Page 1
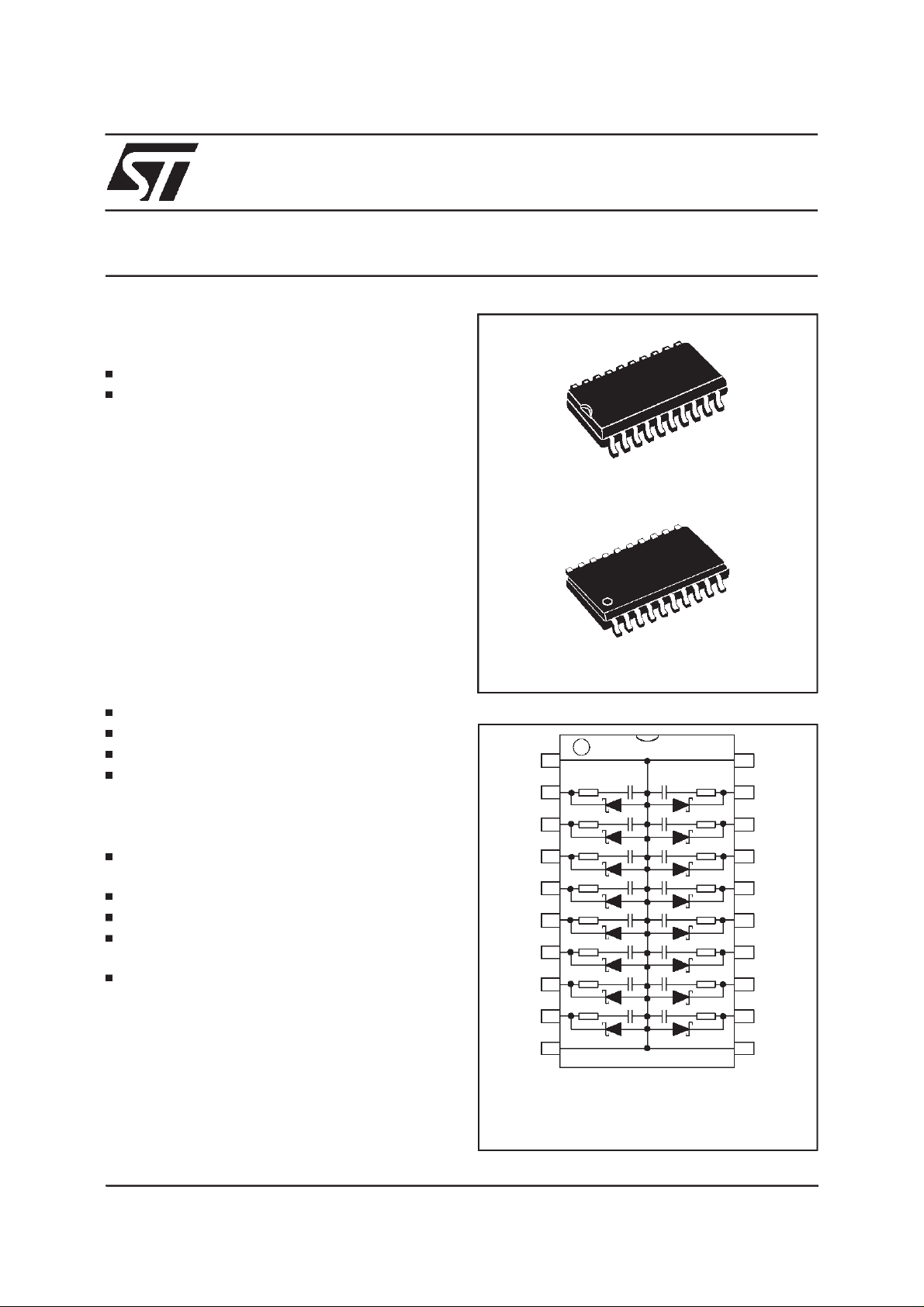
RCD16-47B
Application Specific Discretes
A.S.D.
MAINAPPLICATIONS
In any electronic equipment where a suitable bus
terminationis requiredtoavoidsignalreflectionsand
distortions:
PC and workstationcomputer
Data-lineanalyzers
DESCRIPTION
With the increasing speed of data transmission,
line reflections provide signal distorsions and the
overshootsor undershootsproducedon the signal
edges can cause the malfunction of the whole
system.
To avoid these negative effects from leading to
problems, a suitable termination is required.
Dedicated to bus termination, the RCD16-47B
provides by far the best method to minimise stray
emissionsfrom PCB tracks.
FEATURES
NETWORKOF16R-C-DLINETERMINATIONS
RESISTANCE:R = 47
CAPACITANCE: C=33pF,TOLERANCE+/-10%
SCHOTTKY DIODE: (D)
TM
Ω
, TOLERANCE+/-10%
RCD NETWORK
FOR BUS TERMINATION
SO20
SSOP20
FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM
1
2
20
19
BENEFITS
Provides impedance matching, thus increasing
noiseimmunityand minimizingdistortion.
LowersEMI / RFI radiation.
No DC powerdissipation.
Eliminates negative voltages : no current will
changethebias of the protecteddevice.
Usesthe best of allterminationschemes.
COMPLIESWITHTHEFOLLOWINGSTANDARDS:
MILSTD 883C - Method 3015-6
= 2 kV C=100 pF R = 1500 Ω
-V
PP
-3 positivestrikesand 3 negativestrikes (F=1Hz)
October 1998 - Ed : 2A
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
R=47 Ω, tolerance +/−
10
%
C= 33 pF, tolerance +/- 10 %
D= Schottkydiode
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
1/7
Page 2
RCD16-47B
APPLICATION NOTE : BUS TERMINATION
Withtheincreasingspeedof datatransmission(PC,TV,...),engineersare naturallyconfrontedwith effects
that were of less significance with slowercircuits. Amongthese are the effectsdescribedin transmission
linetheory : line reflectionsprovide signal distortionsand the overshootsor undershootsproducedon the
signaledges can finally cause themalfunctionof thewhole system.
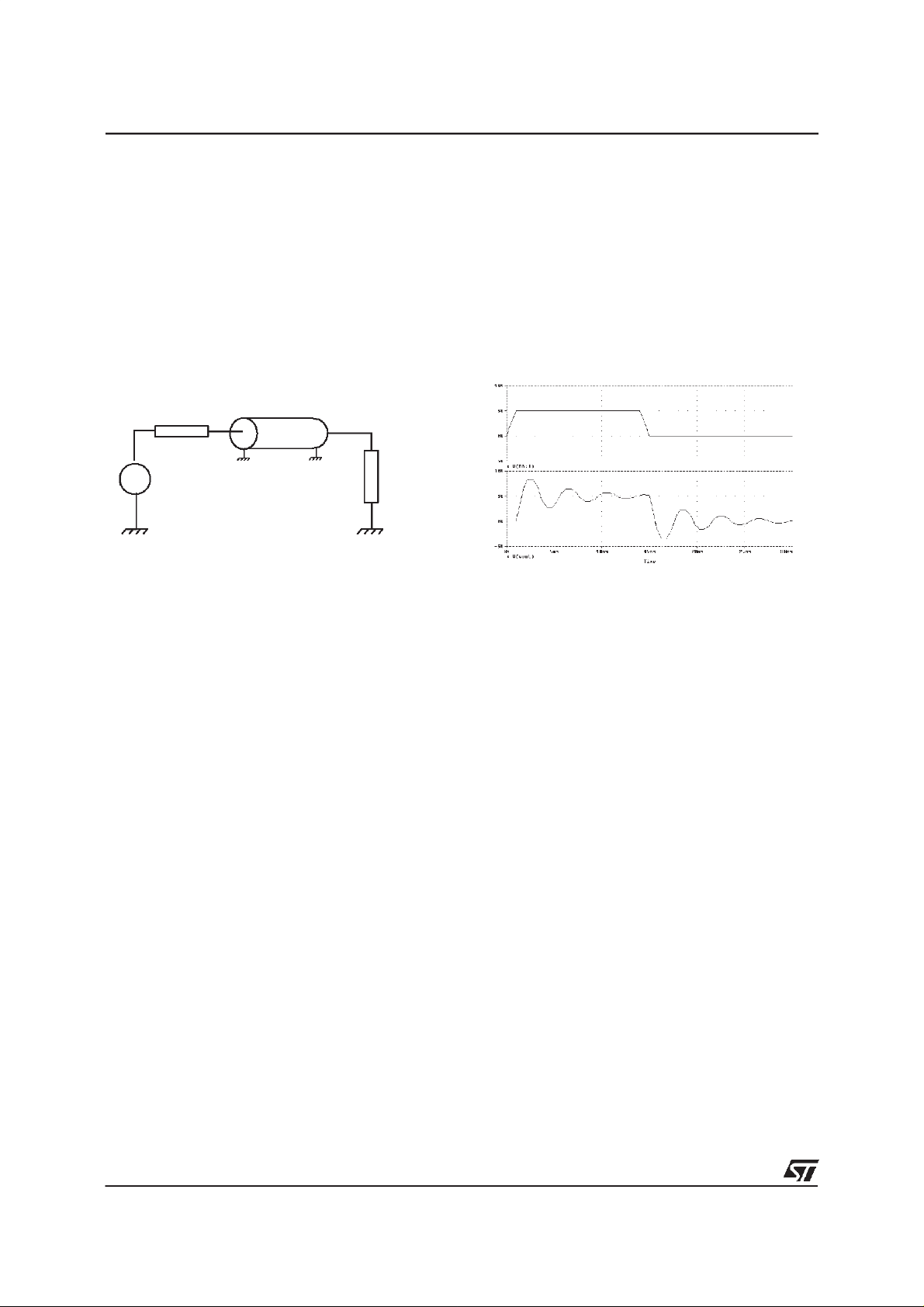
1. Reflectionat a non terminatedline
Thefigure below showsthe circuitof a transmissionsystemin whicha memorydevice(input impedance of
100kΩ) is connectedat the endof a line with lineimpedanceZo.
10 Ω
100 kΩ
If thisline is notproperlyterminated, a certain amount of the energy isreflected back,inducing a reflection
phenomenathat can distortthe signal.This can resultin improper operation ofthe system.
Thesimulation shownon the abovefigure illustratesthe signal distortionproducedby line reflection at the
endof theline whichis not well terminated.
Evenif thesignalat thestartof theline hasthe correctform(uppercurve),considerabledistortion arisesat
theend of the line (lower curve). On the positive edge, the overshootcan exceed themaximumoperating
voltageof the usedcircuittechnologywhichwill then bedestroyed.Also, the following negativeundershoot
mayreach a level low enoughtochangethe value of thelogicstate. If it affectsof an addressline, a wrong
memorycell will be addressed,and in the caseof adata line, the data can be corrupted.
Thisphenomenaalso occurson thefalling edge.
To avoid these negative effects from leading to problems in a system, a suitable termination is
required.
2/7
Page 3

RCD16-47B
2. The RCD termination
The traditional solution to properly match each line of the bus consists of the use of several discrete
resistances,capacitorsand smallschottky diodes. For a 16-bit bus, thisrequires48 discretecomponents.
TM
SGS-THOMSONoffers an innovatingsolutionwith a monolithicstructureusing
TM
ASD
The
device. The
technologyenablestointegratemonolithically16 oftheseRCD ”basiccells”onto a singlechip
RCD16-47B
reduces component cost and assemblycost, saves board space and improves
reliability.
ASD
technology(*).
Thesimulationillustratesthe signal distortionproduced by linereflectionat the endof the line when sucha
terminationis used.
The resistorprovidesthe pathterminationfor PCB track,thusresulting inlow reflectionphenomena.
The capacitor of 33 pF blocks DC currents while acting as a shortcircuit during signaltransitions,and
holdsthe busat the last logic level. It reducespowerconsumptionand avoidsexcessivecurrent.
The small Schottkydiode clampsthe negativeremainingundershoots whichcanresultfrom impedance
mismatch.This dampsnegative voltages and preventsthe logic signal from rising above the logic level
’0’ thresholdafter a falling edge.
TheRCD terminationprovides optimal solution compared to all other terminationtechniques.
(*)ASD = ApllicaionSpecificDiscretes.
3/7
Page 4

RCD16-47B
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(0°C≤ T
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
P Totalpower dissipationper package 500 mW
amb
≤ 70°C)
V
I
RRM
V
PP
F
Continuousforwardcurrentper Schottkydiode 50 mA
Repetitivepeak reversevoltage 7.5 V
Maximumelectrostaticdischarge
2kV
MIL STD 883C -METHOD 3015-6
T
stg
T
Storagetemperaturerange
Maximumjunctiontemperature
j
- 55 to +150
150
THERMAL RESISTANCE
Symbol Parameter Package Value Unit
R
th(j-a)
Junctionto ambient SO20
SSOP20
100
140
ELECTRICALCHARACTERISTICS
Symbol Parameterand testconditions Typ. Max. Unit
R
C
C
I
R
Connectionresistance(note1)
Totalcapacitance F = 1 MHz, VR=0V, V
t
Leakagecurrent VR=V
RRM
=25°C 0.25 Ω
T
amb
=30mV 45 pF
RMS
Tj=25°C
T
=70°C
j
1
10
°
C
°C
°C/W
µ
A
V
F
Forwardvoltage IF=1mA
=16mA
I
F
T
=25°C
j
=25°C
T
j
Note 1 : Rc isthe resistance betweenpin 1 andpin 11 orbetweenpin 10and pin 20
4/7
0.5
1
V
Page 5

PSPICEMODEL per RCD CELL
RCD16-47B
Dschotparameters
L
3 nH SO20
1.75 nH SSOP20
R1 3Ω R3 9Ω
R2 47Ω
Cvar
C1 33pF
Cvar
Cvarparameters
Dschot
t
SO20Package
Z magnitudeversus frequency
Ω
SSOP20 Package
Z magnitudeversus frequency
Ω
Phaseversus frequency
°
Phaseversus frequency
°
5/7
Page 6

RCD16-47B
ORDERCODE
RCD 16
Product
16cells
Product Package
RCD16-47B SO20 40 1000
RCD16-47B6 SSOP20 66 2000
MARKING
47 B RL
-
R=47Ω
Tube Tape& reel
package:
B = SO20
B6 = SSOP20
Base Qty
Packaging:
: tube
RL : tape & reel
Type Package Marking
RCD16-47B SO20 RCD1647B
RCD1647B6 SSOP20 RCD1647B6
Packging: Preferredpackagingis tapeand reel.
6/7
Page 7

PACKAGEMECHANICAL DATA
SO20(Plastic)
D
A
K
e
A1B
EH
SSOP20(Plastic)
hx45°
RCD16-47B
DIMENSIONS
REF.
A 2.35 2.65 0.092 0.104
CL
A1 0.10 0.20 0.004 0.008
B 0.33 0.51 0.013 0.020
C 0.23 0.32 0.009 0.013
D 12.6 13.0 0.484 0.512
E 7.40 7.60 0.291 0.299
e 1.27 0.050
H 10.0 10.65 0.394 0.419
h 0.25 0.75 0.010 0.029
L 0.50 1.27 0.020 0.050
K8°(max)
Millimeters Inches
Min. Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max.
DIMENSIONS
L
REF.
Millimeters Inches
Min. Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max.
A2
A
b
D
e
k
E
A1 c
A 2.00 0.079
A1 0.25 0.010
A2 1.51 2.00 0.059 0.079
b 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.010 0.012 0.014
c 0.10 0.35 0.004 0.014
20
11
E1
101
D 7.05 8.05 0.278 0.317
E 7.60 8.70 0.299 0.343
E1 5.02 6.10 6.22 0.198 0.240 0.245
e 0.65 0.026
k0° 10° 0° 10°
L 0.25 0.50 0.80 0.010 0.020 0.031
Informationfurnished is believedtobe accurate and reliable.However, STMicroelectronicsassumes no responsibility for the consequences of
use of such information nor for any infringementof patentsor other rights of third parties which may result from its use.No license is grantedby
implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics.Specifications mentioned in this publication are subject to
change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
STMicroelectronics products are not authorized for use as criticalcomponents in life support devices or systems without express writtenapproval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is a registeredtrademark ofSTMicroelectronics
1998 STMicroelectronics - Printed in Italy - All rights reserved.
STMicroelectronics GROUP OF COMPANIES
Australia - Brazil - Canada - China - France - Germany - Italy - Japan - Korea - Malaysia - Malta - Mexico - Morocco -
The Netherlands - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - Taiwan - Thailand - United Kingdom - U.S.A.
http://www.st.com
7/7
 Loading...
Loading...