Page 1
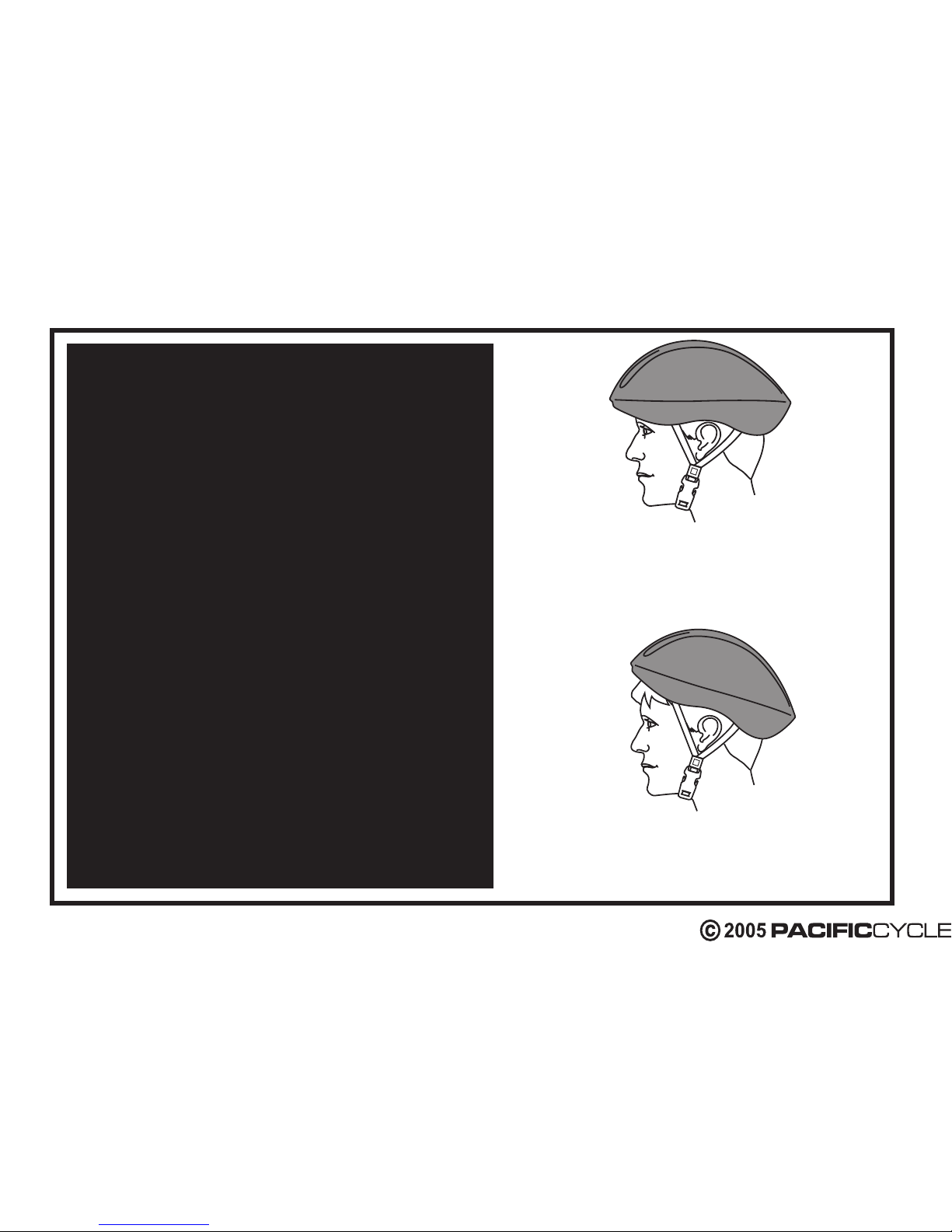
CORRECT FITTING - MAKE
SURE YOUR HELMET COVERS
YOUR FOREHEAD.
INCORRECT FITTING. FOREHEAD
IS EXPOSED AND VULNERABLE
TO SERIOUS INJURY.
ALWAYS WEAR A PROPERLY
FITTED HELMET WHEN
YOU RIDE YOUR SCOOTER.
DO NOT RIDE AT NIGHT.
AVOID RIDING IN WET
CONDITIONS.
HELMETS
SAVE
LIVES !!!
Page 2

Please Retain your Sales Receipt
as Proof of Purchase.
Notes: _______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________
Page 3

The following manual is only a guide to assist you and is not a complete or comprehensive manual of all aspects of
maintaining and repairing your scooter. The scooter you have purchased is a complex object. We recommend that you
consult a professional bicycle dealer if you have doubts or concerns as to your experience or ability to properly assemble,
repair, or maintain your scooter. You will save time and the inconvenience of having to go back to the store if you choose
to write or call us concerning missing parts, service questions, operating advice, and/or assembly questions.
SERVICE
CALL TOLL FREE 1.800.626.2811
Monday - Friday 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. Central Time
PACIFIC CYCLE, INC.
4902 Hammersley Road
Madison, WI 53711
Customer Service 1.800.626.2811
www.pacific-cycle.com
Serial number is located
on the bottom of the frame
behind the kickstand.
Page 4

D I R EC TO RY
PART 1
PART 2
PART 3
PART 4
PART 5
PART 7
Parts Identification ...................................................... 01-03
Before You Ride ............................................................04-11
Assembly ..................................................................... 12-29
Servicing ...................................................................... 30-32
Detailed Maintenance .................................................. 33-45
Purchase Record and Warranty ................................. 51-52
Warning / Important
Take notice of this symbol throughout this manual and pay particular
attention to the instructions blocked off and preceded by this symbol.
PART 6
How Things Work ........................................................ 46-50
PACIFIC CYCLE
P.O. Box 344 • 4730 E. Radio Tower Ln. • Olney, IL 62450
Customer Service 1.800.626.2811 • www.pacific-cycle.com
?
Page 5
02
Your new scooter was assembled and tuned in the factory and then partially disassembled for shipping.
You may have purchased the scooter already fully assembled and ready to ride OR in the shipping carton in
the partially disassembled form. The following instructions will enable you to prepare your scooter for years
of enjoyable scooter riding. For more details on inspection, lubrication, maintenance and adjustment of any
area please refer to the relevant sections in this manual. If you have questions about your ability to properly
assemble this unit, please consult a qualified specialist before riding. If you need replacement parts or have
questions pertaining to assembly of your scooter, call the service line direct at:
SERVICE AND TECHNICAL SUPPORT:
1.800.626.2811
Monday - Friday 8:00 a.m. - 5:00 p.m. Central Time.
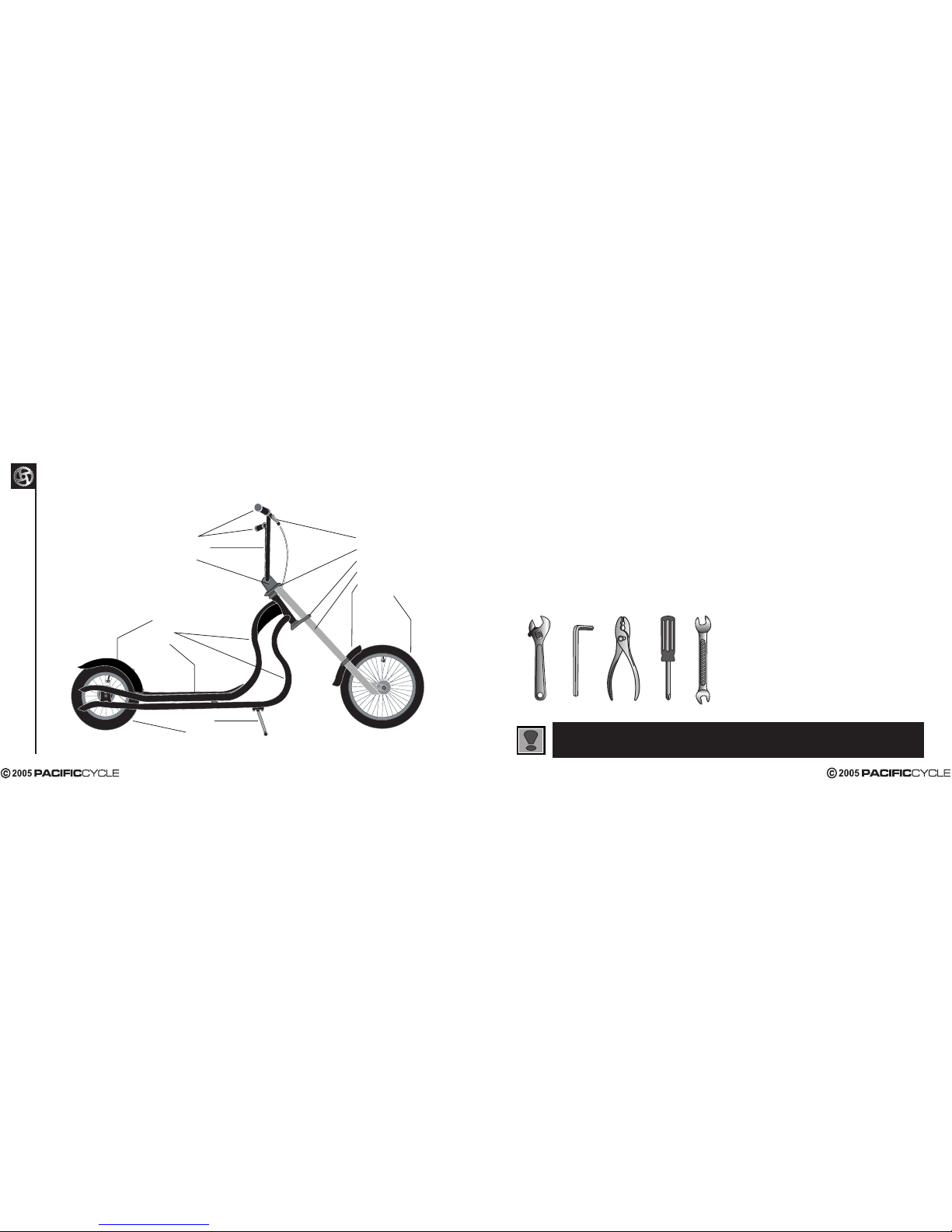
Tools Required:
• Phillips head screw driver
• 4mm, 5mm 6mm & 8mm Allen keys
• Adjustable wrench or a 9mm, 10mm,
14mm & 15mm open and box end wrenches
• A pair of pliers with cable cutting ability
To avoid injury, this product must be properly assembled before use. If your scooter was
obtained assembled, we strongly recommend that you review the complete assembly
instructions and perform checks specified in this manual before riding.
01
SCHWINN STINGRAY SCOOTER BASIC PARTS BREAKDOWN
Brake Lever
Upper Fork Crown
Lower Fork Crown
Fork Leg
Front Fender
Front Wheel
Grips
Handlebar
Stem
Rear Fender
Frame
Deck
Kickstand
Rear Wheel
Page 6
04
PART 2 - BEFORE YOU RIDE
03
ABOUT THIS MANUAL
It is important for you to understand your new scooter. By reading this manual before you go out on your first ride, you’ll know how
to get better performance, comfort, and enjoyment from your new scooter.
It is also important that your first ride on your new scooter is taken in a controlled environment, away from cars, obstacles,
and other cyclists.
GENERAL WARNING
Scooter riding can be a hazardous activity even under the best of circumstances. Proper maintenance of your scooter is your responsibility as it helps reduce the risk of injury. This manual contains many “Warnings” and “Cautions” concerning the consequences of failure
to maintain or inspect your scooter. Many of the warnings and cautions say “you may lose control and fall.” Because any fall can result
in serious injury or even death, we do not repeat the warning of possible injury or death whenever the risk of falling is mentioned.
A SPECIAL NOTE FOR PARENTS
It is a tragic fact that most scooter accidents involve children. As a parent or guardian, you bear the responsibility for the activities and
safety of your minor child. Among these responsibilities are to make sure that the scooter which your child is riding is properly fitted
to the child; that it is in good repair and safe operating condition; that you and your child have learned, understand and obey not only
the applicable local motor vehicle, scooter, and traffic laws, but also the common sense rules of safe and responsible scooter riding.
As a parent, you should read this manual before letting your child ride the scooter. Please make sure that your child always wears an
approved bicycle helmet when riding.
Age/Weight Range
Age
6 years to adult
Weight
Up to 200 lbs.
Handlebar Height
Maximum comfort is usually obtained when the handlebar height is
equal to the height of the seat. You may wish to try different heights
to find the most comfortable position.
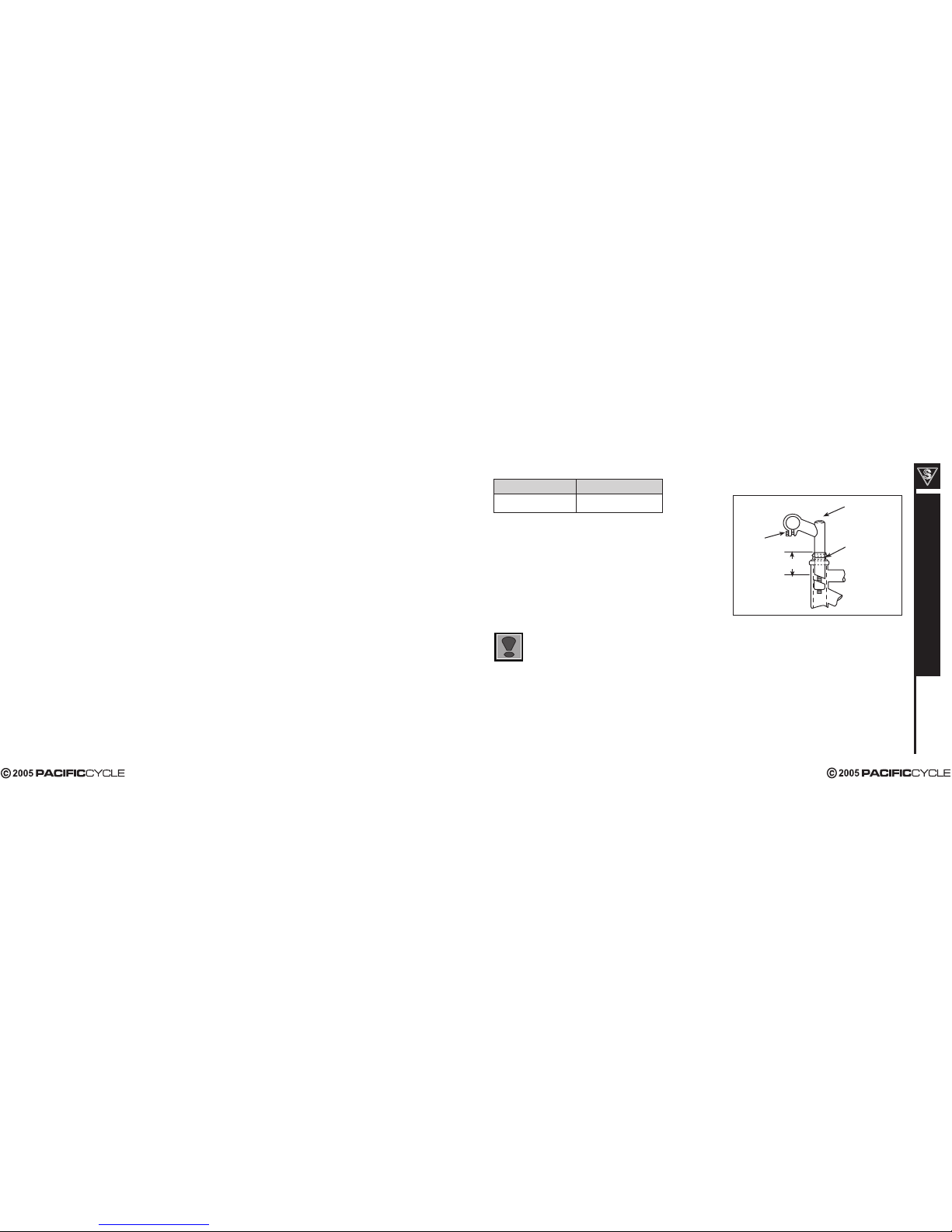
Stem Wedge Bolt
Maximum Height/
Minimum Insertion
Mark
Handlebar Binder Bolt
Exceeds 2 1/2”
(64mm)
Threadless headsets and clamp-on stems are not adjustable. Please refer to page 14
for instructions on installation.
The stem’s “Minimum Insertion” mark must not be visible above the top of the headset.
If the stem is extended beyond this mark, the stem may break or damage the fork’s
steerer tube, which could cause you to lose control and fall.
Failure to properly tighten the stem binder bolt, the handlebar binder bolt, or the bar
end extension clamping bolts may compromise steering action, which could cause you
to lose control and fall. Place the front wheel of the scooter between your legs and
attempt to twist the handlebar/stem assembly using a reasonable amount of force. If
you can twist the stem in relation to the front wheel, turn the handlebars in relation to
the stem, or turn the bar end extensions in relation to the handlebar, you must tighten
the appropriate bolts accordingly.
Page 7
06
05
SAFETY CHECKLIST
Before every ride, it is important to carry out the following safety checks:
1. Brakes
- Ensure front and rear brakes work properly.
- Ensure brake shoe pads are not over worn and are correctly positioned in relation to the rims.
- Ensure brake control cables are lubricated, correctly adjusted and display no obvious wear.
- Ensure brake control levers are lubricated and tightly secured to the handlebar.
2. Wheels and Tires
- Ensure tires are inflated to within the recommended limit as displayed on the tire sidewall.
- Ensure tires have tread and have no bulges or excessive wear.
- Ensure rims run true and have no obvious wobbles or kinks.
- Ensure all wheel spokes are tight and not broken.
- Check that axle nuts are tight. If your scooter is fitted with quick release axles,
make sure locking levers are correctly tensioned and in the closed position.
3. Steering
- Ensure handlebar and stem are correctly adjusted and tightened, and allow proper steering.
- Ensure that the handlebars are set correctly in relation to the forks and the direction of travel.
- Check that the headset locking mechanism is properly adjusted and tightened.
- If the scooter is fitted with handlebar end extensions, ensure they are properly positioned and tightened.
4. Bearings
- Ensure all bearings are lubricated, run freely and display no excess movement, grinding or rattling.
- Check headset, wheel bearings, pedal bearings and bottom bracket bearings.
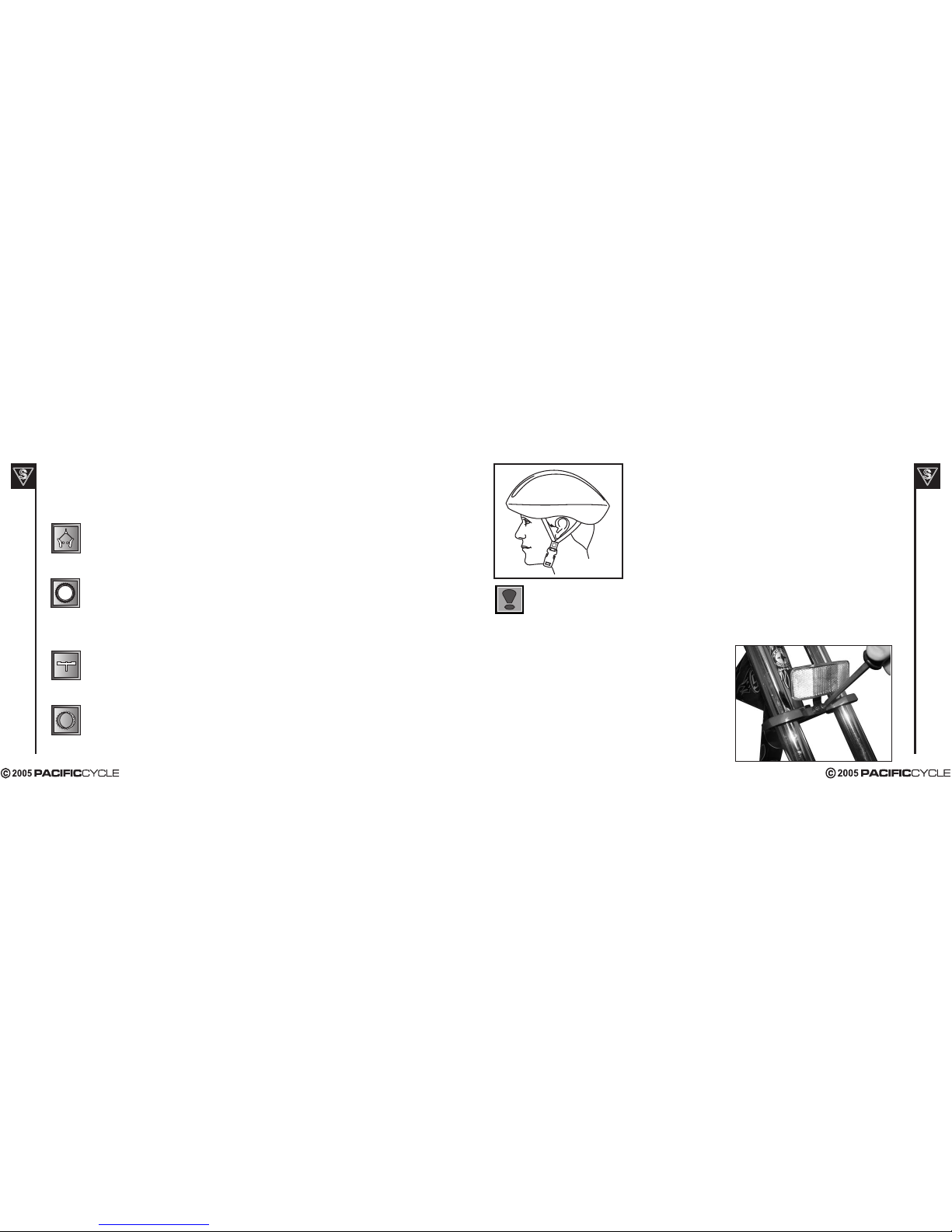
Helmets
It is strongly advised that a properly fitting, ANSI or SNELL approved,
bicycle safety helmet be worn at all times when riding your scooter.
The correct helmet should:
- be comfortable
- be lightweight
- have good ventilation
- fit correctly
- cover forehead
Always wear a properly fitted helmet which covers the forehead when riding a scooter. Many states
require specific safety devices. It is your responsibility to familiarize yourself with the laws of the state
where you ride and to comply with all applicable laws, including properly equipping yourself and your
scooter as the law requires. Reflectors are important safety devices which are designed as an integral
part of your scooter.
FRONT REFLECTOR ASSEMBLY
Locate front reflector brackets and screws in the parts box.
Assemble clear front reflector to lower fork crown using
(2) screws provided. Face reflector forward and tighten
(2) screws securely. Reflector bracket should be +/- 3
degrees from vertical (90 degrees).
1.
2.
Page 8
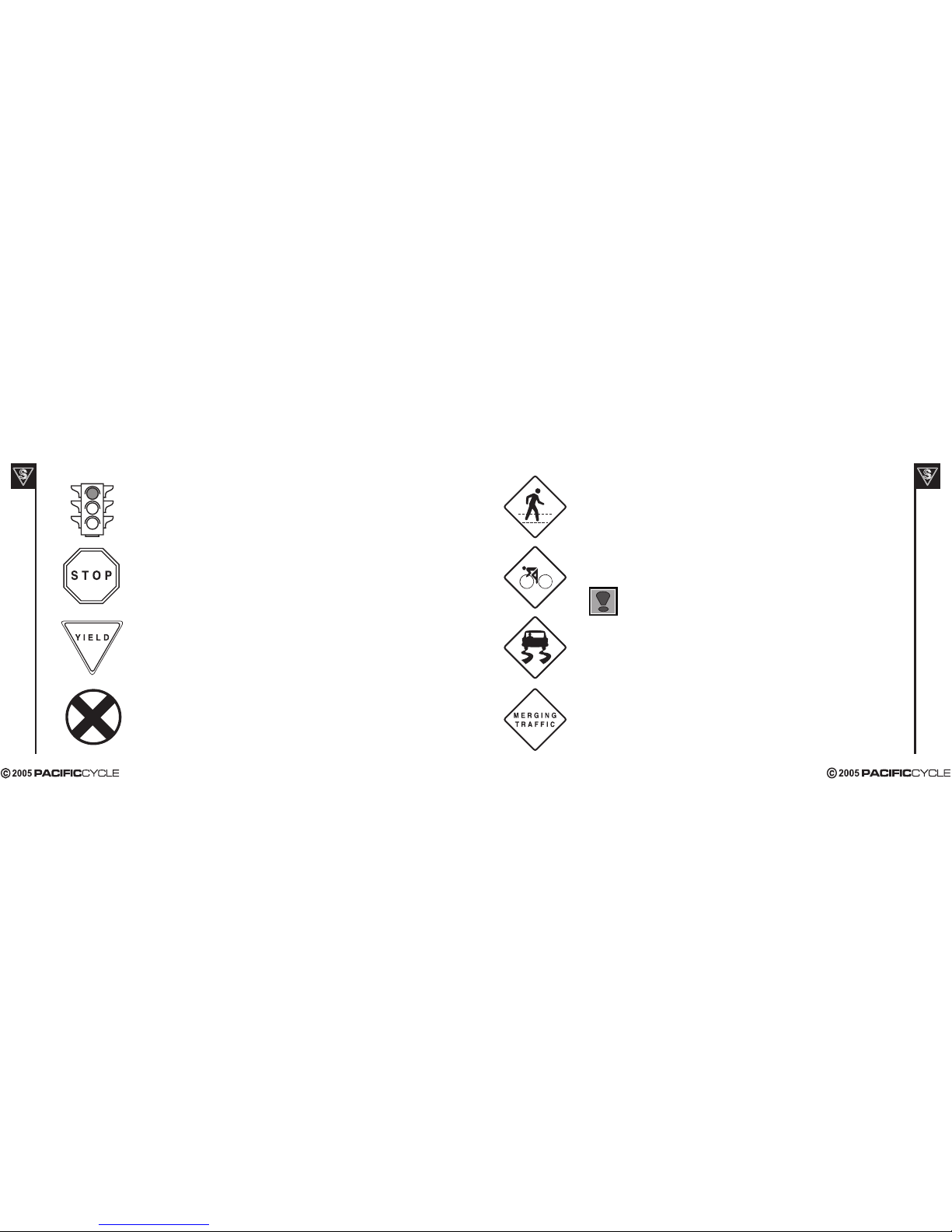
RIDING SAFELY
Scooters are intended for sidewalk riding, and should not be ridden in streets, parking lots
or anywhere that motor vehicles are present. Please consult your local traffic laws for more
information. These safety guidelines are included for your re
ference.
General Rules
When riding obey the same road laws as all other road vehicles, including giving way to
pedestrians, and stopping at red lights and stop signs.
For further information, contact the Road Traffic Authority in your State.
Ride predictably and in a straight line. Never ride against traffic.
Ride defensively. To other road users, you may be hard to see.
Concentrate on the path ahead. Avoid pot holes, gravel, wet road markings, oil, curbs, speed
bumps, drain grates and other obstacles.
Cross train tracks at a 90 degree angle or walk your scooter across.
Expect the unexpected such as opening car doors or cars backing out of concealed driveways.
Be extra careful at intersections and when preparing to pass other vehicles.
Familiarize yourself with all the scooter's features. Practice braking.
Don't carry packages or passengers that will interfere with your visibility or control of the scooter.
Don't use items that may restrict your hearing.
Do not lock up the brakes.
Maintain a comfortable stopping distance from all other riders, vehicles and objects.
Safe braking distances and forces are subject to the prevailing weather conditions.
Wet Weather
IT IS RECOMMENDED TO NOT RIDE IN WET WEATHER
- In wet weather you need to take extra care.
- Brake earlier, you will take a longer distance to stop.
- Decrease your riding speed, avoid sudden braking and take corners with
additional caution.
- Be more visible on the road.
- Wear reflective clothing and use safety lights.
- Pot holes and slippery surfaces such as line markings and train tracks all become
more hazardous when wet.
Night Riding
- Ensure scooter is equipped with a full set of correctly positioned and clean reflectors.
- Refer to page 6 of this manual.
- Use a properly functioning lighting set comprising of a white front lamp and a red rear lamp.
- If using battery powered lights, make sure batteries are well charged.
- Some rear lights available have a flashing mechanism which enhances visibility.
- Wear reflective and light colored clothing.
- Ride at night only if necessary. Slow down and use familiar roads with street lighting, if possible.
IT IS RECOMMENDED TO NOT RIDE AT NIGHT
07
08
Page 9
10
Avoid streets and surfaces with water, sand, gravel, dirt, leaves, and other debris.
Wet weather impairs traction,braking, and visibility.
Do not ride at night.
Brake will get hot from continuous use. Do not touch after braking.
Avoid excessive speed associated with downhill rides.
Adults must assist children in the initial adjustment procedures to unfold scooter,
adjust handlebar and steering to height, and finally to fold scooter.
Obey all local traffic and scooter riding laws and regulations.
Watch out for pedestrians.
Check and secure all fasteners before every ride.
Replace worn or broken parts immediately.
SCOOTER CARE
Security
It is advisable that the following steps be taken to prepare for and help prevent possible theft.
1. Maintain a record of the scooter’s serial number, located on the bottom
of the frame behind the kickstand.
2. Register the scooter with the local police.
3. Invest in a high quality scooter lock that will resist hack saws and bolt cutters.
Always lock your scooter to an immovable object if it is left unattended.
Cornering Technique
Brake slightly before cornering and prepare to lean your body into the corner.
Please refer to pages 47-48 for braking techniques
.
Rules for Children
To avoid accidents, teach children good riding skills with an emphasis on safety from an early age.
Children should be supervised by an adult.
1. Always wear a properly fitted helmet.
2. Do not play in driveways or the road.
3. Do not ride on busy streets.
4. Do not ride at night.
5. Obey all the traffic laws, especially stop signs and red lights.
6. Be aware of other road vehicles behind and nearby.
7. Before entering a street: Stop, look right, left, and right again for traffic. If there's no traffic, proceed into the roadway.
8. If riding downhill, be extra careful. Slow down using the brakes and maintain control of the steering.
9. Never take your hands off the handlebars
.
09
The Consumer Protection Safety Commission advises that the riding of small wheel diameter
scooters at excessive speeds can lead to instability and is not recommended.
Children should be made aware of all possible riding hazards and correct riding behavior before they take to the streets.
- Do not leave it up to trial and error.
Always wear safety equipment such as helmet, knee pads and elbow pads. Always wear a helmet when riding your scooter
and keep the chinstrap securely buckled. Always wear shoes.
Ride on smooth, paved surfaces away from motor vehicles.
Avoid sharp bumps, drainage grates, and sudden surface changes. Scooter may suddenly stop.
Page 10
12
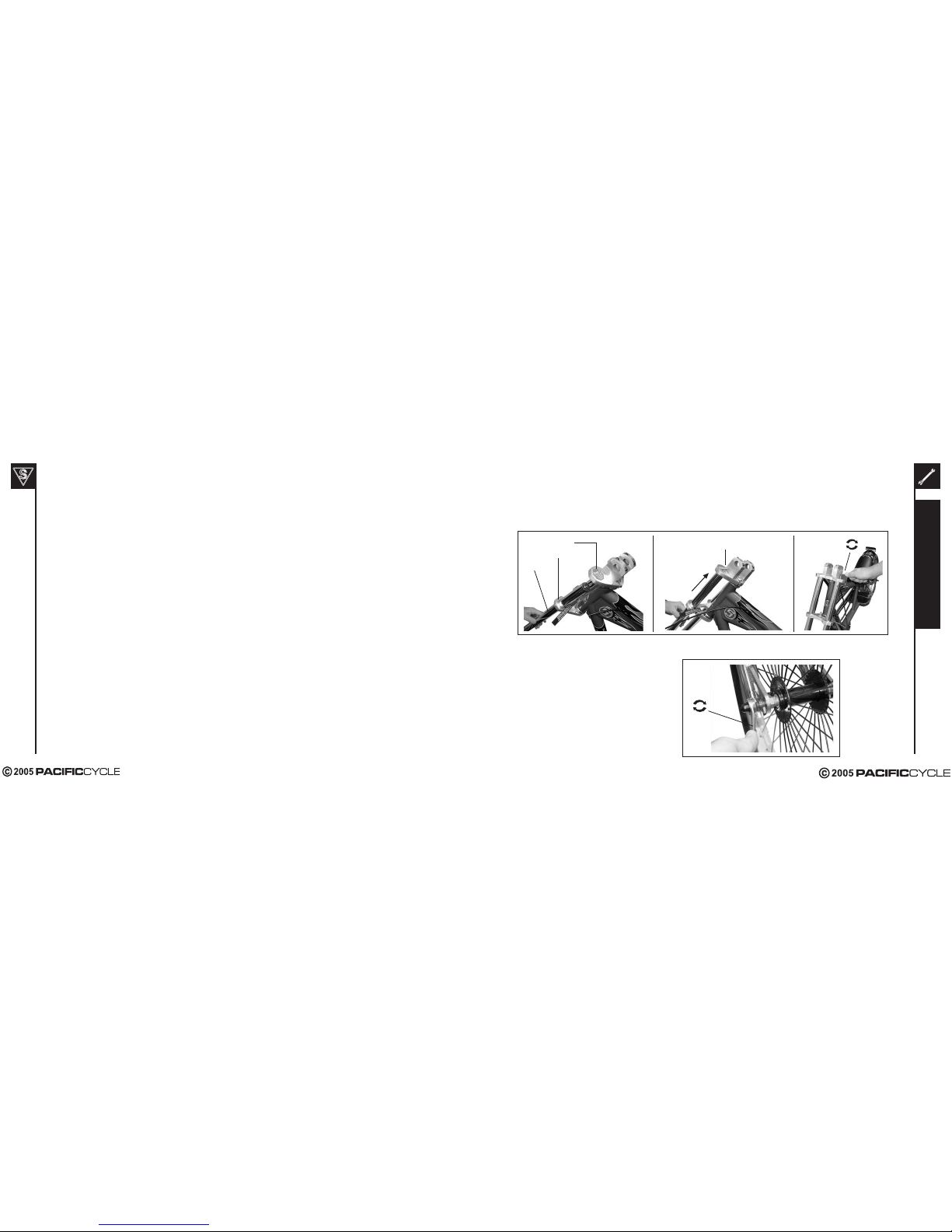
Stingray Scooter Fork Assembly
Step #1
Insert one fork leg through the lower crown, and slide it up until it contacts the bolt in the upper crown. Push the leg
up to remove the red stop sign decal from the fork leg. Using a 5mm hex (Allen) wrench align the upper crown bolt
with the fork leg, and tighten upper crown bolt completely into the fork leg. Repeat for other fork leg.
PART 3 - ASSEMBLY
Basic Maintenance
The following procedures will help you maintain your scooter for years of enjoyable riding.
For painted frames, dust the surface and remove any loose dirt with a dry cloth. To clean, wipe with a damp cloth
soaked in a mild detergent mixture. Dry with a cloth and polish with car or furniture wax. Use soap and water to clean
plastic parts and rubber tires. Chrome plated bikes should be wiped over with a rust preventative fluid.
Store your scooter under shelter. Avoid leaving it in the rain or exposed to corrosive materials. Riding on the beach or
in coastal areas exposes your scooter to salt which is very corrosive. Wash your scooter frequently and wipe or spray
all unpainted parts with an anti-rust treatment. Make sure wheel rims are dry so braking performance is not affected.
After rain, dry your scooter and apply anti-rust treatment.
If the hub and bottom bracket bearings of your scooter have been submerged in water, they should be taken out and
re-greased. This will prevent accelerated bearing deterioration.
If paint has become scratched or chipped to the metal, use touch up paint to prevent rust. Clear nail polish can also
be used as a preventative measure.
Regularly clean and lubricate all moving parts, tighten components and make adjustments as required. (Refer to
Parts 4 and 5 of this manual for further details). The use of alloy components and BED, SATIN and TITANIUM surface
treatments minimizes the number of places where rust can surface.
Storage
Keep your scooter in a dry location away from the weather and the sun. Ultraviolet rays may cause paint to fade or
rubber and plastic parts to crack. Before storing your scooter for a long period of time, clean and lubricate all components and wax the frame. Deflate the tires to half pressure and hang the scooter off the ground. Don't store near
electric motors as ozone emissions may effect the rubber and paint. Don't cover with plastic as "sweating” will result
which may cause rusting. Please notice that your scooter warranty does not cover paint damage, rust, corrosion, dry
rot or theft.
Step #
2
Align the two fork legs so that the axle dropouts
face forward. Install front wheel, making sure that
the step washers seat into the fork dropouts as
you tighten the axle nuts. Tighten front axle nuts
completely using 15mm wrench.
Upper Fork Crown
Lower Fork Crown
Fork Leg
Remove Decal
12
11
Page 11

14
13
Tightening/Preloading Aheadset
Stem Installation
(Should be assembled on the bike already)
1. Insert the compression bolt through the top
cap and the stem. Begin threading into the
star nut.
2.Tighten compression bolt so it removes all
play from the fork, but allows the fork to rotate
smoothly.
3. Align the stem with the front wheel. Tighten
the stem clamp bolts to secure the stem to the
steerer tube.
Handlebar Installation
1. Remove the stem cap bolts and stem cap.
2. Insert handlebar into the stem cap.
3. Tighten the stem cap bolts equally. Note
the distance between the stem and stem cap:
It should be equal on the top and bottom of the
stem cap.
A must be equal distance.
Installed
by
factory
Compression Bolt
Top Cap
Stem Clamp Bolts
Spacer
Headset Wedge
Bearing Race
Bearing Dust Cover
Bearing Retainer
Star Nut
(Inside Steerer Tube)
Upper Headset Cup
Headtube
Lower Headset Cup
Bearing Retainer
Bearing Dust Cover
Headset Crown Race
fork
Steerer Tube
Handlebar
Stem Cap
Bolts
Stem Cap
Stingray Scooter Front
Fender Assembly
After the first fork leg is installed:
1. Assemble front fender to fork l
eg and hand
tighten bolt. When installing second fork leg,
remove fender mounting bolt first, assemble
fork leg, and re-install fender mounting bolt.
Hand tighten.
At the end of fork assembly:
2. After fork and front wheel
are completely
assembled, center fender and tighten both
mounting bolts securely.
Step #3
Using 5mm hex (Allen) wrench, tighten the two
lower fork crown pinch bolts completely. Please
note that these bolts should be tightened until the
fork is secure only,
DO NOT OVER TIGHTEN,
or damage to the lower fork crown may occur.
1.
2.
Page 12

16
Band Brake Series Installation
Step 1
Assemble the inner drum clockwise onto
the rear hub. Make sure the re-entrant side
is fixed toward you.
Step 2
Assemble the outer shell onto the hub axle
covering inner drum and fasten the nut.
Step 3
Thread inner wire through the adjusterscrew then connect and fix its end on the
brake pad control lever.
Step 4
Finely adjust the adjuster-screw to reach
the perfect braking performance.
Note:
1. Lubricating the drum can cause faulty braking.
2. Brake pad will wear over time. Turn adjusting barrel to compensate
for pad wear. Replace brake pad before it is completely worn.
Hub
Inner Drum
Clockwise
Outer Shell
Pad Control Lever
Fixing Nut
Inner Wire
Adjuster Screws
15
If the stem is not inserted into the top nut to at least the “Minimum Insertion” mark, it is possible to over-tighten the stem
bolt and damage the fork steerer tube. If these instructions are
not followed, it could cause an unsafe condition and risk injury
to the rider. Check steering tightness prior to riding by strad
dling the front wheel. Try turning the handlebar. If you can
turn it without turning the front wheel, the stem is too loose.
Re-align the handlebar with the front wheel and re-tighten the
stem bolt.
Sunken Stem Bolt System
1. Remove the protective shipping cap from the stem wedge.
2. Remove the Stem Plug from the stem. Loosen the Stem Bolt
with a 6mm allen wrench.
3. Insert the stem into the headtube of the scooter. Ensure that
the Minimum Insertion Line is below the top nut of the headset.
4. Align the stem and handlebar so it is in line with the front wheel.
5. Tighten the Stem Bolt with the 6mm allen wrench. Reinsert the
Stem Plug into the stem.
WARNING: MINIMUM INSERTION LINE MUST BE HIDDEN WITHIN
THE HEADTUBE OF THE SCOOTER.
Page 13

18
While holding the shoe against the
rim, tighten the shoe fixing nut.
3.
Adjust the balance with the spring
tension adjustment screws.
5.
Depress the brake lever about 10 times as
far as the grip to check that everything is
operating correctly and that the shoe
clearance is correct before using the brakes.
6.
Pass the inner cable through the inner
cable lead. Set the cable with a clear
ance
of 1mm between each brake pad and the
rim, tighten the cable fixing bolt.
4.
5 mm Allen key
5 mm Allen key
1mm 1mm
1mm
Spring tension
adjustment screw
Spring tension
adjustment screw
Depress about
10 times
1 mm 1 mm
shoe fixing nut
17
V - Brake
If fitted with V-Brakes, insert the brake
body into the center spring hole in the frame
mounting boss, and then secure the brake
body to the frame with the link fixing bolt.
1.
While holding the shoe against the rim, adjust the
amount of shoe protrusion by interchanging the
position of the B washers (i.e. 6 mm and 3 mm) so
that dimension A is kept at 39 mm or more.
2.
5 mm Allen key
Washer
Link
fixing
bolt
Stopper pin
Spring
hole
39 mm or more
A
3 mm washer B 6 mm washer B
Washer A
Shoe fixing link
Washer A
Washer
Shoe fixing nut
Page 14

20
Check your Brakes
Press each brake lever to make sure that there is no binding and that the brake pads press hard enough on the rims
to stop the bike. The brake pads should be adjusted so they are 1 mm to 2 mm away from the rim when the brakes
are not applied. Brake pads should be centered on the rim and “toed-in” so the rear portion of each brake pad is about
0.5 - 1.0 mm farther from the rim than the front portion of the brake pad.
Do not ride the scooter until the brakes are functioning
properly. To test, apply the brakes while trying to push
the bike forward to make sure they will stop the scooter.
Never ride a scooter that is not functioning properly.
Do not lock up brakes. Sudden or excessive application
of the front brake may pitch the rider over the handlebars,
causing serious injury or death. When braking, always
apply the rear brake first, then the front.
Brake pad aligned with the rim surface Pad and rim should be parallel.
Direction of rim
rotation
0.5 - 1.0 mm
1- 2 mm
19
V-Style Brakes
If not already assembled, take the brake noodle from the parts box
and slide the cable through the larger opening. The cable housing
will then seat into the end of the noodle. Slide the cable through the
cable lead on the end of the left brake arm, this will cause the noodle
to fit into the lead. Slip the brake cable boot over the cable and posi
tion it between both brake arms. Next, loosen the 5mm anchor bolt
at the end of the right brake arm and slide the cable under the retain
ing washer. Pull the slack out of the cable making sure a distance of
39mm or more remains between the end of the lead and the start of
the anchor bolt. Once the cable is secured to the brake arms, engage
the brake lever several times, checking the position of the brake
shoes at the rim. The brake shoes should be 1mm away from the
rim when in a relaxed position. When the brake lever is engaged, the
brake shoe should hit the rim flush (never the tire) with the front brake
pad touching the rim slightly before the rear. This is called “toeing-in”
your brake shoe. If this position is not achieved, adjustments to the
brake shoe are required. Loosen the brake shoe hardware and reposi
tion the brake shoe. It may take several shoe and cable adjustments
before the required position is accomplished.
Brake
Noodle
Outer
Cable
Lead
Brake
Cable
Boot
Anchor
Bolt
Brake
Arm
Tension
Screw
Brake
Shoe
Pivot
Bolt
Page 15

22
Fork Leg
Brake Cable
Housing
Rotating
Rod
Cable Boot
with Spring
inside
Cable Anchor
Bolt
Caliper
Body
Actuating
Arm
Caliper Mounting
Bolts with spacers
Quick Release
lever
Fork Drop Out
Disc
Disc Mounting
Bolts
Hub
Centering Bolt
Centering Bolt (inside)
These brakes require breaking in! Ride and use the brakes gently for 13
miles before using the brakes in downhill conditions, for sudden stops,
or any other serious braking. Please be aware that your brake system will
change in performance throughout the wear-in process. The disc brake
should be cleaned before the first ride using rubbing alcohol. NEVER use oil
or similar products to clean your disc brake system.
21
Disc Brakes
If fitted with a front disc brake, the components should already
be attached. However, please check all connections before
attempting to ride the scooter. Secure tightly the 6 bolts that
hold the disc to the front wheel hub and the 2 bolts that hold
the brake mechanism to the fork. Insert the front wheel into the
fork dropouts ensuring that the disc fits into the brake mecha
nism between the enclosed brake pads. Secure the front wheel
to the scooter by tightening the quick release mechanism and
clamping the lever to the closed position. Please refer to
section 6 for further instruction on quick release mechanisms.
Next, attach the cable to the brake lever by inserting the cable
end into the cable end holder after the barrel adjuster and lock
nut slots have been aligned with the cable end holder. After
the cable is secured to the lever, rotate the barrel adjuster and
lock nut so the slots no longer line up. Ensure the cable hous
ing seats appropriately into the end of the barrel adjuster and
check for any kinks or damage.
Slide the exposed brake cable through the rotating rod located
on the caliper body and seat the housing into the same stop.
Insert the cable into the spring and spring boot.
Next, slide the cable through the cable anchor and pull all the
slack out. Secure the cable in place by tightening the bolts that
comprise the anchor assembly. Some disc brakes will have a
centering devise while others are a free-floating mechanism.
If your caliper body is equipped with centering bolts, apply the
brake lever after the cable has been connected. While engag
ing
the lever, tighten the centering bolts securely. This will center
the caliper body on the disc.
Brake Pads
“C” Clip
Actuating Arm
Rotating Rod
Cable Anchor
Bolt
Caliper
Mounting
Bolt with
spacers
Caliper
Mounting
Bolt with
spacers
Barrel Adjuster
Brake Cable
Housing
Cable
Insertion
Slot
Brake Cable
Cable End
Holder
Brake Type
Selector
Brake Lever
DISC GETS HOT! Severe injury could result from
contact with the hot disc! Mind your legs, as well
as your hands.
Lock Nut
Page 16

24
SCOOTER
Handlebars
Remove the protective cap from the stem wedge and loosen the stem
bolt using the 6mm Allen key. Some models may use a 13mm
hexagonal bolt instead of an Allen key bolt. Place the handlebar stem
into the head tube, observing the minimum insertion mark on the
handlebar stem and ensuring that all cables are free of tangles. Check
that the fork and the handlebar are facing forward, and that they are
properly aligned with the front wheel. Tighten the stem bolt. Rotate the
handlebar to the desired position. Tighten stem cap bolt 1 (see picture)
two turns, tighten stem cap bolt 2 two turns and so on. Repeat until
handle bar is secure to the stem. See picture for a 4 or 6-bolt system.
Also check that the stem binder bolts are tightened equally and securely.
The handlebar must be inserted so that the minimum insertion
mark cannot be seen.
WARNING: Over tightening the stem
bolt or headset assembly may cause damage to the scooter and/
or injury to the rider.
Stem
Bolt
Minimum
Insertion Mark
Head
Tube
Foreword: Assembling a scooter is an important responsibility. Proper assembly not only gives the rider more enjoyment
of the scooter; it also offers an important measure of safety.
Stem Cap Binder Bolts
Stem Wedge
Four Bolt
Face
Plate
Six Bolt
Face
Plate
Getting Started
Open the carton from the top and remove the scooter. Remove the straps and protective wrapping from the scooter.
Inspect the scooter and all accessories and parts for possible shortages. It is recom
mended that the threads and all moving
parts in the parts package be lubricated prior to installation. Do not discard packing materials until assembly is complete
to insure that no required parts are accidentally discarded. Assemble your scooter following the steps that pertain to
your model.
Note: Your scooter may be equipped with different style components than the ones illustrated.
23
Final Check
- If you encounter any problems, refer to the appropriate section
and make any necessary adjustments.
- Check the tire pressure and inflate each tube to the recom
mended
psi as stated on the sidewall of the tire.
- Check that the kickstand operates smoothly and the
kickstand bolt is secured tightly.
- Finally, examine the scooter. Make sure all accessories are
attached and all quick releases, nuts and bolts have been
tightened securely.
- Correct maintenance of your scooter will ensure many years
of happy riding. Service your scooter regularly by referring
to the relevant sections of this manual, OR take it to a
professional bicycle shop.
Remember: Always wear a helmet and obey all
traffic laws.
Never inflate a tire beyond the maximum
pressure marked on the tire’s sidewall.
Exceeding the recommended pressure
may blow the tire off the rim, which
could cause damage to the scooter and
injury to the rider and bystanders.
Tighten both rear wheel axle nuts or the
quick release mechanism securely. Failure
to do this may cause the rear wheel to
dislodge from the frame dropouts resulting
in serious damage or injury.
Page 17

26
Rotors
Some freestyle BMX bicycles come equipped with a detan
gler
system that will allow the handlebar to spin 360-degrees without
binding the cables. It is very important that this system is adjusted
correctly. Installation should only be done by a qualified scooter
mechanic with the correct tools.
Upper Cable
1. First connect the barrel end of the upper cable to the
rear brake lever. Make sure the long cable casing is on
top of the short cable casing; otherwise, the upper cable
will have a twist in it.
2. Route the upper cable through the handlebars (below
the crossbar) with the short cable casing on the same
side as the rear brake lever.
3. Connect the upper cable to the upper plate by passing
the football ends of the upper cable through the threaded
holes in the upper plate and connecting them to the bearing.
4. Screw the adjusting barrels into the upper plate. Don’t
tighten the locknuts at this time.
Lower Cable
1. Slide the cable casing through the cable guide on the frame.
2. Connect the lower cable to the lower plate by passing
the football ends of the lower cable through the threaded
holes in the lower plate and connecting them to the bearing.
3. Screw the adjusting barrels into the lower plate. Don’t
tighten the locknuts at this time.
4. Connect the lower cable to the rear brake. Don’t adjust
the rear brake at this time.
NOTE: Check to make sure all 11 cable casing ends on
the upper and lower cables are seated correctly, and that
the spring tension of the rear brake is pulling the bearing down.
Adjustment
1. Screw the cable adjusters on the rear brake lever and the
upper cable splitter all the way in.
2. Screw the adjusting barrels in the upper plate in (or out)
to set the bearing for maximum travel. The bearing should
be as far down as it can go without resting on the lower
plate or the adjusting barrels screwed into the lower plate.
3. Use the adjusting barrels that are screwed into the
upper plate to make the bearing parallel to the upper
plate. Use a 10mm wrench to tighten the locknut on the
left adjusting barrel of the upper cable. Leave the right
adjusting barrel loose.
4. Screw the lower cable adjusting barrel into (or out of)
the lower plate until they are as close to the bearing as
they can get without touching it.
5. Screw the cable adjuster on the upper cable splitter out
until all slack is removed from the upper cable. Then
screw the cable adjuster out one more turn to raise the
bearing an additional 1mm away from the lower cable
adjusting barrels.
CAUTION: Don’t screw the cable adjuster on the upper
cable splitter out more than 8mm. Use the cable adjuster
on the rear brake lever if more adjustment is needed.
6. Check for bearing flop by placing the handlebars in the
normal riding position, then quickly rotate the handlebars
back and forth. Perform the following steps to eliminate
bearing flop.
NOTE: The bearing should never be allowed to rest on
the lower plate or lower cable adjusting barrels.
a) Screw the lower cable adjusting barrels out of (or
into) the lower plate until all bearing flop is eliminated.
b) Tighten the locknut of the right adjusting barrel on the
lower cable.
c) Rotate the handlebars 180 degrees and recheck
for bearing flop. If there is any bearing flop, use the
“loose” adjusting barrels on the upper and lower cable to
remove it.
d) Repeat steps (6a) and (6c) until the handlebars can be
rotated 360 degrees without any bearing flop.
7. Finish adjusting the rear brakes.
25
Front Wheel
1. Make sure the brakes are loose enough to allow the wheel to
pass through the brake pads easily.
2. Place wheel into fork drop outs.
3. Install retaining washers with raised lip pointed towards the fork,
and insert into the small hole of the fork blade.
NOTE: Some scooters may have step retaining washers in place
of the retaining washer (shown in dotted box). If so, install the
step retaining washer, raised portion sliding in to the fork dropouts.
4. Install axle nut and tighten.
Make sure the wheel is centered between the fork blades.
5. Spin the wheel to make sure that it is centered and clears the
brake shoes. Tighten the brakes if necessary.
6. Turn the scooter upright using the kickstand to support it.
It is very important to check the front wheel
connection to the scooter. Failure to properly tight
en
may cause the front wheel to dislodge.
Axle Nut
Axle
Hub
Cone Nuts
Fork Drop Out
Retaining
Washer
Step
Retaining
Washer
Page 18

28
Axle Peg Assembly Instructions
Non-Threaded
First remove the axle nut from the wheel. There will be either
a retaining washer or a step retaining washer included. Place
this washer between the peg and the frame of the scooter. Slide
the peg onto the axle, followed by a flat washer and lastly the
axle nut. Tighten the axle nut clockwise until the peg fits snugly
against the frame or fork. Repeat for all the remaining pegs.
Non-Threaded
Threaded
Threaded
This style of peg is threaded to fit the axle. Make sure the axle
nut is tight with a 15mm wrench. Place a screw driver through
the mounting holes of the peg and attach the peg to the axle by
turning clockwise. Tighten against the frame or fork for a snug
fit. Repeat for all the remaining pegs.
PLEASE NOTE: Not all axles are able to accept axle pegs.
Please consult the Pacific Cycle Service Department if
you have any questions. Some scooters come with two
or four pegs.
27
Failure to adjust correctly may result in
loss of braking power and personal injury.
Barrel End
Single Cable Casing
Cable Adjuster
Cable Splitter
Upper Cable
(short casing)
Upper Cable
(long casing)
Upper Plate
Bearing
Football Ends
Lower Plate
Lower Cable
Adjusting Barrel
Locknut
Keyed Washer
Locknut
Adjusting Barrel
37mm + or - 1mm
Set for Max. Travel
Minimum 1mm (1/32”)
Page 19

30
PART 4 - SERVICING
Correct routine maintenance of your new bike will ensure:
Smooth running - Longer lasting components - Safer riding - Lower running costs
Every time you ride your scooter, its condition changes. The more you ride, the more frequently maintenance will be
required. We recommend you spend a little time on regular maintenance tasks. The following schedules are a useful guide
and by referring to Part 5 of this manual, you should be able to accomplish most tasks. If you require assistance, we
recommend you see a scooter specialist.
Weekly
Every Six Months
Yearly
brake calipers
brake levers
brake cables
wheel bearings
headset
oil
oil
lithium based grease
lithium based grease
lithium based grease
3 drops from oil can
2 drops from oil can
disassemble
disassemble
disassemble
Schedule 1 - Lubrication
Note: The frequency of maintenance should increase with use in wet or dusty conditions. Do not over
lubricate - remove excess lubricant to prevent dirt build up. Never use a degreaser to lubricate your chain (WD-40™)
ComponentFrequency Lubricant
How to Lubricate
29
Final Check
Install any additional parts that are supplied with your bike.
NOTE: Your scooter may be equipped with different style components than the ones illustrated.
Reflectors: Attach the white reflector to the front bracket and the red reflector to the rear bracket using an 8mm
wrench or a Phillips head screwdriver. Attach the brackets to the scooter using the hardware provided. For some models,
the front reflector bracket will be mounted on the front brake assembly bolt that fits through the fork. It is important to
make sure all connections are tightened securely and that the reflectors are properly angled.
Tire Pressure: Check tire pressure, inflate to the range recommended on the tire sidewalls.
Pegs: There are many different types of pegs-too many to deal with individually in this manual.
Please see your dealer for specific information regarding peg installation.
Before riding, ensure all nuts, bolts and fittings
on the scooter have been correctly tightened.
Page 20

32
Tools Required
1. Open ended wrench or ring
wrenches: 8mm, 9mm, 10mm,
12mm, 13mm, 14mm, 15mm
2. Open end or pedal wrench 15mm
3. Allen key wrenches: 4mm, 5mm,
6mm, 8mm
4. Adjustable wrench
5. Standard flat head screwdriver
6. Standard Phillips head screwdriver
7. Standard slip joint pliers
8. Tire pump
9 Tube repair kit
10. Tire levers
Travel Tools
1. Spare Tube
2. Patch kit
3. Pump
4. Tire levers
5. Multi-tool
6. Change (phone call)
31
Task
Check tire pressure
Check brake operation
Check wheels for loose spokes
Make sure nothing is loose
Quick wipe down with damp cloth
Lubrication as per schedule 1
Lubrication as per schedule 1
Check brake adjustment
Check brake and gear cable adjustment
Check tire wear and pressure
Check wheels are true and spokes tight
Check hub, head set
Check handlebars are tight
Check frame and fork for trueness
Check all nuts and bolts are tight
Lubrication as per schedule 1
Check all points as per monthly service
Check and replace brake pads, if required
Lubrication as per schedule 1
Frequency
Before every ride
After every ride
Weekly
Monthly
Every Six Months
Yearly
Page Reference
34
40-43
33
33
13
30
30
40-43
38
34
33
35, 39
37-38
44
30
31
40-43
30
Schedule 2 - Service Checklist
Page 21

34
Tire Inspection
Tires must be maintained properly to ensure road holding and stability. Check the following areas:
Inflation: Ensure tires are inflated to the pressure indicated on the tire sidewalls.
It is better to use a tire gauge and a hand pump than a service station pump.
Caution: If inflating tires with a service station pump, take care that sudden over inflation
does not cause tire to blow out.
Bead
Seating: When inflating or refitting tire, make sure that the bead is properly seated in the rim.
Tread:
Check that the tread shows no signs of excessive wear or flat spots, and that there are no cuts or other damage.
Caution: Excessively worn or damaged tires should be replaced.
Valves: Make sure valve caps are fitted and that valves are free from dirt. A slow leak caused by the entry of the dirt can
lead to a flat tire, and possibly a dangerous situation.
Recommended Tire pressure:
The recommended pressure is molded on the sidewall of your scooter tires.
33
WHEELS AND TIRES
Wheel Inspection
It is most important that wheels are kept in top condition. Properly maintaining your scooter's wheels will help braking
performance and stability when riding. Be aware of the following potential problems:
• Dirty or greasy rims:
Caution: These can render your brakes ineffective. Do not clean them with oily or greasy materials.
When cleaning, use a clean rag or wash with soapy water, rinse and air dry. Don't ride while they're wet.
When lubricating your scooter, don't get oil on the rim braking surfaces.
• Wheels not straight:
Lift each wheel off the ground and spin them to see if they are crooked or out of true. If wheels are not straight, they
will need to be adjusted. This is quite difficult and is best left to a professional bicycle dealer.
• Broken or loose spokes:
Check that all spokes are tight and that none are missing or damaged.
Caution: Such damage can result in severe instability and possibly an accident if not corrected.
Again, spoke repairs are best handled by a specialist.
• Loose hub bearings:
Lift each wheel off the ground and try to move the wheel from side to side.
Caution: If there is movement between the axle and the hub, do not ride the scooter. Adjustment is required.
•Axle nuts:
Check that these are tight before each ride.
PART 5 - DETAILED MAINTENANCE
Page 22

36
Remove tire bead from the rim.
Pull tire back onto the rim.
6. Match the position of the leak in the tube with the tire to locate the possible
cause and mark the location on the tire.
7. Remove the tire completely and inspect for a nail, glass, etc. and remove if
located. Also inspect the inside of the rim to ensure there are no protruding
spokes, rust or other potential causes. Replace the rim tape which covers the
spoke ends, if damaged.
8. Remount one side of the tire onto the rim.
9. Using a hand pump, inflate the tube just enough to give it some shape.
10. Place the valve stem through the hole in the rim and work the tube into the
tire. Note: Do not let it twist.
11. Using your hands only, remount the other side of the tire by pushing the edge
toward the center of the rim. Start on either side of the valve and work around
the rim.
12. Before the tire is completely mounted, push the valve up into the rim to make
sure the tire can sit squarely in position.
13. Fit the rest of the tire, rolling the last, most difficult part on using your thumbs.
Note: Avoid using tire levers as these can easily puncture the tube or damage
the tire.
14. Check that the tube is not caught between the rim and the tire bead at any point.
15. Using a hand pump, inflate the tube until the tire begins to take shape, and check
that the tire bead is evenly seated all the way around the rim. When properly
seated, fully inflate the tire to the pressure marked on the sidewall. Use a tire air
pressure gauge to check.
16. Replace the wheel into the frame checking that safety washers are engaged and
wheel is centered.
35
Hub Bearing Adjustment
When checked, the hub bearings of either wheel will require
adjustment if there is any more than slight side play.
1. Check to make sure neither locknut is loose.
2. To adjust, remove wheel from scooter and loosen the locknut on
one side of the hub while holding the bearing cone on the same
side with a flat open end wrench.
3. Rotate the adjusting cone as needed to eliminate free play.
4. Re-tighten the locknut while holding the adjusting cone in position.
5. Re-check that the wheel can turn freely without excessive side play.
How To Fix a Flat Tire
If yo u need to repair a tire, fo llow these steps:
1. Remove the wheel from the scooter.
2. Deflate the tire completely via the valve.
Loosen the tire bead by pushing it inward all the way around.
3. Press one side of the tire bead up over the edge of the rim.
Note: Use tire levers, not a screwdriver, otherwise you may
damage the rim.
4. Remove the tube, leaving the tire on the rim.
5. Locate the leaks and patch using a tube repair kit, carefully
following the instructions, or replace the tube.
Note: Ensure that the replacement tube size matches the size
stated on the tire sidewall and that the valve is the correct type
for your scooter.
Lock
Washer
Axle
Lock Nut
Hub Body
Ball Bearings
Bearing
Cone
Washer
Axle Nut
Push tire bead
into the center
of the rim.
Page 23

38
Cables and Cable Housing
Cables and housing are one of the most overlooked
parts on the scooter. The first indication that your
cables and housing need to be replaced is an
increased amount of pressure needed to operate the
brakes or shifters. Before every ride, check that there
are no kinks or frays in the cables and housing. Also
check that the housing is seated properly into each
cable stop of the scooter. It is recommended
that the cables and housing are replaced at least
every riding season to prolong the life of your bike.
Do not ride a scooter that is not
operating properly.
When re-fitting the stem, make sure the handlebars are correctly aligned and tightened using the appropriate
hex wrench or allen key.
Do not over tighten.
Test the security of the handlebar within the stem, and the stem within the fork steerer tube, by clamping the front
wheel between your knees and trying to move the handlebar up and down, and from side to side. The handlebar
should not move when applying turning pres
sure.
Never ride unless the handlebar clamping
mechanism has been securely tightened.
kink
fray
good cable
Handlebars
The exact positioning of the handlebar is a matter
of personal comfort.
Rider should be able to comfortably steer, balance and apply
the brakes. If this is not the case, adjust handlebar position.
37
HANDLEBARS AND STEM
Handlebar Stem
The handlebar stem fits into the steering column and is held firm by
the action of a binder bolt and expander wedge which, when tight
ened,
binds with the inside of the fork steerer tube.
When removing the stem, loosen the stem bolt two or three turns,
then give it a tap to loosen the wedge inside.
Lubricate by first wiping off any old grease and grime, then applying a
thin film of grease to the part, including the wedge, that will be inser
ted
into the frame.
The height of the handlebar can be adjusted to suit your
comfort preference.
If the stem is removed from the steering column, you will notice a
mark about 65mm up from the bottom with the words “max. height” or
“minimum insertion".
Never ride a scooter if the stem has
been raised so that the max. height/
minimum insertion line can be seen.
Handlebar Clamp Bolts
Handlebar Binder Bolt
Stem Bolt
Max. Height/
Min. Insertion Mark
Stem Bolt Wedge
Max. Height/
Minimum Insertion
Mark
Warning: Over tightening the stem
bolt or headset assembly may cause
damage to the scooter and/or injury
to the rider.
Page 24

40
BRAKES
The correct adjustment and operation of your scooter's brakes is extremely important for safe operation. Brakes should be
checked for effective operation before every ride. Frequent checking of adjustment is necessary as the control cables will
stretch and the brake pads will become worn with use.
Never ride a scooter unless the brakes are functioning properly.
There are several of hand operated scooter brakes in common use: sidepull calipers, cantilever calipers, linearpull, Band,
and disc brake. Both utilize a handlebar mounted lever which controls a cable to operate the brake. Sidepull brakes
are mounted to the frame or fork via a single pivot point. Cantilever brakes use two brake pivot arms, each mounted on
separate pivots on either side of the frame/fork.
Inspection
Brake levers should be checked for tightness at least every three
months. They should be set in a comfortable position within easy
reach of the rider's hands, and must not be able to move on the
handlebar. Some brake levers make use of a reach adjustment screw,
which can be altered to the distance between the handlebar grip and
the lever, as required. The brake pads should be checked for correct
positioning and tightness before every ride, and the various bolts and
nuts at least every three months. Squeeze each brake lever to make
sure they operate freely and that the brake pads press hard enough
on the rims to stop the bike. There should be about 1mm - 2mm
clearance between each pad and the rim when the brakes are not
applied. The brake pads must be properly centered for maximum
contact with the rim. Replace the brake pads if they are over worn so
that the grooves or pattern cannot be seen. The brake cable wires
should be checked for kinks, rust, broken strands or frayed ends. The
outer casing should also be checked for kinks, stretched coils and
other damage. If the cables are damaged, they should be replaced.
Cantilever Brakes
Brake Cable
Brake Arm
Straddle Cable
39
HEADSET
Inspection
The headset bearing adjustment should be checked every month.
This is important as it is the headset which locks the fork into the
frame, and if loose, can cause damage or result in an accident.
While standing over the frame top tube with both feet on the ground,
apply the front brake firmly and rock the scooter back and forth; if you
detect any looseness in the headset, it will need adjustment. Check
that the headset is not over tight by slowly rotating the fork to the right
and left. If the fork tends to stick or bind at any point, the bearings
are too tight.
Note: If your bike is equipped with a threadless headset, please see
a qualified specialist for repairs and adjustments.
Adjustment
Loosen the headset top locknut or remove it completely along with the
reflector bracket, if fitted. Turn the adjusting cup clockwise until finger
tight. Replace the lock washer or reflector bracket and re-tighten the
lock nut using a suitable wrench.
Note: Do not over tighten or bearing damage will occur.
Lock Nut
Lock Washer
Adjusting Cup/Cone
Ball Retainer
Top Head Cup
Bottom Head Cup
Ball Retainer
Crown Race
Always make sure that the headset is properly
adjusted and that the headset locknut is fully
tightened before riding.
Warning: Over tightening the stem bolt or headset
assembly may cause damage to the scooter and/or
injury to the rider.
Standard Headset
Page 25

42
Some brakes have a special mechanism which enables you to set the
clearance on either side of the rim using a screwdriver. Brake pads
should finally be adjusted so that the leading edge of the pad makes
first contact with the rim. Some brakes have special curved washers
to allow this, but on less complex models it will be necessary to apply
a little force to the pad and its mounting.
Adjustment - Cantilever Calipers
Minor brake adjustment can be made via the barrel cable adjusters
which are located on each brake lever. To adjust, squeeze the brake
pads against the rim, loosen the lock nut, and turn the adjuster to pull
the brake pads closer to, or spread them away from the rim as required.
Brake pad clearance should be a maximum 2mm from the rim.
When correct, re-tighten the lock nut. If the pads cannot be set close
enough to the rim in this manner, you may have to adjust either the
length of the straddle cable or the length of the brake cable.
If the brakes use a separate brake cable and straddle cable, adjust
the straddle length by first screwing the barrel adjuster 3/4 of the way
in, then loosening the straddle cable fixing bolt, then pulling or push
ing
the cable through the fixing bolt to adjust the length, and finally
re-tightening the fixing bolt.
Check that the straddle bridge is in the middle of the cable to ensure
even brake pad contact. Apply full force to the brake lever to test,
then fine tune using the barrel adjuster.
To adjust the brake cable length, loosen the brake cable fixing bolt on
the cable straddle bridge, adjust the length until the brake shoes are
the correct distance from the rim, then re-tighten and test.
Parallel
Parallel
Fully Adjustable Brake Shoes
Curved
Adjustment
Washer
Curved
Adjustment
Washer
2mm clearance
41
Some brakes have a quick release mechanism to allow easier wheel removal. Whenever you adjust the brakes,
make sure the quick release mechanism is in the closed position.
Never ride unless the quick release is firmly locked in the closed position.
Lubrication
The brake lever and brake caliper pivot points should be oiled with
2-3 drops of light oil at least every three months to ensure smooth
operation and to reduce wear. Cables should be greased along
their entire length, after removing them from their casings, at least
every six months. Always grease new cables before fitting.
Adjustment - Sidepull Calipers
Minor brake adjustment can be made via the cable adjusting barrel, usually located at the upper cable arm. To adjust, squeeze
the brake pads against the rim, loosen the lock nut and turn the
adjuster Brake pad clearance should be a maximum 2mm from
the rim. When correct, re-tighten the lock nut. If the pads cannot
be set close enough to the rim in this manner, you may have to
adjust the cable length. Screw the barrel adjuster 3/4 of the way in,
squeeze the pads against the rim, undo the cable anchor bolt and
pull the cable through with pliers. Re-tighten the cable anchor bolt
and apply full force to the brake lever to test, then fine tune using
the barrel adjuster. If one pad is closer to the rim than the other,
loosen the fixing nut at the back of the brake, apply the brake to
hold it centered, and re-tighten the fixing nut.
Brake Lever
Brake Lever Housing
Cable Adjusting Barrel
Lock nut
Cable Adjusting Barrel
Center Bolt
Brake Shoe
Side-Pull Brakes
Fixing Nut
in Back
Cable
Anchor
Bolt
Ensure the Brake fixing nut is secured tightly.
Failure to do this may cause the Brake assembly
to dislodge from the fork.
Page 26

44
Problem
Brakes not working effectively
When applying the brakes
they squeal/squeak
Knocking or shuddering when
applying brakes
Wobbling wheel
Steering not accurate
Possible Cause
- Brake blocks worn down
- Brake blocks/rim greasy, wet or dirty
- Brake cables are
binding/stretched/damaged
- Brake levers are binding
- Brakes out of adjustment
- Brake blocks worn down
- Brake block toe-in incorrect
- Brake blocks/rim dirty or wet
- Brake arms loose
- Bulge in the rim or rim out of true
- Brake mounting bolts loose
- Brakes out of adjustment
- Fork loose in head tube
- Axle broken
- Wheel out of true
- Hub comes loose
- Headset binding
- Hub bearings collapsed
-
QR mechanism loose
- Wheels not aligned in frame
- Headset loose or binding
- Front forks or frame bent
Remedy
- Replace brake blocks
- Clean blocks and rim
- Clean/adjust/replace cables
- Adjust brake levers
- Center brakes
- Replace blocks
- Correct block toe-in
- Clean blocks and rim
- Tighten mounting bolts
- True wheel or take to a bike shop
for repair
- Tighten bolts
- Center brakes and/or adjust brake
block toe-in
- Tighten headset
- Replace axle
- True wheel
- Adjust hub bearings
- Adjust headset
- Replace bearings
-
Adjust QR mechanism
- Align wheels correctly
- Adjust/tighten headset
- Take scooter to a bike shop for
possible frame realignment
43
On some newer type cantilever brakes, the main brake cable
continues through the central cable carrier to an anchor bolt on one
of the brake arms. A shorter link cable reaches from the carrier and
the hook on the other brake arm. Adjustment of the cable length is
made after loosening the anchor bolt on the brake arm.
Adjust the brake pad position so that it is parallel to the wheel rim
and so that the leading edge makes first contact. To do this, fit an
Allen key into the brake pad holding bolt, loosen the fixing nut and
adjust. Move the brake pad along its mounting post to alter the
distance from the rim, and move the curved adjustment washer to
alter the angle of the pad.
On some models there is a spring-force adjustment screw on the
brake arm which allows further fine tuning of the brake shoe position.
Scooters with cantilever brakes must be fitted with safety devices
to prevent a possible accident in the event of the brake control
cable or the straddle bridge becoming loose or breaking while
riding. These are usually the reflector brackets, and must be fitted
in the front and rear. The bracket will prevent the straddle cable
from interfering with the wheel should the cable become discon
nected from the control cable. If the reflector brackets are not fitted
in this position, then alternative emergency cable safety stops must still
be fitted.
Usable Brake Shoe Worn Out Brake Shoe (Replace)
Tread Tread Worn Off
Align brake shoe with rim surface
Direction of rim
rotation
0.5 - 1.0 mm
Brake Shoe Holding Nut
Page 27

46
6. How Things Work
It’s important to your performance, enjoyment and safety to understand how things work on your scooter. Even if you’re an
experienced scooter rider, don’t assume that the way things work on your new scooter is the same as how they work on older
scooters. Be sure to read and to understand this section of the Manual. If you have even the slightest doubt as to whether
you understand something, talk to a qualified specialist.
A. Wheel Installation
1. Removing and Installing Bolt-On Wheels
a. Removing a Bolt-On Front Wheel
(1) Open up the brake shoes.
(2) With a 15mm box wrench or a six inch adjustable wrench, loosen the two axle nuts.
(3) If your front fork has a clip-on type secondary retention device, disengage it and go to step (4).
If your front fork has an integral secondary retention device, loosen the axle nuts about six full turns;
then go to step (4).
(4) Raise the front wheel a few inches off the ground and tap the top of the wheel with the palm of your
hand to knock the wheel out of the fork ends.
b. Installing a Bolt-On Front Wheel
(1) With the steering fork facing forward, insert the wheel between the fork blades so that the axle seats
firmly at the top of the slots which are at the tips of the fork blades. The axle nut washers should be on the
outside, between the fork blade and the axle nut. If your bike has a clip-on type secondary retention
device, engage it.
(2) While pushing the wheel firmly to the top of the slots in the fork dropouts, and at the same time center
ing the wheel rim in the fork, use a six-inch adjustable wrench or a 15mm box wrench to tighten the axle
nuts as tight as you can.
(3) Close the brake shoes; then spin the wheel to make sure that it is centered in the frame and clears the
brake shoes.
PART 6 - HOW THINGS WORK
?
45
Remedy
- Replace Inner tube
- Replace tire
- Replace with correct tire
- Remove sharp object embedded
in tire
- Correct tire pressure
- File down spoke
Problem
Frequent punctures
Possible Cause
- Inner tube old or faulty
- Tire tread/casing worn
- Tire unsuited to rim
- Tire not checked after previous
puncture
- Tire pressure too low
- Spoke protruding into rim
Page 28

48
WARNING: Some scooter brakes, such as linear-pull and disc brakes, are extremely powerful. You should take extra care
in becoming familiar with these brakes and exercise particular care when using them. Applying these brakes too hard or too
suddenly can lock up a wheel, which could cause you to lose control and fall.
When you apply one or both brakes, the scooter begins to slow, but your body wants to continue at the speed at which it was
going. This causes a transfer of weight to the front wheel (or, under heavy braking, around the front wheel hub, which could
send you flying over the handlebars). A wheel with more weight on it will accept greater brake pressure before lockup; a wheel
with less weight will lock up with less brake pressure. So, as you apply brakes and your weight shifts forward, you need to shift
your body toward the rear of the bike, to transfer weight back on to the rear wheel; and at the same time, you need to both
decrease rear braking and increase front braking force. This is even more important on steep descents, because descents
shift weight forward. The keys to effective speed control and safe stopping are controlling wheel lockup and weight transfer.
Practice braking and weight transfer techniques where there is no traffic or other hazards and distractions.
Everything changes when you ride on loose surfaces or in wet weather. Tire adhesion is reduced, so the wheels have less
cornering and braking traction and can lock up with less brake force. Moisture or dirt on the brake shoes reduces their ability
to grip. The way to maintain control on loose or wet surfaces is to go more slowly to begin with.
2. Adjusting your brakes
If either brake lever on your scooter fails the Mechanical Safety Check you can restore brake lever travel by turning the
brake cable adjusting barrel counterclockwise, then lock the adjustment in by turning the barrel’s lock nut clockwise as far as
it will go. If the lever still fails the Mechanical Safety Check, or you have any question about whether your brakes are working
properly have your dealer check the brakes.
?
47
B. Brakes
NOTE: For most effective braking, use both brakes and apply them simultaneously.
WARNING: Sudden or excessive application of the front brake may pitch the rider over the handlebars, causing serious
injury or death.
1. How brakes work
It’s important to your safety that you instinctively know which brake lever controls which brake on your bike. In the U.S.,
scooters are required to be set up with the right brake lever controlling the rear brake, and the left lever controlling the
front brake.
The braking action of a scooter is a function of the friction between the brake surfaces – usually the brake shoes and the
wheel rim. To make sure that you have maximum friction available, keep your wheel rims and brake shoes clean and free
of lubricants, waxes or polishes.
Make sure that your hands can reach and squeeze the brake levers comfortably. If your hands are too small to operate the
levers comfortably, consult your dealer before riding the bike. The lever reach may be adjustable; or you may need a different
brake lever design.
Most brakes have some form of quick release mechanism to allow the brake shoes to clear the tire when a wheel is removed
or reinstalled. When the brake quick release is in the open position, the brakes are inoperative. Make sure that you under
stand the way the brake quick release works on your scooter and check each time to make sure both brakes work correctly
before you get on the bike.
Brakes are designed to control your speed, not just to stop the bike. Maximum braking force for each wheel occurs at the
point just before the wheel “locks up” (stops rotating) and starts to skid. Once the tire skids, you actually lose most of your
stopping force and all directional control. You need to practice slowing and stopping smoothly without locking up a wheel.
The technique is called progressive brake modulation. Instead of jerking the brake lever to the position where you thinkyou’ll
generate appropriate braking force, squeeze the lever, progressively increasing the braking force. If you feel the wheel begin
to lock up, release pressure just a little to keep the wheel rotating just short of lockup. It’s important to develop a feel for
the amount of brake lever pressure required for each wheel at different speeds and on different surfaces. To better under
stand this, experiment a little by walking your bike and applying different amounts of pressure to each brake lever, until
the wheel locks.
?
Page 29

50
?
Some special high-performance tires have unidirectional treads: their tread pattern is designed to work better in one direction
than in the other. The sidewall marking of a unidirectional tire will have an arrow showing the correct rotation direction. If your
bike has unidirectional tires, be sure that they are mounted to rotate in the correct direction.
2. Tire Valves
The tire valve allows air to enter the tire’s inner tube under pressure, but doesn’t let it back out unless you want it to. There
are primarily two kinds of scooter tube valves (actually, there are other designs, but they are seldom seen in the US any
more): The Schraeder Valve and the Presta Valve. The scooter pump you use must have the fitting appropriate to the valve
stems on your scooter.
The Schraeder is like the valve on a car tire. To inflate a Schraeder valve tube, remove the valve cap and push the air hose
or pump fitting onto the end of the valve stem. To let air out of a Schraeder valve, depress the pin in the end of the valve
stem with the end of a key or other appropriate object.
The Presta valve has a narrower diameter and is only found on scooter tires. To inflate a Presta valve tube using a Presta
headed scooter pump, remove the valve cap; unscrew (counterclockwise) the valve stem lock nut; and push down on the
valve stem to free it up. Then push the pump head on to the valve head, and inflate. To inflate a Presta valve with a gas
station air hose, you’ll need a Presta adapter (available at your bike shop) which screws on to the valve stem once you’ve
freed up the valve. The adapter fits the end of the air hose fitting. Close the valve after inflation. To let air out of a Presta
valve, open up the valve stem lock nut and depress the valve stem.
49
C. Tires and Tubes
1. Tires
Scooter tires are available in many designs and specifications, ranging from general-purpose designs to tires designed to
perform best under very specific weather or terrain conditions. Your scooter has been equipped with tires which the scooter ’s
manufacturer felt were the best balance of performance and value for the use for which the scooter was intended. If, once
you’ve gained experience with your new scooter, you feel that a different tire might better suit your riding needs, your dealer
can help you select the most appropriate design.
The size, pressure rating, and on some high-performance tires the specific recommended use, are marked on the sidewall of
the tire. The part of this information which is most important to you is Tire Pressure.
WARNING: Never inflate a tire beyond the maximum pressure marked on the tire’s sidewall. Exceeding the recommended
maximum pressure may blow the tire off the rim, which could cause damage to the bike and injury to the rider and bystanders.
The best way to inflate a scooter tire to the correct pressure is with a bicycle pump.
CAUTION: Gas station air hoses move a large volume of air very rapidly, and will raise the pressure in your tire very rapidly.
To avoid over inflation when using a gas station air hose, put air into your tire in short, spaced bursts.
Tire pressure is given either as maximum pressure or as a pressure range. How a tire performs under different terrain or
weather conditions depends largely on tire pressure. Inflating the tire to near its maximum recommended pressure gives the
lowest rolling resistance; but also produces the harshest ride. High pressures work best on smooth, dry pavement. Very low
pressures, at the bottom of the recommended pressure range, give the best performance on smooth, slick terrain such as
hard-packed clay, and on deep, loose surfaces such as deep, dry sand. Tire pressure that is too low for your weight and the
riding conditions can cause a puncture of the tube by allowing the tire to deform sufficiently to pinch the inner tube between
the rim and the riding surface.
CAUTION: Pencil type automotive tire gauges and gas station air hose pressure settings can be inaccurate and should not be
relied upon for consistent, accurate pressure readings. Instead, use a high quality dial gauge.
Check inflation as described in you’ll know how correctly inflated tires should look and feel. Some tires may need to be
brought up to pressure every week or two.
?
Page 30

52
LIMITED WARRANTY
AND POLICY ON REPLACEMENT PROCEDURES AND RESPONSIBILITIES
Your purchase includes the following warranty which is in lieu of all other express warranties. This warranty is extended only to the initial consumer purchaser. No
warranty registration is required. This warranty gives you specific legal rights and you may have other rights which vary from state to state.
FRAME
Steel, aluminum and dual suspension frames are guaranteed against faulty materials and workmanship for as long as the initial consumer purchaser has the scooter, subject to the
Terms and Conditions of this Limited Warranty. If frame failure should occur due to faulty materials or workmanship during the guarantee period, the frame will be replaced. For
frame replacement under this Pacific Limited Warranty, contact us, stating the nature of the failure, model number, date received and the name of the store from which the bike was
received, at the address given on this page. Frame must be returned for inspection at customer's expense. Please note: the fork is not part of the frame. A lifetime warranty on your
frame does not guarantee that the product will last forever. The length of the useful life cycle will vary depending on the type of bike, riding conditions and care the scooter receives.
Competition, jumping, downhill racing, trick riding, trial riding, riding in severe conditions or climates, riding with heavy loads or any other non-standard use can substantially shorten
the useful product life cycle. Any one or a combination of these conditions may result in an unpredictable failure that is not covered by this warranty. All bicycles and frame sets
should be periodically checked by an authorized dealer for indications of potential problems, inappropriate use or abuse. These are important safety checks and are very important
to help prevent accidents, bodily injury to the rider and shortened useful product life cycle.
PARTS
All other parts of the unit except Normal Wear Parts are warranted against defective materials and workmanship for as long as the initial consumer purchaser has the scooter, subject
to the Terms and Conditions of this Limited Warranty. If failure of any part should occur due to faulty materials or workmanship during the warranty period, the part will be replaced.
All warranty claims must be submitted to the address below and must be shipped prepaid and accompanied by proof of purchase. Any other warranty claims not included in this
statement are void. This especially includes installation, assembly, and disassembly costs. This warranty does not cover paint damage, rust, or any modifications made to the scooter.
Normal Wear Parts are defined as grips, tires, tubes, cables, brake shoes and saddle covering. These parts are warranted to be free from defects in material and workmanship as
delivered with the product. Any claim for repair or replacement of Normal Wear Parts (grips, tubes, tires, cables, brake shoes and saddle covering) and missing parts must be made
within thirty (30) days of the date of purchase. The warranty does not cover normal wear and tear, improper assembly or maintenance, or installation of parts or accessories not
originally intended or compatible with the scooter as sold. The warranty does not apply to damage or failure due to accident, abuse, misuse, neglect, or theft. Claims involving these
issues will not be honored.
CONDITIONS OF WARRANTY
1. Your scooter has been designed for general transportation and recreational use, but has not been designed to withstand abuse associated with stunting and jumping.
This warranty ceases when you rent, sell, or give away the scooter, ride with more than one person, or use the scooter for stunting or jumping.
2. This warranty does not cover ordinary wear and tear or anything you break accidentally or deliberately.
3. It is the responsibility of the individual consumer purchaser to assure that all parts included in the factory-sealed carton are properly installed, all functional parts are
initially adjusted properly, and subsequent normal maintenance services and adjustments necessary to keep the scooter in good operating condition are properly made.
This warranty does not apply to damage due to improper installation of parts or failure to properly maintain or adjust the scooter.
NOTICE: Scooter specifications
subject to change without notice.
PACIFIC CYCLE, INC.
4902 Hammersley Road
Madison, WI 53711
Call Toll Free 1.800.626.2811
Monday -Friday 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. Central Time
51
Purchase Record Card
Fill in Immediately and retain as a record of your purchase.
Your Name: ______
Address: _____________________________________________________
Date Purchased: _______________ Place of Purchase: _____________
Model & Brand Information: _____________________________________
Wheel Size: ____________________
Color: _________________________
Serial Number: __________________
*Please retain your sales receipt for any possible warranty claims.
PART 7 - P URCHASE RE CORD
Serial number is located
on the bottom of the frame
behind the kickstand.
Page 31

 Loading...
Loading...