. Press:
2. Press 1 to store a number or 2 to clear a number.
3. Enter a 2-digit Speed Dial number (from 01 to 05 for Rapid Key Dialing, or 06 to
4. Enter the full fax/telephone number.
5. Press:
6. Enter the name of the location by pressing number keys (Refer to the letter
7. Press:
FUNCTION
3
Display shows: FAX/TEL # MODE
40 for Speed Dialing) (If you are clearing a number, go to Step 7.)
START
entry table in
ENTERING YOUR NAME AND NUMBER
START
STOP
.)
FAX mode: The fax machine automatically answers on the set number of rings
and receives the incoming document.
TEL mode:
START
Beep
RECEIVING
TEL/FAX mode: This mode is convenient for receiving both fax es and v oice calls.
When a call comes in, the fax will detect whether it is a voice call (including manually dialed fax transmissions), or an automatically dialed fax.
A.M. mode: Select this mode when an answering machine is connected to the f ax
and the answering machine is turned on.
1 – 9
Page 12

FO-50A
FO-70A
M E M O
1 – 10
Page 13
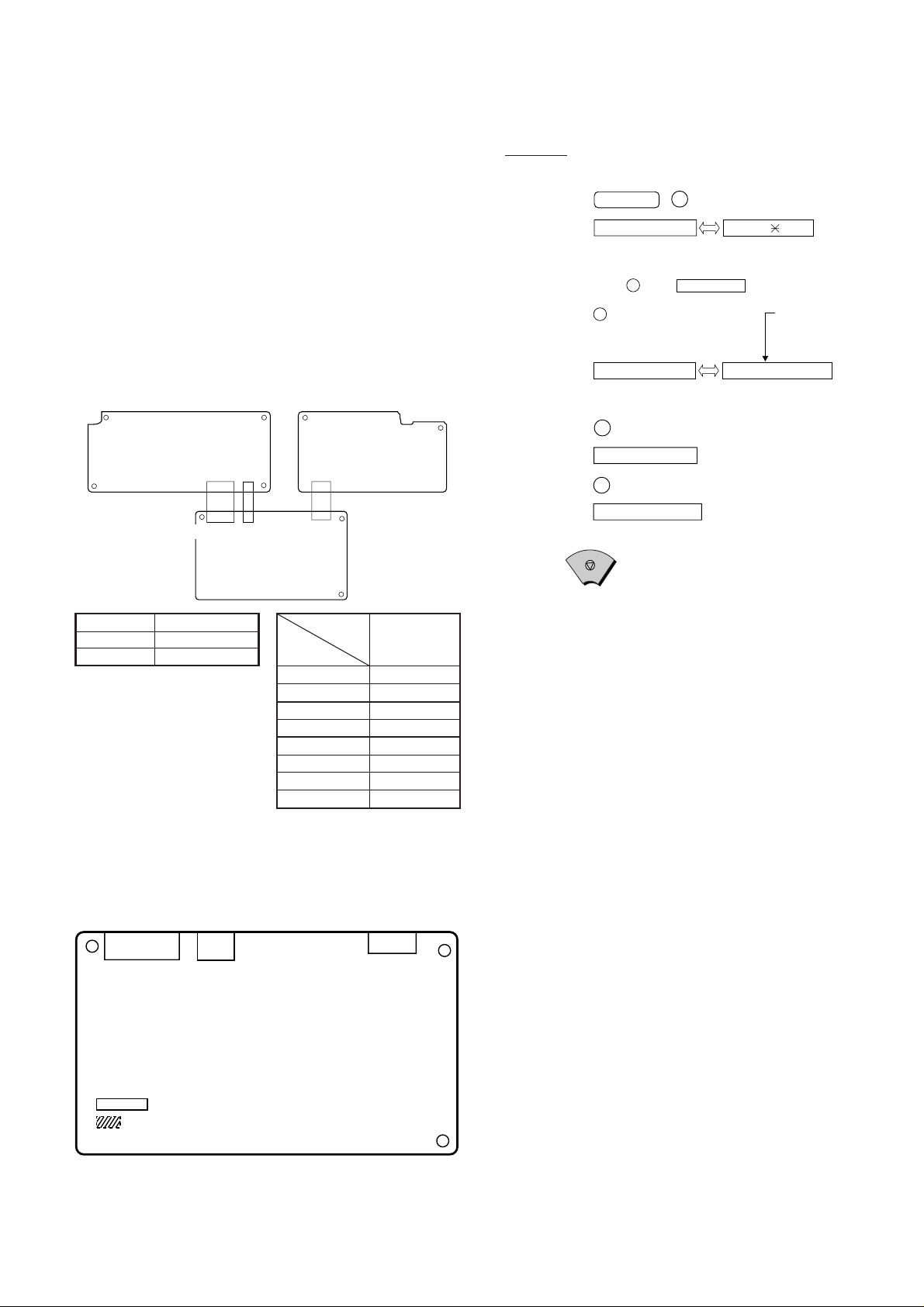
CHAPTER 2. ADJUSTMENTS
(step 1) Select "OPTION SETTING".
KEY : FUNCTION 4
DISPLAY: OPTION SETTING PRESS OR #
(step 2) Select "DIAL MODE".
KEY: Push # until " DAIL MODE " is
indicated because the number of
# s changes by the model.
DISPLAY: DIAL MODE
(step 3) Select, using "1" or "2".
KEY: 1
DISPLAY: TONE SELECTED
KEY: 2
DISPLAY: PULSE SELECTED
(step 4) End, using the "STOP" key.
KEY:
Cursor
When initially registering,
the mode shows 1=TONE.
When registering again, the
mode which was registered
formerly is shown.
STOP
1=TONE, 2=PULSE
[1] Adjustments
General
Since the following adjustments and settings are provided f or this model,
make adjustments and/or setup as necessary.
1. Adjustments
Adjustments of output voltage (FACTORY ONLY)
1. Install the power supply unit in the machine.
2. Set the recording paper and document.
3. When the document is loaded, power is supplied to the output lines.
Confirm that outputs are within the limits below.
Output voltage settings
FO-50A
FO-70A
3. Settings
Dial mode selector
DIAL mode (Soft Switch No. SWB4 DATA No. 2)
TEL/LIU PWB
CNL IUA
Output Voltage limits
+5V 4.75V ∼ 5.25V
+24V 24.0V ∼ 26.0V
2. IC protectors replacement
ICPs (IC Protectors) are installed to protect the motor driver circuit.
ICPs protect various ICs and electronic circuits from an overcurrent condition.
The location of ICPs are shown below:
CNLIUA
CONTROL PWB
CNL IUB
CNLIUB
Pin No.
POWER SUPPLY PWB
CN2
CNPW
Connector
No. CNPW
1DG
2 +5V
3MG
4MG
5 +24V
6 +24V
7DG
8 PSAVE
CNLIUA
CNMT
FU100
(1)FU100 (KAB2402) is installed in order to protect IC’s from an over-
current generated in the motor drive circuit. If FU100 is open, replace it with a new one.
CNLIUB
CONTROL PWB
(TOP SIDE)
CNPW
2 – 1
Page 14
FO-50A
FO-70A
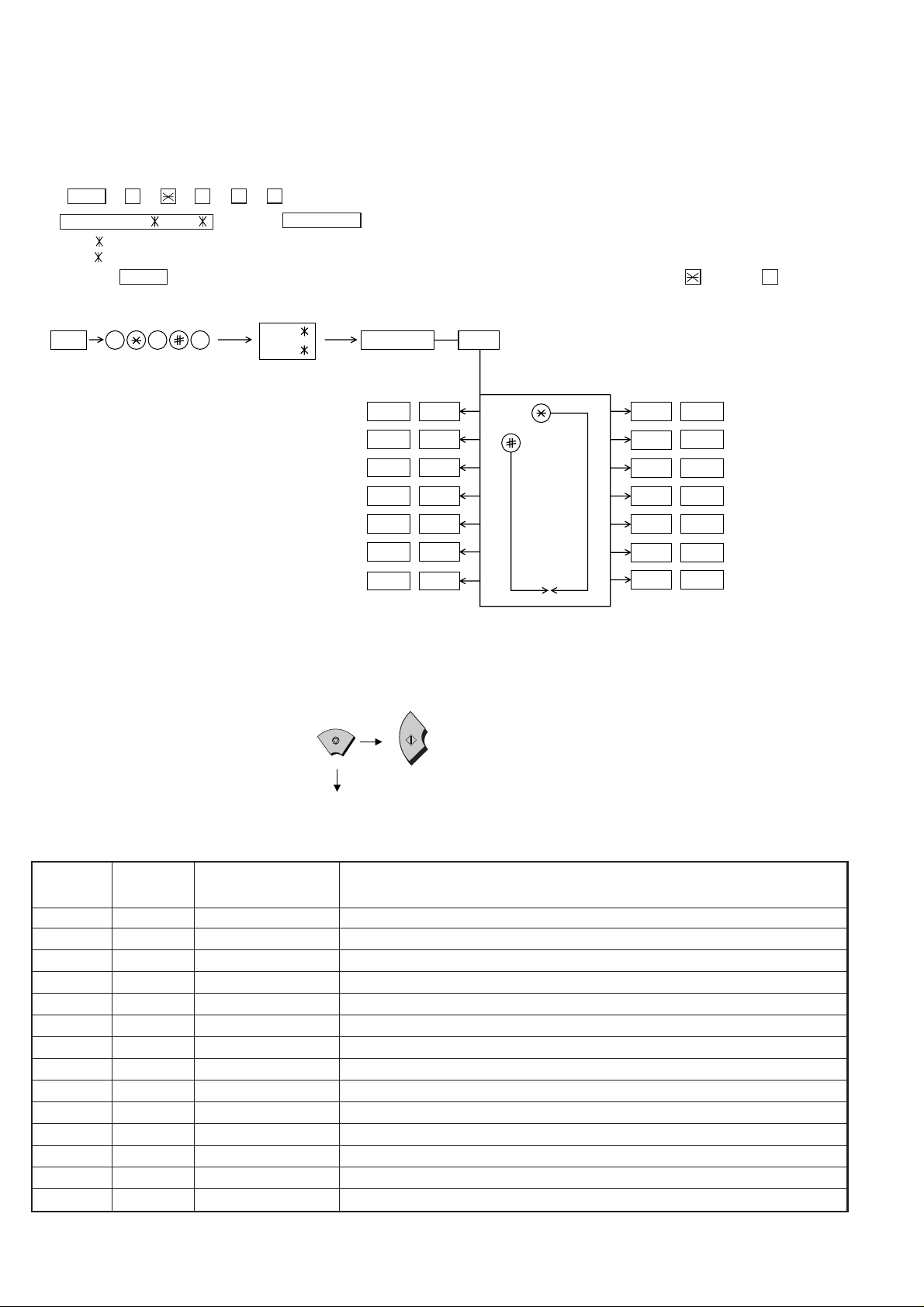
[2] Diagnostics and service soft switch
1. Operating procedure
(1) Entering the diagnostic mode
Press FUNC → 9 → → 8 → # → 7 , and the following display will appear.
ROM Ver. FZK0 (FZL0 ) After 2 sec: DIAG MODE
FZK0 (FO-50A)
FZL0 (FO-70A)
Then press the START key and country name selected by country select will appear. Select the desired item with the key or the # key or select
with the direct key. Enter the mode with the START key.
(Diag•specifications)
FUNC
9 8 7
FZK0
FZL0
DIAG MODE
START
START —Soft switch mode
START
START
START
START
START CSignal send mode
START —Memory clear
If the diag mode cannot be set, repeat the diag mode operation, performing the following operation.
After the power is turned on and "WAIT A MOMENT" is indicated, press
the STOP key.
START
KEY
"Power ON"
STOP
KEY
+
Memory clear
(Work + Backup)
AROM & RAM check
—Aging mode
—Panel check mode
BCheck pattern
In relation with the process response (request from Production
Engineering) "WAIT A MOMENT" clock indication may appear depending
on STOP ke y timing. If the ST OP key is held do wn, "MEMORY CLEAR?"
appears.
—
—
—
—
E
D
—
2. Diagnostic items
ITEM DIRECT
No. key
1 — SOFT SWITCH MODE Soft switches are displayed and changed. List can be output.
2 A ROM & RAM CHECK ROM is sum-checked, and RAM is matched. Result list is output.
3 — AGING MODE 10 sheets of check patterns are output every 5 minutes per sheet.
4 — PANEL CKECK MODE Panel keys are tested. Result list is output.
5 B CHECK PATTERN 2 sheets of check patterns are output.
6 C SIGNAL SEND MODE Various signals of FAX communication are output.
7 — MEMORY CLEAR Back-up memory is cleared, and is set at delivery.
8 — SHADING MODE Shading compensation is performed in this mode.
9 D ALL BLACK PRINT To check the print head, whole dots are printed over the interval of 2 m.
10 E AUTO FEEDER MODE Insertion and discharge of document are tested.
11 — ENTRY DATA SEND Registered content is sent.
12 — ENTRY DATA RECEIVE Registered content is received, and its list is output.
13 — CUTTER AGING Recording paper is successively cut. (Cutter model only)
14 — COUNTRY SELECT The software parameter that it agreed in each country name is set up.
Contents Function
START
START
START
START
START
START
START
Country select
Cutter aging
(Cutter model only)
Entry data receive
Entry data send
Auto feeder mode
All black mode
Shading mode
2 – 2
Page 15

3. Diagnostic items description
3. 1. Soft switch mode
The soft switches are provided so that each operation mode can be set
by using the operation panel.
In this mode, these switches can be checked and set.
The contents of these switches are backed up.
The available soft switches are SW-A1 to SW-K1.
The content of soft switches is shown in page 2-5 to 2-17.
The contents are set to factory default settings.
3. 2. ROM & RAM check
ROM executes the sum check, and RAM executes the matching test.
The result will be notified with the number of short sounds of the buzzer
as well as by printing the ROM & RAM check list.
Number of short sounds of buzzer 0 → No error
1 → ROM error
2 → RAM error (32Kbyte)
3. 3. Aging mode
If any document is first present, copying will be ex ecuted sheet by sheet.
If no document is present, the check pattern will be printed sheet by
sheet. This operation will be executed at a rate of one sheet per 5minutes, and will be ended at a total of 10 sheets.
3. 4. Panel check mode
This mode is used to check whether each key oper ates properly or not.
Press the key on the operation panel, and the key will be displayed on
the display. Theref ore, press all k eys . At this time,finally press the STOP
key.
When the STOP key is pressed, the keys which are not judged as
"pressed" will be printed on the result list.
• LED part of the contact image sensor (CIS) is kept on during the term
from when "ST AR T" of the panel test mode to end with the STOP k ey .
FO-50A
FO-70A
3. 6. Signal send mode
This mode is used to send various signals to the circuit during F AX communication. Ever y push of START key sends a signal in the following
sequence. Moreover , the signal sound is also output to the speaker when
the line monitor of the soft switch is on.
[1] No signal (CML signal turned on)
[2] 9600bps
[3] 7200bps
[4] 4800bps
[5] 2400bps
[6] 300bps (FLAG)
[7] 2100Hz (CED)
[8] 1100Hz (CNG)
[9] Pseudo Ring (models with auto TEL/FAX changeover function)
[10] END
3. 7. Memory clear
This mode is used to clear the backup memory and to reset to the factory default settings.
The content of each setting will be cleared.
Note: Be sure to ex ecute the memory clear mode whenev er you change
the country select setting. The def ault settings of the soft switches
vary according to the destinations. Theref ore, if you do not e xecute
the memory clear after changing the country select setting, some
functions may not work.
3. 8. Shading mode
The mode is used for the shooting compensation. For reading, set up
the special original paper.
The shooting compensation memorizes the reference data of white and
black for reading.
Moreover, the memorized data is not er ased ev en if memory clear mode
is executed.
3. 5. Check pattern
This mode is used to check the status of print head. Two sheets of check
pattern are printed. The f ollowing inf ormation of check pattern is printed.
1
Vertical stripes (alternate white and black lines) Approx. 35 mm
2
Full black Approx. 70 mm
3
Full white Approx. 35 mm
1
2
3
RANK 0 or 1
Note:
There is a selection RANK 0 or 1 depending on resistance value of the
thermal head. RANK 0 or RANK 1 is printed at the tail of check pattern
to identify.
3. 9. All black print
This mode is used to check the state of the printing head and intentionally overheat it. Whole dots are printed over the interval of 2 m. If it is
overheated or the printing sheet is jammed, press STOP k ey for the end.
3. 10. Auto feeder mode
In this mode, a document is inserted and discharged to check the auto
feed function.
After this mode is started, set a document, and the document feed will
be automatically tested.
3. 11. Entry data send
This mode is used to send the registered data to the other machine and
to make the other machine copy the registered content. Before sending
in this mode, it is necessary to set the other machine at the entry data
receive mode.
The contents to be sent are as follows (the machine prints each list after
the transmission has completed):
1. Telephone list data
2. Sender (cover sheet) register data
3. Optional setting content
4. Soft switch content
5. Junk fax number list
6. Country setting content
2 – 3
Page 16
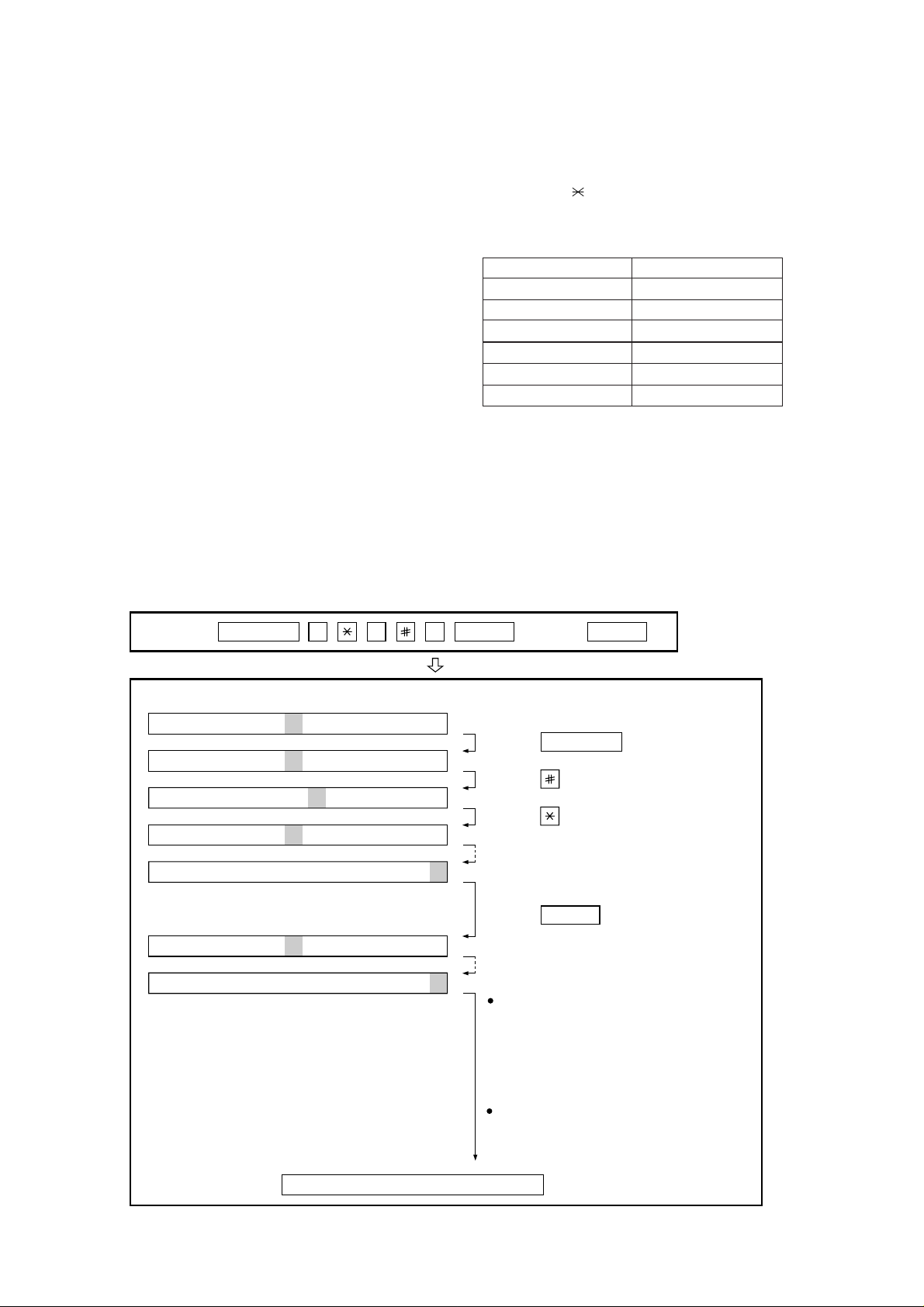
FO-50A
FO-70A
3. 12. Entry data receive
This mode is used to receive the registered data from the other machine
and to make your machine register the received data. Before receiving
in this mode, it is necessary to set the other machine at the entry data
send mode.
After receiving is completed, the machine prints the following lists:
1. Telephone list data
2. Soft switch list
3. Junk fax number list
3. 13. Cutter aging (Cutter model only)
This mode is used to consecutively cut the recording paper about 10
mm long and to display the number of cutting times.
(The number of cutting times is cumulatively counted unless you execute the memory clear.)
The operation is stopped in the following cases:
1. Hold down the stop key. (The cutter aging is stopped.)
2. No recording paper. (The cut operation is stopped.)
3. Recording paper jam. (The cut operation is stopped.)
3. 14. Country select
This mode is used to set line connecting parameters which correspond
to each destination.
When the country select mode is selected, and then the START key is
pressed, the destination (country name) currently set will be displayed.
By pressing the # or k ey, selectable destinations (country names) are
displayed. When the destination (country name) you want to choose is
displayed, press the START key. Each par ameter will be stored in RAM.
Destinations (Country names) you can select are as follows:
COUNTRY NAME COUNTRY NAME
HONG KONG (HK) TAIWAN (AU)
INDIA (IN) THAILAND (TH)
MALAYSIA (MY) GENERAL AREA (GRU)
RUSSIAN (RA) GENERAL AREA (GRH)
SINGAPORE (SG) AUSTRALIA (A)
SOUTH AFRICA (ZA) CHINA (CN)
Note: Be sure to execute the memor y clear mode whenever you
change the country select setting. The default settings of the
soft switches vary according to the destinations. Therefore, if
you do not execute the memory clear after changing the country select setting, some functions may not work.
Do not set a country select setting which is different from that
of the destination of the machine. Some functions will not work
because the function and the PWB specifications are different.
4. How to make soft switch setting
To enter the soft switch mode, press the following key entries in sequence.
Press
FUNCTION
9 8 7 START START
DATA No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
S F T SW-A1 = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T SW-A1 = 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T SW-A1 = 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T SW-A1 = 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T SW-A1 = 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T SW-A2 = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
S F T SW-M2 = 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Press FUNCTION key.
Press key.
Press key.
Bit1 - 8 are set.
Press key during setting.
START
Soft SW-A2 - SW-K1 are set.
To finish the settings halfway between
SW-A1 and SW-K1, press the STOP
key. In this case, the setting being done
to the SW No. on display will be nullified
while settings done to the preceding
SW Nos. remain in effect.
When the COPY key is pressed, the
contents of soft switches are printed.
The soft switch mode is terminated.
2 – 4
Page 17
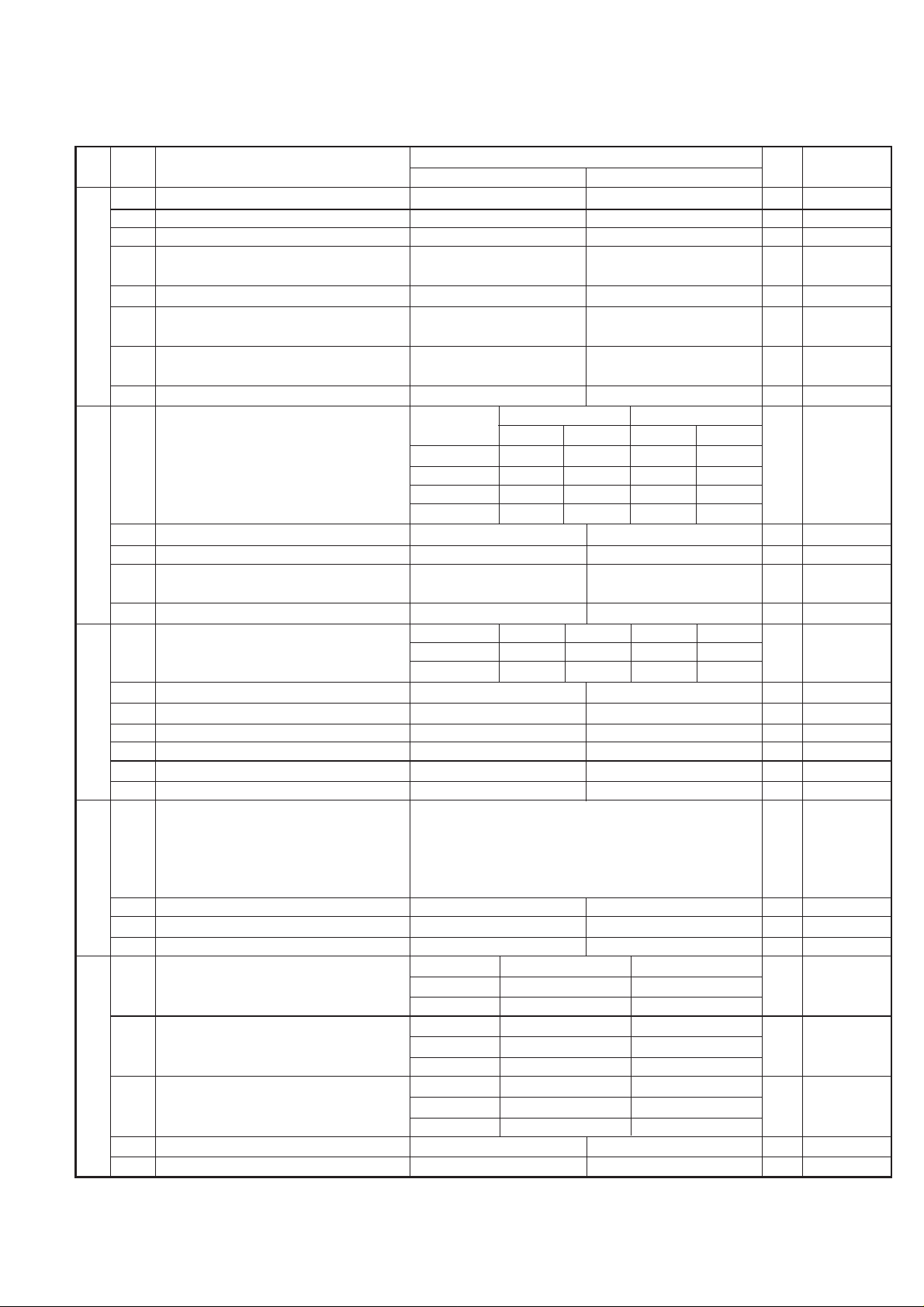
5. Soft switch description
• Soft switch
FO-50A
FO-70A
SW
DATA
NO.
NO.
1 Protect from echo No Yes 0
2 Forced 4800bps reception Yes No 0
3 Footer Print Yes No 0
4 Length limitation of copy/send/receive No limit Copy/Send:60cm 0
SW
5 CSI transmission Not transmitted Transmitted 0
l
A1
6 DIS receive acknowledgement during G3 Twice NSF:Once 0
transmission DIS:Twice
7 Non modulated carrier for V29 transmission Yes No 0
mode
8 Reserved 0
Modem speed V.29 V.27 ter
1No. 100000
2No. 200000
3No. 301100
SW
4No. 411001
l
A2
5 Reserved 0
6 H2 mode No Yes 0
7 Communication error treatment in RTN No communication error Communication error 0
sending mode(Reception)
8 CNG transmission No Yes 0
CED tone signal interval 1000ms 750ms 500ms 75ms
1No. 111000
2No. 210100
3 MR Coding No Yes 0
SW
l
4 Reserved 0
A3
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Signal T r ansmission level Binary input 0
2 (0~-31 dBm setting by 1dBm step) No. = 16 8 4 2 1 1
3 1 2 3 4 5 1
SW
4 0 1 1 1 1 1
l
5 1
A4
6 Protocol monitor(Error print) Printed at com. error Not printed 0
7 Protocol monitor Yes No 0
8 Line monitor Yes No 0
Digital equalization setting(Reception) 7.2km 0km
1No. 1101
2No. 2101
Digital equalization setting(Transmitter) 7.2km 0km
3No. 3100
SW
4No. 4100
l
A5
Digital equalization setting(Reception 7.2km 0km
5 for Caller ID) No. 5 1 0 0
6No. 6100
7 Error criterion 10 ~ 20 % 5 ~ 10 % 0
8 Anti junk fax check Yes No 1
ITEM
Switch setting and function
10
Receive:1.5m
9600bps 7200bps 4800bps 2400bps
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 5
Page 18
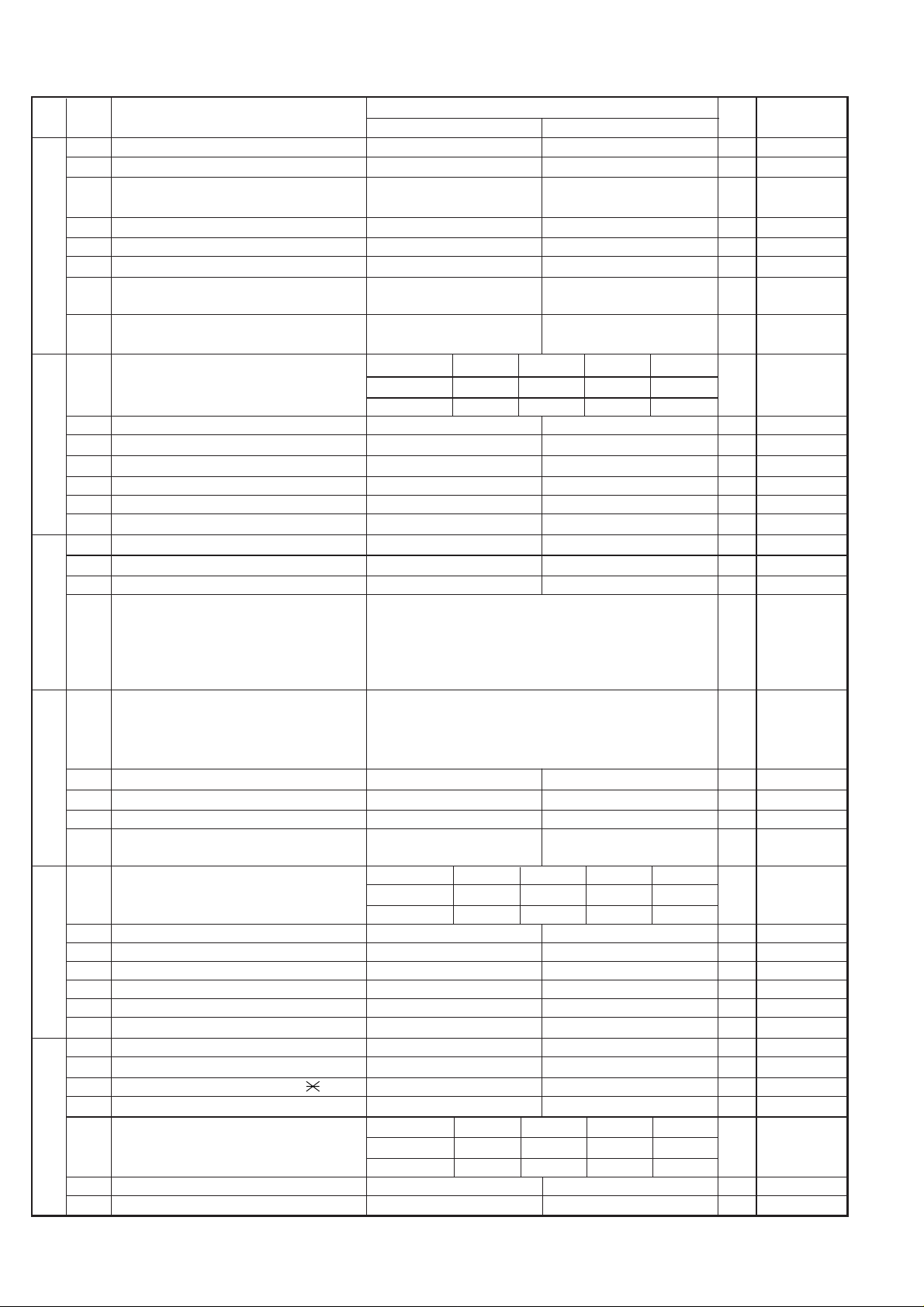
FO-50A
FO-70A
SW
DA TA
NO.
NO.
1 Auto gain control(MODEM) Enable Disable 1
2 End Buzzer Yes No 1
3 Disconnect the line when DIS is received in No Yes 1
SW
l
A6
SW
l
A7
SW
l
B1
SW
l
B2
SW
l
B3
SW
l
B4
RX mode
4 Equalizer freeze control(MODEM) On Off 0
5 Equalizer freeze control 7200 bps only No Yes 0
6 CNG transmission in manual TX mode Yes No 1
7 Initial compression scheme for sharp fax in MR mode H2 mode 0
TX mode
8 Modem speed automatic down when RX Yes No 0
level is under -40dBm
EOL detect timer 5 seconds 13 seconds 20 seconds25 seconds
1No. 100110
2No. 201011
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Hold key Enable Disable 1
2 Auto dial fax transmission by REDIAL key Yes No 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Recall interval Binary input 0
5 (0~15.5min setting by 0.5min step) No. = 16 8 4 2 1 1
6 4 5 6 7 8 0
7 0 1 0 1 0 1
8 0
1 Recall times(0~15times setting) Binary input 0
2 No. = 8 4 2 1 0
3 1 2 3 4 1
4 0 0 1 0 0
5 Dial tone detection(Before auto dial) No Yes 1
6 Reserved 0
7 Busy tone detection(After auto dial) No Yes 1
8 Busy tone detection pulse number 4 pulses 2 pulses 0
(After auto dial)
Waiting time after dialing
1No. 100110
2No. 201010
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Dial pausing(sec/pause) 4 sec 2 sec 0
2 Dial mode Tone Pulse 1 OPTION
3 Pulse → Tone change function by key Enable Disable 1
4 Dial pulse make/break ratio(%) 40/60 33/67 0
Auto dial mode Delay timer of before line
5 connect No. 5 0 0 1 1 1
6 No. 601010
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
45 seconds 55 seconds 90 seconds 140 seconds
0 second 1.5 seconds 3.0 seconds 4.5 seconds
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 6
Page 19
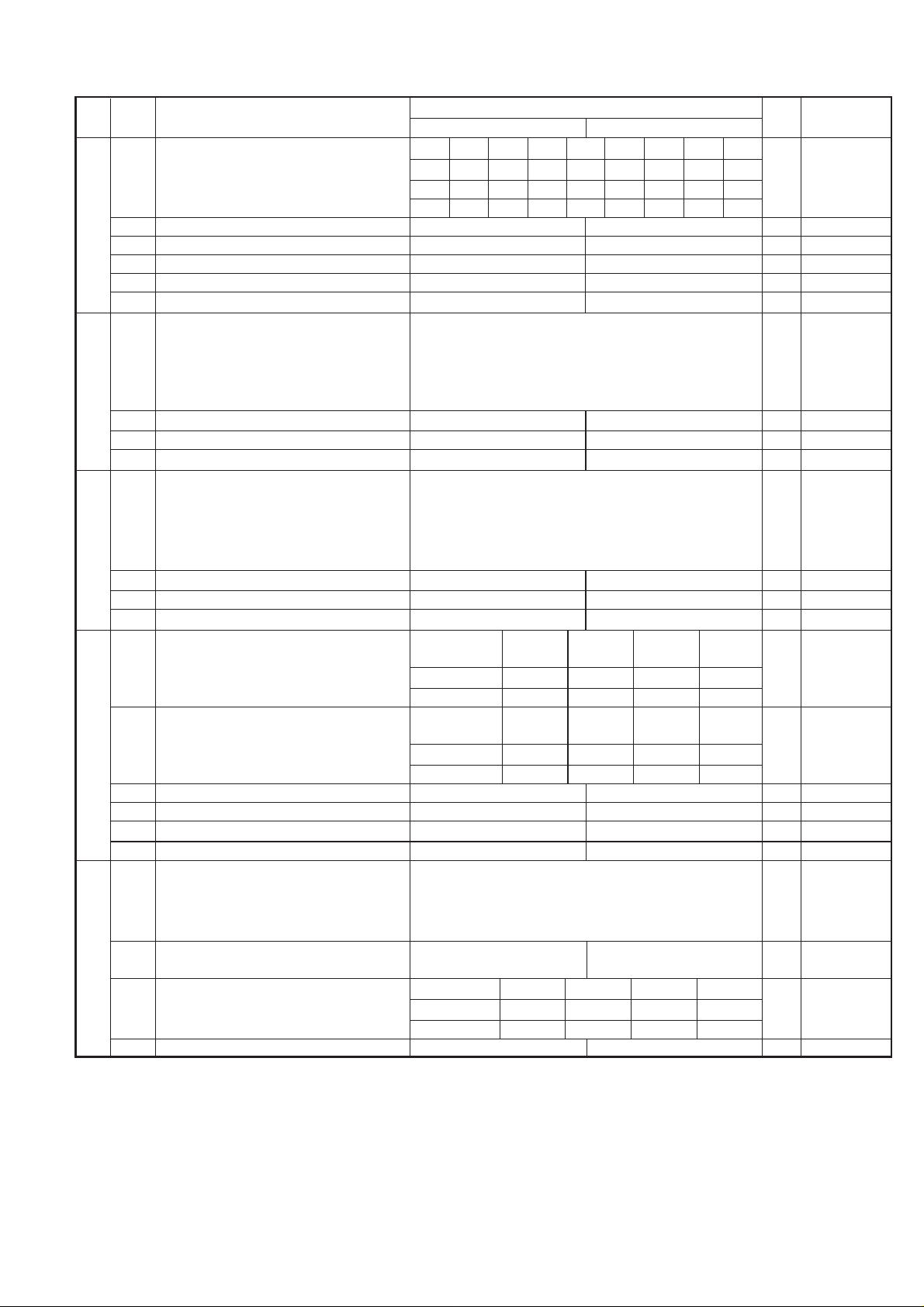
FO-50A
FO-70A
SW
DATA
NO.
NO.
Auto dial mode Delay timer of after line 1.7s 2.0s 2.5s 3.0s 3.6s 4.0s 5.5s 7.0s
1 connect No. 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0
2 No. 2001100111
3 No. 3010101011
SW
4
l
B5
SW
l
B6
SW
l
B7
SW
l
C1
SW
l
D1
Fax signal detection after telephone mode dial
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 DTMF signal transmission level Binary input 1
2 (Low frequency 0~15.5dBm setting No. = 16 8 4 2 1 0
3 by 0.5dBm step) 1 2 3 4 5 0
4 1 0 0 1 1 1
5 1
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 DTMF signal transmission level Binary input 1
2 (High frequency 0~15.5dBm setting No. = 16 8 4 2 1 0
3 by 0.5dBm step) 1 2 3 4 5 0
4 1 0 0 0 0 0
5 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
Reading Slice(Binary) Factory Dark Light Daker in
1No. 100110
2No. 201010
Reading Slice(Half tone) Factory Dark Light Daker in
3No. 300110
4No. 401010
5 Line density selection Fine Standard 0
6 Reserved 0
7 MTF correction in half tone mode No Yes 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Number of rings for auto receive Binary input 0 OPTION
2 (0~15rings setting) No. = 8 4 2 1 0
3 1 2 3 4 1
4 0 0 1 0 0
5 Automatic swiching manual to auto receive Yes No 0
function
CI detect frequency
6No. 600110
7No. 701010
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
Yes No 0
Switch setting and function
1
setting dark
setting dark
As PTT 11.5Hz 13.0Hz 20.0Hz
0
I
nitial
setting
Remarks
2 – 7
Page 20
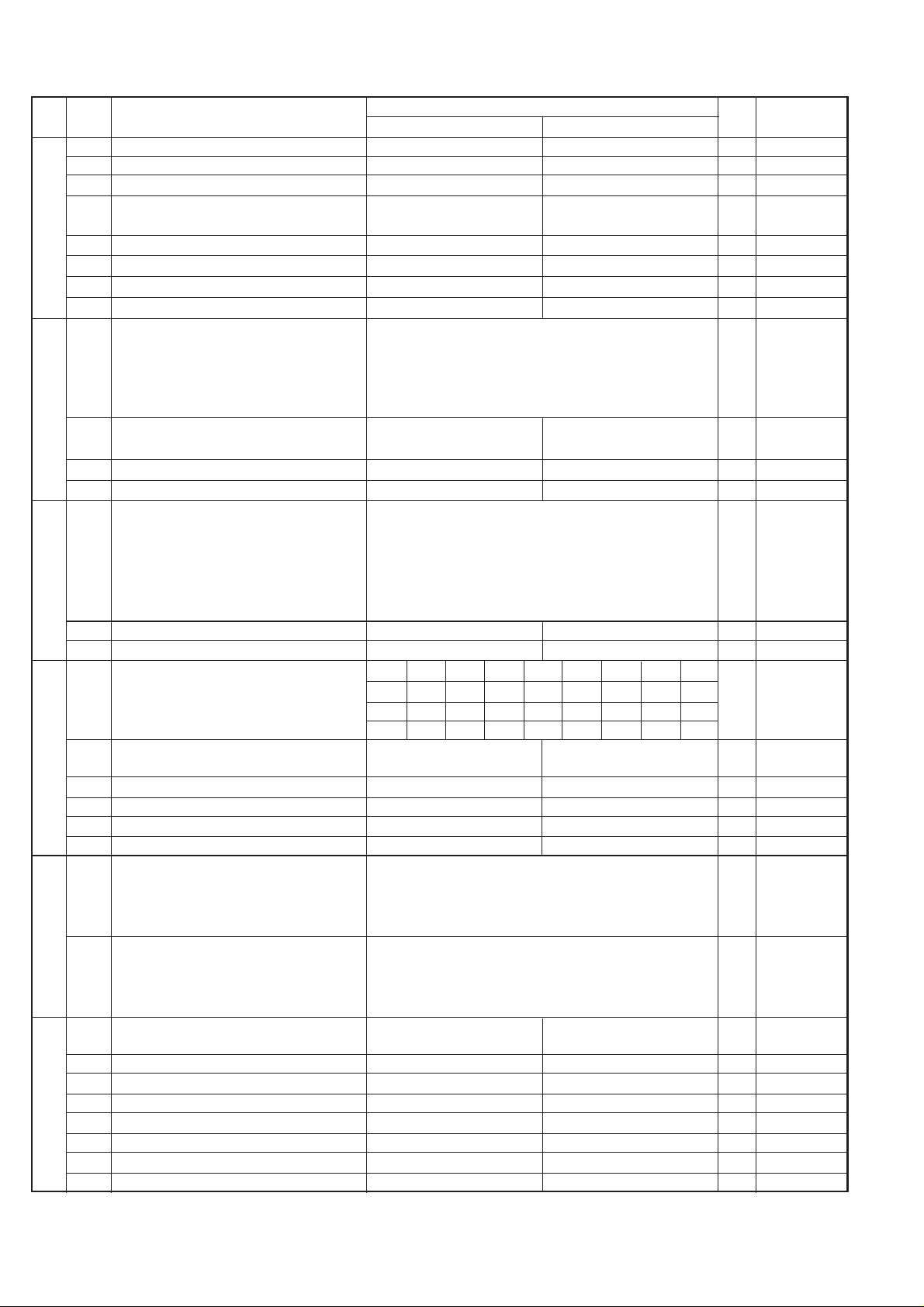
FO-50A
FO-70A
SW
NO.
SW
D2
SW
D3
SW
D4
SW
E1
SW
E2
SW
E3
DA TA
NO.
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Australia/New Zealand distinctive ring Yes No 0 OPTION
l
l
l
l
l
l
detection
5 Reserved 0
6 Caller ID function Yes No 0 OPTION
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 CI off detection timer Binary input 0
2 (0~1550ms setting by 50ms step) No. = 16 8 4 2 1 1
3 1 2 3 4 5 1
4 0 1 1 1 0 1
5 0
6 Caller-ID country select for Australia/ New Zealand Australia 0 OPTION
New Zealand
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 DTMF type Caller ID RX level Binary input 1
2 (0~-44dBm setting by 1dBm step) No. = 32 16 8 4 2 1 0
3 1 2 3 4 5 6 1
4 1 0 1 1 0 0 1
5 0
6 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
Pseudo ringing time at the TEL/FAX
1 automatic switching mode No. 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0
2 No. 2001100111
3 No. 3010101010
4 Number of CNG signal detection at the Twice Once 1
TEL/FAX automatic switching mode
5 CNG detect time at TEL/FAX mode 3 sec 5 sec 0
6 Post answer tone(TEL/FAX mode) No Yes 0
7 Type of post answer tone LA-SI-DO tone 800Hz single tone 1
8 Pseudo ringer ON/OFF cycle 1 sec ON / 4 sec OFF 1 sec ON / 2 sec OFF 0
1 Pseudo ringer sound output level to the line Binary input 1
2 (0~-15dBm setting by 1dBm step) No. = 8 4 2 1 0
3 1 2 3 4 1
4 1 0 1 0 0
5 Post answer tone transmission level Binary input 0
6 (0~-15dBm setting by 1dBm step) No. = 8 4 2 1 1
7 5 6 7 8 1
8 0 1 1 1 1
1
Disconnect the line when DTMF "#" is received
during TEL/FAX automatic switching mode
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
9sec 15sec 30sec 60sec 90sec 120sec 150sec 180sec
Yes No 0
Switch setting and function
1
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 8
Page 21
FO-50A
FO-70A
SW
DATA
NO.
NO.
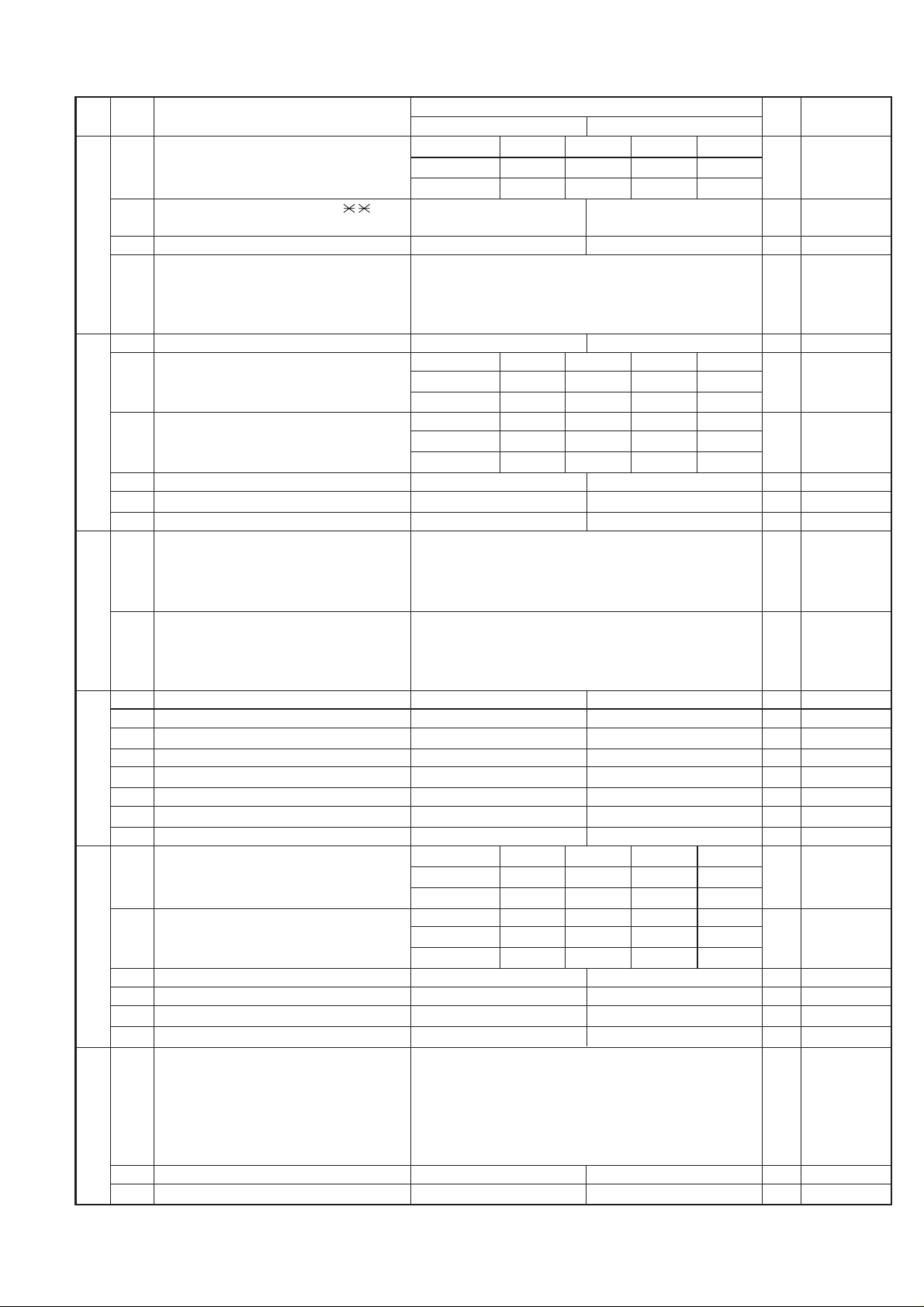
DTMF detection time 50ms 80ms 100ms 120ms
1No. 100110
2No. 201010
3 Protection of remote reception(5 )Yes No 0
SW
l
F1
SW
l
F2
SW
l
G1
SW
l
G2
SW
l
G3
SW
l
G4
detection
4 Remote reception with GE telephone Compatible Not compatible 1
5 Remote operation code figure by external Binary input 0 OPTION
6 TEL (0~9) No. = 8 4 2 1 1
7 5 6 7 8 0
8 0 1 0 1 1
1 CNG detection in STAND-BY mode Yes No 1 OPTION
Number of CNG detect(AM mode) 1 pulse 2 pulses 3 pulses 4 pulses
2No. 200110
3No. 301011
Number of CNG detect(STAND-BY mode) 1 pulse 2 pulses 3 pulses 4 pulses
4No. 400110
5No. 501011
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Quiet detect time Binary input 0 OPTION
2 (0~15sec setting by 1sec step) No. = 8 4 2 1 1
3 1 2 3 4 0
4 0 1 0 0 0
5 Quiet detect start timing Binary input 0 OPTION
6 (0~15sec setting by 1sec step) No. = 8 4 2 1 1
7 5 6 7 8 0
8 0 1 0 1 1
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
OGM detect timer Not work 100ms 200ms 300ms
1No. 100110
2No. 201011
Section time of quiet detection 30s 40s 50s 60s
3No. 300110
4No. 401011
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Quiet detect level setting Binary input 1
2 (0~-44dBm setting by 1dBm step) No. = 32 16 8 4 2 1 0
3 1 2 3 4 5 6 1
4 1 0 1 1 0 0 1
5 0
6 0
7 Fax switching when A.M. full Yes No 0 OPTION
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
Initial
0
setting
Remarks
2 – 9
Page 22
FO-50A
FO-70A
SW
NO.
SW
H1
SW
H2
SW
I1
SW
I2
SW
I3
SW
I4
DA TA
NO.
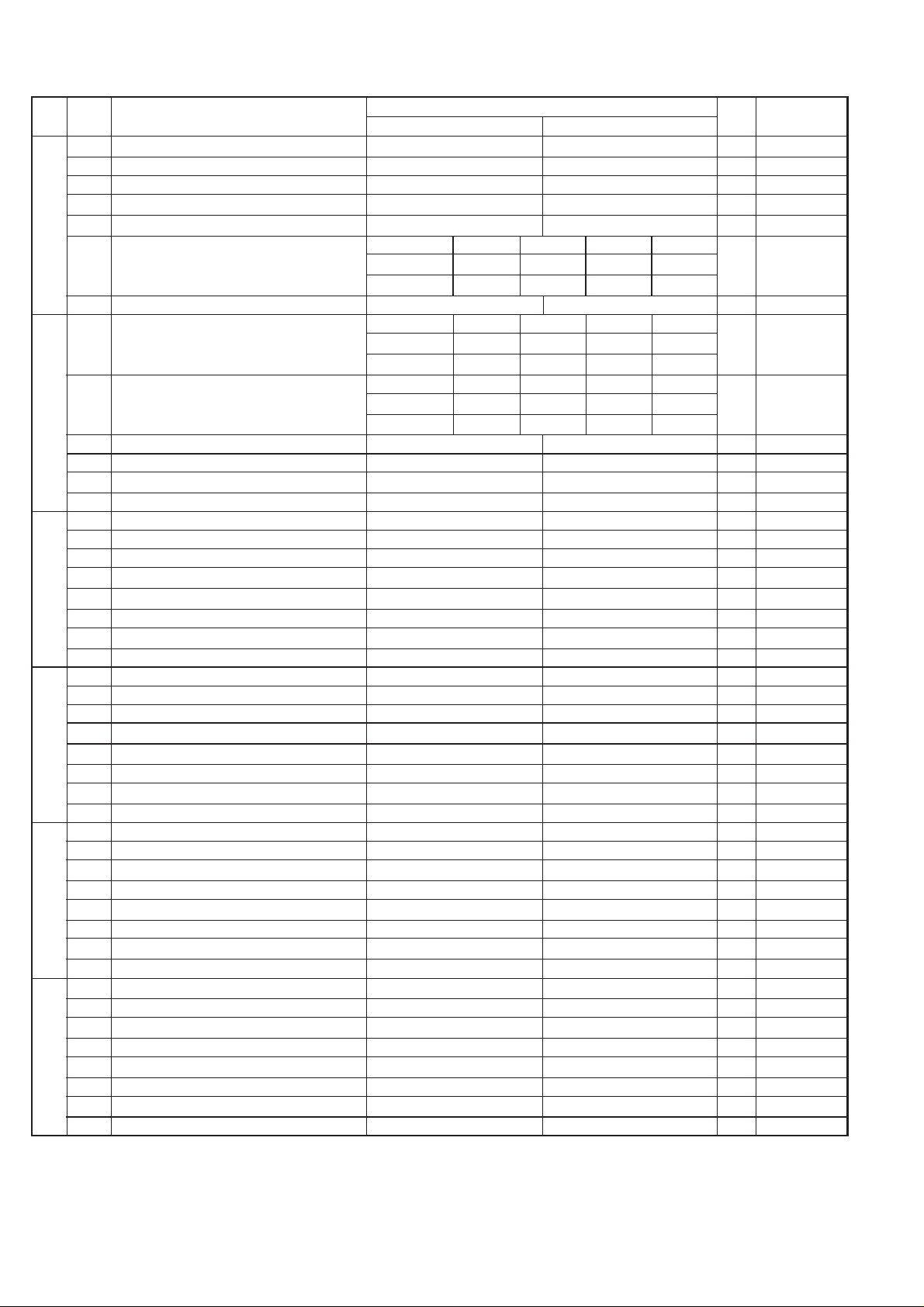
1 Busy tone continuous sound detect time 5 sec 10 sec 1
2 Reserved 0
3 Busy tone detect continuation sound detect No Yes 0
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Busy tone detect intermittent sound detect No Yes 0
Busy tone detection pulse number 2 pulses 4 pulses 6 pulses 10 pulses
6No. 600110
7No. 701011
8 Reserved 0
Busy tone detection ON/OFF time(Lower limit)
1No. 100110
2No. 201010
Busy tone detection ON/OFF time(Upper limit)
3No. 300110
l
4No. 401011
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
150 ms 200 ms 250 ms 350 ms
650 ms 900 ms 1500 ms 2700 ms
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 10
Page 23
FO-50A
FO-70A
SW
DATA
NO.
NO.
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
SW
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Reserved 0
I5
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
SW
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Reserved 0
I6
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
SW
l
5 Reserved 0
I7
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
SW
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Reserved 0
I8
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Sender’s phone number setting Cannot change Change allowed 0
2 Reserved 0
Ringer volume Off Low Middle High OPTION
3No. 300111
SW
4No. 401010
l
J1
SW
l
J2
Speaker volume Low Low Middle High OPTION
5No. 500111
6No. 601010
7 Polling key Yes No 0 OPTION
8 Reserved 0
1 Reserved 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Saving energy start timing 5 sec 180 sec 0
8 Saving energy mode Enable Disable 1
ITEM
Switch setting and function
1
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 11
Page 24
FO-50A
FO-70A
SW
NO.
SW
J3
SW
K1
DA TA
NO.
Communication results printout Error Send only Always No print OPTION
(Transaction report)
1
2No. 200110
3No. 301010
l
4 Time format 12 hour 24 hour 0
5 Date format Month-Day-Year Day-Month-Year 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
1 Entering diag mode by pressing SPEED key Yes No 0
2 Reserved 0
3 Reserved 0
4 Reserved 0
l
5 Reserved 0
6 Reserved 0
7 Reserved 0
8 Reserved 0
ITEM
No. 1 0 0 0 0 0
Switch setting and function
1
0
Initial
setting
Remarks
2 – 12
Page 25
• Soft switch function description
SW-A1 No. 1 Protect from echo
Used to protect from echo in reception.
SW-A1 No. 2 Forced 4800BPS reception
When line conditions warrant that receptions take place at 4800 BPS
repeatedly.
It may improve the success of receptions by setting at 4800BPS.
This improves the receiving document quality and reduces handshake
time due to fallback during training.
SW-A1 No. 3 Footer print
When set to "1", the date of reception, the sender machine No., and the
page No. are automatically recorded at the end of reception.
SW-A1 No. 4 Length limitation of copy/send/receive
Used to set the maximum page length.
To avoid possible paper jam, the page length is normally limited to 0.6
meter for copy or transmit, and 1.5 meters for receive.
It is possible to set it to "No limit" to transmit a long document, such as a
computer print form, etc. (In this case, the receiver must also be set to
no limit.)
SW-A1 No. 5 CSI transmission
(CSI TRANSMISSION) is a s witch to set whether the machine sends or
does not send the signal (CSI signal) informing its own telephone No. to
the remote fax machine when information is received. When "nonsending"
is set, the telephone No. is not output on the remote transmitting machine if the remote transmitting machine has the function to display or
print the telephone No. of receiving machine, using this CSI signal.
SW-A1 No. 6 DIS receive ackno wledgment during G3 transmission
Used to make a choice of whether reception of DIS(NSF) is acknowledged after receiving two DISs(NSFs) or receiving one DIS (two NSFs).
It may be useful for ov erseas comm unication to av oid an echo suppression problem, if set to 1.
SW-A1 No. 7 Non modulated carrier for V29 transmission mode
Though transmission of a nonmodulated carrier is not required for transmission by the V29 modem according to the CCITT Recommendation, it
may be permitted to a send nonmodulated carrier before the image signal to avoid an echo suppression problem.
It may be useful for ov erseas comm unication to av oid an echo suppression problem, if set to 1.
SW-A1 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-A2 No. 1 ~ No. 4 Modem speed
Used to set the initial modem speed. The default is 9600BPS.
It may be necessary to program it to a slower speed when frequent line
fallback is encountered, in order to save the time required for fallback
procedure.
SW-A2 No. 5 Reserved
Set to "0".
FO-50A
FO-70A
SW-A2 No. 6 H2 mode
Used to determine reception of H2 mode (15 sec transmission mode).
When set to OFF, H2 mode reception is inhibited even though the transmitting machine has H2 mode function.
SW-A2 No. 7 Communication err or treatment in RTN sending mode
(Reception)
Used to determine communication error treatment when RTN is sent by
occurrence of a received image error in G3 reception. When it is set to
"1", communication error is judged as no error.
SW-A2 No. 8 CNG transmission
When set to "0", this model allows CNG transmission by pressing the
Start key in the key pad dialing mode. When set to "1", CNG transmission in the key pad dialing mode cannot be perfor med. In either case,
CNG transmission can be performed in the auto dial mode.
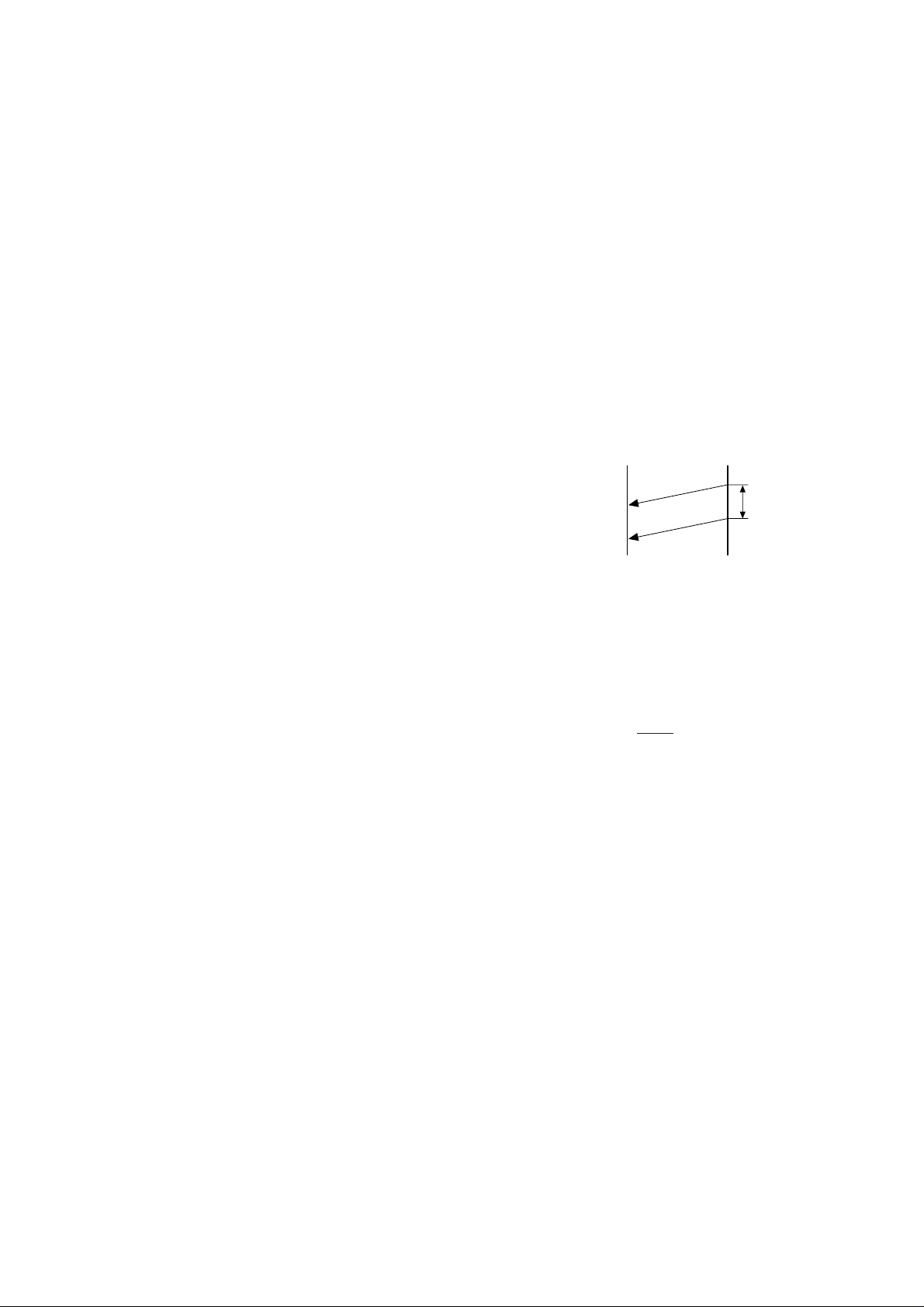
SW-A3 No. 1, No. 2 CED tone signal interval
For international communication, the 2100Hz CED tone may act as an
echo suppression switch, causing a communication problem.
Though SW-A3 No . 1 and No . 2 are normally set to 0, this selfing is used
to change the time between the CED tone signal to eliminate the communication caused by echo.
TX RX
CED
T
DIS
SW-A3 No. 3 MR coding
Used to select the MR coding enable or disable.
SW-A3 No. 4 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-A4 No. 1 ~ No. 5 Signal transmission level
(0~-31 dBm setting by 1dBm step)
Used to control the signal transmission level in the range of -0dB to
-31dB.
The factory setting is at -10dB (MODEM output).
SW-A4 No. 6 Protocol monitor (Error Print)
If set to "1", protocol is printed at communication error.
SW-A4 No. 7 Protocol monitor
Normally set to "0". If set to "1", communication can be chec ked, in case
of trouble, without using a G3 tester or other tools.
When communication FSK data transmission or reception is made, the
data is taken into the buffer . When communication is finished, the data is
analyzed and printed out. When data is received with the line monitor
(SW4-No. 8) set to "1" the reception level is also printed out.
SW-A4 No. 8 Line monitor
Normally set to "0". If set to "1", the transmission speed and the reception level are displayed on the LCD. Used for line tests.
SW-A5 No. 1, No. 2 Digital equalization setting (Reception)
Line equalization when reception is to be set according to the line characteristics.
Setting should be made according to distance between the telephone
and the telephone company central switching station.
SW-A5 No. 3, No. 4 Digital equalization setting (Transmitter)
Line equalization when transmission is to be set according to the line
characteristics.
Setting should be made according to distance between the telephone
and the telephone company central switching station.
2 – 13
Page 26
FO-50A
FO-70A
SW-A5 No. 5, No. 6 Digital equalization setting
(Reception for Caller ID)
Line equalization when reception for CALLER ID is to be set according
to the line characteristics.
Setting should be made according to distance between the telephone
and the telephone company central switching station.
SW-A5 No. 7 Error criterion
Used to select error criterion for sending back RTN when receiving image data.
SW-A5 No. 8 Anti junk fax check
When using the Anti junk fax function, set to "1".
SW-A6 No. 1 Auto gain control(MODEM)
When this mode is enabled, if the reception signal lev el is under 31dBm,
the modem itself controls the signal gain automatically.
SW-A6 No. 2 End buzzer
Setting this bit to 0 will disable the end buzzer (including the error b uzzer/
on-hook buzzer).
SW-A6 No. 3 Disconnect the line when DIS is received in RX mode
Bit1 = 0 : When DIS signal is received during RX mode, disconnect the
line immediately.
Bit1 = 1 : When DIS signal is receiv ed during RX mode, wait f or the ne xt
signal.
SW-A6 No. 4 Equalizer freeze control (MODEM)
This switch is used to perform reception operation by fixing the equalizer control of modem for the line which is always in unfavorable state
and picture cannot be received.
* Usually , the control is e xecuted according to the state of line where the
equalizer setting is changed always.
SW-A6 No.5 Equalizer freeze 7200BPS only
Setting which specifies SW-A6 No . 4 control only in condition of 7200BPS
modem speed.
SW-A6 No. 6 CNG transmission in manual TX mode
When set to "1", fax transmit the CNG signal in case of manual
transmissiom mode (User press the START key after waiting f or the fax
answering signal from handset or speaker).
SW-A6 No. 7 Initial compression scheme for sharp fax in TX mode
When set to "0", if the other fax is Sharp model, fax transmit the document by H2 mode.
When set to "1", even if the other fax is Sharp model, fax transmit the
document by MR mode.
SW-A6 No. 8 Modem speed automatic down when RX level is under
-40dBm
When set to "1", if fax signal level is under -40dBm during reception,
machine selects the slower modem speed automatically.
It is effective when noises occur on the received document due to the
long distance communications.
SW-A7 No. 1, No. 2 EOL (End Of Line) detect timer
Used to make a choice of whether to use the 5 or 13 or 20 or 25 seconds
timer for detection of EOL.
This is effective to override communication failures with some facsimile
models that have longer EOL detection.
SW-A7 No. 3 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-B1 No. 1 Hold key
Used to set YES/NO of holding function by the HOLD key.
SW-B1 No. 2 Auto dial fax transmission by REDIAL key
When set to "1", if original documents are set to the feeder and you
press REDIAL key, machine will dial and transmit the ducuments automatically.
When set to "0", operator needs to press the START key after FAX reception tone is heard.
SW-B1 No. 3 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-B1 No. 4 ~ No. 8 Recall interval
(0~15.5min setting by 0.5min step)
Choice is made for a redial interval for speed and rapid dial calls.
Use a binary number to program this with 0.5min steps. If set to 0 accidentally, 0.5min will be assumed.
SW-B2 No. 1 ~ No.4 Recall times (0~15times setting)
Choice is made as to how many redials there should be.
SW-B2 No. 5 Dial tone detection (Before auto dial)
Used to set YES/NO of dial tone detection in auto dialing.
SW-B2 No. 6 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-B2 No. 7 Busy tone detection (After auto dial)
Used to set YES/NO of busy tone detection after auto dialing.
SW-B2 No. 8 Busy tone detection pulse number (After auto dial)
Used for detection of busy tone in 2 or 4 pulses.
SW-B3 No. 1, No. 2 Waiting time after dialing
This is waiting time for the opponent's signals after dialing.
45 / 55 / 90 / 140 seconds settings are available.
SW-B3 No. 3 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-B4 No. 1 Dialing pause (sec/pause)
Pauses can be inserted between telephone numbers of direct dial connection. Selection of 4 sec or 2 sec pause is available.
SW-B4 No. 2 Dial mode
When using the pulse dial, set to 0. When using the tone dial, set to 1.
SW-B4 No. 3 Pulse → Tone change function by key
When setting to 1, the mode is changed by pressing the key from the
pulse dial mode to the tone dial mode.
SW-B4 No. 4 Dial pulse make/break ratio (%)
When using the 33% make ratio pulse dial, set to 0.
When using the 40% make ratio pulse dial, set to 1.
SW-B4 No. 5, No. 6 Auto dial mode Delay timer of before line connect
Delay time between the dial key input and line connection under the
auto dial mode.
RAPID A CML RELAY ON
DIALLING
No.5=0 No.6=0 : 0sec
No.5=0 No.6=1 : 1.5sec
No.5=1 No.6=0 : 3.0sec
No.5=1 No.6=1 : 4.5sec
SW-B4 No. 7, No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
2 – 14
Page 27
SW-B5 No. 1 ~ No. 3 Auto dial mode Delay timer of after line connect
Delay time between the line connection and dial data output under the
auto dial mode.
This setting is available when dial tone detection(SW -B2 No. 5) is set to
"NO".
RAPID A CML RELAY ON
No. 1 No. 2 No. 3
0 0 0 1.7sec
0 0 1 2.0sec
0 1 0 2.5sec
0 1 1 3.0sec
1 0 0 3.6sec
1 0 1 4.0sec
1 1 0 5.5sec
1 1 1 7.0sec
SW-B5 No. 4 Fax signal detection after telephone mode dial
When set to "1", if machine detects the fax answering signal after telephone calling (handset off-hook or speaker mode dial), machine starts
to receive the documents automatically.
SW-B5 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-B6 No. 1 ~ No. 5 DTMF signal transmission level
(Low frequency 0~15.5dBm setting by 0.5dBm step)
The transmission level of DTMF signal is adjusted. (lower frequency)
00000: 0dBm
↓
11111: -15.5 dBm (-0.5dBm x 31)
SW-B6 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-B7 No. 1 ~ No. 5 DTMF signal transmission level
(High frequency 0~15.5dBm setting by 0.5dBm step)
The transmission level of DTMF signal is adjusted. (higher frequency)
00000: 0dBm
↓
11111: -15.5 dBm (-0.5dBm x 31)
SW-B7 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-C1 No. 1, No. 2 Reading slice (Binary)
Used to determine the set value of reading density in standard/fine/super-fine mode.
The standard setting is "00"(Factory setting is "00").
SW-C1 No. 3, No. 4 Reading slice (Half tone)
Used to determine the set value of reading density in half tone mode.
The standard setting is "00"(Factory setting is "00").
DIAL DATA
FO-50A
FO-70A
SW-C1 No. 5 Line density selection
Used to set the transmission mode which is automatically selected when
the Resolution key is not pressed. In the copy mode, however, the fine
mode is automatically selected unless the Resolution key is manually
set to another mode.
SW-C1 No. 6 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-C1 No. 7 MTF correction in half tone mode
This allows selection of MTF correction (dimness correction) in the half
tone mode.
When "NO" (=1) is selected, the whole image becomes soft and mild.
Clearness of characters will be reduced. Normally set to "YES" (=0).
SW-C1 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-D1 No.1 ~ No. 4 Number of rings for auto receive
(0~15rings setting)
When the machine is set in the auto receive mode, the number of rings
before answering can be selected. It may be set from one to nine rings
using a binary number. Since the facsimile telephone could be used as
an ordinary telephone if the handset is taken off the hook, it should be
programmed to the user's choice. If the soft switch was set to 1, direct
connection is made to the facsimile.
If a facsimile calling beep was heard when the handset is taken off the
hook, press the START key and put the handset on the hook to hav e the
facsimile start receiving. If it w as set to 0 accidentally, receive ring is set
to 1.
NOTE: If the machine is set to answer after a large number of rings, it
may not be able to receive faxes successfully.
If you have difficulty receiving f ax es, reduce the number of rings
to a maximum of 5.
SW-D1 No. 5 Automatic switching manual to auto receive function
This soft switch is used to select whether the machine should switch to
the auto receive mode after 5 rings in the manual receive mode or remain in the same way as SW -D1 No. 1, No . 2, No . 3 and No. 4 "0"1"0"1"(5
rings).
SW-D1 No. 6, No. 7 CI detect frequency
Detection frequency of ring signal for auto reception is set.
When set to No. 6=0, No. 7=0,frequency is set to PTT recommendation.
When set to No. 6=0, No. 7=1, frequency is set to 11.5Hz or more.
When set to No. 6=1, No. 7=0, frequency is set to 13.0Hz or more.
When set to No. 6=1, No. 7=1, frequency is set to 20.0Hz or more.
SW-D1 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-D2 No. 1 ~ No. 3 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-D2 No. 4 Australia/New Zealand distinctive ring detection
When set to "1", machine recognize the CI signal FAX ringing or TEL
ringing automatically .
SW-D2 No. 5 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-D2 No. 6 Caller ID Function
Used for Caller ID function.
SW-D2 No. 7, No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
2 – 15
Page 28
FO-50A
FO-70A
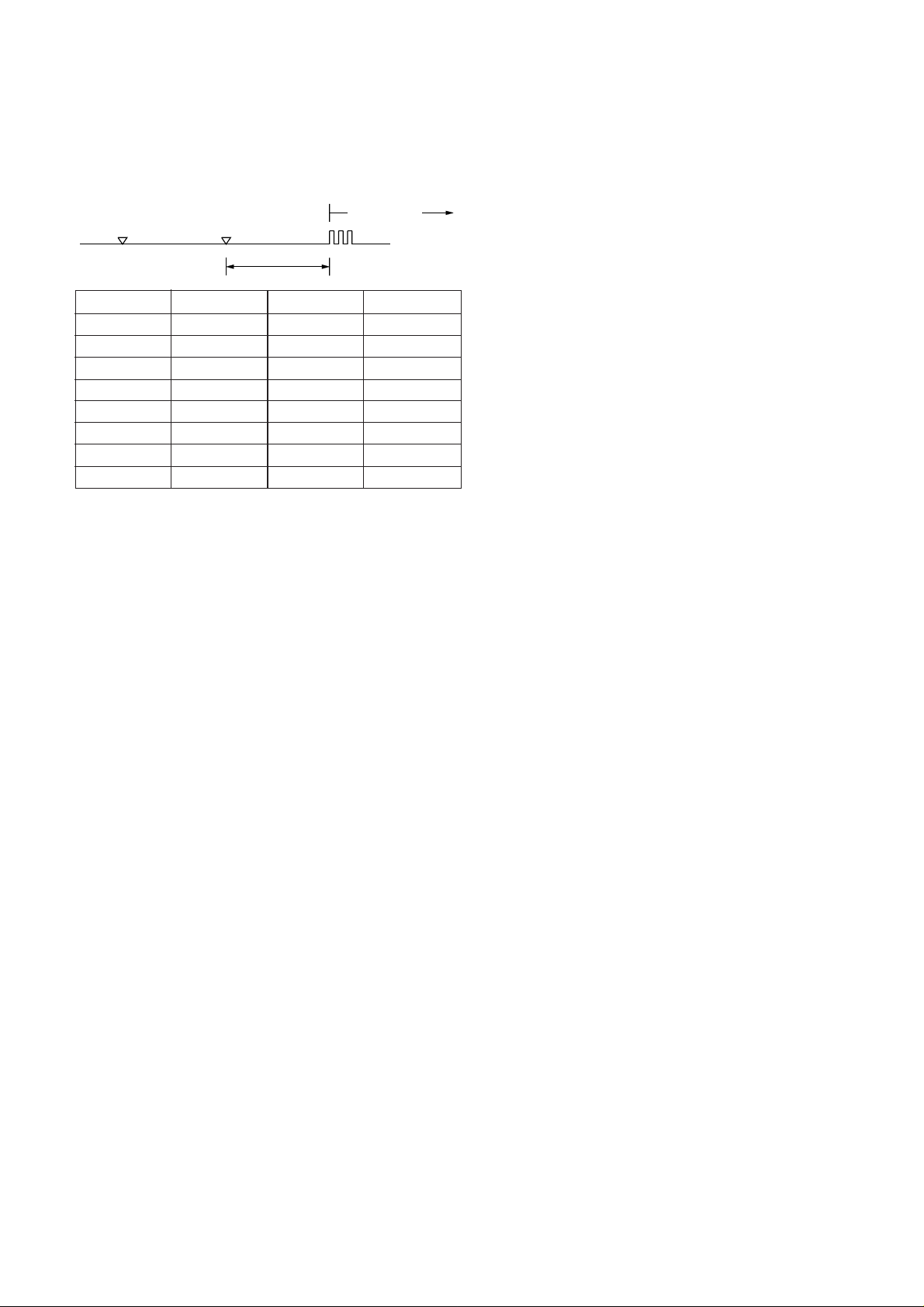
SW-D3 No. 1 ~ No. 5 CI off detection timer
(0~1550ms setting by 50ms step)
Set the minimum time period of CI signal interruption which affords to be
judged as a CI OFF section with 50ms steps.
(Example)
AB
400msec
1
0 1 1 1 0 (50ms~14) : 700ms(CI interruption>700ms:Judged as a CI
OFF section)
The section 1 is not judged as a CI OFF section, the CI signal A is counted as one signal.
The section 2 is judged as a CI OFF section,
the CI signal B is considered as the second signal.
0 0 1 1 1 (50ms~7) : 350ms(CI interruption>350ms:J udged as a CI
OFF section)
The section 1 is judged as a CI OFF section,
and the CI signal A is counted as two signals.
The section 2 is judged as a CI OFF section,
and the CI signal B is considered as the third
signal.
SW-D3 No. 6 Caller-ID country select for Australia/New Zealand
This is used for selecting whether Australia or New Zealand Caller-ID
system.
SW-D3 No. 7, No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-D4 No. 1 ~ No. 6 DTMF type Caller ID RX level
(0~-44dBm setting by 1dBm step)
This is used for DTMF type Caller ID detection level setting.
SW-D4 No. 7, No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-E1 No. 1 ~ No. 3 Pseudo ringing time at the TEL/FAX automatic
switching mode
Choice is made as to how long to rumble the dummy ringer on TEL/FAX
automatic switching mode.
SW-E1 No. 4 Number of CNG signal detection at the TEL/FAX automatic switching mode
Used for detection of CNG in one tone or two tones in the TEL/FAX
automatic switching mode.
SW-E1 No. 5 CNG detect time at TEL/FAX mode
The switch which sets the time from the start of CNG detection to the
end of detection.
SW-E1 No. 6 Post answer tone (TEL/FAX mode)
When set to "0", machine send the tones in TEL/FAX auto changeover
mode.
SW-E1 No. 7 Type of post answer tone
When set to "0", post answer tone is 800Hz single tone.
When set to "1", post answer tone is 880Hz/988Hz/1046Hz(LA-SI-DO)
tone.
SW-E1 No. 8 Pseudo ringer ON/OFF cycle
When set to "0", pseudo ringer is 1 sec ON and 2 sec OFF cycles.
When set to "1", pseudo ringer is 1 sec ON and 4 sec OFF cycles.
SW-E2 No. 1 ~ No. 4 Pseudo ringer sound output level to the line
(0~-15dBm setting by 1dBm step)
Used to adjust the sound volume of pseudo ringer to the line (ring back
tone) generated on selecting TEL/FAX.
2000msec
2
SW-E2 No. 5 ~ No. 6 Post answer tone transmission level
(0~-15dBm setting by 1dBm step)
Used to adjust the sound volume of post answer tone to the line generated on selecting TEL/FAX.
SW-E3 No. 1 Disconnect the line when DTMF "#" is received during
TEL/FAX automatic switching mode
When set to "1", if machine detects the DTMF code # during phone/fax
automatic switching mode, stop the pseudo ringer and disconnect the
line.
This effect when operator want to stop the pseudo ringer from e xtension
phone connected with parallel.
SW-E3 No. 2 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-F1 No. 1, No. 2 DTMF detection time
Used to set detect time of DTMF (Dual Tone Multi Frequency) used in
remote reception(5 ).
The longer the detect time is, the less the error detection is caused by
noises.
SW-F1 No. 3 Protection of remote reception (5 ) detection
Used to set the function of remote reception (5 ). When set to "1",
the remote reception function is disabled.
SW-F1 No. 4 Remote reception with GE telephone
"1": Compatible with TEL mode by GE
"0": Not compatible
• When sending (5 ) for remote reception with a GE manufactured
telephone remote reception may not take place because of special
specifications in their DTMF.
To overcome this, a soft SW is provided to change the modem setting
to allow for remote reception.
• If this soft SW is set to "1", other telephone sets may be adversely
affected.
SW-F1 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Remote operation code figure by external TEL
(0~9)
Remote operation codes can be changed from 0 through 9. If set to
greater than 9, it defaults to 9. The "5 " is not changed.
Ex- 7 (Default : 5 )
SW-F2 No. 1 CNG detection in STAND-BY mode
When setting to "1", the CNG signal detection function during standby
stops.
SW-F2 No. 2, No. 3 Number of CNG detect (AM mode)
Used for detection of CNG in 1 to 4 pulses.
SW-F2 No. 4, No. 5 Number of CNG detect (STAND-BY mode)
Used for detection of CNG in 1 to 4 pulses.
SW-F2 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0"
SW-G1 No. 1 ~ No. 4 Quiet detect time
(0~15sec setting by 1sec step)
When an answering machine is connected, if a no sound state is detected for a certain period of time, the machine judges it as a transmission from a facsimile machine and automatically switches to the FAX
mode.
SW-G1 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Quiet detect start timing
(0~15sec setting by 1sec step)
Inserts a pause before commencing quiet detection.
SW-G2 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0"
SW-G3 No. 1, No. 2 OGM detect timer
This is used to change the OGM detection time for answering machine
hook up detection.
2 – 16
Page 29

SW-G3 No. 3, No. 4 Section time of quiet detection
The switch which sets the time from the start of detection function to the
end of the function.
SW-G3 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0"
SW-G4 No. 1 ~ No. 6 Quiet detect level setting
(0~-44dBm setting by 1dBm step)
This is used to change the quiet detect level setting.
If quiet detection is difficult due to noise, reduce this setting level.
(Example)
Factory setting : 1 0 1 1 0 0 (- 44dBm)
↓
1 0 1 0 0 0 (- 40dBm)
SW-G4 No. 7 Fax switching when A.M. full
If the answering machine’s memory (tape) is full and there is no response,
the machine automatically switches to Fax reception.
SW-G4 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-H1 No. 1 Busy tone continuous sound detect time
Set detecting time busy tone continuous sound for 5 seconds or 10 seconds.
SW-H1 No. 2 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-H1 No. 3 Busy tone detect continuation sound detect
Used to select detection of the continuous sound of certain frequency.
SW-H1 No. 4 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-H1 No. 5 Busy tone detect intermittent sound detect
Used to select detection of the intermittent sound of certain frequency.
SW-H1 No. 6, No. 7 Busy tone detection pulse number
Used to set detection of Busy tone intermittent sounds.
SW-H1 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-H2 No. 1, No. 2 Busy tone detection ON/OFF time (Lower limit)
The initial value of detection is set according to electric condition.
The set value is changed according to the local switch board. (Errone-
ous detection of sound is reduced.)
If erroneous detection is caused by sound, etc., adjust the detection
range.
The lower limit can be set in the range of 150msec to 350msec.
SW-H2 No. 3, No. 4 Busy tone detection ON/OFF time (Upper limit)
Similarly to SW-H2 No. 1, No. 2, the set value can be varied.
The upper limit can be set in the range of 650msec to 2700msec.
SW-H2 No. 5 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-I1 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-I2 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-I3 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-I4 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-I5 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
FO-50A
FO-70A
SW-I6 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-I7 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-I8 No. 1 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-J1 No. 1 Sender's phone number setting
Used to make a choice of whether the registered sender's phone number
can be changed or not. If the switch is set to "1", new registration of the
sender's phone number is disabled to prevent accidental wrong input.
SW-J1 No. 2 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-J1 No. 3, No. 4 Ringer Volume
Used to adjust ringing volume.
SW-J1 No. 5, No. 6 Speaker Volume
Used to adjust sound volume from a speaker.
SW-J1 No. 7 Polling key
If this switch is set to 1, the last of Rapid key works as polling key.
SW-J1 No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-J2 No. 1 ~ No. 6 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-J2 No. 7 Saving energy start timing
Used to set the time between the machine’s stand-by state (clock indication) after operation and saving energy mode.
It is possible to set the time to either 5 sec or 180 sec (default).
SW-J2 No. 8 Saving energy mode
Used to select whether to make the saving energy mode valid or not.
SW-J3 No. 1 ~ No. 3 Communication results printout
(Transaction report)
It is possible to obtain transaction results after each communication.
Normally,the switch is set (No. 1 : 0, No. 2 : 0, No. 3 : 0) so that the
transaction report is produced only when a communication error is encountered.
If No.1 was set to 0 and No. 2 to 1 and No. 3 to 0, the transaction report
will be produced every time a communicaion is done, even if the
communicaion was successful.
Setting No. 1 to 0 and No . 2 to 1 and No. 3 to 1 will disable this function.
No transaction report printed.
SW-J3 No. 4 Time format
When set to "0", 24hour time format is used.
When set to "1", 12hour time format is used.
SW-J3 No. 5 Date format
When set to "0", Day-Month-Year format is used.
When set to "1", Month-Day-Year format is used.
SW-J3 No. 6 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
SW-K1 No. 1 Entering diag mode by pressing SPEED key
A bit which is used in the production process only . When the SPEED ke y
is pressed, the switch is changed from the stand-by state to the diag
mode.
SW-K1 No. 2 ~ No. 8 Reserved
Set to "0".
2 – 17
Page 30
FO-50A
y
FO-70A
[3] T roubleshooting
Refer to the follo wing actions to troub leshoot any of the problems mentioned in 1-4.
[1] A communication error occurs.
[2] Image distortion produced.
[3] Unable to do overseas communication.
[4] Communication speed slow due to FALLBACK.
• Increase the transmission level SOFT SWITCH A4-1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
May be used in case [1] [2] [3].
• Decrease the transmission level SOFT SWITCH A4-1, 2, 3, 4,
5. May be used in case [3].
TO: ATT: Ref.No.:
CC: ATT: Date :
FM: Dept :
***** Facsimile communication problem *****
From: Mr . Fax Tel No.:
Our customer Name Tel No.
Address Fax No.
Contact person Model name
Other party Name Tel No.
Address Fax No.
Contact person Model name
Problem mode Line: Domestic / international Model: G3 Phase: A, B, C, D.
Reception / Transmission
Frequency: % ROM version:
Confirmation
item
Our customer
Automatic reception / Manual reception
Automatic dialing / Manual dialing / Others
B1
B2
• Apply line equalization SOFT SWITCH A5-1, 2.
May be used in case [1] [2] [3] [4].
• Slow down the transmission speed SOFT SWITCH A2-1, 2, 3,
4. May be used in case [2] [3].
• Replace the TEL/LIU PWB.
May be used in all cases.
• Replace the control PWB.
May be used in all cases.
* If transmission problems still exist on the machine, use the following
format and check the related matters.
Sign :
Other party
Please mark problem with an X.
No problem is: 0.
A1 A2 B1 B2 C1 C2 D1 D2 E1 E2
Ref.No.:
Date:
A1 A2
C1 D2
C2 D1
E1
E2
Our service
Comment
Countermeasure
**** Please attach the G3 data and activity report on problem. ****
* Please complete this report before calling the “TAC” hotline if problem still occurs.
Other part
's service
Transmission level setting is ( ) dB at our
customer
Transmission level ( ) dBm
Reception level ( ) dBm
By level meter at B1 and B2
2 – 18
Page 31

[4] Error code table
1. Communication error code table
G3 Transmission
Code Final received signal Error Condition (Receiver side)
0 Incomplete signal frame Cannot recognize bit stream after flag
1 NSF, DIS Cannot recognize DCS signal by echo etc.
Cannot recognize NSS signal (FIF code etc)
2 CFR Disconnects line during reception (carrier missing etc)
3 FTT Disconnects line by fall back
4 MCF Disconnects line during reception of multi page
Cannot recognize NSS, DCS signal in the case of mode change
5 PIP or PIN The line is hung up without replying to telephone request from the receiving party.
6 RTN or RTP Cannot recognize NSS, DCS signal after transmit RTN or RTP signal.
7 No signal or DCN No response in receiver side or DCN signal received* (transmitter side)
8 − Owing to error in some page the error could not be corrected although the specified number of
error retransmissions were attempted.
11 − Error occurred after or while reception by the remote (receiving) machine was revealed to be
impossible.
12 − Error occurred just after fallback.
13 − Error occurred after a response to retransmission end command was received.
FO-50A
FO-70A
G3 Reception
Code Final received signal Error Condition (Receiver side)
0 Incomplete signal frame Cannot recognize bit stream after flag
1 NSS, DCS Cannot recognize CFR or FTT signal
Disconnects line during transmission (line error)
2 NSC, DTC Cannot recognize NSS signal (FIF code etc)
3 EOP Cannot recognize MCF, PIP, PIN, RTN, RTP signal
4 EOM Cannot recognize MCF, PIP, PIN, RTN, RTP signal in the case of mode change
5 MPS The line is hung up without replying to communication request.
6 PR1-Q Cannot recognize PIP, PIN signal in the case of TALK request
7 No signal or DCN No response in transmitter (cannot recognize DIS signal) or DCN signal received* (receiver side)
8 − Error occurred upon completion of reception of all pages.
9 − Error occurred when mode was changed or Transmission/Reception switching was performed.
10 − Error occurred during partial page or physical page reception.
11 − Error occurred after or during inquiry from the remote (transmitting) machine as to whether
reception is possible or not.
12 − Error occurred during or just after fallback.
13 − Error occurred after the retransmission end command was received.
2 – 19
Page 32

FO-50A
FO-70A
CHAPTER 3. MECHANISM BLOCKS
[1] General description
1. Document feed block and diagram
3-2. Automatic document feed
1) Use of the paper feed roller and separation rubber plate ensures error-free transport and separation of documents. The plate spring
presses the document to the paper feed roller to assure smooth feeding of the document.
2) Document separation method: Separation rubber plate
Separator rubber
Separator plate
Document sensor
Back roller
Operation panel PWB
CIS unit
Fig. 1
Hopper guide
Document
Front sensor
Paper feed roller
2. Document feed operation
1) The original, which is set in the document hopper, feeds automatically when the front sensor is activated. This in turn activates the
pulse motor which drives the document supply roller. The document
stops when the lead edge is detected by the document sensor.
2) The lead edge of the original is fed a specified number of pulses after
the lead edge of the document is detected for the reading process to
begin.
3) The trailing edge of the original is fed a specific number of pulses
after the trailing edge of the document deactivates the document
sensor. The read process then stops and the original is discharged.
4) When the front sensor is in the OFF state (any document is not set
up in the hopper guide), the drive will be stopped when the document is discharged.
Separation rubber
Feed plate
Document
Paper feed roller
Fig. 3
3-3. Documents applicable for automatic feed
4x6 series
(788mm x 1091mm x
1000mm sheets)
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
Feeder capacity 10 sheets, max.
Paper weight 45kg 69.2kg 52g/m
Paper thickness (ref.)
Paper size 148mm x 140mm ~
NOTE: Double-side coated documents and documents on facsimile re-
cording paper should be inserted manually. The document feed
quantity may be changed according to the document thickness.
Documents corresponding to a paper weight heavier than 69.2kg (80g/
m2 ) and lighter than 135kg (157g/m2 ) are acceptable for manual feed.
Documents heavier than 135kg in terms of the paper weight must be
duplicated on a copier to make it operative in the facsimile.
0.06mm 0.09mm 0.06mm 0.09mm
A4 (210mm x 297mm), Letter (216mm x 279mm)
Square
meter series
2
80g/m
2
3. Hopper mechanism
3-1. General view
Fig. 2
The hopper section contains document guides that are used to adjust
the hopper to the width of the original document. This ensures that the
original feeds straight into the fax machine for scanning.
Document width: 148 mm to 216 mm (A5 longitudinal size to Letter
longitudinal size)
NOTE: Adjust the document guide after setting up the document.
3-4. Loading the documents
1) Make sure that the documents are of suitable size and thickness, and
free from creases, folds, curls, wet glue, wet ink, clips, staples and
pins.
2) Place documents face down in the hopper.
i) Adjust the document guides to the document size.
ii) Align the top edge of documents and gently place them into the
hopper. The first page under the stac k will be taken up b y the feed
roller to get ready for transmission.
NOTES: 1) Curled edge of documents, if any, must be straightened
out.
2) Do not load the documents of different sizes and/or
thicknesses together.
3 – 1
Page 33

Separation rubber
Recording paper
Scanner frame
Platen roller
Cutter guide
Pinch roller
PO roller
Cutter unit
Thermal head
Head guide
Paper guide
Recording paper
Scanner frame
Platen roller
PO guide
Thermal head
Head guide
Paper guide
(CUTTER MODEL)
(NON CUTTER MODEL)
Last page of document
Back of document
First page of document
Feed plate
Paper feed roller
Fig. 4
3-5. Documents requiring use of document carrier
1) Documents smaller than 148mm x 140mm.
2) Documents thinner than the thickness of 0.06mm.
3) Documents containing creases, folds, or curls, especially those whose
surface is curled (maximum allowable curl is 5mm).
4) Documents containing tears.
5) Carbon-backed documents. (Insert a white sheet of paper between
the carbon back and the document carrier to avoid transfer of carbon
to the carrier.)
6) Documents containing an easily separable writing material (e.g., those
written with a lead pencil).
7) Transparent documents.
8) Folded or glued documents.
Document in document carrier should be inserted manually into the
feeder.
FO-50A
FO-70A
5. Recording block
5-1. General view
Fig. 6
4. Document release
4-1. General
To correct a jammed document or to clean the document running surface, pull the insertion side of document center of the operation panel.
T o open the upper document guide, the operation panel m ust be opened
first.
4-2. Cross section view
Operation panel unit
CIS release lever
Lower cabinet
Scanner frame unit
Fig. 5
PWB case unit
5-2. Driving
Via the pulse motor gear shaft, the reduction gear, and the recording
paper feed gear, rotation of the pulse motor is con ve yed to the recording
paper feed roller to feed the recording paper.
5-3. Recording
Use of a thermal head permits easier maintenance and low operating
costs.
1) Thermal head
The thermal head consists of 1728-dot heat elements arranged in a single row and has the resolution of 8 dots/mm. The maximum recording
speed is 10ms/line. The thermal head also incorporates a 1728-dot shift
register latch and output control driver circuit. Low po wer consumption is
achieved by dividing the head into nine segments.
2) Structure of the recording mechanism
Recording is accomplished by pressing the thermal head on the recording paper against the platen roller.
The main scan (horizontal) is electronically achieved, while the subscan
(vertical) is achieved by moving the recording paper by the recording
platen roller.
Usually, the cause for uneven print tone is caused by misalignment of
the thermal head or uneven contact with the roller.
It can by checked in the following manner.
1) Check if the thermal head power and signal cables are properly routed.
2) Check that the thermal head pivot moves smoothly up and down.
3) Check that the thermal head support bracket is secured without any
play.
4) Check to see that the recording platen roller has proper concentricity,
in the case of a print tone variation evenly repeated down the page.
5) Replace the thermal head with a new one and check to see if the
same trouble occurs.
3 – 2
Page 34

FO-50A
FO-70A
[2] Disassembly and assembly procedures
• This chapter mainly describes the disassembly procedures. For the assembly procedures, reverse the disassembly procedures.
• Easy and simple disassembly/assembly procedures of some parts and units are omitted. For disassembly and assembly of such parts and units,
refer to the Parts List.
• The numbers in the illustration, the parts list and the flowchart in a same section are common to each other.
• To assure reliability of the product, the disassembly and the assembly procedures should be performed carefully and deliberately.
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
Paper support guide, handset cover
and scanner unit
12
12
10
7
12
8
9
10
11
3
10
Parts list (Fig. 1)
No. Part name Q’ty No. Part name Q’ty
1 Mechanism unit 1
2 Screw (3×12) 2
3 Paper support guide 1
4 Paper sensor lever 1
5
Paper sensor lever spring
6 Panel stopper 1
2
Hook
4
2
7 Screw (3×8) 1
8 Handset cover 1
9 Hook switch lever 1
10 Screw (3×12) 2
1
11 Connector 2
12 Scanner unit 1
Fix position of spring
4
12
8
Hook
Hook
Hook
5
9
7
11
Hook
Control
PWB
Hook
1
5
6
Fig. 1
3 – 3
Page 35

FO-50A
2
3
4
5
1
7
8
9
6
12
13
13
14
14
13
14
15
15
17
15
11
17
17
18
19
10
20
16
Hook
Hook
2
3
4
5
1
7
8
9
6
12
13
11
15
10
14
17
16
20
19
18
OK
NG
Fix position
Fix position of CSI spring
,,
20
FO-70A
2
CIS unit and scanner frame
Parts list (Fig. 2)
No. Part name Q’ty No. Part name Q’ty
1 Document guide lower 1
2 Back roller gear 1
3 Back roller bearing, left 1
4 CIS release lever , left 1
5 Back roller 1
6 CIS release lever, right 1
7
Back roller bearing, right
8 Reduction gear, 17/28z 1
9 Reduction gear, 17/23z 1
10 Feed roller shaft 1
11 Feed roller 1
12 Connector 1
13 CIS support, left 1
14 CIS support, right 1
15 CIS unit 1
16 CIS protect sheet 1
17 CIS spring 2
1
18 Connector 1
19 Front sensor 1
20 Scanner frame 1
Fig. 2
3 – 4
Page 36

FO-50A
FO-70A
3
Operation panel unit, drive unit, hopper
guide
1
2
4
3
5
10
6
7
11
8
13
14
15
16
17
12
18
Parts list (Fig. 3)
No. Part name Q’ty No. Part name Q’ty
1 Mechanism unit 1
2 Connector 2
3 Operation panel unit 1
4 Connector (FO-70) 3
4 Connector (FO-50) 2
5 Screw (3×8) 1
(FO-70 only)
6 Cutter cam spring 1
(FO-70 only)
7 Screw (3×12) 1
8 Drive unit 1
9 Cutter arm (FO-70 only) 1
10 Screw (3×8) 2
11 Hopper guide unit 1
12
Operation panel unit/
document guide upper unit
13 Screw 1
14 Pinion gear 1
15 Hopper spring 1
16 Hopper guide, left 1
17 Hopper guide, right 1
18 Hopper guide 1
1
9
FO-50
2
4
3
FO-70
2
3
4
7
Control
Control
PWB
PWB
2
8
5
6
7
Control
PWB
2
8
9
UP
1
1
10
12
11
13
18
14
15
16
Fix position
30°
15
boss
Confirm of HOPPER GUIDE position.
HOPPER
GUIDE(R)
17
GAP 0
Rib
R
Rib
GAP 0
L
HOPPER
GUIDE(L)
Fig. 3
3 – 5
Page 37

FO-50A
FO-70A
4
Upper cabinet and document guide
upper
Parts list (Fig. 4)
No. Part name Q’ty No. Part name Q’ty
1 Screw (3×8) 2
2 Connector 1
3 Door sensor 1
4 Blind sheet 1
5
Document guide upper unit
6 Operation panel unit 1
7 Separate spring 1
8 Separator plate 1
9 Separator rubber 1
10 Feed spring 1
11 Feed plate 1
12 Document guide upper 1
13 Screw (2×6) 3
1
14 Connector 1
15
Operation panel PWB unit
16 Direct key 1
17 Start key 1
18 12 key 1
19 Upper cabinet 1
1
1
2
3
1
5
4
4
Fix position
11
7
12
8
10
7
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
16
17
18
2
9
3
12
6
LCD CABLE
19
14
15
LCD PWB
LCD PWB
Rib
Rib
Note) The LCD PWB should
be securely locked by the
click of the panel case.
15
Fig. 4
3 – 6
13
Page 38

FO-50A
FO-70A
5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Drive unit frame (Cutter model)
11
12
15
16
13 14
17 18
29
30
31
29
19
22
21
20
28
23 24 25
26
27
28
2
Parts list (Fig. 5)
No. Part name Q’ty No. Part name Q’ty No. Part name Q’ty
1 Cutter switch 1
2 Cutter gear 1
3 Cutter gear spring 1
4 Cutter plate 1
5 Cam spring 1
6 Cam switch 1
7 Cam gear 1
8 Reduction gear, 17/30Z 1
9 Idler gear, 30Z 1
10 Idler gear, 25Z 1
11 Idler gear, 25Z 1
12 Planet lever C 1
13 Planet gear 1
14 Planet gear spring 1
15 Reduction gear, 17/36Z 1
16 Mode lever 1
17 Planet gear 1
18 Planet gear spring 1
19 Reduction gear, 17/30Z 1
20 Planet lever A 1
21 Planet gear 1
22 Planet gear spring 1
23 Planet lever B 1
24 Planet gear 1
25 Planet gear spring 1
26 Reduction gear, 17/43Z 1
27 Idler gear, 25Z 1
28 Screw (3×8) 1
29 Motor 1
30 Motor plate 1
31 Drive unit frame 1
30
5
OK NG
12
, ,
20
, ,
Grease
13
21
18
17
/
14
16
, ,
/
22
Grease
Nail be doing lock.
12
, ,
20
, ,
21
13
23
24
, ,
14
22
25
/
/
16
23
, ,
, ,
10
17
24
18
25
27
26
24
6
OK NG
21
23
22
25
20
3
1
31
15
19
8
13
4
9
17
18
7
16
14
12
OK NG
11
Fig. 5
3 – 7
Page 39

FO-50A
FO-70A
1
2
3
4
7
10
13
14
15
6
Drive unit frame (Non cutter model)
17
16
6
5
8 9
11
12
16
17
18
19
18
19
Parts list (Fig. 6)
No. Part name Q’ty No. Part name Q’ty
1 Cam spring 1
2 Cam switch 1
3 Cam gear 1
4 Mode lever 1
5 Planet gear 1
6 Planet gear spring 1
7 Planet lever A 1
8 Planet gear 1
9 Planet gear spring 1
10 Planet lever B 1
11 Planet gear 1
12 Planet gear spring 1
13 Reduction gear, 17/30Z 1
14 Reduction gear, 17/43Z 1
15 Idler gear, 25Z 1
16 Screw (3×8) 1
17 Motor 1
18 Motor plate 1
19 Drive unit frame 1
1
OK NG
2
14
OK NG
5
4
, ,
11
10
, ,
Grease
Nail be doing lock.
6
12
Grease
4
10
/
, ,
, ,
11
12
10
8
9
7
9
8
7
, ,
15
11
13
3
9
8
/
6
5
7
, ,
12
5
4
6
Fig. 6
3 – 8
Page 40

FO-50A
FO-70A
7
Head guide, PO guide, cutter guide
upper and cutter
1
2
3 4 5
6
6
Parts list (Fig. 7)
No. Part name Q’ty No. Part name Q’ty
1 Mechanism unit 1
2 Cutter guide upper 1
(FO-70 only)
3 PO guide unit 1
(FO-70 only)
4 Pinch roller spring 2
(FO-70 only)
5 Pinch roller 2
(FO-70 only)
6 PO guide (FO-70 only) 1
7 Screw (3×8) 1
(FO-50 only)
8 PO guide (FO-50 only) 1
9 Release lever 1
(FO-50 only)
10 Head guide 1
11 Screw (3×6) 1
(FO-70 only)
12 Cutter cushion 1
(FO-70 only)
13 Cutter (FO-70 only) 1
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
4
Fix position
5
3
4
OK
NG
1
10
2
11
9
7
RELEASE
8
13
12
Fig. 7
3 – 9
Page 41

FO-50A
2
3
4
5
1
7
7
8
9
6
13
13
14
14
12
2
3
4
5
1
7
8
9
6
12
13
11
10
Control
PWB
Hook
8
7
7
10
14
11
11
FO-70A
8
PO roller guide and head frame unit
Parts list (Fig. 8)
No. Part name Q’ty No. Part name Q’ty
1 Mechanism unit 1
2 Screw (3×6) 1
3 Connector 1
4 Screw (3×12) 1
(FO-70 only)
PO roller guide unit
5
(FO-70 only)
6 PO gear 1
(FO-70 only)
7 PO roller rubber 2
(FO-70 only)
8 PO roller 1
(FO-70 only)
9 PO roller guide 1
1
(FO-70 only)
10 Screw (3×12) 1
11 Head earth cable 1
12 Head frame unit 1
13 Screw (3×8) 2
14 Panel lock lever spring 2
Fig. 8
3 – 10
Page 42

FO-50A
FO-70A
9
1
2
3
Head frame and thermal head
4
12
5
13
6
14
Parts list (Fig. 9)
No. Part name Q’ty No. Part name Q’ty
1 Platen gear 1
2 Platen bearing 2
3 Platen roller 1
4 Connector 1
5 Screw (3×6) 1
6 Head holder, left 1
7 Screw (3×6) 1
8 Head holder, right 1
9 Thermal head 1
10 Document sensor lever 1
(FO-70 only)
11 Document sensor lever 1
spring (FO-70 only)
12 Head spring 2 2
13 Head spring 1 3
14 Head frame 1
7
8
9
2
10
11
3
1
6
2
9
5
4
14
11
12
Fix position of Document
Sensor lever spring
OK
8
13
7
12
13
10
NG
Fig. 9
3 – 11
Page 43

FO-50A
FO-70A
10
PWB case top, bottom, PWB and
speaker
1
11
2
3
12
4
13
5
14
6
15
7
16
8
17
9
18
10
19
20
7
3
Parts list (Fig. 10)
No. Part name Q’ty No. Part name Q’ty
1 Mechanism unit 1
2 Screw (3×8) 1
3 Connector 1
4 Connector 3
5
PWB case unit
6 Screw (3×8) 1
7 Control PWB unit 1
8 Screw (3×8) 1
9
Speaker holder lever spring
10 Speaker ass’y 1
6
8
9
10
2
4
4
11 Screw (3×8) 2
12 Hook switch joint lever 1
13
PWB case, top
14
PWB case, bottom unit
15 Screw (3×6) 1
1
16 TEL/LIU PWB unit 1
17 Screw (4×6) 1
18 AC cord ass’y 1
19 Power supply PWB unit 1
1
20 PWB case, bottom 1
5
1
1
4
17
Fix position
19
18
17
18
19
12
13
11
16
15
Hook
20
14
11
Fig. 10
3 – 12
Page 44

FO-50A
FO-70A
11
Wire treatment
Panel cable
Door
sensor
cable
Hopper cover
Door sensor cable
Panel
cable
Parts list (Fig. 11)
No. Part name Q’ty
1 Core (F2125) 2
2 Scre w (3 ×6) 1
3 Scre w (4 ×6) 1
4 Scre w (3 ×6) 1
5 Band (100mm) 3
6 Core (F2123) 1
7 Scre w (3 ×8) 1
Operation
panel PWB
Operation
panel unit
Rib
Door sensor
cable
Rib
Rib
1
Rib
FO-70
Cam
switch
cable
Rib
Rib
6
5
Front
sensor cable
CIS
cable
Rib
Scanner
frame
Rib
The panel cable and
door sensor cable
pass to the core 2
times.
Cam
switch
cable
Motor
cable
Cutter cable
Drive unit
Motor cable
Rib
5
6
5
5
CIS
cable
6
CIS
cable
Front
sensor
cable
CIS
cable
Rib
Cutter
cable
(FO-70
ONLY)
Front
sensor
cable
Front
sensor
cable
Rib
Speaker
cable
CIS
cable
Panel
cable
1
Door
sensor
cable
TEL/LIU PWB
Speaker
cable
Control
PWB
Head
cable
Rib
Power
Supply PWB
2
Rib
Speaker
Head
earth
cable
The head cable and
head earth cable
pass to the core 2 times.
1
5
5
Speaker
7
TEL/LIU PWB
PWB
case, bottom
ARG
cable
FO-50
Cam
switch
cable
Rib
4
AC
cord
earth
3
cable
Power
supply
PWB
1
Rib
Drive unit
Motor cable
3
AC cord
earth cable
AC
cord
Fig. 11
3 – 13
Page 45

M E M O
FO-50A
FO-70A
3 – 14
Page 46

FO-50A
SRAM
256kbit
ROM
1Mbit
CPU
CPU I/F
TIMER
RTC
PIO
WATCHDOG
TIMER
CLOCK
32.768kHz
INTERRUPT
CONTROLLER
CIS I/F
MOTOR I/F
SENSOR I/F
SIO
THERMAL
HEAD I/F
PANEL I/F
PM
OPERATION
PANEL
CONTROL PWB UNIT
1CHIP FAX ENGINE (FC200)
HANDSET
SPEAKER
+5V +24V
OPERATION
PANEL
TEL/LIU
PWB UNIT
DRIVER
THERMAL
HEAD
PM
CONTACT
IMAGE
SENSOR
DOCUMENT
SENSOR
(FO-70 ONLY)
POWER SUPPLY
PWB UNIT
STABILIZER
MODEM
FM209
AMPLIFIER
AMPLIFIER
SURGE
PROTECT/
FILTER
CML TRANSFORMER
CI
VBT
RECTIFIER
TRANSFORMER
RECTIFIER
DIODE
TRANS
SURGE
ABSORBER
FILTER
LINE
PAPER
SENSOR
RESET IC
AMPLIFIER
BZ
CLOCK
32.256MHz
LCD
D-FF
16MHz
+3.3V
+5V
REGULATOR
CUTTER
(FO-70 ONLY)
AMPLIFIER
FO-70A
CHAPTER 4. DIAGRAMS
[1] Block diagram
4 – 1
Page 47

[2] Wiring diagram
CNCIS
CNDR
CNTH
DOOR
SENSOR
CNPW
CN2
CNLIUA
CNLNJ
8
12
CNLIUA
CNFRS
FRONT
SENSOR
CNSP
CNCUTCNCSWCNMT
CUTTER
SW
CAM SW
TX/RX
MOTOR
6
2
3
2
2
CNPN
SPEAKER
16
CNPN
CNLCD
OPERATION
PANEL PWB
UNIT
LCD UNIT
16
7
THERMAL HEAD
CIS(CONTACT IMAGE SENSOR)UNIT
HANDSET
FG
ARG
CNHJ
TEL/LIU
PWB UNIT
POWER SUPPLY
PWB UNIT
CONTROL
PWB UNIT
FG
14
AC CORD
2
CNTLJ
CNLIUB CNLIUB
4
(FO-70 ONLY)
FO-50A
FO-70A
4 – 2
Page 48

FO-50A
FO-70A
[3] Point- to-point diagram
TX/RX
MOTOR
THERMAL
HEAD
TPAD
TPBD
TPAD
TPBD
VMT
VMT
VTH
VTH
STRB1
STRB2
THI
N.C.
MG
MG
MG
+5V
STRB3
STRB4
LATCH
PCLK
DATA
VTH
1
2
3
4
5
6
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
CNMT
1
2
3
4
5
6
CNTH
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
TPAD
TPBD
TPAD
TPBD
VMT
VMT
VTH
VTH
STRB1
STRB2
THI
RANK
MG
MG
MG
+5V
STRB3
STRB4
LATCH
PCLK
DATA
VTH
TELOUT
TELIN
TELMUTE
CI
HS
RHS
RXIN
TXOUT
CML
+5V
DG
+24V
RLYCNT
TXMUTE
DPON
DPMUTE
E-RLY
(FO-70 ONLY)
CNCUT
CUT
N.C.
DG
10
11
12
CNLIUACNLIUA
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
CNLIUBCNLIUB
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
TELOUT
TELIN
TELMUTE
CI
HS
RHS
RXIN
TXOUT
CML
+5V
DG
+24V
N.C.
N.C.
DPON
DPMUTE
E-RLY
CUT
DG
TEL/LIU
PWB
CUTTER
SENSOR
OPERATION
PANEL
PWB
CIS
DG
+5V
SEN4
E
SEN0
SEN1
SEN2
SEN3
SEN5
SEN6
SEN7
ORGSNS
KEN4A
KEN3A
KEN2A
KEN1A
VO
DG
+5V
øT
CISCLK
GLED
+24V
CNPN CNPN
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
CNCIS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
DG
+5V
SEN4
E
SEN0
SEN1
SEN2
SEN3
SEN5
SEN6
SEN7
ORGSNS
KEN4A
KEN3A
KEN2A
KEN1A
VO
DG
+5V
øT
CISCLK
GLED
+24V
CONTROL
PWB
DRSNS
DG
DG
+5V
MG
MG
+24V
+24V
DG
PSAVE
CNCSW
CSW
DG
SP+
SP-
FRSNS
DG
CNDR
1
2
CNPW
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
CNSP
1
2
CNFRS
1
2
1
2
CN2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1
2
1
2
1
2
DRSNS
DG
DG
+5V
MG
MG
+24V
+24V
DG
PSAVE
CSW
DG
SP+
SP-
FRSNS
DG
DOOR
SENSOR
POWER
SUPPLY
PWB
CAM
SWITCH
SPEAKER
FRONT
SENSOR
4 – 3
Page 49

CHAPTER 5. CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
[1] Circuit description
1. General description
The compact design of the control PWB is obtained by using CONEXANT
fax engine in the main control section and high density printing of surface mounting parts. Each PWB is independent according to its function
as shown in Fig. 1.
2. PWB configuration
TEL/LIU
PWB
CIS
CONTROL
LCD
PWB
PANEL
PWB
1) Control PWB
The control PWB controls peripheral PWBs, mechanical parts, transmission, and performs overall control of the unit.
This machine employs a 1 chip modem (FM209) which is installed on
the control PWB.
2) TEL/LIU PWB
This PWB controls connection of the telephone line to the unit.
3) Power supply PWB
This PWB provides voltages of +5V and +24V to the other PWBs.
4) Panel PWB
The panel PWB allows input of the operation keys.
PWB
POWER
SUPPLY
PWB
AC CORD
TX/RX
MOTOR
Fig. 1
FO-50A
FO-70A
3. Operational description
Operational descriptions are given below:
• Transmission operation
When a document is loaded in standby mode, the state of the document sensor is sensed via the 1 chip fax engine (FC200). If the sensor signal was on, the motor is started to bring the document into the
standby position. With depression of the START key in the off-hook
state, transmission takes place.
Then, the procedure is sent out from the modem and the motor is
rotated to move the document down to the scan line. In the scan
processor, the signal scanned by the CIS is sent to the internal image processor and the AD converter to convert the analog signal into
binary data. This binary data is transferred from the scan processor
to the image buffer within the RAM and encoded and stored in the
transmit buffer of the RAM. The data is then converted from parallel
to serial form by the modem where the serial data is modulated and
sent onto the line.
• Receive operation
There are two ways of starting reception, manual and automatic.
Depression of the START key in the off-hook mode in the case of
manual receive mode, or CI signal detection by the LIU in the automatic receive mode.
First, the FC200 controls the procedure signals from the modem to
be ready to receive data. When the program goes into phase C, the
serial data from the modem is converted to parallel form in the modem interface of the 1 chip fax engine (FC200) which is stored in the
receive buffer of the RAM. The data in the receive buffer is decoded
software-wise to reproduce it as binary image data in the image buffer .
The data is DMA transferred to the recording processor within the
FC200 which is then converted from parallel to serial form to be sent
to the thermal head. The data is printed line by line by the FC200
which is assigned to control the motor rotation and strobe signal.
• Copy operation
T o mak e a cop y on this facsimile , the COPY ke y is pressed when the
machine is in stand-by with a document on the document table and
the telephone set is in the on-hook state.
First, depression of the COPY key advances the document to the
scan line. Similar to the transmitting operation, the image signal from
the CIS is converted to a binary signal in the DMA mode via the 1
chip fax engine (FC200) which is then sent to the image buff er of the
RAM. Next, the data is transferred to the recording processor in the
DMA mode to send the image data to the thermal head which is
printed line by line. The copying takes place as the operation is repeated.
5) LCD PWB
This PWB controls the LCD display.
5 – 1
Page 50

FO-50A
FO-70A
[2] Circuit description of control PWB
1. General description
Fig. 2 shows the functional blocks of the control PWB, which is composed of 4 blocks.
MAIN CONTROL BLOCK
(3) ROM
MODEM BLOCK
3) 27E010 (IC5): pin-32 DIP (ROM)
ROM of 1 Mbit equipped with software for the main CPU.
4) W24258S-70LE (IC3): pin-28 SOP (SRAM)
Line memory for the main CPU system RAM area and coding/decoding
process. Used as the transmission buffer.
Memory of recorded data such as daily report and auto dials. When the
power is turned off, this memory is backed up by the lithium battery.
(1) FAX ENGINE
(2) MODEM
(4) SRAM
Fig. 2 Control PWB functional block diagram
2. Description of each block
(1) Main control block
The main control block is composed of CONEXANT 1 chip fax engine
(FC200), ROM (1Mbit), SRAM (256kbit) and Modem (FM209).
Devices are connected to the bus to control the whole unit.
1) FC200 (IC2) : pin-144 QFP (FAX ENGINE)
2) FM209 (IC4) : pin-128 QFP (MODEM)
The FAX ENGINE Integrated Facsimile Controllers.
FC200, contains an internal 8 bit microprocessor with an external 16
Mbyte address space and dedicated circuitry optimized for facsimile
image processing and facsimile machine control and monitoring.
MIRQN
A[23:0]
D[7:0]
RDN
WRN
ROMCSN
CSN[1:0]
MCSN
SYNC
REGDMA
WAITN
RASN
CASN[1:0]
DWRN
TONE
GPIO[0]
GPIO[1]/SASTXD
GPIO[2]/SASRXD
GPIO[3]/SASCLK
GPIO[4]/CPCIN
GPIO[5]/SSCLK2
GPIO[6]/SSTXD2
GPIO[7]/SSRXD2
GPIO[8]/FWRN
GPIO[9]/FRDN
GPIO[10]/SSSTAT2
GPIO[11]/BE/SERINP
GPIO[12]/CS2N
GPIO[13]/CS3N
GPIO[14]/CS4N
GPIO[15]/CS5N
GPIO[16]/IRQ8
GPIO[17]/IRQ5N
GPIO[18]/IRQ9N
GPIO[19]/RDY/SEROUT
GPIO[20]/ALTTONE
SM[3:0]/GPO[7:4]
PM[3:0]/GPO[3:0]
EXTERNAL CPU BUS
GENERAL I/O
TONE/ALTTONE
GPIO
CALLING PARTY
CONTROL
AUTOBAUD
SYNC-ASYNC SASIF
SYNC SERIF 2
FLASH MEMORY IF
AUTOBAUD
SCANNER CONTROL & VIDEO PROCESSING
8-BIT PADC
CCD/CIS SCANNER
5 ms,A4/B4 LINES
SHADING CORRECTION(1:1,1:8)
DITHERING
MULTILEVEL B4-A4 REDUCTION
ERROR DIFFUSION
MTF
2.6kBYTE VIDEO RAM
INTERNAL & EXTERNAL BUS CONTROL
INTERNAL & EXTERNAL DECODE
BUS INTERFACE
DRAM CONTROL
DMA CONTROLLER
BI-LEVEL RESOLUTION
CONVERSION
PROGRAMMABLE
REDUCTION &
EXPANSION
MC24 CPU CONTROL IF
MC24 MEGACELL(8BIT DATA,24BIT ADDRESS)
WATCHDOG TIMER
REAL TIME CLOCK
CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR
BATTERY BACK-UP CIRCUIT
INTERRUPT CONTROLLER
CPU BUS
OPERATOR PANEL IF
32 KEYS
8 LEDS
LCD MODULE
MOTOR POWER
CONTROL RINGER
SYNC SERIF 1
INTERNAL CPU BUS
T.4/T.6 CODEC
MH,MR,MMR
HARDWARE,ALTERNATE
COMPRESSION &
DECOMPRESSION
THERMAL PRINTER IF
5 ms LINE TIME
A4/B4 LINES
TPH ADC
4 STROBE TPH
LATCHLESS TPH
EXTEMAL DMA I/F
DMA BUS
WRPROTN
SYSCLK
TSTCLK
DEBUGN
RESETN
XIN
XOUT
PWRDWNN
BATRSTN
SEE
"OPIF
OUTPUTS"
BELOW
SEE
"OPIF
INPUTS"
BELOW
THADIN
PCLK
PDAT
PLAT
STRB[3:0]
STRBPOL
START
CLK1
CLK1N
CLK2
VIDCTL0/FCS1N
VIDCTL1/FCS2N
+VREF
–VREF
VIN
PWR/GND TEST
OPIF INPUTS
OPI[0]/GPIO[21]/SSRXD1
OPI[1]/GPIO[22]/SSSTAT1
OPI[2]/GPIO[23]/SSCLK1
OPI[3]/GPIO[24]
Fig. 3
5 – 2
OPIF OUTPUTS
LEDCTL/GPO[16]
LCDCS/GPO[17]
OPO[0]/GPO[8]/SINPWR CTRL
OPO[1]/GPO[9]/PMPWR CTRL
OPO[2]/GPO[10]/RINGER
OPO[3]/GPO[11]
OPO[4]/GPO[12]/SSTXD1
OPO[5]/GPO[13]
OPO[6]/GPO[14]
OPO[7]/GPO[15]
Page 51

FC200 (IC2) Terminal descriptions
Pin Name Pin No. I/O
MIRQn 135 I HU − Modem interrupt, active low. (Hysteresis In, Internal Pullup.)
SYSCLK 133 I H − System clock. (Hysteresis In.)
TSTCLK 130 O − 123XT T est clock.
A[23:0] [1:6][8:13] O TU 123XT Address bus (24-bit).
[15:20][22:27]
D[7:0] [136:139] I/O TU 123XT Data bus (8-bit).
[141:144]
RDn 128 O − 123XT Read strobe.
WRn 127 O − 123XT Write strobe.
ROMCSn 120 O − 123XT ROM chip select.
CS1n 122 O − 123XT I/O chip select.
CS0n 57 O − 123XT SRAM chip select. (Battery powered.)
MCSn 121 O − 123XT Modem chip select.
SYNC 126 O − 123XT Indicates CPU op code fetch cycle (active high).
REGDMA 124 O − 123XT Indicates REGSEL cycle and DMA cycle.
WAITn 125 O − 123XT Indicates current TSTCLK cycle is a wait state or a halt state.
RASn 113 O − 123XT DRAM row address select. (Battery powered.)
CAS[1:0]n [111:112] O − 123XT DRAM column address select. (Battery powered.)
DWRn 109 O − 123XT DRAM write. (Battery powered.)
DEBUGn 129 I HU − External non-maskable input (NMI).
RESETn 131 I/O HU 2XO FC100/FC200 Reset.
TEST 58 I C − Sets Test mode (Battery powered).
XIN 59 I OSC − Crystal oscillator input pin.
XOUT 60 O − OSC Crystal oscillator output pin.
PWRDWNn 62 I H −
BATRSTn 61 I H − Battery power reset input.
WRPROTn 110 O − 1XC
START 101 O − 2XS Scanner shift gate control.
CLK1 100 O − 2XS Scanner clock.
CLK1n 99 O − 2XS Scanner clock-inverted.
CLK2 98 O − 2XS Scanner reset gate control (or clock for CIS scanner).
FCS1n/VIDCTL0 96 O − 2XT Flash memory chip select or Video Control signal.
FCS2n/VIDCTL1 97 O − 2XT Flash memory chip select or Video Control signal.
PCLK/DMAACK 29 O − 3XC Thermal Print Head (TPH) clock, or external DMAACK.
PDAT 30 O − 2XP Serial printing data (to TPH).
PLAT 31 O − 3XP TPH data latch.
STRB[3:0] [33:36] O − 1XP Strobe signals for the TPH.
STRBPOL/DMAREQ
OPO[0]/GPO[8]/ 47 O − 2XL Keyboard/LED strobe [0] or GPO[8] or Scan Motor Power Control
SMPWRCTRL
OPO[1]/GPO[9]/ 46 O − 2XL Keyboard/LED strobe [1] or GPO[9] or Print Motor Power Control
PMPWRCTRL
OPO[2]/GPO[10]/ 44 O − 2XCT Keyboard/LED strobe [2] or GPO[10] or RINGER
RINGER
OPO[3]/GPO[11] 43 O − 2XL Keyboard/LED strobe [3] or GPO[11]
OPO[4]/GPO[12]/ 42 O − 2XL Keyboard/LED strobe [4] or GPO[12] or SSTXD1 (for SSIF1)
SSTXD1
OPO[5]/GPO[13] 40 O − 2XL Keyboard/LED strobe [5] or GPO[13]
OPO[6]/GPO[14] 39 O − 2XL Keyboard/LED strobe [6] or GPO[14]
OPO[7]/GPO[15] 38 O − 2XL Keyboard/LED strobe [7] or GPO[15]
OPI[0]/GPIO[21]/ 52 I/O HU 2XC (Pullup, Hysteresis In) Keyboard return [0] or GPIO[21] or SSRXD1
SSRXD1 (for SSIF1)
OPI[1]/GPIO[22]/ 51 I/O HU 2XC (Pullup, Hysteresis In) Keyboard return [1] or GPIO[22] or SSSTAT1
SSSTAT1 (for SSIF1)
37 I C − Sets strobe polarity, active high/low or external DMA request.
Input Output Pin Description
Ty pe Type (Note: Active low signals have an "n" pin name ending.)
CPU Control Interface
Bus Control Interface
Prime Power Reset Logic and Test
Battery Power Control and Reset Logic
Used by external system to indicate -to FC200 - loss of prime power.
(Results in NMI)
(Battery powered.) Write protect during loss of VDD power.
NOTE:The functional logic is powered by battery power, but the output drive
is powered by DRAM battery power.
Scanner Interface
Printer Interface
Operator Panel Interface
FO-50A
FO-70A
5 – 3
Page 52

FO-50A
FO-70A
FC200 (IC2) Terminal descriptions
Pin Name Pin No. I/O
OPI[2]/GPIO[23]/ 50 I/O HU 2XC (Pullup, Hysteresis In) Keyboard return [2] or GPIO[23] or SSCLK1
SSCLK1 (for SSIF1)
OPI[3]/GPIO[24] 49 I/O HU 2XC (Pullup, Hysteresis In) Keyboard return [3] or GPIO[24]
LEDCTL 55 O − 4XC Indicates outputs OPO[7:0] are for LEDs.
LCDCS 54 O − 1XC LCD chip select.
GPIO[0] 94 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[0].
GPIO[1]/SASTXD 93 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[1] or SASTXD (for SERIF).
GPIO[2]/SASRXD 92 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[2] or SASRXD (for SERIF).
GPIO[3]/SASCLK 91 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[3] or SASCLK (for SERIF).
GPIO[4]/CPCIN 90 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[4] or Calling Party Control Input.
GPIO[5]/SSCLK2 89 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[5] or SSCLK2 (for SSIF2).
GPIO[6]/SSTXD2 87 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[6] or SSTXD2 (for SSIF2).
GPIO[7]/SSRXD2 86 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[7] or SSRXD2 (for SSIF2).
GPIO[8]/FWRn 85 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[8] or flash write enable signal for NAND-type flash
GPIO[9]/FRDn 84 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[9] or flash read enable signal for NAND-type flash
GPIO[10]/SSSTAT2
GPIO[11]/BE/ 82 I/O H 1XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[11] or bus enable or serial port data input for
SERINP autobaud detection.
GPIO[12]/CS[2]n 80 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[12] or I/O chip select [2].
GPIO[13]/CS[3]n 79 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[13] or I/O chip select [3].
GPIO[14]/CS[4]n 78 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[14] or I/O chip select [4].
GPIO[15]/CS[5]n 77 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[15] or I/O chip select [5].
GPIO[16]/IRQ[8] 76 I/O H 1XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[16] or external interrupt 8.
GPIO[17] 75 I/O H 1XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[17].
GPIO[18]/IRQ[9]n 74 I/O H 1XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[18] or external interrupt 9.
GPIO[19]/RDY/ 73 I/O H 1XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[19] or ready signal or Serial port data output for
SEROUT autobaud detection.
GPIO[20]/ALTTONE
SM[3:0]/GPO[7:4] [103:106] O − 1XC Programmable: scan motor control pins or GPO pins.
PM[3:0]/GPO[3:0] [115:118] O − 1XC Programmable: print motor control pins or GPO pins.
TONE 119 O − 1XC Tone output signal.
-Vref/CLREF 66 I -VR − Negative Reference Voltage for Video A/D or Reference Voltage for the
ADXG 68 I VXG − A/D Internal GND. (NOTE: This pin requires an external 0.22µF decoupling
ADGA 69 VADG A/D Analog Ground
ADVA 70 VADV A/D Analog Power
ADGD 72 VADG A/D Digital Ground
+Vref 71 I +VR Positive Reference Voltage for Video A/D.
VIN 67 I VA − Analog Video A/D input.
THAD1 65 I T A − Analog Thermal A/D input.
VSS(12) 7,21,28,45, Digital Ground
VDD(8) 14,32,41,48, Digital Power
VBAT 63 Battery Power
VDRAM 114 DRAM Battery Power
83 I/O H 2XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[10] or SSSTAT2 (for SSIF2).
107 I/O H 1XC (Hysteresis In) GPIO[20] or ALTTONE.
53,56,64,88,
95,108,132,
134
81,102,123,
140
Input Output
Type Type
Operator Panel Interface
General Purpose I/O
memory.
memory.
Miscellaneous
Power, Reference Voltages, Ground
Clamp Circuit.
capacitor to ADGA.)
Power and Ground
Pin Description
5 – 4
Page 53

(2) Panel control block
The following controls are performed by the FC200.
• Operation panel key scanning
• Operation panel LCD display
(3) Mechanism/recording control block
• Recording control block diagram (1)
FO-50A
FO-70A
PANEL/LCD PWB
THERMAL HEAD
MOTOR
CIS
OPERATOR
PANEL,
KEYPAD,
LEDS & LCD
PRINTER DATA
CONTROI &
SENSORS
PRINTER &
SCANNER
MOTOR DRIVERS
SCANNER
CONTROLS &
SENSORS
SCANNER
VIDEO
PREPROCESSING
SYNC PORTS (2)
(SSIF)
PURPOSE I/O
SYNC/ASYNC
SERIAL
PORT
OPO[7:0]*
OPI[3:0]*
LEDCTL*
LCDCS*
STRB[3:0]
STRBPOL
THADI
PDAT
PCLK
PLAT
PM[3:0]*
SM[3:0]*
START
CLK2
CLK1
CLK1N
VIDCTL[1:0]
VIN
+VREF
–VREF
SSCLK[2:1]*
SSTXD[2:1]*
SSRXD[2:1]*
SSSTAT[2:1]*
GPIOGENERAL
SASCLK
SASTXD
SASRXD
EXTENDED
FACSIMILE
CONTROLLER
TEST
BATRSTN
RESETN
TONE/ALTTONE
TSTCLK
REGDMA
WAITN
SYNC
PWRDWNN
XIN
XOUT
SYSCLK
MIRON
MCSN
EXTERNAL BUS
A[23:0]
D[7:0]
RDN
WRN
ROMSCN
CS[5:0]N*
WRPROTN
FRDN*
FRWN*
FCLE*
FCS[0:2]
DEBUGN
VDD
VDRAM
VBAT
VSS
RTC
CRYSTAL
A[4:0]
D[7:0]
RDN
WRN
TXOUT
TXA1
MONOFAX
FACSIMILE
MODEM
GPIO
CAS[0,1]N,RASN,DWRN
D[7:0]
FLASH MEMORY
RXIN
TXA2
TELEPHONE
LINE
LINE
INTERFACE
RIN
SPKR
RXDAT
TXDAT
RMODE
TMODE
CLKIN
SLEEPN
NOTES:*ALTERNATIVE GPO,GPI OR GPIO LINES
SPEAKER
MICROPHONE
CIRCUIT
TXA
MIC RIN
SPKR
RXA
ANALOG
SWITCH
SPKRLO
SPKRHI
XIA
GPIO
DRAM
(OPTION)
SPEAKERPHONE ONLY
VOICE OR SPEAKERPHONE
Fig. 4
5 – 5
Page 54

FO-50A
FO-70A
(4) Modem (FM209) block
INTRODUCTION
The CONEXANT FM209 MONOFAX modem is a synchronous 9600
bits per second (bps) half-duplex modem with error detection and DTMF
reception. It has low power consumption and requires a single +5V and
+3.3V DC power supply. The modem is housed in a single VLSI device
package.
The modem can operate over the public switched telephone network
(PSTN) through line terminations provided by a data access arrangement (DAA).
The FM209 is designed for use in Group 3 facsimile machines.
The modem satisfies the requirements specified in CCITT recommendations V.29, V.27 ter, V.21 Channel 2 and T.4, and meets the binary
signaling requirements of T.30.
The modem can operate at 9600, 7200, 4800, 2400, or 300 bps, and
also includes the V.27 ter short training sequence option.
The modem can also perform HDLC framing according to T.30 at 9600,
7200, 4800, 2400, or 300 bps.
The modem features a programmable DTMF receiver and three programmable tone detectors which operate concurrently with the V.21
channel 2 receiver.
The voice mode allows the host computer to efficiently transmit and
receive audio signals and messages.
The modem is available in either a 128-pin plastic quad flat pac k (TQFP).
General purpose input/output (GPIO) pins are available for host as
signment in the 128-pin TQFP.
The modem’s small size, single voltage supply, and low power consumption allow the design of compact system enclosures for use in both
office and home environments.
MONOFAX is a registered trademark of CONEXANT.
+3.3V
OFFHOOK
EYEXY
EYECLK
EYESYNC
GND
TALK
RINGD
LINEOUT
LINEIN
SPKRP
SPKRM
DAA
SPEAKER
DRIVER
(OPTIONAL)
EYE
PATTERN
GENERATOR
(OPTIONAL)
TELEPHONE
(DTE)
HOST
PROCESSOR
USART
(OPTIONAL)
DECODER
CRYSTAL
TXD
RXD
DCLK
RTS#
CTS#
RLSD#
READ#
WRITE#
DATA BUS
ADDR BUS
CS#
RESET#
IRQ1#
IRQ2#
XTLI
XTLO
FM209
MONOFAX
MODEM
+5V
LINE
FEATURES
• Group 3 facsimile transmission/reception
- ITU-T V.29, V.27 ter, T.30, V.21 Channel 2, T.4
- ITU-T V.17 and V.27 ter short train
- HDLC framing at all speeds
- Receive dynamic range: 0 dBm to -43 dBm
- Automatic adaptive equalization
- Fixed and programmable digital compromise equalization
- DTMF detect and tone detect
- ITU-T V.21 Channel 2 FSK 7E Flag Detect
- Ring detector
- Programmable transmits level
- Programmable single/dual tone transmission
• V.23 and Type I Caller ID
- Full-duplex modes:
TX = 75 bps. RX = 1200 bps
TX = 1200 bps. RX = 75 bps
- Half-duplex mode:
TX = RX = 1200 bps
- Serial and parallel data modes
- Programmable parallel data mode
- 5, 6, 7 or 8 data bits
- 1 or 2 Stop bits
- Mark, Space, Even, or Odd Parity
- Break function
- Transmitter squelch
- Compromise equalizer
• Programmable interface memory interrupt
• Eight General Purpose Input (GPI) and eight General Purpose Out-
put (GPO) pins for host assignment
• DTE interface: two alternate ports
- Selectable microprocessor bus (6500 or 8085)
- ITU-T V.24 (EIA/TIA-232-E compatible) interface
• TTL and CMOS compatible
• 3.3V/5V operation
• Power consumption
- Operating Mode: 200 mW (Basic), 275 mW (-V option). 300 mW
(-VS option)
- Sleep Mode: 1 ma (Basic. -V option and -VS option)
• Packaging
- 128-pin TQFP (thin quad flat pack)
Fig. 5
POWER
SUPPLY
5 – 6
Page 55

FM209 (IC4) Hardware Interface Signals
Pin Signals – 128-Pin TQFP
Pin No. Signal Name I/O Type Pin Description
1 SR4IN/RESERVED MI Modem Interconnect
2 SR3OUT/RESERVED MI Modem Interconnect
3 EYESYNC OA Eye Pattern Circuit
4 EYECLK OA Eye Pattern Circuit
5 RXD OA DTE serial interface
6 SR1IO MI Modem Interconnect
7 NC — No Connection
8 EYEXY OA Eye Pattern Circuit
9 SR4OUT MI Modem Interconnect
10 VDD1 PWR 3.3V Digital Supply for DSP
11 RLSD# OB DTE Serial Interface
12 DCLK OB DTE Serial Interface
13 EN85# IA Host Parallel Interface
14 GPI0 IA Host Parallel Interface
15 RTS# IA DTE Serial Interface
16 DGND1 GND DSP Digital Ground
17 TXD IA DTE Serial Interface
18 SA1CLK MI Modem Interconnect
19 RS4 IB Host Parallel Interface
20 RS3 IB Host Parallel Interface
21 RS2 IB Host Parallel Interface
22 RS1 IB Host Parallel Interface
23 RS0 IB Host Parallel Interface
24 YCLK I Modem Interconnect
25 IACLK MI Modem Interconnect
26 IA1CLK MI Modem Interconnect
27 CTRLSIN S/NC MI Modem Interconnect
28 RESERVED/NC MI Modem Interconnect
29 SOUT S/NC MI Modem Interconnect
30 SIN S/NC MI Modem Interconnect
31 FSYNC S/NC MI Modem Interconnect
32 IARESET S#/NC MI Modem Interconnect
33 AGND1 GND IA Analog Ground
34 LINEIN S/NC I Line Interface
35 MICP S/NC I Microphone Input
36 MICM S/NC I Microphone Input
37 MICBIAS S/NC O Microphone Bias Output
38 NC — No Connection
39 NC — No Connection
40 VREF S/NC MI Modem Interconnect
41 VC S/NC MI Modem Interconnect
42 VAA S/NC PWR 5V IA Analog power
43 LINEOUT S/NC O Line Interface
44 NC — No Connection
45 AGND2 GND IA Analog Ground
46 SPKRP S/NC O Speaker Interface Output
47 SPKRM S/NC O Speaker Interface Output
48 AVDD S/NC PWR 5V IA Digital power
49 RESERVED/NC MI Modem Interconnect
50 ICLK S/NC MI Modem Interconnect
51 MCLK P MI Modem Interconnect
52 CTRLSIN P MI Modem Interconnect
53 RESERVED MI Modem Interconnect
54 SOUT P MI Modem Interconnect
55 SIN P MI Modem Interconnect
56 FSYNC P MI Modem Interconnect
57 IARESET P# MI Modem Interconnect
58 AGND3 GND IA Analog Ground
59 NC — No Connection
60 LINEIN P I Line Interface
61 MICP P I Microphone Input
62 MICM P I Microphone Input
63 MICBIAS P O Microphone Bias Output
64 NC — No Connection
65 NC NC No Connection
66 VREF P MI Modem Interconnect
67 VC P MI Modem Interconnect
68 VAA P PWR 5V Analog Supply for IA
69 LINEOUT P O Line Interface
70 AGND4 GND IA Analog Ground
71 SPKRP P O Speaker Interface Output
FO-50A
FO-70A
5 – 7
Page 56

FO-50A
FO-70A
FM209 (IC4) Hardware Interface Signals
Pin Signals – 128-Pin TQFP
Pin No. Signal Name I/O Type Pin Description
72 SPKRM P O Speaker Interface Output
73 AVDD P PWR 5V Digital power for IA
74 NC — No Connection
75 ICLK P MI Modem Interconnect
76 MCLK S/NC MI Modem Interconnect
77 VDD2 PWR 3.3V Digital Supply for DSP
78 D7 IB/OC Host Parallel Interface
79 D6 IB/OC Host Parallel Interface
80 D5 IB/OC Host Parallel Interface
81 D4 IB/OC Host Parallel Interface
82 D3 IB/OC Host Parallel Interface
83 D2 IB/OC Host Parallel Interface
84 DGND2 GND DSP Digital Ground
85 VDD3 PWR 3.3V Digital Supply for DSP
86 D1 IB/OC Host Parallel Interface
87 DGND3 GND DSP Digital Ground
88 D0 IB/OC Host Parallel Interface
89 CSBR# IB Host Parallel Interface
90 WRITE# IB Host Parallel Interface
91 CS# IB Host Parallel Interface
92 READ# IB Host Parallel Interface
93 GPI2 IA General purpose input
94 GPI3 IA General purpose input
95 GPI4 IA General purpose input
96 GPI5 IA General purpose input
97 GPI6 IA General purpose input
98 GPI7 IA General purpose input
99 GPO7 OC General pur pose output
100 VDD4 PWR 3.3V DSP Digital Power
101 GPO6 OC General purpose output
102 GPO5 OC General purpose output
103 RESERVED MI Modem Interconnect
104 GPO4 OC General purpose output
105 GPO3 OC General purpose output
106 DGND4 GND DSP Digital Ground
107 CTS# OB DTE Serial Interface
108 IRQ1# OB Interrupt request
109 GPO2 OC General purpose output
110 GPO1 OC General purpose output
111 GPO0 OC GPO0 (IA reset)
112 VDD5 PWR 3.3V DSP Digital Power
113 VGG PWR 5V DSP Digital
114 DGND5 GND DSP Digital Ground
115 RESET# IB External reset
116 XTALI I Crystal in
117 XTALO O Crystal out
118 RESERVED MI Modem Interconnect
119 XCLK OB X clock output
120 GPI1 IA General purpose input
121 IRQ2# OA Interrupt request
122 SR3IN MI Modem Interconnect
123 RESERVED MI Modem Interconnect
124 RESERVED MI Modem Interconnect
125 DGND6 GND DSP Digital Ground
126 DVAA PWR 3.3V DSP analog power
127 AGND5 GND DSP Analog Ground
128 RESERVED MI Modem Interconnect
Notes:
I/O types: MI = Modem interconnect.
P Signals: Primary IA
S Signals: Secondary IA
Reserved = No external connection allowed.
IA, IB, = digital input
OA, OB, OC = digital output
I = analog input
O = analog output
5 – 8
Page 57

[3] Circuit description of TEL/LIU PWB
(1) TEL/LIU block operational description
1) Block diagram
FO-50A
FO-70A
L1
L2
CML
M
C
B
~~+
–
BIT7 BIT6 BIT5 BIT4 BIT3 BIT2 BIT1 BIT0
DAC
GAIN
TXRX
LOOP
MIC GAIN L/O E
IACR1
IACR2
IACR3
DPON
DPON
CI
H
L
DPMUTE
HANDSET
RX
TX
SPKR E
LINEOUT
ATTENUATION
L
H
HS
ADC
GAIN
RXTXLOOP
L/I E MIC E
MICBIAS
SEL
LINE SEL
TXOUT
RXIN
TELIN
TELMUTE
TELOUT
CONTROL PWBTEL/LIU PWB
SPEAKER
SPMUTE
Fig. 6
SPKRP-P
MICP
LINEIN
LINEOUT
LINEOUT
ENABLE
SP OUT
ENABLE
0,20,25,30dB
SP
DRIVER
MIC
GAIN
LINE
DRIVER
MUTE,0,
–6,–12dB
RTLOOP
MIC IN
LPF
LINE IN
LPF
LNINSEL
(0:1)
(1:0)
(0:0)
(1:1)
MIC ENABLE
MIC
ENABLE
1
0
LINE IN
ENABLE
1
0
(0:0)
(1:1)
(1:0)
MODEM
FM209
DAC GAIN
0,6dB
ADC GAIN
0,–4dB
BZOUT
CML
SPMUTE
RCVOL
VTHON
DAC
ADC
SIN
SOUT
FAX
ENGINE
FC200
RHS
RANK
DRSNS
TXMUTE
TELMUTE
IA-RESET
CUTI
HS
CI
CSWI
PESNS
FRSNS
ORGSNS
PSNS
VREFCONT
MDMRST
LEDON
2) Circuit description
The TEL/LIU PWB is composed of the following 6 blocks.
1. Speech circuit section
2. Dial transmission section
3. Speaker amplifier section
4. Ringer circuit section
5. Externally connected TEL OFF HOOK detection circuit
6. CI detection circuit
3) Block description
1. Speech circuit section
• The receiver volume is an electronic volume type, this model is
switched in 2 steps.
2. Dial transmission section
• D.P. transmission: The CML relay and PC1 are turned on and off
for control in the DP calling system. (Refer to the attached sheet.)
• DTMF transmission: It is formed in the modem, and is output.
3. Speaker amplifier section
• Ringer volume : It is controlled by the combination of the attenuator
value of the LINE DRIVER in the modem and the
ringer sending level sent from the modem.
• Speaker volume: It is controlled by the attenuator value of the LINE
DRIVER in the modem.
4. Ringer circuit section
• The ringer sound is formed in the tone of modem when CI signal is
detected. The amplifier circuit driv es the speaker of the main body.
5 – 9
Page 58

FO-50A
FO-70A
5. Externally connected TEL OFF HOOK detection circuit section
• The circuit current detection is turned on together with OFF HOOK
of main body or OFF HOOK of externally connected TEL. ON of
CML OFF (HS=L) is judged as OFF HOOK of externally connected
TEL.
6. CI detection circuit
• CI is detected by the photocoupler which is integrated in series in
the primary side TEL circuit well proven in the existing unit.
4) Signal selection
The following signals are used to control the transmission line of TEL/
FAX signal. For details, refer to the signal selector matrix table.
[Control signals from output port]
Signal Name Description
CML Line connecting relay and DP generating relay
(The circuit is located H: Line make
in the TEL/LIU PWB.) L: Line break
SP MUTE Speaker tone mute control signal
(The circuit is located H: Muting (Power down mode)
in the TEL/LIU PWB.) L: Muting cancel (Normal operation)
Handset reception mute control signal
TEL MUTE H: Muting
L: Muting cancel
VOLUME SETTING
DTMF T ransmission Fixed
volume setting (Receiver)
Key buzzer volume setting Fixed
Speaker volume setting Low 1 1
Middle 1 0
High 0 1
Ringer volume setting Low 1 1
Middle 1 0
High 0 1
DTMF speaker volume setting Low 1 1
Middle 1 0
High 0 1
LINEOUT A
(HIGH) (LOW)
5 – 10
Page 59

[Signals for status recognition according to input signals]
Signal Name Function
RHS
H:The handset is in the on-hook state.
L: The handset is in the off-hook state.
CI Incoming call (CI) detection signal
[Other signals]
Signal Name Function
TEL IN Receiving signal from line or modem
TEL OUT Transfer signal to line
SPOUT Speaker output signal
TXOUT
RXIN
Transmission (DTMF) analog signal output
from modem
Reception (DTMF, others) analog signal
into modem
(Example: TEL speaking)
input
NO Signal Name (CNLIUA)
1 TELOUT
2 TELIN
3 TELMUTE
4CI
5
HS
6 RHS
NO Signal Name (CNLIUB)
1N. C.
2
N. C.
3 DPON
FO-50A
FO-70A
NO Signal Name (CNLIUA)
7 RXIN
8 TXOUT
9 CML
10
11
12 +24V
NO Signal Name (CNLIUB)
4 DPMUTE
5
+5V
DG
E-RLY
CONTROL PWBTEL/LIU PWB
TELMUTE
L/I E MIC E
MICBIAS
SEL
LINE SEL
TXOUT
RXIN
TELIN
TELOUT
SPEAKER
SPMUTE
L1
L2
CML
M
C
B
~~+
BIT7 BIT6 BIT5 BIT4 BIT3 BIT2 BIT1 BIT0
DAC
GAIN
TXRX
LOOP
MIC GAIN L/O E
IACR1
IACR2
IACR3
CI
DPON
H
L
–
DPON
HANDSET
RX
TX
ATTENUATION
DPMUTE
L
LINEOUT
H
SPKR E
HS
ADC
GAIN
RXTXLOOP
SP OUT
ENABLE
SPKRP-P
MICP
0,20,25,30dB
LINEIN
LINEOUT
LINEOUT
ENABLE
TEL SPEAKING:
FAX SENDING/RECEIVING:
SP
DRIVER
MIC
GAIN
LINE
DRIVER
MUTE,0,
–6,–12dB
RTLOOP
MIC IN
LPF
LINE IN
LPF
LNINSEL
(0:1)
(1:0)
(0:0)
(1:1)
MIC ENABLE
MIC
ENABLE
1
0
LINE IN
ENABLE
1
0
(0:0)
(1:1)
(1:0)
MODEM
FM209
DAC GAIN
0,6dB
ADC GAIN
0,–4dB
BZOUT
CML
SPMUTE
RCVOL
VTHON
DAC
ADC
SIN
SOUT
FAX
ENGINE
FC200
RHS
RANK
DRSNS
TXMUTE
TELMUTE
IA-RESET
CUTI
HS
CI
CSWI
PESNS
FRSNS
ORGSNS
PSNS
VREFCONT
MDMRST
LEDON
Fig. 7
5 – 11
Page 60

FO-50A
FO-70A
[4] Circuit description of power supply PWB
1. Block diagram
F1
1.6A/250V
AC IN
Noise
Filter
Circuit
Rectifying
Smoothing
Circuit
F2
1.6A/250V
2-1. Noise filter circuit
The input noise filter section is composed of L1, C1, C15 and C21 which
reduces normal mode noise from the AC line and common mode noise
to the AC line.
2-2. Rectifying/smoothing circuit
The AC input voltage is rectified by diode D1, 2, 3, 4 and smoothed by
capacitor C2 to supply DC voltage to the switching circuit section.
Power thermistor TH1 suppresses inrush current at power switch-on.
2-3. Switching circuit
This circuit includes MOS FET Q1 and the gate drive circuit, and components around Q1.
In this circuit, the DC voltage supplied from the rectifying/smoothing
section is converted into high frequency pulses by ON/OFF repetition of
Q1.
Switching
Circuit
(RCC system)
Regulator
Circuit
+5V
+24V
Control
Circuit
Fig. 8
Photo Coupler
2-4. Control circuit
This circuit controls output voltage of 24V by adjusting ON period of Q1,
looking at signal from photo-coupler PC1.
In this operation IC1 takes charge of important part .
The over current protection is performed by br inging Q1 to OFF state
through detection of voltage of T1 subwiding .
The over voltage protection is performed by operating the over current
protection circuit through detection of zener diode ZD4 anb short-circuiting
of load.
2-5. +5V circuit
DC voltage supplied by rectifying the output of transf ormer T1 with diode
D8 is stabilized by 3-terminal regulator IC1.
[5] Circuit description of CIS unit
1. CIS (Contact Image Sensor)
Cis is an image sensor which puts the original paper in close contact
with the full-size sensor for scanning, being a monochromatic type
with the pixel number of 1,728 dots and the main scanning density of
8 dots/mm.
It is composed of sensor, rod lens, LED light source , light-conductive
plate, control circuit and so on, and the reading line and focus are
previously adjusted as the unit.
Due to the full-size sensor, the f ocus distance is so short that the set
is changed from the light weight type to the compact type.
2. Waveforms
The following clock is supplied from FC200 of the control board, and
VO is output.
5ms
øT
1.984µs
CISCLK
VO
Fig. 9
Approx.5V
0V
2V(TYP)
(White original paper)
5 – 12
Page 61

CHAPTER 6. CIRCUIT SCHEMATICS AND PARTS LAYOUT
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
107
7374757677
798082838485868789909192939496
97
100
99
98
101
33343536293031
37
38
39
40
42
43
44
46
47
54
55
49
50
51
52
114
115
116
117
118
103
104
105
106
119
65
67
66
71
59
60
62
63
61
78
70
72
69
68
140
123
102
81
48
32
14
21
28
45
53.56
64.88
95.108
132
7.134
58
129
131
135
133
130
136
137
138
139
+5V
C145
0.1
C146
1
DG
+5V
141
142
143
144
(3-3A)
(3-3B)
SYSCLK
MIRQ
R150
10K
C116
1000P
DG
R108
33K
R109
33K
R111
33K
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
RA3
270 x 4
RA2
270 x 4
(2-5B)
(3-4B)
M
LN
41
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
DG
C127
1000P
C152 1000P
C175 1000P
C149 1000P
C147 1000P
C126 1000P
C114 1000P
C130 1000P
1
2345689
111213151617181920222324252627
128
127
120
12257121
126
124
125
113
112
111
109
110
10
ABCDEFG
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2A1
A0
RA6
270 x 4
RA14
270 x 4
IJK
H
(2-5B)
(3-4B)
(2-4E)(3-3B)
(2-4B)
(2-4E)
(3-3B)
R106 100
R107 100
VBT
C169
1
R149
1M
C172
0.1
DG
BATRST
DG
+5V
VCC
GND
OUT
C168
1
MCS
CE1
ROMCS
WR
RD
(1-1F)
RESET
IC9
XC61
(1-1I)
RESET
DG
DG
C170
2200P
R151
10M
C173
22P
C174
22P
X2
32.768kHz
(5-2D)
+VREF
(5-2D)
–VREF
(5-6D)
VIN
(5-1I)
THADI
(6-4I)
BZOUT
(5-5F)
TPA
(5-5F)
TPB
(5-5F)
TPA
(5-5F)
TPB
DG
DGDG
DG
DG
DG
DG
C113 1000P
C111 1000P
C107 1000P
C106 1000P
RA5
270 x 4
(5-5F)
VTHON
(5-5F)
LEDON
(3-2C)
MDMRST
(6-6C)(6-2A)
RCVOL
DG
C112
0.1
+5V
CNPN-16
CNPN-15
CNPN-14
CNPN-13
CNPN-4
CNPN-5
CNPN-6
CNPN-7
CNPN-8
CNPN-3
CNPN-9
CNPN-10
CNPN-11
KEN1A
KEN2A
KEN3A
KEN4A
E
SEN0
SEN1
SEN2
SEN3
SEN4
SEN5
SEN6
SEN7
L107
HM601
R152
120
RA9
470 x 4
RA15
470 x 4
A23
A22
A21
A20
A19
A18
A17
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2A1
A0
RD
WR
ROMCS
CS1
CS0
MCS
SYNC
REGDMA
WAIT
RAS
CAS0
CAS1
DWR
WRPROT
VBAT
CNTH-13
LATCH
CNTH-15
DATA
CNTH-14
PCLK
CNTH-3
STRB1
CNTH-4
STRB2
CNTH-11
STRB3
CNTH-12
STRB4
RA12
470 x 4
RA13
270 x 4
DG
C154 22P
DG
C155 22P
DG
C133 22P
DG
C134 22P
DG
C177 22P
DG
C176 22P
DG
C178 22P
CNCIS-4
CNCIS-5
CISCLK
D[7-0]
A[16-0]
R120 150
R122 470
L102
HM601
(4-2D)
PSNS
(4-5D)
ORGSNSI
(4-5D)
FRSNSI
(4-3D)
PESNS
CNLIUB-4
DPMUTE
C213
100P
R121
470
RA4
470 x 4
R126
R125
R124
R123
CNLIUB-5
E-RLY
CNLIUB-3
DPON
CNPW-8
PSAVE
CNLIUB-1
RLYCNT
(4-6D)
CSWI
C214
C202
C189
C212
100P x 4
RA11
470 x 4
R103
470
R136
33K
CI
(1-6B)
HS
(6-4I)
SPMUTE
(1-6B)
CML
(5-2A)
VREFCONT
(4-4D)
CUTI
CML
GPIO20
GPIO19
GPIO18
GPIO17
GPIO16
GPIO15
GPIO14
GPIO13
GPIO12
GPIO11
GPIO10
GPIO9
GPIO8
GPIO7
GPIO6
GPIO5
GPIO4
GPIO3
GPIO2
GPIO1
GPIO0
VIDCTL0
VIDCTL1
CLK1
CLK1
CLK2
START
STRB3
STRB2
STRB1
STRB0
PCLK
PDAT
PLAT
STRBPOL
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
TSTCLK
SYSCLK
MIRQ
RESET
DEBUG
TEST
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VSS
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
VDD
ADXG
ADGA
ADGD
ADVA
BATRST
PWRDWN
XOUT
XIN
+VREF
–VREF / CLREF
VIN
THADI
TONE
SM0
SM1
SM2
SM3
GPO0
GPO1
GPO2
GPO3
VDRAM
OPI0
OPI1
OPI2
OPI3
LEDCTL
LCDCS
OPO0
OPO1
OPO2
OPO3
OPO4
OPO5
OPO6
38 : OPO7
2
1
3
DG
R168
10K
RA1
470 x 4
R137
10K
RA10
470 x 4
R102(*1)
R145
470
R105(*1)
R133 33K
R135 33K
R134 33K
(2-4B)(3-3B)
DG
DG
IC2
FC200
FAX ENGINE
CNLIUA-9
CML
(1-5A)(6-3E)
C171
1
RA16
470 x 4
N.M.
CA1
CA2
DG DG
PHIT
C161
C162
N.M.
(1-6B)
HS
CNLIUA-5
HS
(1-5A)
CI
CNLIUA-4
CI
(1-5A)
R102 R105
N.M. N.M.
470 33K
MODEL
FO-50
FO-70
(*1)
C128
1
C153
1
C150
1
C151
1
C148
1
C125
1
C115
1
C117
1
R110 270
RA7
270 x 4
RA8
270 x 4
DGDG
C118
68P
C119
68P
C196
100P
C209
100P
C190
100P
33K x 4
FO-50A
FO-70A
[1] Control PWB circuit 1/6
Main control block
6 – 1
Page 62

FO-50A
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
21
2029192818
172515231426132731
32
1
10
11
16
22
24
1
IO8
19
26
IO7
18
A14
2
A14
IO6
17
A13
23
A13
IO5
16
A12
21
A12
IO4
15
A11
24
A11
IO3
13
A10
25
A10
IO2
12
A9
3
A9
IO1
11
A8
4
A8
A7
5
A7
A6
6
A6
A5
7
A5 VDD
28
A4
8
A4
VSS
14
A3
9
A3
A2
10
A2
A1
A0
27A022
CS2/OE
A[16~0]
(1-5I)
D[7~0]
(1-6I)
(1-3I)RD(1-3I)
+5V
DG
C205
0.1
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
D0
IC5
27E010
ROM
3
A15 DQ8
A14 DQ7
A13 DQ6
A12 DQ54A11 DQ4
A10 DQ3
A9 DQ2
A8 DQ1
A75A66A57A4
VCC
8
A3
VPP
9
A2A1A0 GNDEG
IC3
W24258S-70LE
SRAM
A1
WE
D7D6D5D4D3D2D1
D0
VBT
DG
C129
0.1
WR
(1-3I)
VBT
R127
22K
ROMCS
2
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10A9A8A7A6A5A4A3A2A1A0
A16
12
(A17)
20
CS1
CE1
(1-3I)
L108
0
FO-70A
Memory block 2/6
6 – 2
Page 63

FO-50A
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
D7
A0
C108
0.01
R115
270
D6D5D4D3D2D1D0
A1A2A3
A4
1920212223
RS4
RS3
RS2
RS1
RS0
78D779D680D581D482D383D286D188D091CS92
READ90WRITE
108
IRQ1
115
RESET13EN85
DG
D[7~0]
RD
WR
(1-3I)
(1-3I)
(1-3I)
R189 0
MIRQ
(1-6F)
A[4~0]
MDMRST
(1-1D)
MCS
MAG
121
IRQ2
15
107
17
12
5
RTS
CTS
TXD
DCLK
RXD11RLSD
R132
10K
RESERVED/CSBR
DG
89
119
24
R117
270
+5V
SYSCLK
(1-6F)
621
7
3
5
8
XCLK
YCLK
CLR
D
CLK
PRE
C2
Q
L100
HM601
R104
470
L103
HM601
C124
1
IC1
WT74
L101
HM601
99
101
102
104
105
109
110
111
R139
470
R147
470
R131
10K
TXMUTE
TELMUTE
57
32
3
4
8
DGDG DG DG DG DG DG
R101
120
C105
12P
C104
10P
R100
200
6
52
27
56
18
31
51
25
76
9
55
30
26
75
50
54
122
29
116
117
DG
414043344746373635
1,2,53,103,118,123,124,128
38,39,44,49,59,64,65,74
MAG
67
66
C164
0.1
C165
0.1
C2
10/50C110/50
MAG
69
(6-5E)
SPOUT
60
(6-4C)
TELOUTI
(6-4E)
SIGTX
(6-4E)
SIGRX
72
71
63
62
61
C163
0.1
R141
2.2K
R142
1K
MAG
CNDR-1
DRSNS
C138
2200P
R129
470
+5V
R113
100K
98
97
96
95
94
93
120
14
CNTH-6
RANK
CNLIUA-6
RHS
R118
470
+3.3V
L106
HM601
10
77
85
100
112
73
16
84
87
106
114
125
113
126
33
45
+5V
L104
HM601
C123
0.1
+3.3V
C3
47/25
C166
1
58
70
127
68
C136
1
+5V
L105
HM601
MAG
DG
MAG
MICP-P
MICM-P
MICBIAS-P
SPKRP-P
SPKRM-P
LINEIN-P
LINEOUT-P
VREF-P
VC-P
RESERVED
N.C./MICM-S
N.C./SPKRP-S
N.C./LINEIN-S
N.C./VREF-S
N.C./MICP-S
N.C./MICBIAS-S
N.C./SPKRM-S
N.C./LINEOUT-S
N.C./VC-S
N.C.
XTL0
XTL1
N.C./SOUT-S
SR3IN
SOUT-P
N.C./ICLK-S
ICLK-P
IA1CLK
N.C./SIN-S
SIN-P
SR4OUT
N.C./MCLK-S
IACLK
MCLK-P
N.C./FSYNC-S
SA1CLK
FSYNC-P
N.C./CTRLSIN-S
CTRLSIN-P
SR1IO
EYEXY
EYECLK
EYESYNC
N.C./IARESET-S
IARESET-P
GPO0
GPO1
GPO2
GPO3
GPO4
GPO5
GPO6
GPO7
GPI7
GPI6
GPI5
GPI4
GPI3
GPI2
GPI1
GPI0
VDD1(+3.3VDD)
VDD2(+3.3VDD)
VDD3(+3.3VDD)
VDD4(+3.3VDD)
VDD5(+3.3VDD)
AVDD-P(+3.3VIAD)
DGND1
DGND2
DGND3
DGND4
DGND5
DGND6
VGG(+5VDD)
DVAA(+3.3VDA)
AGND1
AGND2
AGND3
AGND4
AGND5
VAA-P(+5VIAA)
42
R165
33K
R119
33K
R144
0
DG
X1
32.256MHz
DG
CNLIUA-3
CNLIUB-2
(1-6H)
(1-5I)
IC4
FM209
MODEM
C132
0.1
C217
100P
(6-4E)
TXMUTE
C208
100P
R143 0
R116 0
R130 0
C109
N.M.
4
DG
C110
0.1
C141
N.M.
R114
100K
R146
470
C210
100P
DG
DG
DG
C143
1
C144
1
C221 1
C220 1
C219 1
C218 1
C142 1
R162
3
C167
0.1
C140
0.1
48
42 : VAA-S(+5VIAA)
48 : N.C./AVDD-S(+3.3VIAD)
FO-70A
Modem block 3/6
6 – 3
Page 64

FO-50A
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
CNCSW-1
CNCSW-2
CSW
DG
(1-4A)
CNFRS-1
CNFRS-2
FRSNS
DG
(1-3A)
CNPN-12
ORGSNS
(1-3A)
(1-4A)
+24V
C120
2200P
DG
CSWI
C122
2200P
DG
FRSNSI
C180
2200P
DG
ORGSNSI
PESNS
R169
1K
DG
R128 (*1)
(1-3A)
PSNS
13
24
DG
DGDG
13
24
PESNS
PSNS
PI2
SG206
PI1 (*1)
CNCUT-1
CNCUT-3
CUT
DG
(1-5A)
C139 (*1)
DG
CUTI
DG
+5V
R184
5.6K
BAT1
CR2032
D5
HRW0202
VBT
<VBT>
+3.3V
23
1
D6
1SS355
REG100
XC62
C207
0.1
+5V
+24V
+24VA
C5
22/50
C215
0.1/50
R182
N.M.
R181
FG
N.M.
C6
47/25
C216
0.1
+5V
DG
DG
+24V
+24V
MG
MG
+5V
+5V
DG
DG
+24V
CNLIUA-10
CNPN-2
CNLIUA-11
CNPN-1
CNLIUA-12
CNPW-2
CNPW-1
CNPW-7
CNPW-5
CNPW-6
CNPW-3
CNPW-4
R186
200
C8
100/50
DG
MG
DG
CNCUT-2
N.C.
R183
DG
C211
1000P
+5V
C191
1000P
I
R
O
(*1)
MODEL PI1 R128 R139 CNCUT
FO-50 N.M. 0 N.M. N.M.
FO-70 SG206S N.M. 2200P 3PIN
FO-70A
Sensor/Reset/Power supply block 4/6
6 – 4
Page 65

FO-50A
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
R138
5.1K
+5V
DG
Q1
2SA1037
CNCIS-1
<VO>
VO
(1-1F)
<VIN>
VIN
C160
1000P
+5V
CNCIS-3
CNCIS-2
<DG>
DG
+5V
+24V
CNCIS-7
DG
+24V
C159
1
C137
0.1
GLED
CNCIS-6
DG
C135
0.1
LEDON
R148
5.1K
DG
Q5
2SA1037
(1-5A)
VREFCONT
(1-1F)
VREF+
+5V
R180
20K
(1-1F)
VREF–
R167
30K
DG
R166
43K
9161514131211
10
1234567
8
TPA
TPB
TPA
TPB
VTHON
LEDON
(1-1E)
(1-1E)
(1-1E)
(1-1E)
(1-1E)
(3-1D)
+24V
FU100
KAB2402
D1
100(1W)
VMT
VMT
TPBD
TPAD
TPBD
TPAD
VTHON
LEDON
CNMT-5
CNMT-6
CNMT-1
CNMT-2
CNMT-3
CNMT-4
(5-3E)
(5-4B)
IC8
ULN2003A
1B2B3B4B5B6B7B
E
COM
1C2C3C4C5C6C7C
VTHON
(5-5I)
+24V
D4
1SS355
RY1
DQ1U24VDC
12
34
+24V
VTH
CNTH-1
VTH
CNTH-2
VTH
CNTH-16MGCNTH-7MGCNTH-8MGCNTH-9
R112
22K
MG
+5V
CNTH-10
+5V
(1-1F)
CNTH-5
THI
THADI
C157
1
R185
20K
R187
470K
MG
C7
10/50
MG
MG
C10
R188
0
N.M.
(5-5I)
DG
C222
N.M.
MG
DG
+5V
MG
C156
1000P
MG
C131
1000P
DG
C102 1000P
DG
C103 1000P
DG
C101 1000P
DG
C100 1000P
C121
1000P
FO-70A
Video processing/Motor drive / Thermal block 5/6
6 – 5
Page 66

FO-50A
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
–
+
+5V
+5VA
+5V
–
+
–
+
+5VA
+5V
(1-1D)
RCVOL
TELOUT
CNLIUA-1
C192
1
R170
51K
C195
820P
R171
3.3K
1
2
3
IC7
2904
R172
15K
R154
100
N.M.
C179
Q2
RNC1402
R153
6.8K
R155
12K
C183
1
D2
1SS355
TELOUTI
(3-4H)
SIGTX
(3-4H)
TXOUT
CNLIUA-8
(3-3H)
SPOUT
6
4
5
2
3
1
7
8
+5V
R178
100K
C201
220P
R161
220K
C4
47/25
SP+
DG
SP–
CNSP-1
CNSP-2
(1-5A)
SPMUTE
C200
1
DG DG
(1-1F)
BZOUT
R177
1K
C206
4700P
R164
20K
RXIN
CNLIUA-7
C198
1
R175
118K
R156
0
7
6
5
R157
3.3K
R159
118K
C182
33P
DG
R160
0
C184
1
R158
N.M.
SIGRX
(3-4H)
CML
(1-5A)
Q4
TELIN
CNLIUA-2
C197
0.1
C194
0.022
R176
47K
RCVOL
(1-1D)
R173
30K
R174
Q3
RNC1402
DG
DG
C223
0.1
D3
1SS355
IC7
2904
DG DG
R179
100K
C204
0.01
R163
15K
C188
0.1
IC6
NJM2113
C186
1
(3-1D)
TXMUTE
DG
Q6
RNC1402
L109
0
DG
L110
0
+24VA
DG
C193
1
DG
8
4
N.M.
DG
C9
47/25
DG
DG
R181
1
C185
0
C203
C187
C199
N.M.
DG
FO-70A
Analog signal block 6/6
6 – 6
Page 67

Control PWB parts layout (Top side)
FO-50A
FO-70A
6 – 7
Page 68

FO-50A
FO-70A
Control PWB parts layout (Bottom side)
6 – 8
Page 69

FO-50A
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
–
+
+5VA
+5VA
–
+
+5VA
+24VA
+5V
VREF
+5V
–
+
VREF
+5V
–
+
VREF
L3B
R-5C
TLJ-2
CNLNJ-2
L4
JP13
JP10
JP8
CNLNJ-3
JP9
JP6
CNLNJ-4
VA2
RA-501P-V6
VA1
RA-501P-V6
ARG
CNLNJ-5
JP11
TLJ-1
JP12
L1
JP1
JP15
C102
L5
4.7mH
C101
L2
N.M.
N.M.
L3A
R-5C
JP3
N.M.
C
M
B
CML2
C3
0.56
R101
43K
R3
22K(1/2W)
D1
1SS133
ZD4
MTZJ20B
PC5
TLP521
R1
C1
0.33
R103
300
C2
1
N.M.
2
1
4
3
T1
I2164
C103
0.068
C116
N.M.
~
~
+
–
REC1
S1ZB60
CNLNJ-6
PC4
PC1
TLP627
PC2
TLP521
R104
10K
ZD1
MTZJ6R8B
R105
15K
C4
10/50
R102
15
R107
15
PC3
R106
D
G
S
Q1
BS108
R2
0
N.M.
ZD8
HZ2A1
ZD7
HZ2A1
JP4
C11
JP2
DG
+5V
C10
22/50
N.M.
R117
10
R129
620
JP14
C9
C127
0
C123
0.033
R133
470
7
6
5
R116
3.3K
DG
C115
R115
220K
IC102
2904
R114
10K
TXOUT
CNLIUA-8
R137
6.8K
C125
0.1
R139
510
C126
0.022
R138
270
C124
0
C122
0
R134
22K
R140
22K
R141
47K
C120
820P
C121
1000P
R143
36K
2
3
1
IC102
2904
RXIN
CNLIUA-7
R142
3.3K
DG
8
4
DG
C112
0.1
C114
0.1
8
4
DG
IC101
2904
IC102
2904
R111
20K
R113
20K
R112
1K
C7
10/50
DGDG
CNHJ-4
CNHJ1-4
CNHJ-1
CNHJ1-1
TX+
TX–
C104
0.01
CNHJ1-2
CNHJ-2
CNHJ1-3
CNHJ-3
RX+
RX–
L8
R-5C
R108
1.5K
R109
1K
C6
22/50
DG
C105
0.01
DG
C106
0.01
R110
15K
ZD5 ZD6
N.M.
C108
2700P
R114
43K
C109
220P
R131
3.3K
C113
1000P
C8
C107
1000P
DGDGDG
N.M.
IC101
2904
1
2
3
R130
0
TELOUT
CNLIUA-1
D3
1SS133
D2
1SS133
DG
L7
R-5C
L6
R-5C
C5
4.7/50
R123
150
R124
2.2K
DG
DG
R125
3.3K
DG
7
6
5
IC101
2904
C111
1000P
R126
82K
C14
N.M.
TELIN
CNLIUA-2
R127
24K
R128
8.2K
TELMUTE
CNLIUA-3
R132
0
DG
Q107
RNC1402
JP7
AR1
DSS301L
ZD2
MTZJ30B
DG
Q101
2SC2412K
JP5
ZD3
0
N.M.
N.M.
NOTE:
These marks are all satety-cirtical parts.
N.M.
N.M.
N.M.
N.M.
N.M.
JP18
N.M.
JP17
N.M.
JP16
N.M.
N.M.
N.M.
N.M.
N.M.
FO-70A
[2] TEL/LIU PWB circuit 1/2
6 – 9
Page 70

FO-50A
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
+5V
DPON
CNLIUB-3
DPMUTE
CNLIUB-4
E-RLY
CNLIUB-5
R119
470
PC1
TLP627
Q105
RNC1402
DG
Q106
RNC1402
DG
Q108
DG
R120
470
R121
PC2
TLP521
PC4
CI
CNLIUA-4
R122
100K
DGDG
C110
0.1
PC5
TLP521
HS
CNLIUA-5
R136
DGDG
C119
PC3
N.M.
N.M.
RHS
CNLIUA-6DGCNHS-1
CNHS-2
SW1
HOOK SW
CNLIUA-10
+5V
CNLIUA-11DGCNLIUA-12
+24V
R118
10
C13
100/50
C12
100/50
C117
0.1
C118
0.1
+5VA
DG
+24VA
R135
1K
CNLIUA-9
CML
D4
1SS133
DG
Q104
RNC1402
CML
NOTE:
These marks are all satety-cirtical parts.
FO-70A
TEL/LIU PWB circuit 2/2
6 – 10
Page 71

TEL/LIU PWB parts layout (Top side)
FO-50A
FO-70A
6 – 11
Page 72

FO-50A
FO-70A
TEL/LIU PWB parts layout (Bottom side)
6 – 12
Page 73

FO-50A
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
D7
S3L20U-4004P15
C13
T1
PTTP124
FB1
R11
39
ZD7
RD20ESAB
PC2
PC123YS
Q5
2SC4210
R21
150K
Q6
2SC4210
R12
180K
ZD4
RD30FB
R20
4.7K
IC1
UPC29M05AHF
R19
4.7K
L3
JUMPER
F3
CCP2E100(4A)
R25
10K
C16
100/10
C9
0.47
R16
22K
C12
0.1
R15
330K
R14
1.5K
R13
4.7K
PC1
PC123YS
R18
27K
Q4
2SC2412K
ZD5
RD6.2SB
VR1
1K
R17
8,2K
C10
2200/16
D8
SR140
N.M.
D9
C23
R24
ZD6
L2
RS208
R4
330
C4
2200P
PC2
PC123YS
ZD2
RD2.0SB
C6
0
D5
1SS355
PC1
C17
1000P
C24
0.22
R7
33
D6
R2
R3
Q1
FS5KM
C3
1000P
ZD1
RD27SB
Q2
2SD2114K
Q3
2SC2412K
R9
470
R10
0.33
R8
47K
C7
3900P
F2
1.6A/250V
CN1
F1
1.6A/250V
C1
0.22
R1
3.3M
1
2
V1
ERZV07D471
L1
ELF15N003A
C15
2200P
D3
D4
C21
D2D1
TH1
89.2
N.M.
N.M.
CN2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
DG
+5V
MG
MG
+24V
+24V
DG
PSAVE
C2
68/400
C8
560/35
*R5
1.5K
*R6
18K
*:ADJUSTMENT RESISTOR
ERA15-06 x 4
CH2 W1
450V
5.02ms
-50V
-4.9Sms
GND
50V/div
1ms/div
CH2 W1
1200V
25.00us
-800V
-25.00us
GND
200V/div
5us/div
CH2 W1
100.0V
25.00us
-100.0V
-25.00us
GND
20V/div
5us/div
CH2 W1
50.0V
25.00us
-50.0V
-25.00us
GND
10V/div
5us/div
CH2 W1
50.0V
25.00us
-50.0V
-25.00us
GND
10V/div
5us/div
FO-70A
[3] Power supply PWB circuit
6 – 13
Page 74

FO-50A
FO-70A
Power supply PWB parts layout (Top side)
C8
C13
J7
D7
D8
FB1
C10
IC1
J5
ZD7
L3
C16
ZD4
CN2
1
T1
R3
Q1
C3
C21
J4
R2
TH1
JW1
D4
R10
C2
L1
V1
C15
C1
D3
D1
D2
J6
F2
R1
F1
CN1
2
1
D9
J3
ZD6
R24
L2
C7
VR1
PC2
C24
J1
J11
PC1
J10
8
C9
J12
Power supply PWB parts layout (Bottom side)
ZD1
R8R9Q3
D6
R6
D5
C6
R5
C5
R7
ZD2
Q2
C4R4
C17
C23
R13
Q5
R14
R21
R18
C12
Q4
R15
ZD5
Q6
R12
R19
R17
R11
R20
F3
R16
R25
6 – 14
Page 75

FO-50A
1
2
6
4
3
5
BDEFG
I
HCA
BDEFG
I
HCA
1
2
6
4
3
5
LD4
D4
1SS270
CNLCD-11
CNPN-5
LD5
D3
1SS270
CNLCD-12
CNPN-6
123
456
VOLUME
SEN0
SEN1
LD6
D2
1SS270
CNLCD-13
CNPN-7
789
FUNC
SEN2
LD7
D5
1SS270
CNLCD-14
CNPN-8
0
#
RESO/MODE
SEN3
RS
D1
1SS270
CNLCD-4
CNPN-3
03
01
SEN4
02 04
D6
1SS270
CNPN-9
STOP
05
SEN5
START COPY
D7
1SS270
CNPN-10
HOLD
REDIAL
SEN6
SPEED SPEAKER
D8
CNPN-11
PLAY
REC
SEN7
REPEAT DELETE
CNPN-16
KEN1A
CNPN-15
KEN2A
CNPN-14
KEN3A
CNPN-13
KEN4A
N.M.
CNPN-12
ORGSNS
ORGSNS
DG
SW-169-72AU
CNLCD-6
E
CNPN-4
E
CNLCD-2
+5V
CNPN-2
+5V
CNLCD-1
DG
CNPN-1
DG
CNLCD-5
R/W
CNLCD-3
VO
DG
C2 C1
R1
1K
R2
6.2K
12345678910
11 12
13 14
15 16
CNPN
DG
SEN4
SEN0
SEN2
SEN5
SEN7
KEN4A
KEN2A
E
SEN1
SEN3
SEN6
ORGSNS
KEN3A
KEN1A
+5V
12345678910
11 12
13 14
CNLCD
DGVOR/W
N.C.
N.C.
LD4
LD6
RSEN.C.
N.C.
LD5
LD7
+5V
ORGSNS
N.M.
NOTE: Since the parts of PWB cannot be supplied, change it as a unit.
FO-70A
[4] Operation panel PWB circuit
6 – 15
Page 76

FO-50A
FO-70A
CHAPTER 7. OPERATION FLOWCHART
[1] Protocol
Receive side
G3 communication
Transmitter side
(Document inserted into
document sensor during
standby)
To recording
position
CED
NSF
CSI
DIS
(DCS)
CFR
TSI
NSS
TCF
IMAGE
SIGNAL
TSI
NSS
TCF
IMAGE
CED
NSF
CSI
DIS
Document inserted to
the reading position
(DCS)
CFR
1st page
SIGNAL
Cut line printed
Cut line printed
MCF
MCF
RTC
MPS
IMAGE
RTC
EOP
SIGNAL
RTC
MPS
IMAGE
RTC
EOP
Next page insert
command
MCF
SIGNAL
MCF
DCN
DCN
Document ejectedRecording papor ejected
7 – 1
Page 77

[2] Power on sequence
FO-50A
FO-70A
START
CPU initialized
MODEM initialized
“WAIT A MOMENT” display
STOP key ?
NO
“MEMORY CLEAR ?” display
YES
1
YES
2
YES
START key ?
NO
COPY key ?
NO
STOP key ?
NO
3 sec ?
YES
STAND-BY
NO
3 sec ?
YES
STAND-BY
“MEMORY CLEARED” display
Memory clear
STAND-BY
NO
21
“MEMORY CLEARED” display
Memory clear
PROCESS CHECK MODE
7 – 2
Page 78

FO-50A
FO-70A
CHAPTER 8. OTHERS
[1] Service tools
1. List
NO. PARTS CODE DESCRIPTION Q’TY
1 C P W B S 3 0 4 5 S C S 1 Extension board unit (Control PWB) 1AR
2 P S H E Z 3 3 5 4 S C Z Z Shading wave memory standard paper 1AD
Extension board unit
PRICE
RANK
EXTENSION CONTROL PWB
C17
DG1
PESNS
R145
(BOTTOM
C
E
PI2
A
K
SIDE)
PI1
A
K
E
C
PSNS
NO. PARTS CODE DESCRIPTION Q’TY
1 C C N W – 4 7 5 6 S C 0 1 SPEAKER RELAY CABLE 1AK
2 C C N W – 4 7 5 8 S C 0 1 CIS RELAY CABLE 1AQ
3 C C N W – 4 7 5 9 S C 0 1 HEAD RELAY CABLE 1AX
4 C C N W – 4 7 6 0 S C 0 1 CAM SWITCH RELAY CABLE 1AK
5 C C N W – 4 7 6 1 S C 0 1 FRONT SENSOR RELAY CABLE 1AK
6 C C N W – 4 7 6 3 S C 0 1 MOTOR RELAY CABLE 1AP
7 Q C N W – 4 9 6 9 S C Z Z SENSOR RELAY CABLE 1BF
8 C C N W - 2 7 4 A S C 0 1 PANEL RELAY CABLE 1AU
9 C C N W - 2 7 5 A S C 0 1 DOOR SWITCH RELAY CABLE 1AL
10 C C N W - 2 7 6 A S C 0 1 CUTTER RELAY CABLE 1AH
11 V R S – T S 2 A D 1 0 2 J RESISTOR (1/10W 1KΩ ±5%)[R145
12 V H P S G 2 0 6 S / / –1 PHOTO TRANSISTOR [PI1
13 V H P S G 2 0 6 S / / –1 PHOTO TRANSISTOR [PI2
]
]
]
PRICE
RANK
1AA
1AG
1AG
8 – 1
Page 79

2. Description
2-1. Relay board unit
1. Remove the TEL/LIU PWB, control PWB and Power Supply PWB
from this unit, and mount the relay board unit instead.
• Before connecting the wiring to the relay board unit, set the test
PWB switches to the fixed position.
2. The setting is as follows.
• The relay cables are used as one pair.
Relay
cable
• The cover swich and hook switch are manually operated.
FO-50A
FO-70A
CNLIUA
CNLIUB
CNPW
CHECK
CONTROL
PWB
NOTE
12
The recording paper sensor (PI1) and the hook switch are operated by
OR of the mechanical unit switch and the test PWB switch. When
1
1
CNLIUA
TEL/LIU
PWB
1
CNLIUB
5
CN2
UNIT
POWER
SUPPLY
PWB
DON'T SEPARATE
RELAY CABLE
performing installation in the machine unit, set the test PWB switches to
the fixed position.
Mechanical unit PWB to be tested
Actual operation with mechanical unit
Recording paper
sensor
Hook SW
Recording paper
sensor
Hook SW ON-HOOK
* Recording paper: ON
No recording paper: OFF
ON/OFF operation
ON/OFF operation
PWB sensor check
OFF
CHECK
CONTROL
PWB
TEL/LIU
PWB
OFF (Photo interrupter
is interrupted.)
ON-HOOK
ON/OFF operation
ON/OFF operation
TO
EXTENSION
PWB
+24V(C17(+side))
DG(DG1)
PESNS
PSNS
Not used
Not used
SENSOR RELAY CABLE (QCNW-4969SCZZ)
WHITE
BLACK
BROWN
RED
ORANGE
YELLOW
8 – 2
POWER
SUPPLY
PWB
TO
CHECK
PWB
Page 80

FO-50A
FO-70A
3. Shading paper
The white and black basis is applied to remember the shading waveform. Be sure to perform this operation when replacing the battery or
replacing the control PWB. Execute in the shading mode of DIAG mode.
UX-108 SERIES SHADING WAVE MEMORY STANDARD PAPER (PSHEZ3354SCZZ)
8 – 3
Page 81

[2] IC signal name
3
2
1
1 2
3
VIN
VOUT
VSS
VREF
VIN
VOUT
VSS
3
1
–
+
2
1
2
3
VIN VOUT
VSS
VIN
VOUT
VSS
CURRENT
LIMITER
PEFERENCE VOLTAGE
SOURCE
CONTROL PWB UNIT
IC101: VHiXC61AN45M1 (XC61AN4502ML)
FO-50A
FO-70A
REG100: VHi62FP332P-1 (XC62FP3302P)
8 – 4
Page 82

FO-50A
FO-70A
IC3: VHiW24258S7LE (W24258S-70LE)
IC5: VHiW27E010-12 (27E010)
ROM
A14
A12
I/O1
I/O2
I/O3
VSS
(TOP VIEW)
1
2
3
A7
4
A6
5
A5
6
A4
7
A3
8
A2
9
A1
10
A0
11
12
13
14
28
VDD
27
WE
26
A13
25
A8
24
A9
23
A11
22
OE
21
A10
20
CS
19
I/O8
18
I/O7
17
I/O6
16
I/O5
15 I/O4
Pin name
A0~A14
CS
WE
OE
I/O1~I/O8
VDD
VSS
VPP
A16
A15
A12
Signal
Address input
Chip select input
Write enable input
Output enable input
Data I/O
Power source
Ground
DQ1
DQ2
DQ3
GND
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
(TOP VIEW)
32
VCC
31
PGM
30
A17
29
A14
28
A13
27
A8
26
A9
25
A11
24
G
23
A10
22
E
21
DQ8
20
DQ7
19
DQ6
18
DQ5
17
DQ4
Pin name
A0~A17
DQ1~DQ8
(*) Only in the program mode
Address input
E
Chip enable
G
Output enable
GND
Ground
PGM
Program
Data output (Program input)
VCC
+5V power
VPP
+12.5V power(*)
Signal
IC1: VHiTC7WT74FU1 (TC7WT74)
1
CK
2
D
3
Q
4
GND
IC8: VHiULN2003AN/ (ULN2003ANS)
1C 2C 3C 4C 5C 6C 7C COM
16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9
IC6: VHiNJM2113M-1 (NJM2113M)
8
VCC
7
PR
CD
FC2
FC1
6
CLR
VIN
5
Q
1
2
3
4
8
VO2
7
GND
6
VCC
5 VO1
(TOP VIEW)
12345678
1B 2B 3B 4B 5B 6B 7B E
8 – 5
Page 83

IC2: VHiFC2FM209-1 (FC200)
D0D1D2D3VDDD4D5D6D7
142
143
141
A23
A22
A21
A20
A19
A18
VSS
A17
A16
A15
A14
A13
A12
VDD
A11
A10
VSS
VSS
PCLK/DMAACK
PDAT
PLAT 31
VDD 32
STRB3 33
STRB2 34
STRB1 35
STRB0
144
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
A9
18
A8
19
A7
20
A6
21
22
A5
23
A4
24
A3
25
A2
26
A1
27
A0
28
29
30
36
140
139
138
137
136
MIRQN
135
VSS
134
SYSCLK
VSS
133
132
RESETN
TSTCLK
131
130
RDN
DEBUGN
129
128
WRN
127
SYNC
126
WAITN
125
REGDMA
VDD
124
123
CS1N
122
MCSN
121
ROMCSN
TONE
120
119
PM0/GPO0
PM1/GPO1
118
117
PM2/GPO2
PM3/GPO3
116
115
VDRAM
114
RASN
113
CAS0N
112
CAS1N
111
CAS2N
110
DWRN
109
FO-50A
FO-70A
108
VSS
107
GPIO20/ALTTONE
106
SM0/GPO4
105
SM1/GPO5
104
SM2/GPO6
103
SM3/GPO7
102
VDD
START
101
CLK1
100
CLK1N
99
CLK2
98
FCS2N/VIDCTL1
97
FCS1N/VIDCTL0
96
VSS
95
GPIO0
94
GPIO1/SASTXD
93
GPIO2/SASRXD
92
GPIO3/SASCLK
91
GPIO4/CPCIN
90
GPIO5/SSCLK2
89
VSS
88
GPIO6/SSTXD2
87
GPIO7/SSRXD2
86
GPIO8/FWRN
85
GPIO9/FRDN
84
GPIO10/SSSTAT2
83
GPIO11/BE/SERINP
82
VDD
81
GPIO12/CS2N80
GPIO13/CS3N79
GPIO14/CS4N78
GPIO15/CS5N77
GPIO16/IRQ876
GPIO1775
GPIO18/IRQ9N74
GPIO19/RDY/SEROUT73
373839
STRBPOL
OPO7/GPO15
40414243444546
VDD
OPO6G/PO14
OPO5/GPO13
OPO3/GPO11
OPO4/GPO12/SSTXD1
47
48
VSS
OPO2/GPO10/RINGER
VDD
OPO1/GPO9/PMPWRCTRL
OPO0/GPO8/SMPWRCTRL
51
49
OPI3/GPIO24
52
50
OPI1/GPIO22/SSTAT1
OPI2/GPIO23/SSCLK1
OPI0/GPIO21/SSRXD1
53
54
VSS
VCDCS/GPIO17
8 – 6
55
56
57
VSS
CS0N
LEDCTL/GPIO16
58
TEST
59
XIN
60
XOUT
61
62
BATRSTN
PWRDWNN
63
VBAT
64
VSS
65
66
THAD1
–VREF/CLREF
67
VIN
69
ADXG68ADGA
70
ADVA
71
+VREF
72
ADGD
Page 84

FO-50A
FO-70A
IC4: VHiFC2FM209-1 (FM209)
RESERVED
128
1SR4IN1/RESERVED2
2SR3OUT1/RESERVED2
3EYESYNC
4EYECLK
5RXD
6SR1IO
7NC
8EYEXY
9SR4OUT
10VDD1
11RLSD#
12DCLK
13EN85#
14GPI0
15RTS#
16DGND1
17TXD
18SA1CLK
19RS4
20RS3
21RS2
22RS1
23RS0
24YCLK
25IACLK
26IA1CLK
27CTRLSIN_S1/NC2
28RESERVED1/NC2
29SOUT_S1/NC2
30SIN_S1/NC2
31FSYNC_S1/NC2
32IARESET_S1/NC2
33AGND1
34LINEIN_S1/NC2
35MICP_S1/NC2
36MICM_S1/NC2
37MICBIAS_S1/NC2
38NC
39
AGND5
DVAA
126
127
41
RESERVED
DGND6
124
125
42
43
RESERVED
SR3IN
IRQ2#
121
122
123
44NC45
GPI1
120
47
RESERVED
XCLK
118
119
48
49
XTLO
117
50
XTLI
116
51
RESET#
DGND5
114
115
53
VGG
113
54
VDD5
112
GPO0
111
GPO1
110
GPO2
109
58
IRQ1#
108
CTS#
107
DGND4
GPO3
105
106
RESERVED
GPO4
103
104
102 GPO5
101 GPO6
100 VDD4
99 GPO7
98 GPI7
97 GPI6
96 GPI5
95 GPI4
94 GPI3
93 GPI2
92 READ#
91 CS#
90 WRITE#
89 CSBR#3/RESERVED2
88 D0
87 DGND3
86 D1
85 VDD3
84 DGND2
83 D2
82 D3
81 D4
80 D5
79 D6
78 D7
77 VDD2
76 MCLK_S1/NC2
75 ICLK_P
74 NC
73 AVDD_P
72 SPKRM_P
71 SPKRP_P
70 AGND4
69 LINEOUT_P
68 VAA_P
67 VC_P
66 VREF_P
65 NC
64
NC40VREF_S1/NC2
NOTES:
1 FOR -S OPTIONS
2 FOR ALL OTHER OPTIONS
3 FOR -R OPTIONS
VC_S1/NC2
VAA_S1/NC2
LINEOUT_S1/NC2
AGND246SPKRP_S1/NC2
SPKRM_S1/NC2
AVDD_S1/NC2
RESERVED1/NC2
ICLK_S1/NC2
MCLK_P52CTRLSIN_P
RESERVED
8 – 7
SOUT_P55SIN_P56FSYNC_P57IARESET_P#
AGND359NC60LINEIN_P61MICP_P62MICM_P63MICBIAS_P
NC
Page 85

PARTS GUIDE
FO-50
MODEL FO-70
Non Cutter model Cutter model
FO-50 FO-70
FO-50A
FO-70A
1 Cabinet, etc.
2 Scanner unit
3 Upper cabinet
4 Document guide upper
5 Drive unit (Non cutter model)
(FO-50)
CONTENTS
6 Drive unit (Cutter model)
(FO-70)
7 Packing material & Accessories
8 Control PWB unit
9 TEL-Liu PWB unit
10 Power supply PWB unit
Index
Because parts marked with " " is indispensable for the machine safety maintenance and operation, it must be
replaced with the parts specific to the product specification.
Page 86

FO-50A
FO-70A
[1] Cabinet, etc.
49
46
(CUTTER MODEL)
27
25
26
(NON CUTTER MODEL)
B7
B3
DOCUMENT
GUIDE UPPER
(NON CUTTER MODEL)
25
30
41
54
RELEASE
53
58
2
SCANNER
UNIT
39
B3
1
2
11
7
9
8
B3
B3
47
B7x2
22
5
6
B1
B3
B7x2
DRIVE
UNIT
(CUTTER MODEL)
50
43
42
48
B6
51
57
B7
B3
14
B3
B3
36
B4
28
43
DRIVE
UNIT
14
29
(CUTTER
MODEL)
38
44
B3
62
35
B3
45
34
37
31
B4
33
34
32
28
(NON CUTTER MODEL)
B3
B3
B3
15
12
13
B3
53
39
40
52
27
19
B4
17
40
59
18
16
24
23
61
56
60
B4
B5
20
21
55
– 1 –
B3x2
Page 87

FO-50A
FO-70A
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[1] Cabinet etc.
1 DCEKP481BXH05 AP N E Operation panel unit
2 CCNW-212AXH01 AK N C Panel cable ass’y
5 MSPRC2954XHZZ AC C Hopper spring
6 NGERP2318XHZZ AD C Pinion gear
7 PGIDM2560XHSD AE N C Hopper,guide,left
8 PGIDM2561XHSD AC N C Hopper,guide,right
9 PHOP-2104XHSD AF N C Hopper cover
11 QSW-M2296XHZZ AD B Door sensor
12 CCNW-215AXH01 AG N C Speaker ass’y
13 GCABB2343XHSC AK N D Lower cabinet
14 MSPRP3119XHZZ AC N C Panel lock lever spring
15 MSPRP3123XHZZ AC N C Speaker holder lever spring
16 DCEKL483BXH06 BD N E TEL/Liu PWB unit
17 GCASP2110XHSE AK N C PWB case,top
18 GCASP2111XHSC AH N C PWB case,bottom
19 MLEVP2320XHZZ AC N C Hook switch joint lever
20 QACCL2045XHZZ AR N B AC cord ass’y
21 RDENT2144XHZZ BA N E Power supply PWB unit
!
22 GDAI-2083XHZZ AF N C Paper support guide
23 MLEVP2316XHZZ AC N C Paper sensor lever
24 MSPRD3116XHZZ AB N C Paper sensor lever spring
25 MSPRT3114XHZZ AC N C Pinch roller spring [70]
26 NROLP2426XHZZ AC N C Pinch roller [70]
27 PGIDM2563XHSC AC N C PO guide [50]
PGIDM2559XHSC AE N C PO guide [70]
28 LBSHP2112XHZZ AB N C Platen bearing
29 LFRM-2208XHZZ AF N C Head frame
30 LHLDZ2184XHZZ AC N C Head holder,left
31 LHLDZ2185XHZZ AC N C Head holder,right
32 MLEVP2315XHZZ AC N C Document sensor lever [70]
33 MSPRC3112XHZZ AC N C Head spring 1
34 MSPRC3148XHZZ AC N C Head spring 2
35 MSPRD3115XHZZ AB N C Document sensor lever spring [70]
36 NGERH2478XHZZ AB N C Platen gear
37 NROLR2425XHZZ AP N C Platen roller
38 PGIDM2558XHZZ AD N C Cutter guide upper [70]
39 QCNW-209AXHZZ AH N C Head cable
40 QCNW-210AXHZZ AC N C Head earth cable
41 RHEDZ2059XHZZ BF N B Thermal head
42 NROLR2427XHZZ AC N C PO roller [70]
43 PGUMR2168XHZZ AF N C PO roller rubber [70]
44 PGIDM2564XHZZ AD N C PO roller guide [70]
45 DCEKC686MXHZZ BP N E Control PWB unit(Within ROM) [50]
DCEKC684MXHZZ BP N E Control PWB unit(Within ROM) [70]
46 GDAI-2082XHSD AD N C Handset cover
47 LSTPP2054XHZZ AC N C Panel stopper
48 MARMP2023XHZZ AB N C Cutter arm [70]
49 MLEVP2319XHZZ AC N C Hook switch lever
50 NGERH2477XHZZ AC N C PO gear [70]
51 PCUT-2040SCZZ AV N C Cutter [70]
52 PGIDM2566XHZZ AC N C Head guide
53 RCORF2125XHZZ AE B Core(TRA31)
!
54 HPNLH2392XHS3 AE N D Decoration panel [50]
HPNLH2392XHSR AE N D Decoration panel [70]
55 LBNDJ2006XHZZ AA C Band(100mm)
56 PSHEZ3410XHZZ AB C Jack sheet
57 MSPRD3169XHZZ AD N C Cutter arm spring [70]
58 MLEVP2321XHZZ AN N C Release lever [50]
59 TLABS389AXHZZ AD N D New Zealand label [50]
TLABS388AXHZZ AD N D New Zealand label [70]
60 TLABS4335XHZZ AD D AUSSIE label
61 TLABZ3418XHZZ AA D Telephone set label
62 PCUSU2132XHZZ AC N C Cutter cushion
B1 LX-BZ2138XHZZ AB C Screw(2x6)
B3 XEBSD30P08000 AA C Screw(3x8)
B4 XBBSD30P06000 AA C Screw(3x6)
B5 XBPSN40P06K00 AA C Screw(4x6)
B6 XHBSD30P06000 AA C Screw(3x6) [70]
B7 XEBSD30P12000 AA C Screw(3x12)
– 2 –
Page 88

FO-50A
FO-70A
[2] Scanner unit
20
16
19
15
13
12
5
20
15
1
10
11
8
2
2
19
16
7
9
20
15
17
5
1
16
16
6
15
2
3
6
14
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
[2] Scanner unit
1 LBSHP2110XHZZ AB N C Back roller bearing
2 LFRM-2209XHZZ AF N C Scanner frame
3 LHLDZ2180XHZZ AC N C CIS support,left
4 LHLDZ2181XHZZ AC N C CIS support,right
5 MLEVP2317XHZZ AB N C CIS release lever
6 MSPRC3117XHZZ AB N C CIS spring
7 NGERH2479XHZZ AB N C Back roller gear
8 NGERH2480XHZZ AB N C Reduction gear,17/28Z
9 NGERH2481XHZZ AB N C Reduction gear,17/23Z
10 NROLR2375XHZZ AL C Feed roller
11 NROLR2428XHZZ AP N C Back roller
12 NSFTZ2273XHZZ AF C Feed roller shaft
13 PGIDM2562XHZZ AD N C Document guide lower
14 PSHEZ3436XHZZ AC C CIS protect sheet
15 QCNW-4814XHZZ AG N C CIS cable
16 QCNW-213AXHZZ AC N C Front sensor cable
17 QSW-M2293XHZZ AE N B Front sensor
18 RUNTZ2054XHZZ BE N B CIS unit
19 LBNDJ2006XHZZ AA C Band(100mm)
20 RCORF2123XHZZ AD N B Core
!
19
18
4
DESCRIPTION
– 3 –
Page 89

[3] Upper cabinet
FO-50A
FO-70A
6
5
3
1
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
[3] Upper cabinet
1 CCNW-212AXH01 AK N C Panel cable ass’y
3 GCABA2342XHSC AH N D Upper cabinet
4 JBTN-2257XHSD AD N C 12 key
5 JBTN-2258XHSC AC N C Start key
6 JBTN-2261XHSC AC N C Direct key
7 DCEKP482BXH01 AQ N E Operation panel PWB unit
B2 XUBSD20P06000 AA C Screw(2x6)
901 DCEKP481BXH05 AP N E Operation panel unit
(Unit)
4
7
B2x3
DESCRIPTION
[4] Document guide upper
NO.
PARTS CODE
[4] Document guide upper
1 LPLTG2911XHZZ AE C Separator rubber
2 LPLTP2908XHZZ AE C Separator plate
3 LPLTP3051XHZZ AB N C Feed plate
4 MSPRT3140XHZZ AA N C Separate spring
5 MSPRT3139XHZZ AA N C Feed spring
6 PGIDM2554XHZZ AF N C Document guide upper
7 PSHEZ3517XHZZ AE N C Blind sheet [50]
PSHEZ3510XHZZ AE N C Blind sheet [70]
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
3
2
5
4
1
6
7
DESCRIPTION
– 4 –
Page 90

FO-50A
FO-70A
[5] Drive unit (Non cutter model) (FO-50)
22
B3
2
20
21
12
17
12
1
9
6
9
5
13
15
10
4
12
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
[5] Drive unit(Non cutter model)(FO-50)
1 LFRM-2207XHZZ AF N C Drive unit frame
2 LPLTM3049XHZZ AD N C Motor plate
4 MCAMP2027XHZZ AC N C Cam
5 MLEVP2311XHZZ AB N C Planet lever A
6 MLEVP2312XHZZ AB N C Planet lever B
8 MLEVP2314XHZZ AB N C Mode lever
9 MSPRC2735XHZZ AC C Planet gear spring
10 MSPRC3110XHZZ AB N C Cam spring
12 NGERH2278XHZZ AC C Planet gear
13 NGERH2379XHZZ AC C Idler gear,25Z
15 NGERH2391XHZZ AC C Reduction gear,17/30Z
17 NGERH2475XHZZ AB N C Reduction gear,17/43Z
20 QCNW-4933XHZZ AC C Cam switch cable
21 QSW-F2224SCZZ AE B Cam switch
22 RMOTZ2148XHZZ AT N B Motor
B3 XEBSD30P08000 AA C Screw(3x8)
9
8
DESCRIPTION
– 5 –
Page 91

[6] Drive unit (Cutter model) (FO-70)
22
FO-50A
FO-70A
19
B3
21
18
2
10
20
13
17
12
21
12
6
9
9
5
11
1
14
15
15
3
16
13
13
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
[6] Drive unit(Cutter model)(FO-70)
1 LFRM-2206XHZZ AF N C Drive unit frame
2 LPLTM3049XHZZ AD N C Motor plate
3 LPLTP3050XHZZ AB N C Cutter plate
4 MCAMP2027XHZZ AC N C Cam
5 MLEVP2311XHZZ AB N C Planet lever A
6 MLEVP2312XHZZ AB N C Planet lever B
7 MLEVP2313XHZZ AC N C Planet lever C
8 MLEVP2314XHZZ AB N C Mode lever
9 MSPRC2735XHZZ AC C Planet gear spring
10 MSPRC3110XHZZ AB N C Cam spring
11 MSPRC3127XHZZ AB N C Cutter gear spring
12 NGERH2278XHZZ AC C Planet gear
13 NGERH2379XHZZ AC C Idler gear,25Z
14 NGERH2380XHZZ AC C Reduction gear,17/36Z
15 NGERH2391XHZZ AC C Reduction gear,17/30Z
16 NGERH2451XHZZ AB C Idler gear,30Z
17 NGERH2475XHZZ AB N C Reduction gear,17/43Z
18 NGERH2476XHZZ AB N C Cutter gear
19 QCNW-207AXHZZ AC N C Cutter cable
20 QCNW-4933XHZZ AC C Cam switch cable
21 QSW-F2224SCZZ AE B Cam switch
22 RMOTZ2148XHZZ AT N B Motor
B3 XEBSD30P08000 AA C Screw(3x8)
12
9
4
DESCRIPTION
12
9
7
8
– 6 –
Page 92

FO-50A
FO-70A
[7] Packing material & Accessories
2
23
FAX PAPER
24
7
TAPE
6
TAPE
R
25
8
TAPE
27
ORIGINAL DOCUMENT
SUPPORT SIDE
5
26
21
17
16
1
TAPE
AC CORD
3
9
4
18
(2)
(3)
(4)
(1)
22
10
11
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[7] Packing material & Accessories
1 TINSE4028XHZZ AL N D Operation manual
2 DUNTK204CXHPU AH N E Handset
3 QCNW-3976XHOW AK C Handset cord
4 PHOP-2105XHZZ AD N C Original document support
5 QCNWG0376AFZZ AM C Telephone line cord
6 SPAKP296BXHZZ AE N D Vinyl cover
7 SPAKA287BXHZZ AE N D Packing add.,left
8 SPAKA288BXHZZ AE N D Packing add.,right
9 SPAKA289BXHZZ AC N D Pad
10 SPAKC324BXHZZ AH N D Packing case [50]
SPAKC329BXHZZ AH N D Packing case [70]
11 TLABM320BXHZZ AD N D Box label [50]
TLABM324BXHZZ AD N D Box label [70]
16 PGIDM2578XHZZ AE N C Paper roll shim,right
17 PGIDM2579XHZZ AE N C Paper roll shim,left
18 NSFTZ2320XHZZ AF N C Paper shaft
21 TCADZ2264XHZZ AD D Installation card
22 TLABV363AXHZZ AC N D Bar cord label [50]
TLABV366AXHZZ AC N D Bar cord label [70]
23 TCADZ2935XHZZ AA N D Caution sheet
24 SPAKA388BXHZZ AE N D Protection sheet,left
25 SPAKA389BXHZZ AE N D Protection sheet,right
26 QPLGZ9065AFZZ AP C Australia plug
27 QCNWG0381AFZZ AM C New Zealand cable
– 7 –
Page 93

FO-50A
FO-70A
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[8] Control PWB unit
1 UBATL2046SCZZ AK B Battery(CR2032T34) [BAT1]
2 VCEAGA1HW106M AA C Capacitor(50WV 10µF) [C1]
3 VCEAGA1HW106M AA C Capacitor(50WV 10µF) [C2]
4 VCEAGA1EW476M AA C Capacitor(25WV 47µF) [C3]
5 VCEAGA1EW476M AA C Capacitor(25WV 47µF) [C4]
6 VCEAGA1HW226M AB C Capacitor(50WV 22µF) [C5]
7 VCEAGA1EW476M AA C Capacitor(25WV 47µF) [C6]
8 VCEAGA1HW106M AA C Capacitor(50WV 10µF) [C7]
9 VCEAGA1HW107M AA C Capacitor(50WV 100µF) [C8]
10 VCEAGA1EW476M AA C Capacitor(25WV 47µF) [C9]
11 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C100]
12 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C101]
13 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C102]
14 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C103]
15 VCCCTV1HH100D AA C Capacitor(50WV 10PF) [C104]
16 VCCCTV1HH120J AA C Capacitor(50WV 12PF) [C105]
17 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C106]
18 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C107]
19 VCKYTV1HB103K AB C Capacitor(50WV 0.01µF) [C108]
20 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C110]
21 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C111]
22 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C112]
23 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C113]
24 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C114]
25 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C115]
26 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C116]
27 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C117]
28 VCCCTV1HH680J AA C Capacitor(50WV 68PF) [C118]
29 VCCCTV1HH680J AA C Capacitor(50WV 68PF) [C119]
30 VCKYTV1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C120]
31 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C121]
32 VCKYTV1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C122]
33 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C123]
34 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C124]
35 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C125]
36 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C126]
37 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C127]
38 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C128]
39 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C129]
40 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C130]
41 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C131]
42 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C132]
43 VCCCTV1HH220J AA C Capacitor(50WV 22PF) [C133]
44 VCCCTV1HH220J AA C Capacitor(50WV 22PF) [C134]
45 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C135]
46 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C136]
47 VCKYTV1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C137]
48 VCKYTV1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C138]
49 VCKYTV1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C139][70]
50 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C140]
51 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C142]
52 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C143]
53 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C144]
54 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C145]
55 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C146]
56 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C147]
57 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C148]
58 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C149]
59 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C150]
60 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C151]
61 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C152]
62 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C153]
63 VCCCTV1HH220J AA C Capacitor(50WV 22PF) [C154]
64 VCCCTV1HH220J AA C Capacitor(50WV 22PF) [C155]
65 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C156]
66 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C157]
67 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C159]
68 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C160]
69 VCKYTV1EB104K AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C163]
70 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C164]
71 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C165]
72 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C166]
73 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C167]
74 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C168]
75 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C169]
76 VCKYTV1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C170]
77 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C171]
78 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C172]
79 VCCCTV1HH220J AA C Capacitor(50WV 22PF) [C173]
80 VCCCTV1HH180J AA C Capacitor(50WV 18PF) [C174]
– 8 –
Page 94

FO-50A
FO-70A
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[8] Control PWB unit
81 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C175]
82 VCCCTV1HH220J AA C Capacitor(50WV 22PF) [C176]
83 VCCCTV1HH220J AA C Capacitor(50WV 22PF) [C177]
84 VCCCTV1HH220J AA C Capacitor(50WV 22PF) [C178]
85 VCKYTV1HB222K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2200PF) [C180]
86 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C181]
87 VCCCTV1HH330J AA C Capacitor(50WV 33PF) [C182]
88 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C183]
89 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C184]
90 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [C185]
91 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C186]
92 VCKYTV1EB104K AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C188]
93 VCCCTV1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C189]
94 VCCCTV1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C190]
95 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C191]
96 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C192]
97 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C193]
98 VCKYTV1HB223K AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.022µF) [C194]
99 VCKYTV1HB821K AA C Capacitor(50WV 820PF) [C195]
100 VCCCTV1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C196]
101 VCKYTV1EB104K AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C197]
102 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C198]
103 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C200]
104 VCKYTV1HB221K AA C Capacitor(50WV 220PF) [C201]
105 VCCCTV1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C202]
106 VCKYTV1HB103K AB C Capacitor(50WV 0.01µF) [C204]
107 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C205]
108 VCKYTV1HB472K AA C Capacitor(50WV 4700PF) [C206]
109 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C207]
110 VCCCTV1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C208]
111 VCCCTV1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C209]
112 VCCCTV1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C210]
113 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C211]
114 VCCCTV1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C212]
115 VCCCTV1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C213]
116 VCCCTV1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C214]
117 VCKYTV1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C215]
118 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C216]
119 VCCCTV1HH101J AA C Capacitor(50WV 100PF) [C217]
120 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C218]
121 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C219]
122 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C220]
123 VCKYTV1CF105Z AB C Capacitor(16WV 1µF) [C221]
124 VCKYTV1EB104K AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C223]
125 QCNCM7014SC0G AB C Connector(7pin) [CNCIS]
126 QCNCM2442SC0B AB C Conector(2pin) [CNCSW]
127 QCNCM7014SC0C AA C Connector(3pin) [CNCUT][70]
128 QCNCM705BAF06 AB C Connector(2pin) [CNDR]
129 QCNCM7014SC0B AD C Connector(2pin) [CNFRS]
130 QCNCW2500SC1B AF C Connector(12pin) [CNLIUA]
131 QCNCW2500SC0D AG C Connector(4pin) [CNLIUB]
132 QCNCM7014SC0F AB C Connector(6pin) [CNMT]
133 QCNCM7014SC1F AD C Connector(16pin) [CNPN]
134 QCNCW2500SC0H AF C Connector(8pin) [CNPW]
135 QCNCM2401SC0B AA C Connector(2pin) [CNSP]
136 QCNCM7014SC1F AD C Connector(16pin) [CNTH]
137 VRS-HT3AA101J AA C Resistor(1W 100Ω ±5%) [D1]
138 VHD1SS355//-1 AB B Diode(1SS355) [D2]
139 VHD1SS355//-1 AB B Diode(1SS355) [D3]
140 VHD1SS355//-1 AB B Diode(1SS355) [D4]
141 VHDHRW0202B-1 AD C Diode(HRW0202B) [D5]
142 VHD1SS355//-1 AB B Diode(1SS355) [D6]
143 QFS-P2010SCZZ AD N B IC protector(KAB2402) [FU100]
144 VHITC7WT74FU1 AF N B IC(TC7WT74) [IC1]
145 VHIFC2FM209-1 BD N B IC(FC200)(Within IC2 and IC4 pair) [IC2]
146 VHIW24258S7LE AQ B IC(W24258S-70LE) [IC3]
147 VHIFC2FM209-1 BD N B IC(FM209)(Within IC2 and IC4 pair) [IC4]
148 QSOCZ2051SC32 AC C IC socket(32pin) [IC5]
VHI27010FZK0A BM N B IC,EPROM(1MB) [IC5][50]
VHI27010FZL0C BM N B IC,EPROM(1MB) [IC5][70]
150 VHINJM2113M-1 AG B IC(NJM2113) [IC6]
151 VHINJM2904M-2 AG B IC(NJM2904M) [IC7]
152 VHIULN2003AN/ AE B IC(ULN2003A) [IC8]
153 VHIXC61AN45M1 AE N B IC(XC61AN4502ML) [IC9]
154 RCILZ2145XHZZ AF C Coil(Z2145) [L100]
155 RCILZ2145XHZZ AF C Coil(Z2145) [L101]
156 RCILZ2145XHZZ AF C Coil(Z2145) [L102]
157 RCILZ2145XHZZ AF C Coil(Z2145) [L103]
158 RCILZ2145XHZZ AF C Coil(Z2145) [L104]
159 RCILZ2145XHZZ AF C Coil(Z2145) [L105]
– 9 –
Page 95

FO-50A
FO-70A
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[8] Control PWB unit
160 RCILZ2145XHZZ AF C Coil(Z2145) [L106]
161 RCILZ2145XHZZ AF C Coil(Z2145) [L107]
162 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [L108]
163 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [L109]
164 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [L110]
165 VHPSG206S//-1 AG B Photo transistor(SG206S) [PI1][70]
166 VHPSG206S//-1 AG B Photo transistor(SG206S) [PI2]
167 VS2SA1037KS-1 AB B Transistor(2SA1037KS) [Q1]
168 VSRNC1402//-1 AC B Transistor(RNC1402) [Q2]
169 VSRNC1402//-1 AC B Transistor(RNC1402) [Q3]
170 VS2SA1037KS-1 AB B Transistor(2SA1037KS) [Q5]
171 VSRNC1402//-1 AC B Transistor(RNC1402) [Q6]
172 VRS-TS2AD201J AG C Resistor(1/10W 200Ω ±5%) [R100]
173 VRS-TS2AD121J AA C Resistor(1/10W 120Ω ±5%) [R101]
174 VRS-TS2AD471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R102][70]
175 VRS-TS2AD471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R103]
176 VRS-TS2AD471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R104]
177 VRS-TS2AD333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R105][70]
178 VRS-TS2AD101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R106]
179 VRS-TS2AD101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R107]
180 VRS-TS2AD333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R108]
181 VRS-TS2AD333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R109]
182 VRS-TS2AD271J AA C Resistor(1/10W 270Ω ±5%) [R110]
183 VRS-TS2AD333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R111]
184 VRS-TS2AD223J AA C Resistor(1/10W 22KΩ ±5%) [R112]
185 VRS-TS2AD104J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100KΩ ±5%) [R113]
186 VRS-TS2AD104J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100KΩ ±5%) [R114]
187 VRS-TS2AD271J AA C Resistor(1/10W 270Ω ±5%) [R115]
188 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R116]
189 VRS-TS2AD271J AA C Resistor(1/10W 270Ω ±5%) [R117]
190 VRS-TS2AD471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R118]
191 VRS-TS2AD333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R119]
192 VRS-TS2AD151J AA C Resistor(1/10W 150Ω ±5%) [R120]
193 VRS-TS2AD471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R121]
194 VRS-TS2AD471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R122]
195 VRS-TS2AD333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R123]
196 VRS-TS2AD333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R124]
197 VRS-TS2AD333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R125]
198 VRS-TS2AD333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R126]
199 VRS-TS2AD223J AA C Resistor(1/10W 22KΩ ±5%) [R127]
200 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R128][50]
201 VRS-TS2AD471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R129]
202 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R130]
203 VRS-TS2AD103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R131]
204 VRS-TS2AD103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R132]
205 VRS-TS2AD333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R133]
206 VRS-TS2AD333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R134]
207 VRS-TS2AD333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R135]
208 VRS-TS2AD333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R136]
209 VRS-TS2AD103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R137]
210 VRS-TS2AD512J AA C Resistor(1/10W 5.1KΩ ±5%) [R138]
211 VRS-TS2AD471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R139]
212 VRS-TS2AD222J AA C Resistor(1/10W 2.2KΩ ±5%) [R141]
213 VRS-TS2AD102J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1.0KΩ ±5%) [R142]
214 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R143]
215 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R144]
216 VRS-TS2AD471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R145]
217 VRS-TS2AD471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R146]
218 VRS-TS2AD471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R147]
219 VRS-TS2AD512J AA C Resistor(1/10W 5.1KΩ ±5%) [R148]
220 VRS-TS2AD105J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1.0MΩ ±5%) [R149]
221 VRS-TS2AD103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R150]
222 VRS-TS2AD106J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10MΩ ±5%) [R151]
223 VRS-TS2AD121J AA C Resistor(1/10W 120Ω ±5%) [R152]
224 VRS-TS2AD682J AA C Resistor(1/10W 6.8KΩ ±5%) [R153]
225 VRS-TS2AD101J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100Ω ±5%) [R154]
226 VRS-TS2AD123J AA C Resistor(1/10W 12KΩ ±5%) [R155]
227 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R156]
228 VRS-TS2AD332J AA C Resistor(1/10W 3.3KΩ ±5%) [R157]
229 VRSTS2AD1183F AA C Resistor(1/10W 118KΩ ±1%) [R159]
230 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R160]
231 VRS-TS2AD224J AA C Resistor(1/10W 220KΩ ±5%) [R161]
232 VRS-TS2AD3R0J AA C Resistor(1/10W 3.0Ω ±5%) [R162]
233 VRS-TS2AD153J AA C Resistor(1/10W 15KΩ ±5%) [R163]
234 VRS-TS2AD203J AA C Resistor(1/10W 20KΩ ±5%) [R164]
235 VRS-TS2AD333J AA C Resistor(1/10W 33KΩ ±5%) [R165]
236 VRS-TS2AD433J AA C Resistor(1/10W 43KΩ ±5%) [R166]
237 VRS-TS2AD303J AA C Resistor(1/10W 30KΩ ±5%) [R167]
238 VRS-TS2AD103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R168]
239 VRS-TS2AD102J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1.0KΩ ±5%) [R169]
– 10 –
Page 96

FO-50A
FO-70A
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[8] Control PWB unit
240 VRS-TS2AD513J AA C Resistor(1/10W 51KΩ ±5%) [R170]
241 VRS-TS2AD332J AA C Resistor(1/10W 3.3KΩ ±5%) [R171]
242 VRS-TS2AD153J AA C Resistor(1/10W 15KΩ ±5%) [R172]
243 VRS-TS2AD303J AA C Resistor(1/10W 30KΩ ±5%) [R173]
244 VRSTS2AD1183F AA C Resistor(1/10W 118KΩ ±1%) [R175]
245 VRS-TS2AD473J AA C Resistor(1/10W 47KΩ ±5%) [R176]
246 VRS-TS2AD102J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1.0KΩ ±5%) [R177]
247 VRS-TS2AD104J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100KΩ ±5%) [R178]
248 VRS-TS2AD104J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100KΩ ±5%) [R179]
249 VRS-TS2AD203J AA C Resistor(1/10W 20KΩ ±5%) [R180]
250 VRS-TS2AD562J AA C Resistor(1/10W 5.6KΩ ±5%) [R184]
251 VRS-TS2AD203J AA C Resistor(1/10W 20KΩ ±5%) [R185]
252 VRS-TS2AD201J AG C Resistor(1/10W 200Ω ±5%) [R186]
253 VRS-TS2AD474J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470KΩ ±5%) [R187]
254 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R188]
255 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R189]
256 RR-TZ3018SCZZ AC C Block resistor(470Ωx4) [RA1]
257 RR-TZ3017SCZZ AC C Block resistor(270Ωx4) [RA2]
258 RR-TZ3017SCZZ AC C Block resistor(270Ωx4) [RA3]
259 RR-TZ3018SCZZ AC C Block resistor(470Ωx4) [RA4]
260 RR-TZ3018SCZZ AC C Block resistor(470Ωx4) [RA5]
261 RR-TZ3017SCZZ AC C Block resistor(270Ωx4) [RA6]
262 RR-TZ3017SCZZ AC C Block resistor(270Ωx4) [RA7]
263 RR-TZ3017SCZZ AC C Block resistor(270Ωx4) [RA8]
264 RR-TZ3018SCZZ AC C Block resistor(470Ωx4) [RA9]
265 RR-TZ3018SCZZ AC C Block resistor(470Ωx4) [RA10]
266 RR-TZ3018SCZZ AC C Block resistor(470Ωx4) [RA11]
267 RR-TZ3018SCZZ AC C Block resistor(470Ωx4) [RA12]
268 RR-TZ3017SCZZ AC C Block resistor(270Ωx4) [RA13]
269 RR-TZ3017SCZZ AC C Block resistor(270Ωx4) [RA14]
270 RR-TZ3018SCZZ AC C Block resistor(470Ωx4) [RA15]
271 RR-TZ3018SCZZ AC C Block resistor(470Ωx4) [RA16]
272 VHI62FP332P-1 AF B IC(XC62FP3302P) [REG100]
273 RRLYD3138XHZZ AG B Relay [RY1]
274 RCRSQ2157SCZZ AF B Crystal(32.256MHz) [X1]
275 RCRSB0297AFZZ AD B Crystal(32.768kHz) [X2]
901 DCEKC686MXHZZ BP N E Control PWB unit(Within ROM) [50]
DCEKC684MXHZZ BP N E Control PWB unit(Within ROM) [70]
(Unit)
[9] TEL/Liu PWB unit
1 VHVDSS301L/-U AF B Varistor(DSS-301L) [AR1]
2 QCNW-4753XHZZ AE C Cable [ARG]
3 VCQYNA1HM334K AD C Capacitor(50WV 0.33µF) [C1]
4 RC-FZ2020SCZZ AE C Capacitor(250WV 1.0µF) [C2]
5 RC-FZ3028SCZZ AG C Capacitor(250WV 0.56µF) [C3]
6 VCEAGA1HW106M AA C Capacitor(50WV 10µF) [C4]
7 VCEAGA1HW475M AA C Capacitor(50WV 4.7µF) [C5]
8 VCEAGA1HW226M AB C Capacitor(50WV 22µF) [C6]
9 VCEAGA1HW106M AA C Capacitor(50WV 10µF) [C7]
10 VCEAGA1HW226M AB C Capacitor(50WV 22µF) [C10]
11 VCEAGA1HW107M AA C Capacitor(50WV 100µF) [C12]
12 VCEAGA1HW107M AA C Capacitor(50WV 100µF) [C13]
13 VCKYTQ1HB683K AB C Capacitor(50WV 0.068µF) [C103]
14 VCKYTV1HB103K AB C Capacitor(50WV 0.01µF) [C104]
15 VCKYTV1HB103K AB C Capacitor(50WV 0.01µF) [C105]
16 VCKYTV1HB103K AB C Capacitor(50WV 0.01µF) [C106]
17 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C107]
18 VCKYTV1HB272K AA C Capacitor(50WV 2700PF) [C108]
19 VCKYTV1HB221K AA C Capacitor(50WV 220PF) [C109]
20 VCKYTV1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C110]
21 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C111]
22 VCKYTV1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C112]
23 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C113]
24 VCKYTV1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C114]
25 VCKYTV1EF104Z AA C Capacitor(25WV 0.1µF) [C117]
26 VCKYTV1HF104Z AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C118]
27 VCKYTV1HB821K AA C Capacitor(50WV 820PF) [C120]
28 VCKYTV1HB102K AA C Capacitor(50WV 1000PF) [C121]
29 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [C122]
30 VCKYTQ1HB333K AA C Capacitor(50WV 0.033µF) [C123]
31 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [C124]
32 VCKYTQ1HB104K AB C Capacitor(50WV 0.1µF) [C125]
33 VCKYTQ1HB223K AB C Capacitor(50WV 0.022µF) [C126]
34 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [C127]
35 RRLYZ3427SCZZ AN B Relay [CML2]
!
– 11 –
Page 97

FO-50A
FO-70A
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[9] TEL/Liu PWB unit
36 QJAKZ2079XH0D AD N C Jack [CNHJ]
37 QCNCM2548SC1B AH C Connector(12pin) [CNLIUA]
38 QCNCM2548SC0D AF C Connector(4pin) [CNLIUB]
39 QJAKZ2060SC0D AE C Jack [CNLNJ]
40 QJAKZ2060SC0B AD C Jack [CNTLJ]
41 VHDDSS133//-1 AA B Diode(1SS133) [D1]
42 VHDDSS133//-1 AA B Diode(1SS133) [D2]
43 VHDDSS133//-1 AA B Diode(1SS133) [D3]
44 VHDDSS133//-1 AA B Diode(1SS133) [D4]
45 QSW-Z2263XHZZ AG B Hook switch [HOOK SW]
46 VHINJM2904M-2 AG B IC(NJM2904M) [IC101]
47 VHINJM2904M-2 AG B IC(NJM2904M) [IC102]
48 RFILN2027XHZZ AC C Coil(R-5C) [L3A]
49 RFILN2027XHZZ AC C Coil(R-5C) [L3B]
50 RCILZ2120SCZZ AD C Coil(4.7mH) [L5]
51 RFILN2027XHZZ AC C Coil(R-5C) [L6]
52 RFILN2027XHZZ AC C Coil(R-5C) [L7]
53 RFILN2027XHZZ AC C Coil(R-5C) [L8]
54 VHPTLP627//-1 AH B Photo coupler(TLP627) [PC1]
!
55 VHPTLP521-1BL AE B Photo coupler(TLP521) [PC2]
!
56 VHPTLP521-1BL AE B Photo coupler(TLP521) [PC5]
!
57 VSBS108////-1 AE B FET(BS108) [Q1]
58 VS2SC2412KR-1 AD B Transistor(2SC2412K) [Q101]
59 VSRNC1402//-1 AC B Transistor(RNC1402) [Q104]
60 VSRNC1402//-1 AC B Transistor(RNC1402) [Q105]
61 VSRNC1402//-1 AC B Transistor(RNC1402) [Q106]
62 VSRNC1402//-1 AC B Transistor(RNC1402) [Q107]
63 VRD-HT2HY223J AA C Resistor(1/2W 22KΩ ±5%) [R3]
64 VRS-TS2AD433J AA C Resistor(1/10W 43KΩ ±5%) [R101]
65 VRS-TP2BD150J AA C Resistor(1/8W 15Ω ±5%) [R102]
66 VRS-TS2AD301J AA C Resistor(1/10W 300Ω ±5%) [R103]
67 VRS-TS2AD103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R104]
68 VRS-TS2AD153J AA C Resistor(1/10W 15KΩ ±5%) [R105]
69 VRS-TP2BD150J AA C Resistor(1/8W 15Ω ±5%) [R107]
70 VRS-TS2AD152J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1.5KΩ ±5%) [R108]
71 VRS-TS2AD102J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1KΩ ±5%) [R109]
72 VRS-TS2AD153J AA C Resistor(1/10W 15KΩ ±5%) [R110]
73 VRS-TS2AD203J AA C Resistor(1/10W 20KΩ ±5%) [R111]
74 VRS-TS2AD102J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1KΩ ±5%) [R112]
75 VRS-TS2AD203J AA C Resistor(1/10W 20KΩ ±5%) [R113]
76 VRS-TS2AD433J AA C Resistor(1/10W 43KΩ ±5%) [R114]
77 VRS-TS2AD224J AA C Resistor(1/10W 220KΩ ±5%) [R115]
78 VRS-TS2AD332J AA C Resistor(1/10W 3.3KΩ ±5%) [R116]
79 VRS-TS2AD100J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10Ω ±5%) [R117]
80 VRS-TS2AD100J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10Ω ±5%) [R118]
81 VRS-TS2AD471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R119]
82 VRS-TS2AD471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R120]
83 VRS-TS2AD104J AA C Resistor(1/10W 100KΩ ±5%) [R122]
84 VRS-TS2AD151J AA C Resistor(1/10W 150Ω ±5%) [R123]
85 VRS-TS2AD222J AA C Resistor(1/10W 2.2KΩ ±5%) [R124]
86 VRS-TS2AD332J AA C Resistor(1/10W 3.3KΩ ±5%) [R125]
87 VRS-TS2AD823J AA C Resistor(1/10W 82KΩ ±5%) [R126]
88 VRS-TS2AD243J AA C Resistor(1/10W 24KΩ ±5%) [R127]
89 VRS-TS2AD822J AA C Resistor(1/10W 8.2KΩ ±5%) [R128]
90 VRS-TS2AD621J AA C Resistor(1/10W 620Ω ±5%) [R129]
91 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R130]
92 VRS-TS2AD332J AA C Resistor(1/10W 3.3KΩ ±5%) [R131]
93 VRS-TS2AD000J AA C Resistor(1/10W 0Ω ±5%) [R132]
94 VRS-TS2AD471J AA C Resistor(1/10W 470Ω ±5%) [R133]
95 VRS-TS2AD223J AA C Resistor(1/10W 22KΩ ±5%) [R134]
96 VRS-TS2AD102J AA C Resistor(1/10W 1KΩ ±5%) [R135]
97 VRS-TS2AD682J AA C Resistor(1/10W 6.8KΩ ±5%) [R137]
98 VRS-TS2AD271J AA C Resistor(1/10W 270Ω ±5%) [R138]
99 VRS-TS2AD511J AA C Resistor(1/10W 510Ω ±5%) [R139]
100 VRS-TS2AD223J AA C Resistor(1/10W 22KΩ ±5%) [R140]
101 VRS-TS2AD473J AA C Resistor(1/10W 47KΩ ±5%) [R141]
102 VRS-TS2AD332J AA C Resistor(1/10W 3.3KΩ ±5%) [R142]
103 VRS-TS2AD363J AA C Resistor(1/10W 36KΩ ±5%) [R143]
104 VRS-TS2AD103J AA C Resistor(1/10W 10KΩ ±5%) [R144]
105 RH-DX2007SCZZ AC B Diode bridge(S1ZB60) [REC1]
106 RTRNI2165XHZZ AG N B Transformer [T1]
!
107 VHVRA501PV6-1 AE B Varistor(RA-501P-V6-2) [VA1]
108 VHVRA501PV6-1 AE B Varistor(RA-501P-V6-2) [VA2]
109 VHEMTZJ6R8B-1 AC B Zener diode(MTZJ6R8B) [ZD1]
110 VHEMTZJ300B-1 AA B Zener diode(MTZJ30B) [ZD2]
111 VHEMTZJ200B-1 AC B Zener diode(MTZJ20B) [ZD4]
112 VHEHZ2A1///-1 AC B Zener diode(HZ2A1) [ZD7]
113 VHEHZ2A1///-1 AC B Zener diode(HZ2A1) [ZD8]
901 DCEKL483BXH06 BD N E TEL/Liu PWB unit
(Unit)
– 12 –
Page 98

FO-50A
FO-70A
NO.
PARTS CODE
PRICE
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
DESCRIPTION
[10] Power supply PWB unit
1 0CBUGFM224KR/ AF C Capacitor(RE224-C) [C1]
2 0CBUGZ1072ZZ/ AN C Capacitor(KMF400VB68M) [C2]
3 0CBUGCV102HZ/ AD N C Capacitor(ECKZ3D102KBP) [C3]
4 0CBUGXAEF222/ AC N C Capacitor(GRM40B222K50PT) [C4]
5 0CBUEXCAO000/ AB N C Resistor(MCR10EZHJ000) [C6]
6 0CBUGCM392BJ/ AF N C Capacitor(DE1510-1E392M-KX) [C7]
7 0CBUGAE561TS/ AH N C Capacitor(LXJ35VB560(M)) [C8]
8 0CBUGFF474JA/ AF C Capacitor(ECQV1H474JL3) [C9]
9 0CBUGAC222VV/ AK N C Capacitor(LXZ16VB2200(K)) [C10]
10 0CBUGXAED104/ AC N C Capacitor(GRM40B104K25PT) [C12]
11 0CBUGZ1041ZZ/ AF N C Capacitor(DE1007E222M-KH) [C15]
12 0CBUGAB101RV/ AF C Capacitor(KME10VB100(M)) [C16]
13 0CBUGXAEF102/ AC N C Capacitor(GRM40B102K50PT) [C17]
14 0CBUGCU681BR/ AC C Capacitor(DEO805R681K1K-MHR) [C21]
15 0CBUGFF223EH/ AC N C Capacitor(AMZV-223J50) [C24]
16 0CBPKZ0194ZZ/ AC C Base post ass’y(B 2P3-VH) [CN1]
17 0CBPCZ0275ZZ/ AD N C Connector(8PL-FJ) [CN2]
18 0CBUBC0125DK/ AD B Diode(ERA15-06) [D1]
19 0CBUBC0125DK/ AD B Diode(ERA15-06) [D2]
20 0CBUBC0125DK/ AD B Diode(ERA15-06) [D3]
21 0CBUBC0125DK/ AD B Diode(ERA15-06) [D4]
22 0CBUBY0020AK/ AD N B Diode(1SS355) [D5]
23 0CBUBC0336AZ/ AL B Diode(S3L20U-4004P15) [D7]
24 0CBUBC0302BZ/ AE B Diode(SR140) [D8]
25 0CBPJCEJ1601/ AH A Current fuse(21501.6 ME600) [F1]
26 0CBPJCEJ1601/ AH A Current fuse(21501.6 ME600) [F2]
27 0CBPZZ0906ZZ/ AH A Circuit protect chip(CCP2E100) [F3]
28 0CBBFZ89256Z/ AD B Beads core(BL02RNI-R62T4) [FB1]
29 0CBUCB0199AZ/ AR N B IC(UPC29M05AHF) [IC1]
30 0CBUKZ0826ZZ/ AK C Filter(ELF15N003A) [L1]
31 0CBUZZ0156ZZ/ AN C Coil(RS208) [L2]
32 0CBPZZ0940ZZ/ AB N C Jumper(J1/6Z-T26-A) [L3]
33 0CBLRZ6616ZN/ AQ N C Heat sink(MN903-5001AT) [MT1]
34 0CBLRZ6619ZQ/ AQ N C Heat sink(MF903-5002AT) [MT2]
35 0CBUDC0163CZ/ AG B Photo coupler(PC123YS) [PC1]
36 0CBUDC0163CZ/ AG B Photo coupler(PC123YS) [PC2]
37 0CBUAG0161AC/ AQ B FET(FS5KM-18A-AN) [Q1]
38 0CBUDA0128AK/ AD N B Transistor(2SD2114K) [Q2]
39 0CBUAY0016CK/ AD N B Transistor(2SC2412K) [Q3]
40 0CBUAY0016CK/ AD N B Transistor(2SC2412K) [Q4]
41 0CBUAC0289AK/ AD N B Transistor(2SC4210) [Q5]
42 0CBUAC0289AK/ AD N B Transistor(2SC4210) [Q6]
43 0CBUEEC335CH/ AC N C Resistor(RDM12TB335J) [R1]
44 0CBUEEC105CH/ AC N C Resistor(RDM12TB105J) [R2]
45 0CBUEEC105CH/ AC N C Resistor(RDM12TB105J) [R3]
46 0CBUEXCAS331/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR331J) [R4]
47 0CBUEXCAS152/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR152J) [R5]
48 0CBUEXCAS183/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR183J) [R6]
49 0CBUEXCAS330/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR330J) [R7]
50 0CBUEXCAS473/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR473J) [R8]
51 0CBUEXCAS471/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR471J) [R9]
52 0CBUEFDR33DB/ AE C Resistor(RSMF1TBR33G) [R10]
53 0CBUEXCAS390/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR390J) [R11]
54 0CBUEXCAS184/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR184J) [R12]
55 0CBUEXCAS472/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR472J) [R13]
56 0CBUEXCAS152/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR152J) [R14]
57 0CBUEXCAS334/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR334J) [R15]
58 0CBUEXCAS223/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR223J) [R16]
59 0CBUEXCAS822/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR822J) [R17]
60 0CBUEXCAS273/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR273J) [R18]
61 0CBUEXCAS472/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR472J) [R19]
62 0CBUEXCAS472/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR472J) [R20]
63 0CBUEXCAS154/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR154J) [R21]
64 0CBUEXCAS103/ AB N C Resistor(CR21TR103J) [R25]
65 0CB829655027/ BE N B Transformer(PTTP124-KTT) [T1]
66 0CBUDC0232AK/ AF B Thermistor(KL07L8R2TB) [TH1]
67 0CBUEZ0507ZZ/ AD B Varistor(ERZV07D471) [V1]
68 0CBUFBA102FE/ AD N B Variable resistor(ENV CYA A01 B13) [VR1]
69 0CBUBDAX270A/ AD N B Zener diode(RD27SB) [ZD1]
70 0CBUBXAD2R0A/ AD N B Zener diode(RD2.0SB) [ZD2]
71 0CBUBDBM300D/ AC B Zener diode(RD30FB) [ZD4]
72 0CBUBXAD6R2C/ AD N B Zener diode(RD6.2SB) [ZD5]
73 0CBUBDBE200D/ AD B Zener diode(RD20ESAB) [ZD7]
901 RDENT2144XHZZ BA N E Power supply PWB unit
!
(Unit)
– 13 –
Page 99

I n d e x
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
PRICE
PARTS CODE
[C]
CCNW-212AXH01 1-2 AK N C
″ 3-1 AK N C
CCNW-215AXH01 1-12 AG N C
[D]
DCEKC684MXHZZ 1-45 BP N E
″ 8-901 BP N E
DCEKC686MXHZZ 1-45 BP N E
″ 8-901 BP N E
DCEKL483BXH06 1-16 BD N E
″ 9-901 BD N E
DCEKP481BXH05 1-1 AP N E
″ 3-901 AP N E
DCEKP482BXH01 3-7 AQ N E
DUNTK204CXHPU 7-2 AH N E
[G]
GCABA2342XHSC 3-3 AH N D
GCABB2343XHSC 1-13 AK N D
GCASP2110XHSE 1-17 AK N C
GCASP2111XHSC 1-18 AH N C
GDAI-2082XHSD 1-46 AD N C
GDAI-2083XHZZ 1-22 AF N C
[H]
HPNLH2392XHSR 1-54 AE N D
HPNLH2392XHS3 1-54 AE N D
[J]
JBTN-2257XHSD 3-4 AD N C
JBTN-2258XHSC 3-5 AC N C
JBTN-2261XHSC 3-6 AC N C
[L]
LBNDJ2006XHZZ 1-55 AA C
″ 2-19 AA C
LBSHP2110XHZZ 2-1 AB N C
LBSHP2112XHZZ 1-28 AB N C
LFRM-2206XHZZ 6-1 AF N C
LFRM-2207XHZZ 5-1 AF N C
LFRM-2208XHZZ 1-29 AF N C
LFRM-2209XHZZ 2-2 AF N C
LHLDZ2180XHZZ 2-3 AC N C
LHLDZ2181XHZZ 2-4 AC N C
LHLDZ2184XHZZ 1-30 AC N C
LHLDZ2185XHZZ 1-31 AC N C
LPLTG2911XHZZ 4-1 AE C
LPLTM3049XHZZ 5-2 AD N C
″ 6-2 AD N C
LPLTP2908XHZZ 4-2 AE C
LPLTP3050XHZZ 6-3 AB N C
LPLTP3051XHZZ 4-3 AB N C
LSTPP2054XHZZ 1-47 AC N C
LX-BZ2138XHZZ 1-B1 AB C
[M]
MARMP2023XHZZ 1-48 AB N C
MCAMP2027XHZZ 5-4 AC N C
″ 6-4 AC N C
MLEVP2311XHZZ 5-5 AB N C
″ 6-5 AB N C
MLEVP2312XHZZ 5-6 AB N C
″ 6-6 AB N C
MLEVP2313XHZZ 6-7 AC N C
MLEVP2314XHZZ 5-8 AB N C
″ 6-8 AB N C
MLEVP2315XHZZ 1-32 AC N C
MLEVP2316XHZZ 1-23 AC N C
MLEVP2317XHZZ 2-5 AB N C
MLEVP2319XHZZ 1-49 AC N C
MLEVP2320XHZZ 1-19 AC N C
MLEVP2321XHZZ 1-58 AN N C
MSPRC2735XHZZ 5-9 AC C
″ 6-9 AC C
MSPRC2954XHZZ 1-5 AC C
MSPRC3110XHZZ 5-10 AB N C
″ 6-10 AB N C
MSPRC3112XHZZ 1-33 AC N C
MSPRC3117XHZZ 2-6 AB N C
MSPRC3127XHZZ 6-11 AB N C
MSPRC3148XHZZ 1-34 AC N C
MSPRD3115XHZZ 1-35 AB N C
MSPRD3116XHZZ 1-24 AB N C
MSPRD3169XHZZ 1-57 AD N C
MSPRP3119XHZZ 1-14 AC N C
No.
RANK
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
PRICE
PARTS CODE
MSPRP3123XHZZ 1-15 AC N C
MSPRT3114XHZZ 1-25 AC N C
MSPRT3139XHZZ 4-5 AA N C
MSPRT3140XHZZ 4-4 AA N C
[N]
NGERH2278XHZZ 5-12 AC C
″ 6-12 AC C
NGERH2379XHZZ 5-13 AC C
″ 6-13 AC C
NGERH2380XHZZ 6-14 AC C
NGERH2391XHZZ 5-15 AC C
″ 6-15 AC C
NGERH2451XHZZ 6-16 AB C
NGERH2475XHZZ 5-17 AB N C
″ 6-17 AB N C
NGERH2476XHZZ 6-18 AB N C
NGERH2477XHZZ 1-50 AC N C
NGERH2478XHZZ 1-36 AB N C
NGERH2479XHZZ 2-7 AB N C
NGERH2480XHZZ 2-8 AB N C
NGERH2481XHZZ 2-9 AB N C
NGERP2318XHZZ 1-6 AD C
NROLP2426XHZZ 1-26 AC N C
NROLR2375XHZZ 2-10 AL C
NROLR2425XHZZ 1-37 AP N C
NROLR2427XHZZ 1-42 AC N C
NROLR2428XHZZ 2-11 AP N C
NSFTZ2273XHZZ 2-12 AF C
NSFTZ2320XHZZ 7-18 AF N C
[P]
PCUSU2132XHZZ 1-62 AC N C
PCUT-2040SCZZ 1-51 AV N C
PGIDM2554XHZZ 4-6 AF N C
PGIDM2558XHZZ 1-38 AD N C
PGIDM2559XHSC 1-27 AE N C
PGIDM2560XHSD 1-7 AE N C
PGIDM2561XHSD 1-8 AC N C
PGIDM2562XHZZ 2-13 AD N C
PGIDM2563XHSC 1-27 AC N C
PGIDM2564XHZZ 1-44 AD N C
PGIDM2566XHZZ 1-52 AC N C
PGIDM2578XHZZ 7-16 AE N C
PGIDM2579XHZZ 7-17 AE N C
PGUMR2168XHZZ 1-43 AF N C
PHOP-2104XHSD 1-9 AF N C
PHOP-2105XHZZ 7-4 AD N C
PSHEZ3410XHZZ 1-56 AB C
PSHEZ3436XHZZ 2-14 AC C
PSHEZ3510XHZZ 4-7 AE N C
PSHEZ3517XHZZ 4-7 AE N C
[Q]
QACCL2045XHZZ 1-20 AR N B
QCNCM2401SC0B 8-135 AA C
QCNCM2442SC0B 8-126 AB C
QCNCM2548SC0D 9-38 AF C
QCNCM2548SC1B 9-37 AH C
QCNCM7014SC0B 8-129 AD C
QCNCM7014SC0C 8-127 AA C
QCNCM7014SC0F 8-132 AB C
QCNCM7014SC0G 8-125 AB C
QCNCM7014SC1F 8-133 AD C
″ 8-136 AD C
QCNCM705BAF06 8-128 AB C
QCNCW2500SC0D 8-131 AG C
QCNCW2500SC0H 8-134 AF C
QCNCW2500SC1B 8-130 AF C
QCNW-207AXHZZ 6-19 AC N C
QCNW-209AXHZZ 1-39 AH N C
QCNW-210AXHZZ 1-40 AC N C
QCNW-213AXHZZ 2-16 AC N C
QCNW-3976XHOW 7-3 AK C
QCNW-4753XHZZ 9-2 AE C
QCNW-4814XHZZ 2-15 AG N C
QCNW-4933XHZZ 5-20 AC C
″ 6-20 AC C
QCNWG0376AFZZ 7-5 AM C
QCNWG0381AFZZ 7-27 AM C
QFS-P2010SCZZ 8-143 AD N B
QJAKZ2060SC0B 9-40 AD C
QJAKZ2060SC0D 9-39 AE C
No.
RANK
FO-50A
FO-70A
NEW
MARK
PART
RANK
PRICE
PARTS CODE
QJAKZ2079XH0D 9-36 AD N C
QPLGZ9065AFZZ 7-26 AP C
QSOCZ2051SC32 8-148 AC C
QSW-F2224SCZZ 5-21 AE B
″ 6-21 AE B
QSW-M2293XHZZ 2-17 AE N B
QSW-M2296XHZZ 1-11 AD B
QSW-Z2263XHZZ 9-45 AG B
[R]
RC-FZ2020SCZZ 9-4 AE C
RC-FZ3028SCZZ 9-5 AG C
RCILZ2120SCZZ 9-50 AD C
RCILZ2145XHZZ 8-154 AF C
″ 8-155 AF C
″ 8-156 AF C
″ 8-157 AF C
″ 8-158 AF C
″ 8-159 AF C
″ 8-160 AF C
″ 8-161 AF C
RCORF2123XHZZ 2-20 AD N B
RCORF2125XHZZ 1-53 AE B
RCRSB0297AFZZ 8-275 AD B
RCRSQ2157SCZZ 8-274 AF B
RDENT2144XHZZ 1-21 BA N E
″ 10-901 BA N E
RFILN2027XHZZ 9-48 AC C
″ 9-49 AC C
″ 9-51 AC C
″ 9-52 AC C
″ 9-53 AC C
RH-DX2007SCZZ 9-105 AC B
RHEDZ2059XHZZ 1-41 BF N B
RMOTZ2148XHZZ 5-22 AT N B
″ 6-22 AT N B
RR-TZ3017SCZZ 8-257 AC C
″ 8-258 AC C
″ 8-261 AC C
″ 8-262 AC C
″ 8-263 AC C
″ 8-268 AC C
″ 8-269 AC C
RR-TZ3018SCZZ 8-256 AC C
″ 8-259 AC C
″ 8-260 AC C
″ 8-264 AC C
″ 8-265 AC C
″ 8-266 AC C
″ 8-267 AC C
″ 8-270 AC C
″ 8-271 AC C
RRLYD3138XHZZ 8-273 AG B
RRLYZ3427SCZZ 9-35 AN B
RTRNI2165XHZZ 9-106 AG N B
RUNTZ2054XHZZ 2-18 BE N B
[S]
SPAKA287BXHZZ 7-7 AE N D
SPAKA288BXHZZ 7-8 AE N D
SPAKA289BXHZZ 7-9 AC N D
SPAKA388BXHZZ 7-24 AE N D
SPAKA389BXHZZ 7-25 AE N D
SPAKC324BXHZZ 7-10 AH N D
SPAKC329BXHZZ 7-10 AH N D
SPAKP296BXHZZ 7-6 AE N D
[T]
TCADZ2264XHZZ 7-21 AD D
TCADZ2935XHZZ 7-23 AA N D
TINSE4028XHZZ 7-1 AL N D
TLABM320BXHZZ 7-11 AD N D
TLABM324BXHZZ 7-11 AD N D
TLABS388AXHZZ 1-59 AD N D
TLABS389AXHZZ 1-59 AD N D
TLABS4335XHZZ 1-60 AD D
TLABV363AXHZZ 7-22 AC N D
TLABV366AXHZZ 7-22 AC N D
TLABZ3418XHZZ 1-61 AA D
[U]
UBATL2046SCZZ 8-1 AK B
[V]
VCCCTV1HH100D 8-15 AA C
No.
RANK
– 14 –
Page 100

FO-50A
FO-70A
NEW
PRICE
PARTS CODE
VCCCTV1HH101J 8-93 AA C
″ 8-94 AA C
″ 8-100 AA C
″ 8-105 AA C
″ 8-110 AA C
″ 8-111 AA C
″ 8-112 AA C
″ 8-114 AA C
″ 8-115 AA C
″ 8-116 AA C
″ 8-119 AA C
VCCCTV1HH120J 8-16 AA C
VCCCTV1HH180J 8-80 AA C
VCCCTV1HH220J 8-43 AA C
″ 8-44 AA C
″ 8-63 AA C
″ 8-64 AA C
″ 8-79 AA C
″ 8-82 AA C
″ 8-83 AA C
″ 8-84 AA C
VCCCTV1HH330J 8-87 AA C
VCCCTV1HH680J 8-28 AA C
″ 8-29 AA C
VCEAGA1EW476M 8-4 AA C
″ 8-5 AA C
″ 8-7 AA C
″ 8-10 AA C
VCEAGA1HW106M 8-2 AA C
″ 8-3 AA C
″ 8-8 AA C
″ 9-6 AA C
″ 9-9 AA C
VCEAGA1HW107M 8-9 AA C
″ 9-11 AA C
″ 9-12 AA C
VCEAGA1HW226M 8-6 AB C
″ 9-8 AB C
″ 9-10 AB C
VCEAGA1HW475M 9-7 AA C
VCKYTQ1HB104K 9-32 AB C
VCKYTQ1HB223K 9-33 AB C
VCKYTQ1HB333K 9-30 AA C
VCKYTQ1HB683K 9-13 AB C
VCKYTV1CF105Z 8-25 AB C
″ 8-27 AB C
″ 8-34 AB C
″ 8-35 AB C
″ 8-38 AB C
″ 8-46 AB C
″ 8-51 AB C
″ 8-52 AB C
″ 8-53 AB C
″ 8-55 AB C
″ 8-57 AB C
″ 8-59 AB C
″ 8-60 AB C
″ 8-62 AB C
″ 8-66 AB C
″ 8-67 AB C
″ 8-72 AB C
″ 8-74 AB C
″ 8-75 AB C
″ 8-77 AB C
″ 8-86 AB C
″ 8-88 AB C
″ 8-89 AB C
″ 8-91 AB C
″ 8-96 AB C
″ 8-97 AB C
″ 8-102 AB C
″ 8-103 AB C
″ 8-120 AB C
″ 8-121 AB C
″ 8-122 AB C
″ 8-123 AB C
VCKYTV1EB104K 8-69 AA C
″ 8-92 AA C
″ 8-101 AA C
″ 8-124 AA C
No.
RANK
MARK
PART
RANK
NEW
PRICE
PARTS CODE
VCKYTV1EF104Z 8-20 AA C
″ 8-22 AA C
″ 8-33 AA C
″ 8-39 AA C
″ 8-42 AA C
″ 8-45 AA C
″ 8-50 AA C
″ 8-54 AA C
″ 8-70 AA C
″ 8-71 AA C
″ 8-73 AA C
″ 8-78 AA C
″ 8-107 AA C
″ 8-109 AA C
″ 8-118 AA C
″ 9-25 AA C
VCKYTV1HB102K 8-11 AA C
″ 8-12 AA C
″ 8-13 AA C
″ 8-14 AA C
″ 8-17 AA C
″ 8-18 AA C
″ 8-21 AA C
″ 8-23 AA C
″ 8-24 AA C
″ 8-26 AA C
″ 8-31 AA C
″ 8-36 AA C
″ 8-37 AA C
″ 8-40 AA C
″ 8-41 AA C
″ 8-56 AA C
″ 8-58 AA C
″ 8-61 AA C
″ 8-65 AA C
″ 8-68 AA C
″ 8-81 AA C
″ 8-95 AA C
″ 8-113 AA C
″ 9-17 AA C
″ 9-21 AA C
″ 9-23 AA C
″ 9-28 AA C
VCKYTV1HB103K 8-19 AB C
″ 8-106 AB C
″ 9-14 AB C
″ 9-15 AB C
″ 9-16 AB C
VCKYTV1HB221K 8-104 AA C
″ 9-19 AA C
VCKYTV1HB222K 8-30 AA C
″ 8-32 AA C
″ 8-48 AA C
″ 8-49 AA C
″ 8-76 AA C
″ 8-85 AA C
VCKYTV1HB223K 8-98 AA C
VCKYTV1HB272K 9-18 AA C
VCKYTV1HB472K 8-108 AA C
VCKYTV1HB821K 8-99 AA C
″ 9-27 AA C
VCKYTV1HF104Z 8-47 AA C
″ 8-117 AA C
″ 9-20 AA C
″ 9-22 AA C
″ 9-24 AA C
″ 9-26 AA C
VCQYNA1HM334K 9-3 AD C
VHDDSS133//-1 9-41 AA B
″ 9-42 AA B
″ 9-43 AA B
″ 9-44 AA B
VHDHRW0202B-1 8-141 AD C
VHD1SS355//-1 8-138 AB B
″ 8-139 AB B
″ 8-140 AB B
″ 8-142 AB B
VHEHZ2A1///-1 9-112 AC B
″ 9-113 AC B
VHEMTZJ200B-1 9-111 AC B
No.
RANK
MARK
PART
RANK
NEW
PRICE
PARTS CODE
VHEMTZJ300B-1 9-110 AA B
VHEMTZJ6R8B-1 9-109 AC B
VHIFC2FM209-1 8-145 BD N B
″ 8-147 BD N B
VHINJM2113M-1 8-150 AG B
VHINJM2904M-2 8-151 AG B
″ 9-46 AG B
″ 9-47 AG B
VHITC7WT74FU1 8-144 AF N B
VHIULN2003AN/ 8-152 AE B
VHIW24258S7LE 8-146 AQ B
VHIXC61AN45M1 8-153 AE N B
VHI27010FZK0A 8-148 BM N B
VHI27010FZL0C 8-148 BM N B
VHI62FP332P-1 8-272 AF B
VHPSG206S//-1 8-165 AG B
″ 8-166 AG B
VHPTLP521-1BL 9-55 AE B
″ 9-56 AE B
VHPTLP627//-1 9-54 AH B
VHVDSS301L/-U 9-1 AF B
VHVRA501PV6-1 9-107 AE B
″ 9-108 AE B
VRD-HT2HY223J 9-63 AA C
VRS-HT3AA101J 8-137 AA C
VRS-TP2BD150J 9-65 AA C
″ 9-69 AA C
VRS-TS2AD000J 8-90 AA C
″ 8-162 AA C
″ 8-163 AA C
″ 8-164 AA C
″ 8-188 AA C
″ 8-200 AA C
″ 8-202 AA C
″ 8-214 AA C
″ 8-215 AA C
″ 8-227 AA C
″ 8-230 AA C
″ 8-254 AA C
″ 8-255 AA C
″ 9-29 AA C
″ 9-31 AA C
″ 9-34 AA C
″ 9-91 AA C
″ 9-93 AA C
VRS-TS2AD100J 9-79 AA C
″ 9-80 AA C
VRS-TS2AD101J 8-178 AA C
″ 8-179 AA C
″ 8-225 AA C
VRS-TS2AD102J 8-213 AA C
″ 8-239 AA C
″ 8-246 AA C
″ 9-71 AA C
″ 9-74 AA C
″ 9-96 AA C
VRS-TS2AD103J 8-203 AA C
″ 8-204 AA C
″ 8-209 AA C
″ 8-221 AA C
″ 8-238 AA C
″ 9-67 AA C
″ 9-104 AA C
VRS-TS2AD104J 8-185 AA C
″ 8-186 AA C
″ 8-247 AA C
″ 8-248 AA C
″ 9-83 AA C
VRS-TS2AD105J 8-220 AA C
VRS-TS2AD106J 8-222 AA C
VRS-TS2AD121J 8-173 AA C
″ 8-223 AA C
VRS-TS2AD123J 8-226 AA C
VRS-TS2AD151J 8-192 AA C
″ 9-84 AA C
VRS-TS2AD152J 9-70 AA C
VRS-TS2AD153J 8-233 AA C
″ 8-242 AA C
″ 9-68 AA C
″ 9-72 AA C
No.
RANK
MARK
PART
RANK
– 15 –
 Loading...
Loading...